
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Biologically Informed Polygenic Scores for Brain Insulin Receptor Network Are Associated with Cardiometabolic Risk Markers and Diabetes in Women
- Jannica S. Selenius, Patricia P. Silveira, Mikaela von Bonsdorff, Jari Lahti, Hannu Koistinen, Riitta Koistinen, Markku Seppälä, Johan G. Eriksson, Niko S. Wasenius
- Received February 10, 2023 Accepted November 25, 2023 Published online March 25, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0039 [Epub ahead of print]
- 687 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
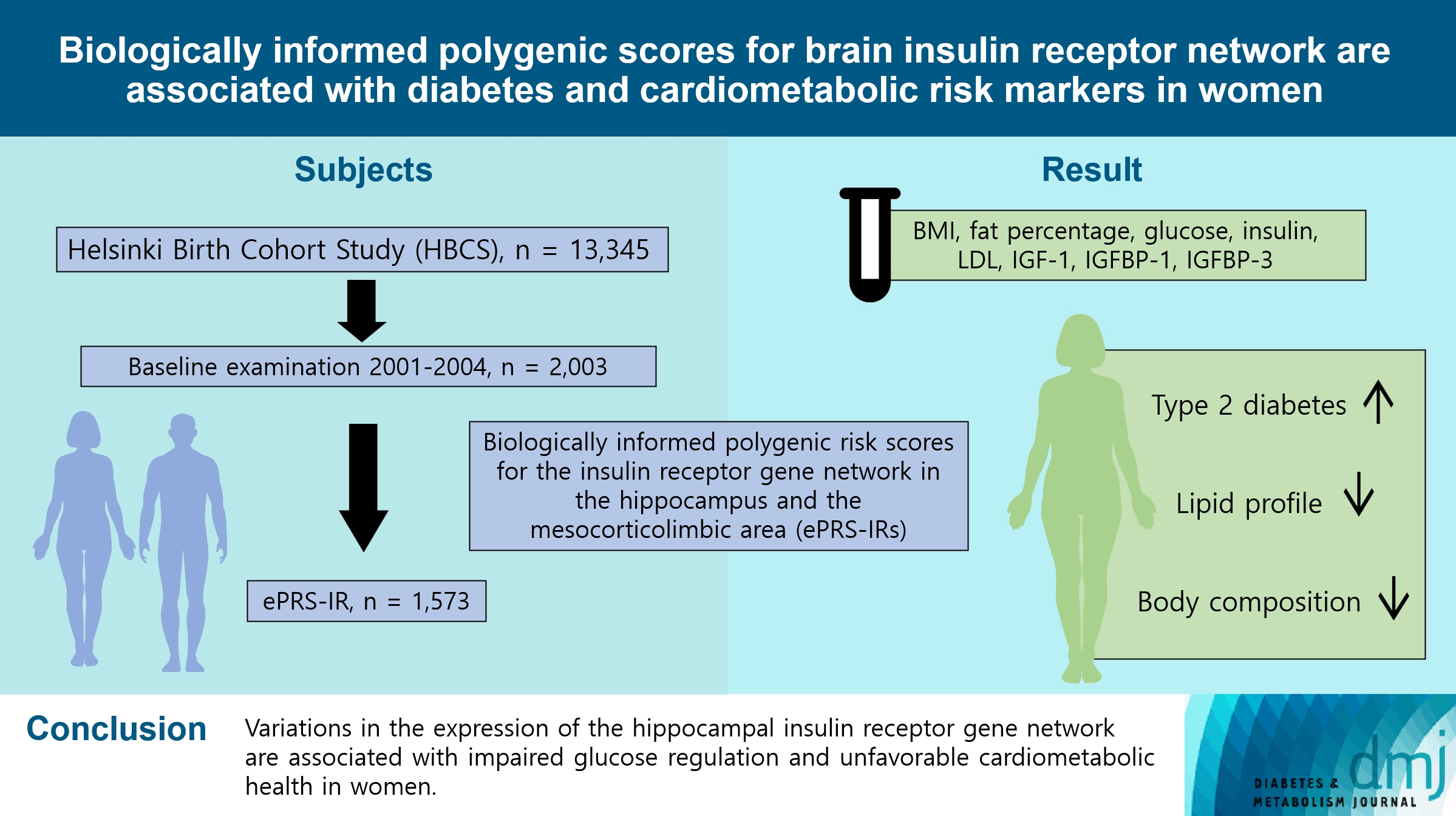
To investigate associations between variations in the co-expression-based brain insulin receptor polygenic score and cardiometabolic risk factors and diabetes mellitus.
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 1,573 participants from the Helsinki Birth Cohort Study. Biologically informed expression-based polygenic risk scores for the insulin receptor gene network were calculated for the hippocampal (hePRS-IR) and the mesocorticolimbic (mePRS-IR) regions. Cardiometabolic markers included body composition, waist circumference, circulating lipids, insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1), and insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 and 3 (IGFBP-1 and -3). Glucose and insulin levels were measured during a standardized 2-hour 75 g oral glucose tolerance test and impaired glucose regulation status was defined by the World Health Organization 2019 criteria. Analyzes were adjusted for population stratification, age, smoking, alcohol consumption, socioeconomic status, chronic diseases, birth weight, and leisure-time physical activity.
Results
Multinomial logistic regression indicated that one standard deviation increase in hePRS-IR was associated with increased risk of diabetes mellitus in all participants (adjusted relative risk ratio, 1.17; 95% confidence interval, 1.01 to 1.35). In women, higher hePRS-IR was associated with greater waist circumference and higher body fat percentage, levels of glucose, insulin, total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, apolipoprotein B, insulin, and IGFBP-1 (all P≤0.02). The mePRS-IR was associated with decreased IGF-1 level in women (P=0.02). No associations were detected in men and studied outcomes.
Conclusion
hePRS-IR is associated with sex-specific differences in cardiometabolic risk factor profiles including impaired glucose regulation, abnormal metabolic markers, and unfavorable body composition in women.
- Complications
- The Risk of Shoulder Adhesive Capsulitis in Individuals with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Longitudinal Nationwide Population-Based Study
- Jong-Ho Kim, Bong-Seoung Kim, Kyung-do Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):869-878. Published online August 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0275

- 1,525 View
- 145 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to investigate the association between type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and shoulder adhesive capsulitis (AC) using a large-scale, nationwide, population-based cohort in the Republic of Korea.
Methods
A total of 3,471,745 subjects aged over 20 years who underwent a National Health Insurance Service medical checkup between 2009 and 2010 were included in this study, and followed from the date of their medical checkup to the end of 2018. Subjects were classified into the following four groups based on the presence of dysglycemia and history of diabetes medication: normal, prediabetes, newly diagnosed T2DM (new-T2DM), and T2DM (claim history for antidiabetic medication). The endpoint was new-onset AC during follow-up. The incidence rates (IRs) in 1,000 person-years and hazard ratios (HRs) of AC for each group were analyzed using Cox proportional hazard regression models.
Results
The IRs of AC were 9.453 (normal), 11.912 (prediabetes), 14.933 (new-T2DM), and 24.3761 (T2DM). The adjusted HRs of AC in the prediabetes, new-T2DM, and T2DM groups were 1.084 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.075 to 1.094), 1.312 (95% CI, 1.287 to 1.337), and 1.473 (95% CI, 1.452 to 1.494) compared to the normal group, respectively. This secular trend of the HRs of AC according to T2DM status was statistically significant (P<0.0001).
Conclusion
This large-scale, longitudinal, nationwide, population-based cohort study of 3,471,745 subjects confirmed that the risk of AC increases in prediabetic subjects and is associated with T2DM status.
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Comparison of on-Statin Lipid and Lipoprotein Levels for the Prediction of First Cardiovascular Event in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):837-845. Published online August 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0217
- 1,443 View
- 173 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
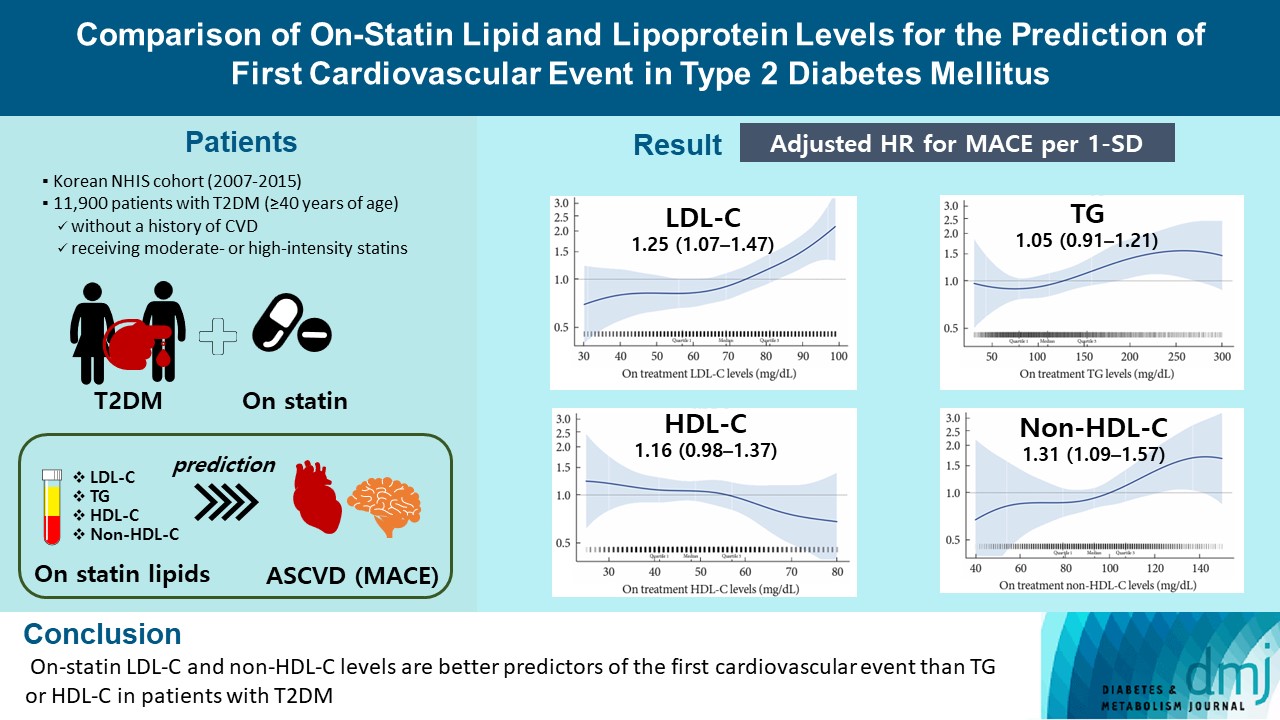
A substantial cardiovascular disease risk remains even after optimal statin therapy. Comparative predictiveness of major lipid and lipoprotein parameters for cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who are treated with statins is not well documented.
Methods
From the Korean Nationwide Cohort, 11,900 patients with T2DM (≥40 years of age) without a history of cardiovascular disease and receiving moderate- or high-intensity statins were included. The primary outcome was the first occurrence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) including ischemic heart disease, ischemic stroke, and cardiovascular death. The risk of MACE was estimated according to on-statin levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglyceride (TG), highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and non-HDL-C.
Results
MACE occurred in 712 patients during a median follow-up period of 37.9 months (interquartile range, 21.7 to 54.9). Among patients achieving LDL-C levels less than 100 mg/dL, the hazard ratios for MACE per 1-standard deviation change in ontreatment values were 1.25 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.07 to 1.47) for LDL-C, 1.31 (95% CI, 1.09 to 1.57) for non-HDL-C, 1.05 (95% CI, 0.91 to 1.21) for TG, and 1.16 (95% CI, 0.98 to 1.37) for HDL-C, after adjusting for potential confounders and lipid parameters mutually. The predictive ability of on-statin LDL-C and non-HDL-C for MACE was prominent in patients at high cardiovascular risk or those with LDL-C ≥70 mg/dL.
Conclusion
On-statin LDL-C and non-HDL-C levels are better predictors of the first cardiovascular event than TG or HDL-C in patients with T2DM.
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- The Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus according to Changes in Obesity Status in Late Middle-Aged Adults: A Nationwide Cohort Study of Korea
- Joon Ho Moon, Yeonhoon Jang, Tae Jung Oh, Se Young Jung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):514-522. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0159

- 2,058 View
- 133 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Although obesity is a well-known risk factor of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), there is scant data on discriminating the contribution of previous obesity and recent weight gain on developing T2DM.
Methods
We analyzed the Korean National Health Insurance Service-Health Screening Cohort data from 2002 to 2015 where Korean residents underwent biennial health checkups. Participants were classified into four groups according to their obesity status (body mass index [BMI] ≥25 kg/m2) before and after turning 50 years old: maintaining normal (MN), becoming obese (BO), becoming normal (BN), and maintaining obese (MO). Cox proportional hazards regression model was used to estimate the risk of T2DM factoring in the covariates age, sex, BMI, presence of impaired fasting glucose or hypertension, family history of diabetes, and smoking status.
Results
A total of 118,438 participants (mean age, 52.5±1.1 years; men, 45.2%) were prospectively evaluated for incident T2DM. A total of 7,339 (6.2%) participants were diagnosed with T2DM during a follow-up period of 4.8±2.6 years. Incidence rates of T2DM per 1,000 person-year were 9.20 in MN, 14.81 in BO, 14.42 in BN, 21.38 in MO. After factoring in covariates, participants in the groups BN (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 1.15; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.04 to 1.27) and MO (aHR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.06 to 1.24) were at increased risk of developing T2DM compared to MN, whereas BO (hazard ratio, 1.06; 95% CI, 0.96 to 1.17) was not.
Conclusion
Having been obese before 50 years old increased the risk of developing T2DM in the future, but becoming obese after 50 did not. Therefore, it is important to maintain normal weight from early adulthood to prevent future metabolic perturbations.
- Complications
- Association of Body Mass Index and Fracture Risk Varied by Affected Bones in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- Se-Won Lee, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):242-254. Published online January 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0001
- 2,898 View
- 164 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
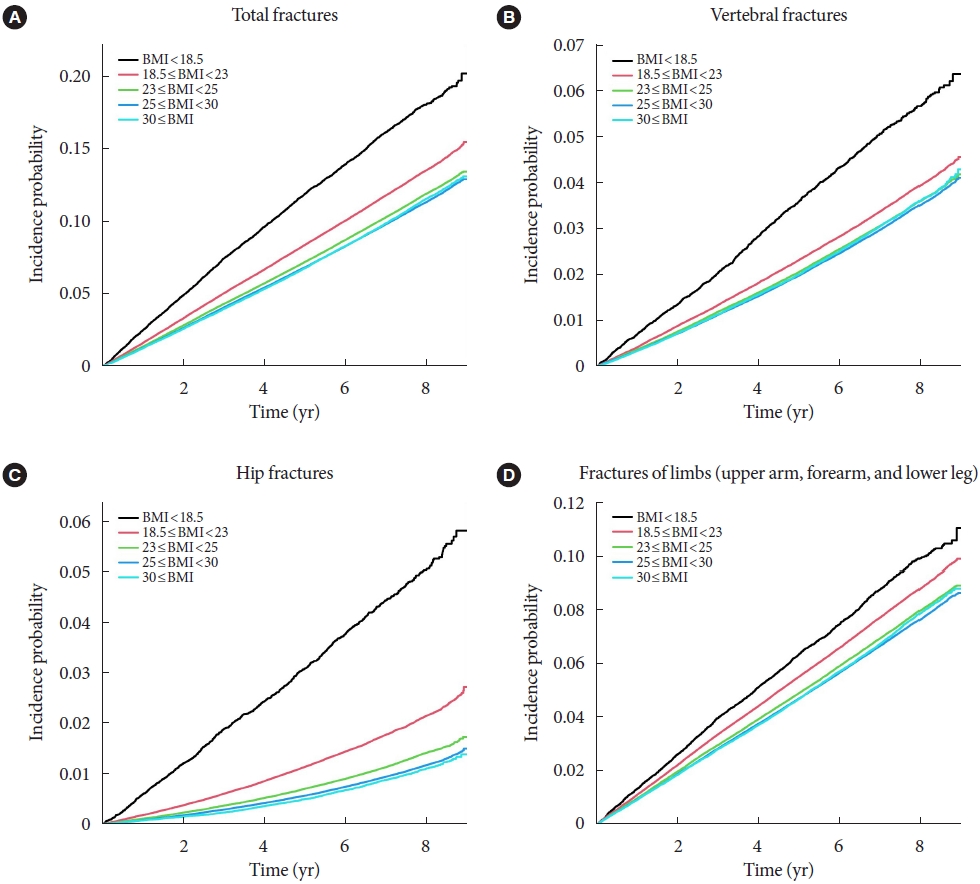
Body mass index (BMI) is a risk factor for the type 2 diabetes (T2DM), and T2DM accompanies various complications, such as fractures. We investigated the effects of BMI and T2DM on fracture risk and analyzed whether the association varied with fracture locations.
Methods
This study is a nationwide population-based cohort study that included all people with T2DM (n=2,746,078) who received the National Screening Program during 2009–2012. According to the anatomical location of the fracture, the incidence rate and hazard ratio (HR) were analyzed by dividing it into four categories: vertebra, hip, limbs, and total fracture.
Results
The total fracture had higher HR in the underweight group (HR, 1.268; 95% CI, 1.228 to 1.309) and lower HR in the obese group (HR, 0.891; 95% CI, 0.882 to 0.901) and the morbidly obese group (HR, 0.873; 95% CI, 0.857 to 0.89), compared to reference (normal BMI group). Similar trends were observed for HR of vertebra fracture. The risk of hip fracture was most prominent, the risk of hip fracture increased in the underweight group (HR, 1.896; 95% CI, 1.178 to 2.021) and decreased in the obesity (HR, 0.643; 95% CI, 0.624 to 0.663) and morbidly obesity group (HR, 0.627; 95% CI, 0.591 to 0.665). Lastly, fracture risk was least affected by BMI for limbs.
Conclusion
In T2DM patients, underweight tends to increase fracture risk, and overweight tends to lower fracture risk, but association between BMI and fracture risk varied depending on the affected bone lesions. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dysuricemia—A New Concept Encompassing Hyperuricemia and Hypouricemia
Naoyuki Otani, Motoshi Ouchi, Einosuke Mizuta, Asuka Morita, Tomoe Fujita, Naohiko Anzai, Ichiro Hisatome
Biomedicines.2023; 11(5): 1255. CrossRef - Association of Body Mass Index and Fracture Risk Varied by Affected Bones in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:242-54)
Se-Won Lee, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 439. CrossRef - Association of Body Mass Index and Fracture Risk Varied by Affected Bones in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:242-54)
So Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 437. CrossRef - Effect of SGLT2 inhibitors on fractures, BMD, and bone metabolism markers in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Xin Wang, Fengyi Zhang, Yufeng Zhang, Jiayi Zhang, Yingli Sheng, Wenbo Wang, Yujie Li
Osteoporosis International.2023; 34(12): 2013. CrossRef
- Dysuricemia—A New Concept Encompassing Hyperuricemia and Hypouricemia
Review
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Screening for Prediabetes and Diabetes in Korean Nonpregnant Adults: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2022
- Kyung Ae Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Suk Chon, Min Kyong Moon, on Behalf of the Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline of Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):819-826. Published online November 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0364

- 4,264 View
- 268 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetes screening serves to identify individuals at high-risk for diabetes who have not yet developed symptoms and to diagnose diabetes at an early stage. Globally, the prevalence of diabetes is rapidly increasing. Furthermore, obesity and/or abdominal obesity, which are major risk factors for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), are progressively increasing, particularly among young adults. Many patients with T2DM are asymptomatic and can accompany various complications at the time of diagnosis, as well as chronic complications develop as the duration of diabetes increases. Thus, proper screening and early diagnosis are essential for diabetes care. Based on reports on the changing epidemiology of diabetes and obesity in Korea, as well as growing evidence from new national cohort studies on diabetes screening, the Korean Diabetes Association has updated its clinical practice recommendations regarding T2DM screening. Diabetes screening is now recommended in adults aged ≥35 years regardless of the presence of risk factors, and in all adults (aged ≥19) with any of the risk factors. Abdominal obesity based on waist circumference (men ≥90 cm, women ≥85 cm) was added to the list of risk factors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oxidative Balance Score and New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Adults without Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study-Health Examinees (KoGES-HEXA) Cohort
Mid-Eum Moon, Dong Hyuk Jung, Seok-Jae Heo, Byoungjin Park, Yong Jae Lee
Antioxidants.2024; 13(1): 107. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Semaglutide Versus Once-Daily Sitagliptin as Metformin Add-on in a Korean Population with Type 2 Diabetes
Byung-Wan Lee, Young Min Cho, Sin Gon Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Soo Lim, Amine Dahaoui, Jin Sook Jeong, Hyo Jin Lim, Jae Myung Yu
Diabetes Therapy.2024; 15(2): 547. CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus more effectively than oral glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity and secretion markers
Min Jin Lee, Ji Hyun Bae, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi, Mi Sook Yun, Yang Ho Kang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111640. CrossRef - Cumulative muscle strength and risk of diabetes: A prospective cohort study with mediation analysis
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Yan Liang, Wenji Chen, Duolao Wang, Zilin Sun, Bo Xie, Tongzhi Wu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 197: 110562. CrossRef - Revisiting the Diabetes Crisis in Korea: Call for Urgent Action
Jun Sung Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef
- Oxidative Balance Score and New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Adults without Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study-Health Examinees (KoGES-HEXA) Cohort
Original Articles
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2021
- Jae Hyun Bae, Kyung-Do Han, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ye Seul Yang, Jong Han Choi, Kyung Mook Choi, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyu Chang Won, on Behalf of the Committee of Media-Public Relation of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):417-426. Published online May 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0106

- 13,719 View
- 1,655 Download
- 76 Web of Science
- 99 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to investigate the prevalence and management of diabetes mellitus, risk-factor control, and comorbidities among Korean adults.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey to assess the prevalence, treatment, risk factors, comorbidities, and self-management behaviors of diabetes mellitus from 2019 to 2020. We also analyzed data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service to evaluate the use of antidiabetic medications in people with diabetes mellitus from 2002 through 2018.
Results
Among Korean adults aged 30 years or older, the estimated prevalence of diabetes mellitus was 16.7% in 2020. From 2019 through 2020, 65.8% of adults with diabetes mellitus were aware of the disease and treated with antidiabetic medications. The percentage of adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) <6.5% was 24.5% despite the increased use of new antidiabetic medications. We found that adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved all three goals of HbA1c <6.5%, blood pressure (BP) <140/85 mm Hg, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol <100 mg/dL were 9.7%. The percentage of self-management behaviors was lower in men than women. Excess energy intake was observed in 16.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus.
Conclusion
The prevalence of diabetes mellitus among Korean adults remained high. Only 9.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus achieved all glycemic, BP, and lipid controls from 2019 to 2020. Continuous evaluation of national diabetes statistics and a national effort to increase awareness of diabetes mellitus and improve comprehensive diabetes care are needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
Jinyoung Kim, Bongseong Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 567. CrossRef - Changes in Fatty Liver Disease and Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Young Korean Adults
Kye-Yeung Park, Hwan-Sik Hwang, Kyungdo Han, Hoon-Ki Park
American Journal of Preventive Medicine.2024; 66(4): 717. CrossRef - Widening disparities in the national prevalence of diabetes mellitus for people with disabilities in South Korea
I. Hwang, S.Y. Kim, Y.Y. Kim, J.H. Park
Public Health.2024; 226: 173. CrossRef - Questionnaire-Based Survey of Diabetes Self-Care Activities and Barriers among Young Korean Adults with Early-Onset Diabetes
Ji In Park, Sang-Wook Kim, Il Sung Nam-Goong, Kee-Ho Song, Ji Hee Yu, Ji Yun Jeong, Eun-Hee Cho
Yonsei Medical Journal.2024; 65(1): 42. CrossRef - Patients with diabetes in regions with population decline and likelihood of receiving diabetes management education and screenings for related complications in Korea
Yeong Jun Ju, Woorim Kim, Kyujin Chang, Tae Hoon Lee, Soon Young Lee
Preventive Medicine.2024; 178: 107793. CrossRef - Association between underweight and risk of heart failure in diabetes patients
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung‐Do Han, Eun‐Jung Rhee, Won‐Young Lee
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2024; 15(2): 671. CrossRef - Gastroparesis might not be uncommon in patients with diabetes mellitus in a real-world clinical setting: a cohort study
Jeongmin Lee, Hye Lim Park, Su Young Park, Chul-Hyun Lim, Min-Hee Kim, Jung Min Lee, Sang-Ah Chang, Jung-Hwan Oh
BMC Gastroenterology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to impaired fasting glucose and gastrointestinal cancer risk: A nationwide cohort study
Byeong Yun Ahn, Bokyung Kim, Sanghyun Park, Sang Gyun Kim, Kyungdo Han, Soo‐Jeong Cho
Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Multidimensional behavioral factors for diabetes management among middle-aged adults: a population-based study
Hyerang Kim, Heesook Son
Journal of Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Semaglutide Versus Once-Daily Sitagliptin as Metformin Add-on in a Korean Population with Type 2 Diabetes
Byung-Wan Lee, Young Min Cho, Sin Gon Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Soo Lim, Amine Dahaoui, Jin Sook Jeong, Hyo Jin Lim, Jae Myung Yu
Diabetes Therapy.2024; 15(2): 547. CrossRef - Association between dietary selenium intake and severe abdominal aortic calcification in the United States: a cross-sectional study
Weiwei Dong, Xiaobai Liu, Lu Ma, Zhiyong Yang, Chunyan Ma
Food & Function.2024; 15(3): 1575. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to hypertriglyceridemia and risk of type 2 diabetes in young adults
Min-Kyung Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Jong-Dai Kim, Moon Jung Kim, Byungpyo Kim, Jung Heo, Jiyeon Ahn, Seo-Young Sohn, Jae-Hyuk Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 208: 111109. CrossRef - Recent evidence on target blood pressure in patients with hypertension
Hack-Lyoung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2024; 6(1): 17. CrossRef - Status and trends in epidemiologic characteristics of diabetic end-stage renal disease: an analysis of the 2021 Korean Renal Data System
Kyeong Min Kim, Seon A Jeong, Tae Hyun Ban, Yu Ah Hong, Seun Deuk Hwang, Sun Ryoung Choi, Hajeong Lee, Ji Hyun Kim, Su Hyun Kim, Tae Hee Kim, Ho-Seok Koo, Chang-Yun Yoon, Kiwon Kim, Seon Ho Ahn, Yong Kyun Kim, Hye Eun Yoon
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 43(1): 20. CrossRef -
In silico
exploration of the potential inhibitory activities of in-house and ZINC database lead compounds against alpha-glucosidase using structure-based virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation approach
Zuhier A. Awan, Haider Ali Khan, Alam Jamal, Sulaiman Shams, Guojun Zheng, Abdul Wadood, Muhammad Shahab, Mohammad Imran Khan, Abdulaziz A. Kalantan
Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Mobile Applications for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Scoping Review
Jung Lim Lee, Youngji Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 368. CrossRef - Current status of remote collaborative care for hypertension in medically underserved areas
Seo Yeon Baik, Kyoung Min Kim, Hakyoung Park, Jiwon Shinn, Hun-Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2024; 6(1): 33. CrossRef - Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: nationwide population based study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
BMJ.2024; : e076388. CrossRef - Comparison of metabolic and neurological comorbidities in Asian patients with psoriasis and atopic dermatitis
Hee Joo Yang, Mi Young Lee, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Chang Jin Jung, Woo Jin Lee, Chong Hyun Won, Mi Woo Lee, Joon Min Jung, Sung Eun Chang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer risk according to fasting blood glucose trajectories: a population-based cohort study
Thi Minh Thu Khong, Thi Tra Bui, Hee-Yeon Kang, Jinhee Lee, Eunjung Park, Jin-Kyoung Oh
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2024; 12(1): e003696. CrossRef - Participation experience in self-care program for type 2 diabetes: A mixed-methods study
Mihwan Kim, Haejung Lee, Gaeun Park, Ah Reum Khang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(1): 31. CrossRef - Fasting GLP-1 Levels and Albuminuria Are Negatively Associated in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Cheol-Won Jang, Tae Yang Yu, Jin Woo Jeong, Se Eun Ha, Rajan Singh, Moon Young Lee, Seungil Ro
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2024; 14(3): 280. CrossRef - The clinical relevance of a polygenic risk score for type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Korean population
Na Yeon Kim, Haekyung Lee, Sehee Kim, Ye-Jee Kim, Hyunsuk Lee, Junhyeong Lee, Soo Heon Kwak, Seunggeun Lee
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic traits and colorectal cancer survival in a cohort of South Korean patients: A Mendelian randomization analysis
So Yon Jun, Sooyoung Cho, Min Jung Kim, Ji Won Park, Seung‐Bum Ryoo, Seung Yong Jeong, Kyu Joo Park, Aesun Shin
Cancer Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 279. CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus more effectively than oral glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity and secretion markers
Min Jin Lee, Ji Hyun Bae, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi, Mi Sook Yun, Yang Ho Kang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111640. CrossRef - Real-World Outcomes of Individualized Targeted Therapy with Insulin Glargine 300 Units/mL in Insulin-Naïve Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes: TOBE Study
Eun-Gyoung Hong, Kyung-Wan Min, Jung Soo Lim, Kyu-Jeung Ahn, Chul Woo Ahn, Jae-Myung Yu, Hye Soon Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Won Kim, Dong Han Kim, Hak Chul Jang
Advances in Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of complicated, untreated and uncontrolled diabetes and pre‐diabetes on treatment outcome among patients with pulmonary tuberculosis
Kyung Hoon Kim, Hyung Woo Kim, Yong Hyun Kim, Yeonhee Park, Sung Soo Jung, Jin Woo Kim, Jee Youn Oh, Heayon Lee, Sung Kyoung Kim, Sun‐Hyung Kim, Jiwon Lyu, Yousang Ko, Sun Jung Kwon, Yun‐Jeong Jeong, Do Jin Kim, Hyeon‐Kyoung Koo, Yangjin Jegal, Sun Young
Respirology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of dietary behavior and intake related to glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes aged 30 years or older in Korea: Utilizing the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Jin-Ah Seok, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(2): 239. CrossRef - Management of Early-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Jin Hwa Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2024; 25(1): 4. CrossRef - Baseline glycated albumin level and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Healthy individuals: a retrospective longitudinal observation in Korea
Kang-Su Shin, Min-Seung Park, Mi Yeon Lee, Eun Hye Cho, Hee-Yeon Woo, Hyosoon Park, Min-Jung Kwon
Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation.2024; : 1. CrossRef - The Potential Role of Presepsin in Predicting Severe Infection in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Eun Yeong Ha, Il Rae Park, Seung Min Chung, Young Nam Roh, Chul Hyun Park, Tae-Gon Kim, Woong Kim, Jun Sung Moon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(8): 2311. CrossRef - Myotonic dystrophy type 1 in South Korea: a comprehensive analysis of cancer and comorbidity risks
Incheol Seo, Jin-Mo Park
Neurological Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Pancreatic Cancer and Use of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score-Matching Analysis
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Soon Jib Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 426. CrossRef - Diabetes screening in South Korea: a new estimate of the number needed to screen to detect diabetes
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kyung Ae Lee, Kyung-Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Dae Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(1): 93. CrossRef - Sex differences in the impact of diabetes mellitus on tuberculosis recurrence: a retrospective national cohort study
Dararat Eksombatchai, Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2023; 127: 1. CrossRef - Response to Letter to the Editor From Han and Xu: “Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes”
Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(4): e58. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in catholic priests compared with general public
Youngmi Eun, Sun Myeong Ock, Se-Hong Kim, Ju Hye Chung, Se Jin Park, Churlmin Kim, Min-Kyun Im, Kyung-do Han
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(5): 655. CrossRef - Blood pressure control and its associated factors in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes
Anan S Jarab, Walid Al-Qerem, Salam Alqudah, Shrouq R Abu Heshmeh, Tareq L Mukattash, Karem H Alzoubi
Electronic Journal of General Medicine.2023; 20(3): em477. CrossRef - Prevalence and associated factors of diabetes mellitus among patients with tuberculosis in South Korea from 2011 to 2018: a nationwide cohort study
Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Jeong Mi Seo, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang
BMJ Open.2023; 13(3): e069642. CrossRef - The association between nutrition label utilization and disease management education among hypertension or diabetes diagnosed in Korea using 2018 Community Health Survey: a cross-sectional study
Miran Jin, Jayeun Kim, Kyuhyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 38. CrossRef - Insulin Fact Sheet in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Trends of Antidiabetic Medication Use in Insulin Users with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: 2002 to 2019
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Bong-Sung Kim, Kyung-Do Han, So Yoon Kwon, So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 211. CrossRef - Comparison of Operational Definition of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Data from Korean National Health Insurance Service and Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Ha Baek, Yong-Moon Park, Kyung Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Han Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 201. CrossRef - Evaluation of pharmacokinetic interactions between lobeglitazone, empagliflozin, and metformin in healthy subjects
Heeyoung Kim, Choon Ok Kim, Hyeonsoo Park, Min Soo Park, Dasohm Kim, Taegon Hong, Yesong Shin, Byung Hak Jin
Translational and Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 31(1): 59. CrossRef - Vascular and metabolic effects of ipragliflozin versus sitagliptin (IVS) in type 2 diabetes treated with sulphonylurea and metformin: IVS study
Seon Mee Kang, Han Mi Yun, Minji Sohn, Soo Lim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(7): 1922. CrossRef - Diabetes and Skin Disease
Jungah Lim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(1): 29. CrossRef - Revisiting the Diabetes Crisis in Korea: Call for Urgent Action
Jun Sung Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between Sleep Duration and Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Healthy Subjects: A 14-Year Longitudinal Cohort Study
Jin ha Jang, Wonjin Kim, Jin Sil Moon, Eun Roh, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm, Ji Hye Huh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(8): 2899. CrossRef - Exercise Frequency Reduction Is Associated With Higher Risk of Infection in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes: A Nationally Representative Cohort Study
Yohwan Lim, Hye Jun Kim, Sung Soo Yoon, Sang Jun Lee, Myeong Hoon Lee, Hyewon Park, Sun Jae Park, Seogsong Jeong, Hyun Wook Han
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Consuming Heat-Treated Dodamssal Brown Rice Containing Resistant Starch on Glucose Metabolism in Humans
Jiyoung Park, Sea-Kwan Oh, Miae Doo, Hyun-Jung Chung, Hyun-Jin Park, Hyejin Chun
Nutrients.2023; 15(10): 2248. CrossRef - Opening the Precision Diabetes Care through Digital Healthcare
Joonyub Lee, Jin Yu, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 307. CrossRef - Fatty Liver & Diabetes Statistics in Korea: Nationwide Data 2009 to 2017
Eugene Han, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-ho Lee, Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Jung Hwan Park, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 347. CrossRef - Trends in the Quality of Primary Care and Acute Care in Korea From 2008 to 2020: A Cross-sectional Study
Yeong Geun Gwon, Seung Jin Han, Kyoung Hoon Kim
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(3): 248. CrossRef - Development and Validation of Multiple Equations for Low-Density Lipoprotein and Apolipoprotein B in Korean Patients Visiting Local Clinics and Hospitals
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Nutrients.2023; 15(12): 2786. CrossRef - The role of retinal vessel geometry as an indicator of systemic arterial stiffness assessed by cardio-ankle vascular index
Dae Joong Ma, Heesun Lee, Ji Min Choi, Hyo Eun Park, Su-Yeon Choi, Hyuk Jin Choi
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between type 2 diabetes mellitus and depression among Korean midlife women: a cross-sectional analysis study
You Lee Yang, Eun-Ok Im, Yunmi Kim
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of updated cardiovascular health metrics, including sleep health, with incident diabetes and cardiovascular events in older adults with prediabetes: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Seung Jin Han
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110820. CrossRef - Paradigm Shift in Management of Hyperglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Glucocentric versus Organ Protection
Jong Chul Won
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(2): 59. CrossRef - Medical nutrition therapy for diabetes mellitus
Suk Chon
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 421. CrossRef - Prevalence and treatment status of diabetes mellitus in Korea
Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 404. CrossRef - The impact of diabetes status on total and site-specific cancer risk in the elderly population: A nationwide cohort study
Kyuho Kim, Bongseong Kim, Hyunho Kim, Hyung Soon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110866. CrossRef - Response to comments of Lai et al. “Proposal of one option for patient-centered, heterogeneous selection of antidiabetic drug”
Sunyoung Kim, Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110864. CrossRef - Association of Dental Diseases and Oral Hygiene Care With the Risk of Heart Failure in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Youn Huh, Jung Eun Yoo, Sang‐Hyun Park, Kyungdo Han, Seon Mee Kim, Hye Soon Park, Kyung Hwan Cho, Jin‐Soo Ahn, Sang Ho Jun, Ga Eun Nam
Journal of the American Heart Association.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bidirectional associations between periodontal disease and systemic diseases: a nationwide population-based study in Korea
Salma Nabila, Jaesung Choi, Ji-Eun Kim, Seokyung Hahn, In-Kyung Hwang, Tae-Il Kim, Hee-Kyung Park, Ji-Yeob Choi
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term Effectiveness of the National Diabetes Quality Assessment Program in South Korea
Ji Hye Huh, Serim Kwon, Gui Ok Kim, Bo Yeon Kim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(9): 1700. CrossRef - Refined Diagnostic Protocol for Diabetic Polyneuropathy: Paving the Way for Timely Detection
Byung-Mo Oh
Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine.2023; 47(4): 234. CrossRef - Analysis of difference in body fluid composition and dietary intake between Korean adults with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yu-Gyeong Kim, Ha-Neul Choi, Jung-Eun Yim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 377. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus in the Elderly Adults in Korea: Based on Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019 to 2020
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Yong-Moon Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Kyuho Kim, Jae-Hyun Bae, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Nan-Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 643. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Association between initial continuity of care status and diabetes-related health outcomes in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A nationwide retrospective cohort study in South Korea
Hyun Woo Jung, Woo-Ri Lee
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(6): 600. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef - Diagnostic performance of the fibrosis-4 index and the NAFLD fibrosis score for screening at-risk individuals in a health check-up setting
Huiyul Park, Eileen L. Yoon, Mimi Kim, Jonghyun Lee, Hye-Lin Kim, Seon Cho, Eun-Hee Nah, Dae Won Jun
Hepatology Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef - The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population
Sunghwan Suh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 522. CrossRef - Comparative Risk of Type 2 Diabetes after Gastrectomy and Endoscopic Resection for Gastric Cancer: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Yeongkeun Kwon, Jin-Won Kwon, Jiyun Kim, Dohyang Kim, Jinseub Hwang, Jane Ha, Shin-Hoo Park, Sungsoo Park
Journal of the American College of Surgeons.2023; 237(6): 902. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Evogliptin Add-on Therapy to Dapagliflozin/Metformin Combinations in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week Multicenter Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel-Design Phase-3 Trial with a 28-Week Extensio
Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Hae Jin Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Chang Won, Kyung Ah Han, Cheol-Young Park, Jong Chul Won, Dong Jun Kim, Gwan Pyo Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Chang Beom Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 808. CrossRef - Association between diabetes mellitus and cause of death in patients with tuberculosis: A Korean nationwide cohort study
Se Hyun Kwak, Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang, Frederick Quinn
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(12): e0295556. CrossRef - Strategies to Maintain the Remission of Diabetes Following Metabolic Surgery
Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Soon Kim
Journal of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery.2023; 12(2): 26. CrossRef - Anti-Diabetic Medications and Osteoporosis
Kyongyoung Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 173. CrossRef - The associations between changes in hepatic steatosis and heart failure and mortality: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Hasung Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: is it preventable?
Seung-Hyun Ko
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(3): 106. CrossRef - Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 552. CrossRef - Current status of obesity treatment in Korea: based on the 2020 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity guidelines for obesity management
Eun-Jung Rhee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(7): 388. CrossRef - 젊은 2형 당뇨병 환자의 관리
재현 배
Public Health Weekly Report.2022; 15(35): 2474. CrossRef - Analysis of the Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Renal Function in Middle-Aged Patients with Diabetes
Yoonjin Park, Su Jung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(18): 11832. CrossRef - The Degree of Glycemic Control for the First Three Months Determines the Next Seven Years
Nami Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Blood Pressure Target in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hyun-Jin Kim, Kwang-il Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 667. CrossRef - Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes
Yewon Na, Soo Wan Kim, Ie Byung Park, Soo Jung Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Jaehun Jung, Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(11): 3022. CrossRef - Education for Insulin Injection in Elderly Diabetic Patients
Gi Yeon Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(3): 201. CrossRef - Recent Updates on Phytoconstituent Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors: An Approach towards the Treatment of Type Two Diabetes
Hamdy Kashtoh, Kwang-Hyun Baek
Plants.2022; 11(20): 2722. CrossRef - Epidemiological characteristics of diabetes mellitus in Korea
Soon Young Lee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(10): 640. CrossRef - Screening for Prediabetes and Diabetes in Korean Nonpregnant Adults: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2022
Kyung Ae Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Suk Chon, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 819. CrossRef - Oldies but Goodies: Thiazolidinedione as an Insulin Sensitizer with Cardioprotection
Eun-Hee Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 827. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Acceptance Action in the Relationship between Diabetes Distress and Self-stigma among Old Adults with Diabetes in South Korea
Hyesun Kim, Kawoun Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(4): 446. CrossRef
- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
- Drug/Regimen
- Comparison of Serum Ketone Levels and Cardiometabolic Efficacy of Dapagliflozin versus Sitagliptin among Insulin-Treated Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Chi-Ho Lee, Mei-Zhen Wu, David Tak-Wai Lui, Darren Shing-Hei Chan, Carol Ho-Yi Fong, Sammy Wing-Ming Shiu, Ying Wong, Alan Chun-Hong Lee, Joanne King-Yan Lam, Yu-Cho Woo, Karen Siu-Ling Lam, Kelvin Kai-Hang Yiu, Kathryn Choon-Beng Tan
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):843-854. Published online April 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0319
- 4,992 View
- 257 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Insulin-treated patients with long duration of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are at increased risk of ketoacidosis related to sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor (SGLT2i). The extent of circulating ketone elevation in these patients remains unknown. We conducted this study to compare the serum ketone response between dapagliflozin, an SGLT2i, and sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, among insulin-treated T2DM patients.
Methods
This was a randomized, open-label, active comparator-controlled study involving 60 insulin-treated T2DM patients. Participants were randomized 1:1 for 24-week of dapagliflozin 10 mg daily or sitagliptin 100 mg daily. Serum β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) levels were measured at baseline, 12 and 24 weeks after intervention. Comprehensive cardiometabolic assessments were performed with measurements of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) cholesterol efflux capacity (CEC), vibration-controlled transient elastography and echocardiography.
Results
Among these 60 insulin-treated participants (mean age 58.8 years, diabetes duration 18.2 years, glycosylated hemoglobin 8.87%), as compared with sitagliptin, serum BHB levels increased significantly after 24 weeks of dapagliflozin (P=0.045), with a median of 27% increase from baseline. Change in serum BHB levels correlated significantly with change in free fatty acid levels. Despite similar glucose lowering, dapagliflozin led to significant improvements in body weight (P=0.006), waist circumference (P=0.028), HDL-C (P=0.041), CEC (P=0.045), controlled attenuation parameter (P=0.007), and liver stiffness (P=0.022). Average E/e’, an echocardiographic index of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction, was also significantly lower at 24 weeks in participants treated with dapagliflozin (P=0.037).
Conclusion
Among insulin-treated T2DM patients with long diabetes duration, compared to sitagliptin, dapagliflozin modestly increased ketone levels and was associated with cardiometabolic benefits. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Serum thrombospondin‐2 level changes with liver stiffness improvement in patients with type 2 diabetes
Jimmy Ho Cheung Mak, David Tak‐Wai Lui, Carol Ho‐Yi Fong, Chloe Yu‐Yan Cheung, Ying Wong, Alan Chun‐Hong Lee, Ruby Lai‐Chong Hoo, Aimin Xu, Kathryn Choon‐Beng Tan, Karen Siu‐Ling Lam, Chi‐Ho Lee
Clinical Endocrinology.2024; 100(3): 230. CrossRef - SGLT-2 inhibitors as novel treatments of multiple organ fibrosis
Junpei Hu, Jianhui Teng, Shan Hui, Lihui Liang
Heliyon.2024; 10(8): e29486. CrossRef - Effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter protein-2 inhibitors on left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Yao Wang, Yujie Zhong, Zhehao Zhang, Shuhao Yang, Qianying Zhang, Bingyang Chu, Xulin Hu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on hepatic fibrosis and steatosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Peipei Zhou, Ying Tan, Zhenning Hao, Weilong Xu, Xiqiao Zhou, Jiangyi Yu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 inhibitors on lipid profile: A meta-analysis of 28 randomized controlled trials
Gang Fan, Dian long Guo, Hong Zuo
European Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 959: 176087. CrossRef
- Serum thrombospondin‐2 level changes with liver stiffness improvement in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Abnormal Responses in Cognitive Impulsivity Circuits Are Associated with Glycosylated Hemoglobin Trajectories in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Impaired Metabolic Control
- Helena Jorge, Isabel C. Duarte, Sandra Paiva, Ana Paula Relvas, Miguel Castelo-Branco
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):866-878. Published online March 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0307
- 4,392 View
- 173 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Risky health decisions and impulse control profiles may impact on metabolic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). We hypothesize that the neural correlates of cognitive impulsivity and decision-making in T1DM relate to metabolic control trajectories.
Methods
We combined functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), measures of metabolic trajectories (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] over multiple time points) and behavioral assessment using a cognitive impulsivity paradigm, the Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART), in 50 participants (25 T1DM and 25 controls).
Results
Behavioral results showed that T1DM participants followed a rigid conservative risk strategy along the iterative game. Imaging group comparisons showed that patients showed larger activation of reward related, limbic regions (nucleus accumbens, amygdala) and insula (interoceptive saliency network) in initial game stages. Upon game completion differences emerged in relation to error monitoring (anterior cingulate cortex [ACC]) and inhibitory control (inferior frontal gyrus). Importantly, activity in the saliency network (ACC and insula), which monitors interoceptive states, was related with metabolic trajectories, which was also found for limbic/reward networks. Parietal and posterior cingulate regions activated both in controls and patients with adaptive decision-making, and positively associated with metabolic trajectories.
Conclusion
We found triple converging evidence when comparing metabolic trajectories, patients versus controls or risk averse (non-learners) versus patients who learned by trial and error. Dopaminergic reward and saliency (interoceptive and error monitoring) circuits show a tight link with impaired metabolic trajectories and cognitive impulsivity in T1DM. Activity in parietal and posterior cingulate are associated with adaptive trajectories. This link between reward-saliency-inhibition circuits suggests novel strategies for patient management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The usefulness of an intervention with a serious video game as a complementary approach to cognitive behavioural therapy in eating disorders: A pilot randomized clinical trial for impulsivity management
Cristina Vintró‐Alcaraz, Núria Mallorquí‐Bagué, María Lozano‐Madrid, Giulia Testa, Roser Granero, Isabel Sánchez, Janet Treasure, Susana Jiménez‐Murcia, Fernando Fernández‐Aranda
European Eating Disorders Review.2023; 31(6): 781. CrossRef - Adaptations of the balloon analog risk task for neuroimaging settings: a systematic review
Charline Compagne, Juliana Teti Mayer, Damien Gabriel, Alexandre Comte, Eloi Magnin, Djamila Bennabi, Thomas Tannou
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Trust-based health decision-making recruits the neural interoceptive saliency network which relates to temporal trajectories of Hemoglobin A1C in Diabetes Type 1
Helena Jorge, Isabel C. Duarte, Miguel Melo, Ana Paula Relvas, Miguel Castelo-Branco
Brain Imaging and Behavior.2023; 18(1): 171. CrossRef
- The usefulness of an intervention with a serious video game as a complementary approach to cognitive behavioural therapy in eating disorders: A pilot randomized clinical trial for impulsivity management
- COVID-19
- Association of Metabolic Syndrome with COVID-19 in the Republic of Korea
- Woo-Hwi Jeon, Jeong-Yeon Seon, So-Youn Park, In-Hwan Oh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):427-438. Published online November 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0105
- 4,423 View
- 242 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
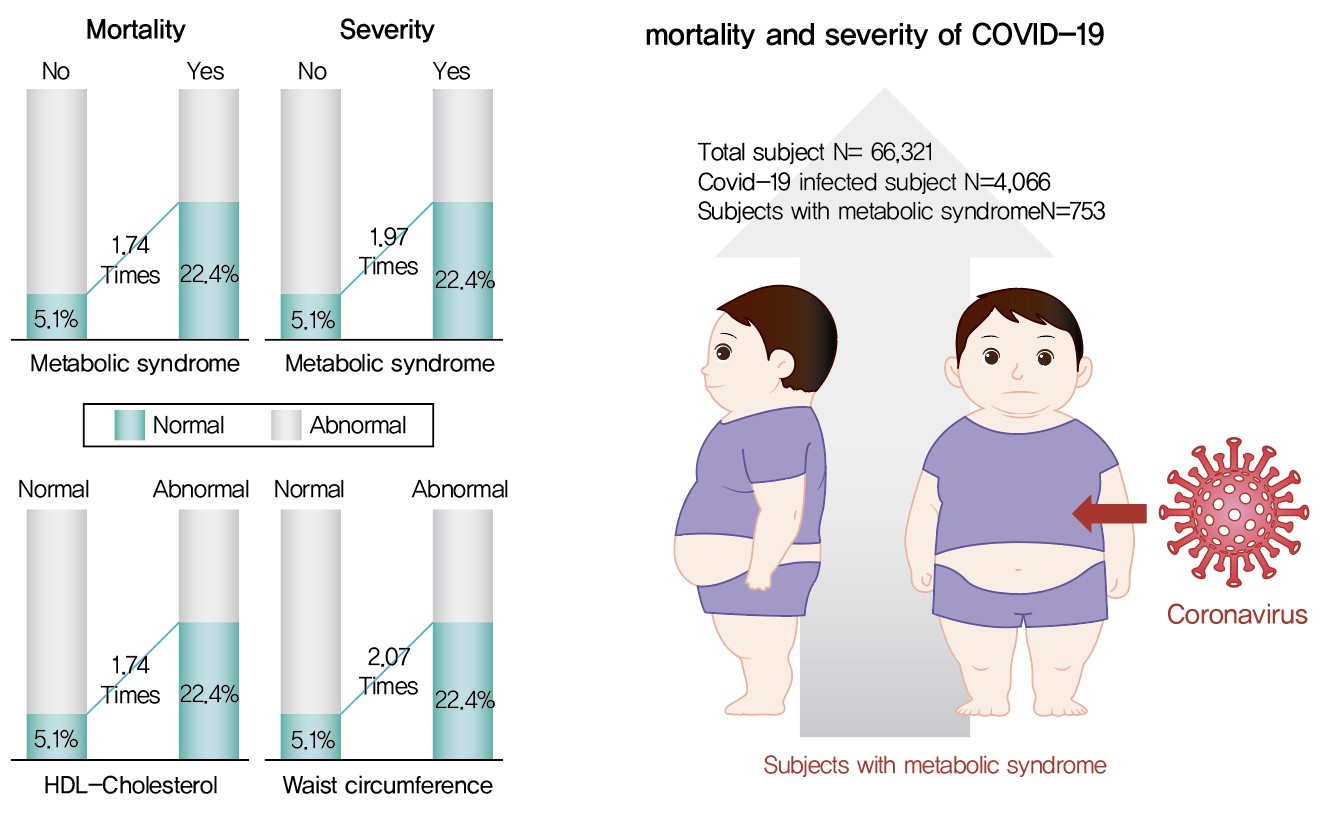
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is reportedly a crucial risk factor for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). Since the epidemiological studies that examine this association are few and include small samples, we investigated the relationship between MetS and COVID-19 severity and death using a larger sample in the Republic of Korea.
Methods
We analyzed 66,321 patients, 4,066 of whom had COVID-19. We used chi-square tests to examine patients’ characteristics. We performed logistic regression analysis to analyze differences in COVID-19 infection and clinical outcomes according to the presence of MetS.
Results
Although MetS was not significantly associated with COVID-19 risk, acquiring MetS was significantly associated with the risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes (odds ratio [OR], 1.97; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.34 to 2.91; P=0.001). The mortality risk was significantly higher in COVID-19 patients with MetS (OR, 1.74; 95% CI, 1.17 to 2.59; P=0.006). Patients with abnormal waist circumference were approximately 2.07 times more likely to develop severe COVID-19 (P<0.001), and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels were significantly associated with COVID-19; the mortality risk due to COVID-19 was 1.74 times higher in men with an HDL-C level of <40 mg/dL and in women with an HDL-C level of <50 mg/dL (P=0.012).
Conclusion
COVID-19 is likely associated with severity and death in patients with MetS or in patients with MetS risk factors. Therefore, patients with MetS or those with abnormal waist circumference and HDL-C levels need to be treated with caution. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Heterogeneity in familial clustering of metabolic syndrome components in the multiethnic GENNID study
Jia Y. Wan, Deborah Goodman, Sukh Makhnoon, Trina M. Norden‐Krichmar, Baolin Wu, Karen L. Edwards
Obesity.2024; 32(1): 176. CrossRef - Associated Factors with Changes of Metabolic Abnormalities among General Population in COVID-19 Pandemic
Eunjoo Kwon, Eun-Hee Nah, Suyoung Kim, Seon Cho, Hyeran Park
Korean Journal of Health Promotion.2023; 23(2): 55. CrossRef - Association between metabolic syndrome and mortality in patients with COVID-19: A nationwide cohort study
Hyo Jin Park, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyungdo Han, Jean Shin, Yoojeong Lee, Yujin Chang, Kyeyeung Park, Yoon Jeong Cho, Youn Seon Choi, Seon Mee Kim, Ga Eun Nam
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2022; 16(6): 484. CrossRef
- Heterogeneity in familial clustering of metabolic syndrome components in the multiethnic GENNID study
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Performance of Diabetes and Kidney Disease Screening Scores in Contemporary United States and Korean Populations
- Liela Meng, Keun-Sang Kwon, Dae Jung Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Jeehyoung Kim, Abhijit V. Kshirsagar, Heejung Bang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):273-285. Published online September 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0054
- 65,535 View
- 238 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Risk assessment tools have been actively studied, and they summarize key predictors with relative weights/importance for a disease. Currently, standardized screening scores for type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) and chronic kidney disease (CKD)—two key global health problems—are available in United States and Korea. We aimed to compare and evaluate screening scores for DM (or combined with prediabetes) and CKD, and assess the risk in contemporary United States and Korean populations.
Methods
Four (2×2) models were evaluated in the United States-National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES 2015–2018) and Korea-NHANES (2016–2018)—8,928 and 16,209 adults. Weighted statistics were used to describe population characteristics. We used logistic regression for predictors in the models to assess associations with study outcomes (undiagnosed DM and CKD) and diagnostic measures for temporal and cross-validation.
Results
Korean adult population (mean age 47.5 years) appeared to be healthier than United States counterpart, in terms of DM and CKD risks and associated factors, with exceptions of undiagnosed DM, prediabetes and prehypertension. Models performed well in own country and external populations regarding predictor-outcome association and discrimination. Risk tests (high vs. low) showed area under the curve >0.75, sensitivity >84%, specificity >45%, positive predictive value >8%, and negative predictive value >99%. Discrimination was better for DM, compared to the combined outcome of DM and prediabetes, and excellent for CKD due to age.
Conclusion
Four easy-to-use screening scores for DM and CKD are well-validated in contemporary United States and Korean populations. Prevention of DM and CKD may serve as first-step in public health, with these self-assessment tools as basic tools to help health education and disparity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A meta‐analysis of diabetes risk prediction models applied to prediabetes screening
Yujin Liu, Sunrui Yu, Wenming Feng, Hangfeng Mo, Yuting Hua, Mei Zhang, Zhichao Zhu, Xiaoping Zhang, Zhen Wu, Lanzhen Zheng, Xiaoqiu Wu, Jiantong Shen, Wei Qiu, Jianlin Lou
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(5): 1593. CrossRef - Performance Analysis and Assessment of Type 2 Diabetes Screening Scores in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Norma Latif Fitriyani, Muhammad Syafrudin, Siti Maghfirotul Ulyah, Ganjar Alfian, Syifa Latif Qolbiyani, Chuan-Kai Yang, Jongtae Rhee, Muhammad Anshari
Mathematics.2023; 11(10): 2266. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Analysis of Chinese, Japanese, Korean, US-PIMA Indian, and Trinidadian Screening Scores for Diabetes Risk Assessment and Prediction
Norma Latif Fitriyani, Muhammad Syafrudin, Siti Maghfirotul Ulyah, Ganjar Alfian, Syifa Latif Qolbiyani, Muhammad Anshari
Mathematics.2022; 10(21): 4027. CrossRef
- A meta‐analysis of diabetes risk prediction models applied to prediabetes screening
Review
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Management of Cardiovascular Risk in Perimenopausal Women with Diabetes
- Catherine Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):492-501. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0262
- 5,649 View
- 154 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
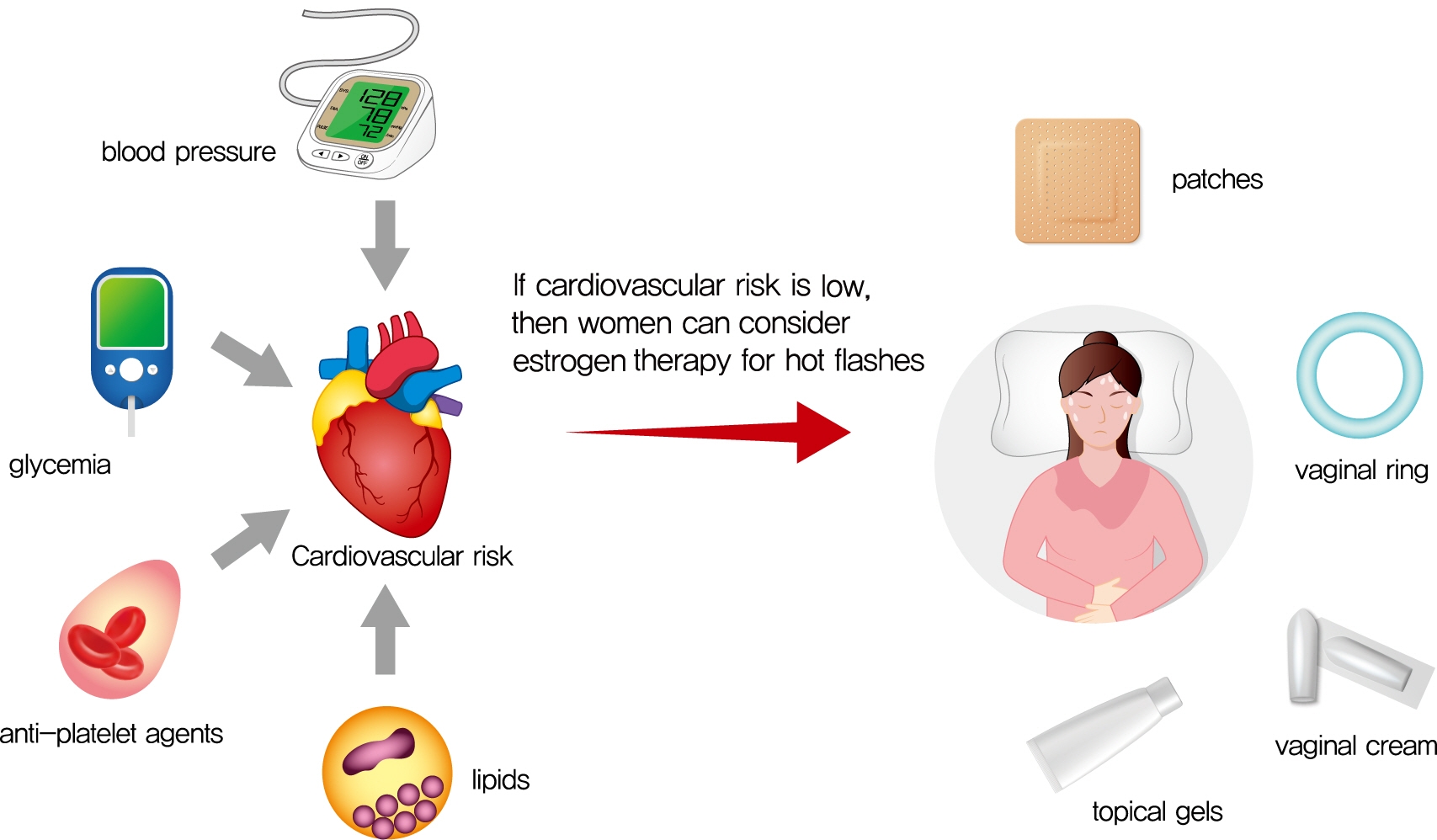
- Cardiovascular disease is the primary cause of mortality in women and men with diabetes. Due to age and worsening of risk factors over the menopausal transition, risk of coronary heart disease events increases in postmenopausal women with diabetes. Randomized studies have conflicted regarding the beneficial impact of estrogen therapy upon intermediate cardiovascular disease markers and events. Therefore, estrogen therapy is not currently recommended for indications other than symptom management. However, for women at low risk of adverse events, estrogen therapy can be used to minimize menopausal symptoms. The risk of adverse events can be estimated using risk engines for the calculation of cardiovascular risk and breast cancer risk in conjunction with screening tools such as mammography. Use of estrogen therapy, statins, and anti-platelet agents can be guided by such calculators particularly for younger women with diabetes. Risk management remains focused upon lifestyle behaviors and achieving optimal levels of cardiovascular risk factors, including lipids, glucose, and blood pressure. Use of pharmacologic therapies to address these risk factors, particularly specific hypoglycemic agents, may provide some additional benefit for risk prevention. The minimal benefit for women with limited life expectancy and risk of complications with intensive therapy should also be considered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurse-led intervention in the management of patients with cardiovascular diseases: a brief literature review
Xiaoqin Qiu
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Determination of the Level of Cardiovascular Risk in 172,282 Spanish Working Women
Ángel Arturo López-González, María Albaladejo Blanco, Cristina Vidal Ribas, Pilar Tomás-Gil, Pere Riutord Sbert, José Ignacio Ramírez-Manent
Diagnostics.2023; 13(17): 2734. CrossRef - Comparison of seven surrogate insulin resistance indexes for predicting the prevalence of carotid atherosclerosis in normal-weight individuals
Zeyu Liu, Bi Deng, Qin Huang, Ruxin Tu, Fang Yu, Jian Xia, Jie Feng
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications
Joon Ho Moon, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 3. CrossRef - Reproductive Life Span and Severe Hypoglycemia Risk in Postmenopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Soyeon Kang, Yong-Moon Park, Dong Jin Kwon, Youn-Jee Chung, Jeong Namkung, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 578. CrossRef - Global hotspots and prospects of perimenopausal depression: A bibliometric analysis via CiteSpace
Mingzhou Gao, Hao Zhang, Zhan Gao, Ya Sun, Jieqiong Wang, Fengqin Wei, Dongmei Gao
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - State of metabolic processes and ways to improve them in premenopausal women due to the life extension strategy
I.V. Lakhno
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY.2021; (61): 51. CrossRef
- Nurse-led intervention in the management of patients with cardiovascular diseases: a brief literature review
Original Article
- Complications
- Screening Tools Based on Nomogram for Diabetic Kidney Diseases in Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Ganyi Wang, Biyao Wang, Gaoxing Qiao, Hao Lou, Fei Xu, Zhan Chen, Shiwei Chen
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):708-718. Published online April 13, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0117
- 6,913 View
- 141 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
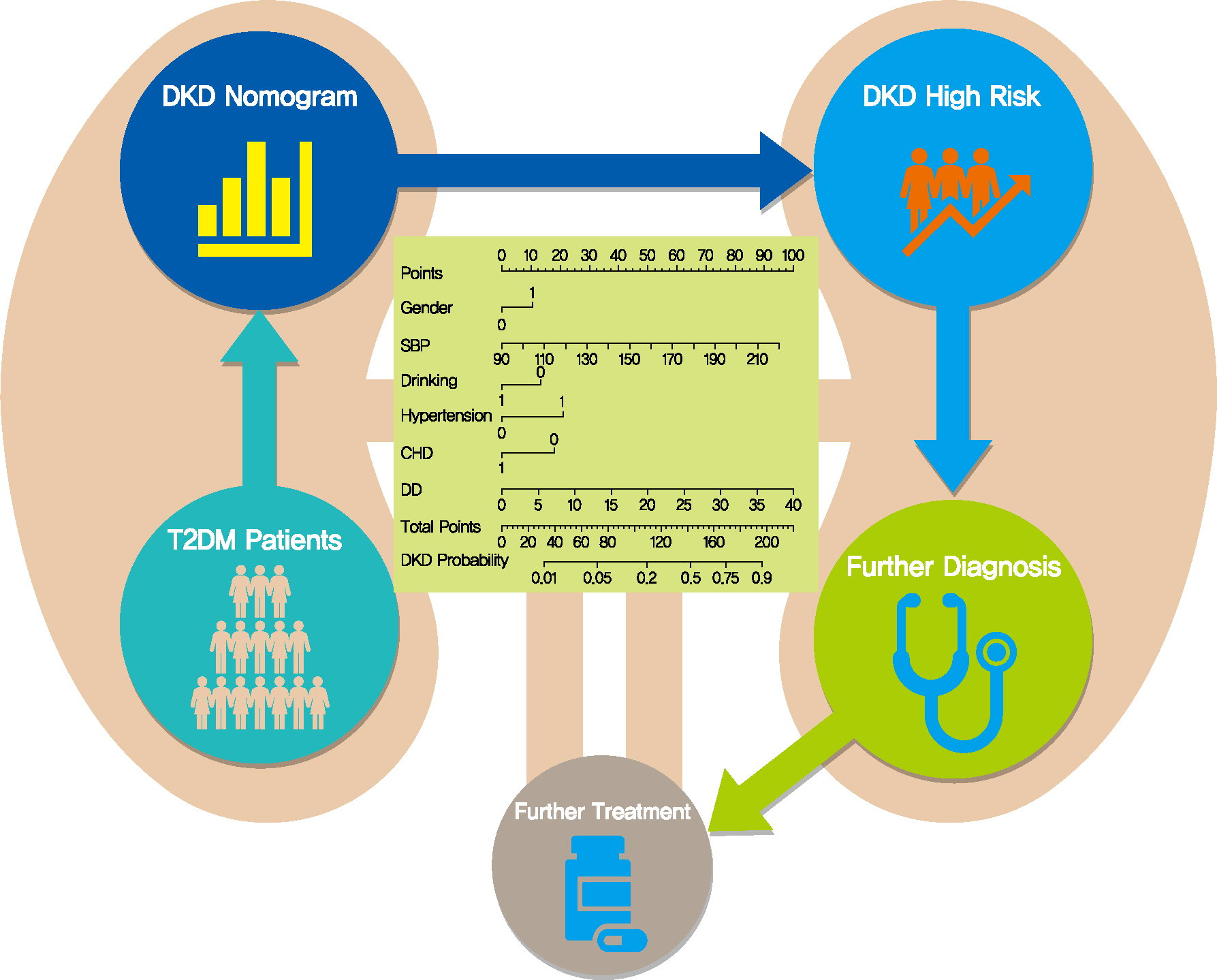
- Background
The influencing factors of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) were explored to develop and validate a DKD diagnostic tool based on nomogram approach for patients with T2DM.
Methods
A total of 2,163 in-hospital patients with diabetes diagnosed from March 2015 to March 2017 were enrolled. Specified logistic regression models were used to screen the factors and establish four different diagnostic tools based on nomogram according to the final included variables. Discrimination and calibration were used to assess the performance of screening tools.
Results
Among the 2,163 participants with diabetes (1,227 men and 949 women), 313 patients (194 men and 120 women) were diagnosed with DKD. Four different screening equations (full model, laboratory-based model 1 [LBM1], laboratory-based model 2 [LBM2], and simplified model) showed good discriminations and calibrations. The C-indexes were 0.8450 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.8202 to 0.8690) for full model, 0.8149 (95% CI, 0.7892 to 0.8405) for LBM1, 0.8171 (95% CI, 0.7912 to 0.8430) for LBM2, and 0.8083 (95% CI, 0.7824 to 0.8342) for simplified model. According to Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test, good agreement between the predicted and observed DKD events in patients with diabetes was observed for full model (χ2=3.2756, P=0.9159), LBM1 (χ2=7.749, P=0.4584), LBM2 (χ2=10.023, P=0.2634), and simplified model (χ2=12.294, P=0.1387).
Conclusion
LBM1, LBM2, and simplified model exhibited excellent predictive performance and availability and could be recommended for screening DKD cases among Chinese patients with diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Development of Serum Lactate Level-Based Nomograms for Predicting Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Chunxia Jiang, Xiumei Ma, Jiao Chen, Yan Zeng, Man Guo, Xiaozhen Tan, Yuping Wang, Peng Wang, Pijun Yan, Yi Lei, Yang Long, Betty Yuen Kwan Law, Yong Xu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2024; Volume 17: 1051. CrossRef - Changes in urinary exosomal protein CALM1 may serve as an early noninvasive biomarker for diagnosing diabetic kidney disease
Tao Li, Tian ci Liu, Na Liu, Man Zhang
Clinica Chimica Acta.2023; 547: 117466. CrossRef - Developing screening tools to estimate the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Xu Cao, Xiaomei Pei
Technology and Health Care.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Development and validation of a novel nomogram to predict diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetic mellitus and proteinuric kidney disease
Hui Zhuan Tan, Jason Chon Jun Choo, Stephanie Fook-Chong, Yok Mooi Chin, Choong Meng Chan, Chieh Suai Tan, Keng Thye Woo, Jia Liang Kwek
International Urology and Nephrology.2022; 55(1): 191. CrossRef - Nomogram-Based Chronic Kidney Disease Prediction Model for Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Patients Using Routine Pathological Data
Nakib Hayat Chowdhury, Mamun Bin Ibne Reaz, Sawal Hamid Md Ali, Shamim Ahmad, María Liz Crespo, Andrés Cicuttin, Fahmida Haque, Ahmad Ashrif A. Bakar, Mohammad Arif Sobhan Bhuiyan
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(9): 1507. CrossRef - Development and assessment of diabetic nephropathy prediction model using hub genes identified by weighted correlation network analysis
Xuelian Zhang, Yao Wang, Zhaojun Yang, Xiaoping Chen, Jinping Zhang, Xin Wang, Xian Jin, Lili Wu, Xiaoyan Xing, Wenying Yang, Bo Zhang
Aging.2022; 14(19): 8095. CrossRef
- Development of Serum Lactate Level-Based Nomograms for Predicting Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Review
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Diabetes Management in Patients with Heart Failure
- Jia Shen, Barry H. Greenberg
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):158-172. Published online March 25, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0296

- 8,077 View
- 493 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Diabetes and heart failure (HF) are common diseases, each affecting large segments of the world population. Moreover, prevalence rates for both are expected to rise dramatically over coming decades. The high prevalence rates of both diseases and wellrecognized association of diabetes as a risk factor for HF make it inevitable that both diseases co-exist in a large number of patients, complicating their management and increasing the risk of a poor outcome. Management of diabetes has been shown to impact clinical events in patients with HF and there is emerging evidence that agents used to treat diabetes can reduce HF events, even in non-diabetic patients. In this review we summarize the clinical course and treatment of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and HF and review the efficacy and safety of pharmacological agents in patients with T2DM at risk for HF and those with established disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Letter to Editor From Banerjee et al: “Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Across the Spectrum of Heart Failure”
Mainak Banerjee, Indira Maisnam, Satinath Mukhopadhyay
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(2): e873. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Prevalence and management of hyperkalemia in chronic kidney disease and heart failure patients in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC)
Ali AlSahow, Mohammad AbdulShafy, Saeed Al‐Ghamdi, Harith AlJoburi, Osama AlMogbel, Fadel Al‐Rowaie, Nizar Attallah, Feras Bader, Hisham Hussein, Mohamed Hassan, Khaldoun Taha, Matthew R. Weir, Faiez Zannad
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2023; 25(3): 251. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Prescription appropriateness of anti-diabetes drugs in elderly patients hospitalized in a clinical setting: evidence from the REPOSI Register
Elena Succurro, Alessio Novella, Alessandro Nobili, Federica Giofrè, Franco Arturi, Angela Sciacqua, Francesco Andreozzi, Antonello Pietrangelo, Giorgio Sesti, Francesco Perticone, Francesco Violi, Salvatore Corrao, Alessandra Marengoni, Mauro Tettamanti,
Internal and Emergency Medicine.2023; 18(4): 1049. CrossRef - Re-evaluation of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in patients with heart failure and diabetes mellitus
Jiaoran Li, Yanping Liu, Panpan Hao
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 202: 110798. CrossRef - Managing heart failure in diabetics with dual acting sotagliflozin—A review
Kushal Seni, Pooja A Chawla
Health Sciences Review.2023; 9: 100130. CrossRef - Effect of Integrated Care on Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials
Yi Li, Wenjing Zhao, Jun Huang, Murui Zheng, Peng Hu, Jiahai Lu, Hai Deng, Xudong Liu
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Pharmacological treatment of type 2 diabetes in elderly patients with heart failure: randomized trials and beyond
Angela Sciacqua, Elena Succurro, Giuseppe Armentaro, Sofia Miceli, Daniele Pastori, Giuseppe Rengo, Giorgio Sesti
Heart Failure Reviews.2021; 28(3): 667. CrossRef
- Letter to Editor From Banerjee et al: “Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Across the Spectrum of Heart Failure”
Original Article
- Complications
- High Incidence of Chronic Kidney Disease among Iranian Diabetic Adults: Using CKD-EPI and MDRD Equations for Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate
- Seyyed Saeed Moazzeni, Reyhane Hizomi Arani, Mitra Hasheminia, Maryam Tohidi, Fereidoun Azizi, Farzad Hadaegh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):684-697. Published online March 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0109
- 5,823 View
- 157 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
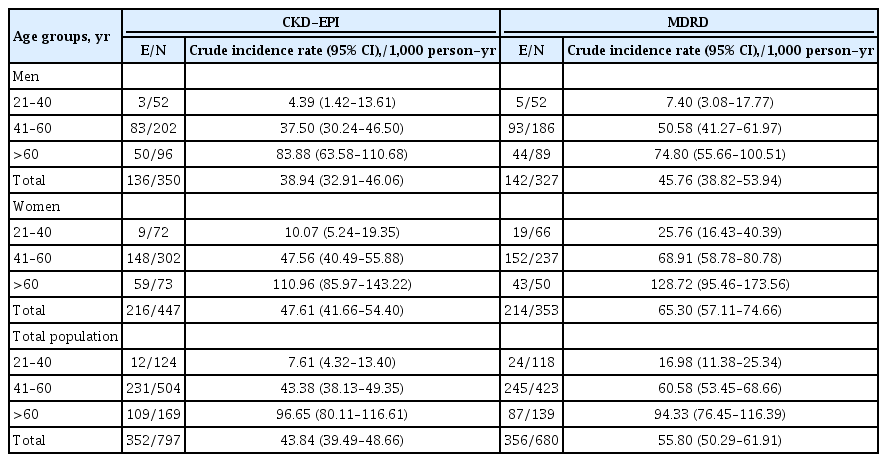
ePub - Background
To investigate the population based incidence rate of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and its potential risk factors among Iranian diabetic adults during over 14 years of follow-up.
Methods
Two different equations (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration [CKD-EPI] and Modification of Diet in Renal Disease [MDRD]) were applied for the calculating the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Among a total of 1,374 diabetic Tehranian adults, 797 and 680 individuals were eligible for CKD-EPI and MDRD analyses, respectively. CKD was defined as eGFR lower than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Multivariable Cox proportional hazard models were used to estimate the hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for all potential risk factors.
Results
The incidence rates (95% CI) of CKD per 1,000 person-years were 43.84 (39.49 to 48.66) and 55.80 (50.29 to 61.91) based on CKD-EPI and MDRD equations, respectively. Being older, a history of cardiovascular disease, and having lower levels of eGFR were significant risk factors in both equations. Moreover, in CKD-EPI, using glucose-lowering medications and hypertension, and in MDRD, female sex and fasting plasma glucose ≥10 mmol/L were also independent risk factors. Regarding the discrimination index, CKD-EPI equation showed a higher range of C-index for the predicted probability of incident CKD in the full-adjusted model, compared to MDRD equation (0.75 [0.72 to 0.77] vs. 0.69 [0.66 to 0.72]).
Conclusion
We found an incidence rate of more than 4%/year for CKD development among our Iranian diabetic population. Compared to MDRD, it can be suggested that CKD-EPI equation can be a better choice to use for prediction models of incident CKD among the Iranian diabetic populations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of the Holy Quran Recitation on Inflammatory Markers in Hemodialysis Patients in Iran: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Maedeh Teimourzadeh, Hassan Babamohamadi, Maliheh Yarmohamadi, Raheb Ghorbani, Harold G. Koenig
Journal of Religion and Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of anemia and its associated factors among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a referral diabetic clinic in the north of Iran
Reyhane Hizomi Arani, Farima Fakhri, Mohammad Naeimi Tabiee, Fatemeh Talebi, Zahra Talebi, Negin Rashidi, Maryam Zahedi
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between fasting plasma glucose variability and incident eGFR decline: evidence from two cohort studies
Niloofar Deravi, Yasaman Sharifi, Fatemeh Koohi, Seyed Saeed Tamehri Zadeh, Soroush Masrouri, Fereidoun Azizi, Farzad Hadaegh
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Low LncRNA LUCAT1 Expression Assists in the Diagnosis of Chronic Heart Failure and Predicts Poor Prognosis
Jian Wang, Xujin Wu, Li Wang, Chengyong Zhao
International Heart Journal.2023; 64(3): 409. CrossRef - Comparison of eGFR formulas (CKD-EPI and MDRD) in patients with multiple myeloma
Osman ERİNÇ, Soner YEŞİLYURT, Meliha NALCACİ
Cukurova Medical Journal.2023; 48(2): 336. CrossRef - Comparison and evaluation of the 2009 and 2021 chronic kidney disease-epidemiological collaboration equations among Jordanian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Randa I. Farah, Abdulrahman Alhajahjeh, Oraib Al-farahid, Hana Abuzaid, Dana Hiasat, Rama Rayyan, Laith Bdier, Izzat AlAwwa, Kamel Ajlouni
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 61(2): 169. CrossRef - Effect of teaching health-promoting behaviors on the care burden of family caregivers of hemodialysis patients: a four-group clinical trial
Mehrdad Hayati, Razieh Bagherzadeh, Mehdi Mahmudpour, Fatemeh Heidari, Hakimeh Vahedparast
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of social and clinical factors on the diagnostic delay of chronic kidney disease: an evaluation study
Mousa Ghelichi-Ghojogh, Mohammad fararouei, Mozhgan Seif, Bahram Shahryari, Maryam Pakfetrat
International Urology and Nephrology.2022; 54(7): 1603. CrossRef - Chronic kidney disease and its health-related factors: a case-control study
Mousa Ghelichi-Ghojogh, Mohammad Fararouei, Mozhgan Seif, Maryam Pakfetrat
BMC Nephrology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidence and risk factors of severe non‐proliferative/proliferative diabetic retinopathy: More than a decade follow up in the Tehran Lipids and Glucose Study
Mahsa Sardarinia, Samaneh Asgari, Reyhane Hizomi Arani, Fatemeh Eskandari, Fereidoun Azizi, Davood Khalili, Farzad Hadaegh
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(2): 317. CrossRef - Pathophysiologic Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Chan-Young Jung, Tae-Hyun Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 181. CrossRef - Prevalence of chronic kidney diseases and its determinants among Iranian adults: results of the first phase of Shahedieh cohort study
Ali Dehghani, Sadegh Alishavandi, Nader Nourimajalan, Hossein Fallahzadeh, Vahid Rahmanian
BMC Nephrology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Construct a classification decision tree model to select the optimal equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate and estimate it more accurately
Zhenliang Fan, Qiaorui Yang, Zhuohan Xu, Ke Sun, Mengfan Yang, Riping Yin, Dongxue Zhao, Junfen Fan, Hongzhen Ma, Yiwei Shen, Hong Xia
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel biomarkers for diabetic kidney disease
Chan-Young Jung, Tae-Hyun Yoo
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 41(Suppl 2): S46. CrossRef - Prevalence and Associated Factors of Kidney Dysfunction in Patients with Hypertension and/or Diabetes Mellitus from a Primary Care Population in Northwest China
Mengyue Lin, Mulalibieke Heizhati, Lin Wang, Lin Gan, Mei Li, Wenbo Yang, Ling Yao, Zhongrong Wang, Zhikang Yang, Reyila Abudoyreyimu, Zihao Wu, Nanfang Li
International Journal of General Medicine.2021; Volume 14: 7567. CrossRef
- The Effect of the Holy Quran Recitation on Inflammatory Markers in Hemodialysis Patients in Iran: A Randomized Clinical Trial

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





