- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 46(3); 2022 > Article
-
Original ArticleGuideline/Fact Sheet Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2021
-
Jae Hyun Bae1*
 , Kyung-Do Han2*
, Kyung-Do Han2* , Seung-Hyun Ko3, Ye Seul Yang4, Jong Han Choi5, Kyung Mook Choi6, Hyuk-Sang Kwon7
, Seung-Hyun Ko3, Ye Seul Yang4, Jong Han Choi5, Kyung Mook Choi6, Hyuk-Sang Kwon7 , Kyu Chang Won8
, Kyu Chang Won8 , on Behalf of the Committee of Media-Public Relation of the Korean Diabetes Association
, on Behalf of the Committee of Media-Public Relation of the Korean Diabetes Association -
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2022;46(3):417-426.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0106
Published online: May 25, 2022
1Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Department of Statistics and Actuarial Science, Soongsil University, Seoul, Korea
3Department of Internal Medicine, St. Vincent’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Suwon, Korea
4Department of Internal Medicine, Uijeongbu St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Uijeongbu, Korea
5Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University Medical Center, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
6Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
7Department of Internal Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
8Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea
-
Corresponding authors: Hyuk-Sang Kwon
 Department of Internal Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, 10 63-ro, Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul 07345, Korea E-mail: drkwon@catholic.ac.kr
Department of Internal Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, 10 63-ro, Yeongdeungpo-gu, Seoul 07345, Korea E-mail: drkwon@catholic.ac.kr -
Kyu Chang Won
 Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, 170 Hyeonchung-ro, Nam-gu, Daegu 42415, Korea E-mail: kcwon@med.yu.ac.kr
Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University Medical Center, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, 170 Hyeonchung-ro, Nam-gu, Daegu 42415, Korea E-mail: kcwon@med.yu.ac.kr - *Jae Hyun Bae and Kyung-Do Han contributed equally to this study as first authors.
Copyright © 2022 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- This study aimed to investigate the prevalence and management of diabetes mellitus, risk-factor control, and comorbidities among Korean adults.
-
Methods
- We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey to assess the prevalence, treatment, risk factors, comorbidities, and self-management behaviors of diabetes mellitus from 2019 to 2020. We also analyzed data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service to evaluate the use of antidiabetic medications in people with diabetes mellitus from 2002 through 2018.
-
Results
- Among Korean adults aged 30 years or older, the estimated prevalence of diabetes mellitus was 16.7% in 2020. From 2019 through 2020, 65.8% of adults with diabetes mellitus were aware of the disease and treated with antidiabetic medications. The percentage of adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) <6.5% was 24.5% despite the increased use of new antidiabetic medications. We found that adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved all three goals of HbA1c <6.5%, blood pressure (BP) <140/85 mm Hg, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol <100 mg/dL were 9.7%. The percentage of self-management behaviors was lower in men than women. Excess energy intake was observed in 16.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus.
-
Conclusion
- The prevalence of diabetes mellitus among Korean adults remained high. Only 9.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus achieved all glycemic, BP, and lipid controls from 2019 to 2020. Continuous evaluation of national diabetes statistics and a national effort to increase awareness of diabetes mellitus and improve comprehensive diabetes care are needed.
- Diabetes mellitus is a major public health problem, leading to morbidity, disability, and mortality globally, with rapidly growing incidence and prevalence [1]. According to the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 537 million adults aged 20 to 79 years had diabetes worldwide in 2021, and the number is estimated to rise to 783 million by 2045 [2]. The causes of the diabetes epidemic are complex, and overweight and obesity, unhealthy diets, and physical inactivity influence the development of diabetes mellitus, in conjunction with genetic and epigenetic predispositions [3]. Therefore, valid and reliable assessments of disease status, risk factors, and comorbidities are essential to reduce the burden of diabetes mellitus.
- Coping with a rise in diabetes mellitus, the Korean Diabetes Association (KDA) has published the Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea since 2012 to provide representative national statistics on diabetes mellitus. Previous reports showed that approximately one out of seven Korean adults aged 30 years or older and three out of 10 aged 65 years had diabetes mellitus and poor glycemic and risk-factor controls [4,5]. In the Korean National Burden of Disease study, diabetes mellitus ranked the highest cause of disability-adjusted life years [6], which further increased given diabetic complications [7]. These findings warrant immediate action to halt the diabetes epidemic in Korea. The importance of managing diabetes mellitus is further heightened during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic because numerous studies showed that diabetes mellitus was associated with an increased risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes [8-11]. On the other hand, preclinical studies reported that severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection might elicit impaired β-cell function [12] or insulin resistance [13]. In addition, the COVID-19 pandemic could have indirect effects on diabetes management by affecting the diagnoses and monitoring of diabetes mellitus [14]. Approval of new antidiabetic medications and changes in clinical practice guidelines based on recent clinical trials also impact diabetes care and support [15,16]. In this respect, understanding the current status of diabetes mellitus has important clinical and public health implications.
- We aimed to investigate the prevalence and management of diabetes mellitus, risk-factor control, and comorbidities among Korean adults and update the Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2020 [17]. In this study, we analyzed data from Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) and the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) to provide representative national estimates of diabetes mellitus.
INTRODUCTION
- Study design and data collection
- We analyzed data from the KNHANES (2019 and 2020) and the Korean NHIS (2002 through 2018). The KNHANES is a series of nationally representative, cross-sectional surveys designed to evaluate health behaviors, health status, and food and nutrient intake of the Korean population [18]. Data are collected from health interviews, health examinations, and nutrition surveys. The response rate for health interviews and health examinations was 71.0% and for nutritional surveys was 79.3% in 2019. We used the KNHANES data to evaluate the prevalence of diabetes mellitus among adults aged 19 years or older and risk-factor control, comorbidities, and self-management behaviors among adults aged 30 years or older. The Korean NHIS is a single, compulsory health insurance system managed by the Korean government, providing healthcare coverage to almost the entire Korean population [19]. The Korean NHIS database includes sociodemographic information, use of medical services, medical claims, and health examinations. We examined the use of antidiabetic medications among adults aged 30 years or older with diabetes mellitus using the Korean NHIS data. We defined diabetes mellitus as the tenth revision of the International Classification of Diseases codes E11–E14 and at least one prescription of antidiabetic medications. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Korea University Anam Hospital (IRB No. 2022AN-0146). Informed consent was waived by the board.
- Definition of diabetes mellitus and comorbidities
- We defined diabetes mellitus as having fasting plasma glucose (FPG) ≥126 mg/dL or glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥6.5% or a previous diagnosis of diabetes mellitus or taking medications for diabetes mellitus [20]. Prediabetes was defined as an FPG of 100 to 125 mg/dL or an HbA1c of 5.7% to 6.4% [16]. We defined hypertension as systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥90 mm Hg or taking antihypertensive medications [20]. We defined hyper-low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterolemia as low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) ≥100 mg/dL or taking lipid-lowering medications [5]. Overweight and obesity were defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 23.0–24.9 and ≥25.0 kg/m2, respectively [16]. Abdominal obesity was defined as waist circumference ≥90 cm in men and ≥85 cm in women [21].
- Risk factors and self-management behaviors
- We defined awareness of diabetes mellitus as the percentage of people previously diagnosed with diabetes mellitus among people with diabetes mellitus [20]. We defined the treatment rate of diabetes mellitus as the percentage of people taking antidiabetic medications among people with diabetes mellitus [20]. The control rate of diabetes mellitus was defined as the percentage of people with HbA1c <6.5% among people with diabetes mellitus [16]. We defined blood pressure (BP) control as SBP <140 mm Hg and DBP <85 mm Hg [16]. We defined lipid control as LDL-C <100 mg/dL [16].
- Current smoking was defined as having smoked five packs (or 100 cigarettes) in his or her lifetime and currently smoking cigarettes [20]. High-risk alcohol consumption was defined as more than seven drinks twice a week for men and more than five for women [20]. Regular walking was defined as a minimum of 30 minutes a day of walking five or more days per week [20]. Excess energy intake was defined as 125% or more of the estimated energy requirement recommended by the Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2015 [22]. We calculated the percentages of energy intake from macronutrients (carbohydrates, protein, and fat) as previously reported [17].
- Use of antidiabetic medications
- We evaluated the management of diabetes mellitus as insulin, oral glucose-lowering medications, non-pharmacologic treatment, and no treatment using a health interview survey of the KNHANES. In addition, we analyzed claims data from the Korean NHIS to further assess changes in the prescription of antidiabetic medication classes (metformin, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 [SGLT2] inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide-1 [GLP-1] receptor agonists, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 [DPP-4] inhibitors, thiazolidinediones, α-glucosidase inhibitors, sulfonylureas/glinides, and insulin) in people with diabetes mellitus from 2002 through 2018.
- Statistical analysis
- We examined descriptive statistics for diabetes mellitus among adult KNHANES and Korean NHIS participants. The estimated prevalence of diabetes mellitus was presented as mean and standard error. The proportions of comorbidities, risk-factor control, and self-management behaviors were presented as percentages. Statistical analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA).
METHODS
- Prevalence of diabetes mellitus
- Among Korean adults aged 30 years or older, approximately 6.05 million people, or 16.7% (19.2% in men and 14.3% in women), had diabetes mellitus in 2020 (Table 1). When defined based on FPG alone, the estimated prevalence of diabetes mellitus was 14.5% (16.8% in men and 12.3% in women). The estimated prevalence of diabetes mellitus among adults aged 19 years or older and aged 65 years was 13.9% (15.8% in men and 12.1% in women) and 30.1% (29.8% in men and 30.2% in women), respectively. The prevalence of diabetes mellitus increased with increasing age. The prevalence of diabetes mellitus was higher in adults with lower equivalized household incomes. Among adults aged 30 years or older, approximately 15.83 million people, or 44.0% (46.9% in men and 41.2% in women), had prediabetes in 2020 (Supplementary Table 1). The estimated prevalence of impaired fasting glucose, defined as an FPG of 100 to 125 mg/dL, was 26.9% (33.1% in men and 20.8% in women). The estimated prevalence of prediabetes among adults aged 19 years or older and aged 65 years was 39.3% (42.3% in men and 36.3% in women) and 50.0% (51.0% in men and 49.1% in women), respectively.
- Diabetes management
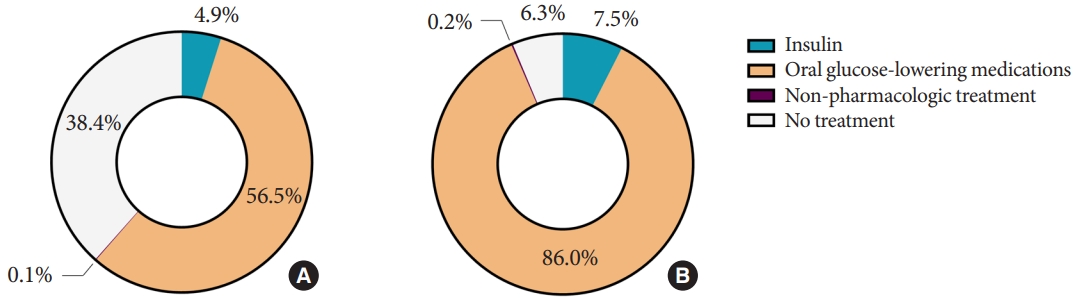
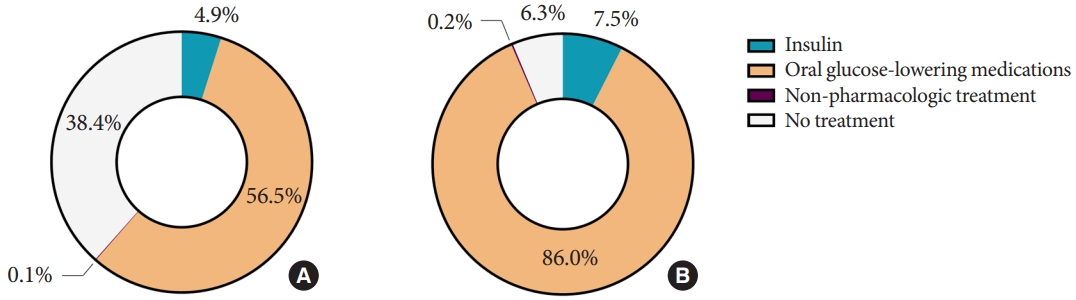
- From 2019 through 2020, awareness of diabetes mellitus in adults was 65.8%, and 61.4% of adults with diabetes mellitus were receiving oral glucose-lowering medications or insulin (Table 2). The proportion of adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved an HbA1c target of <6.5% was 24.5%. We found that 86.0% of adults with previously diagnosed diabetes mellitus were taking oral glucose-lowering medications without insulin, and 7.5% were treated with insulin. However, 6.3% of them were not receiving any treatment for diabetes mellitus (Fig. 1).
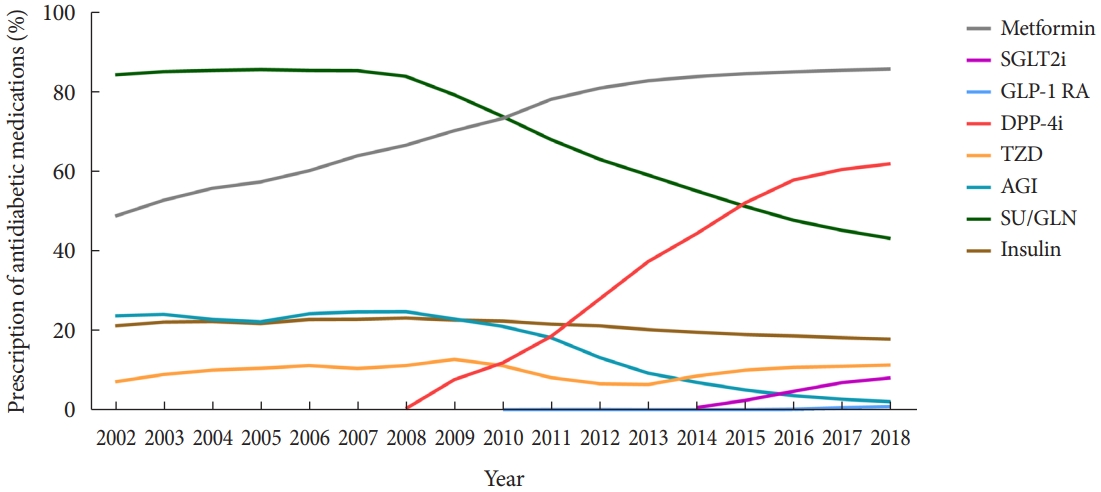
- Among adults with diabetes mellitus, the use of metformin steadily increased from 2002 to 2016 and then leveled off (Fig. 2, Supplementary Table 2). Since 2008, the use of new antidiabetic medications, including DPP-4 inhibitors, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors, had increased. In 2018, 62.0% of adults receiving antidiabetic medications used DPP-4 inhibitors. There was a steady decrease in the use of sulfonylureas/glinides and α-glucosidase inhibitors. The use of insulin and thiazolidinediones remained stable from 2002 to 2018.
- Risk-factor control and comorbidities
- The percentages of adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved an HbA1c level of <6.5%, <7.0%, and <8.0% were 24.5%, 55.6%, and 80.5%, respectively (Table 3, Supplementary Fig. 1). The prevalence of hypertension among adults with diabetes mellitus was 58.6% (57.9% in men and 59.5% in women), and 55.5% of adults with diabetes mellitus achieved BP control (<140/85 mm Hg). The prevalence of hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia among adults with diabetes mellitus was 76.5% (73.3% in men and 80.5% in women). The percentage of adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved lipid control (LDL-C <100 mg/dL) was 38.3%. Only 9.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus achieved all three goals of HbA1c <6.5%, BP <140/85 mm Hg, and LDL-C <100 mg/dL for diabetes care in patients without cardiovascular disease (CVD) based on the 2021 KDA Clinical Practice Guideline [16].
- The prevalence of obesity among adults with diabetes mellitus was 55.1% (57.0% in men and 52.5% in women), of which class I obesity accounted for 41.3% (Table 3). The prevalence of overweight among adults with diabetes mellitus was 23.1%. The prevalence of abdominal obesity among adults with diabetes mellitus was 63.3%, showing slightly higher percentages in women (64.6%) than men (62.2%).
- Self-management behaviors
- Current smoking and high-risk alcohol consumption were observed in 22.3% (36.0% in men and 5.0% in women) and 22.8% (31.1% in men and 4.2% in women) of adults with diabetes mellitus, respectively. Those with regular walking accounted for 38.1% (37.2% in men and 39.4% in women) (Table 3). Total energy intake was higher in adults without diabetes mellitus than those with diabetes mellitus or previously diagnosed diabetes mellitus (Table 4). The percentage of energy intake from carbohydrates was higher in adults with diabetes mellitus, whereas those from protein and fat were higher in those without diabetes mellitus.
RESULTS
- The estimated prevalence of Korean adults aged 30 years or older with diabetes mellitus was 16.7% in 2020. The proportion of adults being aware of and treated for diabetes mellitus did not increase in 2019–2020 compared with 2016–2018 [17]. The percentage of adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved HbA1c <6.5% and LDL-C <100 mg/dL were lower than those who achieved BP <140/85 mm Hg. Only 9.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus achieved all glycemic, BP, and lipid controls. The prevalence of self-management behaviors for diabetes mellitus was lower in men than women.
- This study updated previous findings of the Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2020 [17] using the 2019 and 2020 data from the KNHANES. The most notable change was an increase in the prevalence of diabetes mellitus among adults aged 30 years or older in 2020 (16.7%). The prevalence of diabetes mellitus among Korean adults remained stable, ranging from 11.4% to 14.4% between 2012 and 2018 [5], despite increasing BMI and waist circumference [23], decreasing mortality in diabetes mellitus [24], and increasing young adults with diabetes mellitus [25,26]. Growing evidence suggests that COVID-19 could increase the risk of diabetes mellitus [27]. A recent cohort study in the United States provided further evidence that COVID-19 was significantly associated with an increased risk of incident diabetes mellitus beyond the first 30 days of infection [28]. In Korea, 60,726 confirmed COVID-19 cases were reported from January 2020 to December 2020 [29]. Although the actual effect is difficult to evaluate, the infection and preventive measures, such as social distancing and working from home, may in part have contributed to the increased prevalence of diabetes mellitus during the COVID-19 pandemic. Further investigation on data in 2021 or later will give a clear picture of changes in the prevalence of diabetes mellitus in Korea.
- Risk-factor control among adults with diabetes mellitus worsened in 2019–2020 compared with 2016–2018 [17]. We examined the use of antidiabetic medications from the Korean NHIS data to complement the KNHANES data on the management of diabetes mellitus. The improvement in glycemic control stalled in this period despite the increased use of new antidiabetic medications with additional benefits of weight loss, a low risk of hypoglycemia, and cardiorenal protection. Similar to another study [30], individualized glycemic targets based on patient characteristics and risks and benefits of therapy might affect glycemic control in Korean adults with diabetes mellitus [16]. The prevalence of hypertension and BP control among adults with diabetes mellitus were similar between 2016–2018 [17] and 2019–2020. On the other hand, lipid control significantly worsened in 2019–2020 (38.3%) compared with 2016–2018 (53.3%), with a higher prevalence of hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia (72.0% in 2016–2018 and 76.5% in 2019–2020) [17]. Although additional information is required to elucidate these changes, a substantial increase in abdominal obesity among adults with diabetes mellitus (53.2% in 2016–2018 [17] and 63.3% in 2019–2020) may have influenced the prevalence of hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia and lipid control. In line with these findings, only a small proportion of adults with diabetes mellitus achieved goals of all three risk factors in 2019 to 2020, which was lower than 11.5% in 2016 to 2018 [17]. The decline in risk-factor control in people with diabetes mellitus has public health implications. Compared with nondiabetic individuals, people with type 2 diabetes mellitus had higher cardiovascular morbidity and mortality [31]. However, people with type 2 diabetes mellitus who had risk factors within the target ranges had marginally higher risks of mortality and CVD than the general population [32]. Given the increased prevalence of diabetes mellitus in our study, urgent interventions are needed to improve risk-factor control in Korean adults with diabetes mellitus.
- The prevalence of obesity and abdominal obesity among adults with diabetes mellitus steadily increased from 2013–2018 [4,5] to 2019–2020. Excessive adiposity is intertwined with the incidence and progression of type 2 diabetes mellitus [33]. Asian populations tended to develop type 2 diabetes mellitus at a lower BMI than Western populations, indicating that impaired β-cell function for progressive decline in insulin sensitivity was crucial in the pathophysiology [34]. However, along with a recent rise in obesity in Asia, insulin resistance also largely contributes to developing type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Asian population [35]. In addition, weight loss is beneficial to glycemic and risk-factor controls regardless of heterogeneity of diabetes mellitus [33]. Therefore, lifestyle and pharmacologic interventions should be offered to people with diabetes mellitus considering their effects on weight management.
- With regard to self-management behaviors, current smoking among adults with diabetes mellitus continues to decrease from 2013–2018 to 2019–2020, whereas high-risk alcohol consumption continues to increase [4,5]. Current smoking and high-risk alcohol consumption were approximately seven times more prevalent in men than women. The proportion of patients with regular walking increased in 2019–2020 compared with 2013–2018 [4,5]. Excess energy intake in Korean adults with diabetes mellitus decreased from 18.1% in 2016–2018 [17] to 16.7% in 2019–2020. A total of 66.3% of energy intake came from carbohydrates. A previous study using the KDA-Korean Ministry of Health and Welfare index showed that overall adherence to dietary guidelines was low in Korean adults with diabetes mellitus, particularly non-elderly patients [36]. Maintaining healthy behaviors is fundamental to achieving treatment goals in people with diabetes mellitus [37]. This includes diabetes self-management education and support, medical nutrition therapy, physical activity, smoking cessation, and addressing social determinants of health [38,39]. Person-centered comprehensive care is needed to improve health outcomes in diabetes mellitus.
- This study has several limitations. First, since this study analyzed cross-sectional data, we could not assess causality and may not reflect changes in variables. Second, misclassification of diabetes mellitus is possible because self-reported information was used for medical history. Third, we evaluated the use of antidiabetic medications using the Korean NHIS data, which may have made a difference from other analyses in study participants. Fourth, we did not examine risk-factor control according to cardiovascular risk or established CVD.
- In conclusion, the prevalence of diabetes mellitus among Korean adults remained high. Only 9.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus achieved all glycemic, BP, and lipid controls from 2019 to 2020. Continuous evaluation of national diabetes statistics is important to support and advocate public health policy in reducing the burden of diabetes mellitus and its complication. A national effort to increase awareness of diabetes mellitus and improve comprehensive diabetes care, including preventive practices, is needed to tackle the diabetes epidemic in Korea.
DISCUSSION
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Table 1.
Supplementary Table 2.
Supplementary Fig. 1.
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Seung-Hyun Ko has been executive editor of the Diabetes & Metabolism Journal since 2022. Kyung Mook Choi has been editor-in-chief of the Diabetes & Metabolism Journal since 2022. Kyu Chang Won has been the publisher of the Diabetes & Metabolism Journal since 2022. They were not involved in the review process of this article. Otherwise, there was no conflict of interest.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception or design: J.H.B., K.D.H., S.H.K., H.S.K.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: J.H.B., K.D.H., S.H.K., H.S.K.
Drafting the work or revising: J.H.B., K.D.H., S.H.K., H.S.K.
Final approval of the manuscript: J.H.B., K.D.H., S.H.K., Y.S.Y., J.H.C., K.M.C., H.S.K., K.C.W.
-
FUNDING
None
NOTES
-
Acknowledgements
- We acknowledge the Korean Diabetes Association for supporting this study.

| Variable | Number | Percentage±SE | Estimated population |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age group, yr | |||
| ≥19 | |||
| FPG or HbA1ca | 5,612 | 13.9±0.6 | 6,101,158 |
| FPG | 5,613 | 12.2±0.5 | 5,327,384 |
| ≥30 | |||
| FPG or HbA1ca | 4,848 | 16.7±0.7 | 6,047,618 |
| FPG | 4,849 | 14.5±0.6 | 5,273,844 |
| ≥65 | |||
| FPG or HbA1ca | 1,545 | 30.1±1.3 | 2,450,207 |
| FPG | 1,546 | 27.0±1.2 | 2,202,928 |
| 19–29a | 764 | 0.7±0.3 | 53,540 |
| 30–39a | 734 | 4.4±0.8 | 314,033 |
| 40–49a | 936 | 9.0±1.1 | 740,264 |
| 50–59a | 1,025 | 19.1±1.4 | 1,636,363 |
| 60–69a | 1,068 | 25.1±1.6 | 1,626,599 |
| ≥70a | 1,085 | 31.5±1.6 | 1,730,360 |
| Sexa | |||
| Men | |||
| Age ≥19 yr | 2,516 | 15.8±0.9 | 3,417,978 |
| Age ≥30 yr | 2,135 | 19.2±1.0 | 3,393,466 |
| Age ≥65 yr | 671 | 29.8±2.1 | 1,109,812 |
| Women | |||
| Age ≥19 yr | 3,096 | 12.1±0.7 | 3,212,364 |
| Age ≥30 yr | 2,713 | 14.3±0.8 | 3,187,148 |
| Age ≥65 yr | 874 | 30.2±1.5 | 1,459,697 |
| Equivalized household incomea,b | |||
| Quintile 1 (lowest) | 752 | 30.8±2.0 | - |
| Quintile 2 | 911 | 22.1±1.7 | - |
| Quintile 3 | 981 | 14.3±1.3 | - |
| Quintile 4 | 1,084 | 12.9±1.1 | - |
| Quintile 5 (highest) | 1,104 | 12.3±1.1 | - |
| Variable |
Total diabetes mellitus |
Diagnosed diabetes mellitus |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number | Percentage±SE | Number | Percentage±SE | |
| Awareness or detectiona | ||||
| Age, yr | ||||
| ≥30 | 1,770 | 65.8±1.4 | - | - |
| ≥65 | 914 | 76.4±1.5 | - | - |
| Sex | ||||
| Men | 1,225 | 62.6±1.9 | - | - |
| Women | 1,168 | 69.7±1.8 | - | - |
| Treatment rateb | ||||
| Age, yr | ||||
| ≥30 | 1,770 | 61.4±1.5 | 1,202 | 93.4±1.0 |
| ≥65 | 914 | 73.3±1.6 | 694 | 95.9±0.8 |
| Sex | ||||
| Men | 899 | 57.1±2.1 | 589 | 91.2±1.7 |
| Women | 871 | 66.8±1.8 | 613 | 95.8±0.8 |
| Control ratec | ||||
| Age, yr | ||||
| ≥30 | 1,770 | 24.5±1.2 | 1,202 | 26.8±1.4 |
| ≥65 | 914 | 28.3±1.7 | 694 | 31.3±2.0 |
| Sex | ||||
| Men | 899 | 24.4±1.6 | 589 | 25.3±2.0 |
| Women | 871 | 24.5±1.7 | 613 | 28.5±2.0 |
KNHANES, Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; SE, standard error.
a Awareness of diabetes mellitus was defined as the percentage of people previously diagnosed with diabetes mellitus among people with diabetes mellitus,
b Treatment rate of diabetes mellitus was defined as the percentage of people taking antidiabetic medications among people with diabetes mellitus,
c Control rate of diabetes mellitus was defined as the percentage of people with glycosylated hemoglobin <6.5% among people with diabetes mellitus.
| Variable | Total | Men | Women |
|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c | |||
| <6.5% | 24.5 | 24.4 | 24.5 |
| <7.0% | 55.6 | 55.0 | 56.3 |
| <8.0% | 80.5 | 79.5 | 81.7 |
| <9.0% | 89.9 | 89.3 | 90.5 |
| Hypertensiona | 58.6 | 57.9 | 59.5 |
| BP <140/85 mm Hg | 55.5 | 51.7 | 60.2 |
| Hyper-LDL-cholesterolemiab | 76.5 | 73.3 | 80.5 |
| LDL-C <100 mg/dL | 38.3 | 36.1 | 40.9 |
| Hypertensiona and hyper-LDL- cholesterolemiab | 43.9 | 41.9 | 46.4 |
| HbA1c <6.5% +BP <140/85 mm Hg + LDL-C <100 mg/dL | 9.7 | 11.0 | 8.1 |
| Weight status (BMI, kg/m2) | |||
| Underweight (<18.5) | 1.2 | 1.1 | 1.3 |
| Normal weight (18.5–22.9) | 20.7 | 18.2 | 23.8 |
| Overweight (23.0–24.9) | 23.1 | 23.7 | 22.4 |
| Class I obesity (25.0–29.9) | 41.3 | 43.5 | 38.5 |
| Class II obesity (30.0–34.9) | 11.2 | 11.0 | 11.4 |
| Class III obesity (≥35.0) | 2.6 | 2.5 | 2.6 |
| Abdominal obesity (WC, cm) | |||
| No (<90 in men, <85 in women) | 36.7 | 37.8 | 35.4 |
| Yes (≥90 in men, ≥85 in women) | 63.3 | 62.2 | 64.6 |
| Current smokingc | 22.3 | 36.0 | 5.0 |
| High-risk alcohol consumptiond | 22.8 | 31.1 | 4.2 |
| Regular walkinge | 38.1 | 37.2 | 39.4 |
Values are presented as percentages.
KNHANES, Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; BP, blood pressure; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference.
a Hypertension was defined as systolic BP ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic BP ≥90 mm Hg or taking antihypertensive medications,
b Hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia was defined as LDL-C ≥100 mg/dL or taking lipid-lowering medications,
c Current smoking was defined as having smoked five packs (or 100 cigarettes) in his or her lifetime and currently smoking cigarettes,
d High-risk alcohol consumption was defined as more than seven drinks twice a week for men and more than five for women,
e Regular walking was defined as a minimum of 30 minutes a day of walking five or more days per week.
| Variable | Total diabetes mellitus | Diagnosed diabetes mellitus | Non- diabetes mellitus | P valuea |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total energy intake, kcal | 1,825 | 1,785 | 1,911 | 0.009 |
| Men | 2,127 | 2,111 | 2,251 | 0.013 |
| Women | 1,439 | 1,402 | 1,596 | <0.001 |
| Excess energy intake, %b | 16.7 | 15.8 | 16.9 | 0.914 |
| Men | 19.5 | 18.9 | 20.5 | 0.637 |
| Women | 13.2 | 12.2 | 13.5 | 0.827 |
| Percentages of energy intake from macronutrients | ||||
| Carbohydrates, % | 66.3 | 66.8 | 62.4 | <0.001 |
| Men | 64.5 | 64.7 | 61.5 | <0.001 |
| Women | 68.6 | 69.2 | 63.3 | <0.001 |
| Protein, % | 15.0 | 14.8 | 15.6 | <0.001 |
| Men | 15.5 | 15.5 | 16.0 | 0.008 |
| Women | 14.3 | 14.0 | 15.1 | <0.001 |
| Fat, % | 18.7 | 18.4 | 22.0 | <0.001 |
| Men | 20.0 | 19.8 | 22.4 | <0.001 |
| Women | 17.1 | 16.9 | 21.6 | <0.001 |
KNHANES, Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
a P values are for comparing total diabetes mellitus and non-diabetes mellitus,
b Excess energy intake was defined as 125% or more of the estimated energy requirement recommended by the Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2015 [22].
- 1. GBD 2019 Diseases and Injuries Collaborators. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990-2019: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020;396:1204-22.PubMedPMC
- 2. International Diabetes Federation. IDF diabetes atlas. 10th ed. Brussels: IDF; 2021.
- 3. Zheng Y, Ley SH, Hu FB. Global aetiology and epidemiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus and its complications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2018;14:88-98.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea, 2018. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association; 2018.
- 5. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea, 2020. Seoul: Korean Diabetes Association; 2020.
- 6. Kim YE, Park H, Jo MW, Oh IH, Go DS, Jung J, et al. Trends and patterns of burden of disease and injuries in Korea using disability-adjusted life years. J Korean Med Sci 2019;34(Suppl 1):e75.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 7. Kim J, Yoon SJ, Jo MW. Estimating the disease burden of Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus patients considering its complications. PLoS One 2021;16:e0246635.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Lim S, Bae JH, Kwon HS, Nauck MA. COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2021;17:11-30.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 9. Williamson EJ, Walker AJ, Bhaskaran K, Bacon S, Bates C, Morton CE, et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature 2020;584:430-6.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 10. Barron E, Bakhai C, Kar P, Weaver A, Bradley D, Ismail H, et al. Associations of type 1 and type 2 diabetes with COVID-19-related mortality in England: a whole-population study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2020;8:813-22.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Moon SJ, Rhee EJ, Jung JH, Han KD, Kim SR, Lee WY, et al. Independent impact of diabetes on the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 in 5,307 patients in South Korea: a nationwide cohort study. Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:737-46.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 12. Muller JA, Gross R, Conzelmann C, Kruger J, Merle U, Steinhart J, et al. SARS-CoV-2 infects and replicates in cells of the human endocrine and exocrine pancreas. Nat Metab 2021;3:149-65.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 13. Reiterer M, Rajan M, Gomez-Banoy N, Lau JD, Gomez-Escobar LG, Ma L, et al. Hyperglycemia in acute COVID-19 is characterized by insulin resistance and adipose tissue infectivity by SARS-CoV-2. Cell Metab 2021;33:2174-88.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Carr MJ, Wright AK, Leelarathna L, Thabit H, Milne N, Kanumilli N, et al. Impact of COVID-19 on diagnoses, monitoring, and mortality in people with type 2 diabetes in the UK. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2021;9:413-5.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, Draznin B, Aroda VR, Bakris G, Benson G, Brown FM, et al. 9. Pharmacologic approaches to glycemic treatment: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022;45(Suppl 1):S125-43.
- 16. Hur KY, Moon MK, Park JS, Kim SK, Lee SH, Yun JS, et al. 2021 Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:461-81.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 17. Jung CH, Son JW, Kang S, Kim WJ, Kim HS, Kim HS, et al. Diabetes fact sheets in Korea, 2020: an appraisal of current status. Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:1-10.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 18. Oh K, Kim Y, Kweon S, Kim S, Yun S, Park S, et al. Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 20th anniversary: accomplishments and future directions. Epidemiol Health 2021;43:e2021025.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 19. Choi EK. Cardiovascular research using the Korean National Health Information Database. Korean Circ J 2020;50:754-72.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 20. Ministry of Health and Welfare; Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency. Korea Health Statistics 2020: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES VIII-2). Seoul: KDCA; 2022.
- 21. Kim BY, Kang SM, Kang JH, Kang SY, Kim KK, Kim KB, et al. 2020 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity guidelines for the management of obesity in Korea. J Obes Metab Syndr 2021;30:81-92.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Ministry of Health and Welfare; The Korean Nutritional Society. Dietary Reference Intakes for Koreans 2015. Seoul: KNS; 2015.
- 23. Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. 2021 Obesity fact sheet. Seoul: KSSO; 2021.
- 24. Park JH, Ha KH, Kim BY, Lee JH, Kim DJ. Trends in cardiovascular complications and mortality among patients with diabetes in South Korea. Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:120-4.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 25. Choi HH, Choi G, Yoon H, Ha KH, Kim DJ. Rising incidence of diabetes in young adults in South Korea: a national cohort study. Diabetes Metab J 2022 Jan 11 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0236.Article
- 26. Yang YS, Han K, Sohn TS, Kim NH. Young-onset type 2 diabetes in South Korea: a review of the current status and unmet need. Korean J Intern Med 2021;36:1049-58.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 27. Montefusco L, Ben Nasr M, D’Addio F, Loretelli C, Rossi A, Pastore I, et al. Acute and long-term disruption of glycometabolic control after SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat Metab 2021;3:774-85.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 28. Xie Y, Al-Aly Z. Risks and burdens of incident diabetes in long COVID: a cohort study. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2022;10:311-21.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Ministry of Health and Welfare: Coronavirus (COVID-19), Republic of Korea. Available from: http://ncov.mohw.go.kr/en/ (cited 2022 Apr 28).
- 30. Fang M, Wang D, Coresh J, Selvin E. Trends in diabetes treatment and control in U.S. adults, 1999-2018. N Engl J Med 2021;384:2219-28.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. Wright AK, Suarez-Ortegon MF, Read SH, Kontopantelis E, Buchan I, Emsley R, et al. Risk factor control and cardiovascular event risk in people with type 2 diabetes in primary and secondary prevention settings. Circulation 2020;142:1925-36.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 32. Rawshani A, Rawshani A, Franzen S, Sattar N, Eliasson B, Svensson AM, et al. Risk factors, mortality, and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2018;379:633-44.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Lingvay I, Sumithran P, Cohen RV, le Roux CW. Obesity management as a primary treatment goal for type 2 diabetes: time to reframe the conversation. Lancet 2022;399:394-405.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Yabe D, Seino Y. Type 2 diabetes via β-cell dysfunction in east Asian people. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2016;4:2-3.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Yoshinari M, Hirakawa Y, Hata J, Higashioka M, Honda T, Yoshida D, et al. Comparison of the contributions of impaired beta cell function and insulin resistance to the development of type 2 diabetes in a Japanese community: the Hisayama Study. Diabetologia 2021;64:1775-84.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 36. Jang H, Im J, Park K. Adherence to dietary guidelines among diabetes patients: comparison between elderly and non-elderly groups. Clin Nutr Res 2021;10:14-23.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 37. Powers MA, Bardsley JK, Cypress M, Funnell MM, Harms D, Hess-Fischl A, et al. Diabetes self-management education and support in adults with type 2 diabetes: a consensus report of the American Diabetes Association, the Association of Diabetes Care & Education Specialists, the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, the American Academy of Family Physicians, the American Academy of PAs, the American Association of Nurse Practitioners, and the American Pharmacists Association. Diabetes Care 2020;43:1636-49.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 38. American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee; American Diabetes Association Professional Practice Committee, Aroda VR, Bakris G, Benson G, et al. 5. Facilitating behavior change and well-being to improve health outcomes: standards of medical care in diabetes-2022. Diabetes Care 2022;45(Suppl 1):S60-82.
- 39. Hill-Briggs F, Adler NE, Berkowitz SA, Chin MH, Gary-Webb TL, Navas-Acien A, et al. Social determinants of health and diabetes: a scientific review. Diabetes Care 2020;44:258-79.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
Jinyoung Kim, Bongseong Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 567. CrossRef - Changes in Fatty Liver Disease and Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Young Korean Adults
Kye-Yeung Park, Hwan-Sik Hwang, Kyungdo Han, Hoon-Ki Park
American Journal of Preventive Medicine.2024; 66(4): 717. CrossRef - Widening disparities in the national prevalence of diabetes mellitus for people with disabilities in South Korea
I. Hwang, S.Y. Kim, Y.Y. Kim, J.H. Park
Public Health.2024; 226: 173. CrossRef - Questionnaire-Based Survey of Diabetes Self-Care Activities and Barriers among Young Korean Adults with Early-Onset Diabetes
Ji In Park, Sang-Wook Kim, Il Sung Nam-Goong, Kee-Ho Song, Ji Hee Yu, Ji Yun Jeong, Eun-Hee Cho
Yonsei Medical Journal.2024; 65(1): 42. CrossRef - Patients with diabetes in regions with population decline and likelihood of receiving diabetes management education and screenings for related complications in Korea
Yeong Jun Ju, Woorim Kim, Kyujin Chang, Tae Hoon Lee, Soon Young Lee
Preventive Medicine.2024; 178: 107793. CrossRef - Association between underweight and risk of heart failure in diabetes patients
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung‐Do Han, Eun‐Jung Rhee, Won‐Young Lee
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2024; 15(2): 671. CrossRef - Gastroparesis might not be uncommon in patients with diabetes mellitus in a real-world clinical setting: a cohort study
Jeongmin Lee, Hye Lim Park, Su Young Park, Chul-Hyun Lim, Min-Hee Kim, Jung Min Lee, Sang-Ah Chang, Jung-Hwan Oh
BMC Gastroenterology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to impaired fasting glucose and gastrointestinal cancer risk: A nationwide cohort study
Byeong Yun Ahn, Bokyung Kim, Sanghyun Park, Sang Gyun Kim, Kyungdo Han, Soo‐Jeong Cho
Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Multidimensional behavioral factors for diabetes management among middle-aged adults: a population-based study
Hyerang Kim, Heesook Son
Journal of Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Semaglutide Versus Once-Daily Sitagliptin as Metformin Add-on in a Korean Population with Type 2 Diabetes
Byung-Wan Lee, Young Min Cho, Sin Gon Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Soo Lim, Amine Dahaoui, Jin Sook Jeong, Hyo Jin Lim, Jae Myung Yu
Diabetes Therapy.2024; 15(2): 547. CrossRef - Association between dietary selenium intake and severe abdominal aortic calcification in the United States: a cross-sectional study
Weiwei Dong, Xiaobai Liu, Lu Ma, Zhiyong Yang, Chunyan Ma
Food & Function.2024; 15(3): 1575. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to hypertriglyceridemia and risk of type 2 diabetes in young adults
Min-Kyung Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Jong-Dai Kim, Moon Jung Kim, Byungpyo Kim, Jung Heo, Jiyeon Ahn, Seo-Young Sohn, Jae-Hyuk Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 208: 111109. CrossRef - Recent evidence on target blood pressure in patients with hypertension
Hack-Lyoung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2024; 6(1): 17. CrossRef - Status and trends in epidemiologic characteristics of diabetic end-stage renal disease: an analysis of the 2021 Korean Renal Data System
Kyeong Min Kim, Seon A Jeong, Tae Hyun Ban, Yu Ah Hong, Seun Deuk Hwang, Sun Ryoung Choi, Hajeong Lee, Ji Hyun Kim, Su Hyun Kim, Tae Hee Kim, Ho-Seok Koo, Chang-Yun Yoon, Kiwon Kim, Seon Ho Ahn, Yong Kyun Kim, Hye Eun Yoon
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 43(1): 20. CrossRef -
In silico
exploration of the potential inhibitory activities of in-house and ZINC database lead compounds against alpha-glucosidase using structure-based virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation approach
Zuhier A. Awan, Haider Ali Khan, Alam Jamal, Sulaiman Shams, Guojun Zheng, Abdul Wadood, Muhammad Shahab, Mohammad Imran Khan, Abdulaziz A. Kalantan
Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Mobile Applications for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Scoping Review
Jung Lim Lee, Youngji Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 368. CrossRef - Current status of remote collaborative care for hypertension in medically underserved areas
Seo Yeon Baik, Kyoung Min Kim, Hakyoung Park, Jiwon Shinn, Hun-Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2024; 6(1): 33. CrossRef - Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: nationwide population based study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
BMJ.2024; : e076388. CrossRef - Comparison of metabolic and neurological comorbidities in Asian patients with psoriasis and atopic dermatitis
Hee Joo Yang, Mi Young Lee, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Chang Jin Jung, Woo Jin Lee, Chong Hyun Won, Mi Woo Lee, Joon Min Jung, Sung Eun Chang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer risk according to fasting blood glucose trajectories: a population-based cohort study
Thi Minh Thu Khong, Thi Tra Bui, Hee-Yeon Kang, Jinhee Lee, Eunjung Park, Jin-Kyoung Oh
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2024; 12(1): e003696. CrossRef - Participation experience in self-care program for type 2 diabetes: A mixed-methods study
Mihwan Kim, Haejung Lee, Gaeun Park, Ah Reum Khang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(1): 31. CrossRef - Fasting GLP-1 Levels and Albuminuria Are Negatively Associated in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Cheol-Won Jang, Tae Yang Yu, Jin Woo Jeong, Se Eun Ha, Rajan Singh, Moon Young Lee, Seungil Ro
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2024; 14(3): 280. CrossRef - The clinical relevance of a polygenic risk score for type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Korean population
Na Yeon Kim, Haekyung Lee, Sehee Kim, Ye-Jee Kim, Hyunsuk Lee, Junhyeong Lee, Soo Heon Kwak, Seunggeun Lee
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic traits and colorectal cancer survival in a cohort of South Korean patients: A Mendelian randomization analysis
So Yon Jun, Sooyoung Cho, Min Jung Kim, Ji Won Park, Seung‐Bum Ryoo, Seung Yong Jeong, Kyu Joo Park, Aesun Shin
Cancer Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 279. CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus more effectively than oral glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity and secretion markers
Min Jin Lee, Ji Hyun Bae, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi, Mi Sook Yun, Yang Ho Kang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111640. CrossRef - Real-World Outcomes of Individualized Targeted Therapy with Insulin Glargine 300 Units/mL in Insulin-Naïve Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes: TOBE Study
Eun-Gyoung Hong, Kyung-Wan Min, Jung Soo Lim, Kyu-Jeung Ahn, Chul Woo Ahn, Jae-Myung Yu, Hye Soon Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Won Kim, Dong Han Kim, Hak Chul Jang
Advances in Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of complicated, untreated and uncontrolled diabetes and pre‐diabetes on treatment outcome among patients with pulmonary tuberculosis
Kyung Hoon Kim, Hyung Woo Kim, Yong Hyun Kim, Yeonhee Park, Sung Soo Jung, Jin Woo Kim, Jee Youn Oh, Heayon Lee, Sung Kyoung Kim, Sun‐Hyung Kim, Jiwon Lyu, Yousang Ko, Sun Jung Kwon, Yun‐Jeong Jeong, Do Jin Kim, Hyeon‐Kyoung Koo, Yangjin Jegal, Sun Young
Respirology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of dietary behavior and intake related to glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes aged 30 years or older in Korea: Utilizing the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Jin-Ah Seok, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(2): 239. CrossRef - Management of Early-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Jin Hwa Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2024; 25(1): 4. CrossRef - Baseline glycated albumin level and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Healthy individuals: a retrospective longitudinal observation in Korea
Kang-Su Shin, Min-Seung Park, Mi Yeon Lee, Eun Hye Cho, Hee-Yeon Woo, Hyosoon Park, Min-Jung Kwon
Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation.2024; : 1. CrossRef - The Potential Role of Presepsin in Predicting Severe Infection in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Eun Yeong Ha, Il Rae Park, Seung Min Chung, Young Nam Roh, Chul Hyun Park, Tae-Gon Kim, Woong Kim, Jun Sung Moon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(8): 2311. CrossRef - Myotonic dystrophy type 1 in South Korea: a comprehensive analysis of cancer and comorbidity risks
Incheol Seo, Jin-Mo Park
Neurological Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Pancreatic Cancer and Use of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score-Matching Analysis
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Soon Jib Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 426. CrossRef - Diabetes screening in South Korea: a new estimate of the number needed to screen to detect diabetes
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kyung Ae Lee, Kyung-Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Dae Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(1): 93. CrossRef - Sex differences in the impact of diabetes mellitus on tuberculosis recurrence: a retrospective national cohort study
Dararat Eksombatchai, Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2023; 127: 1. CrossRef - Response to Letter to the Editor From Han and Xu: “Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes”
Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(4): e58. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in catholic priests compared with general public
Youngmi Eun, Sun Myeong Ock, Se-Hong Kim, Ju Hye Chung, Se Jin Park, Churlmin Kim, Min-Kyun Im, Kyung-do Han
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(5): 655. CrossRef - Blood pressure control and its associated factors in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes
Anan S Jarab, Walid Al-Qerem, Salam Alqudah, Shrouq R Abu Heshmeh, Tareq L Mukattash, Karem H Alzoubi
Electronic Journal of General Medicine.2023; 20(3): em477. CrossRef - Prevalence and associated factors of diabetes mellitus among patients with tuberculosis in South Korea from 2011 to 2018: a nationwide cohort study
Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Jeong Mi Seo, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang
BMJ Open.2023; 13(3): e069642. CrossRef - The association between nutrition label utilization and disease management education among hypertension or diabetes diagnosed in Korea using 2018 Community Health Survey: a cross-sectional study
Miran Jin, Jayeun Kim, Kyuhyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 38. CrossRef - Insulin Fact Sheet in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Trends of Antidiabetic Medication Use in Insulin Users with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: 2002 to 2019
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Bong-Sung Kim, Kyung-Do Han, So Yoon Kwon, So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 211. CrossRef - Comparison of Operational Definition of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Data from Korean National Health Insurance Service and Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Ha Baek, Yong-Moon Park, Kyung Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Han Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 201. CrossRef - Evaluation of pharmacokinetic interactions between lobeglitazone, empagliflozin, and metformin in healthy subjects
Heeyoung Kim, Choon Ok Kim, Hyeonsoo Park, Min Soo Park, Dasohm Kim, Taegon Hong, Yesong Shin, Byung Hak Jin
Translational and Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 31(1): 59. CrossRef - Vascular and metabolic effects of ipragliflozin versus sitagliptin (IVS) in type 2 diabetes treated with sulphonylurea and metformin: IVS study
Seon Mee Kang, Han Mi Yun, Minji Sohn, Soo Lim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(7): 1922. CrossRef - Diabetes and Skin Disease
Jungah Lim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(1): 29. CrossRef - Revisiting the Diabetes Crisis in Korea: Call for Urgent Action
Jun Sung Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between Sleep Duration and Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Healthy Subjects: A 14-Year Longitudinal Cohort Study
Jin ha Jang, Wonjin Kim, Jin Sil Moon, Eun Roh, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm, Ji Hye Huh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(8): 2899. CrossRef - Exercise Frequency Reduction Is Associated With Higher Risk of Infection in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes: A Nationally Representative Cohort Study
Yohwan Lim, Hye Jun Kim, Sung Soo Yoon, Sang Jun Lee, Myeong Hoon Lee, Hyewon Park, Sun Jae Park, Seogsong Jeong, Hyun Wook Han
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Consuming Heat-Treated Dodamssal Brown Rice Containing Resistant Starch on Glucose Metabolism in Humans
Jiyoung Park, Sea-Kwan Oh, Miae Doo, Hyun-Jung Chung, Hyun-Jin Park, Hyejin Chun
Nutrients.2023; 15(10): 2248. CrossRef - Opening the Precision Diabetes Care through Digital Healthcare
Joonyub Lee, Jin Yu, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 307. CrossRef - Fatty Liver & Diabetes Statistics in Korea: Nationwide Data 2009 to 2017
Eugene Han, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-ho Lee, Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Jung Hwan Park, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 347. CrossRef - Trends in the Quality of Primary Care and Acute Care in Korea From 2008 to 2020: A Cross-sectional Study
Yeong Geun Gwon, Seung Jin Han, Kyoung Hoon Kim
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(3): 248. CrossRef - Development and Validation of Multiple Equations for Low-Density Lipoprotein and Apolipoprotein B in Korean Patients Visiting Local Clinics and Hospitals
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Nutrients.2023; 15(12): 2786. CrossRef - The role of retinal vessel geometry as an indicator of systemic arterial stiffness assessed by cardio-ankle vascular index
Dae Joong Ma, Heesun Lee, Ji Min Choi, Hyo Eun Park, Su-Yeon Choi, Hyuk Jin Choi
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between type 2 diabetes mellitus and depression among Korean midlife women: a cross-sectional analysis study
You Lee Yang, Eun-Ok Im, Yunmi Kim
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of updated cardiovascular health metrics, including sleep health, with incident diabetes and cardiovascular events in older adults with prediabetes: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Seung Jin Han
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110820. CrossRef - Paradigm Shift in Management of Hyperglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Glucocentric versus Organ Protection
Jong Chul Won
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(2): 59. CrossRef - Medical nutrition therapy for diabetes mellitus
Suk Chon
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 421. CrossRef - Prevalence and treatment status of diabetes mellitus in Korea
Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 404. CrossRef - The impact of diabetes status on total and site-specific cancer risk in the elderly population: A nationwide cohort study
Kyuho Kim, Bongseong Kim, Hyunho Kim, Hyung Soon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110866. CrossRef - Response to comments of Lai et al. “Proposal of one option for patient-centered, heterogeneous selection of antidiabetic drug”
Sunyoung Kim, Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110864. CrossRef - Association of Dental Diseases and Oral Hygiene Care With the Risk of Heart Failure in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Youn Huh, Jung Eun Yoo, Sang‐Hyun Park, Kyungdo Han, Seon Mee Kim, Hye Soon Park, Kyung Hwan Cho, Jin‐Soo Ahn, Sang Ho Jun, Ga Eun Nam
Journal of the American Heart Association.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bidirectional associations between periodontal disease and systemic diseases: a nationwide population-based study in Korea
Salma Nabila, Jaesung Choi, Ji-Eun Kim, Seokyung Hahn, In-Kyung Hwang, Tae-Il Kim, Hee-Kyung Park, Ji-Yeob Choi
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term Effectiveness of the National Diabetes Quality Assessment Program in South Korea
Ji Hye Huh, Serim Kwon, Gui Ok Kim, Bo Yeon Kim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(9): 1700. CrossRef - Refined Diagnostic Protocol for Diabetic Polyneuropathy: Paving the Way for Timely Detection
Byung-Mo Oh
Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine.2023; 47(4): 234. CrossRef - Analysis of difference in body fluid composition and dietary intake between Korean adults with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yu-Gyeong Kim, Ha-Neul Choi, Jung-Eun Yim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 377. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus in the Elderly Adults in Korea: Based on Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019 to 2020
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Yong-Moon Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Kyuho Kim, Jae-Hyun Bae, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Nan-Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 643. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Association between initial continuity of care status and diabetes-related health outcomes in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A nationwide retrospective cohort study in South Korea
Hyun Woo Jung, Woo-Ri Lee
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(6): 600. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef - Diagnostic performance of the fibrosis-4 index and the NAFLD fibrosis score for screening at-risk individuals in a health check-up setting
Huiyul Park, Eileen L. Yoon, Mimi Kim, Jonghyun Lee, Hye-Lin Kim, Seon Cho, Eun-Hee Nah, Dae Won Jun
Hepatology Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef - The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population
Sunghwan Suh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 522. CrossRef - Comparative Risk of Type 2 Diabetes after Gastrectomy and Endoscopic Resection for Gastric Cancer: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Yeongkeun Kwon, Jin-Won Kwon, Jiyun Kim, Dohyang Kim, Jinseub Hwang, Jane Ha, Shin-Hoo Park, Sungsoo Park
Journal of the American College of Surgeons.2023; 237(6): 902. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Evogliptin Add-on Therapy to Dapagliflozin/Metformin Combinations in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week Multicenter Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel-Design Phase-3 Trial with a 28-Week Extensio
Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Hae Jin Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Chang Won, Kyung Ah Han, Cheol-Young Park, Jong Chul Won, Dong Jun Kim, Gwan Pyo Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Chang Beom Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 808. CrossRef - Association between diabetes mellitus and cause of death in patients with tuberculosis: A Korean nationwide cohort study
Se Hyun Kwak, Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang, Frederick Quinn
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(12): e0295556. CrossRef - Strategies to Maintain the Remission of Diabetes Following Metabolic Surgery
Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Soon Kim
Journal of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery.2023; 12(2): 26. CrossRef - Anti-Diabetic Medications and Osteoporosis
Kyongyoung Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 173. CrossRef - The associations between changes in hepatic steatosis and heart failure and mortality: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Hasung Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: is it preventable?
Seung-Hyun Ko
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(3): 106. CrossRef - Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 552. CrossRef - Current status of obesity treatment in Korea: based on the 2020 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity guidelines for obesity management
Eun-Jung Rhee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(7): 388. CrossRef - 젊은 2형 당뇨병 환자의 관리
재현 배
Public Health Weekly Report.2022; 15(35): 2474. CrossRef - Analysis of the Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Renal Function in Middle-Aged Patients with Diabetes
Yoonjin Park, Su Jung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(18): 11832. CrossRef - The Degree of Glycemic Control for the First Three Months Determines the Next Seven Years
Nami Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Blood Pressure Target in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hyun-Jin Kim, Kwang-il Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 667. CrossRef - Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes
Yewon Na, Soo Wan Kim, Ie Byung Park, Soo Jung Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Jaehun Jung, Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(11): 3022. CrossRef - Education for Insulin Injection in Elderly Diabetic Patients
Gi Yeon Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(3): 201. CrossRef - Recent Updates on Phytoconstituent Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors: An Approach towards the Treatment of Type Two Diabetes
Hamdy Kashtoh, Kwang-Hyun Baek
Plants.2022; 11(20): 2722. CrossRef - Epidemiological characteristics of diabetes mellitus in Korea
Soon Young Lee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(10): 640. CrossRef - Screening for Prediabetes and Diabetes in Korean Nonpregnant Adults: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2022
Kyung Ae Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Suk Chon, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 819. CrossRef - Oldies but Goodies: Thiazolidinedione as an Insulin Sensitizer with Cardioprotection
Eun-Hee Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 827. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Acceptance Action in the Relationship between Diabetes Distress and Self-stigma among Old Adults with Diabetes in South Korea
Hyesun Kim, Kawoun Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(4): 446. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite