
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug/Regimen
- Safety and Effectiveness of Dulaglutide in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Korean Real-World Post-Marketing Study
- Jeonghee Han, Woo Je Lee, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyoung Cho, Byung Wan Lee, Cheol-Young Park
- Received February 3, 2023 Accepted July 10, 2023 Published online February 2, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0030 [Epub ahead of print]
- 592 View
- 53 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader - Background
To investigate the real-world safety and effectiveness of dulaglutide in Korean adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
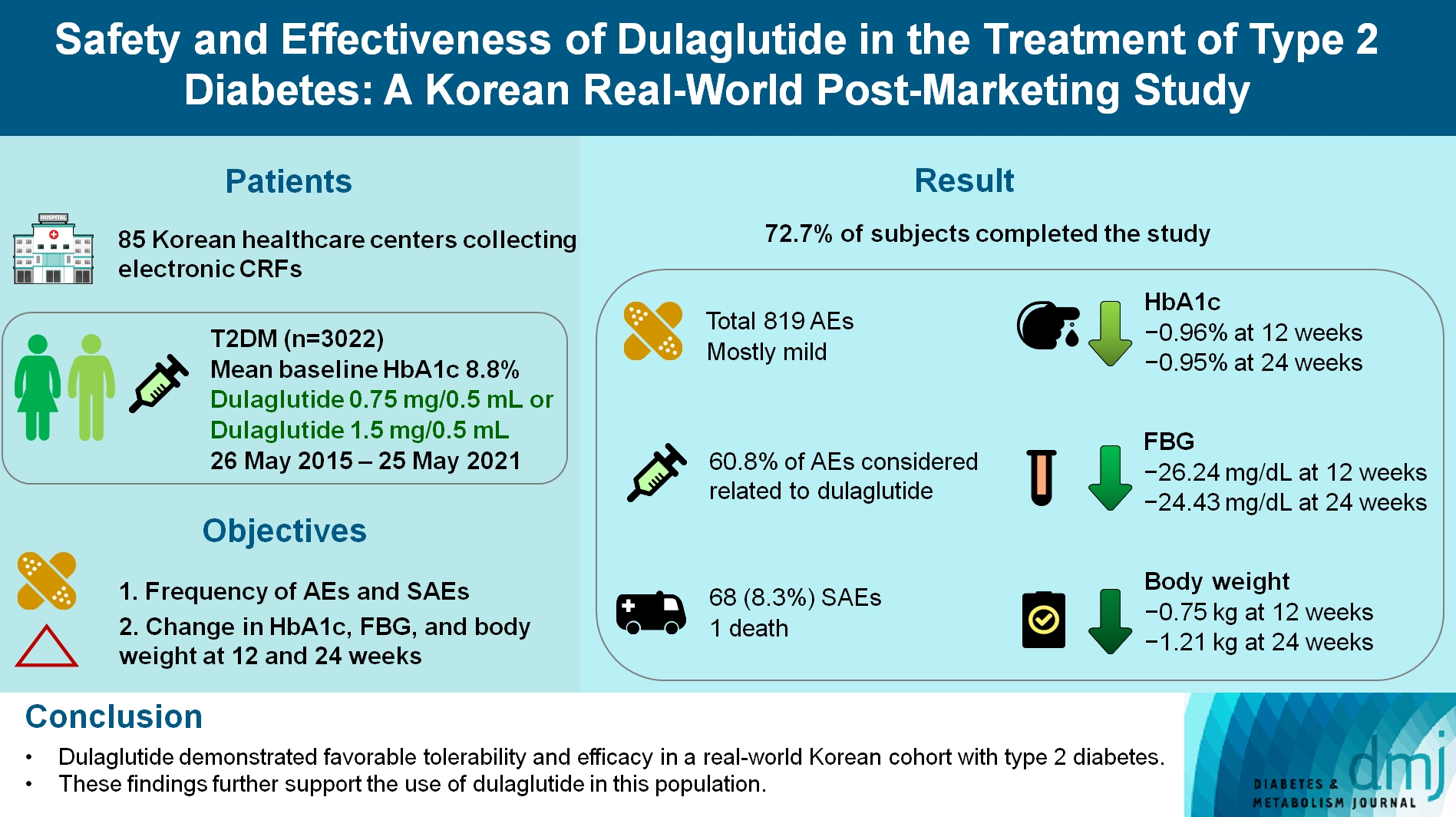
This was a real-world, prospective, non-interventional post-marketing safety study conducted from May 26, 2015 to May 25, 2021 at 85 Korean healthcare centers using electronic case data. Data on patients using dulaglutide 0.75 mg/0.5 mL or the dulaglutide 1.5 mg/0.5 mL single-use pens were collected and pooled. The primary objective was to report the frequency and proportion of adverse and serious adverse events that occurred. The secondary objective was to monitor the effectiveness of dulaglutide at 12 and 24 weeks by evaluating changes in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c ), fasting plasma glucose, and body weight.
Results
Data were collected from 3,067 subjects, and 3,022 subjects who received ≥1 dose (of any strength) of dulaglutide were included in the safety analysis set (53% female, mean age 56 years; diabetes duration 11.2 years, mean HbA1c 8.8%). The number of adverse events reported was 819; of these, 68 (8.3%) were serious adverse events. One death was reported. Adverse events were mostly mild in severity; 60.81% of adverse events were considered related to dulaglutide. This study was completed by 72.73% (2,198/3,022) of subjects. At 12/24 weeks there were significant (P<0.0001) reductions from baseline in least-squares mean HbA1c (0.96%/0.95%), fasting blood glucose (26.24/24.43 mg/dL), and body weight (0.75/1.21 kg).
Conclusion
Dulaglutide was generally well tolerated and effective in real-world Korean individuals with T2DM. The results from this study contribute to the body of evidence for dulaglutide use in this population.
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Hepatic Fibrosis and Cancer: The Silent Threats of Metabolic Syndrome
- Scott L. Friedman
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):161-169. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0240
- 2,239 View
- 273 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
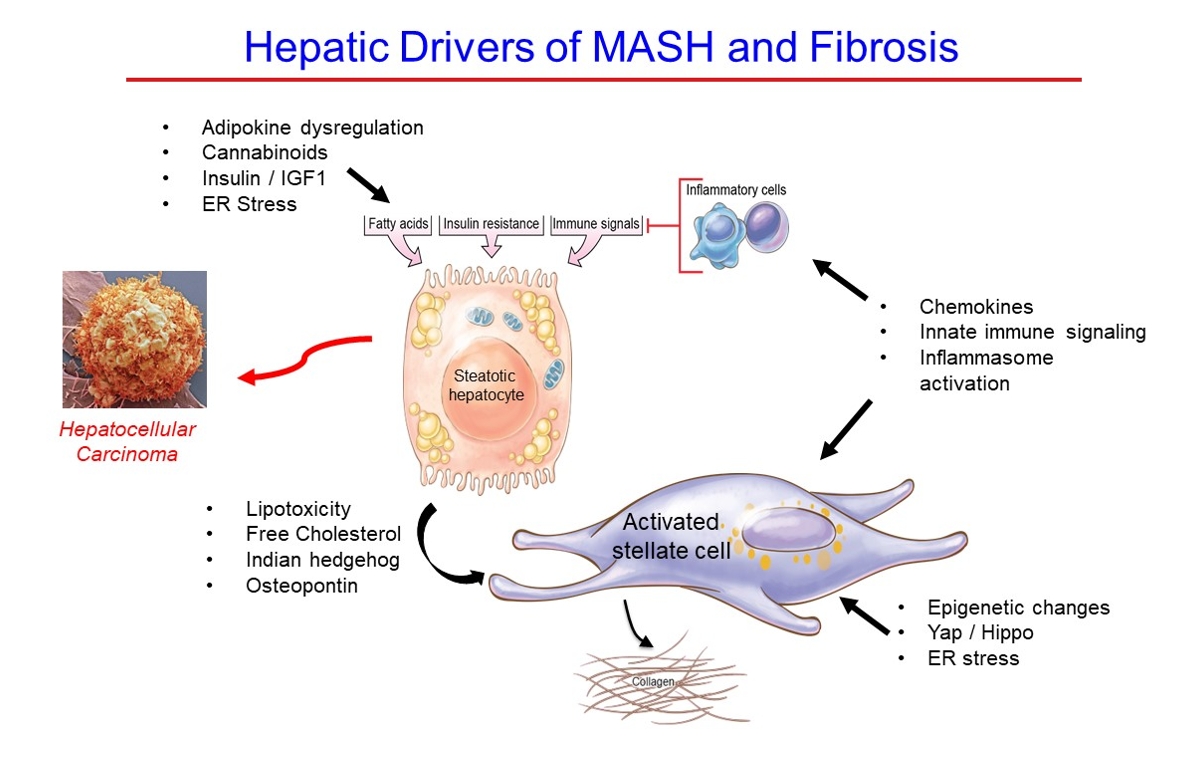
ePub - Metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic (fatty) liver disease (MASLD), previously termed non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, is a worldwide epidemic that can lead to hepatic inflammation, fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The disease is typically a component of the metabolic syndrome that accompanies obesity, and is often overlooked because the liver manifestations are clinically silent until late-stage disease is present (i.e., cirrhosis). Moreover, Asian populations, including Koreans, have a higher fraction of patients who are lean, yet their illness has the same prognosis or worse than those who are obese. Nonetheless, ongoing injury can lead to hepatic inflammation and ballooning of hepatocytes as classic features. Over time, fibrosis develops following activation of hepatic stellate cells, the liver’s main fibrogenic cell type. The disease is usually more advanced in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, indicating that all diabetic patients should be screened for liver disease. Although there has been substantial progress in clarifying pathways of injury and fibrosis, there no approved therapies yet, but current research seeks to uncover the pathways driving hepatic inflammation and fibrosis, in hopes of identifying new therapeutic targets. Emerging molecular methods, especially single cell sequencing technologies, are revolutionizing our ability to clarify mechanisms underlying MASLD-associated fibrosis and HCC.
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae Jin Kim, Hyun Min Kim, Jung Hae Ko, Nam Hoon Kim, Chong Hwa Kim, Jeeyun Ahn, Tae Jung Oh, Soo-Kyung Kim, Jaehyun Kim, Eugene Han, Sang-Man Jin, Won Suk Choi, Min Kyong Moon, Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):575-594. Published online September 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0282
- 5,016 View
- 628 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
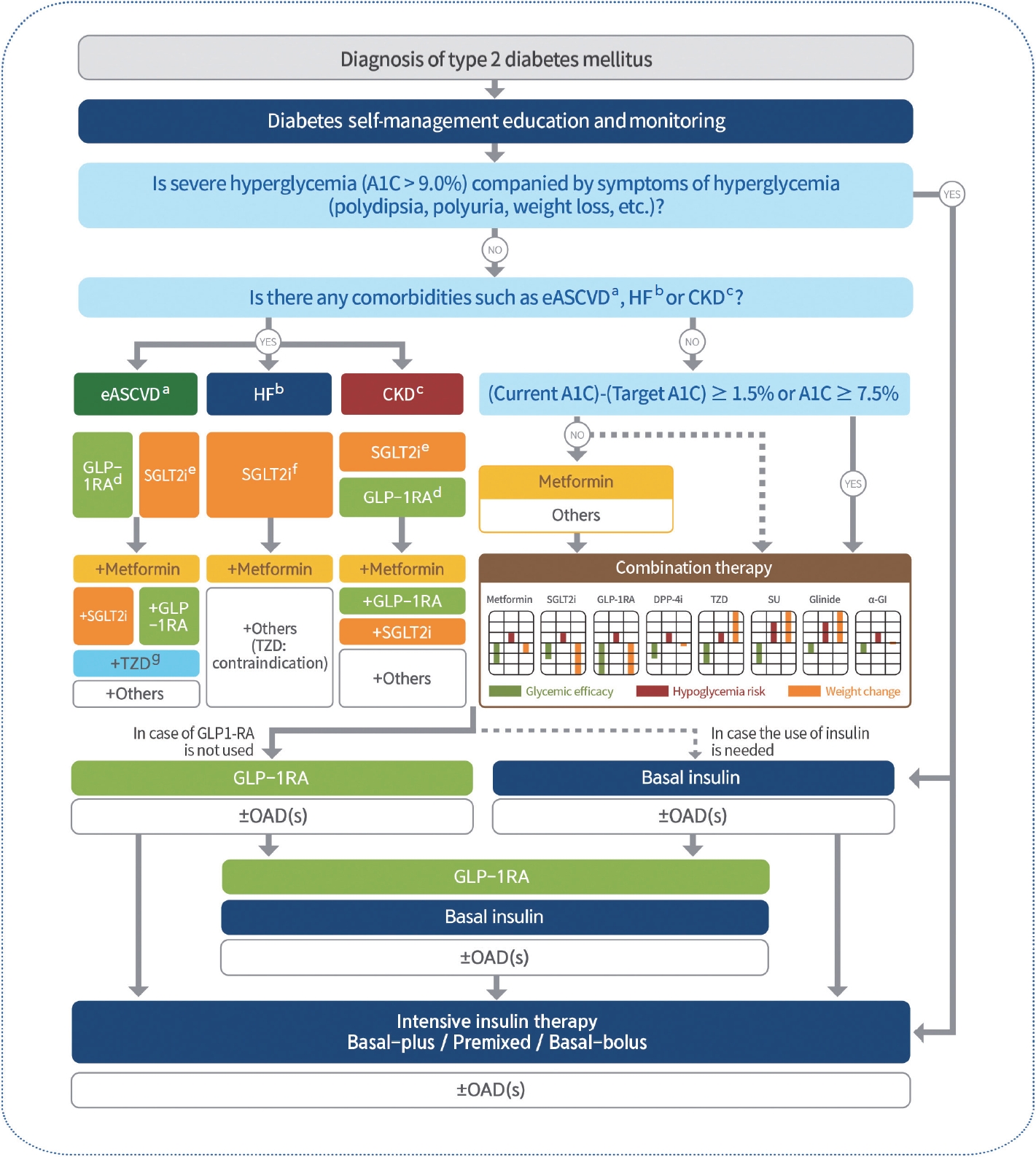
ePub - In May 2023, the Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines of the Korean Diabetes Association published the revised clinical practice guidelines for Korean adults with diabetes and prediabetes. We incorporated the latest clinical research findings through a comprehensive systematic literature review and applied them in a manner suitable for the Korean population. These guidelines are designed for all healthcare providers nationwide, including physicians, diabetes experts, and certified diabetes educators who manage patients with diabetes or individuals at risk of developing diabetes. Based on recent changes in international guidelines and the results of a Korean epidemiological study, the recommended age for diabetes screening has been lowered. In collaboration with the relevant Korean medical societies, recently revised guidelines for managing hypertension and dyslipidemia in patients with diabetes have been incorporated into this guideline. An abridgment containing practical information on patient education and systematic management in the clinic was published separately.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Eugene Han, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Sang Hoon Ahn, Yong-ho Lee, Seung Up Kim
Metabolism.2024; 152: 155789. CrossRef - Letter by In-Kyung Jeong Regarding Article, Trends in Prevalence of Hypertriglyceridemia and Related Factors in Korean Adults: A Serial Cross-Sectional Study
In-Kyung Jeong
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2024; 13(1): 80. CrossRef - Association between cardiovascular disease risk and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus in individuals with prediabetes: A retrospective cohort study
Myung Jin Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 208: 111125. CrossRef - Korea Hypertension Fact Sheet 2023: analysis of nationwide population-based data with a particular focus on hypertension in special populations
Hyeon Chang Kim, Hokyou Lee, Hyeok-Hee Lee, Dasom Son, Minsung Cho, Sojung Shin, Yeeun Seo, Eun-Jin kim, Song Vogue Ahn, Sun Ha Jee, Sungha Park, Hae-Young Lee, Min Ho Shin, Sang-Hyun Ihm, Seung Won Lee, Jong Ku Park, Il Suh, Tae-Yong Lee
Clinical Hypertension.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes Duration, Cholesterol Levels, and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyu Na Lee, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Adding Apolipoprotein B Testing on the Prevalence of Dyslipidemia and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in the Korean Adult Population
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Metabolites.2024; 14(3): 169. CrossRef - A self-powered and supercapacitive microneedle continuous glucose monitoring system with a wide range of glucose detection capabilities
Hye-Jun Kil, Jang Hyeon Kim, Kanghae Lee, Tae-Uk Kang, Ju-Hyun Yoo, Yong-ho Lee, Jin-Woo Park
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2024; 257: 116297. CrossRef - Cardiorenal outcomes and mortality after sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitor initiation in type 2 diabetes patients with percutaneous coronary intervention history
Jin Hwa Kim, Young Sang Lyu, BongSeong Kim, Mee Kyung Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Recommendations for Pharmacological Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
Junghyun Noh
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 127. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Ye Seul Yang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 135. CrossRef - A 33-Year-Old Man Presented with Abdominal Pain and Vomiting Starting a Day Ago
Jong Han Choi
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2023; 98(6): 289. CrossRef - Comorbidity Patterns and Management in Inpatients with Endocrine Diseases by Age Groups in South Korea: Nationwide Data
Sung-Soo Kim, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 14(1): 42. CrossRef
- Mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet in South Korea, 2022
- Eun-Sun Jin, Jee-Seon Shim, Sung Eun Kim, Jae Hyun Bae, Shinae Kang, Jong Chul Won, Min-Jeong Shin, Heung Yong Jin, Jenny Moon, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, In-Kyung Jeong, on Behalf of the Committee of Public Relation of the Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):632-642. Published online August 2, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0135
- 3,050 View
- 315 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
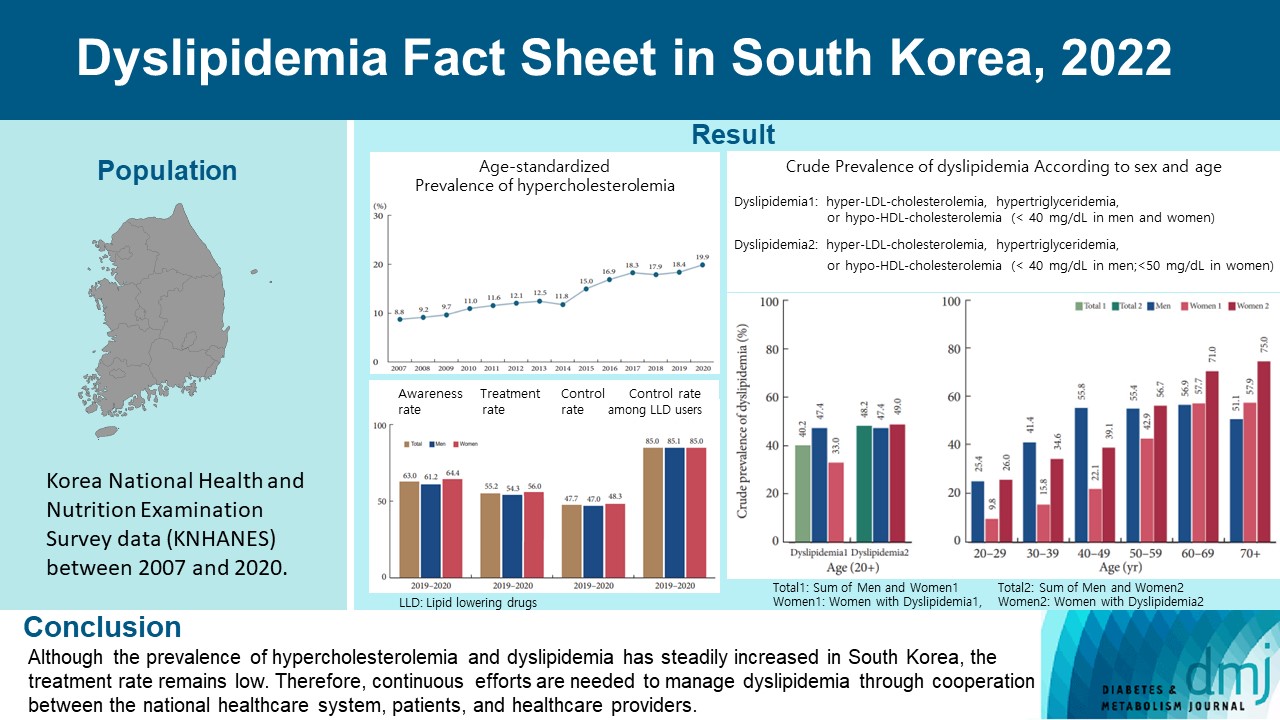
This study aimed to investigate the prevalence and status of dyslipidemia management among South Korean adults, as performed by the Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis under the name Dyslipidemia Fact Sheet 2022.
Methods
We analyzed the lipid profiles, age-standardized and crude prevalence, management status of hypercholesterolemia and dyslipidemia, and health behaviors among Korean adults aged ≥20 years, using the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data between 2007 and 2020.
Results
In South Korea, the crude prevalence of hypercholesterolemia (total cholesterol ≥240 mg/dL or use of a lipid-lowering drug) in 2020 was 24%, and the age-standardized prevalence of hypercholesterolemia more than doubled from 2007 to 2020. The crude treatment rate was 55.2%, and the control rate was 47.7%. The crude prevalence of dyslipidemia—more than one out of three conditions (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol ≥160 or the use of a lipid-lowering drug, triglycerides ≥200, or high-density lipoprotein cholesterol [HDL-C] [men and women] <40 mg/dL)—was 40.2% between 2016 and 2020. However, it increased to 48.2% when the definition of hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia in women changed from <40 to <50 mg/dL.
Conclusion
Although the prevalence of hypercholesterolemia and dyslipidemia has steadily increased in South Korea, the treatment rate remains low. Therefore, continuous efforts are needed to manage dyslipidemia through cooperation between the national healthcare system, patients, and healthcare providers. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Oxidative Balance Score and New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Adults without Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study-Health Examinees (KoGES-HEXA) Cohort
Mid-Eum Moon, Dong Hyuk Jung, Seok-Jae Heo, Byoungjin Park, Yong Jae Lee
Antioxidants.2024; 13(1): 107. CrossRef - Comparison of metabolic and neurological comorbidities in Asian patients with psoriasis and atopic dermatitis
Hee Joo Yang, Mi Young Lee, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Chang Jin Jung, Woo Jin Lee, Chong Hyun Won, Mi Woo Lee, Joon Min Jung, Sung Eun Chang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Adding Apolipoprotein B Testing on the Prevalence of Dyslipidemia and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in the Korean Adult Population
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Metabolites.2024; 14(3): 169. CrossRef - Exploring Utilization and Establishing Reference Intervals for the Apolipoprotein B Test in the Korean Population
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Diagnostics.2023; 13(20): 3194. CrossRef
- Oxidative Balance Score and New-Onset Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Adults without Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study-Health Examinees (KoGES-HEXA) Cohort
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Cardiovascular Outcomes according to Comorbidities and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sang Hyun Park, Hyeon Chang Kim, Byung Jin Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Jin Oh Na, Young Youl Hyun, Bum Joon Kim, Kyung-Do Han, In-Kyung Jeong, on Behalf of the Committee of Practice Guideline of Korean Lipid and Atheroscelerosis
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):45-58. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0344
- 2,947 View
- 259 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
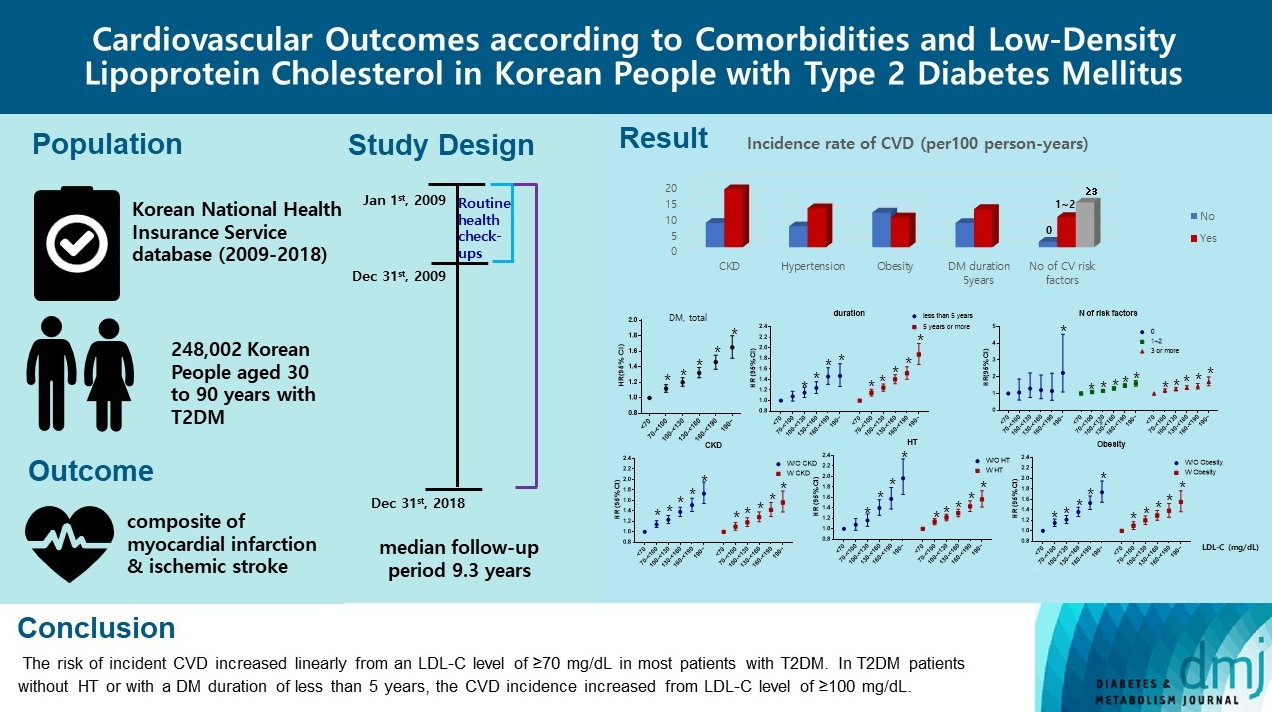
There are no clear data to support the cardiovascular (CV) risk categories and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) treatment goals in Korean people with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We evaluated the incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) according to comorbidities and suggested LDL-C treatment goals in Korean people with T2DM in nationwide cohort data.
Methods
Using the Korean National Health Insurance Service database, 248,002 people aged 30 to 90 years with T2DM who underwent routine health check-ups during 2009 were included. Subjects with previous CVD were excluded from the study. The primary outcome was incident CVD, defined as a composite of myocardial infarction and ischemic stroke during the follow-up period from 2009 to 2018.
Results
The mean age of the study participants was 59.6±10.9 years, and median follow-up period was 9.3 years. CVD incidence increased in the order of DM duration of 5 years or more (12.04/1,000 person-years), hypertension (HT) (12.27/1,000 personyears), three or more CV risk factors (14.10/1,000 person-years), and chronic kidney disease (18.28/1,000 person-years). The risk of incident CVD increased linearly from an LDL-C level of ≥70 mg/dL in most patients with T2DM. In T2DM patients without HT or with a DM duration of less than 5 years, the CVD incidence increased from LDL-C level of ≥100 mg/dL.
Conclusion
For primary prevention of CVD in Korean adults with T2DM, it can be helpful to lower LDL-C targets when there are chronic kidney disease, HT, a long duration of diabetes mellitus, or three or more CV risk factors. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Optimal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level for Primary Prevention in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ji Yoon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 42. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Ye Seul Yang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 135. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Significant Gap Between Guidelines and Practice in the Management of LDL Cholesterol: Insight From the Survey of the Korean Society of Myocardial Infarction
Sang Yeub Lee, Kyung Hoon Cho, Jang Hoon Lee, Young Joon Hong, Jin yong Hwang, Myung Ho Jeong, Weon Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Association between Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Korean Adults: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- Junghyun Noh, Min Kyong Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sang Hyun Park, Hyeon Chang Kim, Byung Jin Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Jin Oh Na, Young Youl Hyun, Bum Joon Kim, Kyung-Do Han, In-Kyung Jeong, on Behalf of the Committee of Practice Guideline of Korean Lipid and Atheroscelerosis
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):59-71. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0320
- 2,726 View
- 224 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
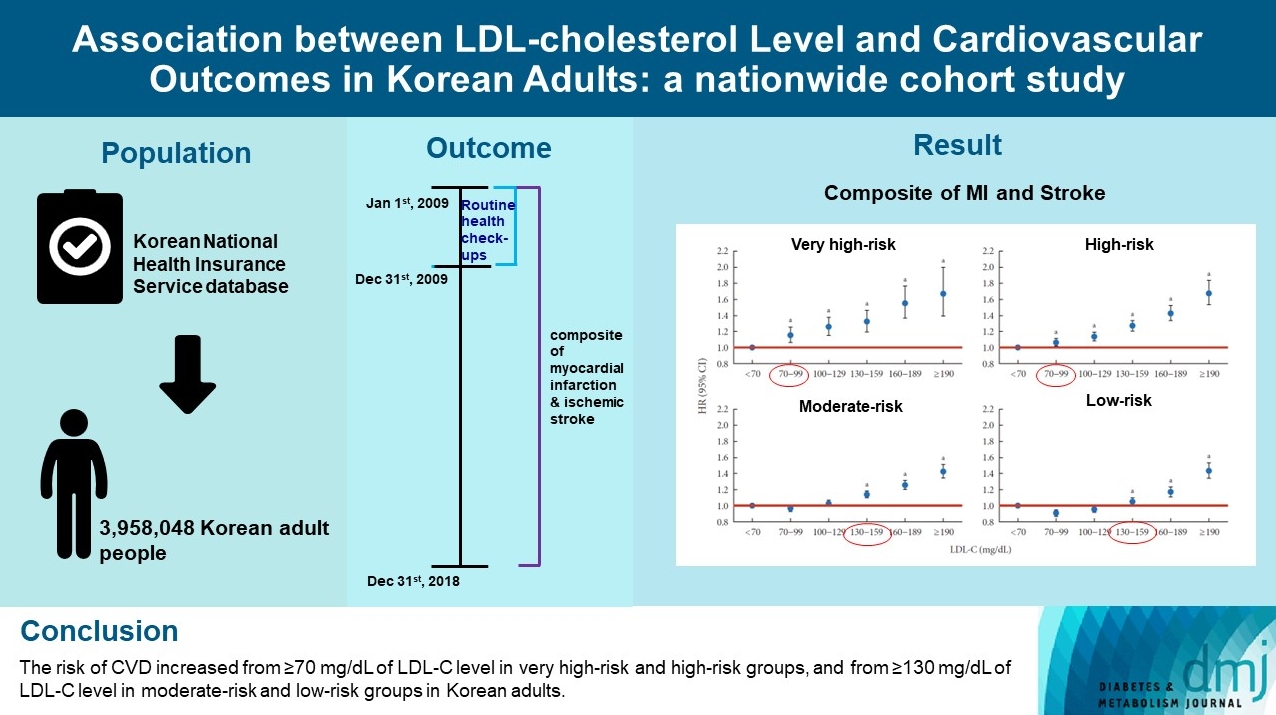
To validate the treatment target of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) level according to the cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk which was recommended by Korean dyslipidemia guideline.
Methods
We used the Korean National Health Insurance Service database which included 3,958,048 people aged 20 to 89 years who underwent regular health screening. The primary outcome was incident CVD, defined as a composite of myocardial infarction and stroke during the follow-up period from 2009 to 2018.
Results
The risk of CVD increased from LDL-C level of 70 mg/dL in very high-risk and high-risk groups and from 130 mg/dL in moderate-risk and low-risk groups. Adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) of LDL-C ranges 70–99, 100–129, 130–159, 160–189, and ≥190 mg/dL were 1.20 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.08–1.33), 1.27 (1.15–1.42), 1.39 (1.23–1.56), 1.69 (1.45–1.96), and 1.84 (1.49– 2.27) in very high-risk group, and 1.07 (1.02–1.13), 1.16 (1.10–1.21), 1.29 (1.22–1.36), 1.45 (1.36–1.55), and 1.73 (1.58–1.90) in high-risk group. Adjusted HRs (95% CI) of LDL-C ranges 130–159, 160–189, and ≥190 mg/dL were 1.15 (1.11–1.20), 1.28 (1.22– 1.34), and 1.45 (1.36–1.54) in moderate-risk group and 1.07 (1.02–1.13), 1.20 (1.13–1.26), and 1.47 (1.37–1.57) in low-risk group.
Conclusion
We confirmed the incidence of CVD was increased in higher LDL-C range. The risk of CVD increased from ≥70 mg/dL of LDL-C in very high-risk and high-risk groups, and from ≥130 mg/dL of LDL-C in moderate-risk and low-risk groups in Korean adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and Safety of a Single-Pill Triple Combination of Olmesartan, Amlodipine, and Rosuvastatin in Hypertensive Patients with Low-to-Moderate Cardiovascular Risk: A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label, Active-Control, Phase IV Clinical Trial
Byung Jin Kim, Kwang Soo Cha, Wook Hyun Cho, Eung Ju Kim, Seung-Hyuk Choi, Moo Hyun Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Jun-Bean Park, Seong-Mi Park, Il Suk Sohn, Kyu Hyung Ryu, In-Ho Chae
Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology and Therapeutics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Efficacy and Safety of a Single-Pill Triple Combination of Olmesartan, Amlodipine, and Rosuvastatin in Hypertensive Patients with Low-to-Moderate Cardiovascular Risk: A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label, Active-Control, Phase IV Clinical Trial
- Others
- Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
- Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):552-563. Published online July 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0193

- 5,718 View
- 277 Download
- 32 Web of Science
- 33 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Recently, medical research using big data has become very popular, and its value has become increasingly recognized. The Korean National Health Information Database (NHID) is representative of big data that combines information obtained from the National Health Insurance Service collected for claims and reimbursement of health care services and results obtained from general health examinations provided to all Korean adults. This database has several strengths and limitations. Given the large size, various laboratory data, and questionnaires obtained from medical check-ups, their longitudinal nature, and long-term accumulation of data since 2002, carefully designed studies may provide valuable information that is difficult to obtain from other forms of research. However, consideration of possible bias and careful interpretation when defining causal relationships is also important because the data were not collected for research purposes. After the NHID became publicly available, research and publications based on this database have increased explosively, especially in the field of diabetes and metabolism. This article reviews the history, structure, and characteristics of the Korean NHID. Recent trends in big data research using this database, commonly used operational diagnosis, and representative studies have been introduced. We expect further progress and expansion of big data research using the Korean NHID.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
Jinyoung Kim, Bongseong Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 567. CrossRef - Repeated detection of non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease increases the incidence risk of type 2 diabetes in young adults
Jin Hwa Kim, Young Sang Lyu, Mee Kyoung Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(1): 180. CrossRef - Diabetes severity and the risk of depression: A nationwide population-based study
Yunjung Cho, Bongsung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 351: 694. CrossRef - Diabetes Duration, Cholesterol Levels, and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases in Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyu Na Lee, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Remnant cholesterol is an independent risk factor for the incidence of chronic kidney disease in newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population-based study
Soo Yeon Jang, Minwoong Kang, Eyun Song, Ahreum Jang, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111639. CrossRef - Association of the Intensive Blood Pressure Target and Cardiovascular Outcomes in the Population With Chronic Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Study in Korea
Soo‐Young Yoon, Ji Yoon Kong, Su Jin Jeong, Jin Sug Kim, Hyeon Seok Hwang, Kyunghwan Jeong
Journal of the American Heart Association.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Depression according to Cumulative Exposure to a Low-Household Income Status in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population- Based Study
So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Kyu-na Lee, Bongsung Kim, So Hyun Cho, So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 290. CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef - A nationwide cohort study on diabetes severity and risk of Parkinson disease
Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Seung Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
npj Parkinson's Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting the Risk of Insulin-Requiring Gestational Diabetes before Pregnancy: A Model Generated from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
Seung-Hwan Lee, Jin Yu, Kyungdo Han, Seung Woo Lee, Sang Youn You, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 129. CrossRef - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Comparison of Operational Definition of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Data from Korean National Health Insurance Service and Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Ha Baek, Yong-Moon Park, Kyung Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Han Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 201. CrossRef - Comorbidity Differences by Trajectory Groups as a Reference for Identifying Patients at Risk for Late Mortality in Childhood Cancer Survivors: Longitudinal National Cohort Study
Hyery Kim, Hae Reong Kim, Sung Han Kang, Kyung-Nam Koh, Ho Joon Im, Yu Rang Park
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e41203. CrossRef - Diabetes severity is strongly associated with the risk of active tuberculosis in people with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study with a 6-year follow-up
Ji Young Kang, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim
Respiratory Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Investigation of the Relationship Between Psychiatry Visit and Suicide After Deliberate Self-harm: Longitudinal National Cohort Study
Hye Hyeon Kim, Chanyoung Ko, Ji Ae Park, In Han Song, Yu Rang Park
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e41261. CrossRef - Reply
Yeonghee Eun, Hyungjin Kim, Jaejoon Lee
Arthritis & Rheumatology.2023; 75(6): 1081. CrossRef - Fatty Liver & Diabetes Statistics in Korea: Nationwide Data 2009 to 2017
Eugene Han, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-ho Lee, Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Jung Hwan Park, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 347. CrossRef - Comparison of Cefepime with Piperacillin/Tazobactam Treatment in Patients with Hospital-Acquired Pneumonia
Bo-Guen Kim, Danbee Kang, Kyung Hoon Min, Juhee Cho, Kyeongman Jeon
Antibiotics.2023; 12(6): 984. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to metabolic syndrome increases thyroid cancer risk in young adults: a population-based cohort study
Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(4): 526. CrossRef - Risk of developing chronic kidney disease in young-onset Type 2 diabetes in Korea
Joonyub Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon, Jae Hyoung Cho, Kyungdo Han, Yeoree Yang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting High Body Weight Variability
Kyungdo Han, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 163. CrossRef - Physical activity and reduced risk of fracture in thyroid cancer patients after thyroidectomy — a nationwide cohort study
Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Jeonghoon Ha, Chaiho Jeong, Jun-Young Heu, Se-Won Lee, Jeongmin Lee, Yejee Lim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Hyun Baek
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of diabetes status on total and site-specific cancer risk in the elderly population: A nationwide cohort study
Kyuho Kim, Bongseong Kim, Hyunho Kim, Hyung Soon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110866. CrossRef - Response to comments of Lai et al. “Proposal of one option for patient-centered, heterogeneous selection of antidiabetic drug”
Sunyoung Kim, Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110864. CrossRef - Risk of Pancreatic Cancer and Use of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score-Matching Analysis
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Soon Jib Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 426. CrossRef - Increased risk of ischemic stroke associated with elevated gamma-glutamyl transferase level in adult cancer survivors: a population-based cohort study
Kyuwoong Kim, Hyeyun Jung, Edvige Di Giovanna, Tae Joon Jun, Young-Hak Kim
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-world data analysis on effectiveness of integrative therapies: A practical guide to study design and data analysis using healthcare databases
Ye-Seul Lee, Yoon Jae Lee, In-Hyuk Ha
Integrative Medicine Research.2023; 12(4): 101000. CrossRef - Possible Applications of the Korean Experience in the Development of Croatian Healthcare System
Predrag Bejakovic, Romina P Družeta, Ohmin Kwon
Science, Art and Religion.2023; 2(1--2): 26. CrossRef - Cumulative effect of impaired fasting glucose on the risk of dementia in middle-aged and elderly people: a nationwide cohort study
Jin Yu, Kyu-Na Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Alcohol consumption and the risk of liver disease: a nationwide, population-based study
Sang Yi Moon, Minkook Son, Yeo Wool Kang, Myeongseok Koh, Jong Yoon Lee, Yang Hyun Baek
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Levels and the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Han-Sang Baek, Bongseong Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Dong-Jun Lim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Sang-Ah Chang, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(6): 770. CrossRef - Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A nationwide propensity-score matched cohort study
Jinyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 194: 110187. CrossRef - Chronic viral hepatitis accelerates lung function decline in smokers
Suh-Young Lee, Sun-Sin Kim, So-Hee Lee, Heung-Woo Park
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2022; 23(6): 2159. CrossRef
- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2021
- Jae Hyun Bae, Kyung-Do Han, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ye Seul Yang, Jong Han Choi, Kyung Mook Choi, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyu Chang Won, on Behalf of the Committee of Media-Public Relation of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):417-426. Published online May 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0106

- 13,719 View
- 1,655 Download
- 76 Web of Science
- 99 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to investigate the prevalence and management of diabetes mellitus, risk-factor control, and comorbidities among Korean adults.
Methods
We conducted a cross-sectional analysis of data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey to assess the prevalence, treatment, risk factors, comorbidities, and self-management behaviors of diabetes mellitus from 2019 to 2020. We also analyzed data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service to evaluate the use of antidiabetic medications in people with diabetes mellitus from 2002 through 2018.
Results
Among Korean adults aged 30 years or older, the estimated prevalence of diabetes mellitus was 16.7% in 2020. From 2019 through 2020, 65.8% of adults with diabetes mellitus were aware of the disease and treated with antidiabetic medications. The percentage of adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) <6.5% was 24.5% despite the increased use of new antidiabetic medications. We found that adults with diabetes mellitus who achieved all three goals of HbA1c <6.5%, blood pressure (BP) <140/85 mm Hg, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol <100 mg/dL were 9.7%. The percentage of self-management behaviors was lower in men than women. Excess energy intake was observed in 16.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus.
Conclusion
The prevalence of diabetes mellitus among Korean adults remained high. Only 9.7% of adults with diabetes mellitus achieved all glycemic, BP, and lipid controls from 2019 to 2020. Continuous evaluation of national diabetes statistics and a national effort to increase awareness of diabetes mellitus and improve comprehensive diabetes care are needed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
Jinyoung Kim, Bongseong Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Ki‐Ho Song, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 567. CrossRef - Changes in Fatty Liver Disease and Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Young Korean Adults
Kye-Yeung Park, Hwan-Sik Hwang, Kyungdo Han, Hoon-Ki Park
American Journal of Preventive Medicine.2024; 66(4): 717. CrossRef - Widening disparities in the national prevalence of diabetes mellitus for people with disabilities in South Korea
I. Hwang, S.Y. Kim, Y.Y. Kim, J.H. Park
Public Health.2024; 226: 173. CrossRef - Questionnaire-Based Survey of Diabetes Self-Care Activities and Barriers among Young Korean Adults with Early-Onset Diabetes
Ji In Park, Sang-Wook Kim, Il Sung Nam-Goong, Kee-Ho Song, Ji Hee Yu, Ji Yun Jeong, Eun-Hee Cho
Yonsei Medical Journal.2024; 65(1): 42. CrossRef - Patients with diabetes in regions with population decline and likelihood of receiving diabetes management education and screenings for related complications in Korea
Yeong Jun Ju, Woorim Kim, Kyujin Chang, Tae Hoon Lee, Soon Young Lee
Preventive Medicine.2024; 178: 107793. CrossRef - Association between underweight and risk of heart failure in diabetes patients
Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung‐Do Han, Eun‐Jung Rhee, Won‐Young Lee
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2024; 15(2): 671. CrossRef - Gastroparesis might not be uncommon in patients with diabetes mellitus in a real-world clinical setting: a cohort study
Jeongmin Lee, Hye Lim Park, Su Young Park, Chul-Hyun Lim, Min-Hee Kim, Jung Min Lee, Sang-Ah Chang, Jung-Hwan Oh
BMC Gastroenterology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to impaired fasting glucose and gastrointestinal cancer risk: A nationwide cohort study
Byeong Yun Ahn, Bokyung Kim, Sanghyun Park, Sang Gyun Kim, Kyungdo Han, Soo‐Jeong Cho
Cancer.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Multidimensional behavioral factors for diabetes management among middle-aged adults: a population-based study
Hyerang Kim, Heesook Son
Journal of Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Once-Weekly Semaglutide Versus Once-Daily Sitagliptin as Metformin Add-on in a Korean Population with Type 2 Diabetes
Byung-Wan Lee, Young Min Cho, Sin Gon Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Soo Lim, Amine Dahaoui, Jin Sook Jeong, Hyo Jin Lim, Jae Myung Yu
Diabetes Therapy.2024; 15(2): 547. CrossRef - Association between dietary selenium intake and severe abdominal aortic calcification in the United States: a cross-sectional study
Weiwei Dong, Xiaobai Liu, Lu Ma, Zhiyong Yang, Chunyan Ma
Food & Function.2024; 15(3): 1575. CrossRef - Cumulative exposure to hypertriglyceridemia and risk of type 2 diabetes in young adults
Min-Kyung Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Jong-Dai Kim, Moon Jung Kim, Byungpyo Kim, Jung Heo, Jiyeon Ahn, Seo-Young Sohn, Jae-Hyuk Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 208: 111109. CrossRef - Recent evidence on target blood pressure in patients with hypertension
Hack-Lyoung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2024; 6(1): 17. CrossRef - Status and trends in epidemiologic characteristics of diabetic end-stage renal disease: an analysis of the 2021 Korean Renal Data System
Kyeong Min Kim, Seon A Jeong, Tae Hyun Ban, Yu Ah Hong, Seun Deuk Hwang, Sun Ryoung Choi, Hajeong Lee, Ji Hyun Kim, Su Hyun Kim, Tae Hee Kim, Ho-Seok Koo, Chang-Yun Yoon, Kiwon Kim, Seon Ho Ahn, Yong Kyun Kim, Hye Eun Yoon
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 43(1): 20. CrossRef -
In silico
exploration of the potential inhibitory activities of in-house and ZINC database lead compounds against alpha-glucosidase using structure-based virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulation approach
Zuhier A. Awan, Haider Ali Khan, Alam Jamal, Sulaiman Shams, Guojun Zheng, Abdul Wadood, Muhammad Shahab, Mohammad Imran Khan, Abdulaziz A. Kalantan
Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Evaluation of Mobile Applications for Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Scoping Review
Jung Lim Lee, Youngji Kim
Healthcare.2024; 12(3): 368. CrossRef - Current status of remote collaborative care for hypertension in medically underserved areas
Seo Yeon Baik, Kyoung Min Kim, Hakyoung Park, Jiwon Shinn, Hun-Sung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2024; 6(1): 33. CrossRef - Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: nationwide population based study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
BMJ.2024; : e076388. CrossRef - Comparison of metabolic and neurological comorbidities in Asian patients with psoriasis and atopic dermatitis
Hee Joo Yang, Mi Young Lee, Jeong Hyeon Lee, Chang Jin Jung, Woo Jin Lee, Chong Hyun Won, Mi Woo Lee, Joon Min Jung, Sung Eun Chang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cancer risk according to fasting blood glucose trajectories: a population-based cohort study
Thi Minh Thu Khong, Thi Tra Bui, Hee-Yeon Kang, Jinhee Lee, Eunjung Park, Jin-Kyoung Oh
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2024; 12(1): e003696. CrossRef - Participation experience in self-care program for type 2 diabetes: A mixed-methods study
Mihwan Kim, Haejung Lee, Gaeun Park, Ah Reum Khang
Journal of Korean Gerontological Nursing.2024; 26(1): 31. CrossRef - Fasting GLP-1 Levels and Albuminuria Are Negatively Associated in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Cheol-Won Jang, Tae Yang Yu, Jin Woo Jeong, Se Eun Ha, Rajan Singh, Moon Young Lee, Seungil Ro
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2024; 14(3): 280. CrossRef - The clinical relevance of a polygenic risk score for type 2 diabetes mellitus in the Korean population
Na Yeon Kim, Haekyung Lee, Sehee Kim, Ye-Jee Kim, Hyunsuk Lee, Junhyeong Lee, Soo Heon Kwak, Seunggeun Lee
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic traits and colorectal cancer survival in a cohort of South Korean patients: A Mendelian randomization analysis
So Yon Jun, Sooyoung Cho, Min Jung Kim, Ji Won Park, Seung‐Bum Ryoo, Seung Yong Jeong, Kyu Joo Park, Aesun Shin
Cancer Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 279. CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index predicts type 2 diabetes mellitus more effectively than oral glucose tolerance test-derived insulin sensitivity and secretion markers
Min Jin Lee, Ji Hyun Bae, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi, Mi Sook Yun, Yang Ho Kang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111640. CrossRef - Real-World Outcomes of Individualized Targeted Therapy with Insulin Glargine 300 Units/mL in Insulin-Naïve Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes: TOBE Study
Eun-Gyoung Hong, Kyung-Wan Min, Jung Soo Lim, Kyu-Jeung Ahn, Chul Woo Ahn, Jae-Myung Yu, Hye Soon Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Won Kim, Dong Han Kim, Hak Chul Jang
Advances in Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of complicated, untreated and uncontrolled diabetes and pre‐diabetes on treatment outcome among patients with pulmonary tuberculosis
Kyung Hoon Kim, Hyung Woo Kim, Yong Hyun Kim, Yeonhee Park, Sung Soo Jung, Jin Woo Kim, Jee Youn Oh, Heayon Lee, Sung Kyoung Kim, Sun‐Hyung Kim, Jiwon Lyu, Yousang Ko, Sun Jung Kwon, Yun‐Jeong Jeong, Do Jin Kim, Hyeon‐Kyoung Koo, Yangjin Jegal, Sun Young
Respirology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of dietary behavior and intake related to glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes aged 30 years or older in Korea: Utilizing the 8th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2019–2021)
Jin-Ah Seok, Yeon-Kyung Lee
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(2): 239. CrossRef - Management of Early-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Jin Hwa Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2024; 25(1): 4. CrossRef - Baseline glycated albumin level and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Healthy individuals: a retrospective longitudinal observation in Korea
Kang-Su Shin, Min-Seung Park, Mi Yeon Lee, Eun Hye Cho, Hee-Yeon Woo, Hyosoon Park, Min-Jung Kwon
Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation.2024; : 1. CrossRef - The Potential Role of Presepsin in Predicting Severe Infection in Patients with Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Eun Yeong Ha, Il Rae Park, Seung Min Chung, Young Nam Roh, Chul Hyun Park, Tae-Gon Kim, Woong Kim, Jun Sung Moon
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(8): 2311. CrossRef - Myotonic dystrophy type 1 in South Korea: a comprehensive analysis of cancer and comorbidity risks
Incheol Seo, Jin-Mo Park
Neurological Sciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Pancreatic Cancer and Use of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Propensity Score-Matching Analysis
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Soon Jib Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 426. CrossRef - Diabetes screening in South Korea: a new estimate of the number needed to screen to detect diabetes
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kyung Ae Lee, Kyung-Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Dae Jung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(1): 93. CrossRef - Sex differences in the impact of diabetes mellitus on tuberculosis recurrence: a retrospective national cohort study
Dararat Eksombatchai, Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2023; 127: 1. CrossRef - Response to Letter to the Editor From Han and Xu: “Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes”
Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(4): e58. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in catholic priests compared with general public
Youngmi Eun, Sun Myeong Ock, Se-Hong Kim, Ju Hye Chung, Se Jin Park, Churlmin Kim, Min-Kyun Im, Kyung-do Han
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(5): 655. CrossRef - Blood pressure control and its associated factors in patients with hypertension and type 2 diabetes
Anan S Jarab, Walid Al-Qerem, Salam Alqudah, Shrouq R Abu Heshmeh, Tareq L Mukattash, Karem H Alzoubi
Electronic Journal of General Medicine.2023; 20(3): em477. CrossRef - Prevalence and associated factors of diabetes mellitus among patients with tuberculosis in South Korea from 2011 to 2018: a nationwide cohort study
Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Jeong Mi Seo, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang
BMJ Open.2023; 13(3): e069642. CrossRef - The association between nutrition label utilization and disease management education among hypertension or diabetes diagnosed in Korea using 2018 Community Health Survey: a cross-sectional study
Miran Jin, Jayeun Kim, Kyuhyun Yoon
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2023; 28(1): 38. CrossRef - Insulin Fact Sheet in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Trends of Antidiabetic Medication Use in Insulin Users with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: 2002 to 2019
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Bong-Sung Kim, Kyung-Do Han, So Yoon Kwon, So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 211. CrossRef - Comparison of Operational Definition of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Data from Korean National Health Insurance Service and Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Ha Baek, Yong-Moon Park, Kyung Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Han Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 201. CrossRef - Evaluation of pharmacokinetic interactions between lobeglitazone, empagliflozin, and metformin in healthy subjects
Heeyoung Kim, Choon Ok Kim, Hyeonsoo Park, Min Soo Park, Dasohm Kim, Taegon Hong, Yesong Shin, Byung Hak Jin
Translational and Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 31(1): 59. CrossRef - Vascular and metabolic effects of ipragliflozin versus sitagliptin (IVS) in type 2 diabetes treated with sulphonylurea and metformin: IVS study
Seon Mee Kang, Han Mi Yun, Minji Sohn, Soo Lim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(7): 1922. CrossRef - Diabetes and Skin Disease
Jungah Lim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(1): 29. CrossRef - Revisiting the Diabetes Crisis in Korea: Call for Urgent Action
Jun Sung Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(1): 1. CrossRef - Association between Sleep Duration and Incident Diabetes Mellitus in Healthy Subjects: A 14-Year Longitudinal Cohort Study
Jin ha Jang, Wonjin Kim, Jin Sil Moon, Eun Roh, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm, Ji Hye Huh
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(8): 2899. CrossRef - Exercise Frequency Reduction Is Associated With Higher Risk of Infection in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes: A Nationally Representative Cohort Study
Yohwan Lim, Hye Jun Kim, Sung Soo Yoon, Sang Jun Lee, Myeong Hoon Lee, Hyewon Park, Sun Jae Park, Seogsong Jeong, Hyun Wook Han
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Consuming Heat-Treated Dodamssal Brown Rice Containing Resistant Starch on Glucose Metabolism in Humans
Jiyoung Park, Sea-Kwan Oh, Miae Doo, Hyun-Jung Chung, Hyun-Jin Park, Hyejin Chun
Nutrients.2023; 15(10): 2248. CrossRef - Opening the Precision Diabetes Care through Digital Healthcare
Joonyub Lee, Jin Yu, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 307. CrossRef - Fatty Liver & Diabetes Statistics in Korea: Nationwide Data 2009 to 2017
Eugene Han, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-ho Lee, Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Jung Hwan Park, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 347. CrossRef - Trends in the Quality of Primary Care and Acute Care in Korea From 2008 to 2020: A Cross-sectional Study
Yeong Geun Gwon, Seung Jin Han, Kyoung Hoon Kim
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2023; 56(3): 248. CrossRef - Development and Validation of Multiple Equations for Low-Density Lipoprotein and Apolipoprotein B in Korean Patients Visiting Local Clinics and Hospitals
Rihwa Choi, Sang Gon Lee, Eun Hee Lee
Nutrients.2023; 15(12): 2786. CrossRef - The role of retinal vessel geometry as an indicator of systemic arterial stiffness assessed by cardio-ankle vascular index
Dae Joong Ma, Heesun Lee, Ji Min Choi, Hyo Eun Park, Su-Yeon Choi, Hyuk Jin Choi
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between type 2 diabetes mellitus and depression among Korean midlife women: a cross-sectional analysis study
You Lee Yang, Eun-Ok Im, Yunmi Kim
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of updated cardiovascular health metrics, including sleep health, with incident diabetes and cardiovascular events in older adults with prediabetes: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Seung Jin Han
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110820. CrossRef - Paradigm Shift in Management of Hyperglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Glucocentric versus Organ Protection
Jong Chul Won
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(2): 59. CrossRef - Medical nutrition therapy for diabetes mellitus
Suk Chon
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 421. CrossRef - Prevalence and treatment status of diabetes mellitus in Korea
Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 404. CrossRef - The impact of diabetes status on total and site-specific cancer risk in the elderly population: A nationwide cohort study
Kyuho Kim, Bongseong Kim, Hyunho Kim, Hyung Soon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Seung Yun
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110866. CrossRef - Response to comments of Lai et al. “Proposal of one option for patient-centered, heterogeneous selection of antidiabetic drug”
Sunyoung Kim, Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110864. CrossRef - Association of Dental Diseases and Oral Hygiene Care With the Risk of Heart Failure in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Youn Huh, Jung Eun Yoo, Sang‐Hyun Park, Kyungdo Han, Seon Mee Kim, Hye Soon Park, Kyung Hwan Cho, Jin‐Soo Ahn, Sang Ho Jun, Ga Eun Nam
Journal of the American Heart Association.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bidirectional associations between periodontal disease and systemic diseases: a nationwide population-based study in Korea
Salma Nabila, Jaesung Choi, Ji-Eun Kim, Seokyung Hahn, In-Kyung Hwang, Tae-Il Kim, Hee-Kyung Park, Ji-Yeob Choi
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term Effectiveness of the National Diabetes Quality Assessment Program in South Korea
Ji Hye Huh, Serim Kwon, Gui Ok Kim, Bo Yeon Kim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(9): 1700. CrossRef - Refined Diagnostic Protocol for Diabetic Polyneuropathy: Paving the Way for Timely Detection
Byung-Mo Oh
Annals of Rehabilitation Medicine.2023; 47(4): 234. CrossRef - Analysis of difference in body fluid composition and dietary intake between Korean adults with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yu-Gyeong Kim, Ha-Neul Choi, Jung-Eun Yim
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2023; 56(4): 377. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus in the Elderly Adults in Korea: Based on Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019 to 2020
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Yong-Moon Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Kyuho Kim, Jae-Hyun Bae, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Nan-Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 643. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - Association between initial continuity of care status and diabetes-related health outcomes in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A nationwide retrospective cohort study in South Korea
Hyun Woo Jung, Woo-Ri Lee
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(6): 600. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes
Min Kyong Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 120. CrossRef - Diagnostic performance of the fibrosis-4 index and the NAFLD fibrosis score for screening at-risk individuals in a health check-up setting
Huiyul Park, Eileen L. Yoon, Mimi Kim, Jonghyun Lee, Hye-Lin Kim, Seon Cho, Eun-Hee Nah, Dae Won Jun
Hepatology Communications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Cause-Specific Mortality across Glucose Spectrum in Elderly People: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Joonyub Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Soon Jib Yoo, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 525. CrossRef - The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population
Sunghwan Suh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 522. CrossRef - Comparative Risk of Type 2 Diabetes after Gastrectomy and Endoscopic Resection for Gastric Cancer: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Yeongkeun Kwon, Jin-Won Kwon, Jiyun Kim, Dohyang Kim, Jinseub Hwang, Jane Ha, Shin-Hoo Park, Sungsoo Park
Journal of the American College of Surgeons.2023; 237(6): 902. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Evogliptin Add-on Therapy to Dapagliflozin/Metformin Combinations in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week Multicenter Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel-Design Phase-3 Trial with a 28-Week Extensio
Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Hae Jin Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Chang Won, Kyung Ah Han, Cheol-Young Park, Jong Chul Won, Dong Jun Kim, Gwan Pyo Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Chang Beom Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 808. CrossRef - Association between diabetes mellitus and cause of death in patients with tuberculosis: A Korean nationwide cohort study
Se Hyun Kwak, Dawoon Jeong, Jeongha Mok, Doosoo Jeon, Hee-Yeon Kang, Hee Jin Kim, Hee-Sun Kim, Hongjo Choi, Young Ae Kang, Frederick Quinn
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(12): e0295556. CrossRef - Strategies to Maintain the Remission of Diabetes Following Metabolic Surgery
Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Soon Kim
Journal of Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery.2023; 12(2): 26. CrossRef - Anti-Diabetic Medications and Osteoporosis
Kyongyoung Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 173. CrossRef - The associations between changes in hepatic steatosis and heart failure and mortality: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Hasung Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: is it preventable?
Seung-Hyun Ko
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(3): 106. CrossRef - Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 552. CrossRef - Current status of obesity treatment in Korea: based on the 2020 Korean Society for the Study of Obesity guidelines for obesity management
Eun-Jung Rhee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(7): 388. CrossRef - 젊은 2형 당뇨병 환자의 관리
재현 배
Public Health Weekly Report.2022; 15(35): 2474. CrossRef - Analysis of the Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Renal Function in Middle-Aged Patients with Diabetes
Yoonjin Park, Su Jung Lee
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(18): 11832. CrossRef - The Degree of Glycemic Control for the First Three Months Determines the Next Seven Years
Nami Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Blood Pressure Target in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hyun-Jin Kim, Kwang-il Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 667. CrossRef - Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes
Yewon Na, Soo Wan Kim, Ie Byung Park, Soo Jung Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Jaehun Jung, Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(11): 3022. CrossRef - Education for Insulin Injection in Elderly Diabetic Patients
Gi Yeon Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(3): 201. CrossRef - Recent Updates on Phytoconstituent Alpha-Glucosidase Inhibitors: An Approach towards the Treatment of Type Two Diabetes
Hamdy Kashtoh, Kwang-Hyun Baek
Plants.2022; 11(20): 2722. CrossRef - Epidemiological characteristics of diabetes mellitus in Korea
Soon Young Lee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2022; 65(10): 640. CrossRef - Screening for Prediabetes and Diabetes in Korean Nonpregnant Adults: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2022
Kyung Ae Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Suk Chon, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 819. CrossRef - Oldies but Goodies: Thiazolidinedione as an Insulin Sensitizer with Cardioprotection
Eun-Hee Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 827. CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Acceptance Action in the Relationship between Diabetes Distress and Self-stigma among Old Adults with Diabetes in South Korea
Hyesun Kim, Kawoun Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(4): 446. CrossRef
- Weight change in patients with new‐onset type 2 diabetes mellitus and its association with remission: Comprehensive real‐world data
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Trends in the Prevalence of Obesity and Its Phenotypes Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey from 2007 to 2017 in Korea
- Sang Ouk Chin, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):808-812. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0226
- 3,873 View
- 215 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - This study used data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey IV–VII from 2007 to identify the prevalence of obesity and its phenotypes (metabolically unhealthy obesity [MUO] and metabolically healthy obesity [MHO]) and their secular changes. The prevalence of obesity in Korea increased with significant secular changes observed (β=0.326, P trend <0.01) between 2007 and 2017, and especially in men (β=0.682, P trend <0.001) but not in women. The changes in the prevalence of obesity during the study period were different between men and women (P=0.001). The prevalence of MUO significantly increased only in men (β=0.565, P trend <0.01), while that of MHO increased only in women (β=0.179, P<0.05), especially in the younger age group (β=0.308, P<0.01).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hormonal Gut–Brain Signaling for the Treatment of Obesity
Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3384. CrossRef - Differences of Regional Fat Distribution Measured by Magnetic Resonance Imaging According to Obese Phenotype in Koreans
Ha-Neul Choi, Hyunjung Lim, Young-Seol Kim, Sang-Youl Rhee, Jung-Eun Yim
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2022; 20(10): 551. CrossRef
- Hormonal Gut–Brain Signaling for the Treatment of Obesity
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Increased Visit-to-Visit Liver Enzyme Variability Is Associated with Incident Diabetes: A Community-Based 12-Year Prospective Cohort Study
- Kyuhoon Bang, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, You-Cheol Hwang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):890-898. Published online March 17, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0208
- 4,810 View
- 155 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
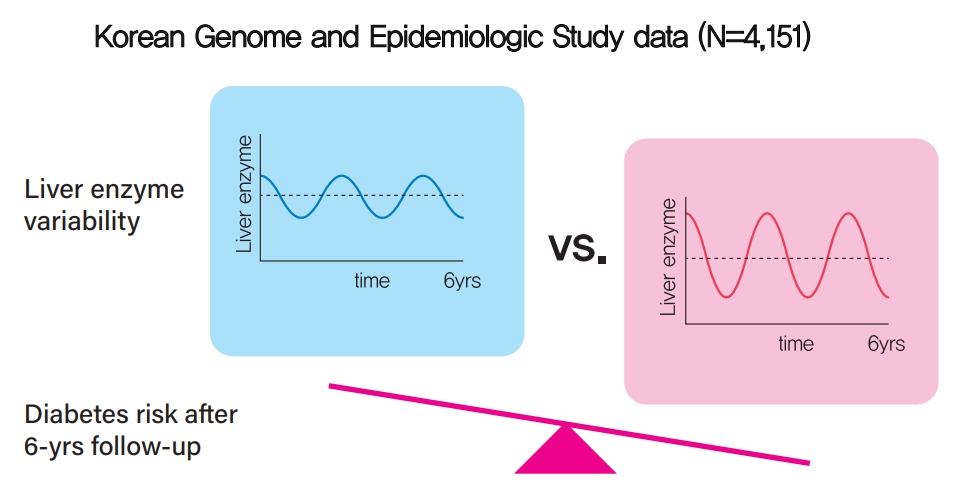
- Background
Fatty liver and/or increased liver enzyme values have been reported to be associated with incident diabetes. We sought to determine whether increased visit-to-visit liver enzyme variability is associated with incident diabetes.
Methods
Study participants were recruited from the Korean Genome and Epidemiologic Study (KoGES). A total of 4,151 people aged 40 to 69 years was recruited and tested every 2 years for up to 12 years. Visit-to-visit aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) variability was evaluated in first the 6-year period through the use of various variability measurements: standard deviation (SD), average successive variability, coefficient of variation (CV), and variation independent of mean (VIM). Oral glucose tolerance test was performed at every visit.
Results
During the 6-year follow‐up appointments, 13.0% (538/4,151) of people developed incident diabetes. Visit-to-visit AST variability was associated with an increased risk of diabetes independent of conventional risk factors for diabetes (hazard ratio per 1-SD increment [95% confidence interval]: 1.06 [1.00 to 1.11], 1.12 [1.04 to 1.21], and 1.13 [1.04 to 1.22] for SD, CV, and VIM, respectively; all P<0.05); however, no such associations were observed in the visit-to-visit ALT variability. According to alcohol consumption status, both AST and ALT variability were independent predictors for incident diabetes in subjects with heavy alcohol consumption; however, neither AST nor ALT variability was associated with diabetes risk in subjects who did not drink alcohol heavily.
Conclusion
Visit-to-visit liver enzyme variability is an independent predictor of incident diabetes. Such association was more evident in those who consumed significant amounts of alcohol.
- Drug/Regimen
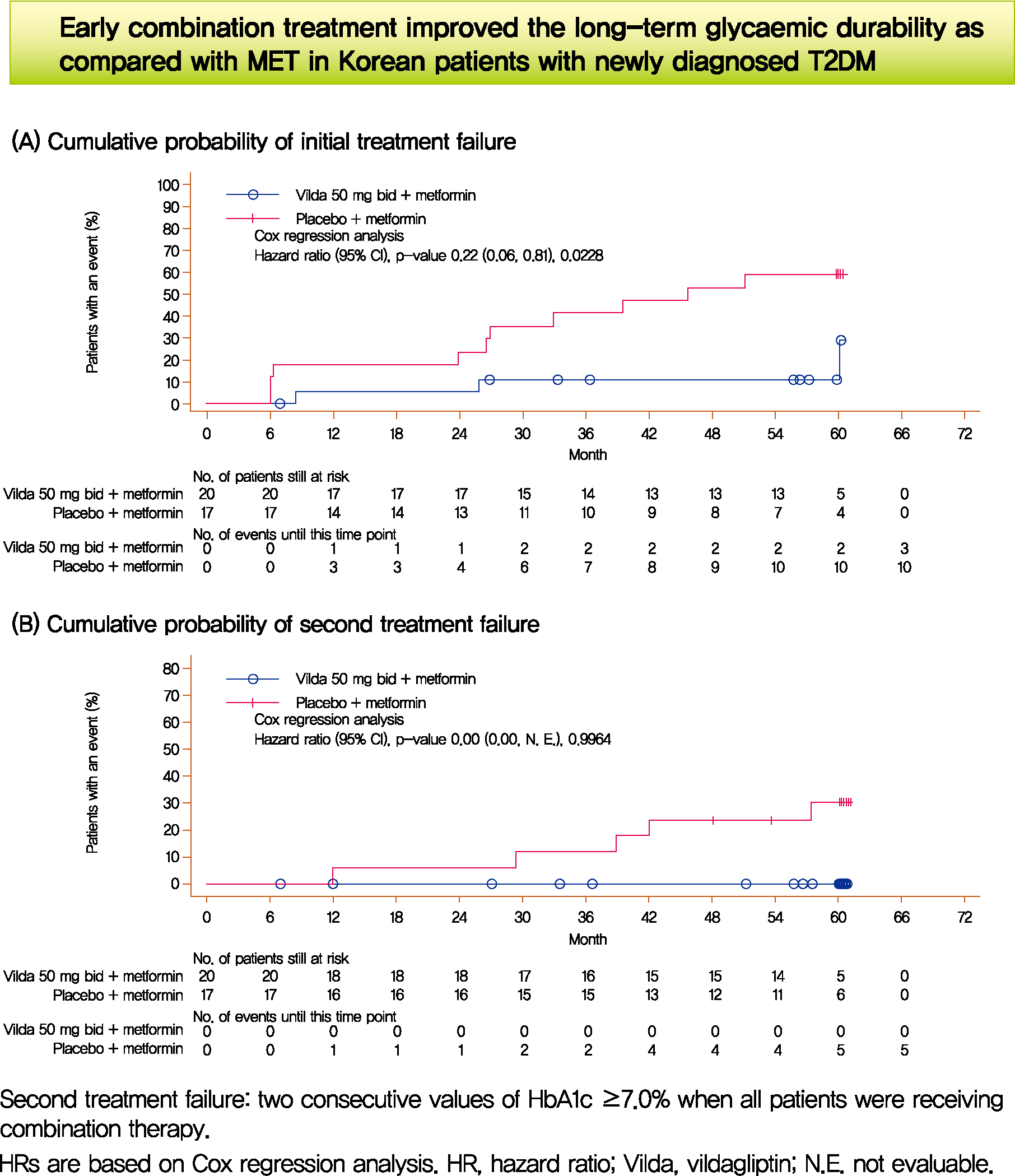
- Long-Term Glycaemic Durability of Early Combination Therapy Strategy versus Metformin Monotherapy in Korean Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Soon-Jib Yoo, Sang-Ah Chang, Tae Seo Sohn, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Jong Min Lee, Sungdae Moon, Pieter Proot, Päivi M Paldánius, Kun Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):954-959. Published online November 12, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0173
- 55,049 View
- 367 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- We assessed the glycaemic durability with early combination (EC; vildagliptin+metformin [MET], n=22) versus MET monotherapy (n=17), among newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) enrolled (between 2012 and 2014) in the VERIFY study from Korea (n=39). Primary endpoint was time to initial treatment failure (TF) (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] ≥7.0% at two consecutive scheduled visits after randomization [end of period 1]). Time to second TF was assessed when both groups were receiving and failing on the combination (end of period 2). With EC the risk of initial TF significantly reduced by 78% compared to MET (n=3 [15%] vs. n=10 [58.7%], P=0.0228). No secondary TF occurred in EC group versus five patients (29.4%) in MET. Patients receiving EC treatment achieved consistently lower HbA1c levels. Both treatment approaches were well tolerated with no hypoglycaemic events. In Korean patients with newly diagnosed T2DM, EC treatment significantly and consistently improved the long-term glycaemic durability as compared with MET.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Kyu Yeon Hur, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Jong Ha Baek, Junghyun Noh, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Ye Seul Yang, Jang Won Son, Jong Han Choi, Kee Ho Song, Nam Hoon Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jin Wha Kim,
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 461. CrossRef
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Technology/Device
- Data Configuration and Publication Trends for the Korean National Health Insurance and Health Insurance Review & Assessment Database
- Hae Kyung Kim, Sun Ok Song, Junghyun Noh, In-Kyung Jeong, Byung-Wan Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):671-678. Published online October 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0207

- 7,190 View
- 243 Download
- 49 Web of Science
- 55 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Big data reports related to diseases and health care for the Korean population have been published since the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) and the Health Insurance Review & Assessment (HIRA) Service provided limited open access to their databases. Here, we reviewed the structure, content, and means of using data from the National Health Insurance (NHI) system for the benefit of Korean researchers and presented the latest publication trends in Korean healthcare data procured from the NHI and HIRA databases.
Methods
Since 2013, researchers have been able to obtain nationwide population-based studies using the NHI and HIRA databases of the insured. We searched publications using the NHI and the HIRA databases between 2013 and 2019 retrieved from PubMed.
Results
The NHI and HIRA databases provide nationwide population-based data. The total number of publications from 2014 to 2019 using NHI and HIRA databases is 2,541 and 655, respectively. A total of 5,465 endocrinology-related studies were performed during 2014 to 2019.
Conclusion
The NHIS and HIRA databases have provided tools for guidelines to approach world-leading population-based epidemiology and disease research. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Medical service utilization patterns among adults with insomnia: A retrospective cohort study
Min Kyung Hyun, Jang Won Lee
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2024; 67: 102325. CrossRef - COVID-19-related cardiovascular disease risk due to weight gain: a nationwide cohort study
Su Kyoung Lee, Yohwan Lim, Seogsong Jeong, Hyun Wook Han
European Journal of Medical Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Kidney Health Plan 2033 in Korea: bridging the gap between the present and the future
Do Hyoung Kim, Young Youl Hyun, Jin Joo Cha, Sua Lee, Hyun Kyung Lee, Jong Wook Choi, Su-Hyun Kim, Sang Youb Han, Cheol Whee Park, Eun Young Lee, Dae Ryong Cha, Sung Gyun Kim, Chun Soo Lim, Sun-Hee Park
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 43(1): 8. CrossRef - Bipolar disorder and the risk of cardiometabolic diseases, heart failure, and all-cause mortality: a population-based matched cohort study in South Korea
You-Bin Lee, Hyewon Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Dongwoo Kang, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hong Jin Jeon, Kyu Yeon Hur
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evidence for the biopsychosocial model of suicide: a review of whole person modeling studies using machine learning
Earvin S. Tio, Melissa C. Misztal, Daniel Felsky
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Nationwide Study of the Epidemiology, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis in Korea
Hae In Jung, Dal Ri Nam, Seung-Hun You, Jae-Woo Jung, Kang-Mo Gu, Sun-Young Jung
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantitative risk factor analysis of prior disease condition and socioeconomic status with the multiple myeloma development: nationwide cohort study
Suein Choi, Eunjin Kim, Jinhee Jung, Sung-Soo Park, Chang-Ki Min, Seunghoon Han
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of physical activity with fractures in kidney transplant recipients: A Korean nationwide cohort study
Sungmi Kim, Jin‐Hyung Jung, Kyungho Lee, Junseok Jeon, Dong Wook Shin, Hye Ryoun Jang, Jung Eun Lee, Kyungdo Han, Wooseong Huh
Clinical Transplantation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Does endometriosis increase the risks of endometrial hyperplasia and endometrial cancer?
Hoon Kim, Hyun Jung Kim, Hyeong Sik Ahn
Gynecologic Oncology.2023; 169: 147. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Outcomes according to Comorbidities and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sang Hyun Park, Hyeon Chang Kim, Byung Jin Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Jin Oh Na, Young Youl Hyun, Bum Joon Kim, Kyung-Do Han, In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 45. CrossRef - Association between Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Korean Adults: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Junghyun Noh, Min Kyong Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sang Hyun Park, Hyeon Chang Kim, Byung Jin Kim, Hae Jin Kim, Seonghoon Choi, Jin Oh Na, Young Youl Hyun, Bum Joon Kim, Kyung-Do Han, In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 59. CrossRef - Predicting the Risk of Insulin-Requiring Gestational Diabetes before Pregnancy: A Model Generated from a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study in Korea
Seung-Hwan Lee, Jin Yu, Kyungdo Han, Seung Woo Lee, Sang Youn You, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 129. CrossRef - Genital tract infection and pelvic surgery contribute to the development of endometriosis
Ae Ra Han, Suehyun Lee, Jaehun Cha, Jong-Yeup Kim, Dong-Kyu Kim, Jae Won Han, Chul Jung Kim, Sung Ki Lee
Journal of Reproductive Immunology.2023; 156: 103831. CrossRef - Big Data Research in the Field of Endocrine Diseases Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Sun Wook Cho, Jung Hee Kim, Han Seok Choi, Hwa Young Ahn, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(1): 10. CrossRef - Comorbidity Differences by Trajectory Groups as a Reference for Identifying Patients at Risk for Late Mortality in Childhood Cancer Survivors: Longitudinal National Cohort Study
Hyery Kim, Hae Reong Kim, Sung Han Kang, Kyung-Nam Koh, Ho Joon Im, Yu Rang Park
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e41203. CrossRef - Investigation of the Relationship Between Psychiatry Visit and Suicide After Deliberate Self-harm: Longitudinal National Cohort Study
Hye Hyeon Kim, Chanyoung Ko, Ji Ae Park, In Han Song, Yu Rang Park
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e41261. CrossRef - Long-term exposure to particulate matter and risk of Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia in Korea: a national population-based Cohort Study
Jung-Im Shim, Garam Byun, Jong-Tae T. Lee
Environmental Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Physical Activity With SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Severe Clinical Outcomes Among Patients in South Korea
YoHwan Lim, Myeong Hoon Lee, Seogsong Jeong, Hyun Wook Han
JAMA Network Open.2023; 6(4): e239840. CrossRef - Age at Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Who Underwent Kidney Transplantation: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Sun Ok Song, Eugene Han, Kang Ju Son, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3160. CrossRef - Nationwide patterns of hydroxychloroquine dosing and monitoring of retinal toxicity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus
Jae-Eun Lee, Dal Ri Nam, Yoon-Kyoung Sung, Yu Jeong Kim, Sun-Young Jung
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of updated cardiovascular health metrics, including sleep health, with incident diabetes and cardiovascular events in older adults with prediabetes: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Seung Jin Han
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110820. CrossRef - Association of Socioeconomic Status With Long-Term Outcome in Survivors After Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest: Nationwide Population-Based Longitudinal Study
Kyung Hun Yoo, Yongil Cho, Jaehoon Oh, Juncheol Lee, Byuk Sung Ko, Hyunggoo Kang, Tae Ho Lim, Sang Hwan Lee
JMIR Public Health and Surveillance.2023; 9: e47156. CrossRef - Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Effects of
Lactiplantibacillus plantarum THK-j112 Isolated from
Kimchi against Streptococcus mutans
Du-Na Yu, Eun-Ji Yi, Je-Yong Jung, Tae-Hoo Yi, Moochang Kook
Current Topic in Lactic Acid Bacteria and Probiotics.2023; 9(1): 9. CrossRef - The Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus according to Changes in Obesity Status in Late Middle-Aged Adults: A Nationwide Cohort Study of Korea
Joon Ho Moon, Yeonhoon Jang, Tae Jung Oh, Se Young Jung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(4): 514. CrossRef - Proton pump inhibitor use and the risk of metachronous gastric cancer after H. pylori eradication in patients who underwent endoscopic resection for gastric neoplasms: A population‐based cohort study
Eun Jeong Gong, Hye‐Kyung Jung, Bora Lee, Jitaek Hong, Jong Wook Kim, Cheol Min Shin, Young Hoon Youn, Kwang Jae Lee
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2023; 58(7): 668. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Lower Extremity Amputation in Patients with End-Stage Kidney Disease: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Min Jun Seo, Dong Geon Lee, Se Yun Ko, Ga Yeong Song, Geon Yeong Lee, Sung Hwa Kim, Dae Ryong Kang, Jiye Kim, Jun Young Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(17): 5641. CrossRef - Poorer outcomes following COVID-19 infection for patients with depression: A cohort analysis in South Korea
Su Kyoung Lee, Yohwan Lim, Seogsong Jeong, Hyun Wook Han
Annals of the Academy of Medicine, Singapore.2023; 52(8): 411. CrossRef - The role of income and frequency of dental visits in the relationship between dental sealant use and resin fillings after extended coverage: a retrospective cohort study
Dong-Hun Han, Hee-Yeon Kang, Jae-In Ryu
BMC Oral Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of changes in the hearing aid subsidy on the prevalence of hearing loss in South Korea
Chul Young Yoon, Junhun Lee, Tae Hoon Kong, Young Joon Seo
Frontiers in Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Visual Impairment Risk After Alcohol Abstinence in Patients With Newly Diagnosed Open-Angle Glaucoma
Yoon Jeong, Su Hwan Kim, Goneui Kang, Hyung-Jin Yoon, Young Kook Kim, Ahnul Ha
JAMA Network Open.2023; 6(10): e2338526. CrossRef - Impact of statin treatment on cardiovascular risk in patients with type 1 diabetes: a population-based cohort study
Joonsang Yoo, Jimin Jeon, Minyoul Baek, Sun Ok Song, Jinkwon Kim
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Socioeconomic Disparities in the Association Between All-Cause Mortality and Health Check-Up Participation Among Healthy Middle-Aged Workers: A Nationwide Study
Byungyoon Yun, Juyeon Oh, Jaesung Choi, Laura S. Rozek, Heejoo Park, Juho Sim, Yangwook Kim, Jongmin Lee, Jin-Ha Yoon
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased Estimated GFR Is Negatively Associated With the Risk of SARS-CoV-2 Infection and Severe COVID-19 Within Normal to Mildly Decreased Levels: Nested Case-Control Study
Yohwan Lim, Myeong Hoon Lee, Su Kyoung Lee, Seogsong Jeong, Hyun Wook Han
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Pregnancy Complications and Low Birth Weight Offsprings in Korean Women With Rheumatic Diseases: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Jin-Su Park, Min Kyung Chung, Hyunsun Lim, Jisoo Lee, Chan Hee Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of variability in body weight and glucose levels with the risk of hip fracture in people with diabetes
Jeongmin Lee, Kyungdo Han, Sang Hyun Park, Mee Kyoung Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Moo-Il Kang, Seung-Hwan Lee
Metabolism.2022; 129: 155135. CrossRef - Travel Time for Dental Care Services Based on Patient Preference in South Korea
Han-A Cho, Bo-Ra Kim, Hosung Shin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(4): 2051. CrossRef - The Basic Concept of Claim Data-based Research
Su Bee Park, Jae Myung Cha
The Korean Journal of Helicobacter and Upper Gastrointestinal Research.2022; 22(1): 70. CrossRef - Trends of severe hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes in Korea: A longitudinal nationwide cohort study
Jae‐Seung Yun, Kyungdo Han, Seung‐Hyun Ko
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(8): 1438. CrossRef - National General Health Screening Program in Korea: history, current status, and future direction
Dong Wook Shin, Juhee Cho, Jae Hyun Park, BeLong Cho
Precision and Future Medicine.2022; 6(1): 9. CrossRef - Cumulative Exposure to High γ-Glutamyl Transferase Level and Risk of Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Ji-Yeon Park, Kyungdo Han, Hun-Sung Kim, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Kun-Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 272. CrossRef - Understanding and Utilizing Claim Data from the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) and Health Insurance Review & Assessment (HIRA) Database for Research
Dae-Sung Kyoung, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(2): 103. CrossRef - Clinical and Cost-Saving Effects of the Drug Utilization Review Modernization Project in Inpatient and Outpatient Settings in Korea
Dongwon Yoon, Inmyung Song, Ha-Lim Jeon, Sungho Bea, Ahhyung Choi, Hyesung Lee, Ju-Young Shin
Journal of Patient Safety.2022; 18(6): 605. CrossRef - Adherence to healthy lifestyle behaviors as a preventable risk factor for severe hypoglycemia in people with type 2 diabetes: A longitudinal nationwide cohort study
Jae‐Seung Yun, Kyungdo Han, Yong‐Moon Park, Eugene Han, Yong‐ho Lee, Seung‐Hyun Ko
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(9): 1533. CrossRef - Analysis of sedation and general anesthesia in patients with special needs in dentistry using the Korean healthcare big data
Jieun Kim, Hyuk Kim, Kwang-Suk Seo, Hyun Jeong Kim
Journal of Dental Anesthesia and Pain Medicine.2022; 22(3): 205. CrossRef - Improvement in Age at Mortality and Changes in Causes of Death in the Population with Diabetes: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 466. CrossRef - Visual Acuity Outcomes in Diseases Associated with Reduced Visual Acuity: An Analysis of the National Health Insurance Service Database in Korea
Sang-Yeob Kim, Byeong-Yeon Moon, Hyun-Gug Cho, Dong-Sik Yu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(14): 8689. CrossRef - Reproductive Life Span and Severe Hypoglycemia Risk in Postmenopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Soyeon Kang, Yong-Moon Park, Dong Jin Kwon, Youn-Jee Chung, Jeong Namkung, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 578. CrossRef - Lipid cutoffs for increased cardiovascular disease risk in non-diabetic young people
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Hun-Sung Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hwan Lee
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2022; 29(14): 1866. CrossRef - Current Trends of Big Data Research Using the Korean National Health Information Database
Mee Kyoung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 552. CrossRef - Increasing trends in mortality and costs of infectious diseases in Korea: trends in mortality and costs of infectious diseases
Dahye Baik, Byung-Woo Kim, Moran Ki
Epidemiology and Health.2022; 44: e2022010. CrossRef - How to Use Health Insurance Data Effectively for Healthcare Research
Ilsu Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2022; 47(Suppl 2): S31. CrossRef - Remnant cholesterol and the risk of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: a nationwide longitudinal cohort study
Ji Hye Huh, Kyung-do Han, Yun Kyung Cho, Eun Roh, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metformin and Cervical Cancer Risk in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea
Hyun Min Kim, Min Jin Kang, Sun Ok Song
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(6): 929. CrossRef - Effect of Sex on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Coronavirus Disease: A Population-Based Study
Kyu Hyang Cho, Sang Won Kim, Jong Won Park, Jun Young Do, Seok Hui Kang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 10(1): 38. CrossRef - Increased Age of Death and Change in Causes of Death Among Persons With Diabetes Mellitus From the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Medical service utilization patterns among adults with insomnia: A retrospective cohort study
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Association of Soybean Food Intake and Cardiometabolic Syndrome in Korean Women: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2007 to 2011)
- Sook-Hyun Jun, Woo-Kyoung Shin, Yookyung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):143-157. Published online December 2, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0078
- 5,722 View
- 68 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Soybean food consumption has been considered as a possible way to lower incidence of cardiometabolic syndrome (CMS) among Asians. However, results from studies investigating its efficacy on CMS in Asians have been inconsistent.
Methods We analyzed the association between soybean intake frequency and prevalence of CMS based on data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007 to 2011. Data of 9,287 women aged 20 to 64 years were analyzed. Food frequency questionnaire was used to assess soybean food consumption frequency. General linear model and multivariable logistic regression model were used to examine the association of soybean intake quintile with CMS and its risk factors. Least square means of metabolic factors mostly showed no significant relevance except liver indexes.
Results Compared to participants in the 1st quintile (<2 times/week of soybean food), odds ratios (OR) for CMS and abdominal obesity (AO) in the 4th quintile (8.5 times/week<soybean food≤17 times/week) were 0.73 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.57 to 0.95) and 0.72 (95% CI, 0.58 to 0.90), respectively. After excluding Tofu products, ORs of CMS, AO, high blood pressure, and hypertriglyceridemia were lower than those without excluding Tofu products. However, results still did not show significant inverse linear trend across frequency quintiles.
Conclusion Our findings suggest that soybean intake of 8.5 to 17 times/week was inversely associated with CMS in Korean women. The relation between soybean intake >17 times/week and CMS varied depending on soybean food items.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Anti-obesogenic effects of plant natural products: A focus on Korean traditional foods
Gitishree Das, Luis Alfonso Jiménez Ortega, Sandra Gonçalves, J. Basilio Heredia, Maria de Lourdes Gomes Pereira, Anabela Romano, Han-Seung Shin, Jayanta Kumar Patra
Trends in Food Science & Technology.2024; : 104470. CrossRef - Sex differences in waist circumference obesity and eating speed: a cross-sectional study of Japanese people with normal body mass index
Yuri Yaguchi, Tsuneo Konta, Nahomi Imaeda, Chiho Goto, Yoshiyuki Ueno, Takamasa Kayama
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Dietary Patterns with Metabolic Syndrome in Chinese Children and Adolescents Aged 7–17: The China National Nutrition and Health Surveillance of Children and Lactating Mothers in 2016–2017
Jia Shi, Hongyun Fang, Qiya Guo, Dongmei Yu, Lahong Ju, Xue Cheng, Wei Piao, Xiaoli Xu, Zizi Li, Di Mu, Liyun Zhao, Li He
Nutrients.2022; 14(17): 3524. CrossRef - What Is the Relationship between Antioxidant Efficacy, Functional Composition, and Genetic Characteristics in Comparing Soybean Resources by Year?
Han-Na Chu, Suji Lee, Xiaohan Wang, Chi-Do Wee, Hye-Myeong Yoon, Eun-Suk Jung, Mi-Kyung Seo, Yongseok Kwon, Kyeong-A Jang, Haeng-Ran Kim
Antioxidants.2022; 11(11): 2249. CrossRef - Longitudinal changes in adherence to the portfolio and DASH dietary patterns and cardiometabolic risk factors in the PREDIMED-Plus study
Andrea J. Glenn, Pablo Hernández-Alonso, Cyril W.C. Kendall, Miguel Ángel Martínez-González, Dolores Corella, Montserrat Fitó, J.Alfredo Martínez, Ángel M. Alonso-Gómez, Julia Wärnberg, Jesús Vioque, Dora Romaguera, José López-Miranda, Ramon Estruch, Fran
Clinical Nutrition.2021; 40(5): 2825. CrossRef - The Effects of Dietary Pattern on Metabolic Syndrome in Jiangsu Province of China: Based on a Nutrition and Diet Investigation Project in Jiangsu Province
Yuanyuan Wang, Yue Dai, Ting Tian, Jingxian Zhang, Wei Xie, Da Pan, Dengfeng Xu, Yifei Lu, Shaokang Wang, Hui Xia, Guiju Sun
Nutrients.2021; 13(12): 4451. CrossRef - Sex-Specific Energy Intakes and Physical Activity Levels According to the Presence of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Elderly People: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2018
Won-Sang Jung, Hun-Young Park, Sung-Woo Kim, Kiwon Lim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(15): 5416. CrossRef
- Anti-obesogenic effects of plant natural products: A focus on Korean traditional foods
- Epidemiology
- Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2018: An Appraisal of Current Status
- Bo-Yeon Kim, Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyuk Lee, Hun-Sung Kim, Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kyu Chang Won, Dae Jung Kim, Kyong Soo Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(4):487-494. Published online July 17, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0067

- 11,227 View
- 178 Download
- 97 Web of Science
- 101 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The objective of this study was to investigate the prevalence, management, and comorbidities of diabetes among Korean adults aged 30 years and older.
Methods This study used 2013 to 2016 data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, a nationally-representative survey of the Korean population. Diabetes was defined as fasting glucose ≥126 mg/dL, current use of antidiabetic medication, a previous history of diabetes, or glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥6.5%.
Results In 2016, 14.4% (approximately 5.02 million) of Korean adults had diabetes. The prevalence of impaired fasting glucose was 25.3% (8.71 million). From 2013 to 2016, the awareness, control, and treatment rates for diabetes were 62.6%, 56.7%, and 25.1%, respectively. People with diabetes had the following comorbidities: obesity (50.4%), abdominal obesity (47.8%), hypertension (55.3%), and hypercholesterolemia (34.9%). The 25.1%, 68.4%, and 44.2% of people with diabetes achieved HbA1c <6.5%, blood pressure <140/85 mm Hg, and low density lipoprotein cholesterol <100 mg/dL. Only 8.4% of people with diabetes had good control of all three targets.
Conclusion This study confirms that diabetes is as an important public health problem. Efforts should be made to increase awareness, detection, and comprehensive management of diabetes to reduce diabetes-related morbidity and mortality.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Social Support, eHealth Literacy, and mHealth Use in Older Adults With Diabetes
Minjin Kim, Beomsoo Kim, Sunhee Park
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(2): 136. CrossRef - Cardiovascular safety of evogliptin dual and triple therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study
Sohee Park, Han Eol Jeong, In-Sun Oh, Sangmo Hong, Sung Hoon Yu, Chang Beom Lee, Ju-Young Shin
BMJ Open.2024; 14(4): e077084. CrossRef - Prognostic value of resting heart rate in predicting undiagnosed diabetes in adults: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2018
Dong-Hyuk Park, Seon Young Goo, Sung Hyun Hong, Ji-hee Min, Ji Yong Byeon, Mi-Kyung Lee, Hae Dong Lee, Byoung Wook Ahn, Heejin Kimm, Sun Ha Jee, Dong Hoon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Justin Y. Jeon
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(1): 141. CrossRef - Levels and correlates of risk factor control in diabetes mellitus –ELSA-Brasil
Bruna Cristine Chwal, Rodrigo Citton Padilha dos Reis, Maria Inês Schmidt, Bruce B. Duncan, Sandhi Maria Barreto, Rosane Harter Griep
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in total cholesterol level and cardiovascular disease risk among type 2 diabetes patients
Jaewon Khil, Sung Min Kim, Jooyoung Chang, Seulggie Choi, Gyeongsil Lee, Joung Sik Son, Sang Min Park, NaNa Keum
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of dapagliflozin compared with glimepiride on body composition in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin: The BEYOND study
Hyeong Kyu Park, Kyoung‐Ah Kim, Kyung‐Wan Min, Tae‐Seo Sohn, In Kyung Jeong, Chul Woo Ahn, Nan‐Hee Kim, Ie Byung Park, Ho Chan Cho, Choon Hee Chung, Sung Hee Choi, Kang Seo Park, Seoung‐Oh Yang, Kwan Woo Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(9): 2743. CrossRef - Comparison of SGLT2 inhibitors with DPP-4 inhibitors combined with metformin in patients with acute myocardial infarction and diabetes mellitus
Young Sang Lyu, Seok Oh, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Myung Ho Jeong
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Smoking Cessation and the Risk of Cholangiocarcinoma and Ampulla of Vater Cancer: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Joo-Hyun Park, Jung Yong Hong, Kyungdo Han
Liver Cancer.2023; 12(5): 457. CrossRef - Achievement of Treatment Goals and Mortality in Individuals with Diabetes: The ELSA-Brasil Study
Bruna Cristine Chwal, Rodrigo Citton P. dos Reis, Maria Inês Schmidt, Sandhi Maria Barreto, Rosane Harter Griep, Bruce B. Duncan
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(24): 7663. CrossRef - Cigarette Smoking and Risk of Infection-Related Mortality: A Cohort Study
Hae Suk Cheong, Yoosoo Chang, Eun-Jeong Joo, Seungho Ryu
Nicotine & Tobacco Research.2022; 24(2): 204. CrossRef - Angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors versus angiotensin receptor blockers: New‐onset diabetes mellitus stratified by statin use
Juyoung Shin, Hyunah Kim, Hyeon Woo Yim, Ju Han Kim, Suehyun Lee, Hun‐Sung Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2022; 47(1): 97. CrossRef - Exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and volatile organic compounds is associated with a risk of obesity and diabetes mellitus among Korean adults: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) 2015–2017
Inae Lee, Hyunwoong Park, Min Joo Kim, Sunmi Kim, Sohyeon Choi, Jeongim Park, Yoon Hee Cho, Sooyeon Hong, Jiyoung Yoo, Gi Jeong Cheon, Kyungho Choi, Young Joo Park, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health.2022; 240: 113886. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Chronic Disease and Health Care Utilization Among Young Adults in South Korea
Jongho Park, Yeaeun Kim
Population Health Management.2022; 25(3): 407. CrossRef - Sleep duration and mortality in patients with diabetes: Results from the 2007–2015 Korea national health and nutrition examination survey
Kang-Mo Gu, Se Hee Min, Jaeyoung Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(3): 101312. CrossRef - Retinal Vascular Caliber Changes in Early Type 2 Diabetic Patients without Retinopathy
Jeong Woo Park, Jeong Hun Bae, Su Jeong Song, Joon Mo Kim
Journal of the Korean Ophthalmological Society.2022; 63(1): 20. CrossRef - Association Between Long Working Hours and Chronic Kidney Disease According to Diabetic Status
Ki Duk Kim, Suk-Yong Jang
Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine.2022; 64(3): 190. CrossRef - Sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors do not increase the risk of fractures in real‐world clinical practice in Korea: A national observational cohort study
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Yong Jun Choi
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(6): 986. CrossRef - Improvement of Lipotoxicity-Induced Islet β Cellular Insulin Secretion Disorder by Osteocalcin
Yafang Zhang, Ling Li, Yongze Zhang, Sunjie Yan, Lingning Huang, Riccardo Calafiore
Journal of Diabetes Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Association between gastric cancer and the risk of depression among South Korean adults
Sinyoung Kwon, Jinyeong Kim, Taeyeon Kim, Wonjeong Jeong, Eun-Cheol Park
BMC Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Performance of Diabetes and Kidney Disease Screening Scores in Contemporary United States and Korean Populations
Liela Meng, Keun-Sang Kwon, Dae Jung Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Jeehyoung Kim, Abhijit V. Kshirsagar, Heejung Bang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 273. CrossRef - Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 464. CrossRef - Normalized Creatinine-to-Cystatin C Ratio and Risk of Diabetes in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Bo Xie, Yang Yuan, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 476. CrossRef - A double‐blind, Randomized controlled trial on glucose‐lowering EFfects and safety of adding 0.25 or 0.5 mg lobeglitazone in type 2 diabetes patients with INadequate control on metformin and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor therapy: REFIND study
Soree Ryang, Sang Soo Kim, Ji Cheol Bae, Ji Min Han, Su Kyoung Kwon, Young Il Kim, Il Seong Nam‐Goong, Eun Sook Kim, Mi‐kyung Kim, Chang Won Lee, Soyeon Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh, Min Jeong Kwon, Jeong Hyun Park, In Joo Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(9): 1800. CrossRef - Long‐term clinical outcomes of oral antidiabetic drugs as fixed‐dose combinations: A nationwide retrospective cohort study
Sang‐Jun Cho, In‐Sun Oh, Han Eol Jeong, Young Min Cho, Yul Hwangbo, Oriana Hoi Yun Yu, Ju‐Young Shin
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(10): 2051. CrossRef - Improvement in Age at Mortality and Changes in Causes of Death in the Population with Diabetes: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 466. CrossRef - Dietary antioxidant consumption and the risk of type 2 diabetes in South Korean adults: a prospective cohort study based on the Health Examinees study
Li-Juan Tan, Su Bin Hwang, Shinyoung Jun, Hyojee Joung, Sangah Shin
BMJ Open.2022; 12(7): e065073. CrossRef - Visual Acuity Outcomes in Diseases Associated with Reduced Visual Acuity: An Analysis of the National Health Insurance Service Database in Korea
Sang-Yeob Kim, Byeong-Yeon Moon, Hyun-Gug Cho, Dong-Sik Yu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(14): 8689. CrossRef - Development of Various Diabetes Prediction Models Using Machine Learning Techniques
Juyoung Shin, Jaewon Kim, Chanjung Lee, Joon Young Yoon, Seyeon Kim, Seungjae Song, Hun-Sung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 650. CrossRef - Real-World Prescription Patterns and Barriers Related to the Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors among Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
Jong Ha Baek, Ye Seul Yang, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Jae Hyeon Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Jong Han Choi, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 701. CrossRef - Remnant cholesterol and the risk of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: a nationwide longitudinal cohort study
Ji Hye Huh, Kyung-do Han, Yun Kyung Cho, Eun Roh, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences in health behavior and nutrient intake status between diabetes-aware and unaware Korean adults based on the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2016–18 data: A cross-sectional study
Anshul Sharma, Chen Lulu, Kee-Ho Song, Hae-Jeung Lee
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effective coverage of diabetes and hypertension: an analysis of Thailand’s national insurance database 2016–2019
Nattadhanai Rajatanavin, Woranan Witthayapipopsakul, Vuthiphan Vongmongkol, Nithiwat Saengruang, Yaowaluk Wanwong, Aniqa Islam Marshall, Walaiporn Patcharanarumol, Viroj Tangcharoensathien
BMJ Open.2022; 12(12): e066289. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Treatment with Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Multi-Center, Retrospective, Observational Study
Jun Sung Moon, Sunghwan Suh, Sang Soo Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Jeong Mi Kim, Min Hee Jang, Kyung Ae Lee, Ju Hyung Lee, Seung Min Chung, Young Sang Lyu, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jung Eun Jang, Tae Nyun Kim, Sung Woo Kim, Eonju Jeon, Nan Hee Cho, Mi-Kyung Ki
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 675. CrossRef - Association between secondhand smoke exposure and diabetes mellitus in 131 724 Korean never smokers using self‐reported questionnaires and cotinine levels: Gender differences
Byung Jin Kim, Ji Hye Kim, Jeong Gyu Kang, Bum Soo Kim, Jin Ho Kang
Journal of Diabetes.2021; 13(1): 43. CrossRef - Importance of Awareness and Treatment for Diabetes in Influenza Vaccination Coverage of Diabetic Patients under 65 Years: A Population-Based Study
Yu Mi Ko, Seung Hyun Ko, Kyoungdo Han, Yong-Moon Park, Joon Young Choi, Shin Young Kim, So Hyang Song, Chi Hong Kim, Sung Kyoung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 55. CrossRef - Associations of urinary concentrations of phthalate metabolites, bisphenol A, and parabens with obesity and diabetes mellitus in a Korean adult population: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) 2015–2017
Inae Lee, Young Joo Park, Min Joo Kim, Sunmi Kim, Sohyeon Choi, Jeongim Park, Yoon Hee Cho, Sooyeon Hong, Jiyoung Yoo, Hyunwoong Park, Gi Jeong Cheon, Kyungho Choi, Min Kyong Moon
Environment International.2021; 146: 106227. CrossRef - Early combination versus initial metformin monotherapy in the management of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: AnEast Asianperspective
Linong Ji, Juliana C. N. Chan, Miao Yu, Kun Ho Yoon, Sin Gon Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Chien‐Ning Huang, Shih Te Tu, Chih‐Yuan Wang, Päivi Maria Paldánius, Wayne H. H. Sheu
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(1): 3. CrossRef - Hypertension and stroke in Asia: A comprehensive review from HOPE Asia
Yuda Turana, Jeslyn Tengkawan, Yook Chin Chia, Michael Nathaniel, Ji‐Guang Wang, Apichard Sukonthasarn, Chen‐Huan Chen, Huynh Van Minh, Peera Buranakitjaroen, Jinho Shin, Saulat Siddique, Jennifer M. Nailes, Sungha Park, Boon Wee Teo, Jorge Sison, Arieska
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2021; 23(3): 513. CrossRef - Glycaemic control with add‐on thiazolidinedione or a sodium‐glucose co‐transporter‐2 inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes after the failure of an oral triple antidiabetic regimen: A 24‐week, randomized controlled trial
Jaehyun Bae, Ji Hye Huh, Minyoung Lee, Yong‐Ho Lee, Byung‐Wan Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(2): 609. CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Jung A Kim, Jinsil Kim, Eun Roh, So-hyeon Hong, You-Bin Lee, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi, Eunjin Noh, Soon Young Hwang, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 171: 108533. CrossRef - Effectiveness and safety of sodium‐glucose co‐transporter‐2 inhibitors compared with dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors in older adults with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population‐based study
Seung Jin Han, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Nami Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(3): 682. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2020: An Appraisal of Current Status
Chan-Hee Jung, Jang Won Son, Shinae Kang, Won Jun Kim, Hun-Sung Kim, Hae Soon Kim, Mihae Seo, Hye-Jung Shin, Seong-Su Lee, Su Jin Jeong, Yongin Cho, Seung Jin Han, Hyang Mi Jang, Mira Rho, Shinbi Lee, Mihyun Koo, Been Yoo, Jung-Wha Moon, Hye Young Lee, Ja
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 1. CrossRef - Prevalence and diagnosis experience of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women over 50: Focusing on socioeconomic factors
Min Hyeok Choi, Ji Hee Yang, Jae Seung Seo, Yoon-ji Kim, Suk-Woong Kang, Jose M. Moran
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(3): e0248020. CrossRef - Metformin use in cancer survivors with diabetes reduces all-cause mortality, based on the Korean National Health Insurance Service between 2002 and 2015
Joungyoun Kim, Yoon-Jong Bae, Jae-woo Lee, Ye-seul Kim, Yonghwan Kim, Hyo-Sun You, Hyeong-Seop Kim, Eun-A Choi, Ye-Eun Han, Hee-Taik Kang
Medicine.2021; 100(11): e25045. CrossRef - Role of obesity-induced inflammation in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: history of the research and remaining questions
Jieun Kim, Jongsoon Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - White Blood Cell Count as a Predictor of Incident Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Non-Obese Adults: A Longitudinal 10-Year Analysis of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Jae-Min Park, Hye Sun Lee, Ju-Young Park, Dong-Hyuk Jung, Ji-Won Lee
Journal of Inflammation Research.2021; Volume 14: 1235. CrossRef - The Association of Hemoglobin A1c and Fasting Glucose Levels with hs-CRP in Adults Not Diagnosed with Diabetes from the KNHANES, 2017
Jeong Woo Seo, Sat Byul Park, Ulrike Rothe
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Effects of Jerusalem Artichoke Extract and Inulin on Blood Glucose Levels and Insulin Secretion in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Mice
Seung Hee Kim, Byung Ki Kim, Boo Yeun Park, Jung Min Kim, Young Jik Lee, Mi Kyung Lee, Sung-Tae Yee, Mi Yeon Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(1): 60. CrossRef - Health State Utility Values for Type 2 Diabetes and Related Complications in East and Southeast Asia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Chiu Hang Mok, Harley H.Y. Kwok, Carmen S. Ng, Gabriel M. Leung, Jianchao Quan
Value in Health.2021; 24(7): 1059. CrossRef - Association between alcohol consumption status and obesity-related comorbidities in men: data from the 2016 Korean community health survey
Bo-Yeon Kim, Hyewon Nam, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Yoon-Young Cho, Dug-Hyun Choi, Chan-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok, Chul-Hee Kim
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease and its risk factors in Korea
Hyeon Chang Kim
Global Health & Medicine.2021; 3(3): 134. CrossRef - Korea Heart Disease Fact Sheet 2020: Analysis of Nationwide Data
Hyeok-Hee Lee, So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jongmin Baek, Jang-Ho Bae, Wook-Jin Chung, Hyeon Chang Kim
Korean Circulation Journal.2021; 51(6): 495. CrossRef - Personalized Type 2 Diabetes Management Using a Mobile Application Integrated with Electronic Medical Records: An Ongoing Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun-Young Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Seon-Ah Cha, Sun-Young Lim, Jin-Hee Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hyun Ko
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(10): 5300. CrossRef - Association between toothbrushing and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Ji-Youn Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Gyu-Na Lee, Hyun Chul Song, Yu-Bae Ahn, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hyun Ko, Houkai Li
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(5): e0243686. CrossRef - Control of Glucose, Blood Pressure, and Cholesterol among Adults with Diabetes: The Brazilian National Health Survey
Rodrigo Citton P. dos Reis, Bruce B. Duncan, Célia Landmann Szwarcwald, Deborah Carvalho Malta, Maria Inês Schmidt
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(15): 3428. CrossRef - Comparison of fracture risk between type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a comprehensive real-world data
J. Ha, C. Jeong, K.-D. Han, Y. Lim, M.K. Kim, H.-S. Kwon, K.-H. Song, M.I. Kang, K.-H. Baek
Osteoporosis International.2021; 32(12): 2543. CrossRef - Treatment Patterns of Type 2 Diabetes Assessed Using a Common Data Model Based on Electronic Health Records of 2000–2019
Kyung Ae Lee, Heung Yong Jin, Yu Ji Kim, Yong-Jin Im, Eun-Young Kim, Tae Sun Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Etiology, diagnosis, complications, and treatments of diabetic foot
Dong-Kyo Seo
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2021; 64(8): 523. CrossRef - Occupational Noise Exposure and Incidence of High Fasting Blood Glucose: A 3-Year, Multicenter, Retrospective Study
Seunghan Kim, Byungyoon Yun, Seunghyun Lee, Changyoung Kim, Juho Sim, Ara Cho, Yeonsuh Oh, Jiho Lee, Jinha Yoon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(17): 9388. CrossRef - Positive association between the ratio of triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and diabetes incidence in Korean adults
Joungyoun Kim, Sang-Jun Shin, Ye-Seul Kim, Hee-Taik Kang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Standard E TB-Feron ELISA and QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus Assays in Patients with Tuberculosis and Healthcare Workers
In Young Yoo, Jaewoong Lee, Ae Ran Choi, Yoon Hee Jun, Hwa Young Lee, Ji Young Kang, Yeon-Joon Park
Diagnostics.2021; 11(9): 1659. CrossRef - Associations between obesity, weight change and decreased renal function in Korean type 2 diabetic patients: a longitudinal follow-up study
Bo-Yeon Kim, Dug-Hyun Choi, Chan-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok, Chul-Hee Kim
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-World Efficacy and Safety of Dulaglutide in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Study in a Tertiary Referral Center
Jee Hee Yoon, A Ram Hong, Wonsuk Choi, Ji Yong Park, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang
Chonnam Medical Journal.2021; 57(3): 211. CrossRef - The History of Insulin Therapy in Korea
Jun Sung Moon, Jong Chul Won, Young Min Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 623. CrossRef - How Can We Adopt the Glucose Tolerance Test to Facilitate Predicting Pregnancy Outcome in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus?
Kyeong Jin Kim, Nam Hoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Ju Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 988. CrossRef - Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Disease in Older Patients With Diabetes: Retrospective Cohort Study
Sangmo Hong, Jung Hwan Park, Kyungdo Han, Chang Beom Lee, Dong Sun Kim, Sung Hoon Yu
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Glycaemic Durability of Early Combination Therapy Strategy versus Metformin Monotherapy in Korean Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Soon-Jib Yoo, Sang-Ah Chang, Tae Seo Sohn, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Jong Min Lee, Sungdae Moon, Pieter Proot, Päivi M Paldánius, Kun Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 954. CrossRef - Short-Term Effects of the Internet-Based Korea Diabetes Prevention Study: 6-Month Results of a Community-Based Randomized Controlled Trial
Jin-Hee Lee, Sun-Young Lim, Seon-Ah Cha, Chan-Jung Han, Ah Reum Jung, Kook-Rye Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 960. CrossRef - Anti-diabetic effects of aqueous extract of Dendropanax morbifera Lev. leaves in streptozotocin-induced diabetic Sprague-Dawley rats
Min-Jae Kim, Ye-Jin Kang, Dong-Eon Lee, Suk Kim, Se-Hun Lim, Hu-Jang Lee
Korean Journal of Veterinary Research.2021; 61(4): e38. CrossRef - The Potential Role of MicroRNA in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 54. CrossRef -
Diabetes and Metabolism Journal in 2020: Good to Great
In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 1. CrossRef - Use of SGLT-2 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Abdominal Obesity: An Asian Perspective and Expert Recommendations
Wayne Huey-Herng Sheu, Siew Pheng Chan, Bien J. Matawaran, Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Ambrish Mithal, Juliana Chan, Ketut Suastika, Chin Meng Khoo, Huu Man Nguyen, Ji Linong, Andrea Luk, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 11. CrossRef - Underweight Increases the Risk of End-Stage Renal Diseases for Type 2 Diabetes in Korean Population: Data From the National Health Insurance Service Health Checkups 2009–2017
Yang-Hyun Kim, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Kyung-do Han, Sung-Hee Ihm, Kyung-Hwan Cho, Yong-Gyu Park
Diabetes Care.2020; 43(5): 1118. CrossRef - The Role of CD36 in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: β-Cell Dysfunction and Beyond
Jun Sung Moon, Udayakumar Karunakaran, Elumalai Suma, Seung Min Chung, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 222. CrossRef - Metformin treatment for patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology consensus statement
Kyu Yeon Hur, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Miyeun Han, Dong Won Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 39(1): 32. CrossRef - Effect of Smartphone-Based Lifestyle Coaching App on Community-Dwelling Population With Moderate Metabolic Abnormalities: Randomized Controlled Trial
So Mi Jemma Cho, Jung Hyun Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hyungseon Yeom, Su Jin Lee, Yong Woo Jeon, Hyeon Chang Kim
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2020; 22(10): e17435. CrossRef - Fasting plasma glucose level and the risk of open angle glaucoma: Nationwide population-based cohort study in Korea
Jin A. Choi, Yong-Moon Park, Kyungdo Han, Jiyoung Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko, Bang V Bui
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(9): e0239529. CrossRef - Smoking as a Target for Prevention of Diabetes
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 402. CrossRef - Association of Snoring with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center Cohort
So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hyeon Chang Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 687. CrossRef - Increased Mortality Burden in Young Asian Subjects with Dysglycemia and Comorbidities
Eun-Jung Rhee, Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Yang-Hyun Kim, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Won-Young Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(4): 1042. CrossRef - Metformin Treatment for Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
Kyu Yeon Hur, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Miyeun Han, Dong Won Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 3. CrossRef - Study of hospitalization and mortality in Korean diabetic patients using the diabetes complications severity index
Hyunju Yoo, Eunjung Choo, Sukhyang Lee
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2020;[Epub] CrossRef Comprehensive Trends and Patterns of Antihypertensive Prescriptions Using a Nationwide Claims Database in Korea
Minji Jung, Eunjung Choo, Sukhyang Lee
Clinical Epidemiology.2020; Volume 12: 963. CrossRef- The effects of climate on the incidence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
Seung Ri Oh, Sung Jin Min, Chang Eurn Kim, Munyoung Chang, Seog-Kyun Mun
International Journal of Biometeorology.2020; 64(12): 2119. CrossRef - Prevalence and Current Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Korean Adults Based on Fact Sheets
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 85. CrossRef - Diabetic Retinopathy and Related Clinical Practice for People with Diabetes in Korea: A 10-Year Trend Analysis
Yoo-Ri Chung, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kihwang Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 928. CrossRef - Association between sleep duration and impaired fasting glucose according to work type in non-regular workers: data from the first and second year (2016, 2017) of the 7th Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination (KNHANE) (a cross-sectional study)
JaeHan Joo, Jae-Gwang Lee, SangWoo Kim, JaeHan Lee, June-Hee Lee, Kyung-Jae Lee
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Young Eun Chon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Sik Yoon, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(2): 135. CrossRef Effect of Switching from Linagliptin to Teneligliptin Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eugene Han, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Soon Kim, Byung-wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4113. CrossRef- Temperature Correction to Enhance Blood Glucose Monitoring Accuracy Using Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy
Ye Sung Lee, Minkook Son, Alexander Zhbanov, Yugyung Jung, Myoung Hoon Jung, Kunsun Eom, Sung Hyun Nam, Jongae Park, Sung Yang
Sensors.2020; 20(21): 6231. CrossRef - Predictors of Health-Related Quality of Life in Korean Adults with Diabetes Mellitus
Mihyun Jeong
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(23): 9058. CrossRef - The triglyceride-glucose index predicts ischemic heart disease risk in Koreans: a prospective study using National Health Insurance Service data
Byoungjin Park, Yong-Jae Lee, Hye Sun Lee, Dong-Hyuk Jung
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Independent Impact of Diabetes on the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 5,307 Patients in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:737-46)
Sun Joon Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 942. CrossRef - Does Diabetes Increase the Risk of Contracting COVID-19? A Population-Based Study in Korea
Sung-Youn Chun, Dong Wook Kim, Sang Ah Lee, Su Jung Lee, Jung Hyun Chang, Yoon Jung Choi, Seong Woo Kim, Sun Ok Song
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 897. CrossRef - Independent Impact of Diabetes on the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 5,307 Patients in South Korea: A Nationwide-Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:737-46)
Kyuho Kim, Tae Jung Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 938. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea
Ji Hong You, Sang Ah Lee, Sung-Youn Chun, Sun Ok Song, Byung-Wan Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Edward J. Boyko
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(4): 901. CrossRef - The Liability Threshold Model for Predicting the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Multi-Cohort Study of Korean Adults
Eun Pyo Hong, Seong Gu Heo, Ji Wan Park
Metabolites.2020; 11(1): 6. CrossRef - Increased Age of Death and Change in Causes of Death Among Persons With Diabetes Mellitus From the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes and Muscle Dysfunction in Older Adults
Hak Chul Jang
Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research.2019; 23(4): 160. CrossRef - Letter: Comparison of the Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy 20 mg with Rosuvastatin 5 mg and Ezetimibe 10 mg Combination Therapy on Lipid Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J2019;43:582–9)
Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 909. CrossRef - Comprehensive Efforts Are Needed to Improve the Quality of Primary Diabetes Care in Korea
Chan-Hee Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(3): 265. CrossRef
- Social Support, eHealth Literacy, and mHealth Use in Older Adults With Diabetes
- Epidemiology
-
- High Proportion of Adult Cases and Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Population in Korea: A Nationwide Study
- You-Bin Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Seung-Eun Lee, Ji Eun Jun, Jiyeon Ahn, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(1):76-89. Published online August 22, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0048
- 5,860 View
- 109 Download
- 26 Web of Science
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background The prevalence and incidence of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) in all age groups and the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with T1DM in Korea were estimated.
Methods The incidence and prevalence of T1DM between 2007 and 2013 were calculated using the Korean National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) datasets of claims. Clinical characteristics and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in individuals with T1DM between 2009 and 2013 were determined using the database of NHIS preventive health checkups.
Results The prevalence of T1DM in Korea between 2007 and 2013 was 0.041% to 0.047%. The annual incidence rate of T1DM in Korea in 2007 to 2013 was 2.73 to 5.02/100,000 people. Although the incidence rate of typical T1DM was highest in teenagers, it remained steady in adults over 30 years of age. In contrast, the incidence rate of atypical T1DM in 2013 was higher in people aged 40 years or older than in younger age groups. Age- and sex-adjusted prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with T1DM was 51.65% to 55.06% between 2009 and 2013.
Conclusion T1DM may be more common in Korean adults than previously believed. Metabolic syndrome may be a frequent finding in individuals with T1DM in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Increased risk of incident mental disorders in adults with new-onset type 1 diabetes diagnosed after the age of 19: A nationwide cohort study
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, So Hyun Cho, Rosa Oh, Ji Yoon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2024; 50(1): 101505. CrossRef - Incidence and trends of type 1 diabetes before and after 2000 in the Western Pacific Region: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Du Wang, Xiaoli Hou, Juan Huang, Jianjing Sun, Takashi Kadowaki, Moon-Kyu Lee, Alicia J. Jenkins, Linong Ji
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 207: 111055. CrossRef - The emergence of obesity in type 1 diabetes
Martin T. W. Kueh, Nicholas W. S. Chew, Ebaa Al-Ozairi, Carel W. le Roux
International Journal of Obesity.2024; 48(3): 289. CrossRef - Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Risk Factors Influence on Microvascular Complications in Patients With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Asad Riaz, Shoaib Asghar, Salman Shahid, Haider Tanvir, Muhammad Hamza Ejaz, Mamuna Akram
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Depression according to Cumulative Exposure to a Low-Household Income Status in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population- Based Study
So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Kyu-na Lee, Bongsung Kim, So Hyun Cho, So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 290. CrossRef - Comparison of Insulin-Treated Patients with Ambiguous Diabetes Type with Definite Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Subjects: A Clinical Perspective
Insa Laspe, Juris J. Meier, Michael A. Nauck
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 140. CrossRef - Clinical and biochemical profile of childhood–adolescent-onset type 1 diabetes and adult-onset type 1 diabetes among Asian Indians
Viswanathan Mohan, Ganesan Uma Sankari, Anandakumar Amutha, Ranjit Mohan Anjana, Saravanan Jeba Rani, Ranjit Unnikrishnan, Ulagamathesan Venkatesan, Coimbatore Subramanian Shanthi Rani
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(4): 579. CrossRef - Subtypes of type 2 diabetes and their association with outcomes in Korean adults - A cluster analysis of community-based prospective cohort
You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung
Metabolism.2023; 141: 155514. CrossRef - Insulin Fact Sheet in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Trends of Antidiabetic Medication Use in Insulin Users with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: 2002 to 2019
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Bong-Sung Kim, Kyung-Do Han, So Yoon Kwon, So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 211. CrossRef - Insulin resistance is more frequent in type 1 diabetes patients with long disease duration
Yuting Xie, Mei Shi, Xiaolin Ji, Fansu Huang, Li Fan, Xia Li, Zhiguang Zhou
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term Effectiveness of the National Diabetes Quality Assessment Program in South Korea
Ji Hye Huh, Serim Kwon, Gui Ok Kim, Bo Yeon Kim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(9): 1700. CrossRef - Low Household Income Status and Death from Pneumonia in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Study
You-Bin Lee, So Hee Park, Kyu-na Lee, Bongsung Kim, So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 682. CrossRef - Impact of statin treatment on cardiovascular risk in patients with type 1 diabetes: a population-based cohort study
Joonsang Yoo, Jimin Jeon, Minyoul Baek, Sun Ok Song, Jinkwon Kim
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Metabolic Syndrome and Microvascular Complications in Chinese Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Qianwen Huang, Daizhi Yang, Hongrong Deng, Hua Liang, Xueying Zheng, Jinhua Yan, Wen Xu, Xiangwen Liu, Bin Yao, Sihui Luo, Jianping Weng
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 93. CrossRef - The Incidence of Adult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review From 32 Countries and Regions
Jessica L. Harding, Pandora L. Wander, Xinge Zhang, Xia Li, Suvi Karuranga, Hongzhi Chen, Hong Sun, Yuting Xie, Richard A. Oram, Dianna J. Magliano, Zhiguang Zhou, Alicia J. Jenkins, Ronald C.W. Ma
Diabetes Care.2022; 45(4): 994. CrossRef - Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Jong Ha Baek, Woo Je Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Soo Kyoung Kim, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 46. CrossRef - Genomic ancestry and metabolic syndrome in individuals with type 1 diabetes from an admixed population: a multicentre, cross‐sectional study in Brazil
B. S. V. Barros, D. C. Santos, L. G. N. Melo, M. H. Pizarro, L. H. Muniz, D. A. Silva, L. C. Porto, M. B. Gomes
Diabetic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Interplay Between Diet and the Epigenome in the Pathogenesis of Type-1 Diabetes
Amira Kohil, Maha Al-Asmakh, Mashael Al-Shafai, Annalisa Terranegra
Frontiers in Nutrition.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of early mortality and cardiovascular disease according to the presence of recently diagnosed diabetes and requirement for insulin treatment: A nationwide study
You‐Bin Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Min Sun Choi, Jiyun Park, Minyoung Kim, Sang‐Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(10): 1855. CrossRef - Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:46-54)
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 277. CrossRef - Comparison of fracture risk between type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a comprehensive real-world data
J. Ha, C. Jeong, K.-D. Han, Y. Lim, M.K. Kim, H.-S. Kwon, K.-H. Song, M.I. Kang, K.-H. Baek
Osteoporosis International.2021; 32(12): 2543. CrossRef - Early mortality and cardiovascular disease, varied association with body mass index and its changes in insulin-treated diabetes: a nationwide study
You-Bin Lee, Bongsung Kim, Jiyun Park, Minyoung Kim, Min Sun Choi, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
International Journal of Obesity.2021; 45(11): 2482. CrossRef - Young-onset type 2 diabetes in South Korea: a review of the current status and unmet need
Ye Seul Yang, Kyungdo Han, Tae Seo Sohn, Nam Hoon Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2021; 36(5): 1049. CrossRef - Positive association between the ratio of triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and diabetes incidence in Korean adults
Joungyoun Kim, Sang-Jun Shin, Ye-Seul Kim, Hee-Taik Kang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Mortality and causes of death in a population with blindness in Korea: A longitudinal follow-up study using a national sample cohort
Hyo Geun Choi, Min Joung Lee, Sang-Mok Lee
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Hospitalization for heart failure incidence according to the transition in metabolic health and obesity status: a nationwide population-based study
You-Bin Lee, Da Hye Kim, Seon Mee Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Yong Gyu Park, Kyungdo Han, Hye Jin Yoo
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Adults
Hye Ryoung Yun
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 156. CrossRef - New Insulin Pumps and Open Source Artificial Pancreas System in Korea
Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(4): 197. CrossRef - Risk of early mortality and cardiovascular disease in type 1 diabetes: a comparison with type 2 diabetes, a nationwide study
You-Bin Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Ji Eun Jun, Jiyeon Ahn, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of end‐stage renal disease from chronic kidney disease defined by decreased glomerular filtration rate in type 1 diabetes: A comparison with type 2 diabetes and the effect of metabolic syndrome
You‐Bin Lee, Kyungdo Han, Bongsung Kim, Ji Eun Jun, Seung‐Eun Lee, Jiyeon Ahn, Gyuri Kim, Sang‐Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Increased risk of incident mental disorders in adults with new-onset type 1 diabetes diagnosed after the age of 19: A nationwide cohort study

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





