- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 43(4); 2019 > Article
-
Original ArticleEpidemiology Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2018: An Appraisal of Current Status
-
Bo-Yeon Kim1
 , Jong Chul Won2, Jae Hyuk Lee3, Hun-Sung Kim4, Jung Hwan Park5, Kyoung Hwa Ha6, Kyu Chang Won7, Dae Jung Kim6
, Jong Chul Won2, Jae Hyuk Lee3, Hun-Sung Kim4, Jung Hwan Park5, Kyoung Hwa Ha6, Kyu Chang Won7, Dae Jung Kim6 , Kyong Soo Park8
, Kyong Soo Park8 -
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2019;43(4):487-494.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0067
Published online: July 17, 2019
1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Center, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
3Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
5Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
6Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
7Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeungnam University College of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
8Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Dae Jung Kim. Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, 164 World cup-ro, Yeongtong-gu, Suwon 16499, Korea. djkim@ajou.ac.kr
Copyright © 2019 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- The objective of this study was to investigate the prevalence, management, and comorbidities of diabetes among Korean adults aged 30 years and older.
-
Methods
- This study used 2013 to 2016 data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, a nationally-representative survey of the Korean population. Diabetes was defined as fasting glucose ≥126 mg/dL, current use of antidiabetic medication, a previous history of diabetes, or glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥6.5%.
-
Results
- In 2016, 14.4% (approximately 5.02 million) of Korean adults had diabetes. The prevalence of impaired fasting glucose was 25.3% (8.71 million). From 2013 to 2016, the awareness, control, and treatment rates for diabetes were 62.6%, 56.7%, and 25.1%, respectively. People with diabetes had the following comorbidities: obesity (50.4%), abdominal obesity (47.8%), hypertension (55.3%), and hypercholesterolemia (34.9%). The 25.1%, 68.4%, and 44.2% of people with diabetes achieved HbA1c <6.5%, blood pressure <140/85 mm Hg, and low density lipoprotein cholesterol <100 mg/dL. Only 8.4% of people with diabetes had good control of all three targets.
-
Conclusion
- This study confirms that diabetes is as an important public health problem. Efforts should be made to increase awareness, detection, and comprehensive management of diabetes to reduce diabetes-related morbidity and mortality.
- Economic and social developments have affected lifestyles and diet habits, resulting in increases in non-communicable diseases, such as obesity, dyslipidemia, hypertension, and diabetes. Diabetes is associated with a high risk of vascular disease. Cardiovascular disease is a primary cause of death among people with type 2 diabetes [12]. In Korea, four million adults aged 30 years or older have diabetes. The prevalence of diabetes has been estimated to be 12.4% in Korea in 2011 [34]. In 2016, diabetes was the sixth leading cause of death and the most common cause of renal replacement therapy in Korea [5]. The increase in diabetes has, consequently, resulted in an increase in diabetes-related morbidity, thus becoming a socioeconomic burden. Therefore, recognizing problems in reaching glycemic target goals and seeking solutions are important to decrease the comorbidities and mortality of diabetes. Since 2012, The Korean Diabetes Association (KDA) has published Diabetes Fact Sheets based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES), a nationwide survey conducted by the Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention to promote the understanding of chronic diseases, provide comprehensive and systematic prevention and management at the national level, and improve public awareness of diabetes and its risk factors. More active, comprehensive management of diabetic patients is a very important health issue. The objective of this study was to investigate the prevalence, management, and comorbidities of diabetes among Korean adults aged 30 years and older by analyzing nationally-representative KNHANES data.
INTRODUCTION
- Study population
- This study analyzed KNHANES data from 2013 to 2016, a nationally representative, cross-sectional survey designed to evaluate the health and nutritional status of the Korean population. KNHANES consists of three surveys: a health interview survey, a health examination survey, and a nutrition survey. The health interview included prior history of diabetes diagnosis, hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, and medication for those conditions. Informed consent was obtained during the KNHANES process. The estimated percentages and the total number of people over the age of 30 with diabetes and prediabetes were determined by reflecting the 2016 demographic structure. We constructed two datasets from KNHANES as follows: (1) KNHANES 2016 and (2) KNHANES 2013 to 2016 (merged 4 years of data). Data form KNHANES 2016 were used to calculate the prevalence of diabetes and impaired fasting glucose (IFG). And, data for KNHANES 2013 to 2016 (4 years of data) were used to identify current status of managing diabetes and comorbidities in diabetes. The study protocol conformed to the ethical guidelines of the World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital (IRB No 2018-11-018).
- Biochemical measurements
- After an overnight fast, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), total cholesterol (TC), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), triglyceride (TG) level, serum creatinine level, and urinary concentration of creatinine were measured using a Hitachi Automatic Analyzer 7600 (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). Low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) was measured by direct assay for persons with TG >200 mg/dL (Hitachi Automatic Analyzer 7600). Thus, we used either directly measured or calculated LDL-C according to the Friedewald formula: LDL-C=TC–HDL-C–(TG/5) [6]. Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels were measured using high-performance liquid chromatography (HLC-723G7; Tosoh, Tokyo, Japan). Urinary albumin levels in random urine samples were measured using a Hitachi Automatic Analyzer 7600.
- Definitions of diabetes and its related comorbidities
- The diagnosis of diabetes was based on FPG ≥126 mg/dL, current use of antidiabetic medication(s), a previous history of diabetes, or HbA1c ≥6.5%. IFG was defined by FPG in the range of 100 to 125 mg/dL among those without diabetes as described above [7]. Glycemic control rate in diabetes was defined as rate of people of HbA1c <6.5% among people with diabetes (%). Obesity was defined as a body mass index (BMI; weight in kilograms divided by the square of height in meters) ≥25.0 kg/m2 in accordance with the Asia-Pacific criteria of the World Health Organization guidelines [8]. Abdominal obesity was defined as waist circumference ≥90 cm in men and ≥85 cm in women. Hypertension was defined ad systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg and/or current use of antihypertensive medications. Control of hypertension was defined as systolic and diastolic blood pressure <140/85 mm Hg according to the KDA Treatment Guideline for Diabetes 2015 (English version is available at www.diabetes.or.kr) [9]. Hypercholesterolemia was defined as TC ≥240 mg/dL or current use of lipid-lowering medication(s), and control of hypercholesterolemia was defined as LDL-C <100 mg/dL [910]. Awareness rate was defined as rate of people diagnosed with diabetes by a doctor among people with diabetes (%). Treatment rate was defined as rate of people treated with oral hypoglycemic agents, or insulin therapy among people with diabetes (%). Definition of health behaviors are as follows: current smoking: smoked at least five packs of cigarettes (100 cigarettes) during lifetime; high-risk drinking: more than seven glasses in men or five glasses in women on the same occasion on each of two or more a week; regular walking exercise: 5 days or more per week and for 30 minutes or more per activity.
- Statistical analysis
- Descriptive statistics were used to evaluate the patient data. Statistical analyses were performed using SAS statistical software version 9.3 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) to reflect the complex sampling design and sampling weights of KNHANES and to provide nationally representative prevalence estimates using a complex sampling design.
METHODS
- Prevalence of diabetes and IFG
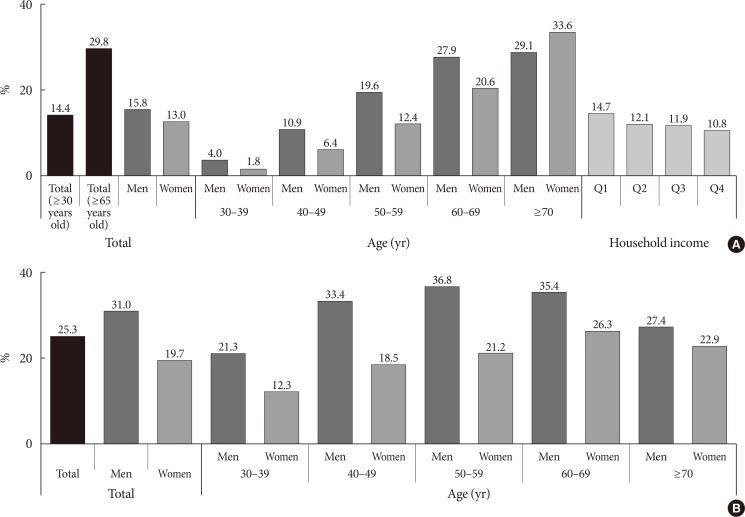
- Among adults aged 30 years or more in 2016, the prevalence of diabetes was 14.4%, representing approximately 5.02 million. There were differences in diabetes prevalence by sex, age group, and household income. The prevalence of diabetes among women in 2016 was 13.0%, which was lower than that in men (15.8%). The prevalence increased with age in both sexes. Specifically, the prevalence exceeded 10% for men in the 40 to 49 age group and for women in the 50 to 59 age group. In addition, the prevalence of diabetes among adults 65 years or older was 29.8%. By household income quartile, the prevalence in the lowest household income quartile was 14.7%, while that in the highest household income quartile was 10.8% (Fig. 1). The prevalence of IFG among adults 30 years or older in 2016 was 25.3%. The number of people with IFG was estimated to be 8.71 million in 2016. The IFG prevalence peaked in the of 50- to 59-year-old age group in men and in the 60- to 69-year-old age group in women (Fig. 1).
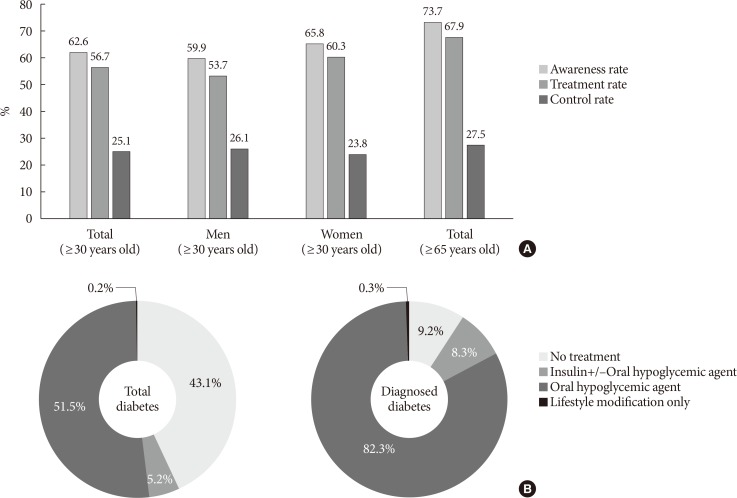
- Current status of managing diabetes
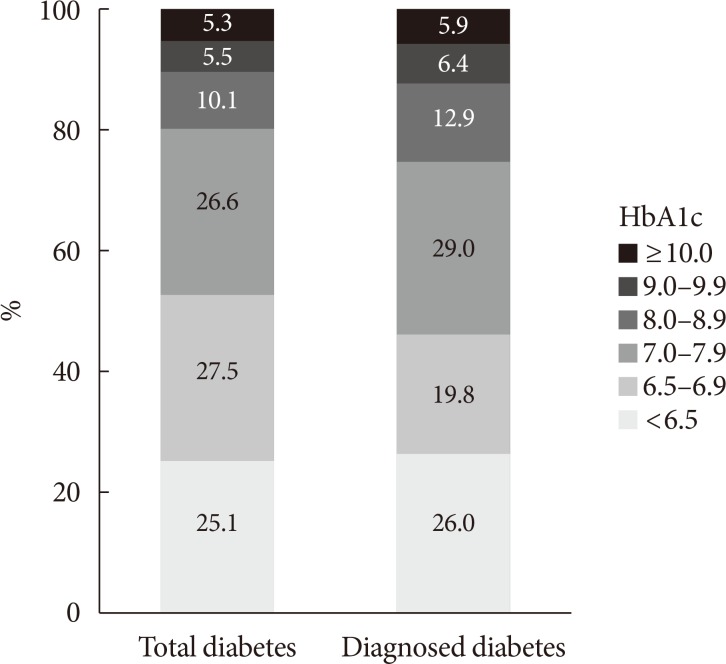
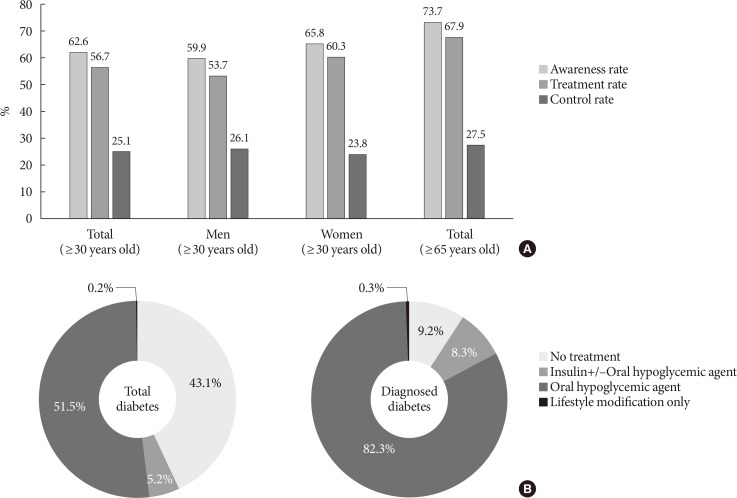
- In 2013 to 2016, among people with diabetes, 62.6% were aware of their condition and 56.7% were using glucose-lowering drugs (oral hypoglycemic agent, 51.5%; insulin therapy, 5.2%). However, 43.1% were not receiving any treatment (glucose-lowering drugs and/or lifestyle modification). Among people who were previously diagnosed with diabetes, 9.2% were not receiving any treatment for their disease. However, most of them were being treated with oral hypoglycemic agents (82.3%) and 8.3% of them were receiving insulin therapy (Fig. 2). Glycemic control rate among people with diabetes was 25.1% for HbA1c <6.5% and 52.6% for HbA1c <7.0%. However, 20.9% of people with diabetes had worse glycemic control (HbA1c ≥8.0%) (Fig. 3).
- Comorbidities in diabetes
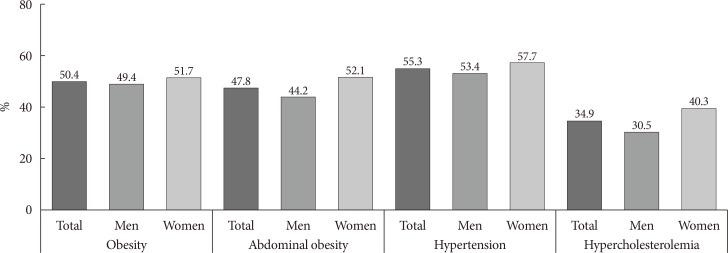
- In 2013 to 2016, the prevalence of obesity (BMI ≥25.0 kg/m2) in people with diabetes was 50.4%. When obesity was categorized as class I to III, obesity class I (BMI 25.0 to 29.9 kg/m2) accounted for 40.2% of the diabetes cases and obesity class II (BMI 30.0 to 34.9 kg/m2) accounted for 8.4%, while obesity class III (BMI ≥35.0 kg/m2) only accounted for 1.8%. Abdominal obesity, based on waist circumference (men ≥90 cm, women ≥85 cm), accounted for 47.8% of the people with diabetes. The prevalence of abdominal obesity was higher in women than in men (men 44.2%, women 52.1%). In diabetes, the prevalence of hypertension was 55.3% and that of hypercholesterolemia was 34.9% (Fig. 4).
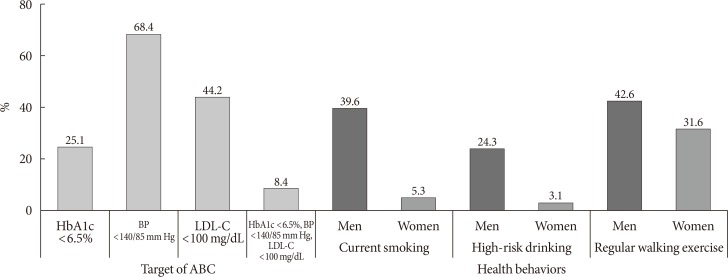
- According to the 2015 KDA treatment guideline, 25.1% of people with diabetes achieved HbA1c <6.5%, 68.4% achieved blood pressure <140/85 mm Hg, and 44.2% achieved LDL-C <100 mg/dL. Only 8.4% of people with diabetes had good control of all three targets. In addition, more men than women were current smokers (men 39.6%, women 5.3%) or high-risk drinkers (men 24.3%, women 3.1%). Only 36.0% of those with diabetes were walking 30 minutes regularly (Fig. 5).
RESULTS
- In a representative sample of Korean adults in 2016, the prevalence of diabetes among adults aged 30 years or more was 14.4% and the estimated number of people with diabetes was 5.02 million. Excluding HbA1c from the definition of diabetes, the prevalence decreased to 13.0%. In addition, the prevalence of IFG was 25.3%.
- In Korea, the prevalence of diabetes has mainly increased due to population aging [11]. This study also showed that the prevalence of diabetes increased with age in both sexes. Specifically, the prevalence of diabetes among adults 65 years or older was 29.8%, which was more than twice the prevalence of diabetes among adults aged 30 years or more. Diabetes in the elderly is accompanied by functional disability, several comorbidities, and premature mortality [12]. Thus, the management of diabetes is necessary, especially considering the prevalence and comorbidities in the elderly.
- This study showed that the lower the income level, the higher the prevalence of diabetes. Previous studies have shown that people with low socioeconomic status (SES) were more likely to develop type 2 diabetes with worse glycemic control that can lead to more diabetic complications [1314]. According to the Korean National Diabetes Program (KNDP) cohort study, men with low SES had worse glycemic control and higher risk for retinopathy [15]. In addition, in Korea, low-income people with diabetes had lower medication adherence and lower levels of utilization of fundus examinations and HbA1c tests than high-income people with diabetes [16].
- Improved awareness of diabetes through early detection should be prioritized in diabetes management. However, from 2013 to 2016, the diabetes awareness rate was only 62.6%, which was lower than that (68.0%) in 2005 [17]. The reason for the decrease in awareness was that the number of undiagnosed diabetes cases increased when HbA1c was included in the diagnosis of diabetes from 2013 to 2016. In addition, 43.1% did not take treatment with glucose-lowering drugs or modify their lifestyle. Although the rate of worse glycemic control (HbA1c ≥8.0%) fell steadily from 33.6% in 2005 to 20.9% in 2013 to 2016 [18], good control (HbA1c <6.5%) was only achieved in 25.1% of the patients.
- In addition, more than half the people with diabetes had comorbidities. According to the KNHANES 2011 study, the prevalence of dyslipidemia, hypertension, and obesity was 79.6%, 54.6%, and 44.4%, respectively, among adults with diabetes [19]. In 2013 to 2016, the prevalence of hypertension and obesity among people with diabetes was higher, while the prevalence of dyslipidemia was lower compared to the data in 2011. However, in 2011, the definition of dyslipidemia included hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia, or hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia. Thus, we could not exactly compare the differences in prevalence.
- Tight glycemic control and treatment of additional cardiovascular risk factors can decrease diabetic complications [202122]. Thus, the management of diabetes through achievement of the ABC clinical targets (A, HbA1c; B, blood pressure; and C, LDL-C) is important. However, only 8.4% of subjects achieved all three ABC targets. Also, 24.1% were current smokers, 14.7% were high-risk drinkers, and only 36.4% were walking 30 minutes regularly. Compared to a previous study, the proportion of current smokers among people with diabetes has decreased and that of people who participate in regular walking exercise activities has significantly increased. However, the proportion of high-risk drinkers among people with diabetes has slightly increased. The incidence of type 2 diabetes is closely related to diet and lifestyle [2324]. Several studies have shown that alcohol consumption can increase the risk of diabetes, even in the case of moderate consumption [2526], while another study reported that moderate alcohol consumption decreased the risk of type 2 diabetes [27]. Although there is still controversy about the effect of moderate alcohol consumption, heavy alcohol drinking is known to potentiate the development of diabetes through pancreatic β-cell dysfunction [2829]. In addition, the prevalence of alcohol dependence and alcohol abuse is much higher in Korea compared to other countries [30]. Thus, it is necessary to inform people with diabetes about the danger of alcohol consumption and the importance of decreasing alcohol intake.
- In conclusion, increasing awareness and strengthening the management of people with diabetes can have a positive impact on the prevention of diabetes-related complications. However, the prevalence of diabetes is constantly increasing, while the awareness and control rates are still low in Korea. Thus, we need to construct a systemic approach to supporting diabetic patients, ranging from early detection to target-driven management.
DISCUSSION
-
Acknowledgements
- This study was supported by The Korean Diabetes Association.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS:
NOTES
- 1. Roglic G, Unwin N, Bennett PH, Mathers C, Tuomilehto J, Nag S, Connolly V, King H. The burden of mortality attributable to diabetes: realistic estimates for the year 2000. Diabetes Care 2005;28:2130-2135. PubMed
- 2. Morrish NJ, Wang SL, Stevens LK, Fuller JH, Keen H. Mortality and causes of death in the WHO multinational study of vascular disease in diabetes. Diabetologia 2001;44(Suppl 2):S14-S21. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Jeon JY, Ko SH, Kwon HS, Kim NH, Kim JH, Kim CS, Song KH, Won JC, Lim S, Choi SH, Jang MJ, Kim Y, Oh K, Kim DJ, Cha BY;. Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes according to fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c. Diabetes Metab J 2013;37:349-357. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 4. Jeon JY, Kim DJ, Ko SH, Kwon HS, Lim S, Choi SH, Kim CS, An JH, Kim NH, Won JC, Kim JH, Cha BY, Song KH. Taskforce Team of Diabetes Fact Sheet of the Korean Diabetes Association. Current status of glycemic control of patients with diabetes in Korea: the fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Diabetes Metab J 2014;38:197-203. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Vital Statistics Division Statistics Korea. Shin HY, Lee JY, Kim JE, Lee S, Youn H, Kim H, Lee J, Park MS, Huh S. Cause-of-death statistics in 2016 in the Republic of Korea. J Korean Med Assoc 2018;61:573-584.ArticlePDF
- 6. Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 1972;18:499-502. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2014;37(Suppl 1):S81-S90. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Oh SW, Shin SA, Yun YH, Yoo T, Huh BY. Cut-off point of BMI and obesity-related comorbidities and mortality in middle-aged Koreans. Obes Res 2004;12:2031-2040. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Korean Diabetes Association. 2015 Treatment guidelines for diabetes updated 2019 Jan 1. Available from: http://www.diabetes.or.kr/bbs/skin/dianews/download.php?code=guide&number=301.
- 10. Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, Benjamin EJ, Berry JD, Blaha MJ, Dai S, Ford ES, Fox CS, Franco S, Fullerton HJ, Gillespie C, Hailpern SM, Heit JA, Howard VJ, Huffman MD, Judd SE, Kissela BM, Kittner SJ, Lackland DT, Lichtman JH, Lisabeth LD, Mackey RH, Magid DJ, Marcus GM, Marelli A, Matchar DB, McGuire DK, Mohler ER 3rd, Moy CS, Mussolino ME, Neumar RW, Nichol G, Pandey DK, Paynter NP, Reeves MJ, Sorlie PD, Stein J, Towfighi A, Turan TN, Virani SS, Wong ND, Woo D, Turner MB. American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Heart disease and stroke statistics: 2014 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2014;129:e28-e92. PubMed
- 11. Ha KH, Kim DJ. Trends in the diabetes epidemic in Korea. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2015;30:142-146. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Sesti G, Antonelli Incalzi R, Bonora E, Consoli A, Giaccari A, Maggi S, Paolisso G, Purrello F, Vendemiale G, Ferrara N. Management of diabetes in older adults. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2018;28:206-218. ArticlePubMed
- 13. Ross NA, Gilmour H, Dasgupta K. 14-Year diabetes incidence: the role of socio-economic status. Health Rep 2010;21:19-28.
- 14. Lee TC, Glynn RJ, Peña JM, Paynter NP, Conen D, Ridker PM, Pradhan AD, Buring JE, Albert MA. Socioeconomic status and incident type 2 diabetes mellitus: data from the Women's Health Study. PLoS One 2011;6:e27670. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Kim SH, Lee SY, Kim CW, Suh YJ, Hong S, Ahn SH, Seo DH, Nam MS, Chon S, Woo JT, Baik SH, Park Y, Lee KW, Kim YS. KNDP Study Group. Impact of socioeconomic status on health behaviors, metabolic control, and chronic complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab J 2018;42:380-393. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 16. Shin WY, Kim HC, Lee T, Jeon DH, Ha KH, Kim DJ, Chang HJ. Combined effects of diabetes and low household income on mortality: a 12-year follow-up study of 505 677 Korean adults. Diabet Med 2018;35:1345-1354. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Choi YJ, Kim HC, Kim HM, Park SW, Kim J, Kim DJ. Prevalence and management of diabetes in Korean adults: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 1998-2005. Diabetes Care 2009;32:2016-2020. PubMedPMC
- 18. Ha KH, Kim DJ. Current status of managing diabetes mellitus in Korea. Korean J Intern Med 2016;31:845-850. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 19. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes fact sheet in Korea 2018 updated 2019 Jan 1. Available from: http://www.diabetes.or.kr/bbs/skin/dianews/download.php?code=admin&number=1859.
- 20. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Nathan DM, Genuth S, Lachin J, Cleary P, Crofford O, Davis M, Rand L, Siebert C. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;329:977-986. ArticlePubMed
- 21. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998;352:837-853. ArticlePubMed
- 22. Nathan DM, Cleary PA, Backlund JY, Genuth SM, Lachin JM, Orchard TJ, Raskin P, Zinman B. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Study Research Group. Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Study Research Group. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2643-2653. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 23. Hu FB, Manson JE, Stampfer MJ, Colditz G, Liu S, Solomon CG, Willett WC. Diet, lifestyle, and the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in women. N Engl J Med 2001;345:790-797. ArticlePubMed
- 24. Mokdad AH, Ford ES, Bowman BA, Dietz WH, Vinicor F, Bales VS, Marks JS. Prevalence of obesity, diabetes, and obesity-related health risk factors, 2001. JAMA 2003;289:76-79. ArticlePubMed
- 25. Ajani UA, Hennekens CH, Spelsberg A, Manson JE. Alcohol consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus among US male physicians. Arch Intern Med 2000;160:1025-1030. ArticlePubMed
- 26. Davies MJ, Baer DJ, Judd JT, Brown ED, Campbell WS, Taylor PR. Effects of moderate alcohol intake on fasting insulin and glucose concentrations and insulin sensitivity in postmenopausal women: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2002;287:2559-2562. ArticlePubMed
- 27. Seike N, Noda M, Kadowaki T. Alcohol consumption and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japanese: a systematic review. Asia Pac J Clin Nutr 2008;17:545-551. PubMed
- 28. Lee DY, Yoo MG, Kim HJ, Jang HB, Kim JH, Lee HJ, Park SI. Association between alcohol consumption pattern and the incidence risk of type 2 diabetes in Korean men: a 12-years follow-up study. Sci Rep 2017;7:7322ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 29. Kim JY, Lee DY, Lee YJ, Park KJ, Kim KH, Kim JW, Kim WH. Chronic alcohol consumption potentiates the development of diabetes through pancreatic β-cell dysfunction. World J Biol Chem 2015;6:1-15. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Min S, Noh S, Shin J, Ahn JS, Kim TH. Alcohol dependence, mortality, and chronic health conditions in a rural population in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 2008;23:1-9. ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Estimated prevalence of adults (≥30 years old) with (A) diabetes and (B) impaired fasting glucose (household income: from the lowest to the highest quintiles [Q]).
Management of (A) diabetes and (B) type of treatment (awareness rate: rate of people diagnosed with diabetes by a doctor among people with diabetes [%]; treatment rate: rate of people treated with oral hypoglycemic agents, and/or insulin therapy among people with diabetes [%]; control rate: rate of people of glycosylated hemoglobin <6.5% among people with diabetes).
Estimated prevalence of comorbidities in diabetes (obesity: body mass index [kg/m2] ≥25.0; abdominal obesity: men ≥90 cm, women ≥85 cm; hypertension: systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg and/or antihypertensive medications; hypercholesterolemia: total cholesterol ≥240 mg/dL and/or lipid-lowering medications).
Control rate of comorbidities and estimated proportion for health behaviors in diabetes (current smoking: smoked at least five packs of cigarettes [100 cigarettes] during lifetime; high-risk drinking: more than seven glasses in men or five glasses in women on the same occasion on each of 2 or more a week; regular walking exercise: 5 days or more per week and for 30 minutes or more per activity). HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; BP, blood pressure; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; ABC, glycosylated hemoglobin, blood pressure, and low density lipoprotein cholesterol.
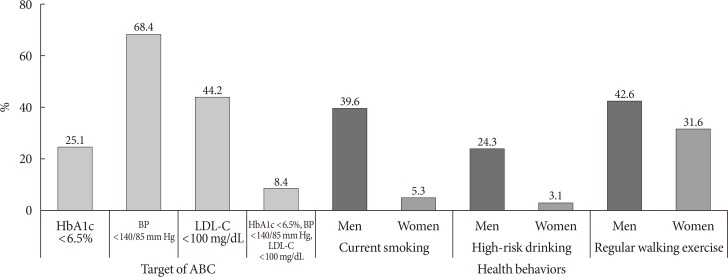
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Social Support, eHealth Literacy, and mHealth Use in Older Adults With Diabetes
Minjin Kim, Beomsoo Kim, Sunhee Park
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2024; 42(2): 136. CrossRef - Cardiovascular safety of evogliptin dual and triple therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: a nationwide cohort study
Sohee Park, Han Eol Jeong, In-Sun Oh, Sangmo Hong, Sung Hoon Yu, Chang Beom Lee, Ju-Young Shin
BMJ Open.2024; 14(4): e077084. CrossRef - Gamma‐glutamyl transferase and the risk of all‐cause and disease‐specific mortality in patients with diabetes: A nationwide cohort study
Goh Eun Chung, Su‐Min Jeong, Su Jong Yu, Jeong‐Ju Yoo, Yuri Cho, Kyu‐na Lee, Dong Wook Shin, Yoon Jun Kim, Jung‐Hwan Yoon, Kyungdo Han, Eun Ju Cho
Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic value of resting heart rate in predicting undiagnosed diabetes in adults: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2018
Dong-Hyuk Park, Seon Young Goo, Sung Hyun Hong, Ji-hee Min, Ji Yong Byeon, Mi-Kyung Lee, Hae Dong Lee, Byoung Wook Ahn, Heejin Kimm, Sun Ha Jee, Dong Hoon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Justin Y. Jeon
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(1): 141. CrossRef - Levels and correlates of risk factor control in diabetes mellitus –ELSA-Brasil
Bruna Cristine Chwal, Rodrigo Citton Padilha dos Reis, Maria Inês Schmidt, Bruce B. Duncan, Sandhi Maria Barreto, Rosane Harter Griep
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in total cholesterol level and cardiovascular disease risk among type 2 diabetes patients
Jaewon Khil, Sung Min Kim, Jooyoung Chang, Seulggie Choi, Gyeongsil Lee, Joung Sik Son, Sang Min Park, NaNa Keum
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of dapagliflozin compared with glimepiride on body composition in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin: The BEYOND study
Hyeong Kyu Park, Kyoung‐Ah Kim, Kyung‐Wan Min, Tae‐Seo Sohn, In Kyung Jeong, Chul Woo Ahn, Nan‐Hee Kim, Ie Byung Park, Ho Chan Cho, Choon Hee Chung, Sung Hee Choi, Kang Seo Park, Seoung‐Oh Yang, Kwan Woo Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(9): 2743. CrossRef - Comparison of SGLT2 inhibitors with DPP-4 inhibitors combined with metformin in patients with acute myocardial infarction and diabetes mellitus
Young Sang Lyu, Seok Oh, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Myung Ho Jeong
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Smoking Cessation and the Risk of Cholangiocarcinoma and Ampulla of Vater Cancer: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Joo-Hyun Park, Jung Yong Hong, Kyungdo Han
Liver Cancer.2023; 12(5): 457. CrossRef - Achievement of Treatment Goals and Mortality in Individuals with Diabetes: The ELSA-Brasil Study
Bruna Cristine Chwal, Rodrigo Citton P. dos Reis, Maria Inês Schmidt, Sandhi Maria Barreto, Rosane Harter Griep, Bruce B. Duncan
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(24): 7663. CrossRef - Cigarette Smoking and Risk of Infection-Related Mortality: A Cohort Study
Hae Suk Cheong, Yoosoo Chang, Eun-Jeong Joo, Seungho Ryu
Nicotine & Tobacco Research.2022; 24(2): 204. CrossRef - Angiotensin‐converting enzyme inhibitors versus angiotensin receptor blockers: New‐onset diabetes mellitus stratified by statin use
Juyoung Shin, Hyunah Kim, Hyeon Woo Yim, Ju Han Kim, Suehyun Lee, Hun‐Sung Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2022; 47(1): 97. CrossRef - Exposure to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and volatile organic compounds is associated with a risk of obesity and diabetes mellitus among Korean adults: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) 2015–2017
Inae Lee, Hyunwoong Park, Min Joo Kim, Sunmi Kim, Sohyeon Choi, Jeongim Park, Yoon Hee Cho, Sooyeon Hong, Jiyoung Yoo, Gi Jeong Cheon, Kyungho Choi, Young Joo Park, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health.2022; 240: 113886. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Chronic Disease and Health Care Utilization Among Young Adults in South Korea
Jongho Park, Yeaeun Kim
Population Health Management.2022; 25(3): 407. CrossRef - Sleep duration and mortality in patients with diabetes: Results from the 2007–2015 Korea national health and nutrition examination survey
Kang-Mo Gu, Se Hee Min, Jaeyoung Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(3): 101312. CrossRef - Retinal Vascular Caliber Changes in Early Type 2 Diabetic Patients without Retinopathy
Jeong Woo Park, Jeong Hun Bae, Su Jeong Song, Joon Mo Kim
Journal of the Korean Ophthalmological Society.2022; 63(1): 20. CrossRef - Association Between Long Working Hours and Chronic Kidney Disease According to Diabetic Status
Ki Duk Kim, Suk-Yong Jang
Journal of Occupational & Environmental Medicine.2022; 64(3): 190. CrossRef - Sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors do not increase the risk of fractures in real‐world clinical practice in Korea: A national observational cohort study
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Yong Jun Choi
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(6): 986. CrossRef - Improvement of Lipotoxicity-Induced Islet β Cellular Insulin Secretion Disorder by Osteocalcin
Yafang Zhang, Ling Li, Yongze Zhang, Sunjie Yan, Lingning Huang, Riccardo Calafiore
Journal of Diabetes Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Association between gastric cancer and the risk of depression among South Korean adults
Sinyoung Kwon, Jinyeong Kim, Taeyeon Kim, Wonjeong Jeong, Eun-Cheol Park
BMC Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Performance of Diabetes and Kidney Disease Screening Scores in Contemporary United States and Korean Populations
Liela Meng, Keun-Sang Kwon, Dae Jung Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Jeehyoung Kim, Abhijit V. Kshirsagar, Heejung Bang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 273. CrossRef - Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 464. CrossRef - Normalized Creatinine-to-Cystatin C Ratio and Risk of Diabetes in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Bo Xie, Yang Yuan, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 476. CrossRef - A double‐blind, Randomized controlled trial on glucose‐lowering EFfects and safety of adding 0.25 or 0.5 mg lobeglitazone in type 2 diabetes patients with INadequate control on metformin and dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitor therapy: REFIND study
Soree Ryang, Sang Soo Kim, Ji Cheol Bae, Ji Min Han, Su Kyoung Kwon, Young Il Kim, Il Seong Nam‐Goong, Eun Sook Kim, Mi‐kyung Kim, Chang Won Lee, Soyeon Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh, Min Jeong Kwon, Jeong Hyun Park, In Joo Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(9): 1800. CrossRef - Long‐term clinical outcomes of oral antidiabetic drugs as fixed‐dose combinations: A nationwide retrospective cohort study
Sang‐Jun Cho, In‐Sun Oh, Han Eol Jeong, Young Min Cho, Yul Hwangbo, Oriana Hoi Yun Yu, Ju‐Young Shin
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(10): 2051. CrossRef - Improvement in Age at Mortality and Changes in Causes of Death in the Population with Diabetes: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 466. CrossRef - Dietary antioxidant consumption and the risk of type 2 diabetes in South Korean adults: a prospective cohort study based on the Health Examinees study
Li-Juan Tan, Su Bin Hwang, Shinyoung Jun, Hyojee Joung, Sangah Shin
BMJ Open.2022; 12(7): e065073. CrossRef - Visual Acuity Outcomes in Diseases Associated with Reduced Visual Acuity: An Analysis of the National Health Insurance Service Database in Korea
Sang-Yeob Kim, Byeong-Yeon Moon, Hyun-Gug Cho, Dong-Sik Yu
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(14): 8689. CrossRef - Development of Various Diabetes Prediction Models Using Machine Learning Techniques
Juyoung Shin, Jaewon Kim, Chanjung Lee, Joon Young Yoon, Seyeon Kim, Seungjae Song, Hun-Sung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 650. CrossRef - Real-World Prescription Patterns and Barriers Related to the Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors among Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
Jong Ha Baek, Ye Seul Yang, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Jae Hyeon Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Jong Han Choi, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 701. CrossRef - Remnant cholesterol and the risk of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes: a nationwide longitudinal cohort study
Ji Hye Huh, Kyung-do Han, Yun Kyung Cho, Eun Roh, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Differences in health behavior and nutrient intake status between diabetes-aware and unaware Korean adults based on the Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2016–18 data: A cross-sectional study
Anshul Sharma, Chen Lulu, Kee-Ho Song, Hae-Jeung Lee
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effective coverage of diabetes and hypertension: an analysis of Thailand’s national insurance database 2016–2019
Nattadhanai Rajatanavin, Woranan Witthayapipopsakul, Vuthiphan Vongmongkol, Nithiwat Saengruang, Yaowaluk Wanwong, Aniqa Islam Marshall, Walaiporn Patcharanarumol, Viroj Tangcharoensathien
BMJ Open.2022; 12(12): e066289. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Treatment with Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Multi-Center, Retrospective, Observational Study
Jun Sung Moon, Sunghwan Suh, Sang Soo Kim, Heung Yong Jin, Jeong Mi Kim, Min Hee Jang, Kyung Ae Lee, Ju Hyung Lee, Seung Min Chung, Young Sang Lyu, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jung Eun Jang, Tae Nyun Kim, Sung Woo Kim, Eonju Jeon, Nan Hee Cho, Mi-Kyung Ki
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 675. CrossRef - Association between secondhand smoke exposure and diabetes mellitus in 131 724 Korean never smokers using self‐reported questionnaires and cotinine levels: Gender differences
Byung Jin Kim, Ji Hye Kim, Jeong Gyu Kang, Bum Soo Kim, Jin Ho Kang
Journal of Diabetes.2021; 13(1): 43. CrossRef - Importance of Awareness and Treatment for Diabetes in Influenza Vaccination Coverage of Diabetic Patients under 65 Years: A Population-Based Study
Yu Mi Ko, Seung Hyun Ko, Kyoungdo Han, Yong-Moon Park, Joon Young Choi, Shin Young Kim, So Hyang Song, Chi Hong Kim, Sung Kyoung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 55. CrossRef - Associations of urinary concentrations of phthalate metabolites, bisphenol A, and parabens with obesity and diabetes mellitus in a Korean adult population: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) 2015–2017
Inae Lee, Young Joo Park, Min Joo Kim, Sunmi Kim, Sohyeon Choi, Jeongim Park, Yoon Hee Cho, Sooyeon Hong, Jiyoung Yoo, Hyunwoong Park, Gi Jeong Cheon, Kyungho Choi, Min Kyong Moon
Environment International.2021; 146: 106227. CrossRef - Early combination versus initial metformin monotherapy in the management of newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: AnEast Asianperspective
Linong Ji, Juliana C. N. Chan, Miao Yu, Kun Ho Yoon, Sin Gon Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Chien‐Ning Huang, Shih Te Tu, Chih‐Yuan Wang, Päivi Maria Paldánius, Wayne H. H. Sheu
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(1): 3. CrossRef - Hypertension and stroke in Asia: A comprehensive review from HOPE Asia
Yuda Turana, Jeslyn Tengkawan, Yook Chin Chia, Michael Nathaniel, Ji‐Guang Wang, Apichard Sukonthasarn, Chen‐Huan Chen, Huynh Van Minh, Peera Buranakitjaroen, Jinho Shin, Saulat Siddique, Jennifer M. Nailes, Sungha Park, Boon Wee Teo, Jorge Sison, Arieska
The Journal of Clinical Hypertension.2021; 23(3): 513. CrossRef - Glycaemic control with add‐on thiazolidinedione or a sodium‐glucose co‐transporter‐2 inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes after the failure of an oral triple antidiabetic regimen: A 24‐week, randomized controlled trial
Jaehyun Bae, Ji Hye Huh, Minyoung Lee, Yong‐Ho Lee, Byung‐Wan Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(2): 609. CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index and the risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Jung A Kim, Jinsil Kim, Eun Roh, So-hyeon Hong, You-Bin Lee, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi, Eunjin Noh, Soon Young Hwang, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 171: 108533. CrossRef - Effectiveness and safety of sodium‐glucose co‐transporter‐2 inhibitors compared with dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors in older adults with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population‐based study
Seung Jin Han, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Nami Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(3): 682. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheets in Korea, 2020: An Appraisal of Current Status
Chan-Hee Jung, Jang Won Son, Shinae Kang, Won Jun Kim, Hun-Sung Kim, Hae Soon Kim, Mihae Seo, Hye-Jung Shin, Seong-Su Lee, Su Jin Jeong, Yongin Cho, Seung Jin Han, Hyang Mi Jang, Mira Rho, Shinbi Lee, Mihyun Koo, Been Yoo, Jung-Wha Moon, Hye Young Lee, Ja
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 1. CrossRef - Prevalence and diagnosis experience of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women over 50: Focusing on socioeconomic factors
Min Hyeok Choi, Ji Hee Yang, Jae Seung Seo, Yoon-ji Kim, Suk-Woong Kang, Jose M. Moran
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(3): e0248020. CrossRef - Metformin use in cancer survivors with diabetes reduces all-cause mortality, based on the Korean National Health Insurance Service between 2002 and 2015
Joungyoun Kim, Yoon-Jong Bae, Jae-woo Lee, Ye-seul Kim, Yonghwan Kim, Hyo-Sun You, Hyeong-Seop Kim, Eun-A Choi, Ye-Eun Han, Hee-Taik Kang
Medicine.2021; 100(11): e25045. CrossRef - Role of obesity-induced inflammation in the development of insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes: history of the research and remaining questions
Jieun Kim, Jongsoon Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 26(1): 1. CrossRef - White Blood Cell Count as a Predictor of Incident Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Among Non-Obese Adults: A Longitudinal 10-Year Analysis of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Jae-Min Park, Hye Sun Lee, Ju-Young Park, Dong-Hyuk Jung, Ji-Won Lee
Journal of Inflammation Research.2021; Volume 14: 1235. CrossRef - The Association of Hemoglobin A1c and Fasting Glucose Levels with hs-CRP in Adults Not Diagnosed with Diabetes from the KNHANES, 2017
Jeong Woo Seo, Sat Byul Park, Ulrike Rothe
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Effects of Jerusalem Artichoke Extract and Inulin on Blood Glucose Levels and Insulin Secretion in Streptozotocin Induced Diabetic Mice
Seung Hee Kim, Byung Ki Kim, Boo Yeun Park, Jung Min Kim, Young Jik Lee, Mi Kyung Lee, Sung-Tae Yee, Mi Yeon Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(1): 60. CrossRef - Health State Utility Values for Type 2 Diabetes and Related Complications in East and Southeast Asia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Chiu Hang Mok, Harley H.Y. Kwok, Carmen S. Ng, Gabriel M. Leung, Jianchao Quan
Value in Health.2021; 24(7): 1059. CrossRef - Association between alcohol consumption status and obesity-related comorbidities in men: data from the 2016 Korean community health survey
Bo-Yeon Kim, Hyewon Nam, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Yoon-Young Cho, Dug-Hyun Choi, Chan-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok, Chul-Hee Kim
BMC Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease and its risk factors in Korea
Hyeon Chang Kim
Global Health & Medicine.2021; 3(3): 134. CrossRef - Korea Heart Disease Fact Sheet 2020: Analysis of Nationwide Data
Hyeok-Hee Lee, So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jongmin Baek, Jang-Ho Bae, Wook-Jin Chung, Hyeon Chang Kim
Korean Circulation Journal.2021; 51(6): 495. CrossRef - Personalized Type 2 Diabetes Management Using a Mobile Application Integrated with Electronic Medical Records: An Ongoing Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun-Young Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Seon-Ah Cha, Sun-Young Lim, Jin-Hee Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hyun Ko
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(10): 5300. CrossRef - Association between toothbrushing and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Ji-Youn Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Gyu-Na Lee, Hyun Chul Song, Yu-Bae Ahn, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hyun Ko, Houkai Li
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(5): e0243686. CrossRef - Control of Glucose, Blood Pressure, and Cholesterol among Adults with Diabetes: The Brazilian National Health Survey
Rodrigo Citton P. dos Reis, Bruce B. Duncan, Célia Landmann Szwarcwald, Deborah Carvalho Malta, Maria Inês Schmidt
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(15): 3428. CrossRef - Comparison of fracture risk between type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a comprehensive real-world data
J. Ha, C. Jeong, K.-D. Han, Y. Lim, M.K. Kim, H.-S. Kwon, K.-H. Song, M.I. Kang, K.-H. Baek
Osteoporosis International.2021; 32(12): 2543. CrossRef - Treatment Patterns of Type 2 Diabetes Assessed Using a Common Data Model Based on Electronic Health Records of 2000–2019
Kyung Ae Lee, Heung Yong Jin, Yu Ji Kim, Yong-Jin Im, Eun-Young Kim, Tae Sun Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Etiology, diagnosis, complications, and treatments of diabetic foot
Dong-Kyo Seo
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2021; 64(8): 523. CrossRef - Occupational Noise Exposure and Incidence of High Fasting Blood Glucose: A 3-Year, Multicenter, Retrospective Study
Seunghan Kim, Byungyoon Yun, Seunghyun Lee, Changyoung Kim, Juho Sim, Ara Cho, Yeonsuh Oh, Jiho Lee, Jinha Yoon
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(17): 9388. CrossRef - Positive association between the ratio of triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and diabetes incidence in Korean adults
Joungyoun Kim, Sang-Jun Shin, Ye-Seul Kim, Hee-Taik Kang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Standard E TB-Feron ELISA and QuantiFERON-TB Gold Plus Assays in Patients with Tuberculosis and Healthcare Workers
In Young Yoo, Jaewoong Lee, Ae Ran Choi, Yoon Hee Jun, Hwa Young Lee, Ji Young Kang, Yeon-Joon Park
Diagnostics.2021; 11(9): 1659. CrossRef - Associations between obesity, weight change and decreased renal function in Korean type 2 diabetic patients: a longitudinal follow-up study
Bo-Yeon Kim, Dug-Hyun Choi, Chan-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok, Chul-Hee Kim
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-World Efficacy and Safety of Dulaglutide in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Study in a Tertiary Referral Center
Jee Hee Yoon, A Ram Hong, Wonsuk Choi, Ji Yong Park, Hee Kyung Kim, Ho-Cheol Kang
Chonnam Medical Journal.2021; 57(3): 211. CrossRef - The History of Insulin Therapy in Korea
Jun Sung Moon, Jong Chul Won, Young Min Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 623. CrossRef - How Can We Adopt the Glucose Tolerance Test to Facilitate Predicting Pregnancy Outcome in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus?
Kyeong Jin Kim, Nam Hoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Ju Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 988. CrossRef - Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Disease in Older Patients With Diabetes: Retrospective Cohort Study
Sangmo Hong, Jung Hwan Park, Kyungdo Han, Chang Beom Lee, Dong Sun Kim, Sung Hoon Yu
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-Term Glycaemic Durability of Early Combination Therapy Strategy versus Metformin Monotherapy in Korean Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Soon-Jib Yoo, Sang-Ah Chang, Tae Seo Sohn, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Jong Min Lee, Sungdae Moon, Pieter Proot, Päivi M Paldánius, Kun Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 954. CrossRef - Short-Term Effects of the Internet-Based Korea Diabetes Prevention Study: 6-Month Results of a Community-Based Randomized Controlled Trial
Jin-Hee Lee, Sun-Young Lim, Seon-Ah Cha, Chan-Jung Han, Ah Reum Jung, Kook-Rye Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 960. CrossRef - Anti-diabetic effects of aqueous extract of Dendropanax morbifera Lev. leaves in streptozotocin-induced diabetic Sprague-Dawley rats
Min-Jae Kim, Ye-Jin Kang, Dong-Eon Lee, Suk Kim, Se-Hun Lim, Hu-Jang Lee
Korean Journal of Veterinary Research.2021; 61(4): e38. CrossRef - The Potential Role of MicroRNA in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy
Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 54. CrossRef -
Diabetes and Metabolism Journal in 2020: Good to Great
In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 1. CrossRef - Use of SGLT-2 Inhibitors in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Abdominal Obesity: An Asian Perspective and Expert Recommendations
Wayne Huey-Herng Sheu, Siew Pheng Chan, Bien J. Matawaran, Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Ambrish Mithal, Juliana Chan, Ketut Suastika, Chin Meng Khoo, Huu Man Nguyen, Ji Linong, Andrea Luk, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 11. CrossRef - Underweight Increases the Risk of End-Stage Renal Diseases for Type 2 Diabetes in Korean Population: Data From the National Health Insurance Service Health Checkups 2009–2017
Yang-Hyun Kim, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Kyung-do Han, Sung-Hee Ihm, Kyung-Hwan Cho, Yong-Gyu Park
Diabetes Care.2020; 43(5): 1118. CrossRef - The Role of CD36 in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: β-Cell Dysfunction and Beyond
Jun Sung Moon, Udayakumar Karunakaran, Elumalai Suma, Seung Min Chung, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 222. CrossRef - Metformin treatment for patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology consensus statement
Kyu Yeon Hur, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Miyeun Han, Dong Won Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 39(1): 32. CrossRef - Effect of Smartphone-Based Lifestyle Coaching App on Community-Dwelling Population With Moderate Metabolic Abnormalities: Randomized Controlled Trial
So Mi Jemma Cho, Jung Hyun Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hyungseon Yeom, Su Jin Lee, Yong Woo Jeon, Hyeon Chang Kim
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2020; 22(10): e17435. CrossRef - Fasting plasma glucose level and the risk of open angle glaucoma: Nationwide population-based cohort study in Korea
Jin A. Choi, Yong-Moon Park, Kyungdo Han, Jiyoung Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko, Bang V Bui
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(9): e0239529. CrossRef - Smoking as a Target for Prevention of Diabetes
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 402. CrossRef - Association of Snoring with Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center Cohort
So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hyeon Chang Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 687. CrossRef - Increased Mortality Burden in Young Asian Subjects with Dysglycemia and Comorbidities
Eun-Jung Rhee, Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Yang-Hyun Kim, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Won-Young Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(4): 1042. CrossRef - Metformin Treatment for Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
Kyu Yeon Hur, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Miyeun Han, Dong Won Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 3. CrossRef - Study of hospitalization and mortality in Korean diabetic patients using the diabetes complications severity index
Hyunju Yoo, Eunjung Choo, Sukhyang Lee
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2020;[Epub] CrossRef Comprehensive Trends and Patterns of Antihypertensive Prescriptions Using a Nationwide Claims Database in Korea
Minji Jung, Eunjung Choo, Sukhyang Lee
Clinical Epidemiology.2020; Volume 12: 963. CrossRef- The effects of climate on the incidence of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
Seung Ri Oh, Sung Jin Min, Chang Eurn Kim, Munyoung Chang, Seog-Kyun Mun
International Journal of Biometeorology.2020; 64(12): 2119. CrossRef - Prevalence and Current Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Korean Adults Based on Fact Sheets
Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 85. CrossRef - Diabetic Retinopathy and Related Clinical Practice for People with Diabetes in Korea: A 10-Year Trend Analysis
Yoo-Ri Chung, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Kihwang Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 928. CrossRef - Association between sleep duration and impaired fasting glucose according to work type in non-regular workers: data from the first and second year (2016, 2017) of the 7th Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination (KNHANE) (a cross-sectional study)
JaeHan Joo, Jae-Gwang Lee, SangWoo Kim, JaeHan Lee, June-Hee Lee, Kyung-Jae Lee
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Korea between 2012 and 2014: an Analysis of Data from the Korean Nationwide Cancer Registry
Young Eun Chon, Han Ah Lee, Jun Sik Yoon, Jun Yong Park, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joon Lee, Suk Kyun Hong, Dong Hyeon Lee, Hyun-Joo Kong, Eunyang Kim, Young-Joo Won, Jeong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Liver Cancer.2020; 20(2): 135. CrossRef Effect of Switching from Linagliptin to Teneligliptin Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eugene Han, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Soon Kim, Byung-wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4113. CrossRef- Temperature Correction to Enhance Blood Glucose Monitoring Accuracy Using Electrical Impedance Spectroscopy
Ye Sung Lee, Minkook Son, Alexander Zhbanov, Yugyung Jung, Myoung Hoon Jung, Kunsun Eom, Sung Hyun Nam, Jongae Park, Sung Yang
Sensors.2020; 20(21): 6231. CrossRef - Predictors of Health-Related Quality of Life in Korean Adults with Diabetes Mellitus
Mihyun Jeong
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(23): 9058. CrossRef - The triglyceride-glucose index predicts ischemic heart disease risk in Koreans: a prospective study using National Health Insurance Service data
Byoungjin Park, Yong-Jae Lee, Hye Sun Lee, Dong-Hyuk Jung
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Independent Impact of Diabetes on the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 5,307 Patients in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:737-46)
Sun Joon Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 942. CrossRef - Does Diabetes Increase the Risk of Contracting COVID-19? A Population-Based Study in Korea
Sung-Youn Chun, Dong Wook Kim, Sang Ah Lee, Su Jung Lee, Jung Hyun Chang, Yoon Jung Choi, Seong Woo Kim, Sun Ok Song
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 897. CrossRef - Independent Impact of Diabetes on the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 5,307 Patients in South Korea: A Nationwide-Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:737-46)
Kyuho Kim, Tae Jung Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 938. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea
Ji Hong You, Sang Ah Lee, Sung-Youn Chun, Sun Ok Song, Byung-Wan Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Edward J. Boyko
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(4): 901. CrossRef - The Liability Threshold Model for Predicting the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Multi-Cohort Study of Korean Adults
Eun Pyo Hong, Seong Gu Heo, Ji Wan Park
Metabolites.2020; 11(1): 6. CrossRef - Increased Age of Death and Change in Causes of Death Among Persons With Diabetes Mellitus From the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes and Muscle Dysfunction in Older Adults
Hak Chul Jang
Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research.2019; 23(4): 160. CrossRef - Letter: Comparison of the Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy 20 mg with Rosuvastatin 5 mg and Ezetimibe 10 mg Combination Therapy on Lipid Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J2019;43:582–9)
Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 909. CrossRef - Comprehensive Efforts Are Needed to Improve the Quality of Primary Diabetes Care in Korea
Chan-Hee Jung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(3): 265. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA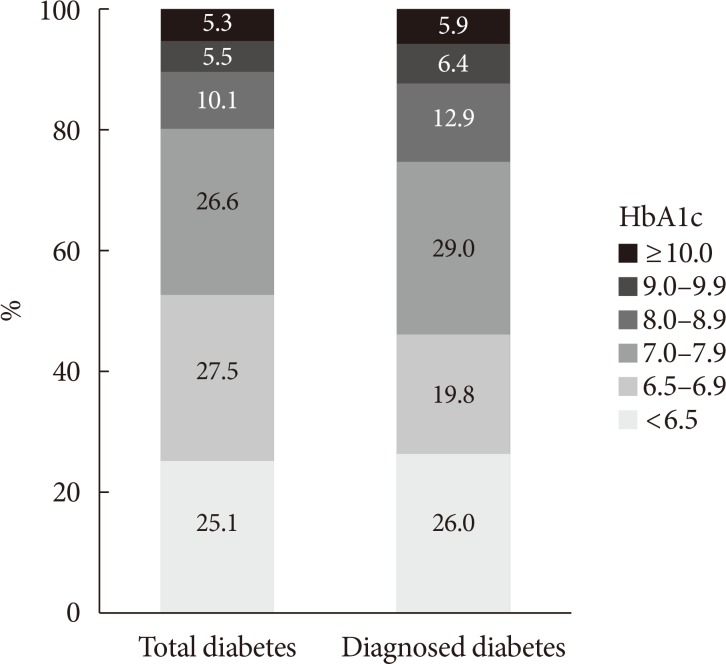
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite