- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Ahead-of print > Article
-
Original ArticleDrug/Regimen Safety and Effectiveness of Dulaglutide in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Korean Real-World Post-Marketing Study
-
Jeonghee Han1
 , Woo Je Lee2, Kyu Yeon Hur3, Jae Hyoung Cho4, Byung Wan Lee5, Cheol-Young Park6
, Woo Je Lee2, Kyu Yeon Hur3, Jae Hyoung Cho4, Byung Wan Lee5, Cheol-Young Park6
-
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0030
Published online: February 2, 2024
- 634 Views
- 55 Download
1Lilly Korea Ltd., Seoul, Korea
2Department of Internal Medicine, Asan Medical Center, University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
3Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
5Department of Internal Medicine, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
6Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding author: Cheol-Young Park Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 29 Saemunan-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul 03181, Korea E-mail: cydoctor@chol.com
Copyright © 2024 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
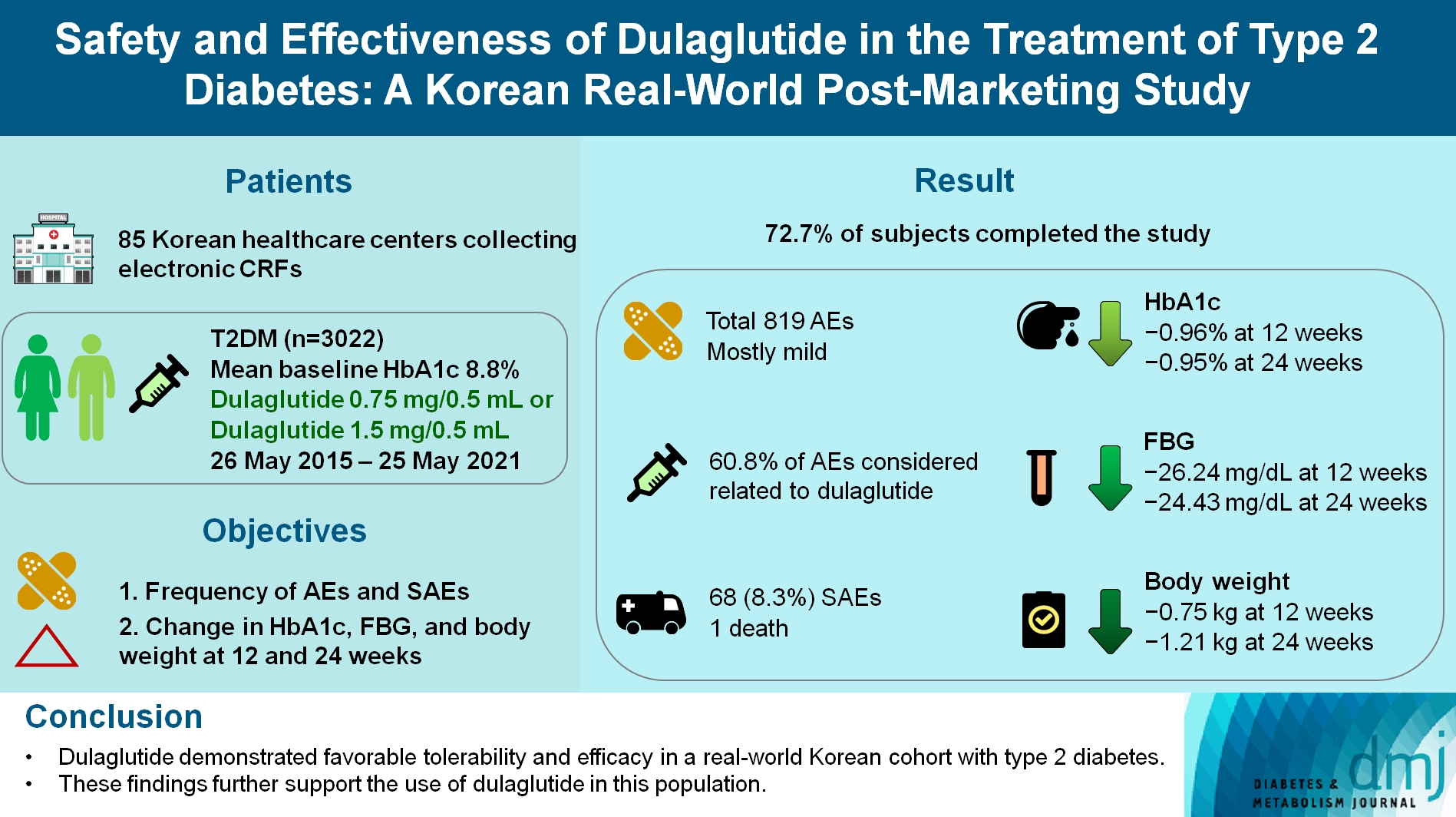
- To investigate the real-world safety and effectiveness of dulaglutide in Korean adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
-
Methods
- This was a real-world, prospective, non-interventional post-marketing safety study conducted from May 26, 2015 to May 25, 2021 at 85 Korean healthcare centers using electronic case data. Data on patients using dulaglutide 0.75 mg/0.5 mL or the dulaglutide 1.5 mg/0.5 mL single-use pens were collected and pooled. The primary objective was to report the frequency and proportion of adverse and serious adverse events that occurred. The secondary objective was to monitor the effectiveness of dulaglutide at 12 and 24 weeks by evaluating changes in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), fasting plasma glucose, and body weight.
-
Results
- Data were collected from 3,067 subjects, and 3,022 subjects who received ≥1 dose (of any strength) of dulaglutide were included in the safety analysis set (53% female, mean age 56 years; diabetes duration 11.2 years, mean HbA1c 8.8%). The number of adverse events reported was 819; of these, 68 (8.3%) were serious adverse events. One death was reported. Adverse events were mostly mild in severity; 60.81% of adverse events were considered related to dulaglutide. This study was completed by 72.73% (2,198/3,022) of subjects. At 12/24 weeks there were significant (P<0.0001) reductions from baseline in least-squares mean HbA1c (0.96%/0.95%), fasting blood glucose (26.24/24.43 mg/dL), and body weight (0.75/1.21 kg).
-
Conclusion
- Dulaglutide was generally well tolerated and effective in real-world Korean individuals with T2DM. The results from this study contribute to the body of evidence for dulaglutide use in this population.
- • This was a post-marketing safety study conducted upon dulaglutide approval in Korea.
- • Real-world data was collected from 3,067 adults with type 2 diabetes from 2015 to 2021.
- • Dulaglutide resulted in reductions in HbA1c, fasting blood glucose, and body weight.
- • Adverse events were consistent with the known safety profile of dulaglutide.
- • Dulaglutide was well-tolerated and effective in Korean adults with type 2 diabetes.
Highlights
- Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a growing global concern with rising prevalence and morbidity/mortality rates [1]. While there are many treatment options available for T2DM, few therapeutic options focus on enhancing the action of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). GLP-1 limits postprandial glucose excursion by stimulating insulin secretion, inhibiting glucagon secretion [2], delaying gastric emptying, and reducing food intake [3]. The actions of GLP-1 are mediated via the GLP-1 receptor, which is found in several body tissues and enhances the action of GLP-1 beyond plasma glucose regulation [2]. However, the short half-life of GLP-1 limits it clinical utility. Since the first approval by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2005, GLP-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have been shown to be effective for glycemic control in adults with T2DM [2]. GLP-1 RAs work by activating the GLP-1 receptor in the pancreas, resulting in the promotion of glucose-dependent insulin secretion and inhibition of glucose-dependent glucagon secretion [3,4]. These effects in addition to other mechanisms cause a modest reduction in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), glucagonemia, and body weight [4,5] with a low risk of hypoglycemia [6]. Despite clinical benefits, the initiation of injectable therapy with GLP-1 RAs can be complex. Adverse events (AEs) have been reported and include gastrointestinal disorders (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea), and pancreatitis [3,4]. In addition, physician-, patient-, or healthcare system-related barriers can exist, where a significant proportion of high-risk patients who are eligible do not obtain the appropriate T2DM treatments [2].
- In 2020, 16.7% of Korean adults aged ≥30 years and 30.1% of adults aged ≥65 years were living with T2DM diabetes [1]; however, there are limited data on the effectiveness and safety of GLP-1 RA use in Korean patients [1,7,8]. This real-world, single-country, prospective, non-interventional, post-marketing safety study (PMSS) was designed to investigate the safety and effectiveness of dulaglutide in Korean adults with T2DM. The primary objective was to report the frequency and proportion of AEs and serious adverse events (SAEs) that occurred during the study. The secondary objectives were to monitor the effectiveness of dulaglutide at 12 and 24 weeks by evaluating changes in HbA1c, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), and body weight.
INTRODUCTION
- The GLP-1 RA dulaglutide was approved by the Korean Ministry of Food and Drug Safety (MFDS) on May 26, 2015 on the condition that a re-examination PMSS would be conducted. This single-country, prospective, non-interventional PMSS was conducted from May 26, 2015 to May 25, 2021. Before initiating the study, the investigators obtained written and dated approval from the Independent Ethics Committee for the study protocol and its amendments. The study was conducted in accordance with the Standard for Re-examination of New Drugs outlined in the Pharmaceutical Affairs Act, the Regulation on Safety of Medicinal Products, and the regulations of the Korean MFDS (IRB number: PMS2016-035). Informed consent was obtained in compliance with the applicable regulatory requirements and adhered to good clinical practice and the ethical principles that have their origin in the Declaration of Helsinki.
- Target populations were recruited from 85 healthcare centers where electronic case report forms (CRFs) were collected, and clinical data had been accurately and completely entered into the CRFs. Study subjects were enrolled via a continuous enrolment method, with their CRFs continuously recorded without omission from the first administered dose of dulaglutide until the contracted number of subjects was reached. A target number of 4,046 subjects were contracted to be recruited from the 85 sites. The subjects were followed up starting from the baseline visit to 24±4 weeks or until the last treatment (in case of the subject discontinuing dulaglutide before 24±4 weeks), whichever came first.
- Clinical characteristics, medical history, comorbidities, and status of dulaglutide treatment were recorded. Any AEs that occurred during the investigation period including AEs of low frequency, unexpected AEs (AEs not reflected in the dulaglutide label), and adverse drug reactions (ADRs) were included in the safety analysis. AEs of low frequency (<5%) were reported regardless of whether their relationship to the study drug could be determined [9,10]. Mild AEs were defined as a symptom that does not cause significant interference with daily life, moderate AEs were defined as symptoms that significantly influence everyday life and may require an adjustment of the medication dose, and severe AEs were defined as a symptom that inhibits a person from living their everyday life as he/she wishes. SAEs were defined as any AE resulting in: death; initial or prolonged inpatient hospitalization; a life-threatening experience (i.e., immediate risk of dying); persistent or significant disability/incapacity; congenital anomaly/birth defect; or an AE considered significant by the investigator for any other reason. The relationship between dulaglutide and any safety events was determined by the investigator. HbA1c, FPG, and body weight data were included in the effectiveness analysis.
- Data were analyzed using three subsets: (1) the safety evaluation included subjects who received at least one dose of the study drug and participated in at least one post-baseline visit; (2) the effectiveness evaluation included subjects who received at least one dose of the study drug, who participated in at least one post-baseline visit, and whose HbA1c, FPG, or body weight were collected at baseline or at a visit within an acceptable period post-baseline (±4 weeks); (3) a sensitivity analysis for effectiveness was conducted and included subjects whose data were collected at baseline or at a visit within a broader acceptable period post-baseline (±6 weeks).
- Descriptive statistics were used to report baseline clinical characteristic data. Univariate analysis (chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test) and multivariable logistic regression were used to identify the incidence and factors that affect AEs and SAEs. A mixed model for repeated measures (MMRM), a paired t-test and an analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) were used to assess, test and measure the difference in change between the HbA1c, FPG, and body weight at baseline and follow-up visits. Multivariable logistic regression and univariate analysis were used to identify the factors associated with the achievement of HbA1c levels of 6.5% or less.
METHODS
- Data were collected from 3,067 subjects’ CRFs; 45 were excluded due to not receiving the drug (n=2), violation of the inclusion/exclusion criteria (n=37), or not having follow-up data (n=6). This resulted in 3,022 subjects being included in the safety evaluation. Of these 3,022 subjects, those whose baseline (±4 weeks) effectiveness data were not collected (n=622) or who did not receive the study drug for at least 8 weeks (n=32) were excluded, leaving 2,368 subjects in the effectiveness evaluation set. An additional subset of 2,590 subjects were included in an effectiveness sensitivity analysis (±6 weeks for visits, as described in the methods).
- In this study, most patients were female, had an average age of 56.22 years, a body mass index (BMI) of 28.31 kg/m2, a HbA1c of 8.84%, and duration of T2DM was 11.19 years. Almost all patients (95.43%) had used concomitant medication for T2DM; data on the classes or types of prior T2DM medication were not collected. Similarly, the majority of patients (82.43%) had used non-T2DM concomitant medication, most commonly lipid-modifying agents (66.98%), agents acting on the renin-angiotensin system (37.39%), and anti-platelet agents (33.98%). Baseline demographics and characteristics are outlined in Table 1.
- The dose of dulaglutide administered during the study period ranged from 0.75 to 114 mg. Patients were started on an initial dose of 0.75 mg (95.8%) or 1.5 mg (4.2%) dulaglutide. During the study period, 48.6% of patients required a dose increase from 0.75 to 1.5 mg. Most patients received dulaglutide for ≥22 weeks (Supplementary Table 1). A total of 2,198 (72.73%) subjects completed the study and 824 (27.27%) discontinued the study. The reasons for discontinuation included AEs (n=221/824; 26.82%), lost to follow-up (n=12/824; 1.46%), patient decision (n=111/824; 13.47%), investigator decision (n=186/824; 22.57%), and other reasons (n=294/824; 35.68%).
- Safety data
- All AEs were reported regardless of the association with dulaglutide. A total of 819 AEs including 498 ADRs, 325 unexpected AEs including 62 unexpected ADRs, 68 SAEs including 15 serious ADRs, 59 unexpected SAEs including 13 unexpected serious ADRs, and one death were reported. The most frequently reported AE was nausea, which was reported in 5.03% (152/3,022 subjects, 154 events), followed by diarrhea reported in 2.08% (63/3,022 subjects, 63 events), and decreased appetite, which was reported in 1.29% (39/3,022 subjects, 39 events) (Table 2). Hypoglycemia occurred in 13 subjects (0.43%; 14 events).
- The severity of the AEs was mostly mild (82.30%; 674/819 events) or moderate (16.85%; 138/819 events), with severe events comprising 0.85% (7/819 events). Outcomes of the AEs included recovery without sequelae (72.04%), recovery with sequelae (0.12%), ongoing recovery (17.22%), did not recover (8.30%), aggravation (0%), death (0.12%), and unknown outcome (2.20%). The frequency of AEs resulting in initial or prolonged inpatient hospitalization was 8.30% (68/819 events). No life-threatening events were reported, and there was one death (metastatic breast cancer).
- The association of AEs with dulaglutide was noted in 60.81% (498/819 events). The most common AEs associated with dulaglutide were gastrointestinal disorders (11.80%) plus general disorders and administration site conditions (8.89%). None of these categories included an aggravation or death. Dose changes due to an AE were reported. The dose was maintained in 59.95%, escalated in 0.37%, reduced in 4.15%, discontinued in 0.85%, and abandoned in 34.68% of study subjects. Discontinued was defined as permanently stopping the medication, while abandoned indicated patient non-adherence to either acquiring or taking the medication. The occurrence of AEs by baseline characteristics is summarized in Table 3. When comparing AEs according to the average weekly dose of dulaglutide received, there was a statistically significant difference in the incidence of AEs according to dose (P=0.0075) (Table 3), but no statistically significant difference in SAEs (P=0.1512).
- A higher incidence of AEs was associated with female sex, normal BMI, previous history of T2DM treatment with medicine, the presence of a medical history and pre-existing conditions, and administration of other non-T2DM concomitant medication, according to univariate analysis.
- A statistical difference was also noted in AEs by dulaglutide administration duration, average weekly dose, and follow-up period. Using multivariable logistic regression, factors that statistically significantly influenced the incidence of AEs were sex, previous history of T2DM treatment with medicine, administration of other concomitant medication, and the administration duration of dulaglutide (Table 4).
- Effectiveness data
- HbA1c, FPG, and body weight were all improved from baseline at 12 and 24 weeks. The mean±standard deviation (SD) HbA1c was 8.85%±1.47% at baseline, 7.88%±1.43% at 12±4 weeks, and 7.89%±1.45% at 24±4 weeks. The mean±SD FPG was 172.79±63.75 mg/dL at baseline, 146.79±48.84 mg/dL at 12±4 weeks, and 148.39±49.27 mg/dL at 24±4 weeks. The mean±SD body weight was 74.90±14.72 kg at baseline, 74.16±14.82 kg at 12±4 weeks, and 73.70±14.98 kg at 24±4 weeks. According to the MMRM analysis, the change from baseline was statistically significant at both 12 and 24 weeks for all parameters (Table 5).
- In the ANCOVA analysis, a statistically significant difference was noted in the least-square (LS) mean reduction in HbA1c by age (patients <40 years showing a greater reduction [1.50% to 1.25%] in HbA1c levels compared to patients >40 years [0.9% to 1.07%]; P=0.0012), BMI (1.08% in patients with BMI ≥30 kg/m2 vs. 0.04%–0.95% in patients with BMI <30 kg/m2; P=0.0109), history of T2DM treatment with medicine (0.92% with yes, 1.10% with no; P=0.0140), pre-existing conditions (0.93% with yes, 1.11% with no; P=0.0229), use of other concomitant medication (0.95% with yes, 1.06% with no; P<0.0001), administration duration of dulaglutide (0.98% and 1.00% for 22–26 and >26 weeks, respectively, and 0.13%–0.92% for <22 weeks; P=0.0014), and follow-up period (≥22 weeks 0.98%, <22 weeks 0.83%; P=0.0499). There was no statistically significant difference noted for the change in HbA1c and the proportion of patients reaching a HbA1c of <6.5% according to average weekly dulaglutide dose (P=0.8021 and P=0.5329, respectively).
- The proportion of subjects who achieved a HbA1c of 6.5% or less was 14.65% (297/2,027 subjects) at 12±4 weeks, 15.52% (225/1,450 subjects) at 24±4 weeks, and 15.38% (344/2,236 subjects) at completion of the study. The proportion of subjects who achieved a HbA1c of 7.0% or less was 27.68% (561/2,027 subjects) at 12±4 weeks, 27.79% (403/1,450 subjects) at 24±4 weeks, and 27.68% (619/2,236 subjects) at completion of the study. Using multivariable logistic regression, factors that statistically significantly influenced the achievement of HbA1c of 6.5% or less are outlined in Table 6.
- The sensitivity analysis used a broader definition of an acceptable time period (within ±6 weeks of the scheduled visit vs. ±4 weeks of the scheduled visit in the main analysis). In this analysis, the proportion of subjects who achieved a HbA1c of 6.5% or less was 14.95% (332/2,220 subjects) at 12±6 weeks and 15.75% (268/1,702 subjects) at 24±6 weeks, which are similar to the results of the main analysis. The MMRM analysis using the time period for the sensitivity analysis showed an LS mean±standard error (SE) reduction from baseline in HbA1c of –0.96%±0.03% at 12±6 weeks and –0.92%±0.03% at 24±6 weeks—a statistically significant decrease from baseline at each visit (both P<0.0001). FPG change from baseline using MMRM analysis revealed an LS mean±SE of –25.36±1.15 mg/dL at 12±6 weeks and –23.42±1.29 mg/dL at 24±6 weeks (both P<0.0001). Using MMRM, LS mean±SE change in body weight from baseline was –0.77±0.07 kg at 12±6 weeks and –1.19±0.07 kg at 24±6 weeks (both P<0.0001).
RESULTS
- The objective of this PMSS study in Korean subjects with T2DM was to evaluate the safety and effectiveness of dulaglutide. The safety profile of dulaglutide in this real-world study was generally as expected; that is, gastrointestinal AEs were common, and rates of hypoglycaemia were low. The factors associated with a statistically significant increase in AEs included female sex, normal BMI, previous history of T2DM treatment with medicine, pre-existing conditions, administration of other concomitant medication, and duration and average weekly dose of dulaglutide, according to univariate analysis. Logistic regression analysis confirmed an association of AEs with sex, previous history of T2DM medication, use of other concomitant medication, and administration duration of dulaglutide. Effectiveness data in this study showed a statistically significant change in HbA1c, body weight, and FPG levels from baseline at both 12 and 24 weeks.
- The numerically higher incidence of AEs and SAEs in females reported in this PMSS study has also been noted in some previous studies [11,12]. In other studies, 10.0% to 31.6% of subjects experienced transient gastrointestinal adverse effects [4,13-15], with more events noted in women [16]. Further studies may be warranted on sex differences [17]. As per the current dulaglutide label, no dose adjustment is needed based upon sex.
- It is not uncommon to experience an increased incidence of serious AEs in subjects who take other concomitant medication [18]. In this real-world study, the incidence of AEs in subjects who received concomitant medications other than glucose-lowering drugs was 2.52 times higher than in subjects who did not (Table 4). This increase in AEs associated with concomitant medication has been noted in other studies [18,19].
- The dose-related change in AEs summarized in Table 3 shows a slightly higher number of AEs (20.67%) in the lower dulaglutide dose of ≤0.75 mg/week when compared to >0.75 to <1.5 mg/week (18.88%). Similar data have been reported in other studies and in Korean populations [20], and where a higher risk of AEs at lower doses occurred, this was associated with age-related changes in pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics, the number of prescribed drugs, comorbidities, sex, and allergies [21,22].
- Comparable with previous real-world, retrospective, and post hoc analyses of randomized controlled trials [23-26], HbA1c reduction from baseline in this study was –0.96% and –0.95% at 12 and 24 weeks, respectively. HbA1c reductions with dulaglutide reported in the literature varied from –1.43% at 26 weeks [15], –1.3% over 24 months [25], –0.61% after 72 months [24], and –1.24% over 10 years [14]. However, the greatest reduction in HbA1c has been noted in the first 12 months with an average reduction of –0.0197% for each month on dulaglutide during this period [24]. The significant factors associated with HbA1c reduction in this study were age, previous history of T2DM treatment with medicine, other concomitant medications, and administration duration of dulaglutide, with longer administration duration associated with greater reductions (≥22 weeks vs. <22 weeks: approximately 1.00% vs. 0.13%–0.92%). The association of HbA1c reduction with administration duration was unexpected; previous studies showed that the reduction in HbA1c was associated with higher baseline HbA1c levels [11,13,14,26], independent of BMI, duration of disease [24], baseline body weight, total daily insulin dose [13], and sex [14]. The real-world nature of our study means that it is possible that the lesser HbA1c reduction with <22 weeks of dulaglutide is due to poor adherence or lack of response resulting in participant discontinuation before 22 weeks.
- In this study, subjects with a previous history of a glucose-lowering drug or other concomitant medication showed a significant reduction of HbA1c in response to dulaglutide treatment. The baseline HbA1c level in this study was 8.84%, which is lower than a study of Korean patients initiating insulin, which reported a baseline HbA1c level of 9.1% [27]. While the difference is small, this suggests that the initiation of the first injectable therapy may occur earlier in the disease course if the injectable is dulaglutide than if it is insulin, highlighting the potential value of dulaglutide in mitigating injection-related barriers.
- The statistically significant change from baseline in MMRM LS mean body weight at 12±4 weeks (–0.75 kg) and 24±4 weeks (–1.21 kg) aligns with previous literature [3,4,6,12,14-16,28,29]. The difference is comparable to other studies using a 0.75 mg dose of dulaglutide that have shown an average weight loss of –0.62 kg at 52 weeks [17], but lower than the weight change observed at 6 months in another Korean study that reported losses of –2.1 kg [14]. Some studies have linked the dulaglutide-associated increase in absolute weight loss to a subject’s higher baseline BMI and HbA1c levels [30]. Other studies have also found significant sex differences in changes in body weight, noting that females experienced greater weight loss or less weight gain when taking dulaglutide [16,17]. Of interest is the lowered risk of weight gain observed with dulaglutide when compared with active comparators [11].
- In general, safety and effectiveness results of this study were comparable with the previous reports [4,11-13]. The safety data for dulaglutide showed that gastrointestinal AEs were lower than previous reports and similar factors were associated with the risk of AEs [11-16]. In total, 221 of the 824 patients who discontinued the study did so because of AEs (26.8%); however, considering the entire safety evaluation population, discontinuation due to AEs was low (221/3,022; 7.31%). Less than 1% of AEs were considered severe, and most AEs resolved without sequelae. The effectiveness data for dulaglutide showed similar reductions in HbA1c, FPG, and body weight compared with previous data [23-26]. Therefore, this study could establish comparable safety and effectiveness of dulaglutide in the Korean population.
- Limitations should be considered when interpreting results due to the study design (single-arm observational study with no comparator group) and the relatively short study duration. Effectiveness results and the P-values of the univariate analysis without correction for multiplicity must be carefully interpreted.
- In conclusion, this real-world, single-country, prospective, non-interventional PMSS was designed to investigate the safety and effectiveness of dulaglutide in Korean adults with T2DM. This study concluded that dulaglutide was generally well tolerated in this study population. The prevalence of AEs and SAEs was comparable to current evidence; the majority were mild, without sequelae and resolved by study completion. The clinical use of dulaglutide in this study population was associated with meaningful reductions in HbA1c, FPG, and body weight during the study period.
DISCUSSION
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Table 1.
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
Jeonghee Han: employed by Eli Lilly and Company Korea; Woo Je Lee: a speaker for Eli Lilly and Company, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Novartis, Astra Zeneca, Viatris Pharmaceuticals, and Boehringer Ingelheim; Kyu Yeon Hur: no conflict of interest; Jae Hyoung Cho: no conflict of interest; Byung Wan Lee: a speaker and advisory board member for Eli Lilly and Company; Cheol-Young Park: a speaker for Eli Lilly and Company.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception or design: J.H., W.J.L., B.W.L., C.Y.P.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: W.J.L., K.Y.H., J.H.C., B.W.L., C.Y.P.
Drafting the work or revising: J.H., B.W.L., C.Y.P.
Final approval of the manuscript: J.H., W.J.L., K.Y.H., J.H.C., B.W.L., C.Y.P.
-
FUNDING
This work was funded by Eli Lilly and Company.
NOTES
-
Acknowledgements
- The sponsors acknowledge the participation of all healthy patients and the study site personnel involved in the clinical trial. Medical writing support was provided by Clare Koning and Sheridan Henness (Rx Communications, Mold, UK), funded by Eli Lilly and Company.
| Category | Number | Statistic |
|---|---|---|
| Female sex | 3,022 | 1,600 (52.95) |
| Age, yr | 3,022 | 56.22±12.56 |
| <30 | 97 (3.21) | |
| ≥30 and <40 | 209 (6.92) | |
| ≥40 and <50 | 533 (17.64) | |
| ≥50 and <60 | 907 (30.01) | |
| ≥60 and <70 | 854 (28.26) | |
| ≥70 and <80 | 372 (12.31) | |
| ≥80 | 50 (1.65) | |
| Patients stratified by age 65 years, yr | ||
| ≥65 | 785 (25.98) | |
| <65 | 2,237 (74.02) | |
| Height, cm | 2,341 | 163.25±9.34 |
| Waist circumference, cm | 1,088 | 91.23±14.19 |
| Baseline weight, kg | 2,335 | 75.45±15.22 |
| Baseline BMI, kg/m2 | 2,148 | 28.31±4.64 |
| Underweight (BMI <18.5) | 9 (0.42) | |
| Normal (18.5≤ BMI <23.0) | 195 (9.08) | |
| Overweight (23.0≤ BMI <25.0) | 294 (13.69) | |
| Obese I (25.0≤ BMI <30.0) | 985 (45.86) | |
| Obese II (BMI ≥30.0) | 665 (30.96) | |
| HbA1c, % | 2,731 | 8.84±1.47 |
| FBG, mg/dL | 2,174 | 172.61±63.24 |
| Duration of T2DM, yrb | 3,022 | 11.19±7.83 |
| Previously received T2DM treatment | 3,022 | 2,449 (81.04) |
| Pre-existing conditions | 3,022 | 2,659 (87.99) |
| Hypertension | 3,022 | 1,599 (52.91) |
| Dyslipidemiac | 3,022 | 1,067 (35.31) |
| Hyperlipidemiad | 3,022 | 838 (27.73) |
| Renal impairmente | 3,022 | 258 (8.54) |
| Hepatic impairmente | 3,022 | 325 (10.75) |
| Allergiese | 3,022 | 84 (2.78) |
| Coronary artery disease | 3,022 | 2 (0.07) |
| Concomitant medication for T2DM | 3,022 | 2,884 (95.43) |
| Other concomitant medication | 3,022 | 2,491 (82.43) |
Values are presented as number (%) or mean±standard deviation.
BMI, body mass index; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; FBG, fasting blood glucose; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
a The safety analysis set (n=3,022) includes subjects from the effectiveness analysis set (n=2,368). The effectiveness set includes subjects whose HbA1c, FBG, or body weight data were collected at baseline,
b The diagnosis date of T2DM for 19 subjects is the same date as starting date for dulaglutide,
c Dyslipidaemia refers to the imbalance of lipids in the blood (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, and high-density lipoprotein),
d Hyperlipidaemia refers to high levels of lipids or fats in the blood (low-density lipoprotein cholesterol only),
e Renal impairment, hepatic impairment, allergy definitions were not formally defined for this study, and were noted in the case report forms by the treating physician as part of routine clinical practice.
| Event type | No. of events | No. of subjects (%) | Most common symptom (%)a |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse event | 819 | 589 (19.49) | Nausea (5.03) |
| Diarrhea (2.08) | |||
| Decreased appetite (1.29) | |||
| Adverse drug reaction | 498 | 403 (13.34) | Nausea (4.93) |
| Diarrhea (1.75) | |||
| Drug in-effectivity (1.26) | |||
| Unexpected adverse event | 325 | 255 (8.44) | Increased blood glucose (0.86) |
| Dizziness (0.53) | |||
| Hyperglycemia (0.5) | |||
| Unexpected adverse drug reaction | 62 | 60 (1.99) | Increased blood glucose (0.26) |
| Dizziness (0.26) | |||
| Headache (0.20) | |||
| Pruritis (0.20) | |||
| Serious adverse eventb | 68 | 51 (1.69) | Increased blood glucose (0.30) |
| Inadequate DM control (0.1) | |||
| Cardiac failure (0.07) | |||
| Serious adverse drug reaction | 15 | 14 (0.46) | Increased blood glucose (0.26) |
| Inadequate control of DM, diabetic gastropathy, diabetic nephropathy, and urinary disorders (0.03%, respectively) | |||
| Unexpected serious adverse event | 59 | 50 (1.65) | Increased blood glucose (0.3) |
| Inadequate DM control (0.1) | |||
| Cardiac failure (0.07) | |||
| Unexpected serious adverse drug reaction | 13 | 13 (0.43) | Increased blood glucose (0.26) |
| Inadequate DM control, diabetic gastropathy, dizziness, diabetic nephropathy, urinary disorders (0.03, respectively) | |||
| Deathc | 1 | 1 |
DM, diabetes mellitus.
a Preferred term as defined by MedDRA 24.0 (MedDRA-K 24.0) for system organ class and investigations,
b Serious adverse events included adverse events that resulted in death, required either inpatient hospitalization or the prolongation of hospitalization, were life-threatening (immediate risk of death), resulted in a persistent or significant disability/incapacity or resulted in a congenital anomaly/birth defect, or any adverse event that did not result in death or require inpatient hospitalization but was considered significant based on the investigator’s judgement,
c The causal relationship between dulaglutide and this death was considered unlikely by the investigator.
| Factor | Subject | AE incidence | 95% CI | P valuea |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||||
| Male | 1,422 | 232 (16.32) | 14.43–18.34 | <0.0001b |
| Female | 1,600 | 357 (22.31) | 20.29–24.43 | |
| Total | 3,022 | 589 (19.49) | ||
| Age, yr | ||||
| <30 | 97 | 16 (16.49) | 9.73–25.40 | 0.7101 |
| ≥30–<40 | 209 | 39 (18.66) | 13.62–24.61 | |
| ≥40–<50 | 533 | 93 (17.45) | 14.32–20.94 | |
| ≥50–<60 | 907 | 177 (19.51) | 16.98–22.25 | |
| ≥60–<70 | 854 | 181 (21.19) | 18.50–24.09 | |
| ≥70–<80 | 372 | 74 (19.89) | 15.96–24.32 | |
| ≥80 | 50 | 9 (18.00) | 8.58–31.44 | |
| Total | 3,022 | 589 (19.49) | ||
| Patients stratified by age 65 years, yr | ||||
| ≥65 | 785 | 158 (20.13) | 17.38–23.11 | 0.6005 |
| <65 | 2,237 | 431 (19.27) | 17.65–20.96 | |
| Total | 3,022 | 589 (19.49) | ||
| BMI, kg/m2 | ||||
| Underweight (BMI <18.5) | 9 | 2 (22.22) | 2.81–60.01 | 0.0182b |
| Normal (18.5≤ BMI <23.0) | 195 | 55 (28.21) | 22.01–35.08 | |
| Overweight (23.0≤ BMI <25.0) | 294 | 52 (17.69) | 13.50–22.54 | |
| Obese I (25.0≤ BMI <30.0) | 985 | 179 (18.17) | 15.81–20.73 | |
| Obese II (BMI ≥30.0) | 665 | 141 (21.20) | 18.15–24.51 | |
| Total | 2,148 | 429 (19.97) | ||
| Previous history of T2DM treatment | ||||
| Yes | 2,449 | 518 (21.15) | 19.55–22.82 | <0.0001b |
| No | 573 | 71 (12.39) | 9.81–15.37 | |
| Total | 3,022 | 589 (19.49) | ||
| Medical historyc | ||||
| Yes | 270 | 76 (28.15) | 22.87–33.92 | 0.0002b |
| No | 2,752 | 513 (18.64) | 17.20–20.15 | |
| Total | 3,022 | 589 (19.49) | ||
| Pre-existing conditions | ||||
| Yes | 2,659 | 557 (20.95) | 19.41–22.54 | <0.0001b |
| No | 363 | 32 (8.82) | 6.11–12.22 | |
| Total | 3,022 | 589 (19.49) | ||
| Renal impairment | ||||
| Yes | 258 | 56 (21.71) | 16.83–27.24 | 0.3477 |
| No | 2,764 | 533 (19.28) | 17.83–20.80 | |
| Total | 3,022 | 589 (19.49) | ||
| Hepatic impairment | ||||
| Yes | 325 | 70 (21.54) | 17.19–26.41 | 0.3238 |
| No | 2,697 | 519 (19.24) | 17.77–20.78 | |
| Total | 3,022 | 589 (19.49) | ||
| Allergies | 0.1159 | |||
| Yes | 84 | 22 (26.19) | 17.20–36.93 | |
| No | 2,938 | 567 (19.30) | 17.89–20.77 | |
| Total | 3,022 | 589 (19.49) | ||
| Concomitant medication for T2DM | ||||
| Yes | 2,884 | 571 (19.80) | 18.36–21.30 | 0.0503 |
| No | 138 | 18 (13.04) | 7.92–19.83 | |
| Total | 3,022 | 589 (19.49) | ||
| Other concomitant medication | <0.0001b | |||
| Yes | 2,491 | 544 (21.84) | 20.23–23.51 | |
| No | 531 | 45 (8.47) | 6.25–11.18 | |
| Total | 3,022 | 589 (19.49) | ||
| Dulaglutide administration duration, wk | ||||
| <10 | 332 | 106 (31.93) | 26.94–37.24 | <0.0001b |
| 10–14 | 253 | 71 (28.06) | 22.62–34.03 | |
| >14–<22 | 310 | 74 (23.87) | 19.23–29.01 | |
| 22–26 | 905 | 145 (16.02) | 13.69–18.58 | |
| >26 | 1,222 | 193 (15.79) | 13.79–17.96 | |
| Total | 3,022 | 589 (19.49) | ||
| Average weekly dose of dulaglutide, mg/wk | ||||
| ≤0.75 | 1,548 | 320 (20.67) | 18.68–22.78 | 0.0075b |
| >0.75–<1.5 | 1,398 | 264 (18.88) | 16.86–21.04 | |
| ≥1.5 | 76 | 5 (6.58) | 2.17–14.69 | |
| Total | 3,022 | 589 (19.49) | ||
| Follow-up period, wk | ||||
| <22 | 761 | 190 (24.97) | 21.93–28.20 | <0.0001b |
| ≥22 | 2,261 | 399 (17.65) | 16.10–19.28 | |
| Total | 3,022 | 589 (19.49) |
Values are presented as number (%).
AE, adverse event; CI, confidence interval; BMI, body mass index; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus.
a Chi-square test,
b Statistically significant,
c Medical history was not formally defined for this study, and was noted in the case report forms by the treating physician as part of routine clinical practice.
| Factor | Odds ratio (95% CI) | P valuea |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 0.61 (0.49–0.77) | <0.0001b |
| Female | Reference | |
| BMI, 1 kg/m2 | 0.99 (0.96–1.01) | 0.2865 |
| Previous history of T2DM treatment with medicine | ||
| Yes | 1.70 (1.19–2.42) | 0.0034b |
| No | Reference | |
| Medical history | ||
| Yes | 1.34 (0.96–1.87) | 0.0894 |
| No | Reference | |
| Pre-existing conditions | ||
| Yes | 1.64 (0.80–3.37) | 0.1762 |
| No | Reference | |
| Other concomitant medication | ||
| Yes | 2.52 (1.43–4.44) | 0.0014b |
| No | Reference | |
| Administration duration of dulaglutide, 1 week | 0.94 (0.93–0.95) | <0.0001b |
| Factor | LS mean difference (mean±SE) | 95% CI | P valuea |
|---|---|---|---|
| HbA1c change from baseline, %b | |||
| 12±4 weeks | –0.96±0.03 | –1.01 to –0.91 | <0.0001c |
| 24±4 weeks | –0.95±0.03 | –1.01 to –0.89 | <0.0001c |
| FBG change from baseline, mg/dLd | |||
| 12±4 weeks | –26.24±1.19 | –28.56 to –23.91 | <0.0001c |
| 24±4 weeks | –24.43±1.37 | –27.12 to –21.73 | <0.0001c |
| Body weight change from baseline, kge | |||
| 12±4 weeks | –0.75±0.07 | –0.89 to –0.62 | <0.0001c |
| 24±4 weeks | –1.21±0.08 | –1.36 to –1.06 | <0.0001c |
HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; FBG, fasting blood glucose; LS, least-square; SE, standard error; CI, confidence interval.
a P values are tests from mixed model for repeated measure (MMRM),
b MMRM model: change from baseline=β1×visit+β2×baseline HbA1c+β3×visit×baseline HbA1c,
c Statistically significant,
d MMRM model: change from baseline=β1×visit+β2×baseline FBG+β3×visit×baseline FBG,
e MMRM model: change from baseline=β1×visit+β2×baseline weight+β3×visit×baseline weight.
| Factor | Odds ratio (95% CI) | P valuea |
|---|---|---|
| Age, 1 year | 0.97 (0.96–0.98) | <0.0001b |
| BMI, 1 kg/m2 | 1.03 (1.00–1.06) | 0.0542 |
| Hepatic impairment | ||
| Yes | 1.42 (0.96–2.10) | 0.0781 |
| No | Reference | |
| Other concomitant medication | ||
| Yes | 0.62 (0.45–0.87) | 0.0053b |
| No | Reference |
- 1. Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes facts sheet in Korea. Seoul: KDA; 2022.
- 2. Andreasen CR, Andersen A, Knop FK, Vilsboll T. Understanding the place for GLP-1RA therapy: translating guidelines for treatment of type 2 diabetes into everyday clinical practice and patient selection. Diabetes Obes Metab 2021;23 Suppl 3:40-52.PubMed
- 3. Zhang L, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Tong N. Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Sci Rep 2016;6:18904.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 4. Pace E, Tingen J. Dulaglutide (trulicity) for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am Fam Physician 2017;96:540-2.PubMed
- 5. Glaesner W, Vick AM, Millican R, Ellis B, Tschang SH, Tian Y, et al. Engineering and characterization of the long-acting glucagon-like peptide-1 analogue LY2189265, an Fc fusion protein. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2010;26:287-96.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Sheahan KH, Wahlberg EA, Gilbert MP. An overview of GLP-1 agonists and recent cardiovascular outcomes trials. Postgrad Med J 2020;96:156-61.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Oh S, Chon S, Ahn KJ, Jeong IK, Kim BJ, Kang JG. The role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: understanding how data can inform clinical practice in Korea. Diabetes Metab J 2015;39:177-87.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Kang YM, Cho YK, Lee J, Lee SE, Lee WJ, Park JY, et al. Asian subpopulations may exhibit greater cardiovascular benefit from long-acting glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: a meta-analysis of cardiovascular outcome trials. Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:410-21.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 9. Onakpoya I. Rare adverse events in clinical trials: understanding the rule of three. Available from: https://blogs.bmj.com/bmjebmspotlight/2017/11/14/rare-adverse-events-clinical-trials-understanding-rule-three/ (cited 2023 Aug 22).Article
- 10. European Commission. A guideline on summary of product characteristics 2009. Available from: https://health.ec.europa.eu/system/files/2016-11/smpc_guideline_rev2_en_0.pdf (cited 2023 Aug 22).
- 11. Onishi Y, Oura T, Matsui A, Matsuura J, Iwamoto N. Analysis of efficacy and safety of dulaglutide 0.75 mg stratified by sex in patients with type 2 diabetes in 2 randomized, controlled phase 3 studies in Japan. Endocr J 2017;64:553-60.ArticlePubMed
- 12. Gerstein HC, Colhoun HM, Dagenais GR, Diaz R, Lakshmanan M, Pais P, et al. Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): a double-blind, randomized placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019;394:121-30.PubMed
- 13. Yu M, Yuan GY, Zhang B, Wu HY, Lv XF. Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide by baseline HbA1c in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: a post hoc analysis. Diabetes Ther 2020;11:1147-59.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 14. Yoon JH, Hong AR, Choi W, Park JY, Kim HK, Kang HC. Real-world efficacy and safety of dulaglutide in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a retrospective study in a tertiary referral center. Chonnam Med J 2021;57:211-8.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 15. Lee J, Cho YK, Kim HS, Jung CH, Park JY, Lee WJ. Dulaglutide as an add-on to insulin in type 2 diabetes: clinical efficacy and parameters affecting the response in real-world practice. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 2019;12:2745-53.PubMedPMC
- 16. Gallwitz B, Dagogo-Jack S, Thieu V, Garcia-Perez LE, Pavo I, Yu M, et al. Effect of once-weekly dulaglutide on glycated haemoglobin (HbA1c) and fasting blood glucose in patient subpopulations by gender, duration of diabetes and baseline HbA1c. Diabetes Obes Metab 2018;20:409-18.PubMed
- 17. Yu Y, Chen J, Li D, Wang L, Wang W, Liu H. Systematic analysis of adverse event reports for sex differences in adverse drug events. Sci Rep 2016;6:24955.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 18. Bechman K, Clarke BD, Rutherford AI, Yates M, Nikiphorou E, Molokhia M, et al. Polypharmacy is associated with treatment response and serious adverse events: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2019;58:1767-76.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Modesto AC, Silveira EA, de Carvalho Santos AS, dos Santos Rodrigues AP, Lima DM, Provin MP, et al. Prevalence of adverse drug events in severely obese adults and associated factors: clinical trial baseline results. Sci Pharm 2020;88:41.Article
- 20. Woo SD, Yoon J, Doo GE, Park Y, Lee Y, Lee SH, et al. Common causes and characteristics of adverse drug reactions in older adults: a retrospective study. BMC Pharmacol Toxicol 2020;21:87.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 21. Lavan AH, Gallagher P. Predicting risk of adverse drug reactions in older adults. Ther Adv Drug Saf 2016;7:11-22.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 22. Gomes IV, Muniz CR, Vieira RS, Reis RL, Carmo RF, Silva DT. Risk factors for adverse drug events in hospitalized patients: an overview of systematic reviews. Rev Bras Farm Hosp Serv Saude 2022;13:0738.
- 23. Gerstein HC, Colhoun HM, Dagenais GR, Diaz R, Lakshmanan M, Pais P, et al. Dulaglutide and renal outcomes in type 2 diabetes: an exploratory analysis of the REWIND randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2019;394:131-8.PubMed
- 24. Kwan AY, Gerstein HC, Basile J, Xavier D, Maldonado JM, Raha S, et al. HbA1c reduction in dulaglutide-treated patients irrespective of duration of diabetes, microvascular disease, and BMI: a post hoc analysis from the REWIND trial. Diabetes Care 2022;45:547-54.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 25. Mody R, Yu M, Grabner M, Boye K, Teng CC, Kwan AY. Dulaglutide shows sustained reduction in glycosylated hemoglobin values: 2-year US real-world study results. Clin Ther 2020;42:2184-95.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Yoo JH, Cho YK, Lee J, Kim HS, Kang YM, Jung CH, et al. Clinical efficacy and parameters affecting the response to dulaglutide treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective, real-world data study. Diabetes Ther 2019;10:1453-63.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 27. Kim SS, Kim IJ, Kim YK, Yoon KH, Son HY, Park SW, et al. Duration of diabetes and effectiveness of insulin in the management of insulin-naive Korean patients uncontrolled on oral antidiabetic drugs: a sub-analysis of the MOdaliTy of Insulin treatment eValuation (MOTIV) registry results. Acta Diabetol 2014;51:655-61.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 28. Trujillo JM, Nuffer W, Smith BA. GLP-1 receptor agonists: an updated review of head-to-head clinical studies. Ther Adv Endocrinol Metab 2021;12:2042018821997320.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 29. Bonora E, Frias JP, Tinahones FJ, Van J, Malik RE, Yu Z, et al. Effect of dulaglutide 3.0 and 4.5 mg on weight in patients with type 2 diabetes: exploratory analyses of AWARD-11. Diabetes Obes Metab 2021;23:2242-50.PubMedPMC
- 30. Hong YH, Chung IH, Han K, Chung S; Taskforce Team of the Obesity Fact Sheet of the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity. Prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus among Korean children, adolescents, and adults younger than 30 years: changes from 2002 to 2016. Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:297-306.ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Figure
- Related articles
-
- Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Data Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:356-65)
- Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Data Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:356-65)
- Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Data Analysis
- Safety and Effectiveness of Empagliflozin in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from a Nationwide Post-Marketing Surveillance
- Effectiveness of Resistance Exercise on Inflammatory Biomarkers in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis

 KDA
KDA
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite