
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- The Ratio of Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate Based on Cystatin C and Creatinine Reflecting Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetic Patients
- Ah Reum Khang, Min Jin Lee, Dongwon Yi, Yang Ho Kang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):415-425. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0177
- 1,823 View
- 112 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The ratio of estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) based on cystatin C and creatinine (eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio) is related to accumulating atherosclerosis-promoting proteins and increased mortality in several cohorts.
Methods
We assessed whether the eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio is a predictor of arterial stiffness and sub-clinical atherosclerosis in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients, who were followed up during 2008 to 2016. GFR was estimated using an equation based on cystatin C and creatinine.
Results
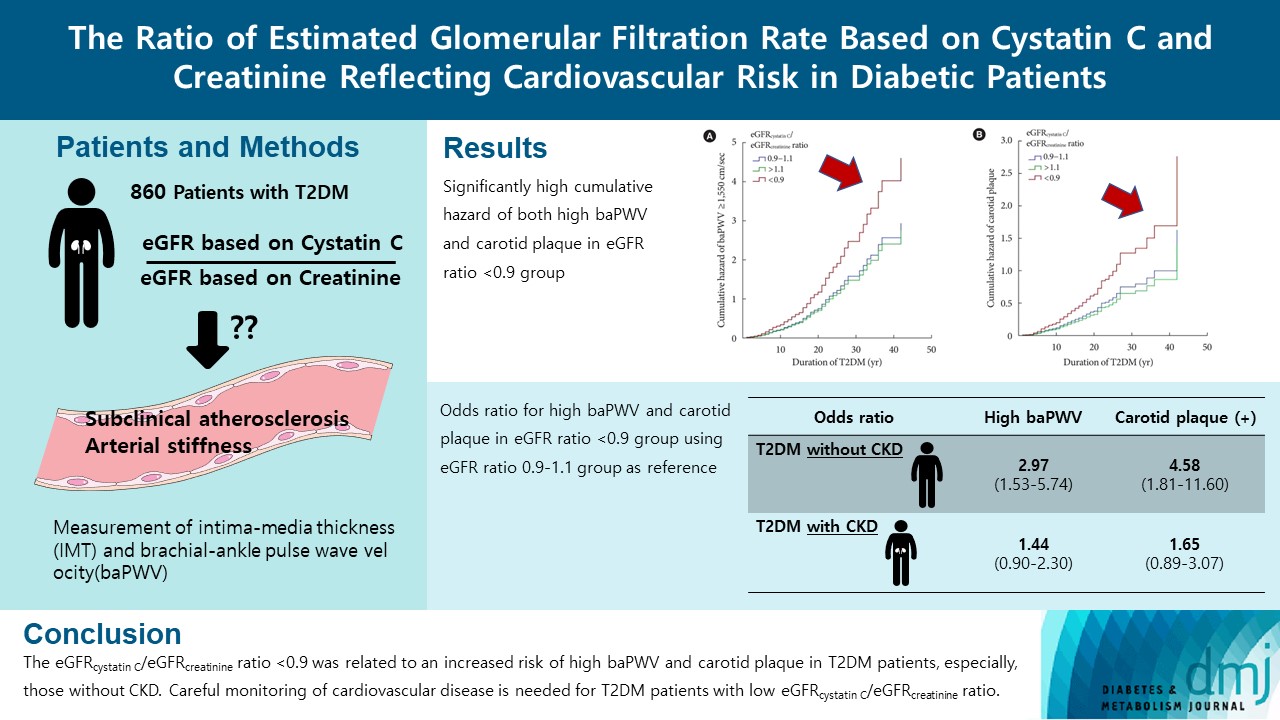
A total of 860 patients were stratified according to their eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio (i.e., <0.9, 0.9–1.1 [a reference group], and >1.1). Intima-media thickness was comparable among the groups; however, presence of carotid plaque was frequent in the <0.9 group (<0.9 group, 38.3%; 0.9–1.1 group, 21.6% vs. >1.1 group, 17.2%, P<0.001). Brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) was faster in the <0.9 group (<0.9 group, 1,656.3±333.0 cm/sec; 0.9–1.1 group, 1,550.5±294.8 cm/sec vs. >1.1 group, 1,494.0±252.2 cm/sec, P<0.001). On comparing the <0.9 group with the 0.9–1.1 group, the multivariate-adjusted odds ratios of prevalence of high baPWV and carotid plaque were 2.54 (P=0.007) and 1.95 (P=0.042), respectively. Cox regression analysis demonstrated near or over 3-fold higher risks of the prevalence of high baPWV and carotid plaque in the <0.9 group without chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Conclusion
We concluded that eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio <0.9 was related to an increased risk of high baPWV and carotid plaque in T2DM patients, especially, those without CKD. Careful monitoring of cardiovascular disease is needed for T2DM patients with low eGFRcystatin C/eGFRcreatinine ratio. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Progress of Creatinine, Cystatin C, and Their Ratio in Renal Diseases
广智 杨
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(04): 976. CrossRef - Muscle mass, creatinine, cystatin C and selective glomerular hypofiltration syndromes
Linnea Malmgren, Anders Grubb
Clinical Kidney Journal.2023; 16(8): 1206. CrossRef - Investigating kidney function changes in young adults with COVID-19: Serum creatinine level, glomerular filtration rate, and biochemical profile analysis
Nikita Matyushin, Dmitriy Ermakov, Inna Vasileva, Roza Vakolyuk, Anastasiya Spaska
Electronic Journal of General Medicine.2023; 20(6): em547. CrossRef - Intraindividual difference in estimated GFR by creatinine and cystatin C, cognitive trajectories and motoric cognitive risk syndrome
Jinqi Wang, Yueruijing Liu, Rui Jin, Xiaoyu Zhao, Zhiyuan Wu, Ze Han, Zongkai Xu, Xiuhua Guo, Lixin Tao
Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Research Progress of Creatinine, Cystatin C, and Their Ratio in Renal Diseases
- Complications
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Sarcopenia and Carotid Plaque Progression Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Yongin Cho, Hye-Sun Park, Byung Wook Huh, Yong-ho Lee, Seong Ha Seo, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):232-241. Published online January 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0355
- 3,598 View
- 222 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We aimed to evaluate whether non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) with or without sarcopenia is associated with progression of carotid atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
We investigated 852 T2DM patients who underwent abdominal ultrasonography, bioelectrical impedance analysis, and carotid artery ultrasonography at baseline and repeated carotid ultrasonography after 6 to 8 years. NAFLD was confirmed by abdominal ultrasonography, and sarcopenia was defined as a sex-specific skeletal muscle mass index (SMI) value <2 standard deviations below the mean for healthy young adults. SMI was calculated by dividing the sum of appendicular skeletal mass by body weight. We investigated the association between NAFLD with or without sarcopenia and the progression of carotid atherosclerosis.
Results
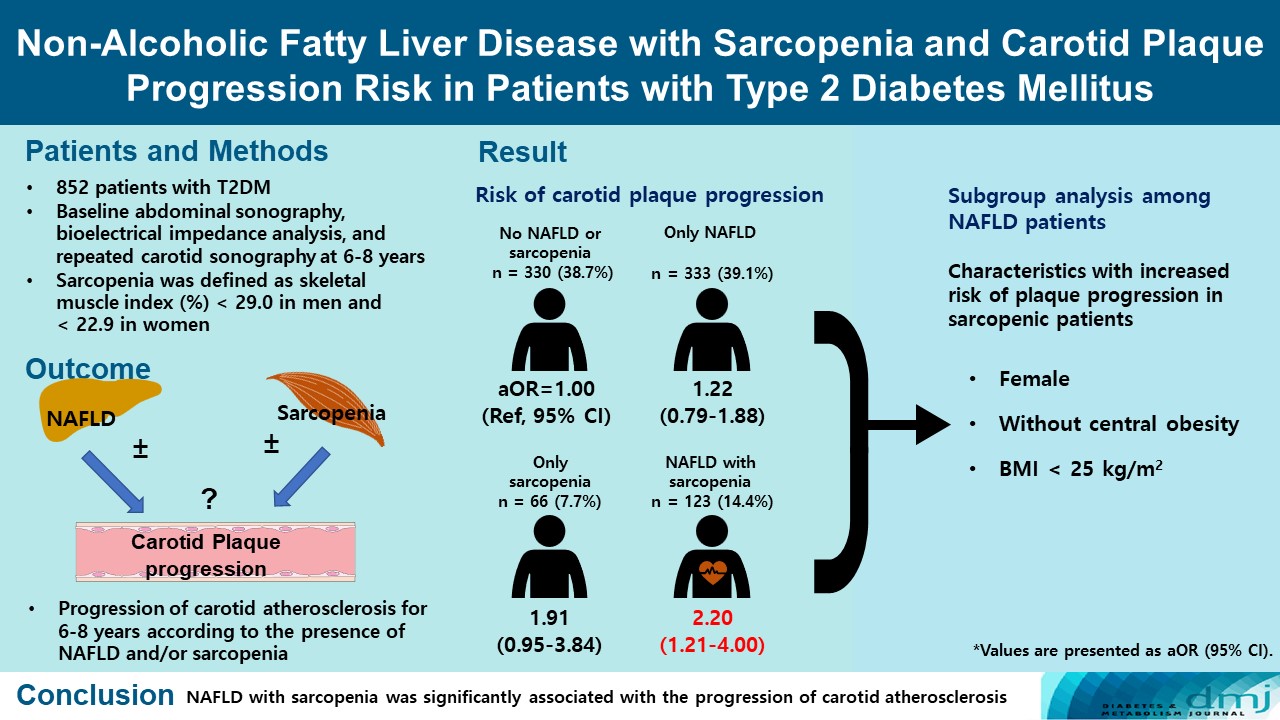
Of the 852 patients, 333 (39.1%) were classified as NAFLD without sarcopenia, 66 (7.7%) were classified as sarcopenia without NAFLD, and 123 (14.4%) had NAFLD with sarcopenia at baseline. After 6 to 8 years, patients with both NAFLD and sarcopenia had a higher risk of atherosclerosis progression (adjusted odds ratio, 2.20; P<0.009) than controls without NAFLD and sarcopenia. When a subgroup analysis was performed on only patients with NAFLD, female sex, absence of central obesity, and non-obesity were significant factors related to increased risk of plaque progression risk in sarcopenic patients.
Conclusion
NAFLD with sarcopenia was significantly associated with the progression of carotid atherosclerosis in T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and sarcopenia: A double whammy
Aditya Viswanath, Sherouk Fouda, Cornelius James Fernandez, Joseph M Pappachan
World Journal of Hepatology.2024; 16(2): 152. CrossRef - Prevalence and outcome of sarcopenia in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Suprabhat Giri, Prajna Anirvan, Sumaswi Angadi, Ankita Singh, Anurag Lavekar
World Journal of Gastrointestinal Pathophysiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and carotid media‐intima thickness: A systematic review and a meta‐analysis
Manouchehr Khoshbaten, Sepideh H. Maleki, Sara Hadad, Amrit Baral, Ana V. Rocha, Laxmi Poudel, Alireza Abdshah
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiometabolic risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes and sarcopenia
Yu. G. Samoilova, M. V. Matveeva, E. A. Khoroshunova, D. V. Podchinenova, L. L. Maksimova, G. G. Gorbach, A. B. Trivozhenko, V. A. Avkhimenko
Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention.2023; 23(1): 3655. CrossRef
- Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease and sarcopenia: A double whammy
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Validation of Risk Prediction Models for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in a Prospective Korean Community-Based Cohort
- Jae Hyun Bae, Min Kyong Moon, Sohee Oh, Bo Kyung Koo, Nam Han Cho, Moon-Kyu Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):458-469. Published online January 13, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0061
- 6,866 View
- 225 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background To investigate the performance of the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Pooled Cohort Equations (PCE) in a large, prospective, community-based cohort in Korea and to compare it with that of the Framingham Global Cardiovascular Disease Risk Score (FRS-CVD) and the Korean Risk Prediction Model (KRPM).
Methods In the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KOGES)-Ansan and Ansung study, we evaluated calibration and discrimination of the PCE for non-Hispanic whites (PCE-WH) and for African Americans (PCE-AA) and compared their predictive abilities with the FRS-CVD and the KRPM.
Results The present study included 7,932 individuals (3,778 men and 4,154 women). The PCE-WH and PCE-AA moderately overestimated the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) for men (6% and 13%, respectively) but underestimated the risk for women (−49% and −25%, respectively). The FRS-CVD overestimated ASCVD risk for men (91%) but provided a good risk prediction for women (3%). The KRPM underestimated ASCVD risk for men (−31%) and women (−31%). All the risk prediction models showed good discrimination in both men (C-statistic 0.730 to 0.735) and women (C-statistic 0.726 to 0.732). Recalibration of the PCE using data from the KOGES-Ansan and Ansung study substantially improved the predictive accuracy in men.
Conclusion In the KOGES-Ansan and Ansung study, the PCE overestimated ASCVD risk for men and underestimated the risk for women. The PCE-WH and the FRS-CVD provided an accurate prediction of ASCVD in men and women, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Factors for Infertility in Korean Women
Juyeon Lee, Chang-Woo Choo, Kyoung Yong Moon, Sang Woo Lyu, Hoon Kim, Joong Yeup Lee, Jung Ryeol Lee, Byung Chul Jee, Kyungjoo Hwang, Seok Hyun Kim, Sue K. Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating cardiovascular disease risk stratification using multiple-polygenic risk scores and pooled cohort equations: insights from a 17-year longitudinal Korean cohort study
Yi Seul Park, Hye-Mi Jang, Ji Hye Park, Bong-Jo Kim, Hyun-Young Park, Young Jin Kim
Frontiers in Genetics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Moderation of Weight Misperception on the Associations Between Obesity Indices and Estimated Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Kayoung Lee
International Journal of Behavioral Medicine.2023; 30(1): 89. CrossRef - Validation of the general Framingham Risk Score (FRS), SCORE2, revised PCE and WHO CVD risk scores in an Asian population
Sazzli Shahlan Kasim, Nurulain Ibrahim, Sorayya Malek, Khairul Shafiq Ibrahim, Muhammad Firdaus Aziz, Cheen Song, Yook Chin Chia, Anis Safura Ramli, Kazuaki Negishi, Nafiza Mat Nasir
The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific.2023; 35: 100742. CrossRef - Principles of cardiovascular risk management in perimenopausal women with type 2 diabetes
F. O. Ushanova, T. Yu. Demidova, T. N. Korotkova
FOCUS. Endocrinology.2023; 4(2): 19. CrossRef - Prediction of the 10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in the Korean population
Sangwoo Park, Yong-Giun Kim, Soe Hee Ann, Young-Rak Cho, Shin-Jae Kim, Seungbong Han, Gyung-Min Park
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023052. CrossRef - Triglyceride-Glucose Index Predicts Future Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases: A 16-Year Follow-up in a Prospective, Community-Dwelling Cohort Study
Joon Ho Moon, Yongkang Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae Hoon Moon, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi, Nam H. Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 406. CrossRef - Validity of the models predicting 10-year risk of cardiovascular diseases in Asia: A systematic review and prediction model meta-analysis
Mahin Nomali, Davood Khalili, Mehdi Yaseri, Mohammad Ali Mansournia, Aryan Ayati, Hossein Navid, Saharnaz Nedjat, Hean Teik Ong
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(11): e0292396. CrossRef - Assessing the Validity of the Criteria for the Extreme Risk Category of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(1): 73. CrossRef - Mediation of Grip Strength on the Association Between Self-Rated Health and Estimated Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Kayoung Lee
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2022; 20(6): 344. CrossRef - Implications of the heterogeneity between guideline recommendations for the use of low dose aspirin in primary prevention of cardiovascular disease
Xiao-Ying Li, Li Li, Sang-Hoon Na, Francesca Santilli, Zhongwei Shi, Michael Blaha
American Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2022; 11: 100363. CrossRef - The Risk of Cardiovascular Disease According to Chewing Status Could Be Modulated by Healthy Diet in Middle-Aged Koreans
Hyejin Chun, Jongchul Oh, Miae Doo
Nutrients.2022; 14(18): 3849. CrossRef - Management of Cardiovascular Risk in Perimenopausal Women with Diabetes
Catherine Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 492. CrossRef - Comparative performance of the two pooled cohort equations for predicting atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Alessandra M. Campos-Staffico, David Cordwin, Venkatesh L. Murthy, Michael P. Dorsch, Jasmine A. Luzum
Atherosclerosis.2021; 334: 23. CrossRef - Usefulness of Relative Handgrip Strength as a Simple Indicator of Cardiovascular Risk in Middle-Aged Koreans
Won Bin Kim, Jun-Bean Park, Yong-Jin Kim
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2021; 362(5): 486. CrossRef
- Risk Factors for Infertility in Korean Women
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Impact of Diabetes Control on Subclinical Atherosclerosis: Analysis from Coronary Computed Tomographic Angiography Registry
- Gyung-Min Park, Chang Hoon Lee, Seung-Whan Lee, Sung-Cheol Yun, Young-Hak Kim, Yong-Giun Kim, Ki-Bum Won, Soe Hee Ann, Shin-Jae Kim, Dong Hyun Yang, Joon-Won Kang, Tae-Hwan Lim, Eun Hee Koh, Woo Je Lee, Min-Seon Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Hong-Kyu Kim, Jaewon Choe, Sang-Gon Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):470-479. Published online November 22, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0073
- 8,662 View
- 69 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background There are limited data on the impact of diabetes control on the risk of subclinical coronary atherosclerosis.
Methods We analyzed 6,434 consecutive asymptomatic individuals without previous history of coronary artery disease who underwent coronary computed tomographic angiography (CCTA) (mean age, 53.7±7.6 years and 4,694 men [73.0%]). The degree and extent of subclinical coronary atherosclerosis were assessed by CCTA, and ≥50% diameter stenosis was defined as significant. A cardiac event was defined as a composite of all-cause death, myocardial infarction, unstable angina, or coronary revascularization. Study participants were categorized as normal (
n =5,319), controlled diabetes (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] <7%,n =747), or uncontrolled diabetes (HbA1c ≥7%,n =368), respectively.Results Compared with normal individuals, there were no statistically significant differences in the risk of for any atherosclerotic plaque (odds ratio [OR], 1.16; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.98 to 1.38;
P =0.086) and significant coronary artery stenosis (OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.82 to 1.42;P =0.583) in controlled diabetic individuals. In contrast, uncontrolled diabetic individuals had consistently higher risks of any atherosclerotic plaque (OR, 2.16; 95% CI, 1.70 to 2.75;P <0.001) and significant coronary artery stenosis (OR, 3.34; 95% CI, 2.52 to 4.43;P <0.001) than normal individuals. During a follow-up of median 5.4 years, there was no significant difference in cardiac events between normal and controlled diabetic individuals (P =0.365). However, uncontrolled diabetes was associated with an increased risk of cardiac events compared with normal individuals (P <0.001) and controlled diabetic individuals (P =0.023).Conclusion Asymptomatic uncontrolled diabetes was associated with significant subclinical coronary atherosclerosis with subsequent high risk for cardiac events.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Carotid Ultrasound Abnormalities of People Living With HIV in Kunming, China: Multiple Correspondence Analysis Approach to Identify Influencing Factors
Shuishui Pan, Haiyan Fu, Zhiqiong Ai, Chongxi Li, Jinsong Bai
International Journal of STD & AIDS.2023; 34(10): 710. CrossRef - Differential Impact of Degree of Hypertension on Subclinical Coronary Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic Subjects With and Without Diabetes Mellitus
Hyun Woo Park, Sangyong Jo, Kyung Sun Park, Hyeji Lee, Young-Jee Jeon, Sangwoo Park, Soe Hee Ann, Yong-Giun Kim, Seong Hoon Choi, Woon Jung Kwon, Young-Rak Cho, Jon Suh, Gyung-Min Park
The American Journal of Cardiology.2023; 203: 343. CrossRef - Exosomal MALAT1 Derived from High Glucose-Treated Macrophages Up-Regulates Resistin Expression via miR-150-5p Downregulation
Kou-Gi Shyu, Bao-Wei Wang, Wei-Jen Fang, Chun-Ming Pan, Chiu-Mei Lin
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(3): 1095. CrossRef - Comparison of Framingham risk score and pooled cohort equations for the prediction of coronary atherosclerosis in patients who meet the target LDL-C level of Korean dyslipidemia guideline
Su Bin Kim, Hae Won Jung
Medicine.2022; 101(47): e31816. CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study
Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyeong Jin Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 368. CrossRef - Frequency and Significance of Right Bundle Branch Block and Subclinical Coronary Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic Individuals
Hyeji Lee, Young-Jee Jeon, Byung Ju Kang, Tae Young Lee, Eun Ji Park, Sangwoo Park, Soe Hee Ann, Yong-Giun Kim, Yongjik Lee, Seong Hoon Choi, Gyung-Min Park
The American Journal of Cardiology.2021; 158: 30. CrossRef - The association between glucose-related variables and plaque morphology in patients with ST-segment elevated myocardial infarction
Jinxin Liu, Shanjie Wang, Can Cui, Hengxuan Cai, Rong Sun, Weili Pan, Shaohong Fang, Bo Yu
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Choosing Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: How to Reduce the Risk of Death
N. A. Koziolova, P. G. Karavaev, A. S. Veklich
Kardiologiia.2020; 60(4): 109. CrossRef
- Carotid Ultrasound Abnormalities of People Living With HIV in Kunming, China: Multiple Correspondence Analysis Approach to Identify Influencing Factors
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Diabetes and Subclinical Coronary Atherosclerosis
- Chang Hoon Lee, Seung-Whan Lee, Seong-Wook Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(5):355-363. Published online October 22, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0041
- 4,702 View
- 58 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader It is well known that diabetic patients have a high risk of cardiovascular events, and although there has been a tremendous effort to reduce these cardiovascular risks, the incidence of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in diabetic patients remains high. Therefore, the early detection of coronary artery disease (CAD) is necessary in those diabetic patients who are at risk of cardiovascular events. Significant medical and radiological advancements, including coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA), mean that it is now possible to investigate the characteristics of plaques, instead of solely evaluating the calcium level of the coronary artery. Recently, several studies reported that the prevalence of subclinical coronary atherosclerosis (SCA) is higher than expected, and this could impact on CAD progression in asymptomatic diabetic patients. In addition, several reports suggest the potential benefit of using CCTA for screening for SCA in asymptomatic diabetic patients, which might dramatically decrease the incidence of cardiovascular events. For these reasons, the medical interest in SCA in diabetic patients is increasing. In this article, we sought to review the results of studies on CAD in asymptomatic diabetic patients and discuss the clinical significance and possibility of using CCTA to screen for SCA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Coronary Artery Calcium Score directed risk stratification of patients with Type-2 diabetes mellitus
Mahmoud Nassar, Nso Nso, Kelechi Emmanuel, Mohsen Alshamam, Most Sirajum Munira, Anoop Misra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2022; 16(6): 102503. CrossRef - Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef - Serum metabolic signatures of subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a preliminary study
Jiaorong Su, Qing Zhao, Aihua Zhao, Wei Jia, Wei Zhu, Jingyi Lu, Xiaojing Ma
Acta Diabetologica.2021; 58(9): 1217. CrossRef - Atherogenic Index of Plasma, Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Monocyte-to-Lymphocyte Ratio for Predicting Subclinical Coronary Artery Disease
Yueqiao Si, Wenjun Fan, Chao Han, Jingyi Liu, Lixian Sun
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2021; 362(3): 285. CrossRef - Cardiologist's approach to the diabetic patient: No further delay for a paradigm shift
Francesco Maranta, Lorenzo Cianfanelli, Carlo Gaspardone, Vincenzo Rizza, Rocco Grippo, Marco Ambrosetti, Domenico Cianflone
International Journal of Cardiology.2021; 338: 248. CrossRef - Co‐expression of glycosylated aquaporin‐1 and transcription factor NFAT5 contributes to aortic stiffness in diabetic and atherosclerosis‐prone mice
Rosalinda Madonna, Vanessa Doria, Anikó Görbe, Nino Cocco, Péter Ferdinandy, Yong‐Jian Geng, Sante Donato Pierdomenico, Raffaele De Caterina
Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine.2020; 24(5): 2857. CrossRef - Recent Updates on Vascular Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Chan-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 260. CrossRef - Quantitative measure of asymptomatic cardiovascular disease risk in Type 2 diabetes: Evidence from Indian outpatient setting
Samit Ghosal, Binayak Sinha, Jignesh Ved, Mansij Biswas
Indian Heart Journal.2020; 72(2): 119. CrossRef - Role of pregnancy hormones and hormonal interaction on the maternal cardiovascular system: a literature review
Vitaris Kodogo, Feriel Azibani, Karen Sliwa
Clinical Research in Cardiology.2019; 108(8): 831. CrossRef - Letter: Comparison of the Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy 20 mg with Rosuvastatin 5 mg and Ezetimibe 10 mg Combination Therapy on Lipid Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J2019;43:582–9)
Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 909. CrossRef - Effects of Diabetes on Motor Recovery After Cerebral Infarct: A Diffusion Tensor Imaging Study
Jun Sung Moon, Seung Min Chung, Sung Ho Jang, Kyu Chang Won, Min Cheol Chang
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2019; 104(9): 3851. CrossRef
- Coronary Artery Calcium Score directed risk stratification of patients with Type-2 diabetes mellitus
- Clinical Diabetes and Therapeutics
- Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index as a Surrogate Marker of Early Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- So Young Park, Sang Ook Chin, Sang Youl Rhee, Seungjoon Oh, Jeong-Taek Woo, Sung Woon Kim, Suk Chon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(4):285-295. Published online July 27, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0080
- 4,804 View
- 52 Download
- 18 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Carotid artery intima medial thickness (IMT), brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV), and ankle-brachial index (ABI) are commonly used surrogate markers of subclinical atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The cardio-ankle vascular index (CAVI) is a complement to the baPWV, which is affected by blood pressure. However, it is unclear which marker is the most sensitive predictor of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD).
Methods This was a retrospective non-interventional study that enrolled 219 patients with T2DM. The correlations among IMT, ABI, and CAVI as well as the relationship of these tests to the 10-year ASCVD risk were also analyzed.
Results Among the 219 patients, 39 (17.8%) had ASCVD. In the non-ASCVD group, CAVI correlated significantly with IMT after adjusting for confounding variables, but ABI was not associated with CAVI or IMT. The analyses after dividing the non-ASCVD group into three subgroups according to the CAVI score (<8, ≥8 and <9, and ≥9) demonstrated the significant increase in the mean IMT, 10-year ASCVD risk and number of metabolic syndrome risk factors, and decrease in the mean ABI in the high-CAVI group. A high CAVI was an independent risk factor in the non-ASCVD group for both a high 10-year ASCVD risk (≥7.5%; odds ratio [OR], 2.42;
P <0.001) and atherosclerosis (mean IMT ≥1 mm; OR, 1.53;P =0.007).Conclusion In Korean patients with T2DM without ASCVD, CAVI was the most sensitive of several surrogate markers for the detection of subclinical atherosclerosis.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effects of severe periodontitis on arterial stiffness using cardio‐ankle vascular index in patients with type 2 diabetes
Gizem Torumtay Cin, Semin Melahat Fenkci, Ismail Doğu Kiliç, Halil Serdar Aslan, Cihan İlyas Sevgican, Hande Şenol
Journal of Periodontal Research.2024; 59(1): 74. CrossRef - Prediction of cardiovascular disease using deep learning algorithms to prevent COVID 19
Malathi S, Arockia Raj Y, Abhishek Kumar, V D Ashok Kumar, Ankit Kumar, Elangovan D, V D Ambeth Kumar, Chitra B, a Abirami
Journal of Experimental & Theoretical Artificial Intelligence.2023; 35(6): 791. CrossRef - Association of cardio-ankle vascular index and future major adverse cardiovascular events in older adults living with HIV
Amaraporn Rerkasem, Arunrat Tangmunkongvorakul, Linda Aurpibul, Patumrat Sripan, Wason Parklak, Sothida Nantakool, Kriengkrai Srithanaviboonchai, Kittipan Rerkasem
AIDS Care.2023; 35(4): 591. CrossRef - Impact of Fasting Blood Glucose Levels on Blood Pressure Parameters among Older Adults with Prediabetes
Thapanee Roengrit, Ruchada Sri-Amad, Nawiya Huipao, Suphawadee Phababpha, Piyapong Prasertsri, Francesco Giallauria
The Scientific World Journal.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - A framework of biomarkers for vascular aging: a consensus statement by the Aging Biomarker Consortium
Le Zhang, Jun Guo, Yuehong Liu, Shimin Sun, Baohua Liu, Qi Yang, Jun Tao, Xiao-Li Tian, Jun Pu, Huashan Hong, Miao Wang, Hou-Zao Chen, Jie Ren, Xiaoming Wang, Zhen Liang, Yuan Wang, Kai Huang, Weiqi Zhang, Jing Qu, Zhenyu Ju, Guang-Hui Liu, Gang Pei, Jian
Life Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diastolic Pressure and ACR Are Modifiable Risk Factors of Arterial Stiffness in T2DM Without Cardiovascular Disease
Gateano Leto, Lida Tartaglione, Silverio Rotondi, Marzia Pasquali, Ernesto Maddaloni, Carmen Mignogna, Luca D’Onofrio, Simona Zampetti, Angela Carlone, Maria Luisa Muci, Daniela Mastroluca, Valeria Fassino, Raffaella Buzzetti, Sandro Mazzaferro
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(9): e3857. CrossRef - Risk assessment indicators and brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity to predict atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Hung-Ju Ko, Chuan-Chuan Liu, Po-Jui Hsu, Kuang-Chun Hu, Chung-Lieh Hung, Lo-Yip Yu, Yun-Chieh Huang, Shou-Chuan Shih
Medicine.2022; 101(32): e29609. CrossRef - Prediction of Cardiovascular Disease Using Machine Learning Technique—A Modern Approach
Jung-Hwa Kim, Jin-Woo Jeong
Computers, Materials & Continua.2022; 71(1): 855. CrossRef - Cardio-ankle vascular index represents the best surrogate for 10-year ASCVD risk estimation in patients with primary hypertension
Mustafa Tarik Agac, Süret Ağaç, Muhammed Necati Murat Aksoy, Mehmet Bülent Vatan
Clinical and Experimental Hypertension.2021; 43(4): 349. CrossRef - Relation between fragmented QRS complex and cardio-ankle vascular index in asymptomatic subjects
Ali Rıza Akyüz, Sinan Şahin, Ömer Faruk Çırakoğlu, Selim Kul, Turhan Turan, Hakan Erkan
Clinical and Experimental Hypertension.2021; 43(4): 368. CrossRef - Progress of clinical evaluation for vascular aging in humans
Yumin Qiu, Yuanya Liu, Jun Tao
Journal of Translational Internal Medicine.2021; 9(1): 17. CrossRef - Effects of long-term air pollution exposure on ankle-brachial index and cardio-ankle vascular index: A longitudinal cohort study using data from the Electricity Generating Authority of Thailand study
Kanawat Paoin, Kayo Ueda, Prin Vathesatogkit, Thammasin Ingviya, Suhaimee Buya, Arthit Phosri, Xerxes Tesoro Seposo, Nisakron Thongmung, Teerapat Yingchoncharoen, Akiko Honda, Hirohisa Takano, Piyamitr Sritara
International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health.2021; 236: 113790. CrossRef The Relationship Between Glycemic Control and Concomitant Hypertension on Arterial Stiffness in Type II Diabetes
Teonchit Nuamchit, Duangduan Siriwittayawan, Piyanuch Thitiwuthikiat
Vascular Health and Risk Management.2020; Volume 16: 343. CrossRef- Relationship between cardio-ankle vascular index and obstructive coronary artery disease
Divya Birudaraju, Lavanya Cherukuri, April Kinninger, Bhanu T. Chaganti, Pishoy Haroun, Sivakrishna Pidikiti, Suvasini Lakshmanan, Sajad Hamal, Ferdinand Flores, Christopher Dailing, Kashif Shaikh, Sion K. Roy, Matthew J. Budoff
Coronary Artery Disease.2020; 31(6): 550. CrossRef - Association of Kidney Function Tests with a Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index in Community-Dwelling Individuals with a Normal or Mildly Decreased Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate
Javad Alizargar, Chyi-Huey Bai, Nan-Chen Hsieh, Shu-Fang Vivienne Wu, Shih-Yen Weng, Jia-Ping Wu
Medicina.2019; 55(10): 657. CrossRef - Cardiovascular remodeling in patients with diabetic сardiomyopathy
A. S. Veklich, N. A. Koziolova, P. G. Karavaev
Russian Journal of Cardiology.2019; (11): 42. CrossRef - Short‑term impact of aged garlic extract on endothelial function in diabetes: A randomized, double‑blind, placebo‑controlled trial
Sajad Hamal, Lavanya Cherukuri, Divya Birudaraju, Suguru Matsumoto, April Kinninger, Bhanu Chaganti, Ferdinand Flores, Kashif Shaikh, Sion Roy, Matthew Budoff
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Breakfast Frequency and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk: A Cross-Sectional Study of KNHANES Data, 2014–2016
Hyeon Ji Lee, Jieun Jang, Sang Ah Lee, Dong-Woo Choi, Eun-Cheol Park
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(10): 1853. CrossRef - Response: Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index as a Surrogate Marker of Early Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2018;42:285-95)
So Young Park, Suk Chon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(5): 449. CrossRef - Letter: Cardio-Ankle Vascular Index as a Surrogate Marker of Early Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Koreans with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2018;42:285-95)
Dongwon Yi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(5): 447. CrossRef
- The effects of severe periodontitis on arterial stiffness using cardio‐ankle vascular index in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: The Emerging Burden in Cardiometabolic and Renal Diseases
- Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(6):430-437. Published online November 17, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.6.430
- 4,934 View
- 86 Download
- 50 Web of Science
- 54 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader As the number of individuals with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) has increased, the influence of NAFLD on other metabolic diseases has been highlighted. Accumulating epidemiologic evidence indicates that NAFLD not only affects the liver but also increases the risk of extra-hepatic diseases such as type 2 diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome, dyslipidemia, hypertension, cardiovascular or cerebrovascular diseases, and chronic kidney disease. Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, an advanced type of NAFLD, can aggravate these inter-organ relationships and lead to poorer outcomes. NAFLD induces insulin resistance and exacerbates systemic chronic inflammation and oxidative stress, which leads to organ dysfunction in extra-hepatic tissues. Although more research is needed to identify the pathophysiological mechanisms and causal relationship between NAFLD and cardiometabolic and renal diseases, screening for heart, brain, and kidney diseases, risk assessment for diabetes, and a multidisciplinary approach for managing these patients should be highly encouraged.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inter‐relationships between cardiovascular, renal and metabolic diseases: Underlying evidence and implications for integrated interdisciplinary care and management
Jiten Vora, David Cherney, Mikhail N. Kosiborod, Jonas Spaak, Naresh Kanumilli, Kamlesh Khunti, Carolyn S. P. Lam, Michael Bachmann, Peter Fenici
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between Uric Acid to High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Ratio and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Nonoverweight/Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Yuliang Cui, Zhenzhen Qu, Wenmei Hu, Haiyan Shi, Faustino R. Perez-Lopez
International Journal of Endocrinology.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Emerging Role of Protein O-GlcNAcylation in Liver Metabolism: Implications for Diabetes and NAFLD
Ziyan Xie, Ting Xie, Jieying Liu, Qian Zhang, Xinhua Xiao
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(3): 2142. CrossRef - Lean or Non-obese Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: Are They Really Lean?
Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 980. CrossRef - Factores de riesgo para fibrosis hepática en pacientes diabéticos con enfermedad renal cronica terminal
Ismael Yepes Barreto, Diana Romero Florez, Jorge Coronado Daza
Revista colombiana de Gastroenterología.2023; 38(3): 278. CrossRef - Circ_0004535/miR-1827/CASP8 network involved in type 2 diabetes mellitus with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Min Li, Ai Zeng, Xinle Tang, Hui Xu, Wei Xiong, Yanying Guo
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease associated with greater herpes zoster risk than alcoholic fatty liver disease
Cheng-Wei Yu, Chia-Hung Chen, Yung-Chi Cheng, Wen-Che Hsieh, Tzu-Ju Hsu, Fuu-Jen Tsai, Chao-Yu Hsu
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A GLP‐1/GLP‐2 receptor dual agonist to treat NASH: Targeting the gut‐liver axis and microbiome
Eun Ran Kim, Jeong Su Park, Jin Hee Kim, Ji Young Oh, In Jeong Oh, Da Hyun Choi, Yu seol Lee, I. Seul Park, SeungWon Kim, Da Hyun Lee, Jae Hee Cheon, Jin‐Woo Bae, Minyoung Lee, Jin Won Cho, In Bok An, Eun Joo Nam, Sang‐In Yang, Myung‐Shik Lee, Soo Han Bae
Hepatology.2022; 75(6): 1523. CrossRef - Analysis of Severe Hypoglycemia Among Adults With Type 2 Diabetes and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Ji-Yeon Lee, Young-eun Kim, Kyungdo Han, Eugene Han, Byung Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Seung-Hyun Ko, Yong-ho Lee
JAMA Network Open.2022; 5(2): e220262. CrossRef - State-of-the-Art Overview of the Pharmacological Treatment of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
Yongin Cho, Yong-ho Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(1): 38. CrossRef - Fatty Liver Index is a valid predictor of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in pregnancy
Iresha Sandamali Koralegedara, Janith Niwanthaka Warnasekara, Ashani Rathnayake, Korale Gedara Dayaratne, Suneth Buddhika Agampodi
BMJ Open Gastroenterology.2022; 9(1): e000913. CrossRef - A Prediction Model of the Incidence of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease With Visceral Fatty Obesity: A General Population-Based Study
Yang Zhou, Xiangping Chai, Tuo Guo, Yuting Pu, Mengping Zeng, Aifang Zhong, Guifang Yang, Jiajia Cai
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and sarcopenia is associated with the risk of albuminuria independent of insulin resistance, and obesity
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Seung-Soon Im, Byoung Kuk Jang, Hye Soon Kim
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2022; 36(8): 108253. CrossRef - Increased Risk of NAFLD in Adults with Glomerular Hyperfiltration: An 8-Year Cohort Study Based on 147,162 Koreans
Dae-Jeong Koo, Mi Yeon Lee, Inha Jung, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Won-Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Se Eun Park
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(7): 1142. CrossRef - Effects of Avocado Oil Supplementation on Insulin Sensitivity, Cognition, and Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Markers in Different Tissues of Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Schérolin de Oliveira Marques, Alexandre Pastoris Muller, Thais Fernandes Luciano, Natália dos Santos Tramontin, Mateus da Silva Caetano, Bruno Luis da Silva Pieri, Tatiane Lima Amorim, Marcone Augusto Leal de Oliveira, Cláudio Teodoro de Souza
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2906. CrossRef - Relationship Between Handgrip Strength and Laboratory Values in Adolescents With Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Si Yeong Lee, Yong Whi Jeong, Hong Koh, Yunkoo Kang
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2022; 25(4): 490. CrossRef - Association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolically healthy deterioration across different body shape phenotypes at baseline and change patterns
Liu Lei, Wang Changfa, Wang Jiangang, Chen Zhiheng, Yuan Ting, Zhu Xiaoling, Deng Yuling, Wang Yaqin
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Muscle fat contents rather than muscle mass determines nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in patients with severe obesity
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Won Lee, Seungwan Ryu, Hye Soon Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Youngsung Suh
Obesity.2022; 30(12): 2440. CrossRef - Prediction of decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate using liver fibrosis markers: a renal biopsy-based study
Akira Mima
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Therapeutic implications of shared mechanisms in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic kidney disease
Mehmet Kanbay, Mustafa C. Bulbul, Sidar Copur, Baris Afsar, Alan A. Sag, Dimitrie Siriopol, Masanari Kuwabara, Silvia Badarau, Adrian Covic, Alberto Ortiz
Journal of Nephrology.2021; 34(3): 649. CrossRef - Taxifolin ameliorate high-fat-diet feeding plus acute ethanol binge-induced steatohepatitis through inhibiting inflammatory caspase-1-dependent pyroptosis
Zi-Ying Zhan, Mei Wu, Yue Shang, Min Jiang, Jian Liu, Chun-Ying Qiao, Huan Ye, Yong-Ce Lin, Mei-Hua Piao, Rong-Hui Sun, Zhi-Hong Zhang, Jing-Ya Jiao, Yan-Ling Wu, Ji-Xing Nan, Li-Hua Lian
Food & Function.2021; 12(1): 362. CrossRef - Albuminuria Is Associated with Steatosis Burden in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 698. CrossRef - The Leg Fat to Total Fat Ratio Is Associated with Lower Risks of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Less Severe Hepatic Fibrosis: Results from Nationwide Surveys (KNHANES 2008–2011)
Hyun Min Kim, Yong-ho Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(6): 1232. CrossRef - A preliminary report about the detection of ventricular repolarisation in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Marwan S. Al-Nimer, Vian A. Esmail, Dler S. Hamid, Mohammad O. Mohammad
Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences.2020; 15(4): 284. CrossRef - Atorvastatin attenuates obese-induced kidney injury and impaired renal organic anion transporter 3 function through inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation
Nattavadee Pengrattanachot, Rada Cherngwelling, Krit Jaikumkao, Anchalee Pongchaidecha, Laongdao Thongnak, Myat Theingi Swe, Varanuj Chatsudthipong, Anusorn Lungkaphin
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2020; 1866(6): 165741. CrossRef - Correlation Between Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver and Chronic Kidney Disease
Hasyim Kasim, St. Rabiul Zatalia, Haerani Rasyid, Syakib Bakri, Muhammad L. Parewangi, Fardah Akil, Arifin Seweng
The Open Urology & Nephrology Journal.2020; 13(1): 1. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Fatty Liver Research Group of the Korean Diabetes Association
Byung-Wan Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Cheol-Young Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee, Nan-Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Keun-Gyu Park, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Bong-Soo Cha, Dae Ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 382. CrossRef - Sarcopenia: an emerging risk factor for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease
Yong-ho Lee, Seung Up Kim
Hepatology International.2020; 14(1): 5. CrossRef - Association between Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis and Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hokyou Lee, Gyuri Kim, Young Ju Choi, Byung Wook Huh, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Jig Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Kap Bum Huh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 267. CrossRef - Ipragliflozin Additively Ameliorates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Controlled with Metformin and Pioglitazone: A 24-Week Randomized Controlled Trial
Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 259. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and progression of carotid atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes: a Korean cohort study
Hyeok-Hee Lee, Yongin Cho, Young Ju Choi, Byung Wook Huh, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Seok Won Park, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Jig Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Kap Bum Huh
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Hepatic fibrosis is associated with total proteinuria in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes
Eugene Han, Yongin Cho, Kyung-won Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-wan Lee
Medicine.2020; 99(33): e21038. CrossRef - Association between NAFLD and risk of prevalent chronic kidney disease: why there is a difference between east and west?
Min Zhang, Su Lin, Ming-fang Wang, Jiao-feng Huang, Shi-ying Liu, Su-mei Wu, Hao-yang Zhang, Zi-mu Wu, Wen-Yue Liu, Dong-Chu Zhang, Chuan-ming Hao, Yue-yong Zhu, Ming-Hua Zheng, Xiao-zhong Wang
BMC Gastroenterology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Serum Bilirubin and the Progression of Carotid Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetes
Inkuk Lee, Hyeok-Hee Lee, Yongin Cho, Young Ju Choi, Byung Wook Huh, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Seok Won Park, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Jig Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Kap Bum Huh
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2020; 9(1): 195. CrossRef - Letter: Sarcopenia Is Significantly Associated with Presence and Severity of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (J Obes Metab Syndr 2019;28:129-38)
Chan-Hee Jung
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2020; 29(2): 158. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome and Abnormal Peri-Organ or Intra-Organ Fat (APIFat) Deposition in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: An Overview
Niki Katsiki, Anca Pantea Stoian, Paschalis Steiropoulos, Nikolaos Papanas, Andra-Iulia Suceveanu, Dimitri P. Mikhailidis
Metabolites.2020; 10(11): 465. CrossRef - Heart Failure and Liver Disease
Andrew Xanthopoulos, Randall C. Starling, Takeshi Kitai, Filippos Triposkiadis
JACC: Heart Failure.2019; 7(2): 87. CrossRef - Risk factors for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatic fibrosis in type 2 diabetes patients
Asieh Mansour, Mohammad Reza Mohajeri-Tehrani, Majid Samadi, Hadis Gerami, Mostafa Qorbani, Nick Bellissimo, Hossein Poustchi, Azita Hekmatdoost
Acta Diabetologica.2019; 56(11): 1199. CrossRef - Targeting CYP4A attenuates hepatic steatosis in a novel multicellular organotypic liver model
Jae-Sung Ryu, Minji Lee, Seon Ju Mun, Sin-Hyoung Hong, Ho-Joon Lee, Hyo-Suk Ahn, Kyung-Sook Chung, Gun-Hwa Kim, Myung Jin Son
Journal of Biological Engineering.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis and type 2 diabetes mellitus: the effects of weight loss versus drug treatment
Niki Katsiki, Vasilios G Athyros
Current Medical Research and Opinion.2019; 35(7): 1305. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Diabetes. Part I: Epidemiology and Diagnosis
Yong-ho Lee, Yongin Cho, Byung-Wan Lee, Cheol-Young Park, Dae Ho Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun-Jung Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(1): 31. CrossRef - Progress in the Study of the Pathogenesis of Chronic Kidney Disease Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
清莲 宋
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2019; 09(09): 1073. CrossRef - Association Between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Future Deterioration of Metabolic Health: A Cohort Study
You‐Cheol Hwang, Hong‐Yup Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park
Obesity.2019; 27(8): 1360. CrossRef - Subfornical organ insulin receptors tonically modulate cardiovascular and metabolic function
Jin Kwon Jeong, Julie A. Horwath, Hayk Simonyan, Katherine A. Blackmore, Scott D. Butler, Colin N. Young
Physiological Genomics.2019; 51(8): 333. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Diabetes: Part II: Treatment
Kyung-Soo Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Yong Jin Kim, Dae Ho Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(2): 127. CrossRef - Chicken Protein Hydrolysates Have Anti-Inflammatory Effects on High-Fat Diet Induced Obesity in Mice
Thomas Aloysius, Ana Carvajal, Rasa Slizyte, Jon Skorve, Rolf Berge, Bodil Bjørndal
Medicines.2018; 6(1): 5. CrossRef - STK25 Regulates Cardiovascular Disease Progression in a Mouse Model of Hypercholesterolemia
Emmelie Cansby, Elin Magnusson, Esther Nuñez-Durán, Manoj Amrutkar, Matteo Pedrelli, Paolo Parini, Jenny Hoffmann, Marcus Ståhlman, Brian W. Howell, Hanns-Ulrich Marschall, Jan Borén, Margit Mahlapuu
Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology.2018; 38(8): 1723. CrossRef - Organ-Specific Mechanisms of Transendothelial Neutrophil Migration in the Lung, Liver, Kidney, and Aorta
Sanne L. Maas, Oliver Soehnlein, Joana R. Viola
Frontiers in Immunology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Visceral adiposity index as a predictor of NAFLD: A prospective study with 4‐year follow‐up
Chaonan Xu, Zhimin Ma, Yunfeng Wang, Xiangtong Liu, Lixin Tao, Deqiang Zheng, Xiuhua Guo, Xinghua Yang
Liver International.2018; 38(12): 2294. CrossRef - Obesity induced alterations in redox homeostasis and oxidative stress are present from an early age
Alfonso M. Lechuga-Sancho, David Gallego-Andujar, Pablo Ruiz-Ocaña, Francisco M. Visiedo, Ana Saez-Benito, Mónica Schwarz, Carmen Segundo, Rosa M. Mateos, Manuel Portero-Otin
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(1): e0191547. CrossRef - Capybara Oil Improves Hepatic Mitochondrial Dysfunction, Steatosis, and Inflammation in a Murine Model of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Polyana C. Marinho, Aline B. Vieira, Priscila G. Pereira, Kíssila Rabelo, Bianca T. Ciambarella, Ana L. R. Nascimento, Erika Cortez, Aníbal S. Moura, Fernanda V. Guimarães, Marco A. Martins, Gonzalo Barquero, Rodrigo N. Ferreira, Jorge J. de Carvalho
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Persistently Increased Resting Energy Expenditure Predicts Short-Term Mortality in Patients with Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure
Jia Yao, Xiaoshuang Zhou, Hui Wang, Lili Yuan, Yu Chen, Zhongping Duan
Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism.2018; 73(1): 2. CrossRef - The Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin Prevents Renal and Liver Disease in Western Diet Induced Obesity Mice
Dong Wang, Yuhuan Luo, Xiaoxin Wang, David Orlicky, Komuraiah Myakala, Pengyuan Yang, Moshe Levi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(1): 137. CrossRef - Association of sex hormone-binding globulin with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in Chinese adults
Jing Luo, Qian Chen, Tianran Shen, Xu Wang, Wanjun Fang, Xiaocai Wu, Zenan Yuan, Gengdong Chen, Wenhua Ling, Yuming Chen
Nutrition & Metabolism.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inter‐relationships between cardiovascular, renal and metabolic diseases: Underlying evidence and implications for integrated interdisciplinary care and management
- Epidemiology
- Application of the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Cholesterol Guideline to the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys from 1998 to 2012
- Young Shin Song, Tae Jung Oh, Kyoung Min Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang, Kyong Soo Park, Soo Lim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(1):38-50. Published online December 16, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.1.38
- 4,265 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background The 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association (ACC/AHA) guideline for the treatment of blood cholesterol recommends statin therapy for individuals at high risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD). The aim of this study was to investigate serial trends in the percentages of Korean adults considered eligible for statin therapy according to the new ACC/AHA cholesterol guideline.
Methods Data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) I (1998,
n =7,698), II (2001,n =5,654), III (2005,n =5,269), IV (2007 to 2009,n =15,727), and V (2010 to 2012,n =16,304), which used a stratified, multistage, probability sampling design, were used as representative of the entire Korean population.Results The percentage of adults eligible for statin therapy according to the ACC/AHA cholesterol guideline increased with time: 17.0%, 19.0%, 20.8%, 20.2%, and 22.0% in KNHANES I, II, III, IV, and V, respectively (
P =0.022). The prevalence of ASCVD was 1.4% in KNHANES I and increased to 3.3% in KNHANES V. The percentage of diabetic patients aged 40 to 75 years with a low density lipoprotein cholesterol levels of 70 to 189 mg/dL increased from 4.8% in KNHANES I to 6.1% in KNHANES V. People with an estimated 10-year ASCVD risk ≥7.5% and aged 40 to 75 years accounted for the largest percentage among the four statin benefit groups: 9.1% in KNHANES I and 11.0% in KNHANES V.Conclusion Application of the 2013 ACC/AHA guideline has found that the percentage of Korean adults in the statin benefit groups has increased over the past 15 years.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sex differences in risk factors for subclinical hypothyroidism
Jeonghoon Ha, Jeongmin Lee, Kwanhoon Jo, Dong-Jun Lim, Moo Il Kang, Bong Yun Cha, Min-Hee Kim
Endocrine Connections.2018; 7(4): 511. CrossRef
- Sex differences in risk factors for subclinical hypothyroidism
- Resistin in Rodents and Humans
- Hyeong Kyu Park, Rexford S. Ahima
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(6):404-414. Published online December 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.6.404
- 5,581 View
- 52 Download
- 121 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Obesity is characterized by excess accumulation of lipids in adipose tissue and other organs, and chronic inflammation associated with insulin resistance and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. Obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases are major health concerns. Resistin was first discovered as an adipose-secreted hormone (adipokine) linked to obesity and insulin resistance in rodents. Adipocyte-derived resistin is increased in obese rodents and strongly related to insulin resistance. However, in contrast to rodents, resistin is expressed and secreted from macrophages in humans and is increased in inflammatory conditions. Some studies have also suggested an association between increased resistin levels and insulin resistance, diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Genetic studies have provided additional evidence for a role of resistin in insulin resistance and inflammation. Resistin appears to mediate the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis by promoting endothelial dysfunction, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, arterial inflammation, and formation of foam cells. Indeed, resistin is predictive of atherosclerosis and poor clinical outcomes in patients with coronary artery disease and ischemic stroke. There is also growing evidence that elevated resistin is associated with the development of heart failure. This review will focus on the biology of resistin in rodents and humans, and evidence linking resistin with type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis, and cardiovascular disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Resistin – A Plausible Therapeutic Target in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis
Manupati Srikanth, Mahaboobkhan Rasool
Immunological Investigations.2024; 53(2): 115. CrossRef - MHO or MUO? White adipose tissue remodeling
Jing Yi Zhao, Li Juan Zhou, Kai Le Ma, Rui Hao, Min Li
Obesity Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistin in endocrine pancreas of sheep: Presence and expression related to different diets
Margherita Maranesi, Elisa Palmioli, Cecilia Dall'Aglio, Daniele Marini, Polina Anipchenko, Elena De Felice, Paola Scocco, Francesca Mercati
General and Comparative Endocrinology.2024; 348: 114452. CrossRef - Adipocytokines levels as potential biomarkers for discriminating patients with a diagnosis of depressive disorder from healthy controls
Elżbieta Małujło-Balcerska, Tadeusz Pietras
Journal of Psychiatric Research.2024; 171: 163. CrossRef - Adipokines in atopic dermatitis: the link between obesity and atopic dermatitis
Shiyun Zhang, Bingjie Zhang, Yuehua Liu, Li Li
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Adipokines in the Control of Pituitary Functions
Barbara Kaminska, Beata Kurowicka, Marta Kiezun, Kamil Dobrzyn, Katarzyna Kisielewska, Marlena Gudelska, Grzegorz Kopij, Karolina Szymanska, Barbara Zarzecka, Oguzhan Koker, Ewa Zaobidna, Nina Smolinska, Tadeusz Kaminski
Animals.2024; 14(2): 353. CrossRef - Adipokine imbalance and its role in the pathogenesis of novel coronavirus infection
I. D. Bespalova, U. M. Mitrichenko, V. V. Kalyuzhin, E. S. Koroleva, Yu. I. Koshchavtseva, D. S. Romanov, D. E. Pershina
Bulletin of Siberian Medicine.2024; 22(4): 164. CrossRef - Association of adipokine levels with obesity in periodontal health and disease: A systematic review with meta‐analysis and meta‐regression
Eswar Kandaswamy, Chun‐Teh Lee, Soumya Bardvalli Gururaj, Sachin Shivanaikar, Vinayak M. Joshi
Journal of Periodontal Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of maternal body composition and diet on breast milk hormones and neonatal growth during the first month of lactation
David Ramiro-Cortijo, Pratibha Singh, Gloria Herranz Carrillo, Andrea Gila-Díaz, María A. Martín-Cabrejas, Camilia R. Martin, Silvia M. Arribas
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Upregulation of peripheral blood mononuclear cells resistin gene expression in severe obstructive sleep apnea and obstructive sleep apnea with coexisting type 2 diabetes mellitus
Branislava Rajkov, Marija Zdravković, Ana Ninić, Milica Brajković, Slobodan Klašnja, Vera Gardijan, Lidija Memon, Jelena Munjas, Marija Mihajlović, Vesna Spasojević- Kalimanovska, Vojislav Radosavljević, Miron Sopić
Sleep and Breathing.2023; 27(5): 2031. CrossRef - Fat-to-heart crosstalk in health and disease
Fleur Lodewijks, Timothy A. McKinsey, Emma L. Robinson
Frontiers in Genetics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipokines as Diagnostic and Prognostic Markers for the Severity of COVID-19
Thomas Grewal, Christa Buechler
Biomedicines.2023; 11(5): 1302. CrossRef - Role of adipokines in sarcopenia
Wenhao Lu, Wenjie Feng, Jieyu Lai, Dongliang Yuan, Wenfeng Xiao, Yusheng Li
Chinese Medical Journal.2023; 136(15): 1794. CrossRef - Resistin, TNF-α, and microRNA 124-3p expressions in peripheral blood mononuclear cells are associated with diabetic nephropathy
Amin Monjezi, Azam Khedri, Mehrnoosh Zakerkish, Ghorban Mohammadzadeh
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2022; 42(1): 62. CrossRef - Resistin in Urine and Breast Milk: Relation to Type of Feeding and Anthropometry at 1-Month
Irena Santosa, Hiromichi Shoji, Kentaro Awata, Yoshiteru Arai, Hiroki Suganuma, Toshiaki Shimizu
Pediatric Reports.2022; 14(1): 86. CrossRef - High Serum Levels of Resistin is Associated With Acute Cerebral Infarction
Kee Ook Lee, Kyung-Yul Lee, Cheol-Young Lee, Ji Hoon Kim, Jaeku Kang, Hoi Young Lee, Sang-Jun Na, Seung-Hun Oh, Ji Hoe Heo
The Neurologist.2022; 27(2): 41. CrossRef - Resistin production does not affect outcomes in a mouse model of acute surgical sepsis
Anthony S. Bonavia, Zissis C. Chroneos, Victor Ruiz-Velasco, Charles H. Lang, Partha Mukhopadhyay
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(3): e0265241. CrossRef - Single-nucleotide polymorphisms as important risk factors of diabetes among Middle East population
Iman Akhlaghipour, Amir Reza Bina, Mohammad Reza Mogharrabi, Ali Fanoodi, Amir Reza Ebrahimian, Soroush Khojasteh Kaffash, Atefeh Babazadeh Baghan, Mohammad Erfan Khorashadizadeh, Negin Taghehchian, Meysam Moghbeli
Human Genomics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Synergistic Effects of Weighted Genetic Risk Scores and Resistin and sST2 Levels on the Prognostication of Long-Term Outcomes in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease
Hsin-Hua Chou, Lung-An Hsu, Jyh-Ming Jimmy Juang, Fu-Tien Chiang, Ming-Sheng Teng, Semon Wu, Yu-Lin Ko
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4292. CrossRef - Hypoxia Increases the Potential for Neutrophil-mediated Endothelial Damage in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Katharine M. Lodge, Arlette Vassallo, Bin Liu, Merete Long, Zhen Tong, Paul R. Newby, Danya Agha-Jaffar, Koralia Paschalaki, Clara E. Green, Kylie B. R. Belchamber, Victoria C. Ridger, Robert A. Stockley, Elizabeth Sapey, Charlotte Summers, Andrew S. Cowb
American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine.2022; 205(8): 903. CrossRef - The Role of the Adipokine Resistin in the Pathogenesis and Progression of Epithelial Ovarian Cancer
Klaudia Parafiniuk, Wiktoria Skiba, Anna Pawłowska, Dorota Suszczyk, Aleksandra Maciejczyk, Iwona Wertel
Biomedicines.2022; 10(4): 920. CrossRef - Resistin Modulates Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Uptake in Human Placental Explants via PCSK9
Sonia Nava-Salazar, Arturo Flores-Pliego, Giovanni Pérez-Martínez, Sandra Parra-Hernández, America Vanoye-Carlo, Francisco Ibarguengoitia-Ochoa, Otilia Perichart-Perera, Enrique Reyes-Muñoz, Juan Mario Solis-Paredes, Salvador Espino y Sosa, Guadalupe Estr
Reproductive Sciences.2022; 29(11): 3242. CrossRef - Differential Association of Selected Adipocytokines, Adiponectin, Leptin, Resistin, Visfatin and Chemerin, with the Pathogenesis and Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (T2DM) in the Asir Region of Saudi Arabia: A Case Control Study
Mohammad Muzaffar Mir, Rashid Mir, Mushabab Ayed Abdullah Alghamdi, Javed Iqbal Wani, Zia Ul Sabah, Mohammed Jeelani, Vijaya Marakala, Shahzada Khalid Sohail, Mohamed O’haj, Muffarah Hamid Alharthi, Mohannad Mohammad S. Alamri
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(5): 735. CrossRef - Immune system and sarcopenia: Presented relationship and future perspective
Xuzhi Zhang, Hengzhen Li, Miao He, Jingyu Wang, Yuxiang Wu, Yusheng Li
Experimental Gerontology.2022; 164: 111823. CrossRef - Adipose Tissue Secretion Pattern Influences β-Cell Wellness in the Transition from Obesity to Type 2 Diabetes
Giuseppina Biondi, Nicola Marrano, Anna Borrelli, Martina Rella, Giuseppe Palma, Isabella Calderoni, Edoardo Siciliano, Pasquale Lops, Francesco Giorgino, Annalisa Natalicchio
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(10): 5522. CrossRef - Supplemental hydroxychloroquine therapy regulates adipokines in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus with stable disease
Risa Wakiya, Kiyo Ueeda, Hiromi Shimada, Shusaku Nakashima, Tomohiro Kameda, Nobuyuki Miyatake, Mikiya Kato, Taichi Miyagi, Koichi Sugihara, Mao Mizusaki, Rina Mino, Norimitsu Kadowaki, Hiroaki Dobashi
Clinical Rheumatology.2022; 41(11): 3345. CrossRef - Can soy isoflavones in combination with soy protein change serum concentration of adiponectin and resistin? A systematic review and meta‐analysis on randomized clinical trials
Mitra Hariri, Bahareh Amirkalali, Ensiyeh Mollanoroozy, Ali Gholami
Food Science & Nutrition.2022; 10(12): 4126. CrossRef - Adipokines: Deciphering the cardiovascular signature of adipose tissue
Joseph C. Galley, Shubhnita Singh, Wanessa M.C. Awata, Juliano V. Alves, Thiago Bruder-Nascimento
Biochemical Pharmacology.2022; 206: 115324. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Anti-Obesity Effect of Zeaxanthin and Exercise in HFD-Induced Obese Rats
Mona Al-thepyani, Salha Algarni, Hana Gashlan, Mohamed Elzubier, Lina Baz
Nutrients.2022; 14(23): 4944. CrossRef - Single High-Dose Vitamin D Supplementation as an Approach for Reducing Ultramarathon-Induced Inflammation: A Double-Blind Randomized Controlled Trial
Jan Mieszkowski, Andżelika Borkowska, Błażej Stankiewicz, Andrzej Kochanowicz, Bartłomiej Niespodziński, Marcin Surmiak, Tomasz Waldziński, Rafał Rola, Miroslav Petr, Jędrzej Antosiewicz
Nutrients.2021; 13(4): 1280. CrossRef - Resistin mitigates stemness and metabolic profile of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells via insulin resistance
Komal Rawal, Kishan M. Purohit, Tushar P. Patel, Neeta Karont, Sarita Gupta
Cytokine.2021; 138: 155374. CrossRef - Resistin is co-secreted with adiponectin in white mouse adipocytes
Saliha Musovic, Man Mohan Shrestha, Ali M. Komai, Charlotta S. Olofsson
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2021; 534: 707. CrossRef - Resistin: Potential biomarker and therapeutic target in atherosclerosis
Li Zhou, Jun-Yi Li, Ping-Ping He, Xiao-Hua Yu, Chao-Ke Tang
Clinica Chimica Acta.2021; 512: 84. CrossRef - The circulating levels of CTRP1 and CTRP5 are associated with obesity indices and carotid intima-media thickness (cIMT) value in patients with type 2 diabetes: a preliminary study
Ziba Majidi, Solaleh Emamgholipour, Abolfazl Omidifar, Soheil Rahmani Fard, Hossein Poustchi, Mehrnoosh Shanaki
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Corylin reduces obesity and insulin resistance and promotes adipose tissue browning through SIRT-1 and β3-AR activation
Chin-Chuan Chen, Chen-Hsin Kuo, Yann-Lii Leu, Shu-Huei Wang
Pharmacological Research.2021; 164: 105291. CrossRef - A Focused Review of the Metabolic Side-Effects of Clozapine
Jessica W. Y. Yuen, David D. Kim, Ric M. Procyshyn, William J. Panenka, William G. Honer, Alasdair M. Barr
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Negative Energy Balance Is Associated with Metabolic Dysfunctions in the Hypothalamus of a Humanized Preclinical Model of Alzheimer’s Disease, the 5XFAD Mouse
Antonio J. López-Gambero, Cristina Rosell-Valle, Dina Medina-Vera, Juan Antonio Navarro, Antonio Vargas, Patricia Rivera, Carlos Sanjuan, Fernando Rodríguez de Fonseca, Juan Suárez
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(10): 5365. CrossRef - Resistin in pregnancy: Analysis of determinants in pairs of umbilical cord blood and maternal serum
Anne Floeck, Nina Ferrari, Christine Joisten, Maria T. Puth, Brigitte Strizek, Ramona Dolscheid-Pommerich, Ulrich Gembruch, Waltraut M. Merz
Cytokine: X.2021; 3(2): 100052. CrossRef - Is resistin the master link between inflammation and inflammation-related chronic diseases?
Mohammed Taouis, Yacir Benomar
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2021; 533: 111341. CrossRef - The dynamics of human bone marrow adipose tissue in response to feeding and fasting
Pouneh K. Fazeli, Miriam A. Bredella, Gisela Pachon-Peña, Wenxiu Zhao, Xun Zhang, Alexander T. Faje, Megi Resulaj, Sai P. Polineni, Tara M. Holmes, Hang Lee, Elizabeth K. O’Donnell, Ormond A. MacDougald, Mark C. Horowitz, Clifford J. Rosen, Anne Klibanski
JCI Insight.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistin: A journey from metabolism to cancer
Ankita Deb, Bhavana Deshmukh, Pranay Ramteke, Firoz Khan Bhati, Manoj Kumar Bhat
Translational Oncology.2021; 14(10): 101178. CrossRef - Obesity is the basis of metabolic syndrome
A. F. Verbovoy, N. I. Verbovaya, Yu. A. Dolgikh
Obesity and metabolism.2021; 18(2): 142. CrossRef - Human Milk Metabolic Hormones: Analytical Methods and Current Understanding
Majed A. Suwaydi, Zoya Gridneva, Sharon L. Perrella, Mary E. Wlodek, Ching Tat Lai, Donna T. Geddes
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(16): 8708. CrossRef - Adipokines as Immune Cell Modulators in Multiple Sclerosis
Merel Rijnsburger, Niek Djuric, Inge A. Mulder, Helga E. de Vries
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(19): 10845. CrossRef - The Role of Adipokines in Cardiovascular Pathology
Valery Podzolkov , Anna Pokrovskaya, Ulyana Bazhanova , Tatyana Vargina , Svetlana Anatolievna Knyazeva , Daria Vanina
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2021; 9(F): 794. CrossRef - Measurement of Plasma Resistin Concentrations in Horses with Metabolic and Inflammatory Disorders
Beatriz Fuentes-Romero, Alberto Muñoz-Prieto, José J. Cerón, María Martín-Cuervo, Manuel Iglesias-García, Escolástico Aguilera-Tejero, Elisa Díez-Castro
Animals.2021; 12(1): 77. CrossRef - EFFECT OF DIET AND EXERCISE-INDUCE WEIGHT LOSS ON LEVEL OF RESISTIN IN PATIENT WITH OBESITY
О. I. Tokarenko, I. O. Andreieva, O. O. Tokarenko, M. M. Surmilo
Modern medical technology.2021; (4): 11. CrossRef - Alteration of gut microbiota affects expression of adiponectin and resistin through modifying DNA methylation in high-fat diet-induced obese mice
Hongyang Yao, Chaonan Fan, Yuanyuan Lu, Xiuqin Fan, Lulu Xia, Ping Li, Rui Wang, Tiantian Tang, Yuanyuan Wang, Kemin Qi
Genes & Nutrition.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistin hormone in diabetic kidney disease and its relation to iron status and hepcidin
Zhian Sherzad Hayder, Zrar Saleem Kareem
International Urology and Nephrology.2020; 52(4): 749. CrossRef - Proteoglycans in Obesity-Associated Metabolic Dysfunction and Meta-Inflammation
Ariane R. Pessentheiner, G. Michelle Ducasa, Philip L. S. M. Gordts
Frontiers in Immunology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistin Is Increased in Periodontal Cells and Tissues: In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
Andressa V. B. Nogueira, Marjan Nokhbehsaim, Sema Tekin, Rafael S. de Molon, Luis C. Spolidorio, Svenja Memmert, Anna Damanaki, Andreas Jäger, Sigrun Eick, James Deschner, Joni A. Cirelli
Mediators of Inflammation.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Adipose Tissue Distribution, Inflammation and Its Metabolic Consequences, Including Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
Alan Chait, Laura J. den Hartigh
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The possible role of endocrine dysfunction of adipose tissue in gestational diabetes mellitus
Patrik Šimják, Kateřina Anderlová, Anna Cinkajzlová, Antonín Pařízek, Michal Kršek, Martin Haluzík
Minerva Endocrinologica.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - High Plasma Resistin Levels Portend the Insulin Resistance-Associated Susceptibility to Early Cognitive Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Chenchen Wang, Xi Huang, Sai Tian, Rong Huang, Dan Guo, Hongyan Lin, Jiaqi Wang, Shaohua Wang
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2020; 75(3): 807. CrossRef - Resistin in metabolism, inflammation, and disease
Deeksha Tripathi, Sashi Kant, Saurabh Pandey, Nasreen Z. Ehtesham
The FEBS Journal.2020; 287(15): 3141. CrossRef - Adipokines: New Potential Therapeutic Target for Obesity and Metabolic, Rheumatic, and Cardiovascular Diseases
Lucia Recinella, Giustino Orlando, Claudio Ferrante, Annalisa Chiavaroli, Luigi Brunetti, Sheila Leone
Frontiers in Physiology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation of CCL18 with Levels of Adi-pokines in the Sera of Patients with Myocardial Infarction in a 6-Month Period: Case Series
Atefeh GamarTalepoor, Ehsan Dowlatshahi, Mehrnoush Doroudchi
Iranian South Medical Journal.2020; 23(3): 222. CrossRef - The Mesentery, Systemic Inflammation, and Crohn’s Disease
Edgardo D Rivera, John Calvin Coffey, Dara Walsh, Eli D Ehrenpreis
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.2019; 25(2): 226. CrossRef - Resistin and adenylyl cyclase-associated protein 1 (CAP1) regulate the expression of genes related to insulin resistance in BNL CL.2 mouse liver cells
Dimiter Avtanski, Karin Chen, Leonid Poretsky
Data in Brief.2019; 25: 104112. CrossRef - Proteomic profile of patients with atrial fibrillation undergoing cardiac surgery†
Ilias P Doulamis, George Samanidis, Aspasia Tzani, Asier Antoranz, Anastasios Gkogkos, Panagiotis Konstantopoulos, Vaia Pliaka, Angeliki Minia, Leonidas G Alexopoulos, Despina N Perrea, Konstantinos Perreas
Interactive CardioVascular and Thoracic Surgery.2019; 28(1): 94. CrossRef - Angiotensin-(1-7), Adipokines and Inflammation
Deborah de Farias Lelis, Daniela Fernanda de Freitas, Amanda Souto Machado, Thaísa Soares Crespo, Sérgio Henrique Sousa Santos
Metabolism.2019; 95: 36. CrossRef - New Insights into Adipokines as Potential Biomarkers for Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
Marta Olivera-Santa Catalina, Pedro C. Redondo, Maria P. Granados, Carlos Cantonero, Jose Sanchez-Collado, Letizia Albarran, Jose J. Lopez
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2019; 26(22): 4119. CrossRef - Myokine–adipokine cross-talk: potential mechanisms for the association between plasma irisin and adipokines and cardiometabolic risk factors in Mexican children with obesity and the metabolic syndrome
Adrian M. Gonzalez-Gil, Mariana Peschard-Franco, Elena C. Castillo, Gustavo Gutierrez-DelBosque, Victor Treviño, Christian Silva-Platas, Luisa Perez-Villarreal, Gerardo Garcia-Rivas, Leticia Elizondo-Montemayor
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Early Life Exposures to Perfluoroalkyl Substances in Relation to Adipokine Hormone Levels at Birth and During Childhood
Colleen Shelly, Philippe Grandjean, Youssef Oulhote, Peter Plomgaard, Ruth Frikke-Schmidt, Flemming Nielsen, Denis Zmirou-Navier, Pal Weihe, Damaskini Valvi
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2019; 104(11): 5338. CrossRef - Overweight and obesity in childhood: Dietary, biochemical, inflammatory and lifestyle risk factors
Samah R. Albataineh, Eman F. Badran, Reema F. Tayyem
Obesity Medicine.2019; 15: 100112. CrossRef - Effects of major adipokines and the −420 C > G resistin gene polymorphism on the long-term outcome of patients with acute ischemic stroke
Stella Bouziana, Konstantinos Tziomalos, Antonis Goulas, Timoleon-Achilleas Vyzantiadis, Maria Papadopoulou, Athanasia Panderi, Apostolos Ι. Ηatzitolios
International Journal of Neuroscience.2019; 129(10): 978. CrossRef - The Complex Interactions Between Obesity, Metabolism and the Brain
Romina María Uranga, Jeffrey Neil Keller
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistin: A reappraisal
E. Acquarone, F. Monacelli, R. Borghi, A. Nencioni, P. Odetti
Mechanisms of Ageing and Development.2019; 178: 46. CrossRef - Implications of resistin in type 2 diabetes mellitus and coronary artery disease: Impairing insulin function and inducing pro‐inflammatory cytokines
Melissa Emamalipour, Khaled Seidi, Ali Jahanban‐Esfahlan, Rana Jahanban‐Esfahlan
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2019; 234(12): 21758. CrossRef - Serum-based soluble markers differentiate psoriatic arthritis from osteoarthritis
Vinod Chandran, Fatima Abji, Anthony V Perruccio, Rajiv Gandhi, Suzanne Li, Richard J Cook, Dafna D Gladman
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.2019; 78(6): 796. CrossRef - Telmisartan prevents diet-induced obesity and preserves leptin transport across the blood-brain barrier in high-fat diet-fed mice
Franziska Schuster, Gianna Huber, Ines Stölting, Emily E. Wing, Kathrin Saar, Norbert Hübner, William A. Banks, Walter Raasch
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology.2018; 470(11): 1673. CrossRef - Adipokines in human breast milk
Juergen Kratzsch, Yoon Ju Bae, Wieland Kiess
Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2018; 32(1): 27. CrossRef - Addressing the Perfect Storm: Biomarkers in Obesity and Pathophysiology of Cardiometabolic Risk
Krasimira Aleksandrova, Dariush Mozaffarian, Tobias Pischon
Clinical Chemistry.2018; 64(1): 142. CrossRef - Adipocytokine Involvement in Innate Immune Mechanisms
Paulina Żelechowska, Elżbieta Kozłowska, Joanna Pastwińska, Justyna Agier, Ewa Brzezińska-Błaszczyk
Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research.2018; 38(12): 527. CrossRef - The effect of a garlic supplement on the pro-inflammatory adipocytokines, resistin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and on pain severity, in overweight or obese women with knee osteoarthritis
Sahar Dehghani, Elham Alipoor, Ahmad Salimzadeh, Mehdi Yaseri, Mostafa Hosseini, Christine Feinle-Bisset, Mohammad Javad Hosseinzadeh-Attar
Phytomedicine.2018; 48: 70. CrossRef - Perivascular adipose tissue (PVAT) in atherosclerosis: a double-edged sword
Xiao-Yan Qi, Shun-Lin Qu, Wen-Hao Xiong, Oren Rom, Lin Chang, Zhi-Sheng Jiang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Usefulness of the Adipokines as Biomarkers of Ischemic Cardiac Dysfunction
Larisa-Diana Mocan Hognogi, Cerasela-Mihaela Goidescu, Anca-Daniela Farcaş
Disease Markers.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 in patients with liver cirrhosis
Sabrina Krautbauer, Lisa Rein-Fischboeck, Elisabeth M Haberl, Rebekka Pohl, Reiner Wiest, Christa Buechler
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2018; 18(1): 63. CrossRef - Association of Cord Blood Resistin with Neonatal Birth Weight and Gestational Age
Shahnaz Pourarian, Saeed Fotouhikia, Forough Saki
Journal of Comprehensive Pediatrics.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Major Adipokines and the −420C>G Resistin Gene Polymorphism as Predictors of Acute Ischemic Stroke Severity and In-Hospital Outcome
Styliani D. Bouziana, Konstantinos Tziomalos, Antonios Goulas, Timoleon-Achilleas Vyzantiadis, Athanasia Panderi, Apostolos Ι. Ηatzitolios
Journal of Stroke and Cerebrovascular Diseases.2018; 27(4): 963. CrossRef - Resistin and NGAL are associated with inflammatory response, endothelial activation and clinical outcomes in sepsis
Stephen P. J. Macdonald, Erika Bosio, Claire Neil, Glenn Arendts, Sally Burrows, Lisa Smart, Simon G. A. Brown, Daniel M. Fatovich
Inflammation Research.2017; 66(7): 611. CrossRef - Reference values for fasting serum resistin in healthy children and adolescents
Ulrik Lausten-Thomsen, Michael Christiansen, Paula Louise Hedley, Tenna Ruest Haarmark Nielsen, Cilius Esmann Fonvig, Oluf Pedersen, Torben Hansen, Jens-Christian Holm
Clinica Chimica Acta.2017; 469: 161. CrossRef - Sarcopenic obesity or obese sarcopenia: A cross talk between age-associated adipose tissue and skeletal muscle inflammation as a main mechanism of the pathogenesis
Alexander Kalinkovich, Gregory Livshits
Ageing Research Reviews.2017; 35: 200. CrossRef - Is There Any Relationship between Plasma 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3, Adipokine Profiles and Excessive Body Weight in Type 2 Diabetic Patients?
Joanna Kocot, Piotr Dziemidok, Małgorzata Kiełczykowska, Jacek Kurzepa, Grzegorz Szcześniak, Irena Musik
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2017; 15(1): 19. CrossRef - Exogenous Adipokine Peptide Resistin Protects Against Focal Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice
Jiangtao Zhu, Di Wu, Chenyu Zhao, Man Luo, Ronald C. Hamdy, Balvin H. L. Chua, Xingshun Xu, Zhigang Miao
Neurochemical Research.2017; 42(10): 2949. CrossRef - Adipokines in Liver Cirrhosis
Christa Buechler, Elisabeth Haberl, Lisa Rein-Fischboeck, Charalampos Aslanidis
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2017; 18(7): 1392. CrossRef - The role of sex steroids in white adipose tissue adipocyte function
A E Newell-Fugate
Reproduction.2017; 153(4): R133. CrossRef - Odanacatib Inhibits Resistin-induced Cardiomyocyte Hypertrophy Through the Inactivation of ERK Signaling Pathway
Xian Zheng, Guanchang Cheng, Jianwei Luo, Qunhui Ye, Yongzhi Deng, Lin Wu
International Journal of Pharmacology.2017; 13(2): 212. CrossRef - Linking resistin, inflammation, and cardiometabolic diseases
Hyeong Kyu Park, Mi Kyung Kwak, Hye Jeong Kim, Rexford S. Ahima
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(2): 239. CrossRef - Translating the biology of adipokines in atherosclerosis and cardiovascular diseases: Gaps and open questions
M. Ruscica, A. Baragetti, A.L. Catapano, G.D. Norata
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2017; 27(5): 379. CrossRef - Differences in Mean Levels of Maternal Resistin Serum between Early Onset Preeclampsia (EOPE) and Late Onset Preeclampsia (LOPE)
Yusrawati ., P. Alfajra, R. Machmud
Research Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.2016; 10(1): 1. CrossRef - Secret talk between adipose tissue and central nervous system via secreted factors—an emerging frontier in the neurodegenerative research
Avinash Parimisetty, Anne-Claire Dorsemans, Rana Awada, Palaniyandi Ravanan, Nicolas Diotel, Christian Lefebvre d’Hellencourt
Journal of Neuroinflammation.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of adipokines in ischemic stroke risk stratification
Styliani Bouziana, Konstantinos Tziomalos, Antonios Goulas, Apostolos Ι Ηatzitolios
International Journal of Stroke.2016; 11(4): 389. CrossRef - The endocrine function of human placenta: an overview
Mariana A. Costa
Reproductive BioMedicine Online.2016; 32(1): 14. CrossRef - Ursolic acid plays a protective role in obesity-induced cardiovascular diseases
Yu-Ting Lin, Ya-Mei Yu, Weng-Cheng Chang, Su-Yin Chiang, Hsu-Chin Chan, Ming-Fen Lee
Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology.2016; 94(6): 627. CrossRef - Determinants of body weight regulation in humans
Milene Moehlecke, Luis Henrique Canani, Lucas Oliveira Junqueira e Silva, Manoel Roberto Maciel Trindade, Rogerio Friedman, Cristiane Bauermann Leitão
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 60(2): 152. CrossRef - Sitagliptin decreases ventricular arrhythmias by attenuated glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP)-dependent resistin signalling in infarcted rats
Tsung-Ming Lee, Wei-Ting Chen, Nen-Chung Chang
Bioscience Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Les adipokines : état des lieux et nouveautés
J.-P. Bastard, C. Bastard, S. Fellahi, C. Vatier, J. Capeau, B. Fève
Obésité.2016; 11(3): 181. CrossRef - Factors that promote macrophage homing to adipose tissue in metabolic syndrome
Ishwarlal Jialal, Beverley Adams-Huet, Sridevi Devaraj
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2016; 30(8): 1434. CrossRef - Uncovering Factors Related to Pancreatic Beta-Cell Function
Aoife M. Curran, Miriam F. Ryan, Elaine Drummond, Eileen R. Gibney, Michael J. Gibney, Helen M. Roche, Lorraine Brennan, Nigel Irwin
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(8): e0161350. CrossRef - Resistin’s, obesity and insulin resistance: the continuing disconnect between rodents and humans
X. Huang, Z. Yang
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2016; 39(6): 607. CrossRef - Adipocytokines in renal transplant recipients
Kristof Nagy, Shankar Prasad Nagaraju, Connie M. Rhee, Zoltan Mathe, Miklos Z. Molnar
Clinical Kidney Journal.2016; 9(3): 359. CrossRef - Endocrine alterations from concentric vs. eccentric muscle actions: A brief review
Robert R. Kraemer, V. Daniel Castracane
Metabolism.2015; 64(2): 190. CrossRef - Non-traditional cytokines: How catecholamines and adipokines influence macrophages in immunity, metabolism and the central nervous system
Mark A. Barnes, Monica J. Carson, Meera G. Nair
Cytokine.2015; 72(2): 210. CrossRef - Local and serum levels of adipokines in patients with obesity after periodontal therapy: one‐year follow‐up
Tiago Eduardo Dias Gonçalves, Glaucia Santos Zimmermann, Luciene Cristina Figueiredo, Monique de Carvalho Souza, Daniele Ferreira da Cruz, Marta Ferreira Bastos, Hélio Doyle Pereira da Silva, Poliana Mendes Duarte
Journal of Clinical Periodontology.2015; 42(5): 431. CrossRef - Newborn Adipokines and Birth Outcomes
Edwina H. Yeung, Alexander C. McLain, Nancy Anderson, David Lawrence, Nansi S. Boghossian, Charlotte Druschel, Erin Bell
Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology.2015; 29(4): 317. CrossRef - The effect of a preparation of minerals, vitamins and trace elements on the cardiac gene expression pattern in male diabetic rats
Márta Sárközy, Gergő Szűcs, Márton Pipicz, Ágnes Zvara, Katalin Éder, Veronika Fekete, Csilla Szűcs, Judit Bárkányi, Csaba Csonka, László G. Puskás, Csaba Kónya, Péter Ferdinandy, Tamás Csont
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Diet-induced variability of the resistin gene (Retn) transcript level and methylation profile in rats
Joanna Nowacka-Woszuk, Ewa Pruszynska-Oszmalek, Maciej Szydlowski, Slawomir Sadkowski, Izabela Szczerbal
BMC Genetics.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - INFLUENCE OF RESISTIN ON THE COURSE OF ISCHEMIC HEART DISEASE IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
A. T. Teplyakov, Sh. D. Akhmedov, T. Ye. Suslova, А. V. Andriyanova, A. V. Kuznetsova, N. V. Protopopova, V. V. Kalyuzhin, O. N. Nasanova
Bulletin of Siberian Medicine.2015; 14(5): 73. CrossRef - The Effects of a Single Developmentally Entrained Pulse of Testosterone in Female Neonatal Mice on Reproductive and Metabolic Functions in Adult Life
Hyeran Jang, Shalender Bhasin, Tyler Guarneri, Carlo Serra, Mary Schneider, Mi-Jeong Lee, Wen Guo, Susan K. Fried, Karol Pencina, Ravi Jasuja
Endocrinology.2015; 156(10): 3737. CrossRef - The Resin fromProtium heptaphyllumPrevents High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity in Mice: Scientific Evidence and Potential Mechanisms
Karine Maria Martins Bezerra Carvalho, José Delano Barreto Marinho Filho, Tiago Sousa de Melo, Ana Jérsia Araújo, Josiane da Silva Quetz, Maria do Perpétuo Socorro Saldanha da Cunha, Karina Moura de Melo, Armenio Andre de Carvalho Almeida da Silva, Adrian
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Evolution of the Vertebrate Resistin Gene Family
Qingda Hu, Huanran Tan, David M. Irwin, Marc Robinson-Rechavi
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(6): e0130188. CrossRef - Obesity, adipokines and neuroinflammation
Argel Aguilar-Valles, Wataru Inoue, Christoph Rummel, Giamal N. Luheshi
Neuropharmacology.2015; 96: 124. CrossRef - Adipokines at the crossroad between obesity and cardiovascular disease
Filippo Molica, Sandrine Morel, Brenda Kwak, Françoise Rohner-Jeanrenaud, Sabine Steffens
Thrombosis and Haemostasis.2015; 113(03): 553. CrossRef - Resistin – 420 C/G polymorphism and serum resistin level in Iranian patients with gestational diabetes mellitus
Mohammad Ali Takhshid, Zinab Zare
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Ictal adipokines are associated with pain severity and treatment response in episodic migraine
Nu Cindy Chai, Bizu Gelaye, Gretchen E. Tietjen, Paul D. Dash, Barbara A. Gower, Linda W. White, Thomas N. Ward, Ann I. Scher, B. Lee Peterlin
Neurology.2015; 84(14): 1409. CrossRef - Inflammation and insulin/IGF-1 resistance as the possible link between obesity and neurodegeneration
Lindsay J. Spielman, Jonathan P. Little, Andis Klegeris
Journal of Neuroimmunology.2014; 273(1-2): 8. CrossRef - Wild Blueberries (Vaccinium myrtillus) Alleviate Inflammation and Hypertension Associated with Developing Obesity in Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet
Otto T. Mykkänen, Anne Huotari, Karl-Heinz Herzig, Thomas W. Dunlop, Hannu Mykkänen, Pirkka V. Kirjavainen, Michael Müller
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(12): e114790. CrossRef - Role of fat and adipokines in intestinal inflammation
LeaI Kredel, Arvind Batra, Britta Siegmund
Current Opinion in Gastroenterology.2014; 30(6): 559. CrossRef -
13C metabolic flux analysis shows that resistin impairs the metabolic response to insulin in L6E9 myotubes
Shirley Guzmán, Silvia Marin, Anibal Miranda, Vitaly A Selivanov, Josep J Centelles, Romain Harmancey, Fatima Smih, Annie Turkieh, Yves Durocher, Antonio Zorzano, Philippe Rouet, Marta Cascante
BMC Systems Biology.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Bee Pollen Improves Muscle Protein and Energy Metabolism in Malnourished Old Rats through Interfering with the Mtor Signaling Pathway and Mitochondrial Activity
Jérôme Salles, Nicolas Cardinault, Véronique Patrac, Alexandre Berry, Christophe Giraudet, Marie-Laure Collin, Audrey Chanet, Camille Tagliaferri, Philippe Denis, Corinne Pouyet, Yves Boirie, Stéphane Walrand
Nutrients.2014; 6(12): 5500. CrossRef
- Resistin – A Plausible Therapeutic Target in the Pathogenesis of Psoriasis
- Risk Factors for the Progression of Intima-Media Thickness of Carotid Arteries: A 2-Year Follow-Up Study in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes
- Sang Ouk Chin, Jin Kyung Hwang, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, You-Cheol Hwang, Seungjoon Oh, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Jeong-taek Woo, Sung-Woon Kim, Young Seol Kim, Ja-Heon Kang, In-Kyung Jeong
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(5):365-374. Published online October 17, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.5.365
- 4,763 View
- 31 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Intima-media thickness (IMT) of the carotid arteries is known to have a positive correlation with the risk of cardiovascular disease. This study was designed to identify risk factors affecting the progression of carotid IMT in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods Patients with newly diagnosed T2DM with carotid IMT measurements were enrolled, and their clinical data and carotid IMT results at baseline and 2 years later were compared.
Results Of the 171 patients, 67.2% of males and 50.8% of females had abnormal baseline IMT of the left common carotid artery. At baseline, systolic blood pressure, body mass index and smoking in male participants, and fasting plasma glucose and glycated hemoglobin levels in females were significantly higher in patients with abnormal IMT than in those with normal IMT. Low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels in males and high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels in females at the 2-year follow-up were significantly different between the nonprogression and the progression groups. Reduction of the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) 10-year coronary heart disease (CHD) risk score after 2 years was generally higher in the nonprogression group than the progression group.
Conclusion LDL-C levels in males and HDL-C levels in females at the 2-year follow-up were significantly different between participants with and without progression of carotid IMT. Furthermore, a reduction in the UKPDS 10-year CHD risk score appeared to delay the advancement of atherosclerosis. Therefore, the importance of establishing the therapeutic goal of lipid profiles should be emphasized to prevent the progression of carotid IMT in newly diagnosed T2DM patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of the Effectiveness of Low Carbohydrate Versus Low Fat Diets, in Type 2 Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Tanefa A. Apekey, Maria J. Maynard, Monia Kittana, Setor K. Kunutsor
Nutrients.2022; 14(20): 4391. CrossRef Nomogram Based on Risk Factors for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Coronary Heart Disease
Rong Shi, Birong Wu, Zheyun Niu, Hui Sun, Fan Hu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 5025. CrossRef- HMGA1 Mediated High-Glucose-Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation in Diabetes Mellitus: Association Between PI3K/Akt Signaling and HMGA1 Expression
Qinghai Zhang, Ling Chen, Zhibo Zhao, Ying Wu, Jing Zhong, Gebo Wen, Renxian Cao, Xuyu Zu, Jianghua Liu
DNA and Cell Biology.2018; 37(4): 389. CrossRef - Relationship between frequency of hypoglycemic episodes and changes in carotid atherosclerosis in insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Tomoya Mita, Naoto Katakami, Toshihiko Shiraiwa, Hidenori Yoshii, Nobuichi Kuribayashi, Takeshi Osonoi, Hideaki Kaneto, Keisuke Kosugi, Yutaka Umayahara, Masahiko Gosho, Iichiro Shimomura, Hirotaka Watada
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of carotid atherosclerosis detection on physician and patient behavior in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a prospective, observational, multicenter study
In-Kyung Jeong, Sin-Gon Kim, Dong Hyeok Cho, Chong Hwa Kim, Chul Sik Kim, Won-Young Lee, Kyu-Chang Won, Doo-Man Kim
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of fibroblast growth factors and advanced glycation end-products on the intima-media complex thickness in patients with coronary heart disease and type 2 diabetes
Ekaterina Vladimirovna Ivannikova, Victor Yurievich Kalashnikov, Olga Mikhailovna Smirnova, Alexander Borisovich Kuznetsov, Сергей Anatolievich Terekhin, Alexander Viktorovich Il'in
Diabetes mellitus.2014; 17(2): 47. CrossRef
- Comparison of the Effectiveness of Low Carbohydrate Versus Low Fat Diets, in Type 2 Diabetes: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Cardiovascular Risk Assessment with Vascular Function, Carotid Atherosclerosis and the UKPDS Risk Engine in Korean Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes
- Choon Sik Seon, Kyung Wan Min, Seung Yup Lee, Kyoung Woo Nho, Se Hwan Park, Bo Kyung Koo, Kyung Ah Han
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(6):619-627. Published online December 26, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.6.619
- 3,805 View
- 29 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Patients with type 2 diabetes have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. Few studies have evaluated the cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk simultaneously using the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) risk engine and non-invasive vascular tests in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes.
Methods Participants (
n =380; aged 20 to 81 years) with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes were free of clinical evidence of CVD. The 10-year coronary heart disease (CHD) and stroke risks were calculated for each patient using the UKPDS risk engine. Carotid intima media thickness (CIMT), flow mediated dilation (FMD), pulse wave velocity (PWV) and augmentation index (AI) were measured. The correlations between the UKPDS risk engine and the non-invasive vascular tests were assessed using partial correlation analysis, after adjusting for age, and multiple regression analysis.Results The mean 10-year CHD and 10-year stroke risks were 14.92±11.53% and 4.03±3.95%, respectively. The 10-year CHD risk correlated with CIMT (
P <0.001), FMD (P =0.017), and PWV (P =0.35) after adjusting for age. The 10-year stroke risk correlated only with the mean CIMT (P <0.001) after adjusting for age. FMD correlated with age (P <0.01) and systolic blood pressure (P =0.09). CIMT correlated with age (P <0.01), HbA1c (P =0.05), and gender (P <0.01).Conclusion The CVD risk is increased at the onset of type 2 diabetes. CIMT, FMD, and PWV along with the UKPDS risk engine should be considered to evaluate cardiovascular disease risk in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of cardiovascular risk estimate with degree of atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Mashkura Riyazuddeen, AliHasan Faiz Karnam, L Gopinath, Nayyar Iqbal
Journal of Current Research in Scientific Medicine.2019; 5(2): 94. CrossRef - Carotid atherosclerosis and its relationship to coronary heart disease and stroke risk in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yan Wu, Jie He, Xue Sun, Yi-Ming Zhao, Han-Yu Lou, Xiao-li Ji, Xiao-Hong Pang, Li-Zhen Shan, Ying-Xiu Kang, Jun Xu, Song-Zhao Zhang, Yong-Jian Wang, Yue-Zhong Ren, Peng-Fei Shan
Medicine.2017; 96(39): e8151. CrossRef - Diabetes Associated to Atherosclerosis Risk Factors in Patients of Family Health Unity
Polyane Medeiros Alves, Raiane dos Santos Pereira, Ariel Gustavo Letti, Álvaro Luís Müller da Fonseca
Open Journal of Preventive Medicine.2015; 05(04): 177. CrossRef - Independent Association of Circulating Level of Chemerin With Functional and Early Morphological Vascular Changes in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Bin Lu, Ming Zhao, Weimin Jiang, Jian Ma, Cuihua Yang, Jiaqing Shao, Ping Gu
Medicine.2015; 94(47): e1990. CrossRef - Assessment of Cardiovascular Risk in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes and Metabolic Syndrome
Chun-Ja Kim, Hee Sun Kang, Elizabeth A. Schlenk, Sun-Mi Chae
The Diabetes Educator.2015; 41(2): 203. CrossRef - Urinary adiponectin concentration is positively associated with micro- and macro-vascular complications
Won Seon Jeon, Ji Woo Park, Namseok Lee, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Won Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Woo Park, Cheol-Young Park, Byung-Soo Youn
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and a Pilot Test of an Internet-Based Cardiovascular Risk Reduction Program for Korean Male Workers With Metabolic Syndrome
CHUN-JA KIM, SEWON KANG
CIN: Computers, Informatics, Nursing.2013; 31(4): 157. CrossRef - Risk Factors for the Progression of Intima-Media Thickness of Carotid Arteries: A 2-Year Follow-Up Study in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes
Sang Ouk Chin, Jin Kyung Hwang, Sang Youl Rhee, Suk Chon, You-Cheol Hwang, Seungjoon Oh, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Jeong-taek Woo, Sung-Woon Kim, Young Seol Kim, Ja-Heon Kang, In-Kyung Jeong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(5): 365. CrossRef - Epicardial adipose tissue thickness is an indicator for coronary artery stenosis in asymptomatic type 2 diabetic patients: its assessment by cardiac magnetic resonance
Hyun Kim, Kwang Kim, Hye-Jeong Lee, Hee Yu, Jae Moon, Eun Kang, Bong Cha, Hyun Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Young Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2012; 11(1): 83. CrossRef - Potential association between coronary artery disease and the inflammatory biomarker YKL-40 in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hyun Min Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Young-Mi Song, Won Jin Kim, Hyuk-Jae Chang, Dong-Hoon Choi, Hee Tae Yu, EunSeok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2012;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association of cardiovascular risk estimate with degree of atherosclerosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Carotid Intimal-Medial Thickness Is Not Increased in Women with Previous Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Yun Hyi Ku, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Young Min Cho, Young Joo Park, Kyong Soo Park, Seong Yeon Kim, Hak Chul Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(5):497-503. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.5.497
- 3,569 View
- 39 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is known to increase the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Measuring the carotid artery intimal-medial thickness (CIMT) is a non-invasive technique used to evaluate early atherosclerosis and to predict future cardiovascular diseases. We examined the association between CIMT and cardiovascular risk factors in young Korean women with previous GDM.
Methods One hundred one women with previous GDM and 19 women who had normal pregnancies (NP) were recruited between 1999 and 2002. At one year postpartum, CIMT was measured using high-resolution B-mode ultrasonography, and oral glucose tolerance tests were performed. Fasting glucose, glycated hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c), insulin levels and lipid profiles were also measured. CIMTs in the GDM and NP groups were compared, and the associations between CIMT and cardiovascular risk factors were analyzed in the GDM group.
Results CIMT results of the GDM group were not significantly different from those of the NP group (GDM, 0.435±0.054 mm; NP, 0.460±0.046 mm;
P =0.069). In the GDM group, a higher HbA1c was associated with an increase in CIMT after age adjustment (P =0.011). CIMT results in the group with HbA1c >6.0% were higher than those of the normal HbA1c (HbA1c ≤6.0%) (P =0.010). Nine of the patients who are type 2 diabetes mellitus converters within one year postpartum but showed no significant difference in CIMT results compared to NP group.Conclusion Higher HbA1c is associated with an increase in CIMT in women with previous GDM. However, CIMT at one year postpartum was not increased in these women compared to that in NP women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The effect of gestational diabetes mellitus on carotid artery intima-media thickness in and after pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Andrea Sonaglioni, Elisabetta Piergallini, Angelo Naselli, Gian Luigi Nicolosi, Anna Ferrulli, Stefano Bianchi, Michele Lombardo, Giuseppe Ambrosio
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 61(2): 139. CrossRef - Prognostic indicators of persistent carotid intima-media thickness increase in postpartum period in a population of normotensive women with gestational diabetes mellitus
Andrea Sonaglioni, Gian Luigi Nicolosi, Valentina Esposito, Stefano Bianchi, Michele Lombardo
European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology.2022; 269: 47. CrossRef - Pharmacotherapy for gestational diabetes
Angelo Maria Patti, Rosaria Vincenza Giglio, Kalliopi Pafili, Manfredi Rizzo, Nikolaos Papanas
Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.2018; 19(13): 1407. CrossRef - Women with a history of gestational diabetes on long-term follow up have normal vascular function despite more dysglycemia, dyslipidemia and adiposity
Olubukola Ajala, Louise A. Jensen, Edmond Ryan, Constance Chik
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2015; 110(3): 309. CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Women: Similarities and Differences from Other Racial/Ethnic Groups
Catherine Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(1): 1. CrossRef - History of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus and Future Risk of Atherosclerosis in Mid‐life: The Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults Study
Erica P. Gunderson, Vicky Chiang, Mark J. Pletcher, David R. Jacobs, Charles P. Quesenberry, Stephen Sidney, Cora E. Lewis
Journal of the American Heart Association.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (GDM) with subclinical atherosclerosis: a systemic review and meta-analysis
Jing-Wei Li, Si-Yi He, Peng Liu, Lin Luo, Liang Zhao, Ying-Bin Xiao
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular Disease Risk in the Offspring of Diabetic Women: The Impact of the Intrauterine Environment
Laura J. Marco, Kate McCloskey, Peter J. Vuillermin, David Burgner, Joanne Said, Anne-Louise Ponsonby
Experimental Diabetes Research.2012; 2012: 1. CrossRef - The Association between Carotid Atherosclerosis and Glucose
Bo Kyung Koo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(5): 466. CrossRef
- The effect of gestational diabetes mellitus on carotid artery intima-media thickness in and after pregnancy: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Basal C-peptide Level as a Surrogate Marker of Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Sung-Tae Kim, Byung-Joon Kim, Dong-Mee Lim, In-Geol Song, Jang-Han Jung, Kang-Woo Lee, Keun-Young Park, Youn-Zoo Cho, Dae-Ho Lee, Gwan-Pyo Koh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(1):41-49. Published online February 28, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.1.41
- 4,026 View
- 37 Download
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Recent studies have revealed that C-peptide induces smooth muscle cell proliferation and causes human atherosclerotic lesions in diabetic patients. The present study was designed to examine whether the basal C-peptide levels correlate with cardiovascular risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients.
Methods Data was obtained from 467 patients with T2DM from two institutions who were followed for four years. The medical findings of all patients were reviewed, and patients with creatinine >1.4 mg/dL, any inflammation or infection, hepatitis, or type 1 DM were excluded. The relationships between basal C-peptide and other clinical values were statistically analyzed.
Results A simple correlation was found between basal C-peptide and components of metabolic syndrome (MS). Statistically basal C-peptide levels were significantly higher than the three different MS criteria used in the present study, the Adult Treatment Panel III (ATP III) of the National Cholesterol Education Program's (NCEP's), World Health Organization (WHO), and the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) criteria (NCEP-ATP III,
P =0.001; IDF,P <0.001; WHO,P =0.029). The multiple regression analysis between intima-media thickness (IMT) and clinical values showed that basal C-peptide significantly correlated with IMT (P =0.043), while the analysis between the 10-year coronary heart disease risk by the United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study risk engine and clinical values showed that basal C-peptide did not correlate with IMT (P =0.226).Conclusion Basal C-peptide is related to cardiovascular predictors (IMT) of T2DM, suggesting that basal C-peptide does provide a further indication of cardiovascular disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Correlation Between C-Peptide and Severity of Peripheral Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Maisa A Wahab, Alshaymaa Alhabibi, Ahmed Khairy Sakr, Mohamed Yahia Zakaria, Ola I Saleh, Inass Hassan Ahmad, Eman Abdelrahman, Randa Taha, Fayka Karem Abdel Azeem Ahmed, Bothayna Ismail, Lamiaa Hosney Azel, Asmaa S Hassan, Hanaa Mohammed Eid El Sayed, Sa
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 2617. CrossRef - Blood C‐peptide concentration as a proxy marker of cardiovascular disease: An observational cross‐sectional study
Laurinda Adusu‐Donkor, Emmanuel Kwaku Ofori, Fleischer C. N. Kotey, Francis Kwaku Dogodzi, Wormenor Dziedzorm, Alfred Buabeng, Segla Kwame Bernard, Seth K. Amponsah, Henry Asare‐Anane
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of insulin induced lipohypertrophy on carotid intima-media thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Cem Onur Kirac, Vehbi Sirikci, Huseyin Avni Findikli
Medicine.2023; 102(39): e34696. CrossRef - Effects of Serum C-Peptide Level on Blood Lipid and Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Injury in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis
Juan Qin, Rongli Sun, Ding Ding, Yuvaraja Teekaraman
Contrast Media & Molecular Imaging.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Correlation between serum C-peptide-releasing effects and the risk of elevated uric acid in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yanyan Liu, Xue Zhao, Zequn Yang, Shurui Wang, Cong Han, Huijuan Zhang
Endocrine Journal.2022; 69(7): 773. CrossRef - Human C-peptide is a ligand of the elastin-receptor-complex and therewith central to human vascular remodelling and disease in metabolic syndrome
Gert Wensvoort
Medical Hypotheses.2022; 168: 110964. CrossRef - Influence of blood glucose fluctuation, C-peptide level and conventional risk factors on carotid artery intima–media thickness in Chinese Han patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Min Liu, Li Ao, Xinyu Hu, Jianning Ma, Kena Bao, Ye Gu, Jing Zhao, Weiping Huang
European Journal of Medical Research.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum C peptide and carotid intima-medial thickness are independent markers of glucose intolerance among patients with ischemic cerebrovascular stroke
Nearmeen M. Rashad, Ghada M. Samir, Hanan M. Sabry, Nesreen M. Mohy, Shereen M. El Shabrawy
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2019; 31(3): 368. CrossRef - Biomarker potential of C-peptide for screening of insulin resistance in diabetic and non-diabetic individuals
Haseeb A. Khan, Samia H. Sobki, Aishah Ekhzaimy, Isra Khan, Mona A. Almusawi
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2018; 25(8): 1729. CrossRef - SERUM C-PEPTIDE LEVEL IN OBESE AND NON-OBESE PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
Shamha Beegum Mariyam, Saboora Beegum Muthubeevi, Sandhya Chandrasekharan Vasantha
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2017; 6(05): 350. CrossRef - Mechanisms of action and therapeutic potential of proinsulin C-peptide
A. O. Shpakov
Journal of Evolutionary Biochemistry and Physiology.2017; 53(3): 180. CrossRef - Hemolysis Affects C‐Peptide Immunoassay
Zhi‐Qi Wu, Ju Lu, Hua‐Guo Xu
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2016; 30(6): 1232. CrossRef - Lipid and inflammatory biomarker profiles in early insulin resistance
Itahisa Marcelino Rodríguez, José Oliva García, José Juan Alemán Sánchez, Delia Almeida González, Santiago Domínguez Coello, Buenaventura Brito Díaz, Fadoua Gannar, María del Cristo Rodríguez Pérez, Roberto Elosua, Antonio Cabrera de León
Acta Diabetologica.2016; 53(6): 905. CrossRef - C-Peptide Is Independently Associated with an Increased Risk of Coronary Artery Disease in T2DM Subjects: A Cross-Sectional Study
Lingshu Wang, Peng Lin, Aixia Ma, Huizhen Zheng, Kexin Wang, Wenjuan Li, Chuan Wang, Ruxing Zhao, Kai Liang, Fuqiang Liu, Xinguo Hou, Jun Song, Yiran Lu, Ping Zhu, Yu Sun, Li Chen, Marta Letizia Hribal
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(6): e0127112. CrossRef - C-peptide as a risk factor of coronary artery disease in the general population
Antonio Cabrera de León, José Gregorio Oliva García, Itahisa Marcelino Rodríguez, Delia Almeida González, José Juan Alemán Sánchez, Buenaventura Brito Díaz, Santiago Domínguez Coello, Vicente Bertomeu Martínez, Armando Aguirre Jaime, María del Cristo Rodr
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2015; 12(3): 199. CrossRef - Gender differences in the association of insulin resistance and high-sensitivity c-reactive protein in obese adolescents
Ramin Alemzadeh, Jessica Kichler
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Cytokinome Profile of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and/or Chronic Hepatitis C Infection
Susan Costantini, Francesca Capone, Eliana Guerriero, Raffaele Marfella, Angela Sorice, Patrizia Maio, Michele Di Stasio, Giuseppe Paolisso, Giuseppe Castello, Giovanni Colonna, Patricia Fitzgerald-Bocarsly
PLoS ONE.2012; 7(6): e39486. CrossRef - Serum glycated albumin predicts the progression of carotid arterial atherosclerosis
Sun Ok Song, Kwang Joon Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
Atherosclerosis.2012; 225(2): 450. CrossRef - C-Peptide: A New Mediator of Atherosclerosis in Diabetes
Dusica Vasic, Daniel Walcher
Mediators of Inflammation.2012; 2012: 1. CrossRef - Letter: Basal C-peptide Level as a Surrogate Marker of Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetes Patients (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:41-9)
Min Suk Lee, Hae Jin Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(2): 188. CrossRef - Response: Basal C-peptide Level as a Surrogate Marker of Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetic Patients (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:41-9)
Sung-Tae Kim, Byung-Joon Kim, Dong-Mee Lim, In-Geol Song, Jang-Han Jung, Kang-Woo Lee, Keun-Young Park, Youn-Zoo Cho, Dae-Ho Lee, Gwan-Pyo Koh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(2): 190. CrossRef
- The Correlation Between C-Peptide and Severity of Peripheral Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Is A1C Variability an Independent Predictor for the Progression of Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetic Patients?
- Chul Sik Kim, So Young Park, Sung Hoon Yu, Jun Goo Kang, Ohk Hyun Ryu, Seong Jin Lee, Eun Gyung Hong, Hyeon Kyu Kim, Doo-Man Kim, Jae Myung Yoo, Sung Hee Ihm, Moon Gi Choi, Hyung Joon Yoo
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(3):174-181. Published online June 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.3.174
- 4,243 View
- 29 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Little is known about the relative contribution of long-term glycemic variability to the risk of macrovascular complications in type 2 diabetes. This study was conducted to evaluate the effect of A1C variability on the progression of carotid artery intima-media thickness (IMT) in type 2 diabetic patients.
Methods Among type 2 diabetic patients who visited Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital from March 2007 to September 2009, 120 patients who had carotid artery IMT measured annually and A1C checked every three months for at least one year were analyzed. Individual A1C variability was defined as the standard deviation (SD) of five A1C levels taken every three months for approximately one year. Change in IMT was defined as an increase in IMT on follow-up measurement. The association between the SD of A1C and changes in IMT was evaluated.
Results With greater A1C variability, there was a greater increase in the mean IMT (
r = 0.350,P < 0.001) of the carotid artery. After adjusting for confounding factors that may influence IMT, A1C variability was significantly associated with the progression of IMT (r = 0.222,P = 0.034). However, the SD of A1C was not a significant independent risk factor for the progression of IMT in multiple regression analysis (β = 0.158,P = 0.093).Conclusion Higher A1C variability is associated with IMT progression in type 2 diabetic patients; however, it is not an independent predictor of IMT progression. Overall glycemic control is the most important factor in the progression of IMT.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Long-Term Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Among Type 2 Diabetes Patients According to Average and Visit-to-Visit Variations of HbA1c Levels During the First 3 Years of Diabetes Diagnosis
Hyunah Kim, Da Young Jung, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Hyeon Woo Yim, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Long-Term Visit-to-Visit Hemoglobin A1c and Cardiovascular Risk in Type 2 Diabetes: The ACCORD Trial
Dan Huang, Yong-Quan Huang, Qun-Ying Zhang, Yan Cui, Tian-Yi Mu, Yin Huang
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Longitudinal Values of Glycated Hemoglobin With Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Multivessel Coronary Artery Disease
Paulo Cury Rezende, Mark Andrew Hlatky, Whady Hueb, Rosa Maria Rahmi Garcia, Luciano da Silva Selistre, Eduardo Gomes Lima, Cibele Larrosa Garzillo, Thiago Luis Scudeler, Gustavo Andre Boeing Boros, Fernando Faglioni Ribas, Carlos Vicente Serrano, Jose An
JAMA Network Open.2020; 3(1): e1919666. CrossRef - Haemoglobin A1c variability as an independent correlate of atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease in Chinese type 2 diabetes
Yifei Mo, Jian Zhou, Xiaojing Ma, Wei Zhu, Lei Zhang, Jie Li, Jingyi Lu, Cheng Hu, Yuqian Bao, Weiping Jia
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2018; 15(5): 402. CrossRef - Relationship of HbA1c variability, absolute changes in HbA1c, and all-cause mortality in type 2 diabetes: a Danish population-based prospective observational study
Mette V Skriver, Annelli Sandbæk, Jette K Kristensen, Henrik Støvring
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2015; 3(1): e000060. CrossRef - Association between hemoglobin A1c variability and subclinical coronary atherosclerosis in subjects with type 2 diabetes
Hae Kyung Yang, Borami Kang, Seung-Hwan Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon, Byung-Hee Hwang, Kiyuk Chang, Kyungdo Han, Gunseog Kang, Jae Hyoung Cho
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2015; 29(6): 776. CrossRef - Glycated hemoglobin as a marker of subclinical atherosclerosis and cardiac remodeling among non-diabetic adults from the general population
Robin Haring, Sebastian E. Baumeister, Wolfgang Lieb, Bettina von Sarnowski, Henry Völzke, Stephan B. Felix, Matthias Nauck, Henri Wallaschofski
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2014; 105(3): 416. CrossRef - HbA1c Variability and Micro- and Macrovascular Complications of Diabetes
Hae Kyung Yang, Seung-Hwan Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2014; 15(4): 202. CrossRef - HbA1c variability and the development of microalbuminuria in type 2 diabetes: Tsukuba Kawai Diabetes Registry 2
A. Sugawara, K. Kawai, S. Motohashi, K. Saito, S. Kodama, Y. Yachi, R. Hirasawa, H. Shimano, K. Yamazaki, H. Sone
Diabetologia.2012; 55(8): 2128. CrossRef
- Long-Term Risk of Cardiovascular Disease Among Type 2 Diabetes Patients According to Average and Visit-to-Visit Variations of HbA1c Levels During the First 3 Years of Diabetes Diagnosis
- The Relationship Between Coronary Artery Calcification and Serum Apolipoprotein A-1 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.
- Hyun Ae Seo, Yeon Kyung Choi, Jae Han Jeon, Jung Eun Lee, Ji Yun Jeong, Seong Su Moon, In Kyu Lee, Bo Wan Kim, Jung Guk Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(6):485-493. Published online December 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.6.485
- 2,423 View
- 20 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The incidence of type 2 diabetes mellitus is increasing annually and patient mortality is high. Coronary artery calcification is a predictor of coronary artery disease. Cardiovascular events, which are the main cause of death in type 2 diabetes patients, may be preventable by addressing risk factors associated with coronary artery calcification. We examined the relationships between coronary artery calcification, lipid profiles, and apolipoprotein levels. METHODS: We calculated the coronary calcium scores (CCS) of 254 subjects with type 2 diabetes (113 males, 141 females) via multi-detector row computed tomography (MDCT). Height, body weight, blood pressure, HbA1c, c-peptide, lipid profile and apolipoprotein were assessed concurrently. RESULTS: In patients with type 2 diabetes, Agatston score and apolipoprotein A-1 were significantly negatively correlated in both males and females (males P = 0.015, females P = 0.021). The negative correlation between Agatston score and apolipoprotein A-1 was retained for the entire patient sample after adjustments for age and sex (P = 0.022). Stepwise multiple regression anaylses with the Agatston score as the dependent variable indicate that apolipoprotein A-1 is a independent predictor (beta coefficient = -0.047, 95%CI = -0.072 ~ -0.021, P < 0.001) of coronary artery calcification. CONCLUSION: The results of our study suggest that apolipoprotein A-1 is a useful independent indicator of coronary artery calcification. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Risk of Coronary Artery Calcification according to Different Lipid Parameters and Average Lipid Parameters
Tae Kyung Yoo, Mi Yeon Lee, Ki-Chul Sung
Journal of Atherosclerosis and Thrombosis.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronary Artery Calcification and Serum Apolipoprotein A-1 in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Ki Won Oh
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(6): 464. CrossRef
- The Risk of Coronary Artery Calcification according to Different Lipid Parameters and Average Lipid Parameters

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





