
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Psychotic Disorders and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases, and All-Cause Mortality: A Population-Based Matched Cohort Study
- You-Bin Lee, Hyewon Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Dongwoo Kang, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim, Hong Jin Jeon, Kyu Yeon Hur
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):122-133. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0431
- 1,115 View
- 144 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The effects of psychotic disorders on cardiometabolic diseases and premature death need to be determined in Asian populations.
Methods
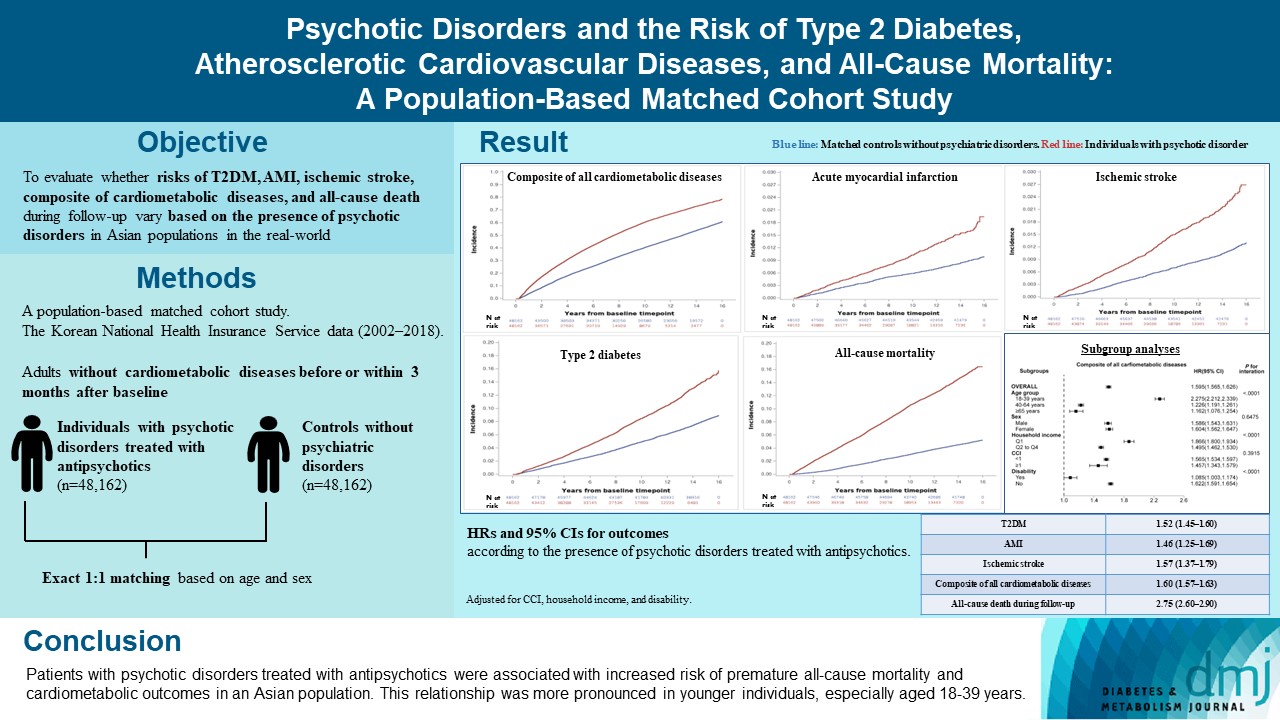
In this population-based matched cohort study, the Korean National Health Insurance Service database (2002 to 2018) was used. The risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), acute myocardial infarction (AMI), ischemic stroke, composite of all cardiometabolic diseases, and all-cause death during follow-up was compared between individuals with psychotic disorders treated with antipsychotics (n=48,162) and 1:1 matched controls without psychiatric disorders among adults without cardiometabolic diseases before or within 3 months after baseline.
Results
In this cohort, 53,683 composite cases of all cardiometabolic diseases (during median 7.38 years), 899 AMI, and 1,216 ischemic stroke cases (during median 14.14 years), 7,686 T2DM cases (during median 13.26 years), and 7,092 deaths (during median 14.23 years) occurred. The risk of all outcomes was higher in subjects with psychotic disorders than matched controls (adjusted hazard ratios [95% confidence intervals]: 1.522 [1.446 to 1.602] for T2DM; 1.455 [1.251 to 1.693] for AMI; 1.568 [1.373 to 1.790] for ischemic stroke; 1.595 [1.565 to 1.626] for composite of all cardiometabolic diseases; and 2.747 [2.599 to 2.904] for all-cause mortality) during follow-up. Similar patterns of associations were maintained in subgroup analyses but more prominent in younger individuals (P for interaction <0.0001) when categorized as those aged 18–39, 40–64, or ≥65 years.
Conclusion
Patients with psychotic disorders treated with antipsychotics were associated with increased risk of premature allcause mortality and cardiometabolic outcomes in an Asian population. This relationship was more pronounced in younger individuals, especially aged 18 to 39 years.
- Complications
- Impact of Hyperglycemia on Complication and Mortality after Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Sun Joon Moon, Chang Ho Ahn, Yun Bin Lee, Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):302-311. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0255
- 777 View
- 114 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Current guidelines regarding periprocedural glycemic control to prevent complications after nonsurgical invasive procedures are insufficient. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a widely used treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. We aimed to investigate the association between diabetes mellitus (DM) per se and the degree of hyperglycemia with postprocedural complications after TACE.
Methods
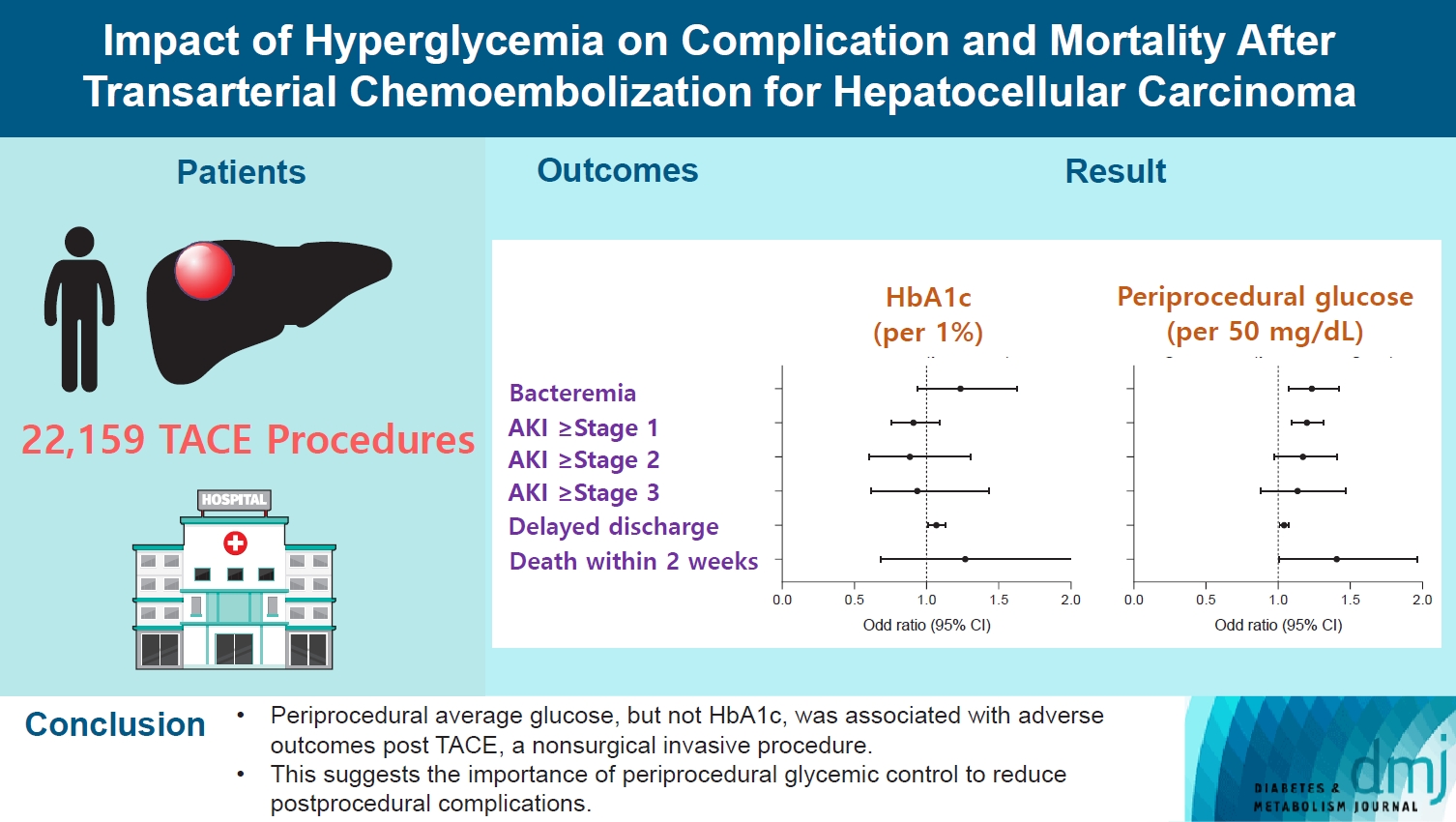
A total of 22,159 TACE procedures performed at Seoul National University Hospital from 2005 to 2018 were retrospectively analyzed. The associations between DM, preprocedural glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and periprocedural average glucose with postprocedural adverse outcomes were evaluated. The primary outcome was occurrence of postprocedural bacteremia. Secondary outcomes were acute kidney injury (AKI), delayed discharge and death within 14 days. Periprocedural glucose was averaged over 3 days: the day of, before, and after the TACE procedures. Propensity score matching was applied for procedures between patients with or without DM.
Results
Periprocedural average glucose was significantly associated with bacteremia (adjusted odds ratio per 50 mg/dL of glucose, 1.233; 95% confidence interval, 1.071 to 1.420; P=0.004), AKI, delayed discharge, and death within 14 days. DM per se was only associated with bacteremia and AKI. Preprocedural HbA1c was associated with delayed discharge. Average glucose levels above 202 and 181 mg/dL were associated with a significantly higher risk of bacteremia and AKI, respectively, than glucose levels of 126 mg/dL or lower.
Conclusion
Periprocedural average glucose, but not HbA1c, was associated with adverse outcomes after TACE, which is a nonsurgical invasive procedure. This suggests the importance of periprocedural glycemic control to reduce postprocedural complications.
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Low Household Income Status and Death from Pneumonia in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Study
- You-Bin Lee, So Hee Park, Kyu-na Lee, Bongsung Kim, So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Kyungdo Han, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(5):682-692. Published online June 22, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0184
- 1,608 View
- 121 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We explored the risk of death from pneumonia according to cumulative duration in low household income state (LHIS) among adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
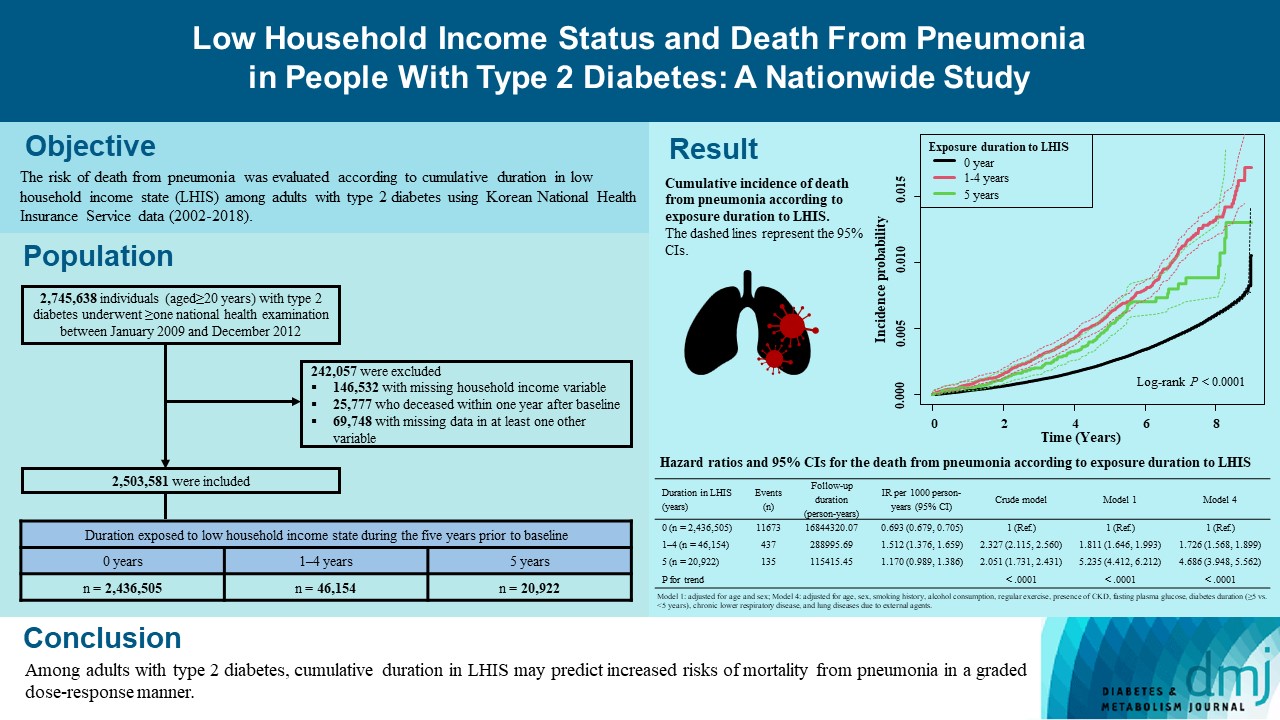
Using Korean National Health Insurance Service data (2002 to 2018), the hazards of mortality from pneumonia were analyzed according to duration in LHIS (being registered to Medical Aid) during the 5 years before baseline (0, 1–4, and 5 years) among adults with T2DM who underwent health examinations between 2009 and 2012 (n=2,503,581). Hazards of outcomes were also compared in six groups categorized by insulin use and duration in LHIS.
Results
During a median 7.18 years, 12,245 deaths from pneumonia occurred. Individuals who had been exposed to LHIS had higher hazards of death from pneumonia in a dose-response manner (hazard ratio [HR], 1.726; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.568 to 1.899 and HR, 4.686; 95% CI, 3.948 to 5.562 in those exposed for 1–4 and 5 years, respectively) compared to the non-exposed reference. Insulin users exposed for 5 years to LHIS exhibited the highest outcome hazard among six groups categorized by insulin use and duration in LHIS.
Conclusion
Among adults with T2DM, cumulative duration in LHIS may predict increased risks of mortality from pneumonia in a graded dose-response manner. Insulin users with the longest duration in LHIS might be the group most vulnerable to death from pneumonia among adults with T2DM.
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Intensified Multifactorial Intervention in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Takayoshi Sasako, Toshimasa Yamauchi, Kohjiro Ueki
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):185-197. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0325
- 5,100 View
- 358 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
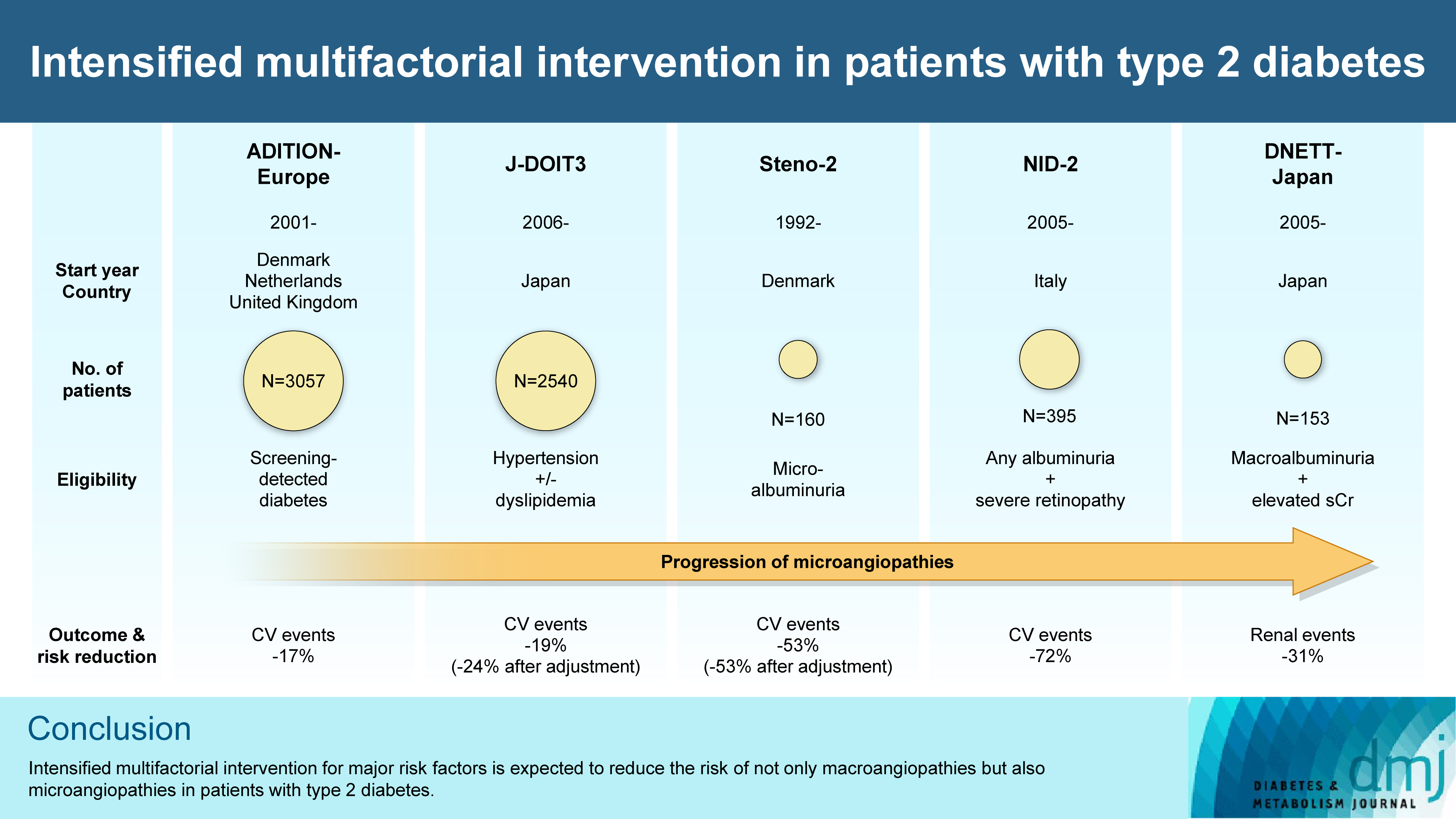
ePub - In the management of diabetes mellitus, one of the most important goals is to prevent its micro- and macrovascular complications, and to that end, multifactorial intervention is widely recommended. Intensified multifactorial intervention with pharmacotherapy for associated risk factors, alongside lifestyle modification, was first shown to be efficacious in patients with microalbuminuria (Steno-2 study), then in those with less advanced microvascular complications (the Anglo-Danish-Dutch Study of Intensive Treatment In People with Screen Detected Diabetes in Primary Care [ADDITION]-Europe and the Japan Diabetes Optimal Treatment study for 3 major risk factors of cardiovascular diseases [J-DOIT3]), and in those with advanced microvascular complications (the Nephropathy In Diabetes-Type 2 [NID-2] study and Diabetic Nephropathy Remission and Regression Team Trial in Japan [DNETT-Japan]). Thus far, multifactorial intervention led to a reduction in cardiovascular and renal events, albeit not necessarily significant. It should be noted that not only baseline characteristics but also the control status of the risk factors and event rates during intervention among the patients widely varied from one trial to the next. Further evidence is needed for the efficacy of multifactorial intervention in a longer duration and in younger or elderly patients. Moreover, now that new classes of antidiabetic drugs are available, it should be addressed whether strict and safe glycemic control, alongside control of other risk factors, could lead to further risk reductions in micro- and macrovascular complications, thereby decreasing all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring mechanisms underlying diabetes comorbidities and strategies to prevent vascular complications
Takayoshi Sasako
Diabetology International.2024; 15(1): 34. CrossRef - Targeting ERS-mitophagy in hippocampal neurons to explore the improvement of memory by tea polyphenols in aged type 2 diabetic rats
Wenjuan Feng, Chenhui Lv, Le Cheng, Xin Song, Xuemin Li, Haoran Xie, Shuangzhi Chen, Xi Wang, Lushan Xue, Cheng Zhang, Jie Kou, Lili Wang, Haifeng Zhao
Free Radical Biology and Medicine.2024; 213: 293. CrossRef - Risk of Dementia Among Patients With Diabetes in a Multidisciplinary, Primary Care Management Program
Kailu Wang, Shi Zhao, Eric Kam-Pui Lee, Susan Zi-May Yau, Yushan Wu, Chi-Tim Hung, Eng-Kiong Yeoh
JAMA Network Open.2024; 7(2): e2355733. CrossRef - Causes of In-Hospital Death and Pharmaceutical Associations with Age of Death during a 10-Year Period (2011–2020) in Individuals with and without Diabetes at a Japanese Community General Hospital
Minae Hosoki, Taiki Hori, Yousuke Kaneko, Kensuke Mori, Saya Yasui, Seijiro Tsuji, Hiroki Yamagami, Saki Kawata, Tomoyo Hara, Shiho Masuda, Yukari Mitsui, Kiyoe Kurahashi, Takeshi Harada, Shingen Nakamura, Toshiki Otoda, Tomoyuki Yuasa, Akio Kuroda, Itsur
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(5): 1283. CrossRef - External validation of a minimal-resource model to predict reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate in people with type 2 diabetes without diagnosis of chronic kidney disease in Mexico: a comparison between country-level and regional performance
Camilla Sammut-Powell, Rose Sisk, Ruben Silva-Tinoco, Gustavo de la Pena, Paloma Almeda-Valdes, Sonia Citlali Juarez Comboni, Susana Goncalves, Rory Cameron
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Gut Microbiota Targeted Approach by Natural Products in Diabetes Management: An Overview
Priyanka Sati, Praveen Dhyani, Eshita Sharma, Dharam Chand Attri, Arvind Jantwal, Rajni Devi, Daniela Calina, Javad Sharifi-Rad
Current Nutrition Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Type 2 Diabetes: Further Insights into the Power of Weight Loss and Exercise
Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(3): 302. CrossRef - Sarcopenia: Loss of mighty armor against frailty and aging
Takayoshi Sasako, Kohjiro Ueki
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(10): 1145. CrossRef
- Exploring mechanisms underlying diabetes comorbidities and strategies to prevent vascular complications
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study
- Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):220-231. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0327

- 65,535 View
- 282 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We investigated whether metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) is associated with an elevated risk of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality using a large-scale health examination cohort.
Methods
A total of 394,835 subjects in the Kangbuk Samsung Health Study cohort were enrolled from 2002 to 2012. Participants were categorized by the presence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and MAFLD as follows: normal subjects; patients with both NAFLD and MAFLD; patients with NAFLD only; and patients with MAFLD only. Cox proportional hazards models were used to analyze the risk of mortality.
Results
During a median 5.7 years of follow-up, 20.69% was patients with both NAFLD and MAFLD, 1.51% was patients with NAFLD only, and 4.29% was patients with MAFLD only. All-cause and cardiovascular death was higher in patients with MAFLD than those without MAFLD (P<0.001, respectively). In patients with MAFLD only, the hazard ratio (HR) of all-cause and cardiovascular death was 1.35 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.13 to 1.60) and 1.90 (95% CI, 1.26 to 2.88) after adjusting for age, which lost its statistical significance by multivariable adjustments. Compared to patients with less than two components of metabolic dysfunction, patients with more than two components of metabolic dysfunction were a higher risk of cardiovascular death (HR, 2.05; 95% CI, 1.25 to 3.38) and only women with more than two components of metabolic dysfunction were a higher risk of all-cause death (HR, 1.44; 95% CI, 1.02 to 2.03).
Conclusion
MAFLD criteria could identify a high-risk group for all-cause and cardiovascular death. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Eugene Han, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Sang Hoon Ahn, Yong-ho Lee, Seung Up Kim
Metabolism.2024; 152: 155789. CrossRef - Association of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with cardiovascular disease and all cause death in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: nationwide population based study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
BMJ.2024; : e076388. CrossRef - Sex differences in mortality and liver‐related events in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Huimin Zhou, Haiyan Chen, Hanxiao Lu, Bo Wu, Shuo Zhang, Yuanlong Gu, Guangwen Zhou, Jie Xiang, Jun Yang
Liver International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between dietary carbohydrate to fiber ratio and metabolic dysfunction associated fatty liver disease in adults: evidence from the NHANES 2017–2020
Zhenmin Liu, Taiyong Fang
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Outcomes Between Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis
Ghazala S Virk, Jaahnavi Vajje, Nausheen K Virk, Raam Mannam, Wajeeh Rehman, Naglaa G Ghobriel , Irfan-ud-din Mian, Muhammad Usama
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in prevalence and all-cause mortality of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease among adults in the past three decades: Results from the NHANES study
Zhi-Qin Xie, Hong-Xia Li, Bing-Kun Wang, Zhao-Ming Yang, Zi-Yu Zhang, Wen-Liang Tan, Wen-Xin Li, Qing-Bin Wang, Lei Yang, Hong-Kai Zhuang, Chen-Wei Tang, Chang-Zhen Shang, Ya-Jin Chen
European Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 110: 62. CrossRef - Comparing the Mortality Risk between Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Han Na Jung, Chang Hee Jung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 198. CrossRef - Increased expression of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 and O-GlcNAcylation in hepatocytes drives non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Hye Jin Chun, Eun Ran Kim, Minyoung Lee, Da Hyun Choi, Soo Hyun Kim, Eugene Shin, Jin-Hong Kim, Jin Won Cho, Dai Hoon Han, Bong-Soo Cha, Yong-ho Lee
Metabolism.2023; 145: 155612. CrossRef - Current understanding and future perspectives on the impact of changing NAFLD to MAFLD on global epidemiology and clinical outcomes
Karl Vaz, Daniel Clayton-Chubb, Ammar Majeed, John Lubel, David Simmons, William Kemp, Stuart K. Roberts
Hepatology International.2023; 17(5): 1082. CrossRef - Mitochondrial Quality Control: Its Role in Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease (MASLD)
Soyeon Shin, Jaeyoung Kim, Ju Yeon Lee, Jun Kim, Chang-Myung Oh
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(4): 289. CrossRef
- Mortality in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Myocardial Infarction, Stroke, and All-Cause Mortality according to Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level in the Elderly, a Nationwide Study
- You-Bin Lee, Minji Koo, Eunjin Noh, Soon Young Hwang, Jung A Kim, Eun Roh, So-hyeon Hong, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):722-732. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0225
- 7,014 View
- 331 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We assessed the myocardial infarction (MI), stroke, and all-cause death risks during follow-up according to the low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) levels among older adults.
Methods
The Korean National Health Insurance Service datasets (2002 to 2020) were used for this population-based cohort study. The hazards of MI, stroke, and all-cause mortality during follow-up were analyzed according to LDL-C level in individuals aged ≥65 years without baseline cardiovascular diseases (n=1,391,616).
Results
During a mean 7.55 years, 52,753 MIs developed; 84,224 strokes occurred over a mean 7.47 years. After a mean 8.50 years, 233,963 died. A decrease in LDL-C was associated with lower hazards of MI and stroke. The decreased hazard of stroke in lower LDL-C was more pronounced in statin users, and individuals with diabetes or obesity. The hazard of all-cause death during follow-up showed an inverted J-shaped pattern according to the LDL-C levels. However, the paradoxically increased hazard of mortality during follow-up in lower LDL-C was attenuated in statin users and individuals with diabetes, hypertension, or obesity. In statin users, lower LDL-C was associated with a decreased hazard of mortality during follow-up.
Conclusion
Among the elderly, lower LDL-C was associated with decreased risks of MI and stroke. Lower LDL-C achieved by statins in the elderly was associated with a decreased risk of all-cause death during follow-up, suggesting that LDL-C paradox for the premature death risk in the elderly should not be applied to statin users. Intensive statin therapy should not be hesitated for older adults with cardiovascular risk factors including diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combination of low- or moderate-intensity statin and ezetimibe vs. high-intensity statin monotherapy on primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and all-cause death: a propensity-matched nationwide cohort study
Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, You-Cheol Hwang
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of Low-density Lipoprotein Cholesterol With All-cause and Cause-specific Mortality in Older Adults in China
Wenqing Ni, Yuebin Lv, Xueli Yuan, Yan Zhang, Hongmin Zhang, Yijing Zheng, Xiaoming Shi, Jian Xu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and all-cause or cardiovascular mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes: a retrospective study
Chin-Huan Chang, Shu-Tin Yeh, Seng-Wei Ooi, Chung-Yi Li, Hua-Fen Chen
PeerJ.2023; 11: e14609. CrossRef - ERCC1 polymorphism and its expression associated with ischemic stroke in Chinese population
Xiao-Dong Deng, Jian-Lin Ke, Tai-Yu Chen, Qin Gao, Zhuo-Lin Zhao, Wei Zhang, Huan Liu, Ming-Liang Xiang, Li-Zhen Wang, Ying Ma, Yun Liu
Frontiers in Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - New, Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Statins
Kyuho Kim, Henry N. Ginsberg, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 517. CrossRef - Association between the Diabetes Drug Cost and Cardiovascular Events and Death in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
Seung Min Chung, Ji-In Lee, Eugene Han, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eonju Jeon, Hye Soon Kim, Ji Sung Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 759. CrossRef
- Combination of low- or moderate-intensity statin and ezetimibe vs. high-intensity statin monotherapy on primary prevention of cardiovascular disease and all-cause death: a propensity-matched nationwide cohort study
- Complications
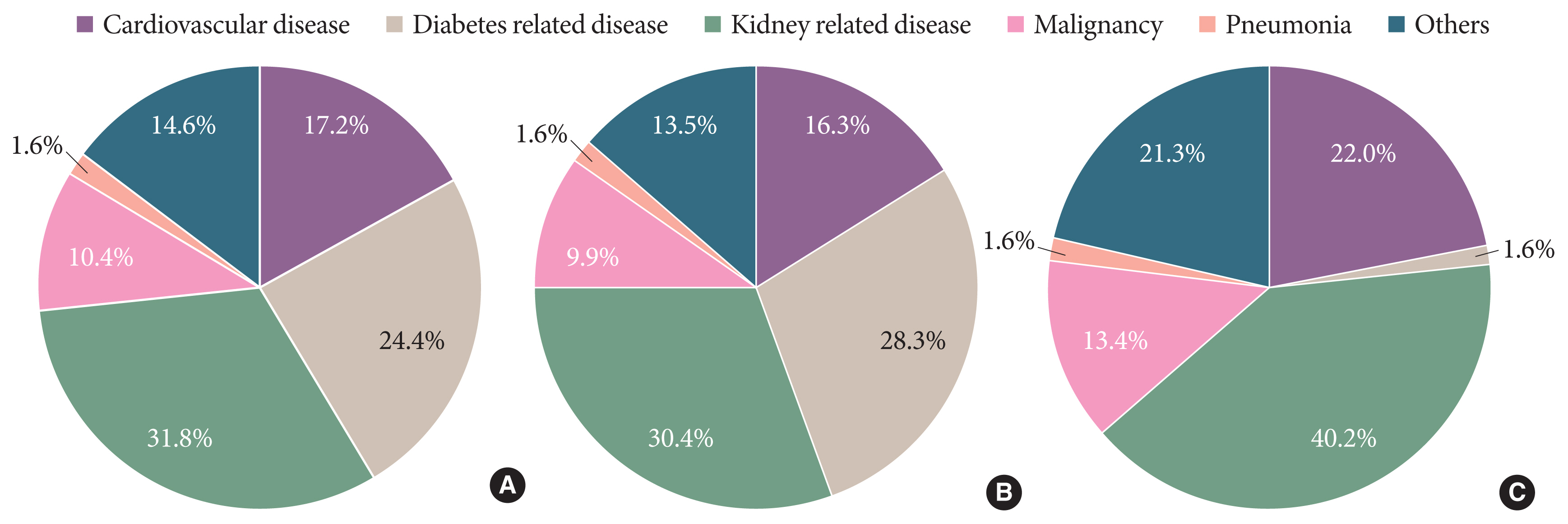
- Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence, and Mortality of End-Stage Kidney Disease in South Korea
- Min-Jeong Lee, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Inwhee Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):933-937. Published online December 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0156
- 5,833 View
- 239 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Knowledge of the epidemiologic characteristics of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) patients is essential. The trends in the prevalence, incidence, and mortality rates of ESKD were analyzed retrospectively using the Korean National Health Insurance ServiceNational Sample Cohort database between 2006 and 2015. From 2006 to 2015, the incidence of ESKD decreased from 28.6 to 24.0 per 100,000 people and showed a decreasing pattern with or without diabetes mellitus. However, the incidence of those aged ≥75 years increased, as did the mean age at the onset of ESKD. From 2007 to 2015, the prevalence of ESKD increased in all age groups, but particularly in those aged ≥75 years. The prevalence of ESKD differed by sex and diabetes mellitus status and this gap widened over time. Mortality rates in ESKD patients remained relatively constant throughout the study period. However, mortality rates in ESKD without diabetes decreased over the same period.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Kidney Health Plan 2033 in Korea: bridging the gap between the present and the future
Do Hyoung Kim, Young Youl Hyun, Jin Joo Cha, Sua Lee, Hyun Kyung Lee, Jong Wook Choi, Su-Hyun Kim, Sang Youb Han, Cheol Whee Park, Eun Young Lee, Dae Ryong Cha, Sung Gyun Kim, Chun Soo Lim, Sun-Hee Park
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 43(1): 8. CrossRef - Remnant cholesterol is an independent risk factor for the incidence of chronic kidney disease in newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population-based study
Soo Yeon Jang, Minwoong Kang, Eyun Song, Ahreum Jang, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111639. CrossRef - Waist circumference and end‐stage renal disease based on glycaemic status: National Health Insurance Service data 2009–2018
Yun Kyung Cho, Ji Hye Huh, Shinje Moon, Yoon Jung Kim, Yang‐Hyun Kim, Kyung‐do Han, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung‐Hee Ihm
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(1): 585. CrossRef - Usefulness of continuous glucose monitoring of blood glucose control in patients with diabetes undergoing hemodialysis: A pilot study
Sua Lee, Soyoung Lee, Kyeong Min Kim, Jong Ho Shin
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between N-Terminal Prohormone Brain Natriuretic Peptide and Decreased Skeletal Muscle Mass in a Healthy Adult Population: A Cross-Sectional Study
Tae Kyung Yoo, Marie Yung-Chen Wu, Moon Soo Kim, Mi-Yeon Lee, Yong-Taek Lee, Kyung Jae Yoon, Chul-Hyun Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 269. CrossRef - Age at Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Who Underwent Kidney Transplantation: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Sun Ok Song, Eugene Han, Kang Ju Son, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3160. CrossRef - Epigenome-wide association study of diabetic chronic kidney disease progression in the Korean population: the KNOW-CKD study
Hye Youn Sung, Sangjun Lee, Miyeun Han, Woo Ju An, Hyunjin Ryu, Eunjeong Kang, Yong Seek Park, Seung Eun Lee, Curie Ahn, Kook-Hwan Oh, Sue K. Park, Jung-Hyuck Ahn
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Dapagliflozin in Asian Patients With Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction in DAPA-HF
Kieran F. Docherty, Inder S. Anand, Chern-En Chiang, Vijay K. Chopra, Akshay S. Desai, Masafumi Kitakaze, Subodh Verma, Pham N. Vinh, Silvio E. Inzucchi, Lars Køber, Mikhail N. Kosiborod, Felipe A. Martinez, Olof Bengtsson, Piotr Ponikowski, Marc S. Sabat
JACC: Asia.2022; 2(2): 139. CrossRef - Glomerular filtration rate as a kidney outcome of diabetic kidney disease: a focus on new antidiabetic drugs
Hyo Jin Kim, Sang Soo Kim, Sang Heon Song
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 37(3): 502. CrossRef - The risk of Parkinson's disease according to diabetic kidney disease status in a Korean population
Seung Eun Lee, Juhwan Yoo, Han Seok Choi, Kyungdo Han, Kyoung-Ah Kim
Parkinsonism & Related Disorders.2022; 100: 13. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - The Incidence and Risk Factors of Renal Insufficiency among Korean HIV infected Patients: The Korea HIV/AIDS Cohort Study
Jun Hyoung Kim, Heeseon Jang, Jung Ho Kim, Joon Young Song, Shin-Woo Kim, Sang Il Kim, Bo Youl Choi, Jun Yong Choi
Infection & Chemotherapy.2022; 54(3): 534. CrossRef - Sex difference in the association among nutrition, muscle mass, and strength in peritoneal dialysis patients
Jun Young Do, Seok Hui Kang
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Additive interaction of diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease in cancer patient mortality risk
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Kidney Health Plan 2033 in Korea: bridging the gap between the present and the future
- Complications
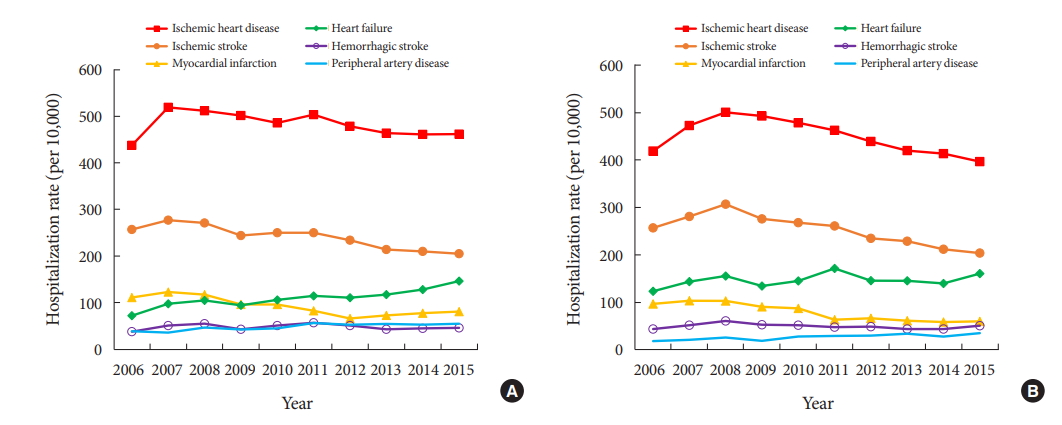
- Trends in Cardiovascular Complications and Mortality among Patients with Diabetes in South Korea
- Jung Hwan Park, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Bo Yeon Kim, Jae Hyuk Lee, Dae Jung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):120-124. Published online December 9, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0175
- Correction in: Diabetes Metab J 2021;45(2):283
- 11,798 View
- 352 Download
- 32 Web of Science
- 37 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- We investigated the cardiovascular complications and mortality rates of patients with diabetes in South Korea. The rates of hospitalization due to cardiovascular complications and mortality were analyzed using the Korean National Health Insurance Service-National Sample Cohort. From 2006 to 2015, the rates of hospitalization due to major cardiovascular complications decreased, while those due to heart failure (from 72 to 146 and 124 to 161 per 10,000 men and women, respectively) and peripheral artery disease (from 39 to 55 and 19 to 35 per 10,000 men and women, respectively) increased. In the period 2007 to 2015, the mortality rates for cancer, cerebrovascular disease, diabetes, heart disease, and hypertensive disease all decreased. However, the mortality rate for pneumonia increased. We observed a continuous reduction in cardiovascular complications and mortality in adults with diabetes. However, with the increase in some diabetes complications, more efforts are needed to prevent diabetes complications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Do Kyeong Song, Young Sun Hong, Yeon-Ah Sung, Hyejin Lee, Hidetaka Hamasaki
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0299035. CrossRef - Remnant cholesterol is an independent risk factor for the incidence of chronic kidney disease in newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population-based study
Soo Yeon Jang, Minwoong Kang, Eyun Song, Ahreum Jang, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111639. CrossRef - Global trends in the incidence of hospital admissions for diabetes-related foot disease and amputations: a review of national rates in the 21st century
Peter A. Lazzarini, Susanna M. Cramb, Jonathan Golledge, Jedidiah I. Morton, Dianna J. Magliano, Jaap J. Van Netten
Diabetologia.2023; 66(2): 267. CrossRef - Inequalities in cancer mortality trends in people with type 2 diabetes: 20 year population-based study in England
Suping Ling, Francesco Zaccardi, Eyad Issa, Melanie J. Davies, Kamlesh Khunti, Karen Brown
Diabetologia.2023; 66(4): 657. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Empagliflozin is associated with lower risk of cardiovascular events and all‐cause mortality in routine care in East Asia: Results from the EMPRISE study
Dae Jung Kim, Wayne H‐H Sheu, Wook‐Jin Chung, Daisuke Yabe, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Masaomi Nangaku, Elise Chia‐Hui Tan, Koichi Node, Atsutaka Yasui, Weiyu Lei, Sunwoo Lee, Laura Saarelainen, Anouk Deruaz‐Luyet, Moe H Kyaw, Yutaka Seino
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(3): 417. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - The effect of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and diabetic kidney disease on the risk of hospitalization of heart failure in type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study
Seung Eun Lee, Juhwan Yoo, Bong-Seong Kim, Han Seok Choi, Kyungdo Han, Kyoung-Ah Kim
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Operational Definition of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Data from Korean National Health Insurance Service and Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Jong Ha Baek, Yong-Moon Park, Kyung Do Han, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Han Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 201. CrossRef - Chronic disease management program applied to type 2 diabetes patients and prevention of diabetic complications: a retrospective cohort study using nationwide data
Min Kyung Hyun, Jang Won Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Present and Future of Artificial Intelligence-Based Medical Image in Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Analytical Methods and Limitations of Clinical Use
Ji-Won Chun, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Echocardiography in Evaluating Cardiovascular Diseases in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Sun Hwa Lee, Jae-Hyeong Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(4): 470. CrossRef - Long-term Effectiveness of the National Diabetes Quality Assessment Program in South Korea
Ji Hye Huh, Serim Kwon, Gui Ok Kim, Bo Yeon Kim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(9): 1700. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Ye Seul Yang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 135. CrossRef - Interpreting global trends in type 2 diabetes complications and mortality
Mohammed K. Ali, Jonathan Pearson-Stuttard, Elizabeth Selvin, Edward W. Gregg
Diabetologia.2022; 65(1): 3. CrossRef - Cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Ja Young Jeon, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(4): 614. CrossRef - Effects of physical activity on cardiovascular outcomes and mortality in Korean patients with diabetes: a nationwide population-based cohort study
Inha Jung, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(1): 42. CrossRef - Editorial: Management of Diabetes and its Complications: A Focus on Endothelial Dysfunction
Shanhu Qiu, Jianhua Ma, Tongzhi Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Smoking, Metabolic Syndrome, and Cardiovascular Disease
Seo Young Kang
Korean Journal of Family Practice.2022; 12(2): 59. CrossRef - Cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus: progress toward personalized management
Cheng-Xu Ma, Xiao-Ni Ma, Cong-Hui Guan, Ying-Dong Li, Dídac Mauricio, Song-Bo Fu
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Adherence to healthy lifestyle behaviors as a preventable risk factor for severe hypoglycemia in people with type 2 diabetes: A longitudinal nationwide cohort study
Jae‐Seung Yun, Kyungdo Han, Yong‐Moon Park, Eugene Han, Yong‐ho Lee, Seung‐Hyun Ko
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(9): 1533. CrossRef - Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 464. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2021
Jae Hyun Bae, Kyung-Do Han, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ye Seul Yang, Jong Han Choi, Kyung Mook Choi, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 417. CrossRef - Advanced Glycation End Products and Their Effect on Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jeongmin Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3086. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - Association between carotid atherosclerosis and presence of intracranial atherosclerosis using three-dimensional high-resolution vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging in asymptomatic patients with type 2 diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, You-Cheol Hwang, Kyu Jeong Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung, Geon-Ho Jahng, Soonchan Park, In-Kyung Jeong, Chang-Woo Ryu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110067. CrossRef - Blood Pressure Target in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hyun-Jin Kim, Kwang-il Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 667. CrossRef - Fenofibrate add-on to statin treatment is associated with low all-cause death and cardiovascular disease in the general population with high triglyceride levels
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Metabolism.2022; 137: 155327. CrossRef - Trends in diabetes-related complications in Singapore, 2013–2020: A registry-based study
Joshua Kuan Tan, Nur Nasyitah Mohamed Salim, Gek Hsiang Lim, Sing Yi Chia, Julian Thumboo, Yong Mong Bee, Ferdinando Carlo Sasso
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(10): e0275920. CrossRef - Association between the Diabetes Drug Cost and Cardiovascular Events and Death in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
Seung Min Chung, Ji-In Lee, Eugene Han, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eonju Jeon, Hye Soon Kim, Ji Sung Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 759. CrossRef - Impact of hypoglycemia at the time of hospitalization for heart failure from emergency department on major adverse cardiovascular events in patients with and without type 2 diabetes
Seon-Ah Cha, Jae-Seung Yun, Gee-Hee Kim, Yu-Bae Ahn
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Heart Failure and Diabetes Mellitus: Dangerous Liaisons
Hae-Young Lee
International Journal of Heart Failure.2022; 4(4): 163. CrossRef - Diabetes and Stroke
Junghyun Noh
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(1): 26. CrossRef - Current trends in epidemiology of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular risk management in type 2 diabetes
Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Metabolism.2021; 123: 154838. CrossRef
- Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- COVID-19
-
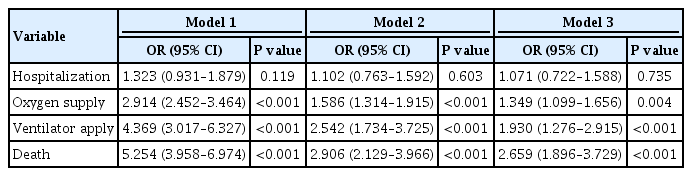
- Independent Impact of Diabetes on the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 5,307 Patients in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
- Sun Joon Moon, Eun-Jung Rhee, Jin-Hyung Jung, Kyung-Do Han, Sung-Rae Kim, Won-Young Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):737-746. Published online October 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0141
- 10,618 View
- 201 Download
- 24 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Inconsistent results have been observed regarding the independent effect of diabetes on the severity of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). We conducted a nationwide population-based cohort study to evaluate the relationship between diabetes and COVID-19 severity in South Korea.
Methods
Patients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19 aged ≥30 years were enrolled and medical claims data were obtained from the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service. Hospitalization, oxygen treatment, ventilator application, and mortality were assessed as severity outcomes. Multivariate logistic regression analyses were performed after adjusting for age, sex, and comorbidities.
Results
Of 5,307 COVID-19 patients, the mean age was 56.0±14.4 years, 2,043 (38.5%) were male, and 770 (14.5%) had diabetes. The number of patients who were hospitalized, who received oxygen, who required ventilator support, and who died was 4,986 (94.0%), 884 (16.7%), 121 (2.3%), and 211 (4.0%), respectively. The proportion of patients with diabetes in the abovementioned outcome groups was 14.7%, 28.1%, 41.3%, 44.6%, showing an increasing trend according to outcome severity. In multivariate analyses, diabetes was associated with worse outcomes, with an adjusted odds ratio (aOR) of 1.349 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.099 to 1.656; P=0.004) for oxygen treatment, an aOR of 1.930 (95% CI, 1.276 to 2.915; P<0.001) for ventilator use, and an aOR of 2.659 (95% CI, 1.896 to 3.729; P<0.001) for mortality.
Conclusion
Diabetes was associated with worse clinical outcomes in Korean patients with COVID-19, independent of other comorbidities. Therefore, patients with diabetes and COVID-19 should be treated with caution. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of COVID-19 on the Microbiome and Inflammatory Status of Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Gratiela Gradisteanu Pircalabioru, Georgiana Alexandra Grigore, Ilda Czobor Barbu, Mariana-Carmen Chifiriuc, Octavian Savu
Biomedicines.2023; 11(1): 179. CrossRef - Bidirectional Relationship between Glycemic Control and COVID-19 and Perspectives of Islet Organoid Models of SARS-CoV-2 Infection
Tongran Zhang, Nannan Wang, Lingqiang Zhu, Lihua Chen, Huisheng Liu
Biomedicines.2023; 11(3): 856. CrossRef - Reasons for Hospitalization Among Australians With Type 1 or Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19
Dunya Tomic, Jonathan E. Shaw, Dianna J. Magliano
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody levels predict outcome in COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study
Sylvia Mink, Christoph H. Saely, Andreas Leiherer, Matthias Frick, Thomas Plattner, Heinz Drexel, Peter Fraunberger
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Mortality-related risk factors of inpatients with diabetes and COVID-19: A multicenter retrospective study in Belgium
Thomas Servais, France Laurent, Thomas Roland, Camelia Rossi, Elodie De Groote, Valérie Godart, Ernestina Repetto, Michel Ponchon, Pascale Chasseur, Laurent Crenier, Sandrine Van Eeckhoudt, John Yango, Philippe Oriot, Mirela Morisca Gavriliu, Stéphanie Ro
Annales d'Endocrinologie.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Screening, diagnosis and management of diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy in clinical practice: International expert consensus recommendations
Dan Ziegler, Solomon Tesfaye, Vincenza Spallone, Irina Gurieva, Juma Al Kaabi, Boris Mankovsky, Emil Martinka, Gabriela Radulian, Khue Thy Nguyen, Alin O Stirban, Tsvetalina Tankova, Tamás Varkonyi, Roy Freeman, Péter Kempler, Andrew JM Boulton
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 186: 109063. CrossRef - The Role of Diabetes and Hyperglycemia on COVID-19 Infection Course—A Narrative Review
Evangelia Tzeravini, Eleftherios Stratigakos, Chris Siafarikas, Anastasios Tentolouris, Nikolaos Tentolouris
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The interrelationship between diabetes mellitus and COVID-19
ThekraAbdulaali Abed, ZainabAdil Ghani Chabuck
Medical Journal of Babylon.2022; 19(1): 1. CrossRef - Impact of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on the Incidence and Outcomes of COVID-19 Needing Hospital Admission According to Sex: Retrospective Cohort Study Using Hospital Discharge Data in Spain, Year 2020
Jose M. de Miguel-Yanes, Rodrigo Jimenez-Garcia, Javier de Miguel-Diez, Valentin Hernández-Barrera, David Carabantes-Alarcon, Jose J. Zamorano-Leon, Ricardo Omaña-Palanco, Ana Lopez-de-Andres
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(9): 2654. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea 2021
Jae Hyun Bae, Kyung-Do Han, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ye Seul Yang, Jong Han Choi, Kyung Mook Choi, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 417. CrossRef - The burden and risks of emerging complications of diabetes mellitus
Dunya Tomic, Jonathan E. Shaw, Dianna J. Magliano
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2022; 18(9): 525. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients Hospitalized with COVID-19 at Case Hospital, Uganda
Mirriam Apiyo, Ronald Olum, Amina Kabuye, Betty Khainza, Anne M. Amate, Vittal Byabashaija, Derrick Nomujuni, Kato Sebbaale, Peter Senfuka, Simon Kazibwe, Gurav Sharma, Lindsay Davidson, Felix Bongomin, Diamantis Kofteridis
Interdisciplinary Perspectives on Infectious Diseases.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Diabetes, obesity, metabolism, and SARS-CoV-2 infection: the end of the beginning
Daniel J. Drucker
Cell Metabolism.2021; 33(3): 479. CrossRef - Effects of a DPP-4 Inhibitor and RAS Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19
Sang Youl Rhee, Jeongwoo Lee, Hyewon Nam, Dae-Sung Kyoung, Dong Wook Shin, Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 251. CrossRef - COVID-19 vaccine acceptance among high-risk populations in Uganda
Felix Bongomin, Ronald Olum, Irene Andia-Biraro, Frederick Nelson Nakwagala, Khalid Hudow Hassan, Dianah Rhoda Nassozi, Mark Kaddumukasa, Pauline Byakika-Kibwika, Sarah Kiguli, Bruce J. Kirenga
Therapeutic Advances in Infectious Disease.2021; 8: 204993612110243. CrossRef - Caracterización clínica, según niveles de glucemia, de pacientes hospitalizados por COVID-19: serie de casos
Irene Stulin, Maria Montes de Oca, Gabriela Blanco, Laura Sánchez, Isabel-Carlota Silva, Jennireth Quevedo, Maria Cristina Arvelo, Nathalia Valera, Irene Papa, Hospital Centro Médico de Caracas, Caracas, Venezuela Bacci, Fátima de Abreu, Héctor Villarroel
Investigación Clínica.2021; 62: 27. CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccination for Endocrine Patients: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Chang Ho Ahn, Jun Sung Moon, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Hee Kyung Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Eun Roh, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 757. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19: Review Article
Mahmoud Nassar, Ahmed Daoud, Nso Nso, Luis Medina, Victoria Ghernautan, Harangad Bhangoo, Andrew Nyein, Mahmoud Mohamed, Ahmed Alqassieh, Karim Soliman, Mostafa Alfishawy, Issac Sachmechi, Anoop Misra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(6): 102268. CrossRef - Dissection of non-pharmaceutical interventions implemented by Iran, South Korea, and Turkey in the fight against COVID-19 pandemic
Mohammad Keykhaei, Sogol Koolaji, Esmaeil Mohammadi, Reyhaneh Kalantar, Sahar Saeedi Moghaddam, Arya Aminorroaya, Shaghayegh Zokaei, Sina Azadnajafabad, Negar Rezaei, Erfan Ghasemi, Nazila Rezaei, Rosa Haghshenas, Yosef Farzi, Sina Rashedi, Bagher Larijan
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(2): 1919. CrossRef - A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Diabetes Associated Mortality in Patients with COVID-19
Puneeta Gupta, Meeta Gupta, Neena KAtoch, Ketan Garg, Bhawna Garg
International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes, Obesity, and COVID-19
Sang Youl Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(3): 174. CrossRef - Diabetes, hypertension, body mass index, smoking and COVID-19-related mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Yahya Mahamat-Saleh, Thibault Fiolet, Mathieu Edouard Rebeaud, Matthieu Mulot, Anthony Guihur, Douae El Fatouhi, Nasser Laouali, Nathan Peiffer-Smadja, Dagfinn Aune, Gianluca Severi
BMJ Open.2021; 11(10): e052777. CrossRef - Independent Impact of Diabetes on the Severity of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in 5,307 Patients in South Korea: A Nationwide-Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:737-46)
Kyuho Kim, Tae Jung Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 938. CrossRef
- Impact of COVID-19 on the Microbiome and Inflammatory Status of Type 2 Diabetes Patients
- Covid-19
-
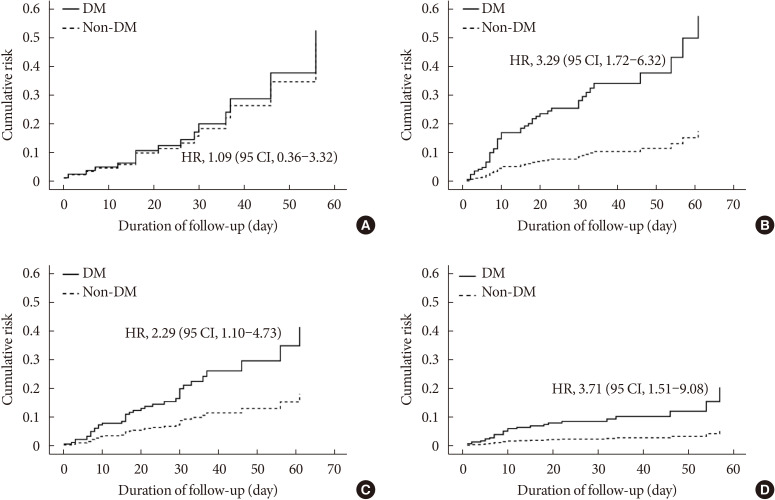
- The Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019 Infection and Diabetes in Daegu, South Korea
- Mi Kyung Kim, Jae-Han Jeon, Sung-Woo Kim, Jun Sung Moon, Nan Hee Cho, Eugene Han, Ji Hong You, Ji Yeon Lee, Miri Hyun, Jae Seok Park, Yong Shik Kwon, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Ki Tae Kwon, Shin Yup Lee, Eon Ju Jeon, Jin-Woo Kim, Hyo-Lim Hong, Hyun Hee Kwon, Chi Young Jung, Yin Young Lee, Eunyeoung Ha, Seung Min Chung, Jian Hur, June Hong Ahn, Na-young Kim, Shin-Woo Kim, Hyun Ha Chang, Yong Hoon Lee, Jaehee Lee, Keun-Gyu Park, Hyun Ah Kim, Ji-Hyun Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):602-613. Published online August 12, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0146
- 13,331 View
- 207 Download
- 67 Web of Science
- 74 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a global pandemic that had affected more than eight million people worldwide by June 2020. Given the importance of the presence of diabetes mellitus (DM) for host immunity, we retrospectively evaluated the clinical characteristics and outcomes of moderate-to-severe COVID-19 in patients with diabetes.
Methods We conducted a multi-center observational study of 1,082 adult inpatients (aged ≥18 years) who were admitted to one of five university hospitals in Daegu because of the severity of their COVID-19-related disease. The demographic, laboratory, and radiologic findings, and the mortality, prevalence of severe disease, and duration of quarantine were compared between patients with and without DM. In addition, 1:1 propensity score (PS)-matching was conducted with the DM group.
Results Compared with the non-DM group (
n =847), patients with DM (n =235) were older, exhibited higher mortality, and required more intensive care. Even after PS-matching, patients with DM exhibited more severe disease, and DM remained a prognostic factor for higher mortality (hazard ratio, 2.40; 95% confidence interval, 1.38 to 4.15). Subgroup analysis revealed that the presence of DM was associated with higher mortality, especially in older people (≥70 years old). Prior use of a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor or a renin-angiotensin system inhibitor did not affect mortality or the clinical severity of the disease.Conclusion DM is a significant risk factor for COVID-19 severity and mortality. Our findings imply that COVID-19 patients with DM, especially if elderly, require special attention and prompt intensive care.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Potential use of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors during acute illness: a systematic review based on COVID-19
Carmen Tisch, Eleni Xourgia, Aristomenis Exadaktylos, Mairi Ziaka
Endocrine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin and Metformin Administration: Unravelling the Multifaceted Association with Mortality across Various Clinical Settings Considering Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19
Łukasz Lewandowski, Agnieszka Bronowicka-Szydełko, Maciej Rabczyński, Dorota Bednarska-Chabowska, Joanna Adamiec-Mroczek, Adrian Doroszko, Małgorzata Trocha, Krzysztof Kujawa, Agnieszka Matera-Witkiewicz, Edwin Kuźnik, Paweł Lubieniecki, Marcin Madziarski
Biomedicines.2024; 12(3): 605. CrossRef - Pre-admission use of sodium glucose transporter-2 inhibitor (SGLT-2i) may significantly improves Covid-19 outcomes in patients with diabetes: A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
Hikmat Permana, Theo Audi Yanto, Timotius Ivan Hariyanto
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 195: 110205. CrossRef - Risk phenotypes of diabetes and association with COVID-19 severity and death: an update of a living systematic review and meta-analysis
Sabrina Schlesinger, Alexander Lang, Nikoletta Christodoulou, Philipp Linnerz, Kalliopi Pafili, Oliver Kuss, Christian Herder, Manuela Neuenschwander, Janett Barbaresko, Michael Roden
Diabetologia.2023; 66(8): 1395. CrossRef - Factors influencing the severity of COVID-19 course for patients with diabetes mellitus in tashkent: a retrospective cohort study
A. V. Alieva, A. A. Djalilov, F. A. Khaydarova, A. V. Alimov, D. Z. Khalilova, V. A. Talenova, N. U. Alimova, M. D. Aripova, A. S. Sadikova
Obesity and metabolism.2023; 20(2): 92. CrossRef - Pituitary Diseases and COVID-19 Outcomes in South Korea: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Jeonghoon Ha, Kyoung Min Kim, Dong-Jun Lim, Keeho Song, Gi Hyeon Seo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(14): 4799. CrossRef - Epidemiological features and consequences of COVID‐19 in patients with and without gastrointestinal symptoms in southwestern Iran. A retrospective observational study
Habibollah Azarbakhsh, Leila Moftakhar, Aliasghar Valipour, Alireza Mirahmadizadeh, Hekmat Allah Moradi, Elahe Piraee
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Long-Term Conditions and Comorbidity Patterns on COVID-19 Infection and Hospitalisation: A Cohort Study
Yun-Ting Huang, Andrew Steptoe, Riyaz S. Patel, Esme Fuller Thomson, Dorina Cadar
Gerontology.2023; 69(10): 1200. CrossRef - Association Between Anti-diabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Tiantian Han, Shaodi Ma, Chenyu Sun, Huimei Zhang, Guangbo Qu, Yue Chen, Ce Cheng, Eric L. Chen, Mubashir Ayaz Ahmed, Keun Young Kim, Raveena Manem, Mengshi Chen, Zhichun Guo, Hongru Yang, Yue Yan, Qin Zhou
Archives of Medical Research.2022; 53(2): 186. CrossRef - Use of DPP4i reduced odds of clinical deterioration and hyperinflammatory syndrome in COVID-19 patients with type 2 diabetes: Propensity score analysis of a territory-wide cohort in Hong Kong
Carlos K.H. Wong, David T.W. Lui, Angel Y.C. Lui, Ashley C.Y. Kwok, Marshall C.H. Low, Kristy T.K. Lau, Ivan C.H. Au, Xi Xiong, Matthew S.H. Chung, Eric H.Y. Lau, Benjamin J. Cowling
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(1): 101307. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-IV) inhibitor was associated with mortality reduction in COVID-19 — A systematic review and meta-analysis
Ahmad Fariz Malvi Zamzam Zein, Wilson Matthew Raffaello
Primary Care Diabetes.2022; 16(1): 162. CrossRef - Prevalence and impact of diabetes in hospitalized COVID‐19 patients: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Sian A. Bradley, Maciej Banach, Negman Alvarado, Ivica Smokovski, Sonu M. M. Bhaskar
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(2): 144. CrossRef - Interplay between Inflammaging, Frailty and Nutrition in Covid-19: Preventive and Adjuvant Treatment Perspectives
A. Padilha de Lima, M. Macedo Rogero, T. Araujo Viel, H.M. Garay-Malpartida, I. Aprahamian, Sandra Maria Lima Ribeiro
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2022; 26(1): 67. CrossRef - Increase in blood glucose level and incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus in the Daegu-Gyeongbuk area during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Mi Seon Lee, Rosie Lee, Cheol Woo Ko, Jung Eun Moon
Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science.2022; 39(1): 46. CrossRef - Interrelationship between 2019-nCov receptor DPP4 and diabetes mellitus targets based on protein interaction network
Qian Gao, Wenjun Zhang, Tingting Li, Guojun Yang, Wei Zhu, Naijun Chen, Huawei Jin
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Can sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor reduce the risk of adverse complications due to COVID-19? – Targeting hyperinflammation
Afnan Alshnbari, Iskandar Idris
Current Medical Research and Opinion.2022; 38(3): 357. CrossRef - Commentary: Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Li-Min Zhao, Xie-Hui Chen, Mei Qiu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID-19 and Diabetes
Awadhesh Kumar Singh, Kamlesh Khunti
Annual Review of Medicine.2022; 73(1): 129. CrossRef - The enzymes in COVID-19: A review
Maria Helena Menezes Estevam Alves, Layla Carvalho Mahnke, Tifany Cerqueira Macedo, Thais Ketinly dos Santos Silva, Luiz Bezerra Carvalho Junior
Biochimie.2022; 197: 38. CrossRef - IMPACT OF ANTIDIABETIC DRUGS ON RISK AND OUTCOME OF COVID-19 INFECTION: A REVIEW
Adnan A. Zainal, Marwan M. Merkhan
Military Medical Science Letters.2022; 91(2): 140. CrossRef - Does metformin affect outcomes in COVID‐19 patients with new or pre‐existing diabetes mellitus? A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Adithan Ganesh, Michael D. Randall
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2022; 88(6): 2642. CrossRef - Diabetes, Metformin and the Clinical Course of Covid-19: Outcomes, Mechanisms and Suggestions on the Therapeutic Use of Metformin
Clifford J. Bailey, Mike Gwilt
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Diabetes and Hyperglycemia on COVID-19 Infection Course—A Narrative Review
Evangelia Tzeravini, Eleftherios Stratigakos, Chris Siafarikas, Anastasios Tentolouris, Nikolaos Tentolouris
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Preadmission use of antidiabetic medications and mortality among patients with COVID-19 having type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis
Nam Nhat Nguyen, Dung Si Ho, Hung Song Nguyen, Dang Khanh Ngan Ho, Hung-Yuan Li, Chia-Yuan Lin, Hsiao-Yean Chiu, Yang-Ching Chen
Metabolism.2022; 131: 155196. CrossRef - Glucose-Lowering Agents and COVID-19
Ah Reum Khang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(1): 1. CrossRef - Impact of diabetes on COVID‐19 mortality and hospital outcomes from a global perspective: An umbrella systematic review and meta‐analysis
Stavroula Kastora, Manisha Patel, Ben Carter, Mirela Delibegovic, Phyo Kyaw Myint
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association Between Antidiabetic Agents and Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients With Diabetes: A Bayesian Network Meta-Analysis
Yidan Chen, Xingfei Lv, Sang Lin, Mohammad Arshad, Mengjun Dai
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Renin‐Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibitors and COVID‐19: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis Revealing Critical Bias Across a Body of Observational Research
Jordan Loader, Frances C. Taylor, Erik Lampa, Johan Sundström
Journal of the American Heart Association.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes and SARS-CoV-2–Is There a Mutual Connection?
Anna P. Jedrzejak, Edyta K. Urbaniak, Jadwiga A. Wasko, Natalia Ziojla, Malgorzata Borowiak
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship of age, sex and prothrombin time related to the severity and mortality of COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta analysis
Audrey Fabianisa Mirza, Ceria Halim, Mutiara Indah Sari
F1000Research.2022; 11: 729. CrossRef - Are lipid ratios and triglyceride-glucose index associated with critical care outcomes in COVID-19 patients?
Marzieh Rohani-Rasaf, Kosar Mirjalili, Akram Vatannejad, Maryam Teimouri, Xiao-Feng Yang
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(8): e0272000. CrossRef - Early glycaemic variability increases 28-day mortality and prolongs intensive care unit stay in critically ill patients with pneumonia
Seong Ho Kim, Ji Young Kim, Eun Song Kim, Il Rae Park, Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Annals of Medicine.2022; 54(1): 2724. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in COVID-19: Beyond glycemic control
Niya Narayanan, Dukhabandhu Naik, Jayaprakash Sahoo, Sadishkumar Kamalanathan
World Journal of Virology.2022; 11(6): 399. CrossRef - Prevalencia de secuelas en pacientes con diabetes mellitus tipo 2 sobrevivientes al COVID-19
Gianela M. Cancino-Castillo, Miguel A. Tresierra-Ayala, Jorge L. Campos-Reyna, Jaime Rosales-Rimache
REVISTA MÉDICA VALLEJIANA/ Vallejian Medical Journal.2022; 11(2): 48. CrossRef - Predictors of adverse in-hospital outcome and recovery in patients with diabetes mellitus and COVID-19 pneumonia in Iraq
Hussein Nafakhi, Mohammed Alareedh, Karrar Al-Buthabhak, Foaad Shaghee, Ahmed Nafakhi, Samet Kasim
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(1): 33. CrossRef - Non-insulin anti-diabetic agents in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: A Critical Appraisal of Literature
Awadhesh Kumar Singh, Ritu Singh, Banshi Saboo, Anoop Misra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(1): 159. CrossRef - COVID-19 associated with diabetes and other noncommunicable diseases led to a global health crisis
Mark Thomaz Ugliara Barone, Belinda Ngongo, Simone Bega Harnik, Lucas Xavier de Oliveira, Dániel Végh, Patrícia Vieira de Luca, Hermelinda Cordeiro Pedrosa, Franco Giraudo, Roque Cardona-Hernandez, Nayanjeet Chaudhury, Luiz Menna-Barreto
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 171: 108587. CrossRef - A meta-analysis on the preadmission use of DPP-4 inhibitors and risk of a fatal or severe course of illness in patients with COVID-19
Chia Siang Kow, Syed Shahzad Hasan
Therapies.2021; 76(4): 361. CrossRef - Disentangling conflicting evidence on DPP-4 inhibitors and outcomes of COVID-19: narrative review and meta-analysis
B. M. Bonora, A. Avogaro, G. P. Fadini
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2021; 44(7): 1379. CrossRef - Prognostic bioindicators in severe COVID-19 patients
L. Bergantini, E. Bargagli, M. d'Alessandro, R.M. Refini, P. Cameli, L. Galasso, C. Scapellato, F. Montagnani, S. Scolletta, F. Franchi, S. Valente, D. Bennett, G. Sebastiani, B. Frediani, F. Dotta
Cytokine.2021; 141: 155455. CrossRef - Epidemiological characteristics and outcomes of COVID-19 in diabetic versus non-diabetic patients
Leila Moftakhar, Parisa Moftakhar, Elahe Piraee, Haleh Ghaem, Aliasghar Valipour, Habibollah Azarbakhsh
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2021; 41(3): 383. CrossRef - DPP-4 inhibition and COVID-19: From initial concerns to recent expectations
André J. Scheen
Diabetes & Metabolism.2021; 47(2): 101213. CrossRef - Use of dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors and prognosis of COVID‐19 in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes: A propensity score analysis from the CORONADO study
Ronan Roussel, Patrice Darmon, Matthieu Pichelin, Thomas Goronflot, Yawa Abouleka, Leila Ait Bachir, Ingrid Allix, Deborah Ancelle, Sara Barraud, Lyse Bordier, Aurélie Carlier, Nicolas Chevalier, Christine Coffin‐Boutreux, Emmanuel Cosson, Anne Dorange, O
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(5): 1162. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use and mortality in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis
Rimesh Pal, Mainak Banerjee, Soham Mukherjee, Ranjitpal Singh Bhogal, Amanpreet Kaur, Sanjay K. Bhadada
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 12: 204201882199648. CrossRef - Renin–angiotensin-system inhibitors and all-cause mortality in patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Chirag Bavishi, Paul K. Whelton, Giuseppe Mancia, Giovanni Corrao, Franz H. Messerli
Journal of Hypertension.2021; 39(4): 784. CrossRef - Evaluation of the Current Therapeutic Approaches for COVID-19: A Systematic Review and a Meta-analysis
Zeinab Abdelrahman, Qian Liu, Shanmei Jiang, Mengyuan Li, Qingrong Sun, Yue Zhang, Xiaosheng Wang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitor and outcome from coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in diabetic patients: a systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
Timotius Ivan Hariyanto, Andree Kurniawan
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(1): 543. CrossRef - Impact of diabetes mellitus on in-hospital mortality in adult patients with COVID-19: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Halla Kaminska, Lukasz Szarpak, Dariusz Kosior, Wojciech Wieczorek, Agnieszka Szarpak, Mahdi Al-Jeabory, Wladyslaw Gawel, Aleksandra Gasecka, Milosz J. Jaguszewski, Przemyslawa Jarosz-Chobot
Acta Diabetologica.2021; 58(8): 1101. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor and mortality in coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) – A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
Iis Inayati Rakhmat, Yudith Yunia Kusmala, Dewi Ratih Handayani, Henny Juliastuti, Eka Noneng Nawangsih, Arief Wibowo, Michael Anthonius Lim, Raymond Pranata
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(3): 777. CrossRef - Post-infection depressive, anxiety and post-traumatic stress symptoms: A prospective cohort study in patients with mild COVID-19
Flavia Ismael, João C.S. Bizario, Tatiane Battagin, Beatriz Zaramella, Fabio E. Leal, Julio Torales, Antonio Ventriglio, Megan E. Marziali, Silvia S. Martins, João M. Castaldelli-Maia
Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry.2021; 111: 110341. CrossRef - Managing diabetes in diabetic patients with COVID: where do we start from?
Angelo Avogaro, Benedetta Bonora, Gian Paolo Fadini
Acta Diabetologica.2021; 58(11): 1441. CrossRef - Is diabetes mellitus a wrongdoer to COVID-19 severity?
Sanjib Sarkar, Dibyendu Das, Sawlang Borsingh Wann, Jatin Kalita, Prasenjit Manna
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 178: 108936. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitor, an Update
Ju Hee Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(2): 91. CrossRef - Correlation Analysis Between Serum Uric Acid, Prealbumin Level, Lactate Dehydrogenase, and Severity of COVID-19
Zhenmu Jin, Mo Zheng, Jichan Shi, Xinchun Ye, Fang Cheng, Que-Lu Chen, Jianping Huang, Xian-Gao Jiang
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonist and Sodium–Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Use and COVID-19 Outcomes
Anna R. Kahkoska, Trine Julie Abrahamsen, G. Caleb Alexander, Tellen D. Bennett, Christopher G. Chute, Melissa A. Haendel, Klara R. Klein, Hemalkumar Mehta, Joshua D. Miller, Richard A. Moffitt, Til Stürmer, Kajsa Kvist, John B. Buse, Tim Q. Duong
Diabetes Care.2021; 44(7): 1564. CrossRef - The effect of metformin on mortality and severity in COVID-19 patients with diabetes mellitus
Wenxing Yang, Xuehong Sun, Jun Zhang, Kui Zhang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 178: 108977. CrossRef - Renin‐Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibitors in Primary Prevention and COVID‐19
Jordan Loader, Erik Lampa, Stefan Gustafsson, Thomas Cars, Johan Sundström
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors influencing on development of COVID-19 pneumonia and association with oral anti-diabetic drugs in hospitalized patients with diabetes mellitus
Ayça Elibol, Didem Eren, Macide Deniz Erdoğan, Merve Elmaağaç, Oguzhan Sıtkı Dizdar, İlhami Çelik, Ali İhsan Günal
Primary Care Diabetes.2021; 15(5): 806. CrossRef - Aging & COVID-19 susceptibility, disease severity, and clinical outcomes: The role of entangled risk factors
Melina Farshbafnadi, Sara Kamali Zonouzi, Mohammadmahdi Sabahi, Mahsa Dolatshahi, Mohammad Hadi Aarabi
Experimental Gerontology.2021; 154: 111507. CrossRef - Classical and Counter-Regulatory Renin–Angiotensin System: Potential Key Roles in COVID-19 Pathophysiology
Moudhi Almutlaq, Abir Abdullah Alamro, Fayhan Alroqi, Tlili Barhoumi
CJC Open.2021; 3(8): 1060. CrossRef - Metformin in Patients With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yin Li, Xue Yang, Peijing Yan, Tong Sun, Zhi Zeng, Sheyu Li
Frontiers in Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pre-existing health conditions and severe COVID-19 outcomes: an umbrella review approach and meta-analysis of global evidence
Marina Treskova-Schwarzbach, Laura Haas, Sarah Reda, Antonia Pilic, Anna Borodova, Kasra Karimi, Judith Koch, Teresa Nygren, Stefan Scholz, Viktoria Schönfeld, Sabine Vygen-Bonnet, Ole Wichmann, Thomas Harder
BMC Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID-19 Vaccination for Endocrine Patients: A Position Statement from the Korean Endocrine Society
Cheol Ryong Ku, Kyong Yeun Jung, Chang Ho Ahn, Jun Sung Moon, Ju Hee Lee, Eun Heui Kim, Hyemi Kwon, Hee Kyung Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Sangmo Hong, Jeonghoon Ha, Eun Roh, Jin Hwa Kim, Mi-kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 757. CrossRef - High Fibrosis-4 Index Is Related with Worse Clinical Outcome in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Diabetes Mellitus: A Multicenter Observational Study
Sung-Woo Kim, Jae-Han Jeon, Jun Sung Moon, Mi Kyung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(4): 800. CrossRef - Mortality Risk of Antidiabetic Agents for Type 2 Diabetes With COVID-19: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Chengxia Kan, Yang Zhang, Fang Han, Qian Xu, Tongtong Ye, Ningning Hou, Xiaodong Sun
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of influence of background therapy for comorbidities in the period before infection on the risk of the lethal COVID outcome. Data from the international ACTIV SARS-CoV-2 registry («Analysis of chronic non-infectious diseases dynamics after COVID-
E. I. Tarlovskaya, A. G. Arutyunov, A. O. Konradi, Yu. M. Lopatin, A. P. Rebrov, S. N. Tereshchenko, A. I. Chesnikova, H. G. Hayrapetyan, A. P. Babin, I. G. Bakulin, N. V. Bakulina, L. A. Balykova, A. S. Blagonravova, M. V. Boldina, A. R. Vaisberg, A. S.
Kardiologiia.2021; 61(9): 20. CrossRef - Association of clinical characteristics, antidiabetic and cardiovascular agents with diabetes mellitus and COVID-19: a 7-month follow-up cohort study
Marzieh Pazoki, Fatemeh Chichagi, Azar Hadadi, Samira Kafan, Mahnaz Montazeri, Sina Kazemian, Arya Aminorroaya, Mehdi Ebrahimi, Haleh Ashraf, Mojgan Mirabdolhagh Hazaveh, Mohammad Reza Khajavi, Reza Shariat Moharari, Seyed Hamidreza Sharifnia, Shahrokh Ka
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(2): 1545. CrossRef - COVID-19 and Diabetes: A Comprehensive Review of Angiotensin Converting Enzyme 2, Mutual Effects and Pharmacotherapy
Lingli Xie, Ziying Zhang, Qian Wang, Yangwen Chen, Dexue Lu, Weihua Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Diabetes on COVID-19 Mortality and Hospital Outcomes, a Global Perspective: An ONTOP Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Stavroula Kastora, Manisha Patel, Ben Carter, Mirela Delibegovic, Phyo Kyaw Myint
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Decision Trees: Predictions of Global Vulnerability to Coronavirus Outbreaks
Moacir José da Silva
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The potential association between common comorbidities and severity and mortality of coronavirus disease 2019: A pooled analysis
Liman Luo, Menglu Fu, Yuanyuan Li, Shuiqing Hu, Jinlan Luo, Zhihui Chen, Jing Yu, Wenhua Li, Ruolan Dong, Yan Yang, Ling Tu, Xizhen Xu
Clinical Cardiology.2020; 43(12): 1478. CrossRef - The Effect of Metformin Consumption on Mortality in Hospitalized COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Antonia Anna Lukito, Raymond Pranata, Joshua Henrina, Michael Anthonius Lim, Sherly Lawrensia, Ketut Suastika
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(6): 2177. CrossRef - Risk Factors on the Progression to Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients in South Korea: Using National Data
Seon-Rye Kim, Seoul-Hee Nam, Yu-Rin Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(23): 8847. CrossRef - Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea
Ji Hong You, Sang Ah Lee, Sung-Youn Chun, Sun Ok Song, Byung-Wan Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Edward J. Boyko
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(4): 901. CrossRef
- Potential use of sodium glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors during acute illness: a systematic review based on COVID-19
- Complications
- Differences in Clinical Outcomes between Patients with and without Hypoglycemia during Hospitalization: A Retrospective Study Using Real-World Evidence
- Jeongmin Lee, Tong Min Kim, Hyunah Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Hun-Sung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):555-565. Published online May 8, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0064
- 6,518 View
- 101 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Some patients admitted to hospitals for glycemic control experience hypoglycemia despite regular meals and despite adhering to standard blood glucose control protocols. Different factors can have a negative impact on blood glucose control and prognosis after discharge. This study investigated risk factors for hypoglycemia and its effects on glycemic control during the hospitalization of patients in the general ward.
Methods This retrospective study included patients who were admitted between 2009 and 2018. Patients were provided regular meals at fixed times according to ideal body weights during hospitalization. We categorized the patients into two groups: those with and those without hypoglycemia during hospitalization.
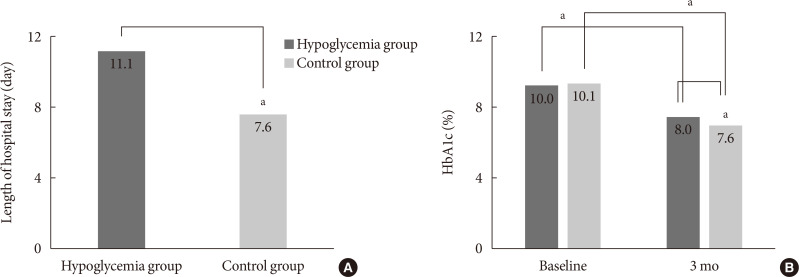
Results Of the 3,031 patients, 379 experienced at least one episode of hypoglycemia during hospitalization (HYPO group). Hypoglycemia occurred more frequently particularly in cases of premixed insulin therapy. Compared with the control group, the HYPO group was older (61.0±16.8 years vs. 59.1±16.5 years,
P =0.035), with more females (60.4% vs. 49.6%,P <0.001), lower body mass index (BMI) (23.5±4.2 kg/m2 vs. 25.1±4.4 kg/m2,P <0.001), and higher prevalence of type 1 diabetes mellitus (6.1% vs. 2.6%,P <0.001), They had longer hospital stay (11.1±13.5 days vs. 7.6±4.6 days,P <0.001). After discharge the HYPO group had lower glycosylated hemoglobin reduction rate (−2.0%±0.2% vs. −2.5%±0.1%,P =0.003) and tended to have more frequent cases of cardiovascular disease.Conclusion Hypoglycemia occurred more frequently in older female patients with lower BMI and was associated with longer hospital stay and poorer glycemic control after discharge. Therefore, clinicians must carefully ensure that patients do not experience hypoglycemia during hospitalization.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Acute kidney injury: a strong risk factor for hypoglycaemia in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes
Ana Carreira, Pedro Castro, Filipe Mira, Miguel Melo, Pedro Ribeiro, Lèlita Santos
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(9): 1179. CrossRef - Adherence to healthy lifestyle behaviors as a preventable risk factor for severe hypoglycemia in people with type 2 diabetes: A longitudinal nationwide cohort study
Jae‐Seung Yun, Kyungdo Han, Yong‐Moon Park, Eugene Han, Yong‐ho Lee, Seung‐Hyun Ko
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(9): 1533. CrossRef - Predicting hypoglycemia in hospitalized patients with diabetes: A derivation and validation study
Michal Elbaz, Jeries Nashashibi, Shiri Kushnir, Leonard Leibovici
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 171: 108611. CrossRef - Hospital care: improving outcomes in type 1 diabetes
Schafer Boeder, Kristen Kulasa
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2021; 28(1): 14. CrossRef - Data Pseudonymization in a Range That Does Not Affect Data Quality: Correlation with the Degree of Participation of Clinicians
Soo-Yong Shin, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Letter: Differences in Clinical Outcomes between Patients with and without Hypoglycemia during Hospitalization: A Retrospective Study Using Real-World Evidence (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:555-65)
Sung-Woo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 775. CrossRef - Response: Differences in Clinical Outcomes between Patients with and without Hypoglycemia during Hospitalization: A Retrospective Study Using Real-World Evidence (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:555-65)
Jeongmin Lee, Hun-Sung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 779. CrossRef - Hypoglycaemia and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Patients with Diabetes
Niki Katsiki, Kalliopi Kotsa, Anca P. Stoian, Dimitri P. Mikhailidis
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2020; 26(43): 5637. CrossRef
- Acute kidney injury: a strong risk factor for hypoglycaemia in hospitalized patients with type 2 diabetes
- Cardiovascular risk/Epidemiology
- Clinical Impact of Dysglycemia in Patients with an Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Jae-Wook Chung, Yeong-Seon Park, Jeong-Eon Seo, Yeseul Son, Cheol-Woo Oh, Chan-Hee Lee, Jong-Ho Nam, Jung-Hee Lee, Jang-Won Son, Ung Kim, Jong-Seon Park, Kyu-Chang Won, Dong-Gu Shin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):270-274. Published online April 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0164
- 5,674 View
- 119 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
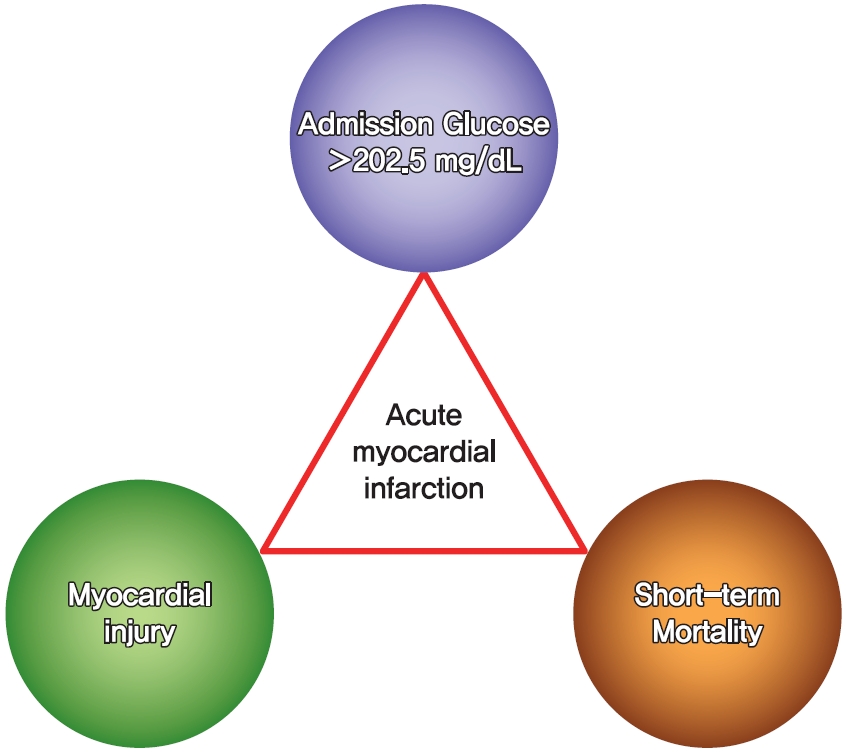
This study aimed to determine the impact of dysglycemia on myocardial injury and cardiac dysfunction in acute myocardial infarctions (AMIs). From 2005 to 2016, a total of 1,593 patients with AMIs who underwent percutaneous coronary intervention were enrolled. The patients were classified into five groups according to the admission glucose level: ≤80, 81 to 140, 141 to 200, 201 to 260, and ≥261 mg/dL. The clinical and echocardiographic parameters and 30-day mortality were analyzed. The peak troponin I and white blood cell levels had a positive linear relationship to the admission glucose level. The left ventricular ejection fraction had an inverted
U -shape trend, and the E/E' ratio wasU -shaped based on euglycemia. The 30-day mortality also increased as the admission glucose increased, and the cut-off value for predicting the mortality was 202.5 mg/dL. Dysglycemia, especially hyperglycemia, appears to be associated with myocardial injury and could be another adjunctive parameter for predicting mortality in patients with AMIs.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Optimal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels in Adults Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study Including More Than 4 Million Individuals From South Korea
Ji Hye Huh, Sang Wook Park, Tae-Hwa Go, Dae Ryong Kang, Sang-Hak Lee, Jang-Young Kim
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of admission hyperglycemia and all-cause mortality in acute myocardial infarction with percutaneous coronary intervention: A dose–response meta-analysis
Shao-Yong Cheng, Hao Wang, Shi-Hua Lin, Jin-Hui Wen, Ling-Ling Ma, Xiao-Ce Dai
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fenofibrate add-on to statin treatment is associated with low all-cause death and cardiovascular disease in the general population with high triglyceride levels
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Metabolism.2022; 137: 155327. CrossRef - Basic types of the first-day glycemia in acute myocardial infarction: Prognostic, diagnostic, threshold and target glycemia
Goran Koracevic, Milan Djordjevic
Primary Care Diabetes.2021; 15(3): 614. CrossRef - Clinical Impact of Dysglycemia in Patients with an Acute Myocardial Infarction (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:270-4)
Bo-Yeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 787. CrossRef - Clinical Impact of Dysglycemia in Patients with an Acute Myocardial Infarction (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:270-4)
Chan-Hee Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 791. CrossRef - The Effects of Glucose Lowering Agents on the Secondary Prevention of Coronary Artery Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 977. CrossRef - Effect of Admission Hyperglycemia on Short-Term Prognosis of Patients with Non-ST Elevation Acute Coronary Syndrome without Diabetes Mellitus
Wei Liu, Zhijuan Li, Shiying Xing, Yanwei Xu, Gaetano Santulli
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Optimal Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels in Adults Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Study Including More Than 4 Million Individuals From South Korea
- Epidemiology
- Diabetes Mellitus and Cause-Specific Mortality: A Population-Based Study
- Sen Li, Jiaxin Wang, Biao Zhang, Xinyi Li, Yuan Liu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(3):319-341. Published online April 19, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0060
- 20,068 View
- 241 Download
- 122 Web of Science
- 135 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background To investigate whether diabetes contributes to mortality for major types of diseases.
Methods Six National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data cycles (1999 to 2000, 2001 to 2002, 2003 to 2004, 2005 to 2006, 2007 to 2008, and 2009 to 2010) and their linked mortality files were used. A population of 15,513 participants was included according to the availability of diabetes and mortality status.
Results Participants with diabetes tended to have higher all-cause mortality and mortality due to cardiovascular disease, cancer, chronic lower respiratory diseases, cerebrovascular disease, influenza and pneumonia, and kidney disease. Confounder-adjusted Cox proportional hazard models showed that both diagnosed diabetes category (yes or no) and diabetes status (diabetes, prediabetes, or no diabetes) were associated with all-cause mortality and with mortality due to cardiovascular disease, chronic lower respiratory diseases, influenza and pneumonia, and kidney disease. No associations were found for cancer-, accidents-, or Alzheimer's disease-related mortality.
Conclusion The current study's findings provide epidemiological evidence that diagnosed diabetes at the baseline is associated with increased mortality risk due to cardiovascular disease, chronic lower respiratory diseases, influenza and pneumonia, and kidney disease, but not with cancer or Alzheimer's disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of type 2 diabetes mellitus with dementia‐related and non–dementia‐related mortality among postmenopausal women: A secondary competing risks analysis of the women's health initiative
Tyler J. Titcomb, Phyllis Richey, Ramon Casanova, Lawrence S. Phillips, Simin Liu, Shama D. Karanth, Nazmus Saquib, Tomas Nuño, JoAnn E. Manson, Aladdin H. Shadyab, Longjian Liu, Terry L. Wahls, Linda G. Snetselaar, Robert B. Wallace, Wei Bao
Alzheimer's & Dementia.2024; 20(1): 234. CrossRef - Antiglycation potential of metal ions and polyphenolic extract of chickpea on thiol-protease inhibitor: A management for diabetic complications
Mohd Shahnawaz Khan, Sheraz Ahmad Bhat, Monnera Saud Albagmi, Mohammed Arshad, Mohammad Tarique, Bilqees Bano
Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal.2024; 32(1): 101916. CrossRef - GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors and noncardiovascular mortality in type 2 diabetes: Insights from a meta-analysis
Mainak Banerjee, Rimesh Pal, Indira Maisnam, Satinath Mukhopadhyay
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2024; 18(1): 102943. CrossRef - Assessment of the radial peripapillary capillary plexus and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in diabetic patients in comparison to normal age-matched individuals
Christina S.I. Farag, Heba M.A. El-Saied, Hala M. El-Mofty, Randa M.A.M. El-Mofty
Journal of the Egyptian Ophthalmological Society.2024; 117(1): 43. CrossRef - Fasting GLP-1 Levels and Albuminuria Are Negatively Associated in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Cheol-Won Jang, Tae Yang Yu, Jin Woo Jeong, Se Eun Ha, Rajan Singh, Moon Young Lee, Seungil Ro
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2024; 14(3): 280. CrossRef - The Benefits and Harms of Lung Cancer Screening in Individuals With Comorbidities
Minal S. Kale, Keith Sigel, Arushi Arora, Bart S. Ferket, Juan Wisnivesky, Chung Yin Kong
JTO Clinical and Research Reports.2024; 5(3): 100635. CrossRef - Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Do Kyeong Song, Young Sun Hong, Yeon-Ah Sung, Hyejin Lee, Hidetaka Hamasaki
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0299035. CrossRef - Liraglutide Attenuates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy via the ILK/PI3K/AKT/PTEN Signaling Pathway in Rats with Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Shatha M. Alobaid, Rahaf M. Alshahrani, Asma S. Alonazi, Nawal M. Alrasheed, Maha A. Alamin, Tahani K. Alshammari, Anfal F. Bin Dayel, Doaa M. Elnagar, Rana R. Alotaibi, Lama A. Almuthnabi, Dalia H. Almasud, Shahad E. Al-Ammar, Shahad O. Almadhi, Reema A.
Pharmaceuticals.2024; 17(3): 374. CrossRef - Effects of high-intensity interval training and its different protocols on lipid profile and glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis
Nandiny Paula Cavalli, Mariana Brondani de Mello, Natiele Camponogara Righi, Felipe Barreto Schuch, Luis Ulisses Signori, Antônio Marcos Vargas da Silva
Journal of Sports Sciences.2024; 42(4): 333. CrossRef - Role of renin-angiotensin system/angiotensin converting enzyme-2 mechanism and enhanced COVID-19 susceptibility in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ashwin Kumar Shukla, Komal Awasthi, Kauser Usman, Monisha Banerjee
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(4): 606. CrossRef - Precision Medicine in Bariatric Procedures
Khushboo Gala, Wissam Ghusn, Andres Acosta
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Clinics of North America.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Gamma‐glutamyl transferase and the risk of all‐cause and disease‐specific mortality in patients with diabetes: A nationwide cohort study
Goh Eun Chung, Su‐Min Jeong, Su Jong Yu, Jeong‐Ju Yoo, Yuri Cho, Kyu‐na Lee, Dong Wook Shin, Yoon Jun Kim, Jung‐Hwan Yoon, Kyungdo Han, Eun Ju Cho
Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in cause-specific mortality among people with type 2 and type 1 diabetes from 2002 to 2019: a Danish population-based study
Tinne Laurberg, Susanne B. Graversen, Annelli Sandbæk, Sarah H. Wild, Rimke C. Vos, Henrik Støvring
The Lancet Regional Health - Europe.2024; 41: 100909. CrossRef - Behavioral Therapy for People With Diabetes Who Smoke: A Scoping Review
Roberta Sammut, Joseph Grech, Riccardo Polosa, Davide Campagna, Agostino Di Ciaula, Tabinda Dugal, Andre Kenge, Anoop Misra, Syed Abbas Raza, Cristina Russo, Noel Somasundaram, Magdalena Walicka, Le Dinh Phoung, Graziella Chiara Prezzavento, Mirko Casu, G
Journal of Primary Care & Community Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 and liver-related complications in individuals with diabetes: a Mendelian randomization and population-based cohort study
Sung Won Chung, Hye-Sung Moon, Hyunjae Shin, Hyein Han, Sehoon Park, Heejin Cho, Jeayeon Park, Moon Haeng Hur, Min Kyung Park, Sung-Ho Won, Yun Bin Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Su Jong Yu, Dong Ki Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Yoon Jun Kim
Hepatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Design of the DAVOS Study: Diabetes Smartphone App, a Fully Automatic Transmission of Data From the Blood Glucose Meter and Insulin Pens Using Wireless Technology to Enhance Diabetes Self-Management—A Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial
Franziska Grosser, Sandra Herrmann, Maxi Bretschneider, Patrick Timpel, Janko Schildt, Markus Bentrup, Peter E. H. Schwarz
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2023; 17(3): 742. CrossRef - Low diet quality is associated with adverse levels of metabolic health markers and clustering of risk factors in adults with type 2 diabetes
Namrata Sanjeevi, Jeanne H. Freeland‐Graves
Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics.2023; 36(1): 31. CrossRef - Need for improving immunization status and preventive care in diabetes mellitus patients
Teresa Gisinger, Alexandra Kautzky-Willer, Michael Leutner
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift.2023; 135(13-14): 336. CrossRef - Nanoparticles encapsulating sesame seeds (Sesamum indicum) oil: Physicochemical, antioxidant and enzymatic inhibition properties
Narimane Lammari, Mehdi Louaer, Ouahida Louaer, Chawki Bensouici, Ahmed Zermane, Abdelhamid Elaissari, Abdeslam Hassen Meniai
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2023; 79: 104003. CrossRef - Significant Association between Subclinical Left Cardiac Dysfunction and Liver Stiffness in Metabolic Syndrome Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Alexandru Apostu, Daniel Malita, Sergiu-Florin Arnautu, Mirela-Cleopatra Tomescu, Dan Gaiță, Alina Popescu, Ruxandra Mare, Ramona Gidea, Diana-Aurora Arnautu
Medicina.2023; 59(2): 328. CrossRef - An examination of causal associations and shared risk factors for diabetes and cardiovascular diseases in the East Asian population: A Mendelian randomization study
Yulin Guo, Jie Gao, Yan Liu, Yanxiong Jia, Xiangguang An, Xitao Zhang, Pixiong Su
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Synthesis, Cytotoxicity and In Vitro α-Glucosidase Inhibition of New N-Substituted Glitazone and Rhodanine Derivatives
N. R. Tshiluka, M. V. Bvumbi, S. S. Mnyakeni-Moleele
Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry.2023; 49(2): 384. CrossRef - Prevalence of QT prolongation and its risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes
Khaled Aburisheh, Mohammad F. AlKheraiji, Saleh I. Alwalan, Arthur C. Isnani, Mohamed Rafiullah, Muhammad Mujammami, Assim A. Alfadda
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adapted Diabetes Complications Severity Index and Charlson Comorbidity Index in predicting all-cause and cause-specific mortality among patients with type 2 diabetes
Yu-Wen Hu, Chiu-Mei Yeh, Chia-Jen Liu, Tzeng-Ji Chen, Nicole Huang, Yiing-Jenq Chou
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2023; 11(2): e003262. CrossRef - Influenza: Diabetes as a risk factor for severe related-outcomes and the effectiveness of vaccination in diabetic population. A meta-analysis of observational studies
Ilaria Dicembrini, Giovanni Antonio Silverii, Alessandra Clerico, Riccardo Fornengo, Giovanni Gabutti, Valeria Sordi, Silvio Tafuri, Ottavia Peruzzi, Edoardo Mannucci
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(6): 1099. CrossRef - Research progress on classification, sources and functions of dietary polyphenols for prevention and treatment of chronic diseases
Wei Li, Haihong Chen, Bing Xu, Yi Wang, Canyang Zhang, Yong Cao, Xinhui Xing
Journal of Future Foods.2023; 3(4): 289. CrossRef - Greater efficiency of polyherbal drug encapsulated biosynthesized chitosan nano-biopolymer on diabetes and its complications
G. Revathi, S. Elavarasi, K. Saravanan, M. Ashokkumar, Chukwuebuka Egbuna
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 240: 124445. CrossRef - Variations in all-cause mortality, premature mortality and cause-specific mortality among persons with diabetes in Ontario, Canada
Laura C Rosella, Kathy Kornas, Ednah Negatu, Limei Zhou
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2023; 11(3): e003378. CrossRef - The relationship between family support and the level of self care in type 2 diabetes patients
Fatma Gul Zeren, Ozlem Canbolat
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(4): 341. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus-related hospital admissions and prescriptions of antidiabetic agents in England and Wales: an ecological study
Gayda Abdel Rahman AbuHammad, Abdallah Y. Naser, Loay Khaled Mohammad Hassouneh
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Administration of alloxan and streptozotocin in Sprague Dawley rats and the challenges in producing diabetes model
Indah Fajarwati, Dedy Duryadi Solihin, Tutik Wresdiyati, Irmanida Batubara
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.2023; 1174(1): 012035. CrossRef - Impacts of SARS-CoV-2 on diabetes mellitus: A pre and post pandemic evaluation
A H M Nurun Nabi, Akio Ebihara, Hossain Uddin Shekhar
World Journal of Virology.2023; 12(3): 151. CrossRef - Risk Stratification for Herpes Simplex Virus Pneumonia Using Elastic Net Penalized Cox Proportional Hazard Algorithm with Enhanced Explainability
Yu-Chiang Wang, Wan-Ying Lin, Yi-Ju Tseng, Yiwen Fu, Weijia Li, Yu-Chen Huang, Hsin-Yao Wang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(13): 4489. CrossRef - Bee Honey Extract Attenuates Hyperglycemia in Induced Type 1 Diabetes: Impact of Antioxidant and Angiogenesis Activities on Diabetic Severity In Vivo
Ahmed H. Alghamdi, Ibrahim M. Shatla, Soliman Shreed, Atif H. Khirelsied, Mohamed F. El-Refaei
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(14): 8045. CrossRef - Increased Left Atrial Stiffness is Significantly Associated with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation in Diabetic Patients
Diana-Aurora Arnautu, Sergiu-Florin Arnautu, Mirela-Cleopatra Tomescu, Silvia Luca, Constantin-Tudor Luca
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 2077. CrossRef - Cost-effectiveness analysis of implementing polygenic risk score in a workplace cardiovascular disease prevention program
Deo Mujwara, Jen Kintzle, Paolo Di Domenico, George B. Busby, Giordano Bottà
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes associates with mortality in critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: No diabetes paradox in COVID-19
Priscila Bellaver, Larissa Schneider, Ariell F. Schaeffer, Lilian Rodrigues Henrique, Joíza Lins Camargo, Fernando Gerchman, Cristiane B. Leitão, Tatiana H. Rech
Heliyon.2023; 9(8): e18554. CrossRef - New Insights into the Role of Oxidative Stress in the Development of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications
Julia Matzenbacher dos Santos, Qing Zhong, Sandra A. Benite-Ribeiro, Thiago Gomes Heck
Journal of Diabetes Research.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - A paradigm shift for cardiovascular outcome evaluation in diabetes: Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) to major adverse vascular events (MAVE)
Ashu Rastogi, Anand Sudhayakumar, Nicolaas C. Schaper, Edward B. Jude
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(11): 102875. CrossRef - Assessing Elevated Blood Glucose Levels Through Blood Glucose Evaluation and Monitoring Using Machine Learning and Wearable Photoplethysmography Sensors: Algorithm Development and Validation
Bohan Shi, Satvinder Singh Dhaliwal, Marcus Soo, Cheri Chan, Jocelin Wong, Natalie W C Lam, Entong Zhou, Vivien Paitimusa, Kum Yin Loke, Joel Chin, Mei Tuan Chua, Kathy Chiew Suan Liaw, Amos W H Lim, Fadil Fatin Insyirah, Shih-Cheng Yen, Arthur Tay, Seng
JMIR AI.2023; 2: e48340. CrossRef - Cost-Utility of an Exercise Referral Scheme Versus Doing Nothing in Flemish Adults: Exploring the Impact of Key Assumptions
Amber Werbrouck, Masja Schmidt, Koen Putman, Steven Simoens, Nick Verhaeghe, Lieven Annemans
Journal of Physical Activity and Health.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Community-based models of care for management of type 2 diabetes mellitus among non-pregnant adults in sub-Saharan Africa: A scoping review
Emmanuel Firima, Lucia Gonzalez, Fabiola Ursprung, Elena Robinson, Jacqueline Huber, Jennifer M. Belus, Fabian Raeber, Ravi Gupta, Gibrilla F. Deen, Alain Amstutz, Bailah Leigh, Maja Weisser, Niklaus Daniel Labhardt, Rehana Abdus Salam
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(11): e0278353. CrossRef - Omega-3 supplementation and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Felipe Mendes Delpino, Lílian Munhoz Figueiredo, Bruna Gonçalves Cordeiro da Silva, Taiciane Gonçalves da Silva, Gicele Costa Mintem, Renata Moraes Bielemann, Denise Petrucci Gigante
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2022; 62(16): 4435. CrossRef - The effect of real‐time monitoring of physical activity intensity in diabetic patients
Rumi Tanaka, Kimie Fujita, Satoko Maeno, Kanako Yakushiji, Satomi Tanaka, Keizo Ohnaka, Kenji Ashida, Shohei Sakamoto, Masatoshi Nomura
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with influenza vaccine coverage among patients with diabetes: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2018
A. Lum Han
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2022; 42(2): 297. CrossRef - Interacción entre el estadio de la enfermedad renal crónica y la diabetes mellitus como factores asociados con mortalidad en pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica: un estudio de cohortes externas
Laura E. Villegas Sierra, Melisa Buriticá Agudelo, Carlos Enrique Yepes Delgado, Yanett Marcela Montoya Jaramillo, Fabián Jaimes Barragan
Nefrología.2022; 42(5): 540. CrossRef - Influence of glucose supplementation on biofilm formation of Candida albicans and Candida glabrata isolated from diabetic and non-diabetic individuals
Pedro Castania Amadio Domingues, Viviane de Cássia Oliveira, Felipe Lazarini Bim, Carolina Patrícia Aires, André Pereira dos Santos, Denise Tornavoi de Castro, Cláudia Helena Silva-Lovato, Denise de Andrade, Evandro Watanabe
Archives of Oral Biology.2022; 134: 105339. CrossRef - The influence of the disclosure of diabetes on the cognitive, physical ability and diabetes self‐management in diabetic employed adults in Saudi Arabia
Sitah Alshutwi, Eman Miligi, Lujain Alhumidan, Adel F. Almutairi
Nursing Open.2022; 9(2): 978. CrossRef - Effect of fermented cassava tuber on the gene expression of PI3K/Akt signaling and AMPK pathway in STZ-NA-induced diabetic rats
Rio Jati Kusuma, Desty Ervira Puspaningtyas, Puspita Mardika Sari
Nutrition & Food Science .2022; 52(2): 213. CrossRef - A fractional order control model for Diabetes and COVID-19 co-dynamics with Mittag-Leffler function
Andrew Omame, Ugochukwu K. Nwajeri, M. Abbas, Chibueze P. Onyenegecha
Alexandria Engineering Journal.2022; 61(10): 7619. CrossRef - Enhancing Choices Regarding the Administration of Insulin Among Patients With Diabetes Requiring Insulin Across Countries and Implications for Future Care
Ileana Mardare, Stephen M. Campbell, Johanna C. Meyer, Israel Abebrese Sefah, Amos Massele, Brian Godman
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dyslipidemia Among Patients With Type 1 Diabetes and Its Associated Factors in Saudi Arabia: An Analytical Cross-Sectional Study
Abdullah A Alrasheed
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prickly Pear Cacti (Opuntia spp.) Cladodes as a Functional Ingredient for Hyperglycemia Management: A Brief Narrative Review
Rao Raahim Kashif, Nathan M. D’Cunha, Duane D. Mellor, Natalie I. Alexopoulos, Domenico Sergi, Nenad Naumovski
Medicina.2022; 58(2): 300. CrossRef - Machine learning for predicting chronic diseases: a systematic review
F.M. Delpino, Â.K. Costa, S.R. Farias, A.D.P. Chiavegatto Filho, R.A. Arcêncio, B.P. Nunes
Public Health.2022; 205: 14. CrossRef - Effects of blueberry and cranberry on type 2 diabetes parameters in individuals with or without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Felipe Mendes Delpino, Lílian Munhoz Figueiredo, Taiciane Gonçalves da Silva, Thaynã Ramos Flores
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2022; 32(5): 1093. CrossRef - Momordica charantia nanoparticles potentiate insulin release and modulate antioxidant gene expression in pancreas of diabetic rats
Olusola Olalekan Elekofehinti
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - GLP-1 receptor agonists in diabetic kidney disease: current evidence and future directions
Ji Hee Yu, So Young Park, Da Young Lee, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 41(2): 136. CrossRef - Pharmacological Study: Synergistic Antidiabetic Activity of Cinnamon Bark and Zingiber Extract in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
Eva Nurinda, Nurul Kusumawardani, Ari Susiana Wulandari , Annisa Fatmawati, E. Emelda, Husnatun Nisa, Nurjani A. Hasan, Wahyu Fajar Iriyanti, Mardiatun Rohmah, Puji Lestari, Veriani Aprilia
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(T8): 1. CrossRef - Integrating a Polygenic Risk Score for Coronary Artery Disease as a Risk‐Enhancing Factor in the Pooled Cohort Equation: A Cost‐Effectiveness Analysis Study
Deo Mujwara, Geoffrey Henno, Stephen T. Vernon, Siyang Peng, Paolo Di Domenico, Brock Schroeder, George B. Busby, Gemma A Figtree, Giordano Bottà
Journal of the American Heart Association.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of mechanistic pathways of bariatric surgery in patients with diabetes mellitus: A Bayesian network meta‐analysis
Chaoxing Lin, Trevor James Jun‐Ming Yeong, Wen Hui Lim, Cheng Han Ng, Chun En Yau, Yip Han Chin, Mark D. Muthiah, Poay Huan Loh, Roger S. Y. Foo, Shao Feng Mok, Asim Shabbir, Georgios K. Dimitriadis, Chin Meng Khoo, Nicholas W. S. Chew
Obesity.2022; 30(7): 1380. CrossRef - Diabetes and COVID-19: Biological profile of type 2 diabetic patients with COVID-19 in Pointe-Noire, Congo
Anicet Boumba Luc Magloire, Batchy Aladin Atandi, Elenga-Bongo Charley, Pouki Freddy Saturnin, Kibouilou Fredy, Balanda Christ Nkouanga, Dabo Tidiane Cheick Ahmed, Wahar Saar Abdoul, Mahouanga Didel Mampassi, Voumbi Ghislain Loubano, Moukassa Donatien
Global Journal of Clinical Virology.2022; 7(1): 001. CrossRef - Integrated Nutritional Supports for Diabetic Patients During COVID-19
Infection: A Comprehensive Review
A.K. Obidul Huq, Abu Naim Mohammad Bazlur Rahim, S.M. Golam Moktadir, Ielias Uddin, Mohammad Zahidul Manir, Muhammad Abu Bakr Siddique, Khaleda Islam, Md. Sirajul Islam
Current Diabetes Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanisms of COVID-19 pathogenesis in diabetes
Chandrakala Aluganti Narasimhulu, Dinender K. Singla
American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology.2022; 323(3): H403. CrossRef - Improvement in Age at Mortality and Changes in Causes of Death in the Population with Diabetes: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 466. CrossRef - Gender difference in association between diabetes mellitus and all-cause mortality in atrial fibrillation patients
Li Tian, Yan-min Yang, Jun Zhu, Han Zhang, Xing-hui Shao
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2022; 36(9): 108265. CrossRef - An Overview of Diabetes Mellitus in Egypt and the Significance of Integrating Preventive Cardiology in Diabetes Management
Mohamed R Abouzid, Karim Ali, Ibrahim Elkhawas, Shorouk M Elshafei
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between diabetes mellitus and functionality in knee osteoarthritis: a cross-sectional study
Serdar KAYMAZ, Sanem Aslıhan AYKAN
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2022; 5(4): 1114. CrossRef - In-hospital hyperglycemia but not diabetes mellitus alone is associated with increased in-hospital mortality in community-acquired pneumonia (CAP): a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies prior to COVID-19
Rahul D Barmanray, Nathan Cheuk, Spiros Fourlanos, Peter B Greenberg, Peter G Colman, Leon J Worth
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(4): e002880. CrossRef - The association between leukocyte telomere length and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is partially mediated by inflammation: a meta-analysis and population-based mediation study
Tieshan Wang, Zhaoqi Jia, Sen Li, Yuxin Li, Tingting Yu, Tao Lu, Yuanyuan Shi
BMC Pulmonary Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy on the Duration of Sciatic Nerve Block with 1.3% Liposomal Bupivacaine and 0.25% Bupivacaine Hydrochloride in a Mouse Model
Liljana Markova, Erika Cvetko, Chiedozie Kenneth Ugwoke, Simon Horvat, Nejc Umek, Tatjana Stopar Pintarič
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(9): 1824. CrossRef - Free, Conjugated, and Bound Phenolics in Peel and Pulp from Four Wampee Varieties: Relationship between Phenolic Composition and Bio-Activities by Multivariate Analysis
Xue Lin, Yousheng Shi, Pan Wen, Xiaoping Hu, Lu Wang
Antioxidants.2022; 11(9): 1831. CrossRef - Protocol: Developing a framework to improve glycaemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo
Jean-Pierre Fina Lubaki, Olufemi Babatunde Omole, Joel Msafiri Francis, David Desseauve
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(9): e0268177. CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index is associated with poor sleep quality in apparently healthy subjects: A cross-sectional study
Daniela Carolina Avelino, Alessandra da Silva, Larissa Oliveira Chaves, Júlia Cristina Cardoso Carraro, Fernanda de Carvalho Vidigal, Josefina Bressan
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms interlinking biological clock and diabetes mellitus: Effective tools for better management
Chandrasekaran Sankaranarayanan, Perumal Subramanian
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2022; 16(11): 102639. CrossRef - Amyloid Fibrillation of Insulin: Amelioration Strategies and Implications for Translation
Megren H. A. Fagihi, Sourav Bhattacharjee
ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science.2022; 5(11): 1050. CrossRef - Potential Roles of Anti-Inflammatory Plant-Derived Bioactive Compounds Targeting Inflammation in Microvascular Complications of Diabetes
Yahia A. Kaabi
Molecules.2022; 27(21): 7352. CrossRef - Additive interaction of diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease in cancer patient mortality risk
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Re-understanding and focusing on normoalbuminuric diabetic kidney disease
Na An, Bi-tao Wu, Yu-wei Yang, Zheng-hong Huang, Jia-fu Feng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Coexistent Lichen Amyloidosis and Acquired Reactive Perforating Collagenosis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Post-Thyroidectomy Hypothyroidism Due to Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Rare Case
Eva Krishna Sutedja, Muhamad Radyn Haryadi Widjaya, Hartati Purbo Dharmadji, Pati Aji Achdiat, Laila Tsaqilah
International Medical Case Reports Journal.2022; Volume 15: 745. CrossRef - Interaction between the stage of chronic kidney disease and diabetes mellitus as factors associated with mortality in chronic kidney disease patients: An external cohort study
Laura E. Villegas Sierra, Melisa Buriticá Agudelo, Carlos Enrique Yepes Delgado, Yanett Marcela Montoya Jaramillo, Fabián Jaimes Barragan
Nefrología (English Edition).2022; 42(5): 540. CrossRef - Effects of Pea Protein on Satiety, Postprandial Glucose Response and Appetite Hormones: A Literature Review
Amy Choi
Undergraduate Research in Natural and Clinical Science and Technology (URNCST) Journal.2022; 6(10): 1. CrossRef - Hemoglobin glycation index is associated with incident chronic kidney disease in subjects with impaired glucose metabolism: A 10-year longitudinal cohort study
Wonjin Kim, Taehwa Go, Dae Ryong Kang, Eun Jig Lee, Ji Hye Huh
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2021; 35(1): 107760. CrossRef - Coronavirus Disease 2019 (SARS-CoV-2) and polycystic ovarian disease: Is there a higher risk for these women?
Giuseppe Morgante, Libera Troìa, Vincenzo De Leo
The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.2021; 205: 105770. CrossRef - Regional differences in diabetes across Europe – regression and causal forest analyses
Péter Elek, Anikó Bíró
Economics & Human Biology.2021; 40: 100948. CrossRef - Active ingredients and mechanisms of Phellinus linteus (grown on Rosa multiflora) for alleviation of Type 2 diabetes mellitus through network pharmacology
Ki Kwang Oh, Md. Adnan, Dong Ha Cho
Gene.2021; 768: 145320. CrossRef - Application of Telemedicine in Diabetes Care: The Time is Now
Felix Aberer, Daniel A. Hochfellner, Julia K. Mader
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(3): 629. CrossRef - Long-term outcomes after kidney transplant failure and variables related to risk of death and probability of retransplant: Results from a single-center cohort study in Brazil
Lúcio R. Requião-Moura, Cássio R. Moreira Albino, Paula Rebello Bicalho, Érika de Arruda Ferraz, Luciana Mello de Mello Barros Pires, Maurício Fregonesi Rodrigues da Silva, Alvaro Pacheco-Silva, Justyna Gołębiewska
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(1): e0245628. CrossRef - Estimating the disease burden of Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus patients considering its complications
Juyoung Kim, Seok-Jun Yoon, Min-Woo Jo, Brecht Devleesschauwer
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(2): e0246635. CrossRef - Susceptibility for Some Infectious Diseases in Patients With Diabetes: The Key Role of Glycemia
Jesús Chávez-Reyes, Carlos E. Escárcega-González, Erika Chavira-Suárez, Angel León-Buitimea, Priscila Vázquez-León, José R. Morones-Ramírez, Carlos M. Villalón, Andrés Quintanar-Stephano, Bruno A. Marichal-Cancino
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediabetes, Diabetes, and the Risk of All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in a Japanese Working Population: Japan Epidemiology Collaboration on Occupational Health Study
Zobida Islam, Shamima Akter, Yosuke Inoue, Huan Hu, Keisuke Kuwahara, Tohru Nakagawa, Toru Honda, Shuichiro Yamamoto, Hiroko Okazaki, Toshiaki Miyamoto, Takayuki Ogasawara, Naoko Sasaki, Akihiko Uehara, Makoto Yamamoto, Takeshi Kochi, Masafumi Eguchi, Tai
Diabetes Care.2021; 44(3): 757. CrossRef - Proportion and mortality of Iranian diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, hypertension and cardiovascular disease patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis
Hamid Mirjalili, Seyed Alireza Dastgheib, Seyed Hossein Shaker, Reza Bahrami, Mahta Mazaheri, Seyed Mohamad Hossein Sadr-Bafghi, Jalal Sadeghizadeh-Yazdi, Hossein Neamatzadeh
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(1): 905. CrossRef - Prevalence and associated factors of diabetes mellitus among tuberculosis patients in Brunei Darussalam: A 6-year retrospective cohort study
Nurfakhrina Omar, Justin Wong, Kyaw Thu, Md Fathi Alikhan, Liling Chaw
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2021; 105: 267. CrossRef - Diabetes and COVID-19
Zohair Jamil Gazzaz
Open Life Sciences.2021; 16(1): 297. CrossRef - Review of potential risk groups for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
M. Naveed, M. Naeem, M. ur Rahman, M. Gul Hilal, M.A. Kakakhel, G. Ali, A. Hassan
New Microbes and New Infections.2021; 41: 100849. CrossRef - COVID-19 from the interdisciplinary standpoint. Round table
M. N. Mamedov, Yu. V. Rodionova, I. S. Yavelov, M. I. Smirnova, E. N. Dudinskaya, V. I. Potievskaya
Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention.2021; 20(3): 2849. CrossRef - Diabetes is a major cause of influenza-associated mortality in Mexico
A. Gómez-Gómez, E.L. Sánchez-Ramos, D.E. Noyola
Revue d'Épidémiologie et de Santé Publique.2021; 69(4): 205. CrossRef - Ameliorative potential of Operculina turpethum against streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats: biochemical and histopathological studies
Neeraj Choudhary, Gopal L. Khatik, Rekha Sharma, Navneet Khurana, Richard Lobo, Shvetank Bhatt, Devesh Tewari, Ashish Suttee
3 Biotech.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Current utilization patterns for long-acting insulin analogues including biosimilars among selected Asian countries and the implications for the future
Brian Godman, Mainul Haque, Santosh Kumar, Salequl Islam, Jaykaran Charan, Farhana Akter, Amanj Kurdi, Eleonora Allocati, Muhammed Abu Bakar, Sagir Abdur Rahim, Nusrat Sultana, Farzana Deeba, M. A. Halim Khan, A. B. M Muksudul Alam, Iffat Jahan, Zubair Ma
Current Medical Research and Opinion.2021; 37(9): 1529. CrossRef - Association between cardiometabolic risk factors and COVID-19 susceptibility, severity and mortality: a review
Yasaman Sharifi, Moloud Payab, Erfan Mohammadi-Vajari, Seyed Morsal Mosallami Aghili, Farshad Sharifi, Neda Mehrdad, Elham Kashani, Zhaleh Shadman, Bagher Larijani, Mahbube Ebrahimpur
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(2): 1743. CrossRef - Association of ACE I/D and PAI-1 4G/5G polymorphisms with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus
Somaye Miri, Mohammad Hasan Sheikhha, Seyed Alireza Dastgheib, Seyed Amir Shaker, Hossein Neamatzadeh
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(2): 1191. CrossRef - Assessment and Management of Diabetic Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Amit K Verma, Mirza Masroor Ali Beg, Deepti Bhatt, Kapil Dev, Mohammed A Alsahli, Arshad Husain Rahmani, Yamini Goyal
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 3131. CrossRef - Higher admission activated partial thromboplastin time, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, serum sodium, and anticoagulant use predict in-hospital COVID-19 mortality in people with Diabetes: Findings from Two University Hospitals in the U.K
Ahmed Iqbal, Marni Greig, Muhammad Fahad Arshad, Thomas H. Julian, Sher Ee Tan, Jackie Elliott
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 178: 108955. CrossRef - Risk factors for severe outcomes in people with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19: a cross-sectional database study
Emilio Ortega, Rosa Corcoy, Mònica Gratacòs, Francesc Xavier Cos Claramunt, Manel Mata-Cases, Ramon Puig-Treserra, Jordi Real, Bogdan Vlacho, Esmeralda Castelblanco, Pere Domingo, Kamlesh Khunti, Josep Franch-Nadal, Didac Mauricio
BMJ Open.2021; 11(7): e051237. CrossRef - Diabetes increases the risk of COVID-19 in an altitude dependent manner: An analysis of 1,280,806 Mexican patients
Juan Alonso Leon-Abarca, Arianna Portmann-Baracco, Mayte Bryce-Alberti, Carlos Ruiz-Sánchez, Roberto Alfonso Accinelli, Jorge Soliz, Gustavo Francisco Gonzales, Chiara Lazzeri
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0255144. CrossRef - Botanical Interventions to Improve Glucose Control and Options for Diabetes Therapy
Peter Smoak, Susan J. Burke, J. Jason Collier
SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine.2021; 3(12): 2465. CrossRef - Antidiabetic bioactive compounds from Tetrastigma angustifolia (Roxb.) Deb and Oxalis debilis Kunth.: Validation of ethnomedicinal claim by in vitro and in silico studies
Julfikar Ali Junejo, Kamaruz Zaman, Mithun Rudrapal, Ismail Celik, Emmanuel Ifeanyi Attah
South African Journal of Botany.2021; 143: 164. CrossRef - SGLT2 Inhibition for Cardiovascular Diseases, Chronic Kidney Disease, and NAFLD
Moein Ala
Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Hospitalization costs with degludec versus glargine U100 for patients with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk: Canadian costs applied to SAEs from a randomized outcomes trial
Jean-Eric Tarride, Mansoor Husain, Andreas Andersen, Jens Gundgaard, Maria Luckevich, Thomas Mark, Lily Wagner, Thomas R. Pieber
Journal of Medical Economics.2021; 24(1): 1318. CrossRef - Traditional Uses, Pharmacological Effects, and Molecular Mechanisms of Licorice in Potential Therapy of COVID-19
Qian-hui Zhang, Hao-zhou Huang, Min Qiu, Zhen-feng Wu, Zhan-chang Xin, Xin-fu Cai, Qiang Shang, Jun-zhi Lin, Ding-kun Zhang, Li Han
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent Updates on Free Fatty Acid Receptor 1 (GPR-40) Agonists for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Lata Rani, Ajmer Singh Grewal, Neelam Sharma, Sukhbir Singh
Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry.2021; 21(4): 426. CrossRef - Low Levels of Influenza Vaccine Uptake among the Diabetic Population in Spain: A Time Trend Study from 2011 to 2020
Jose J. Zamorano-Leon, Rodrigo Jimenez-Garcia, Ana Lopez-de-Andres, Javier de-Miguel-Diez, David Carabantes-Alarcon, Romana Albaladejo-Vicente, Rosa Villanueva-Orbaiz, Khaoula Zekri-Nechar, Sara Sanz-Rojo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 11(1): 68. CrossRef - Effects of Short-term Mobile Application Use on Weight Reduction for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Seung Eun Lee, Su-Kyung Park, Ye-Seul Park, Kyoung-Ah Kim, Han Seok Choi, Sang Woo Oh
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2021; 30(4): 345. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus in combination with COVID-19: modern views on therapy
V.I. Tsymbaliuk, M.D. Tronko, Y.G. Antypkin, S.V. Kushnirenko, V.V. Popova
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY.2021; (57): 8. CrossRef - Dietary aldose reductase inhibitors and prevention of diabetic complications
Ameena Anjum, Janamolla Sreeja, Yarlagadda Swapna, Rajesh Bolleddu, Sama Venkatesh
Indian Journal of Health Sciences and Biomedical Research (KLEU).2021; 14(2): 194. CrossRef - Cohort Profile: The Maule Cohort (MAUCO)
Catterina Ferreccio, Andrea Huidobro, Sandra Cortés, Claudia Bambs, Pablo Toro, Vanessa Van De Wyngard, Johanna Acevedo, Fabio Paredes, Pía Venegas, Hugo Verdejo, Ximena Oyarzún-González, Paz Cook, Pablo F Castro, Claudia Foerster, Claudio Vargas, Jill Ko
International Journal of Epidemiology.2020; 49(3): 760. CrossRef - Treating Dyslipidemias in the Primary Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Older Adults with Diabetes Mellitus
MengHee Tan, Mark Paul MacEachern
Clinics in Geriatric Medicine.2020; 36(3): 457. CrossRef - Increased Mortality Risk in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Lithuania
Donata Linkeviciute-Ulinskiene, Auguste Kaceniene, Audrius Dulskas, Ausvydas Patasius, Lina Zabuliene, Giedre Smailyte
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(18): 6870. CrossRef - Proteinuria Is Associated with Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis in Non-Albuminuric Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jaehyun Bae, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 136. CrossRef - COVID-19 and diabetes: Knowledge in progress
Akhtar Hussain, Bishwajit Bhowmik, Nayla Cristina do Vale Moreira
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 162: 108142. CrossRef - Peripheral arterial endothelial dysfunction predicts future cardiovascular events in diabetic patients with albuminuria: a prospective cohort study
Bo Kyung Koo, Woo-Young Chung, Min Kyong Moon
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk Factors in and Long-Term Survival of Patients with Post-Transplantation Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Ching-Yao Cheng, Cheng-Hsu Chen, Ming-Fen Wu, Ming-Ju Wu, Jun-Peng Chen, Ying-Mei Liu, Yu-Chi Hou, Hue-Yu Wang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(12): 4581. CrossRef - Fasting Plasma Glucose Variability and Gastric Cancer Risk in Individuals Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
So-hyeon Hong, Eunjin Noh, Jinsil Kim, Soon Young Hwang, Jun A. Kim, You-Bin Lee, Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology.2020; 11(9): e00221. CrossRef - Trimetazidine Inhibits Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells to Mesenchymal Transition in Diabetic Rats via Upregulation of Sirt1
Yong Yang, Yong Wang, Zuowen He, Yunchang Liu, Chen Chen, Yan Wang, Dao Wen Wang, Hong Wang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Beta Cell Imaging—From Pre-Clinical Validation to First in Man Testing
Stephane Demine, Michael L. Schulte, Paul R. Territo, Decio L. Eizirik
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(19): 7274. CrossRef - The role of dental insurance in mitigating mortality among working‐age U.S. adults with periodontitis
Naveed Sadiq, Janice C. Probst, Anwar T. Merchant, Amy B. Martin, Deepika Shrestha, M. Mahmud Khan
Journal of Clinical Periodontology.2020; 47(11): 1294. CrossRef - Antidiabetic Activity of Triterpenoids from Anisophyllea disticha
Miftahul Fikriyah, Muhammad Almurdani, Yum Eryanti, Hilwan Y. Teruna
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2020; 1655(1): 012033. CrossRef - Therapeutic efficacy of umbilical cord-derived stem cells for diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis study
Dina H. Kassem, Mohamed M. Kamal
Stem Cell Research & Therapy.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Loss of Smell in COVID-19 Patients: Lessons and Opportunities
Dennis Mathew
Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus and COVID-19: current issues of pathogenesis, clinic and therapy. Literature review
В. І. Цимбалюк, М. Д. Тронько, Ю. Г. Антипкін, В. В. Попова
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY.2020; (54): 8. CrossRef - Increased Age of Death and Change in Causes of Death Among Persons With Diabetes Mellitus From the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Purva Rupeeyam of bhela indriya sthana-an explorative study
Kshama Gupta, Prasad Mamidi
International Journal of Complementary & Alternative Medicine.2020; 13(6): 228. CrossRef - The COVID-19 pandemic and diabetes mellitus
Athanasia Papazafiropoulou, Stavros Antonopoulos
Archives of Medical Science – Atherosclerotic Diseases.2020; 5(1): 200. CrossRef - Diabetes and Cancer: Cancer Should Be Screened in Routine Diabetes Assessment
Sunghwan Suh, Kwang-Won Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 733. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus, Still Major Threat to Mortality from Various Causes
Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(3): 273. CrossRef - The Need to Improve the Quality of Diabetes Care in Korea
Seung Jin Han, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association of type 2 diabetes mellitus with dementia‐related and non–dementia‐related mortality among postmenopausal women: A secondary competing risks analysis of the women's health initiative
- Epidemiology
- The Evidence for an Obesity Paradox in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Seung Jin Han, Edward J. Boyko
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(3):179-187. Published online May 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0055
- 6,375 View
- 122 Download
- 61 Web of Science
- 61 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Although overweight/obesity is a major risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus, there is increasing evidence that overweight or obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus experience lower mortality compared with patients of normal weight. This paradoxical finding, known as the “obesity paradox,” occurs in other chronic diseases, and in type 2 diabetes mellitus is particularly perplexing given that lifestyle intervention with one goal being weight reduction is an important feature of the management of this condition. We summarize in this review the findings from clinical and epidemiologic studies that have investigated the association between overweight and obesity (usually assessed using body mass index [BMI]) and mortality in type 2 diabetes mellitus and discuss potential causes of the obesity paradox. We conclude that most studies show evidence of an obesity paradox, but important conflicting findings still exist. We also evaluate if potential bias might explain the obesity paradox in diabetes, including, for example, the presence of confounding factors, measurement error due to use of BMI as an index of obesity, and reverse causation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between the weight-adjusted waist index and the odds of type 2 diabetes mellitus in United States adults: a cross-sectional study
Dongdong Zheng, Suzhen Zhao, Dan Luo, Feng Lu, Zhishen Ruan, Xiaokang Dong, Wenjing Chen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Racial and Ethnic Disparities in Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease
Mohammad R. Ali, Hadjer Nacer, Claire A. Lawson, Kamlesh Khunti
Canadian Journal of Cardiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Independent and interactive associations of heart rate and obesity with type 2 diabetes mellites: A population‐based study
Tianxin Zhu, Qingyu Chen, Hongxing Chen, Lili You, Dan Liu, Xiaoyun Zhang, Feng Li, Hongshi Wu, Juying Tang, Diaozhu Lin, Kan Sun, Li Yan, Meng Ren
Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Two‐sided roles of adipose tissue: Rethinking the obesity paradox in various human diseases from a new perspective
Jing Pan, Jianqiong Yin, Lu Gan, Jianxin Xue
Obesity Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lean or diabetic subtypes predict increased all-cause and disease-specific mortality in metabolic-associated fatty liver disease
Goh Eun Chung, Su Jong Yu, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Yuri Cho, Kyu-na Lee, Dong Wook Shin, Donghee Kim, Yoon Jun Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon, Kyungdo Han, Eun Ju Cho
BMC Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dynamic changes in prevalence of type 2 diabetes along with associated factors in Bangladesh: Evidence from two national cross-sectional surveys (BDHS 2011 and BDHS 2017–18)
Sabiha Shirin Sara, Ashis Talukder, Ka Yiu Lee, Nayan Basak, Shaharior Rahman Razu, Iqramul Haq, Chuton Deb Nath
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(2): 102706. CrossRef - Association of dietary intake with body mass index and glycemic profile among newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Keddagoda Gamage Piyumi Wasana, Anoja Priyadarshani Attanayake, Thilak Priyantha Weerarathna, Devpura Arachchige Bandumalee Nimalshanthi Amarasekera, Kamani Ayoma Perera Wijewardana Jayatilaka
American Journal of Human Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Can lipophilic pollutants in adipose tissue explain weight change‐related risk in type 2 diabetes mellitus?
Duk‐Hee Lee, In‐Kyu Lee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(4): 528. CrossRef - Visceral fat and attribute-based medicine in chronic kidney disease
Hiroshi Kataoka, Kosaku Nitta, Junichi Hoshino
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A primary care delivered, technology supported lifestyle program for Type 2 Diabetes Management: An evaluation of changes in metabolic health, feasibility, and acceptability – A pilot interventional study protocol
Pennie J. Taylor, Campbell H. Thompson, Thomas P. Wycherley, Grant D. Brinkworth
Contemporary Clinical Trials Communications.2023; 33: 101152. CrossRef - The medical model of “obesity” and the values behind the guise of health
Kayla R. Mehl
Synthese.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Elevated MMP-8 levels, inversely associated with BMI, predict mortality in mechanically ventilated patients: an observational multicenter study
Hang Ruan, Shu-sheng Li, Qin Zhang, Xiao Ran
Critical Care.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity and 30-day case fatality after hyperglycemic crisis hospitalizations in Korea: a national cohort study
Hojun Yoon, Hyun Ho Choi, Giwoong Choi, Sun Ok Song, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2023; 5(3): 74. CrossRef - Normal‐weight central obesity and risk of cardiovascular and microvascular events in adults with prediabetes or diabetes: Chinese and British cohorts
Pingting Zhong, Shaoying Tan, Zhuoting Zhu, Ziyu Zhu, Yi Liang, Wenyong Huang, Wei Wang
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Overweight and obesity are associated with better survival in STEMI patients with diabetes
Hamza Chaudhry, Ramez Bodair, Ziyad Mahfoud, Soha Dargham, Jassim Al Suwaidi, Hani Jneid, Charbel Abi Khalil
Obesity.2023; 31(11): 2834. CrossRef - Influence of diabetes and obesity on ten-year outcomes after coronary artery bypass grafting in the arterial revascularisation trial
Maria Stefil, Mario Gaudino, Umberto Benedetto, Stephen Gerry, Alastair Gray, Belinda Lees, Bruno Podesser, Lukasz Krzych, Lokeswara Rao Sajja, David Taggart, Marcus Flather
Clinical Research in Cardiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Poor glycaemic control: prevalence, factors and implications for the care of patients with type 2 diabetes in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo: a cross-sectional study
Jean-Pierre Fina Lubaki, Olufemi Babatunde Omole, Joel Msafiri Francis
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of obesity indices and triglyceride glucose-related parameters to predict type 2 diabetes mellitus among normal-weight elderly in China
Pan Ke, Xia Wu, Minzhi Xu, Jie Feng, Hongbin Xu, Yong Gan, Chao Wang, Zhenyu Deng, Xiang Liu, Wenning Fu, Qingfeng Tian, Yan He, Lirong Zhong, Heng Jiang, Zuxun Lu
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity.2022; 27(3): 1181. CrossRef - Association Between Obesity and Cardiovascular Disease in Elderly Patients With Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Sangmo Hong, Jung Hwan Park, Kyungdo Han, Chang Beom Lee, Dong Sun Kim, Sung Hoon Yu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(2): e515. CrossRef - The Relationship between the Lipid Accumulation Product and Beta-cell Function in Korean Adults with or without Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The 2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hye Eun Cho, Seung Bum Yang, Mi Young Gi, Ju Ae Cha, so Young Park, Hyun Yoon
Endocrine Research.2022; 47(2): 80. CrossRef - Body mass index and all-cause mortality in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus in South Korea: a retrospective cohort study
Jae-Seok Hong, Hee-Chung Kang
BMJ Open.2022; 12(4): e048784. CrossRef - Social determinants of obesity in American Indian and Alaska Native peoples aged ≥ 50 years
R Turner Goins, Cheryl Conway, Margaret Reid, Luohua Jiang, Jenny Chang, Kimberly R Huyser, Angela G Brega, John F Steiner, Amber L Fyfe-Johnson, Michelle Johnson-Jennings, Vanessa Hiratsuka, Spero M Manson, Joan O’Connell
Public Health Nutrition.2022; 25(8): 2064. CrossRef - Cardiorespiratory Fitness, BMI, Mortality, and Cardiovascular Disease in Adults with Overweight/Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
ANDREW C. WILLS, ELSA VAZQUEZ ARREOLA, MUIDEEN T. OLAIYA, JEFFREY M. CURTIS, MARGARETA I. HELLGREN, ROBERT L. HANSON, WILLIAM C. KNOWLER
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise.2022; 54(6): 994. CrossRef - Spline Longitudinal Multi-response Model for the Detection of Lifestyle-
Based Changes in Blood Glucose of Diabetic Patients
Anna Islamiyati
Current Diabetes Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The obesity paradox: Retinopathy, obesity, and circulating risk markers in youth with type 2 diabetes in the TODAY Study
Lynne L. Levitsky, Kimberly L. Drews, Morey Haymond, Rose A. Glubitosi-Klug, Lorraine E. Levitt Katz, Mihai Mititelu, William Tamborlane, Jeanie B. Tryggestad, Ruth S. Weinstock
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2022; 36(11): 108259. CrossRef - Distribution of lean mass and mortality risk in patients with type 2 diabetes
Li Ding, Yuxin Fan, Jingting Qiao, Jing He, Ruodan Wang, Qing He, Jingqiu Cui, Zhongshu Ma, Fangqiu Zheng, Hua Gao, Chenlin Dai, Hongyan Wei, Jun Li, Yuming Cao, Gang Hu, Ming Liu
Primary Care Diabetes.2022; 16(6): 824. CrossRef - Current Knowledge on the Pathophysiology of Lean/Normal-Weight Type 2 Diabetes
Teresa Salvatore, Raffaele Galiero, Alfredo Caturano, Luca Rinaldi, Livio Criscuolo, Anna Di Martino, Gaetana Albanese, Erica Vetrano, Christian Catalini, Celestino Sardu, Giovanni Docimo, Raffaele Marfella, Ferdinando Carlo Sasso
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 24(1): 658. CrossRef - The obesity paradox and diabetes
Giovanni Gravina, Federica Ferrari, Grazia Nebbiai
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity.2021; 26(4): 1057. CrossRef - Implicating the effect of ketogenic diet as a preventive measure to obesity and diabetes mellitus
Sachin Kumar, Tapan Behl, Monika Sachdeva, Aayush Sehgal, Shilpa Kumari, Arun Kumar, Gagandeep Kaur, Harlokesh Narayan Yadav, Simona Bungau
Life Sciences.2021; 264: 118661. CrossRef - Diagnosis of obesity based on body composition‐associated health risks—Time for a change in paradigm
Anja Bosy‐Westphal, Manfred J. Müller
Obesity Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Body mass index and clinical outcomes in patients with intracerebral haemorrhage: results from the China Stroke Center Alliance
Zhentang Cao, Xinmin Liu, Zixiao Li, Hongqiu Gu, Yingyu Jiang, Xingquan Zhao, Yongjun Wang
Stroke and Vascular Neurology.2021; 6(3): 424. CrossRef - Obesity and Overweight Are Associated with Minimal Extrathyroidal Extension, Multifocality and Bilaterality of Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Krzysztof Kaliszewski, Dorota Diakowska, Marta Rzeszutko, Jerzy Rudnicki
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(5): 970. CrossRef - Obesity paradox in patients with cardiovascular diseases and diabetes mellitus type 2 (analytical review)
Margarita P. Zaikina, Valentina A. Kapustina, Stanislav I. Savel'ev
HEALTH CARE OF THE RUSSIAN FEDERATION.2021; 65(2): 135. CrossRef - Risk factors for adverse outcomes among 35 879 veterans with and without diabetes after diagnosis with COVID-19
Pandora L Wander, Elliott Lowy, Lauren A Beste, Luis Tulloch-Palomino, Anna Korpak, Alexander C Peterson, Bessie A Young, Edward J Boyko
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2021; 9(1): e002252. CrossRef - Obesity and glycemic control among people with type 2 diabetes in the United States: A retrospective cohort study using insurance claims data
Kristina S. Boye, Maureen J. Lage, Vivian Thieu, Shraddha Shinde, Shivanie Dhamija, Jay Patrick Bae
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2021; 35(9): 107975. CrossRef - Differential effects of body mass index on domain-specific cognitive outcomes after stroke
Minwoo Lee, Mi Sun Oh, San Jung, Ju-Hun Lee, Chul-Ho Kim, Min Uk Jang, Young Eun Kim, Hee-Joon Bae, Jaeseol Park, Yeonwook Kang, Byung-Chul Lee, Jae-Sung Lim, Kyung-Ho Yu
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between traditional and non-traditional anthropometric indices and cardiometabolic risk factors among inpatients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study
Sahar Golabi, Sajad Ajloo, Fatemeh Maghsoudi, Maryam Adelipour, Mahshid Naghashpour
Journal of International Medical Research.2021; 49(10): 030006052110499. CrossRef - Impact of preexisting type 2 diabetes mellitus and antidiabetic drugs on all-cause and cause-specific mortality among Medicaid-insured women diagnosed with breast cancer
Wayne R. Lawrence, Akiko S. Hosler, Margaret Gates Kuliszewski, Matthew C. Leinung, Xiuling Zhang, Maria J. Schymura, Francis P. Boscoe
Cancer Epidemiology.2020; 66: 101710. CrossRef - Serum Adiponectin and Progranulin Level in Patients with Benign Thyroid Nodule or Papillary Thyroid Cancer
Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Ji-Sup Yun, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 396. CrossRef - Obesity, sleep apnea, and cancer
Isaac Almendros, Miguel A. Martinez-Garcia, Ramon Farré, David Gozal
International Journal of Obesity.2020; 44(8): 1653. CrossRef - Association of Body Mass Index With Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Atrial Fibrillation: A Report From the FANTASIIA Registry
Vicente Bertomeu‐Gonzalez, José Moreno‐Arribas, María Asunción Esteve‐Pastor, Inmaculada Roldán‐Rabadán, Javier Muñiz, Paula Raña‐Míguez, Martín Ruiz‐Ortiz, Ángel Cequier, Vicente Bertomeu‐Martínez, Lina Badimón, Manuel Anguita, Gregory Y. H. Lip, Francis
Journal of the American Heart Association.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of type 2 diabetes according to the cumulative exposure to metabolic syndrome or obesity: A nationwide population‐based study
You‐Bin Lee, Da Hye Kim, Seon Mee Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Yong Gyu Park, Kyungdo Han, Hye Jin Yoo
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2020; 11(6): 1583. CrossRef - Gut microbiota of obese and diabetic Thai subjects and interplay with dietary habits and blood profiles
Lucsame Gruneck, Niwed Kullawong, Kongkiat Kespechara, Siam Popluechai
PeerJ.2020; 8: e9622. CrossRef Multistate Models to Predict Development of Late Complications of Type 2 Diabetes in an Open Cohort Study
Roqayeh Aliyari, Ebrahim Hajizadeh, Ashraf Aminorroaya, Farshad Sharifi, Iraj Kazemi, Ahmad-Reza Baghestani
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 1863. CrossRef- Early weaning induces short‐ and long‐term effects on pancreatic islets in Wistar rats of both sexes
Carla Bruna Pietrobon, Rosiane Aparecida Miranda, Iala Milene Bertasso, Paulo Cezar de Freitas Mathias, Maria Lúcia Bonfleur, Sandra Lucinei Balbo, Marise Auxiliadora de Barros Reis, Márcia Queiroz Latorraca, Vanessa Cristina Arantes, Elaine de Oliveira,
The Journal of Physiology.2020; 598(3): 489. CrossRef - A negative impact of recent weight loss on in-hospital mortality is not modified by overweight and obesity
Rocco Barazzoni, Isabella Sulz, Karin Schindler, Stephan C. Bischoff, Gianluca Gortan Cappellari, Michael Hiesmayr
Clinical Nutrition.2020; 39(8): 2510. CrossRef - Body mass index and mortality among middle-aged Japanese individuals with diagnosed diabetes: The Japan Public Health Center-based prospective study (JPHC study)
Chiho Yamazaki, Atsushi Goto, Motoki Iwasaki, Norie Sawada, Shino Oba, Mitsuhiko Noda, Hiroyasu Iso, Hiroshi Koyama, Shoichiro Tsugane
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 164: 108198. CrossRef Is the Obesity Paradox in Type 2 Diabetes Due to Artefacts of Biases? An Analysis of Pooled Cohort Data from the Heinz Nixdorf Recall Study and the Study of Health in Pomerania
Bernd Kowall, Andreas Stang, Raimund Erbel, Susanne Moebus, Astrid Petersmann, Antje Steveling, Karl-Heinz Jöckel, Henry Völzke
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 1989. CrossRef- Associations between BMI, waist circumference, central obesity and outcomes in type II diabetes mellitus: The ACCORD Trial
Charles A. German, Brian Laughey, Alain G. Bertoni, Joseph Yeboah
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2020; 34(3): 107499. CrossRef - Trends in mechanical ventilation use and mortality over time in patients receiving mechanical ventilation in Spain from 2001 to 2015.
Javier de-Miguel-Díez, Rodrigo Jiménez-García, Valentín Hernández-Barrera, Jose J Zamorano-Leon, Rosa Villanueva-Orbaiz, Romana Albaladejo-Vicente, Ana López-de-Andrés
European Journal of Internal Medicine.2020; 74: 67. CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes mellitus: pathogenesis and genetic diagnosis
D. Himanshu, Wahid Ali, Mohd Wamique
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2020; 19(2): 1959. CrossRef - Prevalence and factors associated with overweight and obesity among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Uganda—a descriptive retrospective study
Salome Tino, Billy N Mayanja, Michael Charles Mubiru, Emmanuel Eling, Edward Ddumba, Pontiano Kaleebu, Moffat Nyirenda
BMJ Open.2020; 10(11): e039258. CrossRef - Nutrition Therapy in Critically Ill Overweight Elderly Patient with Heart Failure, Myocardial Infarction, Pneumonia, and Chronic Kidney Disease
Christina RUSLI, Agussalim BUKHARI, Nurpudji A. TASLIM, Suryani AS’AD, Haerani RASYID
Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology.2020; 66(Supplement): S25. CrossRef - Obesity and childhood asthma
Jason E. Lang
Current Opinion in Pulmonary Medicine.2019; 25(1): 34. CrossRef - Why primary obesity is a disease?
Antonino De Lorenzo, Santo Gratteri, Paola Gualtieri, Andrea Cammarano, Pierfrancesco Bertucci, Laura Di Renzo
Journal of Translational Medicine.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Impaired compensatory hyperinsulinemia among nonobese type 2 diabetes patients: a cross-sectional study
Jit Sarkar, Sujay Krishna Maity, Abhishek Sen, Titli Nargis, Dipika Ray, Partha Chakrabarti
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 10: 204201881988902. CrossRef - Sedentary behaviour is associated with diabetes mellitus in adults: findings of a cross-sectional analysis from the Brazilian National Health System
Ítalo Ribeiro Lemes, Xuemei Sui, Bruna Camilo Turi-Lynch, Duck-chul Lee, Steven N Blair, Rômulo Araújo Fernandes, Jamile Sanches Codogno, Henrique Luiz Monteiro
Journal of Public Health.2019; 41(4): 742. CrossRef - Obesity Paradox in Chronic Liver Diseases: Product of Bias or a Real Thing?
Ines Bilic Curcic, Maja Cigrovski Berkovic, Lucija Kuna, Hrvoje Roguljic, Robert Smolic, Silvija Canecki Varzic, Lucija Virovic Jukic, Martina Smolic
Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology.2019; 7(3): 1. CrossRef - From the Obesity Tsunami to the Diabetes Avalanche: Primordial Prevention of the Diabesity-Related Cardiovascular Epidemic by Diabeto-Cardiologists
Mustafa Karakurt, Burak Acar, Ozcan Ozeke, Mustafa Bilal Ozbay, Yasin Ozen, Sefa Unal, Mustafa Karanfil, Cagri Yayla, Serkan Cay, Orhan Maden, Dursun Aras, Serkan Topaloglu, Sinan Aydogdu, Zehra Golbasi
Angiology.2019; 70(4): 371. CrossRef - Increased Plasma Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 (DPP4) Activity Is an Obesity-Independent Parameter for Glycemic Deregulation in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Jit Sarkar, Titli Nargis, Om Tantia, Sujoy Ghosh, Partha Chakrabarti
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - INVESTIGATING INDIVIDUAL FACTORS RELATED TO READMISSION OF PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES- A CROSS-SECTIONAL STUDY
Valiallah Dashtpour, Mehran Hesaraki, Mahnaz Abavisani, Mahdieh Sari, Sudabeh Ahmadidarrehsima
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2018; 7(53): 5604. CrossRef
- Association between the weight-adjusted waist index and the odds of type 2 diabetes mellitus in United States adults: a cross-sectional study
- Epidemiology
- Ten-Year Mortality Trends for Adults with and without Diabetes Mellitus in South Korea, 2003 to 2013
- Kyeong Jin Kim, Tae Yeon Kwon, Sungwook Yu, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Dong Seop Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Yousung Park, Nam Hoon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(5):394-401. Published online April 26, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0088
- 4,868 View
- 58 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background To estimate and compare the trends of all-cause and cause-specific mortality rates for subjects with and without diabetes in South Korea, from 2003 to 2013.
Methods Using a population-based cohort (2003 to 2013), we evaluated annual mortality rates in adults (≥30 years) with and without diabetes. The number of subjects in this analysis ranged from 585,795 in 2003 to 670,020 in 2013.
Results Age- and sex-adjusted all-cause mortality rates decreased consistently in both groups from 2003 to 2013 (from 14.4 to 9.3/1,000 persons in subjects with diabetes and from 7.9 to 4.4/1,000 persons in those without diabetes). The difference in mortality rates between groups also decreased (6.61 per 1,000 persons in 2003 to 4.98 per 1,000 persons in 2013). The slope associated with the mortality rate exhibited a steeper decrease in subjects with diabetes than those without diabetes (regression coefficients of time: −0.50 and −0.33, respectively;
P =0.004). In subjects with diabetes, the mortality rate from cardiovascular disease decreased by 53.5% (from 2.73 to 1.27 per 1,000 persons,P for trend <0.001). Notably, the decrease in mortality from ischemic stroke (79.2%, from 1.20 to 0.25 per 1,000 persowns) was more profound than that from ischemic heart disease (28.3%, from 0.60 to 0.43 per 1,000 persons).Conclusion All-cause and cardiovascular mortality rates decreased substantially from 2003 to 2013, and the decline in ischemic stroke mortality mainly contributed to the decreased cardiovascular mortality in Korean people with diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Green tea consumption and incidence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetic patients with overweight/obesity: a community-based cohort study
Bingyue Liu, Shujun Gu, Jin Zhang, Hui Zhou, Jian Su, Sudan Wang, Qian Sun, Zhengyuan Zhou, Jinyi Zhou, Chen Dong
Archives of Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in all-cause and cause-specific mortality in older adults with and without diabetes: A territory-wide analysis in one million older adults in Hong Kong
Aimin Yang, Tingting Chen, Mai Shi, Eric Lau, Raymond SM Wong, Jones Chan, Juliana CN Chan, Elaine Chow
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111618. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2023; 12(1): 12. CrossRef - Lipid Management in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Lipid and Atherosclerosis Consensus Statement
Ye Seul Yang, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 1. CrossRef - Letter: Triglyceride-Glucose Index Predicts Cardiovascular Outcome in Metabolically Unhealthy Obese Population: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study (J Obes Metab Syndr 2022;31:178-86)
Gwanpyo Koh
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 179. CrossRef - Management of Dyslipidemia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung Ae Lee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 111. CrossRef - 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes: Management of Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Ye Seul Yang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 135. CrossRef - The Characteristics and Risk of Mortality in the Elderly Korean Population
Sunghwan Suh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 522. CrossRef - Current Status of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Target Achievement in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea Compared with Recent Guidelines
Soo Jin Yun, In-Kyung Jeong, Jin-Hye Cha, Juneyoung Lee, Ho Chan Cho, Sung Hee Choi, SungWan Chun, Hyun Jeong Jeon, Ho-Cheol Kang, Sang Soo Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Gwanpyo Koh, Su Kyoung Kwon, Jae Hyuk Lee, Min Kyong Moon, Junghyun Noh, Cheol-Young Park, Sung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 464. CrossRef - Health-related Quality of Life Instrument With 8 Items for Use in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Validation Study in Korea
Juyoung Kim, Hyeon-Jeong Lee, Min-Woo Jo
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2022; 55(3): 234. CrossRef - Improvement in Age at Mortality and Changes in Causes of Death in the Population with Diabetes: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 466. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - Diabetic Ketoacidosis and COVID-19: A Retrospective Observational Study
Govind Nagdev, Gajanan Chavan, Charuta Gadkari, Gaurav Sahu
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in the effects of pre‐transplant diabetes on mortality and cardiovascular events after kidney transplantation
Ja Young Jeon, Soo Jung Kim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Ji Hyun Park, Bumhee Park, Chang‐Kwon Oh, Seung Jin Han
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(5): 811. CrossRef - Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports
Na-young Kim, Eunyeong Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Yong-Hoon Lee, Eun Young Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 349. CrossRef - Polysomnographic phenotyping of obstructive sleep apnea and its implications in mortality in Korea
Jeong-Whun Kim, Tae-Bin Won, Chae-Seo Rhee, Young Mi Park, In-Young Yoon, Sung-Woo Cho
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Peripheral arterial endothelial dysfunction predicts future cardiovascular events in diabetic patients with albuminuria: a prospective cohort study
Bo Kyung Koo, Woo-Young Chung, Min Kyong Moon
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Metformin treatment for patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology consensus statement
Kyu Yeon Hur, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Miyeun Han, Dong Won Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 39(1): 32. CrossRef - Outcomes for Inappropriate Renal Dose Adjustment of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Population-Based Study
Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Mayo Clinic Proceedings.2020; 95(1): 101. CrossRef - Metformin Treatment for Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
Kyu Yeon Hur, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Miyeun Han, Dong Won Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 3. CrossRef - A systematic review of trends in all-cause mortality among people with diabetes
Lei Chen, Rakibul M. Islam, Joanna Wang, Thomas R. Hird, Meda E. Pavkov, Edward W. Gregg, Agus Salim, Maryam Tabesh, Digsu N. Koye, Jessica L. Harding, Julian W. Sacre, Elizabeth L. M. Barr, Dianna J. Magliano, Jonathan E. Shaw
Diabetologia.2020; 63(9): 1718. CrossRef - Diabetic ketoacidosis precipitated by COVID-19: A report of two cases and review of literature
Pavan Kumar Reddy, Mohammad Shafi Kuchay, Yatin Mehta, Sunil Kumar Mishra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(5): 1459. CrossRef - Prognostic value of long-term gamma-glutamyl transferase variability in individuals with diabetes: a nationwide population-based study
Da Young Lee, Kyungdo Han, Ji Hee Yu, Sanghyun Park, Ji A Seo, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Sin Gon Kim, Seon Mee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Yong Gyu Park, Nan Hee Kim
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Arterial stiffness is an independent predictor for risk of mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: the REBOUND study
Jeong Mi Kim, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, Jong Ho Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Soon Hee Lee, Chang Won Lee, Min Chul Kim, Jun Hyeob Ahn, Jinmi Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The triglyceride glucose index is a simple and low-cost marker associated with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: a population-based study
Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
BMC Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased Age of Death and Change in Causes of Death Among Persons With Diabetes Mellitus From the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Letter: Comparison of the Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy 20 mg with Rosuvastatin 5 mg and Ezetimibe 10 mg Combination Therapy on Lipid Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J2019;43:582–9)
Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 909. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus, Still Major Threat to Mortality from Various Causes
Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(3): 273. CrossRef - Diabetes and Cancer: Cancer Should Be Screened in Routine Diabetes Assessment
Sunghwan Suh, Kwang-Won Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 733. CrossRef - Trends of Diabetes Epidemic in Korea
Ji Cheol Bae
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(5): 377. CrossRef
- Green tea consumption and incidence of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetic patients with overweight/obesity: a community-based cohort study

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





