
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- A Prospective 1-Year Follow-Up of Glycemic Status and C-Peptide Levels of COVID-19 Survivors with Dysglycemia in Acute COVID-19 Infection
- David Tak Wai Lui, Chi Ho Lee, Ying Wong, Carol Ho Yi Fong, Kimberly Hang Tsoi, Yu Cho Woo, Kathryn Choon Beng Tan
- Received June 5, 2023 Accepted October 13, 2023 Published online March 11, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0175 [Epub ahead of print]
- 745 View
- 35 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We evaluated changes in glycemic status, over 1 year, of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) survivors with dysglycemia in acute COVID-19.
Methods
COVID-19 survivors who had dysglycemia (defined by glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] 5.7% to 6.4% or random glucose ≥10.0 mmol/L) in acute COVID-19 were recruited from a major COVID-19 treatment center from September to October 2020. Matched non-COVID controls were recruited from community. The 75-g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) were performed at baseline (6 weeks after acute COVID-19) and 1 year after acute COVID-19, with HbA1c, insulin and C-peptide measurements. Progression in glycemic status was defined by progression from normoglycemia to prediabetes/diabetes, or prediabetes to diabetes.
Results
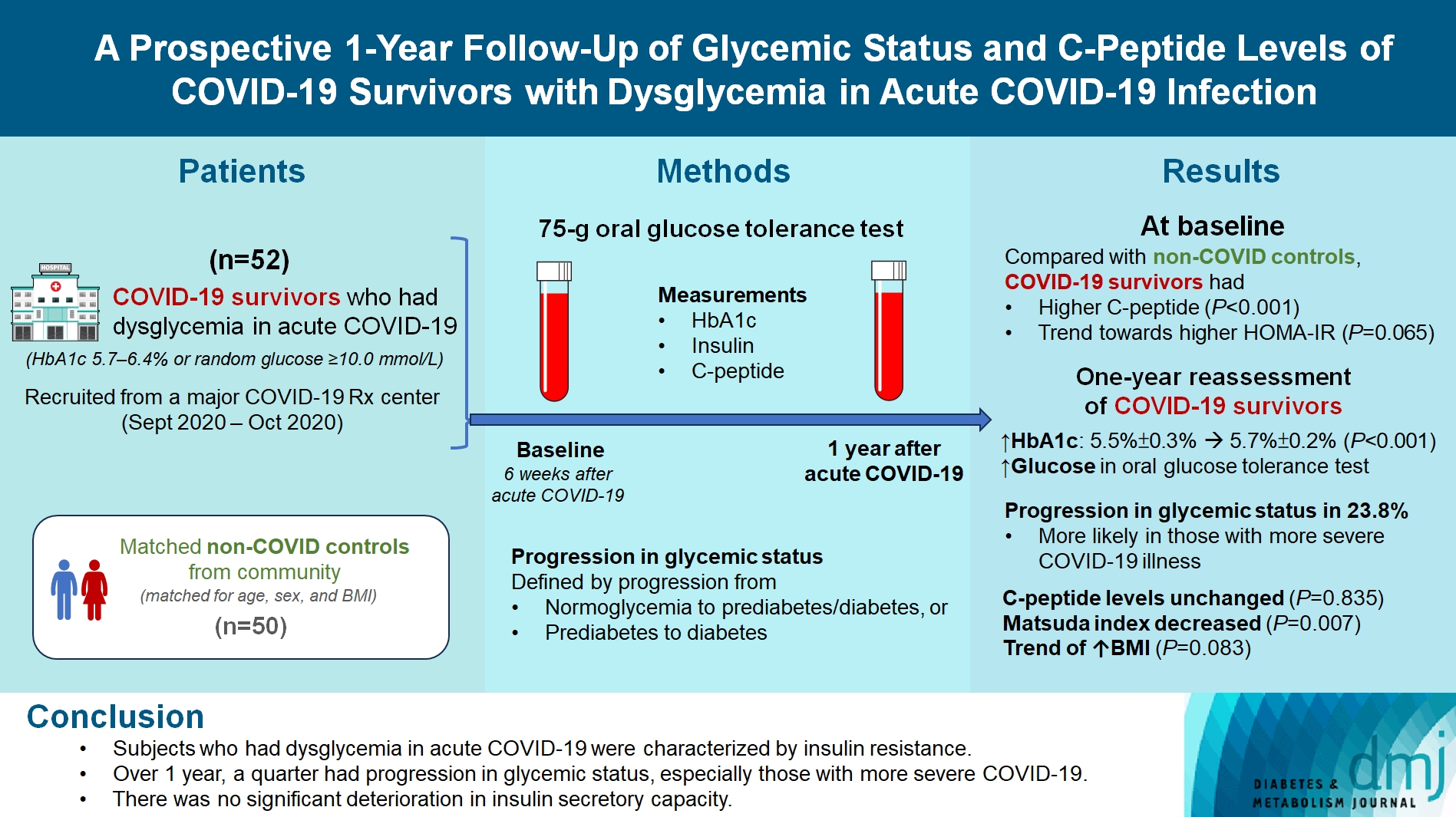
Fifty-two COVID-19 survivors were recruited. Compared with non-COVID controls, they had higher C-peptide (P< 0.001) and trend towards higher homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (P=0.065). Forty-three COVID-19 survivors attended 1-year reassessment. HbA1c increased from 5.5%±0.3% to 5.7%±0.2% (P<0.001), with increases in glucose on OGTT at fasting (P=0.089), 30-minute (P=0.126), 1-hour (P=0.014), and 2-hour (P=0.165). At baseline, 19 subjects had normoglycemia, 23 had prediabetes, and one had diabetes. Over 1 year, 10 subjects (23.8%; of 42 non-diabetes subjects at baseline) had progression in glycemic status. C-peptide levels remained unchanged (P=0.835). Matsuda index decreased (P=0.007) and there was a trend of body mass index increase from 24.4±2.7 kg/m2 to 25.6±5.2 (P=0.083). Subjects with progression in glycemic status had more severe COVID-19 illness than non-progressors (P=0.030). Reassessment was not performed in the control group.
Conclusion
Subjects who had dysglycemia in acute COVID-19 were characterized by insulin resistance. Over 1 year, a quarter had progression in glycemic status, especially those with more severe COVID-19. Importantly, there was no significant deterioration in insulin secretory capacity.
Sulwon Lecture 2023
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Insulin Resistance, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Clinical and Experimental Perspective
- Inha Jung, Dae-Jeong Koo, Won-Young Lee
- Received October 4, 2023 Accepted December 26, 2024 Published online February 2, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0350 [Epub ahead of print]
- 976 View
- 59 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
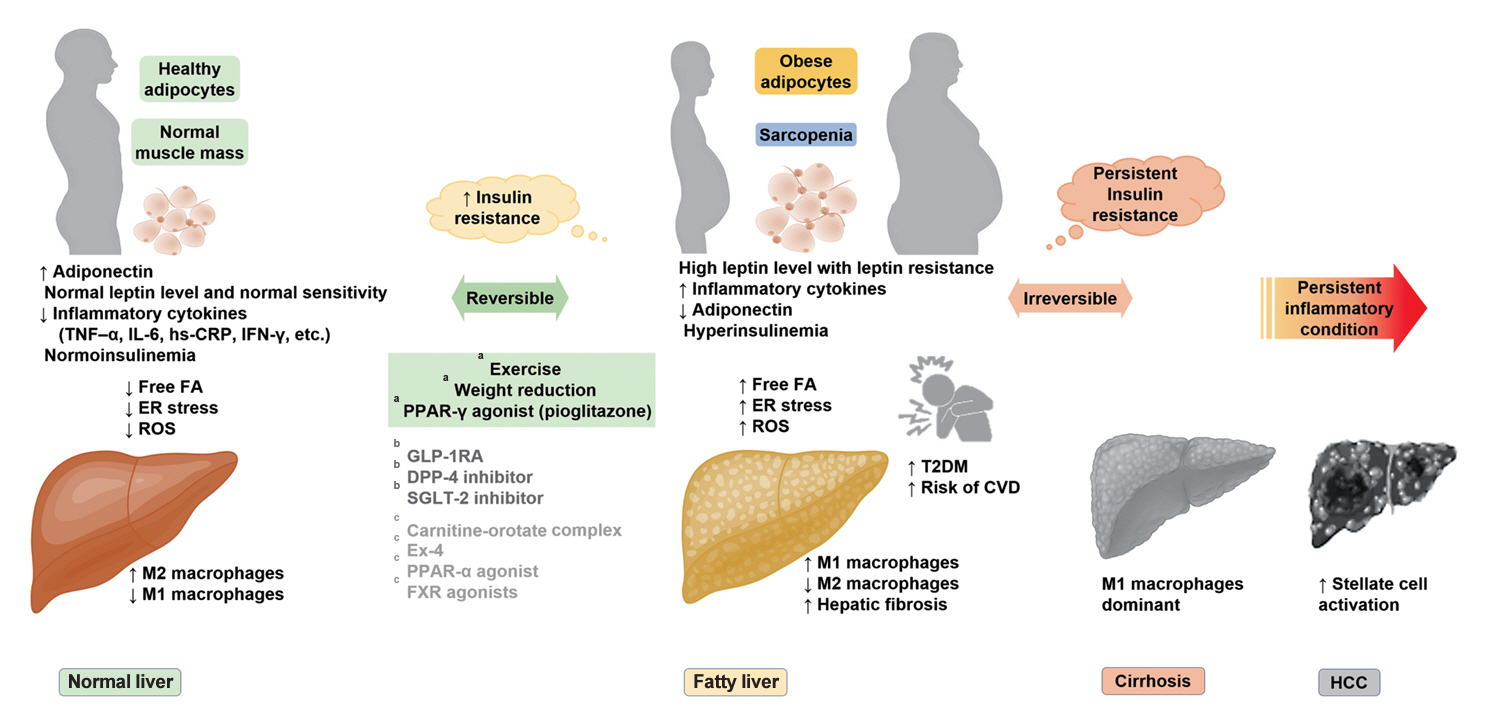
ePub - It has been generally accepted that insulin resistance (IR) and reduced insulin secretory capacity are the basic pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). In addition to genetic factors, the persistence of systemic inflammation caused by obesity and the associated threat of lipotoxicity increase the risk of T2DM. In particular, the main cause of IR is obesity and subjects with T2DM have a higher body mass index (BMI) than normal subjects according to recent studies. The prevalence of T2DM with IR has increased with increasing BMI during the past three decades. According to recent studies, homeostatic model assessment of IR was increased compared to that of the 1990s. Rising prevalence of obesity in Korea have contributed to the development of IR, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and T2DM and cutting this vicious cycle is important. My colleagues and I have investigated this pathogenic mechanism on this theme through clinical and experimental studies over 20 years and herein, I would like to summarize some of our studies with deep gratitude for receiving the prestigious 2023 Sulwon Award.
Original Articles
- Drug/Regimen
- Pioglitazone as Add-on THERAPY in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Inadequately Controlled with Dapagliflozin and Metformin: Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
- Ji Hye Heo, Kyung Ah Han, Jun Hwa Hong, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Jae Myung Yu, Hye Seung Jung, Bong-Soo Cha
- Received September 1, 2023 Accepted October 25, 2023 Published online February 2, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0314 [Epub ahead of print]
- 1,208 View
- 114 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study assessed the efficacy and safety of triple therapy with pioglitazone 15 mg add-on versus placebo in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) inadequately controlled with metformin and dapagliflozin.
Methods
In this multicenter, double-blind, randomized, phase 3 study, patients with T2DM with an inadequate response to treatment with metformin (≥1,000 mg/day) plus dapagliflozin (10 mg/day) were randomized to receive additional pioglitazone 15 mg/day (n=125) or placebo (n=125) for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was the change in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels from baseline to week 24 (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT05101135).
Results
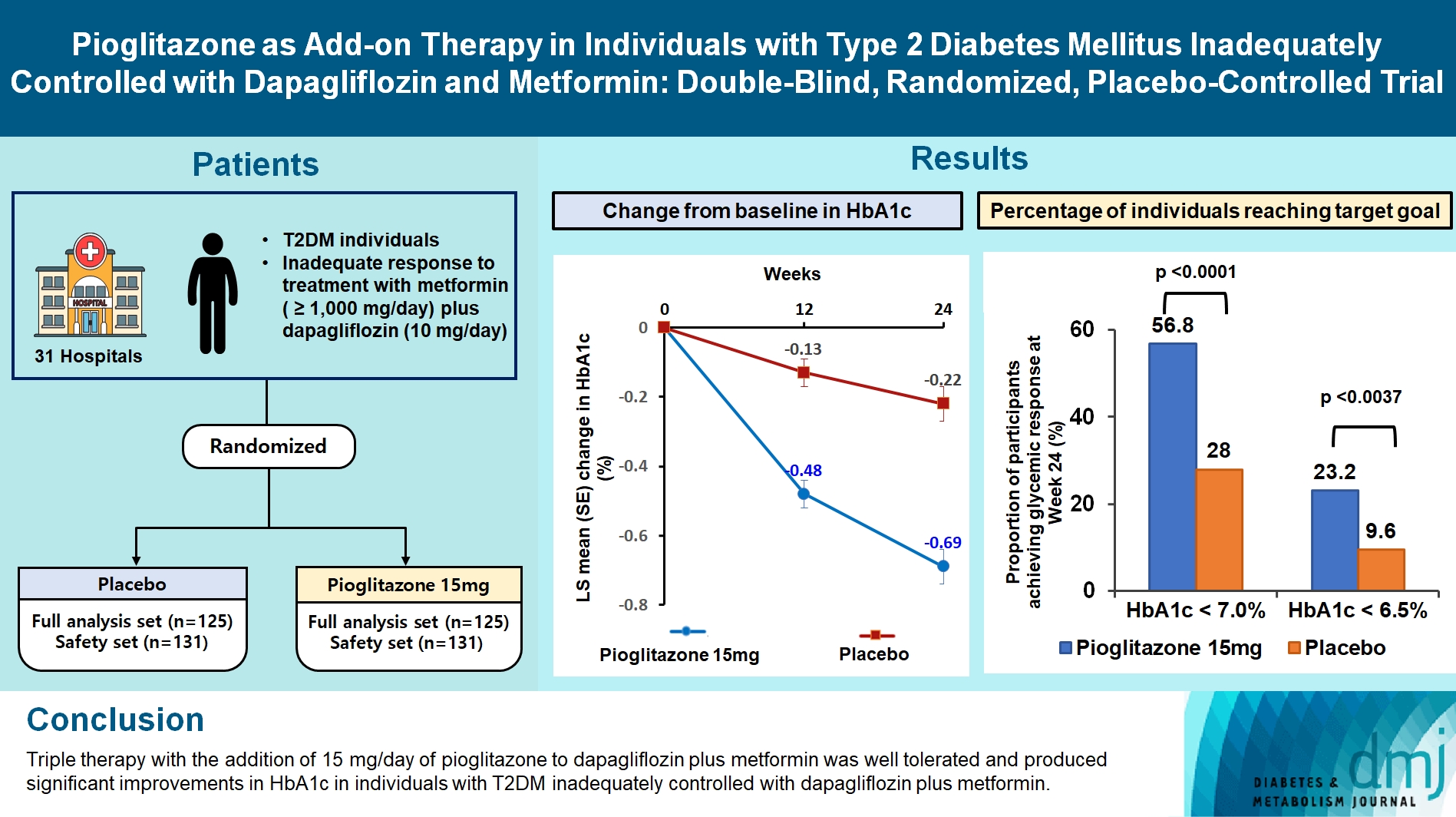
At week 24, the adjusted mean change from baseline in HbA1c level compared with placebo was significantly greater with pioglitazone treatment (–0.47%; 95% confidence interval, –0.61 to –0.33; P<0.0001). A greater proportion of patients achieved HbA1c <7% or <6.5% at week 24 with pioglitazone compared to placebo as add-on to 10 mg dapagliflozin and metformin (56.8% vs. 28% for HbA1c <7%, and 23.2% vs. 9.6% for HbA1c <6.5%; P<0.0001 for all). The addition of pioglitazone also significantly improved triglyceride, highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol levels, and homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance levels, while placebo did not. The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events was similar between the groups, and the incidence of fluid retention-related side effects by pioglitazone was low (1.5%).
Conclusion
Triple therapy with the addition of 15 mg/day of pioglitazone to dapagliflozin plus metformin was well tolerated and produced significant improvements in HbA1c in patients with T2DM inadequately controlled with dapagliflozin plus metformin.
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Harnessing Metabolic Indices as a Predictive Tool for Cardiovascular Disease in a Korean Population without Known Major Cardiovascular Event
- Hyun-Jin Kim, Byung Sik Kim, Yonggu Lee, Sang Bong Ahn, Dong Wook Kim, Jeong-Hun Shin
- Received June 22, 2023 Accepted August 18, 2023 Published online February 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0197 [Epub ahead of print]

- 931 View
- 25 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study evaluated the usefulness of indices for metabolic syndrome, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and insulin resistance (IR), as predictive tools for cardiovascular disease in middle-aged Korean adults.
Methods
The prospective data obtained from the Ansan-Ansung cohort database, excluding patients with major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE). The primary outcome was the incidence of MACCE during the follow-up period.
Results
A total of 9,337 patients were included in the analysis, of whom 1,130 (12.1%) experienced MACCE during a median follow-up period of 15.5 years. The metabolic syndrome severity Z-score, metabolic syndrome severity score, hepatic steatosis index, and NAFLD liver fat score were found to significantly predict MACCE at values above the cut-off point and in the second and third tertiles. Among these indices, the hazard ratios of the metabolic syndrome severity score and metabolic syndrome severity Z-score were the highest after adjusting for confounding factors. The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) of the 10-year atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) score for predicting MACCE was 0.716, and the metabolic syndrome severity Z-score had an AUC of 0.619.
Conclusion
The metabolic syndrome severity score is a highly reliable indicator and was closely associated with the 10-year ASCVD risk score in predicting MACCE in the general population. Given the specific characteristics and limitations of metabolic syndrome severity scores as well as the indices of NAFLD and IR, a more practical scoring system that considers these factors is essential to achieve greater accuracy in forecasting cardiovascular outcomes.
- Pathophysiology
- Deficiency of ASGR1 Alleviates Diet-Induced Systemic Insulin Resistance via Improved Hepatic Insulin Sensitivity
- Xiaorui Yu, Jiawang Tao, Yuhang Wu, Yan Chen, Penghui Li, Fan Yang, Miaoxiu Tang, Abdul Sammad, Yu Tao, Yingying Xu, Yin-Xiong Li
- Published online February 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0124 [Epub ahead of print]
- 853 View
- 59 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Insulin resistance (IR) is the key pathological basis of many metabolic disorders. Lack of asialoglycoprotein receptor 1 (ASGR1) decreased the serum lipid levels and reduced the risk of coronary artery disease. However, whether ASGR1 also participates in the regulatory network of insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism remains unknown.
Methods
The constructed ASGR1 knockout mice and ASGR1-/- HepG2 cell lines were used to establish the animal model of metabolic syndrome and the IR cell model by high-fat diet (HFD) or drug induction, respectively. Then we evaluated the glucose metabolism and insulin signaling in vivo and in vitro.
Results
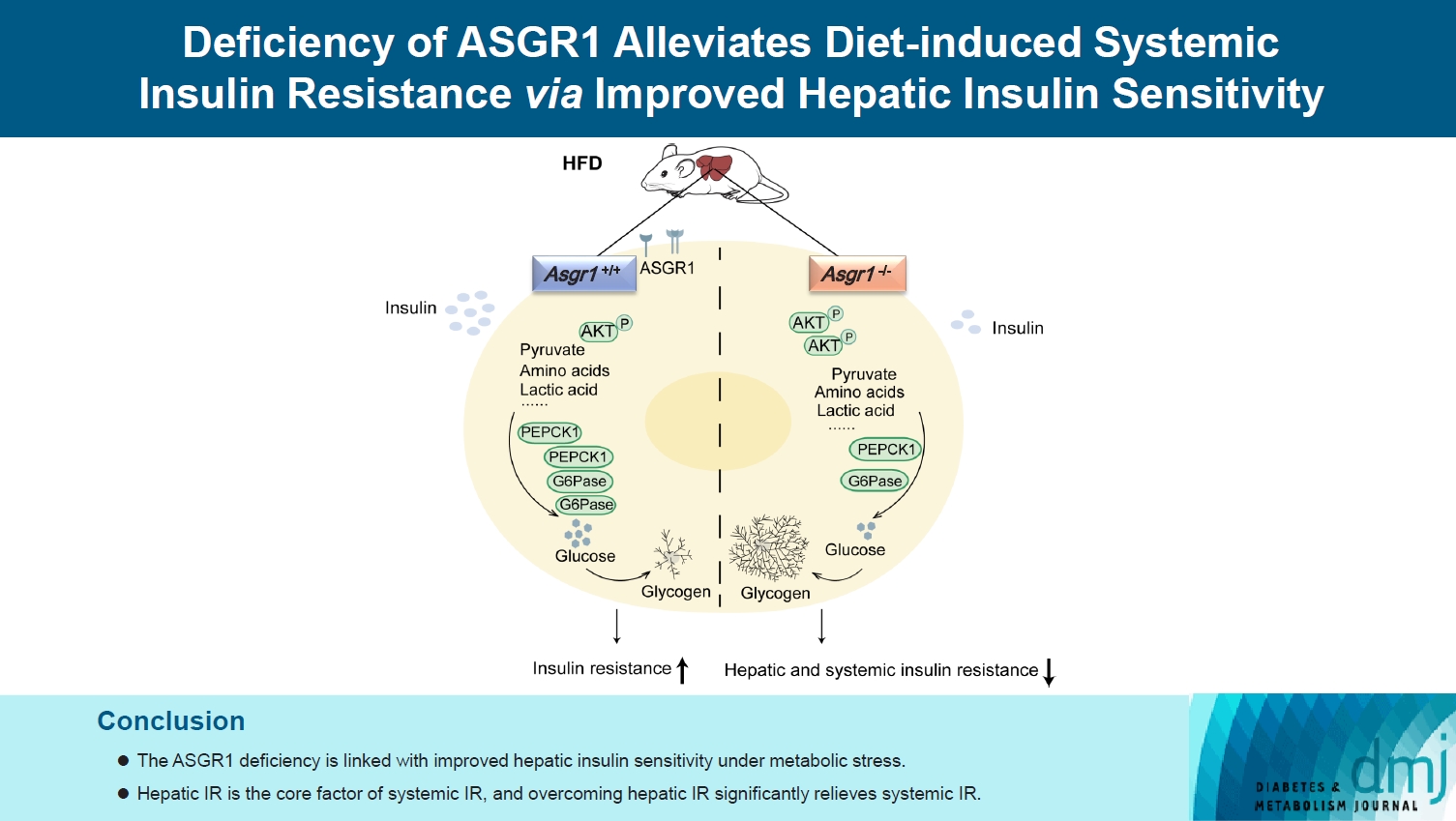
ASGR1 deficiency ameliorated systemic IR in mice fed with HFD, evidenced by improved insulin intolerance, serum insulin, and homeostasis model assessment of IR index, mainly contributed from increased insulin signaling in the liver, but not in muscle or adipose tissues. Meanwhile, the insulin signal transduction was significantly enhanced in ASGR1-/- HepG2 cells. By transcriptome analyses and comparison, those differentially expressed genes between ASGR1 null and wild type were enriched in the insulin signal pathway, particularly in phosphoinositide 3-kinase-AKT signaling. Notably, ASGR1 deficiency significantly reduced hepatic gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis.
Conclusion
The ASGR1 deficiency was consequentially linked with improved hepatic insulin sensitivity under metabolic stress, hepatic IR was the core factor of systemic IR, and overcoming hepatic IR significantly relieved the systemic IR. It suggests that ASGR1 is a potential intervention target for improving systemic IR in metabolic disorders.
Review
- Pathophysiology
- Primordial Drivers of Diabetes Heart Disease: Comprehensive Insights into Insulin Resistance
- Yajie Fan, Zhipeng Yan, Tingting Li, Aolin Li, Xinbiao Fan, Zhongwen Qi, Junping Zhang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):19-36. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0110
- 2,170 View
- 182 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
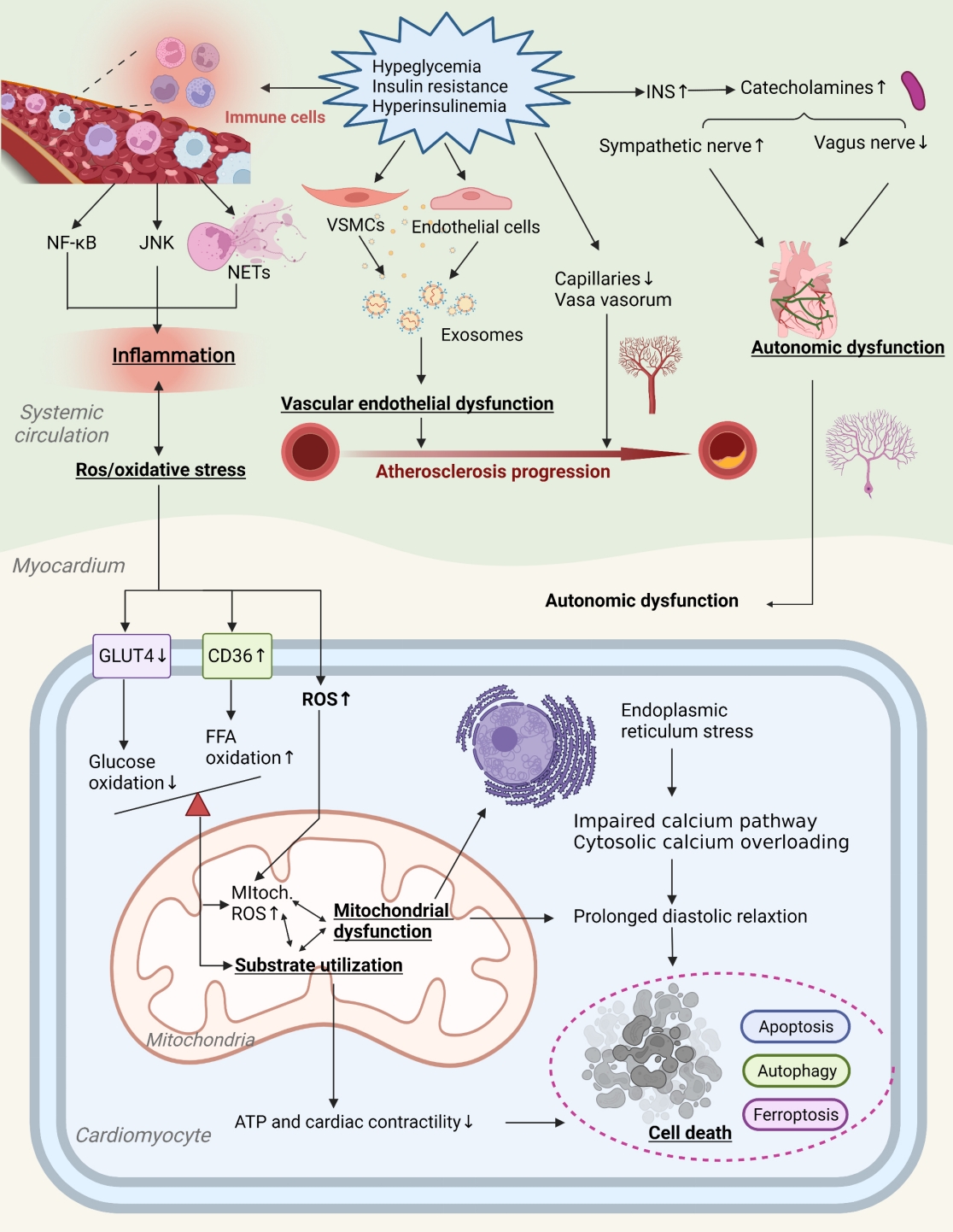
ePub - Insulin resistance has been regarded as a hallmark of diabetes heart disease (DHD). Numerous studies have shown that insulin resistance can affect blood circulation and myocardium, which indirectly cause cardiac hypertrophy and ventricular remodeling, participating in the pathogenesis of DHD. Meanwhile, hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia associated with insulin resistance can directly impair the metabolism and function of the heart. Targeting insulin resistance is a potential therapeutic strategy for the prevention of DHD. Currently, the role of insulin resistance in the pathogenic development of DHD is still under active research, as the pathological roles involved are complex and not yet fully understood, and the related therapeutic approaches are not well developed. In this review, we describe insulin resistance and add recent advances in the major pathological and physiological changes and underlying mechanisms by which insulin resistance leads to myocardial remodeling and dysfunction in the diabetic heart, including exosomal dysfunction, ferroptosis, and epigenetic factors. In addition, we discuss potential therapeutic approaches to improve insulin resistance and accelerate the development of cardiovascular protection drugs.
Original Articles
- Drug/Regimen
- Comparative Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy and Rosuvastatin/Ezetimibe Combination Therapy on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammatory Response in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ji Hye Han, Kyong Hye Joung, Jun Choul Lee, Ok Soon Kim, Sorim Choung, Ji Min Kim, Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Ju Hee Lee, Bon Jeong Ku, Hyun Jin Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):112-121. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0402
- 2,021 View
- 222 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
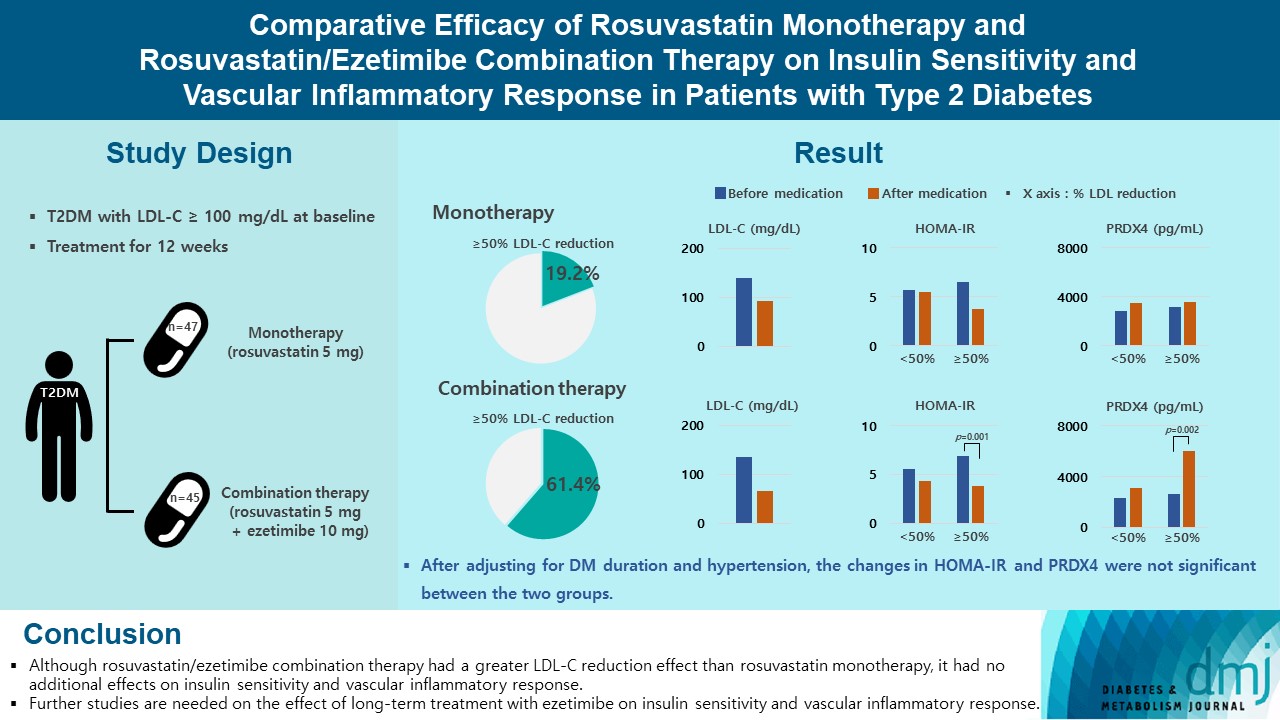
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) induces endothelial dysfunction and inflammation, which are the main factors for atherosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. The present study aimed to compare the effects of rosuvastatin monotherapy and rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy on lipid profile, insulin sensitivity, and vascular inflammatory response in patients with T2DM.
Methods
A total of 101 patients with T2DM and dyslipidemia were randomized to either rosuvastatin monotherapy (5 mg/day, n=47) or rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy (5 mg/10 mg/day, n=45) and treated for 12 weeks. Serum lipids, glucose, insulin, soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1), and peroxiredoxin 4 (PRDX4) levels were determined before and after 12 weeks of treatment.
Results
The reduction in low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) by more than 50% from baseline after treatment was more in the combination therapy group. The serum sICAM-1 levels increased significantly in both groups, but there was no difference between the two groups. The significant changes in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) and PRDX4 were confirmed only in the subgroup in which LDL-C was reduced by 50% or more in the combination therapy group. However, after adjusting for diabetes mellitus duration and hypertension, the changes in HOMA-IR and PRDX4 were not significant between the two groups.
Conclusion
Although rosuvastatin/ezetimibe combination therapy had a greater LDL-C reduction effect than rosuvastatin monotherapy, it had no additional effects on insulin sensitivity and vascular inflammatory response. Further studies are needed on the effect of long-term treatment with ezetimibe on insulin sensitivity and vascular inflammatory response. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Combining Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin: Impacts on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Roh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 55. CrossRef
- Combining Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin: Impacts on Insulin Sensitivity and Vascular Inflammation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Basic Research
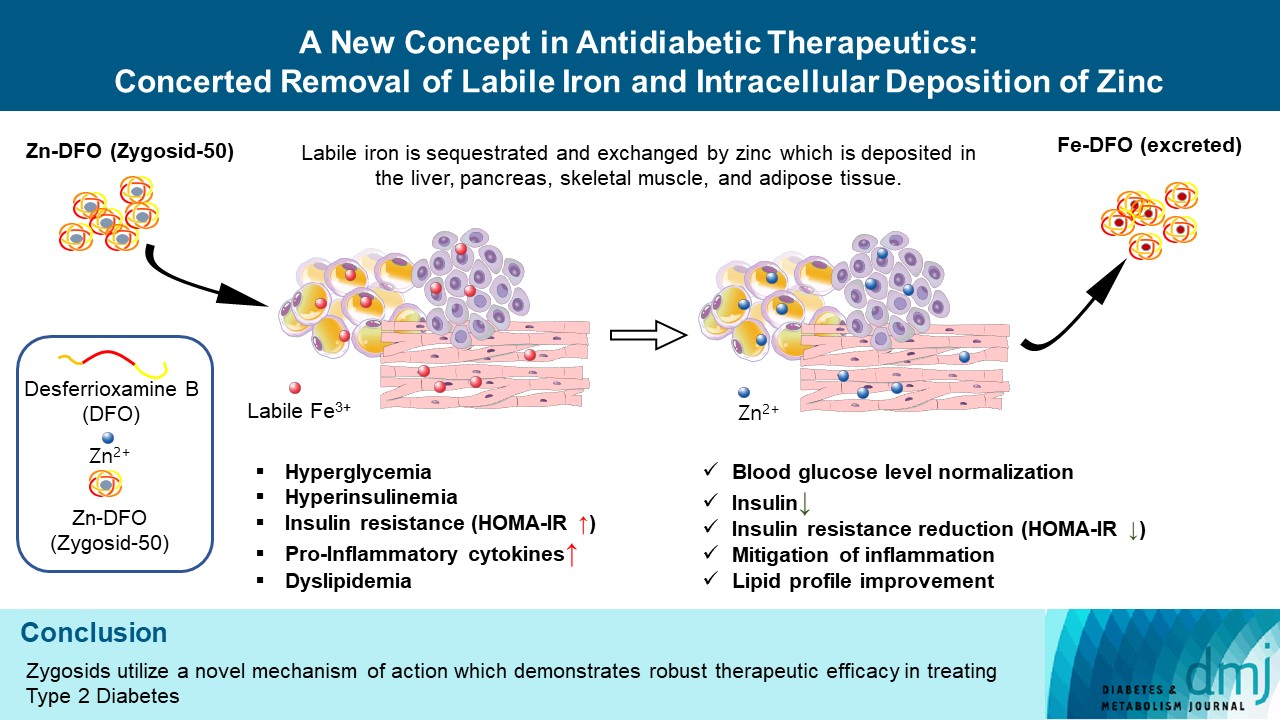
- A New Concept in Antidiabetic Therapeutics: A Concerted Removal of Labile Iron and Intracellular Deposition of Zinc
- Vladimir Vinokur, Eduard Berenshtein, Mordechai Chevion, Dror Chevion
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):59-71. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0292
- Retraction in: Diabetes Metab J 2024;48(2):325
- 1,568 View
- 178 Download
- Basic Research
- Long Non-Coding RNA TUG1 Attenuates Insulin Resistance in Mice with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus via Regulation of the MicroRNA-328-3p/SREBP-2/ERK Axis
- Xuwen Tang, Qingxin Qin, Wenjing Xu, Xuezhen Zhang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):267-286. Published online January 19, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0216
- 2,851 View
- 188 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
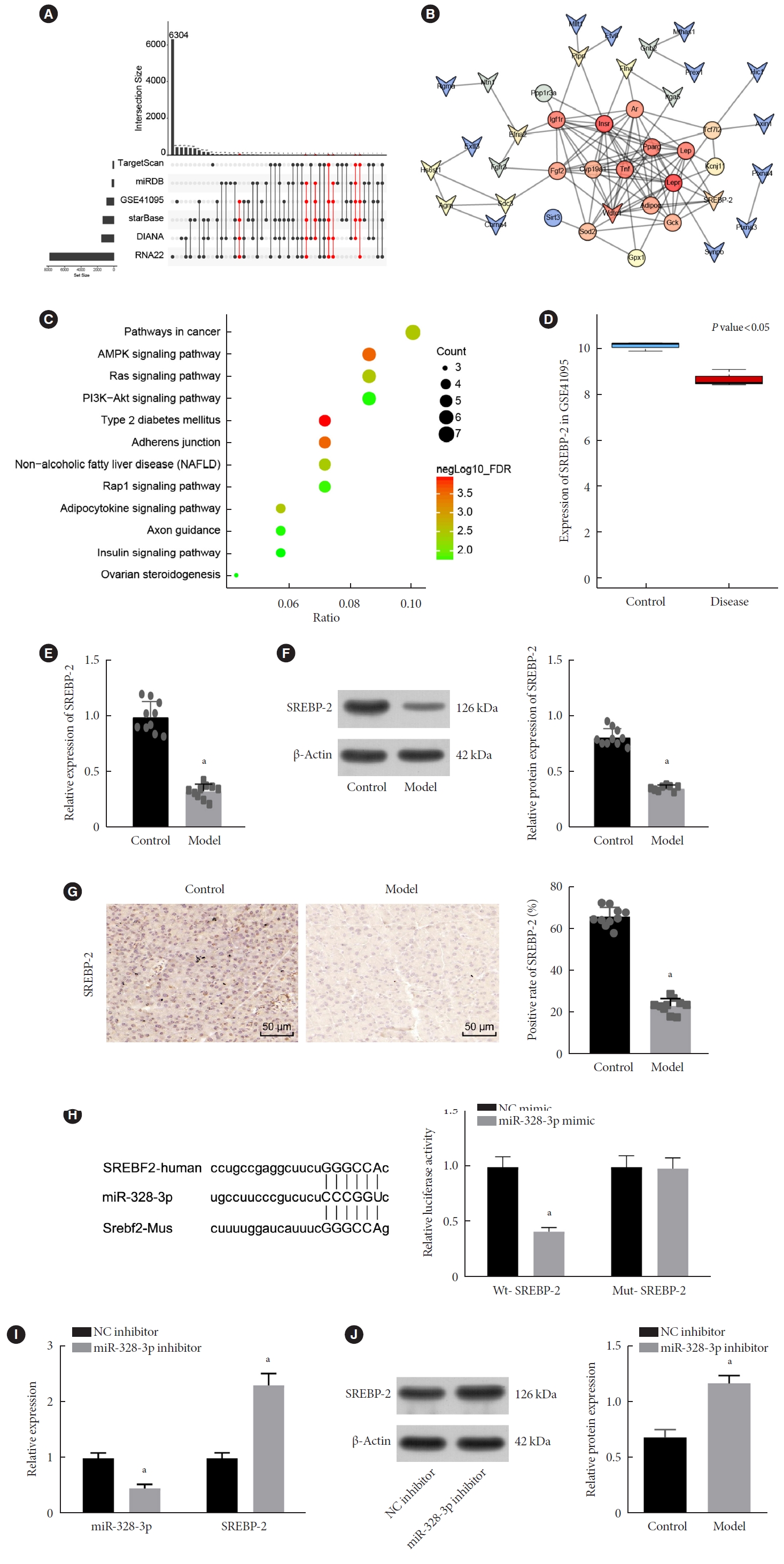
Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) have been illustrated to contribute to the development of gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). In the present study, we aimed to elucidate how lncRNA taurine upregulated gene 1 (TUG1) influences insulin resistance (IR) in a high-fat diet (HFD)-induced mouse model of GDM.
Methods
We initially developed a mouse model of HFD-induced GDM, from which islet tissues were collected for RNA and protein extraction. Interactions among lncRNA TUG1/microRNA (miR)-328-3p/sterol regulatory element binding protein 2 (SREBP-2) were assessed by dual-luciferase reporter assay. Fasting blood glucose (FBG), fasting insulin (FINS), homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), HOMA pancreatic β-cell function (HOMA-β), insulin sensitivity index for oral glucose tolerance tests (ISOGTT) and insulinogenic index (IGI) levels in mouse serum were measured through conducting gain- and loss-of-function experiments.
Results
Abundant expression of miR-328 and deficient expression of lncRNA TUG1 and SREBP-2 were characterized in the islet tissues of mice with HFD-induced GDM. LncRNA TUG1 competitively bound to miR-328-3p, which specifically targeted SREBP-2. Either depletion of miR-328-3p or restoration of lncRNA TUG1 and SREBP-2 reduced the FBG, FINS, HOMA-β, and HOMA-IR levels while increasing ISOGTT and IGI levels, promoting the expression of the extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling pathway-related genes, and inhibiting apoptosis of islet cells in GDM mice. Upregulation miR-328-3p reversed the alleviative effects of SREBP-2 and lncRNA TUG1 on IR.
Conclusion
Our study provides evidence that the lncRNA TUG1 may prevent IR following GDM through competitively binding to miR-328-3p and promoting the SREBP-2-mediated ERK signaling pathway inactivation. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetes and diabetic associative diseases: An overview of epigenetic regulations of TUG1
Mohammed Ageeli Hakami
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2024; 31(5): 103976. CrossRef - Effect of Tinospora cordifolia on gestational diabetes mellitus and its complications
Ritu Rani, Havagiray Chitme, Avinash Kumar Sharma
Women & Health.2023; 63(5): 359. CrossRef - Therapeutic Effect of Tinospora cordifolia (Willd) Extracts on Letrozole-Induced Polycystic Ovarian Syndrome and its Complications in Murine Model
Ritu Rani, Avinash Kumar Sharma, Havagiray R Chitme
Clinical Medicine Insights: Endocrinology and Diabetes.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of ncRNA regulatory mechanisms in diseases—case on gestational diabetes
Dong Gao, Liping Ren, Yu-Duo Hao, Nalini Schaduangrat, Xiao-Wei Liu, Shi-Shi Yuan, Yu-He Yang, Yan Wang, Watshara Shoombuatong, Hui Ding
Briefings in Bioinformatics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - lncRNA TUG1 as potential novel biomarker for prognosis of cardiovascular diseases
Habib Haybar, Narjes Sadat Sadati, Daryush Purrahman, Mohammad Reza Mahmoudian-Sani, Najmaldin Saki
Epigenomics.2023; 15(23): 1273. CrossRef
- Diabetes and diabetic associative diseases: An overview of epigenetic regulations of TUG1
Short Communication
- Others
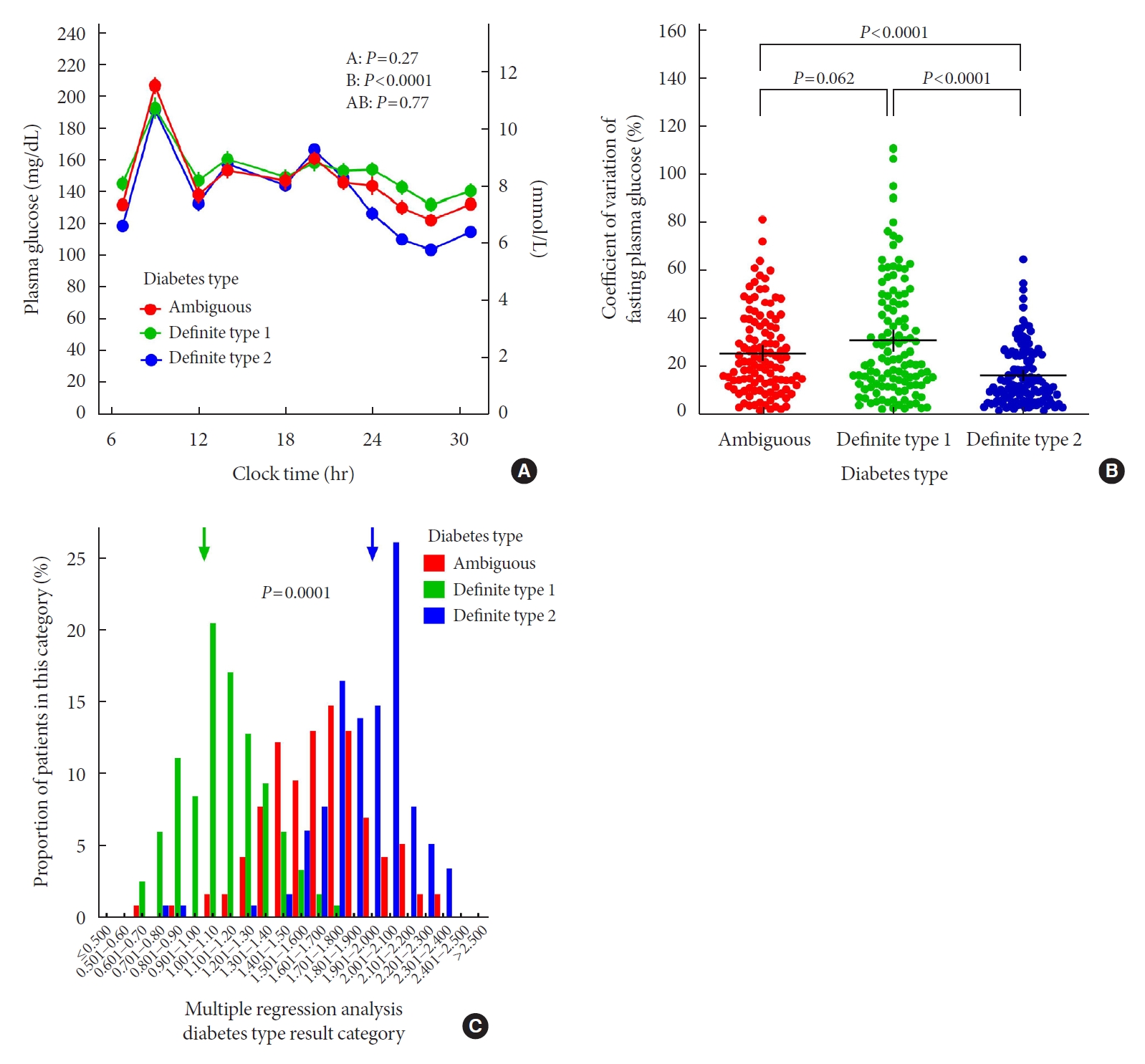
- Comparison of Insulin-Treated Patients with Ambiguous Diabetes Type with Definite Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Subjects: A Clinical Perspective
- Insa Laspe, Juris J. Meier, Michael A. Nauck
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):140-146. Published online March 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0322
- 65,535 View
- 183 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - In clinical practice, the distinction between type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) can be challenging, leaving patients with “ambiguous” diabetes type. Insulin-treated patients (n=115) previously diagnosed with T2DM had to be re-classified based on clinical phenotype and laboratory results, and were operationally defined as having an ambiguous diabetes type. They were compared against patients with definite T1DM and T2DM regarding 12 clinical and laboratory features typically different between diabetes types. Characteristics of patients with ambiguous diabetes type, representing approximately 6% of all patients with T1DM or T2DM seen at our specialized clinic, fell in between those of patients with definite T1DM and T2DM, both regarding individual features and with respect to a novel classification based on multi-variable regression analysis (P<0.0001). In conclusion, a substantial proportion of diabetes patients in a tertiary care centre presented with an “ambiguous” diabetes type. Their clinical characteristics fall in between those of definite T1DM or T2DM patients.
Original Articles
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
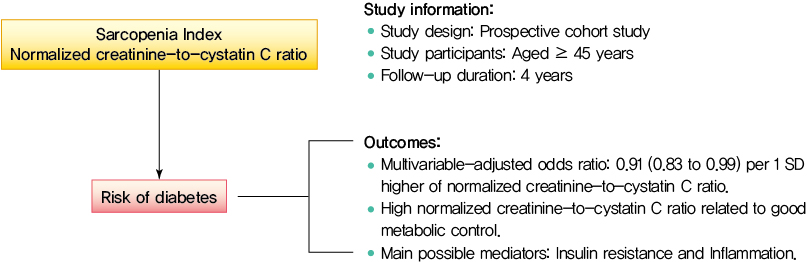
- Normalized Creatinine-to-Cystatin C Ratio and Risk of Diabetes in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
- Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Bo Xie, Yang Yuan, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):476-485. Published online March 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0074
- 4,726 View
- 204 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio is recently suggested to be a surrogate marker for sarcopenia. However, little is known about its association with diabetes. This study aimed to fill in this gap based on a large-scale prospective cohort.
Methods
A population-based representative sample of 5,055 participants aged ≥45 years from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study was enrolled between 2011 and 2012 and followed at least once during the subsequent surveys at 2013, 2015, or 2018. Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio was calculated and normalized by body weight. Incident diabetes was ascertained by plasma glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, self-reported history, or use of anti-diabetic drugs. Logistic regression analysis and mediation analysis were employed.
Results
During follow-up, 634 participants developed diabetes. The risk of diabetes was gradually and significantly decreased with increased normalized creatinine–cystatin C ratio. The multivariable-adjusted odds ratio for diabetes was 0.91 (95% confidence interval, 0.83 to 0.99) per 1 standard deviation higher of normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio, and this relationship remained significant after controlling for muscle strength. The risk reduction in diabetes was significantly larger in participants with normal-weight and high normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio compared with those with overweight/obesity and high normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio (Pinteraction=0.01). Insulin resistance and inflammation appeared to be key mediators accounting for the observed relationship between normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio and risk of diabetes, with their mediating effect being 93.1% and 22.0%, respectively.
Conclusion
High normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio is associated with reduced risk of diabetes in middle-aged and older adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Muscle Quality in Relation to Prediabetes Phenotypes: A Population-Based Study With Mediation Analysis
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Xiaoying Zhou, Jinshui Xu, Zilin Sun, Haijian Guo, Tongzhi Wu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1151. CrossRef - Sex‐specific associations between skeletal muscle mass and incident diabetes: A population‐based cohort study
Dan Liu, Nan Li, Yiling Zhou, Miye Wang, Peige Song, Changzheng Yuan, Qingyang Shi, Hui Chen, Kaixin Zhou, Huan Wang, Tao Li, Xiong‐Fei Pan, Haoming Tian, Sheyu Li
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(3): 820. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus Should Be Considered While Analysing Sarcopenia-Related Biomarkers
Justyna Rentflejsz, Zyta Beata Wojszel
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(4): 1107. CrossRef - Associations of muscle mass and strength with new-onset diabetes among middle-aged and older adults: evidence from the China health and retirement longitudinal study (CHARLS)
Yun-Yun He, Mei-Ling Jin, Xiang-Yang Fang, Xiao-Juan Wang
Acta Diabetologica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The serum creatinine to cystatin C to waist circumference ratios predicts risk for type 2 diabetes: A Chinese cohort study
Yinfei Chen, Weiheng Wen, Zhiliang Mai, Ming Wang, Hong Chen, Jia Sun
Journal of Diabetes.2023; 15(10): 808. CrossRef - Associations of sarcopenia with peak expiratory flow among community-dwelling elderly population: based on the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS)
Yun-Yun He, Mei-Ling Jin, Jing Chang, Xiao-Juan Wang
European Geriatric Medicine.2023; 15(1): 95. CrossRef - Additive impact of diabetes and sarcopenia on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: A longitudinal nationwide population-based study
Eyun Song, Soon Young Hwang, Min Jeong Park, Ahreum Jang, Kyeong Jin Kim, Ji Hee Yu, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 148: 155678. CrossRef
- Muscle Quality in Relation to Prediabetes Phenotypes: A Population-Based Study With Mediation Analysis
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Iron Overload and the Risk of Diabetes in the General Population: Results of the Chinese Health and Nutrition Survey Cohort Study
- He Gao, Jinying Yang, Wenfei Pan, Min Yang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):307-318. Published online March 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0287
- 5,036 View
- 196 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Recent studies have found that there are significant associations between body iron status and the development of diabetes. In the present study, we aimed to analyze the association among iron overload (IO), insulin resistance (IR), and diabetes in Chinese adults, and to explore the sex difference.
Methods
Men and women (age >19 years) who participated in the Chinese Health and Nutrition Survey and did not have diabetes at baseline were followed between 2009 and 2015 (n=5,779). Over a mean of 6 years, 75 participants were diagnosed with incident diabetes. Logistic regression was used to assess the risk factors associated with IO. Cox proportional hazard regression was used to estimate the risk of incident diabetes and to determine whether the risk differed among subgroups. Causal mediation analysis (CMA) was used to explore the mechanism linking IO and diabetes.
Results
According to sex-stratified multivariable-adjusted Cox proportional hazards regression, IO increased the risk of incident diabetes. Women with IO had a higher risk of diabetes than men. Subgroup analysis with respect to age showed that the association between IO and diabetes was stronger in older women and younger men (P<0.001). CMA showed that liver injury (alanine transaminase) and lipid metabolism abnormalities (triglyceride, apolipoprotein B) contributed to the association between IO and diabetes.
Conclusion
IO is associated with diabetes and this association is sex-specific. IO may indirectly induce IR via liver injury and lipid metabolism abnormalities, resulting in diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Quantitative susceptibility mapping for iron monitoring of multiple subcortical nuclei in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Sana Mohammadi, Sadegh Ghaderi, Fatemeh Sayehmiri, Mobina Fathi
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma Ferritin Concentrations in the General Population: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Anthropometric, Metabolic, and Dietary Correlates
Cara Övermöhle, Sabina Waniek, Gerald Rimbach, Katharina Susanne Weber, Wolfgang Lieb
The Journal of Nutrition.2023; 153(5): 1524. CrossRef - Association of Body Iron Metabolism with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Chinese Women of Childbearing Age: Results from the China Adult Chronic Disease and Nutrition Surveillance (2015)
Jie Feng, Xiaoyun Shan, Lijuan Wang, Jiaxi Lu, Yang Cao, Lichen Yang
Nutrients.2023; 15(8): 1935. CrossRef - Iron overload induces islet β cell ferroptosis by activating ASK1/P-P38/CHOP signaling pathway
Ling Deng, Man-Qiu Mo, Jinling Zhong, Zhengming Li, Guoqiao Li, Yuzhen Liang
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15206. CrossRef - The role of ferroptosis in metabolic diseases
Ling Xie, Bin Fang, Chun Zhang
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2023; 1870(6): 119480. CrossRef - Epidemiological and transcriptome data identify potential key genes involved in iron overload for type 2 diabetes
Xuekui Liu, Xiu Hong, Shiqiang Jiang, Rui Li, Qian Lv, Jie Wang, Xiuli Wang, Manqing Yang, Houfa Geng, Yang Li
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between serum iron and liver transaminases based on a large adult women population
Andong He, Zhuoping Zhou, Lili Huang, Ka Cheuk Yip, Jing Chen, Ruiling Yan, Ruiman Li
Journal of Health, Population and Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between serum ferritin and uric acid levels and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in the Chinese population
Fangli Zhou, Xiaoli He, Dan Liu, Yan Ye, Haoming Tian, Li Tian
PeerJ.2023; 11: e16267. CrossRef - The Role of Iron Overload in Diabetic Cognitive Impairment: A Review
Ji-Ren An, Qing-Feng Wang, Gui-Yan Sun, Jia-Nan Su, Jun-Tong Liu, Chi Zhang, Li Wang, Dan Teng, Yu-Feng Yang, Yan Shi
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3235. CrossRef - The Association Between METS-IR and Serum Ferritin Level in United States Female: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on NHANES
Han Hao, Yan Chen, Ji Xiaojuan, Zhang Siqi, Chu Hailiang, Sun Xiaoxing, Wang Qikai, Xing Mingquan, Feng Jiangzhou, Ge Hongfeng
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress on Relationship Between Iron Overload and Lower Limb Arterial Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Zhongjing Wang, Shu Fang, Sheng Ding, Qin Tan, Xuyan Zhang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 2259. CrossRef - Iron deficiency in cardiac surgical patients
L Hof, O Old, A.U. Steinbicker, P Meybohm, S Choorapoikayil, K Zacharowski
Acta Anaesthesiologica Belgica.2022; 73(4): 235. CrossRef
- Quantitative susceptibility mapping for iron monitoring of multiple subcortical nuclei in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Reviews
- Pathophysiology
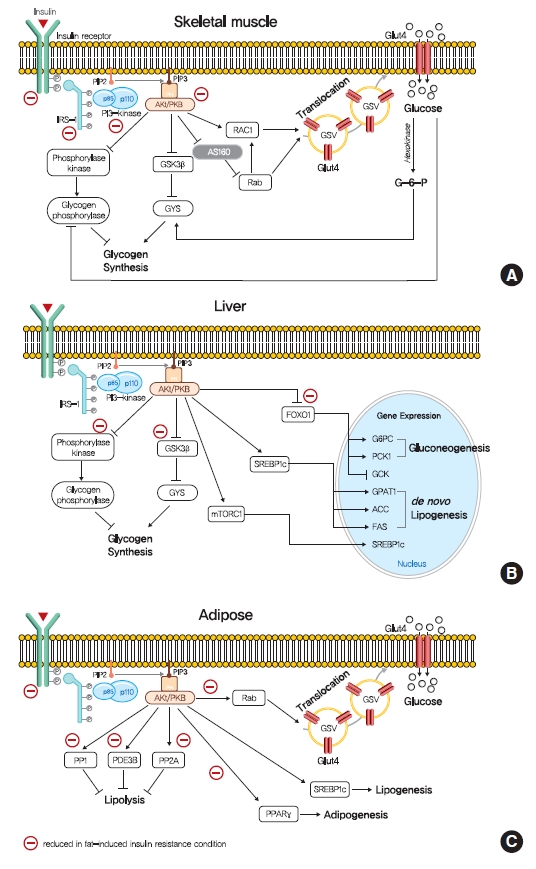
- Insulin Resistance: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Strategies
- Shin-Hae Lee, Shi-Young Park, Cheol Soo Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):15-37. Published online December 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0280
- 30,326 View
- 2,654 Download
- 158 Web of Science
- 191 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Insulin resistance is the pivotal pathogenic component of many metabolic diseases, including type 2 diabetes mellitus, and is defined as a state of reduced responsiveness of insulin-targeting tissues to physiological levels of insulin. Although the underlying mechanism of insulin resistance is not fully understood, several credible theories have been proposed. In this review, we summarize the functions of insulin in glucose metabolism in typical metabolic tissues and describe the mechanisms proposed to underlie insulin resistance, that is, ectopic lipid accumulation in liver and skeletal muscle, endoplasmic reticulum stress, and inflammation. In addition, we suggest potential therapeutic strategies for addressing insulin resistance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetic Encephalopathy: Role of Oxidative and Nitrosative Factors in Type 2 Diabetes
Debashree Mazumdar, Santosh Singh
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry.2024; 39(1): 3. CrossRef - Materials and structure of polysaccharide-based delivery carriers for oral insulin: A review
Xinran Wang, Hongnan Sun, Taihua Mu
Carbohydrate Polymers.2024; 323: 121364. CrossRef - β-Thalassemia and Diabetes Mellitus: Current State and Future
Directions
Jalal Taneera, Eglal Mahgoub, Reem Qannita, Ayah Alalami, Ola Al Shehadat, Mona Youssef, Ayah Dib, Alaa Al Hajji, Amani Al Hajji, Fatheya Al-Khaja, Hany Dewedar, Mawieh Hamad
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2024; 56(04): 272. CrossRef - Mulberry leaf multi-components exert hypoglycemic effects through regulation of the PI-3K/Akt insulin signaling pathway in type 2 diabetic rats
Yue Zhang, Liang Li, Tao Chai, Han Xu, Hong-yan Du, Yan Jiang
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2024; 319: 117307. CrossRef - Thyroid cancer and insulin resistance
Gabriela Brenta, Fernando Di Fermo
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2024; 25(1): 19. CrossRef - Comparative profiling of gut microbiota and metabolome in diet-induced obese and insulin-resistant C57BL/6J mice
Hobby Aggarwal, Jyoti Gautam, Deepika Kumari, Sonu Kumar Gupta, Sneh Bajpai, Kartikey Chaturvedi, Yashwant Kumar, Madhu Dikshit
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2024; 1871(2): 119643. CrossRef - CD248 promotes insulin resistance by binding to the insulin receptor and dampening its insulin-induced autophosphorylation
Patricia O. Benedet, Nooshin S. Safikhan, Maria J. Pereira, Bryan M. Lum, José Diego Botezelli, Cheng-Hsiang Kuo, Hua-Lin Wu, Barbara P. Craddock, W. Todd Miller, Jan W. Eriksson, Jessica T.Y. Yue, Edward M. Conway
eBioMedicine.2024; 99: 104906. CrossRef - The Antiobesity Effects and Potential Mechanisms of Theaflavins
Yi Fang, Jun Wang, Yu Cao, Wenrui Liu, Lianxiang Duan, Jing Hu, Jinghua Peng
Journal of Medicinal Food.2024; 27(1): 1. CrossRef - The role of zinc finger proteins in the fate determination of mesenchymal stem cells during osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation
Bolun Li, Shibo Liu, Ze He, En Luo, Hanghang Liu
The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology.2024; 167: 106507. CrossRef - Gentianella turkestanorum (Gand.) Holub, a Chinese Herbal Medicine that can Alleviate T2DM in Db/db Mice, and its Active Mechanism of Action
Ying Wei, Jiaxin Sun, Liya Su, Tunhai Xu
Pharmacognosy Magazine.2024; 20(2): 646. CrossRef - Hyperglycemia affects axial signs in patients with Parkinson’s disease through mechanisms of insulin resistance or non-insulin resistance
Ruidan Wang, Zhaohui Jin, Qiaoxia Zhen, Lin Qi, Cui Liu, Ping Wang, Yonghong Liu, Jinping Fang, Yanjun Liu, Yuan Su, Yixuan Wang, Detao Meng, Hongjiao Yan, Yi Zhen, Zhenzhen Li, Boyan Fang
Neurological Sciences.2024; 45(5): 2011. CrossRef - Insulin resistance: Risk factors, diagnostic approaches and mathematical models for clinical practice, epidemiological studies, and beyond
Janusz Krzymien, Piotr Ladyzynski
Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering.2024; 44(1): 55. CrossRef - Effects of silybin supplementation on growth performance, serum indexes and liver transcriptome of Peking ducks
Ziyue Zhang, Bozhi Shi, Xueze Lv, Yingchao Dong, Lei Li, Zhaofei Xia
Frontiers in Veterinary Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Consuming Beverages Sweetened with Fructose, Glucose, High-Fructose Corn Syrup, Sucrose, or Aspartame on OGTT-Derived Indices of Insulin Sensitivity in Young Adults
Bettina Hieronimus, Valentina Medici, Vivien Lee, Marinelle V. Nunez, Desiree M. Sigala, Andrew A. Bremer, Chad L. Cox, Nancy L. Keim, Jean-Marc Schwarz, Giovanni Pacini, Andrea Tura, Peter J. Havel, Kimber L. Stanhope
Nutrients.2024; 16(1): 151. CrossRef - Association Between Insulin Resistance Markers and Poor Prognosis in Patients With Acute Ischemic Stroke After Intravenous Thrombolysis
Haimei Liu, Denglu Liu, Peng Zuo
The Neurologist.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Interplay of Angiotensin Peptides, Vasopressin, and Insulin in the Heart: Experimental and Clinical Evidence of Altered Interactions in Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus
Ewa Szczepanska-Sadowska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(2): 1310. CrossRef - High-Density Lipoprotein Is Located Alongside Insulin in the Islets of Langerhans of Normal and Rodent Models of Diabetes
Sahar Mohsin, Haba Elabadlah, Mariam K. Alotaiba, Suhail AlAmry, Shamma J. Almehairbi, Maha M. K. Harara, Aisha M. H. Almuhsin, Saeed Tariq, Frank Christopher Howarth, Ernest A. Adeghate
Nutrients.2024; 16(2): 313. CrossRef - Sweet triterpenoid glycoside from Cyclocarya paliurus ameliorates obesity-induced insulin resistance through inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB/NLRP3 inflammatory pathway
Jie Li, Junyu He, Haibo He, Xiao Wang, Shuran Zhang, Yumin He, Jihong Zhang, Chengfu Yuan, HongWu Wang, Daoxiang Xu, Chaowang Pan, Huifan Yu, Kun Zou
Current Research in Food Science.2024; 8: 100677. CrossRef - Effect of supplementation with probiotics or synbiotics on cardiovascular risk factors in patients with metabolic syndrome: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
TingRui Chen, Jing Wang, ZeKun Liu, Fei Gao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus progression in β-thalassaemia major patients: The impact of iron overload
Eglal Omer Mahgoub, Reem Qannita, Ayah Alalami, Ola Al Shehadat, Rabah Al Mahmoud, Ayah Dib, Alaa Al Hajji, Amani Al Hajji, Fatheya Al Khaja, Hany Dewedar, Mawieh Hamad, Jalal Taneera
Advances in Biomedical and Health Sciences.2024; 3(1): 5. CrossRef - Dietary Tomato Pectin Attenuates Hepatic Insulin Resistance and Inflammation in High-Fat-Diet Mice by Regulating the PI3K/AKT Pathway
Jing Sun, Kongyan Wu, Pan Wang, Yubin Wang, Dan Wang, Wenting Zhao, Yuanyuan Zhao, Chunhong Zhang, Xiaoyan Zhao
Foods.2024; 13(3): 444. CrossRef - Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz. and Cuscuta chinensis Lam. extract relieves insulin resistance via PI3K/Akt signalling in diabetic Drosophila
Yinghong Li, Ye Xu, Biwei Zhang, Zhigang Wang, Leilei Ma, Longyu Sun, Xiuping Wang, Yimin Lin, Ji-an Li, Chenxi Wu
Journal of Traditional and Complementary Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ketogenic diet ameliorates high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance in mouse skeletal muscle by alleviating endoplasmic reticulum stress
Qin Ma, Lincheng Jiang, Yuehua You, Hongbing Ni, Li Ma, Xiaojing Lin, Zhuyun Wang, Weiyan Yan, Xiaoqiu Xiao, Xinyu Li, Jibin Li
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2024; 702: 149559. CrossRef - Brain insulin resistance and Alzheimer’s disease: a systematic review
Luis Jesuino de Oliveira Andrade, Luís Matos de Oliveira, Alcina Maria Vinhaes Bittencourt, Letícia Góes de Carvalho Lourenço, Gabriela Correia Matos de Oliveira
Dementia & Neuropsychologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Poorly controlled glycemia and worse beta cell function associate with higher resting and total energy expenditure in adults with obesity and type 2 diabetes: A doubly labeled water study
Kate Lillegard, John A. Del Castillo, Heidi J. Silver
Clinical Nutrition.2024; 43(3): 729. CrossRef - Gut microbiota in insulin resistance: a bibliometric analysis
Weiwei Tian, Li Liu, Ruirui Wang, Yunyun Quan, Bihua Tang, Dongmei Yu, Lei Zhang, Hua Hua, Junning Zhao
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of the triglyceride glucose index with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in a general population of Iranian adults
Ghazaal Alavi Tabatabaei, Noushin Mohammadifard, Hamed Rafiee, Fatemeh Nouri, Asieh Maghami mehr, Jamshid Najafian, Masoumeh Sadeghi, Maryam Boshtam, Hamidreza Roohafza, Fahimeh Haghighatdoost, Marzieh Taheri, Nizal Sarrafzadegan
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in Cells Associated with Insulin Resistance
Leszek Szablewski
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(4): 2397. CrossRef - Evaluación de la resistencia a la insulina mediante el índice HOMA: un enfoque comparativo entre mujeres premenopáusicas y posmenopáusicas
Carlos Fernando Yauli Flores, Ericka Jazmín Tubón Luisa
Salud, Ciencia y Tecnología.2024; 4: 729. CrossRef - Insulin Resistance: The Increased Risk of Cancers
Leszek Szablewski
Current Oncology.2024; 31(2): 998. CrossRef - Muscle strength and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease/metabolic-associated fatty liver disease
Xuan-Yu Hao, Kai Zhang, Xing-Yong Huang, Fei Yang, Si-Yu Sun
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2024; 30(7): 636. CrossRef - Outcomes With Finerenone in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes by Baseline Insulin Resistance
Thomas Ebert, Stefan D. Anker, Luis M. Ruilope, Paola Fioretto, Vivian Fonseca, Guillermo E. Umpierrez, Andreas L. Birkenfeld, Robert Lawatscheck, Charlie Scott, Katja Rohwedder, Peter Rossing
Diabetes Care.2024; 47(3): 362. CrossRef - Influence of Obesity and Insulin Resistance on the Reproductive Outcome of Iraqi Women Undergoing Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection
Sundus Ali Dawood, Hayder Ali Lafta Mossa, Mufeeda Ali Jwad
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2024; 6(1): 179. CrossRef - Metabolic memory: mechanisms and diseases
Hao Dong, Yuezhang Sun, Lulingxiao Nie, Aimin Cui, Pengfei Zhao, Wai Keung Leung, Qi Wang
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of preoperative oral carbohydrates on insulin resistance in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a randomized controlled trial
Xiaohan Wang, Jingwen Zhuang, Jianxin Cheng, Zeyang Wang, Jingyi Sheng, Shanshan Guo, Rui Wang, Zhiping Wang
Langenbeck's Archives of Surgery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Beta‐Cell Tipe1 Orchestrates Insulin Secretion and Cell Proliferation by Promoting Gαs/cAMP Signaling via USP5
Lu Ding, Yang Sun, Yan Liang, Jie Zhang, Zhendong Fu, Caiyue Ren, Pengfei Li, Wen Liu, Rong Xiao, Hao Wang, Zhaoying Zhang, Xuetian Yue, Chunyang Li, Zhuanchang Wu, Yuemin Feng, Xiaohong Liang, Chunhong Ma, Lifen Gao
Advanced Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome awareness in the general Korean population: results from a nationwide survey
Hyun-Jin Kim, Mi-Seung Shin, Kyung-Hee Kim, Mi-Hyang Jung, Dong-Hyuk Cho, Ju-Hee Lee, Kwang Kon Koh
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2024; 39(2): 272. CrossRef - Pregnane X receptor knockout mitigates weight gain and hepatic metabolic dysregulation in female C57BL/6 J mice on a long-term high-fat diet
Lidya H. Gebreyesus, Sora Choi, Prince Neequaye, Mattia Mahmoud, Mia Mahmoud, Malvin Ofosu-Boateng, Elizabeth Twum, Daniel O. Nnamani, Lijin Wang, Nour Yadak, Sujoy Ghosh, Frank J. Gonzalez, Maxwell A. Gyamfi
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2024; 173: 116341. CrossRef - TyG-GGT is a Reliable Non-Invasive Predictor of Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Overweight or Obese Individuals
Lei Jin, Jing Gu, Zhe Zhang, Cheng-Fei Du, Fei-Qi Xu, Xiao-Kun Huang, Zhen-Yu Gao, Ying Li, Li-Li Yu, Xin Zhang, Guo-Qing Ru, Jun-Wei Liu, Lei Liang, Xiao-Dong Sun, Zun-Qiang Xiao
Obesity Surgery.2024; 34(4): 1333. CrossRef - Excess homocysteine inhibits pancreatic β-cell secretory function by repressing Zbtb20 expression
Tianqi Ding, Bo Wen, Jian Chen, Wenbin Chu, Rong Fan, Xuewei Chen
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2024; 586: 112195. CrossRef - Testosterone therapy reduces insulin resistance in men with adult‐onset testosterone deficiency and metabolic syndrome. Results from the Moscow Study, a randomized controlled trial with an open‐label phase
Yuliya Tishova, Svetlana Kalinchenko, George Mskhalaya, Geoffrey Hackett, Mark Livingston, Carola König, Richard Strange, Michael Zitzmann, Amar Mann, Amro Maarouf, Sudarshan Ramachandran
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Preoperative contributing factors and the remission of diabetes after metabolic surgery: the mediating role of preoperative triglyceride
Lijuan Niu, Liqian Mu, Runda Wu, Shan Tong, Zhongqi Mao, Yi Yang, Jun Yin
Eating and Weight Disorders - Studies on Anorexia, Bulimia and Obesity.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanisms of Action of Potentilla discolor Bunge in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Based on Network Pharmacology and Experimental Verification in Drosophila
Yinghong Li, Fanwu Wu, Jianbo Zhang, Ye Xu, Hong Chang, Yueyue Yu, Chunhua Jiang, Xiujuan Gao, Huijuan Liu, Zhen Chen, Chenxi Wu, Ji-An Li
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2024; Volume 18: 747. CrossRef - Diabetes and diabetic associative diseases: An overview of epigenetic regulations of TUG1
Mohammed Ageeli Hakami
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2024; 31(5): 103976. CrossRef - Sleep quality of patients with diabetes mellitus: association with anxiety trait and state
Lidiane Bernardes Faria Vilela, Larissa Cristina dos Santos Camargos, Guilherme Rocha Rodrigues, Adelzí Auto Alves Júnior, Renato Canevari Dutra da Silva, Elton Brás Camargo Júnior
Revista Gaúcha de Enfermagem.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Qualidade do sono de pacientes com diabetes mellitus: associação com ansiedade traço e estado
Lidiane Bernardes Faria Vilela, Larissa Cristina dos Santos Camargos, Guilherme Rocha Rodrigues, Adelzí Auto Alves Júnior, Renato Canevari Dutra da Silva, Elton Brás Camargo Júnior
Revista Gaúcha de Enfermagem.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of the triglyceride-glucose index with severity of coronary stenosis and in-hospital mortality in patients with acute ST elevation myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention: a multicentre retrospective analysis cohort stud
Xin Lu, Xin Lin, Yingying Cai, Xiaoxiao Zhang, Haoyu Meng, Weiwei Chen, Peng Yu, Xiaohu Chen
BMJ Open.2024; 14(3): e081727. CrossRef - Effects of a Diabetic Microenvironment on Neurodegeneration: Special Focus on Neurological Cells
Vishal Chavda, Dhananjay Yadav, Snehal Patel, Minseok Song
Brain Sciences.2024; 14(3): 284. CrossRef - Mechanisms of body fat distribution and gluteal-femoral fat protection against metabolic disorders
Maha Alser, Khaled Naja, Mohamed A. Elrayess
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Regulation of lipid metabolism by E3 ubiquitin ligases in lipid-associated metabolic diseases
Yuanming Zou, Ying Zhang, Mohan Li, Kexin Cao, Chunyu Song, Zhaobo Zhang, Kexin Cai, Danxi Geng, Shuxian Chen, Yanjiao Wu, Naijin Zhang, Guozhe Sun, Jing Wang, Yixiao Zhang, Yingxian Sun
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2024; 265: 130961. CrossRef - METS-IR and all-cause mortality in Korean over 60 years old: Korean genome and epidemiology study-health examinees (KoGES-HEXA) cohorts
Ha Eun Ryu, Dong Hyuk Jung, Seok-Jae Heo, Byoungjin Park, Yong Jae Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of vitamin family members on insulin resistance and diabetes complications
Hong-Jin Chen, Min Wang, Ding-Min Zou, Gui-You Liang, Si-Yuan Yang
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(3): 568. CrossRef - Alleviative effects of the parthenolide derivative ACT001 on insulin resistance induced by sodium propionate combined with a high-fat diet and its potential mechanisms
Qian Yu, Xiang Zuo, Huijuan Bai, Shuhui Zhang, Jialu Luan, Qili Zhao, Xin Zhao, Xizeng Feng
European Journal of Pharmacology.2024; 971: 176529. CrossRef - The genetic causal relationship between type 2 diabetes, glycemic traits and venous thromboembolism, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study
Mingyi Yang, Xianjie Wan, Yani Su, Ke Xu, Pengfei Wen, Binfei Zhang, Lin Liu, Zhi Yang, Peng Xu
Thrombosis Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Transgenerational inheritance of insulin resistance in offspring of white rice-fed female fruit flies
Kehinde Ahmad Adeshina, Kasimu Ghandi Ibrahim, Murtala Bello Abubakar, Mustapha Umar Imam
Scientific African.2024; 24: e02208. CrossRef - PPARβ/δ as a promising molecular drug target for liver diseases: A focused review
Xin Meng, Lin Wang, Yan-Chao Du, Dong Cheng, Tao Zeng
Clinics and Research in Hepatology and Gastroenterology.2024; 48(6): 102343. CrossRef - EPA and DHA Differentially Improve Insulin Resistance by Reducing Adipose Tissue Inflammation — Targeting GPR120/PPARγ Pathway
Xian Yang, Xudong Li, Manjiang Hu, Jie Huang, Siyan Yu, Huanting Zeng, Limei Mao
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2024; : 109648. CrossRef - The impact of diabetes mellitus on the development of psychiatric and neurological disorders
Olivia Kelly, Jillian Sullivan, Natalie Carris, Samantha Geci, Athena Martinez, Varvara Liashenko, James Colvin, Emily Misko, Gary Vanderlaan, He Liu, Prasad S. Dalvi
Brain Disorders.2024; 14: 100135. CrossRef - Oligonucleotide therapies for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Sixu Li, Feng Xiong, Songbo Zhang, Jinghua Liu, Guangping Gao, Jun Xie, Yi Wang
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids.2024; 35(2): 102184. CrossRef - The Contribution of Type 2 Diabetes to Parkinson’s Disease Aetiology
Samo Ribarič
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(8): 4358. CrossRef - Dose-response associations of triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and triglyceride–glucose index with arterial stiffness risk
Wenkai Zhang, Weifeng Huo, Huifang Hu, Tianze Li, Lijun Yuan, Jinli Zhang, Yifei Feng, Yuying Wu, Xueru Fu, Yamin Ke, Mengmeng Wang, Longkang Wang, Yaobing Chen, Yajuan Gao, Xi Li, Liang Sun, Jinyuan Pang, Zeqiang Zheng, Fulan Hu, Ming Zhang, Yu Liu, Dong
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Unraveling PCOS: Exploring its causes and diagnostic challenges
Mohd Altaf Dar, Mudasir Maqbool, Zulfkar Qadrie, Irfat Ara, Afshana Qadir
Open Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Triglyceride-Glucose Index and Diabetic
Retinopathy: A Meta-Analysis
Lanchu Yu, Bingqing Li
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum Klotho and insulin resistance: Insights from a cross-sectional analysis
Laisha Yan, Xiaoyan Hu, Shanshan Wu, Shunying Zhao
Medicine.2024; 103(17): e37971. CrossRef - Research Progress of Correlation between Triglyceride Glucose Index and Kidney Disease
伊琳 黄
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(04): 2137. CrossRef - Oxygen-Dependent Aspects of Asprosin Action
V. V. Zinchuk, J. S. O. Al-Jebur
Journal of Evolutionary Biochemistry and Physiology.2024; 60(2): 818. CrossRef - Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome and Insulin Resistance in Adult Patients with Acne: Association with Traditional Cardiovascular Risk Factors and Acne Severity
Ana Cecília Arcanjo Carneiro, Jozélio Freire de Carvalho, Daniel Coelho de Sá, Carlos Ewerton Maia Rodrigues
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2023; 21(2): 109. CrossRef - Metabolic and Genetic Association of Vitamin D with Calcium Signaling and Insulin Resistance
Najeebul Tarfeen, Khair Ul Nisa, Mir Bilal Ahmad, Ajaz Ahmad Waza, Bashir Ahmad Ganai
Indian Journal of Clinical Biochemistry.2023; 38(4): 407. CrossRef - Tinosporaside from Tinospora cordifolia Encourages Skeletal Muscle Glucose Transport through Both PI-3-Kinase- and AMPK-Dependent Mechanisms
Akansha Mishra, Khushbu Sharma, Jyotsana Pandey, Kapil Dev, Sleman Kadan, Mahendra Sahai, Ishbal Ahmad, Arvind K. Srivastava, Akhilesh K. Tamrakar, Hilal Zaid, Rakesh Maurya
Molecules.2023; 28(2): 483. CrossRef - Pathophysiology of obesity and its associated diseases
Xin Jin, Tingting Qiu, Li Li, Rilei Yu, Xiguang Chen, Changgui Li, Christopher G. Proud, Tao Jiang
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B.2023; 13(6): 2403. CrossRef - Hypertension, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and p53 mutations negatively correlate with metastatic colorectal cancer patients’ survival
Alessandro Ottaiano, Mariachiara Santorsola, Luisa Circelli, Francesco Perri, Marco Cascella, Francesco Sabbatino, Maurizio Capuozzo, Vincenza Granata, Silvia Zappavigna, Angela Lombardi, Marianna Scrima, Nadia Petrillo, Monica Ianniello, Marika Casillo,
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride glucose index and poor sleep patterns in non-diabetic adults: Evidence from NHANES 2005–2016
Chi-Feng Liu, Li-Wei Chien
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Polyphenol-Rich Extract of Fermented Chili Pepper Alleviates Insulin Resistance in HepG2 Cells via Regulating INSR, PTP1B, PPAR-γ, and AMPK Pathways
Tao Wang, Meiqi Li, Shengbao Cai, Linyan Zhou, Xiaosong Hu, Junjie Yi
Fermentation.2023; 9(2): 84. CrossRef - Effects of preoperative oral enzyme-hydrolyzed rice flour solution on gastric emptying and insulin resistance in patients undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: a prospective randomized controlled trial
Yang Yuan, Guangjun Shi, Huailong Chen, Mingshan Wang, Haofei Liu, Xiao Zhang, Bin Wang, Gaofeng Zhang, Lixin Sun
BMC Anesthesiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the pathophysiology of polycystic ovary syndrome
Hiroshi Koike, Miyuki Harada, Akari Kusamoto, Zixin Xu, Tsurugi Tanaka, Nanoka Sakaguchi, Chisato Kunitomi, Jerilee M. K. Azhary, Nozomi Takahashi, Yoko Urata, Yutaka Osuga
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance (METS-IR) Predicts Cardiovascular Disease and Its Subtypes in Patients with Hypertension and Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Wenbo Yang, Xintian Cai, Junli Hu, Wen Wen, Heizhati Mulalibieke, Xiaoguang Yao, Ling Yao, Qing Zhu, Jing Hong, Qin Luo, Shasha Liu, Nanfang Li
Clinical Epidemiology.2023; Volume 15: 177. CrossRef - Sperm DNA damage: The possible link between obesity and male infertility, an update of the current literature
Andrew Peel, Anmol Saini, Joshua C. Deluao, Nicole O. McPherson
Andrology.2023; 11(8): 1635. CrossRef - Glucose Homeostasis, Diabetes Mellitus, and Gender-Affirming Treatment
Charalampos Milionis, Ioannis Ilias, Evangelia Venaki, Eftychia Koukkou
Biomedicines.2023; 11(3): 670. CrossRef - From Metabolic Syndrome to Type 2 Diabetes in Youth
Dario Iafusco, Roberto Franceschi, Alice Maguolo, Salvatore Guercio Nuzio, Antonino Crinò, Maurizio Delvecchio, Lorenzo Iughetti, Claudio Maffeis, Valeria Calcaterra, Melania Manco
Children.2023; 10(3): 516. CrossRef - Kcnma1 is involved in mitochondrial homeostasis in diabetes‐related skeletal muscle atrophy
Shan‐Yan Gao, Yong‐Ping Liu, Ri Wen, Xin‐Mei Huang, Ping Li, Yu‐Hang Yang, Ni Yang, Tie‐Ning Zhang
The FASEB Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Capsaicin and Zinc Signalling Pathways as Promising Targets for Managing Insulin Resistance and Type 2 Diabetes
Parisa Vahidi Ferdowsi, Kiran D. K. Ahuja, Jeffrey M. Beckett, Stephen Myers
Molecules.2023; 28(6): 2861. CrossRef - Mouse Models with SGLT2 Mutations: Toward Understanding the Role of SGLT2 beyond Glucose Reabsorption
Keiko Unno, Kyoko Taguchi, Yoshiichi Takagi, Tadashi Hase, Shinichi Meguro, Yoriyuki Nakamura
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(7): 6278. CrossRef - Association between triglyceride-glucose index and carotid atherosclerosis in patients with psoriatic arthritis
Wenhui Xie, Wei Bian, Zhibo Song, Xuerong Deng, Jiahao Qu, Zhuoli Zhang
Rheumatology.2023; 62(11): 3584. CrossRef - The relationship between HMGB1 and autophagy in the pathogenesis of diabetes and its complications
Kun Yang, Feng Cao, Weili Wang, Zhenyu Tian, Lu Yang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of long-term triglyceride-glucose index level and change with the risk of cardiometabolic diseases
Wenqi Xu, Haiyan Zhao, Lishu Gao, Lu Guo, Jianrong Liu, Haixia Li, Junyan Sun, Aijun Xing, Shuohua Chen, Shouling Wu, Yuntao Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - White Adipose Tissue Dysfunction: Pathophysiology and Emergent Measurements
Natalia Santillana, Camila Astudillo-Guerrero, Amanda D’Espessailles, Gonzalo Cruz
Nutrients.2023; 15(7): 1722. CrossRef - Soy protein compared with whey protein ameliorates insulin resistance by regulating lipid metabolism, AMPK/mTOR pathway and gut microbiota in high-fat diet-fed mice
Andong Ji, Wei Chen, Chang Liu, Tianyu Zhang, Runjia Shi, Xinqi Wang, Huina Xu, Duo Li
Food & Function.2023; 14(12): 5752. CrossRef - Hepatic Insulin Resistance Model in the Male Wistar Rat Using Exogenous Insulin Glargine Administration
Victor Enrique Sarmiento-Ortega, Diana Moroni-González, Alfonso Diaz, Miguel Ángel García-González, Eduardo Brambila, Samuel Treviño
Metabolites.2023; 13(4): 572. CrossRef - Pathophysiological Effects of Contemporary Lifestyle on Evolutionary-Conserved Survival Mechanisms in Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
Jim Parker
Life.2023; 13(4): 1056. CrossRef - Metabolic dysfunction correction as a method of restoring the function of the reproductive system in women
G. E. Chernukha, V. A. Pronina
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2023; (5): 90. CrossRef - Associations between TyG-BMI and normal-high blood pressure values and hypertension: cross-sectional evidence from a non-diabetic population
Nan Peng, Maobin Kuang, Yi Peng, Hang Yu, Shuhua Zhang, Guobo Xie, Guotai Sheng, Yang Zou
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Inverse Correlation of Superoxide Dismutase and Catalase with Type 2 Diabetes among Rural Thais
Natnicha Promyos, Pornpimol Panprathip Phienluphon, Naruemon Wechjakwen, Jirayu Lainampetch, Pattaneeya Prangthip, Karunee Kwanbunjan
Nutrients.2023; 15(9): 2071. CrossRef - Interplay of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: sarcopenic obesity
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 144: 155577. CrossRef - Oxygen-binding properties of blood in insulin resistance with different asprosin content
V.V. Zinchuk, J.S.O. Al-Jebur, N.V. Glutkina
Biomeditsinskaya Khimiya.2023; 69(2): 133. CrossRef - Associations between basal metabolic rate and insulin resistance in non-diabetic obese adults: Evidence from NHANES 2011–2018
Hai Guo, Dilihumaier Duolikun, Qiaoling Yao
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2023; 43(6): 946. CrossRef - Biomarkers of Spinal Cord Injury in Patients Undergoing Complex Endovascular Aortic Repair Procedures—A Narrative Review of Current Literature
Anna Sotir, Johannes Klopf, Christine Brostjan, Christoph Neumayer, Wolf Eilenberg
Biomedicines.2023; 11(5): 1317. CrossRef - The Hypoglycemic Activities and Underlying Mechanisms of Two Saponins‐Rich Components from Fried Ziziphus jujuba Mill. Kernel
Yi‐Meng Li, Ke‐xin Hao, Hong Xie, Jian‐Guo Jiang
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Long-term outcomes and potential mechanisms of offspring exposed to intrauterine hyperglycemia
Yi-Shang Yan, Chun Feng, Dan-Qing Yu, Shen Tian, Yin Zhou, Yi-Ting Huang, Yi-Ting Cai, Jian Chen, Miao-Miao Zhu, Min Jin
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Function of MondoA and ChREBP Nutrient—Sensing Factors in Metabolic Disease
Byungyong Ahn
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(10): 8811. CrossRef - An Update on the Molecular and Cellular Basis of Pharmacotherapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Mohamed Omer Mahgoub, Ifrah Ismail Ali, Jennifer O. Adeghate, Kornélia Tekes, Huba Kalász, Ernest A. Adeghate
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(11): 9328. CrossRef - Study on the therapeutic effect and mechanism of Tangningtongluo Tablet on diabetic mice
Zengxiaorui Cai, Xiangka Hu, Liuming Gui, Mushuang Qi, Wanjun Zhu, Ying Ren, Shuyu Yang, Chunmei Dai
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(8): 108523. CrossRef - A Descriptive Review of the Action Mechanisms of Berberine, Quercetin and Silymarin on Insulin Resistance/Hyperinsulinemia and Cardiovascular Prevention
Paolo Bellavite, Serafino Fazio, Flora Affuso
Molecules.2023; 28(11): 4491. CrossRef - Relationships of neck circumference and abdominal obesity with insulin resistance considering relative handgrip strength in middle-aged and older individuals
Kayoung Lee
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2023; 114: 105097. CrossRef - Acute exposure to realistic concentrations of Bisphenol-A trigger health damage in fish: Blood parameters, gene expression, oxidative stress
Gustavo Axel Elizalde-Velázquez, Leobardo Manuel Gómez-Oliván, Selene Elizabeth Herrera-Vázquez, Karina Elisa Rosales-Pérez, Nely SanJuan-Reyes, Sandra García-Medina, Marcela Galar-Martínez
Aquatic Toxicology.2023; 261: 106610. CrossRef - Gαi‐coupled GPR41 activation increases Ca2+ influx in C2C12 cells and shows a therapeutic effect in diabetic animals
Do‐Hyung Lee, Kyung‐Sun Heo, Chang‐Seon Myung
Obesity.2023; 31(7): 1871. CrossRef - Physical inactivity induces insulin resistance in plantaris muscle through protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B activation in mice
Saori Kakehi, Yoshifumi Tamura, Shin-ichi Ikeda, Naoko Kaga, Hikari Taka, Yuya Nishida, Ryuzo Kawamori, Hirotaka Watada
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance: A Review of Complex Interlinks
Thomas M. Barber, Stefan Kabisch, Andreas F. H. Pfeiffer, Martin O. Weickert
Metabolites.2023; 13(6): 757. CrossRef - Metabolic Markers Associated with Progression of Type 2 Diabetes Induced by High-Fat Diet and Single Low Dose Streptozotocin in Rats
Maria Andonova, Petko Dzhelebov, Krastina Trifonova, Penka Yonkova, Nikola Kostadinov, Krasimira Nancheva, Veselin Ivanov, Krasimira Gospodinova, Nikola Nizamov, Ilia Tsachev, Chavdar Chernev
Veterinary Sciences.2023; 10(7): 431. CrossRef - Research Progress Into Adipose Tissue Macrophages and Insulin Resistance
M Fu, L Yang, H Wang, Y Chen, X Chen, Q Hu, H Sun
Physiological Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of aerobic exercises in prediabetes patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yifei Wang, Honglei Li, Dongxue Yang, Mengzhao Wang, Yanbai Han, Hongli Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of C-peptide with cardiometabolic parameters in women aged 25–44 years with different metabolic phenotypes
S. V. Mustafina, V. I. Alferova, L. V. Shcherbakova, E. V. Kashtanova, D. V. Denisova
Ateroscleroz.2023; 19(2): 115. CrossRef - Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Therapy as a new Treatment Option for Diabetes Mellitus
Agnieszka Mikłosz, Adrian Chabowski
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(8): 1889. CrossRef - Anthropometric Indices With Insulin Resistance in Obese Patients: A Literature Review
Khalid Khan, Anil Wanjari, Sourya Acharya, Sabiha Quazi
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Preventive and therapeutic effects of natural products and herbal extracts on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Yiming Cao, Xiaoxue Fang, Mingyang Sun, Yegang Zhang, Mengyao Shan, Xintian Lan, Difu Zhu, Haoming Luo
Phytotherapy Research.2023; 37(9): 3867. CrossRef - Tuina (Chinese massage) for insulin resistance and sensitivity: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis of animal and human studies
Zhixuan Zhao, Jun Yan, Yuxin Ding, Yingji Wang, Yan Li, Ricardo Ney Oliveira Cobucci
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(7): e0288414. CrossRef - Rubus chingii Hu relieved the polycystic ovary syndrome with enhanced insulin sensitivity through inhibiting TXNIP/NLRP3 inflammasome signaling
Huizhen Li, Yongping Li, Ying Zhang, Li Tong, Yuping Sa, Wenping Sun
Gynecological Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Research Role of Triglyceride Glucose Index in Pre-Type 2 Diabetes
士博 徐
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(07): 11762. CrossRef - Underlying mechanisms and molecular targets of genistein in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus and related complications
Tao Jiang, Yuhe Dong, Wanying Zhu, Tong Wu, Linyan Chen, Yuantong Cao, Xi Yu, Ye Peng, Ling Wang, Ying Xiao, Tian Zhong
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Gentiopicroside modulates glucose homeostasis in high-fat-diet and streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic mice
Xing Wang, Dongmei Long, Xianghong Hu, Nan Guo
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Review of the Case Reports on Metformin, Sulfonylurea, and Thiazolidinedione Therapies in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Elis Susilawati, Jutti Levita, Yasmiwar Susilawati, Sri Adi Sumiwi
Medical Sciences.2023; 11(3): 50. CrossRef - Effects of AIM2 and IFI16 on Infectious Diseases and Inflammation
Zhen Fan, Rui Chen, Wen Yin, Xiaomei Xie, Shan Wang, Chunbo Hao
Viral Immunology.2023; 36(7): 438. CrossRef - PREDICTING PROGRESSION TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS: A 3-YEAR FOLLOW-UP STUDY EXAMINING RISK FACTORS FOR TYPE 2 DIABETES IN PATIENTS WITH PREDIABETES
Taras I. Griadil, Mykhaylo V. Bychko, Mykhaylo M. Hechko, Ksenia I. Chubirko, Ivan V. Chopey
Polski Merkuriusz Lekarski.2023; 51(3): 245. CrossRef - GABA Prevents Age-Related Sarcopenic Obesity in Mice with High-Fat-Diet-Induced Obesity
Heegu Jin, Hyun-Ji Oh, Boo-Yong Lee
Cells.2023; 12(17): 2146. CrossRef - Bio-Hacking Better Health—Leveraging Metabolic Biochemistry to Maximise Healthspan
Isabella D. Cooper, Yvoni Kyriakidou, Lucy Petagine, Kurtis Edwards, Bradley T. Elliott
Antioxidants.2023; 12(9): 1749. CrossRef - Hyperinsulinemia Impairs Clathrin-Mediated Endocytosis of the Insulin Receptor and Activation of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase in Brain Endothelial Cells
Stephanie G. DiLucia, B. Jacob Kendrick, Catrina Sims-Robinson
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(19): 14670. CrossRef - Validation of a physiological type 2 diabetes model in human periodontal ligament stem cells
Dongqing Ai, Yuanyuan Yin, Xuyun Xia, Sihan Yang, Yu Sun, Jie Zhou, Han Qin, Xiaohui Xu, Jinlin Song
Oral Diseases.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Flavonoids from Lophatherum gracile Brongn. Ameliorate Liver Damages in High-Fat Diet and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice by Regulating PI3K/AKT and NF-Kappa B Pathways
Jian-Hua Zheng, Song-Xia Lin, Xiao-Yi Li, Chun-Yan Shen, Shao-Wei Zheng, Wen-Bin Chen, Walid Elfalleh
Journal of Food Biochemistry.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Asprosin, a novel glucogenic adipokine implicated in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hongcui Diao, Xue Li, Yeqiu Xu, Xiuli Xing, Shuguang Pang
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(11): 108614. CrossRef - Impact of Fixed Combination of Metformin and Pioglitazone on Insulin Resistance of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Results of a Randomized Open-Label Study
Rui Sun, Lu Yuan, Yun Shen, Ziyang Shen, Bo Ding, Jianhua Ma
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 2911. CrossRef - Integrating network analysis and experimental validation to reveal the mechanism of pinocembrin in alleviating high glucose and free fatty acid-induced lipid accumulation in HepG2 cells
Kun Hu, Yongjin Sun, Jie Wang, Shaojun Wu, Jie Ren, Dan Su, Lidan Tang, Jinhong Gong, Hufeng Fang, Shan Xu, Hao Yang
Journal of Functional Foods.2023; 110: 105879. CrossRef - A Literature Review and a Proposed Classification of the Relationships between Ovulatory Infertility and Lifestyle Factors Based on the Three Groups of Ovulation Disorders Classified by WHO
Magdalena Skowrońska, Michał Pawłowski, Robert Milewski
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(19): 6275. CrossRef - Targeting of insulin receptor endocytosis as a treatment to insulin resistance
Bryce Tim, Valentina L. Kouznetsova, Santosh Kesari, Igor F. Tsigelny
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(11): 108615. CrossRef - A U-shaped association between the triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio and the risk of incident type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japanese men with normal glycemic levels: a population-based longitudinal cohort study
Bei Song, Kun Wang, Weilin Lu, Xiaofang Zhao, Tianci Yao, Ting Liu, Guangyu Gao, Haohui Fan, Chengyun Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of triglyceride-glucose index levels with gestational diabetes mellitus in the US pregnant women: a cross-sectional study
Yan Zeng, Li Yin, Xiaoping Yin, Danqing Zhao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The protective role of resveratrol in diabetic wound healing
Minglei Bi, Yonghong Qin, Lerong Wang, Jin Zhang
Phytotherapy Research.2023; 37(11): 5193. CrossRef - Correlation between alternative insulin resistance indexes and diabetic kidney disease: a retrospective study
Xiaodie Mu, Aihua Wu, Huiyue Hu, Min Yang, Hua Zhou
Endocrine.2023; 84(1): 136. CrossRef - Enhancing Muscle Intracellular Ca2+ Homeostasis and Glucose Uptake: Passive Pulsatile Shear Stress Treatment in Type 2 Diabetes
Arkady Uryash, Jordan Umlas, Alfredo Mijares, Jose A. Adams, Jose R. Lopez
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2596. CrossRef - Review of Related Research on Type 2 Diabetes Related Macroangiopathy
珊珊 李
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(09): 15001. CrossRef - Association between lipoprotein(a) and insulin resistance in Chinese adults: results from the China health and nutrition survey
Heng Wang, Jia-Li Fan
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between the Triglyceride–Glucose Index and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in patients with Atrial Fibrillation
Xiaozhong Li, Fenfang Zhan, Tian Peng, Zhen Xia, Juxiang Li
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Resveratrol as a potential protective compound against skeletal muscle insulin resistance
Arash Bahramzadeh, Kosar Bolandnazar, Reza Meshkani
Heliyon.2023; 9(11): e21305. CrossRef - The Potential Role of C-Reactive Protein in Metabolic-Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Aging
Zheng Ding, Yuqiu Wei, Jing Peng, Siyu Wang, Guixi Chen, Jiazeng Sun
Biomedicines.2023; 11(10): 2711. CrossRef - Obesity and Bone Mineral Density Protection Paradox in Chronic Kidney Disease: Secreted Protein Acidic and Rich in Cysteine as a Piece of the Puzzle?
Abdelaziz Ghanemi, Fabrice Mac-Way
Life.2023; 13(11): 2172. CrossRef - Correlation of Lipid Profile and Apolipoprotein B/A-I Ratio with Insulin Resistance in Non-Diabetes Mellitus Subjects
Andi Heriadi Palloge, Liong Boy Kurniawan, Yuyun Widyaningsih, Husaini Umar, Nurahmi Nurahmi, Andi Alfian Zainuddin
INDONESIAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY AND MEDICAL LABORATORY.2023; 30(1): 6. CrossRef - Endothelial progenitor cells as biomarkers of diabetes-related cardiovascular complications
Josefa Benítez-Camacho, Antonio Ballesteros, Lucía Beltrán-Camacho, Marta Rojas-Torres, Antonio Rosal-Vela, Margarita Jimenez-Palomares, Ismael Sanchez-Gomar, Mª Carmen Durán-Ruiz
Stem Cell Research & Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of ginseng peptides on the hypoglycemic activity and gut microbiota of a type 2 diabetes mellitus mice model
Caijing Han, Xiaoting Kong, Xiaohong Xia, Xinyu Huang, Zhaojie Mao, Jiaxin Han, Fuyan Shi, Yaohui Liang, Anning Wang, Fengxiang Zhang
Journal of Functional Foods.2023; 111: 105897. CrossRef - Effects of theasaponin E1 on the regulationglucose uptake of C2C12 myoblasts PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
Ming Zhang, Zhiyun Chen, Di Tian, Zaiqiao Li, Shaning Wang, Yujie Huo, Ling Song, Juan Lu, Jun Sheng, Xu Ji, Xiao Ma
CyTA - Journal of Food.2023; 21(1): 682. CrossRef - Efficacy and underlying mechanisms of berberine against lipid metabolic diseases: a review
Yajie Cai, Qiaoning Yang, Yanqiao Yu, Furong Yang, Ruina Bai, Xiaodi Fan
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipocyte-derived exosomal miR-22-3p modulated by circadian rhythm disruption regulates insulin sensitivity in skeletal muscle cells
Haohao Zhang, Xiaoning Zhang, Saifei Wang, Lu Zheng, Hengru Guo, Yanqi Ren, Bo Qiao, Jing Wu, Di Zhao, Lijun Xu, Shengnan Ma, Xiao Hao, Yushan Yan
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2023; 299(12): 105476. CrossRef - Total Astragalus saponins can reverse type 2 diabetes mellitus-related intestinal dysbiosis and hepatic insulin resistance in vivo
Leilei Ma, Xiaojin La, Biwei Zhang, Wenxuan Xu, Chunyu Tian, Qianru Fu, Meng Wang, Chenxi Wu, Zhen Chen, Hong Chang, Ji-an Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Interplay between Vitamin D and Adipose Tissue: Implications for Adipogenesis and Adipose Tissue Function
Shiqi Lu, Zhen-Bo Cao
Nutrients.2023; 15(22): 4832. CrossRef - Alanine aminotransferase to high- density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio is positively correlated with the occurrence of diabetes in the Chinese population: a population-based cohort study
Shiming He, Changhui Yu, Maobin Kuang, Jiajun Qiu, Ruijuan Yang, Shuhua Zhang, Guotai Sheng, Yang Zou
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between the metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS-IR) index and urinary incontinence in the United States: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2001–2018
Shangqi Cao, Linghao Meng, Lede Lin, Xu Hu, Xiang Li
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipose Tissue, Non-Communicable Diseases, and Physical Exercise: An Imperfect Triangle
Francisco A. Monsalve, Fernando Delgado-López, Barbra Fernández-Tapia, Daniel R. González
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(24): 17168. CrossRef - Risk of metabolic abnormalities in osteoarthritis: a new perspective to understand its pathological mechanisms
Guizheng Wei, Ke Lu, Muhammad Umar, Zhenglin Zhu, William W. Lu, John R. Speakman, Yan Chen, Liping Tong, Di Chen
Bone Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Sociodemographic Variables and Healthy Habits on the Values of Insulin Resistance Indicators in 386,924 Spanish Workers
Miguel Mestre Font, Carla Busquets-Cortés, José Ignacio Ramírez-Manent, Pilar Tomás-Gil, Hernán Paublini, Ángel Arturo López-González
Nutrients.2023; 15(24): 5122. CrossRef - Konjac flour-mediated gut microbiota alleviates insulin resistance and improves placental angiogenesis of obese sows
Deyuan Wu, Wenyu Xiong, Shuo Ma, Jinxi Luo, Hongxuan Ye, Shuangbo Huang, Fuyong Li, Xi’en Xiang, Qiling Chen, Binghui Gao, Jinping Deng, Yulong Yin, Chengquan Tan
AMB Express.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Physiological Adaptations to Life in Space: An Update
Isadora de Carvalho e Silva, Thais Russomano, Ricardo Alves Ferreira, Marli do Carmo Cupertino, Fabíola Alves Alcântara, Mauro Geller, Oswaldo Monteiro Del Cima, Rodrigo Siqueira-Batista
Journal of Aerospace Technology and Management.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Blood and Brain Metabolites after Cerebral Ischemia
Eva Baranovicova, Dagmar Kalenska, Peter Kaplan, Maria Kovalska, Zuzana Tatarkova, Jan Lehotsky
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(24): 17302. CrossRef - Key Therapeutic Targets to Treat Hyperglycemia-Induced Atherosclerosis Analyzed Using a Petri Net-Based Model
Agnieszka Rybarczyk, Dorota Formanowicz, Piotr Formanowicz
Metabolites.2023; 13(12): 1191. CrossRef - Exploration of the Mechanism of the Comorbidity Relationship between Alzheimer’s Disease and Diabetes Mellitus
涛 温
Medical Diagnosis.2023; 13(04): 440. CrossRef - Postbiyotikler ve İnsülin Direnci
Betül SARIDAĞ DEVRAN, Mendane SAKA
Van Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2023; 16(3): 268. CrossRef - The Anti-Diabetic Potential of Baicalin: Evidence from Rodent Studies
Tomasz Szkudelski, Katarzyna Szkudelska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 25(1): 431. CrossRef - Clinical application of Momordica charantia (Bitter Melon) for reducing blood sugar in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ashley Dahlquist, Dana Jandali, Mirielle C. Nauman, Jeremy J. Johnson, Sasho Stoleski
International Journal of Nutrition.2023; 7(4): 8. CrossRef - Alkaloids as Promising Agents for the Management of Insulin Resistance:
A Review
Ayoub Amssayef, Mohamed Eddouks
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2023; 29(39): 3123. CrossRef - Potential Mechanisms for How Long-Term Physical Activity May Reduce Insulin Resistance
Sindre Lee-Ødegård, Thomas Olsen, Frode Norheim, Christian Andre Drevon, Kåre Inge Birkeland
Metabolites.2022; 12(3): 208. CrossRef - Pathophysiological Link between Insulin Resistance and Adrenal Incidentalomas
Jordan A. Higgs, Alyssa P. Quinn, Kevin D. Seely, Zeke Richards, Shad P. Mortensen, Cody S. Crandall, Amanda E. Brooks
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4340. CrossRef - The Dose-Response Effects of Consuming High Fructose Corn Syrup-Sweetened Beverages on Hepatic Lipid Content and Insulin Sensitivity in Young Adults
Desiree M. Sigala, Bettina Hieronimus, Valentina Medici, Vivien Lee, Marinelle V. Nunez, Andrew A. Bremer, Chad L. Cox, Candice A. Price, Yanet Benyam, Yasser Abdelhafez, John P. McGahan, Nancy L. Keim, Michael I. Goran, Giovanni Pacini, Andrea Tura, Clau
Nutrients.2022; 14(8): 1648. CrossRef - Association of β-cell function and cognitive impairment in patients with abnormal glucose metabolism
Mengyi Guo, Jiaokun Jia, Jia Zhang, Mingyue Zhou, Anxin Wang, Shengyun Chen, Xingquan Zhao
BMC Neurology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Insulin Resistance in Fueling NAFLD Pathogenesis: From Molecular Mechanisms to Clinical Implications
Rossella Palma, Annamaria Pronio, Mario Romeo, Flavia Scognamiglio, Lorenzo Ventriglia, Vittorio Maria Ormando, Antonietta Lamazza, Stefano Pontone, Alessandro Federico, Marcello Dallio
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(13): 3649. CrossRef - Crosstalk between Schizophrenia and Metabolic Syndrome: The Role of Oxytocinergic Dysfunction
Kah Kheng Goh, Cynthia Yi-An Chen, Tzu-Hua Wu, Chun-Hsin Chen, Mong-Liang Lu
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(13): 7092. CrossRef - TyG index is positively associated with risk of CHD and coronary atherosclerosis severity among NAFLD patients
Jianqi Zhao, Hongxuan Fan, Ting Wang, Bing Yu, Shaobin Mao, Xun Wang, Wenjing Zhang, Leigang Wang, Yao Zhang, Zhaoyu Ren, Bin Liang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association of Acute Phase Proteins in Stress and Inflammation-Induced T2D
Tammy Speelman, Lieke Dale, Ann Louw, Nicolette J. D. Verhoog
Cells.2022; 11(14): 2163. CrossRef - Probiotic Mechanisms Affecting Glucose Homeostasis: A Scoping Review
Maša Pintarič, Tomaž Langerholc
Life.2022; 12(8): 1187. CrossRef - Potential Molecular Targets of Oleanolic Acid in Insulin Resistance and Underlying Oxidative Stress: A Systematic Review
Ángel Fernández-Aparicio, María Correa-Rodríguez, Jose M. Castellano, Jacqueline Schmidt-RioValle, Javier S. Perona, Emilio González-Jiménez
Antioxidants.2022; 11(8): 1517. CrossRef - Impact of Highly Saturated versus Unsaturated Fat Intake on Carbohydrate Metabolism and Vascular Reactivity in Rat
Youzan Ferdinand Djohan, Fabrice Raynaud, Karen Lambert, Jean-Paul Cristol, Charles Coudray, Christine Feillet-Coudray, Anne Virsolvy, Eric Badia, Néstor Gutiérrez-Méndez
Biochemistry Research International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Mitophagy: A potential therapeutic target for insulin resistance
Peng Ning, Xiaobo Jiang, Jing Yang, Jiaxing Zhang, Fan Yang, Hongyi Cao
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Higher neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio is associated with renal dysfunction and cardiac adverse remodeling in elderly with metabolic syndrome
Yuqi Zhu, Gang Li, Jari A. Laukkanen, Xing Song, Jing Zhang, Linping Wei, Xinrui Chen, Yufeng Li, Cheng Liu
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipid droplet accumulation in β cells in patients with type 2 diabetes is associated with insulin resistance, hyperglycemia and β cell dysfunction involving decreased insulin granules
Tomomi Horii, Junji Kozawa, Yukari Fujita, Satoshi Kawata, Harutoshi Ozawa, Chisaki Ishibashi, Sho Yoneda, Takao Nammo, Jun-ichiro Miyagawa, Hidetoshi Eguchi, Iichiro Shimomura
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing the long non-coding RNA expression profiles of skeletal muscle and kidney tissues from patients with diabetes
Young-Kook Kim, Takahiro Nemoto
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(9): e0274794. CrossRef - The CCR2+ Monocyte Subsets Increase in Obese Boys but Not Girls with Abnormally High Carotid Intima-Media Thickness: A Pilot Study
María José Garcés-Hernández, Karen Pedraza-Escudero, Nayely Garibay-Nieto, Joselin Hernández-Ruiz, Jessica Lakshmi Prieto-Chávez, Lourdes Andrea Arriaga-Pizano, Eréndira Villanueva-Ortega, Galileo Escobedo, Aaron Noe Manjarrez-Reyna, Juan Carlos López-Alv
Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease.2022; 9(10): 330. CrossRef - Effect of honey bee venom on the histological changes of testes and hormonal disturbance in diabetic mice
Sattar J. J. AL-Shaeli, Talal Jabal Hussen, Ali M. Ethaeb
Veterinary World.2022; : 2357. CrossRef - Establishment and Validation of a New Predictive Model for Insulin Resistance based on 2 Chinese Cohorts: A Cross-Sectional Study
Shi Zhang, Xin-Cheng Wang, Jing Li, Xiao-He Wang, Yi Wang, Yan-Ju Zhang, Mei-Yang Du, Min-Ying Zhang, Jing-Na Lin, Chun-Jun Li, Aman Rajpal
International Journal of Endocrinology.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Zishen Pill alleviates diabetes in Db/db mice via activation of PI3K/AKT pathway in the liver
You Wu, Boju Sun, Xiaoyuan Guo, Lili Wu, Yaomu Hu, Lingling Qin, Tao Yang, Mei Li, Tianyu Qin, Miao Jiang, Tonghua Liu
Chinese Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of Insulin and Pioglitazone on Protein Phosphatase 2A Interaction Partners in Primary Human Skeletal Muscle Cells Derived from Obese Insulin-Resistant Participants
Lana Alghanem, Xiangmin Zhang, Ruchi Jaiswal, Berhane Seyoum, Abdullah Mallisho, Zaher Msallaty, Zhengping Yi
ACS Omega.2022; 7(47): 42763. CrossRef - Dietary Plant Protein Intake Can Reduce Maternal Insulin Resistance during Pregnancy
Yuting Hong, Chen Yang, Jinjing Zhong, Yanmei Hou, Kui Xie, Linlin Wang
Nutrients.2022; 14(23): 5039. CrossRef - Preventive effect of probiotics supplementation on occurrence of gestational diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Azin Pakmehr, Hanieh-Sadat Ejtahed, Nooshin Shirzad, Mahboobeh Hemmatabadi, Sara Farhat, Bagher Larijani
Frontiers in Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin resistance in ischemic stroke: Mechanisms and therapeutic approaches
Peng-Fei Ding, Hua-Sheng Zhang, Jie Wang, Yong-Yue Gao, Jian-Nan Mao, Chun-Hua Hang, Wei Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Long Noncoding RNAs in the Pathogenesis of Insulin Resistance
Weili Yang, Yixiang Lyu, Rui Xiang, Jichun Yang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(24): 16054. CrossRef - Predictability of HOMA-IR for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Early Pregnancy Based on Different First Trimester BMI Values
Yanbei Duo, Shuoning Song, Yuemei Zhang, Xiaolin Qiao, Jiyu Xu, Jing Zhang, Zhenyao Peng, Yan Chen, Xiaorui Nie, Qiujin Sun, Xianchun Yang, Ailing Wang, Wei Sun, Yong Fu, Yingyue Dong, Zechun Lu, Tao Yuan, Weigang Zhao
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 13(1): 60. CrossRef - MODERN CONCEPTS OF THE PATHOGENESIS OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS
D.V. Kurkin, E.I. Morkovin, D.A. Bakulin, Yu.V. Gorbunova, A.V. Strygin, A.I. Robertus, I.E. Makarenko, V.B. Saparova, R.V. Drai, V.I. Petrov
Journal of Volgograd State Medical University.2022; 19(4): 34. CrossRef
- Diabetic Encephalopathy: Role of Oxidative and Nitrosative Factors in Type 2 Diabetes
- Metabolic risk/Epidemiology
- Obesity, Diabetes, and Increased Cancer Progression
- Dae-Seok Kim, Philipp E. Scherer
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):799-812. Published online November 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0077

- 14,156 View
- 666 Download
- 70 Web of Science
- 76 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Rates of obesity and diabetes have increased significantly over the past decades and the prevalence is expected to continue to rise further in the coming years. Many observations suggest that obesity and diabetes are associated with an increased risk of developing several types of cancers, including liver, pancreatic, endometrial, colorectal, and post-menopausal breast cancer. The path towards developing obesity and diabetes is affected by multiple factors, including adipokines, inflammatory cytokines, growth hormones, insulin resistance, and hyperlipidemia. The metabolic abnormalities associated with changes in the levels of these factors in obesity and diabetes have the potential to significantly contribute to the development and progression of cancer through the regulation of distinct signaling pathways. Here, we highlight the cellular and molecular pathways that constitute the links between obesity, diabetes, cancer risk and mortality. This includes a description of the existing evidence supporting the obesity-driven morphological and functional alternations of cancer cells and adipocytes through complex interactions within the tumor microenvironment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Triglyceride‐glucose index (TyG index) and endometrial carcinoma risk: A retrospective cohort study
Haimeng Shi, Feifei Guo, Kang Zheng, Rong Li, Huaijun Zhou
International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics.2024; 164(1): 298. CrossRef - Association between total cholesterol levels and all-cause mortality among newly diagnosed patients with cancer
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, So Hyun Cho, Rosa Oh, Ji Yoon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Adipokines in Tumor Progression and Its Association with Obesity
Jae Won Kim, Jun Hyeok Kim, Yoon Jae Lee
Biomedicines.2024; 12(1): 97. CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index is a risk factor for breast cancer in China: a cross-sectional study
Jinghua Zhang, Binbin Yin, Ya Xi, Yongying Bai
Lipids in Health and Disease.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin Resistance: The Increased Risk of Cancers
Leszek Szablewski
Current Oncology.2024; 31(2): 998. CrossRef - Epigenetic modifications in obesity‐associated diseases
Yiqian Long, Chao Mao, Shuang Liu, Yongguang Tao, Desheng Xiao
MedComm.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Juncture of Diabetes, Cancer, and Observational Population-based Studies: Novel Insights From Canadian Provincial Health Records
Terra Arnason, Kerry Mansell
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2024; 48(3): 145. CrossRef - The impact of chemotherapy on adipose tissue remodeling: The molecular players involved in this tissue wasting
Samuel Barbosa, Mafalda Barbosa Pedrosa, Rita Ferreira, Daniel Moreira-Gonçalves, Lúcio Lara Santos
Biochimie.2024; 223: 1. CrossRef - Epidemiological and transcriptome data identify shared gene signatures and immune cell infiltration in type 2 diabetes and non-small cell lung cancer
Qian Yuan, Long Li, Liu-shun Wang, Shi-gui Xing
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - THE INFLUENCE OF DIABETES-ASSOCIATED FACTORS OF ONCOGENESIS ON THE RISK OF BREAST AND ENDOMETRIAL CANCER AND ON THE SURVIVAL OF WOMEN WITH THIS CANCER
Tamara S. Vatseba, Liubov K. Sokolova, Vasyl Ye. Neyko, Valentyna V. Dzvonkovska, Oksana V. Muravlova, Volodymyr V. Derpak
Clinical and Preventive Medicine.2024; (2): 99. CrossRef - Associations between diabetes and cancer: A 10-year national population-based retrospective cohort study
Heléna Safadi, Ágnes Balogh, Judit Lám, Attila Nagy, Éva Belicza
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 211: 111665. CrossRef - Colorectal Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Prevention
Gholamreza Roshandel, Fatemeh Ghasemi-Kebria, Reza Malekzadeh
Cancers.2024; 16(8): 1530. CrossRef - Metabolic Alteration Bridging the Prediabetic State and Colorectal Cancer
Antonino Colloca, Isabella Donisi, Camilla Anastasio, Maria Luisa Balestrieri, Nunzia D’Onofrio
Cells.2024; 13(8): 663. CrossRef - Changes in physical activity and diabetes risk after cancer diagnosis: a nationwide cohort study
Wonyoung Jung, In Young Cho, Jinhyung Jung, Mi Hee Cho, Hye Yeon Koo, Yong-Moon Mark Park, Jong-Ha Baek, Kyungdo Han, Dong Wook Shin
Journal of Cancer Survivorship.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Ultra‐processed food consumption and the risk of pancreatic cancer in the Prostate, Lung, Colorectal and Ovarian Cancer Screening Trial
Guo‐Chao Zhong, Qian Zhu, Dong Cai, Jie‐Jun Hu, Xin Dai, Jian‐Ping Gong, Wei‐Ping Sun
International Journal of Cancer.2023; 152(5): 835. CrossRef - Advances in “adiponcosis”: Insights in the inner mechanisms at the base of adipose and tumour tissues interplay
Cristina Pagano, Erika di Zazzo, Giorgio Avilia, Beatrice Savarese, Giovanna Navarra, Maria Chiara Proto, Donatella Fiore, Monica Rienzo, Patrizia Gazzerro, Chiara Laezza, Maurizio Bifulco
International Journal of Cancer.2023; 152(12): 2464. CrossRef - Metabolites as signalling molecules
Steven Andrew Baker, Jared Rutter
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology.2023; 24(5): 355. CrossRef - Characterization of neuroendocrine regulation- and metabolism-associated molecular features and prognostic indicators with aid to clinical chemotherapy and immunotherapy of patients with pancreatic cancer
Biao Zhang, Qihang Yuan, Bolin Zhang, Shuang Li, Zhizhou Wang, Hangyu Liu, Fanyue Meng, Xu Chen, Dong Shang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Concentration of Selected Adipokines and Factors Regulating Carbohydrate Metabolism in Patients with Head and Neck Cancer in Respect to Their Body Mass Index
Jarosław Nuszkiewicz, Jolanta Czuczejko, Wiktor Dróżdż, Alina Woźniak, Bogdan Małkowski, Karolina Szewczyk-Golec
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3283. CrossRef - Hormonal Gut–Brain Signaling for the Treatment of Obesity
Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3384. CrossRef - A novel five-gene metabolism-related risk signature for predicting prognosis and immune infiltration in endometrial cancer: A TCGA data mining
Huaqing Huang, Xintong Cai, Jiexiang Lin, Qiaoling Wu, Kailin Zhang, Yibin Lin, Bin Liu, Jie Lin
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2023; 155: 106632. CrossRef - Green Antimicrobials as Therapeutic Agents for Diabetic Foot Ulcers
Ines D. Teixeira, Eugenia Carvalho, Ermelindo C. Leal
Antibiotics.2023; 12(3): 467. CrossRef - Impact of abdominal obesity on the risk of glioma development in patients with diabetes: A nationwide population-based cohort study in Korea
Hyunji Sang, Yun Kyung Cho, Kyungdo Han, Eun Hee Koh, Sandar Tin Tin
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(3): e0283023. CrossRef - Relationship Between Physical Exercise and Cognitive Impairment Among Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: Chain Mediating Roles of Sleep Quality and Depression
Han Zhang, Yefan Zhang, Sen Sheng, Yang Xing, Zhongchen Mou, Yanqiu Zhang, Zhixue Shi, Zhenjie Yu, Qianqian Gao, Weiqin Cai, Qi Jing
Psychology Research and Behavior Management.2023; Volume 16: 817. CrossRef - The Mediterranean Lifestyle to Contrast Low-Grade Inflammation Behavior in Cancer
Rosa Divella, Graziella Marino, Stefania Infusino, Laura Lanotte, Gaia Gadaleta-Caldarola, Gennaro Gadaleta-Caldarola
Nutrients.2023; 15(7): 1667. CrossRef - Distribution of ABO blood groups and Rh factor in benign and malign thyroid nodules
Muzaffer Serdar DENİZ
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2023; 6(2): 462. CrossRef - The Role of Selected Adipocytokines in Ovarian Cancer and Endometrial Cancer
Sebastian Stępień, Paweł Olczyk, Joanna Gola, Katarzyna Komosińska-Vassev, Aleksandra Mielczarek-Palacz
Cells.2023; 12(8): 1118. CrossRef - Coronary Revascularization in Patients With Cancer
Bala Pushparaji, Teodora Donisan, Dinu Valentin Balanescu, Jong Kun Park, Dominique J. Monlezun, Abdelrahman Ali, Ibrahim Halil Inanc, Jaime Caballero, Mehmet Cilingiroglu, Konstantinos Marmagkiolis, Cezar Iliescu
Current Treatment Options in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023; 25(6): 143. CrossRef - Hepatocellular carcinoma in a large cohort of type 2 diabetes patients
Carlo B. Giorda, Roberta Picariello, Barbara Tartaglino, Elisa Nada, Giuseppe Costa, Roberta Manti, Luca Monge, Roberto Gnavi
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 200: 110684. CrossRef - Prediction of Hypoglycemia in Diabetic Patients During Colonoscopy
Preparation
Xiaohua Lu, Lingqiao Xie, Wane Zhao, Chuangbiao Zhang, Xixi Luo, Yan Zhou
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2023; 131(05): 274. CrossRef - Interplay of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: sarcopenic obesity
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 144: 155577. CrossRef - PIK3CA mutation in endometriotic epithelial cells promotes viperin-dependent inflammatory response to insulin
Mike R. Wilson, Shannon Harkins, Jake J. Reske, Rebecca A. Siwicki, Marie Adams, Victoria L. Bae-Jump, Jose M. Teixeira, Ronald L. Chandler
Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Function of MondoA and ChREBP Nutrient—Sensing Factors in Metabolic Disease
Byungyong Ahn
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(10): 8811. CrossRef - Mechanism of Cephalophyllum cephalus Intervention in Diabetes Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking Technology
志梁 范
Hans Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2023; 11(02): 81. CrossRef - Development and validation of a prognostic model based on metabolic risk score to predict overall survival of endometrial cancer in Chinese patients
Xingchen Li, Xiao Yang, Yuan Cheng, Yangyang Dong, Jingyuan Wang, Jianliu Wang
Journal of Gynecologic Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nε-(1-Carboxymethyl)-L-lysine, an advanced glycation end product, exerts malignancy on chondrosarcoma via the activation of cancer stemness
Ting-Yu Chang, Kuo-Cheng Lan, Chia-Hung Wu, Meei-Ling Sheu, Rong-Sen Yang, Shing-Hwa Liu
Archives of Toxicology.2023; 97(8): 2231. CrossRef - The Link between Diabetes, Pancreatic Tumors, and miRNAs—New Players for Diagnosis and Therapy?
Małgorzata Kozłowska, Agnieszka Śliwińska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(12): 10252. CrossRef - Obesity, diabetes, and cancer: epidemiology, pathophysiology, and potential interventions
Leonardo de Andrade Mesquita, Laura Fink Wayerbacher, Gilberto Schwartsmann, Fernando Gerchman
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Distinct Lipid Phenotype of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts (CAFs) Isolated From Overweight/Obese Endometrial Cancer Patients as Assessed Using Raman Spectroscopy
Tze Hua Yeu, Intan Sofia Omar, S.F. Abdul Sani, Dharini Pathmanathan, Boon Tong Goh, Nithyialakshmi Ravindran, Ik Hui Teo, Yogeeta Gunasagran, Noor Azmi Mat Adenan, Ivy Chung, Amira Hajirah Abd Jamil
Applied Spectroscopy.2023; 77(7): 723. CrossRef - Global, Regional, and National Epidemiology of Diabetes in Children From 1990 to 2019
Kexin Zhang, Chengxia Kan, Fang Han, Jingwen Zhang, Chuanhua Ding, Zhentao Guo, Na Huang, Yang Zhang, Ningning Hou, Xiaodong Sun
JAMA Pediatrics.2023; 177(8): 837. CrossRef - The effects of physical exercise therapy on weight control: its regulation of adipocyte physiology and metabolic capacity
Hyun Jung Park, Sung Ja Rhie, Insop Shim
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2023; 19(3): 141. CrossRef - The Ephrin tyrosine kinase a3 (EphA3) is a novel mediator of RAGE-prompted motility of breast cancer cells
Marianna Talia, Francesca Cirillo, Asia Spinelli, Azzurra Zicarelli, Domenica Scordamaglia, Lucia Muglia, Salvatore De Rosis, Damiano Cosimo Rigiracciolo, Gianfranco Filippelli, Ida Daniela Perrotta, Mariano Davoli, Rosanna De Rosa, Rachele Macirella, Elv
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Signal detection in real‐world data and confirmation in clinical trials: Diabetes as a case study for a conversation worth having
Elad Sharon, Megan Othus, Zoe Eloise Quandt
Cancer.2023; 129(18): 2769. CrossRef - Ultra-Processed Food Consumption and Obesity in Korean Adults
Jee-Seon Shim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Hyeon Chang Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(4): 547. CrossRef - Decoding the role of leptin and adiponectin in obesity-related gastrointestinal cancer
Vanda Marques, Fabiola Arella, Marta B. Afonso, André A. Santos, Cecília M.P. Rodrigues
Clinical Science.2023; 137(15): 1095. CrossRef - Diabetes and two kinds of primary tumors in a patient with thalassemia: a case report and literature review
Xiaoyan Yu, Yi Peng, Tingting Nie, Wenjia Sun, Yajuan Zhou
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Additive impact of diabetes and sarcopenia on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: A longitudinal nationwide population-based study
Eyun Song, Soon Young Hwang, Min Jeong Park, Ahreum Jang, Kyeong Jin Kim, Ji Hee Yu, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 148: 155678. CrossRef - Obesity and Colorectal Cancer
Jundeok Lee, Su Young Kim
The Korean Journal of Gastroenterology.2023; 82(2): 63. CrossRef - Cognitive Behavioural Therapies for Weight-Loss in Adults: A Scoping Review Protocol
Laura María Compañ-Gabucio, Diana Mancheño-Bañón, Laura Torres-Collado, Jesús Vioque, Manuela García-de-la-Hera
Healthcare.2023; 11(18): 2473. CrossRef - Saxagliptin, a selective dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, alleviates somatic cell aneugenicity and clastogenicity in diabetic mice
Sabry M. Attia, Sheikh F. Ahmad, Ahmed Nadeem, Mohamed S.M. Attia, Mushtaq A. Ansari, Abdelkader E. Ashour, Norah A. Albekairi, Mohammed A. Al-Hamamah, Ali A. Alshamrani, Saleh A. Bakheet
Mutation Research/Genetic Toxicology and Environmental Mutagenesis.2023; 892: 503707. CrossRef - Mechanisms of Linggui Zhugan Decoction in the Treatment of Obesity Based on Network Pharmacology
Chunmei Liu, Li Zhang, Yubin Yang
Science of Advanced Materials.2023; 15(9): 1265. CrossRef - Beyond Body Size: Adiponectin as a Key Player in Obesity-Driven Cancers
Maurizio Capuozzo, Venere Celotto, Loris Landi, Francesco Ferrara, Francesco Sabbatino, Francesco Perri, Marco Cascella, Vincenza Granata, Mariachiara Santorsola, Alessandro Ottaiano
Nutrition and Cancer.2023; 75(10): 1848. CrossRef - Impact of sarcopenic obesity on post-hepatectomy bile leakage for hepatocellular carcinoma
Hikaru Hayashi, Akira Shimizu, Koji Kubota, Tsuyoshi Notake, Hitoshi Masuo, Takahiro Yoshizawa, Kiyotaka Hosoda, Hiroki Sakai, Koya Yasukawa, Yuji Soejima, Ezio Lanza
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(10): e0286353. CrossRef - Colorectal Cancer: From Risk Factors to Oncogenesis
Vlad Alexandru Ionescu, Gina Gheorghe, Nicolae Bacalbasa, Alexandru Laurentiu Chiotoroiu, Camelia Diaconu
Medicina.2023; 59(9): 1646. CrossRef - The impact of poor metabolic health on aggressive breast cancer: adipose tissue and tumor metabolism
Barbara Mensah Sankofi, Estefania Valencia-Rincón, Malika Sekhri, Adriana L. Ponton-Almodovar, Jamie J. Bernard, Elizabeth A. Wellberg
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and growth hormone deficiency: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Tingting Kong, Yunpeng Gu, Lei Sun, Run Zhou, Jie Li, Junping Shi
Endocrine Journal.2023; 70(10): 959. CrossRef - Impact of Caloric Restriction in Breast Cancer Patients Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: A Prospective Case Control Study
Isabella Castellano, Francesco Gallo, Paola Durelli, Taira Monge, Maurizio Fadda, Jasna Metovic, Paola Cassoni, Fulvio Borella, Carlo Raucci, Monica Menischetti, Alessandra Beano, Giuseppe Migliaretti, Concetta Finocchiaro
Nutrients.2023; 15(21): 4677. CrossRef - Metabolomic and lipidomic studies on the intervention of taurochenodeoxycholic acid in mice with hyperlipidemia
Na Cui, Wensen Zhang, Fazhi Su, Zhihong Zhang, Biao Li, Donghui Peng, Yanping Sun, Yuanning Zeng, Bingyou Yang, Haixue Kuang, Qiuhong Wang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Is MG53 a potential therapeutic target for cancer?
Yunyu Du, Tieying Li, Muqing Yi
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Blood Biomarkers Panels for Screening of Colorectal Cancer and Adenoma on a Machine Learning-Assisted Detection Platform
Hui Wang, Zhiwei Zhou, Haijun Li, Weiguang Xiang, Yilin Lan, Xiaowen Dou, Xiuming Zhang
Cancer Control.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Post-treatment serum triglyceride: An effective biomarker for body fat mass and overall survival in esophageal squamous cell cancer patients treated with chemoradiotherapy
Jiahua Lyu, Ningjing Yang, Wang Guan, Ling Xiao, Xinyu Nie, Long Liang, Hansong Bai, Churong Li, Hao Kuang, Xiao Wang, Tao Li
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress of MicroRNA-122 in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
路路 潘
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(06): 5706. CrossRef - Cancer and Obesity: An Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) Clinical Practice Statement (CPS) 2022
Ethan Lazarus, Harold Edward Bays
Obesity Pillars.2022; 3: 100026. CrossRef - Obesity Fact Sheet in Korea, 2021: Trends in Obesity Prevalence and Obesity-Related Comorbidity Incidence Stratified by Age from 2009 to 2019
Ye Seul Yang, Byoung-Duck Han, Kyungdo Han, Jin-Hyung Jung, Jang Won Son
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2022; 31(2): 169. CrossRef - Fried food consumption and the risk of pancreatic cancer: A large prospective multicenter study
Guo-Chao Zhong, Qian Zhu, Jian-Ping Gong, Dong Cai, Jie-Jun Hu, Xin Dai, Jun-Hua Gong
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Intermittent Fasting Is Associated With a Decreased Risk of Age-Related Macular Degeneration
Eun Young Choi, Min Kim, Christopher Seungkyu Lee, Suk Ho Byeon, Sung Soo Kim, Minyoung Lee
American Journal of Ophthalmology.2022; 243: 1. CrossRef - Metformin Mitigated Obesity-Driven Cancer Aggressiveness in Tumor-Bearing Mice
Chun-Jung Chen, Chih-Cheng Wu, Cheng-Yi Chang, Jian-Ri Li, Yen-Chuan Ou, Wen-Ying Chen, Su-Lan Liao, Jiaan-Der Wang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(16): 9134. CrossRef - Visceral fat area and body fat percentage measured by bioelectrical impedance analysis correlate with glycometabolism
Shuying Li, Shaoping Li, Jie Ding, Weihong Zhou
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Insight on the Role of Leptin: A Bridge from Obesity to Breast Cancer
Roberto Buonaiuto, Fabiana Napolitano, Sara Parola, Pietro De Placido, Valeria Forestieri, Giovanna Pecoraro, Alberto Servetto, Luigi Formisano, Pietro Formisano, Mario Giuliano, Grazia Arpino, Sabino De Placido, Carmine De Angelis
Biomolecules.2022; 12(10): 1394. CrossRef - Adipokines as Regulators of Autophagy in Obesity-Linked Cancer
Alin García-Miranda, Alejandra Garcia-Hernandez, Eduardo Castañeda-Saucedo, Napoleon Navarro-Tito, Paola Maycotte
Cells.2022; 11(20): 3230. CrossRef - Roles of hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids in diabetes (HETEs and diabetes)
Linyue Dong, Heyao Wang, Kaixian Chen, Yiming Li
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 156: 113981. CrossRef - Changes in the Fecal Metabolome Accompany an Increase in Aberrant Crypt Foci in the Colon of C57BL/6 Mice Fed with a High-Fat Diet
Huawei Zeng, Bryan D. Safratowich, Wen-Hsing Cheng, Andrew D. Magnuson, Matthew J. Picklo
Biomedicines.2022; 10(11): 2891. CrossRef - Targeting Adiponectin in Breast Cancer
Rawan Nehme, Mona Diab-Assaf, Caroline Decombat, Laetitia Delort, Florence Caldefie-Chezet
Biomedicines.2022; 10(11): 2958. CrossRef - Multidisciplinary Progress in Obesity Research
Xiaoqing Lu, Yuxin Jin, Dexin Li, Jingxin Zhang, Jingyan Han, Yin Li
Genes.2022; 13(10): 1772. CrossRef - The association between serum copper and obesity and all-cause mortality: the NHANES 2011–2016
Hongrong Wu, Qingqi Li, Kaifang Zhang, Jianfeng Zhao
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2022; 30(11): 31395. CrossRef - The crosstalk within the breast tumor microenvironment in type II diabetes: Implications for cancer disparities
Christina S. Ennis, Pablo Llevenes, Yuhan Qiu, Ruben Dries, Gerald V. Denis
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Triglyceride‐glucose index (TyG index) and endometrial carcinoma risk: A retrospective cohort study
- Technology/Device
- Assessment of Insulin Secretion and Insulin Resistance in Human
- So Young Park, Jean-François Gautier, Suk Chon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):641-654. Published online September 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0220

- 14,148 View
- 879 Download
- 47 Web of Science
- 23 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- The impaired insulin secretion and increased insulin resistance (or decreased insulin sensitivity) play a major role in the pathogenesis of all types of diabetes mellitus (DM). It is very important to assess the pancreatic β-cell function and insulin resistance/ sensitivity to determine the type of DM and to plan an optimal management and prevention strategy for DM. So far, various methods and indices have been developed to assess the β-cell function and insulin resistance/sensitivity based on static, dynamic test and calculation of their results. In fact, since the metabolism of glucose and insulin is made through a complex process related with various stimuli in several tissues, it is difficult to fully reflect the real physiology. In order to solve the theoretical and practical difficulties, research on new index is still in progress. Also, it is important to select the appropriate method and index for the purpose of use and clinical situation. This review summarized a variety of traditional methods and indices to evaluate pancreatic β-cell function and insulin resistance/sensitivity and introduced novel indices.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Polyphenol-Rich Extract of Fermented Chili Pepper Alleviates Insulin Resistance in HepG2 Cells via Regulating INSR, PTP1B, PPAR-γ, and AMPK Pathways
Tao Wang, Meiqi Li, Shengbao Cai, Linyan Zhou, Xiaosong Hu, Junjie Yi
Fermentation.2023; 9(2): 84. CrossRef - 2,3-Dihydrosorbicillin and chrysopanol stimulate insulin secretion in INS-1 cells
Dahae Lee, Jaekyung Kim, Sungyoul Choi, Jinwon Choi, Jin Woo Lee, Ki Sung Kang, Sang Hee Shim
Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters.2023; 83: 129186. CrossRef - Insulin: A connection between pancreatic β cells and the hypothalamus
Brenda De la Cruz Concepción, Yaccil Adilene Flores Cortez, Martha Isela Barragán Bonilla, Juan Miguel Mendoza Bello, Monica Espinoza Rojo
World Journal of Diabetes.2023; 14(2): 76. CrossRef - The Metabolic Score for Insulin Resistance (METS-IR) Predicts Cardiovascular Disease and Its Subtypes in Patients with Hypertension and Obstructive Sleep Apnea
Wenbo Yang, Xintian Cai, Junli Hu, Wen Wen, Heizhati Mulalibieke, Xiaoguang Yao, Ling Yao, Qing Zhu, Jing Hong, Qin Luo, Shasha Liu, Nanfang Li
Clinical Epidemiology.2023; Volume 15: 177. CrossRef - Association between dietary patterns and biomarkers in connection with diabetes mellitus in adolescents: A systematic review
Bernardo Paz Barboza, Camila Tureck, Liliana Paula Bricarello, Mariane de Almeida Alves, Anabelle Retondario, Amanda de Moura Souza, Ricardo Fernandes, Francisco de Assis Guedes de Vasconcelos
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(4): 685. CrossRef - PNPLA3 rs738409 risk genotype decouples TyG index from HOMA2-IR and intrahepatic lipid content
Ákos Nádasdi, Viktor Gál, Tamás Masszi, Anikó Somogyi, Gábor Firneisz
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Ethnic Variability in Glucose and Insulin Response to Rice Among Healthy Overweight Adults: A Randomized Cross-Over Study
Amena Sadiya, Vidya Jakapure, Vijay Kumar
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 993. CrossRef - Familial partial lipodystrophy type 2 and obesity, two adipose tissue pathologies with different inflammatory profiles
Guillaume Treiber, Marie-Paule Gonthier, Alice Guilleux, Samir Medjane, Oriane Bonfanti, Muriel Cogne, Olivier Meilhac, Estelle Nobecourt
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Discriminant Model for Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Erislandis López-Galán, Rafael Barrio-Deler, Manuel Alejandro Fernández-Fernández, Yaquelin Del Toro-Delgado, Isaac Enrique Peñuela-Puente, Miguel Enrique Sánchez-Hechavarría, Mario Eugenio Muñoz-Bustos, Gustavo Alejandro Muñoz-Bustos
Medicina.2023; 59(5): 839. CrossRef - Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress in Metabolic Syndrome
Sepiso K. Masenga, Lombe S. Kabwe, Martin Chakulya, Annet Kirabo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(9): 7898. CrossRef - Estimated Glucose Disposal Rate Predicts Renal Progression in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Juan Peng, Aimei Li, Liangqingqing Yin, Qi Yang, Jinting Pan, Bin Yi
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Transfer RNA Mutation Associated with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Fanny Rizki Rahmadanthi, Iman Permana Maksum
Biology.2023; 12(6): 871. CrossRef - Honokiol improves endothelial function in type 2 diabetic rats via alleviating oxidative stress and insulin resistance
An He, Huilin Yu, Yu Hu, Huiling Chen, Xiang Li, Jian Shen, Rongjuan Zhuang, Yi Chen, Bryan Richard Sasmita, Minghao Luo, Dingyi Lv
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2022; 600: 109. CrossRef - Relationship of Vitamin A and Thyroid Function in Individuals With Obesity and After Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
Bingwei Ma, Peng Yang, Jingyang Gao, Lei Du, Chunjun Sheng, Taofeek Usman, Xingchun Wang, Shen Qu
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of Personalized Diabetes Self-care Using an Electronic Medical Record–Integrated Mobile App in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: 6-Month Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun Young Lee, Seon-Ah Cha, Jae-Seung Yun, Sun-Young Lim, Jin-Hee Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Kun-Ho Yoon, Min Kyung Hyun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2022; 24(7): e37430. CrossRef - Acyclovir alleviates insulin resistance via activating PKM1 in diabetic mice
Zhuozhou Hu, Jing Zhou, Liang Han, Xiangxiang Li, Chun Li, Tongyu Wu, Jingjing Liu, Wenyang Zhao, Jia Kang, Xinping Chen
Life Sciences.2022; 304: 120725. CrossRef - Identifying Glucose Metabolism Status in Nondiabetic Japanese Adults Using Machine Learning Model with Simple Questionnaire
Tomoki Uchida, Takeshi Kanamori, Takanori Teramoto, Yuji Nonaka, Hiroki Tanaka, Satoshi Nakamura, Norihito Murayama, Rajesh Kaluri
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Elevated triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index predicts impaired islet β-cell function: A hospital-based cross-sectional study
Zi Chen, Jie Wen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Maternal Glycaemic and Insulinemic Status and Newborn DNA Methylation: Findings in Women With Overweight and Obesity
Marion Lecorguillé, Fionnuala M McAuliffe, Patrick J Twomey, Karien Viljoen, John Mehegan, Cecily C Kelleher, Matthew Suderman, Catherine M Phillips
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 108(1): 85. CrossRef - Acanthosis Nigricans: Pointer of Endocrine Entities
Andreea-Maria Radu, Mara Carsote, Mihai Cristian Dumitrascu, Florica Sandru
Diagnostics.2022; 12(10): 2519. CrossRef - Relationship between Insulin Resistance Risk Scales and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis Scales in 219,477 Spanish Workers
José Ignacio Ramírez-Manent, Emilio Martínez-Almoyna, Carlos López, Carla Busquets-Cortés, Hilda González San Miguel, Ángel Arturo López-González
Metabolites.2022; 12(11): 1093. CrossRef - Investigation of Insulin Secretion in Glucose Tolerance Test by the Intake of Novel Imeglimin (Twymeeg)
Hiroshi BANDO, Hiroko OGAWA, Hirohisa URASAKI, Shinji NAGAHIRO, Hiroko URASAKI, Miwako NAKANISHI, Osami WATANABE
Asploro Journal of Biomedical and Clinical Case Reports.2022; 5(3): 113. CrossRef - Evaluation and Screening of Hypoglycemic Activity of Total Ginsenosides GBE-5 Fraction From Panax Ginseng Berry Based on UHPLC–MS Metabolomics
Heyu Wang, Yu Tong, Anqi Wang, Ying Li, Bofan Lu, Hui Li, Lili Jiao, Wei Wu
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Polyphenol-Rich Extract of Fermented Chili Pepper Alleviates Insulin Resistance in HepG2 Cells via Regulating INSR, PTP1B, PPAR-γ, and AMPK Pathways

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





