
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Optimal Coefficient of Variance Threshold to Minimize Hypoglycemia Risk in Individuals with Well-Controlled Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jee Hee Yoo, Seung Hee Yang, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Received March 14, 2023 Accepted August 12, 2023 Published online March 4, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0083 [Epub ahead of print]

- 512 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study investigated the optimal coefficient of variance (%CV) for preventing hypoglycemia based on real-time continuous glucose monitoring (rt-CGM) data in people with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) already achieving their mean glucose (MG) target.
Methods
Data from 172 subjects who underwent rt-CGM for at least 90 days and for whom 439 90-day glycemic profiles were available were analyzed. Receiver operator characteristic analysis was conducted to determine the cut-off value of %CV to achieve time below range (%TBR)<54 mg/dL <1 and =0.
Results
Overall mean glycosylated hemoglobin was 6.8% and median %TBR<54 mg/dL was 0.2%. MG was significantly higher and %CV significantly lower in profiles achieving %TBR<54 mg/dL <1 compared to %TBR<54 mg/dL ≥1 (all P<0.001). The cut-off value of %CV for achieving %TBR<54 mg/dL <1 was 37.5%, 37.3%, and 31.0%, in the whole population, MG >135 mg/dL, and ≤135 mg/dL, respectively. The cut-off value for %TBR<54 mg/dL=0% was 29.2% in MG ≤135 mg/dL. In profiles with MG ≤135 mg/dL, 94.2% of profiles with a %CV <31 achieved the target of %TBR<54 mg/dL <1, and 97.3% with a %CV <29.2 achieved the target of %TBR<54 mg/ dL=0%. When MG was >135 mg/dL, 99.4% of profiles with a %CV <37.3 achieved %TBR<54 mg/dL <1.
Conclusion
In well-controlled T1DM with MG ≤135 mg/dL, we suggest a %CV <31% to achieve the %TBR<54 mg/dL <1 target. Furthermore, we suggest a %CV <29.2% to achieve the target of %TBR<54 mg/dL =0 for people at high risk of hypoglycemia.
- Technology/Device
- Clinical and Lifestyle Determinants of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Metrics in Insulin-Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Da Young Lee, Namho Kim, Inha Jung, So Young Park, Ji Hee Yu, Ji A Seo, Jihee Kim, Kyeong Jin Kim, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sung-Min Park, Nan Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):826-836. Published online August 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0273

- 1,790 View
- 191 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
There was limited evidence to evaluate the association between lifestyle habits and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) metrics. Thus, we aimed to depict the behavioral and metabolic determinants of CGM metrics in insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
This is a prospective observational study. We analyzed data from 122 insulin-treated patients with T2DM. Participants wore Dexcom G6 and Fitbit, and diet information was identified for 10 days. Multivariate-adjusted logistic regression analysis was performed for the simultaneous achievement of CGM-based targets, defined by the percentage of time in terms of hyper, hypoglycemia and glycemic variability (GV). Intake of macronutrients and fiber, step counts, sleep, postprandial C-peptide-to-glucose ratio (PCGR), information about glucose lowering medications and metabolic factors were added to the analyses. Additionally, we evaluated the impact of the distribution of energy and macronutrient during a day, and snack consumption on CGM metrics.
Results
Logistic regression analysis revealed that female, participants with high PCGR, low glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and daytime step count had a higher probability of achieving all targets based on CGM (odds ratios [95% confidence intervals] which were 0.24 [0.09 to 0.65], 1.34 [1.03 to 1.25], 0.95 [0.9 to 0.99], and 1.15 [1.03 to 1.29], respectively). And participants who ate snacks showed a shorter period of hyperglycemia and less GV compared to those without.
Conclusion
We confirmed that residual insulin secretion, daytime step count, HbA1c, and women were the most relevant determinants of adequate glycemic control in insulin-treated patients with T2DM. In addition, individuals with snack consumption were exposed to lower times of hyperglycemia and GV. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Explanatory variables of objectively measured 24-h movement behaviors in people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review
Lotte Bogaert, Iris Willems, Patrick Calders, Eveline Dirinck, Manon Kinaupenne, Marga Decraene, Bruno Lapauw, Boyd Strumane, Margot Van Daele, Vera Verbestel, Marieke De Craemer
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2024; 18(4): 102995. CrossRef
- Explanatory variables of objectively measured 24-h movement behaviors in people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review
- Technology/Device
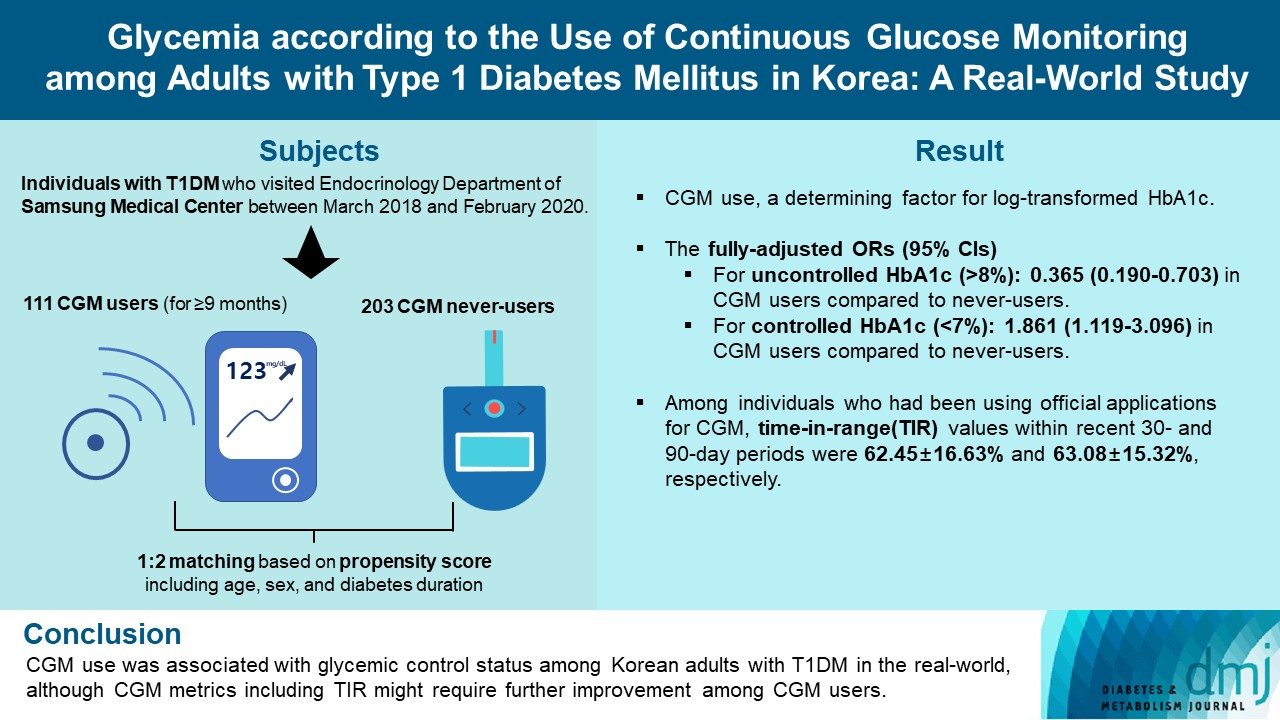
- Glycemia according to the Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring among Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A Real-World Study
- You-Bin Lee, Minjee Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):405-414. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0032
- 3,258 View
- 122 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We explored the association between continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) use and glycemia among adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and determined the status of CGM metrics among adults with T1DM using CGM in the real-world.
Methods
For this propensity-matched cross-sectional study, individuals with T1DM who visited the outpatient clinic of the Endocrinology Department of Samsung Medical Center between March 2018 and February 2020 were screened. Among them, 111 CGM users (for ≥9 months) were matched based on propensity score considering age, sex, and diabetes duration in a 1:2 ratio with 203 CGM never-users. The association between CGM use and glycemic measures was explored. In a subpopulation of CGM users who had been using official applications (not “do-it-yourself” software) such that Ambulatory Glucose Profile data for ≥1 month were available (n=87), standardized CGM metrics were summarized.
Results
Linear regression analyses identified CGM use as a determining factor for log-transformed glycosylated hemoglobin. The fully-adjusted odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for uncontrolled glycosylated hemoglobin (>8%) were 0.365 (95% CI, 0.190 to 0.703) in CGM users compared to never-users. The fully-adjusted OR for controlled glycosylated hemoglobin (<7%) was 1.861 (95% CI, 1.119 to 3.096) in CGM users compared to never-users. Among individuals who had been using official applications for CGM, time in range (TIR) values within recent 30- and 90-day periods were 62.45%±16.63% and 63.08%±15.32%, respectively.
Conclusion
CGM use was associated with glycemic control status among Korean adults with T1DM in the real-world, although CGM metrics including TIR might require further improvement among CGM users. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Sarah Andrade, Boyang Chen, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Accuracy and Safety of the 15-Day CareSens Air Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Won Sang Yoo, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024; 26(4): 222. CrossRef - Navigating the Seas of Glycemic Control: The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 345. CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef
- Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
- Technology/Device
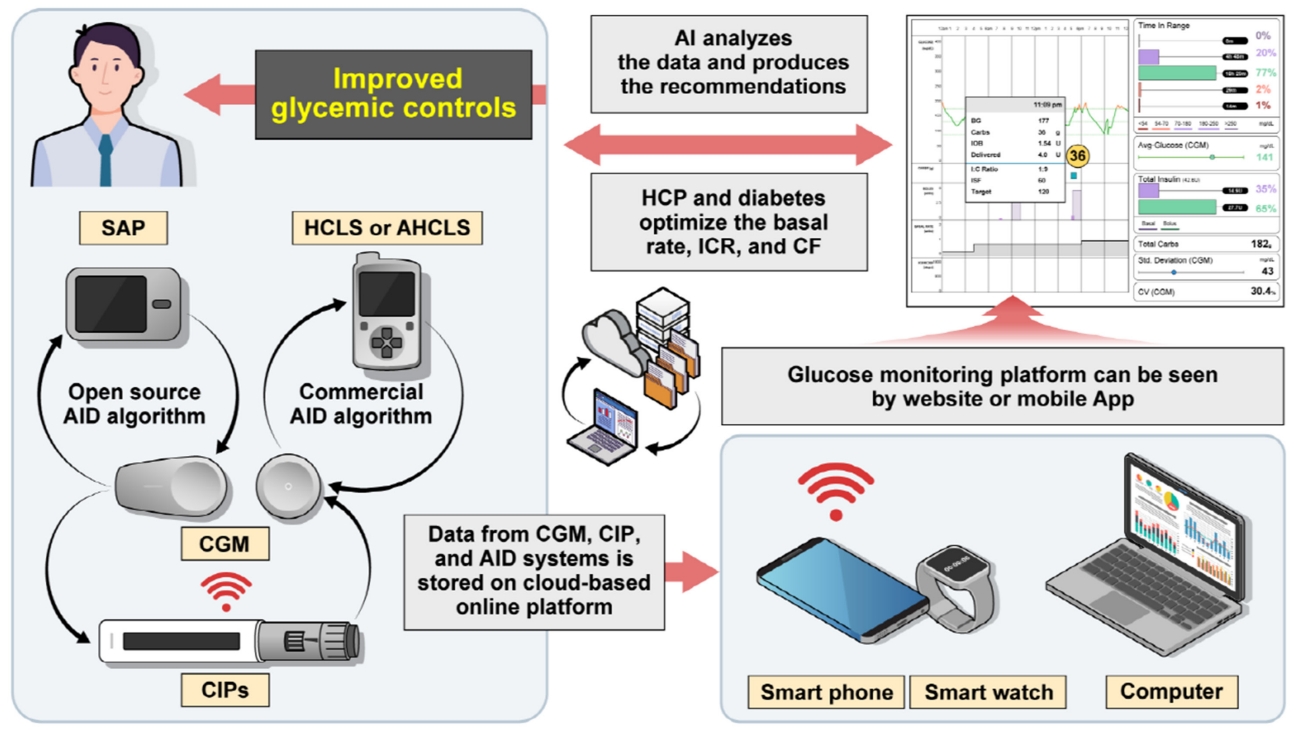
- Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
- Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):27-41. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0271
- 6,235 View
- 384 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) technology has evolved over the past decade with the integration of various devices including insulin pumps, connected insulin pens (CIPs), automated insulin delivery (AID) systems, and virtual platforms. CGM has shown consistent benefits in glycemic outcomes in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) treated with insulin. Moreover, the combined effect of CGM and education have been shown to improve glycemic outcomes more than CGM alone. Now a CIP is the expected future technology that does not need to be worn all day like insulin pumps and helps to calculate insulin doses with a built-in bolus calculator. Although only a few clinical trials have assessed the effectiveness of CIPs, they consistently show benefits in glycemic outcomes by reducing missed doses of insulin and improving problematic adherence. AID systems and virtual platforms made it possible to achieve target glycosylated hemoglobin in diabetes while minimizing hypoglycemia, which has always been challenging in T1DM. Now fully automatic AID systems and tools for diabetes decisions based on artificial intelligence are in development. These advances in technology could reduce the burden associated with insulin treatment for diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Accuracy and Safety of the 15-Day CareSens Air Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Won Sang Yoo, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024; 26(4): 222. CrossRef - Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Sarah Andrade, Boyang Chen, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent advances in the precision control strategy of artificial pancreas
Wuyi Ming, Xudong Guo, Guojun Zhang, Yinxia Liu, Yongxin Wang, Hongmei Zhang, Haofang Liang, Yuan Yang
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital Health in Diabetes and Cardiovascular Disease
Dorothy Avoke, Abdallah Elshafeey, Robert Weinstein, Chang H. Kim, Seth S. Martin
Endocrine Research.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring with structured education in adults with type 2 diabetes managed by multiple daily insulin injections: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kang Hee Sim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Jun Sung Moon, Soo Lim, Eun Seok Kang, Cheol-Young Park, Sin Gon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic Outcomes During Early Use of the MiniMed™ 780G Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop System with Guardian™ 4 Sensor
Toni L. Cordero, Zheng Dai, Arcelia Arrieta, Fang Niu, Melissa Vella, John Shin, Andrew S. Rhinehart, Jennifer McVean, Scott W. Lee, Robert H. Slover, Gregory P. Forlenza, Dorothy I. Shulman, Rodica Pop-Busui, James R. Thrasher, Mark S. Kipnes, Mark P. Ch
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(9): 652. CrossRef - Navigating the Seas of Glycemic Control: The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 345. CrossRef - APSec1.0: Innovative Security Protocol Design with Formal Security Analysis for the Artificial Pancreas System
Jiyoon Kim, Jongmin Oh, Daehyeon Son, Hoseok Kwon, Philip Virgil Astillo, Ilsun You
Sensors.2023; 23(12): 5501. CrossRef - Advances and Development of Electronic Neural Interfaces
Xue Jiaxiang, Liu Zhixin
Journal of Computing and Natural Science.2023; : 147. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) and Metabolic Control in a Cohort of Patients with Type 1 Diabetes and Coeliac Disease
Flavia Amaro, Maria Alessandra Saltarelli, Marina Primavera, Marina Cerruto, Stefano Tumini
Endocrines.2023; 4(3): 595. CrossRef - Comparison of Glycemia Risk Index with Time in Range for Assessing Glycemic Quality
Ji Yoon Kim, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(12): 883. CrossRef - The Benefits Of Continuous Glucose Monitoring In Pregnancy
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(5): 472. CrossRef - The Growing Challenge of Diabetes Management in an Aging Society
Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 630. CrossRef - Recent advances in artificial intelligence-assisted endocrinology and diabetes
Ioannis T. Oikonomakos, Ranjit M. Anjana, Viswanathan Mohan, Charlotte Steenblock, Stefan R. Bornstein
Exploration of Endocrine and Metabolic Disease.2023; 1(1): 16. CrossRef - An Observational Pilot Study of a Tailored Environmental Monitoring and Alert System for Improved Management of Chronic Respiratory Diseases
Mohammed Alotaibi, Fady Alnajjar, Badr A Alsayed, Tareq Alhmiedat, Ashraf M Marei, Anas Bushnag, Luqman Ali
Journal of Multidisciplinary Healthcare.2023; Volume 16: 3799. CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef
- Accuracy and Safety of the 15-Day CareSens Air Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
- Comprehensive Understanding for Application in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus of the Consensus Statement on Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets by Korean Diabetes Association, Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and Korean Society of Hypertension
- Jong Han Choi, Jee-Hyun Kang, Suk Chon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):377-390. Published online May 25, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0051
- 4,949 View
- 249 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The Joint Committee of the Korean Diabetes Association, the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and the Korean Society of Hypertension announced a consensus statement on carbohydrate-restricted diets and intermittent fasting, representing an emerging and popular dietary pattern. In this statement, we recommend moderately-low-carbohydrate or low-carbohydrate diets, not a very-low-carbohydrate diet, for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. These diets can be considered a dietary regimen to improve glycemic control and reduce body weight in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus. This review provides the detailed results of a meta-analysis and systematic literature review on the potential harms and benefits of carbohydrate-restricted diets in patients with diabetes. We expect that this review will help experts and patients by fostering an in-depth understanding and appropriate application of carbohydrate-restricted diets in the comprehensive management of diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy of convenience meal-type foods designed for diabetes in the management of metabolic syndrome based on a 3-week trial
Do Gyeong Lee, In Gyeong Kang, Tae Seok Kim, Yun Ahn, Sang Yun Lee, Hye Jin Ahn, Yoo Kyoung Park
Nutrition.2024; 118: 112287. CrossRef - Long-Term Results of a Digital Diabetes Self-Management and Education Support Program Among Adults With Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Ashley Berthoumieux, Sarah Linke, Melinda Merry, Alison Megliola, Jessie Juusola, Jenna Napoleone
The Science of Diabetes Self-Management and Care.2024; 50(1): 19. CrossRef - Medical nutrition therapy for diabetes mellitus
Suk Chon
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 421. CrossRef
- Efficacy of convenience meal-type foods designed for diabetes in the management of metabolic syndrome based on a 3-week trial
- Technology/Device
- Comparison of Laser and Conventional Lancing Devices for Blood Glucose Measurement Conformance and Patient Satisfaction in Diabetes Mellitus
- Jung A Kim, Min Jeong Park, Eyun Song, Eun Roh, So Young Park, Da Young Lee, Jaeyoung Kim, Ji Hee Yu, Ji A Seo, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo, Nan Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):936-940. Published online March 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0293
- 5,272 View
- 256 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Self-monitoring of capillary blood glucose is important for controlling diabetes. Recently, a laser lancing device (LMT-1000) that can collect capillary blood without skin puncture was developed. We enrolled 150 patients with type 1 or 2 diabetes mellitus. Blood sampling was performed on the same finger on each hand using the LMT-1000 or a conventional lancet. The primary outcome was correlation between glucose values using the LMT-1000 and that using a lancet. And we compared the pain and satisfaction of the procedures. The capillary blood sampling success rates with the LMT-1000 and lancet were 99.3% and 100%, respectively. There was a positive correlation (r=0.974, P<0.001) between mean blood glucose levels in the LMT-1000 (175.8±63.0 mg/dL) and conventional lancet samples (172.5±63.6 mg/dL). LMT-1000 reduced puncture pain by 75.0% and increased satisfaction by 80.0% compared to a lancet. We demonstrated considerable consistency in blood glucose measurements between samples from the LMT-1000 and a lancet, but improved satisfaction and clinically significant pain reduction were observed with the LMT-1000 compared to those with a lancet.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison between a laser-lancing device and automatic incision lancet for capillary blood sampling from the heel of newborn infants: a randomized feasibility trial
Chul Kyu Yun, Eui Kyung Choi, Hyung Jin Kim, Jaeyoung Kim, Byung Cheol Park, Kyuhee Park, Byung Min Choi
Journal of Perinatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Comparison between a laser-lancing device and automatic incision lancet for capillary blood sampling from the heel of newborn infants: a randomized feasibility trial
- Technology/Device
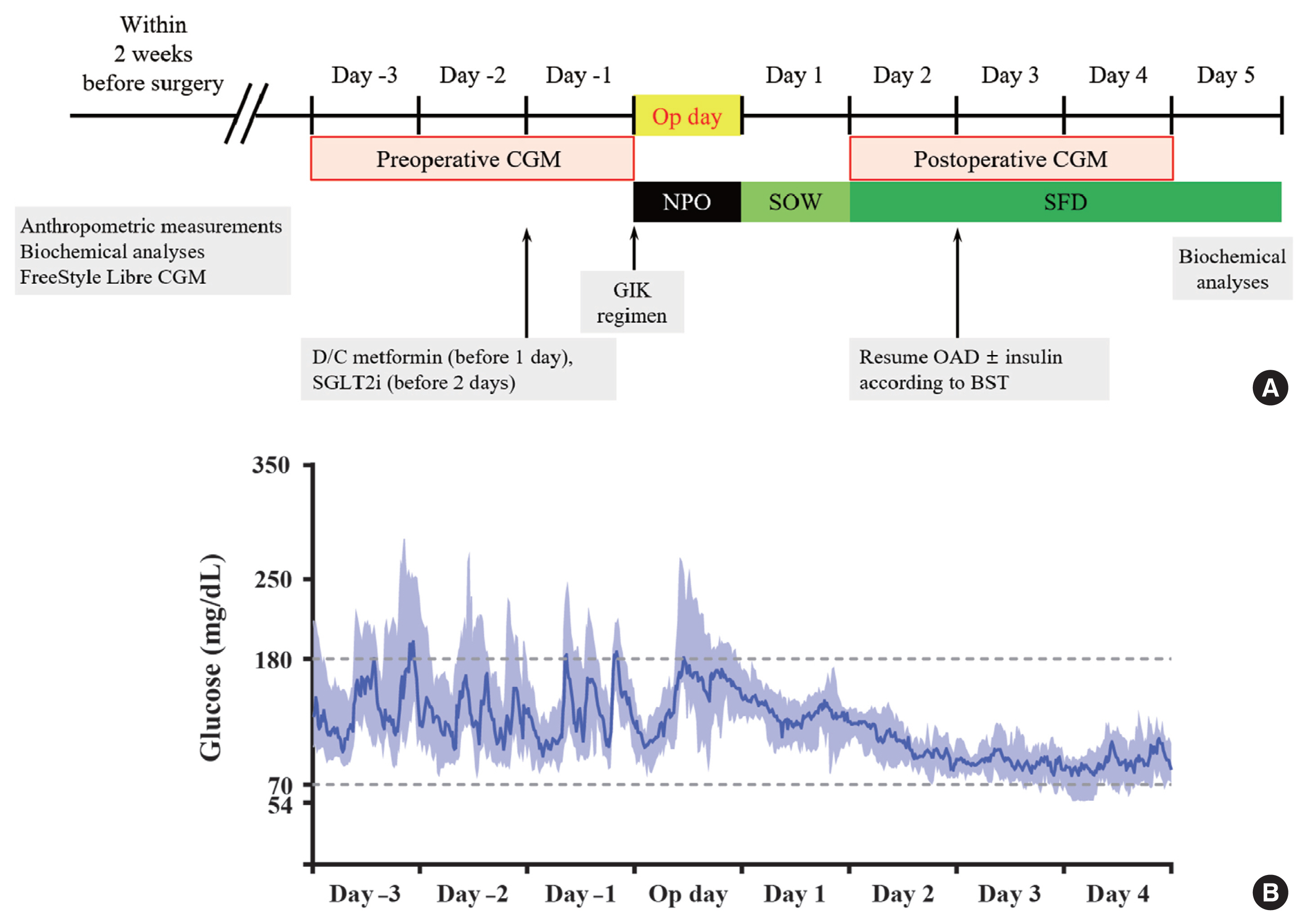
- Glucose Profiles Assessed by Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring System during the Perioperative Period of Metabolic Surgery
- Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang, Young Suk Park, Tae Jung Oh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):713-721. Published online January 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0164
- 4,790 View
- 317 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has been widely used in the management of diabetes. However, the usefulness and detailed data during perioperative status were not well studied. In this study, we described the immediate changes of glucose profiles after metabolic surgery using intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM) in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
This was a prospective, single-center, single-arm study including 20 participants with T2DM. The isCGM (FreeStyle Libre CGM) implantation was performed within 2 weeks before surgery. We compared CGM metrics of 3 days before surgery and 3 days after surgery, and performed the correlation analyses with clinical variables.
Results
The mean glucose significantly decreased after surgery (147.0±40.4 to 95.5±17.1 mg/dL, P<0.001). Time in range (TIR; 70 to 180 mg/dL) did not significantly change after surgery in total. However, it was significantly increased in a subgroup of individuals with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥8.0%. Time above range (>250 or 180 mg/dL) was significantly decreased in total. In contrast, time below range (<70 or 54 mg/dL) was significantly increased in total and especially in a subgroup of individuals with HbA1c <8.0% after surgery. The coefficient of variation significantly decreased after surgery. Higher baseline HbA1c was correlated with greater improvement in TIR (rho=0.607, P=0.005).
Conclusion
The isCGM identified improvement of mean glucose and glycemic variability, and increase of hypoglycemia after metabolic surgery, but TIR was not significantly changed after surgery. We detected an increase of TIR only in individuals with HbA1c ≥8.0%. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Effect of Glucose-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Ji Soo Kim, Gyeongsil Lee, Kyung-Il Park, Seung-Won Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 312. CrossRef - Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients Following Bariatric Surgery: A Scoping Review
Yang Yu, Susan W. Groth
Obesity Surgery.2023; 33(8): 2573. CrossRef - Asymptomatic Hypoglycemia after Metabolic Surgery: New Insights from Perioperative Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Sang-Man Jin
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 675. CrossRef
- Comparative Effect of Glucose-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- Technology/Device
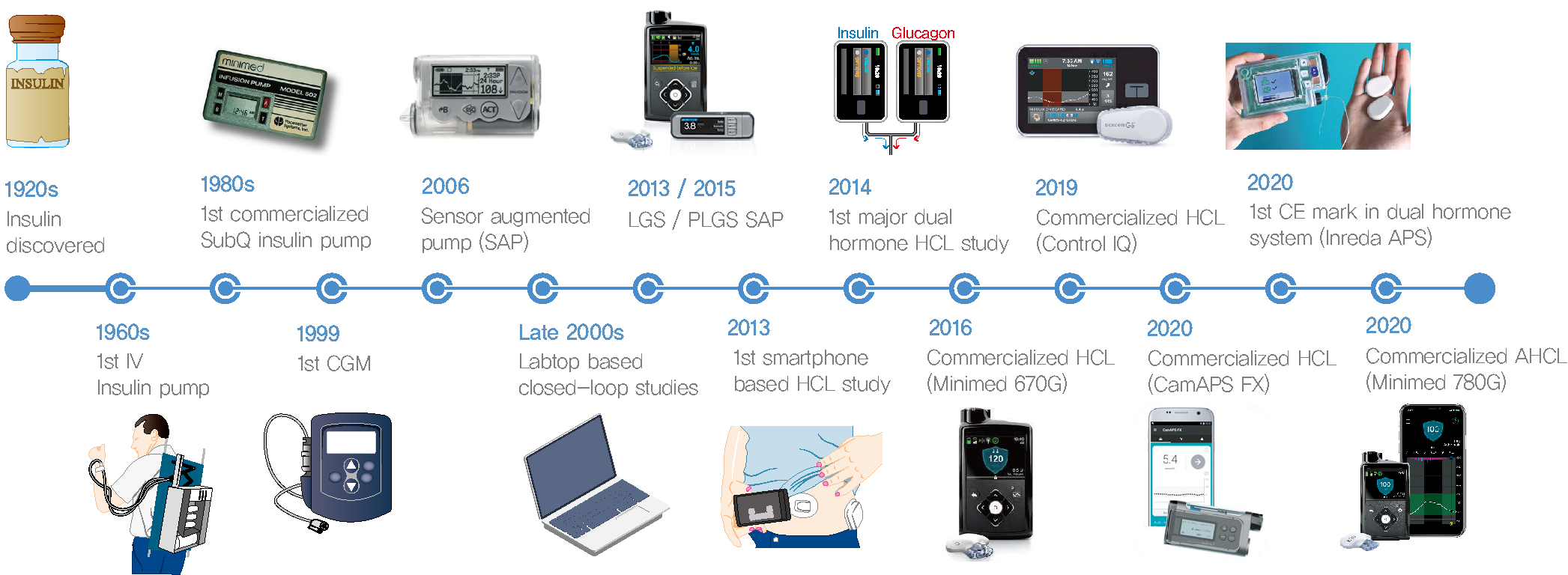
- Current Advances of Artificial Pancreas Systems: A Comprehensive Review of the Clinical Evidence
- Sun Joon Moon, Inha Jung, Cheol-Young Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):813-839. Published online November 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0177
- 14,424 View
- 796 Download
- 28 Web of Science
- 28 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Since Banting and Best isolated insulin in the 1920s, dramatic progress has been made in the treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). However, dose titration and timely injection to maintain optimal glycemic control are often challenging for T1DM patients and their families because they require frequent blood glucose checks. In recent years, technological advances in insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring systems have created paradigm shifts in T1DM care that are being extended to develop artificial pancreas systems (APSs). Numerous studies that demonstrate the superiority of glycemic control offered by APSs over those offered by conventional treatment are still being published, and rapid commercialization and use in actual practice have already begun. Given this rapid development, keeping up with the latest knowledge in an organized way is confusing for both patients and medical staff. Herein, we explore the history, clinical evidence, and current state of APSs, focusing on various development groups and the commercialization status. We also discuss APS development in groups outside the usual T1DM patients and the administration of adjunct agents, such as amylin analogues, in APSs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integration of a Safety Module to Prevent Rebound Hypoglycemia in Closed-Loop Artificial Pancreas Systems
María F. Villa-Tamayo, Patricio Colmegna, Marc D. Breton
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2024; 18(2): 318. CrossRef - The effects of acute hyperglycaemia on sports and exercise performance in type 1 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Bonar McGuire, Hashim Dadah, Dominic Oliver
Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport.2024; 27(2): 78. CrossRef - A new approach to stabilize diabetes systems with time-varying delays and disturbance rejection
S. Syafiie, Fahd Alharbi, Abdullah Ali Alshehri, Bassam Hasanain
Journal of the Franklin Institute.2024; 361(1): 543. CrossRef - Effects of Low-Dose Glucagon on Subcutaneous Insulin Absorption in Pigs
Ingrid Anna Teigen, Marte Kierulf Åm, Misbah Riaz, Sverre Christian Christiansen, Sven Magnus Carlsen
Current Therapeutic Research.2024; 100: 100736. CrossRef - Robust Online Correlation Method for Identification of a Nonparametric Model of Type 1 Diabetes
Martin Dodek, Eva Miklovičová
IEEE Access.2024; 12: 35899. CrossRef - 100 Years of insulin: A chemical engineering perspective
B. Wayne Bequette
Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering.2023; 40(1): 1. CrossRef - Efficacy of intermittent short‐term use of a real‐time continuous glucose monitoring system in non‐insulin–treated patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial
Sun Joon Moon, Kyung‐Soo Kim, Woo Je Lee, Mi Yeon Lee, Robert Vigersky, Cheol‐Young Park
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(1): 110. CrossRef - Identifiable prediction animal model for the bi-hormonal intraperitoneal artificial pancreas
Karim Davari Benam, Hasti Khoshamadi, Marte Kierulf Åm, Øyvind Stavdahl, Sebastien Gros, Anders Lyngvi Fougner
Journal of Process Control.2023; 121: 13. CrossRef - Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 27. CrossRef - CGM accuracy: Contrasting CE marking with the governmental controls of the USA (FDA) and Australia (TGA): A narrative review
John S Pemberton, Emma G Wilmot, Katharine Barnard‐Kelly, Lalantha Leelarathna, Nick Oliver, Tabitha Randell, Craig E Taplin, Pratik Choudhary, Peter Adolfsson
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(4): 916. CrossRef - Evaluation of awareness and attitude of paediatric nursing students, nurses, and adolescents regarding type one diabetes advanced devices and virtual nursing
Howaida Moawad Ahmed Ali
Kontakt.2023; 25(2): 100. CrossRef - Predicting the output error of the suboptimal state estimator to improve the performance of the MPC-based artificial pancreas
Martin Dodek, Eva Miklovičová
Control Theory and Technology.2023; 21(4): 541. CrossRef - A Markov Model of Gap Occurrence in Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data for Realistic in Silico Clinical Trials
Martina Vettoretti, Martina Drecogna, Simone Del Favero, Andrea Facchinetti, Giovanni Sparacino
Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine.2023; 240: 107700. CrossRef - Drug delivery breakthrough technologies – A perspective on clinical and societal impact
Beate Bittner, Manuel Sánchez-Félix, Dennis Lee, Athanas Koynov, Joshua Horvath, Felix Schumacher, Simon Matoori
Journal of Controlled Release.2023; 360: 335. CrossRef - Importance of continuous glucose monitoring in the treatment of diabetes mellitus
Sun Joon Moon, Won-Young Lee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 432. CrossRef - Constrained Versus Unconstrained Model Predictive Control for Artificial Pancreas
Chiara Toffanin, Lalo Magni
IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology.2023; 31(5): 2288. CrossRef - Intelligent Insulin vs. Artificial Intelligence for Type 1 Diabetes: Will the Real Winner Please Stand Up?
Valentina Maria Cambuli, Marco Giorgio Baroni
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(17): 13139. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Efficient Diabetes Care
Gopal Bhagwan Khodve, Sugato Banerjee
Current Diabetes Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The artificial pancreas: two alternative approaches to achieve a fully closed-loop system with optimal glucose control
M. K. Åm, I. A. Teigen, M. Riaz, A. L. Fougner, S. C. Christiansen, S. M. Carlsen
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2023; 47(3): 513. CrossRef - Multivariable Automated Insulin Delivery System for Handling Planned and Spontaneous Physical Activities
Mohammad Reza Askari, Mohammad Ahmadasas, Andrew Shahidehpour, Mudassir Rashid, Laurie Quinn, Minsun Park, Ali Cinar
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2023; 17(6): 1456. CrossRef - Advanced Technology (Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop Systems) in Diabetes from the Perspective of Gender Differences
Maria Grazia Nuzzo, Marciano Schettino
Diabetology.2023; 4(4): 519. CrossRef - Artificial Pancreas under a Zone Model Predictive Control based on Gaussian Process models: toward the personalization of the closed loop
Marco Polver, Beatrice Sonzogni, Mirko Mazzoleni, Fabio Previdi, Antonio Ferramosca
IFAC-PapersOnLine.2023; 56(2): 9642. CrossRef - Personalized Constrained MPC for glucose regulation
Chiara Toffanin, Lalo Magni
IFAC-PapersOnLine.2023; 56(2): 9648. CrossRef - Automated Insulin Delivery Systems in Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Outpatient Randomized Controlled Trials
Baoqi Zeng, Le Gao, Qingqing Yang, Hao Jia, Feng Sun
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(12): 2300. CrossRef - Novel Glycemic Index Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Predict Poor Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Il Rae Park, Yin Young Lee, Eun Young Choi, Jun Sung Moon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dual‐hormone artificial pancreas for glucose control in type 1 diabetes: A meta‐analysis
Baoqi Zeng, Hao Jia, Le Gao, Qingqing Yang, Kai Yu, Feng Sun
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(10): 1967. CrossRef - Dual-Hormone Insulin-and-Pramlintide Artificial Pancreas for Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review
Alezandra Torres-Castaño, Amado Rivero-Santana, Lilisbeth Perestelo-Pérez, Andrea Duarte-Díaz, Analia Abt-Sacks, Vanesa Ramos-García, Yolanda Álvarez-Pérez, Ana M. Wäagner, Mercedes Rigla, Pedro Serrano-Aguilar
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(20): 10262. CrossRef - History of insulin treatment of pediatric patients with diabetes in Korea
Jae Hyun Kim, Choong Ho Shin, Sei Won Yang
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 26(4): 237. CrossRef
- Integration of a Safety Module to Prevent Rebound Hypoglycemia in Closed-Loop Artificial Pancreas Systems
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Real-World Analysis of Therapeutic Outcome in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus at a Tertiary Care Center
- Antonia Kietaibl, Michaela Riedl, Latife Bozkurt
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):149-153. Published online July 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0267
- 4,355 View
- 144 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Insulin replacement in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) needs intensified treatment, which can either be performed by multiple daily injections (MDI) or continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII). This retrospective analysis of a real-world scenario aimed to evaluate whether glycaemic and cardiovascular risk factors could be controlled with CSII outclass MDI as suggested by recent evidence. Data from patients with either insulin pump (n=68) or injection (n=224) therapy at an Austrian tertiary care centre were analysed between January 2016 and December 2017. There were no significant differences with regard to the latest glycosylated hemoglobin, cardiovascular risk factor control or diabetes-associated late complications. Hypoglycaemia was less frequent (P<0.001), sensor-augmented therapy was more common (P=0.003) and mean body mass index (BMI) was higher (P=0.002) with CSII treatment. This retrospective analysis of real-world data in T1DM did not demonstrate the superiority of insulin pump treatment with regard to glycaemic control or cardiovascular risk factor control.
- Drug/Regimen
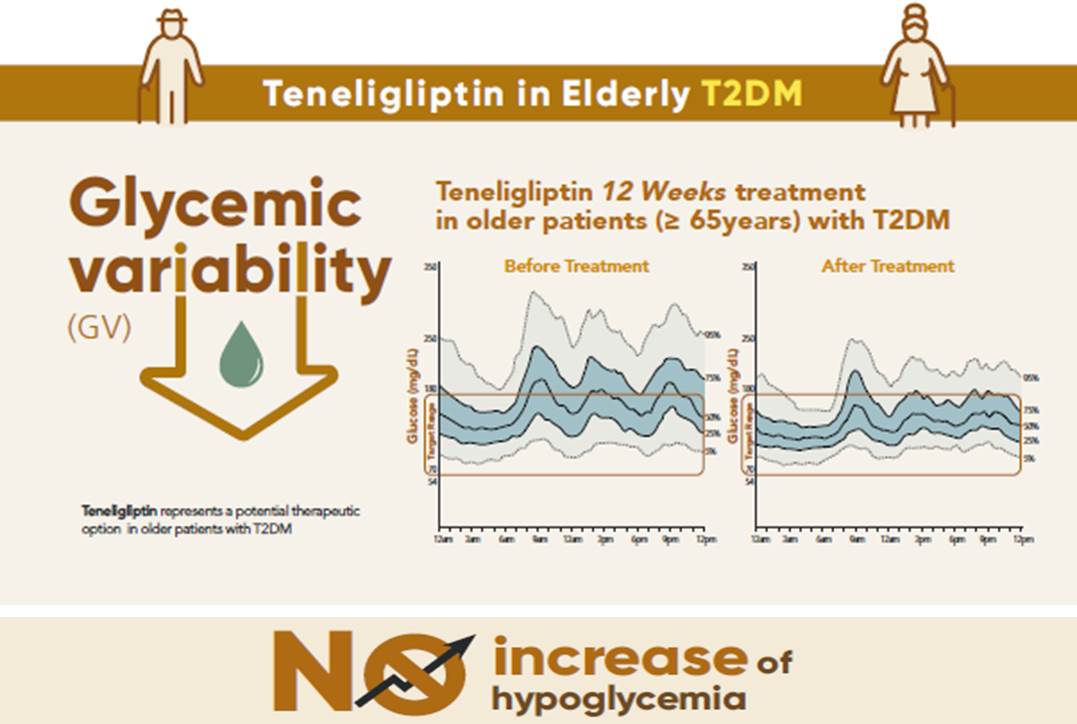
- Effects of Teneligliptin on HbA1c levels, Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Time in Range and Glycemic Variability in Elderly Patients with T2DM (TEDDY Study)
- Ji Cheol Bae, Soo Heon Kwak, Hyun Jin Kim, Sang-Yong Kim, You-Cheol Hwang, Sunghwan Suh, Bok Jin Hyun, Ji Eun Cha, Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyeon Kim
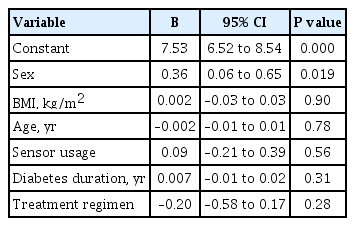
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):81-92. Published online June 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0016
- 7,563 View
- 431 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To evaluate the effects of teneligliptin on glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM)-derived time in range, and glycemic variability in elderly type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Methods
This randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study was conducted in eight centers in Korea (clinical trial registration number: NCT03508323). Sixty-five participants aged ≥65 years, who were treatment-naïve or had been treated with stable doses of metformin, were randomized at a 1:1 ratio to receive 20 mg of teneligliptin (n=35) or placebo (n=30) for 12 weeks. The main endpoints were the changes in HbA1c levels from baseline to week 12, CGM metrics-derived time in range, and glycemic variability.
Results
After 12 weeks, a significant reduction (by 0.84%) in HbA1c levels was observed in the teneligliptin group compared to that in the placebo group (by 0.08%), with a between-group least squares mean difference of –0.76% (95% confidence interval [CI], –1.08 to –0.44). The coefficient of variation, standard deviation, and mean amplitude of glycemic excursion significantly decreased in participants treated with teneligliptin as compared to those in the placebo group. Teneligliptin treatment significantly decreased the time spent above 180 or 250 mg/dL, respectively, without increasing the time spent below 70 mg/dL. The mean percentage of time for which glucose levels remained in the 70 to 180 mg/dL time in range (TIR70–180) at week 12 was 82.0%±16.0% in the teneligliptin group, and placebo-adjusted change in TIR70–180 from baseline was 13.3% (95% CI, 6.0 to 20.6).
Conclusion
Teneligliptin effectively reduced HbA1c levels, time spent above the target range, and glycemic variability, without increasing hypoglycemia in our study population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of teneligliptin and other gliptin-based regimens in addressing insulin resistance and glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients: a cross-sectional study
Harmanjit Singh, Ravi Rohilla, Shivani Jaswal, Mandeep Singla
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 19(1): 81. CrossRef - Potential approaches using teneligliptin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: current status and future prospects
Harmanjit Singh, Jasbir Singh, Ravneet Kaur Bhangu, Mandeep Singla, Jagjit Singh, Farideh Javid
Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 16(1): 49. CrossRef - Mechanism of molecular interaction of sitagliptin with human DPP4 enzyme - New Insights
Michelangelo Bauwelz Gonzatti, José Edvar Monteiro Júnior, Antônio José Rocha, Jonathas Sales de Oliveira, Antônio José de Jesus Evangelista, Fátima Morgana Pio Fonseca, Vânia Marilande Ceccatto, Ariclécio Cunha de Oliveira, José Ednésio da Cruz Freire
Advances in Medical Sciences.2023; 68(2): 402. CrossRef - A prospective multicentre open label study to assess effect of Teneligliptin on glycemic control through parameters of time in range (TIR) Metric using continuous glucose monitoring (TOP-TIR study)
Banshi Saboo, Suhas Erande, A.G. Unnikrishnan
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2022; 16(2): 102394. CrossRef - Association between Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors and Cardiometabolic Outcomes
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 49. CrossRef
- Comparison of teneligliptin and other gliptin-based regimens in addressing insulin resistance and glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients: a cross-sectional study
- Drug/Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Self-Titration Algorithms of Insulin Glargine 300 units/mL in Individuals with Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (The Korean TITRATION Study): A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Jae Hyun Bae, Chang Ho Ahn, Ye Seul Yang, Sun Joon Moon, Soo Heon Kwak, Hye Seung Jung, Kyong Soo Park, Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):71-80. Published online June 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0274

- 7,958 View
- 434 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To compare the efficacy and safety of two insulin self-titration algorithms, Implementing New Strategies with Insulin Glargine for Hyperglycemia Treatment (INSIGHT) and EDITION, for insulin glargine 300 units/mL (Gla-300) in Korean individuals with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
In a 12-week, randomized, open-label trial, individuals with uncontrolled T2DM requiring basal insulin were randomized to either the INSIGHT (adjusted by 1 unit/day) or EDITION (adjusted by 3 units/week) algorithm to achieve a fasting self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) in the range of 4.4 to 5.6 mmol/L. The primary outcome was the proportion of individuals achieving a fasting SMBG ≤5.6 mmol/L without noct urnal hypoglycemia at week 12.
Results
Of 129 individuals (age, 64.1±9.5 years; 66 [51.2%] women), 65 and 64 were randomized to the INSIGHT and EDITION algorithms, respectively. The primary outcome of achievement was comparable between the two groups (24.6% vs. 23.4%, P=0.876). Compared with the EDITION group, the INSIGHT group had a greater reduction in 7-point SMBG but a similar decrease in fasting plasma glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin. The increment of total daily insulin dose was significantly higher in the INSIGHT group than in the EDITION group (between-group difference: 5.8±2.7 units/day, P=0.033). However, body weight was significantly increased only in the EDITION group (0.6±2.4 kg, P=0.038). There was no difference in the occurrence of hypoglycemia between the two groups. Patient satisfaction was significantly increased in the INSIGHT group (P=0.014).
Conclusion
The self-titration of Gla-300 using the INSIGHT algorithm was effective and safe compared with that using the EDITION algorithm in Korean individuals with uncontrolled T2DM (ClinicalTrials.gov number: NCT03406663). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Basal insulin titration algorithms in patients with type 2 diabetes: the simplest is the best (?)
V.I. Katerenchuk
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(1): 72. CrossRef - Issues of insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes and ways to solve them
V.I. Katerenchuk, A.V. Katerenchuk
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(3): 240. CrossRef - Time for Using Machine Learning for Dose Guidance in Titration of People With Type 2 Diabetes? A Systematic Review of Basal Insulin Dose Guidance
Camilla Heisel Nyholm Thomsen, Stine Hangaard, Thomas Kronborg, Peter Vestergaard, Ole Hejlesen, Morten Hasselstrøm Jensen
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2022; : 193229682211459. CrossRef
- Basal insulin titration algorithms in patients with type 2 diabetes: the simplest is the best (?)
- Type 1 Diabetes
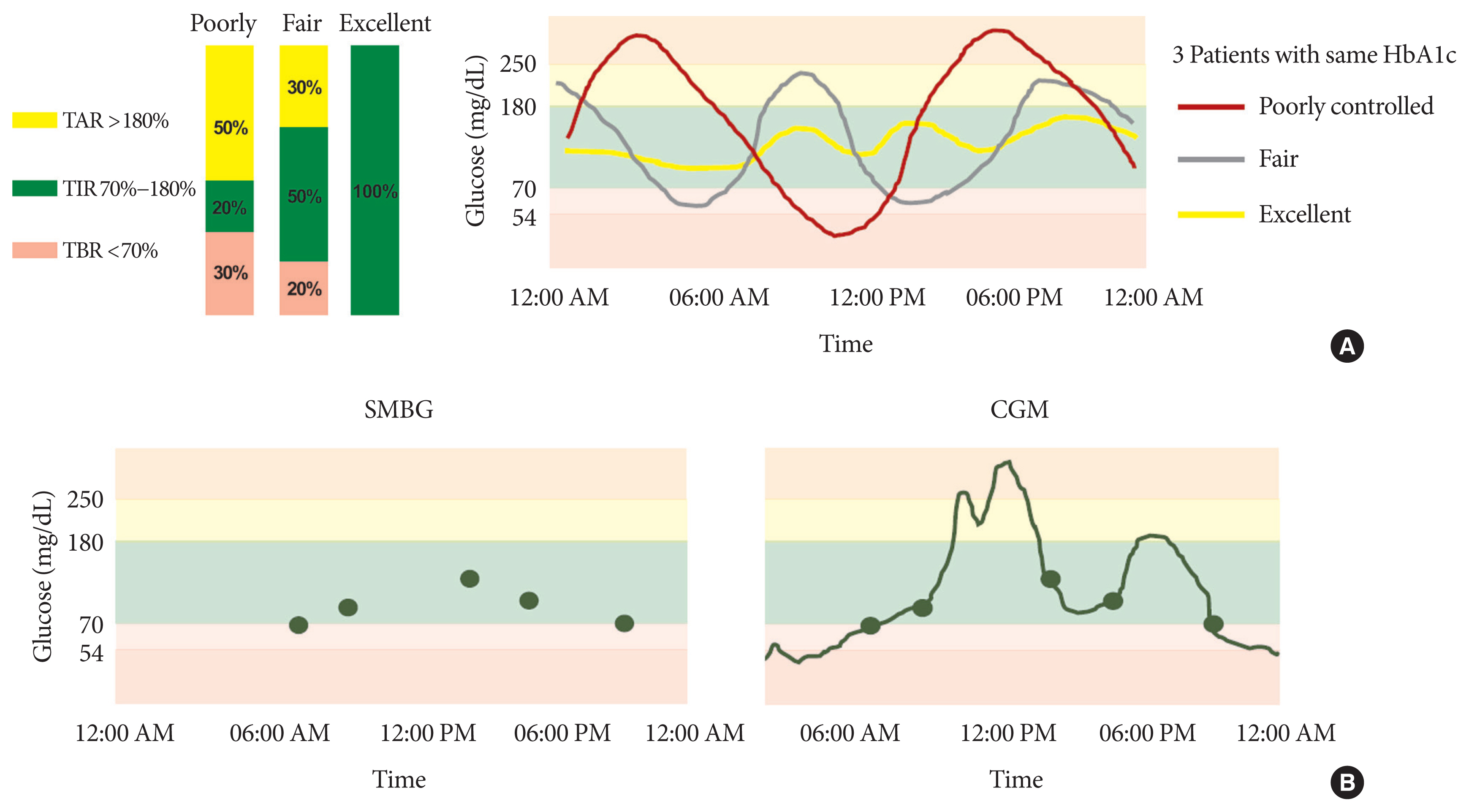
- Time in Range from Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Novel Metric for Glycemic Control
- Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):828-839. Published online December 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0257
- Correction in: Diabetes Metab J 2021;45(5):795
- 9,824 View
- 467 Download
- 31 Web of Science
- 36 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) has been the sole surrogate marker for assessing diabetic complications. However, consistently reported limitations of HbA1c are that it lacks detailed information on short-term glycemic control and can be easily interfered with by various clinical conditions such as anemia, pregnancy, or liver disease. Thus, HbA1c alone may not represent the real glycemic status of a patient. The advancement of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has enabled both patients and healthcare providers to monitor glucose trends for a whole single day, which is not possible with HbA1c. This has allowed for the development of core metrics such as time spent in time in range (TIR), hyperglycemia, or hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability. Among the 10 core metrics, TIR is reported to represent overall glycemic control better than HbA1c alone. Moreover, various evidence supports TIR as a predictive marker of diabetes complications as well as HbA1c, as the inverse relationship between HbA1c and TIR reveals. However, there are more complex relationships between HbA1c, TIR, and other CGM metrics. This article provides information about 10 core metrics with particular focus on TIR and the relationships between the CGM metrics for comprehensive understanding of glycemic status using CGM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Acute and Chronic Adverse Outcomes of Type 1 Diabetes
Rachel Longendyke, Jody B. Grundman, Shideh Majidi
Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America.2024; 53(1): 123. CrossRef - La plongée sous-marine en scaphandre autonome avec un diabète de type 1. Une belle histoire du dernier millénaire
Lise Dufaitre Patouraux, Agnès Sola-Gazagnes, Boris Lormeau, Corinne Lormeau
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2024; 18(1): 67. CrossRef - S100A9 exerts insulin-independent antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory effects
Gloria Ursino, Giulia Lucibello, Pryscila D. S. Teixeira, Anna Höfler, Christelle Veyrat-Durebex, Soline Odouard, Florian Visentin, Luca Galgano, Emmanuel Somm, Claudia R. Vianna, Ariane Widmer, François R. Jornayvaz, Andreas Boland, Giorgio Ramadori, Rob
Science Advances.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hybrid Closed-Loop Versus Manual Insulin Delivery in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: A Post Hoc Analysis Using the Glycemia Risk Index
Melissa H. Lee, Sara Vogrin, Timothy W. Jones, David N. O’Neal
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinically relevant stratification of patients with type 2 diabetes by using continuous glucose monitoring data
Xiaopeng Shao, Jingyi Lu, Rui Tao, Liang Wu, Yaxin Wang, Wei Lu, Hongru Li, Jian Zhou, Xia Yu
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a 2-Week Kinect-Based Mixed-Reality Exercise Program on Prediabetes: A Pilot Trial during COVID-19
So Young Ahn, Si Woo Lee, Hye Jung Shin, Won Jae Lee, Jun Hyeok Kim, Hyun-Jun Kim, Wook Song
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2024; 33(1): 54. CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring with structured education in adults with type 2 diabetes managed by multiple daily insulin injections: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kang Hee Sim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Jun Sung Moon, Soo Lim, Eun Seok Kang, Cheol-Young Park, Sin Gon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison between a tubeless, on-body automated insulin delivery system and a tubeless, on-body sensor-augmented pump in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Eun Seok Kang, Soo Heon Kwak, Yeoree Yang, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyun Bae, Jun Sung Moon, Chang Hee Jung, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh, Sun Joon Moon, Sun Ok Song, Suk Chon, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Anagliptin twice‐daily regimen improves glycaemic variability in subjects with type 2 diabetes: A double‐blind, randomized controlled trial
Yong‐ho Lee, Doo‐Man Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Kyung Mook Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Kang Seo Park, Hyun‐Shik Son, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Soon Hee Lee, Ki‐Ho Song, Su Kyoung Kwon, Hyeong Kyu Park, Kyu Chang Won, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(5): 1174. CrossRef - Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 27. CrossRef - Status of continuous glucose monitoring use and management in tertiary hospitals of China: a cross-sectional study
Liping Chen, Xiaoqin Liu, Qin Lin, Hongmei Dai, Yong Zhao, Zumin Shi, Liping Wu
BMJ Open.2023; 13(2): e066801. CrossRef - Real-world outcomes of continuous glucose monitoring in adults with diabetes mellitus attending an Irish tertiary hospital
Aoife Courtney, Diarmuid Smith, Hannah Forde
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2023; 192(6): 2763. CrossRef - Insight into continuous glucose monitoring: from medical basics to commercialized devices
Ayman Chmayssem, Małgorzata Nadolska, Emily Tubbs, Kamila Sadowska, Pankaj Vadgma, Isao Shitanda, Seiya Tsujimura, Youssef Lattach, Martin Peacock, Sophie Tingry, Stéphane Marinesco, Pascal Mailley, Sandrine Lablanche, Pierre Yves Benhamou, Abdelkader Zeb
Microchimica Acta.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of polyethylene glycol loxenatide versus insulin glargine on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, open-label, parallel-group trial
Shuo Zhang, Chuanyan Zhang, Jingxian Chen, Feiying Deng, Zezhen Wu, Dan Zhu, Fengwu Chen, Yale Duan, Yue Zhao, Kaijian Hou
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control and its derived metrics in type 1 diabetes: a longitudinal study
So Hyun Cho, Seohyun Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Glycemia Risk Index and Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes
Jee Hee Yoo, Ji Yoon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(10): 726. CrossRef - Acute Glycemic Variability and Early Outcomes After Cardiac Surgery:
A Meta-Analysis
Shuo Chang, Mian Xu, Yu Wang, Yanbo Zhang
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2023; 55(11): 771. CrossRef - Comparison of Glycemia Risk Index with Time in Range for Assessing Glycemic Quality
Ji Yoon Kim, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(12): 883. CrossRef - Correlação entre tempo no alvo e hemoglobina glicada de pessoas com diabetes mellitus: revisão sistemática
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlación entre tiempo en rango y hemoglobina glicosilada en personas con diabetes mellitus: revisión sistemática
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation between time on target and glycated hemoglobin in people with diabetes mellitus: systematic review
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef - Novel Glycemic Index Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Predict Poor Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Il Rae Park, Yin Young Lee, Eun Young Choi, Jun Sung Moon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypoglycemic agents and glycemic variability in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
SuA Oh, Sujata Purja, Hocheol Shin, Minji Kim, Eunyoung Kim
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2022; 19(3): 147916412211068. CrossRef - Advanced Glycation End Products and Their Effect on Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jeongmin Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3086. CrossRef - Influence of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on glycemic variability in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Shangyu Chai, Ruya Zhang, Ye Zhang, Richard David Carr, Yiman Zheng, Swapnil Rajpathak, Miao Yu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Glucose Profiles Assessed by Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring System during the Perioperative Period of Metabolic Surgery
Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang, Young Suk Park, Tae Jung Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 713. CrossRef - Deterioration in glycemic control on schooldays among children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A continuous glucose monitoring-based study
Yu Ding, Wenhao Zhang, Xiumei Wu, Tian Wei, Xulin Wang, Xueying Zheng, Sihui Luo
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of repeated bolus and continuous glucose infusion on a panel of circulating biomarkers in healthy volunteers
Roland Feldbauer, Matthias Wolfgang Heinzl, Carmen Klammer, Michael Resl, Johannes Pohlhammer, Klemens Rosenberger, Verena Almesberger, Florian Obendorf, Lukas Schinagl, Thomas Wagner, Margot Egger, Benjamin Dieplinger, Martin Clodi, Stephen L. Atkin
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(12): e0279308. CrossRef - Relationship between glycemic intraday variations evaluated in continuous glucose monitoring and HbA1c variability in type 2 diabetes: pilot study
Akemi Tokutsu, Yosuke Okada, Keiichi Torimoto, Yoshiya Tanaka
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Time-in-range for monitoring glucose control: Is it time for a change?
Virginia Bellido, Pedro José Pinés-Corrales, Rocío Villar-Taibo, Francisco Javier Ampudia-Blasco
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 177: 108917. CrossRef - Glucose Management Indicator for People with Type 1 Asian Diabetes Is Different from That of the Published Equation: Differences by Glycated Hemoglobin Distribution
Jee Hee Yoo, Seung Hee Yang, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life, Family Conflicts and Fear of Injecting: Perception Differences between Preadolescents and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes and Their Mothers
Marta Tremolada, Maria Cusinato, Sabrina Bonichini, Arianna Fabris, Claudia Gabrielli, Carlo Moretti
Behavioral Sciences.2021; 11(7): 98. CrossRef - Daytime Glycemic Variability and Frailty in Older Patients with Diabetes: a Pilot Study Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Seung Min Chung, Yun Hee Lee, Chang Oh Kim, Ji Yeon Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Seung-Hyun Yoo, Jun Sung Moon, Kwang Joon Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Benefits of a Switch from Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring (isCGM) to Real-Time (rt) CGM in Diabetes Type 1 Suboptimal Controlled Patients in Real-Life: A One-Year Prospective Study §
Yannis Préau, Sébastien Galie, Pauline Schaepelynck, Martine Armand, Denis Raccah
Sensors.2021; 21(18): 6131. CrossRef - Recent Advances of Integrative Bio-Omics Technologies to Improve Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) Care
Nisha Karwal, Megan Rodrigues, David D. Williams, Ryan J. McDonough, Diana Ferro
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(24): 11602. CrossRef
- Acute and Chronic Adverse Outcomes of Type 1 Diabetes
- Basic Research
- Role of Intestinal Microbiota in Metabolism of Voglibose In Vitro and In Vivo
- Mahesh Raj Nepal, Mi Jeong Kang, Geon Ho Kim, Dong Ho Cha, Ju-Hyun Kim, Tae Cheon Jeong
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):908-918. Published online April 6, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0147

- 5,666 View
- 114 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Voglibose, an α-glucosidase inhibitor, inhibits breakdown of complex carbohydrates into simple sugar units in intestine. Studies showed that voglibose metabolism in the liver might be negligible due to its poor intestinal absorption. Numerous microorganisms live in intestine and have several roles in metabolism and detoxification of various xenobiotics. Due to the limited information, the possible metabolism of voglibose by intestinal microbiota was investigated
in vitro andin vivo .Methods For the
in vitro study, different concentrations of voglibose were incubated with intestinal contents, prepared from both vehicle- and antibiotics-treated mice, to determine the decreased amount of voglibose over time by using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Similarly,in vivo pharmacodynamic effect of voglibose was determined following the administration of voglibose and starch in vehicle- and antibiotic-pretreated non-diabetic and diabetic mice, by measuring the modulatory effects of voglibose on blood glucose levels.Results The
in vitro results indicated that the remaining voglibose could be significantly decreased when incubated with the intestinal contents from normal mice compared to those from antibiotic-treated mice, which had less enzyme activities. Thein vivo results showed that the antibiotic pretreatment resulted in reduced metabolism of voglibose. This significantly lowered blood glucose levels in antibiotic-pretreated mice compared to the control animals.Conclusion The present results indicate that voglibose would be metabolized by the intestinal microbiota, and that this metabolism might be pharmacodynamically critical in lowering blood glucose levels in mice.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Pharmacomicrobiomics and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A novel perspective towards possible treatment
Liyang Jia, Shiqiong Huang, Boyu Sun, Yongguang Shang, Chunsheng Zhu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Phenolics from endophytic fungi as natural α-glucosidase inhibitors: A comprehensive review
Muhammad Imran Tousif, Saba Tauseef, Sadeer Nabeelah, Jugreet Sharmeen, Gokhan Zengin, Lesetja Legoabe, Muhammad Imran, Mohamad Fawzi Mahomoodally
Journal of Molecular Structure.2023; 1291: 135852. CrossRef - Ligand-targeted fishing of α-glucosidase inhibitors from Tribulus terrestris L. based on chitosan-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes with immobilized α-glucosidase
Xin Meng, Hou Zong, Zhong Zheng, Junpeng Xing, Zhiqiang Liu, Fengrui Song, Shu Liu
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry.2023; 415(14): 2677. CrossRef - Isolation, structure elucidation, and biological activities of sesquiterpenes and phthalides from two edible mushrooms Pleurotus species
Jewel C De Padua, Emi Fukushima-Sakuno, Kotomi Ueno, Thomas Edison E dela Cruz, Atsushi Ishihara
Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry.2023; 87(12): 1429. CrossRef - Effects of Oral Glucose-Lowering Agents on Gut Microbiota and Microbial Metabolites
Dongmei Wang, Jieying Liu, Liyuan Zhou, Qian Zhang, Ming Li, Xinhua Xiao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - 18:0 Lyso PC, a natural product with potential PPAR-γ agonistic activity, plays hypoglycemic effect with lower liver toxicity and cardiotoxicity in db/db mice
Yiming Ma, Xinyi Du, Dandan Zhao, Kegong Tang, Xiaona Wang, Shaoting Guo, Xiaobei Li, Song Mei, Na Sun, Jiaqi Liu, Chengyu Jiang
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2021; 579: 168. CrossRef
- Pharmacomicrobiomics and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A novel perspective towards possible treatment
- Others
- Continuous Glucose Monitoring Sensors for Diabetes Management: A Review of Technologies and Applications
- Giacomo Cappon, Martina Vettoretti, Giovanni Sparacino, Andrea Facchinetti
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(4):383-397. Published online July 25, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0121
- 21,335 View
- 984 Download
- 178 Web of Science
- 188 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader By providing blood glucose (BG) concentration measurements in an almost continuous-time fashion for several consecutive days, wearable minimally-invasive continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) sensors are revolutionizing diabetes management, and are becoming an increasingly adopted technology especially for diabetic individuals requiring insulin administrations. Indeed, by providing glucose real-time insights of BG dynamics and trend, and being equipped with visual and acoustic alarms for hypo- and hyperglycemia, CGM devices have been proved to improve safety and effectiveness of diabetes therapy, reduce hypoglycemia incidence and duration, and decrease glycemic variability. Furthermore, the real-time availability of BG values has been stimulating the realization of new tools to provide patients with decision support to improve insulin dosage tuning and infusion. The aim of this paper is to offer an overview of current literature and future possible developments regarding CGM technologies and applications. In particular, first, we outline the technological evolution of CGM devices through the last 20 years. Then, we discuss about the current use of CGM sensors from patients affected by diabetes, and, we report some works proving the beneficial impact provided by the adoption of CGM. Finally, we review some recent advanced applications for diabetes treatment based on CGM sensors.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Continuous glucose monitoring metrics following sub-Tenon’s injection of triamcinolone acetonide for diabetic macular edema
Rei Sotani-Ogawa, Sentaro Kusuhara, Yushi Hirota, Kyung Woo Kim, Wataru Matsumiya, Wataru Ogawa, Makoto Nakamura
Graefe's Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology.2024; 262(2): 449. CrossRef - Identifying and mapping measures of medication safety during transfer of care in a digital era: a scoping literature review
Catherine Leon, Helen Hogan, Yogini H Jani
BMJ Quality & Safety.2024; 33(3): 173. CrossRef - Highly sensitive and stable glucose sensing using N-type conducting polymer based organic electrochemical transistor
Gang Zhou, Zhu Cao, Yangxuan Liu, Haoyu Zheng, Kai Xu
Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry.2024; 952: 117961. CrossRef - Effectiveness and User Perception of an In-Vehicle Voice Warning for Hypoglycemia: Development and Feasibility Trial
Caterina Bérubé, Vera Franziska Lehmann, Martin Maritsch, Mathias Kraus, Stefan Feuerriegel, Felix Wortmann, Thomas Züger, Christoph Stettler, Elgar Fleisch, A Baki Kocaballi, Tobias Kowatsch
JMIR Human Factors.2024; 11: e42823. CrossRef - Can Electrochemical Aptasensors Achieve the Commercial Success of Glucose Biosensors?
Sina Ardalan, Anna Ignaszak
Advanced Sensor Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Digital Health and Machine Learning Technologies for Blood Glucose Monitoring and Management of Gestational Diabetes
Huiqi Y. Lu, Xiaorong Ding, Jane E. Hirst, Yang Yang, Jenny Yang, Lucy Mackillop, David A. Clifton
IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering.2024; 17: 98. CrossRef - Effects of Digitization of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose Records Using a Mobile App and the Cloud System on Outpatient Management of Diabetes: Single-Armed Prospective Study
Tomoko Handa, Takeshi Onoue, Tomoko Kobayashi, Ryutaro Maeda, Keigo Mizutani, Ayana Yamagami, Tamaki Kinoshita, Yoshinori Yasuda, Shintaro Iwama, Takashi Miyata, Mariko Sugiyama, Hiroshi Takagi, Daisuke Hagiwara, Hidetaka Suga, Ryoichi Banno, Yoshinori Az
JMIR Diabetes.2024; 9: e48019. CrossRef - The Association of Macronutrient Consumption and BMI to Exhaled Carbon Dioxide in Lumen Users: Retrospective Real-World Study
Shlomo Yeshurun, Tomer Cramer, Daniel Souroujon, Merav Mor
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2024; 12: e56083. CrossRef - Generative adversarial network-based data augmentation for improving hypoglycemia prediction: A proof-of-concept study
Wonju Seo, Namho Kim, Sung-Woon Park, Sang-Man Jin, Sung-Min Park
Biomedical Signal Processing and Control.2024; 92: 106077. CrossRef - Pre‐dinner walks may be superior to post‐dinner walks for glucose time in range in adults with type 1 diabetes on hybrid closed‐loop insulin delivery systems
Lauren V. Turner, Michael C. Riddell
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-world effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor agonist-based treatment strategies on “time in range” in patients with type 2 diabetes
Yongru Chen, Jingxian Chen, Shuo Zhang, Dan Zhu, Feiying Deng, Rui Zuo, Yufei Hu, Yue Zhao, Yale Duan, Benwei Lin, Fengwu Chen, Yun Liang, Jiaxiong Zheng, Barkat Ali Khan, Kaijian Hou
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Utility of Flash Glucose Monitoring to Determine Glucose Variation Induced by Different Doughs in Persons with Type 2 Diabetes
Maria Antonietta Taras, Sara Cherchi, Ilaria Campesi, Valentina Margarita, Gavino Carboni, Paola Rappelli, Giancarlo Tonolo
Diabetology.2024; 5(1): 129. CrossRef - Facile chemiresistive biosensor functionalized with PANI/GOx and novel green synthesized silver nanoparticles for glucose sensing
Jitendra B. Zalke, N.P. Narkhede, Dinesh R. Rotake, Shiv Govind Singh
Microchemical Journal.2024; 200: 110339. CrossRef - A novel questionnaire for evaluating digital tool use (DTUQ-D) among individuals with type 2 diabetes: exploring the digital landscape
Ora Peleg, Efrat Hadar, Meyran Boniel-Nissim
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring with structured education in adults with type 2 diabetes managed by multiple daily insulin injections: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kang Hee Sim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Jun Sung Moon, Soo Lim, Eun Seok Kang, Cheol-Young Park, Sin Gon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a Novel Insulin Sensor for Clinical Decision-Making
Eva Vargas, Eleonora M. Aiello, Jordan E. Pinsker, Hazhir Teymourian, Farshad Tehrani, Mei Mei Church, Lori M. Laffel, Francis J. Doyle, Mary-Elizabeth Patti, Eyal Dassau, Joseph Wang
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2023; 17(4): 1029. CrossRef - Diabetes technology and sexual health: which role?
V. Zamponi, J. Haxhi, G. Pugliese, A. Faggiano, R. Mazzilli
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Discordance Between Glycated Hemoglobin A1c and the Glucose Management Indicator in People With Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
Philippe Oriot, Claire Viry, Antoine Vandelaer, Sébastien Grigioni, Malanie Roy, Jean Christophe Philips, Gaëtan Prévost
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2023; 17(6): 1553. CrossRef - Expertenaustausch zum Einsatz von kontinuierlichem Glukosemonitoring (CGM) im Diabetesmanagement: Eine aktuelle Bestandsaufnahme und Blick in die Zukunft
Andreas Thomas, Thomas Haak, Astrid Tombek, Bernhard Kulzer, Dominic Ehrmann, Olga Kordonouri, Jens Kroeger, Oliver Schubert-Olesen, Ralf Kolassa, Thorsten Siegmund, Nicola Haller, Lutz Heinemann
Diabetologie und Stoffwechsel.2023; 18(01): 57. CrossRef - Evaluation of the performance and usability of a novel continuous glucose monitoring system
Li Yan, Qiang Li, Qingbo Guan, Mingsong Han, Yu Zhao, Junfei Fang, Jiajun Zhao
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2023; 43(4): 551. CrossRef - Efficacy of intermittent short‐term use of a real‐time continuous glucose monitoring system in non‐insulin–treated patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial
Sun Joon Moon, Kyung‐Soo Kim, Woo Je Lee, Mi Yeon Lee, Robert Vigersky, Cheol‐Young Park
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(1): 110. CrossRef - Intermittent-scanned continuous glucose monitoring with low glucose alarms decreases hypoglycemia incidence in middle-aged adults with type 1 diabetes in real-life setting
Philippe Oriot, Michel P. Hermans
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(2): 108385. CrossRef - Applications of Microwaves in Medicine
J.-C. Chiao, Changzhi Li, Jenshan Lin, Robert H. Caverly, James C. M. Hwang, Harel Rosen, Arye Rosen
IEEE Journal of Microwaves.2023; 3(1): 134. CrossRef - A Double-Needle Gold-Silver Electrodes Continuous Glucose Monitoring Device
C. Ben Ali Hassine, A. Tekin
IRBM.2023; 44(3): 100752. CrossRef - Accuracy of Flash Glucose Monitoring in Hemodialysis Patients With
and Without Diabetes Mellitus
Michèle R. Weber, Matthias Diebold, Peter Wiesli, Andreas D. Kistler
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2023; 131(03): 132. CrossRef - Minimally invasive electrochemical continuous glucose monitoring sensors: Recent progress and perspective
Yuanyuan Zou, Zhengkang Chu, Jiuchuan Guo, Shan Liu, Xing Ma, Jinhong Guo
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2023; 225: 115103. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Enterally Fed Children with Severe Central Nervous System Impairment
Marlena Górska, Joanna Kudzin, Anna Borkowska, Agnieszka Szlagatys-Sidorkiewicz, Agnieszka Szadkowska, Małgorzata Myśliwiec, Ewa Toporowska-Kowalska
Nutrients.2023; 15(3): 513. CrossRef - Prevalence of type 2 diabetes complications and its association with diet knowledge and skills and self‐care barriers in Tabriz, Iran: A cross‐sectional study
Habib Jalilian, Elnaz Javanshir, Leila Torkzadeh, Saeedeh Fehresti, Nazanin Mir, Majid Heidari‐Jamebozorgi, Somayeh Heydari
Health Science Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Status of continuous glucose monitoring use and management in tertiary hospitals of China: a cross-sectional study
Liping Chen, Xiaoqin Liu, Qin Lin, Hongmei Dai, Yong Zhao, Zumin Shi, Liping Wu
BMJ Open.2023; 13(2): e066801. CrossRef - Diboronic-Acid-Based Electrochemical Sensor for Enzyme-Free Selective and Sensitive Glucose Detection
Joong-Hyun Kim, Hongsik Choi, Chul-Soon Park, Heung-Seop Yim, Dongguk Kim, Sungmin Lee, Yeonkeong Lee
Biosensors.2023; 13(2): 248. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence biosensors for continuous glucose monitoring
Xiaofeng Jin, Andrew Cai, Tailin Xu, Xueji Zhang
Interdisciplinary Materials.2023; 2(2): 290. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Dogs and Cats
Francesca Del Baldo, Federico Fracassi
Veterinary Clinics of North America: Small Animal Practice.2023; 53(3): 591. CrossRef - Accurate Post-Calibration Predictions for Noninvasive Glucose Measurements in People Using Confocal Raman Spectroscopy
Anders Pors, Kaspar G. Rasmussen, Rune Inglev, Nina Jendrike, Amalie Philipps, Ajenthen G. Ranjan, Vibe Vestergaard, Jan E. Henriksen, Kirsten Nørgaard, Guido Freckmann, Karl D. Hepp, Michael C. Gerstenberg, Anders Weber
ACS Sensors.2023; 8(3): 1272. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus in der Akut- und Notfallmedizin
Leo Benning, Julian Krehl, Felix Patricius Hans
Notfallmedizin up2date.2023; 18(01): 45. CrossRef - Empowering People with Diabetes: Role of Continuous Glucose Monitor Systems
Sneha B Srivastava
American Journal of Lifestyle Medicine.2023; 17(3): 359. CrossRef - Diabétologie connectée : quelles sont les attentes des médecins et des patients ?
Nicolas Naïditch, Jean-Pierre Riveline
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2023; 17(2): 2S3. CrossRef - Association of Vibrotactile Biofeedback With Reduced Ergonomic Risk for Surgeons During Tonsillectomy
Natalie A. Kelly, Abdulrahman Althubaiti, Aashika D. Katapadi, Adam G. Smith, Sarah C. Nyirjesy, Jane H. Yu, Amanda J. Onwuka, Tendy Chiang
JAMA Otolaryngology–Head & Neck Surgery.2023; 149(5): 397. CrossRef - The Evolution of Diabetes Technology – Options Toward Personalized Care
Maleeha Zahid, Samaneh Dowlatshahi, Abhishek H. Kansara, Archana R. Sadhu
Endocrine Practice.2023; 29(8): 653. CrossRef - A Personalized and Adaptive Insulin Bolus Calculator Based on Double Deep Q- Learning to Improve Type 1 Diabetes Management
Giulia Noaro, Taiyu Zhu, Giacomo Cappon, Andrea Facchinetti, Pantelis Georgiou
IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics.2023; 27(5): 2536. CrossRef - Celebrating a Century of Insulin Discovery: A Critical Appraisal of the
Emerging Alternative Insulin Delivery Systems
Ntethelelo Sibiya, Bonisiwe Mbatha, Phikelelani Ngubane, Andile Khathi
Current Drug Delivery.2023; 20(6): 656. CrossRef - Machine Learning–Based Time in Patterns for Blood Glucose Fluctuation Pattern Recognition in Type 1 Diabetes Management: Development and Validation Study
Nicholas Berin Chan, Weizi Li, Theingi Aung, Eghosa Bazuaye, Rosa M Montero
JMIR AI.2023; 2: e45450. CrossRef - Drug Delivery Systems for Personal Healthcare by Smart Wearable Patch System
Bikram Khadka, Byeongmoon Lee, Ki-Taek Kim
Biomolecules.2023; 13(6): 929. CrossRef - Wearable Electrochemical Glucose Sensors in Diabetes Management: A Comprehensive Review
Tamoghna Saha, Rafael Del Caño, Kuldeep Mahato, Ernesto De la Paz, Chuanrui Chen, Shichao Ding, Lu Yin, Joseph Wang
Chemical Reviews.2023; 123(12): 7854. CrossRef - Real-life 24-week changes in glycemic parameters among European users of flash glucose monitoring with type 1 and 2 diabetes and different levels of glycemic control
Annel Lameijer, Julia J. Bakker, Kalvin Kao, Yongjin Xu, Rijk O.B. Gans, Henk J.G. Bilo, Timothy C. Dunn, Peter R. van Dijk
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 201: 110735. CrossRef - Les médicaments anti-diabétiques : ce que le médecin anesthésiste réanimateur doit savoir
Michael Joubert
Anesthésie & Réanimation.2023; 9(3): 251. CrossRef - Glycemia control using remote technologies
L. A. Suplotova, O. O. Alieva
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2023; 17(9): 81. CrossRef - Data-enabled learning and control algorithms for intelligent glucose management: The state of the art
Deheng Cai, Wenjing Wu, Marzia Cescon, Wei Liu, Linong Ji, Dawei Shi
Annual Reviews in Control.2023; 56: 100897. CrossRef - A Markov Model of Gap Occurrence in Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data for Realistic in Silico Clinical Trials
Martina Vettoretti, Martina Drecogna, Simone Del Favero, Andrea Facchinetti, Giovanni Sparacino
Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine.2023; 240: 107700. CrossRef - Volumetric Electron Transfer from Metabolites to Chemically Doped Polymer Electrodes
Siew Ting Melissa Tan, Gijun Lee, Kalee Rozylowicz, Adam Marks, Alberto Salleo
Advanced Functional Materials.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes and hypertension MobileHealth systems: a review of general challenges and advancements
Bliss Utibe-Abasi Stephen, Benedicta C. Uzoewulu, Phillip Michael Asuquo, Simeon Ozuomba
Journal of Engineering and Applied Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - THE ASSESSMENT OF COMPENSATION OF CARBOHYDRATE METABOLISM IN PATIENTS WITH TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS WITH METABOLIC SYNDROME BEYOND THE LIMITS OF GLYCATED HEMOGLOBIN
Taras V. Romaniv, Nadiya V. Skrypnyk, Ulyana V. Synko, Nataliia M. Voronych-Semchenko, Oleh V. Melnyk, Anna O. Hryb, Igor B. Boruchok
Wiadomości Lekarskie.2023; 76(6): 1385. CrossRef - Pros and cons of continous glucose monitoring
Marcin Ciechański, Edyta Witkowska, Agnieszka Ostańska, Adrianna Szafran, Klaudia Wiśniewska, Laura Piasek, Grzegorz Godek, Kacper Więcław, Katarzyna Stańko, Wiktor Terelak
Journal of Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring by Insulin-Treated Pilots Flying Commercial Aircraft Within the ARA.MED.330 Diabetes Protocol: A Preliminary Feasibility Study
Gillian L. Garden, Fariba Shojaee-Moradie, Ewan J. Hutchison, Brian M. Frier, Kenneth M. Shaw, Simon R. Heller, Gerd Koehler, Julia K. Mader, Declan Maher, Graham A. Roberts, David L. Russell-Jones
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(8): 543. CrossRef - Importance of continuous glucose monitoring in the treatment of diabetes mellitus
Sun Joon Moon, Won-Young Lee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 432. CrossRef - DiaTrend: A dataset from advanced diabetes technology to enable development of novel analytic solutions
Temiloluwa Prioleau, Abigail Bartolome, Richard Comi, Catherine Stanger
Scientific Data.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Testing the Real-World Accuracy of the Dexcom G6 Pro CGM During the Insulin-Only Bionic Pancreas Pivotal Trial
Martin Chase Marak, Peter Calhoun, Edward R. Damiano, Steven J. Russell, Katrina J. Ruedy, Roy W. Beck
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(11): 817. CrossRef - Use of continuous glucose monitoring in pediatric gastroenterology allows for personalized nutrition support care – Potential for collaboration between pediatric endocrinologists and gastroenterologists
Kathryn Hitchcock, Stephanie Oliveira
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Diabetes.2023; 3: 34. CrossRef - Anti-biofouling strategies for implantable biosensors of continuous glucose monitoring systems
Yan Zheng, Dunyun Shi, Zheng Wang
Frontiers of Chemical Science and Engineering.2023; 17(12): 1866. CrossRef - A novel strategy for therapeutic drug monitoring: application of biosensors to quantify antimicrobials in biological matrices
Quanfang Wang, Sihan Li, Jiaojiao Chen, Luting Yang, Yulan Qiu, Qian Du, Chuhui Wang, Mengmeng Teng, Taotao Wang, Yalin Dong
Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy.2023; 78(11): 2612. CrossRef - Hypoglycemic Effect of an Herbal Decoction (Modified Gangsimtang) in a Patient with Severe Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Refusing Oral Anti-Diabetic Medication: A Case Report
Sungjun Joo, Hyonjun Chun, Jisu Lee, Seungmin Seo, Jungmin Lee, Jungtae Leem
Medicina.2023; 59(11): 1919. CrossRef - GluGAN: Generating Personalized Glucose Time Series Using Generative Adversarial Networks
Taiyu Zhu, Kezhi Li, Pau Herrero, Pantelis Georgiou
IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics.2023; 27(10): 5122. CrossRef - Millifluidic valves and pumps made of tape and plastic
Josue U. Amador-Hernandez, Pablo E. Guevara-Pantoja, Diana F. Cedillo-Alcantar, Gabriel A. Caballero-Robledo, Jose L. Garcia-Cordero
Lab on a Chip.2023; 23(20): 4579. CrossRef - Offline Deep Reinforcement Learning and Off-Policy Evaluation for Personalized Basal Insulin Control in Type 1 Diabetes
Taiyu Zhu, Kezhi Li, Pantelis Georgiou
IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics.2023; 27(10): 5087. CrossRef - Flash Glucose Monitoring in Croatia: The Optimal Number of Scans per Day to Achieve Good Glycemic Control in Type 1 Diabetes
Silvija Canecki-Varzic, Ivana Prpic-Krizevac, Maja Cigrovski Berkovic, Dario Rahelic, Ema Schonberger, Marina Gradiser, Ines Bilic-Curcic
Medicina.2023; 59(11): 1893. CrossRef - The importance of interpreting machine learning models for blood glucose prediction in diabetes: an analysis using SHAP
Francesco Prendin, Jacopo Pavan, Giacomo Cappon, Simone Del Favero, Giovanni Sparacino, Andrea Facchinetti
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - SHMAD: A Smart Health Care System to Monitor Alzheimer’s Disease Patients
Shabana R. Ziyad, May Altulyan, Meshal Alharbi
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2023; 95(4): 1545. CrossRef - Séquelles fonctionnelles après résection pancréatique carcinologique. Un sujet d’actualité pour les patients et les praticiens
Andrea Mulliri, Michael Joubert, Marie-Astrid Piquet, Arnaud Alves, Benoît Dupont
Journal de Chirurgie Viscérale.2023; 160(6): 470. CrossRef - Functional sequelae after pancreatic resection for cancer
Andrea Mulliri, Michael Joubert, Marie-Astrid Piquet, Arnaud Alves, Benoît Dupont
Journal of Visceral Surgery.2023; 160(6): 427. CrossRef - Characteristics of glucose change in diabetes mellitus generalized through continuous wavelet transform processing: A preliminary study
Yoichi Nakamura, Shinya Furukawa
World Journal of Diabetes.2023; 14(10): 1562. CrossRef - Evaluating passive physiological data collection during Spravato treatment
Todd M. Solomon, Matus Hajduk, Martin Majernik, Jamileh Jemison, Alexander Deschamps, Jenna Scoggins, Adam Kolar, Miguel Amável Pinheiro, Peter Dubec, Ondrej Skala, Owen Muir, Amanda Tinkelman, Daniel R. Karlin, Robert Barrow
Frontiers in Digital Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fabrication of conductive Ag/AgCl/Ag nanorods ink on Laser-induced graphene electrodes on flexible substrates for non-enzymatic glucose detection
Rana Bagheri, Saeid Alikhani, Ebrahim Miri-Moghaddam
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Co-design of Human-centered, Explainable AI for Clinical Decision Support
Cecilia Panigutti, Andrea Beretta, Daniele Fadda, Fosca Giannotti, Dino Pedreschi, Alan Perotti, Salvatore Rinzivillo
ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems.2023; 13(4): 1. CrossRef - Analysis of blood glucose monitoring – a review on recent advancements and future prospects
Gayathri Priyadarshini R, Sathiya Narayanan
Multimedia Tools and Applications.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Nafion based biosensors: a review of recent advances and applications
Roya Mohammadzadeh Kakhki
International Journal of Polymeric Materials and Polymeric Biomaterials.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Overview of modern sensors for continuous glucose monitoring
K. T. Momynaliev, M. V. Prokopiev, I. V. Ivanov
Diabetes mellitus.2023; 26(6): 575. CrossRef - A Prospective Multicenter Clinical Performance Evaluation of the C-CGM System
Mihailo Rebec, Kevin Cai, Ralph Dutt-Ballerstadt, Ellen Anderson
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2022; 16(2): 390. CrossRef - Perceived Burdens and Benefits Associated With Continuous Glucose Monitor Use in Type 1 Diabetes Across the Lifespan
Vidita Divan, Margaret Greenfield, Christopher P. Morley, Ruth S. Weinstock
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2022; 16(1): 88. CrossRef - Technologies for Diabetes Self-Monitoring: A Scoping Review and Assessment Using the REASSURED Criteria
Jessica Hanae Zafra-Tanaka, David Beran, Beatrice Vetter, Rangarajan Sampath, Antonio Bernabe-Ortiz
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2022; 16(4): 962. CrossRef - Temporal Trends for Diabetes Management and Glycemic Control Between 2010 and 2019 in Korean Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
Jaewon Choe, Seung Hyun Won, Yunsoo Choe, Sang Hee Park, Yun Jeong Lee, Jieun Lee, Young Ah Lee, Han Hyuk Lim, Jae-Ho Yoo, Seong Yong Lee, Eun Young Kim, Choong Ho Shin, Jae Hyun Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2022; 24(3): 201. CrossRef - International comparison of glycaemic control in people with type 1 diabetes: an update and extension
Regina Prigge, John A. McKnight, Sarah H. Wild, Aveni Haynes, Timothy W. Jones, Elizabeth A. Davis, Birgit Rami‐Merhar, Maria Fritsch, Christine Prchla, Astrid Lavens, Kris Doggen, Suchsia Chao, Ronnie Aronson, Ruth Brown, Else H. Ibfelt, Jannet Svensson,
Diabetic Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial intelligence perspective in the future of endocrine diseases
Mandana Hasanzad, Hamid Reza Aghaei Meybodi, Negar Sarhangi, Bagher Larijani
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2022; 21(1): 971. CrossRef - Telehealth Technologies and Their Benefits to People With Diabetes
Chinenye O. Usoh, Kristine Kilen, Carolyn Keyes, Crystal Paige Johnson, Joseph A. Aloi
Diabetes Spectrum.2022; 35(1): 8. CrossRef - Acetylated Trifluoromethyl Diboronic Acid Anthracene with a Large Stokes Shift and Long Excitation Wavelength as a Glucose-Selective Probe
Hongsik Choi, Inhyeok Song, Chul Soon Park, Heung-seop Yim, Joong Hyun Kim
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(6): 2782. CrossRef - Suitability of the Unified Theory of Acceptance and Use of Technology 2 Model for Predicting mHealth Acceptance Using Diabetes as an Example: Qualitative Methods Triangulation Study
Patrik Schretzlmaier, Achim Hecker, Elske Ammenwerth
JMIR Human Factors.2022; 9(1): e34918. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring System Based on Percutaneous Microneedle Array
Ming-Nan Chien, Yu-Jen Chen, Chin-Han Bai, Jung-Tung Huang
Micromachines.2022; 13(3): 478. CrossRef - Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on the Metabolic Control Parameters in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ifan Ali Wafa, Nando Reza Pratama, Nurizzah Farahiyah Sofia, Elsha Stephanie Anastasia, Tiffany Konstantin, Maharani Ayuputeri Wijaya, M. Rifqi Wiyono, Lilik Djuari, Hermina Novida
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 260. CrossRef - Expert Roundtable on Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Cheryl Rosenfeld, Thomas Blevins, Grazia Aleppo, Gregory Forlenza, Diana Isaacs, Javier Morales, Jane Seley, Jeffrey Unger
Endocrine Practice.2022; 28(6): 622. CrossRef - Glucose variability and predicted cardiovascular risk after gastrectomy
Jun Shibamoto, Takeshi Kubota, Takuma Ohashi, Hirotaka Konishi, Atsushi Shiozaki, Hitoshi Fujiwara, Kazuma Okamoto, Eigo Otsuji
Surgery Today.2022; 52(11): 1634. CrossRef - Efficacy of once-weekly tirzepatide versus once-daily insulin degludec on glycaemic control measured by continuous glucose monitoring in adults with type 2 diabetes (SURPASS-3 CGM): a substudy of the randomised, open-label, parallel-group, phase 3 SURPASS
Tadej Battelino, Richard M Bergenstal, Angel Rodríguez, Laura Fernández Landó, Ross Bray, Zhentao Tong, Katelyn Brown
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2022; 10(6): 407. CrossRef - Towards the Integration of an Islet-Based Biosensor in Closed-Loop Therapies for Patients With Type 1 Diabetes
Loïc Olçomendy, Louis Cassany, Antoine Pirog, Roberto Franco, Emilie Puginier, Manon Jaffredo, David Gucik-Derigny, Héctor Ríos, Alejandra Ferreira de Loza, Julien Gaitan, Matthieu Raoux, Yannick Bornat, Bogdan Catargi, Jochen Lang, David Henry, Sylvie Re
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of divergent continuous glucose monitoring technologies on glycaemic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomised controlled trials
Mona Elbalshy, Jillian Haszard, Hazel Smith, Sarahmarie Kuroko, Barbara Galland, Nick Oliver, Viral Shah, Martin I. de Bock, Benjamin J. Wheeler
Diabetic Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel Glycemic Index Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Predict Poor Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Il Rae Park, Yin Young Lee, Eun Young Choi, Jun Sung Moon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Selection of Noninvasive Features in Wrist-Based Wearable Sensors to Predict Blood Glucose Concentrations Using Machine Learning Algorithms
Brian Bogue-Jimenez, Xiaolei Huang, Douglas Powell, Ana Doblas
Sensors.2022; 22(9): 3534. CrossRef - Generation of post-meal insulin correction boluses in type 1 diabetes simulation models for in-silico clinical trials: More realistic scenarios obtained using a decision tree approach
N. Camerlingo, M. Vettoretti, S. Del Favero, A. Facchinetti, P. Choudhary, G. Sparacino
Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine.2022; 221: 106862. CrossRef - A Miniaturized Optofluidic Glucose Monitoring System Based on Enzyme Colorimetry
Qingmei Xu, Chongwei Zou, Chengtao Sun, Xingguo Zhang, Haixia Yu, Dachao Li
IEEE Sensors Journal.2022; 22(10): 9246. CrossRef - Use and Trends of Diabetes Self-Management Technologies: A Correlation-Based Study
Jesús Fontecha, Iván González, Alfonso Barragán, Theodore Lim, Dario Pitocco
Journal of Diabetes Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Nanotechnology in Diabetes Mellitus: Overview for Nurses
R Priya, Baba Vajrala
Pondicherry Journal of Nursing.2022; 15(1): 22. CrossRef - Effect of Different Glucose Monitoring Methods on Bold Glucose Control: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yeling Wang, Congcong Zou, Han Na, Weixin Zeng, Xiaoyan Li, Xi Lou
Computational and Mathematical Methods in Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Noninvasive Blood Glucose Monitoring Systems Using Near-Infrared Technology—A Review
Aminah Hina, Wala Saadeh
Sensors.2022; 22(13): 4855. CrossRef - Performance of islets of Langerhans conformally coated via an emulsion cross-linking method in diabetic rodents and nonhuman primates
Aaron A. Stock, Grisell C. Gonzalez, Sophia I. Pete, Teresa De Toni, Dora M. Berman, Alexander Rabassa, Waldo Diaz, James C. Geary, Melissa Willman, Joy M. Jackson, Noa H. DeHaseth, Noel M. Ziebarth, Anthony R. Hogan, Camillo Ricordi, Norma S. Kenyon, Ali
Science Advances.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Review—Electrochemistry and Other Emerging Technologies for Continuous Glucose Monitoring Devices
Saroj Kumar Das, Kavya K. Nayak, P. R. Krishnaswamy, Vinay Kumar, Navakanta Bhat
ECS Sensors Plus.2022; 1(3): 031601. CrossRef - Design Strategies and Prospects in Developing Wearable Glucose Monitoring System Using Printable Organic Transistor and Microneedle: A Review
Fazliyatul Azwa Md Rezali, Norhayati Soin, Sharifah Fatmadiana Wan Muhamad Hatta, Mohamad Hazwan Mohd Daut, Muhammad Hafizuddin Al-Helmy Nouxman, Hanim Hussin
IEEE Sensors Journal.2022; 22(14): 13785. CrossRef - Review of Automated Insulin Delivery Systems for Type 1 Diabetes and Associated Time in Range Outcomes
Armaan Nallicheri, Katherine M Mahoney, Hanna A Gutow, Natalie Bellini, Diana Isaacs
Endocrinology.2022; 18(1): 27. CrossRef - Evaluation of Mesoporous TiO2 Layers as Glucose Optical Sensors
David Ortiz de Zárate, Sara Serna, Salvador Ponce-Alcántara, Jaime García-Rupérez
Sensors.2022; 22(14): 5398. CrossRef - A Prospective Study on Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Glycogen Storage Disease Type Ia: Toward Glycemic Targets
Alessandro Rossi, Annieke Venema, Petra Haarsma, Lude Feldbrugge, Rob Burghard, David Rodriguez-Buritica, Giancarlo Parenti, Maaike H Oosterveer, Terry G J Derks
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(9): e3612. CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring as a close to real life alternative to meal studies – a pilot study with a functional drink containing amino acids and chromium
Azat Samigullin, Per M. Humpert, Elin Östman
Frontiers in Medical Technology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - An overview of recent advances in insulin delivery and wearable technology for effective management of diabetes
Sujeet Kumar Raj, M. Ravindra Babu, Sukriti Vishwas, M.V.N.L. Chaitanya, Vancha Harish, Gaurav Gupta, Dinesh Kumar Chellappan, Kamal Dua, Sachin Kumar Singh
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2022; 75: 103728. CrossRef - Medical Certification of Pilots Through the Insulin-Treated Diabetes Mellitus Protocol at the FAA
Lynn K. Stanwyck, James R. DeVoll, Joyce Pastore, Zykevise Gamble, Anna Poe, Gabrielle V. Gui
Aerospace Medicine and Human Performance.2022; 93(8): 627. CrossRef - Rate of glycaemic control and associated factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with insulin-based therapy at selected hospitals in Northwest Ethiopia: a multicentre cross-sectional study
Ashenafi Kibret Sendekie, Eyayaw Ashete Belachew, Ephrem Mebratu Dagnew, Adeladlew Kassie Netere
BMJ Open.2022; 12(9): e065250. CrossRef - Glucose Profiles Assessed by Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring System during the Perioperative Period of Metabolic Surgery
Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang, Young Suk Park, Tae Jung Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 713. CrossRef - Hypoglycemic events and glycemic control effects between NPH and premixed insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A real-world experience at a comprehensive specialized hospital in Ethiopia
Ashenafi Kibret Sendekie, Adeladlew Kassie Netere, Eyayaw Ashete Belachew, Rekha Samuel
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(9): e0275032. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring for the Diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Pilot Study
Daria Di Filippo, Marrwah Ahmadzai, Melissa Han Yiin Chang, Ksana Horgan, Ru Min Ong, Justine Darling, Mahmood Akhtar, Amanda Henry, Alec Welsh, Daniela Foti
Journal of Diabetes Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Caring for people with diabetes
Martha M. Funnell, Katherine A. Kloss, Robin B. Nwankwo
Nursing.2022; 52(11): 26. CrossRef - Tackling the challenges of developing microneedle-based electrochemical sensors
Hilmee Abdullah, Tonghathai Phairatana, Itthipon Jeerapan
Microchimica Acta.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - A Concise and Systematic Review on Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring for Potential Diabetes Management
Soumyasanta Laha, Aditi Rajput, Suvra S. Laha, Rohan Jadhav
Biosensors.2022; 12(11): 965. CrossRef - Assessment of Seasonal Stochastic Local Models for Glucose Prediction without Meal Size Information under Free-Living Conditions
Francesco Prendin, José-Luis Díez, Simone Del Favero, Giovanni Sparacino, Andrea Facchinetti, Jorge Bondia
Sensors.2022; 22(22): 8682. CrossRef - Wearable Sensor-Based Monitoring of Environmental Exposures and the Associated Health Effects: A Review
Xueer Lin, Jiaying Luo, Minyan Liao, Yalan Su, Mo Lv, Qing Li, Shenglan Xiao, Jianbang Xiang
Biosensors.2022; 12(12): 1131. CrossRef - Acceptability and feasibility of continuous glucose monitoring in people with diabetes: protocol for a mixed-methods systematic review of quantitative and qualitative evidence
Jennifer V. E. Brown, Ramzi Ajjan, Najma Siddiqi, Peter A. Coventry
Systematic Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Utilization of Personalized Machine-Learning to Screen for Dysglycemia from Ambulatory ECG, toward Noninvasive Blood Glucose Monitoring
I-Min Chiu, Chi-Yung Cheng, Po-Kai Chang, Chao-Jui Li, Fu-Jen Cheng, Chun-Hung Richard Lin
Biosensors.2022; 13(1): 23. CrossRef - Effect of hydroxychloroquine on glycemic variability in type 2 diabetes patients uncontrolled on glimepiride and metformin therapy
Rajesh Rajput, Suyasha Saini, Siddhant Rajput, Parankush Upadhyay
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 26(6): 537. CrossRef - GESTATIONAL DIABETES MELLITUS: MODERN GLYCEMIA MONITORING SYSTEMS
YU.A. DUDAREVA, V.A. GURYEVA, G.V. NEMTSEVA
AVICENNA BULLETIN.2022; 24(1): 97. CrossRef - Extraction With Sweat-Sebum Emulsion as a New Test Method for Leachables in Patch-Based Medical Devices, Illustrated by Assessment of Isobornylacrylate (IBOA) in Diabetes Products
Herbert Fink, Nuno M. de Barros Fernandes, Jörg Weissmann, Manfred Frey
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2021; 15(4): 792. CrossRef - Mathematical Models of Meal Amount and Timing Variability With Implementation in the Type-1 Diabetes Patient Decision Simulator
Nunzio Camerlingo, Martina Vettoretti, Simone Del Favero, Andrea Facchinetti, Giovanni Sparacino
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2021; 15(2): 346. CrossRef - Fit‐for‐Purpose Biometric Monitoring Technologies: Leveraging the Laboratory Biomarker Experience
Alan Godfrey, Benjamin Vandendriessche, Jessie P. Bakker, Cheryl Fitzer‐Attas, Ninad Gujar, Matthew Hobbs, Qi Liu, Carrie A. Northcott, Virginia Parks, William A. Wood, Vadim Zipunnikov, John A. Wagner, Elena S. Izmailova
Clinical and Translational Science.2021; 14(1): 62. CrossRef - Self-charging wearables for continuous health monitoring
Jiyong Kim, Salman Khan, Peng Wu, Sungjin Park, Hwanjoo Park, Choongho Yu, Woochul Kim
Nano Energy.2021; 79: 105419. CrossRef - Impact of Switching from Intermittently Scanned to Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring Systems in a Type 1 Diabetes Patient French Cohort: An Observational Study of Clinical Practices
Yannis Préau, Martine Armand, Sébastien Galie, Pauline Schaepelynck, Denis Raccah
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2021; 23(4): 259. CrossRef - Individualizing Time-in-Range Goals in Management of Diabetes Mellitus and Role of Insulin: Clinical Insights From a Multinational Panel
Sanjay Kalra, Shehla Shaikh, Gagan Priya, Manas P. Baruah, Abhyudaya Verma, Ashok K. Das, Mona Shah, Sambit Das, Deepak Khandelwal, Debmalya Sanyal, Sujoy Ghosh, Banshi Saboo, Ganapathi Bantwal, Usha Ayyagari, Daphne Gardner, Cecilia Jimeno, Nancy E. Barb
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(2): 465. CrossRef - Machine-Learning Based Model to Improve Insulin Bolus Calculation in Type 1 Diabetes Therapy
Giulia Noaro, Giacomo Cappon, Martina Vettoretti, Giovanni Sparacino, Simone Del Favero, Andrea Facchinetti
IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Engineering.2021; 68(1): 247. CrossRef - Efficacy of telemedicine for persons with type 1 diabetes during Covid19 lockdown
Federico Boscari, Sara Ferretto, Ambra Uliana, Angelo Avogaro, Daniela Bruttomesso
Nutrition & Diabetes.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Technological innovation of Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) as a tool for commercial aviation pilots with insulin-treated diabetes and stakeholders/regulators: A new chance to improve the directives?
F. Strollo, A. Furia, P. Verde, A. Bellia, M. Grussu, A. Mambro, M.D. Petrelli, S. Gentile
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 172: 108638. CrossRef - Machine Learning Techniques for Hypoglycemia Prediction: Trends and Challenges
Omer Mujahid, Ivan Contreras, Josep Vehi
Sensors.2021; 21(2): 546. CrossRef - Time in range–A1c hemoglobin relationship in continuous glucose monitoring of type 1 diabetes: a real-world study
Marina Valenzano, Ivan Cibrario Bertolotti, Adriano Valenzano, Giorgio Grassi
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2021; 9(1): e001045. CrossRef - Machine learning for the diagnosis of early-stage diabetes using temporal glucose profiles
Woo Seok Lee, Junghyo Jo, Taegeun Song
Journal of the Korean Physical Society.2021; 78(5): 373. CrossRef - Forecasting of Glucose Levels and Hypoglycemic Events: Head-to-Head Comparison of Linear and Nonlinear Data-Driven Algorithms Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data Only
Francesco Prendin, Simone Del Favero, Martina Vettoretti, Giovanni Sparacino, Andrea Facchinetti
Sensors.2021; 21(5): 1647. CrossRef - A “Slide Rule” to Adjust Insulin Dose Using Trend Arrows in Adults with Type 1 Diabetes: Test in Silico and in Real Life
Daniela Bruttomesso, Federico Boscari, Giuseppe Lepore, Giulia Noaro, Giacomo Cappon, Angela Girelli, Lutgarda Bozzetto, Andrea Tumminia, Giorgio Grassi, Giovanni Sparacino, Luigi Laviola, Andrea Facchinetti
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(5): 1313. CrossRef - Glycemic variability and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Marcela Martinez, Jimena Santamarina, Adrian Pavesi, Carla Musso, Guillermo E Umpierrez
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2021; 9(1): e002032. CrossRef - Hypoglycaemia detection and prediction techniques: A systematic review on the latest developments
Omar Diouri, Monika Cigler, Martina Vettoretti, Julia K. Mader, Pratik Choudhary, Eric Renard
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Smartphone-based colorimetric detection systems for glucose monitoring in the diagnosis and management of diabetes
Özlem Kap, Volkan Kılıç, John G. Hardy, Nesrin Horzum
The Analyst.2021; 146(9): 2784. CrossRef - The impact of hypoglycaemia on the quality of life of family members of adults with type 1 or type 2 diabetes: A qualitative systematic review
Mette Valdersdorf Jensen, Melanie Broadley, Jane Speight, Alison Scope, Louise Preston, Simon Heller, Bastiaan E. de Galan, Frans Pouwer, Christel Hendrieckx
Diabetic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A review of biosensor technology and algorithms for glucose monitoring
Yaguang Zhang, Jingxue Sun, Liansheng Liu, Hong Qiao
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2021; 35(8): 107929. CrossRef - Optical glucose biosensor built-in disposable strips and wearable electronic devices
Abdullah Reda, Sherif A. El-Safty, Mahmoud M. Selim, Mohamed A. Shenashen
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2021; 185: 113237. CrossRef - Advances, Challenges, and Cost Associated with Continuous Glucose Monitor Use in Adolescents and Young Adults with Type 1 Diabetes
Karishma A. Datye, Daniel R. Tilden, Angelee M. Parmar, Eveline R. Goethals, Sarah S. Jaser
Current Diabetes Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Is HbA1c an ideal biomarker of well-controlled diabetes?
Georgia Kaiafa, Stavroula Veneti, George Polychronopoulos, Dimitrios Pilalas, Stylianos Daios, Ilias Kanellos, Triantafyllos Didangelos, Stamatina Pagoni, Christos Savopoulos
Postgraduate Medical Journal.2021; 97(1148): 380. CrossRef - Technology in the management of type 2 diabetes: Present status and future prospects
Aideen Daly, Roman Hovorka
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(8): 1722. CrossRef - A Non-Invasive Flexible Glucose Monitoring Sensor Using a Broadband Reject Filter
Moussa Bteich, Jessica Hanna, Joseph Costantine, Rouwaida Kanj, Youssef Tawk, Ali H. Ramadan, Assaad A. Eid
IEEE Journal of Electromagnetics, RF and Microwaves in Medicine and Biology.2021; 5(2): 139. CrossRef - Wearable patch delivery system for artificial pancreas health diagnostic-therapeutic application: A review
Nur Farrahain Nadia Ahmad, Nik Nazri Nik Ghazali, Yew Hoong Wong
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2021; 189: 113384. CrossRef - Technological Ecological Momentary Assessment Tools to Study Type 1 Diabetes in Youth: Viewpoint of Methodologies
Mary Katherine Ray, Alana McMichael, Maria Rivera-Santana, Jacob Noel, Tamara Hershey
JMIR Diabetes.2021; 6(2): e27027. CrossRef - Designing biomaterials for the modulation of allogeneic and autoimmune responses to cellular implants in Type 1 Diabetes
Magdalena M. Samojlik, Cherie L. Stabler
Acta Biomaterialia.2021; 133: 87. CrossRef - Evaluation of a continuous glucose monitoring system in neonatal foals
David Wong, Caitlin Malik, Katarzyna Dembek, Krista Estell, Megan Marchitello, Katie Wilson
Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine.2021; 35(4): 1995. CrossRef - Flash Glucose Monitoring in the Netherlands: Increased monitoring frequency is associated with improvement of glycemic parameters
Annel Lameijer, Nicole Lommerde, Timothy C. Dunn, Marion J. Fokkert, Mireille A. Edens, Kalvin Kao, Yongjin Xu, R.O.B. Gans, Henk J.G. Bilo, Peter R. van Dijk
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 177: 108897. CrossRef - Utilisation, access and recommendations regarding technologies for people living with type 1 diabetes: consensus statement of the ADS/ADEA/APEG/ADIPS Working Group
Anthony J Pease, Sofianos Andrikopoulos, Mary B Abraham, Maria E Craig, Brett Fenton, Jane Overland, Sarah Price, David Simmons, Glynis P Ross
Medical Journal of Australia.2021; 215(10): 473. CrossRef - Catalytic effects of magnetic and conductive nanoparticles on immobilized glucose oxidase in skin sensors
Lilian C Alarcón-Segovia, Amay J Bandodkar, John A Rogers, Ignacio Rintoul
Nanotechnology.2021; 32(37): 375101. CrossRef - Optical Glucose Sensor Using Pressure Sensitive Paint
Jongwon Park
Sensors.2021; 21(13): 4474. CrossRef - Type 1 diabetes glycemic management: Insulin therapy, glucose monitoring, and automation
Bruce A. Perkins, Jennifer L. Sherr, Chantal Mathieu
Science.2021; 373(6554): 522. CrossRef - Clinical Utilities of Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Insulin Pumps in Pediatric Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
Jieun Lee, Jae Hyun Kim
The Ewha Medical Journal.2021; 44(3): 55. CrossRef - Personalized Postprandial Glucose Response–Targeting Diet Versus Mediterranean Diet for Glycemic Control in Prediabetes
Orly Ben-Yacov, Anastasia Godneva, Michal Rein, Smadar Shilo, Dmitry Kolobkov, Netta Koren, Noa Cohen Dolev, Tamara Travinsky Shmul, Bat Chen Wolf, Noa Kosower, Keren Sagiv, Maya Lotan-Pompan, Niv Zmora, Adina Weinberger, Eran Elinav, Eran Segal
Diabetes Care.2021; 44(9): 1980. CrossRef - Lack of Acceptance of Digital Healthcare in the Medical Market: Addressing Old Problems Raised by Various Clinical Professionals and Developing Possible Solutions
Jong Il Park, Hwa Young Lee, Hyunah Kim, Jisan Lee, Jiwon Shinn, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Benefits of a Switch from Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring (isCGM) to Real-Time (rt) CGM in Diabetes Type 1 Suboptimal Controlled Patients in Real-Life: A One-Year Prospective Study §
Yannis Préau, Sébastien Galie, Pauline Schaepelynck, Martine Armand, Denis Raccah
Sensors.2021; 21(18): 6131. CrossRef - A Hybrid Automata Approach for Monitoring the Patient in the Loop in Artificial Pancreas Systems
Aleix Beneyto, Vicenç Puig, B. Wayne Bequette, Josep Vehi
Sensors.2021; 21(21): 7117. CrossRef - Editors’ Choice—Review—From Polarography to Electrochemical Biosensors: The 100-Year Quest for Selectivity and Sensitivity
William R. Heineman, Peter T. Kissinger, Kenneth R. Wehmeyer
Journal of The Electrochemical Society.2021; 168(11): 116504. CrossRef - Digital health and diabetes: experience from India
Jothydev Kesavadev, Gopika Krishnan, Viswanathan Mohan
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 12: 204201882110546. CrossRef - Current Advances of Artificial Pancreas Systems: A Comprehensive Review of the Clinical Evidence
Sun Joon Moon, Inha Jung, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(6): 813. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Adherence to Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose Among Young People with Type 1 Diabetes in China: A Cross-Sectional Study
Wencong Lv, Jiaxin Luo, Qing Long, Jundi Yang, Xin Wang, Jia Guo
Patient Preference and Adherence.2021; Volume 15: 2809. CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring devices: A brief presentation (Review)
Doina Mihai, Diana Stefan, Daniela Stegaru, Georgiana Bernea, Ileana Vacaroiu, Toma Papacocea, Mircea Lupușoru, Adriana Nica, Ovidiu Stiru, Dorin Dragos, Octavian Olaru
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Acute glycemic variability on admission predicts the prognosis in hospitalized patients with coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis
Zhaokun Pu, Lihong Lai, Xishan Yang, Yanyu Wang, Pingshuan Dong, Dan Wang, Yingli Xie, Zesen Han
Endocrine.2020; 67(3): 526. CrossRef - Glycemic profile of women with normoglycemia and gestational diabetes mellitus during early pregnancy using continuous glucose monitoring system
Charandeep Singh, Yashdeep Gupta, Alpesh Goyal, Mani Kalaivani, Vineeta Garg, Juhi Bharti, Seema Singhal, Garima Kachhawa, Vidushi Kulshrestha, Rajesh Kumari, Reeta Mahey, Jai B Sharma, Neerja Bhatla, Rajesh Khadgawat, Nandita Gupta, Nikhil Tandon
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 169: 108409. CrossRef - Efficacy of Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Prevention of Recurrent Severe Hypoglycemia
Timothy M.E. Davis, Penny Dwyer, Michelle England, P. Gerry Fegan, Wendy A. Davis
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2020; 22(5): 367. CrossRef - How was the Diabetes Metabolism Journal added to MEDLINE?
Hye Jin Yoo
Science Editing.2020; 7(2): 201. CrossRef - Applying Nanomaterials to Modern Biomedical Electrochemical Detection of Metabolites, Electrolytes, and Pathogens
Itthipon Jeerapan, Thitaporn Sonsa-ard, Duangjai Nacapricha
Chemosensors.2020; 8(3): 71. CrossRef - Clinical Opportunities for Continuous Biosensing and Closed-Loop Therapies
Jason Li, Jia Y. Liang, Steven J. Laken, Robert Langer, Giovanni Traverso
Trends in Chemistry.2020; 2(4): 319. CrossRef - A single-blind, randomised, crossover study to reduce hypoglycaemia risk during postprandial exercise with closed-loop insulin delivery in adults with type 1 diabetes: announced (with or without bolus reduction) vs unannounced exercise strategies
Sémah Tagougui, Nadine Taleb, Laurent Legault, Corinne Suppère, Virginie Messier, Inès Boukabous, Azadeh Shohoudi, Martin Ladouceur, Rémi Rabasa-Lhoret
Diabetologia.2020; 63(11): 2282. CrossRef - Bimetallic PtAu alloy nanomaterials for nonenzymatic selective glucose sensing at low potential
Lingling Lin, Shaohuang Weng, Yanjie Zheng, Xiyao Liu, Shaoming Ying, Feng Chen, Donghong You
Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry.2020; 865: 114147. CrossRef - Type 1 Diabetes in Youth and Technology-Based Advances in Management
Christopher Ferber, Catherine S. Mao, Jennifer K. Yee
Advances in Pediatrics.2020; 67: 73. CrossRef - Advanced Diabetes Management Using Artificial Intelligence and Continuous Glucose Monitoring Sensors
Martina Vettoretti, Giacomo Cappon, Andrea Facchinetti, Giovanni Sparacino
Sensors.2020; 20(14): 3870. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of evogliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, active‐controlled, randomized, double‐blind study with open‐label extension (the EVERGREEN study)
Gyuri Kim, Soo Lim, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon, Ie B. Park, Kyu J. Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park, Su K. Kwon, Hye S. Kim, Seok W. Park, Sin G. Kim, Min K. Moon, Eun S. Kim, Choon H. Chung, Kang S. Park, Mikyung Kim, Dong J. Chung, Chang B. Lee, Tae H. Kim, Moon‐Kyu Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(9): 1527. CrossRef - Association Between Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Time in Range, Other Core Metrics, and Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes
Jee Hee Yoo, Min Sun Choi, Jiyeon Ahn, Sung Woon Park, Yejin Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Sang-Man Jin, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2020; 22(10): 768. CrossRef - A New Approach to Determining Liquid Concentration Using Multiband Annular Ring Microwave Sensor and Polarity Correlator
Waleed Sethi, Ahmed Ibrahim, Khaled Issa, Ali Albishi, Saleh Alshebeili
Electronics.2020; 9(10): 1616. CrossRef - Estrategia terapéutica en el paciente diabético (I). Empoderamiento del paciente y formación. Objetivos terapéuticos. Estilo de vida, alimentación, vacunación y consejos al paciente diabético
F.B. Rivas Sánchez, J. Sanz Cánovas, J. Martín Carmona, S. Jansen Chaparro
Medicine - Programa de Formación Médica Continuada Acreditado.2020; 13(17): 943. CrossRef - Current status of continuous glucose monitoring among Korean children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Jae Hyun Kim
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2020; 25(3): 145. CrossRef - Towards sensor-based calving detection in the rangelands: a systematic review of credible behavioral and physiological indicators
Anita Z Chang, David L Swain, Mark G Trotter
Translational Animal Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Electrochemical glucose sensors in diabetes management: an updated review (2010–2020)
Hazhir Teymourian, Abbas Barfidokht, Joseph Wang
Chemical Society Reviews.2020; 49(21): 7671. CrossRef - An analytical approach to determine the optimal duration of continuous glucose monitoring data required to reliably estimate time in hypoglycemia
Nunzio Camerlingo, Martina Vettoretti, Andrea Facchinetti, Giovanni Sparacino, Julia K. Mader, Pratik Choudhary, Simone Del Favero
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Smartphone-Based Data Collection in Ophthalmology
Florian Philipp Raber, Rokas Gerbutavicius, Armin Wolf, Karsten Kortüm
Klinische Monatsblätter für Augenheilkunde.2020; 237(12): 1420. CrossRef - Glycemic Status Assessment by the Latest Glucose Monitoring Technologies
Ilaria Malandrucco, Benedetta Russo, Fabiana Picconi, Marika Menduni, Simona Frontoni
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(21): 8243. CrossRef - Medical Nutrition Therapy Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
Mee Ra Kweon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(4): 216. CrossRef - Use of Flash Glucose Monitoring in Patients on Intensive Insulin Treatment
Jun Sung Moon
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(4): 184. CrossRef - Data Analysis and Accuracy Evaluation of a Continuous Glucose-Monitoring Device
Lijun Cai, Wancheng Ge, Zhigang Zhu, Xueling Zhao, Zhanhong Li
Journal of Sensors.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Development of an Error Model for a Factory-Calibrated Continuous Glucose Monitoring Sensor with 10-Day Lifetime
Martina Vettoretti, Cristina Battocchio, Giovanni Sparacino, Andrea Facchinetti
Sensors.2019; 19(23): 5320. CrossRef
- Continuous glucose monitoring metrics following sub-Tenon’s injection of triamcinolone acetonide for diabetic macular edema
- Epidemiology
- Low-Normal Free Thyroxine Levels in Euthyroid Male Are Associated with Prediabetes
- Sung Woo Kim, Jae-Han Jeon, Jun Sung Moon, Eon Ju Jeon, Mi-Kyung Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Jung Beom Seo, Keun-Gyu Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):718-726. Published online March 19, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0222
- 4,318 View
- 51 Download
- 2 Web of Science
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Abnormal thyroid function is associated with impaired glucose homeostasis. This study aimed to determine whether free thyroxine (FT4) influences the prevalence of prediabetes in euthyroid subjects using a cross-sectional survey derived from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, conducted between 2013 and 2015. We studied 2,399 male participants of >20 years of age who were euthyroid and non-diabetic. Prediabetic participants had lower FT4 concentrations than those without prediabetes, but their thyrotropin concentrations were similar. We stratified the population into tertiles according to FT4 concentration. After adjusting for multiple confounding factors, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels significantly decreased with increasing FT4 tertile, whereas fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels were not associated with FT4 tertiles (HbA1c,
P <0.01 in T3 vs. T1; FPG,P =0.489 in T3 vs. T1). The prevalence of prediabetes was significantly higher in T1 (odds ratio, 1.426; 95% confidence interval, 1.126 to 1.806;P <0.01) than in T3. In conclusion, subjects with low-normal serum FT4 had high HbA1c and were more likely to have prediabetes. These results suggest that low FT4 concentration is a risk factor for prediabetes in male, even when thyroid function is within the normal range.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





