- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 44(6); 2020 > Article
-
ReviewType 1 Diabetes Time in Range from Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Novel Metric for Glycemic Control
-
Jee Hee Yoo1
 , Jae Hyeon Kim2
, Jae Hyeon Kim2
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2020;44(6):828-839.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0257
Published online: December 23, 2020
1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea
2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding author: Jae Hyeon Kim, https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5001-963X, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 81 Irwon-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul 06351, Korea, E-mail: jaehyeon@skku.edu
Copyright © 2020 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
- Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) has been the sole surrogate marker for assessing diabetic complications. However, consistently reported limitations of HbA1c are that it lacks detailed information on short-term glycemic control and can be easily interfered with by various clinical conditions such as anemia, pregnancy, or liver disease. Thus, HbA1c alone may not represent the real glycemic status of a patient. The advancement of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has enabled both patients and healthcare providers to monitor glucose trends for a whole single day, which is not possible with HbA1c. This has allowed for the development of core metrics such as time spent in time in range (TIR), hyperglycemia, or hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability. Among the 10 core metrics, TIR is reported to represent overall glycemic control better than HbA1c alone. Moreover, various evidence supports TIR as a predictive marker of diabetes complications as well as HbA1c, as the inverse relationship between HbA1c and TIR reveals. However, there are more complex relationships between HbA1c, TIR, and other CGM metrics. This article provides information about 10 core metrics with particular focus on TIR and the relationships between the CGM metrics for comprehensive understanding of glycemic status using CGM.
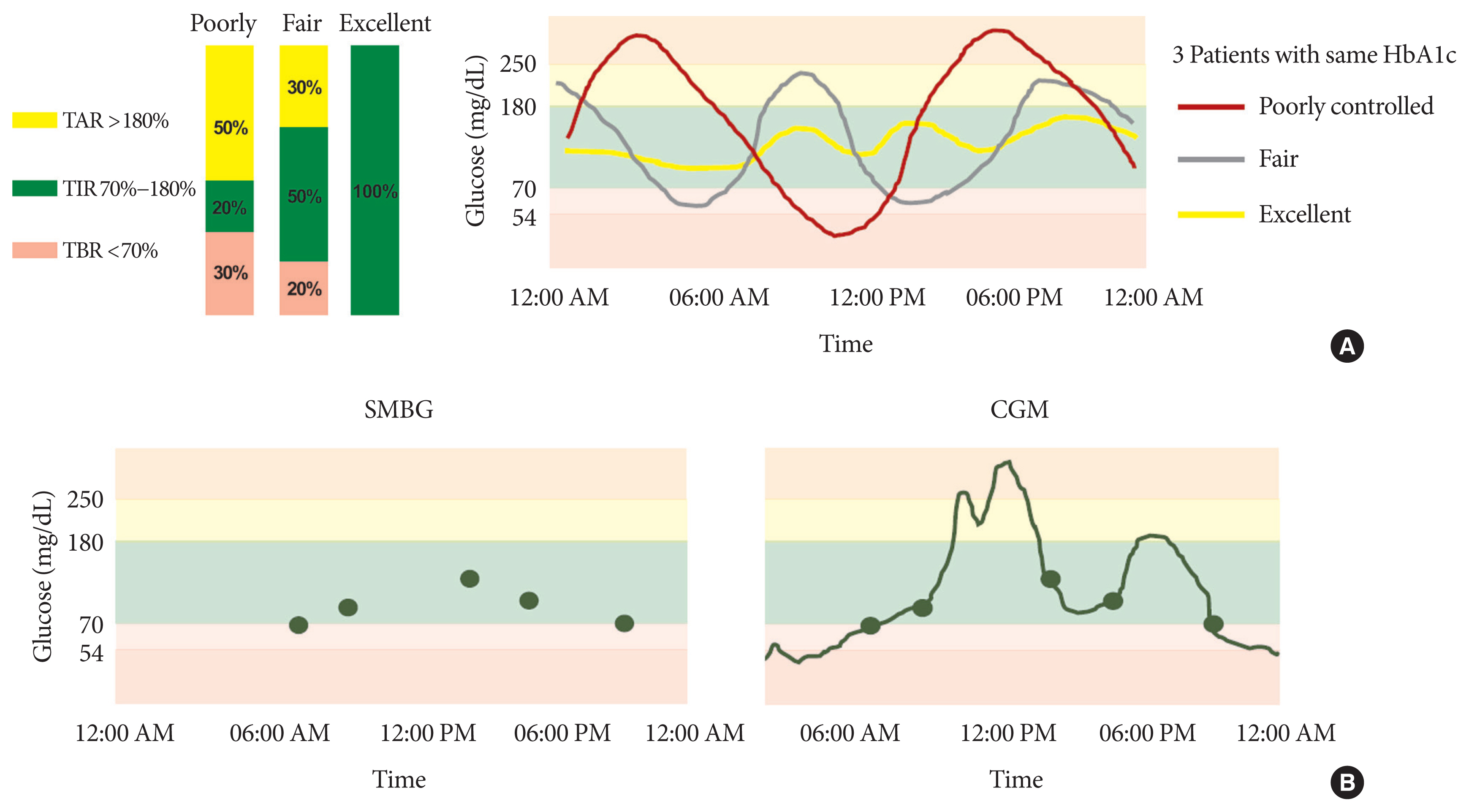
- Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) has been the sole surrogate marker for optimal glycemic control and predicting diabetic complications [1,2]. However, its accuracy for reflecting an individual’s glycemic control is limited because it does not provide detailed information such as glycemic variability, acute excursion of glucose change, or severity of hypo- or hyperglycemia. Hemoglobinopathies, pregnancy, chronic kidney disease, and liver disease also interfere with HbA1c measurement. Thus, a patient’s glycemic status can vary between excellent, fair, and poor, even among individuals with similar HbA1c (Fig. 1A) [3,4]. While fingerstick glucose monitoring can make up for some HbA1c limitations, such as short-term glycemic variability, it cannot fully capture actual glycemic fluctuation. In short, treatment decisions cannot be made by HbA1c alone or complemented by self-monitoring blood glucose (SMBG) (Fig. 1B).
- As is well known, in the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial (DCCT), intensive therapy effectively delayed the progression of long-term microvascular complications [1]. On the contrary, in the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) trial, increased mortality was observed in the intensive treatment group, which had high glycemic variability and incidence of hypoglycemia [5,6]. Thus, these results also support that HbA1c alone is not a reliable indicator for development of diabetic complications, and the paradigm has shifted beyond HbA1c.
- Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) overcomes the problems inherent in HbA1c and SMBG by informing consequent glucose level with various CGM metrics to better understand an individual’s unique glycemic profiles, eventually leading to improved glycemic control. Moreover, since the sensor accuracy [7], convenience of use [8], and reimbursement has improved and numerous studies have shown improvement in glycemic control regardless of diabetes type and insulin delivery method [9], CGM use is rapidly expanding.
- In February 2019, consensus statements on 10 CGM core metrics, including time spent in the time in range (TIR, 70 to 180 mg/dL), which has emerged as an important metric to complement HbA1c, were published [10]. In this review, as CGM use continues to increase as a new standard of care in diabetes, we provide detailed information about the core CGM metrics, especially focusing on TIR, to effectively use and interpret them in clinical practice. Furthermore, we provide crucial information about the importance of CGM-specific structured education and differences between personal CGM and professional CGM to use CGM more effectively in clinical practice.
INTRODUCTION
- CGM allows users to obtain a complete glucose profile by measuring interstitial glucose level every 5 to 15 minutes (96 to 288 measurements/day). It also allowed for development of core metrics for comprehensive understanding of glycemic status, such as time spent in TIR, hyperglycemia, or hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability (See Table 2 of reference 10 for more information about core metrics and therapeutic targets) [10]. Before interpreting the CGM data, adequate information on glucose data are needed for the sake of accuracy. At least 14 days with 70% more action times are necessary to provide good estimates for a 3-month period of TIR and hyperglycemic metrics [11,12]. However, more than 14 days of data might be needed to obtain accurate hypoglycemic metrics and coefficient of variance (CV) [12].
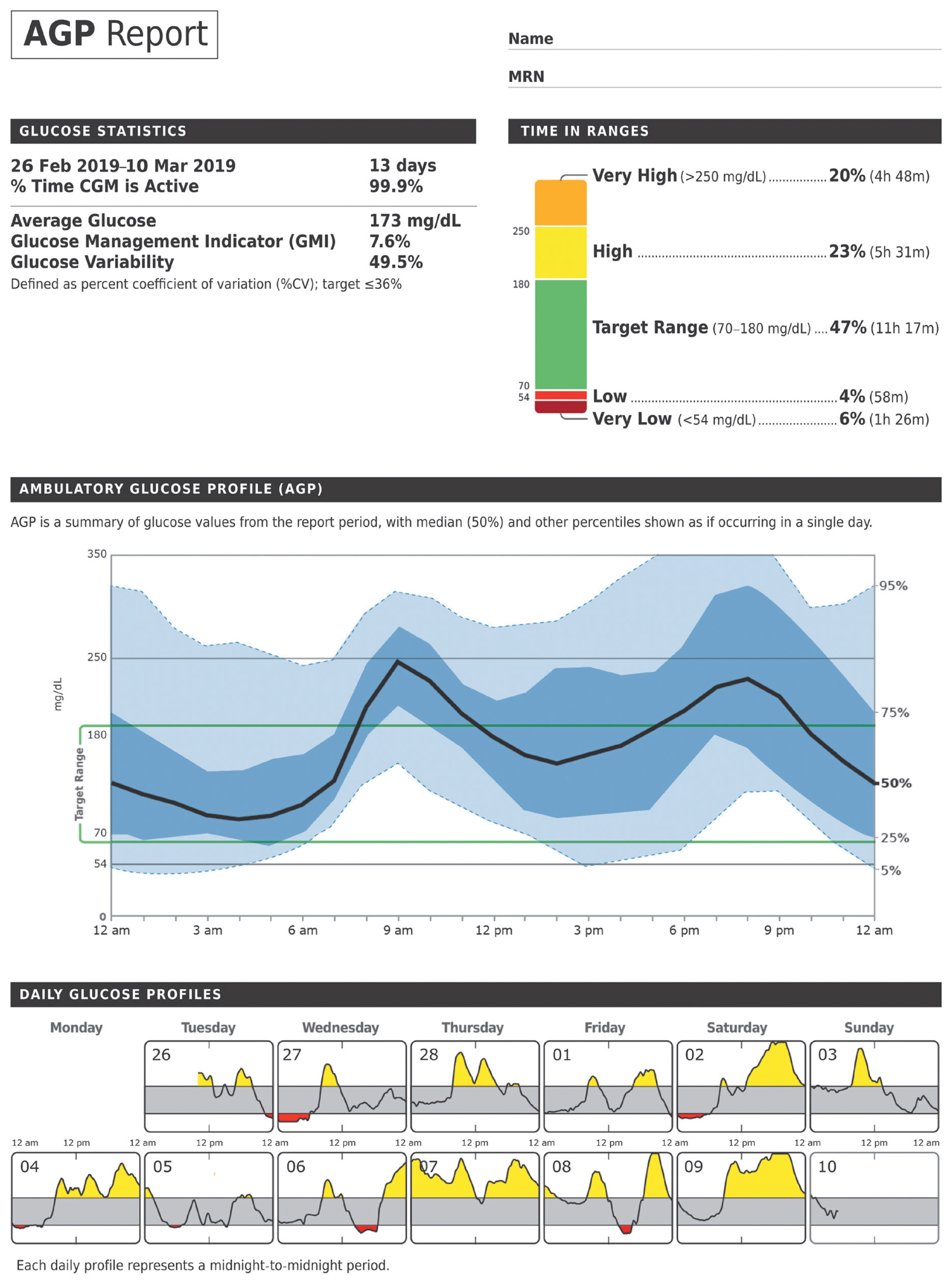
- When sufficient data have been collected to interpret it, an Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP) report (Fig. 2) [13], which visualizes the CGM metrics and targets for a multiple days into a single 24-hour period in a paper, can be used for a therapeutic decisions [14]. The 10 core metrics are further described below.
- Mean glucose and glucose management indicator
- CGM-derived mean glucose and glucose management indicator (GMI) are included in the core metrics. GMI is the estimated HbA1c from CGM-measured mean glucose. By GMI, we can even estimate HbA1c during short periods, as the laboratory HbA1c reflects long-term glycemic status over 2 to 3 months. This makes GMI a much more personalized metric in diabetes management than laboratory HbA1c when used along with the other core metrics. Recently, Bergenstal et al. [15] suggested that GMI should be widely used alongside CGM. The formula was derived using regression analysis of laboratory-measured HbA1c and CGM-measured mean glucose based on population from three clinical trials using specific sensor types (Dexcom G4 and G5; Dexcom, San Diego, CA, USA) in non-Hispanic whites [15–19]. The study reported that each 25 mg/dL increase in mean glucose corresponds to a GMI increase of 0.6%. In addition, mean glucose of 100, 150, and 200 mg/dL corresponded to a GMI of 5.7%, 6.9%, and 8.1%, respectively.
- However, the published GMI is limited with the populations being restricted to the pooled data of clinical trials. Populations with HbA1c higher than 9.9% and those with hypoglycemia unawareness were excluded. In addition, data sets were restricted to specific races (non-Hispanic whites) and sensor types (real time CGM [rt-CGM], e.g., Dexcom G4 and G5). Thus, the published GMI may be inaccurate for those with high or low mean glucose concentrations. When using the published GMI for treatment decisions, race and sensor type must be considered. Several studies have reported that the laboratory HbA1c is much higher than GMI derived from flash glucose monitoring (FGM, e.g., Freestyle Libre; Abbott, Abbott Park, IL, USA), especially in those with a mean glucose level below 200 mg/dL and in Asians [20,21].
- Time in range, time above range, time below range
- A recent international consensus on the use of CGM emphasized the importance of how much time the patients spent in target range, or in hyper- and hypoglycemia, as well as HbA1c [10]. They provide information on not only mean glucose but also glycemic variability when in conjunction with HbA1c. These metrics are classified to TIR (70 to 180 mg/dL), time above range (TAR, hyperglycemic metrics), and time below range (TBR, hypoglycemic metrics). TBR was differentiated to level 1 (TBR, 54 to 69 mg/dL), and level 2 (TBR <54 mg/dL). TAR was also differentiated to level 1 (TAR, 180 to 250 mg/dL) and level 2 (TAR >250 mg/dL).
- A TIR of >70% (16 hours, 48 minutes), level 1 TAR of <25% (6 hours), level 2 TAR of <5% (1 hour, 12 minutes), level 1 TBR of <4% (1 hour), and level 2 TBR of <1% (15 minutes) is recommended in both type 1 and 2 diabetes mellitus (T1DM and T2DM), respectively. Every 1% change in time equals 14 min/day (1 day=1,440 minutes). The 70% and 80% of each TIR approximately corresponds to HbA1c 7.0% and 6.5% [22–24]. Thus, a TIR target of 70% or more was chosen to achieve an HbA1c target of 7.0% or 6.5%. Beck et al. [22] also reported that an HbA1c of 7.0% equals 25% of TAR (>180 mg/dL). A TBR (<70 mg/dL) <4% has been evaluated in various trials in T1DM which provides the basis for consensus [17,25,26]. The targets are different for older and high-risk groups to emphasize reducing hypoglycemia [10].
- The relationship between TIR and HbA1c
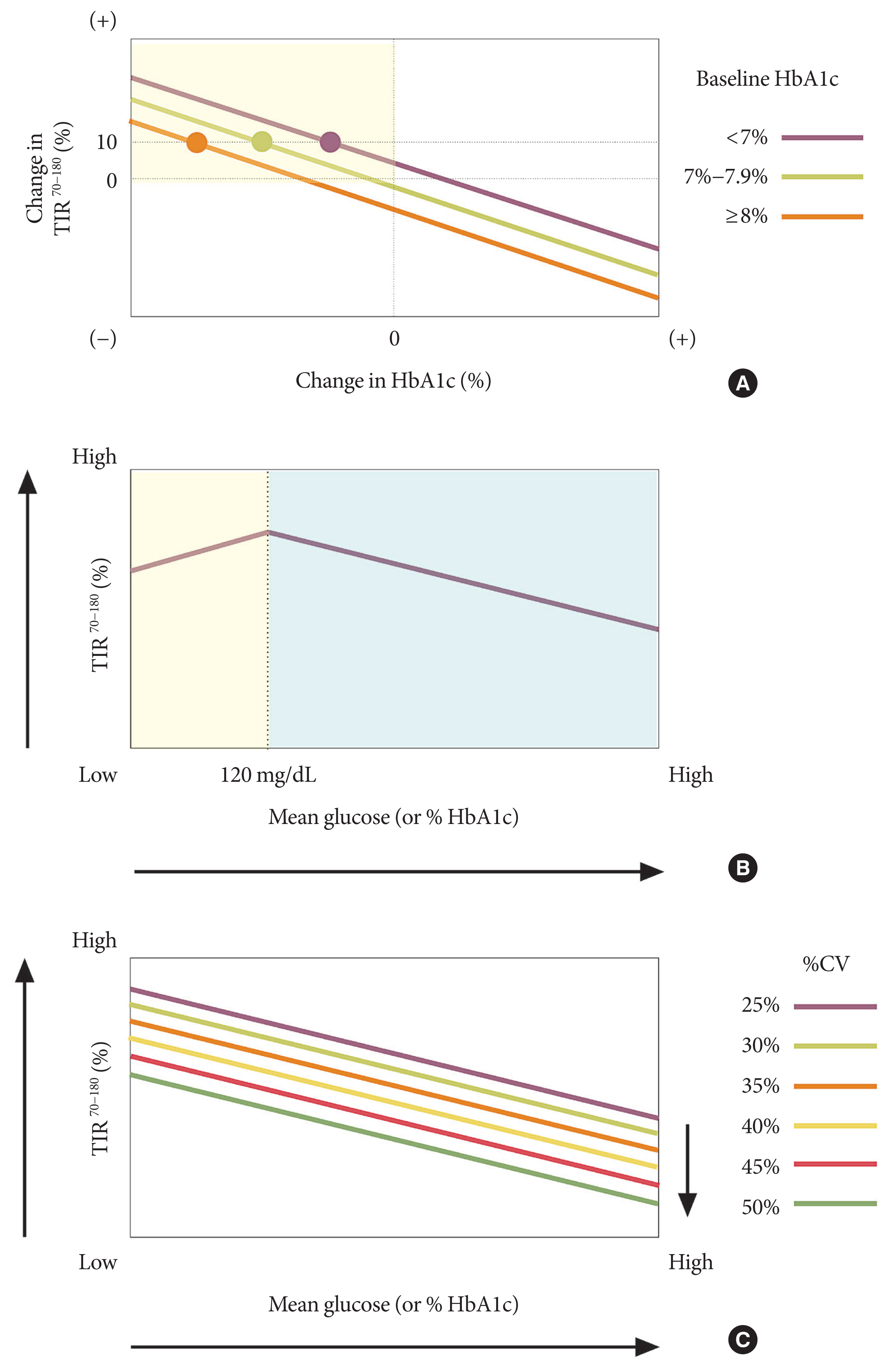
- TIR has been shown to have inversely linear relationship with HbA1c and hyperglycemic metrics (Table 1). Beck et al. [22] evaluated the relationship between HbA1c and TIR at baseline and at month 6, and further analyzed the relationship between the change in HbA1c and change in TIR in 545 T1DM. Ten percentages of TIR (2 hours, 24 minutes) represented an approximately 0.5% decrease in HbA1c, and every 10% change in TIR was associated with a change in HbA1c of 0.4%. By extension, Fabris et al. [24] estimated the HbA1c from a full 3 months of data of CGM-derived TIR for accuracy in T1DM. Their results were similar to the previous study.
- However, while TIR has high correlation (more than 0.9 by Spearman correlation) with other CGM metrics for hyperglycemia, only moderate correlation (about 0.6 to 0.7 by Spearman correlation) was found with HbA1c [22]. Indeed, a wide range of TIR exists for a given HbA1c level, and this suggests TIR is not a metric that can simply transform to predicting HbA1c. Beck et al. [22] found the change in HbA1c for TIR increased by baseline HbA1c (Fig. 3A). This means that a 10% increase in TIR only decreases −0.4% of HbA1c in those with baseline HbA1c <7.0% but decreases −1.0% in HbA1c in those with baseline HbA1c ≥8.0%. We can also see in Table 1 that the slope for estimated HbA1c for TIR is lower at month 6 (slope, 0.041) than at baseline (slope, 0.048), because of the reduction in HbA1c during using CGM over 6 months [22]. Vigersky and McMahon [23] reported that a 10% increase in TIR equals an approximately 0.8% reduction in HbA1c in 1,137 T1DM and T2DM in 18 studies, which was slightly higher than the previous studies [22,24]. This result might be related to high baseline HbA1c. Among the 18 studies, eight studies included participants with baseline HbA1c more than 8.0%.
- Recently, Rodbard [27] revealed the inverse linear relationship between TIR and mean glucose is preserved only in glucose values between 120 and 200 mg/dL, and reversely falls when the glucose level decreases below 120 mg/dL (Fig. 3B). Moreover, the linear relationship remained when %CV for glucose ranges from 20% to 50%, and the relationship with TIR and HbA1c were different by %CV. TIR was much lower in those with high %CV, even in those with the same HbA1c (Fig. 3C).
- Another notable finding is that TIR has a weak correlation to hypoglycemic and glycemic variability metrics. Reducing the mean glucose level while minimizing hypoglycemia has always been challenging in diabetes treatment. Thus, TIR always needs to be complemented with HbA1c and hypoglycemic metrics such as TBR or CV to guide therapeutic decisions.
- Association between TIR and diabetic complications
- HbA1c has been the only prospectively evaluated tool for assessing the risk for diabetes complications. However, as TIR emerges as a new metric for assessing glycemic control in addition to HbA1c, numerous studies have reported TIR as a metric for correlation with diabetes complications (Table 2) [28–33]. At first, a TIR of target glucose and TAR computed from 7-point SMBG but not CGM were retrospectively investigated for retinopathy and microalbuminuria outcomes using DCCT data and the associations have been reported [34]. Since then, Lu et al. [28–30] published a cross-sectional study correlating three-day TIR with diabetic retinopathy and intima-media thickness in patients with T2DM. Yoo et al. [33] have shown a relationship between TIR and albuminuria, a predictor of cardiovascular disease, in T2DM. Ranjan et al. [31] proved the relationship between the two in the longitudinal study in T1DM. Also, TIR was reported to be associated with painful diabetic polyneuropathy [32]. However, the TIR cuff-offs for reducing diabetes complications are lacking. Until now, whether long-term cardiovascular outcomes and TIR are related has not been established. However, we predict TIR to be the preferred metric for determining the outcome of clinical studies, the long-term risk of diabetes complications, and assessment of individual patient glycemic control, though further prospective studies are needed.
- CV as a surrogate metric for glycemic variability
- The only preferred metric for glycemic variability presented in a recently published consensus report is CV. Percentage CV can be easily calculated from the following formula: [%CV= 100×(SD of glucose)/mean glucose]. It reflects amplitude of glycemic variability relative to mean blood glucose, thus, the linear relationship with mean glucose disappears and more precisely reflects the hypoglycemic excursion than SD [35,36]. For example, even if the SD is same with 40 mg/dL, if the mean glucose is 150 mg/dL, the CV is 26.7% and, if the mean glucose is 80 mg/dL, the CV will be 50%. Other metrics such as the mean amplitude of glycemic excursion (MAGE), low or high glucose index (LBGI, HBGI), area under curve (AUC), and others are excluded due to the complexity of calculation [35,37].
- There is tangible evidence from a number of studies that have shown correlation of CV with hypoglycemic metrics, including TBR [38–40]. Fear of hypoglycemia is a major barrier to intensifying treatment in diabetics. As we intensify treatment to approach the target HbA1c level, the CV and frequency of hypoglycemic events increase [39,41,42]. CV is also considered a risk factor for chronic complications in diabetes [43–46]. Thus, experts recently suggested that CV should be assessed in diabetes care to reduce hypoglycemia and associated complications.
- The recent consensus recommended a threshold of 36% or less as stable glucose homeostasis. Monnier found that diabetes without insulinotropic agents had no CV higher than 36%, and hypoglycemia episodes were significantly higher in people who had a value of %CV >36 than those who were below the threshold [41]. Similar results were found in various studies, suggesting a cutoff value of 36% [35,47]. But there are still debates on the target of %CV. Some propose that those with insulin or sulfonylurea regimen should lower the target to 33% to protect against hypoglycemia [36,47]. In another study, %CV below 34% was suggested for people who desire strict glycemic control [38].
TEN CORE CGM METRICS AND AMBULATORY GLUCOSE PROFILE
- Two types of CGM are now available: professional (blind) and personal (real time). The characteristics according to the type of CGM are outlined in Table 3. Professional CGM are owned by healthcare providers and provide data for retrospective analysis; thus, the glucose data is blinded (or masked) during CGM. Personal CGM obtains data for real time or intermittent scanning in which the patient can observe the changes and is thus used by those who are on regimens with insulin requiring long-term monitoring. Both types of CGM show increasing evidence of benefits eventually leading to optimal therapy in T1DM and T2DM in clinical practice [48]. However, the role and indications for the two forms of CGM are different.
- Professional CGM have huge advantages over personal CGM when using CGM blindly in clinical trials to obtain individual short-term glycemic status for determining the efficacy and safety of new drugs and devices, comparing drugs in improving glycemic status, or evaluating the correlation with chronic diabetic complications [30,33,49–51]. When using real-time CGM, the patient can modify behavior such as diet, exercise, medication, or insulin dose in response to real-time changing data, which can affect the outcome of the study [52,53]. However, by using a professional CGM, because of an unawareness of CGM data in real-time, we can avoid the bias caused by a personal CGM.
- Professional CGM can accurately diagnose glycemic status and can be used as an education tool because it does not alter patients’ temporary behavior as can occur with personal CGM use. It also gives actional information by uncovering the presence of hypo- and hyperglycemia [54]. However, it has no alarms for hypo- and hyperglycemia and has limitations in long-term monitoring whereas personal CGM are both available. With personal CGM, the patient can directly adjust diet and exercise behavior or insulin dose with adequate patient education and training.
DIFFERENCES BETWEEN PROFESSIONAL AND PERSONAL CGM
- The use of CGM is gradually increasing but is still not widespread. Multiple challenges remain to be overcome in patients, providers, and even in technology aspects [55,56].
- The main barriers include alarm fatigue, issues remaining in insurance, cost, device discomfort or unfamiliarity of device, pain, and possibility of infection. Sometimes the device leads to depressive mood [56]. However, alarm fatigue is limited to rt-CGM and not FGM [57]. A solution can be changing rt-CGM to FGM for those who are suffering from alarm fatigue but without history of hypoglycemia unawareness.
- Barriers exist in the patient’s point of view, but also to the healthcare providers in CGM use expansion. There is a time constraint to review and interpret CGM in outpatient clinics. Problems for accuracy still remain in the hypoglycemic and/or hyperglycemic range, though CGM systems typically have a higher accuracy in the euglycemic range [55]. This suggests that both providers and patients should be cautious in interpreting the glycemic data in hypo-or hyperglycemic ranges.
BARRIERS TO THE USE OF CGM SYSTEMS
- CGM is reported to improve glycemic control of patients with T1DM or T2DM [9]. In the meta-analysis identified with 15 randomized controlled trials, lasting 12 to 36 weeks and involving 2,461 patients with T1DM and T2DM, CGM led to an overall 0.17% reduction in HbA1c, with a 70-minute (4.9%) increase in TIR, 30-minute (2.1%) decrease in TAR (>180 mg/dL), and 30-minute (2.1%) decrease in TBR (<70 mg/dL).
- Among three of the studies using FGM without structured education, TIR increased by 53.9 minutes (3.7%), and TBR decreased by 56.3 minutes (3.7%), but without any significant change in HbA1c [9]. One study was evaluated for the efficacy of FGM on reducing HbA1c in poorly controlled (HbA1c range, 7.5% to 12.0%) T2DM [58], and two others for reducing hypoglycemia in well-controlled (HbA1c ≤7.5) T1DM [59,60]. These studies were investigated without any training provided. A crucial point to note from these studies is that while FGM without education has a greater effect on reducing hypoglycemia, even in poorly controlled patients, it does not lead to a decrease in HbA1c.
- However, compared to previous studies, Hermanns et al. [61] showed significant differences with a HbA1c reduction of −0.17% in an FGM with education group compared to an FGM without education group. This study was designed to have structured education with four educational sessions lasting 90 minutes each in intervention group. These conflicting results suggest that the lack of education for CGM use might underwhelm the efficacy of CGM. In addition, it might be crucial to know how to interpret the data and adjust behavior or insulin-dose in response to real-time data received from the system.
- Structured diabetes education has been recognized as an essential part of diabetes therapy for a long time. There is also a study emphasizing the importance and effectiveness of CGM-specific education [62]. HbA1c reduction was compared between a group that used FGM with complement diabetes management instruction and a control group with instruction for routine SMBG in T2DM on multiple daily insulin injections for at least one year. The changes in HbA1c (−0.82%) were much higher in the FGM group with structured education than in the control group (−0.33%) with SMBG instruction at the same time given for education. From this perspective, effective CGM-specific education programs that can lead to improvement in CGM efficacy are in great need.
IMPACT OF STRUCTURED EDUCATION WHILE USING CGM
- CGM technology has rapidly expanded. By measuring glucose level continuously, the 10 core CGM metrics emerged, making the understanding of an individual’s glycemic status more comprehensive. This has helped both health providers and patients make better treatment decisions than when using HbA1c alone. TIR in particular is similar to HbA1c but provides more information and can also reflect short-term periods of glycemic status. Evidence for TIR predicting diabetic complications is regularly being published, although prospective studies are currently lacking. Consistent efforts are needed to overcome barriers in using CGM. In the near future, we expect CGM metrics, including TIR, to be widely used in clinical practice and eventually replace HbA1c.
CONCLUSIONS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
NOTES
-
Acknowledgements
- None
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS


| TIR (70–180 mg/dL) | Vigersky et al.a [23] (n=1,137 participants with T1DM or T2DM) | Beck et al.b [22] at baseline (n=455 participants with T1DM) | Beck et al.b [22] in month 6 (n=545 participants with T1DM) | Fabris et al.c [24] (n=168 participants with T1DM) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20% | 10.6 | 9.4 | 8.8 | 9.3 |
| 30% | 9.8 | 8.9 | 8.4 | 8.9 |
| 40% | 9.0 | 8.4 | 8.0 | 8.5 |
| 50% | 8.3 | 7.9 | 7.6 | 8.1 |
| 60% | 7.5 | 7.4 | 7.2 | 7.7 |
| 70% | 6.7 | 7.0 | 6.8 | 7.3 |
| 80% | 5.9 | 6.5 | 6.4 | 6.9 |
| 90% | 5.1 | 6.0 | 6.0 | 6.5 |
| Baseline HbA1c, % | NA | 7.5±1.0 | 7.2±0.8 | NA |
| Equation | HbA1c=12.32–0.081×TIR | HbA1c=10.31–0.048×TIR | HbA1c=9.65–0.041×TIR | HbA1c=10.12–0.04×TIR |
| Every 10% increase in TIR | ~0.8% HbA1c reduction | ~0.5% HbA1c reduction | ~0.4% HbA1c reduction | ~0.4% HbA1c reduction |
HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; CGM, continuous glucose monitoring; TIR, time in range; T1DM, type 1 diabetes mellitus; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; NA, not applicable.
a Data sets were from 18 clinical trials using CGM for a minimum of 3 days,
b Data used in analyses were from four randomized trials using CGM for a minimum of 10 days for baseline and 14 days in month 6,
c Linear regression analysis was used to analyze 3-month full CGM data for this equation.
| Study | Populations | Outcome | Results |
|---|---|---|---|
| Beck et al. (2019) [34] | 1,440 Patients with T1DM in DCCT | Retinopathy, albuminuria | HRs for retinopathy and microalbuminuria by TIR; 7-point SMBG (each 10% decrease in TIR): 1.64 (1.51–1.78) and 1.40 (1.25–1.56) |
| Lu et al. (2018) [30] | 3,262 Patients with T2DM | Retinopathy | OR for any retinopathy by TIR; CGM (each 10% increase in TIR): 0.92 (0.88–0.96) |
| Lu et al. (2020) [29] | 2,215 Patients with T2DM | CIMT | OR for CIMT by TIR; CGM (each 10% increase in TIR): 0.936 (0.878–0.998) |
| Yoo et al. (2020) [33] | 866 Patients with T2DM | Albuminuria | OR for albuminuria by TIR; CGM (each 10% increase in TIR): 0.94 (0.88–0.99) |
| Ranjan et al. (2020) [31] | 26 Patients with T1DM with SAP | Albuminuria | HR for albuminuria by TIR; CGM (each 10% increase in TIR): 0.81 (0.72–0.90) |
| Yang et al. (2020) [32] | 364 Patients with diabetic polyneuropathy | Painful diabetic polyneuropathy | OR for painful diabetic polyneuropathy by TIR; CGM (quartile): 2.66 (1.16–6.10) |
TIR, time in range; T1DM, type 1 diabetes mellitus; DCCT, Diabetes Control and Complications Trial; HR, hazard ratio; SMBG, self-monitoring blood glucose; T2DM, type 2 diabetes mellitus; OR, odds ratio; CGM, continuous glucose monitoring; CIMT, carotid intima-media thickness; SAP, sensor-augmented insulin pump.
| Professional CGM | Personal CGM | |
|---|---|---|
| Methods for obtaining glucose metrics | Blind, retrospective | Real-time (RT) observation or flash glucose monitoring (FGM) |
|
|
||
| Duration | Intermittent use by healthcare providers | Continuous use by patients |
|
|
||
| Device available in Korea | Medtronic ipro2 |
Medtronic Guardian Connect Dexcom G5, G6 (possible sooner) Freestyle Libre |
|
|
||
| Advantages | The results cannot bias patient and investigator use of trial products because they are unaware of the glucose values. | Patient can directly adjust their diet and exercise behavior or insulin dose with adequate patient education and training. |
| Healthcare providers can make appropriate therapy changes with T1DM and even T2DM patients with unrecognized hypo- and hyperglycemia. | Useful for long-term monitoring in patients who are on regimens with basal and prandial insulin. | |
| Both provide optimal therapy adjustment | ||
|
|
||
| Limitations | No alarms for hypo- and hyperglycemia | Clinical trial results may be affected by response to real-time data (e.g., temporary behavior change, insulin dose adjustment, medication inherence, unethical behavior). |
| Not allowed for long-term monitoring | Alarm or calibration fatiguea, cost | |
| Time consuming for reviewing CGM data | ||
- 1. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Nathan DM, Genuth S, Lachin J, Cleary P, Crofford O, Davis M, Rand L, Siebert C. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;329:977-86.ArticlePubMed
- 2. UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998;352:837-53.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Beck RW, Connor CG, Mullen DM, Wesley DM, Bergenstal RM. The fallacy of average: how using HbA1c alone to assess glycemic control can be misleading. Diabetes Care 2017;40:994-9.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 4. Suh S, Kim JH. Glycemic variability: how do we measure it and why is it important? Diabetes Metab J 2015;39:273-82.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group. Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, Goff DC Jr, Bigger JT, Buse JB, Cushman WC, Genuth S, Ismail-Beigi F, Grimm RH Jr, Probstfield JL, Simons-Morton DG, Friedewald WT. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;358:2545-59.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Sheng CS, Tian J, Miao Y, Cheng Y, Yang Y, Reaven PD, Bloomgarden ZT, Ning G. Prognostic significance of long-term HbA1c variability for all-cause mortality in the ACCORD trial. Diabetes Care 2020;43:1185-90.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Kovatchev BP, Patek SD, Ortiz EA, Breton MD. Assessing sensor accuracy for non-adjunct use of continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Technol Ther 2015;17:177-86.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Rodbard D. Continuous glucose monitoring: a review of successes, challenges, and opportunities. Diabetes Technol Ther 2016;18(Suppl 2):S3-13.Article
- 9. Maiorino MI, Signoriello S, Maio A, Chiodini P, Bellastella G, Scappaticcio L, Longo M, Giugliano D, Esposito K. Effects of continuous glucose monitoring on metrics of glycemic control in diabetes: a systematic review with meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Care 2020;43:1146-56.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 10. Battelino T, Danne T, Bergenstal RM, Amiel SA, Beck R, Biester T, Bosi E, Buckingham BA, Cefalu WT, Close KL, Cobelli C, Dassau E, DeVries JH, Donaghue KC, Dovc K, Doyle FJ 3rd, Garg S, Grunberger G, Heller S, Heinemann L, Hirsch IB, Hovorka R, Jia W, Kordonouri O, Kovatchev B, Kowalski A, Laffel L, Levine B, Mayorov A, Mathieu C, Murphy HR, Nimri R, Norgaard K, Parkin CG, Renard E, Rodbard D, Saboo B, Schatz D, Stoner K, Urakami T, Weinzimer SA, Phillip M. Clinical targets for continuous glucose monitoring data interpretation: recommendations from the international consensus on time in range. Diabetes Care 2019;42:1593-603.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 11. Xing D, Kollman C, Beck RW, Tamborlane WV, Laffel L, Buckingham BA, Wilson DM, Weinzimer S, Fiallo-Scharer R, Ruedy KJ. Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group. Optimal sampling intervals to assess long-term glycemic control using continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Technol Ther 2011;13:351-8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Riddlesworth TD, Beck RW, Gal RL, Connor CG, Bergenstal RM, Lee S, Willi SM. Optimal sampling duration for continuous glucose monitoring to determine long-term glycemic control. Diabetes Technol Ther 2018;20:314-6.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Ambulatory Glucose Profile. AGP reports: CGM AGP Report (Continuous Glucose Monitor) New v4.0 Available from: http://agpreport.org/agp/agpreports(cited 2020 Nov 30).
- 14. Bergenstal RM, Ahmann AJ, Bailey T, Beck RW, Bissen J, Buckingham B, Deeb L, Dolin RH, Garg SK, Goland R, Hirsch IB, Klonoff DC, Kruger DF, Matfin G, Mazze RS, Olson BA, Parkin C, Peters A, Powers MA, Rodriguez H, Southerland P, Strock ES, Tamborlane W, Wesley DM. Recommendations for standardizing glucose reporting and analysis to optimize clinical decision making in diabetes: the Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP). Diabetes Technol Ther 2013;15:198-211.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Bergenstal RM, Beck RW, Close KL, Grunberger G, Sacks DB, Kowalski A, Brown AS, Heinemann L, Aleppo G, Ryan DB, Riddlesworth TD, Cefalu WT. Glucose management indicator (GMI): a new term for estimating A1C from continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care 2018;41:2275-80.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 16. Aleppo G, Ruedy KJ, Riddlesworth TD, Kruger DF, Peters AL, Hirsch I, Bergenstal RM, Toschi E, Ahmann AJ, Shah VN, Rickels MR, Bode BW, Philis-Tsimikas A, Pop-Busui R, Rodriguez H, Eyth E, Bhargava A, Kollman C, Beck RW. REPLACE-BG Study Group. REPLACE-BG: a randomized trial comparing continuous glucose monitoring with and without routine blood glucose monitoring in adults with well-controlled type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2017;40:538-45.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 17. Beck RW, Riddlesworth T, Ruedy K, Ahmann A, Bergenstal R, Haller S, Kollman C, Kruger D, McGill JB, Polonsky W, Toschi E, Wolpert H, Price D. DIAMOND Study Group. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes using insulin injections: the DIAMOND randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2017;317:371-8.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Beck RW, Riddlesworth TD, Ruedy K, Ahmann A, Haller S, Kruger D, McGill JB, Polonsky W, Price D, Aronoff S, Aronson R, Toschi E, Kollman C, Bergenstal R. DIAMOND Study Group. Continuous glucose monitoring versus usual care in patients with type 2 diabetes receiving multiple daily insulin injections: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 2017;167:365-74.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Heinemann L, Freckmann G, Ehrmann D, Faber-Heinemann G, Guerra S, Waldenmaier D, Hermanns N. Real-time continuous glucose monitoring in adults with type 1 diabetes and impaired hypoglycaemia awareness or severe hypoglycaemia treated with multiple daily insulin injections (HypoDE): a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2018;391:1367-77.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Grimsmann JM, von Sengbusch S, Freff M, Ermer U, Placzek K, Danne T, Hammer E, Holl RW. DPV Initiative. Glucose management indicator based on sensor data and laboratory HbA1c in people with type 1 diabetes from the DPV database: differences by sensor type. Diabetes Care 2020;43:e111-2.PubMed
- 21. Angellotti E, Muppavarapu S, Siegel RD, Pittas AG. The calculation of the glucose management indicator is influenced by the continuous glucose monitoring system and patient race. Diabetes Technol Ther 2020;22:651-7.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Beck RW, Bergenstal RM, Cheng P, Kollman C, Carlson AL, Johnson ML, Rodbard D. The relationships between time in range, hyperglycemia metrics, and HbA1c. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2019;13:614-26.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 23. Vigersky RA, McMahon C. The relationship of hemoglobin A1C to time-in-range in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 2019;21:81-5.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Fabris C, Heinemann L, Beck R, Cobelli C, Kovatchev B. Estimation of hemoglobin A1c from continuous glucose monitoring data in individuals with type 1 diabetes: is time in range all we need? Diabetes Technol Ther 2020;22:501-8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Bergenstal RM, Klonoff DC, Garg SK, Bode BW, Meredith M, Slover RH, Ahmann AJ, Welsh JB, Lee SW, Kaufman FR. AS-PIRE In-Home Study Group. Threshold-based insulin-pump interruption for reduction of hypoglycemia. N Engl J Med 2013;369:224-32.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Bergenstal RM, Garg S, Weinzimer SA, Buckingham BA, Bode BW, Tamborlane WV, Kaufman FR. Safety of a hybrid closed-loop insulin delivery system in patients with type 1 diabetes. JAMA 2016;316:1407-8.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Rodbard D. Glucose time in range, time above range, and time below range depend on mean or median glucose or HbA1c, glucose coefficient of variation, and shape of the glucose distribution. Diabetes Technol Ther 2020;22:492-500.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Lu J, Home PD, Zhou J. Comparison of multiple cut points for time in range in relation to risk of abnormal carotid intima-media thickness and diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 2020;43:e99-101.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 29. Lu J, Ma X, Shen Y, Wu Q, Wang R, Zhang L, Mo Y, Lu W, Zhu W, Bao Y, Vigersky RA, Jia W, Zhou J. Time in range is associated with carotid intima-media thickness in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 2020;22:72-8.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Lu J, Ma X, Zhou J, Zhang L, Mo Y, Ying L, Lu W, Zhu W, Bao Y, Vigersky RA, Jia W. Association of time in range, as assessed by continuous glucose monitoring, with diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2018;41:2370-6.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 31. Ranjan AG, Rosenlund SV, Hansen TW, Rossing P, Andersen S, Norgaard K. Improved time in range over 1 year is associated with reduced albuminuria in individuals with sensor-augmented insulin pump-treated type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2020;43:2882-5.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 32. Yang J, Yang X, Zhao D, Wang X, Wei W, Yuan H. Association of time in range, as assessed by continuous glucose monitoring, with painful diabetic polyneuropathy. J Diabetes Investig 2020 Sep 3 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdi.13394 .Article
- 33. Yoo JH, Choi MS, Ahn J, Park SW, Kim Y, Hur KY, Jin SM, Kim G, Kim JH. Association between continuous glucose monitoring-derived time in range, other core metrics, and albuminuria in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 2020;22:768-76.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Beck RW, Bergenstal RM, Riddlesworth TD, Kollman C, Li Z, Brown AS, Close KL. Validation of time in range as an outcome measure for diabetes clinical trials. Diabetes Care 2019;42:400-5.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 35. Rodbard D. Clinical interpretation of indices of quality of glycemic control and glycemic variability. Postgrad Med 2011;123:107-18.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Rodbard D. Hypo- and hyperglycemia in relation to the mean, standard deviation, coefficient of variation, and nature of the glucose distribution. Diabetes Technol Ther 2012;14:868-76.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Chon S. How can we easily measure glycemic variability in diabetes mellitus? Diabetes Metab J 2015;39:114-6.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Monnier L, Wojtusciszyn A, Molinari N, Colette C, Renard E, Owens D. Respective contributions of glycemic variability and mean daily glucose as predictors of hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes: are they equivalent? Diabetes Care 2020;43:821-7.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 39. Kovatchev B, Cobelli C. Glucose variability: timing, risk analysis, and relationship to hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2016;39:502-10.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 40. Jin SM, Kim TH, Bae JC, Hur KY, Lee MS, Lee MK, Kim JH. Clinical factors associated with absolute and relative measures of glycemic variability determined by continuous glucose monitoring: an analysis of 480 subjects. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2014;104:266-72.ArticlePubMed
- 41. Monnier L, Colette C, Wojtusciszyn A, Dejager S, Renard E, Molinari N, Owens DR. Toward defining the threshold between low and high glucose variability in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2017;40:832-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 42. Cryer PE. Individualized glycemic goals and an expanded classification of severe hypoglycemia in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2017;40:1641-3.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 43. Jun JE, Jin SM, Baek J, Oh S, Hur KY, Lee MS, Lee MK, Kim JH. The association between glycemic variability and diabetic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2015;14:70.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 44. Jun JE, Lee SE, Lee YB, Ahn JY, Kim G, Hur KY, Lee MK, Jin SM, Kim JH. Continuous glucose monitoring defined glucose variability is associated with cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2019;35:e3092.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 45. Matsutani D, Sakamoto M, Iuchi H, Minato S, Suzuki H, Kayama Y, Takeda N, Horiuchi R, Utsunomiya K. Glycemic variability in continuous glucose monitoring is inversely associated with baroreflex sensitivity in type 2 diabetes: a preliminary report. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2018;17:36.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 46. Ha WC, Oh SJ, Kim JH, Lee JM, Chang SA, Sohn TS, Son HS. Severe hypoglycemia is a serious complication and becoming an economic burden in diabetes. Diabetes Metab J 2012;36:280-4.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 47. Rama Chandran S, Tay WL, Lye WK, Lim LL, Ratnasingam J, Tan AT, Gardner DS. Beyond HbA1c: comparing glycemic variability and glycemic indices in predicting hypoglycemia in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 2018;20:353-62.ArticlePubMed
- 48. Park C, Le QA. The effectiveness of continuous glucose monitoring in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review of literature and meta-analysis. Diabetes Technol Ther 2018;20:613-21.ArticlePubMed
- 49. Lee SH, Min KW, Lee BW, Jeong IK, Yoo SJ, Kwon HS, Choi YH, Yoon KH. Effect of dapagliflozin as an add-on therapy to insulin on the glycemic variability in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus (DIVE): a multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized study. Diabetes Metab J 2020 May 28 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0203 .Article
- 50. Kim G, Lim S, Kwon HS, Park IB, Ahn KJ, Park CY, Kwon SK, Kim HS, Park SW, Kim SG, Moon MK, Kim ES, Chung CH, Park KS, Kim M, Chung DJ, Lee CB, Kim TH, Lee MK. Efficacy and safety of evogliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: a multicentre, active-controlled, randomized, double-blind study with open-label extension (the EVERGREEN study). Diabetes Obes Metab 2020;22:1527-36.PubMedPMC
- 51. Kwak SH, Hwang YC, Won JC, Bae JC, Kim HJ, Suh S, Lee EY, Lee S, Kim SY, Kim JH. Comparison of the effects of gemigliptin and dapagliflozin on glycaemic variability in type 2 diabetes: a randomized, open-label, active-controlled, 12-week study (STABLE II study). Diabetes Obes Metab 2020;22:173-81.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 52. Fonda SJ, Salkind SJ, Walker MS, Chellappa M, Ehrhardt N, Vigersky RA. Heterogeneity of responses to real-time continuous glucose monitoring (RT-CGM) in patients with type 2 diabetes and its implications for application. Diabetes Care 2013;36:786-92.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 53. Vigersky R, Shrivastav M. Role of continuous glucose monitoring for type 2 in diabetes management and research. J Diabetes Complications 2017;31:280-7.ArticlePubMed
- 54. Gehlaut RR, Dogbey GY, Schwartz FL, Marling CR, Shubrook JH. Hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes: more common than you think: a continuous glucose monitoring study. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2015;9:999-1005.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 55. Schrangl P, Reiterer F, Heinemann L, Freckmann G, Del Re L. Limits to the evaluation of the accuracy of continuous glucose monitoring systems by clinical trials. Biosensors (Basel) 2018;8:50.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 56. Messer LH, Tanenbaum ML, Cook PF, Wong JJ, Hanes SJ, Driscoll KA, Hood KK. Cost, hassle, and on-body experience: barriers to diabetes device use in adolescents and potential intervention targets. Diabetes Technol Ther 2020;22:760-7.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Wong JC, Foster NC, Maahs DM, Raghinaru D, Bergenstal RM, Ahmann AJ, Peters AL, Bode BW, Aleppo G, Hirsch IB, Kleis L, Chase HP, DuBose SN, Miller KM, Beck RW, Adi S. T1D Exchange Clinic Network. Real-time continuous glucose monitoring among participants in the T1D Exchange clinic registry. Diabetes Care 2014;37:2702-9.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 58. Haak T, Hanaire H, Ajjan R, Hermanns N, Riveline JP, Rayman G. Flash glucose-sensing technology as a replacement for blood glucose monitoring for the management of insulin-treated type 2 diabetes: a multicenter, open-label randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Ther 2017;8:55-73.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 59. Oskarsson P, Antuna R, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn P, Kroger J, Weitgasser R, Bolinder J. Impact of flash glucose monitoring on hypoglycaemia in adults with type 1 diabetes managed with multiple daily injection therapy: a pre-specified subgroup analysis of the IMPACT randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2018;61:539-50.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 60. Bolinder J, Antuna R, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn P, Kroger J, Weitgasser R. Novel glucose-sensing technology and hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre, non-masked, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016;388:2254-63.ArticlePubMed
- 61. Hermanns N, Ehrmann D, Schipfer M, Kroger J, Haak T, Kulzer B. The impact of a structured education and treatment programme (FLASH) for people with diabetes using a flash sensor-based glucose monitoring system: results of a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2019;150:111-21.ArticlePubMed
- 62. Yaron M, Roitman E, Aharon-Hananel G, Landau Z, Ganz T, Yanuv I, Rozenberg A, Karp M, Ish-Shalom M, Singer J, Wainstein J, Raz I. Effect of flash glucose monitoring technology on glycemic control and treatment satisfaction in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2019;42:1178-84.ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Acute and Chronic Adverse Outcomes of Type 1 Diabetes
Rachel Longendyke, Jody B. Grundman, Shideh Majidi
Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America.2024; 53(1): 123. CrossRef - La plongée sous-marine en scaphandre autonome avec un diabète de type 1. Une belle histoire du dernier millénaire
Lise Dufaitre Patouraux, Agnès Sola-Gazagnes, Boris Lormeau, Corinne Lormeau
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2024; 18(1): 67. CrossRef - S100A9 exerts insulin-independent antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory effects
Gloria Ursino, Giulia Lucibello, Pryscila D. S. Teixeira, Anna Höfler, Christelle Veyrat-Durebex, Soline Odouard, Florian Visentin, Luca Galgano, Emmanuel Somm, Claudia R. Vianna, Ariane Widmer, François R. Jornayvaz, Andreas Boland, Giorgio Ramadori, Rob
Science Advances.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hybrid Closed-Loop Versus Manual Insulin Delivery in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: A Post Hoc Analysis Using the Glycemia Risk Index
Melissa H. Lee, Sara Vogrin, Timothy W. Jones, David N. O’Neal
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinically relevant stratification of patients with type 2 diabetes by using continuous glucose monitoring data
Xiaopeng Shao, Jingyi Lu, Rui Tao, Liang Wu, Yaxin Wang, Wei Lu, Hongru Li, Jian Zhou, Xia Yu
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a 2-Week Kinect-Based Mixed-Reality Exercise Program on Prediabetes: A Pilot Trial during COVID-19
So Young Ahn, Si Woo Lee, Hye Jung Shin, Won Jae Lee, Jun Hyeok Kim, Hyun-Jun Kim, Wook Song
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2024; 33(1): 54. CrossRef - Anagliptin twice‐daily regimen improves glycaemic variability in subjects with type 2 diabetes: A double‐blind, randomized controlled trial
Yong‐ho Lee, Doo‐Man Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Kyung Mook Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Kang Seo Park, Hyun‐Shik Son, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Soon Hee Lee, Ki‐Ho Song, Su Kyoung Kwon, Hyeong Kyu Park, Kyu Chang Won, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(5): 1174. CrossRef - Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 27. CrossRef - Status of continuous glucose monitoring use and management in tertiary hospitals of China: a cross-sectional study
Liping Chen, Xiaoqin Liu, Qin Lin, Hongmei Dai, Yong Zhao, Zumin Shi, Liping Wu
BMJ Open.2023; 13(2): e066801. CrossRef - Real-world outcomes of continuous glucose monitoring in adults with diabetes mellitus attending an Irish tertiary hospital
Aoife Courtney, Diarmuid Smith, Hannah Forde
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2023; 192(6): 2763. CrossRef - Insight into continuous glucose monitoring: from medical basics to commercialized devices
Ayman Chmayssem, Małgorzata Nadolska, Emily Tubbs, Kamila Sadowska, Pankaj Vadgma, Isao Shitanda, Seiya Tsujimura, Youssef Lattach, Martin Peacock, Sophie Tingry, Stéphane Marinesco, Pascal Mailley, Sandrine Lablanche, Pierre Yves Benhamou, Abdelkader Zeb
Microchimica Acta.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of polyethylene glycol loxenatide versus insulin glargine on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, open-label, parallel-group trial
Shuo Zhang, Chuanyan Zhang, Jingxian Chen, Feiying Deng, Zezhen Wu, Dan Zhu, Fengwu Chen, Yale Duan, Yue Zhao, Kaijian Hou
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control and its derived metrics in type 1 diabetes: a longitudinal study
So Hyun Cho, Seohyun Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Glycemia Risk Index and Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes
Jee Hee Yoo, Ji Yoon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(10): 726. CrossRef - Acute Glycemic Variability and Early Outcomes After Cardiac Surgery:
A Meta-Analysis
Shuo Chang, Mian Xu, Yu Wang, Yanbo Zhang
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2023; 55(11): 771. CrossRef - Comparison of Glycemia Risk Index with Time in Range for Assessing Glycemic Quality
Ji Yoon Kim, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(12): 883. CrossRef - Correlação entre tempo no alvo e hemoglobina glicada de pessoas com diabetes mellitus: revisão sistemática
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlación entre tiempo en rango y hemoglobina glicosilada en personas con diabetes mellitus: revisión sistemática
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation between time on target and glycated hemoglobin in people with diabetes mellitus: systematic review
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef - Novel Glycemic Index Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Predict Poor Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Il Rae Park, Yin Young Lee, Eun Young Choi, Jun Sung Moon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypoglycemic agents and glycemic variability in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
SuA Oh, Sujata Purja, Hocheol Shin, Minji Kim, Eunyoung Kim
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2022; 19(3): 147916412211068. CrossRef - Advanced Glycation End Products and Their Effect on Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jeongmin Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3086. CrossRef - Influence of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on glycemic variability in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Shangyu Chai, Ruya Zhang, Ye Zhang, Richard David Carr, Yiman Zheng, Swapnil Rajpathak, Miao Yu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Glucose Profiles Assessed by Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring System during the Perioperative Period of Metabolic Surgery
Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang, Young Suk Park, Tae Jung Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 713. CrossRef - Deterioration in glycemic control on schooldays among children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A continuous glucose monitoring-based study
Yu Ding, Wenhao Zhang, Xiumei Wu, Tian Wei, Xulin Wang, Xueying Zheng, Sihui Luo
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of repeated bolus and continuous glucose infusion on a panel of circulating biomarkers in healthy volunteers
Roland Feldbauer, Matthias Wolfgang Heinzl, Carmen Klammer, Michael Resl, Johannes Pohlhammer, Klemens Rosenberger, Verena Almesberger, Florian Obendorf, Lukas Schinagl, Thomas Wagner, Margot Egger, Benjamin Dieplinger, Martin Clodi, Stephen L. Atkin
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(12): e0279308. CrossRef - Relationship between glycemic intraday variations evaluated in continuous glucose monitoring and HbA1c variability in type 2 diabetes: pilot study
Akemi Tokutsu, Yosuke Okada, Keiichi Torimoto, Yoshiya Tanaka
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Time-in-range for monitoring glucose control: Is it time for a change?
Virginia Bellido, Pedro José Pinés-Corrales, Rocío Villar-Taibo, Francisco Javier Ampudia-Blasco
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 177: 108917. CrossRef - Glucose Management Indicator for People with Type 1 Asian Diabetes Is Different from That of the Published Equation: Differences by Glycated Hemoglobin Distribution
Jee Hee Yoo, Seung Hee Yang, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life, Family Conflicts and Fear of Injecting: Perception Differences between Preadolescents and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes and Their Mothers
Marta Tremolada, Maria Cusinato, Sabrina Bonichini, Arianna Fabris, Claudia Gabrielli, Carlo Moretti
Behavioral Sciences.2021; 11(7): 98. CrossRef - Daytime Glycemic Variability and Frailty in Older Patients with Diabetes: a Pilot Study Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Seung Min Chung, Yun Hee Lee, Chang Oh Kim, Ji Yeon Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Seung-Hyun Yoo, Jun Sung Moon, Kwang Joon Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Benefits of a Switch from Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring (isCGM) to Real-Time (rt) CGM in Diabetes Type 1 Suboptimal Controlled Patients in Real-Life: A One-Year Prospective Study §
Yannis Préau, Sébastien Galie, Pauline Schaepelynck, Martine Armand, Denis Raccah
Sensors.2021; 21(18): 6131. CrossRef - Recent Advances of Integrative Bio-Omics Technologies to Improve Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) Care
Nisha Karwal, Megan Rodrigues, David D. Williams, Ryan J. McDonough, Diana Ferro
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(24): 11602. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite