- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 47(3); 2023 > Article
-
Original ArticleTechnology/Device Glycemia according to the Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring among Adults with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A Real-World Study
-
You-Bin Lee1
 , Minjee Kim2
, Minjee Kim2 , Jae Hyeon Kim1
, Jae Hyeon Kim1
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2023;47(3):405-414.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0032
Published online: March 6, 2023
1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding author: Jae Hyeon Kim https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5001-963X Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 81 Irwon-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul 06351, Korea E-mail: jaehyeon@skku.edu
- * You-Bin Lee and Minjee Kim contributed equally to this study as first authors.
Copyright © 2023 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- We explored the association between continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) use and glycemia among adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and determined the status of CGM metrics among adults with T1DM using CGM in the real-world.
-
Methods
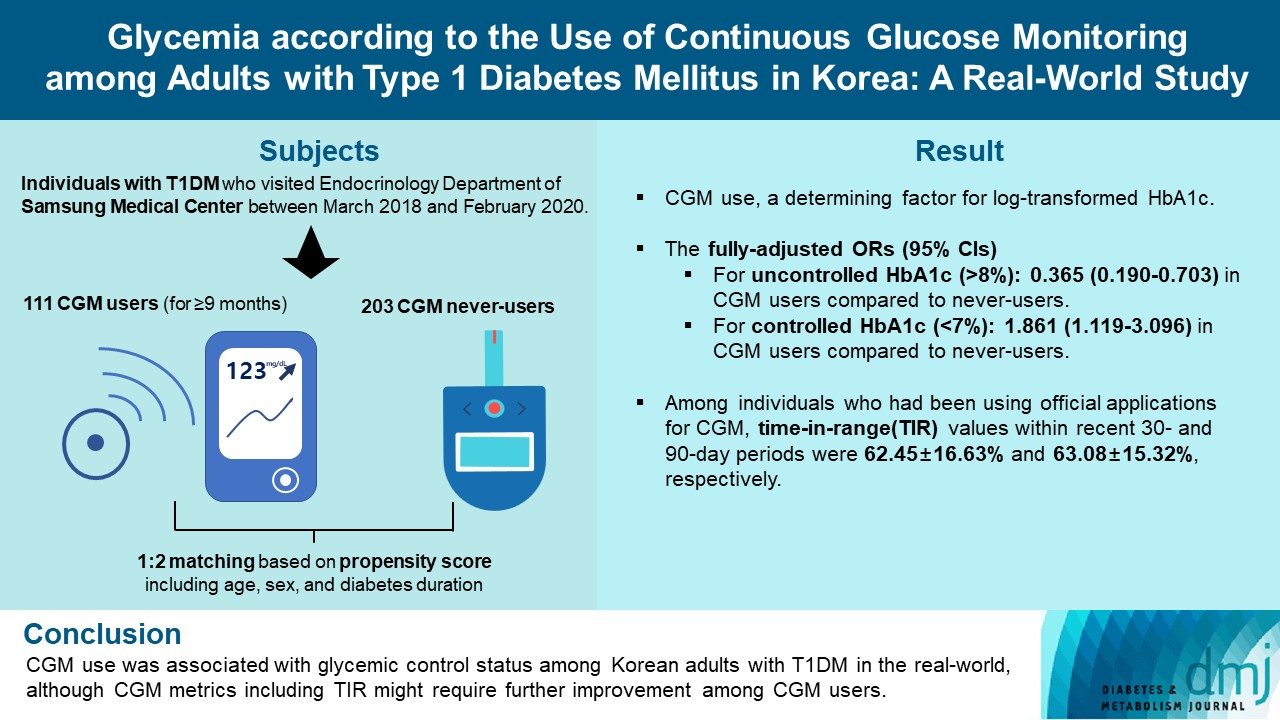
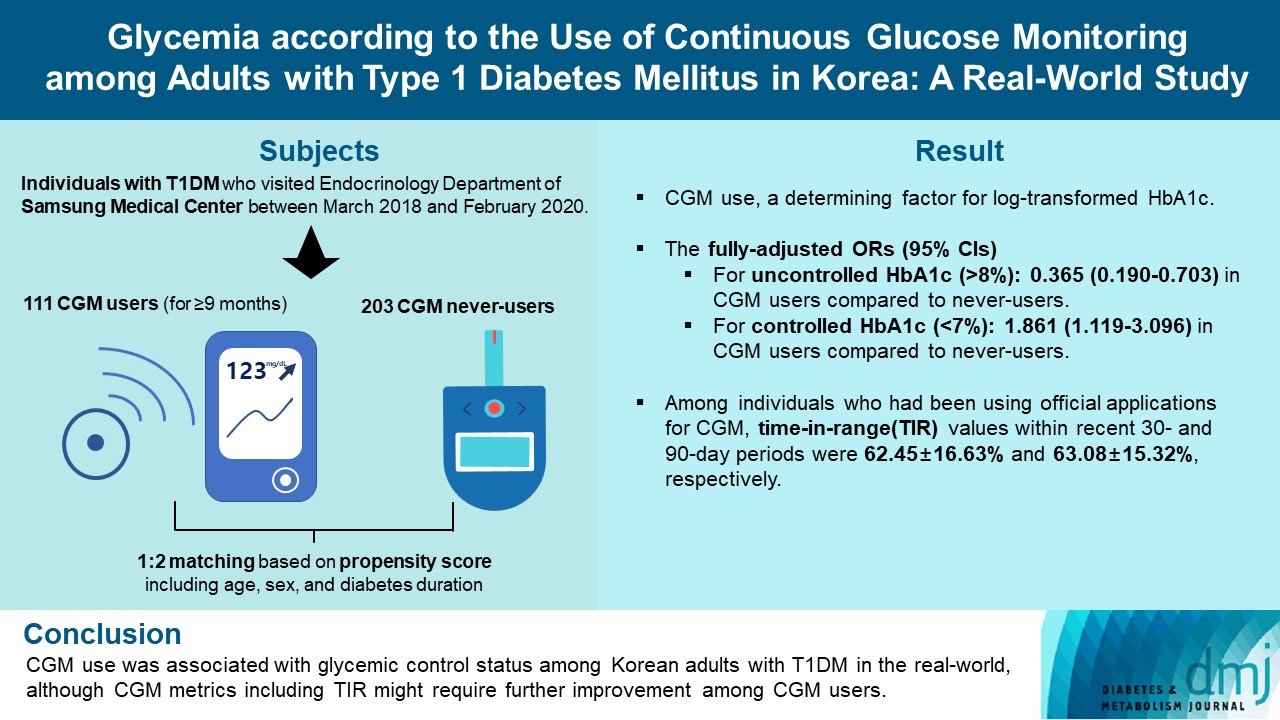
- For this propensity-matched cross-sectional study, individuals with T1DM who visited the outpatient clinic of the Endocrinology Department of Samsung Medical Center between March 2018 and February 2020 were screened. Among them, 111 CGM users (for ≥9 months) were matched based on propensity score considering age, sex, and diabetes duration in a 1:2 ratio with 203 CGM never-users. The association between CGM use and glycemic measures was explored. In a subpopulation of CGM users who had been using official applications (not “do-it-yourself” software) such that Ambulatory Glucose Profile data for ≥1 month were available (n=87), standardized CGM metrics were summarized.
-
Results
- Linear regression analyses identified CGM use as a determining factor for log-transformed glycosylated hemoglobin. The fully-adjusted odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) for uncontrolled glycosylated hemoglobin (>8%) were 0.365 (95% CI, 0.190 to 0.703) in CGM users compared to never-users. The fully-adjusted OR for controlled glycosylated hemoglobin (<7%) was 1.861 (95% CI, 1.119 to 3.096) in CGM users compared to never-users. Among individuals who had been using official applications for CGM, time in range (TIR) values within recent 30- and 90-day periods were 62.45%±16.63% and 63.08%±15.32%, respectively.
-
Conclusion
- CGM use was associated with glycemic control status among Korean adults with T1DM in the real-world, although CGM metrics including TIR might require further improvement among CGM users.
- Adoption of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in people with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) has expanded rapidly in the past decade [1,2]. With this rapid growth in CGM use, the Advanced Technologies and Treatments for Diabetes consensus summarized the standardized CGM metrics, including time in range (TIR) and glycemic variability, and specified their target values for clinical care [1]. Furthermore, CGM data presentation and visualization were standardized using a standard template, the Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP) report [1]. TIR, the time spent in the target glucose range (70 to 180 mg/dL), has been inversely associated with glycosylated hemoglobin and risk of microvascular complications [3].
- Previous clinical trials have demonstrated the benefits of CGM use in terms of reducing glycosylated hemoglobin among adults with T1DM [4–10]. However, for optimal implementation of CGM and subsequent clinical benefits, robust and systematic diabetes education, training, and support should be offered [11–13]. For example, in a small trial conducted in underserved, less educated adults with T1DM, a glycosylated hemoglobin reduction in the CGM group was not achieved [14]. Furthermore, adherence to wearing CGM device might also affect the capability of CGM to improve glycemia [6,7]. Therefore, in the real-world, the association between CGM use and glycemia among adults with T1DM can vary. Even though CGM use has substantially increased in recent years, racial disparities remain in use of technology and glycemic control [15].
- Nevertheless, to the best of our knowledge, no previous study has evaluated the glycemic control state of Korean adults with T1DM according to CGM use in the real-world. In this study, we explored an association between CGM use and glycemia among adults with T1DM in Korea. In addition, we summarized the standardized CGM metrics among adults with T1DM using CGM continuously in the real-world for the first time in Korea.
INTRODUCTION
- Study population and design
- This propensity-matched, cross-sectional study was conducted at Samsung Medical Center, a hospital-based tertiary referral center in Republic of Korea. Using medical records, 588 individuals with T1DM who visited the outpatient clinic of the Endocrinology Department of Samsung Medical Center between March 2018 and February 2020 were screened. The timepoint of the last outpatient visit between March 2018 and February 2020 was considered as the index date (baseline). We excluded individuals who visited the outpatient clinic only once (n=17); those with missing glycosylated hemoglobin variables (n=11); those with uncertain information about the initiation date or duration of CGM use (n=9); and irregular users/short-term users (those with consecutive duration of CGM use <9 months), or past users (those who had ever used CGM but not using it at baseline) of CGM (n=17). Through these processes, 111 continuous users of personal CGM (for ≥9 months) and 423 never-users of CGM were selected. We only included individuals who had been using CGM for at least 9 months as CGM users to select people adherent to continuous CGM use and expected to have been educated three times or more in interpreting CGM data, considering that the intervals between outpatient visits are generally 3 months at our center. The Endocrinology Department of our center operates specialized clinics for the systematic care of people with T1DM. At these specialized clinics, patient education on interpretation of their CGM data are provided for CGM users. CGM devices in use included Dexcom G5 and G6 (real-time CGM [RT-CGM]) (Dexcom, San Diego, CA, USA), the Guardian Connect Mobile system (RT-CGM) (Medtronic, Northridge, CA, USA), and the FreeStyle Libre Flash system (intermittently-scanned CGM [isCGM]) (Abbott Diabetes Care, Witney, UK). Propensity score (PS) matching (1:2) of CGM users and never-users was performed. The PS model was obtained from a multiple logistic regression analysis that included age, sex, and diabetes duration. We applied a greedy nearest neighbor matching on the logit of PS using calipers of width 0.2 of the standard deviation (SD) of the logit of the PS. Finally, 111 CGM users (for ≥9 months) and 203 matched CGM never-users were enrolled (Fig. 1). The distributions of PSs are shown in Supplementary Fig. 1 and indicate that the two groups were well-matched.
- This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board (IRB) of Samsung Medical Center (IRB file no. SMC 2020-11-008-001) and was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. An exemption from informed consent was granted by the IRB because all data were analyzed anonymously.
- Data collection
- Demographic and clinical data of baseline, including age, sex, diabetes duration, total daily dose of insulin, use of an insulin pump, history of cerebral infarction and/or acute myocardial infarction (AMI) during the previous 5 years from baseline, presence of diabetic retinopathy or end-stage renal disease (ESRD), height, weight, blood pressure (BP), and laboratory results were retrospectively extracted from electronic medical records. Collected laboratory data, which were gathered after an 8-hour overnight fast, included glycosylated hemoglobin; glycated albumin (GA); fasting plasma glucose; aspartate aminotransferase; alanine aminotransferase; blood urea nitrogen; creatinine; and lipid profiles including total cholesterol, triglycerides, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. The fasting plasma glucose level was determined using the glucose oxidase method, and lipid profiles were measured using a Hitachi 7600 autoanalyzer (Hitachi Instruments Service, Tokyo, Japan). High-performance liquid chromatography on a VARIANT II TURBO analyzer (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA) was used to measure glycosylated hemoglobin. Serum GA level was determined by an enzymatic method using a Lucica GA-L kit (Asahi Kasei Pharma Corporation, Tokyo, Japan). Body mass index (BMI) was calculated as body weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared (kg/m2). Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated using Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration equations [16]. We defined uncontrolled glycosylated hemoglobin as >8% and controlled glycosylated hemoglobin as <7% of the baseline level.
- Statistical analysis
- All statistical analyses were conducted using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc, Cary, NC, USA) and MedCalc statistical software version 20.100 (MedCalc Software, Ostend, Belgium). Two-tailed P values <0.05 were considered statistically significant. The characteristics of the study population are presented as mean with SD, median with interquartile range, or number with percentage. To compare characteristics between two PS-matched groups, Student’s t-test or the Mann–Whitney U test was used for continuous variables, while the chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test was applied for categorical variables. After the Shapiro–Wilk test that demonstrated non-normal distribution (P<0.0001), glycosylated hemoglobin was log-transformed to achieve a normal distribution of skewed data. Linear regression analyses using log-transformed glycosylated hemoglobin level as a dependent variable were conducted to determine the relative contribution of specific variables, including CGM use. In addition to the CGM use, age, sex, BMI, and systolic and diastolic BPs were used as potential independent variables. Additional multivariable analysis including age, sex, BMI, systolic BP, use of insulin pump, eGFR, and diabetes duration in addition to the CGM use was also conducted. Logistic regression analyses with uncontrolled (>8%) and controlled glycosylated hemoglobin (<7%) as dependent variables were performed to identify whether CGM use could influence these outcome variables. These analyses were performed in the crude (unadjusted) model and three multivariable-adjusted models (models 1, 2, and 3). Model 1 was adjusted for age, sex, diabetes duration, and BMI; model 2 was additionally adjusted for history of cerebral infarction and AMI during the previous 5 years from baseline, and presence of diabetic retinopathy and ESRD at baseline; and model 3 was adjusted for the use of insulin pump, and eGFR in addition to the potential confounders included in model 1. In subpopulations of CGM users who had been using official applications (i.e., not “do-it-yourself” [DIY] software) with at least 1 (n=87) or 3 (n=86) months of AGP data, standardized CGM metrics (including mean glucose, glycemic variability expressed as % coefficient of variation [CV], TIR, time above range, time below range, and percentage of time CGM is active) were summarized.
- Subgroup and sensitivity analyses
- We compared the glycosylated hemoglobin according to CGM use in subgroups categorized by age (<40 years vs. ≥40 years) and use of insulin pump, and after excluding isCGM users, RT-CGM users, users of CGM with official applications, users of CGM with DIY software, and those who initiated CGM at <40 or ≥40 years. Logistic regression analyses with uncontrolled (>8%) or controlled (<7%) glycosylated hemoglobin as dependent variables were also conducted in these subpopulations except for in insulin pump users because of too small number of subjects (n=16 including only four CGM users).
METHODS
- Baseline characteristics
- The study population consisted of 314 subjects, including CGM users (n=111) and 1:2 PS-matched (based on age, sex, and diabetes duration) CGM never-users (n=203). After PS matching, age, sex, and diabetes duration were well-balanced (Table 1, Supplementary Fig. 1). The baseline characteristics of the study population are presented according to CGM use (Table 1). Glycosylated hemoglobin and GA were significantly lower in CGM users than never-users. The mean±SD glycosylated hemoglobin level in CGM users was 7.13%±0.94%, while that in CGM never-users was 7.66%±1.37%. Other baseline characteristics were not significantly different between the two groups. Glycosylated hemoglobin level was also significantly lower in CGM users than never-users when analyzed by analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) with age, sex, diabetes duration, BMI, use of insulin pump, and eGFR values as covariate (Supplementary Table 1).
- CGM use was independently associated with log-transformed glycosylated hemoglobin level
- Linear regression analyses were conducted to identify independent predictors of log-transformed glycosylated hemoglobin level (Table 2). In univariable analysis, CGM use was independently associated with log-transformed glycosylated hemoglobin (P=0.0004). In multivariable analyses, among the potential covariates, log-transformed glycosylated hemoglobin concentration was independently associated with CGM use (P<0.0001 and P=0.0002).
- Association of uncontrolled (>8%) or controlled (<7%) glycosylated hemoglobin with CGM use
- Table 3 summarizes the results of logistic regression analysis with odds ratios predicting uncontrolled (>8%) or controlled (<7%) glycosylated hemoglobin according to CGM use. CGM users had 0.365 times odds (95% confidence interval, 0.190 to 0.703) of uncontrolled glycosylated hemoglobin (>8%) compared to never-users in the fully-adjusted model 3. CGM users had 1.861 times the odds (95% confidence interval, 1.119 to 3.096) of controlled glycosylated hemoglobin (<7%) compared to never-users in the fully-adjusted model 3.
- CGM metrics in CGM users with official applications
- Among CGM users with AGP data for at least 1 month (n=87) or 3 months (n=86), standardized CGM metrics were summarized (Table 4). In this analysis, individuals using non-official applications (DIY software), from which official AGP data were unavailable, were excluded. CGM metrics within recent 90-day periods were comparable to those within recent 30-day periods. The mean±SD TIRs within recent 30- and 90-day periods, respectively, were 62.45%±16.63% and 63.08%± 15.32%. Proportions of individuals with TIR >70% during recent 30- and 90-day periods were 32.2% (28 of 87) and 31.4% (27 of 86), respectively. The mean±SD glycemic variability, expressed as %CV, was 36.63%±5.46% during the recent 30-day period and 37.30%±7.94% during the recent 90-day period. The mean action time (percentage of time CGM is active) within the recent 30- and 90-day periods was maintained as >85%.
- Subgroup and sensitivity analyses
- Glycosylated hemoglobin levels were compared according to CGM use in various subpopulations (Supplementary Table 2). CGM users tended to have lower levels of glycosylated hemoglobin compared to never-users although statistical significance was not secured in three subpopulations (insulin pump users, subpopulation without RT-CGM users, and subpopulation including only CGM never-users and those who initiated CGM at ≥40 years) probably due to lack of number of subjects in a group. Logistic regression analyses with uncontrolled (>8%) or controlled (<7%) glycosylated hemoglobin as dependent variables conducted in various subpopulations (Supplementary Tables 3–7) also demonstrated trends of results consistent to the main analyses.
RESULTS
- This propensity-matched, cross-sectional, real-world study demonstrated that personal CGM use (for ≥9 months) was associated with glycemic control status of Korean adults with T1DM, and it presented the current CGM metrics among Korean adults with T1DM in a real-world clinical setting. In our study population with T1DM, glycosylated hemoglobin and GA levels were significantly lower in CGM users compared to PS-matched never-users, and CGM use was a determining factor of log-transformed glycosylated hemoglobin. CGM use, compared with non-use, was associated with 1.9 times greater odds of controlled glycosylated hemoglobin (<7%) and approximately one-third of the odds for uncontrolled glycosylated hemoglobin (>8%) among adults with T1DM in the real-world. These associations were consistently observed in subgroup and sensitivity analyses.
- Our findings are consistent with those of previous trials that demonstrated the benefits of CGM in improving glycemia in adults with T1DM [4–10]. In several randomized trials of adults with T1DM, CGM use with educational support was shown to reduce glycosylated hemoglobin [4–10] and frequency of hypoglycemia [17–20]. However, to obtain these clinical benefits of CGM, systematic educational support and training are mandatory [11,12]. A small, randomized trial in underserved, less educated adults with T1DM failed to show a significant reduction in glycosylated hemoglobin with CGM use [14]. In the United States, according to an analysis of the type 1 diabetes (T1D) Exchange registry [15], the mean glycosylated hemoglobin changed little between 2010–2012 and 2016–2018 and seemed to have worsened especially in adolescents, although CGM use, which was associated with lower glycosylated hemoglobin level, has expanded substantially in recent years. Nevertheless, our study provided evidence of an association between CGM use and glycemia among Korean adults with T1DM in the real-world. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first study to assess the relationship between CGM use and glycemic control state of Korean adults with T1DM in the real-world. Our findings suggest that clinical benefits of CGM can be obtained also in the real-world. Similarly, a recent analysis of 752 Korean children and adolescents with T1DM during 2010 to 2019 reported that CGM use was associated with lower mean glycosylated hemoglobin level and a reduced incidence of diabetic ketoacidosis [2].
- Among CGM users with available AGP data included in our study, the mean TIR was 62.45% for the recent 30-day period and 63.08% for the recent 90-day period. Less than one-third of those with available AGP data exhibited TIR of >70% during recent 30- and 90-day periods. The mean glycemic variability (%CV) was 36.63% during the recent 30-day period and 37.30% during the recent 90-day period. Even though glycemic targets should be individualized based on patient characteristics, standard targets for general populations with T1DM are >70% for TIR and ≤36% for glycemic variability presented as %CV [1]. Several studies have demonstrated correlations of TIR with diabetes complications, including diabetic retinopathy and albuminuria [21–23], as well as an inverse relationship between TIR and glycosylated hemoglobin [24,25]. Among adults with T1DM, a TIR of 70% strongly corresponded with a glycosylated hemoglobin concentration of approximately 7%, and a 10% increase in TIR corresponded with an approximately 0.5% decrease in glycosylated hemoglobin [24]. A higher %CV has been associated with a minimum glucose level <70 mg/dL during three-day CGM, regardless of diabetes type [26]. Furthermore, in individuals with diabetes, particularly insulin-treated people, the frequency of hypoglycemia has been reported to vary significantly with a %CV threshold of 36%, supporting a %CV of 36% as a reasonable criterion to discriminate between stable and unstable glycemia in diabetes [27]. Considering these standard targets based on an increasing body of evidence, CGM metrics among Korean adults with T1DM in this real-world study might need further improvement.
- Nevertheless, TIR values of CGM users with available AGP data in our study were relatively favorable compared to those reported in previous studies of people with T1DM. TIR within recent 90 days was stable enough to be comparable to that within recent 30-day periods and showed similar values to that observed in clinical trials that provided structured education combined with CGM use. Previously, CGM metrics of 545 adults with T1DM from four randomized trials were analyzed [24]. Participants included in their analyses were in an intervention arm of trials that assessed CGM as an intervention over a 6-month period. In their analyses [24], mean TIR at baseline was 58%, and ranged from 46% to 64% according to trials. In month 6, mean TIR changed to 61% (51% to 70% according to trials), which is comparable to that of our study (62.45% during recent 30 days and 63.08% during recent 90 days). Furthermore, in a single-center, 3-month, randomized controlled trial conducted at our center among people with T1DM, TIR was significantly higher in participants provided with structured individualized education combined with CGM use than in controls with CGM alone [13]. In this clinical trial [13], mean TIR at week 12 was only 44.5% in the control group whereas that in the education group was 63.4%, comparable to that in our study population with available AGP data. These favorable TIR values and better glycemia among CGM users than never-users in our study may have originated from the inclusion of continuous CGM users for at least 9 months (considered to be adherent to continuous CGM use) and education programs at our center. At our Endocrinology Department, specialized clinics are operated for the systematic education and training of people with T1DM. The education program provided at these clinics include interpretation of CGM metrics and adjustment of insulin regimen based on these interpretations for CGM users.
- Several limitations of this study should be acknowledged. First, the cross-sectional design of this study can limit the clarification of causal relationships. Second, despite PS matching based on age, sex, and diabetes duration, and an adjustment for potential confounders during logistic regression analyses, the possibility of residual confounding effects cannot be excluded. For example, CGM users might include people more motivated to manage their diabetes. Third, as a single-center study conducted at a hospital-based tertiary referral center, our study population might not represent general Korean adults with T1DM. Also, the diabetes education and support systems at our center may differ from those of other centers. Fourth, standardized CGM metrics were analyzed only among CGM users who had been using official applications so that AGP data were available. Individuals who had been using non-official applications (DIY software) were excluded, which raises the possibility of selection bias. Considering that the median glycosylated hemoglobin level in DIY software users (6.70%) was significantly lower than that in official application users (7.10%) (P=0.0181) and DIY software users are likely to be active patient groups, these patients might have had more favorable CGM metrics and have contributed to the improved glycemia among CGM users. Last, we could not address the effect of CGM on glycemia according to educational status, support system, and adherence of patients. CGM users (for ≥9 months) included in our study are presumed to be adherent to CGM use and repeatedly educated for better implementation of CGM considering the routine education programs provided at our center.
- In conclusion, CGM use, compared to never-use, was associated with better glycemia among Korean adults with T1DM in the real-world. Our findings indicate that potential clinical benefits of CGM can be expected even in a real-world setting where appropriate user trainings are provided for individuals adherent to continuous CGM use. Regarding the standard targets for general populations with T1DM, standardized CGM metrics, including TIR and %CV of Korean adults with T1DM, in this real-world study might need further improvement. Further research encompassing participants with diverse educational status, support system and compliance in the real-world may be needed to further clarify the individual role of these factors.
DISCUSSION
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Fig. 1.
-
Acknowledgements
- The authors thank the Biostatistics Department of Samsung Biomedical Research Institute for its statistical assistance.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception or design: Y.B.L., J.H.K.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: Y.B.L., M.K.
Drafting the work or revising: Y.B.L., M.K., J.H.K.
Final approval of the manuscript: Y.B.L., M.K., J.H.K.
-
FUNDING
None
NOTES
| Characteristic | Total (n=314) | CGM never-users (n=203) | CGM users (n=111) | P value | SMD before matching | SMD after 1:2 PS matching |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matching variables | ||||||
| Ageb, yr | 38.00 (31.00–49.00) | 38.00 (31.00–50.00) | 38.00 (30.00–48.00) | 0.7072 | 0.664 | 0.037 |
| Male sex | 137 (43.63) | 91 (44.83) | 46 (41.44) | 0.5630 | 0.194 | 0.068 |
| Diabetes durationb, yr | 10.00 (4.00–18.00) | 10.00 (4.00–18.00) | 10.00 (5.00–18.00) | 0.8739 | 0.352 | 0.073 |
|
|
||||||
| Other variables | Missing (n) in CGM never-users | Missing (n) in CGM users | ||||
| BMIb, kg/m2 | 22.47 (21.02–24.14) | 22.47 (21.02–24.02) | 22.47 (20.92–24.20) | 0.7339 | 0 | 0 |
| Systolic BPa, mm Hg | 121.88±16.28 | 121.62±16.51 | 122.34±15.94 | 0.7230 | 25 | 12 |
| Diastolic BPa, mm Hg | 69.66±11.67 | 68.98±11.71 | 70.88±11.55 | 0.1957 | 25 | 12 |
| Total daily dose of insulinb, IU | 40.00 (28.10–54.00) | 40.00 (28.00–55.00) | 40.00 (29.00–50.00) | 0.8746 | 1 | 12 |
| Use of insulin pump | 16 (5.10) | 12 (5.91) | 4 (3.60) | 0.4341 | 0 | 0 |
| Total cholesterolb, mg/dL | 161.00 (141.50–185.00) | 159.00 (142.00–185.00) | 166.00 (141.00–187.00) | 0.2511 | 5 | 1 |
| Triglyceridesb, mg/dL | 69.00 (54.00–90.00) | 71.00 (54.00–96.00) | 65.50 (53.00–85.00) | 0.2413 | 6 | 1 |
| HDL-Cb, mg/dL | 66.00 (55.00–81.00) | 65.00 (54.00–80.00) | 67.50 (56.00–81.00) | 0.3493 | 6 | 1 |
| LDL-Cb, mg/dL | 89.00 (72.00–114.00) | 89.00 (72.00–110.00) | 93.00 (76.00–120.00) | 0.1822 | 6 | 1 |
| ASTb, U/L | 20.00 (16.00–24.00) | 20.00 (17.00–25.00) | 19.00 (16.00–23.00) | 0.1078 | 5 | 1 |
| ALTb, U/L | 16.00 (11.00–22.50) | 17.00 (11.00–23.00) | 15.00 (10.00–22.00) | 0.1423 | 5 | 1 |
| BUNb, mg/dL | 12.90 (10.80–16.80) | 13.05 (10.80–17.10) | 12.80 (10.50–16.20) | 0.3756 | 5 | 1 |
| Creatinineb, mg/dL | 0.77 (0.65–0.90) | 0.77 (0.66–0.90) | 0.77 (0.64–0.90) | 0.4402 | 10 | 8 |
| eGFRb,c, mL/min/1.73 m2 | 108.70 (92.20–117.40) | 107.80 (91.80–117.20) | 109.80 (95.40–119.20) | 0.3515 | 10 | 8 |
| Glycosylated hemoglobinb, % | 7.20 (6.70–8.00) | 7.40 (6.90–8.30) | 7.00 (6.50–7.60) | 0.0005 | 0 | 0 |
| Fasting plasma glucoseb, mg/dL | 146.00 (114.00–190.00) | 144.00 (111.00–188.00) | 149.50 (122.00–193.00) | 0.2313 | 40 | 5 |
| Glycated albuminb, % | 21.55 (18.60–25.10) | 21.80 (18.90–25.80) | 20.80 (18.50–23.60) | 0.0387 | 26 | 2 |
| Cerebral infarction | 1 (0.32) | 0 | 1 (0.90) | 0.3535 | 0 | 0 |
| Acute myocardial infarction | 1 (0.32) | 0 | 1 (0.90) | 0.3535 | 0 | 0 |
| Diabetic retinopathy | 69 (21.97) | 49 (24.14) | 20 (18.02) | 0.2106 | 0 | 0 |
| End-stage renal disease | 23 (7.32) | 15 (7.39) | 8 (7.21) | 0.9528 | 0 | 0 |
Values are presented as median (interquartile range), number (%), or mean±standard deviation. Chi-square test or Fisher’s exact test was applied for categorical variables.
CGM, continuous glucose monitoring; SMD, standardized mean difference; PS, propensity score; BMI, body mass index; BP, blood pressure; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate.
a Continuous variables with normal distributions were compared using Student’s t-test,
b Continuous variables with non-normal distributions were compared using Mann–Whitney U test,
c The Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration (CKD-EPI) equation was used to calculate the eGFR.
Logistic regression analysis with uncontrolled glycosylated hemoglobin (>8%) as a dependent variable was performed to identify whether CGM use could influence this outcome variable. Model 1: Adjusted for age, sex, diabetes duration and body mass index; Model 2: Adjusted for model 1 plus history of cerebral infarction and acute myocardial infarction during the previous 5 years from baseline, and presence of diabetic retinopathy and end-stage renal disease at baseline; Model 3: Adjusted for model 1 plus use of insulin pump, and estimated glomerular filtration rate.
CGM, continuous glucose monitoring.
- 1. Battelino T, Danne T, Bergenstal RM, Amiel SA, Beck R, Biester T, et al. Clinical targets for continuous glucose monitoring data interpretation: recommendations from the international consensus on time in range. Diabetes Care 2019;42:1593-603.PubMedPMC
- 2. Choe J, Won SH, Choe Y, Park SH, Lee YJ, Lee J, et al. Temporal trends for diabetes management and glycemic control between 2010 and 2019 in Korean children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 2022;24:201-11.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Danne T, Nimri R, Battelino T, Bergenstal RM, Close KL, DeVries JH, et al. International consensus on use of continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care 2017;40:1631-40.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 4. Beck RW, Riddlesworth T, Ruedy K, Ahmann A, Bergenstal R, Haller S, et al. Effect of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes using insulin injections: the DIAMOND Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017;317:371-8.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Lind M, Polonsky W, Hirsch IB, Heise T, Bolinder J, Dahlqvist S, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring vs conventional therapy for glycemic control in adults with type 1 diabetes treated with multiple daily insulin injections: the GOLD Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017;317:379-87.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Tumminia A, Crimi S, Sciacca L, Buscema M, Frittitta L, Squatrito S, et al. Efficacy of real-time continuous glucose monitoring on glycaemic control and glucose variability in type 1 diabetic patients treated with either insulin pumps or multiple insulin injection therapy: a randomized controlled crossover trial. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2015;31:61-8.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Juvenile Diabetes Research Foundation Continuous Glucose Monitoring Study Group. Tamborlane WV, Beck RW, Bode BW, Buckingham B, Chase HP, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring and intensive treatment of type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;359:1464-76.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Battelino T, Conget I, Olsen B, Schutz-Fuhrmann I, Hommel E, Hoogma R, et al. The use and efficacy of continuous glucose monitoring in type 1 diabetes treated with insulin pump therapy: a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2012;55:3155-62.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Deiss D, Bolinder J, Riveline JP, Battelino T, Bosi E, Tubiana-Rufi N, et al. Improved glycemic control in poorly controlled patients with type 1 diabetes using real-time continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Care 2006;29:2730-2.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 10. O’Connell MA, Donath S, O’Neal DN, Colman PG, Ambler GR, Jones TW, et al. Glycaemic impact of patient-led use of sensor-guided pump therapy in type 1 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2009;52:1250-7.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 11. American Diabetes Association. 7. Diabetes technology: standards of medical care in diabetes-2021. Diabetes Care 2021;44(Suppl 1):S85-99.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Hur KY, Moon MK, Park JS, Kim SK, Lee SH, Yun JS, et al. 2021 Clinical practice guidelines for diabetes mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association. Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:461-81.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 13. Yoo JH, Kim G, Lee HJ, Sim KH, Jin SM, Kim JH. Effect of structured individualized education on continuous glucose monitoring use in poorly controlled patients with type 1 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2022;184:109209.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Sequeira PA, Montoya L, Ruelas V, Xing D, Chen V, Beck R, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring pilot in low-income type 1 diabetes patients. Diabetes Technol Ther 2013;15:855-8.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Foster NC, Beck RW, Miller KM, Clements MA, Rickels MR, DiMeglio LA, et al. State of type 1 diabetes management and outcomes from the T1D exchange in 2016–2018. Diabetes Technol Ther 2019;21:66-72.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Levey AS, Stevens LA, Schmid CH, Zhang YL, Castro AF 3rd, Feldman HI, et al. A new equation to estimate glomerular filtration rate. Ann Intern Med 2009;150:604-12.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Bolinder J, Antuna R, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn P, Kroger J, Weitgasser R. Novel glucose-sensing technology and hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre, non-masked, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2016;388:2254-63.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Seyed Ahmadi S, Westman K, Pivodic A, Olafsdottir AF, Dahlqvist S, Hirsch IB, et al. The association between HbA1c and time in hypoglycemia during CGM and self-monitoring of blood glucose in people with type 1 diabetes and multiple daily insulin injections: a randomized clinical trial (GOLD-4). Diabetes Care 2020;43:2017-24.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 19. Heinemann L, Freckmann G, Ehrmann D, Faber-Heinemann G, Guerra S, Waldenmaier D, et al. Real-time continuous glucose monitoring in adults with type 1 diabetes and impaired hypoglycaemia awareness or severe hypoglycaemia treated with multiple daily insulin injections (HypoDE): a multicentre, randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2018;391:1367-77.ArticlePubMed
- 20. van Beers CA, DeVries JH, Kleijer SJ, Smits MM, Geelhoed-Duijvestijn PH, Kramer MH, et al. Continuous glucose monitoring for patients with type 1 diabetes and impaired awareness of hypoglycaemia (IN CONTROL): a randomised, open-label, crossover trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 2016;4:893-902.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Lu J, Ma X, Zhou J, Zhang L, Mo Y, Ying L, et al. Association of time in range, as assessed by continuous glucose monitoring, with diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2018;41:2370-6.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 22. Beck RW, Bergenstal RM, Riddlesworth TD, Kollman C, Li Z, Brown AS, et al. Validation of time in range as an outcome measure for diabetes clinical trials. Diabetes Care 2019;42:400-5.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 23. Yoo JH, Choi MS, Ahn J, Park SW, Kim Y, Hur KY, et al. Association between continuous glucose monitoring-derived time in range, other core metrics, and albuminuria in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 2020;22:768-76.ArticlePubMed
- 24. Beck RW, Bergenstal RM, Cheng P, Kollman C, Carlson AL, Johnson ML, et al. The relationships between time in range, hyperglycemia metrics, and HbA1c. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2019;13:614-26.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 25. Vigersky RA, McMahon C. The relationship of hemoglobin A1C to time-in-range in patients with diabetes. Diabetes Technol Ther 2019;21:81-5.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Jin SM, Kim TH, Bae JC, Hur KY, Lee MS, Lee MK, et al. Clinical factors associated with absolute and relative measures of glycemic variability determined by continuous glucose monitoring: an analysis of 480 subjects. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2014;104:266-72.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Monnier L, Colette C, Wojtusciszyn A, Dejager S, Renard E, Molinari N, et al. Toward defining the threshold between low and high glucose variability in diabetes. Diabetes Care 2017;40:832-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Real-World Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data from a Population with Type 1 Diabetes in South Korea: Nationwide Single-System Analysis
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Sarah B. Andrade, Boyang Chen, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Accuracy and Safety of the 15-Day CareSens Air Continuous Glucose Monitoring System
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Won Sang Yoo, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2024; 26(4): 222. CrossRef - Navigating the Seas of Glycemic Control: The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(3): 345. CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef
- Figure
- Related articles
-
- Risk of Depression according to Cumulative Exposure to a Low-Household Income Status in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population- Based Study
- Clinical and Lifestyle Determinants of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Metrics in Insulin-Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Navigating the Seas of Glycemic Control: The Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Data Analysis
- Real-World Prescription Patterns and Barriers Related to the Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors among Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease

 KDA
KDA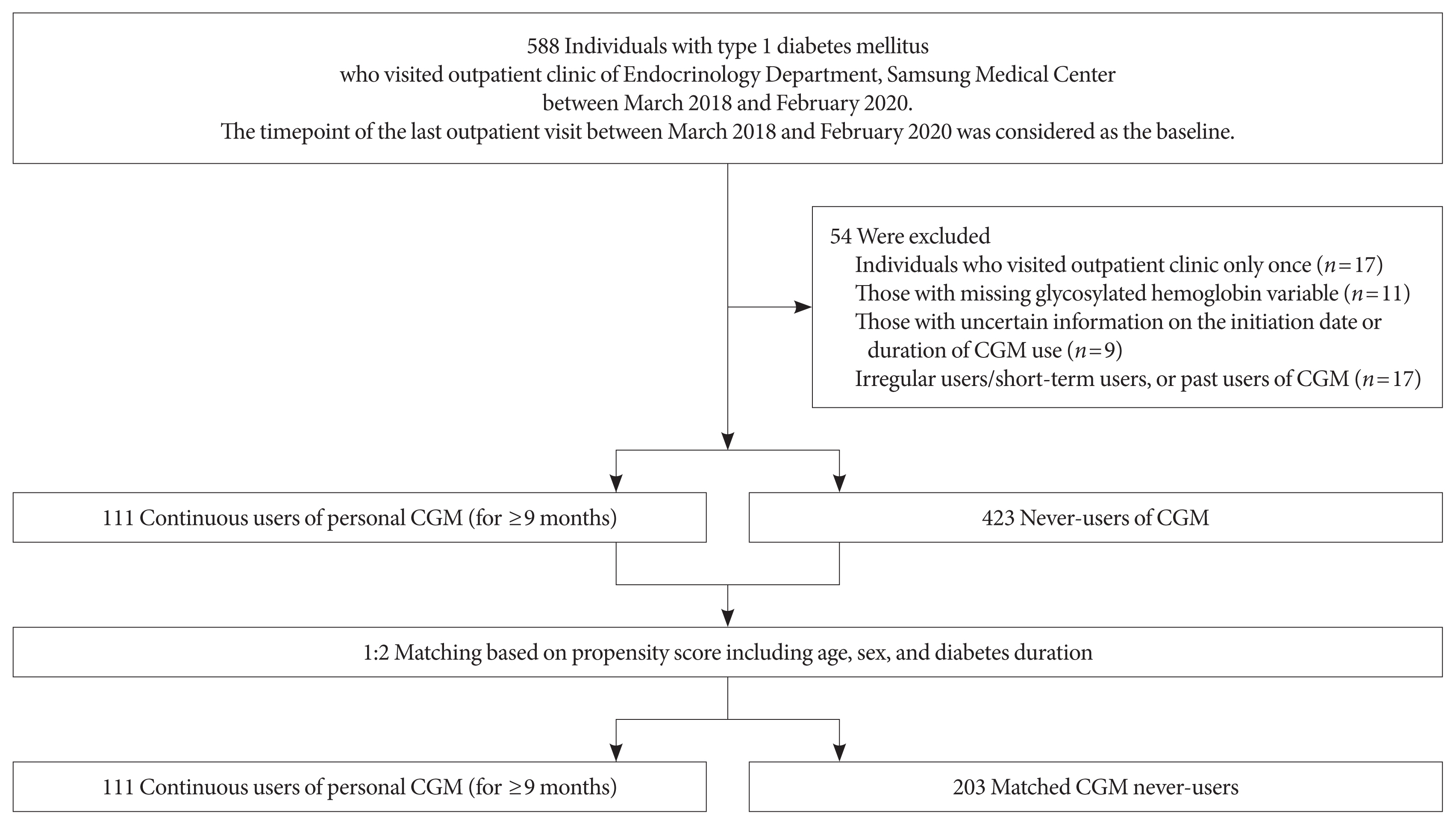
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite