
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 40(2); 2016 > Article
-
Original ArticleClinical Care/Education Clinical Evaluation of OneTouch Diabetes Management Software System in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
-
Jung Min Kim1, Hey Jean Lee2, Keum Ok Kim1, Jong Chul Won1, Kyung Soo Ko1
 , Byung Doo Rhee1
, Byung Doo Rhee1 -
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2016;40(2):129-139.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.2.129
Published online: April 5, 2016
1Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
2Department of Preventive Medicine, Kangwon National University Hospital, Kangwon National University School of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Kyung Soo Ko. Department of Internal Medicine, Cardiovascular and Metabolic Disease Center, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, 1342 Dongil-ro, Nowon-gu, Seoul 01757, Korea. kskomd@paik.ac.kr
• Received: May 19, 2015 • Accepted: October 2, 2015
Copyright © 2016 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Quality improvement strategies for diabetes care: Effects on outcomes for adults living with diabetes
Kristin J Konnyu, Sharlini Yogasingam, Johanie Lépine, Katrina Sullivan, Mostafa Alabousi, Alun Edwards, Michael Hillmer, Sathya Karunananthan, John N Lavis, Stefanie Linklater, Braden J Manns, David Moher, Sameh Mortazhejri, Samir Nazarali, P. Alison Pap
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Emerging technologies for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Nirali A. Shah, Carol J. Levy
Journal of Diabetes.2021; 13(9): 713. CrossRef - Peripartum Management of Gestational Diabetes Using a Digital Health Care Service: A Pilot, Randomized Controlled Study
Ji-Hee Sung, Da Young Lee, Kyoung Pil Min, Cheol-Young Park
Clinical Therapeutics.2019; 41(11): 2426. CrossRef - Impact of initial active engagement in self-monitoring with a telemonitoring device on glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes
Min-Kyung Lee, Kwang-Hyeon Lee, Seung-Hyun Yoo, Cheol-Young Park
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential of OneTouch Diabetes Management Software System in Real Field for Korean Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Borami Kang, Jae Hyoung Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(2): 115. CrossRef
- Figure
- Related articles
-
- Risk Prediction and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in People Living with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Clinical and Lifestyle Determinants of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Metrics in Insulin-Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- The Role of Echocardiography in Evaluating Cardiovascular Diseases in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- Clinical Effects of a Home Care Pilot Program for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- Safety of COVID-19 Vaccines among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Data Analysis

 KDA
KDA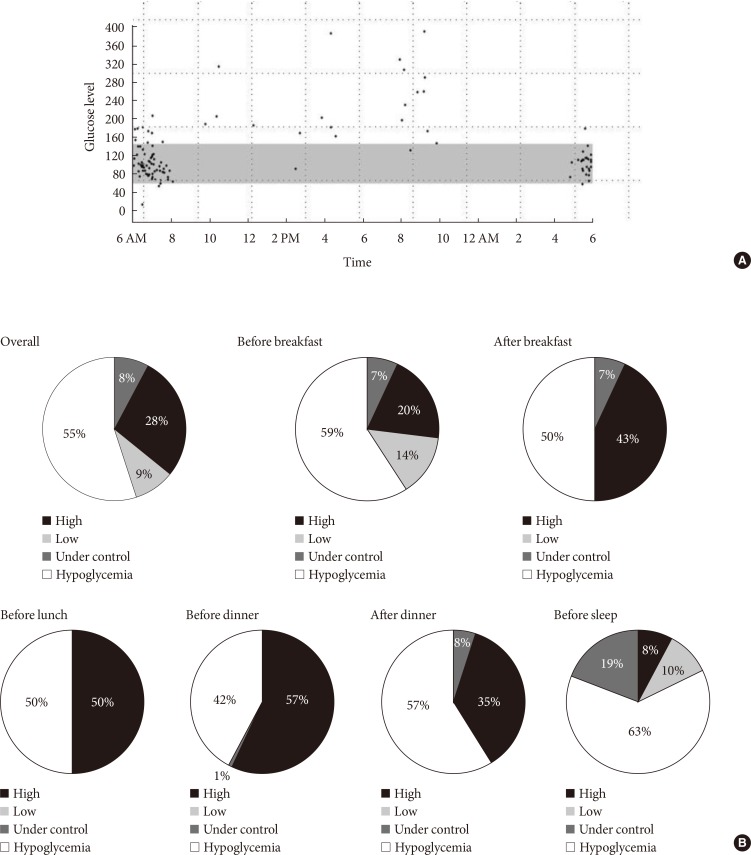
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite




