
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Others
- Risk Prediction and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in People Living with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ying-Guat Ooi, Tharsini Sarvanandan, Nicholas Ken Yoong Hee, Quan-Hziung Lim, Sharmila S. Paramasivam, Jeyakantha Ratnasingam, Shireene R. Vethakkan, Soo-Kun Lim, Lee-Ling Lim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):196-207. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0244
- 1,838 View
- 350 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
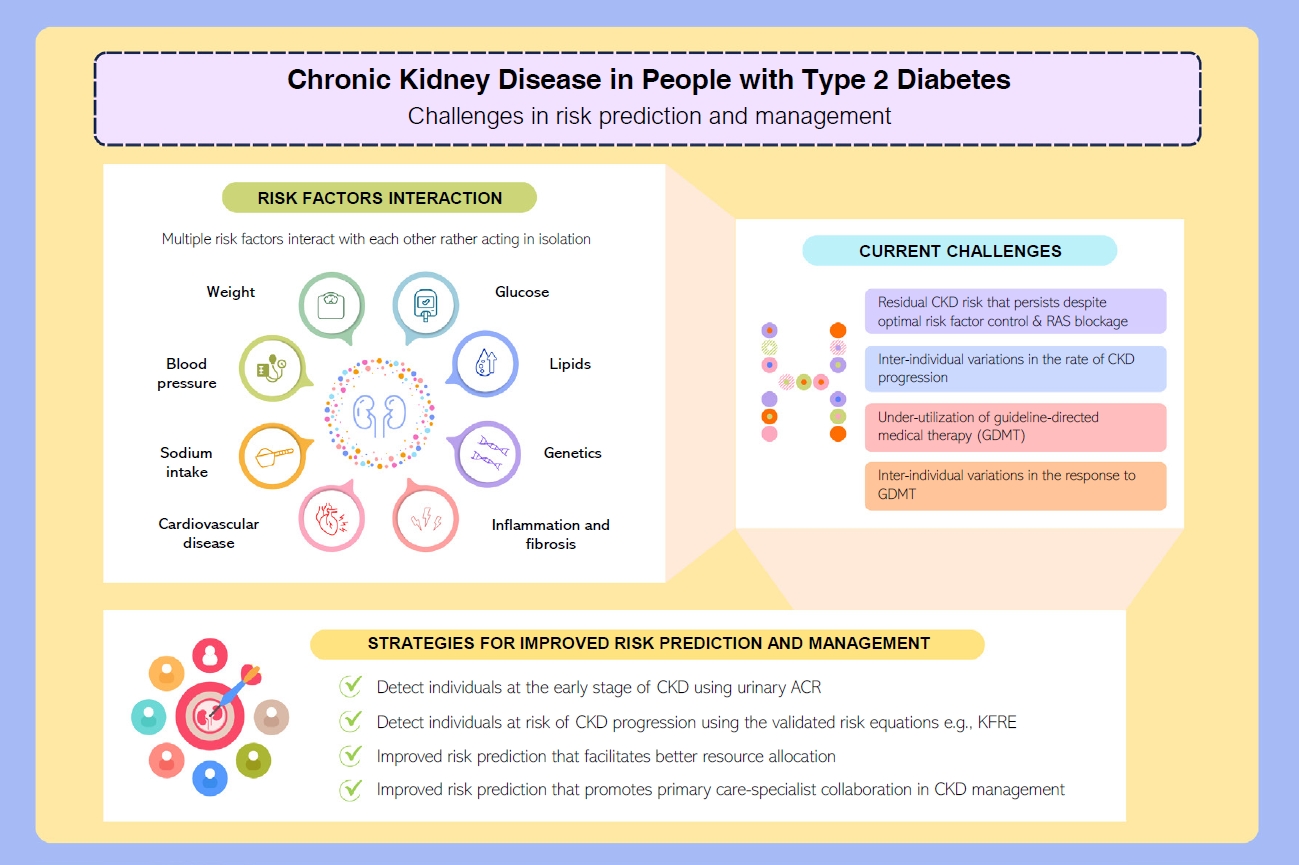
ePub - People with type 2 diabetes mellitus have increased risk of chronic kidney disease and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Improved care delivery and implementation of guideline-directed medical therapy have contributed to the declining incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in high-income countries. By contrast, the global incidence of chronic kidney disease and associated mortality is either plateaued or increased, leading to escalating direct and indirect medical costs. Given limited resources, better risk stratification approaches to identify people at risk of rapid progression to end-stage kidney disease can reduce therapeutic inertia, facilitate timely interventions and identify the need for early nephrologist referral. Among people with chronic kidney disease G3a and beyond, the kidney failure risk equations (KFRE) have been externally validated and outperformed other risk prediction models. The KFRE can also guide the timing of preparation for kidney replacement therapy with improved healthcare resources planning and may prevent multiple complications and premature mortality among people with chronic kidney disease with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. The present review summarizes the evidence of KFRE to date and call for future research to validate and evaluate its impact on cardiovascular and mortality outcomes, as well as healthcare resource utilization in multiethnic populations and different healthcare settings.
- Others
- Development of Various Diabetes Prediction Models Using Machine Learning Techniques
- Juyoung Shin, Jaewon Kim, Chanjung Lee, Joon Young Yoon, Seyeon Kim, Seungjae Song, Hun-Sung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):650-657. Published online March 11, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0115
- 4,792 View
- 293 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
There are many models for predicting diabetes mellitus (DM), but their clinical implication remains vague. Therefore, we aimed to create various DM prediction models using easily accessible health screening test parameters.
Methods
Two sets of variables were used to develop eight DM prediction models. One set comprised 62 easily accessible examination results of commonly used variables from a tertiary university hospital. The second set comprised 27 of the 62 variables included in the national routine health checkups. Gradient boosting and random forest algorithms were used to develop the models. Internal validation was performed using the stratified 10-fold cross-validation method.
Results
The area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC-AUC) for the 62-variable DM model making 12-month predictions for subjects without diabetes was the largest (0.928) among those of the eight DM prediction models. The ROC-AUC dropped by more than 0.04 when training with the simplified 27-variable set but still showed fairly good performance with ROC-AUCs between 0.842 and 0.880. The accuracy was up to 11.5% higher (from 0.807 to 0.714) when fasting glucose was included.
Conclusion
We created easily applicable diabetes prediction models that deliver good performance using parameters commonly assessed during tertiary university hospital and national routine health checkups. We plan to perform prospective external validation, hoping that the developed DM prediction models will be widely used in clinical practice. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictive modeling for the development of diabetes mellitus using key factors in various machine learning approaches
Marenao Tanaka, Yukinori Akiyama, Kazuma Mori, Itaru Hosaka, Kenichi Kato, Keisuke Endo, Toshifumi Ogawa, Tatsuya Sato, Toru Suzuki, Toshiyuki Yano, Hirofumi Ohnishi, Nagisa Hanawa, Masato Furuhashi
Diabetes Epidemiology and Management.2024; 13: 100191. CrossRef - Validation of the Framingham Diabetes Risk Model Using Community-Based KoGES Data
Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park, Young Sun Hong
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrated Embedded system for detecting diabetes mellitus using various machine learning techniques
Rishita Konda, Anuraag Ramineni, Jayashree J, Niharika Singavajhala, Sai Akshaj Vanka
EAI Endorsed Transactions on Pervasive Health and Technology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Present and Future of Artificial Intelligence-Based Medical Image in Diabetes Mellitus: Focus on Analytical Methods and Limitations of Clinical Use
Ji-Won Chun, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine learning for predicting diabetic metabolism in the Indian population using polar metabolomic and lipidomic features
Nikita Jain, Bhaumik Patel, Manjesh Hanawal, Anurag R. Lila, Saba Memon, Tushar Bandgar, Ashutosh Kumar
Metabolomics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Retrospective cohort analysis comparing changes in blood glucose level and body composition according to changes in thyroid‐stimulating hormone level
Hyunah Kim, Da Young Jung, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Jae‐Hyoung Cho, Hyeon Woo Yim, Hun‐Sung Kim
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(9): 620. CrossRef - Improving Machine Learning Diabetes Prediction Models for the Utmost Clinical Effectiveness
Juyoung Shin, Joonyub Lee, Taehoon Ko, Kanghyuck Lee, Yera Choi, Hun-Sung Kim
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(11): 1899. CrossRef
- Predictive modeling for the development of diabetes mellitus using key factors in various machine learning approaches
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Validation of Risk Prediction Models for Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in a Prospective Korean Community-Based Cohort
- Jae Hyun Bae, Min Kyong Moon, Sohee Oh, Bo Kyung Koo, Nam Han Cho, Moon-Kyu Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):458-469. Published online January 13, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0061
- 6,866 View
- 225 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background To investigate the performance of the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Pooled Cohort Equations (PCE) in a large, prospective, community-based cohort in Korea and to compare it with that of the Framingham Global Cardiovascular Disease Risk Score (FRS-CVD) and the Korean Risk Prediction Model (KRPM).
Methods In the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KOGES)-Ansan and Ansung study, we evaluated calibration and discrimination of the PCE for non-Hispanic whites (PCE-WH) and for African Americans (PCE-AA) and compared their predictive abilities with the FRS-CVD and the KRPM.
Results The present study included 7,932 individuals (3,778 men and 4,154 women). The PCE-WH and PCE-AA moderately overestimated the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) for men (6% and 13%, respectively) but underestimated the risk for women (−49% and −25%, respectively). The FRS-CVD overestimated ASCVD risk for men (91%) but provided a good risk prediction for women (3%). The KRPM underestimated ASCVD risk for men (−31%) and women (−31%). All the risk prediction models showed good discrimination in both men (C-statistic 0.730 to 0.735) and women (C-statistic 0.726 to 0.732). Recalibration of the PCE using data from the KOGES-Ansan and Ansung study substantially improved the predictive accuracy in men.
Conclusion In the KOGES-Ansan and Ansung study, the PCE overestimated ASCVD risk for men and underestimated the risk for women. The PCE-WH and the FRS-CVD provided an accurate prediction of ASCVD in men and women, respectively.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk Factors for Infertility in Korean Women
Juyeon Lee, Chang-Woo Choo, Kyoung Yong Moon, Sang Woo Lyu, Hoon Kim, Joong Yeup Lee, Jung Ryeol Lee, Byung Chul Jee, Kyungjoo Hwang, Seok Hyun Kim, Sue K. Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating cardiovascular disease risk stratification using multiple-polygenic risk scores and pooled cohort equations: insights from a 17-year longitudinal Korean cohort study
Yi Seul Park, Hye-Mi Jang, Ji Hye Park, Bong-Jo Kim, Hyun-Young Park, Young Jin Kim
Frontiers in Genetics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Moderation of Weight Misperception on the Associations Between Obesity Indices and Estimated Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Kayoung Lee
International Journal of Behavioral Medicine.2023; 30(1): 89. CrossRef - Validation of the general Framingham Risk Score (FRS), SCORE2, revised PCE and WHO CVD risk scores in an Asian population
Sazzli Shahlan Kasim, Nurulain Ibrahim, Sorayya Malek, Khairul Shafiq Ibrahim, Muhammad Firdaus Aziz, Cheen Song, Yook Chin Chia, Anis Safura Ramli, Kazuaki Negishi, Nafiza Mat Nasir
The Lancet Regional Health - Western Pacific.2023; 35: 100742. CrossRef - Principles of cardiovascular risk management in perimenopausal women with type 2 diabetes
F. O. Ushanova, T. Yu. Demidova, T. N. Korotkova
FOCUS. Endocrinology.2023; 4(2): 19. CrossRef - Prediction of the 10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in the Korean population
Sangwoo Park, Yong-Giun Kim, Soe Hee Ann, Young-Rak Cho, Shin-Jae Kim, Seungbong Han, Gyung-Min Park
Epidemiology and Health.2023; 45: e2023052. CrossRef - Triglyceride-Glucose Index Predicts Future Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Diseases: A 16-Year Follow-up in a Prospective, Community-Dwelling Cohort Study
Joon Ho Moon, Yongkang Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Jae Hoon Moon, Soo Heon Kwak, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi, Nam H. Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(4): 406. CrossRef - Validity of the models predicting 10-year risk of cardiovascular diseases in Asia: A systematic review and prediction model meta-analysis
Mahin Nomali, Davood Khalili, Mehdi Yaseri, Mohammad Ali Mansournia, Aryan Ayati, Hossein Navid, Saharnaz Nedjat, Hean Teik Ong
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(11): e0292396. CrossRef - Assessing the Validity of the Criteria for the Extreme Risk Category of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2022; 11(1): 73. CrossRef - Mediation of Grip Strength on the Association Between Self-Rated Health and Estimated Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Kayoung Lee
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2022; 20(6): 344. CrossRef - Implications of the heterogeneity between guideline recommendations for the use of low dose aspirin in primary prevention of cardiovascular disease
Xiao-Ying Li, Li Li, Sang-Hoon Na, Francesca Santilli, Zhongwei Shi, Michael Blaha
American Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2022; 11: 100363. CrossRef - The Risk of Cardiovascular Disease According to Chewing Status Could Be Modulated by Healthy Diet in Middle-Aged Koreans
Hyejin Chun, Jongchul Oh, Miae Doo
Nutrients.2022; 14(18): 3849. CrossRef - Management of Cardiovascular Risk in Perimenopausal Women with Diabetes
Catherine Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 492. CrossRef - Comparative performance of the two pooled cohort equations for predicting atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease
Alessandra M. Campos-Staffico, David Cordwin, Venkatesh L. Murthy, Michael P. Dorsch, Jasmine A. Luzum
Atherosclerosis.2021; 334: 23. CrossRef - Usefulness of Relative Handgrip Strength as a Simple Indicator of Cardiovascular Risk in Middle-Aged Koreans
Won Bin Kim, Jun-Bean Park, Yong-Jin Kim
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2021; 362(5): 486. CrossRef
- Risk Factors for Infertility in Korean Women
- Epidemiology
- Development and Validation of the Korean Diabetes Risk Score: A 10-Year National Cohort Study
- Kyoung Hwa Ha, Yong-ho Lee, Sun Ok Song, Jae-woo Lee, Dong Wook Kim, Kyung-hee Cho, Dae Jung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(5):402-414. Published online July 6, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0014
- 5,825 View
- 114 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background A diabetes risk score in Korean adults was developed and validated.
Methods This study used the National Health Insurance Service-National Health Screening Cohort (NHIS-HEALS) of 359,349 people without diabetes at baseline to derive an equation for predicting the risk of developing diabetes, using Cox proportional hazards regression models. External validation was conducted using data from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study. Calibration and discrimination analyses were performed separately for men and women in the development and validation datasets.
Results During a median follow-up of 10.8 years, 37,678 cases (event rate=10.4 per 1,000 person-years) of diabetes were identified in the development cohort. The risk score included age, family history of diabetes, alcohol intake (only in men), smoking status, physical activity, use of antihypertensive therapy, use of statin therapy, body mass index, systolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, fasting glucose, and γ glutamyl transferase (only in women). The C-statistics for the models for risk at 10 years were 0.71 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.70 to 0.73) for the men and 0.76 (95% CI, 0.75 to 0.78) for the women in the development dataset. In the validation dataset, the C-statistics were 0.63 (95% CI, 0.53 to 0.73) for men and 0.66 (95% CI, 0.55 to 0.76) for women.
Conclusion The Korean Diabetes Risk Score may identify people at high risk of developing diabetes and may be an effective tool for delaying or preventing the onset of condition as risk management strategies involving modifiable risk factors can be recommended to those identified as at high risk.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Alanine to glycine ratio is a novel predictive biomarker for type 2 diabetes mellitus
Kwang Seob Lee, Yong‐ho Lee, Sang‐Guk Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(3): 980. CrossRef - Associations of updated cardiovascular health metrics, including sleep health, with incident diabetes and cardiovascular events in older adults with prediabetes: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Seung Jin Han
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 203: 110820. CrossRef - Comparisons of the prediction models for undiagnosed diabetes between machine learning versus traditional statistical methods
Seong Gyu Choi, Minsuk Oh, Dong–Hyuk Park, Byeongchan Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Sun Ha Jee, Justin Y. Jeon
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk prediction models for incident type 2 diabetes in Chinese people with intermediate hyperglycemia: a systematic literature review and external validation study
Shishi Xu, Ruth L. Coleman, Qin Wan, Yeqing Gu, Ge Meng, Kun Song, Zumin Shi, Qian Xie, Jaakko Tuomilehto, Rury R. Holman, Kaijun Niu, Nanwei Tong
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Gamma-glutamyl transferase to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio: A valuable predictor of type 2 diabetes mellitus incidence
Wangcheng Xie, Bin Liu, Yansong Tang, Tingsong Yang, Zhenshun Song
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Low aspartate aminotransferase/alanine aminotransferase (DeRitis) ratio assists in predicting diabetes in Chinese population
Wangcheng Xie, Weidi Yu, Shanshan Chen, Zhilong Ma, Tingsong Yang, Zhenshun Song
Frontiers in Public Health.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction Models for Type 2 Diabetes Risk in the General Population: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies
Samaneh Asgari, Davood Khalili, Farhad Hosseinpanah, Farzad Hadaegh
International Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development of a clinical risk score for incident diabetes: A 10‐year prospective cohort study
Tae Jung Oh, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Nam H Cho, Hak Chul Jang
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(4): 610. CrossRef - Association between longitudinal blood pressure and prognosis after treatment of cerebral aneurysm: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Jinkwon Kim, Jang Hoon Kim, Hye Sun Lee, Sang Hyun Suh, Kyung-Yul Lee, Yan Li
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(5): e0252042. CrossRef - Development of a predictive risk model for all-cause mortality in patients with diabetes in Hong Kong
Sharen Lee, Jiandong Zhou, Keith Sai Kit Leung, William Ka Kei Wu, Wing Tak Wong, Tong Liu, Ian Chi Kei Wong, Kamalan Jeevaratnam, Qingpeng Zhang, Gary Tse
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2021; 9(1): e001950. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Deep Learning Based Diabetes Prediction System Using a Nationwide Population-Based Cohort
Sang Youl Rhee, Ji Min Sung, Sunhee Kim, In-Jeong Cho, Sang-Eun Lee, Hyuk-Jae Chang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 515. CrossRef - Development and validation of a new diabetes index for the risk classification of present and new-onset diabetes: multicohort study
Shinje Moon, Ji-Yong Jang, Yumin Kim, Chang-Myung Oh
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - New risk score model for identifying individuals at risk for diabetes in southwest China
Liying Li, Ziqiong Wang, Muxin Zhang, Haiyan Ruan, Linxia Zhou, Xin Wei, Ye Zhu, Jiafu Wei, Sen He
Preventive Medicine Reports.2021; 24: 101618. CrossRef - Multiple Biomarkers Improved Prediction for the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Singapore Chinese Men and Women
Yeli Wang, Woon-Puay Koh, Xueling Sim, Jian-Min Yuan, An Pan
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 295. CrossRef - Smoking as a Target for Prevention of Diabetes
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 402. CrossRef - Middle-aged men with type 2 diabetes as potential candidates for pancreatic cancer screening: a 10-year nationwide population-based cohort study
Dong-Hoe Koo, Kyung-Do Han, Hong Joo Kim, Cheol-Young Park
Acta Diabetologica.2020; 57(2): 197. CrossRef - Systematic review with meta-analysis of the epidemiological evidence relating smoking to type 2 diabetes
Peter N Lee, Katharine J Coombs
World Journal of Meta-Analysis.2020; 8(2): 119. CrossRef - Biomarker Score in Risk Prediction: Beyond Scientific Evidence and Statistical Performance
Heejung Bang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 245. CrossRef - Research progress on Traditional Chinese Medicine syndromes of diabetes mellitus
Jingkang Wang, Quantao Ma, Yaqi Li, Pengfei Li, Min Wang, Tieshan Wang, Chunguo Wang, Ting Wang, Baosheng Zhao
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2020; 121: 109565. CrossRef - Cardiometabolic risk prediction algorithms for young people with psychosis: a systematic review and exploratory analysis
B. I. Perry, R. Upthegrove, O. Crawford, S. Jang, E. Lau, I. McGill, E. Carver, P. B. Jones, G. M. Khandaker
Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica.2020; 142(3): 215. CrossRef - Impact of obesity, fasting plasma glucose level, blood pressure, and renal function on the severity of COVID-19: A matter of sexual dimorphism?
Kyungmin Huh, Rugyeom Lee, Wonjun Ji, Minsun Kang, In Cheol Hwang, Dae Ho Lee, Jaehun Jung
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 170: 108515. CrossRef
- Alanine to glycine ratio is a novel predictive biomarker for type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Clinical Care/Education
- A Clinical Practice Guideline to Guide a System Approach to Diabetes Care in Hong Kong
- Ip Tim Lau
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(2):81-88. Published online April 14, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.2.81
- 3,724 View
- 54 Download
- 33 Web of Science
- 33 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader The Hospital Authority of Hong Kong is a statutory body that manages all the public medical care institutions in Hong Kong. There are currently around 400,000 diabetic patients under its care at 17 hospitals (providing secondary care for 40%) and 73 General Outpatient Clinics (providing primary care for 60%). The patient population has been growing at 6% to 8% per year over the past 5 years, estimated to include over 95% of all diagnosed patients in Hong Kong. In order to provide equitable and a minimal level of care within resources and local system factors constraints, a Clinical Practice Guideline on the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus was drawn in 2013 to guide a system approach to providing diabetes care. There is an algorithm for the use of various hypoglycemic agents. An organizational drug formulary governs that less expansive options have to be used first. A number of clinical care and patient empowerment programs have been set up to support structured and systematic diabetes care. With such a system approach, there have been overall improvements in diabetes care with the percentage of patients with glycosylated hemoglobin <7% rising from 40% in 2010 to 52% in 2015.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of Dementia Among Patients With Diabetes in a Multidisciplinary, Primary Care Management Program
Kailu Wang, Shi Zhao, Eric Kam-Pui Lee, Susan Zi-May Yau, Yushan Wu, Chi-Tim Hung, Eng-Kiong Yeoh
JAMA Network Open.2024; 7(2): e2355733. CrossRef - Evaluating different low‐density lipoprotein cholesterol thresholds to initiate statin for prevention of cardiovascular diseases in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A target trial emulation study
Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Wanchun Xu, Anna Hoi Ying Mok, Weng Yee Chin, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Celine Sze Ling Chui, Esther Wai Yin Chan, Ian Chi Kei Wong, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam, Goodarz Danaei
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(5): 1877. CrossRef - SGLT2i reduces risk of developing HCC in patients with co-existing type 2 diabetes and hepatitis B infection: A territory-wide cohort study in Hong Kong
Chi-Ho Lee, Lung-Yi Mak, Eric Ho-Man Tang, David Tak-Wai Lui, Jimmy Ho-Cheung Mak, Lanlan Li, Tingting Wu, Wing Lok Chan, Man-Fung Yuen, Karen Siu-Ling Lam, Carlos King Ho Wong
Hepatology.2023; 78(5): 1569. CrossRef - Team-Based Diabetes Care in Ontario and Hong Kong: a Comparative Review
Calvin Ke, Emaad Mohammad, Juliana C. N. Chan, Alice P. S. Kong, Fok-Han Leung, Baiju R. Shah, Douglas Lee, Andrea O. Luk, Ronald C. W. Ma, Elaine Chow, Xiaolin Wei
Current Diabetes Reports.2023; 23(7): 135. CrossRef - Association of eGFR slope with all-cause mortality, macrovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with type 2 diabetes and early-stage chronic kidney disease
Qiao Jin, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam, Eric Yuk Fai Wan
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 205: 110924. CrossRef - Association Between SGLT2 Inhibitors vs DPP-4 Inhibitors and Risk of Pneumonia Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Philip C M Au, Kathryn C B Tan, Bernard M Y Cheung, Ian C K Wong, Ying Wong, Ching-Lung Cheung
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(4): e1719. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Integrative Chinese–Western Medicine for Chronic Kidney Disease and Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Kam Wa Chan, Tak Yee Chow, Kam Yan Yu, Yibin Feng, Lixing Lao, Zhaoxiang Bian, Vivian Taam Wong, Sydney Chi-Wai Tang
The American Journal of Chinese Medicine.2022; 50(02): 371. CrossRef - Association Between SGLT2 Inhibitors vs DPP4 Inhibitors and Renal Outcomes Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Philip C M Au, Kathryn C B Tan, Bernard M Y Cheung, Ian C K Wong, Hang-Long Li, Ching-Lung Cheung
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(7): e2962. CrossRef - Association Between Team-Based Continuity of Care and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases Among Patients With Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Kam Suen Chan, Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Weng Yee Chin, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Ivy Lynn Mak, Will Ho Gi Cheng, Margaret Kay Ho, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Diabetes Care.2022; 45(5): 1162. CrossRef - mRNA (BNT162b2) and Inactivated (CoronaVac) COVID-19 Vaccination and Risk of Adverse Events and Acute Diabetic Complications in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Population-Based Study
Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Celine Sze Ling Chui, Anna Hoi Ying Mok, Wanchun Xu, Vincent Ka Chun Yan, Francisco Tsz Tsun Lai, Xue Li, Carlos King Ho Wong, Esther Wai Yin Chan, David Tak Wai Lui, Kathryn Choon Beng Tan, Ivan Fan Ngai Hung, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam, Gabriel
Drug Safety.2022; 45(12): 1477. CrossRef - Evaluation of Fracture Risk Among Patients With Type 2 Diabetes and Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation Receiving Different Oral Anticoagulants
David Tak Wai Lui, Eric Ho Man Tang, Ivan Chi Ho Au, Tingting Wu, Chi Ho Lee, Chun Ka Wong, Chloe Yu Yan Cheung, Carol Ho Yi Fong, Wing Sun Chow, Yu Cho Woo, Kathryn Choon Beng Tan, Karen Siu Ling Lam, Carlos King Ho Wong
Diabetes Care.2022; 45(11): 2620. CrossRef - Ten-Year Effectiveness of the Multidisciplinary Risk Assessment and Management Programme–Diabetes Mellitus (RAMP-DM) on Macrovascular and Microvascular Complications and All-Cause Mortality: A Population-Based Cohort Study
Eric Ho Man Tang, Ivy Lynn Mak, Emily Tsui Yee Tse, Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Julie Yun Chen, Weng Yee Chin, David Vai Kiong Chao, Wendy Wing Sze Tsui, Tony King Hang Ha, Carlos King Ho Wong, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Diabetes Care.2022; 45(12): 2871. CrossRef - An Intervention to Change Illness Representations and Self-Care of Individuals With Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Virginia W.Y. Chan, Alice P.S. Kong, Joseph T.F. Lau, Winnie W.S. Mak, Linda D. Cameron, Phoenix K.H. Mo
Psychosomatic Medicine.2021; 83(1): 71. CrossRef - Risk of mortality and complications in patients with schizophrenia and diabetes mellitus: population-based cohort study
Joe Kwun Nam Chan, Corine Sau Man Wong, Philip Chi Fai Or, Eric Yu Hai Chen, Wing Chung Chang
The British Journal of Psychiatry.2021; 219(1): 375. CrossRef - Screening for diabetic retinopathy with different levels of financial incentive in a randomized controlled trial
Jin Xiao Lian, Sarah Morag McGhee, Ching So, Alfred Siu Kei Kwong, Rita Sum, Wendy Wing Sze Tsui, David Vai Kiong Chao, Jonathan Cheuk Hung Chan
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(9): 1632. CrossRef - Greater variability in lipid measurements associated with kidney diseases in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a 10-year diabetes cohort study
Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Weng Yee Chin, Christie Sze Ting Lau, Anna Hoi Ying Mok, Yuan Wang, Ian Chi Kei Wong, Esther Wai Yin Chan, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of the CHIME simulation model to assess lifetime health outcomes of prediabetes and type 2 diabetes in Chinese populations: A modeling study
Jianchao Quan, Carmen S. Ng, Harley H. Y. Kwok, Ada Zhang, Yuet H. Yuen, Cheung-Hei Choi, Shing-Chung Siu, Simon Y. Tang, Nelson M. Wat, Jean Woo, Karen Eggleston, Gabriel M. Leung, Weiping Jia
PLOS Medicine.2021; 18(6): e1003692. CrossRef - Age‐Specific Associations of Usual Blood Pressure Variability With Cardiovascular Disease and Mortality: 10‐Year Diabetes Mellitus Cohort Study
Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Weng Yee Chin, Jessica K. Barrett, Ian Chi Kei Wong, Esther Wai Yin Chan, Celine Sze Ling Chui, Shiqi Chen, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Journal of the American Heart Association.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes complication burden and patterns and risk of mortality in people with schizophrenia and diabetes: A population-based cohort study with 16-year follow-up
Joe Kwun Nam Chan, Corine Sau Man Wong, Philip Chi Fai Or, Eric Yu Hai Chen, Wing Chung Chang
European Neuropsychopharmacology.2021; 53: 79. CrossRef - Age‐specific associations of glycated haemoglobin variability with cardiovascular disease and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A 10‐ year cohort study
Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Weng Yee Chin, Florence Ting Yan Ng, Shu Ming Cheryl Chia, Ian Chi Kei Wong, Esther Wai Yin Chan, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(8): 1316. CrossRef - The Impact of Cardiovascular Disease and Chronic Kidney Disease on Life Expectancy and Direct Medical Cost in a 10-Year Diabetes Cohort Study
Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Weng Yee Chin, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Ian Chi Kei Wong, Esther Wai Yin Chan, Shirley Xue Li, Nico Kwan Lok Cheung, Yuan Wang, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Diabetes Care.2020; 43(8): 1750. CrossRef - Greater variability in lipid measurements associated with cardiovascular disease and mortality: A 10‐year diabetes cohort study
Eric Y. F. Wan, Esther Y. T. Yu, Weng Y. Chin, Jessica K. Barrett, Anna H. Y. Mok, Christie S. T. Lau, Yuan Wang, Ian C. K. Wong, Esther W. Y. Chan, Cindy L. K. Lam
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(10): 1777. CrossRef - Age at diagnosis, glycemic trajectories, and responses to oral glucose-lowering drugs in type 2 diabetes in Hong Kong: A population-based observational study
Calvin Ke, Thérèse A. Stukel, Baiju R. Shah, Eric Lau, Ronald C. Ma, Wing-Yee So, Alice P. Kong, Elaine Chow, Juliana C. N. Chan, Andrea Luk, Sanjay Basu
PLOS Medicine.2020; 17(9): e1003316. CrossRef - Age‐Specific Associations Between Systolic Blood Pressure and Cardiovascular Disease: A 10‐Year Diabetes Mellitus Cohort Study
Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Weng Yee Chin, Ian Chi Kei Wong, Esther Wai Yin Chan, Shiqi Chen, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Journal of the American Heart Association.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between usual glycated haemoglobin and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A 10‐year diabetes cohort study
Eric YF Wan, Esther YT Yu, Julie Y Chen, Ian CK Wong, Esther WY Chan, Cindy LK Lam
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(12): 2325. CrossRef - Cultural adaptation and psychometric properties of the Chinese Burden of Treatment Questionnaire (C-TBQ) in primary care patients with multi-morbidity
Weng Yee Chin, Carlos King Ho Wong, Cherry Cheuk Wai Ng, Edmond Pui Hang Choi, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Family Practice.2019; 36(5): 657. CrossRef - Association of Blood Pressure and Risk of Cardiovascular and Chronic Kidney Disease in Hong Kong Hypertensive Patients
Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Weng Yee Chin, Daniel Yee Tak Fong, Edmond Pui Hang Choi, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Hypertension.2019; 74(2): 331. CrossRef - Burden of CKD and Cardiovascular Disease on Life Expectancy and Health Service Utilization: a Cohort Study of Hong Kong Chinese Hypertensive Patients
Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Weng Yee Chin, Daniel Yee Tak Fong, Edmond Pui Hang Choi, Eric Ho Man Tang, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Journal of the American Society of Nephrology.2019; 30(10): 1991. CrossRef - Effect of Achieved Systolic Blood Pressure on Cardiovascular Outcomes in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study
Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Weng Yee Chin, Colman Siu Cheung Fung, Daniel Yee Tak Fong, Edmond Pui Hang Choi, Anca Ka Chun Chan, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Diabetes Care.2018; 41(6): 1134. CrossRef - Evolution of Diabetes Care in Hong Kong: From the Hong Kong Diabetes Register to JADE-PEARL Program to RAMP and PEP Program
Ivy H.Y. Ng, Kitty K.T. Cheung, Tiffany T.L. Yau, Elaine Chow, Risa Ozaki, Juliana C.N. Chan
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(1): 17. CrossRef - Relation between HbA1c and incident cardiovascular disease over a period of 6 years in the Hong Kong population
E.Y.F. Wan, E.Y.T. Yu, C.S.C. Fung, W.Y. Chin, D.Y.T. Fong, A.K.C. Chan, C.L.K. Lam
Diabetes & Metabolism.2018; 44(5): 415. CrossRef - Five-Year Effectiveness of the Multidisciplinary Risk Assessment and Management Programme–Diabetes Mellitus (RAMP-DM) on Diabetes-Related Complications and Health Service Uses—A Population-Based and Propensity-Matched Cohort Study
Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Colman Siu Cheung Fung, Fang Fang Jiao, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Weng Yee Chin, Daniel Yee Tak Fong, Carlos King Ho Wong, Anca Ka Chun Chan, Karina Hiu Yen Chan, Ruby Lai Ping Kwok, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Diabetes Care.2018; 41(1): 49. CrossRef - Do We Need a Patient-Centered Target for Systolic Blood Pressure in Hypertensive Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus?
Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Colman Siu Cheung Fung, Weng Yee Chin, Daniel Yee Tak Fong, Anca Ka Chun Chan, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Hypertension.2017; 70(6): 1273. CrossRef
- Risk of Dementia Among Patients With Diabetes in a Multidisciplinary, Primary Care Management Program
- Agreement between Framingham Risk Score and United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study Risk Engine in Identifying High Coronary Heart Disease Risk in North Indian Population
- Dipika Bansal, Ramya S. R. Nayakallu, Kapil Gudala, Rajavikram Vyamasuni, Anil Bhansali
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(4):321-327. Published online July 8, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.4.321
- 2,960 View
- 30 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of the study is to evaluate the concurrence between Framingham Risk score (FRS) and United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) risk engine in identifying coronary heart disease (CHD) risk in newly detected diabetes mellitus patients and to explore the characteristics associated with the discrepancy between them.
Methods A cross-sectional study involving 489 subjects newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus was conducted. Agreement between FRS and UKPDS in classifying patients as high risk was calculated using kappa statistic. Subjects with discrepant scores between two algorithms were identified and associated variables were determined.
Results The FRS identified 20.9% subjects (range, 17.5 to 24.7) as high-risk while UKPDS identified 21.75% (range, 18.3 to 25.5) as high-risk. Discrepancy was observed in 17.9% (range, 14.7 to 21.7) subjects. About 9.4% had high risk by UKPDS but not FRS, and 8.6% had high risk by FRS but not UKPDS. The best agreement was observed at high-risk threshold of 20% for both (κ=0.463). Analysis showed that subjects having high risk on FRS but not UKPDS were elderly females having raised systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Patients with high risk on UKPDS but not FRS were males and have high glycosylated hemoglobin.
Conclusion The FRS and UKPDS (threshold 20%) identified different populations as being at high risk, though the agreement between them was fairly good. The concurrence of a number of factors (e.g., male sex, low high density lipoprotein cholesterol, and smoking) in both algorithms should be regarded as increasing the CHD risk. However, longitudinal follow-up is required to form firm conclusions.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Endocan is Related to Increased Cardiovascular Risk in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Aleksandra Klisic, Jelena Kotur-Stevuljevic, Ana Ninic
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2023; 21(7): 362. CrossRef - Estimated risk of cardiovascular events and long-term complications: The projected future of diabetes patients in Delhi from the DEDICOM-II survey
Swapnil Rawat, Ramasheesh Yadav, Siddhi Goyal, Jitender Nagpal
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(11): 102880. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Biomarkers and Calculated Cardiovascular Risk in
Orally Treated Type 2 Diabetes Patients: Is There a Link?
Aleksandra Markova, Mihail Boyanov, Deniz Bakalov, Atanas Kundurdjiev, Adelina Tsakova
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2021; 53(01): 41. CrossRef - Risk of coronary heart disease and stroke based on United Kingdom prospective diabetes study in type 2 DM patients in Medan
R Amelia, J Harahap, H Wijaya, I I Fujiati
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.2021; 912(1): 012081. CrossRef - Cardiovascular/stroke risk prevention: A new machine learning framework integrating carotid ultrasound image-based phenotypes and its harmonics with conventional risk factors
Ankush Jamthikar, Deep Gupta, Narendra N. Khanna, Luca Saba, John R. Laird, Jasjit S. Suri
Indian Heart Journal.2020; 72(4): 258. CrossRef - Current Data Regarding the Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Risk Factors
Cosmin Mihai Vesa, Loredana Popa, Amorin Remus Popa, Marius Rus, Andreea Atena Zaha, Simona Bungau, Delia Mirela Tit, Raluca Anca Corb Aron, Dana Carmen Zaha
Diagnostics.2020; 10(5): 314. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence framework for predictive cardiovascular and stroke risk assessment models: A narrative review of integrated approaches using carotid ultrasound
Ankush D. Jamthikar, Deep Gupta, Luca Saba, Narendra N. Khanna, Klaudija Viskovic, Sophie Mavrogeni, John R. Laird, Naveed Sattar, Amer M. Johri, Gyan Pareek, Martin Miner, Petros P. Sfikakis, Athanasios Protogerou, Vijay Viswanathan, Aditya Sharma, Georg
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2020; 126: 104043. CrossRef - Additive and Synergistic Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors and HIV Disease Markers' Effects on White Matter Microstructure in Virally Suppressed HIV
Maëliss Calon, Kritika Menon, Andrew Carr, Roland G. Henry, Caroline D. Rae, Bruce J. Brew, Lucette A. Cysique
JAIDS Journal of Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndromes.2020; 84(5): 543. CrossRef - Performance evaluation of 10-year ultrasound image-based stroke/cardiovascular (CV) risk calculator by comparing against ten conventional CV risk calculators: A diabetic study
Narendra N. Khanna, Ankush D. Jamthikar, Deep Gupta, Andrew Nicolaides, Tadashi Araki, Luca Saba, Elisa Cuadrado-Godia, Aditya Sharma, Tomaz Omerzu, Harman S. Suri, Ajay Gupta, Sophie Mavrogeni, Monika Turk, John R. Laird, Athanasios Protogerou, Petros P.
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2019; 105: 125. CrossRef - Cardiovascular risk estimated by UKPDS risk engine algorithm in diabetes
Nebojsa Kavaric, Aleksandra Klisic, Ana Ninic
Open Medicine.2018; 13(1): 610. CrossRef - Differential Association of Metabolic Risk Factors with Open Angle Glaucoma according to Obesity in a Korean Population
Hyun-Ah Kim, Kyungdo Han, Yun-Ah Lee, Jin A Choi, Yong-Moon Park
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association between Diabetic Retinopathy and Framingham Risk Score in Koreans with Type II Diabetes
Da Yeong Kim, Su Jeong Song, Jeong Hun Bae, Cheol-Young Park, Eun-Jung Rhee
Journal of the Korean Ophthalmological Society.2016; 57(5): 779. CrossRef
- Endocan is Related to Increased Cardiovascular Risk in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Metabolic Syndrome versus Framingham Risk Score for Association of Self-Reported Coronary Heart Disease: The 2005 Korean Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Hye Mi Kang, Dong-Jun Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(3):237-244. Published online June 14, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.3.237
- 3,329 View
- 27 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Several studies in Western populations have indicated that metabolic syndrome (MetS) is inferior to the Framingham risk score (FRS) in predicting coronary heart disease (CHD). However there has been no study about the predictability of MetS vs. FRS for CHD in Korea.
Methods Among the 43,145 persons from the third Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey in 2005, laboratory test and nutritional survey data from 5,271 persons were examined. Participants were also asked to recall a physician's diagnosis of CHD.
Results The median age was 46 (range, 20 to 78) in men (
n =2,257) and 44 (range, 20 to 78) years in women (n =3,014). Prevalence of self-reported CHD was 1.7% in men and 2.1% in women. Receiver operating characteristic curves and their respective area under the curve (AUC) were used to compare the ability of the FRS and the number of components of MetS to predict self-reported CHD in each sex. In men, AUC of FRS was significantly larger than that of MetS (0.767 [0.708 to 0.819] vs. 0.677 [0.541 to 0.713],P <0.01). In women, AUC of FRS was comparable to that of MetS (0.777 [0.728 to 0.826] vs. 0.733 [0.673 to 0.795]), and was not significant.Conclusion The data suggested that FRS was more closely associated with CHD compared to MetS in Korean men.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intakes of Milk and Soymilk and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Korean Adults: A Study Based on the 2012~2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Ae Wha Ha, Woo Kyoung Kim, Sun Hyo Kim
Journal of the Korean Society of Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 52(5): 522. CrossRef - Cow’s Milk Intake and Risk of Coronary Heart Disease in Korean Postmenopausal Women
Ae-Wha Ha, Woo-Kyoung Kim, Sun-Hyo Kim
Nutrients.2022; 14(5): 1092. CrossRef - Prognostic Modelling Studies of Coronary Heart Disease—A Systematic Review of Conventional and Genetic Risk Factor Studies
Nayla Nasr, Beáta Soltész, János Sándor, Róza Adány, Szilvia Fiatal
Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease.2022; 9(9): 295. CrossRef - Framingham Risk Score Assessment in Subjects with Pre-diabetes and Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study in Korea
Hyuk Sang Kwon, Kee Ho Song, Jae Myung Yu, Dong Sun Kim, Ho Sang Shon, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Sung Hee Choi, Seung Hyun Ko, Won Kim, Kyoung Hwa Lee, Il Seong Nam-Goong, Tae Sun Park
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2021; 30(3): 261. CrossRef - Cardiometabolic risk prediction algorithms for young people with psychosis: a systematic review and exploratory analysis
B. I. Perry, R. Upthegrove, O. Crawford, S. Jang, E. Lau, I. McGill, E. Carver, P. B. Jones, G. M. Khandaker
Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica.2020; 142(3): 215. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome and Mortality in Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Patients: A 5-Year Prospective Cohort Study
WenLong Gu, Chunyan Yi, Xueqing Yu, Xiao Yang
Kidney and Blood Pressure Research.2019; 44(5): 1026. CrossRef - Comparison Between Metabolic Syndrome and the Framingham Risk Score as Predictors of Cardiovascular Diseases Among Kazakhs in Xinjiang
Wenwen Yang, Rulin Ma, Xianghui Zhang, Heng Guo, Jia He, Lei Mao, Lati Mu, Yunhua Hu, Yizhong Yan, Jiaming Liu, Jiaolong Ma, Shugang Li, Yusong Ding, Mei Zhang, Jingyu Zhang, Shuxia Guo
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediction of Coronary Heart Disease Risk in Korean Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Bo Kyung Koo, Sohee Oh, Yoon Ji Kim, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2018; 7(2): 110. CrossRef - Epidemiology and cardiovascular comorbidities in patients with psoriasis: A Korean nationwide population‐based cohort study
Eui Hyun Oh, Young Suck Ro, Jeong Eun Kim
The Journal of Dermatology.2017; 44(6): 621. CrossRef - Pattern of Thyroid Dysfunction in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome and Its Relationship with Components of Metabolic Syndrome
Prabin Gyawali, Jyoti Shrestha Takanche, Raj Kumar Shrestha, Prem Bhattarai, Kishor Khanal, Prabodh Risal, Rajendra Koju
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(1): 66. CrossRef - The Effects of Menopause on the Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Women
SoYoun Bang, IlGu Cho
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(4): 2704. CrossRef - Evaluation of Nutrient Intake and Food Variety in Korean Male Adults according to Framingham Risk Score
Mi-Kyeong Choi, Yun-Jung Bae
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2014; 27(3): 484. CrossRef - Cardiometabolic implication of sarcopenia: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Study (KNHANES) 2008–2010
Kyoung Min Kim, Soo Lim, Sung Hee Choi, Jung Hee Kim, Chan Soo Shin, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang
IJC Metabolic & Endocrine.2014; 4: 63. CrossRef - Different tools for estimating cardiovascular risk in Brazilian postmenopausal women
Eliana A. P. Nahas, Aline M. Andrade, Mayra C. Jorge, Claudio L. Orsatti, Flavia B. Dias, Jorge Nahas-Neto
Gynecological Endocrinology.2013; 29(10): 921. CrossRef - Hemoglobin A1c Is Positively Correlated with Framingham Risk Score in Older, Apparently Healthy Nondiabetic Korean Adults
Ji Hye Shin, Ji In Kang, Yun Jung, Young Min Choi, Hyun Jung Park, Jung Hae So, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Hak Yeon Bae
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2013; 28(2): 103. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Disease Risk of Bus Drivers in a City of Korea
Seung Shin, Chul Lee, Han Song, Sul Kim, Hyun Lee, Min Jung, Sang Yoo
Annals of Occupational and Environmental Medicine.2013; 25(1): 34. CrossRef
- Intakes of Milk and Soymilk and Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Korean Adults: A Study Based on the 2012~2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





