
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cardiovascular risk/Epidemiology
- Risk of Cardiovascular Disease according to Baseline Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Level in Different Age Groups in Korean Diabetes Population: A Cohort Study
- Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung-Do Han, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):265-278. Published online February 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0443
- 707 View
- 137 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The association between low-density lipoprotein (LDL-C) levels and cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk in different age groups within the diabetes mellitus (DM) population remains unclear. The cohort study was conducted to investigate this relationship.
Methods
We assessed the 2009 to 2012 Korean National Health Screening and National Health Insurance Service records, with follow-up to the primary outcome (myocardial infarction [MI] or stroke) or December 2018. After excluding the participants with a history of MI or stroke, 2,227,394 participants with DM were included and categorized according to baseline LDL-C levels and age. Cox proportional hazards modeling was conducted. The CVD risk of age <40 years and LDL-C <70 mg/dL was set as the reference. In each age group, LDL-C <70 mg/dL was used as a reference for the subgroup analysis.
Results
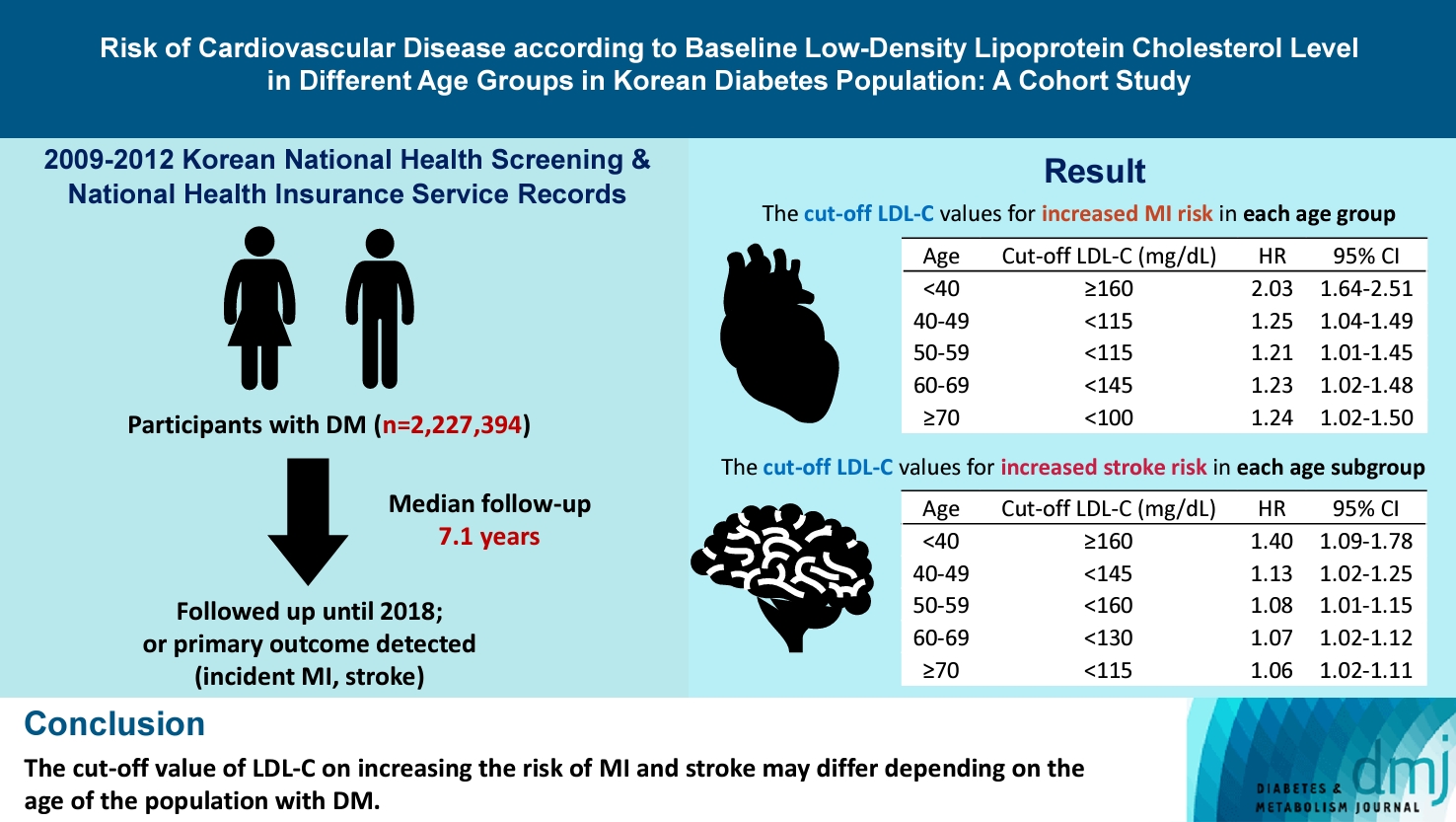
The cut-off LDL-C value for increased MI risk in each age group varied (<40 years old, LDL-C ≥160 mg/dL: hazard ratios [HR], 2.03; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.644 to 2.506) (40–49-year-old, LDL-C <115 mg/dL: HR, 1.245; 95% CI, 1.04 to 1.489) (50–59-year-old, LDL-C <115 mg/dL: HR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.014 to 1.445) (60-69-year-old, LDL-C <145 mg/dL: HR, 1.229; 95% CI, 1.022 to 1.479) (≥70 years old group, LDL-C <100 mg/dL: HR, 1.238; 95% CI, 1.018 to 1.504). The cut-off LDL-C values for increased stroke risk varied in each age subgroup (<40 years old, LDL-C ≥160 mg/dL: HR, 1.395; 95% CI, 1.094 to 1.779) (40–49-year-old, LDL-C <145 mg/dL: HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.019 to 1.253) (50–59-year-old, LDL-C <160 mg/dL: HR, 1.079; 95% CI, 1.008 to 1.154) (60–69-year-old, LDL-C <130 mg/dL: HR, 1.07; 95% CI, 1.022 to 1.119) (≥70 years old, LDL-C <115 mg/dL: HR, 1.064; 95% CI, 1.019 to 1.112).
Conclusion
The effect of LDL-C on the risk of CVD differs depending on the age of the population with DM.
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- A Composite Blood Biomarker Including AKR1B10 and Cytokeratin 18 for Progressive Types of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Seung Joon Choi, Sungjin Yoon, Kyoung-Kon Kim, Doojin Kim, Hye Eun Lee, Kwang Gi Kim, Seung Kak Shin, Ie Byung Park, Seong Min Kim, Dae Ho Lee
- Received June 18, 2023 Accepted August 16, 2023 Published online February 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0189 [Epub ahead of print]
- 755 View
- 44 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We aimed to evaluate whether composite blood biomarkers including aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 (AKR1B10) and cytokeratin 18 (CK-18; a nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [NASH] marker) have clinically applicable performance for the diagnosis of NASH, advanced liver fibrosis, and high-risk NASH (NASH+significant fibrosis).
Methods
A total of 116 subjects including healthy control subjects and patients with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) were analyzed to assess composite blood-based and imaging-based biomarkers either singly or in combination.
Results
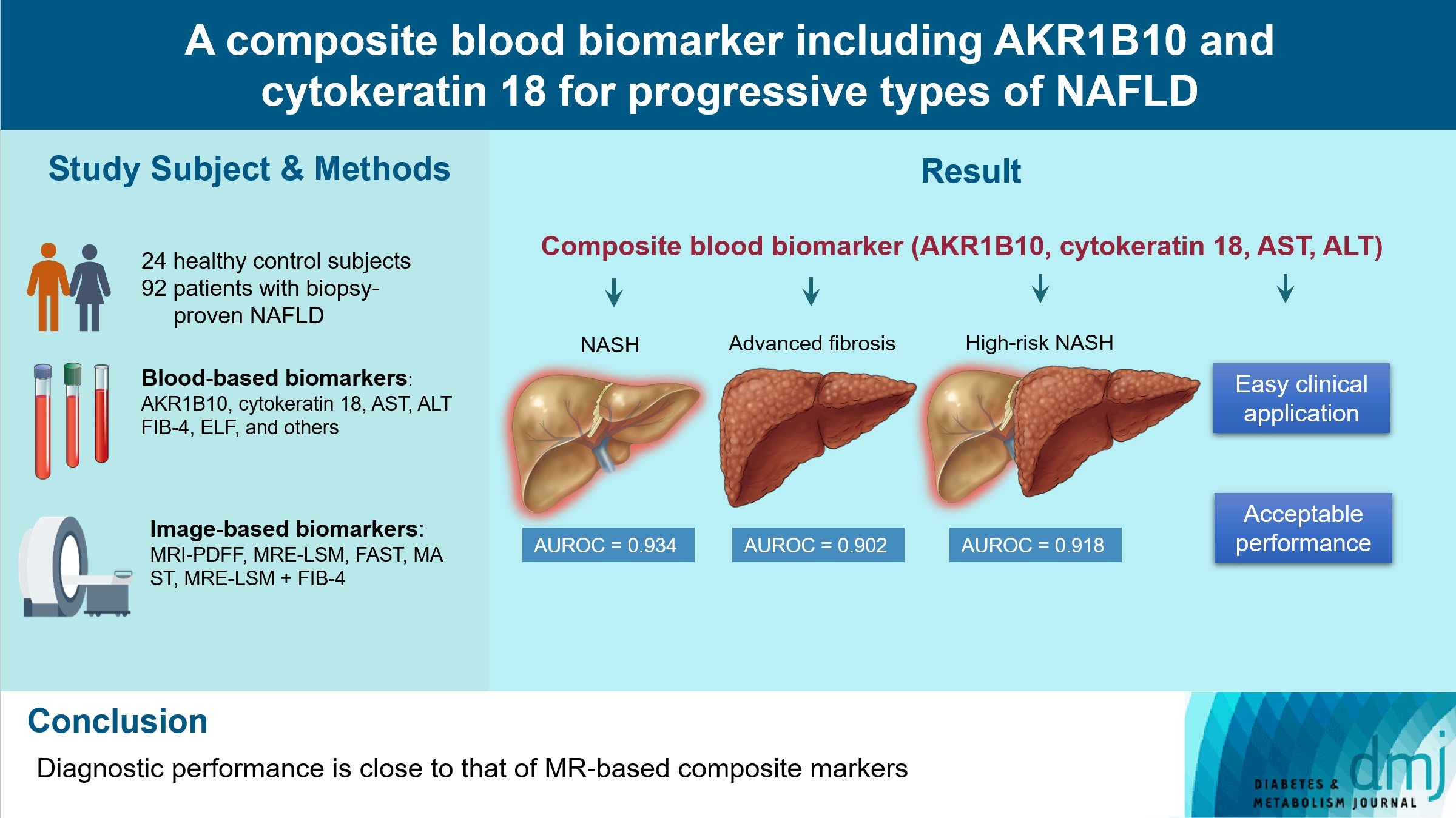
A composite blood biomarker comprised of AKR1B10, CK-18, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) showed excellent performance for the diagnosis of, NASH, advanced fibrosis, and high-risk NASH, with area under the receiver operating characteristic curve values of 0.934 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.888 to 0.981), 0.902 (95% CI, 0.832 to 0.971), and 0.918 (95% CI, 0.862 to 0.974), respectively. However, the performance of this blood composite biomarker was inferior to that various magnetic resonance (MR)-based composite biomarkers, such as proton density fat fraction/MR elastography- liver stiffness measurement (MRE-LSM)/ALT/AST for NASH, MRE-LSM+fibrosis-4 index for advanced fibrosis, and the known MR imaging-AST (MAST) score for high-risk NASH.
Conclusion
Our blood composite biomarker can be useful to distinguish progressive forms of NAFLD as an initial noninvasive test when MR-based tools are not available.
- Lifestyle
- Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Sarcopenia as Comorbid Chronic Diseases in Older Adults: Established and Emerging Treatments and Therapies
- Jakub Mesinovic, Jackson J. Fyfe, Jason Talevski, Michael J. Wheeler, Gloria K.W. Leung, Elena S. George, Melkamu T. Hunegnaw, Costas Glavas, Paul Jansons, Robin M. Daly, David Scott
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):719-742. Published online September 14, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0112
- 4,556 View
- 438 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
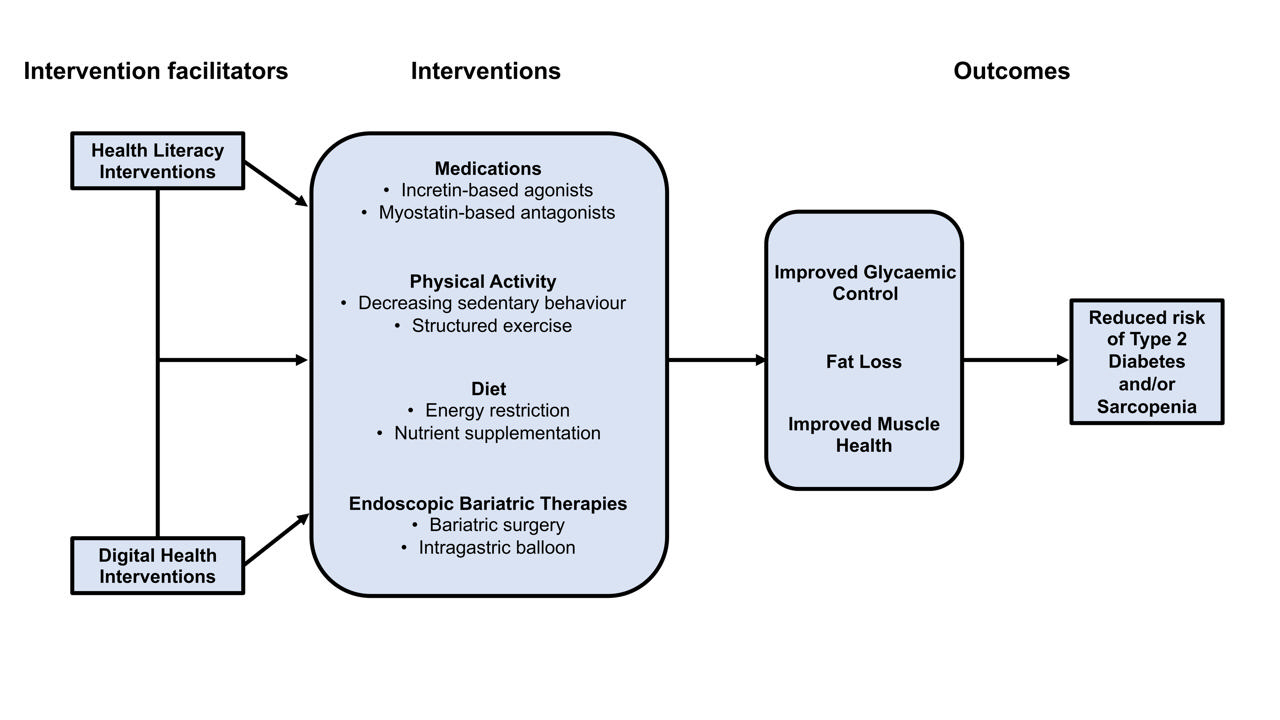
ePub - Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and sarcopenia (low skeletal muscle mass and function) share a bidirectional relationship. The prevalence of these diseases increases with age and they share common risk factors. Skeletal muscle fat infiltration, commonly referred to as myosteatosis, may be a major contributor to both T2DM and sarcopenia in older adults via independent effects on insulin resistance and muscle health. Many strategies to manage T2DM result in energy restriction and subsequent weight loss, and this can lead to significant declines in muscle mass in the absence of resistance exercise, which is also a first-line treatment for sarcopenia. In this review, we highlight recent evidence on established treatments and emerging therapies targeting weight loss and muscle mass and function improvements in older adults with, or at risk of, T2DM and/or sarcopenia. This includes dietary, physical activity and exercise interventions, new generation incretin-based agonists and myostatin-based antagonists, and endoscopic bariatric therapies. We also highlight how digital health technologies and health literacy interventions can increase uptake of, and adherence to, established and emerging treatments and therapies in older adults with T2DM and/or sarcopenia.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fucoidan ameliorates diabetic skeletal muscle atrophy through PI3K/Akt pathway
Caixia Li, Yaping Liu, Mingzhi Yang, Haoyue Huang, Lulu Tang, Yufan Miao, Wenjie Li, Xing Li
Journal of Functional Foods.2024; 114: 106076. CrossRef
- Fucoidan ameliorates diabetic skeletal muscle atrophy through PI3K/Akt pathway
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Prediabetes Progression and Regression on Objectively- Measured Physical Function: A Prospective Cohort Study
- Shanhu Qiu, Yiming Zhu, Bo Xie, Wenji Chen, Duolao Wang, Xue Cai, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):859-868. Published online August 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0377

- 1,289 View
- 122 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Prediabetes leads to declines in physical function in older adults, but the impact of prediabetes progression or regression on physical function is unknown. This study assessed this longitudinal association, with physical function objectivelymeasured by grip strength, walking speed, and standing balance, based on the Health and Retirement Study enrolling United States adults aged >50 years.
Methods
Participants with prediabetes were followed-up for 4-year to ascertain prediabetes status alteration (maintained, regressed, or progressed), and another 4-year to assess their impacts on physical function. Weak grip strength was defined as <26 kg for men and <16 kg for women, slow walking speed was as <0.8 m/sec, and poor standing balance was as an uncompleted fulltandem standing testing. Logistic and linear regression analyses were performed.
Results
Of the included 1,511 participants with prediabetes, 700 maintained as prediabetes, 306 progressed to diabetes, and 505 regressed to normoglycemia over 4 years. Grip strength and walking speed were declined from baseline during the 4-year followup, regardless of prediabetes status alteration. Compared with prediabetes maintenance, prediabetes progression increased the odds of developing weak grip strength by 89% (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.04 to 2.44) and exhibited larger declines in grip strength by 0.85 kg (95% CI, –1.65 to –0.04). However, prediabetes progression was not related to impairments in walking speed or standing balance. Prediabetes regression also did not affect any measures of physical function.
Conclusion
Prediabetes progression accelerates grip strength decline in aging population, while prediabetes regression may not prevent physical function decline due to aging.
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Differential Impact of Obesity on the Risk of Diabetes Development in Two Age Groups: Analysis from the National Health Screening Program
- Tae Kyung Yoo, Kyung-Do Han, Yang-Hyun Kim, Ga Eun Nam, Sang Hyun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):846-858. Published online August 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0242
- 1,185 View
- 141 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The effect of obesity on the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) in different age groups remains unclear. We assessed the impact of obesity on the development of DM for two age groups (40-year-old, middle age; 66-year-old, older adults) in the Korean population.
Methods
We analyzed Korean National Health Insurance Service data of 4,145,321 Korean adults with 40- and 66-year-old age without DM, between 2009 and 2014. Participants were followed up until 2017 or until the diagnosis of DM. We assessed the risk of DM based on the body mass index and waist circumference of the participants. Multiple confounding factors were adjusted.
Results
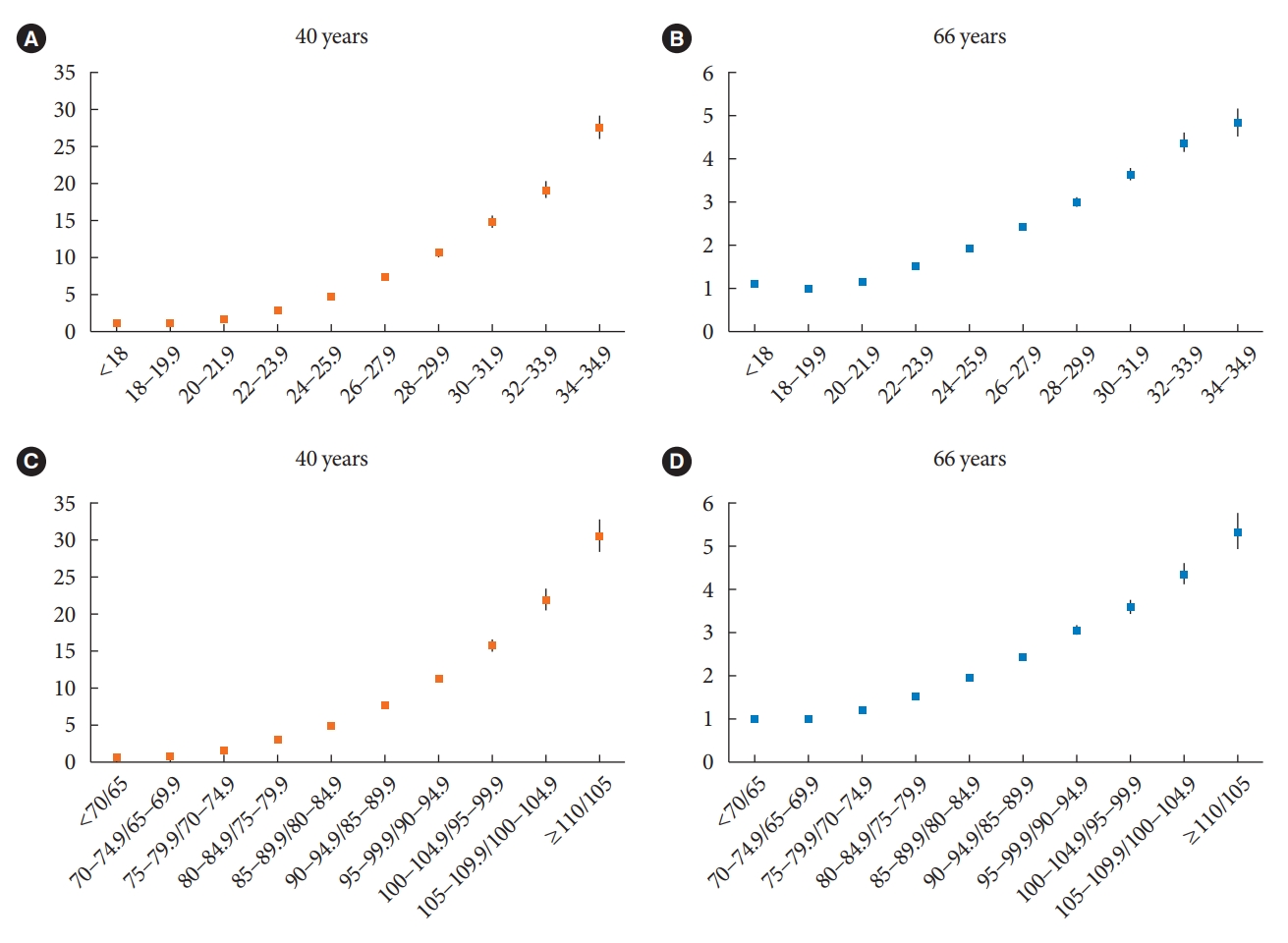
The median follow-up duration was 5.6 years. The association of general and abdominal obesity with the risk of DM development was stronger in the 40-year-old group (general obesity: hazard ratio [HR], 3.566, 95% confidence interval [CI], 3.512 to 3.622; abdominal obesity: HR, 3.231; 95% CI, 3.184 to 3.278) than in the 66-year-old group (general obesity: HR, 1.739; 95% CI, 1.719 to 1.759; abdominal obesity: HR, 1.799; 95% CI, 1.778 to 1.820). In the 66-year-old group, abdominal obesity had a stronger association with the development of DM as compared to general obesity. In the 40-year-old group, general obesity had a stronger association with the risk of DM development than abdominal obesity.
Conclusion
The influence of general and abdominal obesity on the development of DM differed according to age. In older adults, abdominal obesity had a stronger association with DM development than general obesity.
- Basic Research
- Regulation of Cellular Senescence in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: From Mechanisms to Clinical Applications
- Kanako Iwasaki, Cristian Abarca, Cristina Aguayo-Mazzucato
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):441-453. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0416

- 4,687 View
- 417 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Cellular senescence is accelerated by hyperglycemia through multiple pathways. Therefore, senescence is an important cellular mechanism to consider in the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and an additional therapeutic target. The use of drugs that remove senescent cells has led to improvements in blood glucose levels and diabetic complications in animal studies. Although the removal of senescent cells is a promising approach for the treatment of T2DM, two main challenges limit its clinical application: the molecular basis of cellular senescence in each organ is yet to be understood, and the specific effect of removing senescent cells in each organ has to be determined. This review aims to discuss future applications of targeting senescence as a therapeutic option in T2DM and elucidate the characteristics of cellular senescence and senescence-associated secretory phenotype in the tissues important for regulating glucose levels: pancreas, liver, adipocytes, and skeletal muscle.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Amide Alkaloids as Privileged Sources of Senomodulators for Therapeutic Purposes in Age-Related Diseases
Mazzarine Dotou, Aurore L’honoré, Roba Moumné, Chahrazade El Amri
Journal of Natural Products.2024; 87(3): 617. CrossRef - Study on the Pathogenesis of Cell Senescence in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver
丽媛 黄
Medical Diagnosis.2024; 14(01): 76. CrossRef - Senescent adipocytes and type 2 diabetes – current knowledge and perspective concepts
Weronika Kruczkowska, Julia Gałęziewska, Mateusz Kciuk, Adrianna Gielecińska, Elżbieta Płuciennik, Zbigniew Pasieka, Lin-Yong Zhao, Yi-Jin Yu, Damian Kołat, Żaneta Kałuzińska-Kołat
Biomolecular Concepts.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Long-Term Passage on Porcine SMCs’ Function and the Improvement of TGF-β1 on Porcine SMCs’ Secretory Function in Late Passage
Yan-Yan Zheng, Ze-Nan Hu, Zheng Liu, Yi-Chen Jiang, Ren-Peng Guo, Shi-Jie Ding, Guang-Hong Zhou
Foods.2023; 12(14): 2682. CrossRef - Exploring the Relationship between Cellular Senescence Markers and Aging-Related Diseases
怡 罗
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(08): 12298. CrossRef
- Amide Alkaloids as Privileged Sources of Senomodulators for Therapeutic Purposes in Age-Related Diseases
- Basic Research
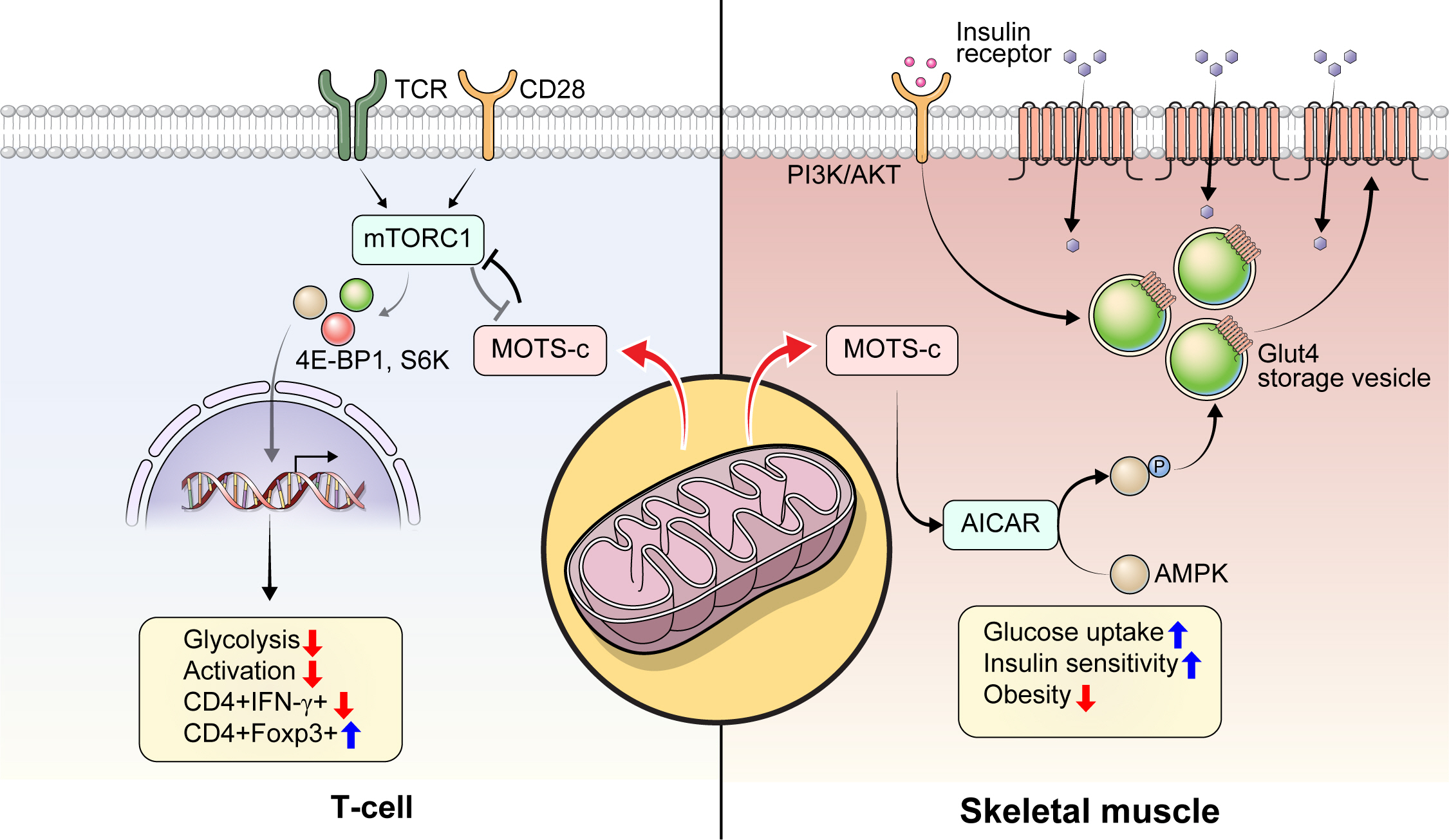
- Mitochondrial-Encoded Peptide MOTS-c, Diabetes, and Aging-Related Diseases
- Byung Soo Kong, Changhan Lee, Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):315-324. Published online February 24, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0333
- 5,719 View
- 284 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Mitochondria are complex metabolic organelles with manifold pathophysiological implications in diabetes. Currently published mitochondrial-encoded peptides, which are expressed from the mitochondrial open reading frame of the 12S ribosomal RNA type-c (MOTS-c), 16S rRNA (humanin and short humanin like peptide 1-6 [SHLP1-6]), or small human mitochondrial open reading frame over serine tRNA (SHMOOSE) are associated with regulation of cellular metabolism and insulin action in age-related diseases, such as type 2 diabetes mellitus. This review focuses mainly on recent advances in MOTS-c research with regards to diabetes, including both type 1 and type 2. The emerging understanding of MOTS-c in diabetes may provide insight into the development of new therapies for diabetes and other age or senescence-related diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Mitochondrial-derived peptides: Antidiabetic functions and evolutionary perspectives
Satadeepa Kal, Sumana Mahata, Suborno Jati, Sushil K. Mahata
Peptides.2024; 172: 171147. CrossRef - Mitochondrial Stress and Mitokines: Therapeutic Perspectives for the Treatment of Metabolic Diseases
Benyuan Zhang, Joon Young Chang, Min Hee Lee, Sang-Hyeon Ju, Hyon-Seung Yi, Minho Shong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 1. CrossRef - Mitochondrial bioenergetics, metabolism, and beyond in pancreatic β-cells and diabetes
Alejandra María Rivera Nieves, Brian Michael Wauford, Accalia Fu
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2024;[Epub] CrossRef
- Mitochondrial-derived peptides: Antidiabetic functions and evolutionary perspectives
- Complication
- Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Brain Atrophy: A Meta-Analysis
- Tianqi Zhang, Marnie Shaw, Nicolas Cherbuin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):781-802. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0189
- 6,429 View
- 296 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 20 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is known to be associated with cognitive decline and brain structural changes. This study systematically reviews and estimates human brain volumetric differences and atrophy associated with T2DM.
Methods
PubMed, PsycInfo and Cochrane Library were searched for brain imaging studies reporting on brain volume differences between individuals with T2DM and healthy controls. Data were examined using meta-analysis, and association between age, sex, diabetes characteristics and brain volumes were tested using meta-regression.
Results
A total of 14,605 entries were identified; after title, abstract and full-text screening applying inclusion and exclusion criteria, 64 studies were included and 42 studies with compatible data contributed to the meta-analysis (n=31,630; mean age 71.0 years; 44.4% male; 26,942 control; 4,688 diabetes). Individuals with T2DM had significantly smaller total brain volume, total grey matter volume, total white matter volume and hippocampal volume (approximately 1% to 4%); meta-analyses of smaller samples focusing on other brain regions and brain atrophy rate in longitudinal investigations also indicated smaller brain volumes and greater brain atrophy associated with T2DM. Meta-regression suggests that diabetes-related brain volume differences start occurring in early adulthood, decreases with age and increases with diabetes duration.
Conclusion
T2DM is associated with smaller total and regional brain volume and greater atrophy over time. These effects are substantial and highlight an urgent need to develop interventions to reduce the risk of T2DM for brain health. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetes, antidiabetic medications and risk of dementia: A systematic umbrella review and meta‐analysis
Alvin Kuate Defo, Veselko Bakula, Alessandro Pisaturo, Christopher Labos, Simon S. Wing, Stella S. Daskalopoulou
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 441. CrossRef - Cognitive deficits among people with schizophrenia and prediabetes or diabetes
Alexander Panickacheril John, Thynn Mya, Darren Haywood
Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica.2024; 149(1): 65. CrossRef - The association of glucose metabolism measures and diabetes status with Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers of amyloid and tau: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Veerle van Gils, Marianna Rizzo, Jade Côté, Wolfgang Viechtbauer, Giuseppe Fanelli, Jordi Salas-Salvadó, Theresa Wimberley, Mònica Bulló, Fernando Fernandez-Aranda, Søren Dalsgaard, Pieter Jelle Visser, Willemijn J. Jansen, Stephanie J.B. Vos
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2024; 159: 105604. CrossRef - ECHDC3 Variant Regulates the Right Hippocampal Microstructural Integrity and Verbal Memory in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Qiyu Zhao, Xin Du, Feng Liu, Yang Zhang, Wen Qin, Quan Zhang
Neuroscience.2024; 538: 30. CrossRef - The hemodynamic response function as a type 2 diabetes biomarker: a data-driven approach
Pedro Guimarães, Pedro Serranho, João V. Duarte, Joana Crisóstomo, Carolina Moreno, Leonor Gomes, Rui Bernardes, Miguel Castelo-Branco
Frontiers in Neuroinformatics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - What have clinical trials taught us about brain health?
Keon-Joo Lee, Hee-Joon Bae
Cerebral Circulation - Cognition and Behavior.2024; 6: 100199. CrossRef - Understanding the relationship between type-2 diabetes, MRI markers of neurodegeneration and small vessel disease, and dementia risk: a mediation analysis
Leslie Grasset, Eric Frison, Catherine Helmer, Gwénaëlle Catheline, Geneviève Chêne, Carole Dufouil
European Journal of Epidemiology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Vulnerability of the Hippocampus to Insults: Links to Blood–Brain Barrier Dysfunction
Terry L. Davidson, Richard J. Stevenson
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(4): 1991. CrossRef - The gut microbiota‐astrocyte axis: Implications for type 2 diabetic cognitive dysfunction
Zi‐Han Li, Ya‐Yi Jiang, Cai‐Yi Long, Qian Peng, Ren‐Song Yue
CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics.2023; 29(S1): 59. CrossRef - NHANES 2011–2014 Reveals Decreased Cognitive Performance in U.S. Older Adults with Metabolic Syndrome Combinations
Edgar Díaz-Camargo, Juan Hernández-Lalinde, María Sánchez-Rubio, Yudy Chaparro-Suárez, Liseth Álvarez-Caicedo, Alexandra Fierro-Zarate, Marbel Gravini-Donado, Henry García-Pacheco, Joselyn Rojas-Quintero, Valmore Bermúdez
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(7): 5257. CrossRef - People with Diabetes Have Poorer Self-Rated Health (SRH) and Diabetes Moderates the Association between Age and SRH
Weixi Kang, Antonio Malvaso
Diseases.2023; 11(2): 73. CrossRef - Cognitive dysfunction in diabetes: abnormal glucose metabolic regulation in the brain
Shan Zhang, Yueying Zhang, Zhige Wen, YaNan Yang, Tianjie Bu, Xiangwei Bu, Qing Ni
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The psychological basis of hunger and its dysfunctions
Richard J Stevenson
Nutrition Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of Glucose Metabolism Status with Brain Macrostructure and Microstructure: Findings from the UK Biobank
Ruyi Li, Tingting Geng, Lin Li, Qi Lu, Rui Li, Xue Chen, Yunjing Ou, Sen Liu, Xiaoyu Lin, Qingying Tian, Zixin Qiu, Kai Zhu, Ziyue Tang, Kun Yang, An Pan, Gang Liu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 109(1): e234. CrossRef - Association Between Frequency of Social Contact and Brain Atrophy in Community-Dwelling Older People Without Dementia
Naoki Hirabayashi, Takanori Honda, Jun Hata, Yoshihiko Furuta, Mao Shibata, Tomoyuki Ohara, Yasuko Tatewaki, Yasuyuki Taki, Shigeyuki Nakaji, Tetsuya Maeda, Kenjiro Ono, Masaru Mimura, Kenji Nakashima, Jun-ichi Iga, Minoru Takebayashi, Toshiharu Ninomiya,
Neurology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A diagnosis model for brain atrophy using deep learning and MRI of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Saba Raoof Syed, Saleem Durai M. A.
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes: a tipping point in neurodegenerative diseases
Jose A. Santiago, Mridula Karthikeyan, Madison Lackey, Diana Villavicencio, Judith A. Potashkin
Trends in Molecular Medicine.2023; 29(12): 1029. CrossRef - Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Brain Atrophy: A Meta-Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:781-802)
Tianqi Zhang, Marnie Shaw, Nicolas Cherbuin
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 815. CrossRef - Association between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Brain Atrophy: A Meta-Analysis (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:781-802)
Se Hee Min
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 813. CrossRef - MORPHOFUNCTIONAL CHANGES OF THE BRAIN IN DIABETES MELLITUS
A. V. Smirnov, A. I Bisinbekova, T. I Faibisovich
Journal of Volgograd State Medical University.2022; 19(3): 3. CrossRef
- Diabetes, antidiabetic medications and risk of dementia: A systematic umbrella review and meta‐analysis
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
-
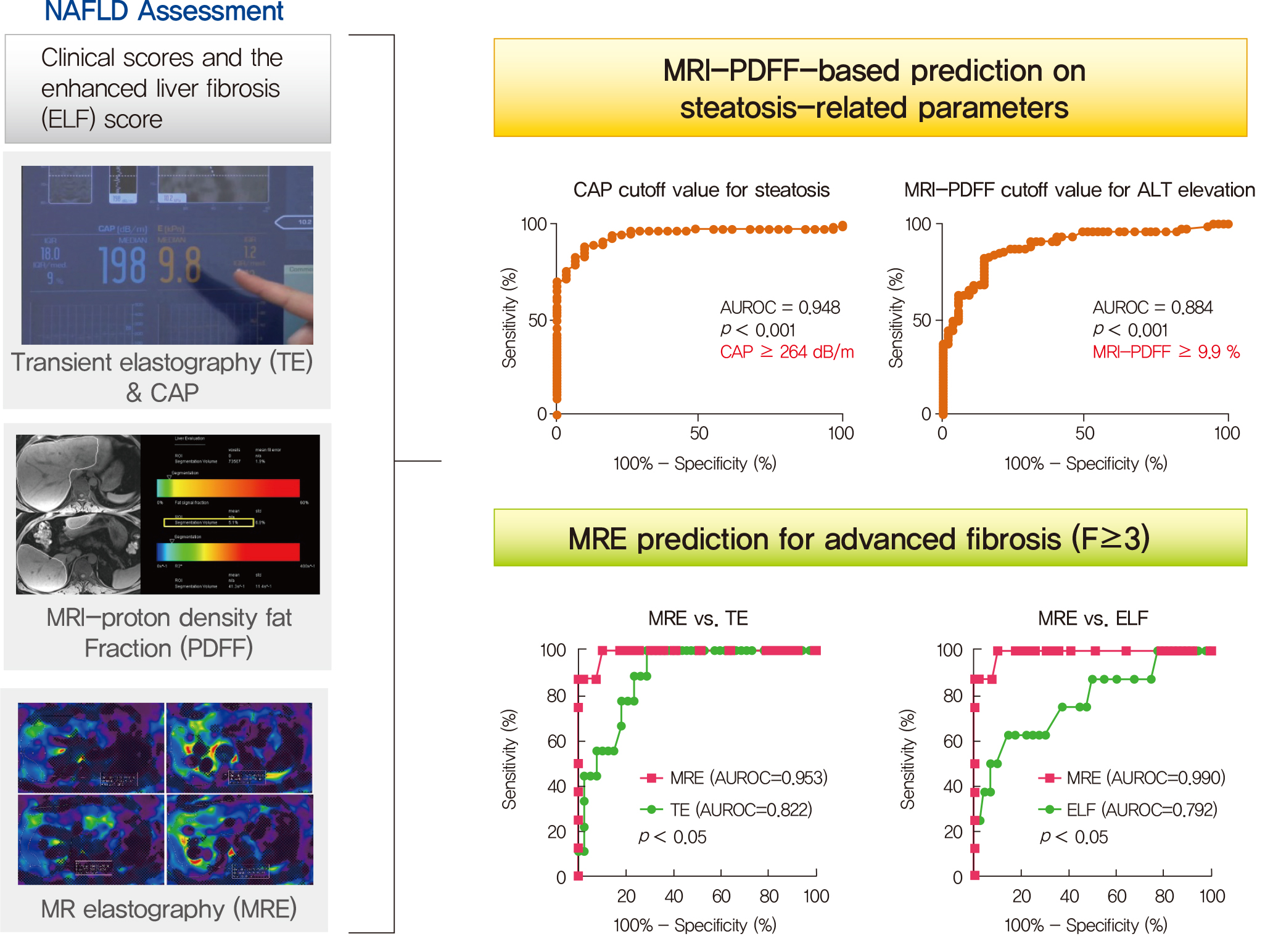
- Magnetic Resonance-Based Assessments Better Capture Pathophysiologic Profiles and Progression in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Seung Joon Choi, Seong Min Kim, Yun Soo Kim, Oh Sang Kwon, Seung Kak Shin, Kyoung Kon Kim, Kiyoung Lee, Ie Byung Park, Cheol Soo Choi, Dong Hae Chung, Jaehun Jung, MunYoung Paek, Dae Ho Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):739-752. Published online October 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0137
- 8,709 View
- 218 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Several noninvasive tools are available for the assessment of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) including clinical and blood biomarkers, transient elastography (TE), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) techniques, such as proton density fat fraction (MRI-PDFF) and magnetic resonance elastography (MRE). In the present study, we aimed to evaluate whether magnetic resonance (MR)-based examinations better discriminate the pathophysiologic features and fibrosis progression in NAFLD than other noninvasive methods.
Methods
A total of 133 subjects (31 healthy volunteers and 102 patients with NAFLD) were subjected to clinical and noninvasive NAFLD evaluation, with additional liver biopsy in some patients (n=54).
Results
MRI-PDFF correlated far better with hepatic fat measured by MR spectroscopy (r=0.978, P<0.001) than with the TE controlled attenuation parameter (CAP) (r=0.727, P<0.001). In addition, MRI-PDFF showed stronger correlations with various pathophysiologic parameters for cellular injury, glucose and lipid metabolism, and inflammation, than the TE-CAP. The MRI-PDFF and TE-CAP cutoff levels associated with abnormal elevation of serum alanine aminotransferase were 9.9% and 270 dB/m, respectively. The MRE liver stiffness measurement (LSM) showed stronger correlations with liver enzymes, platelets, complement component 3, several clinical fibrosis scores, and the enhanced liver fibrosis (ELF) score than the TE-LSM. In an analysis of only biopsied patients, MRE performed better in discriminating advanced fibrosis with a cutoff value of 3.9 kPa than the TE (cutoff 8.1 kPa) and ELF test (cutoff 9.2 kPa).
Conclusion
Our results suggest that MRI-based assessment of NAFLD is the best non-invasive tool that captures the histologic, pathophysiologic and metabolic features of the disease. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Novel Score Based on Controlled Attenuation Parameter Accurately Predicts Hepatic Steatosis in Individuals With Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Derivation and Independent Validation Study
Zi-Ming An, Qiao-Hong Liu, Xin-Jian Ye, Qian Zhang, Hua-Fu Pei, Xin Xin, Jie Yuan, Qian Huang, Kun Liu, Fang Lu, Zhi-Han Yan, Yu Zhao, Yi-Yang Hu, Ming-Hua Zheng, Qin Feng
Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology.2024; 15(3): e00680. CrossRef - Imaging Methods Applicable in the Diagnostics of Alzheimer’s Disease, Considering the Involvement of Insulin Resistance
Petra Hnilicova, Ema Kantorova, Stanislav Sutovsky, Milan Grofik, Kamil Zelenak, Egon Kurca, Norbert Zilka, Petra Parvanovova, Martin Kolisek
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3325. CrossRef - Polyunsaturated and Saturated Oxylipin Plasma Levels Allow Monitoring the Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Progression to Severe Stages
Miguel D. Ferrer, Clara Reynés, Margalida Monserrat-Mesquida, Magdalena Quetglas-Llabrés, Cristina Bouzas, Silvia García, David Mateos, Miguel Casares, Cristina Gómez, Lucía Ugarriza, Josep A. Tur, Antoni Sureda, Antoni Pons
Antioxidants.2023; 12(3): 711. CrossRef - An individual patient data meta-analysis to determine cut-offs for and confounders of NAFLD-fibrosis staging with magnetic resonance elastography
Jia-xu Liang, Javier Ampuero, Hao Niu, Kento Imajo, Mazen Noureddin, Jaideep Behari, Dae Ho Lee, Richard L. Ehman, Fredrik Rorsman, Johan Vessby, Juan R. Lacalle, Ferenc E. Mózes, Michael Pavlides, Quentin M. Anstee, Stephen A. Harrison, Javier Castell, R
Journal of Hepatology.2023; 79(3): 592. CrossRef - Relationship between controlled attenuated parameter and magnetic resonance imaging–proton density fat fraction for evaluating hepatic steatosis in patients with NAFLD
Ziming An, Qiaohong Liu, Wenli Zeng, Yan Wang, Qian Zhang, Huafu Pei, Xin Xin, Shuohui Yang, Fang Lu, Yu Zhao, Yiyang Hu, Qin Feng
Hepatology Communications.2022; 6(8): 1975. CrossRef - Noninvasive imaging of hepatic dysfunction: A state-of-the-art review
Ting Duan, Han-Yu Jiang, Wen-Wu Ling, Bin Song
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2022; 28(16): 1625. CrossRef - Diagnosis and Pathogenesis of Sarcopenia in Chronic Liver Disease Using Liver Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Atsushi Nakamura, Tsubasa Yoshimura, Tomomi Sato, Takeshi Ichikawa
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasma Aldo-Keto Reductase Family 1 Member B10 as a Biomarker Performs Well in the Diagnosis of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Fibrosis
Aron Park, Seung Joon Choi, Sungjin Park, Seong Min Kim, Hye Eun Lee, Minjae Joo, Kyoung Kon Kim, Doojin Kim, Dong Hae Chung, Jae Been Im, Jaehun Jung, Seung Kak Shin, Byung-Chul Oh, Cheolsoo Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Dae Ho Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(9): 5035. CrossRef - Contribution of a genetic risk score to ethnic differences in fatty liver disease
Maddie J. Kubiliun, Jonathan C. Cohen, Helen H. Hobbs, Julia Kozlitina
Liver International.2022; 42(10): 2227. CrossRef - Plasma Metabolomics and Machine Learning-Driven Novel Diagnostic Signature for Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
Moongi Ji, Yunju Jo, Seung Joon Choi, Seong Min Kim, Kyoung Kon Kim, Byung-Chul Oh, Dongryeol Ryu, Man-Jeong Paik, Dae Ho Lee
Biomedicines.2022; 10(7): 1669. CrossRef - Updated S2k Clinical Practice Guideline on Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) issued by the German Society of Gastroenterology, Digestive and Metabolic Diseases (DGVS) – April 2022 – AWMF Registration No.: 021–025
Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie.2022; 60(09): e733. CrossRef - Aktualisierte S2k-Leitlinie nicht-alkoholische Fettlebererkrankung der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Gastroenterologie, Verdauungs- und Stoffwechselkrankheiten (DGVS) – April 2022 – AWMF-Registernummer: 021–025
E. Roeb, A. Canbay, H. Bantel, J. Bojunga, J. de Laffolie, M. Demir, U. W. Denzer, A. Geier, W. P. Hofmann, C. Hudert, T. Karlas, M. Krawczyk, T. Longerich, T. Luedde, M. Roden, J. Schattenberg, M. Sterneck, A. Tannapfel, P. Lorenz, F. Tacke
Zeitschrift für Gastroenterologie.2022; 60(09): 1346. CrossRef - Ultrasound Methods for the Assessment of Liver Steatosis: A Critical Appraisal
Dorotea Bozic, Kristian Podrug, Ivana Mikolasevic, Ivica Grgurevic
Diagnostics.2022; 12(10): 2287. CrossRef - Significance of liver fat loss in chronic liver disease: Usefulness of hepatic proton density fat fraction measurement by magnetic resonance imaging in evaluating malnutrition
Atsushi Nakamura, Haruka Okada, Tsubasa Yoshimura, Manami Deguchi, Yuei Hosokawa, Tomomi Satoh, Takeshi Ichikawa, Keiji Okuyama, Yoshihiro Yoshioka, Hitoshi Asakura
Kanzo.2021; 62(9): 525. CrossRef - Screening for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-when, who and how?
Christoph G Dietrich, Monika Rau, Andreas Geier
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2021; 27(35): 5803. CrossRef
- A Novel Score Based on Controlled Attenuation Parameter Accurately Predicts Hepatic Steatosis in Individuals With Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Derivation and Independent Validation Study
- Drug/Regimen
-
- Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Differentially Affects Brain Activation in Response to Visual Food Cues in Lean and Obese Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jae Hyun Bae, Hyung Jin Choi, Kang Ik Kevin Cho, Lee Kyung Kim, Jun Soo Kwon, Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):248-259. Published online November 4, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0018
- 7,368 View
- 222 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background To investigate the effects of a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist on functional brain activation in lean and obese individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in response to visual food cues.
Methods In a randomized, single-blinded, crossover study, 15 lean and 14 obese individuals with T2DM were administered lixisenatide or normal saline subcutaneously with a 1-week washout period. We evaluated brain activation in response to pictures of high-calorie food, low-calorie food, and nonfood using functional magnetic resonance imaging and measured appetite and caloric intake in participants who were given access to an
ad libitum buffet.Results Obese individuals with T2DM showed significantly greater activation of the hypothalamus, pineal gland, parietal cortex (high-calorie food vs. low-calorie food,
P <0.05), orbitofrontal cortex (high-calorie food vs. nonfood,P <0.05), and visual cortex (food vs. nonfood,P <0.05) than lean individuals with T2DM. Lixisenatide injection significantly reduced the functional activation of the fusiform gyrus and lateral ventricle in obese individuals with T2DM compared with that in lean individuals with T2DM (nonfood vs. high-calorie food,P <0.05). In addition, in individuals who decreased their caloric intake after lixisenatide injection, there were significant interaction effects between group and treatment in the posterior cingulate, medial frontal cortex (high-calorie food vs. low-calorie food,P <0.05), hypothalamus, orbitofrontal cortex, and temporal lobe (food vs. nonfood,P <0.05).Conclusion Brain responses to visual food cues were different in lean and obese individuals with T2DM. In addition, acute administration of lixisenatide differentially affected functional brain activation in these individuals, especially in those who decreased their caloric intake after lixisenatide injection.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Altered Metabolic Phenotypes and Hypothalamic Neuronal Activity Triggered by Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:784-95)
Jae Hyun Bae
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 157. CrossRef - Diabetes remission and relapse following an intensive metabolic intervention combining insulin glargine/lixisenatide, metformin and lifestyle approaches: Results of a randomised controlled trial
Natalia McInnes, Stephanie Hall, Heather A. Lochnan, Stewart B. Harris, Zubin Punthakee, Ronald J. Sigal, Irene Hramiak, Mohammed Azharuddin, Joanne F. Liutkus, Jean‐François Yale, Farah Sultan, Ada Smith, Rose E. Otto, Diana Sherifali, Yan Yun Liu, Hertz
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(11): 3347. CrossRef - Glucagon-like peptide-1 analog therapy in rare genetic diseases: monogenic obesity, monogenic diabetes, and spinal muscular atrophy
Hussein Zaitoon, Ronit Lubetzky, Achiya Z. Amir, Hadar Moran-Lev, Liora Sagi, Michal Yacobi-Bach, Ophir Borger, Efrat Chorna, Yael Lebenthal, Avivit Brener
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(8): 1099. CrossRef - What can functional brain imaging teach us about remission of type 2 diabetes?
Dhruti Hirani, Shahd Alabdulkader, Alexander. D. Miras, Victoria Salem
Diabetic Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fasting oxyntomodulin, glicentin, and gastric inhibitory polypeptide levels are associated with activation of reward‐ and attention‐related brain centres in response to visual food cues in adults with obesity: A cross‐sectional functional MRI study
Nikolaos Perakakis, Olivia M. Farr, Christos S. Mantzoros
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(5): 1202. CrossRef - Aberrant Brain Functional Connectivity Strength and Effective Connectivity in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Xi Guo, Su Wang, Yu-Chen Chen, Heng-Le Wei, Gang-Ping Zhou, Yu-Sheng Yu, Xindao Yin, Kun Wang, Hong Zhang, Eusebio Chiefari
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Altered Metabolic Phenotypes and Hypothalamic Neuronal Activity Triggered by Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:784-95)
- Clinical Care/Education
- Hyperglycemia Is Associated with Impaired Muscle Quality in Older Men with Diabetes: The Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging
- Ji Won Yoon, Yong-Chan Ha, Kyoung Min Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Young Joo Park, Jae Young Lim, Ki Woong Kim, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(2):140-146. Published online March 31, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.2.140
- 7,302 View
- 78 Download
- 86 Web of Science
- 89 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The study aimed to investigate the influence of hyperglycemia on muscle quality in older men with type 2 diabetes.
Methods This was a subsidiary study of the Korean Longitudinal Study of Health and Aging. Among 326 older men consenting to tests of body composition and muscle strength, 269 men were ultimately analyzed after the exclusion because of stroke (
n =30) and uncertainty about the diagnosis of diabetes (n =27). Body composition was measured using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and computed tomography. Muscle strength for knee extension was measured using an isokinetic dynamometer. Muscle quality was assessed from the ratio of leg strength to the entire corresponding leg muscle mass.Results The muscle mass, strength, and quality in patients with type 2 diabetes did not differ significantly from controls. However, when patients with diabetes were subdivided according to their glycemic control status, patients with a glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level of ≥8.5% showed significantly decreased leg muscle quality by multivariate analysis (odds ratio, 4.510;
P =0.045) after adjustment for age, body mass index, smoking amount, alcohol consumption, physical activity, and duration of diabetes. Physical performance status was also impaired in subjects with an HbA1c of ≥8.5%.Conclusion Poor glycemic control in these older patients with diabetes was associated with significant risk of decreased muscle quality and performance status. Glycemic control with an HbA1c of <8.5% might be needed to reduce the risk of adverse skeletal and functional outcomes in this population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Downhill running and caloric restriction attenuate insulin resistance associated skeletal muscle atrophy via the promotion of M2-like macrophages through TRIB3-AKT pathway
Wei Luo, Yue Zhou, Qiang Tang, Yuhang Wang, Yansong Liu, Lei Ai
Free Radical Biology and Medicine.2024; 210: 271. CrossRef - Diabetic Sarcopenia. A proposed muscle screening protocol in people with diabetes
Daniel de Luis Román, Juana Carretero Gómez, José Manuel García-Almeida, Fernando Garrachón Vallo, German Guzmán Rolo, Juan José López Gómez, Francisco José Tarazona-Santabalbina, Alejandro Sanz-Paris
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Dynapenia and sarcopenia: association with the diagnosis, duration and complication of type 2 diabetes mellitus in ELSA-Brasil
Débora Noara Duarte dos Santos, Carolina Gomes Coelho, Maria de Fátima Haueisen Sander Diniz, Bruce Bartholow Duncan, Maria Inês Schmidt, Isabela Judith Martins Bensenor, Claudia Szlejf, Rosa Weiss Telles, Sandhi Maria Barreto
Cadernos de Saúde Pública.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Breaking Down Cachexia: A Narrative Review on the Prevalence of Cachexia in Cancer Patients and Its Associated Risk Factors
Mahmathi Karuppannan, Fares M. S. Muthanna, Fazlin Mohd Fauzi
Nutrition and Cancer.2024; 76(5): 404. CrossRef - Mechanism of muscle atrophy in a normal-weight rat model of type 2 diabetes established by using a soft-pellet diet
Sayaka Akieda-Asai, Hao Ma, Wanxin Han, Junko Nagata, Fumitake Yamaguchi, Yukari Date
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Morphological and functional changes in skeletal muscle in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Jardeson Rocha Filgueiras, Cleudiane Pereira Sales, Ivanilson Gomes da Silva, Cristiana Maria Dos Santos, Elias de Carvalho Magalhães Neto, Rebeca Barbosa da Rocha, Vinicius Saura Cardoso
Physiotherapy Theory and Practice.2023; 39(9): 1789. CrossRef - Hypoglycemic drug liraglutide alleviates low muscle mass by inhibiting the expression of MuRF1 and MAFbx in diabetic muscle atrophy
Dongmei Fan, Yue Wang, Bowei Liu, Fuzai Yin
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2023; 86(2): 166. CrossRef - Mechanisms underlying altered neuromuscular function in people with DPN
Antonin Le Corre, Nathan Caron, Nicolas A. Turpin, Georges Dalleau
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2023; 123(7): 1433. CrossRef - Effects of body compositions on the associations between ferritin and diabetes parameters among Japanese community dwellers
Kyi Mar Wai, Rei Akuzawa, Yoko Umeda, Wataru Munakata, Yoshiko Takahashi, Shigeyuki Nakaji, Kazushige Ihara
Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology.2023; 78: 127174. CrossRef - Effects of glycemic control on frailty: a multidimensional perspective
Ahmed H Abdelhafiz
Hospital Practice.2023; 51(3): 124. CrossRef - Hand grip strength is inversely associated with total daily insulin dose requirement in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a cross-sectional study
Da-shuang Chen, Yun-qing Zhu, Wen-ji Ni, Yu-jiao Li, Guo-ping Yin, Zi-yue Shao, Jian Zhu
PeerJ.2023; 11: e15761. CrossRef - Sarcopenia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Study of the Modifiable Risk Factors Involved
Surapaneni Lakshmi Sravya, Jayshree Swain, Abhay Kumar Sahoo, Swayamsidha Mangaraj, Jayabhanu Kanwar, Pooja Jadhao, Srijit Das
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(17): 5499. CrossRef - Salbutamol ameliorates skeletal muscle wasting and inflammatory markers in streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic rats
Anand Kumar, Priyanka Prajapati, Vinit Raj, Seong-Cheol Kim, Vikas Mishra, Chaitany Jayprakash Raorane, Ritu Raj, Dinesh Kumar, Sapana Kushwaha
International Immunopharmacology.2023; 124: 110883. CrossRef - Decreased serum musclin concentration is independently associated with the high prevalence of sarcopenia in Chinese middle‐elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Lei Fu, Qing Zhang, Juan Liu, Xiaoqing Yuan, Xinhua Ye
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(12): 1412. CrossRef - Association between relative muscle strength and hypertension in middle-aged and older Chinese adults
Jin-hua Luo, Tu-ming Zhang, Lin-lin Yang, Yu-ying Cai, Yu Yang
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus in the Elderly Adults in Korea: Based on Data from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2019 to 2020
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Yong-Moon Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Kyuho Kim, Jae-Hyun Bae, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Nan-Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 643. CrossRef - Management of Hyperglycemia in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes
Gunjan Y. Gandhi, Arshag D. Mooradian
Drugs & Aging.2022; 39(1): 39. CrossRef - Deleterious Effect of High-Fat Diet on Skeletal Muscle Performance Is Prevented by High-Protein Intake in Adult Rats but Not in Old Rats
Eleonora Poggiogalle, Fanny Rossignon, Aude Carayon, Fréderic Capel, Jean-Paul Rigaudière, Sarah De Saint Vincent, Olivier Le-Bacquer, Jérôme Salles, Christophe Giraudet, Véronique Patrac, Patrice Lebecque, Stéphane Walrand, Yves Boirie, Vincent Martin, C
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic phenotypes explain the relationship between dysglycaemia and frailty in older people with type 2 diabetes
A.H. Abdelhafiz, A.J. Sinclair
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2022; 36(4): 108144. CrossRef - Altered features of body composition in older adults with type 2 diabetes and prediabetes compared with matched controls
Kirsten E. Bell, Michael T. Paris, Egor Avrutin, Marina Mourtzakis
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2022; 13(2): 1087. CrossRef - A modern approach to glucose-lowering therapy in frail older people with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ahmed H. Abdelhafiz, Daniel Pennells, Alan J. Sinclair
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 17(2): 95. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome and its association with components of sarcopenia in older community-dwelling Chinese
Qiangwei Tong, Xiao Wang, Yunlu Sheng, Shu Chen, Bin Lai, Rong Lv, Jing Yu
The Journal of Biomedical Research.2022; 36(2): 120. CrossRef - Sarcopenia is associated with the Geriatric Nutritional Risk Index in elderly patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus
Shun Matsuura, Koji Shibazaki, Reiko Uchida, Yukiko Imai, Takuya Mukoyama, Shoko Shibata, Hiroshi Morita
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(8): 1366. CrossRef - Increased serum levels of advanced glycation end products are negatively associated with relative muscle strength in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Tsung-Hui Wu, Shiow-Chwen Tsai, Hsuan-Wei Lin, Chiao-Nan Chen, Chii-Min Hwu
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical outcomes of multidimensional association of type 2 diabetes mellitus, COVID-19 and sarcopenia: an algorithm and scoping systematic evaluation
Anmar Al-Taie, Oritsetimeyin Arueyingho, Jalal Khoshnaw, Abdul Hafeez
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Hypoglycaemic therapy in frail older people with type 2 diabetes mellitus—a choice determined by metabolic phenotype
Alan J. Sinclair, Daniel Pennells, Ahmed H. Abdelhafiz
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2022; 34(9): 1949. CrossRef - Insulin in Frail, Older People with Type 2 Diabetes—Low Threshold for Therapy
Ahmed Abdelhafiz, Shail Bisht, Iva Kovacevic, Daniel Pennells, Alan Sinclair
Diabetology.2022; 3(2): 369. CrossRef - Sex-Specific Associations Between Low Muscle Mass and Glucose Fluctuations in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Xiulin Shi, Wenjuan Liu, Lulu Zhang, Fangsen Xiao, Peiying Huang, Bing Yan, Yiping Zhang, Weijuan Su, Qiuhui Jiang, Mingzhu Lin, Wei Liu, Xuejun Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Lifestyle factors associated with muscle quality in community‐dwelling older people with type 2 diabetes in Japan and Taiwan: a cross‐sectional study
Yuko Yamaguchi, Chieko Greiner, Shu‐Chun Lee, Hirochika Ryuno, Hsin‐Yen Yen, Chiou‐Fen Lin, Ting‐I Lee, Pi‐Hsia Lee
Psychogeriatrics.2022; 22(5): 736. CrossRef - Relationship between Echo Intensity of Vastus Lateralis and Knee Extension Strength in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yoshikazu HIRASAWA, Ryosuke MATSUKI, Hideaki TANINA
Physical Therapy Research.2022; 25(3): 113. CrossRef - Time trends (2012–2020) in glycated hemoglobin and adherence to the glycemic targets recommended for elderly patients by the Japan Diabetes Society/Japan Geriatrics Society Joint Committee among memory clinic patients with diabetes mellitus
Taiki Sugimoto, Hisashi Noma, Yujiro Kuroda, Nanae Matsumoto, Kazuaki Uchida, Yoshinobu Kishino, Naoki Saji, Shumpei Niida, Takashi Sakurai
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(12): 2038. CrossRef - Relationship between Diabetes Status and Sarcopenia in Community-Dwelling Older Adults
Kazuhei Nishimoto, Takehiko Doi, Kota Tsutsumimoto, Sho Nakakubo, Satoshi Kurita, Yuto Kiuchi, Hiroyuki Shimada
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2022; 23(10): 1718.e7. CrossRef - Low relative hand grip strength is associated with a higher risk for diabetes and impaired fasting glucose among the Korean population
Min Jin Lee, Ah Reum Khang, Dongwon Yi, Yang Ho Kang, Giacomo Pucci
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(10): e0275746. CrossRef - Association between Lower-to-Upper Ratio of Appendicular Skeletal Muscle and Metabolic Syndrome
Hyun Eui Moon, Tae Sic Lee, Tae-Ha Chung
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(21): 6309. CrossRef - Association of plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and frailty in community-dwelling older adults
Eun Roh, Soon Young Hwang, Eyun Song, Min Jeong Park, Hye Jin Yoo, Sei Hyun Baik, Miji Kim, Chang Won Won, Kyung Mook Choi
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Organokines, Sarcopenia, and Metabolic Repercussions: The Vicious Cycle and the Interplay with Exercise
Giulia Minniti, Letícia Maria Pescinini-Salzedas, Guilherme Almeida dos Santos Minniti, Lucas Fornari Laurindo, Sandra Maria Barbalho, Renata Vargas Sinatora, Lance Alan Sloan, Rafael Santos de Argollo Haber, Adriano Cressoni Araújo, Karina Quesada, Jesse
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(21): 13452. CrossRef - Multimorbidity, Frailty and Diabetes in Older People–Identifying Interrelationships and Outcomes
Alan J. Sinclair, Ahmed H. Abdelhafiz
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(11): 1911. CrossRef - Determinants of High-Dose Insulin Usage and Upper Extremity Muscle Strength in Adult Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Eren Imre, Tugce Apaydin, Hatice Gizem Gunhan, Dilek Gogas Yavuz
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2021; 45(4): 341. CrossRef - Glycemic Control and Insulin Improve Muscle Mass and Gait Speed in Type 2 Diabetes: The MUSCLES-DM Study
Ken Sugimoto, Hiroshi Ikegami, Yasunori Takata, Tomohiro Katsuya, Masahiro Fukuda, Hiroshi Akasaka, Yasuharu Tabara, Haruhiko Osawa, Yoshihisa Hiromine, Hiromi Rakugi
Journal of the American Medical Directors Association.2021; 22(4): 834. CrossRef - A Narrative Review on Sarcopenia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Prevalence and Associated Factors
Anna Izzo, Elena Massimino, Gabriele Riccardi, Giuseppe Della Pepa
Nutrients.2021; 13(1): 183. CrossRef - Decreased handgrip strength in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study in a tertiary care hospital in north India
Parjeet Kaur, Ritesh Bansal, Bharti Bhargava, Sunil Mishra, Harmandeep Gill, Ambrish Mithal
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(1): 325. CrossRef - Factors associated with relative muscle strength in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chiao-Nan Chen, Ting-Chung Chen, Shiow-Chwen Tsai, Chii-Min Hwu
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2021; 95: 104384. CrossRef - Newer anti-diabetic therapies with low hypoglycemic risk-potential advantages for frail older people
Demelza Emmerton, Ahmed Abdelhafiz
Hospital Practice.2021; 49(3): 164. CrossRef - Influence of glucose, insulin fluctuation, and glycosylated hemoglobin on the outcome of sarcopenia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yuxi Lin, Yongze Zhang, Ximei Shen, Lingning Huang, Sunjie Yan
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2021; 35(6): 107926. CrossRef - Presence and Implications of Sarcopenia in Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis
Gregory Habig, Christa Smaltz, Dina Halegoua-DeMarzio
Metabolites.2021; 11(4): 242. CrossRef - Sensory-Motor Mechanisms Increasing Falls Risk in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Neil D. Reeves, Giorgio Orlando, Steven J. Brown
Medicina.2021; 57(5): 457. CrossRef - Impact of frailty metabolic phenotypes on the management of older people with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ahmed H Abdelhafiz, Demelza Emmerton, Alan J Sinclair
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2021; 21(8): 614. CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes mellitus in older adults: clinical considerations and management
Srikanth Bellary, Ioannis Kyrou, James E. Brown, Clifford J. Bailey
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2021; 17(9): 534. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome and Sarcopenia
Hiroki Nishikawa, Akira Asai, Shinya Fukunishi, Shuhei Nishiguchi, Kazuhide Higuchi
Nutrients.2021; 13(10): 3519. CrossRef - Angiotensin II inhibition: a potential treatment to slow the progression of sarcopenia
Jeffrey Kingsley, Keiichi Torimoto, Tomoki Hashimoto, Satoru Eguchi
Clinical Science.2021; 135(21): 2503. CrossRef - Muscle strength, an independent determinant of glycemic control in older adults with long-standing type 2 diabetes: a prospective cohort study
Bo Kyung Koo, Seoil Moon, Min Kyong Moon
BMC Geriatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between homocysteine, inflammatory cytokines and sarcopenia in Chinese older adults with type 2 diabetes
Zhi-Jing Mu, Jun-Ling Fu, Li-Na Sun, Piu Chan, Shuang-Ling Xiu
BMC Geriatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association Between Diabetes Mellitus and Risk of Sarcopenia: Accumulated Evidences From Observational Studies
Yu-Shun Qiao, Yin-He Chai, Hong-Jian Gong, Zhiyessova Zhuldyz, Coen D. A. Stehouwer, Jian-Bo Zhou, Rafael Simó
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The utility of the ultrasonographic assessment of the lower leg muscles to evaluate sarcopenia and muscle quality in older adults
Masaaki Isaka, Ken Sugimoto, Taku Fujimoto, Yukiko Yasunobe, Keyu Xie, Yuri Onishi, Shino Yoshida, Toshimasa Takahashi, Hitomi Kurinami, Hiroshi Akasaka, Yasushi Takeya, Koichi Yamamoto, Hiromi Rakugi
JCSM Clinical Reports.2021; 6(2): 53. CrossRef - Associations between grip strength and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus: an analysis of data from the 2014-2019 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Harim Choe, Hoyong Sung, Geon Hui Kim, On Lee, Hyo Youl Moon, Yeon Soo Kim
Epidemiology and Health.2021; 43: e2021080. CrossRef - Uncontrolled Diabetes as an Associated Factor with Dynapenia in Adults Aged 50 Years or Older: Sex Differences
Clarice Cavalero Nebuloni, Roberta de Oliveira Máximo, Cesar de Oliveira, Tiago da Silva Alexandre, Anne Newman
The Journals of Gerontology: Series A.2020; 75(6): 1191. CrossRef - Identification and prevalence of frailty in diabetes mellitus and association with clinical outcomes: a systematic review protocol
Peter Hanlon, Isabella Fauré, Neave Corcoran, Elaine Butterly, Jim Lewsey, David A McAllister, Frances S Mair
BMJ Open.2020; 10(9): e037476. CrossRef - Longitudinal association of type 2 diabetes and insulin therapy with muscle parameters in the KORA-Age study
Uta Ferrari, Cornelia Then, Marietta Rottenkolber, Canan Selte, Jochen Seissler, Romy Conzade, Birgit Linkohr, Annette Peters, Michael Drey, Barbara Thorand
Acta Diabetologica.2020; 57(9): 1057. CrossRef - Triad of impairment in older people with diabetes-reciprocal relations and clinical implications
A.H. Abdelhafiz, P.C. Davies, A.J. Sinclair
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 161: 108065. CrossRef - Physical activity and exercise: Strategies to manage frailty
Javier Angulo, Mariam El Assar, Alejandro Álvarez-Bustos, Leocadio Rodríguez-Mañas
Redox Biology.2020; 35: 101513. CrossRef - Handgrip measurement as a useful benchmark for locomotive syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A KAMOGAWA‐DM cohort study
Noriyuki Kitagawa, Takuro Okamura, Nobuko Kitagawa, Yoshitaka Hashimoto, Masahide Hamaguchi, Michiaki Fukui
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2020; 11(6): 1602. CrossRef - Edmonton frail score is associated with diabetic control in elderly type 2 diabetic subjects
Satilmis Bilgin, Gulali Aktas, Ozge Kurtkulagi, Burcin M. Atak, Tuba T. Duman
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2020; 19(1): 511. CrossRef - Comparison of field- and laboratory-based estimates of muscle quality index between octogenarians and young older adults: an observational study
Dahan da Cunha Nascimento, Jonato Prestes, Joyce de Sousa Diniz, Pedro Rodrigues Beal, Vicente Paulo Alves, Whitley Stone, Fabiani Lage Rodrigues Beal
Journal of Exercise Rehabilitation.2020; 16(5): 458. CrossRef - Tip 2 Diyabetli Hastalarda Kan Glukoz Seviyesi ile Kas Gücü, Propriosepsiyon ve Vücut Kompozisyonu Arasındaki İlişki
Zahide Betül TAYFUR, Esra ATILGAN
Turkish Journal of Diabetes and Obesity.2020; 4(3): 207. CrossRef - Challenges and Strategies for Diabetes Management in Community-Living Older Adults
Alan J. Sinclair, Ahmed H. Abdelhafiz
Diabetes Spectrum.2020; 33(3): 217. CrossRef - Association between deterioration in muscle strength and peripheral neuropathy in people with diabetes
Tae Jung Oh, Sunyoung Kang, Jie-Eun Lee, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Hak Chul Jang
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(8): 598. CrossRef - The Association between Body Composition using Dual energy X-ray Absorptiometry and Type-2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational studies
Preeti Gupta, Carla Lanca, Alfred T. L. Gan, Pauline Soh, Sahil Thakur, Yijin Tao, Neelam Kumari, Ryan E. K. Man, Eva K. Fenwick, Ecosse L. Lamoureux
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - MECHANISMS OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Sarcopenia in endocrine and non-endocrine disorders
Victoria Zeghbi Cochenski Borba, Tatiana Lemos Costa, Carolina Aguiar Moreira, Cesar Luiz Boguszewski
European Journal of Endocrinology.2019; 180(5): R185. CrossRef - Hyperglycemia induces skeletal muscle atrophy via a WWP1/KLF15 axis
Yu Hirata, Kazuhiro Nomura, Yoko Senga, Yuko Okada, Kenta Kobayashi, Shiki Okamoto, Yasuhiko Minokoshi, Michihiro Imamura, Shin’ichi Takeda, Tetsuya Hosooka, Wataru Ogawa
JCI Insight.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Hyperglycemia in non‐obese patients with type 2 diabetes is associated with low muscle mass: The Multicenter Study for Clarifying Evidence for Sarcopenia in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
Ken Sugimoto, Yasuharu Tabara, Hiroshi Ikegami, Yasunori Takata, Kei Kamide, Tome Ikezoe, Eri Kiyoshige, Yukako Makutani, Hiroshi Onuma, Yasuyuki Gondo, Kazunori Ikebe, Noriaki Ichihashi, Tadao Tsuboyama, Fumihiko Matsuda, Katsuhiko Kohara, Mai Kabayama,
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2019; 10(6): 1471. CrossRef - Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy as a Risk Factor for Sarcopenia
Tae Jung Oh, Yoojung Song, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research.2019; 23(4): 170. CrossRef - Diabetes and frailty
Mariam El Assar, Olga Laosa, Leocadio Rodríguez Mañas
Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition & Metabolic Care.2019; 22(1): 52. CrossRef - Association of Glucose Fluctuations with Sarcopenia in Older Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Noriko Ogama, Takashi Sakurai, Shuji Kawashima, Takahisa Tanikawa, Haruhiko Tokuda, Shosuke Satake, Hisayuki Miura, Atsuya Shimizu, Manabu Kokubo, Shumpei Niida, Kenji Toba, Hiroyuki Umegaki, Masafumi Kuzuya
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(3): 319. CrossRef - Diabetes in the elderly
Ahmed H. Abdelhafiz, Alan J. Sinclair
Medicine.2019; 47(2): 119. CrossRef - Diabetes and Muscle Dysfunction in Older Adults
Hak Chul Jang
Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research.2019; 23(4): 160. CrossRef - Factors influencing safe glucose-lowering in older adults with type 2 diabetes: A PeRsOn-centred ApproaCh To IndiVidualisEd (PROACTIVE) Glycemic Goals for older people
C.E. Hambling, K. Khunti, X. Cos, J. Wens, L. Martinez, P. Topsever, S. Del Prato, A. Sinclair, G. Schernthaner, G. Rutten, S. Seidu
Primary Care Diabetes.2019; 13(4): 330. CrossRef - Effects of resistance training on neuromuscular parameters in elderly with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized clinical trial
Cíntia E. Botton, Daniel Umpierre, Anderson Rech, Lucinéia O. Pfeifer, Carlos L.F. Machado, Juliana L. Teodoro, Alexandre S. Dias, Ronei S. Pinto
Experimental Gerontology.2018; 113: 141. CrossRef - Management of Elderly Diabetes Patients Who Are Unable to Self-Care
Bok Rye Song
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(4): 232. CrossRef - Decreased Muscle Strength and Quality in Diabetes-Related Dementia
Akito Tsugawa, Yusuke Ogawa, Naoto Takenoshita, Yoshitsugu Kaneko, Hirokuni Hatanaka, Eriko Jaime, Raita Fukasawa, Haruo Hanyu
Dementia and Geriatric Cognitive Disorders Extra.2017; 7(3): 454. CrossRef - Diabetes and Sarcopenia
Dong Hyun Kim, Tae Yang Yu
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2017; 18(4): 239. CrossRef - Frailty and sarcopenia - newly emerging and high impact complications of diabetes
Alan J. Sinclair, Ahmed H. Abdelhafiz, Leocadio Rodríguez-Mañas
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(9): 1465. CrossRef - Association of diabetic retinopathy with both sarcopenia and muscle quality in patients with type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study
Tatsuya Fukuda, Ryotaro Bouchi, Takato Takeuchi, Yujiro Nakano, Masanori Murakami, Isao Minami, Hajime Izumiyama, Koshi Hashimoto, Takanobu Yoshimoto, Yoshihiro Ogawa
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2017; 5(1): e000404. CrossRef - Practical considerations for managing patients with diabetes and dementia
Michelle L Mair, Rohin Athavale, Ahmed H Abdelhafiz
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2017; 12(6): 429. CrossRef - Sarcopenia: An Endocrine Disorder?
Alexis McKee, John E. Morley, Alvin M. Matsumoto, Aaron Vinik
Endocrine Practice.2017; 23(9): 1143. CrossRef - Response: Hyperglycemia Is Associated with Impaired Muscle Quality in Older Men with Diabetes: The Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging (Diabetes Metab J 2016;40:140-6)
Ji Won Yoon, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(3): 250. CrossRef - Salivary lactate dehydrogenase and aminotransferases in diabetic patients
Barbara Malicka, Katarzyna Skoskiewicz-Malinowska, Urszula Kaczmarek
Medicine.2016; 95(47): e5211. CrossRef - Explanatory models of muscle performance in acromegaly patients evaluated by knee isokinetic dynamometry: Implications for rehabilitation
Agnaldo José Lopes, Arthur Sá Ferreira, Evelyn Mendes Walchan, Mauricio Santos Soares, Priscila Santos Bunn, Fernando Silva Guimarães
Human Movement Science.2016; 49: 160. CrossRef - Letter: Hyperglycemia Is Associated with Impaired Muscle Quality in Older Men with Diabetes: The Korean Longitudinal Study on Health and Aging (Diabetes Metab J 2016;40:140-6)
Jun Sung Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(3): 248. CrossRef - Sarcopenia, Frailty, and Diabetes in Older Adults
Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(3): 182. CrossRef
- Downhill running and caloric restriction attenuate insulin resistance associated skeletal muscle atrophy via the promotion of M2-like macrophages through TRIB3-AKT pathway
- The Interplay between Autophagy and Aging
- Jong-Ok Pyo, Seung-Min Yoo, Yong-Keun Jung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(5):333-339. Published online October 17, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.5.333
- 3,784 View
- 37 Download
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Numerous studies have established a link between autophagy and aging; however, the relationship has not been clearly defined. Aging is a very complex process caused by the accumulation of various factors due to the gradual failure of cellular maintenance. Recent studies have shown that autophagy reduces the stress responses induced by starvation, reactive oxygen species, and the accumulation of intracellular proteins and organelles through cytoprotection, clearance of damaged mitochondria, and lysosomal degradation. Here, we summarize our current understanding of the relationship between autophagy and the aging process.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Dysregulation of autophagy activation induced by atorvastatin contributes to new-onset diabetes mellitus in western diet-fed mice
Juhee Kim, Minjune Kim, Minjeong Kim, Young-Hye You, Youngmi Song, Byung-Wan Lee
Metabolism.2024; 153: 155795. CrossRef - The impact of zinc on the molecular signaling pathways in the diabetes disease
Keyvan Asghari, Zahra Shargh, Sina Fatehfar, Leila Chodari, Parsa Sameei
Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology.2022; 72: 126985. CrossRef - Antiaging agents: safe interventions to slow aging and healthy life span extension
Ji-Kai Liu
Natural Products and Bioprospecting.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycans in autophagy, endocytosis and lysosomal functions
Fulvio Reggiori, Hans-Joachim Gabius, Massimo Aureli, Winfried Römer, Sandro Sonnino, Eeva-Liisa Eskelinen
Glycoconjugate Journal.2021; 38(5): 625. CrossRef - Reduced cardiomyocyte Na+ current in the age‐dependent murine Pgc‐1β−/− model of ventricular arrhythmia
Shiraz Ahmad, Haseeb Valli, Robert Smyth, Anita Y. Jiang, Kamalan Jeevaratnam, Hugh R. Matthews, Christopher L.‐H. Huang
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2019; 234(4): 3921. CrossRef - Autophagy in Human Health and Disease: Novel Therapeutic Opportunities
Francesca Giampieri, Sadia Afrin, Tamara Y. Forbes-Hernandez, Massimiliano Gasparrini, Danila Cianciosi, Patricia Reboredo-Rodriguez, Alfonso Varela-Lopez, Jose L. Quiles, Maurizio Battino
Antioxidants & Redox Signaling.2019; 30(4): 577. CrossRef - Molybdenum Disulfide Nanoparticles Resist Oxidative Stress-Mediated Impairment of Autophagic Flux and Mitigate Endothelial Cell Senescence and Angiogenic Dysfunctions
Sunkui Ke, Youlin Lai, Tong Zhou, Lihuang Li, Yange Wang, Lei Ren, Shefang Ye
ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering.2018; 4(2): 663. CrossRef - Phenformin inhibits cell proliferation and induces cell apoptosis and autophagy in cholangiocarcinoma
Shuyang Hu, Qing Ouyang, Qingbao Cheng, Jinghan Wang, Feiling Feng, Liang Qiao, Wei Gan, Yang Shi, Demin Wu, Xiaoqing Jiang
Molecular Medicine Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Ventricular pro-arrhythmic phenotype, arrhythmic substrate, ageing and mitochondrial dysfunction in peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-γ coactivator-1β deficient (Pgc-1β) murine hearts
Shiraz Ahmad, Haseeb Valli, Karan R. Chadda, James Cranley, Kamalan Jeevaratnam, Christopher L.-H. Huang
Mechanisms of Ageing and Development.2018; 173: 92. CrossRef - From Christian de Duve to Yoshinori Ohsumi: More to autophagy than just dining at home
Margaret M. Harnett, Miguel A. Pineda, Perle Latré de Laté, Russell J. Eason, Sébastien Besteiro, William Harnett, Gordon Langsley
Biomedical Journal.2017; 40(1): 9. CrossRef - Metformin Restores Parkin-Mediated Mitophagy, Suppressed by Cytosolic p53
Young Song, Woo Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2016; 17(1): 122. CrossRef - Selected reaction monitoring mass spectrometry for relative quantification of proteins involved in cellular life and death processes
Rune Isak Dupont Birkler, Zahra Nochi, Niels Gregersen, Johan Palmfeldt
Journal of Chromatography B.2016; 1035: 49. CrossRef - Dehydroepiandrosterone prevents linoleic acid-induced endothelial cell senescence by increasing autophagy
Min Jung Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Sang Ah. Lee, Yu Mi Kang, Chang Hee Jung, Hae Kyeong Yoon, So Mi Seol, Yoo La Lee, Woo Je Lee, Joong-Yeol Park
Metabolism.2015; 64(9): 1134. CrossRef - Successful aging: Advancing the science of physical independence in older adults
Stephen D. Anton, Adam J. Woods, Tetso Ashizawa, Diana Barb, Thomas W. Buford, Christy S. Carter, David J. Clark, Ronald A. Cohen, Duane B. Corbett, Yenisel Cruz-Almeida, Vonetta Dotson, Natalie Ebner, Philip A. Efron, Roger B. Fillingim, Thomas C. Foster
Ageing Research Reviews.2015; 24: 304. CrossRef - Autophagy in acute leukemias: A double-edged sword with important therapeutic implications
Cecilia Evangelisti, Camilla Evangelisti, Francesca Chiarini, Annalisa Lonetti, Francesca Buontempo, Luca M. Neri, James A. McCubrey, Alberto M. Martelli
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research.2015; 1853(1): 14. CrossRef - Autophagy: A housekeeper in cardiorenal metabolic health and disease
Guanghong Jia, James R. Sowers
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2015; 1852(2): 219. CrossRef - Autophagy and Lipid Droplets in the Liver
Nuria Martinez-Lopez, Rajat Singh
Annual Review of Nutrition.2015; 35(1): 215. CrossRef - Lysosomal Two-pore Channel Subtype 2 (TPC2) Regulates Skeletal Muscle Autophagic Signaling
Pei-Hui Lin, Pu Duann, Shinji Komazaki, Ki Ho Park, Haichang Li, Mingzhai Sun, Mathew Sermersheim, Kristyn Gumpper, John Parrington, Antony Galione, A. Mark Evans, Michael X. Zhu, Jianjie Ma
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2015; 290(6): 3377. CrossRef - Zinc and autophagy
Juan P. Liuzzi, Liang Guo, Changwon Yoo, Tiffanie S. Stewart
BioMetals.2014; 27(6): 1087. CrossRef - Autophagy in the eye: Implications for ocular cell health
Laura S. Frost, Claire H. Mitchell, Kathleen Boesze-Battaglia
Experimental Eye Research.2014; 124: 56. CrossRef - Can Enhanced Autophagy Be Associated with Human Longevity? Serum Levels of the Autophagy Biomarker Beclin-1 Are Increased in Healthy Centenarians
Enzo Emanuele, Piercarlo Minoretti, Fabian Sanchis-Gomar, Helios Pareja-Galeano, Yusuf Yilmaz, Nuria Garatachea, Alejandro Lucia
Rejuvenation Research.2014; 17(6): 518. CrossRef - Responses and adaptations of intervertebral disc cells to microenvironmental stress: a possible central role of autophagy in the adaptive mechanism
Libo Jiang, Fenglai Yuan, Xiaofan Yin, Jian Dong
Connective Tissue Research.2014; 55(5-6): 311. CrossRef - STOP accelerating lung aging for the treatment of COPD
Kazuhiro Ito, Nicolas Mercado
Experimental Gerontology.2014; 59: 21. CrossRef - In search of antiaging modalities: Evaluation of mTOR‐ and ROS/DNA damage‐signaling by cytometry
Zbigniew Darzynkiewicz, Hong Zhao, H. Dorota Halicka, Jiangwei Li, Yong‐Syu Lee, Tze‐Chen Hsieh, Joseph M. Wu
Cytometry Part A.2014; 85(5): 386. CrossRef - Induction of Covalently Crosslinked p62 Oligomers with Reduced Binding to Polyubiquitinated Proteins by the Autophagy Inhibitor Verteporfin
Elizabeth Donohue, Aruna D. Balgi, Masaaki Komatsu, Michel Roberge, Srinivasa M. Srinivasula
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(12): e114964. CrossRef
- Dysregulation of autophagy activation induced by atorvastatin contributes to new-onset diabetes mellitus in western diet-fed mice
- Effects of Aging and Obesity on Insulin Secretion and Sensitivity.
- J Y Kim, J H Jee, H J Kim, B W Lee, Y J Chung, J H Chung, Y K Min, M S Lee, M K Lee, K W Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2005;29(1):39-47. Published online January 1, 2005
- 788 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Type 2 diabetes is occurring in epidemic proportions worldwide and aging has been defined as one of the risk factors for the progression to diabetes. The mechanism responsible for deterioration of glucose tolerance with aging is still unclear. It has been debated whether this deterioration results from an abnormal beta cell secretory function or/and decreased insulin sensitivity, from the aging process per se, or some other factors, such as an increase in BMI and abdominal fat. The changes in the insulin secretion and sensitivity were assessed in relation to aging and obesity, and the association between obesity and factors influencing glucose homeostasis in obese subjects evaluated. METHODS: 530 individuals, aged 24 to 75 years, having undergone a 75 g OGTT were enrolled, and the insulinogenic index and HOMA-IR calculated for each subject. 212 individuals were obese, i.e. a BMI above 25, which was evaluated from the body composition by CT at the umbilicus and thigh levels. RESULTS: There was negative correlation between the insulinogenic index and age, but not between HOMA-IR and age. In relation to increasing age, the body composition changed toward a metabolically obese state, with increasing WHR, visceral fat area, VSR and VWR. Both the insulinogenic index and HOMA-IR were positively correlated with the anthropometric parameters. CONCLUSION: The age-associated deterioration in glucose tolerance may be due to decreases in both insulin secretion and insulin sensitivity from changes in body composition

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





