- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 35(3); 2011 > Article
-
Original ArticleFactors Associated with Long-Term Oral Hypoglycemic Agent Responsiveness in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Bo-Yeon Kim, Chan-Hee Jung, Ji-Oh Mok, Chul-Hee Kim
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2011;35(3):282-289.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.3.282
Published online: June 30, 2011
Division of Endocrinology & Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Chul-Hee Kim. Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, 1174 Jung-dong, Wonmi-gu, Bucheon 420-767, Korea. chkimem@sch.ac.kr
Copyright © 2011 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- This study was performed to determine the factors associated with long-term oral hypoglycemic agent (OHA) responsiveness in Korean type 2 diabetic patients.
-
Methods
- Two groups of patients were selected among the type 2 diabetic patients who were followed for more than two years at a university hospital diabetes clinic. The OHA responsive group consisted of 197 patients whose HbA1c levels were maintained at ≤7% with OHA for more than two years. The OHA failure group consisted of 180 patients whose HbA1c levels were >8% in spite of optimal combined OHA therapy or patients who required insulin therapy within the two years of the study.
-
Results
- The OHA failure group had higher baseline values of fasting and postprandial glucose, HbA1c, and lower fasting, postprandial, and delta C-peptide compared to those of the OHA responsive group. The OHA failure group also had a higher proportion of female patients, longer diabetic duration, and more family history of diabetes. There were no significant differences in body mass index (BMI) or insulin resistance index between the two groups. Multiple logistic regression analysis showed that the highest quartile of baseline fasting, postprandial glucose, and HbA1c and the lowest quartile of postprandial and delta C-peptide were associated with an increased odds ratio of OHA failure after adjustment for age, sex, body mass index, and family history of diabetes.
-
Conclusion
- Lower baseline values of postprandial and delta C-peptide and elevated fasting glucose and HbA1c are associated with long-term OHA responsiveness in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Defective insulin secretion and insulin resistance are the two main factors causing the development and progression of type 2 diabetes [1]. In the UK Prospective Diabetes Study [2], after an initial improvement, glycemic control continues to deteriorate despite the use of oral agents aimed to enhance insulin secretion and to reduce insulin resistance. This deterioration can be attributed to the progressive decline of β-cell dysfunction, and insulin treatment is usually required in type 2 diabetic patients who are not able to obtain good glycemic control with an oral hypoglycemic agent. Although new treatment options for type 2 diabetic patients are increasingly available, agreement on the most effective treatment approach for individual patients has not been achieved. Prediction of poor response to an oral hypoglycemic agent may be helpful in achieving good glycemic control through earlier administration of insulin therapy.
- Although many previous studies have investigated the association between markers of β-cell function and future insulin use, there is no reliable predictor of responsiveness to oral hypoglycemic agents in clinical practice [3]. Previous studies have reported that plasma glucose, HbA1c, and serum C-peptide are associated with insulin use [4-10]. Those studies focused on predicting future insulin use, but many type 2 diabetic patients who were categorized as non-insulin requiring were not adequately controlled despite the use of an oral hypoglycemic agent. In addition, most of the studies were cross-sectional or had short durations of follow-up and included small numbers of participants. To identify the factors associated with oral hypoglycemic agent responsiveness, we comprehensively examined the association between various clinical factors and oral hypoglycemic agent failure in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
INTRODUCTION
- Participants
- Data for Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who visited the diabetes clinic at Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital during 2001 to 2007 were analyzed. Individuals diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus (fasting serum C-peptide <0.6 ng/mL and postprandial serum C-peptide <1.0 ng/mL or history of diabetic ketoacidosis), with renal insufficiency (serum Cr >1.3 mg/dL), alcoholism, chronic liver disease, chronic infection, endocrine disorders (e.g., thyroid dysfunction, pituitary disease, adrenal disease, or receiving hormone replacement therapy) or malignancy were excluded. Individuals who had been taking drugs that could influence glucose metabolism were also excluded, as were individuals who had been treated with insulin before participation in the study or whose follow-up duration was shorter than two years. In the remaining 1,060 type 2 diabetic patients, fasting and postprandial serum C-peptide levels were measured at baseline, and the evaluation of glycemic control (fasting and postprandial glucose and HbA1c) was performed at baseline and during regular follow-up visits. These follow-up visits occurred at two- to four-month intervals and were conducted by endocrinology specialists, who adjusted anti-diabetic medications as needed to achieve HbA1c <6.5-7%. For the analyses, two groups of patients were selected from the 1,060 patients: the oral hypoglycemic agent (OHA) responsive group consisted of 197 patients whose HbA1c levels were controlled below 7% for more than two years with insulin secretagogues at a less than half maximum dose and/or other oral hypoglycemic agents (biguanide, thiazolidinediones, α-glucosidase inhibitor, or DPP-4 inhibitor). The OHA failure group consisted of 180 patients with the following conditions: 46 patients whose HbA1c levels were greater than 8% despite taking insulin secretagogues at more than the half maximum dose, in addition to other OHAs (biguanide, thiazolidinediones, alpha-glucosidase inhibitor, or DPP-4 inhibitor), and 134 patients who required insulin therapy for glycemic control within two years. A total of 683 patients with the following conditions were excluded: patients who were not followed-up regularly, whose diabetes was controlled with diet only, whose HbA1c levels were between 7% to 8%, who had taken an insufficient dose of OHA despite HbA1c levels greater than 8%, or whose HbA1c levels were controlled below 7% only after administration of the maximum dose of insulin secretagogues. This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital.
- Measurements
- Fasting and postprandial 2-hour glucose and C-peptide levels, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), serum total cholesterol, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein cholesterol, low density lipoprotein cholesterol, and creatinine were determined at baseline. HbA1c was measured using ion-exchange HPLC (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA), and serum C-peptide was determined using an immunoradiometric assay (Immunotech, Prague, Czech Republic). Delta C-peptide was defined as the difference between postprandial serum C-peptide and fasting C-peptide level. The homeostasis model assessment index for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) was calculated with the formula: HOMA-IR=fasting plasma insulin (µU/mL)×fasting plasma glucose (mmol/L)/22.5.
- Statistical analysis
- Data are presented as the mean±standard deviation. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 14.0 for Windows® (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA). Variables that were not distributed normally, such as blood concentrations of glucose, triglycerides, and C-peptide level, were log-transformed before analysis. The unpaired Student's t-test was used to compare differences between the two groups, and the χ2 test was used to compare percentages. Multivariate logistic regression analyses were used to estimate the odds ratios (ORs) for OHA failure after adjusting for other clinical and biochemical variables. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were used to determine the predictive abilities of variables for OHA failure. A P value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
METHODS
- In the OHA responsive group, sulfonylurea was used in 64% of the patients, metformin in 86%, thiazolidinediones in 30%, α-glucosidase inhibitor in 10%, and DPP-4 inhibitor in 5%. In the OHA failure group, sulfonylurea was used in all of the patients, metformin in 73%, thiazolidinediones in 28%, α-glucosidase inhibitor in 6%, and DPP-4 inhibitor in 5%. The baseline characteristics of the study participants are shown in Table 1. Patients in the OHA failure group showed higher baseline values of HbA1c, fasting and postprandial plasma glucose, and lower values of fasting, postprandial, and delta C-peptide levels compared to those of patients in the OHA responsive group. Also, patients in the OHA failure group had a significantly higher proportion of women, more family history of diabetes, and longer duration of diabetes. When the patients were divided into three groups according to diabetic duration, patients with shorter diabetic duration showed a lower rate of OHA failure compared to those of patients with longer diabetic duration (<5 years, 33.5%; 5 to 10 years, 63.4%; >10 years, 81.5%; P<0.001). The proportion of drug-naive patients was higher in the OHA responsive group compared to that in the OHA failure group (29.9% vs. 5.6%, P<0.001). There was no significant difference between the two groups regarding the prevalence of hypertension, body mass index, or HOMA-IR.
- To identify independent factors that are associated with poor response to oral hypoglycemic agent, we performed multiple logistic regression analysis after categorizing HbA1c, fasting and postprandial plasma glucose, fasting and postprandial serum C-peptide, and delta C-peptide into quartiles (Table 2). In the unadjusted model, the highest quartiles of HbA1c and plasma glucose, and lowest quartile of C-peptide were associated with increased risk of oral hypoglycemic agent failure. We adjusted for potential confounding factors which were significantly different between the two groups (sex, family history of diabetes) or that had been reported to be associated with OHA failure in previous studies (age, BMI). Adjustment for age, sex, BMI, and familial history of diabetes attenuated, but did not eliminate associated risks except in the case of fasting C-peptide quartile. Postprandial and delta C-peptide quartiles were more significantly associated with oral hypoglycemic agent failure than was fasting serum C-peptide quartile.
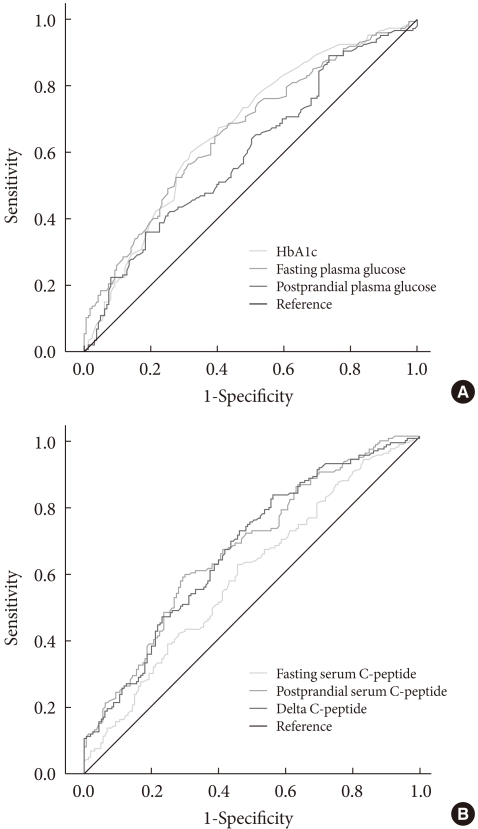
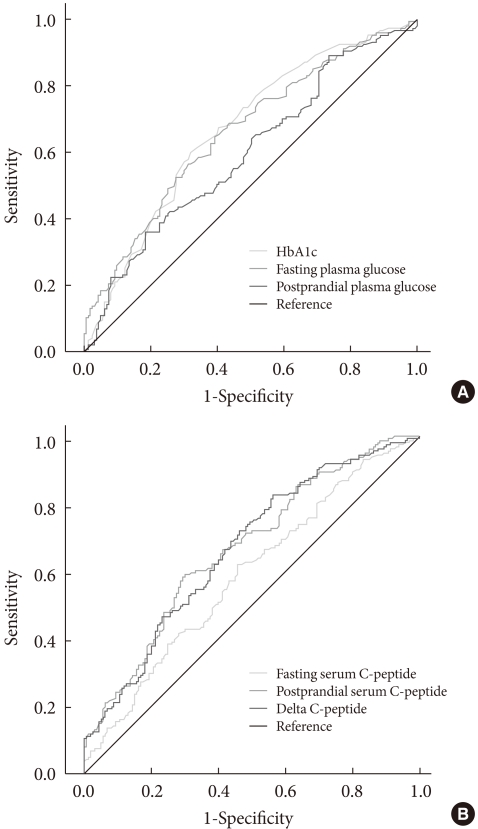
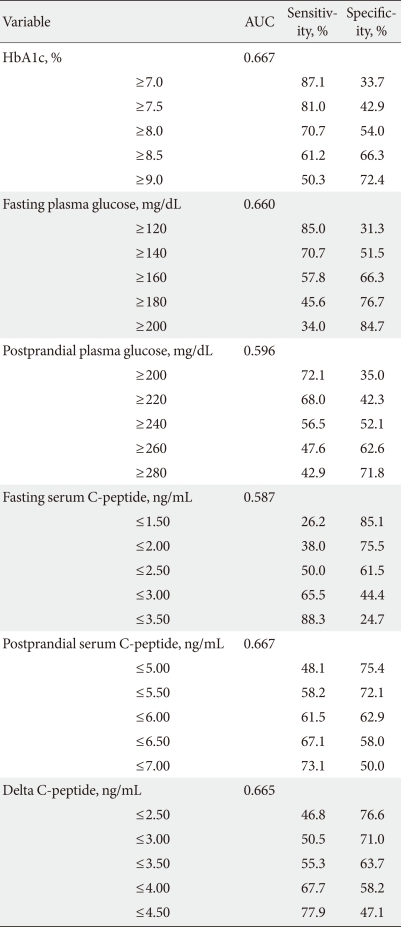
- Receiver operating characteristic curve (Fig. 1) analyses showed that the area under the curve (AUC) for HbA1c, fasting glucose, postprandial glucose, fasting C-peptide, postprandial C-peptide, and delta C-peptide were 0.667, 0.660, 0.596, 0.587, 0.667, and 0.665, respectively. Based on these AUCs, the predictive abilities of HbA1c, fasting glucose, postprandial C-peptide, and delta C-peptide for OHA failure were similar, but slightly higher than those of postprandial glucose and fasting C-peptide. Diagnostic performances, including the sensitivity and specificity, were substantially dependent on the chosen cutoff values (Table 3). The cutoff points showing maximum sensitivity plus specificity were baseline HbA1c 8.5%, fasting glucose 160 mg/dL, postprandial C-peptide 6.5 ng/mL, and delta C-peptide 4.0 ng/mL, which resulted in sensitivity and specificity of around 60% to 70%.
RESULTS
- In the present study conducted in Korean type 2 diabetic patients, we confirmed that lower serum C-peptide and elevated plasma glucose and HbA1c at baseline were associated with long-term OHA failure. These associations were independent of confounding factors, such as age, sex, and BMI. Female sex, longer duration of diabetes, and familial history of diabetes were also associated with OHA failure. In contrast, there was no association between BMI and OHA responsiveness.
- It has been established that severe degree of hyperglycemia and low endogenous insulin secretion are associated with insulin use in type 2 diabetic patients [4,5,7,9,11]. Therefore, it is not surprising that elevated plasma glucose and HbA1c, and low C-peptide quartile at baseline were associated with OHA failure in this study. Among the glycemic variables, fasting glucose and HbA1c had better discriminative ability than did postprandial glucose level. This may be due to greater variability of postprandial glucose level, which is greatly influenced by dietary factors. In contrast, among the C-peptide measures, postprandial or delta C-peptide levels were better markers of OHA failure than was fasting serum C-peptide. This is consistent with previous studies in Korean type 2 diabetic patients that showed postprandial or delta C-peptide levels are more closely correlated with OHA responsiveness than is fasting C-peptide [12-14]. This reflects the fact that a β-cell's capacity to respond to stimulation is more important than basal insulin secretion in determining response to oral hypoglycemic agents. A Japanese study [9] has reported that the serum and urinary C-peptide levels corrected for the fasting plasma glucose were useful for decision making regarding insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. In the present study, however, correction for fasting plasma glucose level did not improve the predictive power of fasting C-peptide (data not shown).
- Our results suggest that impaired β-cell function may be a cause of poor response to OHA. However, reverse causation is also a potential explanation. Unger and Grundy [15] introduced the concept of glucotoxicity, that continuous over-stimulation of β-cells by glucose could lead to depletion of insulin stores, worsening of hyperglycemia, and finally deterioration of β-cell function. Further prospective studies are needed to clarify whether β-cell dysfunction or hyperglycemia is the primary defect.
- Madsbad et al. [16] reported that patients with a post-stimulatory C-peptide level greater than 1.80 ng/mL appeared to be non-insulin dependent. In our analysis, the postprandial C-peptide cutoff value (5.5 to 6.5 ng/mL) was that for good glycemic control with OHA, not for insulin-independence for prevention of life-threatening acute metabolic complications. Therefore, it is natural that much higher insulin secretory capacity is required for good glycemic control compared to that needed for minimal insulin independence for life. Previous studies in Koreans have also reported that postprandial serum C-peptide or glucagon-stimulated serum C-peptide responses are useful indicators of insulin requirement in type 2 diabetic patients [12,13,17-19]. However, most of the studies were cross-sectional analyses including only small numbers of patients, and no study comprehensively examined the associations between various clinical variables with long-term predictors of OHA failure. In addition, in most previous studies performed in the 1980s and 1990s, the target values for glycemic control were much higher than the current guideline. Therefore, the 'good control' in previous studies was inadequate in light of current recommendations. The current study had the strength that it included a relatively large number of Korean type 2 diabetic patients, used strict criteria for OHA responsiveness, and utilized regular follow-up data covering more than two years in all patients.
- Female sex, longer duration of diabetes mellitus, and familial history of diabetes mellitus were also found to be associated with OHA failure. In contrast, there was no association between BMI and OHA responsiveness. A recent study in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients showed that lower BMI had a strong predictive ability for future insulin use, similar to fasting plasma glucose, serum and urine C-peptide levels [11]. The exact reason for these inter-study discrepancies is not clear at present, but there were several differences in study design and patient characteristics between studies. While our study patients were mostly managed in an outpatient clinic, the patients in the Japanese study were those who had admitted for glycemic control. Therefore, their participants generally had poorer glycemic control and longer duration of diabetes compared with those of our study participants. It is also possible that abnormalities in body fat distribution are more important than BMI.
- Little is known about the associations between female sex, family history of diabetes mellitus and OHA failure. There were no significant differences in fasting and postprandial C-peptide levels between male/female groups or positive/negative family history groups. To better understand these results, further studies are needed.
- Our study has several limitations that must be taken into account. First, since this study was a cross-sectional analysis, prospective controlled studies are needed to confirm the usefulness of C-peptide in predicting long-term OHA responsiveness in type 2 diabetes patients. Second, our study population was a cohort of patients cared for in a single center; therefore, our results may not be generalized to the whole Korean type 2 diabetic patients. However, the majority of our study participants were typical type 2 diabetic patients commonly encountered at outpatient-based diabetes clinics in real practice. Third, we used only fasting and postprandial C-peptide levels as a measure of β-cell function. However, it is not practical to perform intravenous glucose tolerance test or hyperglycemic clamp study in clinical settings, and it has been shown that fasting and postprandial C-peptide levels are well-correlated with glucagon-stimulated or 24-hour urine C-peptide [11,13,19,20].
- Despite these limitations, we provided evidence that lower baseline values of postprandial and delta C-peptide, and elevated fasting glucose and HbA1c are useful factors that are associated with OHA failure in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Further large prospective studies are required to confirm the clinical usefulness of those clinical variables in predicting the responsiveness to an oral hypoglycemic agent and in clinical decision making for the choice of therapy in type 2 diabetic patients.
DISCUSSION
- 1. Muoio DM, Newgard CB. Mechanisms of disease: molecular and metabolic mechanisms of insulin resistance and beta-cell failure in type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008;9:193-205. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS). 13: Relative efficacy of randomly allocated diet, sulphonylurea, insulin, or metformin in patients with newly diagnosed non-insulin dependent diabetes followed for three years. BMJ 1995;310:83-88. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. Sacks DB, Bruns DE, Goldstein DE, Maclaren NK, McDonald JM, Parrott M. Guidelines and recommendations for laboratory analysis in the diagnosis and management of diabetes mellitus. Clin Chem 2002;48:436-472. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Peacock I, Tattersall RB. The difficult choice of treatment for poorly controlled maturity onset diabetes: tablets or insulin? Br Med J (Clin Res Ed) 1984;288:1956-1959.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Koskinen P, Viikari J, Irjala K, Kaihola HL, Seppala P. C-peptide determination in the choice of treatment in diabetes mellitus. Scand J Clin Lab Invest 1985;45:589-597. ArticlePubMed
- 6. Kyllastinen M, Elfving S. Serum C-peptide concentrations and their value in evaluating the usefulness of insulin therapy in elderly diabetics. Gerontology 1986;32:317-326. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Nielsen NV, Tronier B. C-peptide in diabetes mellitus treated with insulin. A 3-year epidemiological study on the island of Falster, Denmark. Diabetes Res 1986;3:475-478. PubMed
- 8. Keller U, Pasquel M, Berger W. C-peptide determination in diabetics for the evaluation of insulin requirements. Schweiz Med Wochenschr 1987;117:187-192. PubMed
- 9. Asano T, Kawamura M, Watanabe T, Abe M, Chin R, Miyazaki S, Hirata Y. Indices of urinary and serum C-peptide corrected with fasting plasma glucose for decision-making of insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes-validation and comparison. J Jpn Diabetes Soc 2008;51:759-763.
- 10. Ko GT, So WY, Tong PC, Chan WB, Yang X, Ma RC, Kong AP, Ozaki R, Yeung CY, Chow CC, Chan JC. Effect of interactions between C peptide levels and insulin treatment on clinical outcomes among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. CMAJ 2009;180:919-926. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Goto A, Takaichi M, Kishimoto M, Takahashi Y, Kajio H, Shimbo T, Noda M. Body mass index, fasting plasma glucose levels, and C-peptide levels as predictors of the future insulin use in Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. Endocr J 2010;57:237-244. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Shim WS, Kim SK, Kim HJ, Park SE, Kang ES, Rhee YM, Ahn CW, Lim SK, Kim KR, Lee HC, Cha BS. Clinical meaning of postprandial insulin secretory function in Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus. J Korean Diabetes Assoc 2005;29:367-377.
- 13. Kim RS, Yang IM, Kim JW, Kim YS, Kim KW, Kim SW, Choi YK. Postprandial 2-hr C-peptide concentration as a guide for insulin treatment in patient with NIDDM. Korean J Intern Med 1986;1:120-125. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Yoo HJ, Kim DM, Sung SK, Wee SO. Serum C-peptide concentration as an index of insulin treatment in NIDDM patients. J Korean Diabetes Assoc 1987;11:57-61.
- 15. Unger RH, Grundy S. Hyperglycaemia as an inducer as well as a consequence of impaired islet cell function and insulin resistance: implications for the management of diabetes. Diabetologia 1985;28:119-121. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 16. Madsbad S, Krarup T, McNair P, Christiansen C, Faber OK, Transbol I, Binder C. Practical clinical value of the C-peptide response to glucagon stimulation in the choice of treatment in diabetes mellitus. Acta Med Scand 1981;210:153-156. ArticlePubMed
- 17. Kim YK, Jeon JS, Lee JH, Ahn MA, Shong MH, Ro HK, Song CU, Yoon SI, Ku BJ. Practical clinical value of C-peptide test in the choice of insulin treatment in patients with noninsulin dependent diabetes mellitus. J Korean Diabetes Assoc 1995;19:196-201.
- 18. Hue SH, Shin SH, Kim YS, Seo YK, Seol MJ, Oh YS. Practical value of glucagon test in the choice of treatment in diabetic patients. J Korean Diabetes Assoc 1985;11:63-69.
- 19. Park YS, Kim WB, Hong SK, Kim YS, Lee MK, Kim SY, Cho BY, Lee HK, Koh CS, Min HK, Rhee BD. Fasting plasma C-peptide, glucagon stimulated plasma C-peptide in relation to clinical type of diabetes. J Korean Med Assoc 1991;34:655-665.
- 20. Pasquali R, Buratti P, Biso P, Patrono D, Capelli M, Pasqui F, Melchionda N. Estimation of B-cell function by the urinary excretion rate of C-peptide in diabetic patients: comparison with C-peptide response to glucagon and to a mixed meal. Diabete Metab 1987;13:44-51. PubMed
REFERENCES
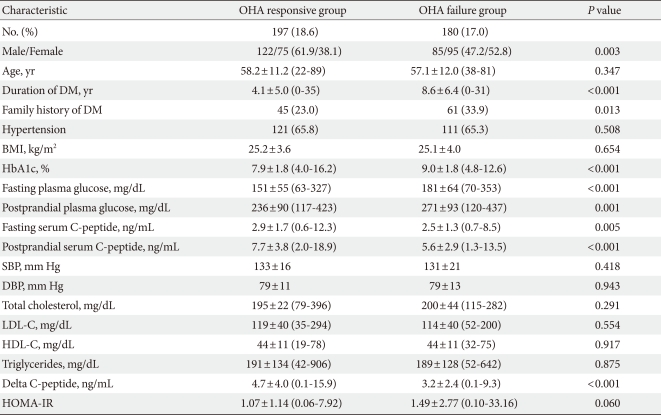
Data are presented as mean±standard deviation (range) or number (%).
P values were determined using the unpaired t-test or χ2 test.
DM, diabetes mellitus; BMI, body mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure, LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment index for insulin resistance.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Therapeutic Effects of Switching to Anagliptin from Other DPP-4 Inhibitors in T2DM Patients with Inadequate Glycemic Control: A Non-interventional, Single-Arm, Open-Label, Multicenter Observational Study
Sang-Yong Kim, Sungrae Kim
Diabetes Therapy.2023; 14(1): 109. CrossRef - Cyanidin-3-glucoside isolated from mulberry fruits protects pancreatic β-cells against glucotoxicity-induced apoptosis
JONG SEOK LEE, YOUNG RAE KIM, JUN MYOUNG PARK, YOUNG EON KIM, NAM IN BAEK, EOCK KEE HONG
Molecular Medicine Reports.2015; 11(4): 2723. CrossRef - The Duration of Sulfonylurea Treatment Is Associated withβ-Cell Dysfunction in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Mi-Seon Shin, Jee Hee Yu, Chang Hee Jung, Jenie Yoonoo Hwang, Woo Je Lee, Min-Seon Kim, Joong-Yeol Park
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2012; 14(11): 1033. CrossRef - The ratio of glycated albumin to glycated haemoglobin correlates with insulin secretory function
Daham Kim, Kwang J. Kim, Ji H. Huh, Byung‐Wan Lee, Eun S. Kang, Bong S. Cha, Hyun C. Lee
Clinical Endocrinology.2012; 77(5): 679. CrossRef
- Figure
- Related articles
-
- Risk Prediction and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in People Living with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- The Beneficial Effect of Glycemic Control against Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Sarcopenia and Carotid Plaque Progression Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Intensified Multifactorial Intervention in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- A Real-World Study of Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Lobeglitazone in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus

 KDA
KDA
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite