- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 46(6); 2022 > Article
-
Original ArticleDrug/Regimen A Real-World Study of Long-Term Safety and Efficacy of Lobeglitazone in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
-
Bo-Yeon Kim1
 , Hyuk-Sang Kwon2, Suk Kyeong Kim3, Jung-Hyun Noh4, Cheol-Young Park5, Hyeong-Kyu Park6, Kee-Ho Song3, Jong Chul Won7, Jae Myung Yu8, Mi Young Lee9, Jae Hyuk Lee10, Soo Lim11, Sung Wan Chun12, In-Kyung Jeong13, Choon Hee Chung9, Seung Jin Han14, Hee-Seok Kim15, Ju-Young Min15, Sungrae Kim16
, Hyuk-Sang Kwon2, Suk Kyeong Kim3, Jung-Hyun Noh4, Cheol-Young Park5, Hyeong-Kyu Park6, Kee-Ho Song3, Jong Chul Won7, Jae Myung Yu8, Mi Young Lee9, Jae Hyuk Lee10, Soo Lim11, Sung Wan Chun12, In-Kyung Jeong13, Choon Hee Chung9, Seung Jin Han14, Hee-Seok Kim15, Ju-Young Min15, Sungrae Kim16
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2022;46(6):855-865.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0264
Published online: March 8, 2022
1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Bucheon, Korea
2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
3Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Goyang, Korea
5Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
6Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
7Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Seoul, Korea
8Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
9Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital, Yonsei University Wonju College of Medicine, Wonju, Korea
10Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Myongji Hospital, Hanyang University College of Medicine, Goyang, Korea
11Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea
12Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Cheonan, Korea
13Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, College of Medicine, Kyung Hee University, Seoul, Korea
14Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea
15Department of Drug Safety Research, Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical Corporation, Seoul, Korea
16Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea
- Corresponding author: Sungrae Kim, Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, 222 Banpo-daero, Seocho-gu, Seoul 06591, Korea, E-mail: kimsungrae@catholic.ac.kr
Copyright © 2022 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
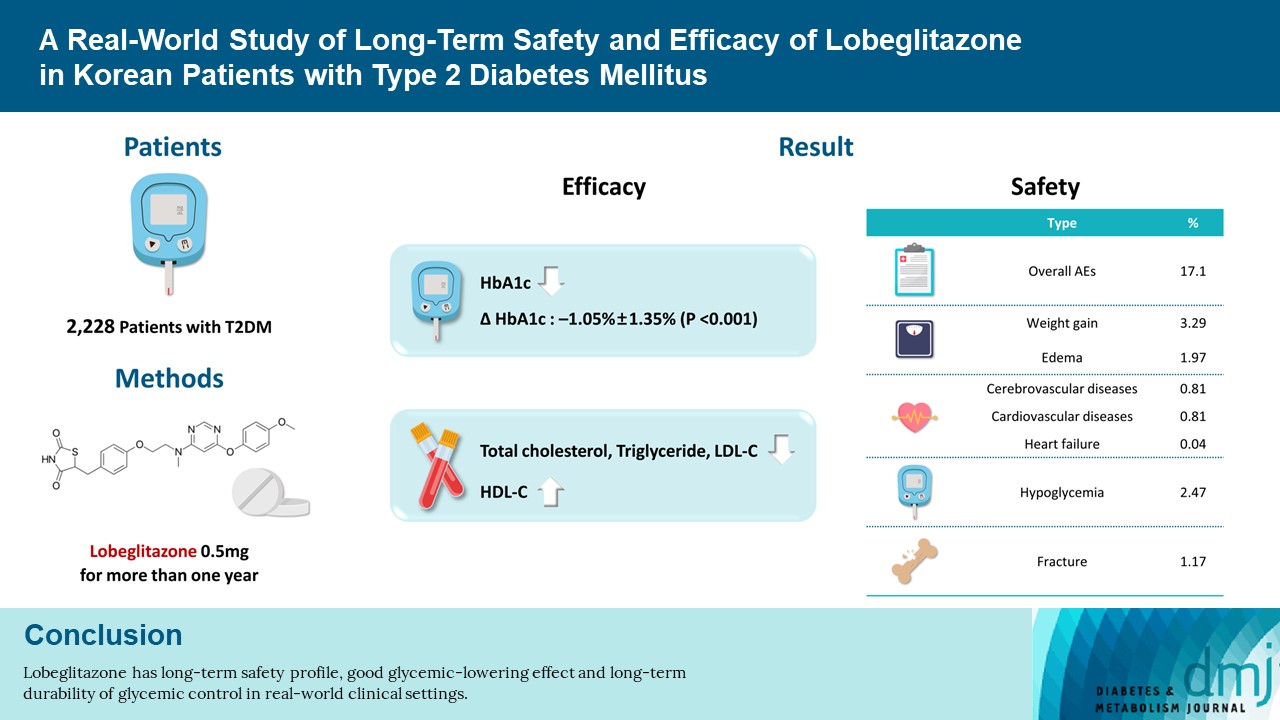
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) have been associated with various safety concerns including weight gain, bladder cancer, and congestive heart failure (CHF). This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of lobeglitazone, a novel TZD in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in real practice.
-
Methods
- In this non-interventional, multi-center, retrospective, and observational study conducted at 15 tertiary or secondary referral hospitals in Korea, a total of 2,228 patients with T2DM who received lobeglitazone 0.5 mg for more than 1 year were enrolled.
-
Results
- Overall adverse events (AEs) occurred in 381 patients (17.10%) including edema in 1.97% (n=44). Cerebrovascular and cardiovascular diseases were identified in 0.81% (n=18) and 0.81% (n=18), respectively. One case of CHF was reported as an AE. Edema occurred in 1.97% (n=44) of patients. Hypoglycemia occurred in 2.47% (n=55) of patients. Fracture occurred in 1.17% (n=26) of all patients. Lobeglitazone significantly decreased HbA1c level, resulting in a mean treatment difference of −1.05%± 1.35% (P<0.001), and decreased total cholesterol, triglyceride, and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. However, it increased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, regardless of statin administration. The patients who received lobeglitazone 0.5 mg showed an apparent reduction in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) from baseline during the first 6 months of treatment. The HbA1c levels remained stable between months 6 and 42.
-
Conclusion
- Lobeglitazone has long-term safety profile, good glycemic-lowering effect and long-term durability of glycemic control in real-world clinical settings.
- Lobeglitazone (trade name, Duvie, Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical Corporation, Seoul, Korea) is a novel thiazolidinedione (TZD). TZD-based drugs improve insulin resistance by regulating the activity of genes involved in glucose and lipid metabolism by stimulating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) receptors [1]. Lobeglitazone increases cell response to insulin without increasing insulin secretion in the pancreas. Therefore, the burden on the pancreas is less than that in other anti-diabetic treatments that increase insulin secretion. In addition, it is reported to be effective in protecting pancreatic β-cells [2,3]. Furthermore, TZD exhibit cardioprotective effects by increasing the secretion of adiponectin [4], expanding blood vessels [5], and alleviating inflammation [5,6]. It is also involved in lipid metabolism, which is known to lower small-dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) [7].
- Lobeglitazone clinical trials were conducted in Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) atients for 6 months to up to 12 months [8,9], and the efficacy and safety results of lobeglitazone are relatively limited. In pre-marketing clinical trials, a controlled group of patients was enrolled but elderly or patients taking concomitant drugs were excluded to minimize other possible effects in determining the efficacy and safety of the drug. Consequently, in real clinical practice, unforeseen events not detected in the pre-marketing stage may occur because of the extensive and longer duration of treatment involving a variety of patients with various underlying conditions and diseases. Therefore, an ongoing safety assessment under real-world settings is needed. TZD use has been associated with the risk of congestive heart failure (CHF), fractures, bladder cancer (long-term use), edema, and weight gain [1,10–12]. Treatment with lobeglitazone has been shown to be safer than other TZDs in patients with bladder cancer and bone fractures [8]. However, currently, there is a lack of large-scale, long-term safety and efficacy data of lobeglitazone in Korea. This is a non-interventional, multi-centered, retrospective and observational study designed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of lobeglitazone in patients with T2DM in real world.
INTRODUCTION
- Subjects and study design
- This non-interventional multi-center observational study (Retrospective study to Evaluate the Safety of DuvieR in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus [DISCOVERY] study) was conducted at 15 tertiary or secondary referral hospitals in Korea. A total of 2,228 patients with T2DM who received lobeglitazone 0.5 mg for more than one year between February 1, 2014 and December 20, 2018 were enrolled. The subjects’ data was collected from anonymized medical records in a clinical setting during the study period, and were recorded in the electronic case report form (eCRF) at the discretion of the researcher. The study protocol was registered at ClinicalTrials.gov (registration number NCT05043467).
- Study assessments
- In brief, the survey items covered baseline demographic characteristics such as age, sex, height, body weight, body mass index (BMI), duration of diabetes, diabetic complications, medical history, lobeglitazone administration information (total treatment period, start and end date of administration, reason for discontinuation of lobeglitazone), and concomitant medication (type and dose).
- Safety assessment items included the incidence of major adverse events (AEs) and any AEs that occurred during the lobeglitazone therapy. Major AEs were: edema, weight gain, fractures, bladder cancer, anemia, hypoglycemia, macular edema, cardiac death, myocardial infarction, stroke, transient ischemic attack, coronary arterial occlusion, and CHF. AEs including blood pressure change, increased liver enzymes (>3×), and dizziness were also identified.
- To assess the efficacy of lobeglitazone 0.5 mg, changes in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and glucose levels, and lipid parameters (total cholesterol, triglyceride, LDL-C, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol [HDL-C]) at 3, 6, 12, 18, 24, 36, 42, and 48 months after administration were identified.
- Ethics statement
- This study proposal was approved by the Institutional Review Boards (IRBs) of each study center listed below: Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital IRB (2020-02-025), Yeouido St. Mary’s Hospital IRB, Konkuk University Hospital IRB, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital IRB, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital IRB, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital IRB, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital IRB, Hallym University Kangnam Sacred Heart Hospital IRB, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital IRB, Myongji Hospital IRB, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital IRB, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital IRB, Kyung Hee University Hospital IRB, Ajou University Hospital IRB, and Bucheon St Mary’s Hospital IRB. Written informed consent by the patients was waived due to a retrospective nature of our study.
- Statistical analysis
- Safety analysis involved all patients who received at least one dose of lobeglitazone and at least one post-safety follow-up. Efficacy analysis involved patients who were naïve to lobeglitazone or lobeglitazone add-on therapy.
- Data management and statistical analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA). The patient characteristics are summarized and tabulated. Data are presented as mean±standard deviation (SD) for continuous variables, whereas the categorical variables are expressed as percentages of patients and number of events. Since the data were not normally distributed, a Wilcoxon signed-rank sum test was performed to evaluate changes in laboratory variables from baseline to follow-up. All tests were two-sided and performed at 5% level of significance.
- According to the retrospective study of Rajagopalan et al. [10], the frequencies of CHF and related hospitalization were 2.0% and 0.7%, respectively. Based on the rates of hospitalization due to CHF, the sample size needed was at least 2,180 to detect a rare serious AE assuming a rate of 0.7% at a fraction of 50% and a two-sided significance level of 0.05.
METHODS
Statistical methods
Sample size
- Patient characteristics
- The baseline characteristics of study participants in the safety set are presented in Table 1. The safety analysis set included total patients (n=2,228), and the efficacy analysis set involved drug-naïve patients at the baseline and following the addition of only lobeglitazone without changing other anti-diabetic agents (n=1,651). Among patients in the safety analysis set, the mean age was 64.07±11.53 years, and males constituted 61.18%. The mean duration of diabetes was 13.01±8.07 years. The mean BMI was 25.09±3.50 kg/m2. In terms of diabetic treatment status, 264 patients (11.85%) in the safety analysis set were drug-naïve and 1,964 patients (88.15%) were exposed to concomitant anti-diabetic medications, which mainly included metformin (n=1,557, 69.88%), dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (n=1,379, 61.89%), sulfonylurea (SU; n=912, 40.93%), sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor (n=42, 1.89%), and insulin (n=228, 10.23%). Mean duration of lobeglitazone treatment was 28.59±9.84 months in the safety analysis set.
- Safety
- The safety analysis set included 2,228 patients. The results of weight gain after taking lobeglitazone 0.5 mg are presented in Table 2. The mean weight change was 2.11±3.85 kg (3.29%± 5.85%). The percentage of the study participants with weight gain exceeding 5% compared to baseline was 16.83% in the safety analysis set. The percentage of patients who gained weight did not vary with age. Overall, AEs occurred 381 patients (17.10%) (Table 3). AEs of special interest are listed in Table 3. Of these AEs, edema was detected in 1.97% (n=44). In this study, edema was observed more frequently in females than in males (n=29 [1.30%] vs. n=15 [0.67%], respectively). Cerebrovascular and cardiovascular diseases occurred in 0.81% (n=18) and 0.81% (n=18), respectively. One case of CHF was reported as an AE. Hypoglycemia occurred in 2.47% (n=55) patients. Insulin or SU was used to treat hypoglycemia in 87.27% of patients. Fractures occurred in 1.17% (n=26) of all patients. Of these, 61.54% were female and the number of fractures increased with age. Increases in aspartate aminotransferase and alanine aminotransferase occurred in 0.22% (n=5) and 0.27% (n=6) of patients, respectively. No cases of jaundice were reported as an AE.
- Efficacy
- The effects of lobeglitazone were analyzed in the efficacy analysis set (n=1,651) and expressed as mean±SD changes in HbA1c, glucose, and lipid parameters from baseline until the end of treatment (Table 4). Lobeglitazone 0.5 mg significantly decreased HbA1c from the baseline level of 8.17%±1.36% to the final level at the end of study, 7.12%±1.13%, resulting in a mean treatment difference of −1.05%±1.35% (P<0.001). Glucose was also improved at the end of treatment (mean treatment difference −34.05±62.00 mg/dL, P<0.001). Treatment with lobeglitazone 0.5 mg significantly decreased the levels of total cholesterol, triglyceride, and LDL-C and increased HDL-C, regardless of statin therapy (not administrated statin, all P<0.001) (Table 4).
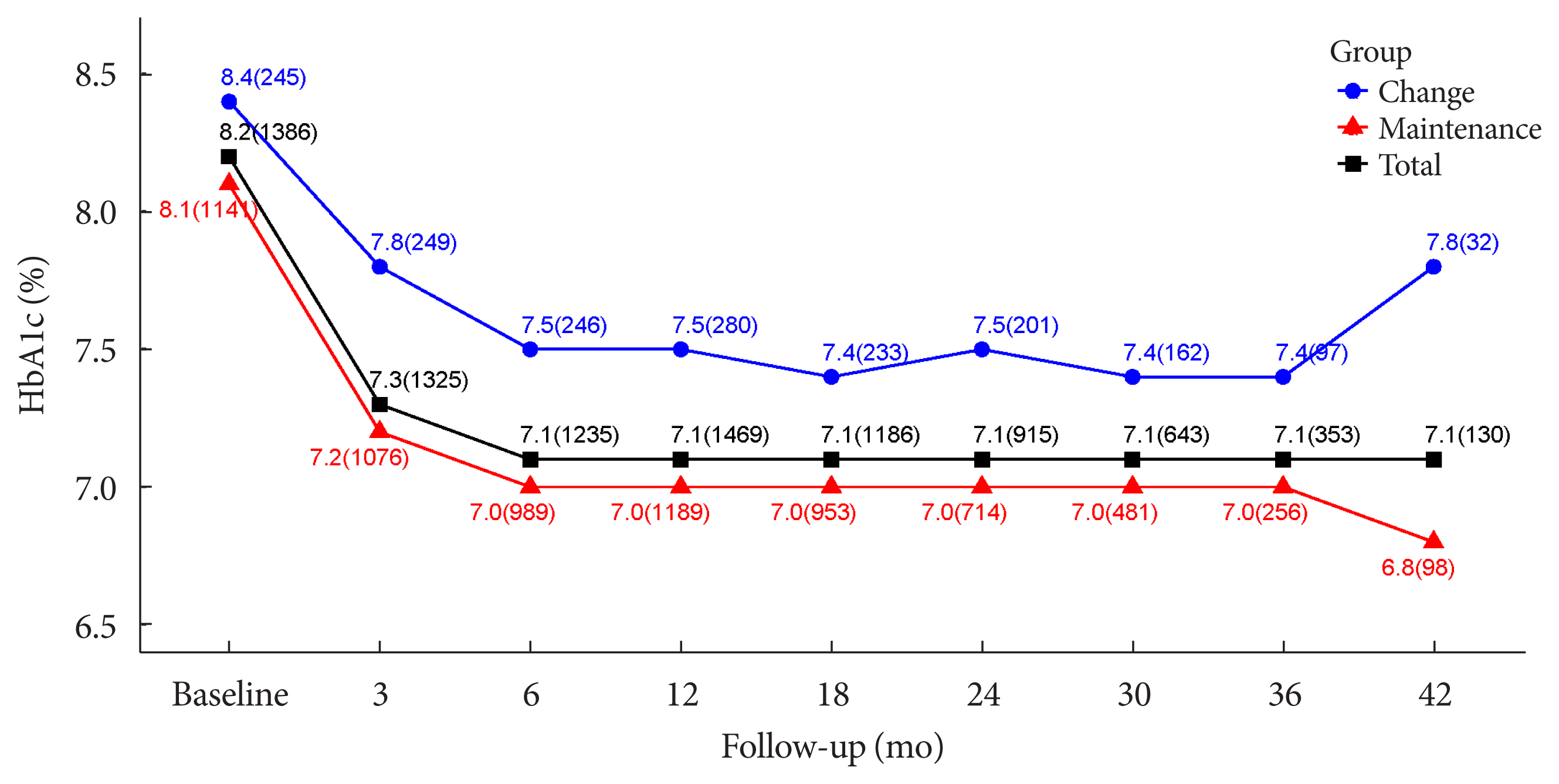
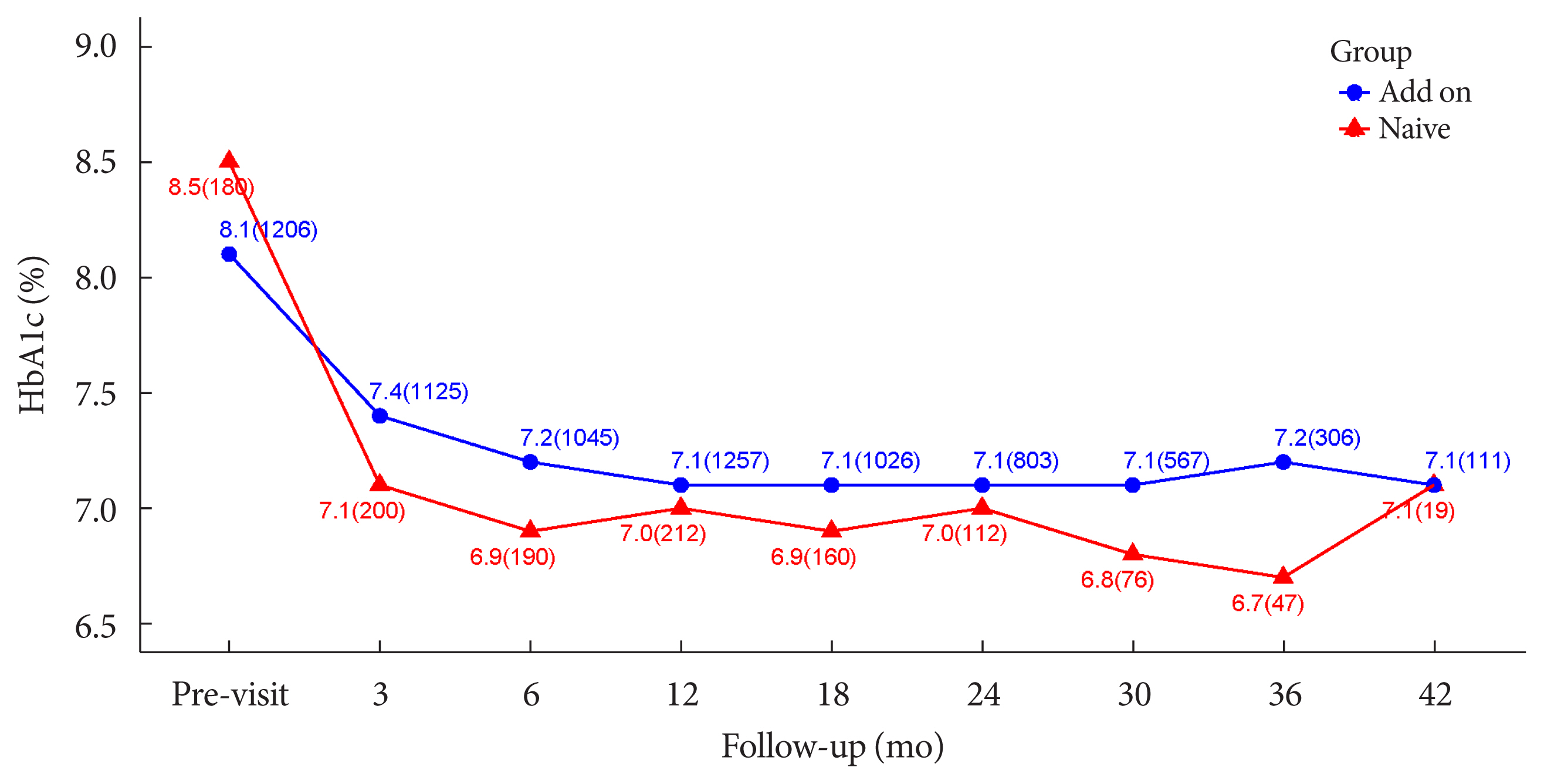
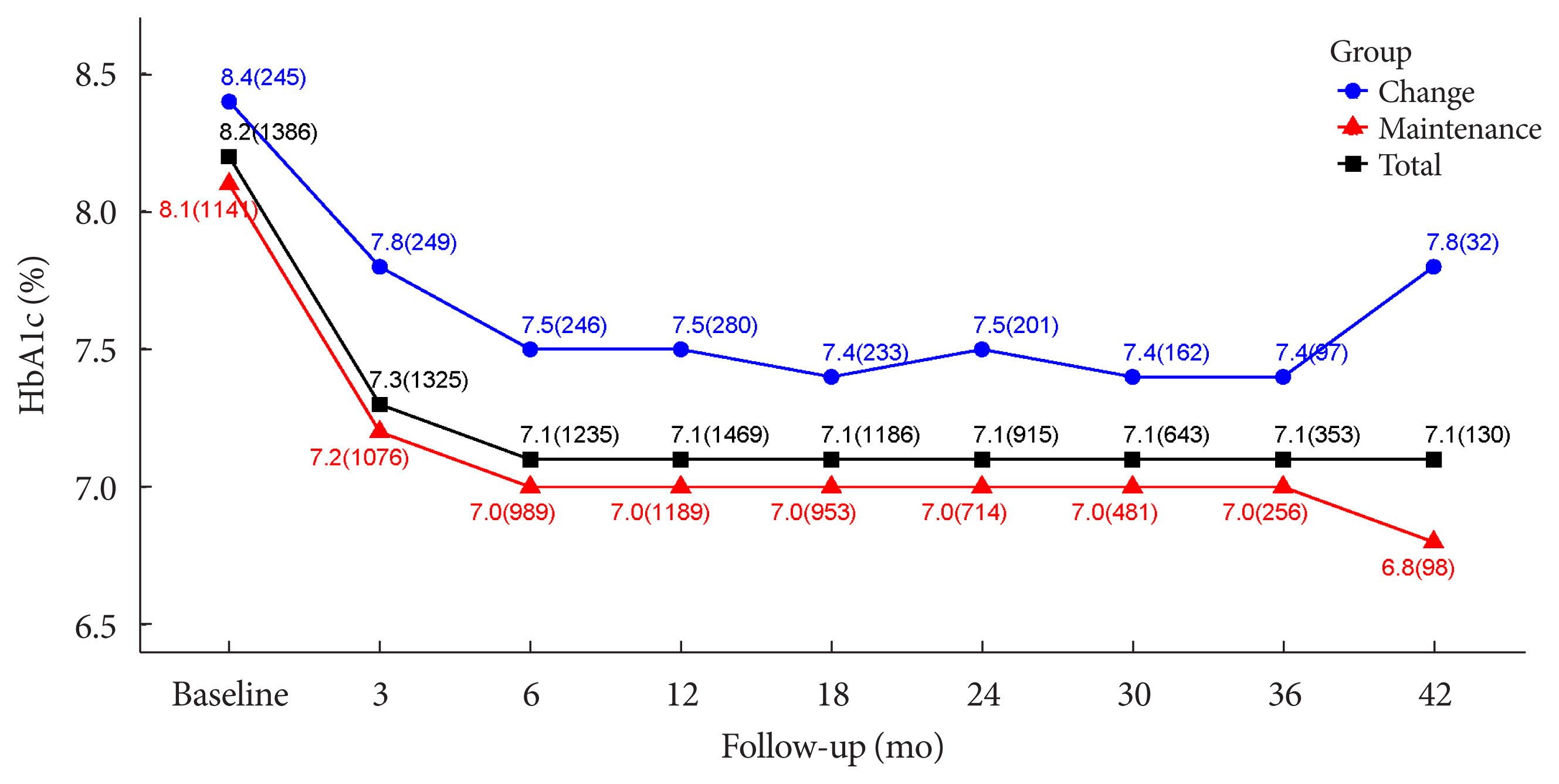
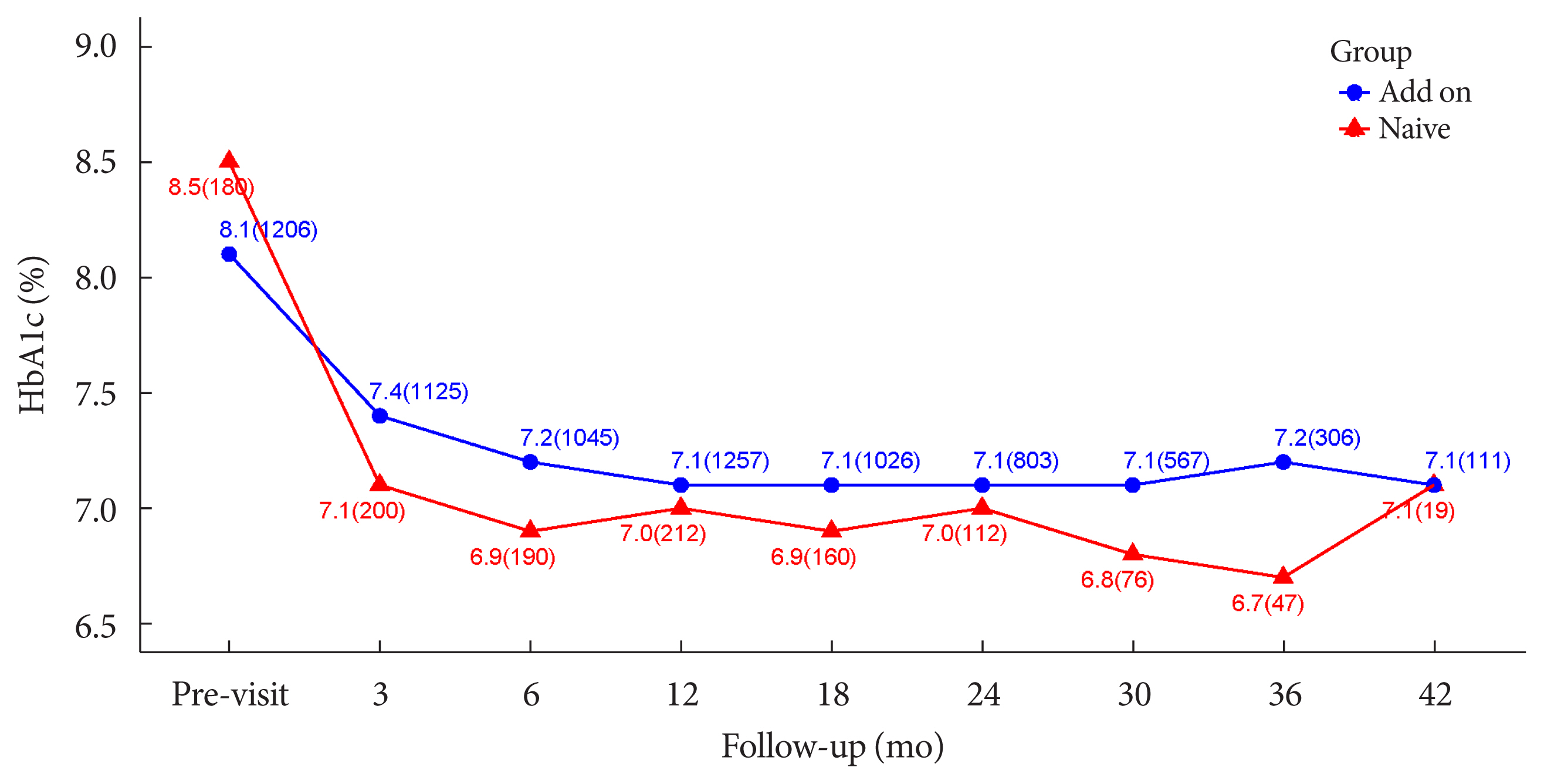
- The durability of glycemic control was analyzed in 1,651 patients. Changes in HbA1c levels for 42 months in different groups are shown in Figs. 1 and 2. Patients who received lobeglitazone 0.5 mg (add-on group vs. drug naïve group) showed an apparent reduction in HbA1c from baseline during the first 6 months of treatment (add-on, 8.1%±1.3% and 7.2%±1.2%, respectively; drug naïve, 8.5%±1.9% and 6.9%±1.2%, respectively), and the HbA1c levels remained stable in both groups of patients between months 6 and 42 (Fig. 1). Fig. 2 showed change in HbA1c levels for 42 months in the three groups (the efficacy analysis set vs. maintenance of anti-diabetic medications vs. change of anti-diabetic medications). HbA1c levels at baseline, 6 and 42 months in the efficacy analysis set were 8.2%±1.4%, 7.1%±1.2%, and 7.1%±1.2%, respectively and the HbA1c levels remained stable between months 6 and 42 (Fig. 2). Treatment in anti-diabetic medications starting from the initial lobeglitazone remained unchanged until the final HbA1c test (maintenance group) in 81.0% (n=1,337) patients. In this group, HbA1c levels at baseline, 6 and 42 months in the efficacy analysis set were 8.1%±1.4%, 7.0%±1.1%, and 6.8%±0.9%, respectively (Fig. 2). Glycemic control and long-term durability were higher in the maintenance group following treatment with anti-diabetic medications than in those who switched to other anti-diabetic medications (Fig. 2).
RESULTS
Effects of lobeglitazone on glucose and lipid parameters
Durability of glycemic control following lobeglitazone therapy
- In the present study, treatment with lobeglitazone 0.5 mg showed a good long-term safety profile. However, lobeglitazone treatment increased body weight by 2.11 kg (3.29%) and led to edema in 1.97% patients during the treatment. Lobeglitazone treatment improved glycemic control in patients with T2DM, and also significantly improved lipid parameters. In particular, lobeglitazone was associated with excellent long-term glycemic control.
- Previous TZDs were associated with various safety concerns including weight gain, bladder cancer, CHF, and so on [1,11,13–18]. Both efficacy and safety are important in determining the clinical benefit of anti-diabetic agents. Weight gain and edema are well known AEs of TZDs. As previously stated, lobeglitazone treatment increased body weight by 2.11 kg (3.29%) and resulted in edema in 1.97% patients during the study period. Lobeglitazone treatment increased body weight by 0.89 and 1.65 kg at 24 and 52 weeks, respectively, in previous efficacy and safety trials of lobeglitazone monotherapy [8,9]. In a meta-analysis, pioglitazone therapy led to a weight gain of 1.76 kg [19]. Compared with previous studies of lobeglitazone and pioglitazone, the present real-world study revealed a higher body weight gain, plausibly due to the effects of other concomitant therapies such as SU and insulin, and also the real-world, retrospective design and long-term treatment duration.
- Overall, AEs occurred in 17.10% of patients in this study. Cerebrovascular and cardiovascular diseases were found in 0.81% and 0.81%, respectively. Lobeglitazone is associated with a very low risk of cerebrovascular and cardiovascular disease in this study. Only a single case of CHF was reported as an AE despite long-term observation of a large number of patients. The findings suggest that clinicians do not need to desist from prescribing lobeglitazone due to the risk of CHF in patients with T2DM. Edema was detected in 1.97% of patients. In this study, edema was observed more frequently in females than in males (1.30% vs. 0.67%, respectively). Edema is already known to be related to TZDs, and it may result from a reduction in the renal excretion of sodium along with an increase in sodium and free water retention [20]. Other possible mechanisms for edema include increased sympathetic nervous system activity, altered interstitial ion transport, and alterations in endothelial permeability [21–23]. In the results of a previous study, more female patients and more insulin users developed TZD-related fluid retention [20]. Hypoglycemia occurred in 2.47% of all patients, but it occurred in 87.27% of those exposed to add-on therapy comprising insulin or SU, suggesting the hypoglycemic effects of concomitant anti-diabetic therapies.
- TZD, a PPARγ agonist, promotes adipogenesis, and inhibits osteoblastogenesis, and its long-term use is associated with impaired bone quality and an increased risk of bone fracture [24–26]. In this study, fractures were reported in 1.17% patients. Although 61.18% of total patients were male, 61.54% of fractures occurred in females and the incidence of fracture increased with age. Compared with clinical studies involving other TZDs [12,27], lobeglitazone showed lower risk of bone fracture (1.17%) than those of other TZDs. Lobeglitazone monotherapy did not significantly alter femur neck and total hip bone mineral density (BMD) compared with placebo [8,9]. Lim et al. [28] evaluated the effects of a 52-week treatment with lobeglitazone 0.5 mg on BMD as a primary end point. The study showed that treatment with lobeglitazone 0.5 mg over 52 weeks was not detrimental to BMD compared with placebo.
- Compared with rosiglitazone or pioglitazone, a novel TZD such as lobeglitazone requires lower doses for glycemic control [29]. Lobeglitazone also affected adipocyte biology in a previous study [30]. Further, in a previous animal study, lobeglitazone had no detrimental effects on osteoblast biology [31]. Therefore, the lower dose and the distinct effect of lobeglitazone on adipocyte biology may contribute to a reduced risk of bone fracture.
- A few observational studies have reported that TZD increases the risk of bladder cancer [11,15,18]. No cases of bladder cancer have been reported in our study. Based on previous preclinical studies [32,33], lobeglitazone does not increase the risk of bladder cancer. Because lobeglitazone shows a lower effective dose—due to its higher affinity to PPARγ—and as it is mainly metabolized by the liver with negligible renal excretion, lobeglitazone may have a lower risk of bladder cancer than other TZDs [34,35]. However, this study cannot confirm the safety of lobeglitazone on bladder cancer, underscoring the need for a further large prospective study to investigate the risk.
- In this study, lobeglitazone showed an apparent reduction in HbA1c from baseline during the first 6 months of treatment (add-on, 8.1%±1.3% and 7.2%±1.2%, respectively; drug naïve, 8.5%±1.9% and 6.9%±1.2%, respectively). Further, the HbA1c levels remained stable in patients in both groups by month 42. These results suggest glycemic efficacy and long-term durability of lobeglitazone. No change in anti-diabetic medications was required in 81.0% of all patients who were treated with upfront lobeglitazone until the final HbA1c test. Glycemic control and long-term durability were better in the maintenance group exposed to anti-diabetic medications. Maintenance therapy without changing anti-diabetic agents implies strong long-term durability in glycemic control. In a previous study investigating the role of different anti-diabetic agents as add-on treatments to metformin in patients with T2DM, the addition of a TZD to metformin yielded the most durable glycemic response [36]. Lobeglitazone, a novel PPARγ agonist, was based on a modification of the rosiglitazone structure to introduce a p-methoxyphenoxy group at the 4-position of the pyrimidine moiety [34,37]. This contributes to the enhanced binding affinity of lobeglitazone for PPARγ; docking analysis suggests that the binding affinity of lobeglitazone is 12 times higher than those of rosiglitazone and pioglitazone [34,38]. TZDs represent peripheral insulin sensitizers [1], but lobeglitazone showed beneficial effects on pancreatic β-cell survival and function in an animal study [2]. These factors may affect the long-term durability of glycemic control with lobeglitazone. Treatment with lobeglitazone also improved lipid parameters in this study consistent with other clinical studies of lobeglitazone [8,9,39].
- This study has several limitations. First, the mean age of participants in this study was 64.07±11.53 years, and the proportion of young patients was extremely low. Further, the mean diabetic duration of participants was relatively long. These limitations may affect the study results. In a previous Korean study, young adults with diabetes were more likely to manifest higher insulin resistance [40]. Second, as this study enrolled patients who had received lobeglitazone 0.5 mg for more than 1 year between February 1, 2014 and December 20, 2018, there were no data on patients who were excluded due to AE or lack of effectiveness within one year. However, in general, there is limited convincing data with a paucity of long-term research in this area, so this study is nonetheless expected to represent a meaningful contribution. Third, due to its retrospective design, the results might have been affected by selection bias. Nonetheless, as our study involved multiple centers including 15 hospitals and various patient groups, the results of the study can be generalized.
- In conclusion, our results reinforce the long-term safety and durability of the glycemic lowering effect of lobeglitazone 0.5 mg in real-world clinical practice.
DISCUSSION
-
Acknowledgements
- We thank all members of DISCOVERY study group involved in conducting and managing this study.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception or design: B.Y.K., J.H.N., C.Y.P., K.H.S., S.K.
Data acquisition, analysis, or interpretation: S.K.K., H.S.K., J.Y.M., S.K.
Drafting the work or revision: B.Y.K., H.S.K., J.H.L., S.L., S.W.C., I.K.J., C.H.C., S.J.H.
Final approval of the manuscript: B.Y.K., H.S.K., S.K.K., J.H.N., C.Y.P., H.K.P., K.H.S., J.C.W., J.M.Y., M.Y.L., J.H.L., S.L., S.W.C., I.K.J., C.H.C., S.J.H., H.S.K., J.Y.M., S.K.
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
In-Kyung Jeong was editor in chief of the Diabetes & Metabolism Journal from 2020 to 2021. Jung Hyun Noh was associate editor of the Diabetes & Metabolism Journal from 2020 to 2021. They were not involved in the review process of this article. Otherwise, there was no conflict of interest. Statistical analysis was supported by Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical Corporation. H.S.K and J.Y.M are employees of Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical Corporation.
-
FUNDING
This work was funded by Chong Kun Dang Pharmaceutical Corporation and partly supported by the Soonchunhyang University Research Fund.
NOTES
| Variable | Safety set (n=2,228) | Efficacy set (n=1,651) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | ||
| Male | 1,363 (61.18) | 1,025 (62.08) |
| Female | 865 (38.82) | 626 (37.92) |
|
|
||
| Age, yr | 64.07±11.53 | 63.94±11.34 |
|
|
||
| Age groups, yr | ||
| <20 | 1 (0.04) | 1 (0.06) |
| ≥20 to <30 | 11 (0.49) | 7 (0.42) |
| ≥30 to <40 | 33 (1.48) | 18 (1.09) |
| ≥40 to <50 | 186 (8.35) | 148 (8.96) |
| ≥50 to <60 | 524 (23.52) | 392 (23.74) |
| ≥60 to <70 | 738 (33.12) | 555 (33.62) |
| ≥70 to <80 | 531 (23.83) | 382 (23.14) |
| ≥80 to <90 | 192 (8.62) | 140 (8.48) |
| ≥90 | 12 (0.54) | 8 (0.48) |
|
|
||
| Duration of diabetes, yr | 13.01±8.07 | 12.87±7.98 |
|
|
||
| Weight, kg | 67.02±11.78a | 67.70±11.27b |
|
|
||
| BMI, kg/m2 | 25.09±3.50c | 25.25±3.38d |
|
|
||
| BMI groups, kg/m2 | ||
| <18.5 | 20 (1.47) | 11 (1.14) |
| ≥18.5 to <22.0 | 225 (16.56) | 137 (14.15) |
| ≥22.0 to <25.0 | 463 (34.07) | 331 (34.19) |
| ≥25.0 to <30.0 | 534 (39.29) | 406 (41.95) |
| ≥30.0 | 117 (8.61) | 83 (8.57) |
|
|
||
| Prescribed antidiabetic drugs | ||
| No (Naïve) | 264 (11.85) | 264 (15.99) |
| Yes | 1,964 (88.15) | 1,387 (84.01) |
| No. of prescribed antidiabetic drugs | ||
| Single class | 384 (17.24) | 226 (13.69) |
| Double classes | 894 (40.12) | 733 (44.40) |
| Triple classes | 642 (28.82) | 410 (24.83) |
| Quadruple classes | 43 (1.93) | 18 (1.09) |
| Quintuple classes | 1 (0.04) | - |
| Types of prescribed antidiabetic drugs | ||
| DPP-4 inhibitors | 1,379 (61.89) | 1,053 (63.78) |
| GLP-1 receptor agonist | 5 (0.22) | 2 (0.12) |
| Insulin | 228 (10.23) | 128 (7.75) |
| Meglitinides | 18 (0.81) | 10 (0.61) |
| Metformin | 1,557 (69.88) | 1,130 (68.44) |
| Pioglitazone | 92 (4.13) | 16 (0.97) |
| Sulfonylurea | 912 (40.93) | 622 (37.67) |
| SGLT-2 inhibitor | 42 (1.89) | 16 (0.97) |
| α-Glucosidase inhibitor | 42 (1.89) | 17 (1.03) |
|
|
||
| History of diabetes complicationsg | ||
| Diabetic foot | 4 (0.18) [4] | 3 (0.18) [3] |
| Diabetic nephropathy | 68 (3.05) [68] | 44 (2.67) [44] |
| Diabetic neuropathy | 312 (14.00) [313] | 219 (13.26) [220] |
| Diabetic retinopathy | 212 (9.52) [212] | 161 (9.75) [161] |
|
|
||
| Liver functiong | ||
| Aspartate aminotransferase | 24.84±10.00e | 24.67±8.69f |
| Alanine aminotransferase | 24.81±14.31e | 26.58±15.19f |
|
|
||
| History of hepatobiliary disordersg,h | 157 (7.05) [172] | 125 (7.57) [133] |
|
|
||
| History of renal failure and impairmentg | 157 (7.05) [160] | 118 (7.15) [120] |
| Acute kidney injury | 5 (0.22) [5] | 4 (0.24) [4] |
| Chronic kidney disease | 146 (6.55) [147] | 109 (6.60) [109] |
| End stage renal disease | 2 (0.09) [2] | 2 (0.12) [2] |
| Renal failure | 4 (0.18) [4] | 4 (0.24) [4] |
| Renal injury | 1 (0.04) [1] | 1 (0.06) [1] |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%) [number of events].
BMI, body mass index; DPP-4, dipeptidyl peptidase-4; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1; SGLT-2, sodium glucose cotransporter-2.
a n=1,361,
b n=970,
c n=1,359,
d n=968,
e n=94,
F n=64,
g By system organ class (MedDRA version 21.1 preferred term),
h Definition of hepatobiliary disorders: alcoholic liver disease, autoimmune hepatitis, bile duct stenosis, bile duct stone, biliary colic, cholangitis, cholecystitis, cholecystitis acute, cholecystitis chronic, cholelithiasis, chronic hepatitis, cirrhosis alcoholic, fatty liver alcoholic, gallbladder polyp, hepatic cirrhosis, hepatic function abnormal, hepatic steatosis, hepatitis, hepatitis alcoholic, hepatorenal syndrome, hepatotoxicity, jaundice, liver disorder, non-alcoholic fatty liver, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, primary biliary cholangitis, steatohepatitis.
| Variable | Safety set (n=2,228) |
|---|---|
| Weight change, kg | 2.11±3.85a |
|
|
|
| Weight change, % | 3.29±5.85a |
|
|
|
| BMI change, kg/m2 | 0.80±1.45b |
|
|
|
| BMI change, % | 3.28±5.86b |
|
|
|
| Weight increased by more than 5% compared to baseline | |
| No | 1,853 (83.17) |
| Yes | 375 (16.83) |
| Weight change, kg | 6.15±2.81 |
| Weight change, % | 9.61±4.24 |
| BMI change, kg/m2 | 2.35±1.04c |
| BMI change, % | 9.62±4.25c |
| Age, yr | 64.62±11.41 |
| Age group, yrd | |
| <20 | 0 |
| ≥20 to <30 | 2 (18.18) |
| ≥30 to <40 | 5 (15.15) |
| ≥40 to <50 | 30 (16.13) |
| ≥50 to <60 | 76 (14.50) |
| ≥60 to <70 | 131 (17.75) |
| ≥70 to <80 | 96 (18.08) |
| ≥80 to <90 | 34 (17.71) |
| ≥90 | 1 (8.33) |
| Variable | Safety set (n=2,228) |
|---|---|
| Any adverse event | 381 (17.10) [623] |
|
|
|
| Aspartate aminotransferase increaseda | 5 (0.22) [5] |
|
|
|
| Alanine aminotransferase increaseda | 6 (0.27) [6] |
|
|
|
| Bronchitis | 2 (0.09) [2] |
|
|
|
| Cancer | |
| Bladder cancer | 0 (0.00) [0] |
| Gastric cancer | 1 (0.04) [1] |
| Lung neoplasm malignant | 1 (0.04) [1] |
| Non-small cell lung cancer | 1 (0.04) [1] |
|
|
|
| Cerebrovascular diseaseb | 18 (0.81) [18] |
|
|
|
| Congestive heart failure | 1 (0.04) [1] |
|
|
|
| Cardiovascular diseasec | 18 (0.81) [19] |
|
|
|
| Constipation | 9 (0.40) [9] |
|
|
|
| Diarrhea | 4 (0.18) [4] |
|
|
|
| Edemad | 44 (1.97) [48] |
| Sexa | |
| Male | 15 (0.67) [16] |
| Female | 29 (1.30) [32] |
|
|
|
| Hypoglycemiae | 55 (2.47) [63] |
| Sex | |
| Male | 30 (1.35) |
| Female | 25 (1.12) |
| Age, yr | 64.78±9.94 |
| Insulin or sulfonylurea administration at occurrence time | |
| No | 7 (0.32) |
| Yes | 48 (2.15) |
|
|
|
| Fracturef | 26 (1.17) [27] |
| Sex | |
| Male | 10 (0.45) |
| Female | 16 (0.72) |
| Age, yr | 72.11±11.92 |
| Age group, yrg | |
| <20 | 0 (0.00) |
| ≥20 to <30 | 0 (0.00) |
| ≥30 to <40 | 0 (0.00) |
| ≥40 to <50 | 1 (0.54) |
| ≥50 to <60 | 3 (0.57) |
| ≥60 to <70 | 6 (0.81) |
| ≥70 to <80 | 7 (1.32) |
| ≥80 to <90 | 8 (4.17) |
| ≥90 | 1 (8.33) |
|
|
|
| Jaundicea | 0 (0.00) [0] |
|
|
|
| Proteinuria | 2 (0.09) [2] |
|
|
|
| Pneumonia | 0 (0.00) [0] |
|
|
|
| Rash | 0 (0.00) [0] |
|
|
|
| Upper respiratory tract infection | 5 (0.22) [5] |
|
|
|
| Urinary tract infection | 4 (0.18) [4] |
|
|
|
| Vomiting | 0 (0.00) [0] |
Values are presented as number of patients (%) [number of events] or mean±standard deviation.
a By system organ class (MedDRA version 21.1 preferred term),
b Definition of cerebrovascular disease: carotid arteriosclerosis, carotid artery stenosis, cerebral arteriosclerosis, cerebral artery stenosis, cerebral infarction, intracranial aneurysm, migraine, neurodegenerative disorder, syncope, vascular dementia,
c Definition of cardiovascular disease: acute myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, angina unstable, atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease, coronary artery occlusion, microvascular coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, tachycardia,
d Definition of edema: face oedema, generalised oedema, oedema, oedema peripheral, lymphoedema, periorbital oedema,
e Definition of hypoglycemia: hypoglycaemia, blood glucose decreased,
F Definition of fracture: ankle fracture, clavicle fracture, facial bones fracture, femoral neck fracture, femur fracture, foot fracture, fracture, lumbar vertebral fracture, open fracture, pelvic fracture, radius fracture, rib fracture, spinal compression fracture, upper limb fracture, wrist fracture, osteoporotic fracture, pathological fracture,
g Number of patients per age group cluster.
| Variable | Efficacy set (n=1,651) | P valuea | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|||
| No. (%) | Mean±SD | ||
| HbA1c, % | |||
| Baseline | 1,386 (83.95) | 8.17±1.36 | |
| Follow-up | 1,624 (98.36) | 7.12±1.13 | |
| Changes | 1,368 (82.86) | −1.05±1.35 | <0.0001 |
| Changes, % | 1,368 (82.86) | −11.53±14.04 | <0.0001 |
|
|
|||
| Glucose, mg/dL | |||
| Baseline | 1,243 (75.29) | 174.71±58.13 | |
| Follow-up | 1,575 (95.40) | 139.10±44.88 | |
| Changes | 1,211 (73.35) | −34.05±62.00 | <0.0001 |
| Changes, % | 1,211 (73.35) | −14.37±29.89 | <0.0001 |
|
|
|||
| Changes by statin administered, mg/dL | |||
| Not administeredb | |||
| Total cholesterol | 380 (23.02) | −12.54±44.05 | <0.0001 |
| Triglyceride | 356 (21.56) | −31.00±110.98 | <0.0001 |
| LDL-C | 324 (19.62) | −9.49±33.00 | <0.0001 |
| HDL-C | 349 (21.14) | 2.06±10.29 | <0.0001 |
| Administeredc | |||
| Total cholesterol | 491 (29.74) | −4.60±32.72 | 0.0257 |
| Triglyceride | 491 (29.74) | −27.10±83.42 | <0.0001 |
| LDL-C | 445 (26.95) | −5.16±28.26 | 0.0008 |
| HDL-C | 487 (29.50) | 4.15±9.79 | <0.0001 |
SD, standard deviation; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
a Wilcoxon signed rank sum test,
b Not administered statin from baseline to last follow-up lab test,
c Kept administering statin from baseline to last follow-up lab test.
- 1. Yki-Jarvinen H. Thiazolidinediones. N Engl J Med 2004;351:1106-18.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Kwon MJ, Lee YJ, Jung HS, Shin HM, Kim TN, Lee SH, et al. The direct effect of lobeglitazone, a new thiazolidinedione, on pancreatic beta cells: a comparison with other thiazolidinediones. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2019;151:209-23.ArticlePubMed
- 3. Xiang AH, Peters RK, Kjos SL, Marroquin A, Goico J, Ochoa C, et al. Effect of pioglitazone on pancreatic beta-cell function and diabetes risk in Hispanic women with prior gestational diabetes. Diabetes 2006;55:517-22.PubMed
- 4. Yu JG, Javorschi S, Hevener AL, Kruszynska YT, Norman RA, Sinha M, et al. The effect of thiazolidinediones on plasma adiponectin levels in normal, obese, and type 2 diabetic subjects. Diabetes 2002;51:2968-74.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 5. Dandona P, Aljada A, Chaudhuri A. Vascular reactivity and thiazolidinediones. Am J Med 2003;115:Suppl 8A. 81S-86S.Article
- 6. Garg R, Kumbkarni Y, Aljada A, Mohanty P, Ghanim H, Hamouda W, et al. Troglitazone reduces reactive oxygen species generation by leukocytes and lipid peroxidation and improves flow-mediated vasodilatation in obese subjects. Hypertension 2000;36:430-5.ArticlePubMed
- 7. Winkler K, Konrad T, Fullert S, Friedrich I, Destani R, Baumstark MW, et al. Pioglitazone reduces atherogenic dense LDL particles in nondiabetic patients with arterial hypertension: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Diabetes Care 2003;26:2588-94.PubMed
- 8. Kim SG, Kim DM, Woo JT, Jang HC, Chung CH, Ko KS, et al. Efficacy and safety of lobeglitazone monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus over 24-weeks: a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo controlled trial. PLoS One 2014;9:e92843.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Kim SH, Kim SG, Kim DM, Woo JT, Jang HC, Chung CH, et al. Safety and efficacy of lobeglitazone monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus over 52 weeks: an open-label extension study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2015;110:e27-30.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Rajagopalan R, Rosenson RS, Fernandes AW, Khan M, Murray FT. Association between congestive heart failure and hospitalization in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving treatment with insulin or pioglitazone: a retrospective data analysis. Clin Ther 2004;26:1400-10.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Mamtani R, Haynes K, Bilker WB, Vaughn DJ, Strom BL, Glanz K, et al. Association between longer therapy with thiazolidinediones and risk of bladder cancer: a cohort study. J Natl Cancer Inst 2012;104:1411-21.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Kahn SE, Zinman B, Lachin JM, Haffner SM, Herman WH, Holman RR, et al. Rosiglitazone-associated fractures in type 2 diabetes: an analysis from A Diabetes Outcome Progression Trial (ADOPT). Diabetes Care 2008;31:845-51.PubMed
- 13. Fonseca V. Effect of thiazolidinediones on body weight in patients with diabetes mellitus. Am J Med 2003;115:Suppl 8A. 42S-48S.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Levin D, Bell S, Sund R, Hartikainen SA, Tuomilehto J, Pukkala E, et al. Pioglitazone and bladder cancer risk: a multipopulation pooled, cumulative exposure analysis. Diabetologia 2015;58:493-504.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Tuccori M, Filion KB, Yin H, Yu OH, Platt RW, Azoulay L. Pioglitazone use and risk of bladder cancer: population based cohort study. BMJ 2016;352:i1541.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Nesto RW, Bell D, Bonow RO, Fonseca V, Grundy SM, Horton ES, et al. Thiazolidinedione use, fluid retention, and congestive heart failure: a consensus statement from the American Heart Association and American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2004;27:256-63.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 17. Singh S, Loke YK, Furberg CD. Thiazolidinediones and heart failure: a teleo-analysis. Diabetes Care 2007;30:2148-53.PubMed
- 18. Mamtani R, Haynes K, Bilker WB, Vaughn DJ, Strom BL, Glanz K, et al. Long-term therapy with thiazolidinediones and the risk of bladder cancer: a cohort study. J Clin Oncol 2012;30(15 Suppl):1503.Article
- 19. Filipova E, Uzunova K, Kalinov K, Vekov T. Effects of pioglitazone therapy on blood parameters, weight and BMI: a meta-analysis. Diabetol Metab Syndr 2017;9:90.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 20. Tang WH, Francis GS, Hoogwerf BJ, Young JB. Fluid retention after initiation of thiazolidinedione therapy in diabetic patients with established chronic heart failure. J Am Coll Cardiol 2003;41:1394-8.ArticlePubMed
- 21. Yoshimoto T, Naruse M, Nishikawa M, Naruse K, Tanabe A, Seki T, et al. Antihypertensive and vasculo- and renoprotective effects of pioglitazone in genetically obese diabetic rats. Am J Physiol 1997;272(6 Pt 1):E989-96.ArticlePubMed
- 22. Hosokawa M, Tsukada H, Fukuda K, Oya M, Onomura M, Nakamura H, et al. Troglitazone inhibits bicarbonate secretion in rat and human duodenum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1999;290:1080-4.PubMed
- 23. Walker AB, Naderali EK, Chattington PD, Buckingham RE, Williams G. Differential vasoactive effects of the insulin sensitizers rosiglitazone (BRL 49653) and troglitazone on human small arteries in vitro. Diabetes 1998;47:810-4.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. Wan Y. PPARγ in bone homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol Metab 2010;21:722-8.ArticlePubMed
- 25. Patel JJ, Butters OR, Arnett TR. PPAR agonists stimulate adipogenesis at the expense of osteoblast differentiation while inhibiting osteoclast formation and activity. Cell Biochem Funct 2014;32:368-77.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Billington EO, Grey A, Bolland MJ. The effect of thiazolidinediones on bone mineral density and bone turnover: systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2015;58:2238-46.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 27. Dormandy J, Bhattacharya M, van Troostenburg de Bruyn AR; PROactive investigators. Safety and tolerability of pioglitazone in high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes: an overview of data from PROactive. Drug Saf 2009;32:187-202.PubMed
- 28. Lim S, Kim KM, Kim SG, Kim DM, Woo JT, Chung CH, et al. Effects of lobeglitazone, a novel thiazolidinedione, on bone mineral density in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus over 52 weeks. Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:377-85.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 29. Lee HW, Kim BY, Ahn JB, Kang SK, Lee JH, Shin JS, et al. Molecular design, synthesis, and hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities of novel pyrimidine derivatives having thiazolidinedione. Eur J Med Chem 2005;40:862-74.ArticlePubMed
- 30. Lim S, Lee KS, Lee JE, Park HS, Kim KM, Moon JH, et al. Effect of a new PPAR-gamma agonist, lobeglitazone, on neointimal formation after balloon injury in rats and the development of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2015;243:107-19.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Kim KM, Jin HJ, Lee SY, Maeng HJ, Lee GY, Oh TJ, et al. Effects of Lobeglitazone, a new thiazolidinedione, on osteoblastogenesis and bone mineral density in mice. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul) 2017;32:389-95.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 32. Lee HS, Chang M, Lee JE, Kim W, Hwang IC, Kim DH, et al. Carcinogenicity study of CKD-501, a novel dual peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors α and γ agonist, following oral administration to Sprague Dawley rats for 94–101 weeks. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol 2014;69:207-16.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Moon KS, Lee JE, Lee HS, Hwang IC, Kim DH, Park HK, et al. CKD-501, a novel selective PPARγ agonist, shows no carcinogenic potential in ICR mice following oral administration for 104 weeks. J Appl Toxicol 2014;34:1271-84.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Bae J, Park T, Kim H, Lee M, Cha BS. Lobeglitazone: a novel thiazolidinedione for the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:326-36.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 35. Kim JW, Kim JR, Yi S, Shin KH, Shin HS, Yoon SH, et al. Tolerability and pharmacokinetics of lobeglitazone (CKD-501), a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ agonist: a single- and multiple-dose, double-blind, randomized control study in healthy male Korean subjects. Clin Ther 2011;33:1819-30.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Mamza J, Mehta R, Donnelly R, Idris I. Important differences in the durability of glycaemic response among second-line treatment options when added to metformin in type 2 diabetes: a retrospective cohort study. Ann Med 2016;48:224-34.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Lee MA, Tan L, Yang H, Im YG, Im YJ. Structures of PPARγ complexed with lobeglitazone and pioglitazone reveal key determinants for the recognition of antidiabetic drugs. Sci Rep 2017;7:16837.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 38. Jang JY, Bae H, Lee YJ, Choi YI, Kim HJ, Park SB, et al. Structural basis for the enhanced anti-diabetic efficacy of lobeglitazone on PPARγ. Sci Rep 2018;8:31.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 39. Jin SM, Park CY, Cho YM, Ku BJ, Ahn CW, Cha BS, et al. Lobeglitazone and pioglitazone as add-ons to metformin for patients with type 2 diabetes: a 24-week, multicentre, randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, active-controlled, phase III clinical trial with a 28-week extension. Diabetes Obes Metab 2015;17:599-602.PubMedPMC
- 40. Ha KH, Park CY, Jeong IK, Kim HJ, Kim SY, Kim WJ, et al. Clinical characteristics of people with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes between 2015 and 2016: difference by age and body mass index. Diabetes Metab J 2018;42:137-46.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Efficacy and safety of novel thiazolidinedione lobeglitazone for managing type-2 diabetes a meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Manoj Kumar, Priyankar K. Datta, Ritin Mohindra, Meha Sharma
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(1): 102697. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of lobeglitazone, a new Thiazolidinedione, as compared to the standard of care in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Shashank R. Joshi, Saibal Das, Suja Xaviar, Shambo Samrat Samajdar, Indranil Saha, Sougata Sarkar, Shatavisa Mukherjee, Santanu Kumar Tripathi, Jyotirmoy Pal, Nandini Chatterjee
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(1): 102703. CrossRef - Will lobeglitazone rival pioglitazone? A systematic review and critical appraisal
Kalyan Kumar Gangopadhyay, Awadhesh Kumar Singh
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(4): 102747. CrossRef - Lobeglitazone
Reactions Weekly.2023; 1948(1): 262. CrossRef - Lobeglitazone, a novel thiazolidinedione, for secondary prevention in patients with ischemic stroke: a nationwide nested case-control study
Joonsang Yoo, Jimin Jeon, Minyoul Baik, Jinkwon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lobeglitazone and Its Therapeutic Benefits: A Review
Balamurugan M, Sarumathy S, Robinson R
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Oldies but Goodies: Thiazolidinedione as an Insulin Sensitizer with Cardioprotection
Eun-Hee Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 827. CrossRef
- Figure
- Related articles
-
- Risk Prediction and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in People Living with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Clinical and Lifestyle Determinants of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Metrics in Insulin-Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Cardiovascular Outcomes according to Comorbidities and Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Korean People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Sarcopenia and Carotid Plaque Progression Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Safety and Effectiveness of Empagliflozin in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from a Nationwide Post-Marketing Surveillance

 KDA
KDA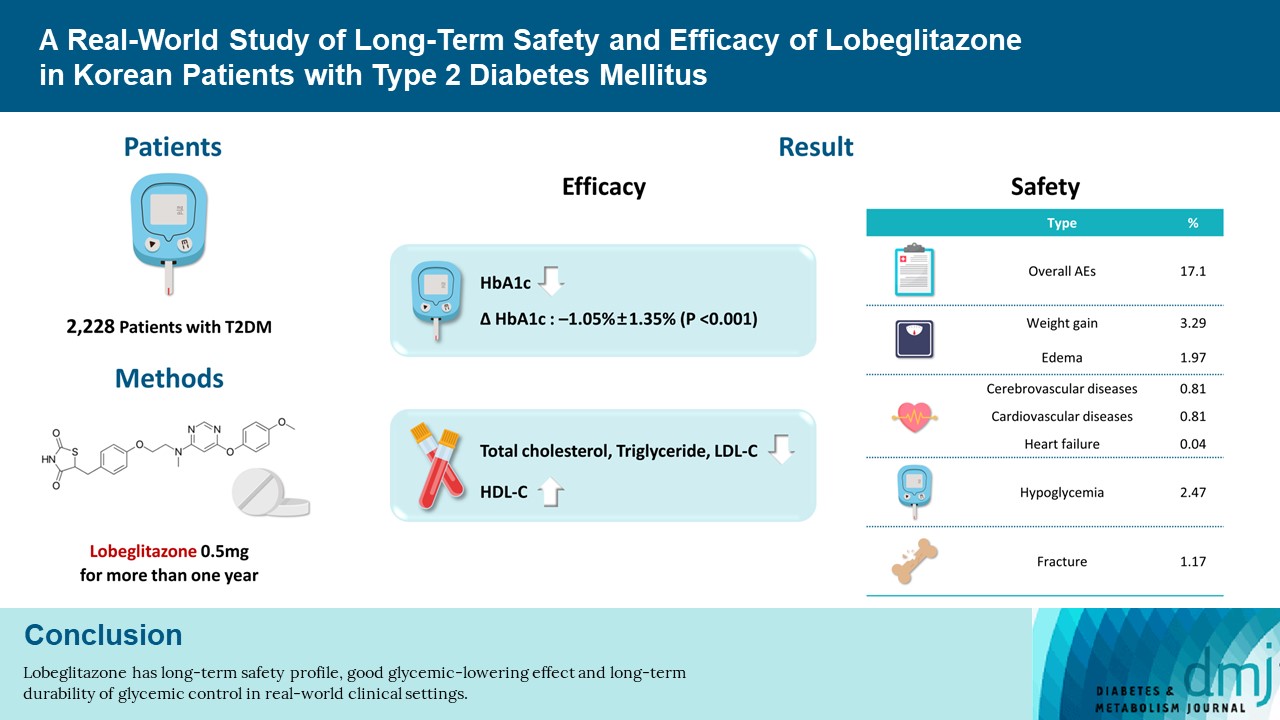
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite