
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Basic Research
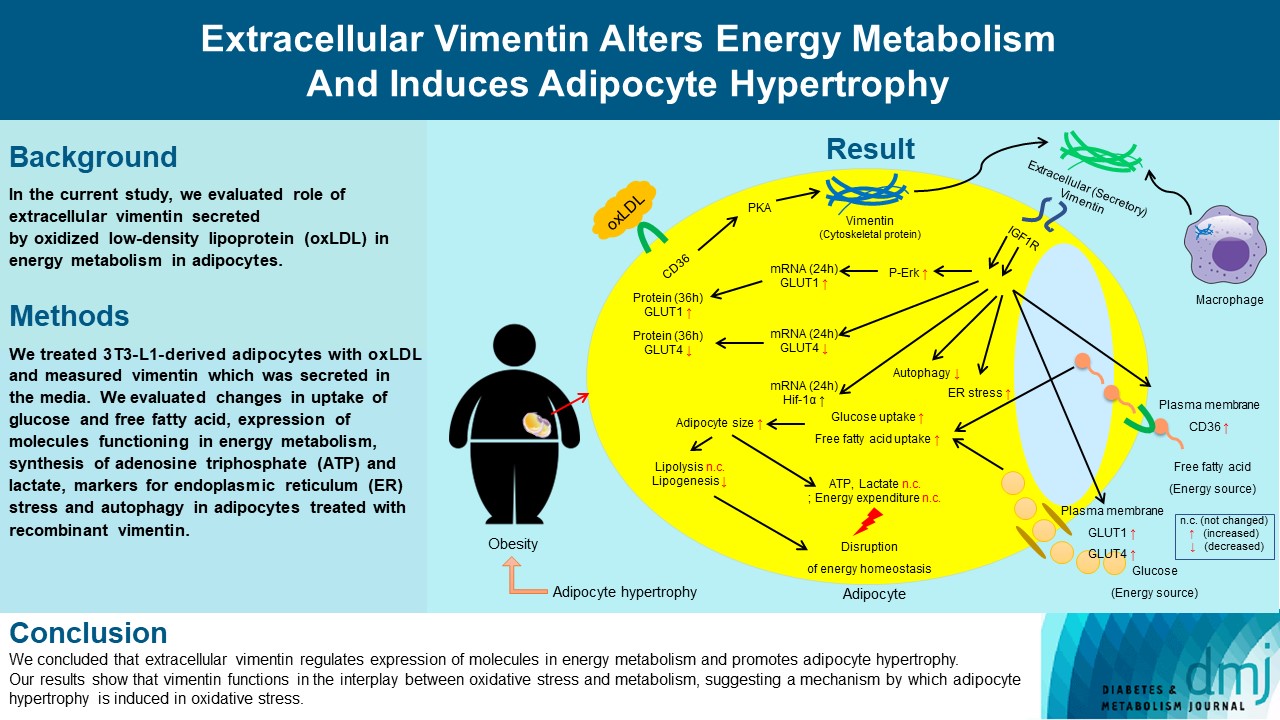
- Extracellular Vimentin Alters Energy Metabolism And Induces Adipocyte Hypertrophy
- Ji-Hae Park, Soyeon Kwon, Young Mi Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):215-230. Published online September 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0332
- 2,286 View
- 190 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Previous studies have reported that oxidative stress contributes to obesity characterized by adipocyte hypertrophy. However, mechanism has not been studied extensively. In the current study, we evaluated role of extracellular vimentin secreted by oxidized low-density lipoprotein (oxLDL) in energy metabolism in adipocytes.
Methods
We treated 3T3-L1-derived adipocytes with oxLDL and measured vimentin which was secreted in the media. We evaluated changes in uptake of glucose and free fatty acid, expression of molecules functioning in energy metabolism, synthesis of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) and lactate, markers for endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and autophagy in adipocytes treated with recombinant vimentin.
Results
Adipocytes secreted vimentin in response to oxLDL. Microscopic evaluation revealed that vimentin treatment induced increase in adipocyte size and increase in sizes of intracellular lipid droplets with increased intracellular triglyceride. Adipocytes treated with vimentin showed increased uptake of glucose and free fatty acid with increased expression of plasma membrane glucose transporter type 1 (GLUT1), GLUT4, and CD36. Vimentin treatment increased transcription of GLUT1 and hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (Hif-1α) but decreased GLUT4 transcription. Adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL), peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ), sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1 (SREBP1), diacylglycerol O-acyltransferase 1 (DGAT1) and 2 were decreased by vimentin treatment. Markers for ER stress were increased and autophagy was impaired in vimentin-treated adipocytes. No change was observed in synthesis of ATP and lactate in the adipocytes treated with vimentin.
Conclusion
We concluded that extracellular vimentin regulates expression of molecules in energy metabolism and promotes adipocyte hypertrophy. Our results show that vimentin functions in the interplay between oxidative stress and metabolism, suggesting a mechanism by which adipocyte hypertrophy is induced in oxidative stress.
- COVID-19
- Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on the Metabolic Control Parameters in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Ifan Ali Wafa, Nando Reza Pratama, Nurizzah Farahiyah Sofia, Elsha Stephanie Anastasia, Tiffany Konstantin, Maharani Ayuputeri Wijaya, M. Rifqi Wiyono, Lilik Djuari, Hermina Novida
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):260-272. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0125
- 5,932 View
- 272 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Abrupt implementation of lockdowns during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic affected the management of diabetes mellitus in patients worldwide. Limited access to health facilities and lifestyle changes potentially affected metabolic parameters in patients at risk. We conducted a meta-analysis to determine any differences in the control of metabolic parameters in patients with diabetes, before and during lockdown.
Methods
We performed searches of five databases. Meta-analyses were carried out using random- or fixed-effect approaches to glycaemic control parameters as the primary outcome: glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), random blood glucose (RBG), fasting blood glucose (FBG), time-in-range (TIR), time-above-range (TAR), time-below-range (TBR). Mean difference (MD), confidence interval (CI), and P value were calculated. Lipid profile was a secondary outcome and is presented as a descriptive analysis.
Results
Twenty-one studies enrolling a total of 3,992 patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes mellitus (T1DM or T2DM) were included in the study. Patients with T1DM showed a significant improvement of TIR and TAR (MD=3.52% [95% CI, 0.29 to 6.74], I2=76%, P=0.03; MD=–3.36% [95% CI, –6.48 to –0.25], I2=75%, P=0.03), while FBG among patients with T2DM significantly worsened (MD=3.47 mg/dL [95% CI, 1.22 to 5.73], I2=0%, P<0.01). No significant difference was found in HbA1c, RBG, and TBR. Use of continuous glucose monitoring in T1DM facilitated good glycaemic control. Significant deterioration of lipid parameters during lockdown, particularly triglyceride, was observed.
Conclusion
Implementation of lockdowns during the COVID-19 pandemic did not worsen glycaemic control in patients with diabetes. Other metabolic parameters improved during lockdown, though lipid parameters, particularly triglyceride, worsened. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Disruption of diabetes and hypertension care during the COVID-19 pandemic and recovery approaches in the Latin America and Caribbean region: a scoping review protocol
Samira Barbara Jabakhanji, Oluwabunmi Ogungbe, Sonia Y Angell, Lawrence Appel, David Byrne, Roopa Mehta, John McCaffrey, Lori Rosman, Edward W Gregg, Kunihiro Matsushita
BMJ Open.2024; 14(1): e074443. CrossRef - Influence of the COVID-19 pandemic on the achievement of guideline targets for HbA1c, blood pressure, and LDL cholesterol in people with diabetes in Japan
Shingo Kuwajima, Takahito Itoh, Tatsuya Sato, Shoya Ino, Satoru Shibata, Kouhei Ohno, Hiroyuki Hotta, Tomoaki Matsumoto, Hitoshi Ooiwa, Hirofumi Kubo, Takayuki Miki
Diabetology International.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic Control in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19: What We Learned From the Lockdown Experience
Catarina Almeida, André Ferreira, Daniela Duarte, Ana Filipa Viegas, André Santos, Alexandra Vaz, Edite Nascimento
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Changes in body weight and glycemic control in association with COVID-19 Shutdown among 23,000 adults with type 2 diabetes
Emily Panza, Kevin E. Kip, Kripa Venkatakrishnan, Oscar C. Marroquin, Rena R. Wing
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(6): 787. CrossRef - The Impact of a Lockdown for the COVID-19 Pandemic on Seasonal HbA1c Variation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Yu-Cheng Cheng, Yu-Hsuan Li, Hsiu-Chen Liu, Chiann-Yi Hsu, Wan-Jen Chang, I-Te Lee, Chin-Li Lu
Life.2023; 13(3): 763. CrossRef - The Impact of Partial Lockdown During COVID-19 Pandemic on Metabolic Control in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ayşe Zülal TOKAÇ, Tuğde Buse UĞUR, Buse Ecem KURUGÖL, Sevilay ALİGÜLÜ, Osman HAYRAN
Journal of Biotechnology and Strategic Health Research.2023; 7(1): 67. CrossRef - Retrospective Study on the Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Northern Taiwan
Hsuan Huang, Hsiao-Ling Su, Chih-Hsung Huang, Yi-Hsin Lin
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 2539. CrossRef - RIPK1 and RIPK3 inhibitors: potential weapons against inflammation to treat diabetic complications
Dan Ke, Zhen Zhang, Jieting Liu, Peijian Chen, Yucen Dai, Xinhai Sun, Yanhui Chu, Luxin Li
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - “Does Physical Exercise Promote Health Benefits for Diabetic Patients during the COVID-19 Pandemic?”: A Systematic Review
Erivaldo de Souza, Daniela Meneses-Santos, Josué Cruz Santos, Felipe J. Aidar, Carla Roberta de Oliveira Carvalho, Jymmys Lopes dos Santos, Anderson Carlos Marçal
Sports.2023; 11(10): 192. CrossRef - Impact of National Lockdown From COVID-19 Pandemic in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: An Observational Study
Nuntakorn Thongtang, Niracha Chanwimol, Lukana Preechasuk, Varisara Boonyuang, Pinyo Rattanaumpawan, Supawadee Likitmaskul, Apiradee Sriwijitkamol
Asia Pacific Journal of Public Health.2022; 34(6-7): 708. CrossRef
- Disruption of diabetes and hypertension care during the COVID-19 pandemic and recovery approaches in the Latin America and Caribbean region: a scoping review protocol
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Comparison of the Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy 20 mg with Rosuvastatin 5 mg and Ezetimibe 10 mg Combination Therapy on Lipid Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- You-Cheol Hwang, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):582-589. Published online January 16, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0124
- 6,572 View
- 184 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The apolipoprotein B/A1 (apoB/A1) ratio is a stronger predictor of future cardiovascular disease than is the level of conventional lipids. Statin and ezetimibe combination therapy have shown additional cardioprotective effects over statin monotherapy.
Methods This was a single-center, randomized, open-label, active-controlled study in Korea. A total of 36 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were randomized to either rosuvastatin monotherapy (20 mg/day,
n =20) or rosuvastatin/ezetimibe (5 mg/10 mg/day,n =16) combination therapy for 6 weeks.Results After the 6-week treatment, low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and apoB reduction were comparable between the two groups (−94.3±15.4 and −62.0±20.9 mg/dL in the rosuvastatin group, −89.9±22.7 and −66.8±21.6 mg/dL in the rosuvastatin/ezetimibe group,
P =0.54 andP =0.86, respectively). In addition, change in apoB/A1 ratio (−0.44±0.16 in the rosuvastatin group and −0.47±0.25 in the rosuvastatin/ezetimibe group,P =0.58) did not differ between the two groups. On the other hand, triglyceride and free fatty acid (FFA) reductions were greater in the rosuvastatin/ezetimibe group than in the rosuvastatin group (−10.5 mg/dL [interquartile range (IQR), −37.5 to 29.5] and 0.0 µEq/L [IQR, −136.8 to 146.0] in the rosuvastatin group, −49.5 mg/dL [IQR, −108.5 to −27.5] and −170.5 µEq/L [IQR, −353.0 to 0.8] in the rosuvastatin/ezetimibe group,P =0.010 andP =0.049, respectively). Both treatments were generally well tolerated, and there were no differences in muscle or liver enzyme elevation.Conclusion A 6-week combination therapy of low-dose rosuvastatin and ezetimibe showed LDL-C, apoB, and apoB/A1 ratio reduction comparable to that of high-dose rosuvastatin monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Triglyceride and FFA reductions were greater with the combination therapy than with rosuvastatin monotherapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Moderate-Intensity Rosuvastatin/Ezetimibe Combination versus Quadruple-Dose Rosuvastatin Monotherapy: A Meta-Analysis and Systemic Review
Yura Kang, Jung Mi Park, Sang-Hak Lee
Yonsei Medical Journal.2024; 65(1): 19. CrossRef - Combination Therapy of Ezetimibe and Rosuvastatin for Dyslipidemia: Current Insights
Maya R Chilbert, Dylan VanDuyn, Sara Salah, Collin M Clark, Qing Ma
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2022; Volume 16: 2177. CrossRef - Ezetimibe and diabetes mellitus:a new strategy for lowering cholesterol
V.A. Serhiyenko, A.A. Serhiyenko
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2022; 18(5): 302. CrossRef - The Effect of Rosuvastatin on Plasma/Serum Levels of High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein, Interleukin-6, and D-Dimer in People Living with Human Immunodeficiency Virus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Akililu Alemu Ashuro, Yin-Guang Fan, Yuan-Sheng Fu, Dong-Sheng Di, Napoleon Bellua Sam, Hai-Feng Pan, Dong-Qing Ye
AIDS Research and Human Retroviruses.2021; 37(11): 821. CrossRef - Comparison of the Efficacy and Safety of Rosuvastatin/Ezetimibe Combination Therapy and Rosuvastatin Monotherapy on Lipoprotein in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Multicenter Randomized Controlled Study
Jiwoo Lee, You-Cheol Hwang, Woo Je Lee, Jong Chul Won, Kee-Ho Song, Cheol-Young Park, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Joong-Yeol Park
Diabetes Therapy.2020; 11(4): 859. CrossRef - Comparison of Renal Effects of Ezetimibe–Statin Combination versus Statin Monotherapy: A Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis
Jaehyun Bae, Namki Hong, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Yong-ho Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(3): 798. CrossRef - Combined use of rosuvastatin and ezetimibe improves hepatic steatosis in patients with dyslipidemia
Won Dong Lee, Beom Kyung Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Kwang-Hyub Han, Seung Up Kim
European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2020; 32(12): 1538. CrossRef - Influence of rosuvastatin dose on total fatty acids and free fatty acids in plasma
Cristian I. Ciucanu, Sonia Olariu, Daliborca C. Vlad, Victor Dumitraşcu
Medicine.2020; 99(48): e23356. CrossRef - The effect of switching from statin-monotherapy to statin/ezetimibe combination therapy on lipid profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes and dyslipidemia: a multicenter open-label study (EUCLID)
Mitsuhide Takeshita, Atsushi Tanaka, Atsushi Kawaguchi, Keiko Sato, Shigeru Toyoda, Teruo Inoue, Koichi Node
Vascular Failure.2020; 4(1): 22. CrossRef - Response: Comparison of the Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy 20 mg with Rosuvastatin 5 mg and Ezetimibe 10 mg Combination Therapy on Lipid Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:582–9)
You-Cheol Hwang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 915. CrossRef - Letter: Comparison of the Efficacy of Rosuvastatin Monotherapy 20 mg with Rosuvastatin 5 mg and Ezetimibe 10 mg Combination Therapy on Lipid Parameters in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J2019;43:582–9)
Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 909. CrossRef - Changes in Plasma Free Fatty Acids Associated with Type-2 Diabetes
Amélie I. S. Sobczak, Claudia A. Blindauer, Alan J. Stewart
Nutrients.2019; 11(9): 2022. CrossRef
- Moderate-Intensity Rosuvastatin/Ezetimibe Combination versus Quadruple-Dose Rosuvastatin Monotherapy: A Meta-Analysis and Systemic Review
- Complications
- Risk Factors for the Development and Progression of Diabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Advanced Diabetic Retinopathy
- Kyung-Jin Yun, Hye Ji Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki-Hyun Baek, Young Jung Roh, Ki-Ho Song
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(6):473-481. Published online September 20, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.6.473
- 4,406 View
- 44 Download
- 25 Web of Science
- 26 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Some patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) do not develop diabetic kidney disease (DKD) despite the presence of advanced diabetic retinopathy (DR). We aimed to investigate the presence of DKD and its risk factors in patients with T2DM and advanced DR.
Methods We conducted a cross-sectional study in 317 patients with T2DM and advanced DR. The phenotypes of DKD were divided into three groups according to the urine albumin/creatinine ratio (uACR, mg/g) and estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2): no DKD (uACR <30 and eGFR ≥60), non-severe DKD (uACR ≥30 or eGFR <60), and severe DKD (uACR ≥30 and eGFR <60). Mean systolic and diastolic blood pressure, mean glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level, and HbA1c variability (standard deviation [SD] of serial HbA1c values or HbA1c-SD) were calculated for the preceding 2 years.
Results The prevalence of no DKD, non-severe DKD, and severe DKD was 37.2% (
n =118), 37.0% (n =117), and 25.8% (n =82), respectively. HbA1c-SD and the triglyceride/high density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio correlated positively with uACR and negatively with eGFR. Multiple linear regression analyses showed that the HbA1c-SD and TG/HDL-C ratio were significantly related with eGFR. Multiple logistic regression analyses after adjusting for several risk factors showed that HbA1c-SD and the TG/HDL-C ratio were significant risk factors for severe DKD.Conclusion The prevalence of DKD was about 60% in patients with T2DM and advanced DR. HbA1c variability and TG/HDL-C ratio may affect the development and progression of DKD in these patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Ocular and Systemic Risk Factors for Disease Worsening Among Patients with NPDR
Charles C. Wykoff, Diana V. Do, Roger A. Goldberg, Dilsher S. Dhoot, Jennifer I. Lim, Weiming Du, Fabiana Q. Silva, Rutvi Desai, Hadi Moini, Kimberly Reed, Alyson J. Berliner, Robert Vitti, W. Lloyd Clark
Ophthalmology Retina.2024; 8(4): 399. CrossRef - Interpretable prediction model for assessing diabetes complication risks in Chinese sufferers
Ye Shiren, Ye Jiangnan, Ye Xinhua, Ni Xinye
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 209: 111560. CrossRef - Dose-response association of diabetic kidney disease with routine clinical parameters in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jianbo Guo, Chen Liu, Yifan Wang, Baoyi Shao, Tung Leong Fong, Ngai Chung Lau, Hui Zhang, Haidi Li, Jianan Wang, Xinyu Lu, Anqi Wang, Cheuk Lung Leung, Xin Wei Chia, Fei Li, Xiaoming Meng, Qingyong He, Haiyong Chen
eClinicalMedicine.2024; 69: 102482. CrossRef - Sex-Specific Computed Tomography Abdominal Fat and Skeletal Muscle Characteristics in Type 2 Diabetic Retinopathy Patients With/Without Comorbid Diabetic Kidney Disease
Jinlei Fan, Liping Zuo, Mingyuan Hou, Bowen Wang, Yueming An, Baoli Hao, Dexin Yu
Academic Radiology.2023; 30(11): 2686. CrossRef - The concordance and discordance of diabetic kidney disease and retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study of 26,809 patients from 5 primary hospitals in China
Zhaoxiang Liu, Xianglan Li, Yanlei Wang, Yanxia Song, Qiang Liu, Junxia Gong, Wenshuang Fan, Chunmei Lv, Chenxiang Cao, Wenhui Zhao, Jianzhong Xiao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Ferroptosis: new insight into the mechanisms of diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy
Luxin Li, Yucen Dai, Dan Ke, Jieting Liu, Peijian Chen, Dong Wei, Tongtong Wang, Yanjie Teng, Xiaohuan Yuan, Zhen Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predicting diabetic kidney disease for type 2 diabetes mellitus by machine learning in the real world: a multicenter retrospective study
Xiao zhu Liu, Minjie Duan, Hao dong Huang, Yang Zhang, Tian yu Xiang, Wu ceng Niu, Bei Zhou, Hao lin Wang, Ting ting Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Developing screening tools to estimate the risk of diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Xu Cao, Xiaomei Pei
Technology and Health Care.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Association between serum complements and kidney function in patients with diabetic kidney disease
Meng-chao Liu, Jia-lin Li, Yue-fen Wang, Yuan Meng, Gui-min Zheng, Zhen Cai, Cun Shen, Meng-di Wang, Xiang-gang Zhu, Yang-zi Chen, Yu-lin Wang, Wen-jing Zhao, Wen-quan Niu, Yao-xian Wang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Coagulation Function and Type 2 Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Real-World Observational Study
Meng-chao Liu, Wen-quan Niu, Yue-fen Wang, Yuan Meng, Gui-min Zheng, Zhen Cai, Cun Shen, Xiang-gang Zhu, Meng-di Wang, Jia-lin Li, Wen-jing Zhao, Yao-xian Wang, Eusebio Chiefari
Journal of Diabetes Research.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - Punicalagin alleviates renal injury via the gut-kidney axis in high-fat diet-induced diabetic mice
Qinglian Hua, Yaling Han, Haifeng Zhao, Haowen Zhang, Bei Yan, Shengjie Pei, Xin He, Yue Li, Xiangyuan Meng, Lei Chen, Feng Zhong, Duo Li
Food & Function.2022; 13(2): 867. CrossRef - Status and Trends of the Association Between Diabetic Nephropathy and Diabetic Retinopathy From 2000 to 2021: Bibliometric and Visual Analysis
Wenwen Lin, Yayong Luo, Fang Liu, Hangtian Li, Qian Wang, Zheyi Dong, Xiangmei Chen
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Risk Threshold for Hemoglobin A1c Associated With Albuminuria: A Population-Based Study in China
Hong Lian, Hongshi Wu, Jie Ning, Diaozhu Lin, Chulin Huang, Feng Li, Ying Liang, Yiqin Qi, Meng Ren, Li Yan, Lili You, Mingtong Xu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Weight change and microvascular outcomes in patients with new-onset diabetes: a nationwide cohort study
Eun Sil Koh, Kyung Do Han, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun Sook Kim, Min-Kyung Lee, Ga Eun Nam, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2021; 36(4): 932. CrossRef - Albuminuria Is Associated with Steatosis Burden in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 698. CrossRef - Effect of Calcium Dobesilate in Preventing Contrast-Induced Nephropathy in Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease
Hao Zhang, Shao-Hua Guo, Zheng-Kai Xue, Ya-Ru Zhang, Jia-Rui Wang, Jing-Jin Che, Tong Liu, Hua-Yue Tao, Guang-Ping Li, Seung-Woon Rha, Swapnil-Zaman Ashraful-Haque, Kang-Yin Chen
Clinics.2021; 76: e2942. CrossRef - Elevated TG/HDL-C and non-HDL-C/HDL-C ratios predict mortality in peritoneal dialysis patients
Wenkai Xia, Xiajuan Yao, Yan Chen, Jie Lin, Volker Vielhauer, Hong Hu
BMC Nephrology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Thermal Perception Abnormalities Can Predict Diabetic Kidney Disease in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Wei-Ching Fang, Kuei-Mei Chou, Chiao-Yin Sun, Chin-Chan Lee, I-Wen Wu, Yung-Chang Chen, Heng-Chih Pan
Kidney and Blood Pressure Research.2020; 45(6): 926. CrossRef - Association between nonalbumin proteinuria and renal tubular damage of N-acetyl-β-d-glucosaminidase and its clinical relevance in patients with type 2 diabetes without albuminuria
Eugene Han, Mi-Kyung Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Soon Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(3): 255. CrossRef - Detection of Lower Albuminuria Levels and Early Development of Diabetic Kidney Disease Using an Artificial Intelligence-Based Rule Extraction Approach
Yoichi Hayashi
Diagnostics.2019; 9(4): 133. CrossRef - Therapeutic effect of liraglutide on expression of CTGF and BMP‐7 in induced diabetic nephropathy
Maggie M. Ramzy, Ahlam M. Abdalla, Nagwa M. Zenhom, Ahmed M. Okasha, Aya E. Abdelkafy, Rabeh K. Saleh
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2019; 120(10): 17512. CrossRef - Are blood lipids associated with microvascular complications among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients? A cross-sectional study in Shanghai, China
Hua Yang, Doris Young, Jian Gao, Yuanzhi Yuan, Minqian Shen, Yuan Zhang, Xueyan Duan, Shanzhu Zhu, Xiaoming Sun
Lipids in Health and Disease.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Discordance in risk factors for the progression of diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ki‐Ho Song, Jee‐Sun Jeong, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon, Ki‐Hyun Baek, Seung‐Hyun Ko, Yu‐Bae Ahn
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2019; 10(3): 745. CrossRef - Risk factors for the development of micro-vascular complications of type 2 diabetes in a single-centre cohort of patients
Marsida Teliti, Giulia Cogni, Lucia Sacchi, Arianna Dagliati, Simone Marini, Valentina Tibollo, Pasquale De Cata, Riccardo Bellazzi, Luca Chiovato
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2018; 15(5): 424. CrossRef - Higher Prevalence and Progression Rate of Chronic Kidney Disease in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Seok Won Park, Yong-Wook Cho, Soo-Kyung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(3): 224. CrossRef - Determinants of the Risk of Diabetic Kidney Disease and Diabetic Retinopathy Independent of Glucose Exposure
Bo Kyung Koo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(6): 444. CrossRef
- Ocular and Systemic Risk Factors for Disease Worsening Among Patients with NPDR
- Impact of Serum Triglyceride and High Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol Levels on Early-Phase Insulin Secretion in Normoglycemic and Prediabetic Subjects
- Masanori Shimodaira, Tomohiro Niwa, Koji Nakajima, Mutsuhiro Kobayashi, Norinao Hanyu, Tomohiro Nakayama
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(4):294-301. Published online August 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.4.294
- 3,213 View
- 28 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Increased triglycerides (TGs) and decreased high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels are established as diabetic risks for nondiabetic subjects. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship among TG, HDL-C, TG/HDL-C ratio, and early-phase insulin secretion in normoglycemic and prediabetic subjects.
Methods We evaluated 663 Japanese subjects who underwent the 75-g oral glucose tolerance test. On the basis of these results, the subjects were divided into four groups: those with normal glucose tolerance (NGT;
n =341), isolated impaired fasting glucose (i-IFG;n =211), isolated impaired glucose tolerance (i-IGT;n =71), and combined IFG and IGT (IFG+IGT;n =40). Insulin secretion was estimated by the insulinogenic index (IGI) (Δinsulin/Δglucose [30 to 0 minutes]) and disposition index (DI) (IGI/homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance).Results In prediabetic subjects (i-IFG, i-IGT, and IFG+IGT), linear regression analyses revealed that IGI and DI were positively correlated with HDL-C levels. Moreover, in subjects with i-IGT and (IFG+IGT), but not with i-IFG, the indices of insulin secretion were negatively correlated with the log-transformed TG and TG/HDL-C ratio. In both the subjects with i-IGT, multivariate linear regression analyses revealed that DI was positively correlated with HDL-C and negatively with log-transformed TG and TG/HDL-C ratio. On the other hand, in subjects with NGT, there was no association between insulin secretion and lipid profiles.
Conclusion These results revealed that serum TG and HDL-C levels have different impacts on early-phase insulin secretion on the basis of their glucose tolerance status.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The protective effects of lipoxin A4 on type 2 diabetes mellitus: A Chinese prospective cohort study
Sudan Wang, Xiaoyan Qian, Chao Shen, Qian Sun, Yang Jing, Bingyue Liu, Kexin Zhang, Mengyuan Li, Junrong Wang, Hui Zhou, Chen Dong
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Interaction between the GCKR rs1260326 variant and serum HDL cholesterol contributes to HOMA-β and ISIMatusda in the middle-aged T2D individuals
Min Shen, Liying Jiang, Hechun Liu, Hao Dai, Hemin Jiang, Yu Qian, Zhixiao Wang, Shuai Zheng, Heng Chen, Tao Yang, Qi Fu, Kuanfeng Xu
Journal of Human Genetics.2023; 68(12): 835. CrossRef - Elevated triglyceride/high-density lipoprotein-cholesterol ratio as a risk factor for progression to prediabetes: a 5-year retrospective cohort study in Japan
Masanori Shimodaira, Yu Minemura, Tomohiro Nakayama
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association ofTG/HDLCratio trajectory and risk of type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study inChina
Yanyan Zhang, Pei Qin, Yanmei Lou, Ping Zhao, Xue Li, Ranran Qie, Xiaoyan Wu, Minghui Han, Shengbing Huang, Yang Zhao, Dechen Liu, Yuying Wu, Yang Li, Xingjin Yang, Yang Zhao, Yifei Feng, Changyi Wang, Jianping Ma, Xiaolin Peng, Hongen Chen, Dan Zhao, Sha
Journal of Diabetes.2021; 13(5): 402. CrossRef - Triglycerides/high-density lipoprotein cholesterol is a predictor similar to the triglyceride–glucose index for the diagnosis of metabolic syndrome using International Diabetes Federation criteria of insulin resistance in obese adolescents: a cross-sectio
Nazlı Nur Aslan Çin, Hülya Yardımcı, Nevra Koç, Seyit Ahmet Uçaktürk, Mehtap Akçil Ok
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 33(6): 777. CrossRef - Comparison of Serum PCSK9 Levels in Subjects with Normoglycemia, Impaired Fasting Glucose, and Impaired Glucose Tolerance
Eugene Han, Nan Hee Cho, Seong-Su Moon, Hochan Cho
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 480. CrossRef - Triglycerides/glucose index is a useful surrogate marker of insulin resistance among adolescents
B Kang, Y Yang, E Y Lee, H K Yang, H-S Kim, S-Y Lim, J-H Lee, S-S Lee, B-K Suh, K-H Yoon
International Journal of Obesity.2017; 41(5): 789. CrossRef - The TyG index may predict the development of cardiovascular events
Laura Sánchez‐Íñigo, David Navarro‐González, Alejandro Fernández‐Montero, Juan Pastrana‐Delgado, Jose Alfredo Martínez
European Journal of Clinical Investigation.2016; 46(2): 189. CrossRef - TyG Index Change Is More Determinant for Forecasting Type 2 Diabetes Onset Than Weight Gain
David Navarro-González, Laura Sánchez-Íñigo, Alejandro Fernández-Montero, Juan Pastrana-Delgado, Jose Alfredo Martinez
Medicine.2016; 95(19): e3646. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the efficacy of omega-3 fatty acids for hypertriglyceridaemia management in Korea
H.-S. Kim, H. Kim, Y. J. Jeong, S. J. Yang, S. J. Baik, H. Lee, S.-H. Lee, J. H. Cho, I.-Y. Choi, H. W. Yim, K.-H. Yoon
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2016; 41(5): 508. CrossRef - Relationship between insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion rate: not necessarily hyperbolic
S. H. Kim, A. Silvers, J. Viren, G. M. Reaven
Diabetic Medicine.2016; 33(7): 961. CrossRef - The triglyceride to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (TG/HDL-C) ratio as a predictor of insulin resistance but not of β cell function in a Chinese population with different glucose tolerance status
Meicen Zhou, Lixin Zhu, Xiangli Cui, Linbo Feng, Xuefeng Zhao, Shuli He, Fan Ping, Wei Li, Yuxiu Li
Lipids in Health and Disease.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Interactive effects of C-reactive protein levels on the association between APOE variants and triglyceride levels in a Taiwanese population
Semon Wu, Lung-An Hsu, Ming-Sheng Teng, Jeng-Feng Lin, Hsin-Hua Chou, Ming-Cheng Lee, Yi-Ming Wu, Cheng-Wen Su, Yu-Lin Ko
Lipids in Health and Disease.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipoproteins and β-Cell Functions: From Basic to Clinical Data
Dae Ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(4): 274. CrossRef
- The protective effects of lipoxin A4 on type 2 diabetes mellitus: A Chinese prospective cohort study
- Postprandial Triglyceride Is Associated with Fasting Triglyceride and HOMA-IR in Korean Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes
- Seo Hee Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Hee Kwan Won, Jae Hoon Moon, Kwang Joon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(4):404-410. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.404
- 4,105 View
- 41 Download
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Recent studies indicate postprandial triglyceride (TG) had a better association with cardiovascular events and metabolic syndrome than fasting TG. The authors of the present study investigated the metabolic and clinical relevance of postprandial TG.
Methods In a cross-sectional retrospective study, the authors of the present study compared fasting and postprandial TG and analyzed the relationship between postprandial TG and various demographic and metabolic parameters in 639 Korean subjects with type 2 diabetes (T2D, group I,
n =539) and impaired fasting glucose (IFG, group II,n =100) after ingestion of a standardized liquid meal (total 500 kcal, 17.5 g fat, 68.5 g carbohydrate, and 17.5 g protein).Results Fasting and postprandial TG were significantly correlated (
r =0.973,r =0.937,P <0.001) in group I and II, respectively. Of the variables, total cholesterol, waist circumference and body mass index were significantly correlated with fasting and postprandial TG in both groups. Only postprandial TG showed a significant correlation with glucose metabolic parameters (e.g., postprandial glucose, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance [HOMA-IR], and fasting C-peptide) in subjects with T2D. Multiple regression analysis showed fasting TG and HOMA-IR could be predictable variables for postprandial TG in subjects with T2D.Conclusion Postprandial TG was very strongly correlated with fasting TG. The authors of the present study suggest insulin resistance may be more associated with postprandial TG than fasting TG in Korean T2D patients on a low-fat diet.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impaired ketogenesis is associated with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes
Sejeong Lee, Jaehyun Bae, Doo Ri Jo, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Postprandial lipaemia following consumption of a meal enriched with medium chain saturated and/or long chain omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. A randomised cross-over study
Grace Austin, Jessica JA. Ferguson, Rohith N. Thota, Harjinder Singh, Tracy Burrows, Manohar L. Garg
Clinical Nutrition.2021; 40(2): 420. CrossRef - Effects of fatty acids composition in a breakfast meal on the postprandial lipid responses: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
Yuanhang Yao, Sheri Xueqi Pek, Darel Wee Kiat Toh, Xuejuan Xia, Jung Eun Kim
International Journal of Food Sciences and Nutrition.2020; 71(7): 793. CrossRef - The Forgotten Lipids: Triglycerides, Remnant Cholesterol, and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk
Pratik B Sandesara, Salim S Virani, Sergio Fazio, Michael D Shapiro
Endocrine Reviews.2019; 40(2): 537. CrossRef - Determinant of postprandial triglyceride levels in healthy young adults
Tri J.E. Tarigan, Anandhara I. Khumaedi, Syahidatul Wafa, Michael Johan, Murdani Abdullah, Ingrid S. Surono, Dicky L. Tahapary
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(3): 1917. CrossRef - Impact of the triglyceride level on coronary plaque components in female patients with coronary artery disease treated with statins
Motoki Yamashita, Atsushi Iwata, Yuta Kato, Makito Futami, Satoshi Imaizumi, Takashi Kuwano, Amane Ike, Makoto Sugihara, Hiroaki Nishikawa, Bo Zhang, Shin’ichiro Yasunaga, Keijiro Saku, Shin-ichiro Miura
Heart and Vessels.2018; 33(10): 1175. CrossRef - Biomarker potential of C-peptide for screening of insulin resistance in diabetic and non-diabetic individuals
Haseeb A. Khan, Samia H. Sobki, Aishah Ekhzaimy, Isra Khan, Mona A. Almusawi
Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences.2018; 25(8): 1729. CrossRef - Postprandial C‐peptide to glucose ratio as a predictor of β‐cell function and its usefulness for staged management of type 2 diabetes
Eun Young Lee, Sena Hwang, Seo Hee Lee, Yong‐ho Lee, A Ra Choi, Youngki Lee, Byung‐Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2014; 5(5): 517. CrossRef - Genetics and Causality of Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease
Robert S. Rosenson, Michael H. Davidson, Benjamin J. Hirsh, Sekar Kathiresan, Daniel Gaudet
Journal of the American College of Cardiology.2014; 64(23): 2525. CrossRef - The effect of insulin resistance on postprandial triglycerides in Korean type 2 diabetic patients
Kyeong Hye Park, Kwang Joon Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
Acta Diabetologica.2014; 51(1): 15. CrossRef - Acute effects of an oral supplement of (−)-epicatechin on postprandial fat and carbohydrate metabolism in normal and overweight subjects
Gabriela Gutiérrez-Salmeán, Pilar Ortiz-Vilchis, Claudia M. Vacaseydel, Ivan Rubio-Gayosso, Eduardo Meaney, Francisco Villarreal, Israel Ramírez-Sánchez, Guillermo Ceballos
Food & Function.2014; 5(3): 521. CrossRef - A comparative study of broccoli sprouts powder and standard triple therapy on cardiovascular risk factors following H.pylori eradication: a randomized clinical trial in patients with type 2 diabetes
Parvin Mirmiran, Zahra Bahadoran, Mahdieh Golzarand, Homayoun Zojaji, Fereidoun Azizi
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of higher resistin levels with inflammatory activation and endothelial dysfunction in patients with essential hypertension
Chang FANG, Juan LEI, Shu-xian ZHOU, Yu-ling ZHANG, Gui-yi YUAN, Jing-feng WANG
Chinese Medical Journal.2013; 126(4): 646. CrossRef - Epicardial adipose tissue thickness is an indicator for coronary artery stenosis in asymptomatic type 2 diabetic patients: its assessment by cardiac magnetic resonance
Hyun Kim, Kwang Kim, Hye-Jeong Lee, Hee Yu, Jae Moon, Eun Kang, Bong Cha, Hyun Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Young Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2012; 11(1): 83. CrossRef
- Impaired ketogenesis is associated with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes
- The Clinical Characteristics of Anemia in Type 2 Diabetic Patients Without Overt Nephropathy.
- Eun Young Ko, Se In Kim, Yong Bum Jang, Kyoung Hun Min, Sung Hun Kim, Kyu Sun Lee, So Ri Kim, Eun Kyoung Choi, Ji Hyun Park, Tae Sun Park, Hong Sun Paek
- Korean Diabetes J. 2004;28(5):425-431. Published online October 1, 2004
- 1,195 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
It is well known that anemia occurs early in diabetic patients before they reach to end stage renal failure. This anemia is considered to be due to the reduced endogenous erythropoietin synthesis, tubulointerstitial damage, autonomic dysfunction, and to the use of angiotensin-converting- enzyme inhibitors. Because anemia has a significant impact on the quality of life for diabetic patients, we examined the clinical characteristics of anemia in those diabetic patients who did not have overt nephropathy. METHODS: We retrospectively reviewed the medical records of 200 type 2 diabetic patients with anemia who had been followed up from 1998 to 2002 by Chonbuk University Medical School Hospital. We measured the total cholesterol, triglycerides, high density lipoprotein, low density lipoprotein, and the presence of complications (retinopathy or neuropathy) for about 90 diabetic patients who were under the age of 65, they were without other underlying disease and they had a hemoglobin concentration 110g/L, GFR 1.0 mL/s. We excluded the causes of anemia as being from malignancy, liver disease, coexisting iron deficiency, chronic inflammatory disease and chronic infection. RESULTS: The clinical characteristics of the patients are as follows; the mean age was 59.6 +/- 8.4 years, the mean HbA1C was 9.4 +/- 2.3%, and the mean Hb concentration was 96 +/- 12 g/L. Our results showed that an inverse relation existeds between Hb concentration and total cholesterol (p<0.04), LDL cholesterol (p<0.05), age (p<0.02), and the duration of diabetes (p<0.01).Our results also showed that a linear relation existed between the Hb concentration, HDL cholesterol (p<0.02), and the GFR (p<0.01). CONCLUSION: Diabrtic patients with anemia are in need of intensive management for the lipid and GFR that causes thair anemia.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





