
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Lifestyle
- Enhancing Diabetes Care through a Mobile Application: A Randomized Clinical Trial on Integrating Physical and Mental Health among Disadvantaged Individuals
- Jae Hyun Bae, Eun Hee Park, Hae Kyung Lee, Kun Ho Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyun Mi Kim, Sin Gon Kim
- Received August 24, 2023 Accepted October 16, 2023 Published online February 2, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0298 [Epub ahead of print]
- 727 View
- 100 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
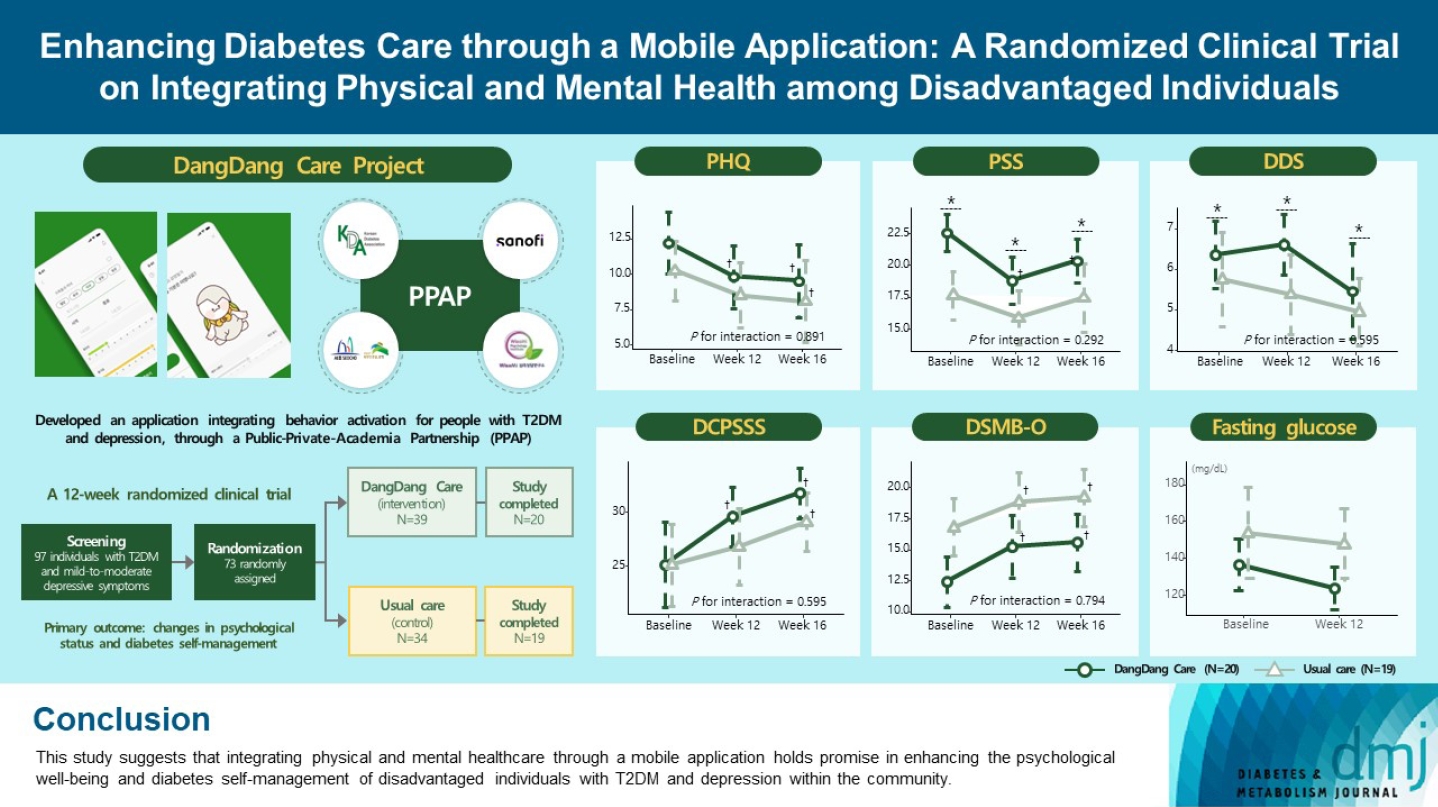
This study examines integrating physical and mental healthcare for disadvantaged persons with type 2 diabetes mellitus and mild-to-moderate depression in the community, using a mobile application within a public-private-academic partnership.
Methods
The Korean Diabetes Association has developed a mobile application combining behavioral activation for psychological well-being and diabetes self-management, with conventional medical therapy. Participants were randomly assigned to receive the application with usual care or only usual care. Primary outcomes measured changes in psychological status and diabetes selfmanagement through questionnaires at week 12 from the baseline. Secondary outcomes assessed glycemic and lipid control, with psychological assessments at week 16.
Results
Thirty-nine of 73 participants completed the study (20 and 19 in the intervention and control groups, respectively) and were included in the analysis. At week 12, the intervention group showed significant reductions in depression severity and perceived stress compared to the control group. Additionally, they reported increased perceived social support and demonstrated improved diabetes self-care behavior. These positive effects persisted through week 16, with the added benefit of reduced anxiety. While fasting glucose levels in the intervention group tended to improve, no other significant differences were observed in laboratory assessments between the groups.
Conclusion
This study provides compelling evidence for the potential efficacy of a mobile application that integrates physical and mental health components to address depressive symptoms and enhance diabetes self-management in disadvantaged individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus and depression. Further research involving larger and more diverse populations is warranted to validate these findings and solidify their implications.
- Drug Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Enavogliflozin versus Dapagliflozin as Add-on to Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week, Double-Blind, Randomized Trial
- Kyung Ah Han, Yong Hyun Kim, Doo Man Kim, Byung Wan Lee, Suk Chon, Tae Seo Sohn, In Kyung Jeong, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Jang Won Son, Jae Jin Nah, Hwa Rang Song, Seong In Cho, Seung-Ah Cho, Kun Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):796-807. Published online February 9, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0315
- 40,168 View
- 579 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
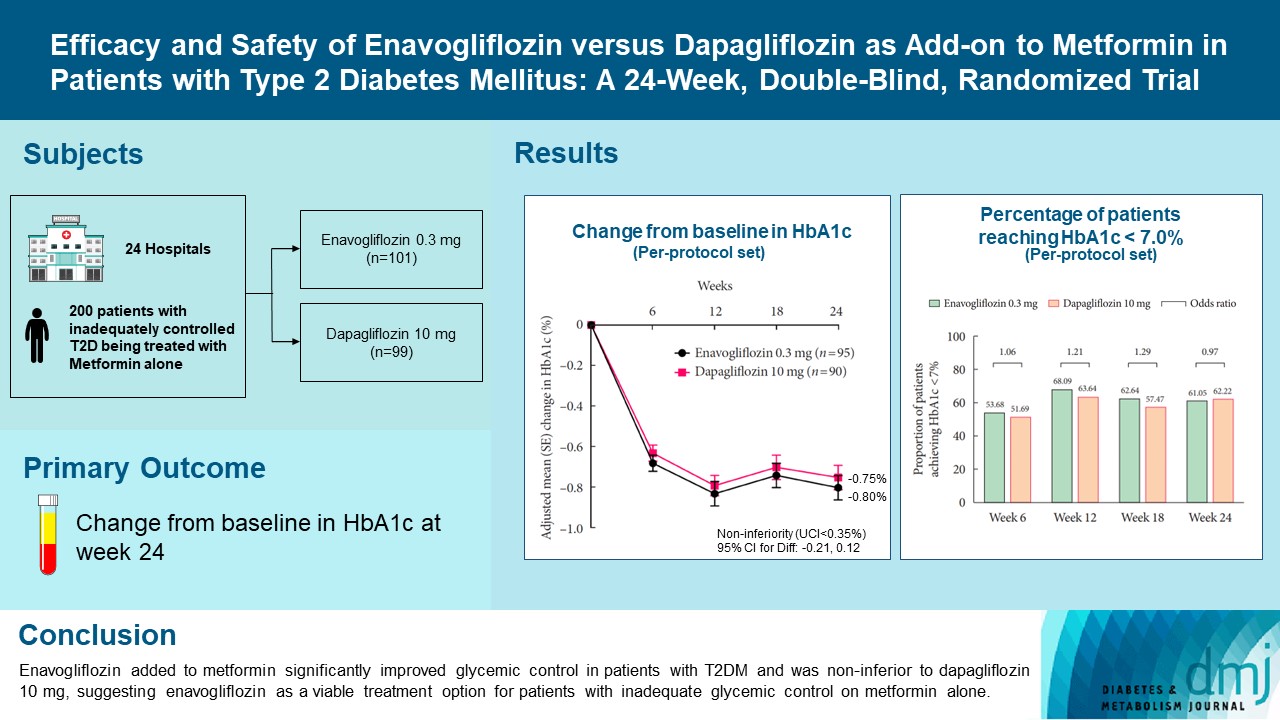
Enavogliflozin is a novel sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor currently under clinical development. This study evaluated the efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin as an add-on to metformin in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) against dapagliflozin.
Methods
In this multicenter, double-blind, randomized, phase 3 study, 200 patients were randomized to receive enavogliflozin 0.3 mg/day (n=101) or dapagliflozin 10 mg/day (n=99) in addition to ongoing metformin therapy for 24 weeks. The primary objective of the study was to prove the non-inferiority of enavogliflozin to dapagliflozin in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) change at week 24 (non-inferiority margin of 0.35%) (Clinical trial registration number: NCT04634500).
Results
Adjusted mean change of HbA1c at week 24 was –0.80% with enavogliflozin and –0.75% with dapagliflozin (difference, –0.04%; 95% confidence interval, –0.21% to 0.12%). Percentages of patients achieving HbA1c <7.0% were 61% and 62%, respectively. Adjusted mean change of fasting plasma glucose at week 24 was –32.53 and –29.14 mg/dL. An increase in urine glucose-creatinine ratio (60.48 vs. 44.94, P<0.0001) and decrease in homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (–1.85 vs. –1.31, P=0.0041) were significantly greater with enavogliflozin than dapagliflozin at week 24. Beneficial effects of enavogliflozin on body weight (–3.77 kg vs. –3.58 kg) and blood pressure (systolic/diastolic, –5.93/–5.41 mm Hg vs. –6.57/–4.26 mm Hg) were comparable with those of dapagliflozin, and both drugs were safe and well-tolerated.
Conclusion
Enavogliflozin added to metformin significantly improved glycemic control in patients with T2DM and was non-inferior to dapagliflozin 10 mg, suggesting enavogliflozin as a viable treatment option for patients with inadequate glycemic control on metformin alone. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
Young Sang Lyu, Sangmo Hong, Si Eun Lee, Bo Young Cho, Cheol-Young Park
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A 52‐week efficacy and safety study of enavogliflozin versus dapagliflozin as an add‐on to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: ENHANCE‐M extension study
Tae Seo Sohn, Kyung‐Ah Han, Yonghyun Kim, Byung‐Wan Lee, Suk Chon, In‐Kyung Jeong, Eun‐Gyoung Hong, Jang Won Son, JaeJin Na, Jae Min Cho, Seong In Cho, Wan Huh, Kun‐Ho Yoon
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of renal function on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of enavogliflozin, a potent and selective sodium‐glucose cotransporter‐2 inhibitor, in type 2 diabetes
Sae Im Jeong, Mu Seong Ban, Jun‐Gi Hwang, Min‐Kyu Park, Soo Lim, Sejoong Kim, Soon Kil Kwon, Yoonjin Kim, Jae Min Cho, Jae Jin Na, Wan Huh, Jae‐Yong Chung
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of novel sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor enavogliflozin in type-2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, B.G. Harish, Beatrice Anne, Lakshmi Nagendra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(8): 102816. CrossRef - Characteristics of the Latest Therapeutic Agent for Diabetes
Nuri Yun
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 148. CrossRef - Prospects of using sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors in patients with metabolic-associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD)
Iryna Kostitska, Nadia Protas, Liliia Petrovska
Diabetes Obesity Metabolic Syndrome.2023; (5): 8. CrossRef - Navigating the Future of Diabetes Treatment with New Drugs: Focusing on the Possibilities and Prospects of Enavogliflozin
Sang Youl Rhee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 769. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
- Drug/Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Self-Titration Algorithms of Insulin Glargine 300 units/mL in Individuals with Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (The Korean TITRATION Study): A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Jae Hyun Bae, Chang Ho Ahn, Ye Seul Yang, Sun Joon Moon, Soo Heon Kwak, Hye Seung Jung, Kyong Soo Park, Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):71-80. Published online June 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0274

- 8,091 View
- 434 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To compare the efficacy and safety of two insulin self-titration algorithms, Implementing New Strategies with Insulin Glargine for Hyperglycemia Treatment (INSIGHT) and EDITION, for insulin glargine 300 units/mL (Gla-300) in Korean individuals with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
In a 12-week, randomized, open-label trial, individuals with uncontrolled T2DM requiring basal insulin were randomized to either the INSIGHT (adjusted by 1 unit/day) or EDITION (adjusted by 3 units/week) algorithm to achieve a fasting self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) in the range of 4.4 to 5.6 mmol/L. The primary outcome was the proportion of individuals achieving a fasting SMBG ≤5.6 mmol/L without noct urnal hypoglycemia at week 12.
Results
Of 129 individuals (age, 64.1±9.5 years; 66 [51.2%] women), 65 and 64 were randomized to the INSIGHT and EDITION algorithms, respectively. The primary outcome of achievement was comparable between the two groups (24.6% vs. 23.4%, P=0.876). Compared with the EDITION group, the INSIGHT group had a greater reduction in 7-point SMBG but a similar decrease in fasting plasma glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin. The increment of total daily insulin dose was significantly higher in the INSIGHT group than in the EDITION group (between-group difference: 5.8±2.7 units/day, P=0.033). However, body weight was significantly increased only in the EDITION group (0.6±2.4 kg, P=0.038). There was no difference in the occurrence of hypoglycemia between the two groups. Patient satisfaction was significantly increased in the INSIGHT group (P=0.014).
Conclusion
The self-titration of Gla-300 using the INSIGHT algorithm was effective and safe compared with that using the EDITION algorithm in Korean individuals with uncontrolled T2DM (ClinicalTrials.gov number: NCT03406663). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Basal insulin titration algorithms in patients with type 2 diabetes: the simplest is the best (?)
V.I. Katerenchuk
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(1): 72. CrossRef - Issues of insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes and ways to solve them
V.I. Katerenchuk, A.V. Katerenchuk
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(3): 240. CrossRef - Time for Using Machine Learning for Dose Guidance in Titration of People With Type 2 Diabetes? A Systematic Review of Basal Insulin Dose Guidance
Camilla Heisel Nyholm Thomsen, Stine Hangaard, Thomas Kronborg, Peter Vestergaard, Ole Hejlesen, Morten Hasselstrøm Jensen
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2022; : 193229682211459. CrossRef
- Basal insulin titration algorithms in patients with type 2 diabetes: the simplest is the best (?)
- Drug/Regimen
- Effect of Dapagliflozin as an Add-on Therapy to Insulin on the Glycemic Variability in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (DIVE): A Multicenter, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Randomized Study
- Seung-Hwan Lee, Kyung-Wan Min, Byung-Wan Lee, In-Kyung Jeong, Soon-Jib Yoo, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):339-348. Published online May 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0203
- 8,342 View
- 334 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
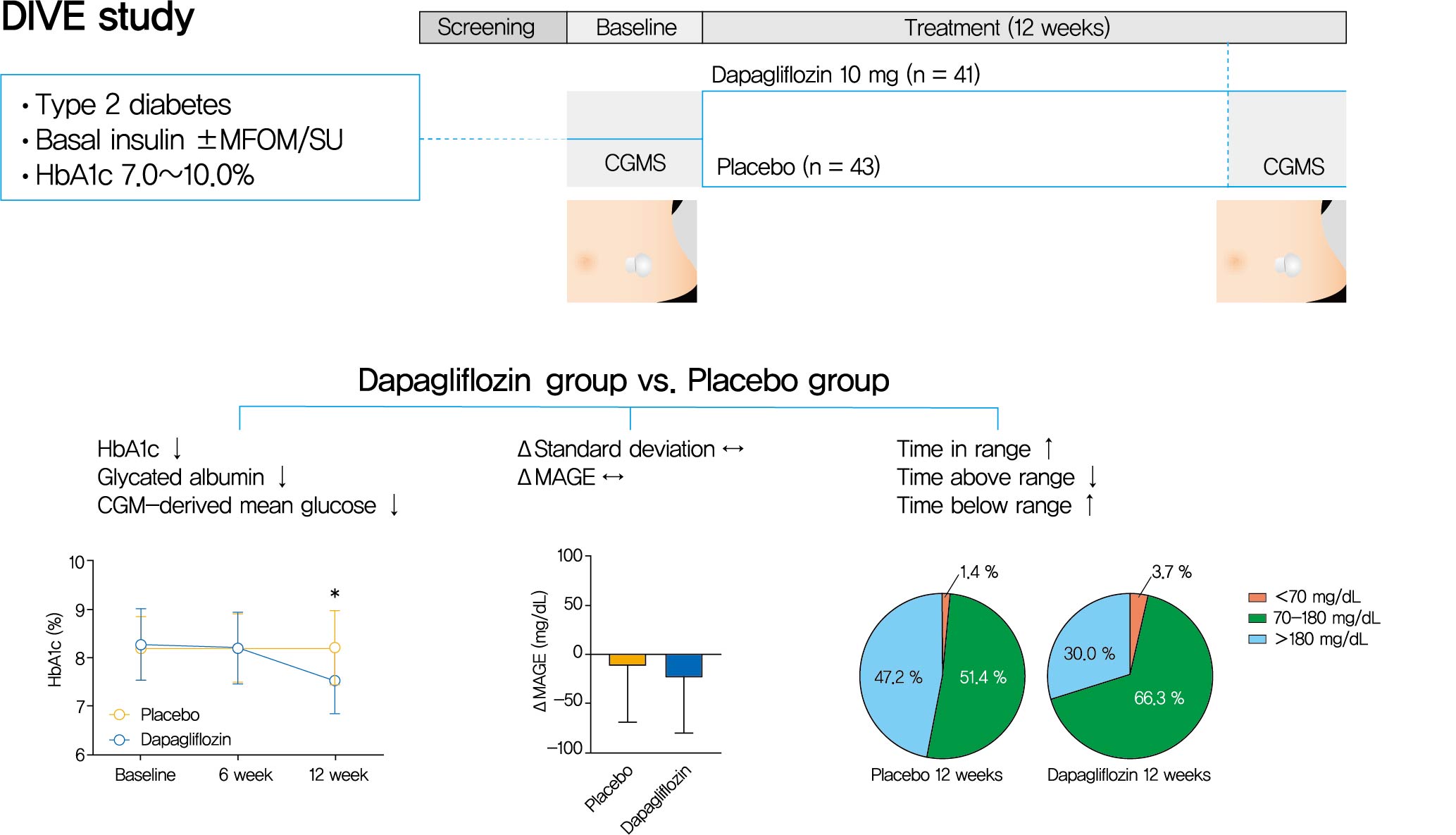
Background Glycemic variability is associated with the development of diabetic complications and hypoglycemia. However, the effect of sodium-glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on glycemic variability is controversial. We aimed to examine the effect of dapagliflozin as an add-on therapy to insulin on the glycemic variability assessed using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods In this multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized study, 84 subjects received 10 mg of dapagliflozin (
n =41) or the placebo (n =43) for 12 weeks. CGM was performed before and after treatment to compare the changes in glycemic variability measures (standard deviation [SD], mean amplitude of glycemic excursions [MAGEs]).Results At week 12, significant reductions in glycosylated hemoglobin (−0.74%±0.66% vs. 0.01%±0.65%,
P <0.001), glycated albumin (−3.94%±2.55% vs. −0.67%±2.48%,P <0.001), and CGM-derived mean glucose (−41.6±39.2 mg/dL vs. 1.1±46.2 mg/dL,P <0.001) levels were observed in the dapagliflozin group compared with the placebo group. SD and MAGE were significantly decreased in the dapagliflozin group, but not in the placebo group. However, the difference in ΔSD and ΔMAGE failed to reach statistical significance between two groups. No significant differences in the incidence of safety endpoints were observed between the two groups.Conclusion Dapagliflozin effectively decreased glucose levels, but not glucose variability, after 12 weeks of treatment in participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus receiving insulin treatment. The role of SGLT2 inhibitors in glycemic variability warrants further investigations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Selective sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in the improvement of hemoglobin and hematocrit in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a network meta-analysis
Yuanyuan Luo, Ruojing Bai, Wei Zhang, Guijun Qin
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring Profiles and Health Outcomes After Dapagliflozin Plus Saxagliptin vs Insulin Glargine
Donald C Simonson, Marcia A Testa, Ella Ekholm, Maxwell Su, Tina Vilsbøll, Serge A Jabbour, Marcus Lind
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of empagliflozin on insulin needs in patients with heart failure and diabetes: An EMPEROR‐Pooled analysis
Khawaja M. Talha, Jennifer Green, Gerasimos Filippatos, Stuart Pocock, Faiez Zannad, Martina Brueckmann, Elke Schueler, Anne Pernille Ofstad, João Pedro Ferreira, Stefan D. Anker, Javed Butler, Julio Rosenstock, Milton Packer
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk of Urinary Tract Infection in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Dapagliflozin: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Zhigui Zheng, Dongyuan He, Jianguo Chen, Xiaohui Xie, Yunan Lu, Binbin Wu, Xinxin Jiang
Clinical Drug Investigation.2023; 43(4): 209. CrossRef - Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitors and Metformin on Inflammatory and Prognostic
Biomarkers in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Yang Cao, Ning Liang, Ting Liu, Jingai Fang, Xiaodong Zhang
Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders - Drug Targets.2023; 23(4): 530. CrossRef - What is Glycaemic Variability and which Pharmacological Treatment Options are Effective? A Narrative Review
Juan Miguel Huertas Cañas, Maria Alejandra Gomez Gutierrez, Andres Bedoya Ossa
European Endocrinology.2023; 19(2): 4. CrossRef - La variabilité glycémique : un facteur de risque singulier à conjuguer au pluriel
Louis Monnier, Claude Colette, Fabrice Bonnet, David Owens
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2022; 16(1): 15. CrossRef - Association between Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors and Cardiometabolic Outcomes
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 49. CrossRef - Effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors on serum urate levels in patients with and without diabetes: a systematic review and meta-regression of 43 randomized controlled trials
Alicia Swee Yan Yip, Shariel Leong, Yao Hao Teo, Yao Neng Teo, Nicholas L. X. Syn, Ray Meng See, Caitlin Fern Wee, Elliot Yeung Chong, Chi-Hang Lee, Mark Y. Chan, Tiong-Cheng Yeo, Raymond C. C. Wong, Ping Chai, Ching-Hui Sia
Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease.2022; 13: 204062232210835. CrossRef - Hypoglycemic agents and glycemic variability in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
SuA Oh, Sujata Purja, Hocheol Shin, Minji Kim, Eunyoung Kim
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2022; 19(3): 147916412211068. CrossRef - The Clinical Effect of Dapagliflozin in Patients with Angiographically Confirmed Coronary Artery Disease and Concomitant Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yana Yu. Dzhun, Yevhen Yu. Marushko, Yanina A. Saienko, Nadiya M. Rudenko, Borys M. Mankovsky
Ukrainian Journal of Cardiovascular Surgery.2022; 30(3): 35. CrossRef - Stress-Induced Hyperglycaemia in Non-Diabetic Patients with Acute Coronary Syndrome: From Molecular Mechanisms to New Therapeutic Perspectives
Alessandro Bellis, Ciro Mauro, Emanuele Barbato, Antonio Ceriello, Antonio Cittadini, Carmine Morisco
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(2): 775. CrossRef - Glycemic Variability Impacted by SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP 1 Agonists in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Heeyoung Lee, Se-eun Park, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(18): 4078. CrossRef - Effect of Dapagliflozin on Glycemic Variability in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes under Insulin Glargine Combined with Other Oral Hypoglycemic Drugs
Menghui Luo, Xiaocen Kong, Huiying Wang, Xiaofang Zhai, Tingting Cai, Bo Ding, Yun Hu, Ting Jing, Xiaofei Su, Huiqin Li, Jianhua Ma, Yoshifumi Saisho
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Time in Range from Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Novel Metric for Glycemic Control
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 828. CrossRef
- Selective sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors in the improvement of hemoglobin and hematocrit in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a network meta-analysis
- Drug/Regimen
- Switching to Once-Daily Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart from Basal Insulin Improves Postprandial Glycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Randomized Controlled Trial
- Kyu Yong Cho, Akinobu Nakamura, Chiho Oba-Yamamoto, Kazuhisa Tsuchida, Shingo Yanagiya, Naoki Manda, Yoshio Kurihara, Shin Aoki, Tatsuya Atsumi, Hideaki Miyoshi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(4):532-541. Published online November 22, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0093
- 5,614 View
- 157 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
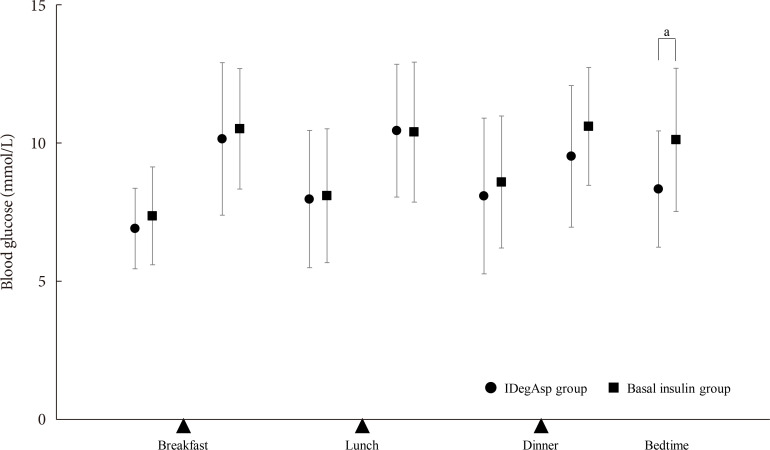
ePub Background To explore the efficacy and safety of switching from once-daily basal insulin therapy to once-daily pre-meal injection insulin degludec/insulin aspart (IDegAsp) with respect to the glycemic control of participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods In this multicenter, open-label, prospective, randomized, parallel-group comparison trial, participants on basal insulin therapy were switched to IDegAsp (IDegAsp group;
n =30) or continued basal insulin (Basal group;n =29). The primary endpoint was the superiority of IDegAsp in causing changes in the daily blood glucose profile, especially post-prandial blood glucose concentration after 12 weeks.Results Blood glucose concentrations after dinner and before bedtime were lower in the IDegAsp group, and the improvement in blood glucose before bedtime was significantly greater in the IDegAsp group than in the Basal group at 12 weeks (−1.7±3.0 mmol/L vs. 0.3±2.1 mmol/L,
P <0.05). Intriguingly, glycemic control after breakfast was not improved by IDegAsp injection before breakfast, in contrast to the favorable effect of injection before dinner on blood glucose after dinner. Glycosylated hemoglobin significantly decreased only in the IDegAsp group (58 to 55 mmol/mol,P <0.05). Changes in daily insulin dose, body mass, and recorded adverse effects, including hypoglycemia, were comparable between groups.Conclusion IDegAsp was more effective than basal insulin at reducing blood glucose after dinner and before bedtime, but did not increase the incidence of hypoglycemia. Switching from basal insulin to IDegAsp does not increase the burden on the patient and positively impacts glycemic control in patients with T2DM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glycaemic outcomes in hospital with IDegAsp versus BIAsp30 premixed insulins
Joshua R. Walt, Julie Loughran, Spiros Fourlanos, Rahul D. Barmanray, Jasmine Zhu, Suresh Varadarajan, Mervyn Kyi
Internal Medicine Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Low fasting glucose‐to‐estimated average glucose ratio was associated with superior response to insulin degludec/aspart compared with basal insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes
Han Na Jang, Ye Seul Yang, Tae Jung Oh, Bo Kyung Koo, Seong Ok Lee, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Hye Seung Jung
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(1): 85. CrossRef - Comparing time to intensification between insulin degludec/insulin aspart and insulin glargine: A single-center experience from India
Rajiv Kovil
Journal of Diabetology.2022; 13(2): 171. CrossRef - Use of Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus: Expert Panel Recommendations on Appropriate Practice Patterns
Tevfik Demir, Serap Turan, Kursad Unluhizarci, Oya Topaloglu, Tufan Tukek, Dilek Gogas Yavuz
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pharmacoeconomic comparison of the second generation insulin analogs and insulins on their base
I. N. Dyakov, S. K. Zyryanov
Kachestvennaya Klinicheskaya Praktika = Good Clinical Practice.2021; 20(1): 4. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Degludec/Insulin Aspart Compared with a Conventional Premixed Insulin or Basal Insulin: A Meta-Analysis
Shinje Moon, Hye-Soo Chung, Yoon-Jung Kim, Jae-Myung Yu, Woo-Ju Jeong, Jiwon Park, Chang-Myung Oh
Metabolites.2021; 11(9): 639. CrossRef - Insulin therapy in diabetic kidney disease
Yan Liu, Chanyue Zhao, Xiaofen Xiong, Ming Yang, Lin Sun
Diabetic Nephropathy.2021; 1(2): 67. CrossRef - Indirect comparison of efficacy and safety of insulin glargine/lixisenatide and insulin degludec/insulin aspart in type 2 diabetes patients not controlled on basal insulin
Anwar Ali Jammah
Primary Care Diabetes.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Glycaemic outcomes in hospital with IDegAsp versus BIAsp30 premixed insulins
- Others
- Addition of Ipragliflozin to Metformin Treatment in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Subgroup Analysis of a Phase 3 Trial
- Kyung-Wan Min, Bon Jeong Ku, Ji-Hyun Lee, Min-Seon Kim, Kyu-Jeung Ahn, Moon-Kyu Lee, Satoshi Kokubo, Satoshi Yoshida, Hyun-Ji Cho, Bong-Soo Cha
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(2):135-145. Published online January 11, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.2.135
- 5,014 View
- 59 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This is a subgroup analysis of Korean patients from a phase 3 clinical trial investigating the efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with metformin.
Methods This multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, parallel-group study was carried out between November 2011 and January 2013. Patients entered a 2-week placebo pretreatment period, followed by a 24-week treatment period with either ipragliflozin (50 mg/day) or placebo, while continuing metformin. Efficacy outcomes (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c], fasting plasma glucose [FPG], and body weight) and safety outcomes (treatment-emergent adverse events [TEAEs]) were measured and compared between the two treatment groups for patients enrolled in all 18 study sites in Korea.
Results Eighty-two Korean patients received ipragliflozin (
n =43) or placebo (n =39) during the study period. Mean changes in HbA1c levels from baseline to the end of treatment were –0.97% in the ipragliflozin group and –0.31% in the placebo group, with an adjusted between-group difference of –0.60% (P <0.001). Compared to placebo, FPG and body weight also decreased significantly (bothP <0.001) from baseline after treatment in the ipragliflozin group, with between-group differences of –21.4 mg/dL and –1.53 kg, respectively. Decreased weight was the most common TEAE in the ipragliflozin group (7.0%); there were no reports of genital and urinary tract infection.Conclusion Ipragliflozin treatment in addition to metformin led to significant improvement in glycemic outcomes and reduction in body weight in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, compared with metformin treatment alone; the safety profile was comparable in both groups.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on bone metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Jing Wang, Xin Li, Yang Li, Chen Lei
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Add-on therapy with dapagliflozin in routine outpatient care of type 2 diabetes patients from Turkey: a retrospective cohort study on HbA1c, body weight, and blood pressure outcomes
Derun Taner Ertugrul, Erdal Kan, Cigdem Bahadir Tura, Haci Bayram Tugtekin, Hayati Ayakta, Mehmet Celebioglu, Ceren Yılmaz, Onur Utebay, Ilhan Yetkin, Eren Gurkan, Kerem Sezer, Ramazan Gen, Suleyman Ozcaylak, Yildiz Okuturlar, Mehmet Coskun, Nilgun Govec
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2022; 42(1): 147. CrossRef SGLT2 Inhibitors as Add-On Therapy to Metformin for People with Type 2 Diabetes: A Review of Placebo-Controlled Trials in Asian versus Non-Asian Patients
André J Scheen
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 2765. CrossRef- Ipragliflozin Additively Ameliorates Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Controlled with Metformin and Pioglitazone: A 24-Week Randomized Controlled Trial
Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 259. CrossRef - Safety of Ipragliflozin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Pooled Analysis of Phase II/III/IV Clinical Trials
Atsunori Kashiwagi, Marina V. Shestakova, Yuichiro Ito, Masahiro Noguchi, Wim Wilpshaar, Satoshi Yoshida, John P. H. Wilding
Diabetes Therapy.2019; 10(6): 2201. CrossRef - Mechanistic effects of SGLT2 inhibition on blood pressure in diabetes
Habib Yaribeygi, Stephen L. Atkin, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(2): 1679. CrossRef - Ipragliflozin as an add-on therapy in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: An evidence-based pharmacoeconomics evaluation
Hongmei Wang, Gaoqiong Yao, Xi Chen, Jing Ouyang, Jiadan Yang
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2019; 157: 107867. CrossRef - Characteristics of Dapagliflozin Responders: A Longitudinal, Prospective, Nationwide Dapagliflozin Surveillance Study in Korea
Eugene Han, Ari Kim, Sung Jae Lee, Je-Yon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim, Woo Je Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
Diabetes Therapy.2018; 9(4): 1689. CrossRef - A phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled trial to assess the efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin as an add-on therapy to metformin in Russian patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus
Marina V. Shestakova, John P.H. Wilding, Wim Wilpshaar, Reiner Tretter, Valeria L. Orlova, Andrey F. Verbovoy
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 146: 240. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin as an add‐on therapy to sitagliptin and metformin in Korean patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial
Kyung‐Ah Han, Suk Chon, Choon Hee Chung, Soo Lim, Kwan‐Woo Lee, SeiHyun Baik, Chang Hee Jung, Dong‐Sun Kim, Kyong Soo Park, Kun‐Ho Yoon, In‐Kyu Lee, Bong‐Soo Cha, Taishi Sakatani, Sumi Park, Moon‐Kyu Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2018; 20(10): 2408. CrossRef - Antihyperglycemic Agent Therapy for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 2017: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Sang Youl Rhee, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 337. CrossRef - Antihyperglycemic agent therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus 2017: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Sang Youl Rhee, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 947. CrossRef - Combination therapy of oral hypoglycemic agents in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Min Kyong Moon, Kyu Yeon Hur, Seung-Hyun Ko, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Nan-Hee Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 974. CrossRef - Combination Therapy of Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Min Kyong Moon, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Seung-Hyun Ko, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Nan-Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 357. CrossRef
- Effects of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on bone metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





