
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Basic Research
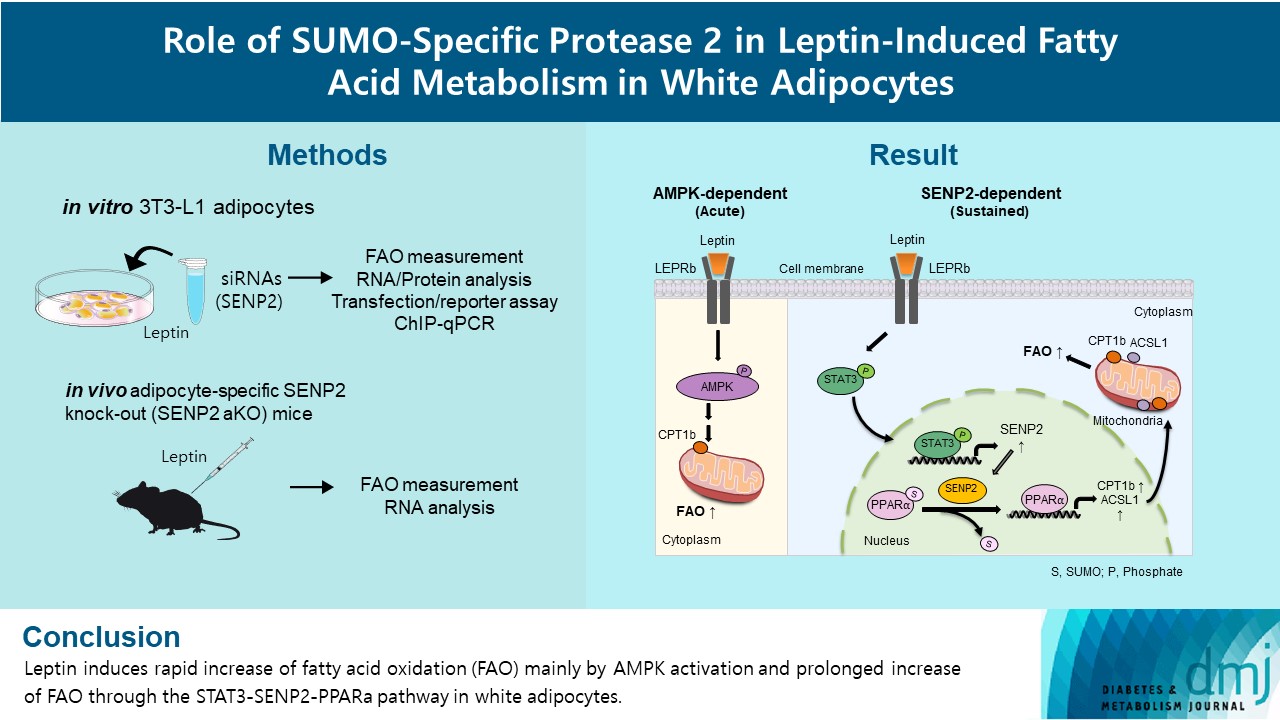
- Role of SUMO-Specific Protease 2 in Leptin-Induced Fatty Acid Metabolism in White Adipocytes
- Praise Chanmee Kim, Ji Seon Lee, Sung Soo Chung, Kyong Soo Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):382-393. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0156
- 3,191 View
- 158 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Leptin is a 16-kDa fat-derived hormone with a primary role in controlling adipose tissue levels. Leptin increases fatty acid oxidation (FAO) acutely through adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and on delay through the SUMO-specific protease 2 (SENP2)–peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ/γ (PPARδ/γ) pathway in skeletal muscle. Leptin also directly increases FAO and decreases lipogenesis in adipocytes; however, the mechanism behind these effects remains unknown. Here, we investigated the role of SENP2 in the regulation of fatty acid metabolism by leptin in adipocytes and white adipose tissues.
Methods
The effects of leptin mediated by SENP2 on fatty acid metabolism were tested by siRNA-mediated knockdown in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The role of SENP2 was confirmed in vivo using adipocyte-specific Senp2 knockout (Senp2-aKO) mice. We revealed the molecular mechanism involved in the leptin-induced transcriptional regulation of carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1b (Cpt1b) and long-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthetase 1 (Acsl1) using transfection/reporter assays and chromatin immunoprecipitation.
Results
SENP2 mediated the increased expression of FAO-associated enzymes, CPT1b and ACSL1, which peaked 24 hours after leptin treatment in adipocytes. In contrast, leptin stimulated FAO through AMPK during the initial several hours after treatment. In white adipose tissues, FAO and mRNA levels of Cpt1b and Acsl1 were increased by 2-fold 24 hours after leptin injection in control mice but not in Senp2-aKO mice. Leptin increased PPARα binding to the Cpt1b and Acsl1 promoters in adipocytes through SENP2.
Conclusion
These results suggest that the SENP2-PPARα pathway plays an important role in leptin-induced FAO in white adipocytes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intermittent cold stimulation affects energy metabolism and improves stress resistance in broiler heart
Tingting Li, Haidong Wei, Shijie Zhang, Xiaotao Liu, Lu Xing, Yuanyuan Liu, Rixin Gong, Jianhong Li
Poultry Science.2024; 103(1): 103190. CrossRef
- Intermittent cold stimulation affects energy metabolism and improves stress resistance in broiler heart
- Basic Research
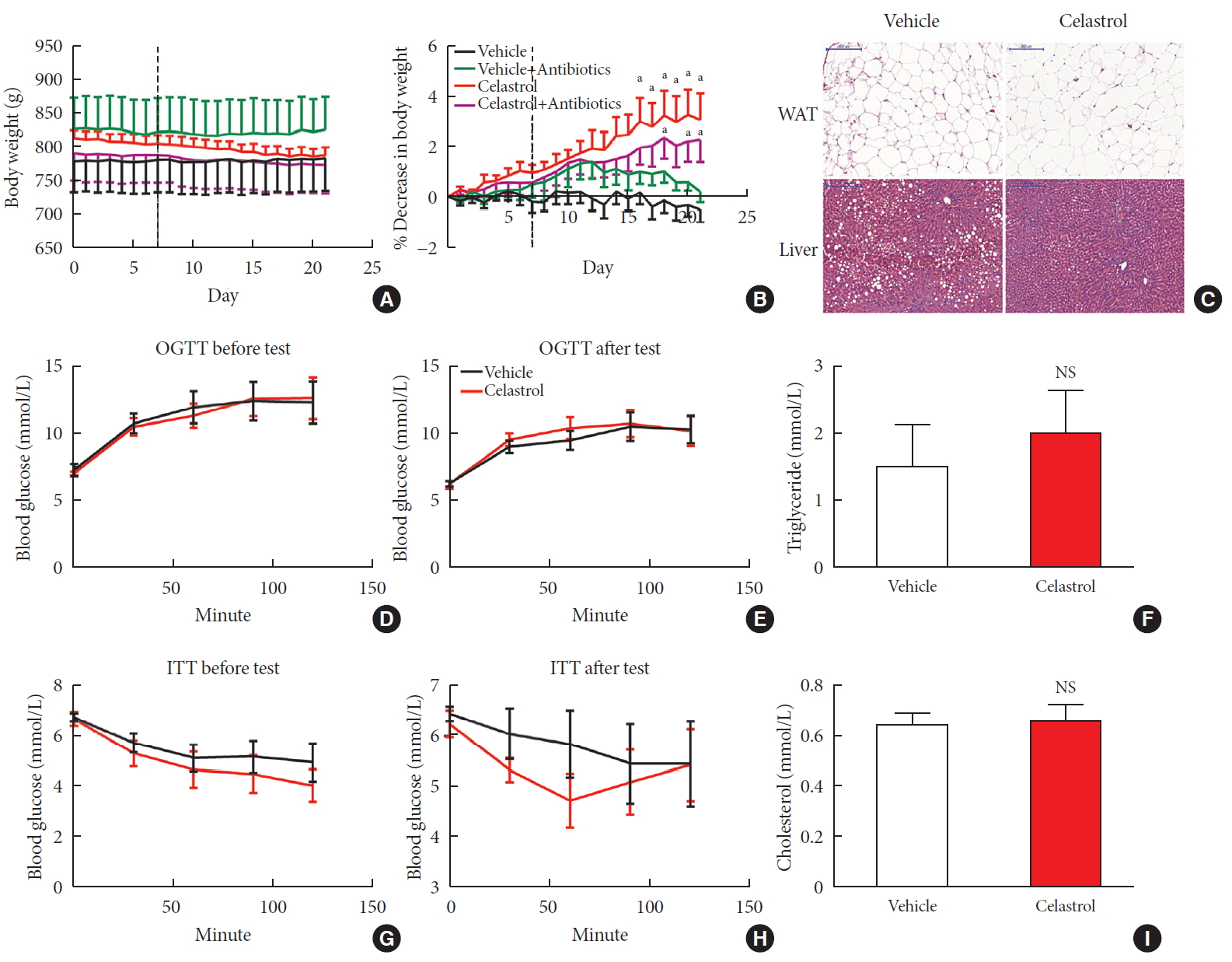
- Effects of Microbiota on the Treatment of Obesity with the Natural Product Celastrol in Rats
- Weiyue Hu, Lingling Wang, Guizhen Du, Quanquan Guan, Tianyu Dong, Ling Song, Yankai Xia, Xinru Wang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):747-763. Published online May 11, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0124
- 9,320 View
- 136 Download
- 16 Web of Science
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Obesity has become one of the most serious issues threatening the health of humankind, and we conducted this study to examine whether and how celastrol protects against obesity.
Methods We fed male Sprague-Dawley rats a high-fat diet and administered celastrol to obese rats for 3 weeks. By recording body weight (BW) and other measures, we identified the effective dose of celastrol for obesity treatment. Feces were collected to perform 16S rRNA sequencing, and hypothalami were extracted for transcriptome sequencing. We then treated leptin knockout rats with celastrol and explored the changes in energy metabolism. Male Institute of Cancer Research (ICR) mice were used to test the acute toxicity of celastrol.
Results We observed that celastrol reduced BW and promoted energy expenditure at a dose of 500 µg/kg BW but that food intake was not changed after administration. The diversity of the gut microbiota was improved, with an increased ratio of
Bacteroidetes toFirmicutes , and the gut microbiota played an important role in the anti-obesity effects of celastrol. Hypothalamic transcriptome analysis showed a significant enrichment of the leptin signaling pathway, and we found that celastrol significantly enhanced energy expenditure, which was mediated by the leptin signaling pathway. Acute lethal toxicity of celastrol was not observed at doses ranging from 0 to 62.5 mg/kg BW.Conclusion Our study revealed that celastrol decreased the BW of obese rats by enhancing energy expenditure but not by suppressing food intake and that this effect was mediated by the improvement of the gut microbiota and the activation of the hypothalamic leptin signaling pathway.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Natural compounds as obesity pharmacotherapies
Xin‐Yuan Zhao, Ji‐Qiu Wang, G. Gregory Neely, Yan‐Chuan Shi, Qiao‐Ping Wang
Phytotherapy Research.2024; 38(2): 797. CrossRef - Celastrol functions as an emerging manager of lipid metabolism: Mechanism and therapeutic potential
Jia Gu, Ya-Ning Shi, Neng Zhu, Hong-Fang Li, Chan-Juan Zhang, Li Qin
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 164: 114981. CrossRef - Tripterygium hypoglaucum extract ameliorates adjuvant-induced arthritis in mice through the gut microbiota
Jianghui HU, Jimin NI, Junping ZHENG, Yanlei GUO, Yong YANG, Cheng YE, Xiongjie SUN, Hui XIA, Yanju LIU, Hongtao LIU
Chinese Journal of Natural Medicines.2023; 21(10): 730. CrossRef - Health improvements of type 2 diabetic patients through diet and diet plus fecal microbiota transplantation
Lili Su, Zhifan Hong, Tong Zhou, Yuanyuan Jian, Mei Xu, Xuanping Zhang, Xiaoyan Zhu, Jiayin Wang
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Tripterygium hypoglaucum (Levl.) Hutch: A systematic review of its traditional uses, botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, pharmacokinetics and toxicology
Jiangping Wei, Liyun Chen, Sijia Gao, Jirui Wang, Yunhong Wang, Zhiwei Zhang, Yuyu Zhang, Xiaomei Zhang, Yong Yang, Dajian Yang
Pharmacological Research - Modern Chinese Medicine.2022; 3: 100094. CrossRef - Celastrol: An Update on Its Hepatoprotective Properties and the Linked Molecular Mechanisms
Mengzhen Li, Faren Xie, Lu Wang, Guoxue Zhu, Lian-Wen Qi, Shujun Jiang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Celastrol inhibits the proliferation and migration of MCF-7 cells through the leptin-triggered PI3K/AKT pathway
Pingping Chen, Bin Wang, Meng Li, Chunxue Cui, Fei Liu, Yonggang Gao
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2022; 20: 3173. CrossRef - Investigating Celastrol’s Anti-DCM Targets and Mechanisms via Network Pharmacology and Experimental Validation
Rui Xi, Yongxin Wan, Lihong Yang, Jingying Zhang, Liu Yang, Shuai Yang, Rui Chai, Fengchen Mu, Qiting Sun, Rui Yan, Zhifang Wu, Sijin Li, Zhijun Liao
BioMed Research International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Celastrol inhibits TXNIP expression to protect pancreatic β cells in diabetic mice
Si-wei Wang, Tian Lan, Fang Zheng, Hui Huang, Hang-fei Chen, Qi Wu, Feng Zhang
Phytomedicine.2022; 104: 154316. CrossRef - Celastrol: A Promising Agent Fighting against Cardiovascular Diseases
Zhexi Li, Jingyi Zhang, Xulei Duan, Guoan Zhao, Min Zhang
Antioxidants.2022; 11(8): 1597. CrossRef - Celastrol: A lead compound that inhibits SARS‐CoV‐2 replication, the activity of viral and human cysteine proteases, and virus‐induced IL‐6 secretion
Carlos A. Fuzo, Ronaldo B. Martins, Thais F. C. Fraga‐Silva, Martin K. Amstalden, Thais Canassa De Leo, Juliano P. Souza, Thais M. Lima, Lucia H. Faccioli, Débora Noma Okamoto, Maria Aparecida Juliano, Suzelei C. França, Luiz Juliano, Vania L. D. Bonato,
Drug Development Research.2022; 83(7): 1623. CrossRef - In vitro activity of celastrol in combination with thymol against carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae isolates
Mahmoud Saad Abdel-Halim, Momen Askoura, Basem Mansour, Galal Yahya, Amira M. El-Ganiny
The Journal of Antibiotics.2022; 75(12): 679. CrossRef - Celastrol alleviates metabolic disturbance in high‐fat diet‐induced obese mice through increasing energy expenditure by ameliorating metabolic inflammation
Xueping Yang, Fan Wu, Lingli Li, Ernest C. Lynch, Linglin Xie, Yan Zhao, Ke Fang, Jingbin Li, Jinlong Luo, Lijun Xu, Xin Zou, Fuer Lu, Guang Chen
Phytotherapy Research.2021; 35(1): 297. CrossRef - Celastrol in metabolic diseases: Progress and application prospects
Shaohua Xu, Yaqian Feng, Weishen He, Wen Xu, Wei Xu, Hongjun Yang, Xianyu Li
Pharmacological Research.2021; 167: 105572. CrossRef - The Anti-Obesity Effect of Traditional Chinese Medicine on Lipid Metabolism
Qijing Fan, Furong Xu, Bin Liang, Xiaoju Zou
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum Metabolome Mediates the Antiobesity Effect of Celastrol-Induced Gut Microbial Alterations
Shaohua Xu, Liwei Lyu, Huaichang Zhu, Xiaoqiang Huang, Wei Xu, Wen Xu, Yaqian Feng, Yong Fan
Journal of Proteome Research.2021; 20(10): 4840. CrossRef - Interrelated Mechanism by Which the Methide Quinone Celastrol, Obtained from the Roots of Tripterygium wilfordii, Inhibits Main Protease 3CLpro of COVID-19 and Acts as Superoxide Radical Scavenger
Francesco Caruso, Manrose Singh, Stuart Belli, Molly Berinato, Miriam Rossi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(23): 9266. CrossRef
- Natural compounds as obesity pharmacotherapies
- Pathophysiology
- Protective Effects of Ginger (
Zingiber officinale ) Extract against Diabetes-Induced Heart Abnormality in Rats - Behrouz Ilkhanizadeh, Alireza Shirpoor, Mohamad hasan Khadem Ansari, Samira Nemati, Yusef Rasmi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(1):46-53. Published online February 19, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.1.46
- 4,635 View
- 69 Download
- 34 Web of Science
- 25 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Diabetic cardiomyopathy is an important causal factor in morbidity and mortality among diabetic patients, and currently, no effective means are available to reverse its pathological progress. The purpose of the present study was to investigate the effect of ginger extract on apolipoproteins (apo) A and B, hyperhomocysteinemia, cathepsin G and leptin changes, as well as cardiac fibrosis and heart muscle cell proliferation under hyperglycemic conditions
in vivo .Methods Twenty-four male Wistar rats were divided into three groups, namely: control, non-treated diabetic, and ginger extract-treated diabetic groups. The ginger extract-treated diabetic group received a 50 mg daily dose of ginger extract intragastrically for 6 weeks.
Results The results revealed concurrent significant increases in plasma C-reactive protein (CRP), homocysteine (Hcy), cathepsin G and apoB levels and decreases in apoA and leptin levels in the non-treated diabetic group compared to the control group. Moreover, heart structural changes, including fibrosis and heart muscle cell proliferation, were observed in non-treated diabetic rats compared to the control rats. Significant amelioration of changes in the heart structure together with restoration of the elevated levels of Hcy and CRP, leptin, cathepsin G, and apoA and B were found in the ginger extract-treated diabetic group compared to the non-treated diabetic group.
Conclusion The findings indicated that ginger extract significantly reduces heart structural abnormalities in diabetic rats and that these effects might be associated with improvements in serum apo, leptin, cathepsin G, and Hcy levels and with the antioxidant properties of ginger extract.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cardioprotective Activities of some Indian Spices: An Insight into
Pharmacology and Phytochemical Investigation
Kalyani Pathak, Manash Pratim Pathak, Riya Saikia, Urvashee Gogoi, Jon Jyoti Sahariah, Aparoop Das, Mohammad Zaki Ahmad, Tirna Paul, Jyotirmoy Das, Saif Aboud M. Alqahtani
Current Traditional Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Network-pharmacology-based research on protective effects and underlying mechanism of Shuxin decoction against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury with diabetes
Ling Yang, Yang Jian, Zai-Yuan Zhang, Bao-Wen Qi, Yu-Bo Li, Pan Long, Yao Yang, Xue Wang, Shuo Huang, Jing Huang, Long-Fu Zhou, Jie Ma, Chang-Qing Jiang, Yong-He Hu, Wen-Jing Xiao
World Journal of Diabetes.2023; 14(7): 1057. CrossRef - Evaluating the effect of Ginger Powder on Bilirubin, Creatinine, Urea and Uric Acid on Experimental Diabetic Wistar Rats in Randomized Control Trial
Maryam Maqsood, Saima Naaz, Huma Bader Ul Ain, Zunaira Mushtaq, Makia Nasir, Aiza Qamar
Pakistan BioMedical Journal.2022; 5(1): 351. CrossRef - The effect of red ginger bread consumption on the physiological parameters of healthy subjects
Titin Sulastri, Marleen Sunyoto, Marvel Reuben Suwitono, Jutti Levita
Journal Of Advanced Pharmacy Education And Research.2022; 12(3): 28. CrossRef - Protective effects of medicinal plant against diabetes induced cardiac disorder: A review
Sadegh Shabab, Zahra Gholamnezhad, Maryam Mahmoudabady
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2021; 265: 113328. CrossRef - Ginger (Zingiber Officinale Roscoe) Extract Protects the Heart Against Inflammation and Fibrosis in Diabetic Rats
Tara Abdi, Maryam Mahmoudabady, Hadi Zare Marzouni, Saeed Niazmand, Majid Khazaei
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2021; 45(3): 220. CrossRef - Combined ginger and garlic extract improves serum lipid profile, oxidative stress markers and reduced IL-6 in diet induced obese rats
Peter Ifeoluwa Adegbola, Olumide Samuel Fadahunsi, Bamidele Stephen Ajilore, Adebola Olayemi Akintola, Olubukola Sinbad Olorunnisola
Obesity Medicine.2021; 23: 100336. CrossRef - The Effects of Medicinal Plants and Bioactive Natural Compounds on Homocysteine
Mohammad Amin Atazadegan, Mohammad Bagherniya, Gholamreza Askari, Aida Tasbandi, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Molecules.2021; 26(11): 3081. CrossRef - Long-chain noncoding RNA-GAS5/hsa-miR-138-5p attenuates high glucose-induced cardiomyocyte damage by targeting CYP11B2
Xiaozhen Zhuo, Kai Bai, Yingxian Wang, Peining Liu, Wen Xi, Jianqing She, Junhui Liu
Bioscience Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Regulation of Apolipoprotein B by Natural Products and Nutraceuticals: A Comprehensive Review
Mohammad Bagherniya, Thomas P. Johnston, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2021; 28(7): 1363. CrossRef - Ameliorative effects of Hydrolea zeylanica in streptozotocin-induced oxidative stress and metabolic changes in diabetic rats
Sandeep Kumar Swain, Umesh Chandra Dash, Satish Kanhar, Atish Kumar Sahoo
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2020; 247: 112257. CrossRef - The effect of 8 weeks of high-intensity interval training and moderate-intensity continuous training on cardiac angiogenesis factor in diabetic male rats
Faramarz Yazdani, Fereshteh Shahidi, Pouran Karimi
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry.2020; 76(2): 291. CrossRef - DNA methyltransferase-1 inactivation of androgen receptor axis triggers homocysteine induced cardiac fibroblast autophagy in diabetic cardiac fibrosis
Hui Tao, Peng Shi, Hai-Yang Xuan, Xuan-Sheng Ding
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics.2020; 692: 108521. CrossRef - Ameliorative and protective effects of ginger and its main constituents against natural, chemical and radiation-induced toxicities: A comprehensive review
Muhammad A. Alsherbiny, Wessam H. Abd-Elsalam, Shymaa A. El badawy, Ehab Taher, Mohamed Fares, Allan Torres, Dennis Chang, Chun Guang Li
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2019; 123: 72. CrossRef - SELECTION OF A FILLER FOR TABLETS MANUFACTURED WITH DIRECT COMPRESSION METHOD CONTAINING DRY GINGER EXTRACT
Оlena Ruban, Malek Alkhalaf, Nataliia Gerbina
EUREKA: Health Sciences.2019; 3: 26. CrossRef - Role of medicinal plants in the management of diabetes mellitus: a review
Bindu Jacob, Narendhirakannan R.T.
3 Biotech.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Ginger (Zingiber officinale Roscoe) in the Prevention of Ageing and Degenerative Diseases: Review of Current Evidence
Nur Fatin Nabilah Mohd Sahardi, Suzana Makpol
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Roles of Spicy Foods and Their Bioactive Compounds in Management of Hypercholesterolemia
Yimin Zhao, Zhen-Yu Chen
Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry.2018; 66(33): 8662. CrossRef - Relaxant and vasoprotective effects of ginger extracts on porcine coronary arteries
Hsing‑Chen Wu, Chi‑Ting Horng, Shih‑Chang Tsai, You‑Li Lee, Shou‑Cheng Hsu, Yi‑Jen Tsai, Fuu‑Jen Tsai, Jo‑Hua Chiang, Daih‑Huang Kuo, Jai‑Sing Yang
International Journal of Molecular Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased hepatic FAT/CD36, PTP1B and decreased HNF4A expression contributes to dyslipidemia associated with ethanol–induced liver dysfunction: Rescue effect of ginger extract
Alireza Shirpoor, Elaheh Heshmati, Fatemeh Kheradmand, Farzaneh Hosseini Gharalari, Leila Chodari, Roya Naderi, Farideh Nezami Majd, Mahrokh Samadi
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2018; 105: 144. CrossRef - Ginger extract mitigates ethanol-induced changes of alpha and beta – myosin heavy chain isoforms gene expression and oxidative stress in the heart of male wistar rats
Alireza Shirpoor, Mitra Zerehpoosh, Mohammad Hasan Khadem Ansari, Fatemeh Kheradmand, Yousef Rasmi
DNA Repair.2017; 57: 45. CrossRef - Single, repeated dose toxicity and genotoxicity assessment of herb formula KIOM2012H
Hwayong Park, Youn-Hwan Hwang, Jin Yeul Ma
Integrative Medicine Research.2017; 6(4): 361. CrossRef - Rescue effects of ginger extract on dose dependent radiation-induced histological and biochemical changes in the kidneys of male Wistar rats
Hassan Saberi, Behnaz Keshavarzi, Alireza Shirpoor, Farzaneh Hosseini Gharalari, Yousef Rasmi
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2017; 94: 569. CrossRef - Promising Antidiabetic Drugs, Medicinal Plants and Herbs: An Update
Mohd Iqbal Yatoo, Archana Saxena, Arumugam Gopalakris, Mahmoud Alagawany, Kuldeep Dhama
International Journal of Pharmacology.2017; 13(7): 732. CrossRef - Cardioprotective effects of rutin via alteration in TNF-α, CRP, and BNP levels coupled with antioxidant effect in STZ-induced diabetic rats
Ravi Saklani, Suresh Kumar Gupta, Ipseeta Ray Mohanty, Binit Kumar, Sushma Srivastava, Rajani Mathur
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2016; 420(1-2): 65. CrossRef
- Cardioprotective Activities of some Indian Spices: An Insight into
Pharmacology and Phytochemical Investigation
- Relation of Absolute or Relative Adiposity to Insulin Resistance, Retinol Binding Protein-4, Leptin, and Adiponectin in Type 2 Diabetes
- You Lim Kim, Tae Kyun Kim, Eun Sun Cheong, Dong Geum Shin, Gyu Sik Choi, Jihye Jung, Kyung-Ah Han, Kyung Wan Min
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(6):415-421. Published online December 12, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.6.415
- 3,909 View
- 30 Download
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Central fat mass (CFM) correlates with insulin resistance and increases the risk of type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular complications; however, peripheral fat mass (PFM) is associated with insulin sensitivity. The aim of this study was to investigate the relation of absolute and relative regional adiposity to insulin resistance index and adipokines in type 2 diabetes.
Methods Total of 83 overweighted-Korean women with type 2 diabetes were enrolled, and rate constants for plasma glucose disappearance (KITT) and serum adipokines, such as retinol binding protein-4 (RBP4), leptin, and adiponectin, were measured. Using dual X-ray absorptiometry, trunk fat mass (in kilograms) was defined as CFM, sum of fat mass on the lower extremities (in kilograms) as PFM, and sum of CFM and PFM as total fat mass (TFM). PFM/TFM ratio, CFM/TFM ratio, and PFM/CFM ratio were defined as relative adiposity.
Results Median age was 55.9 years, mean body mass index 27.2 kg/m2, and mean HbA1c level 7.12±0.84%. KITT was positively associated with PMF/TFM ratio, PMF/CFM ratio, and negatively with CFM/TFM ratio, but was not associated with TFM, PFM, or CFM. RBP4 levels also had a significant relationship with PMF/TFM ratio and PMF/CFM ratio. Adiponectin, leptin, and apolipoprotein A levels were related to absolute adiposity, while only adiponectin to relative adiposity. In correlation analysis, KITT in type 2 diabetes was positively related with HbA1c, fasting glucose, RBP4, and free fatty acid.
Conclusion These results suggest that increased relative amount of peripheral fat mass may aggravate insulin resistance in type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Retinol-binding protein-4 and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Hangkai Huang, Chengfu Xu
Chinese Medical Journal.2022; 135(10): 1182. CrossRef - MANF in POMC Neurons Promotes Brown Adipose Tissue Thermogenesis and Protects Against Diet-Induced Obesity
Qin Tang, Qinhui Liu, Jiahui Li, Jiamin Yan, Xiandan Jing, Jinhang Zhang, Yan Xia, Ying Xu, Yanping Li, Jinhan He
Diabetes.2022; 71(11): 2344. CrossRef - The relation between body fat distribution, plasma concentrations of adipokines and the metabolic syndrome in patients with clinically manifest vascular disease
Ilse M Schrover, Yolanda van der Graaf, Wilko Spiering, Frank LJ Visseren
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2018; 25(14): 1548. CrossRef - Visceral Fat Mass Has Stronger Associations with Diabetes and Prediabetes than Other Anthropometric Obesity Indicators among Korean Adults
Suk Hwa Jung, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Yonsei Medical Journal.2016; 57(3): 674. CrossRef - Adipokines, cytokines and body fat stores in hepatitis C virus liver steatosis
Emilio González-Reimers
World Journal of Hepatology.2016; 8(1): 74. CrossRef - The effect of resveratrol on the expression of AdipoR1 in kidneys of diabetic nephropathy
Hongfei Ji, Lina Wu, Xiaokun Ma, Xiaojun Ma, Guijun Qin
Molecular Biology Reports.2014; 41(4): 2151. CrossRef - Retinol-binding protein 4 and insulin resistance are related to body fat in primary and secondary schoolchildren: the Ouro Preto study
Ana Paula Pereira Castro, Ana Paula Carlos Cândido, Roney Luiz de Carvalho Nicolato, Ivo Santana Caldas, George Luiz Lins Machado-Coelho
European Journal of Nutrition.2014; 53(2): 433. CrossRef - The Effects of Marathon Running on Retinol Binding Protein 4 and C-reactive Protein Levels in Healthy Middle-aged Korean Men
Jisuk Chae, Sungmin Kim, Junga Lee, Justin Y. Jeon
The Korean Journal of Obesity.2014; 23(3): 203. CrossRef - Modeling metabolic homeostasis and nutrient sensing in Drosophila: implications for aging and metabolic diseases
Edward Owusu-Ansah, Norbert Perrimon
Disease Models & Mechanisms.2014; 7(3): 343. CrossRef - Beneficial Effects of Fresh and Fermented Kimchi in Prediabetic Individuals
So-Yeon An, Min Suk Lee, Ja Young Jeon, Eun Suk Ha, Tae Ho Kim, Ja Young Yoon, Chang-Ok Ok, Hye-Kyoung Lee, Won-Sun Hwang, Sun Jung Choe, Seung Jin Han, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Kwan-Woo Lee
Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism.2013; 63(1-2): 111. CrossRef - Regional Adiposity, Adipokines, and Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetes
Jee-Young Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2012; 36(6): 412. CrossRef
- Retinol-binding protein-4 and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- Molecular Mechanisms of Appetite Regulation
- Ji Hee Yu, Min-Seon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(6):391-398. Published online December 12, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.6.391
- 8,966 View
- 215 Download
- 80 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader The prevalence of obesity has been rapidly increasing worldwide over the last several decades and has become a major health problem in developed countries. The brain, especially the hypothalamus, plays a key role in the control of food intake by sensing metabolic signals from peripheral organs and modulating feeding behaviors. To accomplish these important roles, the hypothalamus communicates with other brain areas such as the brainstem and reward-related limbic pathways. The adipocyte-derived hormone leptin and pancreatic β-cell-derived insulin inform adiposity to the hypothalamus. Gut hormones such as cholecystokinin, peptide YY, pancreatic polypeptide, glucagon-like peptide 1, and oxyntomodulin transfer satiety signals to the brain and ghrelin relays hunger signals. The endocannabinoid system and nutrients are also involved in the physiological regulation of food intake. In this article, we briefly review physiological mechanisms of appetite regulation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Regulation of glycose and lipid metabolism and application based on the colloidal nutrition science properties of konjac glucomannan: A comprehensive review
Pengkui Xia, Ying Zheng, Li Sun, Wenxin Chen, Longchen Shang, Jing Li, Tao Hou, Bin Li
Carbohydrate Polymers.2024; 331: 121849. CrossRef - Weight Regain after Metabolic Surgery: Beyond the Surgical Failure
Juan Salazar, Pablo Duran, Bermary Garrido, Heliana Parra, Marlon Hernández, Clímaco Cano, Roberto Añez, Henry García-Pacheco, Gabriel Cubillos, Neidalis Vasquez, Maricarmen Chacin, Valmore Bermúdez
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(4): 1143. CrossRef - Thylakoid supplementation and hunger and fullness perception: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Negin Nikrad, Mehdi Ghaffari Sarghein, Mahdieh Abbasalizad Farhangi
Nutrition Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Stomach clusterin as a gut-derived feeding regulator
Cherl NamKoong, Bohye Kim, Ji Hee Yu, Byung Soo Youn, Hanbin Kim, Evonne Kim, So Young Gil, Gil Myoung Kang, Chan Hee Lee, Young-Bum Kim, Kyeong-Han Park, Min-Seon Kim, Obin Kwon
BMB Reports.2024; 57(3): 149. CrossRef - Anorexigenic neuropeptides as anti-obesity and neuroprotective agents: exploring the neuroprotective effects of anorexigenic neuropeptides
Veronika Strnadová, Andrea Pačesová, Vilém Charvát, Zuzana Šmotková, Blanka Železná, Jaroslav Kuneš, Lenka Maletínská
Bioscience Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The non-conventional edible plant foroba (Parkia biglobosa) has anti-obesity effect, improves lipid peroxidation and reverses colon and hippocampal lesions in healthy and obese rats
Mirela Gouveia-Nhanca, Maria Luiza Rolim Bezerra, Kamila Sabino Batista, Rafael Oliveira Pinheiro, Naís Lira Soares, Maria Carolina de Paiva Sousa, Adriano Francisco Alves, Mateus Duarte Ribeiro, Alexandre Sergio Silva, Marciane Magnani, Marcos dos Santos
Journal of Functional Foods.2023; 108: 105745. CrossRef - Aberrant bone marrow-derived microglia in the hypothalamus may dysregulate appetite in diabetes
Miwako Katagi, Yuki Nakae, Junko Okano, Kazunori Fujino, Tomoki Tanaka, Itsuko Miyazawa, Natsuko Ohashi, Takahiko Nakagawa, Hideto Kojima
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2023; 682: 132. CrossRef - Proteins and peptides from vegetable food sources as therapeutic adjuvants for the type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ivan Chan-Zapata, Carlos Sandoval-Castro, Maira Rubí Segura-Campos
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2022; 62(10): 2673. CrossRef - Differential effects of citalopram on the intake of high fat or high carbohydrates diets in female and male rats
Amparo L. De la Fuente-Reynoso, Eliana Barrios De Tomasi, Jorge Juárez
Nutritional Neuroscience.2022; 25(7): 1477. CrossRef - Egzersizin iştah ve iştah hormonları üzerine etkisinin incelenmesi:
PubMed üzerinden yapılmış sistematik derleme
Esmanur Kaya, Şerife Vatansever
Turkish Journal of Sports Medicine.2022; 57(1): 51. CrossRef - Role of Leu72Met of GHRL and Gln223Arg of LEPR Variants on Food Intake, Subjective Appetite, and Hunger-Satiety Hormones
Tania Sanchez-Murguia, Nathaly Torres-Castillo, Lisset Magaña-de la Vega, Saraí Citlalic Rodríguez-Reyes, Wendy Campos-Pérez, Erika Martínez-López
Nutrients.2022; 14(10): 2100. CrossRef - Appetite ratings and ghrelin concentrations in young adults after administration of a balanced meal. Does sex matter?
Alessandro Leone, Ramona De Amicis, Marta Pellizzari, Simona Bertoli, Simone Ravella, Alberto Battezzati
Biology of Sex Differences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Interplay between fatty acid desaturase2 (FADS2) rs174583 genetic variant and dietary antioxidant capacity: cardio-metabolic risk factors in obese individuals
Mahdieh Khodarahmi, Parisa Javidzade, Mahdieh Abbasalizad Farhangi, Ahmad Hashemzehi, Houman Kahroba
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Appetite-regulating hormones in bipolar disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Błażej Misiak, Krzysztof Kowalski, Bartłomiej Stańczykiewicz, Francesco Bartoli, Giuseppe Carrà, Jerzy Samochowiec, Agnieszka Samochowiec, Dorota Frydecka
Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology.2022; 67: 101013. CrossRef - Association of plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and frailty in community-dwelling older adults
Eun Roh, Soon Young Hwang, Eyun Song, Min Jeong Park, Hye Jin Yoo, Sei Hyun Baik, Miji Kim, Chang Won Won, Kyung Mook Choi
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Gut Hormones in Health and Obesity: The Upcoming Role of Short Chain Fatty Acids
Habeeb Alhabeeb, Ali AlFaiz, Emad Kutbi, Dayel AlShahrani, Abdullah Alsuhail, Saleh AlRajhi, Nemer Alotaibi, Khalid Alotaibi, Saad AlAmri, Saleh Alghamdi, Naji AlJohani
Nutrients.2021; 13(2): 481. CrossRef - Asprosin ve Glikoz Metabolizması Üzerine Etkileri
M. Gizem KESER, Nurhan ÜNÜSAN
Turkish Journal of Diabetes and Obesity.2021; 5(1): 89. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Understanding Peripheral Taste Decoding I: 2010 to 2020
Jea Hwa Jang, Obin Kwon, Seok Jun Moon, Yong Taek Jeong
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 469. CrossRef - Association of increased abdominal adiposity at birth with altered ventral caudate microstructure
Dawn X. P. Koh, Mya Thway Tint, Peter D. Gluckman, Yap Seng Chong, Fabian K. P. Yap, Anqi Qiu, Johan G. Eriksson, Marielle V. Fortier, Patricia P. Silveira, Michael J. Meaney, Ai Peng Tan
International Journal of Obesity.2021; 45(11): 2396. CrossRef - The Crosstalk Between Brain Mediators Regulating Food Intake Behavior in Birds: A Review
Behrouz Rahmani, Elham Ghashghayi, Morteza Zendehdel, Mina Khodadadi, Behnam Hamidi
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics.2021; 27(4): 2349. CrossRef - Oral Semaglutide, the First Ingestible Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist: Could It Be a Magic Bullet for Type 2 Diabetes?
Hwi Seung Kim, Chang Hee Jung
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(18): 9936. CrossRef - Potential Role of Hypothalamic and Plasma Ghrelin in the Feeding Behavior of Obese Type 2 Diabetic Rats with Intraventricular Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Intervention
Ke Lu, Xiaoyan Chen, Xuelian Deng, Juan Long, Jianhua Yan
Obesity Facts.2021; 14(1): 10. CrossRef - Managing obesity through natural polyphenols: A review
Manisha Singh, Thilini Thrimawithana, Ravi Shukla, Benu Adhikari
Future Foods.2020; 1-2: 100002. CrossRef - Neurochemical regulators of food behavior for pharmacological treatment of obesity: current status and future prospects
Gayane Sargis Vardanyan, Hasmik Samvel Harutyunyan, Michail Iosif Aghajanov, Ruben Sargis Vardanyan
Future Medicinal Chemistry.2020; 12(20): 1865. CrossRef - Modulation of feeding behavior and metabolism by dynorphin
Aishwarya Ghule, Ildiko Rácz, Andras Bilkei-Gorzo, Este Leidmaa, Meike Sieburg, Andreas Zimmer
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Possible role of peptide YY (PYY) in the pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS)
Magdy El-Salhy, Jan Gunnar Hatlebakk, Trygve Hausken
Neuropeptides.2020; 79: 101973. CrossRef - Prolactin-releasing peptide increases food intake and affects hypothalamic physiology in Japanese quail (Coturnix japonica)
B.R. McConn, T. Tachibana, E.R. Gilbert, M.A. Cline
Domestic Animal Endocrinology.2020; 72: 106464. CrossRef - Obesity induced by Borna disease virus in rats: key roles of hypothalamic fast-acting neurotransmitters and inflammatory infiltrates
Georg Gosztonyi, Hanns Ludwig, Liv Bode, Moujahed Kao, Manfred Sell, Peter Petrusz, Béla Halász
Brain Structure and Function.2020; 225(5): 1459. CrossRef - D‐methionine improves cisplatin‐induced anorexia and dyspepsia syndrome by attenuating intestinal tryptophan hydroxylase 1 activity and increasing plasma leptin concentration
Yi‐Sin Wong, Meei‐Yn Lin, Pei‐Fen Liu, Jiunn‐Liang Ko, Guan‐Ting Huang, Dom‐Gene Tu, Chu‐Chyn Ou
Neurogastroenterology & Motility.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of oral, smoked, and vaporized cannabis on endocrine pathways related to appetite and metabolism: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, human laboratory study
Mehdi Farokhnia, Gray R. McDiarmid, Matthew N. Newmeyer, Vikas Munjal, Osama A. Abulseoud, Marilyn A. Huestis, Lorenzo Leggio
Translational Psychiatry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Paraventricular Nucleus in Regulation of Feeding Behaviour and the Design of Intranuclear Neuronal Pathway Communications
Shiba Yousefvand, Farshid Hamidi
International Journal of Peptide Research and Therapeutics.2020; 26(3): 1231. CrossRef - Self-Reported Eating Speed and Incidence of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: the Japan Environment and Children’s Study
Jia-Yi Dong, Satoyo Ikehara, Takashi Kimura, Meishan Cui, Yoko Kawanishi, Tadashi Kimura, Kimiko Ueda, Hiroyasu Iso
Nutrients.2020; 12(5): 1296. CrossRef - Effects of a high-fat-diet supplemented with probiotics and ω3-fatty acids on appetite regulatory neuropeptides and neurotransmitters in a pig model
D. Valent, L. Arroyo, E. Fàbrega, M. Font-i-Furnols, M. Rodríguez-Palmero, J.A. Moreno-Muñoz, J. Tibau, A. Bassols
Beneficial Microbes.2020; 11(4): 347. CrossRef - Electro-Acupuncture Alleviates Cisplatin-Induced Anorexia in Rats by Modulating Ghrelin and Monoamine Neurotransmitters
Ji Yun Baek, Tuy An Trinh, Wonsang Huh, Ji Hoon Song, Hyun Young Kim, Juhee Lim, Jinhee Kim, Hyun Jin Choi, Tae-Hun Kim, Ki Sung Kang
Biomolecules.2019; 9(10): 624. CrossRef - Interleukin-6 Expression by Hypothalamic Microglia in Multiple Inflammatory Contexts: A Systematic Review
Vanessa C. D. Bobbo, Carlos P. Jara, Natália F. Mendes, Joseane Morari, Lício A. Velloso, Eliana P. Araújo
BioMed Research International.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Abnormalities in Glucose Metabolism, Appetite-Related Peptide Release, and Pro-inflammatory Cytokines Play a Central Role in Appetite Disorders in Peritoneal Dialysis
Lorena Avila-Carrasco, Mario A. Pavone, Elena González, Álvaro Aguilera-Baca, Rafael Selgas, Gloria del Peso, Secundino Cigarran, Manuel López-Cabrera, Abelardo Aguilera
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Branched chain amino acids stimulate gut satiety hormone cholecystokinin secretion through activation of the umami taste receptor T1R1/T1R3 using an in vitro porcine jejunum model
Min Tian, Jinghui Heng, Hanqing Song, Yufeng Zhang, Fang Chen, Wutai Guan, Shihai Zhang
Food & Function.2019; 10(6): 3356. CrossRef - Multi-Omic Biological Age Estimation and Its Correlation With Wellness and Disease Phenotypes: A Longitudinal Study of 3,558 Individuals
John C Earls, Noa Rappaport, Laura Heath, Tomasz Wilmanski, Andrew T Magis, Nicholas J Schork, Gilbert S Omenn, Jennifer Lovejoy, Leroy Hood, Nathan D Price, David Le Couteur
The Journals of Gerontology: Series A.2019; 74(Supplement): S52. CrossRef - The impact of sugar consumption on stress driven, emotional and addictive behaviors
Angela Jacques, Nicholas Chaaya, Kate Beecher, Syed Aoun Ali, Arnauld Belmer, Selena Bartlett
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2019; 103: 178. CrossRef - Leptin Signaling in the Control of Metabolism and Appetite: Lessons from Animal Models
Alberto A. Barrios-Correa, José A. Estrada, Irazú Contreras
Journal of Molecular Neuroscience.2018; 66(3): 390. CrossRef - Role of paraventricular hypothalamic dopaminergic D1 receptors in food intake regulation of food-deprived rats
Zahra. Mirmohammadsadeghi, Masoud. Shareghi Brojeni, Abbas. Haghparast, Afsaneh. Eliassi
European Journal of Pharmacology.2018; 818: 43. CrossRef - Integrating Thyroid Hormone Signaling in Hypothalamic Control of Metabolism: Crosstalk Between Nuclear Receptors
Soumaya Kouidhi, Marie-Stéphanie Clerget-Froidevaux
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2018; 19(7): 2017. CrossRef - Review article: Role of satiety hormones in anorexia induction by Trichothecene mycotoxins
Chloé Terciolo, Marc Maresca, Philippe Pinton, Isabelle P. Oswald
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2018; 121: 701. CrossRef - Obezite ve Ghrelin/Leptin İlişkisi
Aliye Sağkan Öztürk, Abdullah ARPACI
Mustafa Kemal Üniversitesi Tıp Dergisi.2018; 9(35): 136. CrossRef - Overexpression of Wild-Type Human Alpha-Synuclein Causes Metabolism Abnormalities in Thy1-aSYN Transgenic Mice
Elodie Cuvelier, Mathieu Méquinion, Coline Leghay, William Sibran, Aliçia Stievenard, Alessia Sarchione, Marie-Amandine Bonte, Christel Vanbesien-Mailliot, Odile Viltart, Kevin Saitoski, Emilie Caron, Alexandra Labarthe, Thomas Comptdaer, Pierre Semaille,
Frontiers in Molecular Neuroscience.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Aetiology of eating behaviours: A possible mechanism to understand obesity development in early childhood
Nikki Boswell, Rebecca Byrne, Peter S.W. Davies
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2018; 95: 438. CrossRef - Clinical Phenotype of Depression Affects Interleukin-6 Synthesis
Łukasz Zadka, Piotr Dzięgiel, Michał Kulus, Marcin Olajossy
Journal of Interferon & Cytokine Research.2017; 37(6): 231. CrossRef - Altered Adipogenesis in Zebrafish Larvae Following High Fat Diet and Chemical Exposure Is Visualised by Stimulated Raman Scattering Microscopy
Marjo den Broeder, Miriam Moester, Jorke Kamstra, Peter Cenijn, Valentina Davidoiu, Leonie Kamminga, Freek Ariese, Johannes de Boer, Juliette Legler
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2017; 18(4): 894. CrossRef - SIFamide Translates Hunger Signals into Appetitive and Feeding Behavior in Drosophila
Carlotta Martelli, Ulrike Pech, Simon Kobbenbring, Dennis Pauls, Britta Bahl, Mirjam Vanessa Sommer, Atefeh Pooryasin, Jonas Barth, Carmina Warth Perez Arias, Chrystalleni Vassiliou, Abud Jose Farca Luna, Haiko Poppinga, Florian Gerhard Richter, Christian
Cell Reports.2017; 20(2): 464. CrossRef - Effect of Mulberry Extract on the Lipid Profile and Liver Function in Mice Fed a High Fat Diet
Kyung-Soon Choi, Yong-Hwan Kim, Kyung-Ok Shin
The Korean Journal of Food And Nutrition.2016; 29(3): 411. CrossRef - Helicobacter pylori Infection in Children: Nutritional Status and Associations with Serum Leptin, Ghrelin, and IGF‐1 Levels
Gulin Erdemir, Tanju Basarir Ozkan, Taner Ozgur, Derya Altay, Sinan Cavun, Guher Goral
Helicobacter.2016; 21(4): 317. CrossRef - Dietary Capsaicin Protects Cardiometabolic Organs from Dysfunction
Fang Sun, Shiqiang Xiong, Zhiming Zhu
Nutrients.2016; 8(5): 174. CrossRef - Effects of Short-Term Exenatide Treatment on Regional Fat Distribution, Glycated Hemoglobin Levels, and Aortic Pulse Wave Velocity of Obese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Ju-Young Hong, Keun-Young Park, Byung-Joon Kim, Won-Min Hwang, Dong-Ho Kim, Dong-Mee Lim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(1): 80. CrossRef - The role of the neuropeptide Y (NPY) family in the pathophysiology of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Magdy El-Salhy, Trygve Hausken
Neuropeptides.2016; 55: 137. CrossRef - Proactive and Progressive Approaches in Managing Obesity
Robert H. Eckel, Harold E. Bays, Samuel Klein, Deborah Bade Horn
Postgraduate Medicine.2016; 128(sup1): 21. CrossRef - The role of food intake regulating peptides in cardiovascular regulation
B. Mikulášková, L. Maletínská, J. Zicha, J. Kuneš
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2016; 436: 78. CrossRef - Altered gut and adipose tissue hormones in overweight and obese individuals: cause or consequence?
M E J Lean, D Malkova
International Journal of Obesity.2016; 40(4): 622. CrossRef - Expression of NUCB2/nesfatin-1 in the taste buds of rats
Xun Cao, Xiao Zhou, Yang Cao, Xiao-Min Liu, Li-Hong Zhou
Endocrine Journal.2016; 63(1): 37. CrossRef - Brain Regulation of Energy Metabolism
Eun Roh, Min-Seon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(4): 519. CrossRef - Stopped-Flow Studies of the Reduction of the Copper Centers Suggest a Bifurcated Electron Transfer Pathway in Peptidylglycine Monooxygenase
Shefali Chauhan, Parisa Hosseinzadeh, Yi Lu, Ninian J. Blackburn
Biochemistry.2016; 55(13): 2008. CrossRef - Potential role of bioactive compounds of Phaseolus vulgaris L. on lipid-lowering mechanisms
Aurea K. Ramírez-Jiménez, Rosalía Reynoso-Camacho, M. Elizabeth Tejero, Fabiola León-Galván, Guadalupe Loarca-Piña
Food Research International.2015; 76: 92. CrossRef - Recent developments in the pathophysiology of irritable bowel syndrome
Magdy El-Salhy
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2015; 21(25): 7621. CrossRef - Lifestyle Changes Followed by Bariatric Surgery Lower Inflammatory Markers and the Cardiovascular Risk Factors C3 and C4
Torunn Kristin Nestvold, Erik Waage Nielsen, Judith Krey Ludviksen, Hilde Fure, Anne Landsem, Knut Tore Lappegård
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2015; 13(1): 29. CrossRef - Diet in irritable bowel syndrome
Magdy El-Salhy, Doris Gundersen
Nutrition Journal.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - 3p22.1p21.31 microdeletion identifies CCK as Asperger syndrome candidate gene and shows the way for therapeutic strategies in chromosome imbalances
Ivan Y. Iourov, Svetlana G. Vorsanova, Victoria Y. Voinova, Yuri B. Yurov
Molecular Cytogenetics.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of slow spaced eating on hunger and satiety in overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Theodoros Angelopoulos, Alexander Kokkinos, Christos Liaskos, Nicholas Tentolouris, Kleopatra Alexiadou, Alexander Dimitri Miras, Iordanis Mourouzis, Despoina Perrea, Constantinos Pantos, Nicholas Katsilambros, Stephen R Bloom, Carel Wynard le Roux
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2014; 2(1): e000013. CrossRef - Bisphenol A is related to circulating levels of adiponectin, leptin and ghrelin, but not to fat mass or fat distribution in humans
Monika Rönn, Lars Lind, Jan Örberg, Joel Kullberg, Stefan Söderberg, Anders Larsson, Lars Johansson, Håkan Ahlström, P. Monica Lind
Chemosphere.2014; 112: 42. CrossRef - The modulatory role of alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone administered spinally in the regulation of blood glucose level in d-glucose-fed and restraint stress mouse models
Yun-Beom Sim, Soo-Hyun Park, Sung-Su Kim, Su-Min Lim, Jun-Sub Jung, Hong-Won Suh
Neuropeptides.2014; 48(4): 207. CrossRef - The forgotten members of the glucagon family
Dominique Bataille, Stéphane Dalle
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2014; 106(1): 1. CrossRef - Incretin mimetics as pharmacologic tools to elucidate and as a new drug strategy to treat traumatic brain injury
Nigel H. Greig, David Tweedie, Lital Rachmany, Yazhou Li, Vardit Rubovitch, Shaul Schreiber, Yung-Hsiao Chiang, Barry J. Hoffer, Jonathan Miller, Debomoy K. Lahiri, Kumar Sambamurti, Robert E. Becker, Chaim G. Pick
Alzheimer's & Dementia.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Fatty acid analysis and regulatory effects of citron (Citrus junosSieb. ex TANAKA) seed oil on nitric oxide production, lipid accumulation, and leptin secretion
Tae Woo Kim, Kyoung Kon Kim, Yun Hwan Kang, Dae Jung Kim, Myeon Choe
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2014; 47(4): 221. CrossRef - Analysis of Pine Nut Oil Composition and Its Effects on Obesity
Kyoung Kon Kim, Yun Hwan Kang, Dae Jung Kim, Tae Woo Kim, Myeon Choe
Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology.2014; 46(5): 630. CrossRef - Anti-obesity effects of KR-66195, a synthetic DPP-IV inhibitor, in diet-induced obese mice and obese-diabetic ob/ob mice
Eun Young Lee, Yeon Wook Kim, Hyunhee Oh, Cheol Soo Choi, Jin Hee Ahn, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
Metabolism.2014; 63(6): 793. CrossRef - Position and Length of Fatty Acids Strongly Affect Receptor Selectivity Pattern of Human Pancreatic Polypeptide Analogues
Veronika Mäde, Kathrin Bellmann‐Sickert, Anette Kaiser, Jens Meiler, Annette G. Beck‐Sickinger
ChemMedChem.2014; 9(11): 2463. CrossRef - Regulation of food intake after surgery and the gut brain axis
Nilanjana Tewari, Sherif Awad, Dileep N. Lobo
Current Opinion in Clinical Nutrition and Metabolic Care.2013; 16(5): 569. CrossRef - Effect of ambient temperature during acute aerobic exercise on short-term appetite, energy intake, and plasma acylated ghrelin in recreationally active males
Lucy K. Wasse, James A. King, David J. Stensel, Caroline Sunderland
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2013; 38(8): 905. CrossRef - Peripheral Pathways in the Food-Intake Control towards the Adipose-Intestinal Missing Link
Hugo Mendieta Zerón, Ma. Victoria Domínguez García, María del Socorro Camarillo Romero, Miriam V. Flores-Merino
International Journal of Endocrinology.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef - Alteration of sweet taste in high-fat diet induced obese rats after 4 weeks treatment with exenatide
Xiao-juan Zhang, Yu-qing Wang, Yang Long, Lei Wang, Yun Li, Fa-bao Gao, Hao-ming Tian
Peptides.2013; 47: 115. CrossRef - Decrease of Obesity by Allantoin via Imidazoline I1-Receptor Activation in High Fat Diet-Fed Mice
Hsien-Hui Chung, Kung Shing Lee, Juei-Tang Cheng
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef - Hunger Hormone Profile Monitoring after Gastroplication in an Adolescent
Valeria Calcaterra, Gloria Pelizzo, Ghassan Nakib, Daniela Larizza, Maria Luisa Fonte, Mara De Amici, Hellas Cena
Hormone Research in Paediatrics.2013; 80(3): 213. CrossRef
- Regulation of glycose and lipid metabolism and application based on the colloidal nutrition science properties of konjac glucomannan: A comprehensive review
- Leptin in Relation to the Lipodystrophy-Associated Metabolic Syndrome
- Christos S. Mantzoros
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(3):181-189. Published online June 14, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.3.181
- 2,844 View
- 28 Download
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Leptin, an adipocyte-secreted hormone, regulates energy homeostasis as well as reproductive, neuroendocrine, immune and metabolic functions. Subjects with decreased amounts of fat in their adipose tissue, i.e., lipoatrophy, have low leptin levels. In the context of open-label, uncontrolled studies leptin administration, in physiological replacement doses, has been shown to have metabolically salutary effects in the rare patients with the syndrome of congenital lipodystrophy accompanied by leptin deficiency. Much more patients with lipodystrophy suffer from lipodystrophy and the metabolic syndrome associated with the use of highly active antiretroviral therapy. In this so called highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART)-associated lipodystrophy and metabolic syndrome, patients demonstrate fat maldistribution with dyslipidemia, insulin resistance, and other metabolic complications. Leptin administration has been shown to decrease central fat mass and to improve fasting insulin/glucose levels and insulin sensitivity in human immunodeficiency virus-infected hypoleptinemic patients with HAART induced lipodystrophy and the metabolic syndrome. By contrast, the results of leptin treatment in leptin replete or hyperleptinemic obese individuals with glucose intolerance and diabetes mellitus have been minimal or null, presumably due to leptin tolerance or resistance that impairs leptin action. In this review, we present the emerging clinical applications and potential therapeutic uses of leptin in humans with lipodystrophy and the metabolic syndrome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Milestones in the journey towards addressing obesity; Past trials and triumphs, recent breakthroughs, and an exciting future in the era of emerging effective medical therapies and integration of effective medical therapies with metabolic surgery
Michail Kokkorakis, Angeliki Katsarou, Niki Katsiki, Christos S. Mantzoros
Metabolism.2023; 148: 155689. CrossRef - The common pathophysiologic threads between Asian Indian diabetic’s ‘Thin Fat Phenotype’ and partial lipodystrophy: the peripheral adipose tissue transcriptomic evidences
Aditya Saxena, Pradeep Tiwari, Nitin Wahi, Anshul Kumar, Sandeep Kumar Mathur
Adipocyte.2020; 9(1): 253. CrossRef - The effect of underweight on female and male reproduction
Chrysoula Boutari, Panagiotis D. Pappas, Gesthimani Mintziori, Meletios P. Nigdelis, Loukas Athanasiadis, Dimitrios G. Goulis, Christos S. Mantzoros
Metabolism.2020; 107: 154229. CrossRef - Clinical presentations, metabolic abnormalities and end-organ complications in patients with familial partial lipodystrophy
Baris Akinci, Huseyin Onay, Tevfik Demir, Şenay Savas-Erdeve, Ramazan Gen, Ilgin Yildirim Simsir, Fatma Ela Keskin, Mehmet Sercan Erturk, Ayse Kubat Uzum, Guzin Fidan Yaylali, Nilufer Kutbay Ozdemir, Tahir Atik, Samim Ozen, Banu Sarer Yurekli, Tugce Apayd
Metabolism.2017; 72: 109. CrossRef - CURRENT STATE OF THE PROBLEM OF OVERWEIGHT AND OBESITY IN WOMEN
L. V. Tkachenko, N. I. Sviridova, T. V. Skladanovskaya
Journal of Volgograd State Medical University.2017; 14(4): 3. CrossRef - Leptin and Hormones
Georgios A. Triantafyllou, Stavroula A. Paschou, Christos S. Mantzoros
Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America.2016; 45(3): 633. CrossRef - An allosteric antibody to the leptin receptor reduces body weight and reverses the diabetic phenotype in the Lepob/Lepob mouse
Vinay Bhaskar, Ira D. Goldfine, Resi Gerstner, Kristen Michelson, Catarina Tran, Genevieve Nonet, David Bohmann, Elizabeth Pongo, Jingsong Zhao, Arnold H. Horwitz, Toshihiko Takeuchi, Mark White, John A. Corbin
Obesity.2016; 24(8): 1687. CrossRef - Lipodystrophic Diabetes Mellitus: a Lesson for Other Forms of Diabetes?
Romina Ficarella, Luigi Laviola, Francesco Giorgino
Current Diabetes Reports.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Aldehyde Dehydrogenase 1A1: Friend or Foe to Female Metabolism?
Jennifer Petrosino, David DiSilvestro, Ouliana Ziouzenkova
Nutrients.2014; 6(3): 950. CrossRef - Comparative endocrinology of leptin: Assessing function in a phylogenetic context
Richard L. Londraville, Yazmin Macotela, Robert J. Duff, Marietta R. Easterling, Qin Liu, Erica J. Crespi
General and Comparative Endocrinology.2014; 203: 146. CrossRef - Central obesity and altered peripheral adipose tissue gene expression characterize the NAFLD patient with insulin resistance: Role of nutrition and insulin challenge
J.A. Paniagua, J.M. Escandell-Morales, D. Gil-Contreras, F.J. Berral de la Rosa, M. Romero-Jimenez, A. Gómez-Urbano, A. Sanchez-Lopez, E. Bellido, A. Poyato, B. Calatayud, A.J. Vidal-Puig
Nutrition.2014; 30(2): 177. CrossRef - The complex interaction between obesity, metabolic syndrome and reproductive axis: A narrative review
Konstantinos Michalakis, Gesthimani Mintziori, Athina Kaprara, Basil C. Tarlatzis, Dimitrios G. Goulis
Metabolism.2013; 62(4): 457. CrossRef - Dietary supplementation with long-chain monounsaturated fatty acids attenuates obesity-related metabolic dysfunction and increases expression of PPAR gamma in adipose tissue in type 2 diabetic KK-Ay mice
Zhi-Hong Yang, Hiroko Miyahara, Yusuke Iwasaki, Jiro Takeo, Masashi Katayama
Nutrition & Metabolism.2013; 10(1): 16. CrossRef - Embryo-transfer of the F2 postnatal calorie restricted female rat offspring into a control intra-uterine environment normalizes the metabolic phenotype
Meena Garg, Manikkavasagar Thamotharan, Yun Dai, Paul W.N. Lee, Sherin U. Devaskar
Metabolism.2013; 62(3): 432. CrossRef - Obesity in the ageing man
K. Michalakis, D.G. Goulis, A. Vazaiou, G. Mintziori, A. Polymeris, A. Abrahamian-Michalakis
Metabolism.2013; 62(10): 1341. CrossRef - Acylated and Desacylated Ghrelin, Preptin, Leptin, and Nesfatin-1 Peptide Changes Related to the Body Mass Index
Yusuf Ozkan, Esra Suay Timurkan, Suleyman Aydin, İbrahim Sahin, Mustafa Timurkan, Cihan Citil, Mehmet Kalayci, Musa Yilmaz, Aziz Aksoy, Zekiye Catak
International Journal of Endocrinology.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef - Higher fetuin-A, lower adiponectin and free leptin levels mediate effects of excess body weight on insulin resistance and risk for myelodysplastic syndrome
Maria Dalamaga, Konstantinos Karmaniolas, John Chamberland, Athina Nikolaidou, Antigoni Lekka, Amalia Dionyssiou-Asteriou, Christos S. Mantzoros
Metabolism.2013; 62(12): 1830. CrossRef - Metabolische Korrektur mit Leptin
Konstanze Miehle, Michael Stumvoll, Mathias Fasshauer, Wieland Kiess, Thomas Kapellen
Info Diabetologie.2012; 6(5): 37. CrossRef
- Milestones in the journey towards addressing obesity; Past trials and triumphs, recent breakthroughs, and an exciting future in the era of emerging effective medical therapies and integration of effective medical therapies with metabolic surgery
- The Relationship of Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio with Homeostasis Model Assessment Insulin Resistance Index and Metabolic Syndrome in Apparently Healthy Korean Male Adults
- Chan-Hee Jung, Eun-Jung Rhee, Ji-Hoon Choi, Ji-Cheol Bae, Seung-Hyun Yoo, Won-Jun Kim, Cheol-Young Park, Ji Oh Mok, Chul Hee Kim, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Sun-Woo Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(4):237-243. Published online August 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.4.237
- 4,282 View
- 37 Download
- 45 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We investigated the relationships of adiponectin/leptin (A/L) ratio with cardiovascular risk factors, insulin resistance index, and metabolic syndrome (MS) in apparently healthy Korean male adults.
Methods Sixty-eight male subjects were enrolled among the participants of an annual health check-up program (mean age, 55.1 years). Percent body fat (%) was measured using a bioelectric impedance analyzer. Serum leptin level was measured via radioimmunoassay, and adiponectin level was measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Homeostasis model assessment (HOMA)-insulin resistance (IR) index was calculated, and the presence of metabolic syndrome was assessed.
Results Adiponectin, leptin, and A/L ratio showed significant correlations with percent body fat, lipid profile, and HOMA-IR. Mean leptin and HOMA-IR levels were significantly higher, while A/L ratio was significantly lower in subjects with MS. With increasing number of MS components, the mean values of leptin and HOMA-IR increased and the A/L ratio decreased. In multiple regression analysis, HOMA-IR was significantly correlated with triglyceride, fasting glucose, and A/L ratio, while A/L ratio was significantly correlated with body mass index and HOMA-IR. HOMA-IR and A/L ratio were significant predictors for each other after adjustment for other factors.
Conclusion A/L ratio correlated well with lipid profile, HOMA-IR, and the presence and number of MS components in Korean male subjects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on serum values of adiponectin, leptin, 8-isoprostane and malondialdehyde in women with type 2 diabetes
Mahsa Gholami, Parvin Zarei, Bahman Sadeghi Sedeh, Fatemeh Rafiei, Ali Khosrowbeygi
Gynecological Endocrinology.2024; 34(12): 1059. CrossRef - Serum immunoglobulin G as a predictive marker of early renal affection in type-2 diabetic patients: a single-center study
MohammadH M Abdellah, NabawiaM Tawfik, EffatAbd-Elhady Tony, AmalA A Mahmoud, SehamM Ali, MarwaK Khairallah
Journal of The Egyptian Society of Nephrology and Transplantation.2023; 23(1): 17. CrossRef - Adiponectin/leptin and HOMA/adiponectin ratios in Iranian women with polycystic ovary syndrome
Akram Vatannejad, Asma Kheirollahi
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2023; 192(4): 1793. CrossRef - Insulin resistance in early and advanced diabetic kidney disease
VedavatiB Purandare, ArjunL Kakrani, CharanB Bale, Shalbha Tiwari, AmbikaG Unnikrishnan
Chronicle of Diabetes Research and Practice.2022; 1(1): 3. CrossRef - Changes in adiponectin:leptin ratio among older adults with obesity following a 12-month exercise and diet intervention
Katelyn E. Senkus, Kristi M. Crowe-White, Anneliese C. Bolland, Julie L. Locher, Jamy D. Ard
Nutrition & Diabetes.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Adiponectin, leptin, and leptin/adiponectin ratio with risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: A prospective nested case-control study among Chinese women
Yi Ye, Ping Wu, Yi Wang, Xue Yang, Yixiang Ye, Jiaying Yuan, Yan Liu, Xingyue Song, Shijiao Yan, Ying Wen, Xiaorong Qi, Chunxia Yang, Gang Liu, Chuanzhu Lv, Xiong-Fei Pan, An Pan
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110039. CrossRef - The influence of fasting and energy-restricted diets on leptin and adiponectin levels in humans: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Hamed Varkaneh Kord, Grant M. Tinsley, Heitor O. Santos, Hamid Zand, Ali Nazary, Somaye Fatahi, Zeinab Mokhtari, Ammar Salehi-sahlabadi, Shing Cheng Tan, Jamal Rahmani, Mihnea-Alexandru Gaman, Brijesh Sathian, Amir Sadeghi, Behzad Hatami, Samira Soltanieh
Clinical Nutrition.2021; 40(4): 1811. CrossRef - Galectin-3/adiponectin as a new biological indicator for assessing the risk of type 2 diabetes: a cross-sectional study in a community population
Diaozhu Lin, Xiaosi Hong, Kan Sun, Xiaoyun Zhang, Hong Lian, Jiahuan Wang, Na Mao, Xiuwei Zhang, Meng Ren, Li Yan, Feng Li, Lili You
Aging.2021; 13(11): 15433. CrossRef - Relationship between Adipose Tissue Derived Hormones and Cardiometabolic Risk according to Obesity Status
So Yoon Hwang, Min Joo Seon, Jong Hwa Lee, Oh Yoen Kim
Clinical Nutrition Research.2021; 10(3): 206. CrossRef - Insulin resistance and the adiponectin/leptin ratio as a surrogate measure of insulin resistance in Japanese collegiate baseball players
Kazuto ODA, Hisaya KAWATE, Aya ISHIBASHI, Hiroyuki IMAMURA
The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Variants in ADIPOQ Are Associated with Maternal Circulating Adipokine Profile in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Watip Tangjittipokin, Tassanee Narkdontri, Nipaporn Teerawattanapong, Benyapa Thanatummatis, Prasert Sunsaneevithayakul, Dittakarn Boriboonhirunsarn
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of magnitude of weight loss on Adipo/lep ratio in adolescents with obesity undergoing multicomponent therapy
Yasmin Alaby Martins Ferreira, Ana Claudia Pelissari Kravchychyn, Sofia de Castro Ferreira Vicente, Raquel Munhoz da Silveira Campos, Lian Tock, Lila Missae Oyama, Valter Tadeu Boldarine, Deborah Cristina Landi Masquio, Ana R. Dâmaso
Cytokine.2020; 131: 155111. CrossRef - Association of visceral adiposity index, lipid profile, and serum leptin with glucose intolerance risks in Iraqi obese patients: A cross-sectional study
WaelWaleed Mustafa, SamerShukur Moahammed, WathiqMohammed Al-Jewari, HusseinSaad Abdulrahman, SaadAbdulrahman Hussain
Journal of Pharmacy And Bioallied Sciences.2020; 12(4): 468. CrossRef - Increase of the Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio in Patients with Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes after Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass
Xabier Unamuno, Maitane Izaguirre, Javier Gómez-Ambrosi, Amaia Rodríguez, Beatriz Ramírez, Sara Becerril, Víctor Valentí, Rafael Moncada, Camilo Silva, Javier Salvador, Piero Portincasa, Gema Frühbeck, Victoria Catalán
Nutrients.2019; 11(9): 2069. CrossRef - Elevation of the adiponectin/leptin ratio in women with gestational diabetes mellitus after supplementation with alpha-lipoic acid
Hadise Aslfalah, Mehri Jamilian, Ali Khosrowbeygi
Gynecological Endocrinology.2019; 35(3): 271. CrossRef - Assessing the variability and predictability of adipokines (adiponectin, leptin, resistin and their ratios) in non-obese and obese women with anovulatory polycystic ovary syndrome
Christian Obirikorang, William K. B. A. Owiredu, Sandra Adu-Afram, Emmanuel Acheampong, Evans Adu Asamoah, Enoch Kwabena Antwi-Boasiakoh, Eddie-Williams Owiredu
BMC Research Notes.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - New Insights into the Role of Exercise in Inhibiting mTOR Signaling in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Deborah Agostini, Valentina Natalucci, Giulia Baldelli, Mauro De Santi, Sabrina Donati Zeppa, Luciana Vallorani, Giosuè Annibalini, Francesco Lucertini, Ario Federici, Riccardo Izzo, Vilberto Stocchi, Elena Barbieri
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Increased insulin sensitivity in individuals with neurofibromatosis type 1
Aline Stangherlin Martins, Ann Kristine Jansen, Luiz Oswaldo Carneiro Rodrigues, Camila Maria Matos, Marcio Leandro Ribeiro Souza, Débora Marques Miranda, Nilton Alves de Rezende
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 62(1): 41. CrossRef - Body composition and metabolic changes during a 520-day mission simulation to Mars
F. Strollo, C. Macchi, I. Eberini, M. A. Masini, M. Botta, G. Vassilieva, I. Nichiporuk, M. Monici, D. Santucci, F. Celotti, P. Magni, M. Ruscica
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2018; 41(11): 1267. CrossRef - The relationship between adiposopathy and glucose-insulin homeostasis is not affected by moderate-intensity aerobic training in healthy women with obesity
Andrée-Anne Clément, Eléonor Riesco, Sébastien Tessier, Michel Lacaille, Francine Pérusse, Mélanie Coté, Jean-Pierre Després, John Weisnagel, Jean Doré, Denis R. Joanisse, Pascale Mauriège
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry.2018; 74(4): 591. CrossRef - Effect of personalized moderate exercise training on Wistar rats fed with a fructose enriched water
Julie Dupas, Annie Feray, Anthony Guernec, Morgane Pengam, Manon Inizan, François Guerrero, Jacques Mansourati, Christelle Goanvec
Nutrition & Metabolism.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship of serum leptin with some biochemical, anthropometric parameters and abdominal fat volumes as measured by magnetic resonance imaging
Nawal S. Hijjawi, Ali M. Al-Radaideh, Kholoud I. Al-Fayomi, Nisreen A. Nimer, Hadeel A. Alabadi, Rana M. Al-Zu’bi, Lana M. Agraib, Sabika S. Allehdan, Reema F. Tayyem
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2018; 12(3): 207. CrossRef - Markers of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Defense in Romanian Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Obesity
Ariana Picu, Laura Petcu, Simona Ştefan, Manuela Mitu, Daniela Lixandru, Constantin Ionescu-Tîrgovişte, Grațiela Grădișteanu Pîrcălăbioru, Felicia Ciulu-Costinescu, Maria-Viorica Bubulica, Mariana Carmen Chifiriuc
Molecules.2017; 22(5): 714. CrossRef - Comparisons of physical activity, adipokines, vitamin D status and dietary vitamin D intake among adolescents
K. V. Giudici, R. M. Fisberg, D. M. Marchioni, L. A. Martini
Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics.2017; 30(3): 369. CrossRef - Adiponectin and leptin as first trimester markers for gestational diabetes mellitus: a cohort study
Ida Näslund Thagaard, Lone Krebs, Jens-Christian Holm, Theis Lange, Torben Larsen, Michael Christiansen
Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM).2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Crosstalk Between Bone and Fat Tissue: Associations Between Vitamin D, Osteocalcin, Adipokines, and Markers of Glucose Metabolism Among Adolescents
Kelly Virecoulon Giudici, Regina Mara Fisberg, Dirce Maria Lobo Marchioni, Bárbara Santarosa Emo Peters, Lígia Araújo Martini
Journal of the American College of Nutrition.2017; 36(4): 273. CrossRef - Comparison between body mass index and a body shape index with adiponectin/leptin ratio and markers of glucose metabolism among adolescents
Kelly Virecoulon Giudici, Ligia Araujo Martini
Annals of Human Biology.2017; 44(6): 489. CrossRef - Fitness, adiposopathy, and adiposity are independent predictors of insulin sensitivity in middle-aged men without diabetes
Claire Huth, Étienne Pigeon, Marie-Ève Riou, Josée St-Onge, Hélène Arguin, Erick Couillard, Marie-Julie Dubois, André Marette, Angelo Tremblay, S. John Weisnagel, Michel Lacaille, Pascale Mauriège, Denis R. Joanisse
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry.2016; 72(3): 435. CrossRef - Biomarkers of Metabolic Syndrome: Biochemical Background and Clinical Significance
Harry Robberecht, Nina Hermans
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2016; 14(2): 47. CrossRef - Role of Statins in Glucose Homeostasis and Insulin Resistance
Chanukya Dahagam, Virginia S. Hahn, Aditya Goud, Jason D’Souza, Abdelhai Abdelqader, Roger S. Blumenthal, Seth S. Martin
Current Cardiovascular Risk Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Body Weight Reduction on Plasma Leptin and Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio in Obese Patients With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
F. MUSIL, V. BLAHA, A. TICHA, R. HYSPLER, M. HALUZIK, J. LESNA, A. SMAHELOVA, L. SOBOTKA
Physiological Research.2015; : 221. CrossRef - The Associations of Novel Vitamin D3Metabolic GeneCYP27A1Polymorphism, Adiponectin/Leptin Ratio, and Metabolic Syndrome in Middle-Aged Taiwanese Males
Kai-Hung Cheng, Edward Hsi, Chia-Chu Liu, Chun-Nung Huang, Yung-Chin Lee, Chih-Sheng Chu, Bo-Ying Bao, Chu-Fen Chang, Shu-Pin Huang, Po-Lin Kuo, Wen-Ter Lai
International Journal of Endocrinology.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Effects of tactile massage on metabolic biomarkers in patients with type 2 diabetes
P.E. Wändell, J. Ärnlöv, A. Nixon Andreasson, K. Andersson, L. Törnkvist, A.C. Carlsson
Diabetes & Metabolism.2013; 39(5): 411. CrossRef - Atorvastatin treatment modulates the interaction between leptin and adiponectin, and the clinical parameters in patients with type II diabetes
SAYER I. AL-AZZAM, ASEM M. ALKHATEEB, KAREM H. ALZOUBI, RAYA N. ALZAYADEEN, MERA A. ABABNEH, OMAR F. KHABOUR
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2013; 6(6): 1565. CrossRef - Is the neck circumference an emergent predictor for inflammatory status in obese adults?
G. Jamar, L. P. Pisani, L. M. Oyama, C. Belote, D. C. L. Masquio, V. A. Furuya, J. P. Carvalho-Ferreira, S. G. Andrade-Silva, A. R. Dâmaso, D. A. Caranti
International Journal of Clinical Practice.2013; 67(3): 217. CrossRef - Adiponectin/leptin ratio and insulin resistance in pregnancy
A Skvarca, M Tomazic, R Blagus, B Krhin, A Janez
Journal of International Medical Research.2013; 41(1): 123. CrossRef - Detemir (Levemir): modern paradigms of insulin therapy
L A Ruiatkina, M Iu Sorokin
Problems of Endocrinology.2013; 59(4): 56. CrossRef - Calorie restriction and cancer prevention: a mechanistic perspective
Stephen D Hursting, Sarah M Dunlap, Nikki A Ford, Marcie J Hursting, Laura M Lashinger
Cancer & Metabolism.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - Reduction in the Leptin Concentration as a Predictor of Improvement in Lung Function in Obese Adolescents
Patrícia Leão da Silva, Marco Túlio de Mello, Nadia Carla Cheik, Priscila Lima Sanches, Raquel Munhoz da Silveira Campos, June Carnier, Daniela Inoue, Claudia M.O. do Nascimento, Lila M. Oyama, Lian Tock, Sérgio Tufik, Ana R. Dâmaso
Obesity Facts.2012; 5(6): 806. CrossRef - Relationship between obesity and foot pain and its association with fat mass, fat distribution, and muscle mass
Stephanie K. Tanamas, Anita E. Wluka, Patricia Berry, Hylton B. Menz, Boyd J. Strauss, Miranda Davies‐Tuck, Joseph Proietto, John B. Dixon, Graeme Jones, Flavia M. Cicuttini
Arthritis Care & Research.2012; 64(2): 262. CrossRef - The Homeostasis Model Assessment-adiponectin (HOMA-AD) is the most sensitive predictor of insulin resistance in obese children
Emna Makni, Wassim Moalla, Gérard Lac, Chirine Aouichaoui, Daniel Cannon, Mohamed Elloumi, Zouhair Tabka
Annales d'Endocrinologie.2012; 73(1): 26. CrossRef - Leptin-to-Adiponectin, Adiponectin-to-Leptin Ratios, and Insulin Are Specific and Sensitive Markers Associated with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: A Case–Control Study from Bahrain
Jamal Golbahar, Nagalla Mohan Das, Maha Adel Al-Ayadhi, Khalid Gumaa
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2012; 10(2): 98. CrossRef - Growth Signals, Inflammation, and Vascular Perturbations
Stephen D. Hursting, Marcie J. Hursting
Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology.2012; 32(8): 1766. CrossRef - Hyperleptinemia in obese adolescents deregulates neuropeptides during weight loss
Ana R. Dâmaso, Aline de Piano, Priscila L. Sanches, Flávia Corgosinho, Lian Tock, Lila M. Oyama, Luciana Tock, Claudia M. Oller do Nascimento, Sérgio Tufik, Marco Túlio de Mello
Peptides.2011; 32(7): 1384. CrossRef - Association of the leptin to high-molecular-weight adiponectin ratio with metabolic syndrome
Ji Eu Yun, Soyoung Won, Yejin Mok, Wenying Cui, Heejin Kimm, Sun Ha Jee
Endocrine Journal.2011; 58(9): 807. CrossRef
- Effects of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on serum values of adiponectin, leptin, 8-isoprostane and malondialdehyde in women with type 2 diabetes
- Leptin is Negatively Associated with Femoral Bone Mineral Density in Postmenopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
- Jae Han Jeon, Yeun Kyung Choi, Hyun Ae Seo, Jung Eun Lee, Ji Yun Jeong, Seong Su Moon, Ju Young Lee, Jung Guk Kim, Bo Wan Kim, In Kyu Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(5):421-431. Published online October 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.5.421
- 2,147 View
- 18 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Serum leptin level and bone mineral density (BMD) are widely assumed to be positively associated with body fat mass. Numerous attempts have been made to document the relationship between leptin and BMD, but the results are inconsistent, especially in diabetic patients. METHODS: A total of 60 Korean postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus were included in the present study. The BMDs of lumbar spines (L1 to L4) and proximal femurs (trochanter, neck, and total) were measured by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA), and biochemical markers including leptin, HbA1c, C-peptide and urine albumin-creatinine ratio (ACR) were measured for each patient. RESULTS: Negative associations between leptin and BMD of femoral neck, trochanter, and total femur in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus were documented in a model adjusted for age, body fat mass, and fasting insulin level (r = -0.308, P = 0.020 and r = - 0.303, P = 0.025 and r = - 0.290, P = 0.032 respectively). Multiple linear regression analysis was performed revealing negative associations between leptin and BMD of the femoral neck (beta = -0.369), trochanter (beta = -0.324), and total femur (beta = -0.317). CONCLUSION: The results of the present study suggest a negative relationship between leptin and femoral BMD. In addition, leptin may have a negative effect on BMD in postmenopausal women with type 2 diabetes mellitus. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of bone mineral density in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients before and after treatment
MK Dutta, R Pakhetra, MK Garg
Medical Journal Armed Forces India.2012; 68(1): 48. CrossRef
- Evaluation of bone mineral density in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients before and after treatment
- The Role of Hypothalamic FoxO1 on Hyperphagia in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice.
- Il Seong Nam-Goong, Jae Geun Kim, Se Jin Kim, Seong Jae Hur, Jin Woo Lee, Eun Sook Kim, Chang Ho Yun, Byung Ju Lee, Young Il Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(5):375-381. Published online October 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.5.375
- 1,948 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Streptozotocin-induced diabetic animals are characterized by hyperphagia due to deficiencies of insulin and leptin. Forkhead box-containing protein of the O subfamily-1 (FoxO1) regulates energy homeostasis by regulating energy expenditure and food intake as well as mediating insulin and leptin signals in the hypothalamus. To identify the mediator of diabetic hyperphagia, we examined the effects of insulin or leptin on hypothalamic FoxO1 expression in a diabetic animal model. METHODS: Diabetes was induced in mice (C57BL/6) by intraperitoneal administration of streptozotocin (200 mg/kg). Stainless steel cannula was implanted into the lateral ventricle of the brain in each mouse. After three weeks, the mice were administered saline, insulin or leptin via intracerebroventricular (ICV) route. The medial hypothalamus was isolated to evaluate the mRNA expressions of FoxO1 and neuropeptides. RESULTS: Streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice exhibited significant elevations of blood glucose and food intake and significantly low levels of serum insulin and leptin. The levels of hypothalamic FoxO1 mRNA were significantly increased in diabetic mice. The hypothalamic expression of neuropeptide Y (NPY) mRNA was increased, but the expression of preproopiomelanocortin (POMC) mRNA was decreased in diabetic mice. ICV administration of insulin or leptin attenuated the upregulation of hypothalamic FoxO1 mRNA, and resulted in downregulation of NPY mRNA and upregulation of POMC mRNA in diabetic mice. CONCLUSION: We observed that the expression of hypothalamic FoxO1 mRNA was increased in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice, and that it was significantly attenuated by central administration of insulin or leptin. These results suggest that hypothalamic FoxO1 is the direct mediator of diabetic hyperphagia.
- Adipokine Concentrations in Pregnant Korean Women with Normal Glucose Tolerance and Gestational Diabetes Mellitus.
- Eun Suk Oh, Jung Hee Han, Sung Min Han, Jee Aee Im, Eun Jung Rhee, Cheol Young Park, Ki Won Oh, Won Young Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(4):279-288. Published online August 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.4.279
- 2,451 View
- 22 Download
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The aims of this study were to compare adipokine concentrations of pregnant women in the 24th~28th weeks of gestation to those of non-pregnant women. We compared the concentrations of adipokines in women with gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM), gestational impaired glucose tolerance (GIGT) and normal glucose tolerance (NGT). We also investigated the role of adipokines in the development of gestational glucose intolerance. METHODS: We surveyed 129 pregnant women who underwent a 100 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) during the 24th~28th weeks of gestation. Participants were classified into three groups: (1) NGT (n = 40), (2) GIGT (n = 45), and (3) GDM (n = 44). Pregnant subjects with NGT were matched to non-pregnant controls for BMI and age (n = 41). RESULTS: Pregnant women with NGT exhibited significantly decreased adiponectin levels and elevated leptin levels compared to non-pregnant controls. Mean plasma resistin levels were significantly higher in women with GDM and GIGT than in women with NGT. Resistin and fasting glucose were significant predictors for the development of gestational glucose intolerance. CONCLUSION: Plasma adiponectin levels were decreased and leptin levels were increased in pregnant subjects with NGT compared to BMI and age matched non-pregnant controls. Women with GDM and GIGT exhibit significantly elevated concentrations of resistin compared with women with NGT. Increased resistin levels were also associated with the development of gestational glucose intolerance. Resistin may play an important role on the development of gestational glucose intolerance in Korean women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Maternal serum level of resistin is associated with risk for gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis
Shi-Min Hu, Meng-Shi Chen, Hong-Zhuan Tan
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2019; 7(5): 585. CrossRef - Letter: Adipokines and Insulin Resistance According to Characteristics of Pregnant Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:457-65)
Ohk-Hyun Ryu
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(1): 87. CrossRef - Adipokines and Insulin Resistance According to Characteristics of Pregnant Women with Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Eon Ju Jeon, Seong Yeon Hong, Ji Hyun Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(6): 457. CrossRef
- Maternal serum level of resistin is associated with risk for gestational diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis
- Blood Leptin, Anthropometric and Biochemical Parameters in Type 2 Diabetics.
- Seong su Moon, Jae han Jeon, Jung eun Lee, Soon hong Park, Hee kyung Kim, Jeong yun Doh, Ye dal Jung, In kyu Lee, Bo wan Kim, Jung guk Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2007;31(1):75-82. Published online January 1, 2007
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2007.31.1.75
- 2,082 View
- 29 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Leptin is a hormone which is produced in adipose tissue and regulates food intake and body weight. Leptin is known to correlate with body adiposity such as body mass index. Blood leptin concentration is not different between non-diabetics and diabetics. And It affect not only food intake but may be one of the key factors in the developement of insulin resistance. Recent studies suggest a complex relationship between leptin and insulin resistance or insulin. Therefore we examined the relationship between leptin and anthropometric, biochemical parameters, and insulin resistance in type 2 diabetics. METHOD: The study subjects were 144 patients with type 2 diabetes who visited Kyungpook national university hospital. Anthropometric parameters such as body fat mass, soft lean mass, BMI, arm circumference, skin fold thickness of several sites were measured. Percent body fat were calculated from Brozek fomula, body density were calculated from Jackson and Pollock fomula. Fasting blood leptin and metabolic varables such as C-peptide, HbA1C, insulin, HDL, LDL, TG, total cholesterol, FFA, HOMA-IR were measured. The relationships of blood leptin concentration with clinical data were analyzed with SPSS program. RESULT: Blood leptin concentrations were 8.2 +/- 5.39 ng/mL in women with type 2 diabetes and 5.1 +/- 5.55 ng/mL in men with type 2 diabetes (P-value: 0.01). Percent body fat, FFA were higher in women than men but arm circumference, soft lean mass, waist circumference were higher in men than women (P-value < 0.05). Leptin concentration correlated with BMI, percent body fat, insulin, TG, body fat mass, waist circumference, HOMA-IR. And insulin, C-peptide, total cholesterol, TG were also correlated with leptin only in women with type 2 diabetes. Waist circumference and percent body fat were independent variables which influence blood leptin concentration in multiple regression analysis. CONCLUSION: Blood leptin concentrations are related to parameters such as percent body fat, waist circumference, BMI, body fat mass, insulin, TG, HOMA-IR in type 2 diabetics. The relationship between leptin and obesity or HOMA-IR suggests that leptin may be a one of factors in developement of insulin resistance. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prognostic Value of Leptin in Terminally Ill Cancer Patients
Ji Hyun Hong, So Jin Lee, Sang Mi Kwak, Youn Seon Choi, June Yeong Lee
The Korean Journal of Hospice and Palliative Care.2012; 15(2): 99. CrossRef
- Prognostic Value of Leptin in Terminally Ill Cancer Patients
- Comparison of the Relationship of Leptin to Metabolic Parameters Between Premenopausal Normal Weight and Obese Women.
- Hee Kyoung Kim, Keun Gyu Park, Mi Kyung Kim, Young Yun Jang, Sang Yoon Kim, Eui Dal Jung, Hye Soo Kim, Ju Ho Do, In Kyu Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2005;29(3):223-230. Published online May 1, 2005
- 927 View
- 17 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Leptin is mainly secreted from adipose tissue, and it is a crucial factor for metabolic syndrome that is characterized by obesity, insulin resistance, hypertension and dyslipidemia. We measured the serum leptin concentrations and compared them with the body fat distribution and metabolic risk factors in premenopausal normal weight and obese women. METHODS: 231 premenopausal obese women participated in this study. The subjects were grouped based on their body mass index(BMI). The number of normal weight group women(BMI<25kg/m2) and the number of obese group women(BMI> or = 25kg/m2) were 90 and 141, respectively. We measured the plasma leptin concentration and such metabolic risk factors as fasting glucose, insulin, triglyceride(TG), systolic blood pressure(SBP) and diastolic blood pressure(DBP). The subcutaneous adipose tissue area(SAT) and the visceral adipose tissue area(VAT) were determined by computed tomography. The BMI, waist to hip ratio(WHR) and homeostasis model assessment(HOMA-IR) were calculated. RESULTS: In the obese group, the leptin levels were positively correlated with the BMI and SAT as well as with such metabolic risk factors as fasting serum glucose, insulin, HOMA-IR, TG, SBP and DBP. Although leptin levels were positively correlated with BMI and SAT in the normal weight group, they were not correlated with the metabolic risk factors. CONCLUSION: The present study showed that the leptin levels in the normal weight group were not associated with the metabolic risk factors. Therefore, the degree of obesity must be considered before leptin can be used as a predictor for metabolic syndrome including diabetes and coronary heart disease
- The Effects of Insulin Sensitizers on the Plasma Concentrations of Adipokines in Type 2 Diabetic Patients.
- Hye Seung Jung, Young Min Cho, Kyung Won Kim, Byung Soo Youn, Kang Yeol Yu, Hong Je Park, Chan Soo Shin, Seong Yeon Kim, Hong Kyu Lee, Kyong Soo Park
- Korean Diabetes J. 2003;27(6):476-489. Published online December 1, 2003
- 1,199 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Resistin, leptin and adiponectin are proteins secreted from adipose tissue, and have been suggested to play roles in insulin sensitivity. The effects of the circulating levels of two different types of insulin sensitizer, rosiglitazone and metformin, in type 2 diabetic patients were examined to elucidate the relationship between adipokines and insulin resistance. METHODS: Thirty type 2 diabetic patients, who showed poor glycemic control when administered 4 mg glimepiride a day, without severe diabetic complications or medical illness, were randomized to receive an additional 4mg rosiglitazone or 1000 mg metformin a day. The plasma resistin, leptin and adiponectin concentrations were measured at the baseline and after 6 months of treatment. The anthropometric parameters, fasting plasma glucose, HbA1C, total cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL-cholesterol and free fatty acids were also measured. Certain single nucleotide polymorphisms of adipokine genes were also identified. RESULTS: There were no significant differences in the reductions of the plasma glucose and HbA1C levels, after 6 months of treatment, between the two groups. The plasma resistin concentrations decreased, the adiponectin significantly increased and the leptin showed a tendency to increase in the rosiglitazone group. In the metformin group, only the resistin concentration significantly increased. However, the changes in the adipokines did not correlate with the HOMA-IR in either group. The reduction in the HbA1C due to rosiglitazone was greater if the initial leptin level was high, if there was a G allele on the -420th locus of the resistin gene, or the 45th locus of the APM1 (adiponectin gene) was the T-homozygote or there was a T allele on the 276th locus of the APM1. Those due to metfromin were greater with high initial adiponectin levels. CONCLUSION: In type 2 diabetic patients, showing poor glycemic control with sulfonylurea therapy, rosiglitazone or metformin treatment changed some of the adipokine concentrations, but these changes were not clearly related with insulin resistance. Polymorphisms of certain adipokine genes seem to have a relation to the susceptibility of rosiglitazone.
- Efficacy of Serum Leptin Level as an Indicator to Predict the Clinical Response of Rosiglitazone in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
- Jae Hyuk Lee, Soo Kyung Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Han Seok Choi, Ji Young Jung, Wan Sub Shim, Hyun Joo Lee, Chul Woo Ahn, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Bong Soo Cha
- Korean Diabetes J. 2003;27(5):420-432. Published online October 1, 2003
- 1,322 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Leptin is a protein secreted by adipocytes that regulates food intake by acting on the hypothalamus and is correlated with body fat mass. Insulin resistance is also correlated with body fat mass and obesity. Rosiglitazone (RSG) is known as a highly selective and potent agonist for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARgamma). It improves glycemic control by improving insulin sensitivity in peripheral tissue. This study was performed to evaluate the antidiabetic and insulin sensitizing effects of RSG combination therapy and the efficacy of serum leptin level as an indicator to predict the clinical response of RSG in type 2 diabetic patients with oral agents such as metformin and/or sulfonylurea. METHODS: The study subjects were 140 type 2 diabetic patients (90 male, 50 female) who received a 12-week course of daily 4 mg RSG, in addition to the previous medications. The glucose level, indices of insulin resistance and metabolic parameters were measured. Serum leptin level was measured by radioimmunoassay before and after RSG treatment. Visceral fat and subcutaneous fat were measured by sonography. RESULTS: After 12 weeks of RSG treatment, FPG (12.6+/-28.1 mg/dL), HOMAIR (0.3+/-0.9), serum fasting insulin (1.9+/-4.7 microU/mL), SBP and DBP had all decreased significantly, whereas body weight, BMI, waist circumference, WHR, body fat mass, and subcutaneous fat had all increased. Serum leptin level also tended to increase after RSG treatment, but without significance. deltaFPG (delta=value after treatment- value before treatent) was inversely correlated with basal serum leptin level (r=-0.202), basal HOMAIR (r=-0.226) and basal FPG (r=-0.565). There was no correlation between deltaFPG and basal BMI or serum insulin level. RSG treatment showed significant inverse correlation between serum leptin level and deltaHOMAIR (r=-0.416), delta insulin (r=-0.365) and deltaHbA1c (r=-0.189). Serum leptin level was positively correlated with the subcutaneous fat amount (r=0.548), basal BMI (r=0.521), and basal HOMAIR (r=0.343). CONCLUSION: These results showed that RSG treatment can improve not only hyperglycemia but also insulin resistance in type 2 diabetic patients. The serum leptin level at baseline can be used as an indicator to predict the clinical response of RSG treatment in type 2 diabetes patients.
- Association between Hyperleptinemia and Metabolic Syndrome in an Urban Korean Community.
- Jee Young Oh, Young Sun Hong, Yeon Ah Sung
- Korean Diabetes J. 2003;27(4):313-322. Published online August 1, 2003
- 1,035 View
- 18 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
To determine whether hyperleptinemia is a principal component of metabolic syndrome in a Korean population using factor analysis. METHODS: Metabolic syndrome was defined by the NCEP-ATP III guideline. An oral glucose tolerance test was performed, and plasma samples for leptin and lipid profiles were collected from 199 men and 426 women who had no history of diabetes, hypertension, dyslipidemia, or of taking lipid-lowering, antihypertensive, or antihyperglycemic medications. RESULTS: Leptin level was correlated with overall and central obesity, blood pressure, and glucose or insulin levels in men and women aged 30 to 83. Before and after adjustment for BMI, leptin level was significantly and positively correlated, in women only, with insulin and with insulin resistance, as assessed by a homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) (Ps<0.0001). Factor analysis identified the following four factors from among the metabolic syndrome variables; an obesity/hyperinsulinemia factor, a glucose intolerance factor, a hypertension factor, and a dyslipidemia factor in men. Leptin was clustered as an obesity/ hyperinsulinemia and a dyslipidemia factor in men. In women, four different groups were found: an obesity/hypertension factor, a glucose intolerance factor, an obesity/dyslipidemia factor, and an obesity/hyperinsulinemia factor. Leptin was clustered as an obesity/hyperinsulinemia factor in women. CONCLUSION: Our research suggests that leptin level is associated with metabolic syndrome in relation to obesity and hyperinsulinemia. Moreover, obesity, as opposed to hyperinsulinemia, is related to hypertension or dyslipidemia in women only, and this gender differences may reflect different roles of central adiposity on metabolic abnormalities.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





