
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: New Regulator in Lipid Metabolism
- Tong Bu, Ziyan Sun, Yi Pan, Xia Deng, Guoyue Yuan
- Received August 14, 2023 Accepted January 1, 2024 Published online April 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0277 [Epub ahead of print]
- 623 View
- 22 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
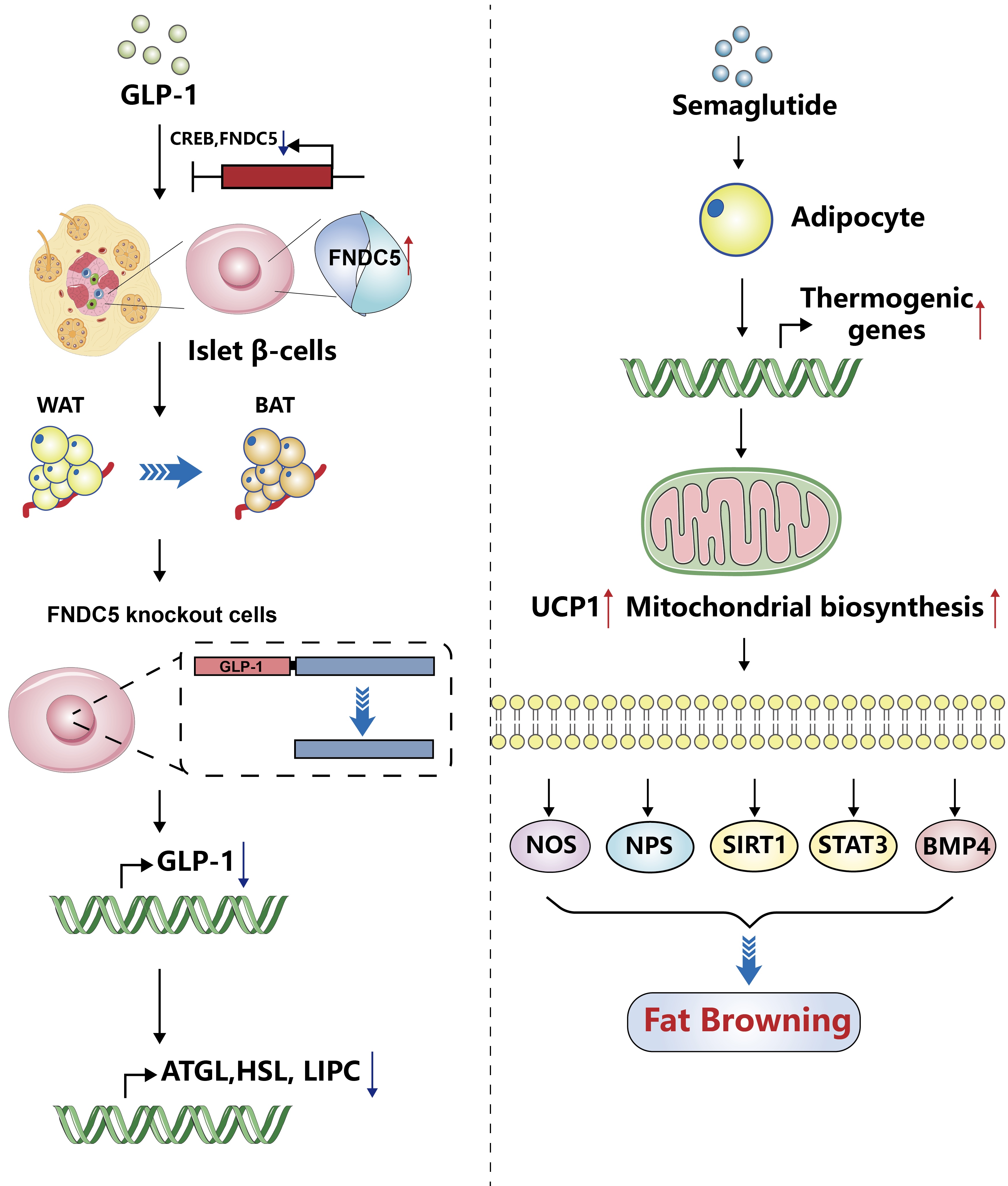
ePub - Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a 30-amino acid peptide hormone that is mainly expressed in the intestine and hypothalamus. In recent years, basic and clinical studies have shown that GLP-1 is closely related to lipid metabolism, and it can participate in lipid metabolism by inhibiting fat synthesis, promoting fat differentiation, enhancing cholesterol metabolism, and promoting adipose browning. GLP-1 plays a key role in the occurrence and development of metabolic diseases such as obesity, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, and atherosclerosis by regulating lipid metabolism. It is expected to become a new target for the treatment of metabolic disorders. The effects of GLP-1 and dual agonists on lipid metabolism also provide a more complete treatment plan for metabolic diseases. This article reviews the recent research progress of GLP-1 in lipid metabolism.
- Basic Research
- Glucagon-Like Peptide Receptor Agonist Inhibits Angiotensin II-Induced Proliferation and Migration in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells and Ameliorates Phosphate-Induced Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Calcification
- Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Min-Jeong Kim, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):83-96. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0363
- 1,756 View
- 168 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
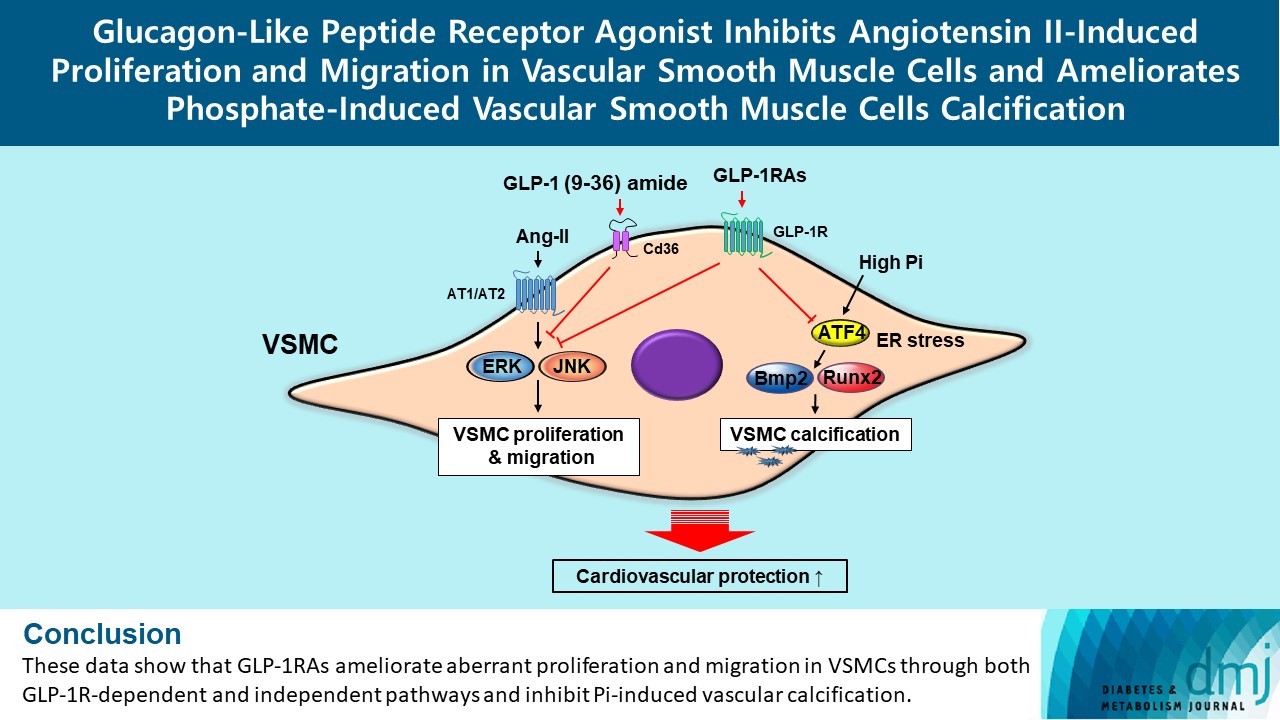
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA), which is a therapeutic agent for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, has a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system.
Methods
To examine the protective effects of GLP-1RAs on proliferation and migration of vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs), A-10 cells exposed to angiotensin II (Ang II) were treated with either exendin-4, liraglutide, or dulaglutide. To examine the effects of GLP-1RAs on vascular calcification, cells exposed to high concentration of inorganic phosphate (Pi) were treated with exendin-4, liraglutide, or dulaglutide.
Results
Ang II increased proliferation and migration of VSMCs, gene expression levels of Ang II receptors AT1 and AT2, proliferation marker of proliferation Ki-67 (Mki-67), proliferating cell nuclear antigen (Pcna), and cyclin D1 (Ccnd1), and the protein expression levels of phospho-extracellular signal-regulated kinase (p-Erk), phospho-c-JUN N-terminal kinase (p-JNK), and phospho-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (p-Pi3k). Exendin-4, liraglutide, and dulaglutide significantly decreased the proliferation and migration of VSMCs, the gene expression levels of Pcna, and the protein expression levels of p-Erk and p-JNK in the Ang II-treated VSMCs. Erk inhibitor PD98059 and JNK inhibitor SP600125 decreased the protein expression levels of Pcna and Ccnd1 and proliferation of VSMCs. Inhibition of GLP-1R by siRNA reversed the reduction of the protein expression levels of p-Erk and p-JNK by exendin-4, liraglutide, and dulaglutide in the Ang II-treated VSMCs. Moreover, GLP-1 (9-36) amide also decreased the proliferation and migration of the Ang II-treated VSMCs. In addition, these GLP-1RAs decreased calcium deposition by inhibiting activating transcription factor 4 (Atf4) in Pi-treated VSMCs.
Conclusion
These data show that GLP-1RAs ameliorate aberrant proliferation and migration in VSMCs through both GLP-1Rdependent and independent pathways and inhibit Pi-induced vascular calcification. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Incretin Hormone Secretion in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Roles of Obesity, Insulin Sensitivity and Treatment with Metformin and GLP-1s
Andrea Etrusco, Mislav Mikuš, Antonio D’Amato, Fabio Barra, Petar Planinić, Trpimir Goluža, Giovanni Buzzaccarini, Jelena Marušić, Mara Tešanović, Antonio Simone Laganà
Biomedicines.2024; 12(3): 653. CrossRef
- Incretin Hormone Secretion in Women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Roles of Obesity, Insulin Sensitivity and Treatment with Metformin and GLP-1s
- Basic Research
- DA-1241, a Novel GPR119 Agonist, Improves Hyperglycaemia by Inhibiting Hepatic Gluconeogenesis and Enhancing Insulin Secretion in Diabetic Mice
- Youjin Kim, Si Woo Lee, Hyejin Wang, Ryeong-Hyeon Kim, Hyun Ki Park, Hangkyu Lee, Eun Seok Kang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):337-348. Published online January 21, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0056
- 5,556 View
- 276 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We investigated the antidiabetic effects of DA-1241, a novel G protein-coupled receptor (GPR) 119 agonist, in vitro and in vivo.
Methods
DA-1241 was administrated to high-fat diet (HFD)-fed C57BL/6J mice for 12 weeks after hyperglycaemia developed. Oral/intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test and insulin tolerance test were performed. Serum insulin and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) levels were measured during oral glucose tolerance test. Insulinoma cell line (INS-1E) cells and mouse islets were used to find whether DA-1241 directly stimulate insulin secretion in beta cell. HepG2 cells were used to evaluate the gluconeogenesis and autophagic process. Autophagic flux was evaluated by transfecting microtubule-associated protein 1 light chain 3-fused to green fluorescent protein and monomeric red fluorescent (mRFP-GFP-LC3) expression vector to HepG2 cells.
Results
Although DA-1241 treatment did not affect body weight gain and amount of food intake, fasting blood glucose level decreased along with increase in GLP-1 level. DA-1241 improved only oral glucose tolerance test and showed no effect in intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test. No significant effect was observed in insulin tolerance test. DA-1241 did not increase insulin secretion in INS-1E cell and mouse islets. DA-1241 reduced triglyceride content in the liver thereby improved fatty liver. Additionally, DA-1241 reduced gluconeogenic enzyme expression in HepG2 cells and mouse liver. DA-1241 reduced autophagic flow in HepG2 cells.
Conclusion
These findings suggested that DA-1241 augmented glucose-dependent insulin release via stimulation of GLP-1 secretion, and reduced hepatic gluconeogenesis, which might be associated with autophagic blockage, leading to improved glycaemic control. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- G protein-coupled receptors driven intestinal glucagon-like peptide-1 reprogramming for obesity: Hope or hype?
Mohan Patil, Ilaria Casari, Leon N. Warne, Marco Falasca
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2024; 172: 116245. CrossRef - GPR119 agonists for type 2 diabetes: past failures and future hopes for preclinical and early phase candidates
Deanne H Hryciw, Rhiannon K Patten, Raymond J Rodgers, Joseph Proietto, Dana S Hutchinson, Andrew J McAinch
Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs.2024; 33(3): 183. CrossRef - Immunomodulation through Nutrition Should Be a Key Trend in Type 2 Diabetes Treatment
Katarzyna Napiórkowska-Baran, Paweł Treichel, Marta Czarnowska, Magdalena Drozd, Kinga Koperska, Agata Węglarz, Oskar Schmidt, Samira Darwish, Bartłomiej Szymczak, Zbigniew Bartuzi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(7): 3769. CrossRef - Discovery of orally active sulfonylphenyl thieno[3,2-d]pyrimidine derivatives as GPR119 agonists
Heecheol Kim, Minjung Kim, Kyujin Oh, Sohee Lee, Sunyoung Lim, Sangdon Lee, Young Hoon Kim, Kwee Hyun Suh, Kyung Hoon Min
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2023; 258: 115584. CrossRef - Increased expression of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 and O-GlcNAcylation in hepatocytes drives non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Hye Jin Chun, Eun Ran Kim, Minyoung Lee, Da Hyun Choi, Soo Hyun Kim, Eugene Shin, Jin-Hong Kim, Jin Won Cho, Dai Hoon Han, Bong-Soo Cha, Yong-ho Lee
Metabolism.2023; 145: 155612. CrossRef - Human skin stem cell-derived hepatic cells as in vitro drug discovery model for insulin-driven de novo lipogenesis
Karolien Buyl, Martine Vrints, Ruani Fernando, Terry Desmae, Thomas Van Eeckhoutte, Mia Jans, Jan Van Der Schueren, Joost Boeckmans, Robim M. Rodrigues, Veerle De Boe, Vera Rogiers, Joery De Kock, Filip Beirinckx, Tamara Vanhaecke
European Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 957: 175989. CrossRef - GPR119 activation by DA-1241 alleviates hepatic and systemic inflammation in MASH mice through inhibition of NFκB signaling
Seung-Ho Lee, Hansu Park, Eun-Kyoung Yang, Bo Ram Lee, Il-Hoon Jung, Tae-Hyoung Kim, Moon Jung Goo, Yuna Chae, Mi-Kyung Kim
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 166: 115345. CrossRef - Characteristics of the Latest Therapeutic Agent for Diabetes
Nuri Yun
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(3): 148. CrossRef - DA-1241, a Novel GPR119 Agonist, Improves Hyperglycaemia by Inhibiting Hepatic Gluconeogenesis and Enhancing Insulin Secretion in Diabetic Mice
Youjin Kim, Si Woo Lee, Hyejin Wang, Ryeong-Hyeon Kim, Hyun Ki Park, Hangkyu Lee, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 337. CrossRef - Autophagy Dysregulation in Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A New Therapeutic Target
Chun-Liang Chen, Yu-Cheng Lin
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(17): 10055. CrossRef
- G protein-coupled receptors driven intestinal glucagon-like peptide-1 reprogramming for obesity: Hope or hype?
- Drug/Regimen
-
- Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Differentially Affects Brain Activation in Response to Visual Food Cues in Lean and Obese Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jae Hyun Bae, Hyung Jin Choi, Kang Ik Kevin Cho, Lee Kyung Kim, Jun Soo Kwon, Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):248-259. Published online November 4, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0018
- 7,407 View
- 222 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background To investigate the effects of a glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist on functional brain activation in lean and obese individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in response to visual food cues.
Methods In a randomized, single-blinded, crossover study, 15 lean and 14 obese individuals with T2DM were administered lixisenatide or normal saline subcutaneously with a 1-week washout period. We evaluated brain activation in response to pictures of high-calorie food, low-calorie food, and nonfood using functional magnetic resonance imaging and measured appetite and caloric intake in participants who were given access to an
ad libitum buffet.Results Obese individuals with T2DM showed significantly greater activation of the hypothalamus, pineal gland, parietal cortex (high-calorie food vs. low-calorie food,
P <0.05), orbitofrontal cortex (high-calorie food vs. nonfood,P <0.05), and visual cortex (food vs. nonfood,P <0.05) than lean individuals with T2DM. Lixisenatide injection significantly reduced the functional activation of the fusiform gyrus and lateral ventricle in obese individuals with T2DM compared with that in lean individuals with T2DM (nonfood vs. high-calorie food,P <0.05). In addition, in individuals who decreased their caloric intake after lixisenatide injection, there were significant interaction effects between group and treatment in the posterior cingulate, medial frontal cortex (high-calorie food vs. low-calorie food,P <0.05), hypothalamus, orbitofrontal cortex, and temporal lobe (food vs. nonfood,P <0.05).Conclusion Brain responses to visual food cues were different in lean and obese individuals with T2DM. In addition, acute administration of lixisenatide differentially affected functional brain activation in these individuals, especially in those who decreased their caloric intake after lixisenatide injection.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Altered Metabolic Phenotypes and Hypothalamic Neuronal Activity Triggered by Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:784-95)
Jae Hyun Bae
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(1): 157. CrossRef - Diabetes remission and relapse following an intensive metabolic intervention combining insulin glargine/lixisenatide, metformin and lifestyle approaches: Results of a randomised controlled trial
Natalia McInnes, Stephanie Hall, Heather A. Lochnan, Stewart B. Harris, Zubin Punthakee, Ronald J. Sigal, Irene Hramiak, Mohammed Azharuddin, Joanne F. Liutkus, Jean‐François Yale, Farah Sultan, Ada Smith, Rose E. Otto, Diana Sherifali, Yan Yun Liu, Hertz
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(11): 3347. CrossRef - Glucagon-like peptide-1 analog therapy in rare genetic diseases: monogenic obesity, monogenic diabetes, and spinal muscular atrophy
Hussein Zaitoon, Ronit Lubetzky, Achiya Z. Amir, Hadar Moran-Lev, Liora Sagi, Michal Yacobi-Bach, Ophir Borger, Efrat Chorna, Yael Lebenthal, Avivit Brener
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(8): 1099. CrossRef - What can functional brain imaging teach us about remission of type 2 diabetes?
Dhruti Hirani, Shahd Alabdulkader, Alexander. D. Miras, Victoria Salem
Diabetic Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Fasting oxyntomodulin, glicentin, and gastric inhibitory polypeptide levels are associated with activation of reward‐ and attention‐related brain centres in response to visual food cues in adults with obesity: A cross‐sectional functional MRI study
Nikolaos Perakakis, Olivia M. Farr, Christos S. Mantzoros
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(5): 1202. CrossRef - Aberrant Brain Functional Connectivity Strength and Effective Connectivity in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Xi Guo, Su Wang, Yu-Chen Chen, Heng-Le Wei, Gang-Ping Zhou, Yu-Sheng Yu, Xindao Yin, Kun Wang, Hong Zhang, Eusebio Chiefari
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef
- Altered Metabolic Phenotypes and Hypothalamic Neuronal Activity Triggered by Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibition (Diabetes Metab J 2023;47:784-95)
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Premeal Consumption of a Protein-Enriched, Dietary Fiber-Fortified Bar Decreases Total Energy Intake in Healthy Individuals
- Chang Ho Ahn, Jae Hyun Bae, Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):879-892. Published online June 25, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0202
- 5,025 View
- 84 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background A premeal load of protein can increase satiety and reduce energy intake. Dietary fiber also conveys metabolic benefits by modulating energy intake. We made a protein-enriched, dietary fiber-fortified bar (PFB) and aimed to investigate its effects on food intake and gut hormone secretion in healthy individuals.
Methods Twenty subjects with normal glucose tolerance were enrolled. On three separate visits, the subjects received, in a randomized order, one of the following: a PFB containing 73 kcal with 10.7 g of protein and 12.7 g of dietary fiber; a usual bar (UB) containing the same calories as the PFB but only 0.9 g of protein and no dietary fiber; or water (control). After 15 minutes, the subjects had
ad libitum intake of a test meal. Food consumption, appetite, and plasma gut hormone levels were measured.Results Total energy intake, including the bar and the test meal, was significantly reduced with the PFB preload compared to the water (904.4±534.9 kcal vs. 1,075.0±508.0 kcal,
P =0.016). With the UB preload, only the intake of the test meal was reduced (P =0.044) but not the total energy intake (P =0.471) than the water. Fullness was also significantly increased after the PFB. In addition, postprandial glucose levels decreased and glucagon-like peptide-1 levels increased with the PFB compared with both the UB and water.Conclusion In healthy individuals, a premeal supplementation of PFB reduced total energy intake and decreased postprandial glucose excursion. This finding necessitates long-term studies regarding clinical use in obesity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Citrus pectin protects mice from burn injury by modulating intestinal microbiota, GLP-1 secretion and immune response
Ji-Wei Hao, Hong-Sheng Liu, Ling-Ying Liu, Qing-Hong Zhang
International Immunopharmacology.2024; 131: 111912. CrossRef - Effect of Two Different Meal Compositions on 1-hour Plasma Ghrelin Levels in Young Men
Brinnell Annette Caszo, Sangeetha Shyam, Purushotham Krishnappa, Justin Vijay Gnanou
Malaysian Journal of Medicine and Health Sciences.2023; 19(5): 185. CrossRef - Intake of Fibre-Associated Foods and Texture Preferences in Relation to Weight Status Among 9–12 Years Old Children in 6 European Countries
Marlies Hörmann-Wallner, Raphaela Krause, Begoña Alfaro, Hannah Jilani, Monica Laureati, Valérie L. Almli, Mari Sandell, Pernilla Sandvik, Gertrude G. Zeinstra, Lisa Methven
Frontiers in Nutrition.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Response: Premeal Consumption of a Protein-Enriched, Dietary Fiber-Fortified Bar Decreases Total Energy Intake in Healthy Individuals (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:879–92)
Chang Ho Ahn, Jae Hyun Bae, Young Min Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 207. CrossRef - Letter: Premeal Consumption of a Protein-Enriched, Dietary Fiber-Fortified Bar Decreases Total Energy Intake in Healthy Individuals (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:879–92)
Mi-kyung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 203. CrossRef - Spent coffee (Coffea arabicaL.) grounds promote satiety and attenuate energy intake: A pilot study
Rocio Campos‐Vega, Andrea Arreguín‐Campos, Miguel A. Cruz‐Medrano, María Dolores Castillo Bilbao
Journal of Food Biochemistry.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Citrus pectin protects mice from burn injury by modulating intestinal microbiota, GLP-1 secretion and immune response
- Pathophysiology
- Factors Related to Blood Intact Incretin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Soyeon Yoo, Eun-Jin Yang, Gwanpyo Koh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(4):495-503. Published online February 20, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0105
- 3,926 View
- 36 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We performed this study to identify factors related to intact incretin levels in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods We cross-sectionally analyzed 336 patients with T2DM. Intact glucagon-like peptide 1 (iGLP-1) and intact glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (iGIP) levels were measured in a fasted state and 30 minutes after ingestion of a standard mixed meal. The differences between 30 and 0 minute iGLP-1 and iGIP levels were indicated as ΔiGLP-1 and ΔiGIP.
Results In simple correlation analyses, fasting iGLP-1 was positively correlated with glucose, C-peptide, creatinine, and triglyceride levels, and negatively correlated with estimated glomerular filtration rate. ΔiGLP-1 was positively correlated only with ΔC-peptide levels. Fasting iGIP showed positive correlations with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and fasting glucose levels, and negative correlations with ΔC-peptide levels. ΔiGIP was negatively correlated with diabetes duration and HbA1c levels, and positively correlated with Δglucose and ΔC-peptide levels. In multivariate analyses adjusting for age, sex, and covariates, fasting iGLP-1 levels were significantly related to fasting glucose levels, ΔiGLP-1 levels were positively related to ΔC-peptide levels, fasting iGIP levels were related to fasting C-peptide levels, and ΔiGIP levels were positively related to ΔC-peptide and Δglucose levels.
Conclusion Taken together, intact incretin levels are primarily related to C-peptide and glucose levels. This result suggests that glycemia and insulin secretion are the main factors associated with intact incretin levels in T2DM patients.
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
-
- Asian Subpopulations May Exhibit Greater Cardiovascular Benefit from Long-Acting Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists: A Meta-Analysis of Cardiovascular Outcome Trials
- Yu Mi Kang, Yun Kyung Cho, Jiwoo Lee, Seung Eun Lee, Woo Je Lee, Joong-Yeol Park, Ye-Jee Kim, Chang Hee Jung, Michael A. Nauck
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(4):410-421. Published online December 27, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0070
- 6,359 View
- 137 Download
- 18 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Based on reported results of three large cardiovascular outcome trials (CVOTs) of glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs), we aimed to investigate the overall effect of GLP-1 RAs on major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) and to identify subpopulations exhibiting the greatest cardiovascular (CV) benefit.
Methods Three CVOTs reporting effects of long-acting GLP-1 RAs were included: LEADER (liraglutide), SUSTAIN-6 (semaglutide), and EXSCEL (exenatide once weekly). In all studies, the primary endpoint was three-point MACE, comprising CV death, non-fatal myocardial infarction, and non-fatal stroke. Overall effect estimates were calculated as hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) using the random-effects model; subgroup analyses reported in the original studies were similarly analyzed.
Results Overall, statistically significant risk reductions in MACE and CV death were observed. Subgroup analysis indicated a significant racial difference with respect to CV benefit (
P for interaction <0.001), and more substantial risk reductions were observed in subjects of African origin (relative risk [RR], 0.78; 95% CI, 0.60 to 0.99) and in Asians (RR, 0.35; 95% CI, 0.09 to 1.32). However,post hoc analysis (Bonferroni method) revealed that only Asians exhibited a significantly greater CV benefit from treatment, compared with white subjects (P <0.0001).Conclusion Long-acting GLP-1 RAs reduced risks of MACE and CV deaths in high-risk patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Our findings of a particularly effective reduction in CV events with GLP-1 RA in Asian populations merits further exploration and dedicated trials in specific populations.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sex, racial, ethnic, and geographical disparities in major adverse cardiovascular outcome of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists among patients with and without diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomized controlled trials,
Frederick Berro Rivera, Nathan Ross B. Bantayan, John Paul Aparece, Linnaeus Louisse A. Cruz, John Vincent Magallong, Polyn Luz Pine, Anne Mira Nicca Idian-Javier, Grace Nooriza O. Lumbang, Edgar V. Lerma, Kyla M. Lara-Breitinger, Martha Gulati, Krishnasw
Journal of Clinical Lipidology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Coronary Artery Disease in South Asian Patients: Cardiovascular Risk Factors, Pathogenesis and Treatments
Vincenzo Sucato, Giuseppe Coppola, Girolamo Manno, Giuseppe Vadalà, Giuseppina Novo, Egle Corrado, Alfredo Ruggero Galassi
Current Problems in Cardiology.2023; 48(8): 101228. CrossRef - Retrospective Analysis of the Effectiveness of Oral Semaglutide in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Its Effect on Cardiometabolic Parameters in Japanese Clinical Settings
Hodaka Yamada, Masashi Yoshida, Shunsuke Funazaki, Jun Morimoto, Shiori Tonezawa, Asuka Takahashi, Shuichi Nagashima, Kimura Masahiko, Otsuka Kiyoshi, Kazuo Hara
Journal of Cardiovascular Development and Disease.2023; 10(4): 176. CrossRef - Efficacy of treatment with glucagon-like peptide receptor agonists-1 in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
L. Yu. Khamnueva, L. S. Andreeva
Problems of Endocrinology.2023; 69(2): 38. CrossRef - Role of diabetes in stroke: Recent advances in pathophysiology and clinical management
Sian A. Bradley, Kevin J. Spring, Roy G. Beran, Dimitrios Chatzis, Murray C. Killingsworth, Sonu M. M. Bhaskar
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity Pillars Roundtable: Obesity and East Asians
Harold Edward Bays, Jennifer Ng, Jeffrey Sicat, Michelle Look
Obesity Pillars.2022; 2: 100011. CrossRef - Pathophysiology, phenotypes and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Indian and Chinese populations
Calvin Ke, K. M. Venkat Narayan, Juliana C. N. Chan, Prabhat Jha, Baiju R. Shah
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2022; 18(7): 413. CrossRef - Effect of race on cardiometabolic responses to once-weekly exenatide: insights from the Exenatide Study of Cardiovascular Event Lowering (EXSCEL)
Timothy M. E. Davis, Anna Giczewska, Yuliya Lokhnygina, Robert J. Mentz, Naveed Sattar, Rury R. Holman
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Generalizability of the Results of Cardiovascular Outcome Trials of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists in Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Xiaoling Cai, Linong Ji
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(7): 1861. CrossRef - Current trends in epidemiology of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular risk management in type 2 diabetes
Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Metabolism.2021; 123: 154838. CrossRef - Sex and ethnic differences in the cardiovascular complications of type 2 diabetes
Jian L. Yeo, Emer M. Brady, Gerry P. McCann, Gaurav S. Gulsin
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 12: 204201882110342. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yuan Zhu, Jiao Xu, Dong Zhang, Xingyu Mu, Yi Shi, Shangtao Chen, Zengxiang Wu, Shuangqing Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of dulaglutide in type 2 diabetes patients in endocrinology clinics of Islamabad, Pakistan
Matiullah Kamin, SajjadAli Khan, UmarYousaf Raja, Osama Ishtiaq, Asmara Malik, Tejhmal Rehman, MuhammadUmar Wahab
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 25(5): 456. CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in South Asians: a Unique Population with a Growing Challenge
Afreen I. Shariff, Nitya Kumar, William S. Yancy, Leonor Corsino
Current Diabetes Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Antihypertensive and Renal Mechanisms of SGLT2 (Sodium-Glucose Linked Transporter 2) Inhibitors
Christopher S. Wilcox
Hypertension.2020; 75(4): 894. CrossRef - Subpopulation Differences in the Cardiovascular Efficacy of Long-Acting Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Liyun He, Na Yang, Lingling Xu, Fan Ping, Wei Li, Yuxiu Li, Huabing Zhang
Diabetes Therapy.2020; 11(9): 2121. CrossRef - 2020 Consensus of Taiwan Society of Cardiology on the pharmacological management of patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases
Chern-En Chiang, Kwo-Chang Ueng, Ting-Hsing Chao, Tsung-Hsien Lin, Yih-Jer Wu, Kang-Ling Wang, Shih-Hsien Sung, Hung-I Yeh, Yi-Heng Li, Ping-Yen Liu, Kuan-Cheng Chang, Kou-Gi Shyu, Jin-Long Huang, Cheng-Dao Tsai, Huei-Fong Hung, Ming-En Liu, Tze-Fan Chao,
Journal of the Chinese Medical Association.2020; 83(7): 587. CrossRef - Beneficial effect of anti-diabetic drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung-Soo Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2020; 26(4): 430. CrossRef
- Sex, racial, ethnic, and geographical disparities in major adverse cardiovascular outcome of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists among patients with and without diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of placebo-controlled randomized controlled trials,
- Effects of a 6-Month Exenatide Therapy on HbA1c and Weight in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study
- Juyoung Shin, Jin-Sun Chang, Hun-Sung Kim, Sun-Hee Ko, Bong-Yun Cha, Ho-Young Son, Kun-Ho Yoon, Jae-Hyoung Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(5):364-370. Published online October 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.5.364
- 3,526 View
- 37 Download
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background While many studies have shown the good efficacy and safety of exenatide in patients with diabetes, limited information is available about exenatide in clinical practice in Korean populations. Therefore, this retrospective cohort study was designed to analyze the effects of exenatide on blood glucose level and body weight in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods We reviewed the records of the patients with diabetes who visited Seoul St. Mary's Hospital and for whom exenatide was prescribed from June 2009 to October 2011. After excluding subjects based on their race/ethnicity, medical history, whether or not they changed more than 2 kinds of oral hypoglycemic agents with exenatide treatment, loss to follow-up, or whether they stopped exenatide therapy within 6 months, a total of 52 subjects were included in the final analysis.
Results The mean glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level and weight remarkably decreased from 8.5±1.7% to 6.7±1.0% (
P <0.001) and from 82.3±15.8 kg to 78.6±16.3 kg (P <0.001), respectively. The multiple regression analysis indicated that the reduction in HbA1c level was significantly associated with a shorter duration of diabetes, a higher baseline HbA1c level, and greater weight reduction, whereas weight loss had no significant correlation with other factors. No severe adverse events were observed.Conclusion These results suggest that a 6-month exenatide injection therapy significantly improved patients' HbA1c levels and body weights without causing serious adverse effects in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical and Genetic Predictors of Glycemic Control and Weight Loss Response to Liraglutide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Artemis Kyriakidou, Angeliki V. Kyriazou, Theocharis Koufakis, Yiannis Vasilopoulos, Maria Grammatiki, Xanthippi Tsekmekidou, Iakovos Avramidis, Stefanos Baltagiannis, Dimitrios G. Goulis, Pantelis Zebekakis, Kalliopi Kotsa
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(3): 424. CrossRef - Insulin receptor signaling and glucagon-like peptide 1 effects on pancreatic beta cells
Nunzia Caporarello, Cristina Parrino, Vincenzo Trischitta, Lucia Frittitta, Claudia Miele
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(8): e0181190. CrossRef - Exenatide versus Insulin Lispro Added to Basal Insulin in a Subgroup of Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kun-Ho Yoon, Elise Hardy, Jenny Han
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(1): 69. CrossRef - Acarbose reduces body weight irrespective of glycemic control in patients with diabetes: results of a worldwide, non-interventional, observational study data pool
Oliver Schnell, Jianping Weng, Wayne H.-H. Sheu, Hirotaka Watada, Sanjay Kalra, Sidartawan Soegondo, Noriyuki Yamamoto, Rahul Rathod, Cheryl Zhang, Wladyslaw Grzeszczak
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2016; 30(4): 628. CrossRef - Determining Predictors of Early Response to Exenatide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Muhammad Khan, Jing Ouyang, Karen Perkins, Sunil Nair, Franklin Joseph
Journal of Diabetes Research.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - The Role of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes: Understanding How Data Can Inform Clinical Practice in Korea
Seungjoon Oh, Suk Chon, Kyu Jeong Ahn, In-Kyung Jeong, Byung-Joon Kim, Jun Goo Kang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(3): 177. CrossRef - Tolerability, effectiveness and predictive parameters for the therapeutic usefulness of exenatide in obese, Korean patients with type 2 diabetes
Sun Ok Song, Kwang Joon Kim, Byung‐Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2014; 5(5): 554. CrossRef - From endocrine to rheumatism: do gut hormones play roles in rheumatoid arthritis?
C.-Y. Chen, C.-Y. Tsai
Rheumatology.2014; 53(2): 205. CrossRef - Early use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) in Type 2 diabetes
Stuart A. Ross, Jane Ballantine
Current Medical Research and Opinion.2013; 29(12): 1617. CrossRef
- Clinical and Genetic Predictors of Glycemic Control and Weight Loss Response to Liraglutide in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- GLP-1 Receptor Agonist and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(4):262-267. Published online August 20, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.4.262
- 5,273 View
- 68 Download
- 57 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), one of the most common liver diseases, is caused by the disruption of hepatic lipid homeostasis. It is associated with insulin resistance as seen in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is an incretin that increases insulin sensitivity and aids glucose metabolism. In recent
in vivo andin vitro studies, GLP-1 presents a novel therapeutic approach against NAFLD by increasing fatty acid oxidation, decreasing lipogenesis, and improving hepatic glucose metabolism. In this report, we provide an overview of the role and mechanism of GLP-1 in relieving NAFLD.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The intestine as an endocrine organ and the role of gut hormones in metabolic regulation
Rula Bany Bakar, Frank Reimann, Fiona M. Gribble
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2023; 20(12): 784. CrossRef - GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Current Evidence and Future Perspectives
Riccardo Nevola, Raffaella Epifani, Simona Imbriani, Giovanni Tortorella, Concetta Aprea, Raffaele Galiero, Luca Rinaldi, Raffaele Marfella, Ferdinando Carlo Sasso
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(2): 1703. CrossRef - From Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease to Liver Cancer: Microbiota and Inflammation as Key Players
Avilene Rodríguez-Lara, Ascensión Rueda-Robles, María José Sáez-Lara, Julio Plaza-Diaz, Ana I. Álvarez-Mercado
Pathogens.2023; 12(7): 940. CrossRef - Investigating the Opposing Effect of Two Different Green Tea Supplements on Oxidative Stress, Mitochondrial Function and Cell Viability in HepG2 Cells
Aparna Shil, Chris Davies, Lata Gautam, Justin Roberts, Havovi Chichger
Journal of Dietary Supplements.2022; 19(4): 459. CrossRef - Antiobesity therapeutics with complementary dual‐agonist activities at glucagon and glucagon‐like peptide 1 receptors
Bong Gyu Park, Gyeong Min Kim, Hye‐Jin Lee, Jae Ha Ryu, Dong‐Hoon Kim, Jae‐Young Seong, Soojeong Kim, Zee‐Yong Park, Young‐Joon Kim, Jaemin Lee, Jae Il Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(1): 50. CrossRef - The anti-inflammatory feature of glucagon-like peptide-1 and its based diabetes drugs—Therapeutic potential exploration in lung injury
Juan Pang, Jia Nuo Feng, Wenhua Ling, Tianru Jin
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B.2022; 12(11): 4040. CrossRef - Deficiency of peroxisomal NUDT7 stimulates de novo lipogenesis in hepatocytes
Jinsoo Song, In-Jeoung Baek, Sujeong Park, Jinjoo Oh, Deokha Kim, Kyung Song, Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Won Lee, Byoung Kuk Jang, Eun-Jung Jin
iScience.2022; 25(10): 105135. CrossRef - Gut–Liver Axis and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Vicious Circle of Dysfunctions Orchestrated by the Gut Microbiome
Salvatore Pezzino, Maria Sofia, Gloria Faletra, Chiara Mazzone, Giorgia Litrico, Gaetano La Greca, Saverio Latteri
Biology.2022; 11(11): 1622. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of semaglutide for weight management: evidence from the STEP program
Anastassia Amaro, Danny Sugimoto, Sean Wharton
Postgraduate Medicine.2022; 134(sup1): 5. CrossRef - Incretin Hormones in Obesity and Related Cardiometabolic Disorders: The Clinical Perspective
Joanna Michałowska, Ewa Miller-Kasprzak, Paweł Bogdański
Nutrients.2021; 13(2): 351. CrossRef - Insights into the Impact of Microbiota in the Treatment of NAFLD/NASH and Its Potential as a Biomarker for Prognosis and Diagnosis
Julio Plaza-Díaz, Patricio Solis-Urra, Jerónimo Aragón-Vela, Fernando Rodríguez-Rodríguez, Jorge Olivares-Arancibia, Ana I. Álvarez-Mercado
Biomedicines.2021; 9(2): 145. CrossRef - A comprehensive review for gut microbes: technologies, interventions, metabolites and diseases
Changlu Qi, Ping Wang, Tongze Fu, Minke Lu, Yiting Cai, Xu Chen, Liang Cheng
Briefings in Functional Genomics.2021; 20(1): 42. CrossRef - Update on the effects of GLP-1 receptor agonists for the treatment of polycystic ovary syndrome
Maka Siamashvili, Stephen N. Davis
Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology.2021; 14(9): 1081. CrossRef - Mechanistic and physiological approaches of fecal microbiota transplantation in the management of NAFLD
Manisha Gupta, Pawan Krishan, Amarjot Kaur, Sandeep Arora, Nirupma Trehanpati, Thakur Gurjeet Singh, Onkar Bedi
Inflammation Research.2021; 70(7): 765. CrossRef - Retrospective analysis (2009–2017) of factors associated with progression and regression of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (Hepatic steatosis) in patients with type 2 diabetes seen at a tertiary diabetes centre in Southern India
Nithyanantham Kamalraj, Madhanagopal Sathishkumar, Mani Arunvignesh, Viswanathan Baskar, Saravanan Jebarani, Anandakumar Amutha, Mohan Deepa, Coimbatore Subramanyam Shanthi Rani, Sundaramoorthy Chandru, Ranjit Unnikrishnan, Ranjit Mohan Anjana, Mardavada
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(5): 102261. CrossRef - Gastrointestinal Hormones in Healthy Adults: Reliability of Repeated Assessments and Interrelations with Eating Habits and Physical Activity
Silke M. Wortha, Katharina A. Wüsten, Veronica A. Witte, Nicole Bössel, Wolfram Keßler, Antje Vogelgesang, Agnes Flöel
Nutrients.2021; 13(11): 3809. CrossRef - Role of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 in suppressing lipid accumulation by glucagon-like peptide-1 agonist in hepatocytes
Jingya Lyu, Hitomi Imachi, Kensaku Fukunaga, Seisuke Sato, Toshihiro Kobayashi, Tao Dong, Takanobu Saheki, Mari Matsumoto, Hisakazu Iwama, Huanxiang Zhang, Koji Murao
Molecular Metabolism.2020; 34: 16. CrossRef - Effects of synbiotic consumption on lipid profile: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled clinical trials
Amir Hadi, Ehsan Ghaedi, Saman Khalesi, Makan Pourmasoumi, Arman Arab
European Journal of Nutrition.2020; 59(7): 2857. CrossRef - Glucagon‐like peptide‐1 receptor agonists (GLP‐1 RAs) for the management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): A systematic review
Xiaodan Lv, Yongqiang Dong, Lingling Hu, Feiyu Lu, Changyu Zhou, Shaoyou Qin
Endocrinology, Diabetes & Metabolism.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Genetic engineering of novel super long-acting Exendin-4 chimeric protein for effective treatment of metabolic and cognitive complications of obesity
Jong Youl Lee, Taehoon Park, Eunmi Hong, Reeju Amatya, Kyung-Ah Park, Young-Hoon Park, Kyoung Ah Min, Minki Jin, Sumi Lee, Seungmi Hwang, Gu Seob Roh, Meong Cheol Shin
Biomaterials.2020; 257: 120250. CrossRef - A look to the future in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: Are glucagon‐like peptide‐1 analogues or sodium‐glucose co‐transporter‐2 inhibitors the answer?
Rebecca K. Vincent, David M. Williams, Marc Evans
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(12): 2227. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta-analysis of probiotic consumption and metabolic status of athletes
Atefeh As’Habi, Maryam Nazari, Hossein Hajianfar, Arman Arab, Zeinab Faghfoori
International Journal of Food Properties.2020; 23(1): 941. CrossRef - The Gut Barrier, Intestinal Microbiota, and Liver Disease: Molecular Mechanisms and Strategies to Manage
Julio Plaza-Díaz, Patricio Solís-Urra, Fernando Rodríguez-Rodríguez, Jorge Olivares-Arancibia, Miguel Navarro-Oliveros, Francisco Abadía-Molina, Ana I. Álvarez-Mercado
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(21): 8351. CrossRef - Pathophysiology of NAFLD and NASH in Experimental Models: The Role of Food Intake Regulating Peptides
L. Kořínková, V. Pražienková, L. Černá, A. Karnošová, B. Železná, J. Kuneš, Lenka Maletínská
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Have a heart: failure to increase GLP-1 caused by heart failure increases the risk of diabetes
Michael J. Ryan
Clinical Science.2020; 134(23): 3119. CrossRef - Unraveling the Role of Leptin in Liver Function and Its Relationship with Liver Diseases
Maite Martínez-Uña, Yaiza López-Mancheño, Carlos Diéguez, Manuel A. Fernández-Rojo, Marta G. Novelle
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(24): 9368. CrossRef - The Role of GLP1 in Rat Steatotic and Non-Steatotic Liver Transplantation from Cardiocirculatory Death Donors
Cindy G. Avalos-de León, Mónica B. Jiménez-Castro, María Eugenia Cornide-Petronio, Araní Casillas-Ramírez, Carmen Peralta
Cells.2019; 8(12): 1599. CrossRef - LRG ameliorates steatohepatitis by activating the AMPK/mTOR/SREBP1 signaling pathway in C57BL/6J mice fed a high‑fat diet
Tao Hao, Hongying Chen, Sisi Wu, Haoming Tian
Molecular Medicine Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Liraglutide alters hepatic metabolism in high-fat fed obese mice: A bioinformatic prediction and functional analysis
Isabelle Arruda Barbosa, Eloá Mangabeira Santos, Alanna Fernandes Paraíso, Pablo Vinicyus Ferreira Chagas, Luís Paulo Oliveira, João Marcus Oliveira Andrade, Lucyana Conceição Farias, Bruna Mara Aparecida de Carvalho, Alfredo Maurício Batista de Paula, An
Meta Gene.2019; 20: 100553. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase‐4 inhibitors and aerobic exercise synergistically protect against liver injury in ovariectomized rats
Nagat Younan, Samah Elattar, Mira Farouk, Laila Rashed, Suzanne Estaphan
Physiological Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Microbial Metabolites Determine Host Health and the Status of Some Diseases
Panida Sittipo, Jae-won Shim, Yun Lee
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(21): 5296. CrossRef - Compound K attenuates glucose intolerance and hepatic steatosis through AMPK-dependent pathways in type 2 diabetic OLETF rats
Yoo-Cheol Hwang, Da-Hee Oh, Moon Chan Choi, Sang Yeoul Lee, Kyu-Jeong Ahn, Ho-Yeon Chung, Sung-Jig Lim, Sung Hyun Chung, In-Kyung Jeong
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2018; 33(2): 347. CrossRef - Liraglutide attenuates partial warm ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat livers
Ahmed A. Abdelsameea, Noha A.T. Abbas, Samar M. Abdel Raouf
Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Archives of Pharmacology.2017; 390(3): 311. CrossRef - Natural alkaloid bouchardatine ameliorates metabolic disorders in high‐fat diet‐fed mice by stimulating the sirtuin 1/liver kinase B‐1/AMPK axis
Yong Rao, Hong Yu, Lin Gao, Yu‐Ting Lu, Zhao Xu, Hong Liu, Lian‐Quan Gu, Ji‐Ming Ye, Zhi‐Shu Huang
British Journal of Pharmacology.2017; 174(15): 2457. CrossRef - Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and dyslipidemia: An update
Niki Katsiki, Dimitri P. Mikhailidis, Christos S. Mantzoros
Metabolism.2016; 65(8): 1109. CrossRef - Exendin-4 Inhibits Hepatic Lipogenesis by Increasing β-Catenin Signaling
Mi Hae Seo, Jinmi Lee, Seok-Woo Hong, Eun-Jung Rhee, Se Eun Park, Cheol Young Park, Ki Won Oh, Sung Woo Park, Won-Young Lee, Catherine Mounier
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(12): e0166913. CrossRef - The Relationship between Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Measured by Controlled Attenuation Parameter
Young Eun Chon, Kwang Joon Kim, Kyu Sik Jung, Seung Up Kim, Jun Yong Park, Do Young Kim, Sang Hoon Ahn, Chae Yoon Chon, Jae Bock Chung, Kyeong Hye Park, Ji Cheol Bae, Kwang-Hyub Han
Yonsei Medical Journal.2016; 57(4): 885. CrossRef - The role of the gut microbiota in NAFLD
Christopher Leung, Leni Rivera, John B. Furness, Peter W. Angus
Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology.2016; 13(7): 412. CrossRef - Extrapancreatic effects of incretin hormones: evidence for weight‐independent changes in morphological aspects and oxidative status in insulin‐sensitive organs of the obese nondiabetic Zucker rat (ZFR)
Ides M. Colin, Henri Colin, Ines Dufour, Charles‐Edouard Gielen, Marie‐Christine Many, Jean Saey, Bernard Knoops, Anne‐Catherine Gérard
Physiological Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - A Guide to Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Childhood and Adolescence
Jonathan Temple, Paul Cordero, Jiawei Li, Vi Nguyen, Jude Oben
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2016; 17(6): 947. CrossRef - Extrapancreatic Effect of Glucagon like Peptide-1
In-Kyung Jeong
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2015; 89(4): 404. CrossRef - Green Tea Extract Rich in Epigallocatechin-3-Gallate Prevents Fatty Liver by AMPK Activation via LKB1 in Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet
Aline B. Santamarina, Juliana L. Oliveira, Fernanda P. Silva, June Carnier, Laís V. Mennitti, Aline A. Santana, Gabriel H. I. de Souza, Eliane B. Ribeiro, Cláudia M. Oller do Nascimento, Fábio S. Lira, Lila M. Oyama, Patricia Aspichueta
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(11): e0141227. CrossRef - Acarbose, lente carbohydrate, and prebiotics promote metabolic health and longevity by stimulating intestinal production of GLP-1
Mark F McCarty, James J DiNicolantonio
Open Heart.2015; 2(1): e000205. CrossRef - The Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Analogue Liraglutide Inhibits Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in the Liver of Rats with Diet-Induced Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Huiting Gao, Zhigang Zeng, Han Zhang, Xiaoli Zhou, Lichang Guan, Weiping Deng, Lishu Xu
Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin.2015; 38(5): 694. CrossRef - Glucagon-like polypeptide agonists in type 2 diabetes mellitus: efficacy and tolerability, a balance
Sri Harsha Tella, Marc S. Rendell
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 6(3): 109. CrossRef - Gut Microbiota: Association with NAFLD and Metabolic Disturbances
E. Lau, D. Carvalho, P. Freitas
BioMed Research International.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and bariatric surgery in adolescents
AiXuan Holterman, Juan Gurria, Smita Tanpure, Nerina DiSomma
Seminars in Pediatric Surgery.2014; 23(1): 49. CrossRef - Pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: New insights and future directions
Pierluigi Marzuillo
World Journal of Hepatology.2014; 6(4): 217. CrossRef - 4Ps medicine of the fatty liver: the research model of predictive, preventive, personalized and participatory medicine—recommendations for facing obesity, fatty liver and fibrosis epidemics
Francesca Maria Trovato, Daniela Catalano, Giuseppe Musumeci, Guglielmo M Trovato
EPMA Journal.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of Medications for the Management of Patients with NAFLD
Natalia Mazzella, Laura M. Ricciardi, Arianna Mazzotti, Giulio Marchesini
Clinics in Liver Disease.2014; 18(1): 73. CrossRef - Randomised clinical trial: the beneficial effects of VSL#3 in obese children with non‐alcoholic steatohepatitis
A. Alisi, G. Bedogni, G. Baviera, V. Giorgio, E. Porro, C. Paris, P. Giammaria, L. Reali, F. Anania, V. Nobili
Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2014; 39(11): 1276. CrossRef - The cardiometabolic benefits of glycine: Is glycine an ‘antidote’ to dietary fructose?
Mark F McCarty, James J DiNicolantonio
Open Heart.2014; 1(1): e000103. CrossRef - Pediatric non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: an increasing public health issue
S. Berardis, E. Sokal
European Journal of Pediatrics.2014; 173(2): 131. CrossRef - Glucagon‐like peptide‐1 analogue, liraglutide, improves liver fibrosis markers in obese women with polycystic ovary syndrome and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
H. Kahal, G. Abouda, A. S. Rigby, A. M. Coady, E. S. Kilpatrick, S. L. Atkin
Clinical Endocrinology.2014; 81(4): 523. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of plasma metabolomics response to metabolic challenge tests in healthy subjects and influence of the FTO obesity risk allele
Simone Wahl, Susanne Krug, Cornelia Then, Anna Kirchhofer, Gabi Kastenmüller, Tina Brand, Thomas Skurk, Melina Claussnitzer, Cornelia Huth, Margit Heier, Christa Meisinger, Annette Peters, Barbara Thorand, Christian Gieger, Cornelia Prehn, Werner Römisch-
Metabolomics.2014; 10(3): 386. CrossRef - Role of thiazolidinediones, insulin sensitizers, in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease
Eugene Chang, Cheol‐Young Park, Sung Woo Park
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2013; 4(6): 517. CrossRef - Therapeutic options in pediatric non alcoholic fatty liver disease: current status and future directions
Pietro Vajro, Selvaggia Lenta, Claudio Pignata, Mariacarolina Salerno, Roberta D’Aniello, Ida De Micco, Giulia Paolella, Giancarlo Parenti
Italian Journal of Pediatrics.2012; 38(1): 55. CrossRef
- The intestine as an endocrine organ and the role of gut hormones in metabolic regulation
- Understanding the Cardiovascular Effects of Incretin
- Ji Sung Yoon, Hyoung Woo Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(5):437-443. Published online October 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.5.437
- 3,279 View
- 43 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Cardiovascular disease (CVD), a leading cause of death in patients with diabetes mellitus, has several pathogenic mechanisms that are well established. However, the traditional hypoglycemic agents do not have proven positive effects on macrovascular disease. Novel therapeutic agents target the incretin pathway including the glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor (GLP-1R) agonists and the dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. The glucose-regulatory actions of these agents function by increasing insulin secretion and suppressing glucagon. They also act to increase weight loss not only by inhibiting gastric emptying, but also by reducing appetite. Although GLP-1 and GLP-1R agonists have demonstrated beneficial effects on myocardium and vascular endothelium including coronary and peripheral mouse vessels, they also have anti-inflammatory and anti-atherogenic actions. These agents also have positive effects on the lipid profile and blood pressure. Although these cardioprotective actions seem to be beyond the effects of glucose control and weight loss, they are mediated through GLP-1R- or GLP-1R-independent actions of cleaved GLP-1 (9-36). Larger randomized controlled trials are necessary to elucidate the clinical promise of these beneficial CVD effects.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cardioprotective Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (9-36) Against Oxidative Injury in H9c2 Cardiomyoblasts: Potential Role of the PI3K/Akt/NOS Pathway
Narawat Nuamnaichati, Warisara Parichatikanond, Supachoke Mangmool
Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology.2022; 79(1): e50. CrossRef - Comparisons of pleiotropic effects of SGLT2 inhibition and GLP-1 agonism on cardiac glucose intolerance in heart dysfunction
Belma Turan, Aysegul Durak, Yusuf Olgar, Erkan Tuncay
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2022; 477(11): 2609. CrossRef - Interrelations of components of metabolic syndrome with the level of the hormones involved in regulation of adipose tissue metabolism
A. Y. Babenko, G. A. Matveev, T. I. Alekseenko, I. V. Derevitskii, M. A. Kokina, E. V. Shlyakhto
"Arterial’naya Gipertenziya" ("Arterial Hypertension").2020; 25(6): 639. CrossRef - Attenuation of carotid neointimal formation after direct delivery of a recombinant adenovirus expressing glucagon-like peptide-1 in diabetic rats
Soo Lim, Gha Young Lee, Ho Seon Park, Dong-Hwa Lee, Oh Tae Jung, Kim Kyoung Min, Young-Bum Kim, Hee-Sook Jun, Jang Hak Chul, Kyong Soo Park
Cardiovascular Research.2017; 113(2): 183. CrossRef - Renoprotective Effects of the Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Sitagliptin: A Review in Type 2 Diabetes
Cristina Mega, Edite Teixeira-de-Lemos, Rosa Fernandes, Flávio Reis
Journal of Diabetes Research.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Letter: Economic Impact of Combining Metformin with Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Diabetic Patients with Renal Impairment in Spanish Patients (Diabetes Metab J2015;39:74-81)
Hannah Seok
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(2): 171. CrossRef - Diuretic and Natriuretic Effects of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Teneligliptin
Masao Moroi, Tetsuya Kubota
Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology.2015; 66(2): 159. CrossRef - The Nonglycemic Actions of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors
Na-Hyung Kim, Taeyang Yu, Dae Ho Lee
BioMed Research International.2014; 2014: 1. CrossRef - Tolerability, effectiveness and predictive parameters for the therapeutic usefulness of exenatide in obese, Korean patients with type 2 diabetes
Sun Ok Song, Kwang Joon Kim, Byung‐Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2014; 5(5): 554. CrossRef - The endothelium in diabetes: Its role in insulin access and diabetic complications
Cathryn M. Kolka, Richard N. Bergman
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2013; 14(1): 13. CrossRef - Is GPR119 agonism an appropriate treatment modality for the safe amelioration of metabolic diseases?
Lauren M Cornall, Michael L Mathai, Deanne H Hryciw, Andrew J McAinch
Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs.2013; 22(4): 487. CrossRef - Effects of GLP-1 on Forearm Vasodilator Function and Glucose Disposal During Hyperinsulinemia in the Metabolic Syndrome
Manfredi Tesauro, Francesca Schinzari, Angelo Adamo, Valentina Rovella, Francesca Martini, Nadia Mores, Angela Barini, Dario Pitocco, Giovanni Ghirlanda, Davide Lauro, Umberto Campia, Carmine Cardillo
Diabetes Care.2013; 36(3): 683. CrossRef - Effect of a Dipeptidyl Peptidase-IV Inhibitor, Des-Fluoro-Sitagliptin, on Neointimal Formation after Balloon Injury in Rats
Soo Lim, Sung Hee Choi, Hayley Shin, Bong Jun Cho, Ho Seon Park, Byung Yong Ahn, Seon Mee Kang, Ji Won Yoon, Hak Chul Jang, Young-Bum Kim, Kyong Soo Park, Alice Y. W. Chang
PLoS ONE.2012; 7(4): e35007. CrossRef - Glucagon-like peptide 1 and cardiac cell survival
Susana Ravassa, Amaia Zudaire, Javier Díez
Endocrinología y Nutrición (English Edition).2012; 59(9): 561. CrossRef - GLP-1 and cardioprotection: from bench to bedside
S. Ravassa, A. Zudaire, J. Diez
Cardiovascular Research.2012; 94(2): 316. CrossRef - Saxagliptin improves glucose tolerance but not survival in a murine model of dilated cardiomyopathy
Arpita Kalla Vyas, Lauren B. Aerni-Flessner, Maria A. Payne, Attila Kovacs, Patrick Y. Jay, Paul W. Hruz
Cardiovascular Endocrinology.2012; 1(4): 74. CrossRef - Péptido similar al glucagón tipo 1 y supervivencia de la célula cardiaca
Susana Ravassa, Amaia Zudaire, Javier Díez
Endocrinología y Nutrición.2012; 59(9): 561. CrossRef
- Cardioprotective Effects of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 (9-36) Against Oxidative Injury in H9c2 Cardiomyoblasts: Potential Role of the PI3K/Akt/NOS Pathway
- Insulin Secretion and Incretin Hormone Concentration in Women with Previous Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
- Sung Hoon Yu, Bongjun Cho, Yejin Lee, Eunhye Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Soo Lim, Ka Hee Yi, Young Joo Park, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(1):58-64. Published online February 28, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.1.58
- 3,576 View
- 35 Download
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We examined the change in the levels of incretin hormone and effects of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) on insulin secretion in women with previous gestational diabetes (pGDM).
Methods A 75-g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) was conducted on 34 women with pGDM. In addition, 11 women with normal glucose tolerance, matched for age, height and weight, were also tested. The insulin, GIP, GLP-1, and glucagon concentrations were measured, and their anthropometric and biochemical markers were also measured.
Results Among 34 women with pGDM, 18 had normal glucose tolerance, 13 had impaired glucose tolerance (IGT) and 1 had diabetes. No significant differences were found in GLP-1 concentration between the pGDM and control group. However, a significantly high level of glucagon was present in the pGDM group at 30 minutes into the OGTT. The GIP concentration was elevated at 30 minutes and 60 minutes in the pGDM group. With the exception of the 30-minute timepoint, women with IGT had significantly high blood glucose from 0 to 120 minutes. However, there was no significant difference in insulin or GLP-1 concentration. The GIP level was significantly high from 0 to 90 minutes in patients diagnosed with IGT.
Conclusion GLP-1 secretion does not differ between pGDM patients and normal women. GIP was elevated, but that does not seem to induce in increase in insulin secretion. Therefore, we conclude that other factors such as heredity and environment play important roles in the development of type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of GLP-1 secretion with parameters of glycemic control in women after gestational diabetes mellitus
Eleni Pappa, Kristina Busygina, Saori Harada, Hana Hermann, Cornelia Then, Andreas Lechner, Uta Ferrari, Jochen Seissler
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2024; 12(1): e003706. CrossRef - Increased Pro-Inflammatory T Cells, Senescent T Cells, and Immune-Check Point Molecules in the Placentas of Patients With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Min-Kyung Yeo, Jung Tae Kim, Danbit Park, Yewon Jung, Ok Soon Kim, Seong Eun Lee, Ji Min Kim, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Bon Jeong Ku, Mina Lee, Hyun Jin Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Simulation of Oral Glucose Tolerance Tests and the Corresponding Isoglycemic Intravenous Glucose Infusion Studies for Calculation of the Incretin Effect
Myeungseon Kim, Tae Jung Oh, Jung Chan Lee, Karam Choi, Min Young Kim, Hee Chan Kim, Young Min Cho, Sungwan Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2014; 29(3): 378. CrossRef - Metabolic, hormonal characteristics and genetic variants of TCF7L2 associated with development of gestational diabetes mellitus in Mexican women
Ruth Reyes‐López, Elva Pérez‐Luque, Juan Manuel Malacara
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2014; 30(8): 701. CrossRef - Reduced postprandial GLP‐1 responses in women with gestational diabetes mellitus
L. Bonde, T. Vilsbøll, T. Nielsen, J. I. Bagger, J. A. Svare, J. J. Holst, S. Larsen, F. K. Knop
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2013; 15(8): 713. CrossRef - Women with normal glucose tolerance and a history of gestational diabetes show significant impairment of β-cell function at normal insulin sensitivity
P. Molęda, K. Homa, K. Safranow, Z. Celewicz, A. Fronczyk, L. Majkowska
Diabetes & Metabolism.2013; 39(2): 155. CrossRef
- Association of GLP-1 secretion with parameters of glycemic control in women after gestational diabetes mellitus
- Triple Combination Therapy Using Metformin, Thiazolidinedione, and a GLP-1 Analog or DPP-IV Inhibitor in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Sun Woo Kim
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(6):331-337. Published online December 31, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.6.331
- 3,259 View
- 40 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Although there is no HbA1c threshold for cardiovascular risk, the American Diabetic Association-recommended goal of HbA1c < 7.0% appears to be unacceptably high. To achieve an optimal HbA1c level goal of 6.0% or less, a high dosage of sulfonylureas and insulin would be required; the trade-off would be the common adverse effects of hypoglycemia and weight gain. In contrast, hypoglycemia is uncommon with insulin sensitizers and GLP-1 analogs, allowing the physician to titrate these drugs to maximum dosage to reduce HbA1c levels below 6.0% and they have been shown to preserve β-cell function. Lastly, weight gain is common with sulfonylurea and insulin therapy, whereas GLP-1 analogs induce weight loss and offset the weight gain associated with TZDs. A treatment paradigm shift is recommended in which combination therapy is initiated with diet/exercise, metformin (which has antiatherogenic effects and improves hepatic insulin sensitivity), a TZD (which improves insulin sensitivity and preserves β-cell function with proven durability), and a GLP-1 analog (which improves β, α-cell function and promotes weight loss) or a dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Design, synthesis and evaluation of l-quebrachitol derivatives against α-glycosidase
Maoying Zhang, Xinjie Liang, Pengcheng Cai, Qixun Feng, Yongsong Chen, Xiaoxi Yu, Kuo Zhang, Xuefei Bao, Guoliang Chen
New Journal of Chemistry.2023; 47(28): 13387. CrossRef - Phase III Study on Efficacy and Safety of Triple Combination (Exenatide/Metformin/Biphasic Insulin Aspart) Therapy for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ke Su, Chunmei Lv, Zongwen Ji, Yishu Wang, Haifeng Wang, Ying Bai, Yaping Liu
American Journal of Therapeutics.2018; 25(6): e609. CrossRef - A Case Report of Diabetes Mellitus with Herniated Intervertebral Lumbar Discs Improved by Korean Medicine Treatment
Dong-geun Han, A-ryun Choi, You-jin Jung, Ah-hyun Kang, Hye-jin Seo, Jae-yeon Sung, Hyung-chul Lee, Gook-hyun Eom, Woo-sub Song
The Journal of Internal Korean Medicine.2017; 38(5): 828. CrossRef - A crossover study of the combination therapy of metformin and exenatide or biphasic insulin aspart 30 in overweight or obese patients newly diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Huibiao Quan, Huachuan Zhang, Weiping Wei, Tuanyu Fang, Daoxiong Chen, Kaining Chen
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2017; 14(4): 3279. CrossRef - Gender-related different effects of a combined therapy of Exenatide and Metformin on overweight or obesity patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Huibiao Quan, Huachuan Zhang, Weiping Wei, Tuanyu Fang
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2016; 30(4): 686. CrossRef - Bioreducible polymers for therapeutic gene delivery
Young Sook Lee, Sung Wan Kim
Journal of Controlled Release.2014; 190: 424. CrossRef - Managing diabetes in Asia: Overcoming obstacles and the role of DPP-IV inhibitors
Yi-Ming Mu, Anoop Misra, John M.F. Adam, Siew Pheng Chan, Francis C.C. Chow, Elaine Cheeay Cunanan, Chaicharn Deerochanawong, Hak Chul Jang, Nguyen Thy Khue, Wayne H.-H. Sheu, Kevin E.K. Tan
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2012; 95(2): 179. CrossRef
- Design, synthesis and evaluation of l-quebrachitol derivatives against α-glycosidase
- Genetic Polymorphism of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
- Kyung Wook Lee, Meihua Jiang, Shanji Piao, Eun A Kim, Seong Bin Hong, Moon Suk Nam, Yong Seong Kim, Kyong Soo Park, Hyun Chul Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2005;29(1):30-38. Published online January 1, 2005
- 1,067 View
- 21 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) is a hormone secreted by intestinal L-cells, which stimulates insulin secretion from cells. The biological action of GLP-1 is mediated by the glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R), which is 463 amino acids in size, with 7 transmembrane domains. Because GLP-1 plays an important modulatory role in regulating glucose-stimulated insulin, the GLP-1R could be a candidate gene contributing to impaired -cell function and the development of this genetically heterogeneous disorder. Recently, four GLP-1R SNPs were identified in Caucasian diabetic individuals, and for the SNP at the Leu- 260Phe (A/C) position, statistically significant differences were detected in the distribution of genotypes between type 2 diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. We replicated the genetic association between the SNP at the leu260Phe (A/C) position in the GLP-1R gene and Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus. METHODS: The Leu260Phe polymorphism in the GLP-1R gene was determined using a PCR- RFLP method (the genotypes were determined according to the results of polymerase chain reaction products after digestion and the digestive enzyme was BbsI) in 419 Korean type 2 diabetic patients and 345 nondiabetic subjects. RESULTS: In contrast to the Caucasian report, there was no significant difference in the frequencies of alleles, and genotypes between Korean type 2 diabetic and nondiabetic subjects. When analyzed according to gender, BMI and age of onset, the genotype distribution of type 2 diabetic subjects was not significantly different from nondiabetic subjects. CONCLUSION: The Leu260Phe polymorphism in the GLP-1R gene was not associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus, and we were unable to replicate the genetic association between this polymorphism and Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





