
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- A Composite Blood Biomarker Including AKR1B10 and Cytokeratin 18 for Progressive Types of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Seung Joon Choi, Sungjin Yoon, Kyoung-Kon Kim, Doojin Kim, Hye Eun Lee, Kwang Gi Kim, Seung Kak Shin, Ie Byung Park, Seong Min Kim, Dae Ho Lee
- Received June 18, 2023 Accepted August 16, 2023 Published online February 1, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0189 [Epub ahead of print]
- 781 View
- 50 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
We aimed to evaluate whether composite blood biomarkers including aldo-keto reductase family 1 member B10 (AKR1B10) and cytokeratin 18 (CK-18; a nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [NASH] marker) have clinically applicable performance for the diagnosis of NASH, advanced liver fibrosis, and high-risk NASH (NASH+significant fibrosis).
Methods
A total of 116 subjects including healthy control subjects and patients with biopsy-proven nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) were analyzed to assess composite blood-based and imaging-based biomarkers either singly or in combination.
Results
A composite blood biomarker comprised of AKR1B10, CK-18, aspartate aminotransferase (AST), and alanine aminotransferase (ALT) showed excellent performance for the diagnosis of, NASH, advanced fibrosis, and high-risk NASH, with area under the receiver operating characteristic curve values of 0.934 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.888 to 0.981), 0.902 (95% CI, 0.832 to 0.971), and 0.918 (95% CI, 0.862 to 0.974), respectively. However, the performance of this blood composite biomarker was inferior to that various magnetic resonance (MR)-based composite biomarkers, such as proton density fat fraction/MR elastography- liver stiffness measurement (MRE-LSM)/ALT/AST for NASH, MRE-LSM+fibrosis-4 index for advanced fibrosis, and the known MR imaging-AST (MAST) score for high-risk NASH.
Conclusion
Our blood composite biomarker can be useful to distinguish progressive forms of NAFLD as an initial noninvasive test when MR-based tools are not available.
- Complications
- Fatty Acid-Binding Protein 4 in Patients with and without Diabetic Retinopathy
- Ping Huang, Xiaoqin Zhao, Yi Sun, Xinlei Wang, Rong Ouyang, Yanqiu Jiang, Xiaoquan Zhang, Renyue Hu, Zhuqi Tang, Yunjuan Gu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):640-649. Published online April 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0195
- 3,443 View
- 193 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Fatty acid-binding protein 4 (FABP4) has been demonstrated to be a predictor of early diabetic nephropathy. However, little is known about the relationship between FABP4 and diabetic retinopathy (DR). This study explored the value of FABP4 as a biomarker of DR in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
A total of 238 subjects were enrolled, including 20 healthy controls and 218 T2DM patients. Serum FABP4 levels were measured using a sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The grade of DR was determined using fundus fluorescence angiography. Based on the international classification of DR, all T2DM patients were classified into the following three subgroups: non-DR group, non-proliferative diabetic retinopathy (NPDR) group, and proliferative diabetic retinopathy (PDR) group. Multivariate logistic regression analyses were employed to assess the correlation between FABP4 levels and DR severity.
Results
FABP4 correlated positively with DR severity (r=0.225, P=0.001). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was used to assess the diagnostic potential of FABP4 in identifying DR, with an area under the curve of 0.624 (37% sensitivity, 83.6% specificity) and an optimum cut-off value of 76.4 μg/L. Multivariate logistic regression model including FABP4 as a categorized binary variable using the cut-off value of 76.4 μg/L showed that the concentration of FABP4 above the cut-off value increased the risk of NPDR (odds ratio [OR], 3.231; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.574 to 6.632; P=0.001) and PDR (OR, 3.689; 95% CI, 1.306 to 10.424; P=0.014).
Conclusion
FABP4 may be used as a serum biomarker for the diagnosis of DR. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Circulating AFABP, FGF21, and PEDF Levels as Prognostic Biomarkers of Sight-threatening Diabetic Retinopathy
Chi-Ho Lee, David Tak-Wai Lui, Chloe Yu-Yan Cheung, Carol Ho-Yi Fong, Michele Mae-Ann Yuen, Yu-Cho Woo, Wing-Sun Chow, Ian Yat-Hin Wong, Aimin Xu, Karen Siu-Ling Lam
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(9): e799. CrossRef - A Prediction Model for Sight-Threatening Diabetic Retinopathy Based on Plasma Adipokines among Patients with Mild Diabetic Retinopathy
Yaxin An, Bin Cao, Kun Li, Yongsong Xu, Wenying Zhao, Dong Zhao, Jing Ke, Takayuki Masaki
Journal of Diabetes Research.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef
- Circulating AFABP, FGF21, and PEDF Levels as Prognostic Biomarkers of Sight-threatening Diabetic Retinopathy
- Complications
- Pathophysiologic Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers in Diabetic Kidney Disease
- Chan-Young Jung, Tae-Hyun Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):181-197. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0329
- 12,139 View
- 793 Download
- 41 Web of Science
- 46 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Although diabetic kidney disease (DKD) remains the leading cause of end-stage kidney disease eventually requiring chronic kidney replacement therapy, the prevalence of DKD has failed to decline over the past 30 years. In order to reduce disease prevalence, extensive research has been ongoing to improve prediction of DKD onset and progression. Although the most commonly used markers of DKD are albuminuria and estimated glomerular filtration rate, their limitations have encouraged researchers to search for novel biomarkers that could improve risk stratification. Considering that DKD is a complex disease process that involves several pathophysiologic mechanisms such as hyperglycemia induced inflammation, oxidative stress, tubular damage, eventually leading to kidney damage and fibrosis, many novel biomarkers that capture one specific mechanism of the disease have been developed. Moreover, the increasing use of high-throughput omic approaches to analyze biological samples that include proteomics, metabolomics, and transcriptomics has emerged as a strong tool in biomarker discovery. This review will first describe recent advances in the understanding of the pathophysiology of DKD, and second, describe the current clinical biomarkers for DKD, as well as the current status of multiple potential novel biomarkers with respect to protein biomarkers, proteomics, metabolomics, and transcriptomics.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Role of polyphenols in the management of diabetic complications
Jeevika Raina, Atika Firdous, Gurvinder Singh, Rajesh Kumar, Charanjit Kaur
Phytomedicine.2024; 122: 155155. CrossRef - Role of MCP-1 as an inflammatory biomarker in nephropathy
Yanlong Liu, Ke Xu, Yuhua Xiang, Boyan Ma, Hailong Li, Yuan Li, Yue Shi, Shuju Li, Yan Bai
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Urinary podocyte stress marker as a prognostic indicator for diabetic kidney disease
Lingfeng Zeng, Jack Kit-Chung Ng, Winston Wing-Shing Fung, Gordon Chun-Kau Chan, Kai-Ming Chow, Cheuk-Chun Szeto
BMC Nephrology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification and validation of immune and cuproptosis - related genes for diabetic nephropathy by WGCNA and machine learning
Yubing Chen, Lijuan Liao, Baoju Wang, Zhan Wu
Frontiers in Immunology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Specific Alternation of Gut Microbiota and the Role of Ruminococcus gnavus in the Development of Diabetic Nephropathy
Jinni Hong, Tingting Fu, Weizhen Liu, Yu Du, Junmin Bu, Guojian Wei, Miao Yu, Yanshan Lin, Cunyun Min, Datao Lin
Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology.2024; 34(3): 547. CrossRef - The Triglyceride-Glucose Index is Superior to Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance in predicting Metabolic Syndrome in an Adult Population in the United States
Beverley Adams-Huet, Rafael Zubirán, Alan T Remaley, Ishwarlal Jialal
Journal of Clinical Lipidology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Narrative Review of New Treatment Options for Diabetic Nephropathy
Aadhira Pillai, Darshna Fulmali
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Bamboo leaf: A review of traditional medicinal property, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and purification technology
Yaqian Cheng, Siqi Wan, Linna Yao, Ding Lin, Tong Wu, Yongjian Chen, Ailian Zhang, Chenfei Lu
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2023; 306: 116166. CrossRef - Molecular Pathways of Diabetic Kidney Disease Inferred from Proteomics
Lan Wei, Yuanyuan Han, Chao Tu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 117. CrossRef - Omics and Artificial Intelligence in Kidney Diseases
Nadja Grobe, Josef Scheiber, Hanjie Zhang, Christian Garbe, Xiaoling Wang
Advances in Kidney Disease and Health.2023; 30(1): 47. CrossRef - Intestinal microbiome diversity of diabetic and non-diabetic kidney disease: Current status and future perspective
Soumik Das, Ramanathan Gnanasambandan
Life Sciences.2023; 316: 121414. CrossRef - Pediatric Diabetic Nephropathy: Novel Insights from microRNAs
Francesca Lanzaro, Annalisa Barlabà, Angelica De Nigris, Federica Di Domenico, Valentina Verde, Emanuele Miraglia del Giudice, Anna Di Sessa
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(4): 1447. CrossRef - Novel Biomarkers of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Jorge Rico-Fontalvo, Gustavo Aroca-Martínez, Rodrigo Daza-Arnedo, José Cabrales, Tomás Rodríguez-Yanez, María Cardona-Blanco, Juan Montejo-Hernández, Dairo Rodelo Barrios, Jhonny Patiño-Patiño, Elber Osorio Rodríguez
Biomolecules.2023; 13(4): 633. CrossRef - Diabetic vascular diseases: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies
Yiwen Li, Yanfei Liu, Shiwei Liu, Mengqi Gao, Wenting Wang, Keji Chen, Luqi Huang, Yue Liu
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic phenotypes and risk of end-stage kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes
Lijun Zhao, Yutong Zou, Yucheng Wu, Linli Cai, Yuancheng Zhao, Yiting Wang, Xiang Xiao, Qing Yang, Jia Yang, Honghong Ren, Nanwei Tong, Fang Liu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of a New RNA and Protein Integrated Biomarker Panel Associated with Kidney Function Impairment in DKD: Translational Implications
Alessandra Scamporrino, Stefania Di Mauro, Agnese Filippello, Grazia Di Marco, Antonino Di Pino, Roberto Scicali, Maurizio Di Marco, Emanuele Martorana, Roberta Malaguarnera, Francesco Purrello, Salvatore Piro
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(11): 9412. CrossRef - Increased serum PCSK9 levels are associated with renal function impairment in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Zhicai Feng, Xiangyu Liao, Hao Zhang, Juan Peng, Zhijun Huang, Bin Yi
Renal Failure.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of Serum Pyrodeath Re-lated Proteins and Renal Injury in Patients with Type 2 DKD
茹洁 马
Asian Case Reports in Emergency Medicine.2023; 11(02): 53. CrossRef - Loganin reduces diabetic kidney injury by inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated pyroptosis
Xiangri Kong, Yunyun Zhao, Xingye Wang, Yongjiang Yu, Ying Meng, Guanchi Yan, Miao Yu, Lihong Jiang, Wu Song, Bingmei Wang, Xiuge Wang
Chemico-Biological Interactions.2023; 382: 110640. CrossRef - Machine-learning algorithm-based prediction of a diagnostic model based on oxidative stress-related genes involved in immune infiltration in diabetic nephropathy patients
Heng-Mei Zhu, Na Liu, Dong-Xuan Sun, Liang Luo
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The roles of gut microbiota and its metabolites in diabetic nephropathy
Hui Zhao, Cheng-E Yang, Tian Liu, Ming-Xia Zhang, Yan Niu, Ming Wang, Jun Yu
Frontiers in Microbiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - High triglyceride levels increase the risk of diabetic microvascular complications: a cross-sectional study
Jiahang Li, Lei Shi, Guohong Zhao, Fei Sun, Zhenxing Nie, Zhongli Ge, Bin Gao, Yan Yang
Lipids in Health and Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation of Kidney Injury Molecule-1 and Nephrin Levels in Iraqi Patients with Diabetic Nephropathy
Raghda Hisham Aljorani, Eman Saadi Saleh , Khalaf Gata Hussein Al Mohammadawi
Al-Rafidain Journal of Medical Sciences ( ISSN 2789-3219 ).2023; 5: 99. CrossRef - Diabetic Nephropathy: Significance of Determining Oxidative Stress and Opportunities for Antioxidant Therapies
Marina Darenskaya, Sergey Kolesnikov, Natalya Semenova, Lyubov Kolesnikova
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(15): 12378. CrossRef - Evaluation of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio, Low-Density Lipoprotein/Albumin Ratio, and Red Cell Distribution Width/Albumin Ratio in the Estimation of Proteinuria in Uncontrolled Diabetic Patients
Duygu Tutan, Murat Doğan
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hedysarum polybotrys polysaccharide attenuates renal inflammatory infiltration and fibrosis in diabetic mice by inhibiting the HMGB1/RAGE/TLR4 pathway
Changqing Xu, Yanxu Cheng, Zongmei Liu, Xiaoyan Fu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Abdominal adipose tissue and type 2 diabetic kidney disease: adipose radiology assessment, impact, and mechanisms
Fei Lu, Jinlei Fan, Fangxuan Li, Lijing Liu, Zhiyu Chen, Ziyu Tian, Liping Zuo, Dexin Yu
Abdominal Radiology.2023; 49(2): 560. CrossRef - Inhibition of MD2 by natural product-drived JM-9 attenuates renal inflammation and diabetic nephropathy in mice
Minxiu Wang, Qianhui Zhang, Shuaijie Lou, Leiming Jin, Gaojun Wu, Wenqi Wu, Qidong Tang, Yi Wang, Xiaohong Long, Ping Huang, Wu Luo, Guang Liang
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 168: 115660. CrossRef - Multifaceted relationship between diabetes and kidney diseases: Beyond diabetes
Pasquale Esposito, Daniela Picciotto, Francesca Cappadona, Francesca Costigliolo, Elisa Russo, Lucia Macciò, Francesca Viazzi
World Journal of Diabetes.2023; 14(10): 1450. CrossRef - Mitochondrial antiviral signaling protein: a potential therapeutic target in renal disease
Meng Wu, Zhiyin Pei, Guangfeng Long, Hongbing Chen, Zhanjun Jia, Weiwei Xia
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Research progress on multiple cell death pathways of podocytes in diabetic kidney disease
Can Yang, Zhen Zhang, Jieting Liu, Peijian Chen, Jialing Li, Haiying Shu, Yanhui Chu, Luxin Li
Molecular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Quantitative profiling of carboxylic compounds by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry for revealing biomarkers of diabetic kidney disease
Rongrong Zhu, Yan Yuan, Rourou Qi, Jianying Liang, Yan Shi, Hongbo Weng
Journal of Chromatography B.2023; 1231: 123930. CrossRef - Jiangtang Decoction Ameliorates Diabetic Kidney Disease Through the Modulation of the Gut Microbiota
Jinni Hong, Tingting Fu, Weizhen Liu, Yu Du, Junmin Bu, Guojian Wei, Miao Yu, Yanshan Lin, Cunyun Min, Datao Lin
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 3707. CrossRef - GLP-1RA Combined with SGLT2 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Meta Analysis
莹 郭
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(11): 18117. CrossRef - Potential application of Klotho as a prognostic biomarker for patients with diabetic kidney disease: a meta-analysis of clinical studies
Li Xia Yu, Min Yue Sha, Yue Chen, Fang Tan, Xi Liu, Shasha Li, Qi-Feng Liu
Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals RAC1 Involvement in Macrophages Efferocytosis in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Yi Song, Yifan Liu, Feng Guo, Lin Zhao, Guijun Qin
Inflammation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Research progress of natural active compounds on improving podocyte function to reduce proteinuria in diabetic kidney disease
Le Gong, Rui Wang, Xinyu Wang, Jing Liu, Zhaodi Han, Qian Li, Yi Jin, Hui Liao
Renal Failure.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Identification of potential crosstalk genes and mechanisms between periodontitis and diabetic nephropathy through bioinformatic analysis
Huijuan Lu, Jia Sun, Jieqiong Sun
Medicine.2023; 102(52): e36802. CrossRef - Mitochondrial RNAs as Potential Biomarkers of Functional Impairment in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Stefania Di Mauro, Alessandra Scamporrino, Agnese Filippello, Maurizio Di Marco, Maria Teresa Di Martino, Francesca Scionti, Antonino Di Pino, Roberto Scicali, Roberta Malaguarnera, Francesco Purrello, Salvatore Piro
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(15): 8198. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - Partial Synthetic PPARƳ Derivative Ameliorates Aorta Injury in Experimental Diabetic Rats Mediated by Activation of miR-126-5p Pi3k/AKT/PDK 1/mTOR Expression
Yasmin M. Ahmed, Raha Orfali, Nada S. Abdelwahab, Hossam M. Hassan, Mostafa E. Rateb, Asmaa M. AboulMagd
Pharmaceuticals.2022; 15(10): 1175. CrossRef - Polydatin attenuates tubulointerstitial fibrosis in diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting YAP expression and nuclear translocation
Manlin He, Lan Feng, Yang Chen, Bin Gao, Yiwei Du, Lu Zhou, Fei Li, Hongbao Liu
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of diabetic nephropathy in the diabetes mellitus population: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis
Sicheng Li, Huidi Xie, Yang Shi, Hongfang Liu
Medicine.2022; 101(42): e31232. CrossRef - Stratification of diabetic kidney diseases via data-independent acquisition proteomics–based analysis of human kidney tissue specimens
Qinghua Huang, Xianming Fei, Zhaoxian Zhong, Jieru Zhou, Jianguang Gong, Yuan Chen, Yiwen Li, Xiaohong Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel biomarkers and therapeutic approaches for diabetic retinopathy and nephropathy: Recent progress and future perspectives
Ziyan Xie, Xinhua Xiao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetic Kidney Disease
Susanne B. Nicholas, Amy K. Mottl
Nephrology Self-Assessment Program.2022; 21(5): 394. CrossRef
- Role of polyphenols in the management of diabetic complications
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Differential Profile of Plasma Circular RNAs in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Yangyang Li, Ying Zhou, Minghui Zhao, Jing Zou, Yuxiao Zhu, Xuewen Yuan, Qianqi Liu, Hanqing Cai, Cong-Qiu Chu, Yu Liu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):854-865. Published online July 13, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0151

- 6,187 View
- 131 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background No currently available biomarkers or treatment regimens fully meet therapeutic needs of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Circular RNA (circRNA) is a recently identified class of stable noncoding RNA that have been documented as potential biomarkers for various diseases. Our objective was to identify and analyze plasma circRNAs altered in T1DM.
Methods We used microarray to screen differentially expressed plasma circRNAs in patients with new onset T1DM (
n =3) and age-/gender-matched healthy controls (n =3). Then, we selected six candidates with highest fold-change and validated them by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in independent human cohort samples (n =12). Bioinformatic tools were adopted to predict putative microRNAs (miRNAs) sponged by these validated circRNAs and their downstream messenger RNAs (mRNAs). Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses were performed to gain further insights into T1DM pathogenesis.Results We identified 68 differentially expressed circRNAs, with 61 and seven being up- and downregulated respectively. Four of the six selected candidates were successfully validated. Curations of their predicted interacting miRNAs revealed critical roles in inflammation and pathogenesis of autoimmune disorders. Functional relations were visualized by a circRNA-miRNA-mRNA network. GO and KEGG analyses identified multiple inflammation-related processes that could be potentially associated with T1DM pathogenesis, including cytokine-cytokine receptor interaction, inflammatory mediator regulation of transient receptor potential channels and leukocyte activation involved in immune response.
Conclusion Our study report, for the first time, a profile of differentially expressed plasma circRNAs in new onset T1DM. Further
in silico annotations and bioinformatics analyses supported future application of circRNAs as novel biomarkers of T1DM.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Non-coding RNAs and exosomal non-coding RNAs in diabetic retinopathy: A narrative review
Yuhong Zhong, Juan Xia, Li Liao, Mohammad Reza Momeni
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2024; 259: 128182. CrossRef - Circular RNAs: Potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets for autoimmune diseases
Ren-Jie Zhao, Wan-Ying Zhang, Xing-Xing Fan
Heliyon.2024; 10(1): e23694. CrossRef - Research progress of circular RNA molecules in aging and age-related diseases
Zhidan Zhang, Yuling Huang, AYao Guo, Lina Yang
Ageing Research Reviews.2023; 87: 101913. CrossRef - CircRNAs and RNA-Binding Proteins Involved in the Pathogenesis of Cancers or Central Nervous System Disorders
Yuka Ikeda, Sae Morikawa, Moeka Nakashima, Sayuri Yoshikawa, Kurumi Taniguchi, Haruka Sawamura, Naoko Suga, Ai Tsuji, Satoru Matsuda
Non-Coding RNA.2023; 9(2): 23. CrossRef - Decrypting the circular RNAs does a favor for us: Understanding, diagnosing and treating diabetes mellitus and its complications
Zi Li, Yuanyuan Ren, Ziwei Lv, Man Li, Yujia Li, Xiaobin Fan, Yuyan Xiong, Lu Qian
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 168: 115744. CrossRef - Circular RNA PIP5K1A Promotes Glucose and Lipid Metabolism Disorders and Inflammation in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ge Song, YiQian Zhang, YiHua Jiang, Huan Zhang, Wen Gu, Xiu Xu, Jing Yao, ZhengFang Chen
Molecular Biotechnology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hsa_circRNA_405498 and hsa_circRNA_100033 Serve as Potential Biomarkers for Differential Diagnosis of Type 1 Diabetes
Ziwei Zhang, Shuoming Luo, Zilin Xiao, Wenfeng Yin, Xiajie Shi, Hongzhi Chen, Zhiguo Xie, Zhenqi Liu, Xia Li, Zhiguang Zhou
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Circular RNA PIP5K1A act as microRNA-552-3p sponge to regulates inflammation, oxidative damage in glucolipotoxicity-induced pancreatic INS-1 β-cells via Janus kinase 1
Lei Ren
Bioengineered.2022; 13(3): 5724. CrossRef - Circular RNAs in diabetes mellitus and its complications
Wenqi Fan, Haipeng Pang, Zhiguo Xie, Gan Huang, Zhiguang Zhou
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus-Related circRNAs Regulate CD4+ T Cell Functions
Jianni Chen, Guanfei Jia, Xue Lv, Shufa Li, Christos K. Kontos
BioMed Research International.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - An intriguing role of circular RNA in insulin resistance and endothelial dysfunction: the future perspectives
Monisha Prasad, Selvaraj Jayaraman, Vishnu Priya Veeraraghavan
Hypertension Research.2022; 45(11): 1843. CrossRef - Circular RNAs in Diabetic Nephropathy: Updates and Perspectives
Miao Liu, Junli Zhao
Aging and disease.2022; 13(5): 1365. CrossRef - CircRNAs: Key molecules in the prevention and treatment of ischemic stroke
Zeyu Liu, Yanhong Zhou, Jian Xia
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 156: 113845. CrossRef - Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Promote the Transcription of Circular RNAs in Human Pancreatic β Cells
Simranjeet Kaur, Caroline Frørup, Aashiq H. Mirza, Tina Fløyel, Reza Yarani, Maikel L. Colli, Jesper Johannesen, Joachim Størling, Decio L. Eizirik, Flemming Pociot
Non-Coding RNA.2022; 8(5): 69. CrossRef - Differential Expression and Bioinformatics Analysis of Plasma-Derived Exosomal circRNA in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Haipeng Pang, Wenqi Fan, Xiajie Shi, Shuoming Luo, Yimeng Wang, Jian Lin, Yang Xiao, Xia Li, Gan Huang, Zhiguo Xie, Zhiguang Zhou, Jinhui Liu
Journal of Immunology Research.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Circular RNAs in diabetes and its complications: Current knowledge and future prospects
Wenfeng Yin, Ziwei Zhang, Zilin Xiao, Xia Li, Shuoming Luo, Zhiguang Zhou
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Circular RNA in autoimmune diseases: special emphasis on regulation mechanism in RA and SLE
Yurong Huang, Qiuyun Xue, Chenglong Cheng, Yuting Wang, Xiao Wang, Jun Chang, Chenggui Miao
Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Emerging roles of circular RNAs in systemic lupus erythematosus
Xin Wang, Rui Ma, Weimin Shi, Zhouwei Wu, Yuling Shi
Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids.2021; 24: 212. CrossRef - Understanding Competitive Endogenous RNA Network Mechanism in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Using Computational and Bioinformatics Approaches
Xuanzi Yi, Xu Cheng
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 3865. CrossRef
- Non-coding RNAs and exosomal non-coding RNAs in diabetic retinopathy: A narrative review
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Sex-, Age-, and Metabolic Disorder-Dependent Distributions of Selected Inflammatory Biomarkers among Community-Dwelling Adults
- So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):711-725. Published online April 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0119
- 5,946 View
- 83 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Inflammatory cytokines are increasingly utilized to detect high-risk individuals for cardiometabolic diseases. However, with large population and assay methodological heterogeneity, no clear reference currently exists.
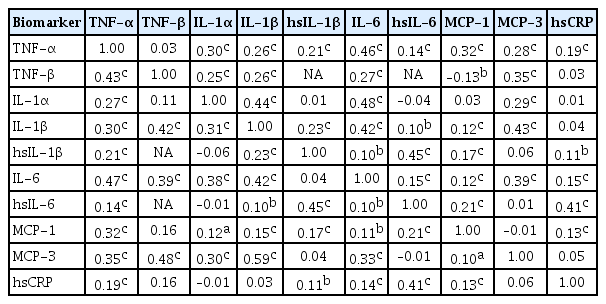
Methods Among participants of the Cardiovascular and Metabolic Diseases Etiology Research Center cohort, of community-dwelling adults aged 30 to 64 without overt cardiovascular diseases, we presented distributions of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α and -β, interleukin (IL)-1α, -1β, and 6, monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 and -3 and high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP) with and without non-detectable (ND) measurements using multiplex enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Then, we compared each markers by sex, age, and prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and dyslipidemia, using the Wilcoxon Rank-Sum Test.
Results In general, there were inconsistencies in direction and magnitude of differences in distributions by sex, age, and prevalence of cardiometabolic disorders. Overall, the median and the 99th percentiles were higher in men than in women. Older participants had higher TNF-α, high sensitivity IL-6 (hsIL-6), MCP-1, hsCRP, TNF-β, and MCP-3 median, after excluding the NDs. Participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus had higher median for all assayed biomarkers, except for TNF-β, IL-1α, and MCP-3, in which the medians for both groups were 0.00 due to predominant NDs. Compared to normotensive group, participants with hypertension had higher TNF-α, hsIL-6, MCP-1, and hsCRP median. When stratifying by dyslipidemia prevalence, the comparison varied significantly depending on the treatment of NDs.
Conclusion Our findings provide sex-, age-, and disease-specific reference values to improve risk prediction and diagnostic performance for inflammatory diseases in both population- and clinic-based settings.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Characterizing CD8+ TEMRA Cells in CP/CPPS Patients: Insights from Targeted Single-Cell Transcriptomic and Functional Investigations
Fei Zhang, Qintao Ge, Jialin Meng, Jia Chen, Chaozhao Liang, Meng Zhang
ImmunoTargets and Therapy.2024; Volume 13: 111. CrossRef - Association between physical activity and inflammatory markers in community-dwelling, middle-aged adults
So Mi Jemma Cho, Hokyou Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Justin Y. Jeon, Hyeon Chang Kim
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2021; 46(7): 828. CrossRef - The monocyte-to-lymphocyte ratio: Sex-specific differences in the tuberculosis disease spectrum, diagnostic indices and defining normal ranges
Thomas S. Buttle, Claire Y. Hummerstone, Thippeswamy Billahalli, Richard J. B. Ward, Korina E. Barnes, Natalie J. Marshall, Viktoria C. Spong, Graham H. Bothamley, Selvakumar Subbian
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0247745. CrossRef
- Characterizing CD8+ TEMRA Cells in CP/CPPS Patients: Insights from Targeted Single-Cell Transcriptomic and Functional Investigations
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Multiple Biomarkers Improved Prediction for the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Singapore Chinese Men and Women
- Yeli Wang, Woon-Puay Koh, Xueling Sim, Jian-Min Yuan, An Pan
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):295-306. Published online November 22, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0020
- 5,532 View
- 101 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Multiple biomarkers have performed well in predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) risk in Western populations. However, evidence is scarce among Asian populations.
Methods Plasma triglyceride-to-high density lipoprotein (TG-to-HDL) ratio, alanine transaminase (ALT), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), ferritin, adiponectin, fetuin-A, and retinol-binding protein 4 were measured in 485 T2DM cases and 485 age-and-sex matched controls nested within the prospective Singapore Chinese Health Study cohort. Participants were free of T2DM at blood collection (1999 to 2004), and T2DM cases were identified at the subsequent follow-up interviews (2006 to 2010). A weighted biomarker score was created based on the strengths of associations between these biomarkers and T2DM risks. The predictive utility of the biomarker score was assessed by the area under receiver operating characteristics curve (AUC).
Results The biomarker score that comprised of four biomarkers (TG-to-HDL ratio, ALT, ferritin, and adiponectin) was positively associated with T2DM risk (
P trend <0.001). Compared to the lowest quartile of the score, the odds ratio was 12.0 (95% confidence interval [CI], 5.43 to 26.6) for those in the highest quartile. Adding the biomarker score to a base model that included smoking, history of hypertension, body mass index, and levels of random glucose and insulin improved AUC significantly from 0.81 (95% CI, 0.78 to 0.83) to 0.83 (95% CI, 0.81 to 0.86;P =0.002). When substituting the random glucose levels with glycosylated hemoglobin in the base model, adding the biomarker score improved AUC from 0.85 (95% CI, 0.83 to 0.88) to 0.86 (95% CI, 0.84 to 0.89;P =0.032).Conclusion A composite score of blood biomarkers improved T2DM risk prediction among Chinese.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The association between retinol-binding protein 4 and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Xiaomeng Tan, Han Zhang, Limin Liu, Zengli Yu, Xinxin Liu, Lingling Cui, Yao Chen, Huanhuan Zhang, Zhan Gao, Zijian Zhao
International Journal of Environmental Health Research.2024; 34(2): 1053. CrossRef - Baseline glycated albumin level and risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Healthy individuals: a retrospective longitudinal observation in Korea
Kang-Su Shin, Min-Seung Park, Mi Yeon Lee, Eun Hye Cho, Hee-Yeon Woo, Hyosoon Park, Min-Jung Kwon
Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Remnant Cholesterol Is an Independent Predictor of Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Ji Hye Huh, Eun Roh, Seong Jin Lee, Sung-Hee Ihm, Kyung-Do Han, Jun Goo Kang
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(2): 305. CrossRef - A FRAMEWORK FOR THE ANALYSIS OF COMORBID CONDITIONS USING INTELLIGENT EXTRACTION OF MULTIPLE FLUID BIOMARKERS
PRIYANKA JADHAV, VINOTHINI SELVARAJU, SARITH P SATHIAN, RAMAKRISHNAN SWAMINATHAN
Journal of Mechanics in Medicine and Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Strikes and Gutters: Biomarkers and anthropometric measures for predicting diagnosed diabetes mellitus in adults in low- and middle-income countries
Sally Sonia Simmons
Heliyon.2023; 9(9): e19494. CrossRef - Association of IL-16 rs11556218 T/G polymorphism with the risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus
Dalia Ghareeb Mohammad, Hamdy Omar, Taghrid B. El-Abaseri, Wafaa Omar, Shaymaa Abdelraheem
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(1): 649. CrossRef - Biomarker Score in Risk Prediction: Beyond Scientific Evidence and Statistical Performance
Heejung Bang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 245. CrossRef
- The association between retinol-binding protein 4 and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Plasma CD36 and Incident Diabetes: A Case-Cohort Study in Danish Men and Women
- Yeli Wang, Jingwen Zhu, Sarah Aroner, Kim Overvad, Tianxi Cai, Ming Yang, Anne Tjønneland, Aase Handberg, Majken K. Jensen
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):134-142. Published online October 18, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0273
- 4,279 View
- 70 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Membrane CD36 is a fatty acid transporter implicated in the pathogenesis of metabolic disease. We aimed to evaluate the association between plasma CD36 levels and diabetes risk and to examine if the association was independent of adiposity among Danish population.
Methods We conducted a case-cohort study nested within the Danish Diet, Cancer and Health study among participants free of cardiovascular disease, diabetes and cancer and with blood samples and anthropometric measurements (height, weight, waist circumference, and body fat percentage) at baseline (1993 to 1997). CD36 levels were measured in 647 incident diabetes cases that occurred before December 2011 and a total of 3,515 case-cohort participants (236 cases overlap).
Results Higher plasma CD36 levels were associated with higher diabetes risk after adjusting for age, sex and other lifestyle factors. The hazard ratio (HR) comparing high versus low tertile of plasma CD36 levels was 1.36 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.00 to 1.86). However, the association lost its significance after further adjustment for different adiposity indices such as body mass index (HR, 1.23; 95% CI, 0.87 to 1.73), waist circumference (HR, 1.21; 95% CI, 0.88 to 1.68) or body fat percentage (HR, 1.20; 95% CI, 0.86 to 1.66). Moreover, raised plasma CD36 levels were moderately associated with diabetes risk among lean participants, but the association was not present among overweight/obese individuals.
Conclusion Higher plasma CD36 levels were associated with higher diabetes risk, but the association was not independent of adiposity. In this Danish population, the association of CD36 with diabetes risk could be either mediated or confounded by adiposity.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Multifunctionality of CD36 in Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications—Update in Pathogenesis, Treatment and Monitoring
Kamila Puchałowicz, Monika Ewa Rać
Cells.2020; 9(8): 1877. CrossRef - The Role of CD36 in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: β-Cell Dysfunction and Beyond
Jun Sung Moon, Udayakumar Karunakaran, Elumalai Suma, Seung Min Chung, Kyu Chang Won
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 222. CrossRef
- The Multifunctionality of CD36 in Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications—Update in Pathogenesis, Treatment and Monitoring
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Increased Serum Angiopoietin-Like 6 Ahead of Metabolic Syndrome in a Prospective Cohort Study
- Jun Namkung, Joon Hyung Sohn, Jae Seung Chang, Sang-Wook Park, Jang-Young Kim, Sang-Baek Koh, In Deok Kong, Kyu-Sang Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(4):521-529. Published online March 29, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0080
- 4,740 View
- 51 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Despite being an anti-obesity hepatokine, the levels of serum angiopoietin-like 6 (ANGPTL6) are elevated in various metabolic diseases. Thus, ANGPTL6 expression may reflect metabolic burden and may have compensatory roles. This study investigated the association between serum ANGPTL6 levels and new-onset metabolic syndrome.
Methods In total, 221 participants without metabolic syndrome were randomly selected from a rural cohort in Korea. Baseline serum ANGPTL6 levels were measured using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Anthropometric and biochemical markers were analyzed before and after follow-up examinations.
Results During an average follow-up period of 2.75 (interquartile range, 0.76) years, 82 participants (37.1%) presented new-onset metabolic syndrome and had higher ANGPTL6 levels before onset than those without metabolic syndrome (48.03±18.84 ng/mL vs. 64.75±43.35 ng/mL,
P =0.001). In the multivariable adjusted models, the odds ratio for the development of metabolic syndrome in the highest quartile of ANGPTL6 levels was 3.61 (95% confidence interval, 1.27 to 10.26). The use of ANGPTL6 levels in addition to the conventional components improved the prediction of new-onset metabolic syndrome (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve: 0.775 vs. 0.807,P =0.036).Conclusion Increased serum ANGPTL6 levels precede the development of metabolic syndrome and its components, including low high density lipoprotein, high triglyceride, and high glucose levels, which have an independent predictive value for metabolic syndrome.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Angiopoietin-Like Proteins: Cardiovascular Biology and Therapeutic Targeting for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases
Eric Thorin, Pauline Labbé, Mélanie Lambert, Pauline Mury, Olina Dagher, Géraldine Miquel, Nathalie Thorin-Trescases
Canadian Journal of Cardiology.2023; 39(12): 1736. CrossRef - Hyperlipidemia and hypothyroidism
Xin Su, Hua Peng, Xiang Chen, Xijie Wu, Bin Wang
Clinica Chimica Acta.2022; 527: 61. CrossRef - Multidimensional Biomarker Analysis Including Mitochondrial Stress Indicators for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Eunha Chang, Jae Seung Chang, In Deok Kong, Soon Koo Baik, Moon Young Kim, Kyu-Sang Park
Gut and Liver.2022; 16(2): 171. CrossRef - Triglyceride and Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins in Atherosclerosis
Bai-Hui Zhang, Fan Yin, Ya-Nan Qiao, Shou-Dong Guo
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship of ANGPTL6 With Neonatal Glucose Homeostasis and Fat Mass Is Disrupted in Gestational Diabetic Pregnancies
Abel Valencia-Martínez, Ute Schaefer-Graf, Encarnación Amusquivar, Emilio Herrera, Henar Ortega-Senovilla
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(10): e4078. CrossRef - Update on dyslipidemia in hypothyroidism: the mechanism of dyslipidemia in hypothyroidism
Huixing Liu, Daoquan Peng
Endocrine Connections.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - RETRACTED ARTICLE: Relationship between the development of hyperlipidemia in hypothyroidism patients
Xin Su, Xiang Chen, Bin Wang
Molecular Biology Reports.2022; 49(11): 11025. CrossRef - Effects of Exercise Intervention on Mitochondrial Stress Biomarkers in Metabolic Syndrome Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Jae Seung Chang, Jun Namkung
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(5): 2242. CrossRef - Angiopoietin-like proteins in atherosclerosis
Yi-Zhang Liu, Chi Zhang, Jie-Feng Jiang, Zhe-Bin Cheng, Zheng-Yang Zhou, Mu-Yao Tang, Jia-Xiang Sun, Liang Huang
Clinica Chimica Acta.2021; 521: 19. CrossRef - Effects of Bariatric Surgeries on Fetuin-A, Selenoprotein P, Angiopoietin-Like Protein 6, and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Concentration
Jakub Poloczek, Wojciech Kazura, Ewa Kwaśnicka, Janusz Gumprecht, Jerzy Jochem, Dominika Stygar, Munmun Chattopadhyay
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Hepatokines and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Linking Liver Pathophysiology to Metabolism
Tae Hyun Kim, Dong-Gyun Hong, Yoon Mee Yang
Biomedicines.2021; 9(12): 1903. CrossRef - Serum levels of angiopoietin-related growth factor in diabetes mellitus and chronic hemodialysis
Semra ÖZKAN ÖZTÜRK, Hilmi ATASEVEN
Cumhuriyet Medical Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - ANGPTL6 Level in Patient with Coronary Heart Disease and Its Relationship with the Severity of Coronary Artery Lesions
蕾 任
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2020; 10(05): 714. CrossRef - Investigating the Role of Myeloperoxidase and Angiopoietin-like Protein 6 in Obesity and Diabetes
Mohammad G. Qaddoumi, Muath Alanbaei, Maha M. Hammad, Irina Al Khairi, Preethi Cherian, Arshad Channanath, Thangavel Alphonse Thanaraj, Fahd Al-Mulla, Mohamed Abu-Farha, Jehad Abubaker
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Letter: Increased Serum Angiopoietin-Like 6 Ahead of Metabolic Syndrome in a Prospective Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:521-9)
Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(5): 727. CrossRef - Response: Increased Serum Angiopoietin-Like 6 Ahead of Metabolic Syndrome in a Prospective Cohort Study (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:521-9)
Jun Namkung, Kyu-Sang Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(5): 729. CrossRef
- Angiopoietin-Like Proteins: Cardiovascular Biology and Therapeutic Targeting for the Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases
- Pathophysiology
- The Phospholipid Linoleoylglycerophosphocholine as a Biomarker of Directly Measured Insulin Resistance
- Maria Camila Pérez-Matos, Martha Catalina Morales-Álvarez, Freddy Jean Karlo Toloza, Maria Laura Ricardo-Silgado, Jose Oscar Mantilla-Rivas, Jairo Arturo Pinzón-Cortes, Maritza Perez-Mayorga, Elizabeth Jiménez, Edwin Guevara, Carlos O Mendivil
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(6):466-473. Published online November 27, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.6.466
- 4,144 View
- 43 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Plasma concentrations of some lysophospholipids correlate with metabolic alterations in humans, but their potential as biomarkers of insulin resistance (IR) is insufficiently known. We aimed to explore the association between plasma linoleoylglycerophosphocholine (LGPC) and objective measures of IR in adults with different metabolic profiles.
Methods We studied 62 men and women, ages 30 to 69 years, (29% normal weight, 59% overweight, 12% obese). Participants underwent a 5-point oral glucose tolerance test (5p-OGTT) from which we calculated multiple indices of IR and insulin secretion. Fifteen participants additionally underwent a hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp for estimation of insulin-stimulated glucose disposal. Plasma LGPC was determined using high performance liquid chromatography/time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Plasma LGPC was compared across quartiles defined by the IR indices.
Results Mean LGPC was 15.4±7.6 ng/mL in women and 14.1±7.3 ng/mL in men. LGPC did not correlate with body mass in-dex, percent body fat, waist circumference, blood pressure, glycosylated hemoglobin, log-triglycerides, or high density lipoprotein cholesterol. Plasma LGPC concentrations was not systematically associated with any of the studied 5p-OGTT-derived IR indices. However, LGPC exhibited a significant negative correlation with glucose disposal in the clamp (Spearman
r =−0.56,P =0.029). Despite not being diabetic, participants with higher plasma LGPC exhibited significantly higher post-challenge plasma glucose excursions in the 5p-OGTT (P trend=0.021 for the increase in glucose area under the curve across quartiles of plasma LGPC).Conclusion In our sample of Latino adults without known diabetes, LGPC showed potential as a biomarker of IR and impaired glucose metabolism.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Identification of potential serum biomarkers associated with HbA1c levels in Indian type 2 diabetic subjects using NMR-based metabolomics
Saleem Yousf, Hitender S. Batra, Rakesh M. Jha, Devika M. Sardesai, Kalyani Ananthamohan, Jeetender Chugh, Shilpy Sharma
Clinica Chimica Acta.2024; 557: 117857. CrossRef - Comparative Metabolomic Profiling of L-Histidine and NEFA Treatments in Bovine Mammary Epithelial Cells
Wenqiang Sun, Mengze Li, Hanjun Ren, Yang Chen, Wei Zeng, Xiong Tan, Xianbo Jia, Shiyi Chen, Jie Wang, Songjia Lai
Animals.2024; 14(7): 1045. CrossRef - Mechanistic Insight of Innovative Biomarkers for Screening of Type II Diabetes
Mellitus
Shubh Deep Yadav, Neelam Singh
Current Indian Science.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Is insulin resistance tissue-dependent and substrate-specific? The role of white adipose tissue and skeletal muscle
Diana Calderón-DuPont, Ivan Torre-Villalvazo, Andrea Díaz-Villaseñor
Biochimie.2023; 204: 48. CrossRef - Causality of genetically determined metabolites and metabolic pathways on osteoarthritis: a two-sample mendelian randomization study
Yifei Gu, Qianmei Jin, Jinquan Hu, Xinwei Wang, Wenchao Yu, Zhanchao Wang, Chen Wang, Yang Liu, Yu Chen, Wen Yuan
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessing the causal effect of genetically predicted metabolites and metabolic pathways on stroke
Tianlong Zhang, Yina Cao, Jianqiang Zhao, Jiali Yao, Gang Liu
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Lipidomics in diabetes
Eun Ji Kim, Radha Ramachandran, Anthony S. Wierzbicki
Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes & Obesity.2022; 29(2): 124. CrossRef - Recent Developments in Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Screening of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Margarita Ortiz-Martínez, Mirna González-González, Alexandro J. Martagón, Victoria Hlavinka, Richard C. Willson, Marco Rito-Palomares
Current Diabetes Reports.2022; 22(3): 95. CrossRef - Discrete Correlation Summation Clustering Reveals Differential Regulation of Liver Metabolism by Thrombospondin-1 in Low-Fat and High-Fat Diet-Fed Mice
Steven M. Bronson, Brian Westwood, Katherine L. Cook, Nancy J. Emenaker, Mark C. Chappell, David D. Roberts, David R. Soto-Pantoja
Metabolites.2022; 12(11): 1036. CrossRef - Metabolic Dysfunction Biomarkers as Predictors of Early Diabetes
Carla Luís, Pilar Baylina, Raquel Soares, Rúben Fernandes
Biomolecules.2021; 11(11): 1589. CrossRef - Serum metabolomics analysis of mice that received repeated airway exposure to a water-soluble PM2.5 extract
Chen Zhao, Mengyuan Niu, Shiyu Song, Jing Li, Zhonglan Su, Yong Wang, Qian Gao, Hongwei Wang
Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety.2019; 168: 102. CrossRef
- Identification of potential serum biomarkers associated with HbA1c levels in Indian type 2 diabetic subjects using NMR-based metabolomics
- Epidemiology
- Serum Betatrophin Concentrations and the Risk of Incident Diabetes: A Nested Case-Control Study from Chungju Metabolic Disease Cohort
- Seung-Hwan Lee, Marie Rhee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Yong-Moon Park, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(1):53-62. Published online November 3, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.1.53
- 3,613 View
- 52 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Betatrophin is a newly identified hormone derived from the liver and adipose tissue, which has been suggested to regulate glucose and lipid metabolism. Circulating levels of betatrophin are altered in various metabolic diseases, although the results are inconsistent. We aimed to examine whether betatrophin is a useful biomarker in predicting the development of diabetes.
Methods A nested case-control study was performed using a prospective Chungju Metabolic disease Cohort Study. During a 4-year follow-up period, we analyzed 167 individuals who converted to diabetes and 167 non-converters, who were matched by age, sex, and body mass index. Serum betatrophin levels were measured by an ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay).
Results Baseline serum betatrophin levels were significantly higher in the converter group compared to the non-converter group (1,315±598 pg/mL vs. 1,072±446 pg/mL,
P <0.001). After adjusting for age, sex, body mass index, fasting plasma glucose, systolic blood pressure, total cholesterol, and family history of diabetes, the risk of developing diabetes showed a stepwise increase across the betatrophin quartile groups. Subjects in the highest baseline quartile of betatrophin levels had more than a threefold higher risk of incident diabetes than the subjects in the lowest quartile (relative risk, 3.275; 95% confidence interval, 1.574 to 6.814;P =0.010). However, no significant relationships were observed between serum betatrophin levels and indices of insulin resistance or β-cell function.Conclusion Circulating levels of betatrophin could be a potential biomarker for predicting new-onset diabetes. Further studies are needed to understand the underlying mechanism of this association.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Maternal and cord blood betatrophin (angiopoietin‐like protein 8) in pregnant women with gestational diabetes and normoglycemic controls: A systematic review, meta‐analysis, and meta‐regression
Faustino R. Pérez‐López, Junhua Yuan, Manuel Sánchez‐Prieto, María T. López‐Baena, Gonzalo R. Pérez‐Roncero, Seshadri Reddy Varikasuvu
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Adiponectin and ANGPTL8 in Women With Metabolic Syndrome in the Madinah Region of Saudi Arabia
Walaa Mohammedsaeed, Ahmed Ahmed, Nada Alharbi, Amjaad Aljohani, Razan Alruwaithi, Reem Alharbi, Shatha Alahmadi
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations Between Betatrophin with Irisin and Metabolic Factors: Effects of Two Exercise Trainings in Diabetic Rats
Hassan Tavassoli, Ali Heidarianpour
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2021; 362(5): 496. CrossRef - Evidences for Expression and Location of ANGPTL8 in Human Adipose Tissue
Leonardo Catalano-Iniesta, Virginia Sánchez Robledo, María Carmen Iglesias-Osma, Amparo Galán Albiñana, Sixto Carrero, Enrique J. Blanco, Marta Carretero-Hernández, José Carretero, María José García-Barrado
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(2): 512. CrossRef - Higher circulating levels of ANGPTL8 are associated with body mass index, triglycerides, and endothelial dysfunction in patients with coronary artery disease
Reza Fadaei, Hossein Shateri, Johanna K. DiStefano, Nariman Moradi, Mohammad Mohammadi, Farzad Emami, Hassan Aghajani, Nasrin Ziamajidi
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2020; 469(1-2): 29. CrossRef - Effects of a diet with or without physical activity on angiopoietin-like protein 8 concentrations in overweight/obese patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial
Hao Hu, Guoyue Yuan, Xinchen Wang, Jin Sun, Zhaohua Gao, Tingting Zhou, Wenwen Yin, Ruonan Cai, Xing Ye, Zhaoling Wang
Endocrine Journal.2019; 66(1): 89. CrossRef - The potential role of angiopoietin-like protein-8 in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a possibility for predictive diagnosis and targeted preventive measures?
Yasmine Amr Issa, Samar Samy Abd ElHafeez, Noha Gaber Amin
EPMA Journal.2019; 10(3): 239. CrossRef - A Short Review on ANGPTL-8 as an Important Regulator in Diabetes
Maryam Esfahani, Mohammad Taghi Goodarzi
Avicenna Journal of Medical Biochemistry.2019; 7(2): 61. CrossRef
- Maternal and cord blood betatrophin (angiopoietin‐like protein 8) in pregnant women with gestational diabetes and normoglycemic controls: A systematic review, meta‐analysis, and meta‐regression
- Functional and Mechanistic Integration of Infection and the Metabolic Syndrome
- Peter Sommer, Gary Sweeney
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(2):71-76. Published online April 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.2.71
- 3,248 View
- 28 Download
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader The metabolic syndrome refers to a well defined group of risk factors, including central obesity and inflammation, for the development of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Interestingly, many studies have recently led to the emergence of somewhat unexpected relationships between several infectious diseases and various aspects of the metabolic syndrome. Our understanding of the mechanisms underlying these interactions is also rapidly developing and some of these are summarized in this article. We will focus first on bacterial infection, and most notably the role of gut microbiota in regulaton of both obesity and inflammation. In particular, we focus on the role of inflammasomes and propose that understanding the role of Toll-like receptors and Nod-like receptors in the pathogenesis of inflammatory disorders with or without infection may provide novel targets for prevention and/or treatment of associated diseases. Secondly, chronic bacterial or viral infection and emerging links with metabolism will be reviewed. Finally, consideratons of biomarkers for metabolic syndrome, in particular lipocalin-2, and their link with infection will be discussed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Antimicrobial Activity of Origanum vulgare L. Correlated with the Gastrointestinal Perturbation in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
Timea Claudia Ghitea, Amina El-Kharoubi, Mariana Ganea, Erika Bimbo-Szuhai, Tiberiu Sebastian Nemeth, Gabriela Ciavoi, Monica Foghis, Luciana Dobjanschi, Annamaria Pallag, Otilia Micle
Molecules.2021; 26(2): 283. CrossRef - COVID-19 severity in relation to sociodemographics and vitamin D use
Darya Saeed Abdulateef, Heshu Sulaiman Rahman, Jamal Mahmood Salih, Sangar Mahmoud Osman, Trifa Abdalla Mahmood, Shirwan Hama Salih Omer, Rana Adnan Ahmed
Open Medicine.2021; 16(1): 591. CrossRef - Iron Reshapes the Gut Microbiome and Host Metabolism
Amy Botta, Nicole G. Barra, Nhat Hung Lam, Samantha Chow, Kostas Pantopoulos, Jonathan D. Schertzer, Gary Sweeney
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2021; 10(2): 160. CrossRef - Alteration in Cellular Signaling and Metabolic Reprogramming during Viral Infection
Anil Pant, Lara Dsouza, Zhilong Yang, Benjamin Gewurz, Vinayaka R. Prasad
mBio.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors increasing the risk of mortality and morbidity due to coronavirus infection in patients with metabolic syndrome
Altansuvd Enkhtur, Joon-Sup Yoon, Chang-Woo Lee
Precision and Future Medicine.2020; 4(3): 83. CrossRef - Holo-lipocalin-2–derived siderophores increase mitochondrial ROS and impair oxidative phosphorylation in rat cardiomyocytes
Erfei Song, Sofhia V. Ramos, Xiaojing Huang, Ying Liu, Amy Botta, Hye Kyoung Sung, Patrick C. Turnbull, Michael B. Wheeler, Thorsten Berger, Derek J. Wilson, Christopher G. R. Perry, Tak W. Mak, Gary Sweeney
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2018; 115(7): 1576. CrossRef - Tuberculosis of the Breast: An Initial Presentation of the Metabolic Syndrome with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in a Young Nigerian Woman
M. A. Adeiza, R. Yusuf, A. A. Liman, P. Abur, F. Bello, A. A. Abba
Case Reports in Infectious Diseases.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Systematic Review of the Relation Between Intestinal Microbiota and Toll-Like Receptors in the Metabolic Syndrome: What Do We Know So Far?
José Pedro Portela-Cidade, Marta Borges-Canha, Adelino Ferreira Leite-Moreira, Pedro Pimentel-Nunes
GE Portuguese Journal of Gastroenterology.2015; 22(6): 240. CrossRef - Impact of Cadmium Exposure on the Association between Lipopolysaccharide and Metabolic Syndrome
Seung Han, Kyoung Ha, Ja Jeon, Hae Kim, Kwan Lee, Dae Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2015; 12(9): 11396. CrossRef - Regulation of Iron and Its Significance in Obesity and Complications
Yee Kwan Chan, Hye Kyoung Sung, Gary Sweeney
The Korean Journal of Obesity.2014; 23(4): 222. CrossRef - Direct effects of adipokines on the heart: focus on adiponectin
Min Park, Gary Sweeney
Heart Failure Reviews.2013; 18(5): 631. CrossRef - The Thioredoxin System as a Therapeutic Target in Human Health and Disease
Dler Faieeq Darweesh Mahmood, Amna Abderrazak, Khadija El Hadri, Thomas Simmet, Mustapha Rouis
Antioxidants & Redox Signaling.2013; 19(11): 1266. CrossRef - Immunoglobulin E and mast cell proteases are potential risk factors of impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance in humans
Zhen Wang, Hong Zhang, Xu-Hui Shen, Kui-Li Jin, Guo-fen Ye, Wei Qiu, Li Qian, Bo Li, Yong-Hong Zhang, Guo-Ping Shi
Annals of Medicine.2013; 45(3): 220. CrossRef - Immunoglobulin E and Mast Cell Proteases Are Potential Risk Factors of Human Pre-Diabetes and Diabetes Mellitus
Zhen Wang, Hong Zhang, Xu-Hui Shen, Kui-Li Jin, Guo-fen Ye, Li Qian, Bo Li, Yong-Hong Zhang, Guo-Ping Shi, Yiqing Song
PLoS ONE.2011; 6(12): e28962. CrossRef
- The Antimicrobial Activity of Origanum vulgare L. Correlated with the Gastrointestinal Perturbation in Patients with Metabolic Syndrome
- Cystatin C is a Valuable Marker for Predicting Future Cardiovascular Diseases in Type 2 Diabetic Patients.
- Seung Hwan Lee, Kang Woo Lee, Eun Sook Kim, Ye Ree Park, Hun Sung Kim, Shin Ae Park, Mi Ja Kang, Yu Bai Ahn, Kun Ho Yoon, Bong Yun Cha, Ho Young Son, Hyuk Sang Kwon
- Korean Diabetes J. 2008;32(6):488-497. Published online December 1, 2008
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2008.32.6.488
- 2,388 View
- 22 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Recent studies suggest that serum Cystatin C is both a sensitive marker for renal dysfunction and a predictive marker for cardiovascular diseases. We aimed to evaluate the association between Cystatin C and various biomarkers and to find out its utility in estimating risk for cardiovascular diseases in type 2 diabetic patients. METHODS: From June 2006 to March 2008, anthropometric measurements and biochemical studies including biomarkers for risk factors of cardiovascular diseases were done in 520 type 2 diabetic patients. A 10-year risk for coronary heart diseases and stroke was estimated using Framingham risk score and UKPDS risk engine. RESULTS: The independent variables showing statistically significant associations with Cystatin C were age (beta = 0.009, P < 0.0001), hemoglobin (beta = -0.038, P = 0.0006), serum creatinine (beta = 0.719, beta < 0.0001), uric acid (beta = 0.048, P = 0.0004), log hsCRP (beta = 0.035, P = 0.0021) and homocysteine (beta = 0.005, P = 0.0228). The levels of microalbuminuria, carotid intima-media thickness, fibrinogen and lipoprotein (a) also correlated with Cystatin C, although the significance was lost after multivariate adjustment. Calculated risk for coronary heart diseases increased in proportion to Cystatin C quartiles: 3.3 +/- 0.4, 6.2 +/- 0.6, 7.6 +/- 0.7, 8.4 +/- 0.7% from Framingham risk score (P < 0.0001); 13.1 +/- 0.9, 21.2 +/- 1.6, 26.1 +/- 1.7, 35.4 +/- 2.0% from UKPDS risk engine (P < 0.0001) (means +/- SE). CONCLUSIONS: Cystatin C is significantly correlated with various emerging biomarkers for cardiovascular diseases. It was also in accordance with the calculated risk for cardiovascular diseases. These findings verify Cystatin C as a valuable and useful marker for predicting future cardiovascular diseases in type 2 diabetic patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lack of Association between Serum Cystatin C Levels and Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Patients
Eun Hee Kim, Ji Hee Yu, Sang Ah Lee, Eui Young Kim, Won Gu Kim, Seung Hun Lee, Eun Hee Cho, Eun Hee Koh, Woo Je Lee, Min-Seon Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Ki-Up Lee
Korean Diabetes Journal.2010; 34(2): 95. CrossRef - Insulin resistance and inflammation may have an additional role in the link between cystatin C and cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients
Seung-Hwan Lee, Shin-Ae Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Hyeon-Woo Yim, Yu-Bae Ahn, Kun-Ho Yoon, Bong-Yun Cha, Ho-Young Son, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Metabolism.2010; 59(2): 241. CrossRef
- Lack of Association between Serum Cystatin C Levels and Coronary Artery Disease in Diabetic Patients

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





