
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Article category
- Page Path
- HOME > Article category > Article category
Erratum
- Hyperinsulinemia in Obesity, Inflammation, and Cancer
- Anni M.Y. Zhang, Elizabeth A. Wellberg, Janel L. Kopp, James D. Johnson
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):622-622. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0131
- Corrects: Diabetes Metab J 2021;45(3):285
- 3,144 View
- 85 Download
- 7 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes mellitus as growing aetiologies of hepatocellular carcinoma
Stephanie Talamantes, Michela Lisjak, Eduardo H. Gilglioni, Camilo J. Llamoza-Torres, Bruno Ramos-Molina, Esteban N. Gurzov
JHEP Reports.2023; : 100811. CrossRef - The impact of poor metabolic health on aggressive breast cancer: adipose tissue and tumor metabolism
Barbara Mensah Sankofi, Estefania Valencia-Rincón, Malika Sekhri, Adriana L. Ponton-Almodovar, Jamie J. Bernard, Elizabeth A. Wellberg
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dietary insulin indices and low-carbohydrate diet and the odds of colorectal cancer: a case-control study
Alireza Bahrami, Karim Parastouei, Maryam Taghdir, Mojtaba Ghadyani
European Journal of Cancer Prevention.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Riesgo cardiovascular en adultos: El papel de la Hiperinsulinemia
María Eugenia Lucena de Ustáriz, Katherine Jazmín Bonilla Adriano, Mónica Gabriela Moncayo Romero, Rosa Elisa Cruz Tenempaguay
Anatomía Digital.2023; 6(4.3): 777. CrossRef - Obesity history, physical exam, laboratory, body composition, and energy expenditure: An Obesity Medicine Association (OMA) Clinical Practice Statement (CPS) 2022
Karlijn Burridge, Sandra M. Christensen, Angela Golden, Amy B. Ingersoll, Justin Tondt, Harold E. Bays
Obesity Pillars.2022; 1: 100007. CrossRef - Special Issue: Emerging Paradigms in Insulin Resistance
J. Jason Collier, Susan J. Burke
Biomedicines.2022; 10(7): 1471. CrossRef - Obesity-Associated ECM Remodeling in Cancer Progression
Junyan Li, Ren Xu
Cancers.2022; 14(22): 5684. CrossRef
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes mellitus as growing aetiologies of hepatocellular carcinoma
Letter
- Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
- Ja Young Jeon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):613-614. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0129
- 3,336 View
- 83 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The relationships between variables of glycated hemoglobin and diabetes distress in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus
V.I. Pankiv, T.Yu. Yuzvenko
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(6): 424. CrossRef
- The relationships between variables of glycated hemoglobin and diabetes distress in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus
Corrigendum
- Early Glycosylated Hemoglobin Target Achievement Predicts Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Joonyub Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):621-621. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0119
- Corrects: Diabetes Metab J 2021;45(3):337
- 2,996 View
- 70 Download
- 1 Crossref
Response
- Effects of a DPP-4 Inhibitor and RAS Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:251-9)
- Sang Youl Rhee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):619-620. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0118
- 3,011 View
- 80 Download
- 2 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- COVID-19 Outcomes and Diabetes Mellitus: A Comprehensive Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study
Karolina Akinosoglou, Georgios Schinas, Evanthia Bletsa, Magdaline Bristianou, Leonidas Lanaras, Charalambos Michailides, Theodoros Katsikas, Fotios Barkas, Evangelos Liberopoulos, Vasileios Kotsis, Konstantinos Tentolouris, Pinelopi Grigoropoulou, Archon
Microorganisms.2023; 11(6): 1416. CrossRef - Baseline moderate-range albuminuria is associated with protection against severe COVID-19 pneumonia
Amir Bashkin, Mona Shehadeh, Lina Shbita, Kamil Namoura, Ronza Haiek, Elena Kuyantseva, Yousef Boulos, Orly Yakir, Etty Kruzel-Davila
World Journal of Diabetes.2022; 13(12): 1154. CrossRef
- COVID-19 Outcomes and Diabetes Mellitus: A Comprehensive Multicenter Prospective Cohort Study
Letter
- Effects of a DPP-4 Inhibitor and RAS Blockade on Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Diabetes and COVID-19 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:251-9)
- Guntram Schernthaner
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):615-616. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0081
- 3,180 View
- 71 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The risk of common hypoglycemic and antihypertensive medications and COVID-19: A 2-sample Mendelian randomization study
Ya Wang, Kai Li, Jiaxing Zeng, Shunyu Lu, Wangsheng Deng
Medicine.2024; 103(6): e36423. CrossRef - The management of type 2 diabetes before, during and after Covid-19 infection: what is the evidence?
Leszek Czupryniak, Dror Dicker, Roger Lehmann, Martin Prázný, Guntram Schernthaner
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef
- The risk of common hypoglycemic and antihypertensive medications and COVID-19: A 2-sample Mendelian randomization study
Reviews
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Computed Tomography-Derived Myosteatosis and Metabolic Disorders
- Iva Miljkovic, Chantal A. Vella, Matthew Allison
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):482-491. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0277
- 6,188 View
- 235 Download
- 41 Web of Science
- 44 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
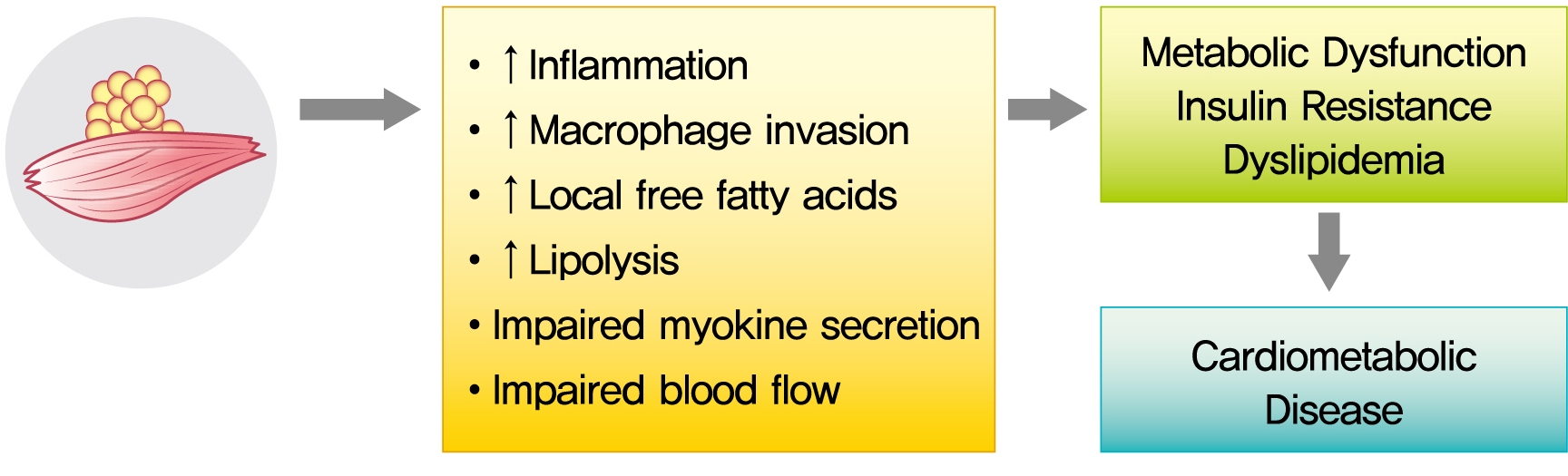
- The role of ectopic adipose tissue infiltration into skeletal muscle (i.e., myosteatosis) for metabolic disorders has received considerable and increasing attention in the last 10 years. The purpose of this review was to evaluate and summarize existing studies focusing on computed tomography (CT)-derived measures of myosteatosis and metabolic disorders. There is consistent evidence that CT-derived myosteatosis contributes to dysglycemia, insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and inflammation, and, to some extent, dyslipidemia, independent of general obesity, visceral fat, and other relevant risk factors, suggesting that it may serve as a tool for metabolic risk prediction. Identification of which muscles should be examined, and the standardized CT protocols to be employed, are necessary to enhance the applicability of findings from epidemiologic studies of myosteatosis. Additional and longer longitudinal studies are necessary to confirm a role of myosteatosis in the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus, and examine these associations in a variety of muscles across multiple race/ethnic populations. Given the emerging role of myosteatosis in metabolic health, well-designed intervention studies are needed to investigate relevant lifestyle and pharmaceutical approaches.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of Muscle Fat Content and Muscle Mass With Impaired Lung Function in Young Adults With Obesity: Evaluation With MRI
Xin Yu, Yan-Hao Huang, You-Zhen Feng, Zhong-Yuan Cheng, Cun-Chuan Wang, Xiang-Ran Cai
Academic Radiology.2024; 31(1): 9. CrossRef - Skeletal muscle alterations indicate poor prognosis in cirrhotic patients: a multicenter cohort study in China
Xin Zeng, Zhi-Wen Shi, Jia-Jun Yu, Li-Fen Wang, Chun-Yan Sun, Yuan-Yuan Luo, Pei-Mei Shi, Yong Lin, Yue-Xiang Chen, Jia Guo, Chun-Qing Zhang, Wei-Fen Xie
Hepatology International.2024; 18(2): 673. CrossRef - Subtype-specific Body Composition and Metabolic Risk in Patients With Primary Aldosteronism
Seung Shin Park, Chang Ho Ahn, Sang Wan Kim, Ji Won Yoon, Jung Hee Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(2): e788. CrossRef - Myosteatosis as a novel predictor of new‐onset diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation
Takahito Wakamiya, Takuya Fujimoto, Takahito Endo, Shun Nishioka, Naoki Yokoyama, Shimpei Yamashita, Kazuro Kikkawa, Yoji Hyodo, Takeshi Ishimura, Yasuo Kohjimoto, Isao Hara, Masato Fujisawa
International Journal of Urology.2024; 31(1): 39. CrossRef - Predictors of visceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue and muscle density: The ShapeUp! Kids study
Gertraud Maskarinec, Yurii Shvetsov, Michael C. Wong, Devon Cataldi, Jonathan Bennett, Andrea K. Garber, Steven D. Buchthal, Steven B. Heymsfield, John A. Shepherd
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2024; 34(3): 799. CrossRef - Association of daily carbohydrate intake with intermuscular adipose tissue in Korean individuals with obesity: a cross-sectional study
Ha-Neul Choi, Young-Seol Kim, Jung-Eun Yim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2024; 18(1): 78. CrossRef - Myosteatosis is associated with poor survival after kidney transplantation: a large retrospective cohort validation
Jie Chen, Yue Li, Chengjie Li, Turun Song
Abdominal Radiology.2024; 49(4): 1210. CrossRef - Regenerative rehabilitation measures to restore tissue function after arsenic exposure
Adam A. Jasper, Kush H. Shah, Helmet Karim, Swathi Gujral, Iva Miljkovic, Caterina Rosano, Aaron Barchowsky, Amrita Sahu
Current Opinion in Biomedical Engineering.2024; 30: 100529. CrossRef - Impact of CFTR modulator therapy on body composition as assessed by thoracic computed tomography: A follow-up study
Víctor Navas-Moreno, Fernando Sebastian-Valles, Víctor Rodríguez-Laval, Carolina Knott-Torcal, Mónica Marazuela, Nuria Sánchez de la Blanca, Jose Alfonso Arranz Martín, Rosa María Girón, Miguel Antonio Sampedro-Núñez
Nutrition.2024; 123: 112425. CrossRef - Myosteatosis predicts postoperative complications and long‐term survival in robotic gastrectomy for gastric cancer: A propensity score analysis
Pingan Ding, Jiaxiang Wu, Haotian Wu, Tongkun Li, Jiaxuan Yang, Li Yang, Honghai Guo, Yuan Tian, Peigang Yang, Lingjiao Meng, Qun Zhao
European Journal of Clinical Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A multifaceted and inclusive methodology for the detection of sarcopenia in patients undergoing bariatric surgery: an in-depth analysis of current evidence
Eunhye Seo, Yeongkeun Kwon, Ahmad ALRomi, Mohannad Eledreesi, Sungsoo Park
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Body Composition at CT and Risk of Future Disease
Michael A. Ohliger
Radiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between hypertension and myosteatosis evaluated by abdominal computed tomography
Han Na Jung, Yun Kyung Cho, Hwi Seung Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Woo Je Lee, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Hypertension Research.2023; 46(4): 845. CrossRef - Muscle fat infiltration in chronic kidney disease: a marker related to muscle quality, muscle strength and sarcopenia
Carla Maria Avesani, Aline Miroski de Abreu, Heitor S. Ribeiro, Torkel B. Brismar, Peter Stenvinkel, Alice Sabatino, Bengt Lindholm
Journal of Nephrology.2023; 36(3): 895. CrossRef - Myosteatosis: a potential missing link between hypertension and metabolic disorder in the Asian population
Minyoung Lee, Sungha Park
Hypertension Research.2023; 46(6): 1603. CrossRef - Interplay of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: sarcopenic obesity
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 144: 155577. CrossRef - Association between sarcopenic obesity and poor muscle quality based on muscle quality map and abdominal computed tomography
Yun Kyung Cho, Han Na Jung, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Joong‐Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Hong‐Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Obesity.2023; 31(6): 1547. CrossRef - Chest CT opportunistic biomarkers for phenotyping high-risk COVID-19 patients: a retrospective multicentre study
Anna Palmisano, Chiara Gnasso, Alberto Cereda, Davide Vignale, Riccardo Leone, Valeria Nicoletti, Simone Barbieri, Marco Toselli, Francesco Giannini, Marco Loffi, Gianluigi Patelli, Alberto Monello, Gianmarco Iannopollo, Davide Ippolito, Elisabetta Maria
European Radiology.2023; 33(11): 7756. CrossRef - Early menopause and premature ovarian insufficiency may increase the risk of sarcopenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Efstathios Divaris, Panagiotis Anagnostis, Nifon K. Gkekas, Evangelia Kouidi, Dimitrios G. Goulis
Maturitas.2023; 175: 107782. CrossRef - The Important Role of Intermuscular Adipose Tissue on Metabolic Changes Interconnecting Obesity, Ageing and Exercise: A Systematic Review
I Gusti Putu Suka Aryana, Ivana Beatrice Paulus, Sanjay Kalra, Dian Daniella, Raden Ayu Tuty Kuswardhani, Ketut Suastika, Sony Wibisono
European Endocrinology.2023; 19(1): 54. CrossRef - Increase in skeletal muscular adiposity and cognitive decline in a biracial cohort of older men and women
Caterina Rosano, Anne Newman, Adam Santanasto, Xiaonan Zhu, Bret Goodpaster, Iva Miljkovic
Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.2023; 71(9): 2759. CrossRef - Myosteatosis and bone marrow adiposity are not associated among postmenopausal women with fragility fractures
Sammy Badr, Héloïse Dapvril, Daniela Lombardo, Huda Khizindar, Claire Martin, Bernard Cortet, Anne Cotten, Julien Paccou
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between trunk intramuscular adipose tissue content and prevalence of metabolic syndrome in middle-aged Japanese men
Noriko I. Tanaka, Masataka Suwa, Hisashi Maeda, Aya Tomita, Takayuki Imoto, Hiroshi Akima
Nutrition.2023; 113: 112083. CrossRef - Sarcopenic obesity and its relation with muscle quality and mortality in patients on chronic hemodialysis
Alice Sabatino, Carla Maria Avesani, Giuseppe Regolisti, Marianna Adinolfi, Giuseppe Benigno, Marco Delsante, Enrico Fiaccadori, Ilaria Gandolfini
Clinical Nutrition.2023; 42(8): 1359. CrossRef - Skeletal muscle adiposity is a novel risk factor for poor cognition in African Caribbean women
Adrianna I. Acevedo‐Fontánez, Ryan K. Cvejkus, Joseph M. Zmuda, Allison L. Kuipers, Emma Barinas‐Mitchell, Akira Sekikawa, Victor Wheeler, Caterina Rosano, Iva Miljkovic
Obesity.2023; 31(9): 2398. CrossRef - Obesity, Sarcopenia and Myosteatosis: Impact on Clinical Outcomes in the Operative Management of Crohn’s Disease
Mark Donnelly, Dorothee Driever, Éanna J Ryan, Jessie A Elliott, John Finnegan, Deirdre McNamara, Ian Murphy, Kevin C Conlon, Paul C Neary, Dara O Kavanagh, James M O’Riordan
Inflammatory Bowel Diseases.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Meld-sarcopenia score and skeletal muscle density predicts short-term readmission of patients with hepatic encephalopathy
Shuo Yang, Lin Zhang, Qian Jin, Jian Wang, Danli Ma, Jie Gao, Rui Huang
European Journal of Radiology.2023; 169: 111178. CrossRef - Muscle Fat Content Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis in Chinese Adults
W. Guo, X. Zhao, D. Cheng, X. Liang, M. Miao, X. Li, J. Lu, N. Xu, Shuang Hu, Qun Zhang
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2023; 27(11): 960. CrossRef - Association between relative muscle strength and hypertension in middle-aged and older Chinese adults
Jin-hua Luo, Tu-ming Zhang, Lin-lin Yang, Yu-ying Cai, Yu Yang
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dynapenic Abdominal Obesity as a Risk Factor for Metabolic Syndrome in Individual 50 Years of Age or Older: English Longitudinal Study of Ageing
P.C. Ramírez, R. de Oliveira Máximo, D. Capra de Oliveira, A.F. de Souza, M. Marques Luiz, M. L. Bicigo Delinocente, A. Steptoe, C. de Oliveira, Tiago da Silva Alexandre
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2023; 27(12): 1188. CrossRef - Editorial Comment to Myosteatosis as a novel predictor of urinary incontinence after robot‐assisted radical prostatectomy
Nobuhiro Haga, Naotaka Gunge, Hiroshi Matsuzaki, Yu Okabe, Takeshi Miyazaki
International Journal of Urology.2022; 29(1): 40. CrossRef - Ammonia and the Muscle: An Emerging Point of View on Hepatic Encephalopathy
Simone Di Cola, Silvia Nardelli, Lorenzo Ridola, Stefania Gioia, Oliviero Riggio, Manuela Merli
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(3): 611. CrossRef - Single skeletal muscle fiber mechanical properties: a muscle quality biomarker of human aging
Jae-Young Lim, Walter R. Frontera
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2022; 122(6): 1383. CrossRef - Sarcopenia in Patients with Cirrhosis after Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt Placement
Jiacheng Liu, Jinqiang Ma, Chongtu Yang, Manman Chen, Qin Shi, Chen Zhou, Songjiang Huang, Yang Chen, Yingliang Wang, Tongqiang Li, Bin Xiong
Radiology.2022; 303(3): 711. CrossRef - Myosteatosis Significantly Predicts Persistent Dyspnea and Mobility Problems in COVID-19 Survivors
Rebecca De Lorenzo, Anna Palmisano, Antonio Esposito, Chiara Gnasso, Valeria Nicoletti, Riccardo Leone, Davide Vignale, Elisabetta Falbo, Marica Ferrante, Marta Cilla, Cristiano Magnaghi, Sabina Martinenghi, Giordano Vitali, Alessio Molfino, Patrizia Rove
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prognostic value of myosteatosis in patients with lung cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Shaofang Feng, Huiwen Mu, Rong Hou, Yunxin Liu, Jianjun Zou, Zheng Zhao, Yubing Zhu
International Journal of Clinical Oncology.2022; 27(7): 1127. CrossRef - Muscle Fat Content Is Strongly Associated With Hyperuricemia: A Cross-Sectional Study in Chinese Adults
Ningxin Chen, Tingting Han, Hongxia Liu, Jie Cao, Wenwen Liu, Didi Zuo, Ting Zhang, Xiucai Lan, Xian Jin, Yurong Weng, Yaomin Hu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Advances in muscle health and nutrition: A toolkit for healthcare professionals
Carla M. Prado, Francesco Landi, Samuel T.H. Chew, Philip J. Atherton, Jeroen Molinger, Tobias Ruck, Maria Cristina Gonzalez
Clinical Nutrition.2022; 41(10): 2244. CrossRef - Factors related to trunk intramuscular adipose tissue content – A comparison of younger and older men
Funa Kitagawa, Madoka Ogawa, Akito Yoshiko, Yoshiharu Oshida, Teruhiko Koike, Hiroshi Akima, Noriko I. Tanaka
Experimental Gerontology.2022; 168: 111922. CrossRef - Association of myosteatosis with various body composition abnormalities and longer length of hospitalization in patients with decompensated cirrhosis
Xiaoyu Wang, Mingyu Sun, Yifan Li, Gaoyue Guo, Wanting Yang, Lihong Mao, Zihan Yu, Yangyang Hui, Xiaofei Fan, Binxin Cui, Kui Jiang, Chao Sun
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Peripheral bone structure, geometry, and strength and muscle density as derived from peripheral quantitative computed tomography and mortality among rural south Indian older adults
Guru Rajesh Jammy, Robert M. Boudreau, Iva Miljkovic, Pawan Kumar Sharma, Sudhakar Pesara Reddy, Susan L. Greenspan, Anne B. Newman, Jane A. Cauley, Bert B. Little
PLOS Global Public Health.2022; 2(10): e0000333. CrossRef - Muscle fat contents rather than muscle mass determines nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in patients with severe obesity
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Won Lee, Seungwan Ryu, Hye Soon Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Youngsung Suh
Obesity.2022; 30(12): 2440. CrossRef - Sex- and region-specific associations of skeletal muscle mass with metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease
Pei Xiao, Pu Liang, Panjun Gao, Jinyi Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Imaging based body composition profiling and outcomes after oncologic liver surgery
Lorenzo Bernardi, Raffaello Roesel, Filippo Vagelli, Pietro Majno-Hurst, Alessandra Cristaudi
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association of Muscle Fat Content and Muscle Mass With Impaired Lung Function in Young Adults With Obesity: Evaluation With MRI
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Management of Cardiovascular Risk in Perimenopausal Women with Diabetes
- Catherine Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):492-501. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0262
- 5,644 View
- 154 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
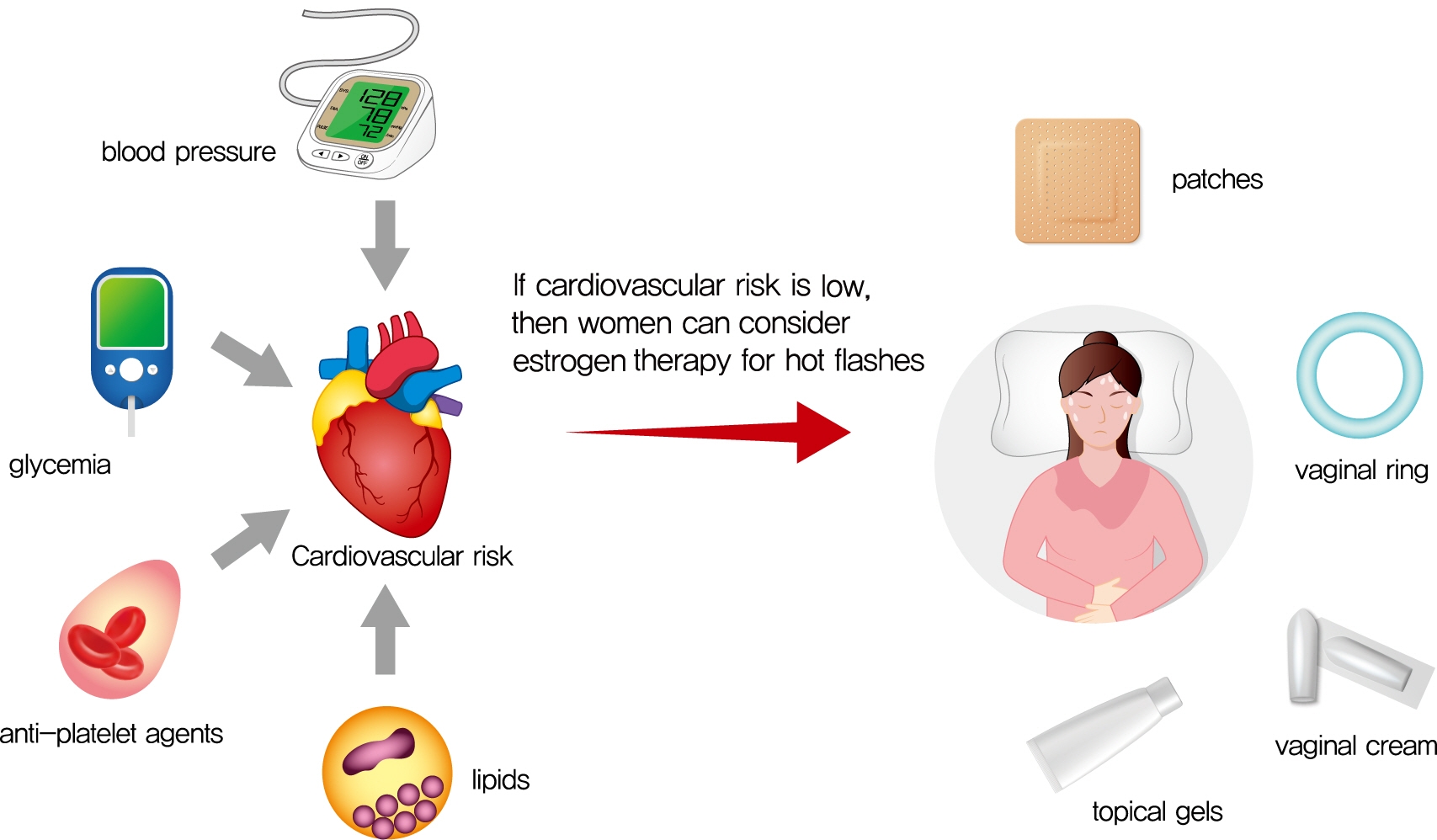
- Cardiovascular disease is the primary cause of mortality in women and men with diabetes. Due to age and worsening of risk factors over the menopausal transition, risk of coronary heart disease events increases in postmenopausal women with diabetes. Randomized studies have conflicted regarding the beneficial impact of estrogen therapy upon intermediate cardiovascular disease markers and events. Therefore, estrogen therapy is not currently recommended for indications other than symptom management. However, for women at low risk of adverse events, estrogen therapy can be used to minimize menopausal symptoms. The risk of adverse events can be estimated using risk engines for the calculation of cardiovascular risk and breast cancer risk in conjunction with screening tools such as mammography. Use of estrogen therapy, statins, and anti-platelet agents can be guided by such calculators particularly for younger women with diabetes. Risk management remains focused upon lifestyle behaviors and achieving optimal levels of cardiovascular risk factors, including lipids, glucose, and blood pressure. Use of pharmacologic therapies to address these risk factors, particularly specific hypoglycemic agents, may provide some additional benefit for risk prevention. The minimal benefit for women with limited life expectancy and risk of complications with intensive therapy should also be considered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurse-led intervention in the management of patients with cardiovascular diseases: a brief literature review
Xiaoqin Qiu
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Determination of the Level of Cardiovascular Risk in 172,282 Spanish Working Women
Ángel Arturo López-González, María Albaladejo Blanco, Cristina Vidal Ribas, Pilar Tomás-Gil, Pere Riutord Sbert, José Ignacio Ramírez-Manent
Diagnostics.2023; 13(17): 2734. CrossRef - Comparison of seven surrogate insulin resistance indexes for predicting the prevalence of carotid atherosclerosis in normal-weight individuals
Zeyu Liu, Bi Deng, Qin Huang, Ruxin Tu, Fang Yu, Jian Xia, Jie Feng
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications
Joon Ho Moon, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 3. CrossRef - Reproductive Life Span and Severe Hypoglycemia Risk in Postmenopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Soyeon Kang, Yong-Moon Park, Dong Jin Kwon, Youn-Jee Chung, Jeong Namkung, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 578. CrossRef - Global hotspots and prospects of perimenopausal depression: A bibliometric analysis via CiteSpace
Mingzhou Gao, Hao Zhang, Zhan Gao, Ya Sun, Jieqiong Wang, Fengqin Wei, Dongmei Gao
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - State of metabolic processes and ways to improve them in premenopausal women due to the life extension strategy
I.V. Lakhno
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY.2021; (61): 51. CrossRef
- Nurse-led intervention in the management of patients with cardiovascular diseases: a brief literature review
Original Articles
- Complications
- Study on Risk Factors of Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Establishment of Prediction Model
- Birong Wu, Zheyun Niu, Fan Hu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):526-538. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0100
- 7,211 View
- 307 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
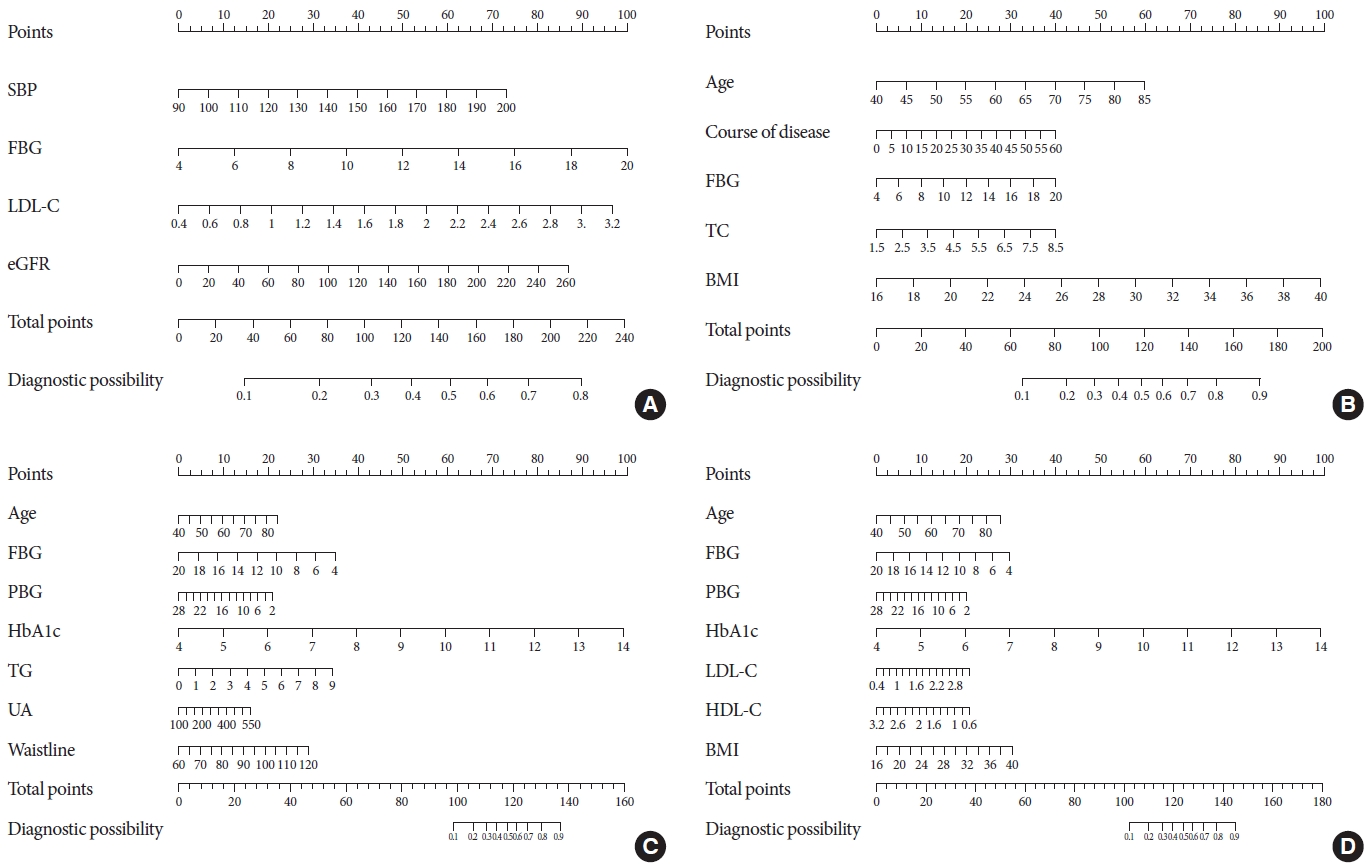
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) is one of the most serious complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). DPN increases the risk of ulcers, foot infections, and noninvasive amputations, ultimately leading to long-term disability.
Methods
Seven hundred patients with T2DM were investigated from 2013 to 2017 in the Sanlin community by obtaining basic data from the electronic medical record system (EMRS). From September 2018 to July 2019, 681 patients (19 missing) were investigated using a questionnaire, physical examination, biochemical index test, and follow-up Toronto clinical scoring system (TCSS) test. Patients with a TCSS score ≥6 points were diagnosed with DPN. After removing missing values, 612 patients were divided into groups in a 3:1 ratio for external validation. Using different Lasso analyses (misclassification error, mean squared error, –2log-likelihood, and area under curve) and a logistic regression analysis of the training set, models A, B, C, and D were established. The receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve, calibration plot, dynamic component analysis (DCA) measurements, net classification improvement (NRI) and integrated discrimination improvement (IDI) were used to validate discrimination and clinical practicality of the model.
Results
Through data analysis, model A (containing four factors), model B (containing five factors), model C (containing seven factors), and model D (containing seven factors) were built. After calibration, ROC curve, DCA, NRI and IDI, models C and D exhibited better accuracy and greater predictive power.
Conclusion
Four prediction models were established to assist with the early screening of DPN in patients with T2DM. The influencing factors in model C and D are more important factors for patients with T2DM diagnosed with DPN. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetes Mellitusu Olan Bireylerde Periferal Nöropati ve Hemşirelik Bakımı
Semanur BİLGİÇ, Burcu BAYRAK KAHRAMAN
Akdeniz Hemşirelik Dergisi.2024; 2(3): 113. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Subclinical Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Li Gao, Jiexing Qin, Ying Chen, Wenqun Jiang, Desheng Zhu, Xiajun Zhou, Jie Ding, Huiying Qiu, Yan Zhou, Qing Dong, Yangtai Guan
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2024; Volume 17: 417. CrossRef - Predictive model and risk analysis for peripheral vascular disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients using machine learning and shapley additive explanation
Lianhua Liu, Bo Bi, Li Cao, Mei Gui, Feng Ju
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Multi‐feature, Chinese–Western medicine‐integrated prediction model for diabetic peripheral neuropathy based on machine learning and SHAP
Aijuan Jiang, Jiajie Li, Lujie Wang, Wenshu Zha, Yixuan Lin, Jindong Zhao, Zhaohui Fang, Guoming Shen
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical significance of vascular endothelial growth factor and endothelin-1 in serum levels as novel indicators for predicting the progression of diabetic nephropathy
Wei Chu, Lin-Lin Ma, Bin-Xian Li, Ming-Cheng Li
European Journal of Inflammation.2023; 21: 1721727X2311515. CrossRef - Common and contrast determinants of peripheral artery disease and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in North Central Nigeria
Felicia Ehusani Anumah, Yakubu Lawal, Rifkatu Mshelia-Reng, Special Odiase Omonua, Kenechukwu Odumodu, Ramatu Shuaibu, Ukamaka Dorothy Itanyi, Amina Ibrahim Abubakar, Hadijat Oluseyi kolade-Yunusa, Zumnan Songden David, Babajide Ogunlana, Andrew Clarke, O
The Foot.2023; 55: 101987. CrossRef - ApoA-I and Diabetes
Thomas W. King, Blake J. Cochran, Kerry-Anne Rye
Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology.2023; 43(8): 1362. CrossRef - Study on risk factors of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and establishment of a prediction model by machine learning
Xiaoyang Lian, Juanzhi Qi, Mengqian Yuan, Xiaojie Li, Ming Wang, Gang Li, Tao Yang, Jingchen Zhong
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Establishment and health management application of a prediction model for high-risk complication combination of type 2 diabetes mellitus based on data mining
Xin Luo, Jijia Sun, Hong Pan, Dian Zhou, Ping Huang, Jingjing Tang, Rong Shi, Hong Ye, Ying Zhao, An Zhang, Yee Gary Ang
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(8): e0289749. CrossRef - Development and validation of risk prediction model for diabetic neuropathy among diabetes mellitus patients at selected referral hospitals, in Amhara regional state Northwest Ethiopia, 2005–2021
Negalgn Byadgie Gelaw, Achenef Asmamaw Muche, Adugnaw Zeleke Alem, Nebiyu Bekele Gebi, Yazachew Moges Chekol, Tigabu Kidie Tesfie, Tsion Mulat Tebeje, Jacopo Sabbatinelli
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(8): e0276472. CrossRef - Machine Learning Models for Blood Glucose Level Prediction in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Kui Liu, Linyi Li, Yifei Ma, Jun Jiang, Zhenhua Liu, Zichen Ye, Shuang Liu, Chen Pu, Changsheng Chen, Yi Wan
JMIR Medical Informatics.2023; 11: e47833. CrossRef - Establishment of models to predict factors influencing periodontitis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Hong-Miao Xu, Xuan-Jiang Shen, Jia Liu
World Journal of Diabetes.2023; 14(12): 1793. CrossRef - Impact of Nutraceuticals on Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus-Induced Micro- and Macrovasculopathies
Philanathi Mabena, Thandi M. D. Fasemore, Pilani Nkomozepi
Applied Sciences.2023; 14(1): 64. CrossRef - Prediction Model for the Risk of HIV Infection among MSM in China: Validation and Stability
Yinqiao Dong, Shangbin Liu, Danni Xia, Chen Xu, Xiaoyue Yu, Hui Chen, Rongxi Wang, Yujie Liu, Jingwen Dong, Fan Hu, Yong Cai, Ying Wang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(2): 1010. CrossRef - Management of Type II Diabetes Mellitus using Adult Autologous Adipose derived stem cells with Platelets Rich Plasma (PRP)
Shahzad Anwar, Ayesha Nawaz, Zaigham Abbas
Pakistan BioMedical Journal.2022; : 270. CrossRef - A Nomogram for Predicting the Possibility of Peripheral Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Wanli Zhang, Lingli Chen
Brain Sciences.2022; 12(10): 1328. CrossRef
- Diabetes Mellitusu Olan Bireylerde Periferal Nöropati ve Hemşirelik Bakımı
- Complications
- Renal Tubular Damage Marker, Urinary N-acetyl-β-D-Glucosaminidase, as a Predictive Marker of Hepatic Fibrosis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Hae Kyung Kim, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):104-116. Published online July 13, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0273
- 5,659 View
- 191 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
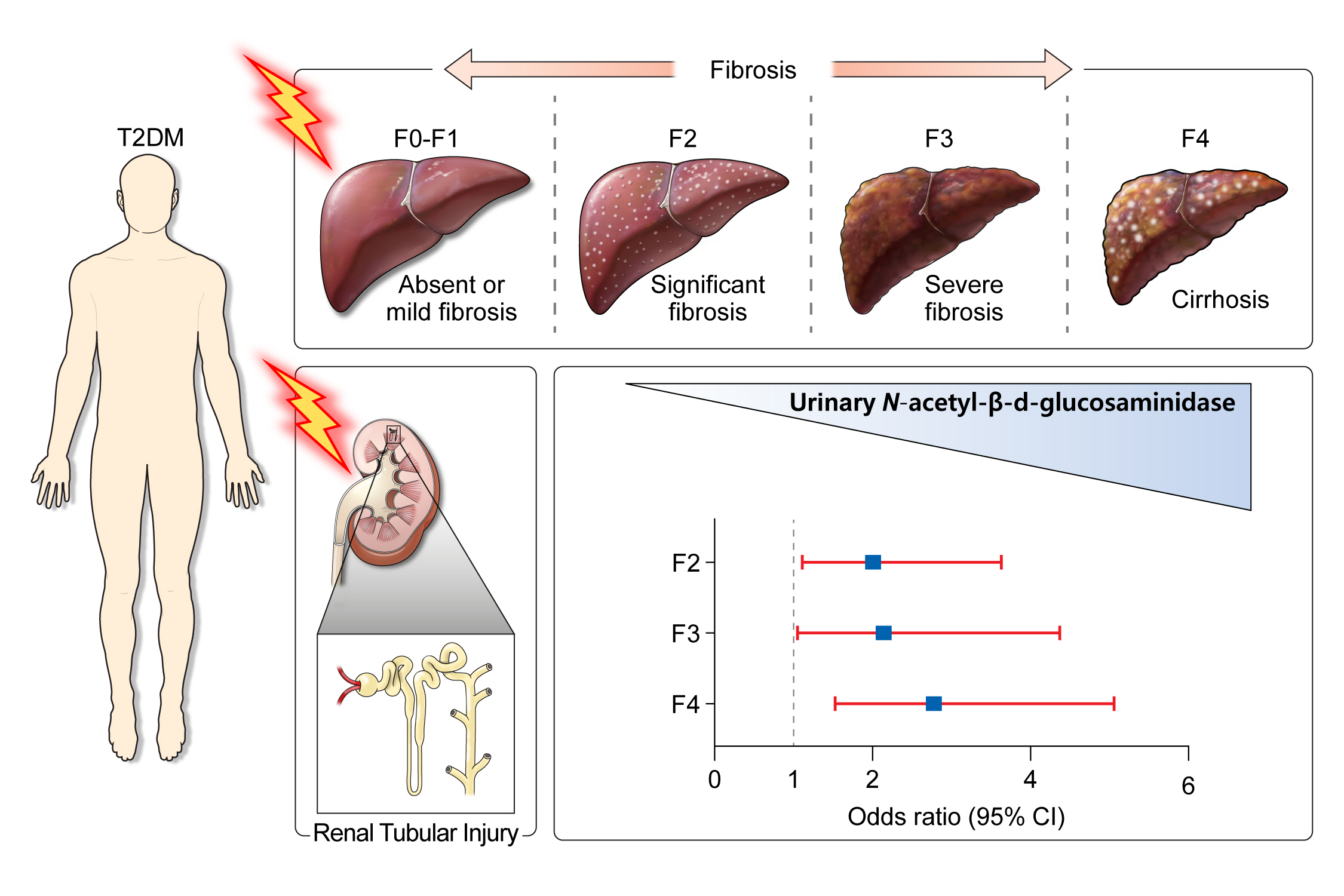
Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis is closely associated with the progression of diabetic kidney disease (DKD) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We investigated whether urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase (u-NAG), an early renal tubular damage biomarker in DKD, could be related to the degree of hepatic fibrosis in patients with T2DM.
Methods
A total of 300 patients with T2DM were enrolled in this study. Hepatic steatosis and fibrosis were determined using transient elastography. The levels of urinary biomarkers, including u-NAG, albumin, protein, and creatinine, and glucometabolic parameters were measured.
Results
Based on the median value of the u-NAG to creatinine ratio (u-NCR), subjects were divided into low and high u-NCR groups. The high u-NCR group showed a significantly longer duration of diabetes, worsened hyperglycemia, and a more enhanced hepatic fibrosis index. A higher u-NCR was associated with a greater odds ratio for the risk of higher hepatic fibrosis stage (F2: odds ratio, 1.99; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.04 to 3.82). Also, u-NCR was an independent predictive marker for more advanced hepatic fibrosis, even after adjusting for several confounding factors (β=1.58, P<0.01).
Conclusion
The elevation of u-NAG was independently associated with a higher degree of hepatic fibrosis in patients with T2DM. Considering the common metabolic milieu of renal and hepatic fibrosis in T2DM, the potential use of u-NAG as an effective urinary biomarker reflecting hepatic fibrosis in T2DM needs to be validated in the future. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intermittent fasting plus early time-restricted eating versus calorie restriction and standard care in adults at risk of type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial
Xiao Tong Teong, Kai Liu, Andrew D. Vincent, Julien Bensalem, Bo Liu, Kathryn J. Hattersley, Lijun Zhao, Christine Feinle-Bisset, Timothy J. Sargeant, Gary A. Wittert, Amy T. Hutchison, Leonie K. Heilbronn
Nature Medicine.2023; 29(4): 963. CrossRef - Significance of Diabetic Kidney Disease Biomarkers in Predicting Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Jaehyun Bae, Byung-Wan Lee
Biomedicines.2023; 11(7): 1928. CrossRef - Abdominal adipose tissue and type 2 diabetic kidney disease: adipose radiology assessment, impact, and mechanisms
Fei Lu, Jinlei Fan, Fangxuan Li, Lijing Liu, Zhiyu Chen, Ziyu Tian, Liping Zuo, Dexin Yu
Abdominal Radiology.2023; 49(2): 560. CrossRef - β‐Amyrin ameliorates diabetic nephropathy in mice and regulates the miR‐181b‐5p/HMGB2 axis in high glucose‐stimulated HK‐2 cells
Wenhua Xu, Hongwu Zhang, Qinfeng Zhang, Jialan Xu
Environmental Toxicology.2022; 37(3): 637. CrossRef - High Glycated Hemoglobin Instead of High Body Mass Index Might Increase the Urine N-Acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase Con-Centration in Children and Adolescents with Diabetes Mellitus
Jin-Soon Suh, Kyoung Soon Cho, Seul Ki Kim, Shin-Hee Kim, Won Kyoung Cho, Min Ho Jung, Moon Bae Ahn
Life.2022; 12(6): 879. CrossRef
- Intermittent fasting plus early time-restricted eating versus calorie restriction and standard care in adults at risk of type 2 diabetes: a randomized controlled trial
Short Communication
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Real-World Analysis of Therapeutic Outcome in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus at a Tertiary Care Center
- Antonia Kietaibl, Michaela Riedl, Latife Bozkurt
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):149-153. Published online July 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0267
- 4,347 View
- 144 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Insulin replacement in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) needs intensified treatment, which can either be performed by multiple daily injections (MDI) or continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII). This retrospective analysis of a real-world scenario aimed to evaluate whether glycaemic and cardiovascular risk factors could be controlled with CSII outclass MDI as suggested by recent evidence. Data from patients with either insulin pump (n=68) or injection (n=224) therapy at an Austrian tertiary care centre were analysed between January 2016 and December 2017. There were no significant differences with regard to the latest glycosylated hemoglobin, cardiovascular risk factor control or diabetes-associated late complications. Hypoglycaemia was less frequent (P<0.001), sensor-augmented therapy was more common (P=0.003) and mean body mass index (BMI) was higher (P=0.002) with CSII treatment. This retrospective analysis of real-world data in T1DM did not demonstrate the superiority of insulin pump treatment with regard to glycaemic control or cardiovascular risk factor control.
Original Article
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018
- Jiun Chae, Moon Young Seo, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):880-889. Published online July 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0185
- 5,855 View
- 239 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
There is a lack of recent research on the changes in risk factors for metabolic syndrome (MetS) in the Asian pediatric population. We aimed to determine the 12-year trends in the prevalence of MetS and relevant lifestyle factors such as smoking, exercise, and calorie intake among Korean adolescents.
Methods
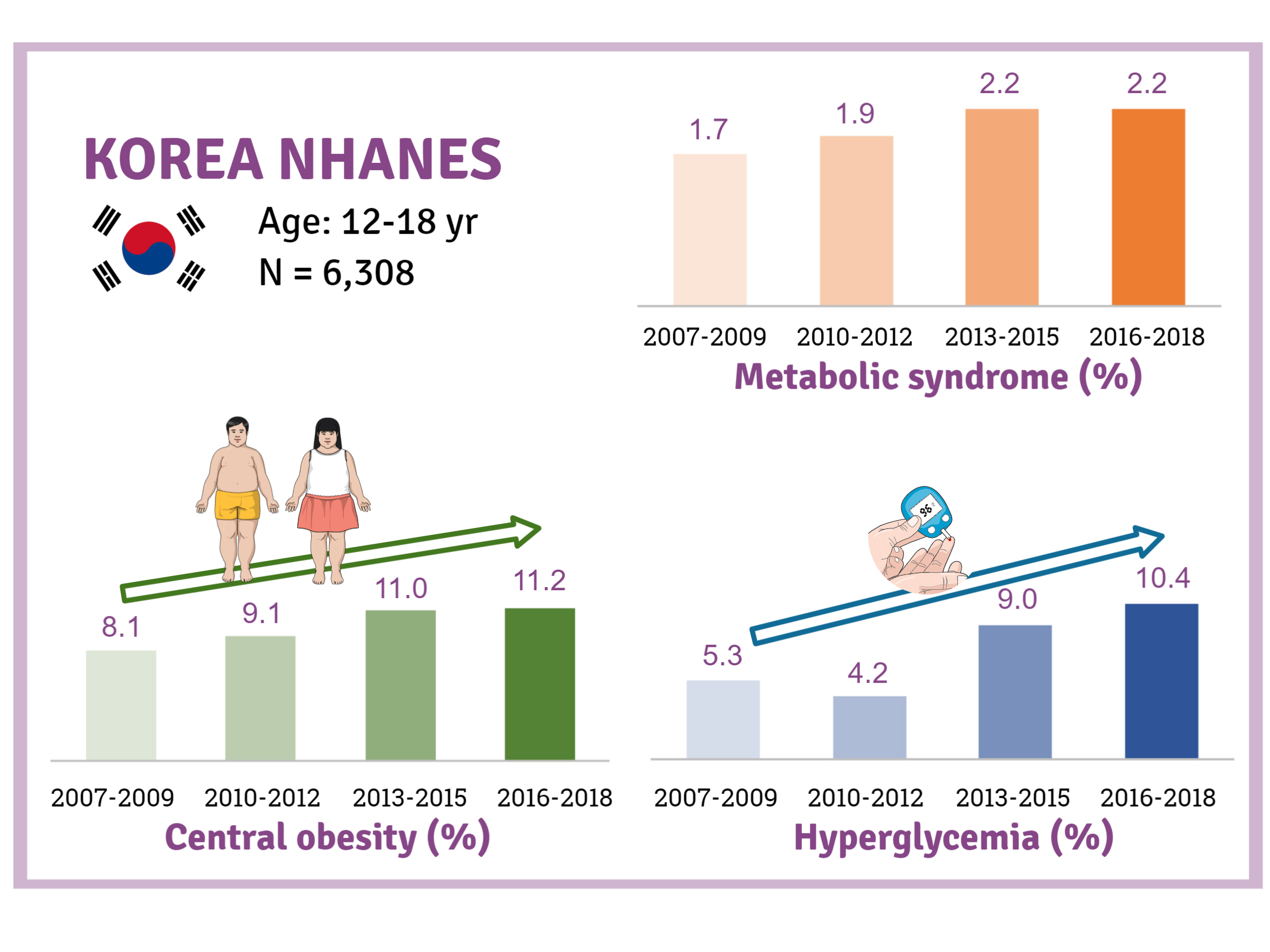
We investigated trends in MetS and lifestyle factors among 6,308 adolescents aged 12 to 18 years from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007 to 2018.
Results
The prevalence of MetS was stable from 2007 to 2018 (1.7% to 2.2%). There were significant increases in the prevalence of central obesity (from 8.1% to 11.2%, P=0.012) and hyperglycemia (from 5.3% to 10.4%, P<0.001) and decreases in hypo-high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterolemia (from 22.4% to 14.8%, P<0.001). Total calorie intake and calorie intake from fat significantly increased (P<0.001), whereas calorie intake from carbohydrates significantly decreased (P<0.001) during the study period. The proportions of tobacco smokers and regular walkers significantly decreased from 2007 to 2018. After controlling for all covariates, total calorie intake was positively correlated with waist circumference (P<0.05). HDL-cholesterol was negatively associated with carbohydrate consumption (P<0.01) and positively associated with fat consumption (P<0.001). Regular walking and regular strength training were associated with lower waist circumference (P<0.05). Smoking was associated with lower fasting glucose levels (P<0.01).
Conclusion
Although the prevalence rate of MetS is stable among Korean adolescents, the prevalence of central obesity and hyperglycemia has increased greatly in the recent decade. Public education on proper dietary intake and lifestyle modification is required. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Overseas Deployment on Fatty Liver and Metabolic Diseases Among Korean Soldiers
Chang In Han, Jaejun Lee
Military Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The impacts of dietary sphingomyelin supplementation on metabolic parameters of healthy adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Chen-Zi Li, Li-Mei Wu, Chen-Xi Zhu, Huan-Yu Du, Guo-Xun Chen, Fang Yang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Thyroid Function and Insulin Resistance Indices in Korean Adolescents: Findings from the 2014–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eunji Mun, Hye Ah Lee, Jung Eun Choi, Rosie Lee, Kyung Hee Kim, Hyesook Park, Hae Soon Kim
Children.2024; 11(3): 370. CrossRef - Ongoing increasing trends in central precocious puberty incidence among Korean boys and girls from 2008 to 2020
Sinyoung Kang, Mi Jung Park, Jung Min Kim, Jin-Sung Yuk, Shin-Hye Kim, Jun Mori
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(3): e0283510. CrossRef - The association between urinary cotinine level and metabolic syndrome profiles among adolescents: findings from the Ewha Birth and growth study
Hyunjin Park, Ui-Jeong Kim, Eun Jeong Choi, Seunghee Jun, Bomi Park, Hye Ah Lee, Hae Soon Kim, Hyesook Park
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence-Based Speech Analysis System for Medical Support
Eui-Sun Kim, Dong Jin Shin, Sung Tae Cho, Kyung Jin Chung
International Neurourology Journal.2023; 27(2): 99. CrossRef - The effect of hypothalamic involvement and growth hormone treatment on cardiovascular risk factors during the transition period in patients with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma
Sang Hee Park, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung-Eun Cheon, Choong Ho Shin, Hae Woon Jung, Young Ah Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(2): 107. CrossRef - Increase of Prevalence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents in Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study Using the KNHANES
Jung Eun Choi, Hye Ah Lee, Sung Won Park, Jung Won Lee, Ji Hyen Lee, Hyesook Park, Hae Soon Kim
Children.2023; 10(7): 1105. CrossRef - The Prevalence of Abdominal Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Children and Adolescents
Ja Hyang Cho
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 103. CrossRef - Temporal Trends of the Prevalence of Abdominal Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Children and Adolescents between 2007 and 2020
Jieun Lee, Sung-Chan Kang, Obin Kwon, Seung-sik Hwang, Jin Soo Moon, Hyun Wook Chae, Jaehyun Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 170. CrossRef - Changes in the Number of Children and Adolescents with Complex Chronic Conditions and Medical Spending: Analyzing National Health Insurance Claims Data from 2011 to 2021
Jeong-Yoon Oh, Su-Jin Cho, Jin-Seon Jung, Jin-Suk Cho, Choon-Seon Park
Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Research.2023; 3(2): 155. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 349. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Jiun Chae, Moon Young Seo, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 351. CrossRef - Comprehensive Understanding for Application in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus of the Consensus Statement on Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets by Korean Diabetes Association, Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and Korean Society of Hyperte
Jong Han Choi, Jee-Hyun Kang, Suk Chon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 377. CrossRef - Environmental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure in relation to metabolic syndrome in US adults
Xue Yang, Qingping Xue, Ying Wen, Yichao Huang, Yi Wang, Gaga Mahai, Tong Yan, Yanjun Liu, Tao Rong, Yixin Wang, Da Chen, Shuqin Zeng, Chun-Xia Yang, Xiong-Fei Pan
Science of The Total Environment.2022; 840: 156673. CrossRef - Commentary on "Single point insulin sensitivity estimator for predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus in obese adolescents"
Shin-Hye Kim
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 27(3): 155. CrossRef
- Impact of Overseas Deployment on Fatty Liver and Metabolic Diseases Among Korean Soldiers
Review
- Basic Research
- Brown Fat as a Regulator of Systemic Metabolism beyond Thermogenesis
- Okamatsu-Ogura Yuko, Masayuki Saito
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):840-852. Published online June 25, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0291

- 9,075 View
- 507 Download
- 16 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Brown adipose tissue (BAT) is a specialized tissue for nonshivering thermogenesis to dissipate energy as heat. Although BAT research has long been limited mostly in small rodents, the rediscovery of metabolically active BAT in adult humans has dramatically promoted the translational studies on BAT in health and diseases. Moreover, several remarkable advancements have been made in brown fat biology over the past decade: The molecular and functional analyses of inducible thermogenic adipocytes (socalled beige adipocytes) arising from a developmentally different lineage from classical brown adipocytes have been accelerated. In addition to a well-established thermogenic activity of uncoupling protein 1 (UCP1), several alternative thermogenic mechanisms have been discovered, particularly in beige adipocytes. It has become clear that BAT influences other peripheral tissues and controls their functions and systemic homeostasis of energy and metabolic substrates, suggesting BAT as a metabolic regulator, other than for thermogenesis. This notion is supported by discovering that various paracrine and endocrine factors are secreted from BAT. We review the current understanding of BAT pathophysiology, particularly focusing on its role as a metabolic regulator in small rodents and also in humans.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Brown adipose tissue evaluation using water and triglyceride as indices by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy
Tomomi Iida, Yukio Ueda, Hideo Tsukada, Dai Fukumoto, Takafumi Hamaoka
Journal of Biophotonics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - White-brown adipose tissue interplay in polycystic ovary syndrome: Therapeutic avenues
Khadijeh Abbasi, Reza Zarezadeh, Amir Valizadeh, Amir Mehdizadeh, Hamed Hamishehkar, Mohammad Nouri, Masoud Darabi
Biochemical Pharmacology.2024; 220: 116012. CrossRef - Brown Adipose Tissue, Batokines, and Bioactive Compounds in Foods: An Update
Fabiane Ferreira Martins, Bruna Cadete Martins, Ananda Vitoria Silva Teixeira, Matheus Ajackson, Vanessa Souza‐Mello, Julio Beltrame Daleprane
Molecular Nutrition & Food Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Plasticity of Adipose Tissues: Interconversion among White, Brown, and Beige Fat and Its Role in Energy Homeostasis
Yanqiu Peng, Lixia Zhao, Min Li, Yunfei Liu, Yuke Shi, Jian Zhang
Biomolecules.2024; 14(4): 483. CrossRef - Thermogenic Brown Fat in Humans: Implications in Energy Homeostasis, Obesity and Metabolic Disorders
Masayuki Saito, Yuko Okamatsu-Ogura
The World Journal of Men's Health.2023; 41(3): 489. CrossRef - Interplay of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: sarcopenic obesity
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 144: 155577. CrossRef - White adipose tissue undergoes browning during preweaning period in association with microbiota formation in mice
Anju Tsukada, Yuko Okamatsu-Ogura, Emi Futagawa, Yuki Habu, Natsumi Takahashi, Mira Kato-Suzuki, Yuko Kato, Satoshi Ishizuka, Kei Sonoyama, Kazuhiro Kimura
iScience.2023; 26(7): 107239. CrossRef - In situ fluorescence-photoacoustic measurement of the changes of brown adipose tissue in mice under hindlimb unloading
Baojie Gong, Jianxin Tang, Xiaoxiao Jiang, Zhe Zhang, Shiying Li, Hongjun Jin, Liming Nie, Guojia Huang
Journal of Applied Physiology.2023; 135(2): 251. CrossRef - Age-Related Expression Dynamics of Uncoupling Protein 1 in Adipose Tissues of ICR Outbred Mice during Postnatal Ontogenesis
A. V. Yakunenkov, E. I. Elsukova, I. O. Natochy
Journal of Evolutionary Biochemistry and Physiology.2023; 59(4): 1020. CrossRef - UNCOUPLING PROTEIN UCP1 EXPRESSION DYNAMICS IN ADIPOSE TISSUES OF THE OUTBRED ICR MICE IN POSTNATAL ONTOGENESIS
A. V. Yakunenkov, E. I. Elsukova, I. O. Natochy
Журнал эволюционной биохимии и физиологии.2023; 59(4): 255. CrossRef - Antibodies Regulate Dual-Function Enzyme IYD to Induce Functional Synergy between Metabolism and Thermogenesis
Sunghyun Kang, Hwan-Woo Park, Kyung Ho Han
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(14): 7834. CrossRef - Machine learning-featured Secretogranin V is a circulating diagnostic biomarker for pancreatic adenocarcinomas associated with adipopenia
Yunju Jo, Min-Kyung Yeo, Tam Dao, Jeongho Kwon, Hyon‐Seung Yi, Dongryeol Ryu
Frontiers in Oncology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Possible roles of exercise and apelin against pregnancy complications
Hamed Alizadeh Pahlavani
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationships between the expression of adipose genes and profiles of hospitalized dogs
Yukina Sugiyama, Fumie Shimokawa, Kazutoshi Sugiyama, Takashi Kobayashi, Yusuke Yamashita, Kei Kazama, Ken Onda, Masayuki Funaba, Masaru Murakami
Veterinary Research Communications.2022; 46(4): 1239. CrossRef - Garlic (Allium sativum L.) in diabetes and its complications: Recent advances in mechanisms of action
Yayi Jiang, Rensong Yue, Guojie Liu, Jun Liu, Bo Peng, Maoyi Yang, Lianxue Zhao, Zihan Li
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Fruit of Gardenia jasminoides Induces Mitochondrial Activation and Non-Shivering Thermogenesis through Regulation of PPARγ
Woo Yong Park, Gahee Song, Ja Yeon Park, Kwan-Il Kim, Kwang Seok Ahn, Hyun Jeong Kwak, Jungtae Leem, Jae-Young Um, Jinbong Park
Antioxidants.2021; 10(9): 1418. CrossRef
- Brown adipose tissue evaluation using water and triglyceride as indices by diffuse reflectance spectroscopy
Original Articles
- Drug/Regimen
- Effects of Teneligliptin on HbA1c levels, Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Time in Range and Glycemic Variability in Elderly Patients with T2DM (TEDDY Study)
- Ji Cheol Bae, Soo Heon Kwak, Hyun Jin Kim, Sang-Yong Kim, You-Cheol Hwang, Sunghwan Suh, Bok Jin Hyun, Ji Eun Cha, Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):81-92. Published online June 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0016
- 7,554 View
- 431 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To evaluate the effects of teneligliptin on glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM)-derived time in range, and glycemic variability in elderly type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Methods
This randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study was conducted in eight centers in Korea (clinical trial registration number: NCT03508323). Sixty-five participants aged ≥65 years, who were treatment-naïve or had been treated with stable doses of metformin, were randomized at a 1:1 ratio to receive 20 mg of teneligliptin (n=35) or placebo (n=30) for 12 weeks. The main endpoints were the changes in HbA1c levels from baseline to week 12, CGM metrics-derived time in range, and glycemic variability.
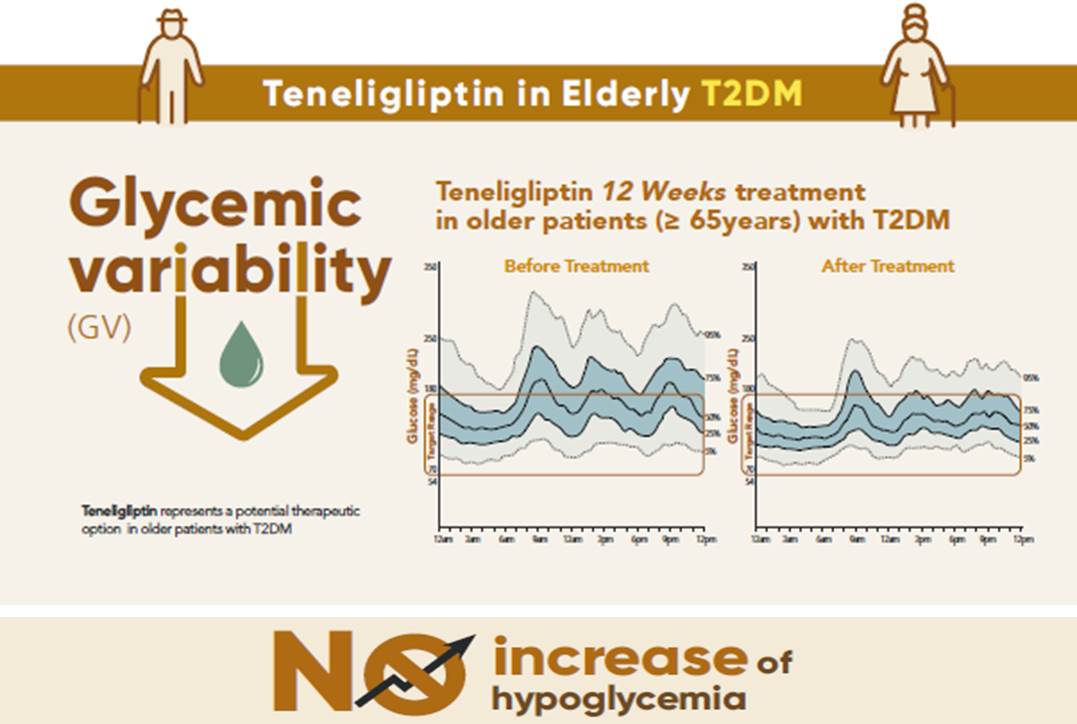
Results
After 12 weeks, a significant reduction (by 0.84%) in HbA1c levels was observed in the teneligliptin group compared to that in the placebo group (by 0.08%), with a between-group least squares mean difference of –0.76% (95% confidence interval [CI], –1.08 to –0.44). The coefficient of variation, standard deviation, and mean amplitude of glycemic excursion significantly decreased in participants treated with teneligliptin as compared to those in the placebo group. Teneligliptin treatment significantly decreased the time spent above 180 or 250 mg/dL, respectively, without increasing the time spent below 70 mg/dL. The mean percentage of time for which glucose levels remained in the 70 to 180 mg/dL time in range (TIR70–180) at week 12 was 82.0%±16.0% in the teneligliptin group, and placebo-adjusted change in TIR70–180 from baseline was 13.3% (95% CI, 6.0 to 20.6).
Conclusion
Teneligliptin effectively reduced HbA1c levels, time spent above the target range, and glycemic variability, without increasing hypoglycemia in our study population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of teneligliptin and other gliptin-based regimens in addressing insulin resistance and glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients: a cross-sectional study
Harmanjit Singh, Ravi Rohilla, Shivani Jaswal, Mandeep Singla
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 19(1): 81. CrossRef - Potential approaches using teneligliptin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: current status and future prospects
Harmanjit Singh, Jasbir Singh, Ravneet Kaur Bhangu, Mandeep Singla, Jagjit Singh, Farideh Javid
Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 16(1): 49. CrossRef - Mechanism of molecular interaction of sitagliptin with human DPP4 enzyme - New Insights
Michelangelo Bauwelz Gonzatti, José Edvar Monteiro Júnior, Antônio José Rocha, Jonathas Sales de Oliveira, Antônio José de Jesus Evangelista, Fátima Morgana Pio Fonseca, Vânia Marilande Ceccatto, Ariclécio Cunha de Oliveira, José Ednésio da Cruz Freire
Advances in Medical Sciences.2023; 68(2): 402. CrossRef - A prospective multicentre open label study to assess effect of Teneligliptin on glycemic control through parameters of time in range (TIR) Metric using continuous glucose monitoring (TOP-TIR study)
Banshi Saboo, Suhas Erande, A.G. Unnikrishnan
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2022; 16(2): 102394. CrossRef - Association between Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors and Cardiometabolic Outcomes
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 49. CrossRef
- Comparison of teneligliptin and other gliptin-based regimens in addressing insulin resistance and glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients: a cross-sectional study
- Drug/Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Self-Titration Algorithms of Insulin Glargine 300 units/mL in Individuals with Uncontrolled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (The Korean TITRATION Study): A Randomized Controlled Trial
- Jae Hyun Bae, Chang Ho Ahn, Ye Seul Yang, Sun Joon Moon, Soo Heon Kwak, Hye Seung Jung, Kyong Soo Park, Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):71-80. Published online June 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0274

- 7,939 View
- 434 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To compare the efficacy and safety of two insulin self-titration algorithms, Implementing New Strategies with Insulin Glargine for Hyperglycemia Treatment (INSIGHT) and EDITION, for insulin glargine 300 units/mL (Gla-300) in Korean individuals with uncontrolled type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
In a 12-week, randomized, open-label trial, individuals with uncontrolled T2DM requiring basal insulin were randomized to either the INSIGHT (adjusted by 1 unit/day) or EDITION (adjusted by 3 units/week) algorithm to achieve a fasting self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) in the range of 4.4 to 5.6 mmol/L. The primary outcome was the proportion of individuals achieving a fasting SMBG ≤5.6 mmol/L without noct urnal hypoglycemia at week 12.
Results
Of 129 individuals (age, 64.1±9.5 years; 66 [51.2%] women), 65 and 64 were randomized to the INSIGHT and EDITION algorithms, respectively. The primary outcome of achievement was comparable between the two groups (24.6% vs. 23.4%, P=0.876). Compared with the EDITION group, the INSIGHT group had a greater reduction in 7-point SMBG but a similar decrease in fasting plasma glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin. The increment of total daily insulin dose was significantly higher in the INSIGHT group than in the EDITION group (between-group difference: 5.8±2.7 units/day, P=0.033). However, body weight was significantly increased only in the EDITION group (0.6±2.4 kg, P=0.038). There was no difference in the occurrence of hypoglycemia between the two groups. Patient satisfaction was significantly increased in the INSIGHT group (P=0.014).
Conclusion
The self-titration of Gla-300 using the INSIGHT algorithm was effective and safe compared with that using the EDITION algorithm in Korean individuals with uncontrolled T2DM (ClinicalTrials.gov number: NCT03406663). -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Basal insulin titration algorithms in patients with type 2 diabetes: the simplest is the best (?)
V.I. Katerenchuk
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(1): 72. CrossRef - Issues of insulin therapy for type 2 diabetes and ways to solve them
V.I. Katerenchuk, A.V. Katerenchuk
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(3): 240. CrossRef - Time for Using Machine Learning for Dose Guidance in Titration of People With Type 2 Diabetes? A Systematic Review of Basal Insulin Dose Guidance
Camilla Heisel Nyholm Thomsen, Stine Hangaard, Thomas Kronborg, Peter Vestergaard, Ole Hejlesen, Morten Hasselstrøm Jensen
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2022; : 193229682211459. CrossRef
- Basal insulin titration algorithms in patients with type 2 diabetes: the simplest is the best (?)
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Longitudinal Change in Myocardial Function and Clinical Parameters in Middle-Aged Subjects: A 3-Year Follow-up Study
- Dong-Hyuk Cho, Hyung Joon Joo, Mi-Na Kim, Hee-Dong Kim, Do-Sun Lim, Seong-Mi Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):719-729. Published online June 15, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0132
- 4,236 View
- 108 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is closely associated with the aging process. However, changes in metabolic conditions and cardiac function that occur in middle aged population remain unclear. We evaluated longitudinal changes in metabolic parameters and cardiac function during a 3-year period in subjects with suspected MetS.
Methods
We studied 191 participants with suspected MetS at baseline and after 3 years. Anthropometric parameters, including waist circumference (WC), and metabolic parameters, including fasting blood glucose and lipid profile were measured. Conventional echocardiography with two-dimensional speckle tracking was performed.
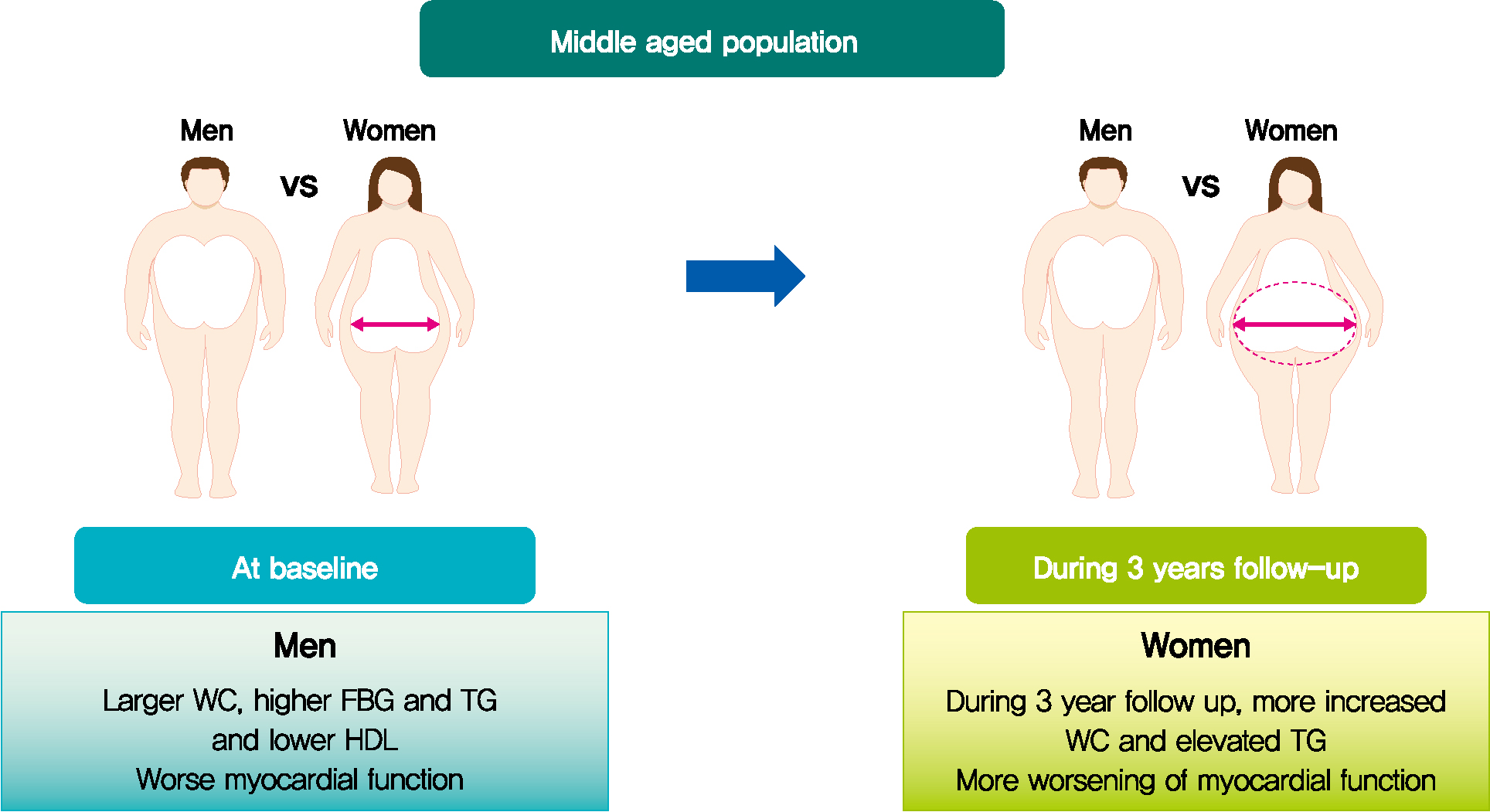
Results
Mean age was 56.2±4.4 years, and there were 97 women (50.8%). Men had increased WC and triglycerides (TG) (WC 91.2±6.8 cm vs. 84.0±8.0 cm, P<0.001; TG 184.4±116.3 mg/dL vs. 128.2±53.6 mg/dL, P<0.001), and reduced global longitudinal strain (GLS) (–15.4%±2.1% vs. –17.1%±2.0%, P<0.001) compared to women. After 3.4 years, values of WC and TG did not change in men but increased in women (all P<0.05). The absolute value of left ventricular (LV) GLS did not change in men but was reduced in women (P=0.011). Change in TG was independently associated with worsening of LV GLS only in women (standardized β, –0.309; 95% confidence interval, –0.130 to –0.009; P=0.025).
Conclusion
In middle aged population, a vulnerable period for metabolic disturbance, cardiac remodeling tended to progress, which was prominent in women. Progression of adiposity and dyslipidemia after menopause may accelerate subclinical cardiac remodeling in middle-aged women. Lifestyle modification and medical interventions may help prevent further cardiac dysfunction in these subjects. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Positive additive interaction effects of age, sex, obesity, and metabolic syndrome on left ventricular dysfunction
Dan Zhou, Zhongwen Ye, Zhiqiang Nie, Chaolei Chen, Songyuan Luo, Mengqi Yan, Jiabin Wang, Yingqing Feng
Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Lung-Heart Outcomes and Mortality through the 2020 COVID-19 Pandemic in a Prospective Cohort of Breast Cancer Radiotherapy Patients
Vincent Vinh-Hung, Olena Gorobets, Nele Adriaenssens, Hilde Van Parijs, Guy Storme, Dirk Verellen, Nam P. Nguyen, Nicolas Magne, Mark De Ridder
Cancers.2022; 14(24): 6241. CrossRef
- Positive additive interaction effects of age, sex, obesity, and metabolic syndrome on left ventricular dysfunction

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





