
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Reviews
- Basic Research
- Mitochondrial Stress and Mitokines: Therapeutic Perspectives for the Treatment of Metabolic Diseases
- Benyuan Zhang, Joon Young Chang, Min Hee Lee, Sang-Hyeon Ju, Hyon-Seung Yi, Minho Shong
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):1-18. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0115
- 2,110 View
- 258 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
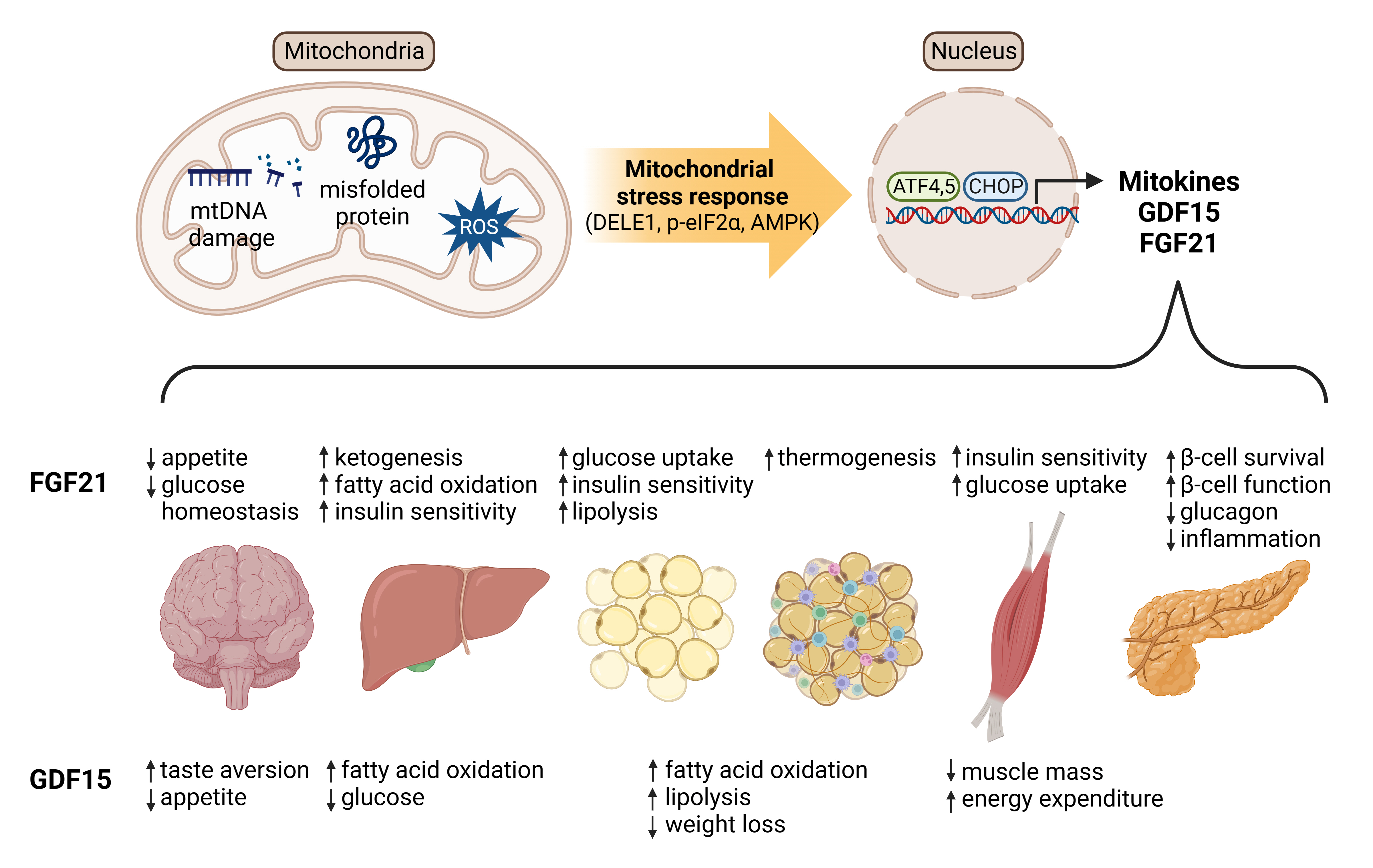
ePub - Mitochondrial stress and the dysregulated mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt) are linked to various diseases, including metabolic disorders, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer. Mitokines, signaling molecules released by mitochondrial stress response and UPRmt, are crucial mediators of inter-organ communication and influence systemic metabolic and physiological processes. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of mitokines, including their regulation by exercise and lifestyle interventions and their implications for various diseases. The endocrine actions of mitokines related to mitochondrial stress and adaptations are highlighted, specifically the broad functions of fibroblast growth factor 21 and growth differentiation factor 15, as well as their specific actions in regulating inter-tissue communication and metabolic homeostasis. Finally, we discuss the potential of physiological and genetic interventions to reduce the hazards associated with dysregulated mitokine signaling and preserve an equilibrium in mitochondrial stress-induced responses. This review provides valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying mitochondrial regulation of health and disease by exploring mitokine interactions and their regulation, which will facilitate the development of targeted therapies and personalized interventions to improve health outcomes and quality of life.
- Pathophysiology
- Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Dysregulated Autophagy in Human Pancreatic Beta Cells
- Seoil Moon, Hye Seung Jung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):533-542. Published online July 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0070
- 4,567 View
- 250 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
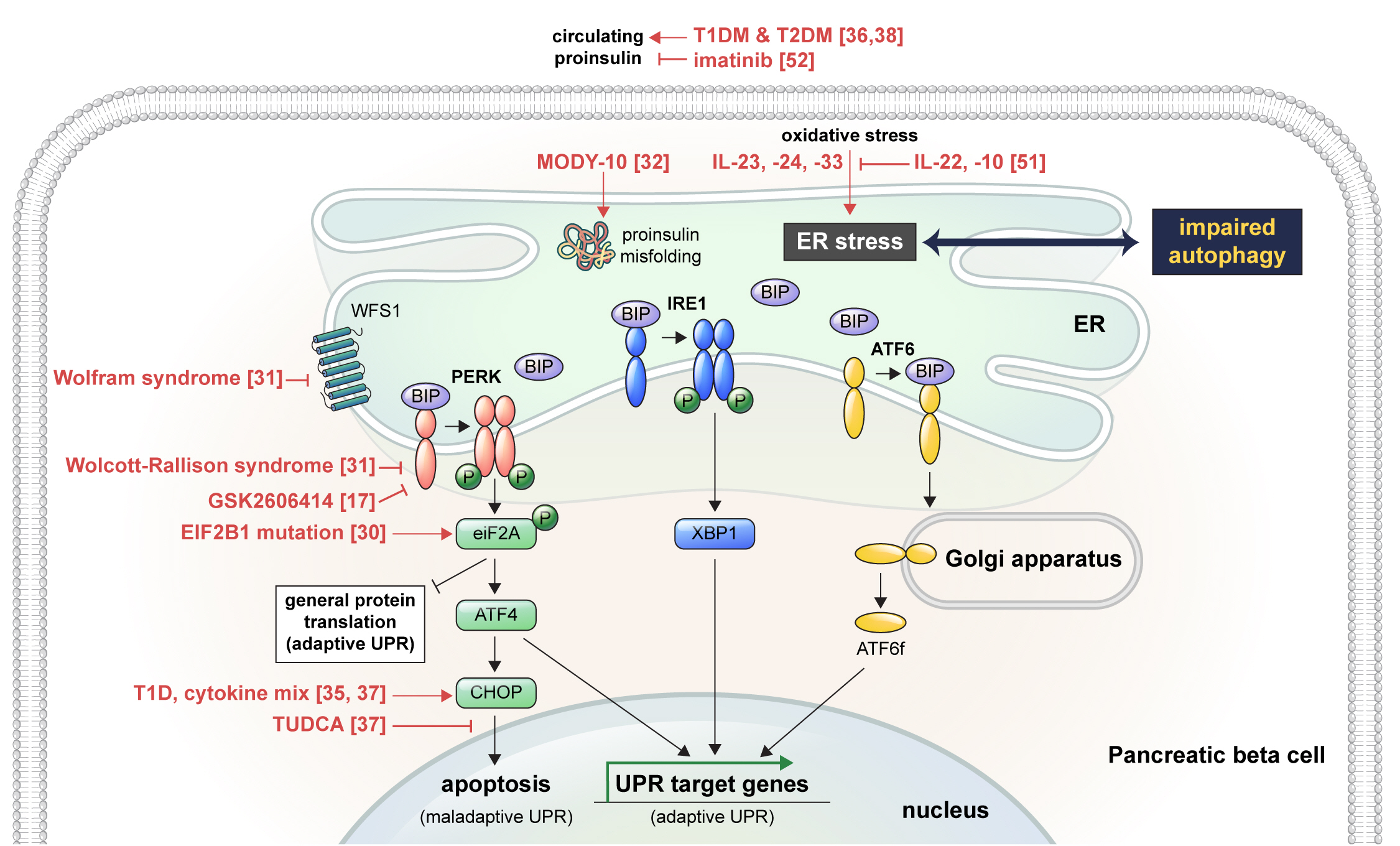
ePub - Pancreatic beta cell homeostasis is crucial for the synthesis and secretion of insulin; disruption of homeostasis causes diabetes, and is a treatment target. Adaptation to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress through the unfolded protein response (UPR) and adequate regulation of autophagy, which are closely linked, play essential roles in this homeostasis. In diabetes, the UPR and autophagy are dysregulated, which leads to beta cell failure and death. Various studies have explored methods to preserve pancreatic beta cell function and mass by relieving ER stress and regulating autophagic activity. To promote clinical translation of these research results to potential therapeutics for diabetes, we summarize the current knowledge on ER stress and autophagy in human insulin-secreting cells.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glucolipotoxicity Suppressed Autophagy and Insulin Contents in Human Islets, and Attenuation of PERK Activity Enhanced Them in an ATG7-Dependent Manner
Seoil Moon, Ji Yoon Lim, Mirang Lee, Youngmin Han, Hongbeom Kim, Wooil Kwon, Jin-Young Jang, Mi Na Kim, Kyong Soo Park, Hye Seung Jung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 231. CrossRef - Endoplasmic reticulum stress: A possible connection between intestinal inflammation and neurodegenerative disorders
Giorgio Vivacqua, Romina Mancinelli, Stefano Leone, Rosa Vaccaro, Ludovica Garro, Simone Carotti, Ludovica Ceci, Paolo Onori, Luigi Pannarale, Antonio Franchitto, Eugenio Gaudio, Arianna Casini
Neurogastroenterology & Motility.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Docosahexanoic Acid Attenuates Palmitate-Induced Apoptosis by Autophagy Upregulation via GPR120/mTOR Axis in Insulin-Secreting Cells
Seok-Woo Hong, Jinmi Lee, Sun Joon Moon, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2024; 39(2): 353. CrossRef - Pancreatic islet remodeling in cotadutide-treated obese mice
Renata Spezani, Thatiany Souza Marinho, Luiz E. Macedo Cardoso, Marcia Barbosa Aguila, Carlos Alberto Mandarim-de-Lacerda
Life Sciences.2023; 327: 121858. CrossRef - Modulation of Unfolded Protein Response Restores Survival and Function of β-Cells Exposed to the Endocrine Disruptor Bisphenol A
Laura Maria Daian, Gabriela Tanko, Andrei Mircea Vacaru, Luiza Ghila, Simona Chera, Ana-Maria Vacaru
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(3): 2023. CrossRef - Interplay of skeletal muscle and adipose tissue: sarcopenic obesity
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 144: 155577. CrossRef - Identification and analysis of type 2 diabetes-mellitus-associated autophagy-related genes
Kun Cui, Zhizheng Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sestrin2 in diabetes and diabetic complications
Xiaodan Zhang, Zirui Luo, Jiahong Li, Yaxuan Lin, Yu Li, Wangen Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Crosstalk between autophagy and insulin resistance: evidence from different tissues
Asie Sadeghi, Maryam Niknam, Mohammad Amin Momeni-Moghaddam, Maryam Shabani, Hamid Aria, Alireza Bastin, Maryam Teimouri, Reza Meshkani, Hamed Akbari
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Beta cell lipotoxicity in the development of type 2 diabetes: the need for species-specific understanding
Patricia Thomas, Meurig T. Gallagher, Gabriela Da Silva Xavier
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Glucolipotoxicity Suppressed Autophagy and Insulin Contents in Human Islets, and Attenuation of PERK Activity Enhanced Them in an ATG7-Dependent Manner
- Pathophysiology
- Nuclear Receptors Resolve Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress to Improve Hepatic Insulin Resistance
- Jae Man Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(1):10-19. Published online February 16, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.1.10
- 4,615 View
- 94 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 13 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Chronic endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress culminating in proteotoxicity contributes to the development of insulin resistance and progression to type 2 diabetes mellitus. Pharmacologic interventions targeting several different nuclear receptors have emerged as potential treatments for insulin resistance. The mechanistic basis for these antidiabetic effects has primarily been attributed to multiple metabolic and inflammatory functions. Here we review recent advances in our understanding of the association of ER stress with insulin resistance and the role of nuclear receptors in promoting ER stress resolution and improving insulin resistance in the liver.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Duality of Nrf2 in iron-overload cardiomyopathy
Enrica Federti, Francesca Vinchi, Iana Iatcenko, Alessandra Ghigo, Alessandro Matte, Serge Cedrick Mbiandjeu Toya, Angela Siciliano, Deborah Chiabrando, Emanuela Tolosano, Steven Zebulon Vance, Veronica Riccardi, Immacolata Andolfo, Manuela Iezzi, Alessia
Haematologica.2023; 108(5): 1335. CrossRef - Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Its Impact on Adipogenesis: Molecular Mechanisms Implicated
Gyuhui Kim, Jiyoon Lee, Joohun Ha, Insug Kang, Wonchae Choe
Nutrients.2023; 15(24): 5082. CrossRef - Qingluotongbi formula regulates the LXRα-ERS-SREBP-1c pathway in hepatocytes to alleviate the liver injury caused by Tripterygium wilfordii Hook. f.
Zhichao Yu, Zhe Feng, Ling Fu, Jing Wang, Changqing Li, Huaxu Zhu, Tong Xie, Jie Zhou, Lingling Zhou, Xueping Zhou
Journal of Ethnopharmacology.2022; 287: 114952. CrossRef - Nuclear‐mitochondrial crosstalk: On the role of the nuclear receptor liver receptor homolog‐1 (NR5A2) in the regulation of mitochondrial metabolism, cell survival, and cancer
Svenja Michalek, Thomas Brunner
IUBMB Life.2021; 73(3): 592. CrossRef - NGBR is required to ameliorate type 2 diabetes in mice by enhancing insulin sensitivity
Yi Chen, Wenquan Hu, Qi Li, Shiwei Zhao, Dan Zhao, Shuang Zhang, Zhuo Wei, Xiaoxiao Yang, Yuanli Chen, Xiaoju Li, Chenzhong Liao, Jihong Han, Qing Robert Miao, Yajun Duan
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2021; 296: 100624. CrossRef - Impaired ferritinophagy flux induced by high fat diet mediates hepatic insulin resistance via endoplasmic reticulum stress
Chunjie Jiang, Shanshan Zhang, Dan Li, Li Chen, Ying Zhao, Guibin Mei, Jingjing Liu, Yuhan Tang, Chao Gao, Ping Yao
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2020; 140: 111329. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor protects against non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in mice by targeting TRAIL receptor-mediated lipoapoptosis via modulating hepatic dipeptidyl peptidase-4 expression
Minyoung Lee, Eugene Shin, Jaehyun Bae, Yongin Cho, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Use of fenofibrate on cardiovascular outcomes in statin users with metabolic syndrome: propensity matched cohort study
Nam Hoon Kim, Ki Hoon Han, Jimi Choi, Juneyoung Lee, Sin Gon Kim
BMJ.2019; : l5125. CrossRef - Inhibition of the Low Molecular Weight Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase (LMPTP) as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Hepatic Progenitor Cells Lipotoxicity—Short Communication
Michalina Alicka, Katarzyna Kornicka-Garbowska, Michael Roecken, Krzysztof Marycz
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(23): 5873. CrossRef - Myricetin prevents thapsigargin-induced CDK5-P66Shc signalosome mediated pancreatic β-cell dysfunction
Udayakumar Karunakaran, Ji Eun Lee, Suma Elumalai, Jun Sung Moon, Kyu Chang Won
Free Radical Biology and Medicine.2019; 141: 59. CrossRef - Spontaneous ketonuria and risk of incident diabetes: a 12 year prospective study
Gyuri Kim, Sang-Guk Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Ele Ferrannini, Yong-ho Lee, Nam H. Cho
Diabetologia.2019; 62(5): 779. CrossRef - CCAAT/enhancer binding protein homologous protein knockdown alleviates hypoxia-induced myocardial injury in rat cardiomyocytes exposed to high glucose
Wenqi Yang, Fang Wu, Ting Luo, Yuelan Zhang
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of changes in ER stress-mediated signaling pathway with lead-induced insulin resistance and apoptosis in rats and their prevention by A-type dimeric epigallocatechin-3-gallate
Chan-Min Liu, Jie-Qiong Ma, Jian-Mei Sun, Zhao-Jun Feng, Chao Cheng, Wei Yang, Hong Jiang
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2017; 110: 325. CrossRef
- Duality of Nrf2 in iron-overload cardiomyopathy

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





