
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Drug/Regimen
- Efficacy and Safety of Alogliptin-Pioglitazone Combination for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Poorly Controlled with Metformin: A Multicenter, Double-Blind Randomized Trial
- Ji-Yeon Park, Joonyub Lee, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kyung Wan Min, Kyung Ah Han, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Soo Lim, Young-Hyun Kim, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Mook Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon, the Practical Evidence of Antidiabetic Combination Therapy in Korea (PEAK) study investigators
- Received August 7, 2023 Accepted November 30, 2023 Published online April 23, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0259 [Epub ahead of print]
- 490 View
- 31 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - Background
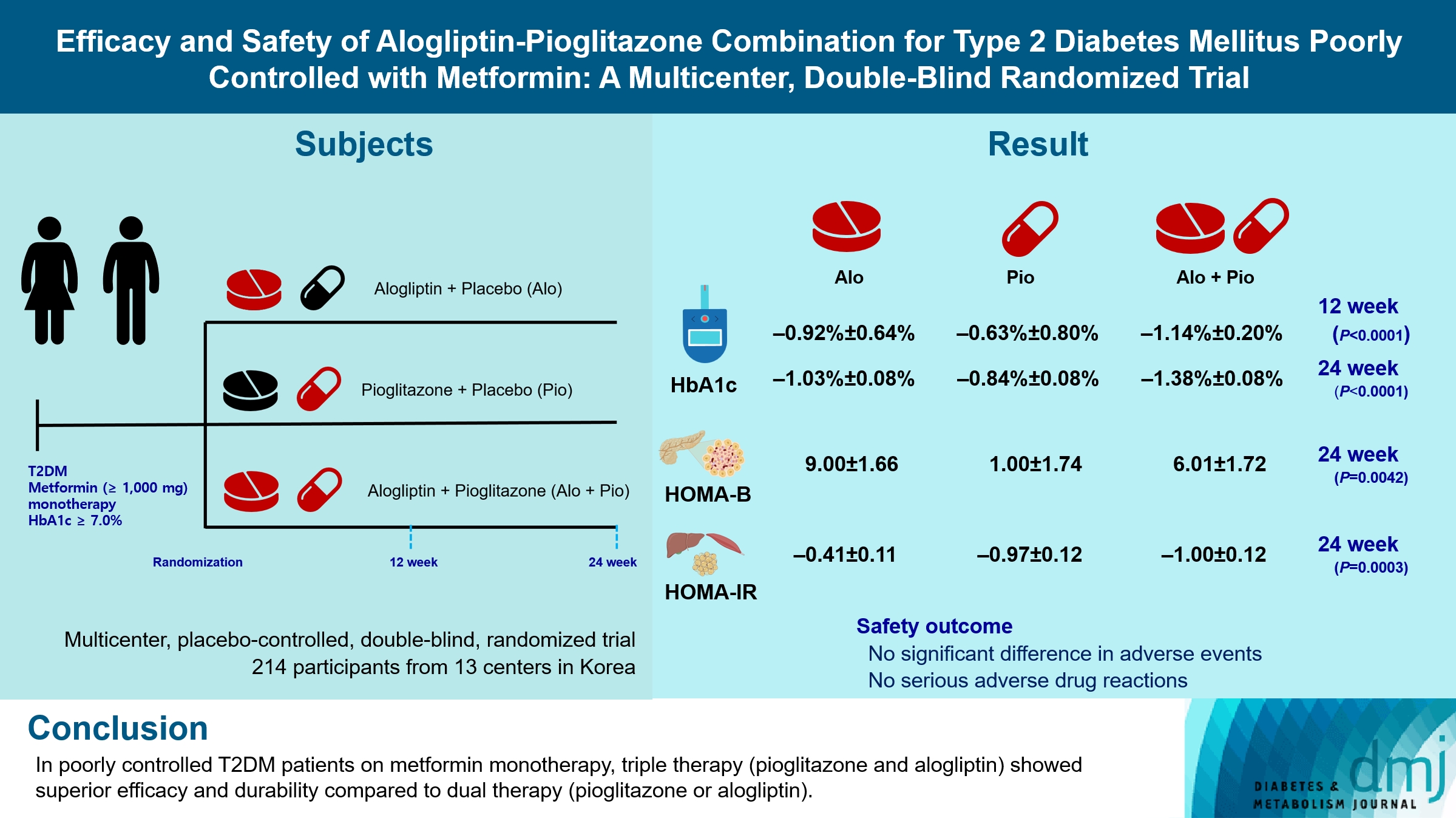
Guidelines for switching to triple combination therapy directly after monotherapy failure are limited. This study investigated the efficacy, long-term sustainability, and safety of either mono or dual add-on therapy using alogliptin and pioglitazone for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who did not achieve their target glycemic range with metformin monotherapy.
Methods
The Practical Evidence of Antidiabetic Combination Therapy in Korea (PEAK) was a multicenter, placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized trial. A total of 214 participants were randomized to receive alogliptin+pioglitazone (Alo+Pio group, n=70), alogliptin (Alo group, n=75), or pioglitazone (Pio group, n=69). The primary outcome was the difference in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels between the three groups at baseline to 24 weeks. For durability, the achievement of HbA1c levels <7% and <6.5% was compared in each group. The number of adverse events was investigated for safety.
Results
After 24 weeks of treatment, the change of HbA1c in the Alo+Pio, Alo, and Pio groups were –1.38%±0.08%, –1.03%±0.08%, and –0.84%±0.08%, respectively. The Alo+Pio group had significantly lower HbA1c levels than the other groups (P=0.0063, P<0.0001) and had a higher proportion of patients with target HbA1c achievement. In addition, insulin sensitivity and β-cell function, lipid profiles, and other metabolic indicators were also improved. There were no significant safety issues in patients treated with triple combination therapy.
Conclusion
Early combination triple therapy showed better efficacy and durability than the single add-on (dual) therapy. Therefore, combination therapy with metformin, alogliptin, and pioglitazone is a valuable early treatment option for T2DM poorly controlled with metformin monotherapy.
- Drug/Regimen
- Comparison of Efficacy of Glimepiride, Alogliptin, and Alogliptin-Pioglitazone as the Initial Periods of Therapy in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: An Open-Label, Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled Study
- Hae Jin Kim, In Kyung Jeong, Kyu Yeon Hur, Soo-Kyung Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Sung Wan Chun, Eun Seok Kang, Eun-Jung Rhee, Sung Hee Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):689-700. Published online March 17, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0183
- 5,721 View
- 377 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The choice of an optimal oral hypoglycemic agent in the initial treatment periods for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients remains difficult and deliberate. We compared the efficacy and safety of glimepiride (GLIM), alogliptin (ALO), and alogliptin-pioglitazone (ALO-PIO) in poorly controlled T2DM patients with drug-naïve or metformin failure.
Methods
In this three-arm, multicenter, open-label, randomized, controlled trial, poorly controlled T2DM patients were randomized to receive GLIM (n=35), ALO (n=31), or ALO-PIO (n=33) therapy for 24 weeks. The primary endpoint was change in the mean glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels at week 24 from baseline. Secondary endpoints were changes in HbA1c level at week 12 from baseline, fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels, lipid profiles at weeks 12 and 24, and parameters of glycemic variability, assessed by continuous glucose monitoring for 24 weeks.
Results
At weeks 12 and 24, the ALO-PIO group showed significant reduction in HbA1c levels compared to the ALO group (–0.96%±0.17% vs. –0.37%±0.17% at week 12; –1.13%±0.19% vs. –0.18%±0.2% at week 24). The ALO-PIO therapy caused greater reduction in FPG levels and significant increase in high-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels at weeks 12 and 24 than the ALO therapy. Compared to low-dose GLIM therapy, ALO-PIO therapy showed greater improvement in glycemic variability. The adverse events were similar among the three arms.
Conclusion
ALO-PIO combination therapy during the early period exerts better glycemic control than ALO monotherapy and excellency in glycemic variability than low-dose sulfonylurea therapy in uncontrolled, drug-naïve or metformin failed T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Comprehensive Review on Weight Loss Associated with Anti-Diabetic Medications
Fatma Haddad, Ghadeer Dokmak, Maryam Bader, Rafik Karaman
Life.2023; 13(4): 1012. CrossRef - Role of Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors in Antidiabetic Treatment
Ruili Yin, Yongsong Xu, Xin Wang, Longyan Yang, Dong Zhao
Molecules.2022; 27(10): 3055. CrossRef
- A Comprehensive Review on Weight Loss Associated with Anti-Diabetic Medications
- Increased Risk of Hospitalization for Heart Failure with Newly Prescribed Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Pioglitazone Using the Korean Health Insurance Claims Database
- Sunghwan Suh, Gi Hyeon Seo, Chang Hee Jung, Mee-Kyoung Kim, Sang-Man Jin, You-Cheol Hwang, Byung-Wan Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2015;39(3):247-252. Published online April 22, 2015
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.3.247
- 4,009 View
- 35 Download
- 21 Web of Science
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background We assessed the association of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP4i) with hospitalization for heart failure (HF) using the Korean Health Insurance claims database.
Methods We collected data on newly prescribed sitagliptin, vildagliptin, and pioglitazone between January 1, 2009 and December 31, 2012 (mean follow-up of 336.8 days) to 935,519 patients with diabetes (518,614 males and 416,905 females) aged 40 to 79 years (mean age of 59.4 years).
Results During the study, 998 patients were hospitalized for primary HF (115.7 per 100,000 patient-years). The incidence rate of hospitalization for HF was 117.7 per 100,000 per patient-years among patients on pioglitazone, 105.7 for sitagliptin, and 135.8 for vildagliptin. The hospitalization rate for HF was greatest in the first 30 days after starting the medication, which corresponded to a significantly higher incidence at days 0 to 30 compared with days 31 to 360 for all three drugs. The hazard ratios were 1.85 (pioglitazone), 2.00 (sitagliptin), and 1.79 (vildagliptin). The incidence of hospitalization for HF did not differ between the drugs for any time period.
Conclusion This study showed an increase in hospitalization for HF in the initial 30 days of the DPP4i and pioglitazone compared with the subsequent follow-up period. However, the differences between the drugs were not significant.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cardioprotective effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors versus sulfonylureas in addition to metformin: A nationwide cohort study of patients with type 2 diabetes
Jui Wang, Hon-Yen Wu, Kuo-Liong Chien
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(3): 101299. CrossRef - Changing Fields-Diabetes Medications Invading the Cardiovascular Space
Lauren D. Breite, Mackenzie Steck, Brandon Tate Cutshall, Samarth P. Shah, Brandon E. Cave
Current Problems in Cardiology.2021; 46(3): 100736. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Safety and Benefits of Noninsulin Antihyperglycemic Drugs for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Part 2
Srikanth Yandrapalli, Aaqib Malik, Adam Horblitt, Gayatri Pemmasani, Wilbert S. Aronow, William H. Frishman
Cardiology in Review.2020; 28(5): 219. CrossRef - Effects of antidiabetic drugs on left ventricular function/dysfunction: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Da-Peng Zhang, Li Xu, Le-Feng Wang, Hong-Jiang Wang, Feng Jiang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor compared with sulfonylurea in combination with metformin: cardiovascular and renal outcomes in a propensity-matched cohort study
Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Juneyoung Lee, Jae Hyun Bae, Jee Hyun An, Hee Young Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparative Cardiovascular Risks of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors: Analyses of Real-world Data in Korea
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Bongseong Kim, Hae Sol Shin, Jinhee Lee, Hansol Choi, Hyeon Chang Kim, Dae Jung Kim
Korean Circulation Journal.2018; 48(5): 395. CrossRef - Worsening Heart Failure During the Use of DPP-4 Inhibitors
Milton Packer
JACC: Heart Failure.2018; 6(6): 445. CrossRef - Resistance exercise improves cardiac function and mitochondrial efficiency in diabetic rat hearts
Tae Hee Ko, Jubert C. Marquez, Hyoung Kyu Kim, Seung Hun Jeong, SungRyul Lee, Jae Boum Youm, In Sung Song, Dae Yun Seo, Hye Jin Kim, Du Nam Won, Kyoung Im Cho, Mun Gi Choi, Byoung Doo Rhee, Kyung Soo Ko, Nari Kim, Jong Chul Won, Jin Han
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology.2018; 470(2): 263. CrossRef - Do DPP-4 Inhibitors Cause Heart Failure Events by Promoting Adrenergically Mediated Cardiotoxicity?
Milton Packer
Circulation Research.2018; 122(7): 928. CrossRef - Comparative safety for cardiovascular outcomes of DPP-4 inhibitors versus glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes
Hyouk-Jun Chin, Jin Hyun Nam, Eui-Kyung Lee, Ju-Young Shin
Medicine.2017; 96(25): e7213. CrossRef - Effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor in insulin-resistant rats with myocardial infarction
Nattayaporn Apaijai, Tharnwimol Inthachai, Suree Lekawanvijit, Siriporn C Chattipakorn, Nipon Chattipakorn
Journal of Endocrinology.2016; 229(3): 245. CrossRef - The current role of thiazolidinediones in diabetes management
Christos V. Rizos, Anastazia Kei, Moses S. Elisaf
Archives of Toxicology.2016; 90(8): 1861. CrossRef - Alternative Interventions to Prevent Oxidative Damage following Ischemia/Reperfusion
Simón Quetzalcoatl Rodríguez-Lara, Ernesto German Cardona-Muñoz, Ernesto Javier Ramírez-Lizardo, Sylvia Elena Totsuka-Sutto, Araceli Castillo-Romero, Teresa Arcelia García-Cobián, Leonel García-Benavides
Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.2016; 2016: 1. CrossRef - Lessons learned from cardiovascular outcome clinical trials with dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) inhibitors
Teresa Vanessa Fiorentino, Giorgio Sesti
Endocrine.2016; 53(2): 373. CrossRef - Letter: Increased Risk of Hospitalization for Heart Failure with Newly Prescribed Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Pioglitazone Using the Korean Health Insurance Claims Database (Diabetes Metab J2015;39:247-52)
Dae Ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(4): 348. CrossRef - Response: Increased Risk of Hospitalization for Heart Failure with Newly Prescribed Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors and Pioglitazone Using the Korean Health Insurance Claims Database (Diabetes Metab J2015;39:247-52)
Sunghwan Suh, Gi Hyeon Seo, Chang Hee Jung, Mee-Kyoung Kim, Sang-Man Jin, You-Cheol Hwang, Byung-Wan Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(4): 350. CrossRef - Cardiovascular, renal and gastrointestinal effects of incretin-based therapies: an acute and 12-week randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, mechanistic intervention trial in type 2 diabetes
Mark M Smits, Lennart Tonneijck, Marcel H A Muskiet, Trynke Hoekstra, Mark H H Kramer, Indra C Pieters, Djuna L Cahen, Michaela Diamant, Daniël H van Raalte
BMJ Open.2015; 5(11): e009579. CrossRef - Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Alarms: Is Heart Failure Caused by a Class Effect?
Yong-ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(3): 204. CrossRef
- Cardioprotective effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors versus sulfonylureas in addition to metformin: A nationwide cohort study of patients with type 2 diabetes
- Glycemic Effectiveness of Metformin-Based Dual-Combination Therapies with Sulphonylurea, Pioglitazone, or DPP4-Inhibitor in Drug-Naïve Korean Type 2 Diabetic Patients
- Young Ki Lee, Sun Ok Song, Kwang Joon Kim, Yongin Cho, Younjeong Choi, Yujung Yun, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun-Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(6):465-474. Published online December 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.6.465
- 5,127 View
- 67 Download
- 17 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study compared the glycemic effectiveness of three metformin-based dual therapies according to baseline hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) to evaluate the appropriateness of the guideline enforced by the National Health Insurance Corporation of Korea for initial medication of type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Methods This prospective observational study was conducted across 24 weeks for drug-naïve Korean T2D patients with HbA1c greater than 7.5%. Subjects were first divided into three groups based on the agent combined with metformin (group 1, gliclazide-modified release or glimepiride; group 2, pioglitazone; group 3, sitagliptin). Subjects were also classified into three categories according to baseline HbA1c (category I, 7.5%≤HbA1c<9.0%; category II, 9.0%≤HbA1c<11.0%; category III, 11.0%≤HbA1c).
Results Among 116 subjects, 99 subjects completed the study, with 88 subjects maintaining the initial medication. While each of the metformin-based dual therapies showed a significant decrease in HbA1c (group 1, 8.9% to 6.4%; group 2, 9.0% to 6.6%; group 3, 9.3% to 6.3%;
P <0.001 for each), there was no significant difference in the magnitude of HbA1c change among the groups. While the three HbA1c categories showed significantly different baseline HbA1c levels (8.2% vs. 9.9% vs. 11.9%;P <0.001), endpoint HbA1c was not different (6.4% vs. 6.6% vs. 6.0%;P =0.051).Conclusion The three dual therapies using a combination of metformin and either sulfonylurea, pioglitazone, or sitagliptin showed similar glycemic effectiveness among drug-naïve Korean T2D patients. In addition, these regimens were similarly effective across a wide range of baseline HbA1c levels.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Benefits and risks of drug combination therapy for diabetes mellitus and its complications: a comprehensive review
Xueqin Xie, Changchun Wu, Yuduo Hao, Tianyu Wang, Yuhe Yang, Peiling Cai, Yang Zhang, Jian Huang, Kejun Deng, Dan Yan, Hao Lin
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimation of Serum Creatinine, Aspartate Aminotransferase, Alanine Transaminase, and Hemoglobin A1c% Levels among Diabetic Patients using Metformin/Dipeptide Peptidase-4 Inhibitor Combination and Insulin – A Cross-Sectional Study
Arshiya Shadab, Ilma Hussain, Praveen Kumar Kandakurti, Marwan Ismail, Ahmed Luay Osman Hashim, Salah Eldin Omar Hussein, Altoum Abd Elgadir
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(B): 959. CrossRef - Acarbose Add-on Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus with Metformin and Sitagliptin Failure: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study
Hae Kyung Yang, Seung-Hwan Lee, Juyoung Shin, Yoon-Hee Choi, Yu-Bae Ahn, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Jung Rhee, Kyung Wan Min, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(3): 287. CrossRef - Initial combination therapy with vildagliptin plus metformin in drug-naïve patients with T2DM: a 24-week real-life study from Asia
Manoj Chawla, Tae Ho Kim, Roberto C. Mirasol, Pathan Faruque, Kathryn Cooke, Peggy Hours-Zesiger, Abhijit Shete
Current Medical Research and Opinion.2018; 34(9): 1605. CrossRef - Consensus recommendations on sulfonylurea and sulfonylurea combinations in the management of Type 2 diabetes mellitus – International Task Force
Sanjay Kalra, Silver Bahendeka, Rakesh Sahay, Sujoy Ghosh, Fariduddin Md, Abbas Orabi, Kaushik Ramaiya, Sameer Al Shammari, Dina Shrestha, Khalid Shaikh, Sachitha Abhayaratna, PradeepK Shrestha, Aravinthan Mahalingam, Mazen Askheta, AlyAhmed A. Rahim, Fat
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 22(1): 132. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin/metformin fixed‐dose combination compared with glimepiride in patients with type 2 diabetes: A multicenter randomized double‐blind study
Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, Kwang Jae Lee, Jeong Hyun Park, Young Il Kim, Young Sil Lee, Sung Chang Chung, Sang Jin Lee
Journal of Diabetes.2017; 9(4): 412. CrossRef - Short‐term intensive insulin therapy could be the preferred option for new onset Type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with HbA1c > 9%
Jianping Weng
Journal of Diabetes.2017; 9(10): 890. CrossRef - The efficacy and safety of adding either vildagliptin or glimepiride to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Gyuri Kim, Sewon Oh, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee
Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.2017; 18(12): 1179. CrossRef - Effects of pioglitazone therapy on blood parameters, weight and BMI: a meta-analysis
Elena Filipova, Katya Uzunova, Krassimir Kalinov, Toni Vekov
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Is insulin the preferred treatment for HbA1c >9%?
Zachary Bloomgarden
Journal of Diabetes.2017; 9(9): 814. CrossRef - The effect of pioglitazone on weight, lipid profile and liver enzymes in type 2 diabetic patients
Nasser Aghamohammadzadeh, Mitra Niafar, Elham Dalir Abdolahinia, Farzad Najafipour, Saeed Mohamadzadeh Gharebaghi, Khadijeh Adabi, Elaheh Dalir Abdolahinia, Hamidreza Ahadi
Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism.2015; 6(2): 56. CrossRef - Glycated Albumin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Increase Relative to HbA1cwith Time
Hye-jin Yoon, Yong-ho Lee, Kwang Joon Kim, So Ra Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
BioMed Research International.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Four-Year Durability of Initial Combination Therapy with Sitagliptin and Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Clinical Practice; COSMIC Study
Eu Jeong Ku, Kyong Yeon Jung, Yoon Ji Kim, Kyoung Min Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Hak Chul Jang, Soo Lim, Bo Ahrén, Giorgio Sesti
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(6): e0129477. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of therapeutic efficiency and costs (experience in Bulgaria) of oral antidiabetic therapies based on glitazones and gliptins
Elena Pavlova Filipova, Katya Hristova Uzunova, Toni Yonkov Vekov
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Interactions of DPP-4 and integrin β1 influences endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Sen Shi, Swayam Prakash Srivastava, Megumi Kanasaki, Jianhua He, Munehiro Kitada, Takako Nagai, Kyoko Nitta, Susumu Takagi, Keizo Kanasaki, Daisuke Koya
Kidney International.2015; 88(3): 479. CrossRef - Sodium Glucose Co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors: New among Antidiabetic Drugs
L. H. Opie
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy.2014; 28(4): 331. CrossRef - Metformin Based Dual-Combination Therapies in Drug Naïve Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Dong-Lim Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(6): 429. CrossRef
- Benefits and risks of drug combination therapy for diabetes mellitus and its complications: a comprehensive review
- The Risk of Bladder Cancer in Korean Diabetic Subjects Treated with Pioglitazone
- Sun Ok Song, Kwang Joon Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(5):371-378. Published online October 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.5.371
- 4,166 View
- 30 Download
- 30 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background There is growing concern regarding the increased incidence of bladder cancer in diabetic patients using pioglitazone. This study aimed to investigate the association between bladder cancer and the use of pioglitazone in Korean diabetics.
Methods This retrospective, matched case-control study included a case group (
n =329) of diabetic patients with bladder cancer who presented at the Severance Hospital from November 2005 to June 2011. The control group consisted of patients without bladder cancer (1:2 ratio matching for sex and age,n =658) who were listed on the Severance Hospital diabetes registry.Results The percentage of subjects who had ever used pioglitazone was significantly lower in the case group than in the control group (6.4% vs. 15.0%,
P <0.001). Multivariate conditional logistic analysis revealed that independent factors affecting bladder cancer were smoking (odds ratio [OR], 11.64; 95% confidence interval [CI], 6.56 to 20.66;P <0.001), coexisting cancer (OR, 6.11; 95% CI, 2.25 to 16.63;P <0.001), and hemoglobin levels (OR, 0.78; 95% CI, 0.69 to 0.88;P <0.001). The OR of the history of pioglitazone use was 2.09 and was not significantly different between the two groups (95% CI, 0.26 to 16.81;P =0.488).Conclusion A relationship between pioglitazone use and incidence of bladder cancer was not observed in Korean diabetic patients. This suggests that the risk for bladder cancer in Korean diabetic subjects treated with pioglitazone might be different from that of Caucasian populations. Large-scale, well-designed and multi-center studies are needed to further evaluate this relationship.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Cancer biology in diabetes update: Focusing on antidiabetic drugs
Emi Kawakita, Keizo Kanasaki
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Pioglitazone, Bladder Cancer, and the Presumption of Innocence
Georgios S. Papaetis
Current Drug Safety.2022; 17(4): 294. CrossRef - A systematic review of observational studies of the association between pioglitazone use and bladder cancer
E. Ripamonti, L. Azoulay, M. Abrahamowicz, R.W. Platt, S. Suissa
Diabetic Medicine.2019; 36(1): 22. CrossRef - Study design choices for evaluating the comparative safety of diabetes medications: An evaluation of pioglitazone use and risk of bladder cancer in older US adults with type‐2 diabetes
Elizabeth M. Garry, John B. Buse, Mugdha Gokhale, Jennifer L. Lund, Matthew E. Nielsen, Virginia Pate, Til Stürmer
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2019; 21(9): 2096. CrossRef - Pioglitazone use and risk of bladder cancer: a systematic literature review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Juha Mehtälä, Houssem Khanfir, Dimitri Bennett, Yizhou Ye, Pasi Korhonen, Fabian Hoti
Diabetology International.2019; 10(1): 24. CrossRef - Thiazolidinedione drugs in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: past, present and future
Melissa A. Davidson, Donald R. Mattison, Laurent Azoulay, Daniel Krewski
Critical Reviews in Toxicology.2018; 48(1): 52. CrossRef - An updated meta-analysis of pioglitazone exposure and bladder cancer and comparison to the drug’s effect on cardiovascular disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis
Mayer B. Davidson, Deyu Pan
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 135: 102. CrossRef - Pioglitazone and risk of bladder cancer in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis of observational studies using real-world data
Mohammad Adil, Rashid Ali Khan, Pinaki Ghosh, Shiva Kumar Venkata, Amit Dattatraya Kandhare, Manju Sharma
Clinical Epidemiology and Global Health.2018; 6(2): 61. CrossRef - Pioglitazone and bladder cancer risk: a systematic review and meta‐analysis
Huilin Tang, Weilong Shi, Shuangshuang Fu, Tiansheng Wang, Suodi Zhai, Yiqing Song, Jiali Han
Cancer Medicine.2018; 7(4): 1070. CrossRef - Global and Regional Effects of Bladder Cancer Risk Associated with Pioglitazone Therapy in Patients with Diabetes
Hua Qu, Yi Zheng, Yuren Wang, Rui Zhang, Xiongzhong Ruan, Gangyi Yang, Zhenqi Liu, Hongting Zheng
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Pioglitazone and the Risk of Bladder Cancer: A Meta-Analysis
Elena Filipova, Katya Uzunova, Krassimir Kalinov, Toni Vekov
Diabetes Therapy.2017; 8(4): 705. CrossRef - Pioglitazone does not increase the risk of type II diabetes in patients with bladder cancer: A retrospective study
YOUHONG DONG, ANPING WANG
Oncology Letters.2016; 12(1): 89. CrossRef - Ten‐year observational follow‐up of PROactive: a randomized cardiovascular outcomes trial evaluating pioglitazone in type 2 diabetes
E. Erdmann, S. Harding, H. Lam, A. Perez
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2016; 18(3): 266. CrossRef - Pioglitazone (Actos) and bladder cancer: Legal system triumphs over the evidence
Mayer B. Davidson
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2016; 30(6): 981. CrossRef - The current role of thiazolidinediones in diabetes management
Christos V. Rizos, Anastazia Kei, Moses S. Elisaf
Archives of Toxicology.2016; 90(8): 1861. CrossRef - Development of vascular complications and bladder carcinoma in diabetics using pioglitazone: A five-year Indian review
Saarwaani Vallabhajosyula, Shashaank Vallabhajosyula, Saraschandra Vallabhajosyula, Suma Nair, Asha Kamath, Karthik N. Rao
Medical Journal Armed Forces India.2016; 72(3): 253. CrossRef - Baseline glycemic status and mortality in 241,499 Korean metropolitan subjects: A Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Eun-Jung Rhee, Se Eun Park, Yoosoo Chang, Seungho Ryu, Won-Young Lee
Metabolism.2016; 65(2): 68. CrossRef - Rosiglitazone Use and the Risk of Bladder Cancer in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Eugene Han, Suk-Yong Jang, Gyuri Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Yeong Choe, Chung Mo Nam, Eun Seok Kang
Medicine.2016; 95(6): e2786. CrossRef - Polemics of pioglitazone: an appraisal in 2015
Awadhesh Kumar Singh
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2015; 10(4): 447. CrossRef - Pioglitazone and bladder cancer risk: a multipopulation pooled, cumulative exposure analysis
Daniel Levin, Samira Bell, Reijo Sund, Sirpa A. Hartikainen, Jaakko Tuomilehto, Eero Pukkala, Ilmo Keskimäki, Ellena Badrick, Andrew G. Renehan, Iain E. Buchan, Samantha L. Bowker, Jasjeet K. Minhas-Sandhu, Zafar Zafari, Carlo Marra, Jeffrey A. Johnson, B
Diabetologia.2015; 58(3): 493. CrossRef - Thiazolidinediones and associated risk of bladder cancer: a systematic review and meta‐analysis
Richard M. Turner, Chun S. Kwok, Chen Chen‐Turner, Chinedu A. Maduakor, Sonal Singh, Yoon K. Loke
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2014; 78(2): 258. CrossRef - A Review on Thiazolidinediones and Bladder Cancer in Human Studies
Chin-Hsiao Tseng
Journal of Environmental Science and Health, Part C.2014; 32(1): 1. CrossRef - Physiological Functions of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor β
Jaap G. Neels, Paul A. Grimaldi
Physiological Reviews.2014; 94(3): 795. CrossRef - Risk of Bladder Cancer among Patients with Diabetes Treated with a 15 mg Pioglitazone Dose in Korea: A Multi-Center Retrospective Cohort Study
Sang-Man Jin, Sun Ok Song, Chang Hee Jung, Jin-Sun Chang, Sunghwan Suh, Seung Min Kang, Inkyung Jung, Cheol-Young Park, Jae Hyeon Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2014; 29(2): 238. CrossRef - Pioglitazone
SS Jadhav, VK Shivane, AR Lila, TR Bandgar, NS Shah
Journal of Postgraduate Medicine.2014; 60(3): 293. CrossRef - Refocusing Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor-α: A New Insight for Therapeutic Roles in Diabetes
Hannah Seok, Bong Soo Cha
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(5): 326. CrossRef - Effects of co-administration of candesartan with pioglitazone on inflammatory parameters in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a preliminary report
Hirofumi Suzuki, Masaya Sakamoto, Takeshi Hayashi, Hiroyuki Iuchi, Kennosuke Ohashi, Tsuyoshi Isaka, Noriko Sakamoto, Yosuke Kayama, Katsuyoshi Tojo, Michihiro Yoshimura, Kazunori Utsunomiya
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2013;[Epub] CrossRef - The Future of Thiazolidinedione Therapy in the Management of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Hanford Yau, Kathya Rivera, Romina Lomonaco, Kenneth Cusi
Current Diabetes Reports.2013; 13(3): 329. CrossRef - Letter: The Risk of Bladder Cancer in Korean Diabetic Subjects Treated with Pioglitazone (Diabetes Metab J2012;36:371-8)
Sheyu Li, Haoming Tian
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2013; 37(1): 81. CrossRef - Metabolic Surgery for Type 2 Diabetes in Patients with a BMI of <35 kg/m2: A Surgeon’s Perspective
Ricardo Cohen, Pedro Paulo Caravatto, Tarissa Petry
Obesity Surgery.2013; 23(6): 809. CrossRef
- Cancer biology in diabetes update: Focusing on antidiabetic drugs
- Long-term Effect of Pioglitazone Treatment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.
- Jae Hoon Moon, Hye Jin Kim, Soo Kyung Kim, Wan Sub Shim, Eun Seuk Kang, Yumie Rhee, Chul Woo Ahn, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Bong Soo Cha
- Korean Diabetes J. 2006;30(4):264-276. Published online July 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2006.30.4.264
- 2,543 View
- 26 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by impaired insulin secretion and/or insulin resistance. Thiazolidinediones have been shown to ameliorate insulin resistance. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the long term serial effect of pioglitazone on anthropometrics and metabolic parameters in Korean type 2 diabetes patients. METHODS: One hundred thirteen type 2 diabetes patients (male, 67; female, 46; mean age, 49.1+/-10.8 years) were evaluated before and after 3 months, 6 months and 12 months of treatment with pioglitazone (Actos(TM), 15 mg/day). Anthropometric parameters and metabolic variables were measured. RESULTS: Body weight and body mass index (BMI) were increased in 3 months after pioglitazone treatment (body weight, 68.8+/-12.2 vs 69.8+/-11.9 kg, P < 0.01) without further increase. In women, body weight and BMI tended to increase more (body weight change after 3 months, 0.6+/-1.7 kg vs 1.6+/-1.7 kg, P < 0.01) and longer (3 months vs 6 months) than in men. Fasting plasma glucose (FPG) and HbA1c were decreased in 3 months after pioglitazone treatment (FPG, 7.97+/-2.29 vs 6.94+/-2.01 mmol/L, P < 0.01; HbA1c, 7.7+/-1.5 vs 7.0+/-1.1%, P < 0.01). Hypoglycemic effect of pioglitazone was prominent in women than in men (FPG change after 12 months, -1.80+/-2.54 vs -0.09+/-1.72 mmol/L, P < 0.001; HbA1c change after 12 months, -0.9+/-1.3 vs -0.4+/-1.1%, P < 0.05). Serum high-density lipoprotein cholesterol was increased after 3 months of pioglitazone treatment (1.16+/-0.24 vs 1.31+/-0.28 mmol/L, P < 0.01) without return until the end of this study. Serum triglycerides level decreased at 3 months (basal vs 3 months, 2.29+/-1.86 vs 1.88+/-1.21 mmol/L, P < 0.01) and 6 months (basal vs 6 months, 2.29+/-1.86 vs 1.97+/-1.40 mmol/L, P < 0.05) of pioglitazone treatment, but returned to basal level at 12 months. Liver enzyme, especially serum alanine transferase level decreased after 3 months of pioglitazone treatment (30.8+/-23.7 vs 24.5+/-18.5 IU/L, P < 0.01) without return until the end of this study. Hypoglycemic effect of pioglitazone was associated with basal BMI, fat contents and serum leptin level. CONCLUSION: Korean type 2 diabetes patients with pioglitazone use showed favorable metabolic effect for glycemic control, lipid metabolism and liverfunction, but pioglitazone induced body weight increase may be limited. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Therapeutic Effect of Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Who Have Insulin Limitations
Won Sang Yoo, Do Hee Kim, Hee Jin Kim, Hyun Kyung Chung
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2019; 20(2): 117. CrossRef
- Therapeutic Effect of Quadruple Oral Hypoglycemic Agents in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Who Have Insulin Limitations
- Effects of Pioglitazone on Cerebral Hemodynamics in Patients of Type 2 Diabetes.
- Jong Suk Park, You Jung Lee, Chul Sik Kim, Hai Jin Kim, Jina Park, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Yul Lee, Hyeong Jin Kim, Young Jun Won, Hun Ju Ha, Hae Sun Kwak, Bong Soo Cha, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee
- Korean Diabetes J. 2006;30(2):96-103. Published online March 1, 2006
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/jkda.2006.30.2.96
- 2,649 View
- 19 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Atherosclerosis is one of the major causes of morbidity and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and pioglitazone has been reported to have antiatherogenic effect. The aim of this study was to investigate whether pioglitazone affects carotid intima-media thickness (IMT) and pulsatility index (PI) in type 2 diabetic patients. METHODS: A total of 40 type 2 diabetic patients were included and divided into two groups: the pioglitazone-treated group (pioglitazone 15 mg/day with gliclazide 80~320 mg/day for 12 weeks) (n = 20) and control group (gliclazide 80~320 mg/day for 12 weeks) (n = 20). The changes in lipid profile, insulin resistance, IMT, and PI were monitored to determine that pioglitazone improves cerebrovascular blood flow. RESULTS: The pioglitazone treatment significantly increased HDL-C, reduced triglyceride, insulin resistance and PI. IMT tended to decrease but the change was not significant. This study revealed that treatment with pioglitazone was associated with the improvement of cerebrovascular blood flow. CONCLUSIONS: Pioglitazone appears to be effective for the improvement of cerebrovascular blood flow in type 2 diabetic patients

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





