
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Brief Report
- Technology/Device
- Do-It-Yourself Open Artificial Pancreas System in Children and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: Real-World Data
- Min Sun Choi, Seunghyun Lee, Jiwon Kim, Gyuri Kim, Sung Min Park, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):154-159. Published online November 23, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0011
- 5,316 View
- 193 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
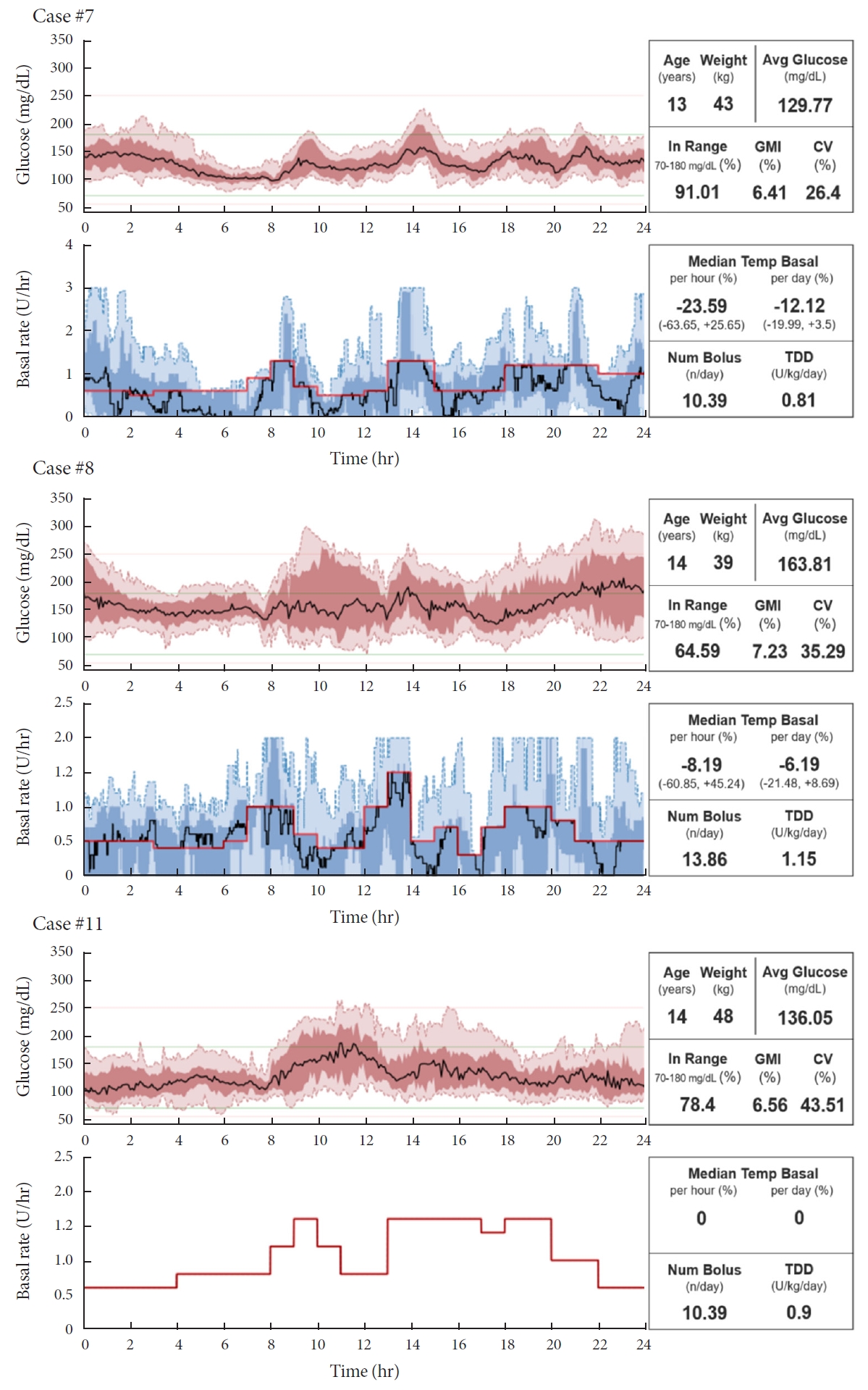
ePub - Few studies have been conducted among Asian children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) using do-it-yourself artificial pancreas system (DIY-APS). We evaluated real-world data of pediatric T1DM patients using DIY-APS. Data were obtained for 10 patients using a DIY-APS with algorithms. We collected sensor glucose and insulin delivery data from each participant for a period of 4 weeks. Average glycosylated hemoglobin was 6.2%±0.3%. The mean percentage of time that glucose level remained in the target range of 70 to 180 mg/dL was 82.4%±7.8%. Other parameters including time above range, time below range and mean glucose were also within the recommended level, similar to previous commercial and DIY-APS studies. However, despite meeting the target range, unadjusted gaps were still observed between the median basal setting and temporary basal insulin, which should be handled by healthcare providers.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 27. CrossRef - Open-source automated insulin delivery systems (OS-AIDs) in a pediatric population with type 1 diabetes in a real-life setting: the AWeSoMe study group experience
Judith Nir, Marianna Rachmiel, Abigail Fraser, Yael Lebenthal, Avivit Brener, Orit Pinhas-Hamiel, Alon Haim, Eve Stern, Noa Levek, Tal Ben-Ari, Zohar Landau
Endocrine.2023; 81(2): 262. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of Android artificial pancreas system use at home among adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus in China: protocol of a 26-week, free-living, randomised, open-label, two-arm, two-phase, crossover trial
Mengyun Lei, Beisi Lin, Ping Ling, Zhigu Liu, Daizhi Yang, Hongrong Deng, Xubin Yang, Jing Lv, Wen Xu, Jinhua Yan
BMJ Open.2023; 13(8): e073263. CrossRef - Barriers to Uptake of Open-Source Automated Insulin Delivery Systems: Analysis of Socioeconomic Factors and Perceived Challenges of Caregivers of Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes From the OPEN Survey
Antonia Huhndt, Yanbing Chen, Shane O’Donnell, Drew Cooper, Hanne Ballhausen, Katarzyna A. Gajewska, Timothée Froment, Mandy Wäldchen, Dana M. Lewis, Klemens Raile, Timothy C. Skinner, Katarina Braune
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Toward Personalized Hemoglobin A1c Estimation for Type 2 Diabetes
Namho Kim, Da Young Lee, Wonju Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Sung-Min Park
IEEE Sensors Journal.2022; 22(23): 23023. CrossRef
- Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
Review
- Technology/Device
- Current Advances of Artificial Pancreas Systems: A Comprehensive Review of the Clinical Evidence
- Sun Joon Moon, Inha Jung, Cheol-Young Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):813-839. Published online November 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0177
- 14,498 View
- 800 Download
- 29 Web of Science
- 28 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
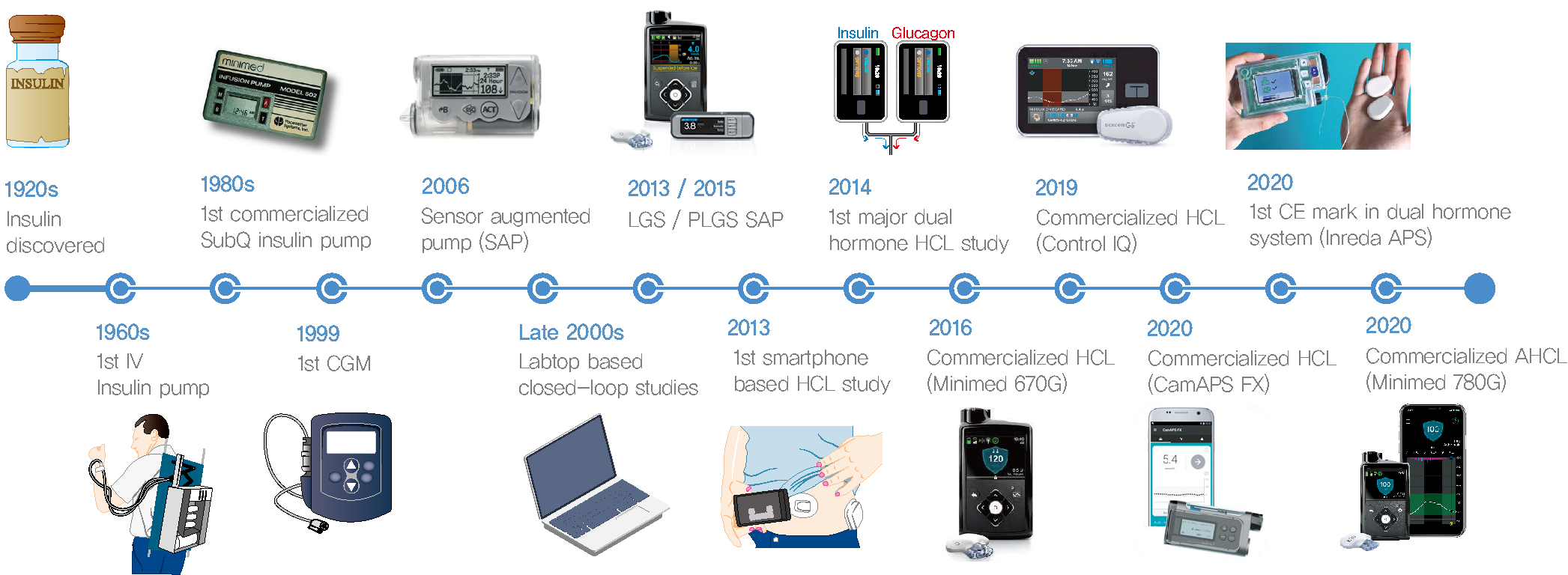
- Since Banting and Best isolated insulin in the 1920s, dramatic progress has been made in the treatment of type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). However, dose titration and timely injection to maintain optimal glycemic control are often challenging for T1DM patients and their families because they require frequent blood glucose checks. In recent years, technological advances in insulin pumps and continuous glucose monitoring systems have created paradigm shifts in T1DM care that are being extended to develop artificial pancreas systems (APSs). Numerous studies that demonstrate the superiority of glycemic control offered by APSs over those offered by conventional treatment are still being published, and rapid commercialization and use in actual practice have already begun. Given this rapid development, keeping up with the latest knowledge in an organized way is confusing for both patients and medical staff. Herein, we explore the history, clinical evidence, and current state of APSs, focusing on various development groups and the commercialization status. We also discuss APS development in groups outside the usual T1DM patients and the administration of adjunct agents, such as amylin analogues, in APSs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Integration of a Safety Module to Prevent Rebound Hypoglycemia in Closed-Loop Artificial Pancreas Systems
María F. Villa-Tamayo, Patricio Colmegna, Marc D. Breton
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2024; 18(2): 318. CrossRef - The effects of acute hyperglycaemia on sports and exercise performance in type 1 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Bonar McGuire, Hashim Dadah, Dominic Oliver
Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport.2024; 27(2): 78. CrossRef - A new approach to stabilize diabetes systems with time-varying delays and disturbance rejection
S. Syafiie, Fahd Alharbi, Abdullah Ali Alshehri, Bassam Hasanain
Journal of the Franklin Institute.2024; 361(1): 543. CrossRef - Effects of Low-Dose Glucagon on Subcutaneous Insulin Absorption in Pigs
Ingrid Anna Teigen, Marte Kierulf Åm, Misbah Riaz, Sverre Christian Christiansen, Sven Magnus Carlsen
Current Therapeutic Research.2024; 100: 100736. CrossRef - Robust Online Correlation Method for Identification of a Nonparametric Model of Type 1 Diabetes
Martin Dodek, Eva Miklovičová
IEEE Access.2024; 12: 35899. CrossRef - 100 Years of insulin: A chemical engineering perspective
B. Wayne Bequette
Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering.2023; 40(1): 1. CrossRef - Efficacy of intermittent short‐term use of a real‐time continuous glucose monitoring system in non‐insulin–treated patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomized controlled trial
Sun Joon Moon, Kyung‐Soo Kim, Woo Je Lee, Mi Yeon Lee, Robert Vigersky, Cheol‐Young Park
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(1): 110. CrossRef - Identifiable prediction animal model for the bi-hormonal intraperitoneal artificial pancreas
Karim Davari Benam, Hasti Khoshamadi, Marte Kierulf Åm, Øyvind Stavdahl, Sebastien Gros, Anders Lyngvi Fougner
Journal of Process Control.2023; 121: 13. CrossRef - Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 27. CrossRef - CGM accuracy: Contrasting CE marking with the governmental controls of the USA (FDA) and Australia (TGA): A narrative review
John S Pemberton, Emma G Wilmot, Katharine Barnard‐Kelly, Lalantha Leelarathna, Nick Oliver, Tabitha Randell, Craig E Taplin, Pratik Choudhary, Peter Adolfsson
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(4): 916. CrossRef - Evaluation of awareness and attitude of paediatric nursing students, nurses, and adolescents regarding type one diabetes advanced devices and virtual nursing
Howaida Moawad Ahmed Ali
Kontakt.2023; 25(2): 100. CrossRef - Predicting the output error of the suboptimal state estimator to improve the performance of the MPC-based artificial pancreas
Martin Dodek, Eva Miklovičová
Control Theory and Technology.2023; 21(4): 541. CrossRef - A Markov Model of Gap Occurrence in Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data for Realistic in Silico Clinical Trials
Martina Vettoretti, Martina Drecogna, Simone Del Favero, Andrea Facchinetti, Giovanni Sparacino
Computer Methods and Programs in Biomedicine.2023; 240: 107700. CrossRef - Drug delivery breakthrough technologies – A perspective on clinical and societal impact
Beate Bittner, Manuel Sánchez-Félix, Dennis Lee, Athanas Koynov, Joshua Horvath, Felix Schumacher, Simon Matoori
Journal of Controlled Release.2023; 360: 335. CrossRef - Importance of continuous glucose monitoring in the treatment of diabetes mellitus
Sun Joon Moon, Won-Young Lee
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 432. CrossRef - Constrained Versus Unconstrained Model Predictive Control for Artificial Pancreas
Chiara Toffanin, Lalo Magni
IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology.2023; 31(5): 2288. CrossRef - Intelligent Insulin vs. Artificial Intelligence for Type 1 Diabetes: Will the Real Winner Please Stand Up?
Valentina Maria Cambuli, Marco Giorgio Baroni
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(17): 13139. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence in Efficient Diabetes Care
Gopal Bhagwan Khodve, Sugato Banerjee
Current Diabetes Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The artificial pancreas: two alternative approaches to achieve a fully closed-loop system with optimal glucose control
M. K. Åm, I. A. Teigen, M. Riaz, A. L. Fougner, S. C. Christiansen, S. M. Carlsen
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2023; 47(3): 513. CrossRef - Multivariable Automated Insulin Delivery System for Handling Planned and Spontaneous Physical Activities
Mohammad Reza Askari, Mohammad Ahmadasas, Andrew Shahidehpour, Mudassir Rashid, Laurie Quinn, Minsun Park, Ali Cinar
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2023; 17(6): 1456. CrossRef - Advanced Technology (Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Advanced Hybrid Closed-Loop Systems) in Diabetes from the Perspective of Gender Differences
Maria Grazia Nuzzo, Marciano Schettino
Diabetology.2023; 4(4): 519. CrossRef - Artificial Pancreas under a Zone Model Predictive Control based on Gaussian Process models: toward the personalization of the closed loop
Marco Polver, Beatrice Sonzogni, Mirko Mazzoleni, Fabio Previdi, Antonio Ferramosca
IFAC-PapersOnLine.2023; 56(2): 9642. CrossRef - Personalized Constrained MPC for glucose regulation
Chiara Toffanin, Lalo Magni
IFAC-PapersOnLine.2023; 56(2): 9648. CrossRef - Automated Insulin Delivery Systems in Children and Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Outpatient Randomized Controlled Trials
Baoqi Zeng, Le Gao, Qingqing Yang, Hao Jia, Feng Sun
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(12): 2300. CrossRef - Novel Glycemic Index Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Predict Poor Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Il Rae Park, Yin Young Lee, Eun Young Choi, Jun Sung Moon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dual‐hormone artificial pancreas for glucose control in type 1 diabetes: A meta‐analysis
Baoqi Zeng, Hao Jia, Le Gao, Qingqing Yang, Kai Yu, Feng Sun
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(10): 1967. CrossRef - Dual-Hormone Insulin-and-Pramlintide Artificial Pancreas for Type 1 Diabetes: A Systematic Review
Alezandra Torres-Castaño, Amado Rivero-Santana, Lilisbeth Perestelo-Pérez, Andrea Duarte-Díaz, Analia Abt-Sacks, Vanesa Ramos-García, Yolanda Álvarez-Pérez, Ana M. Wäagner, Mercedes Rigla, Pedro Serrano-Aguilar
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(20): 10262. CrossRef - History of insulin treatment of pediatric patients with diabetes in Korea
Jae Hyun Kim, Choong Ho Shin, Sei Won Yang
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 26(4): 237. CrossRef
- Integration of a Safety Module to Prevent Rebound Hypoglycemia in Closed-Loop Artificial Pancreas Systems

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





