
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Others
- Risk Prediction and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in People Living with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ying-Guat Ooi, Tharsini Sarvanandan, Nicholas Ken Yoong Hee, Quan-Hziung Lim, Sharmila S. Paramasivam, Jeyakantha Ratnasingam, Shireene R. Vethakkan, Soo-Kun Lim, Lee-Ling Lim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):196-207. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0244
- 2,114 View
- 388 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
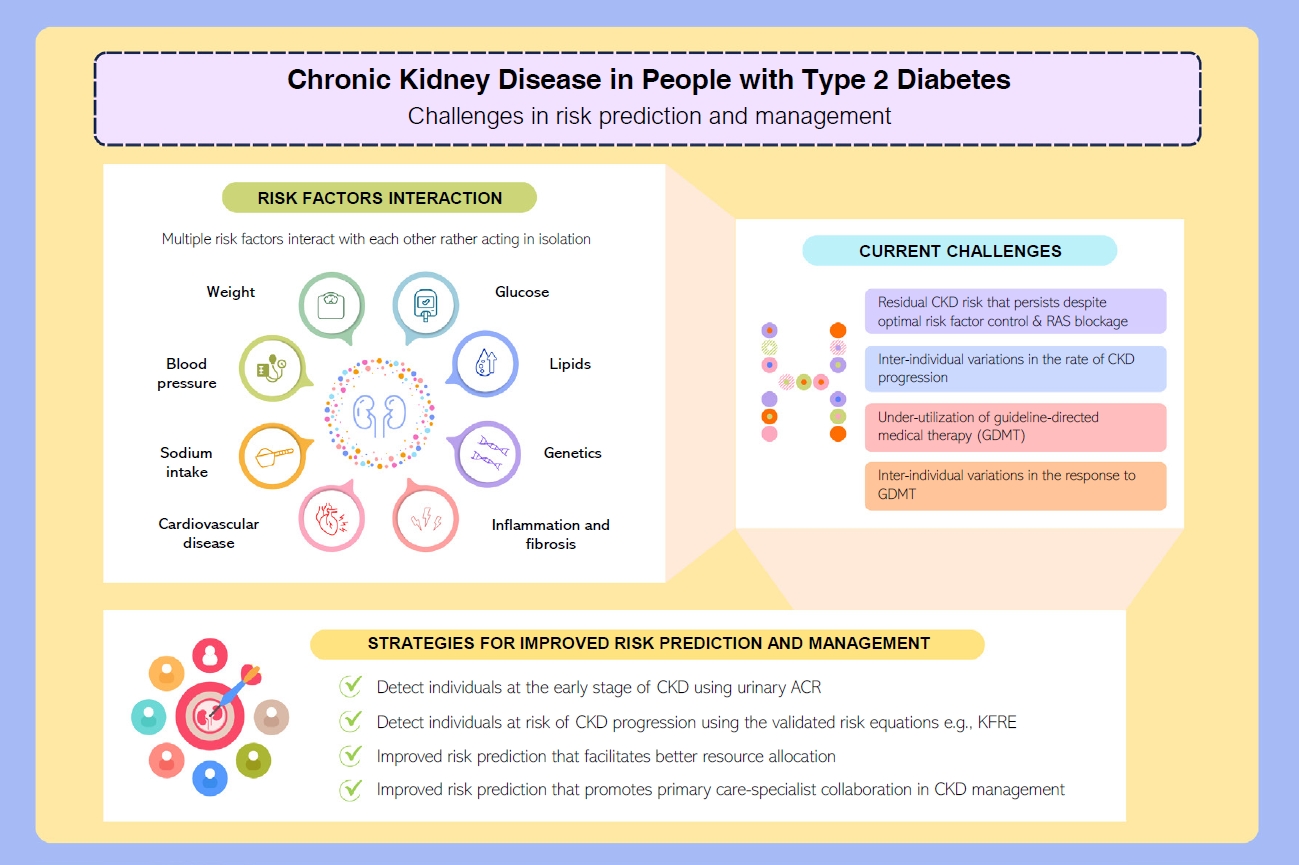
ePub - People with type 2 diabetes mellitus have increased risk of chronic kidney disease and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Improved care delivery and implementation of guideline-directed medical therapy have contributed to the declining incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in high-income countries. By contrast, the global incidence of chronic kidney disease and associated mortality is either plateaued or increased, leading to escalating direct and indirect medical costs. Given limited resources, better risk stratification approaches to identify people at risk of rapid progression to end-stage kidney disease can reduce therapeutic inertia, facilitate timely interventions and identify the need for early nephrologist referral. Among people with chronic kidney disease G3a and beyond, the kidney failure risk equations (KFRE) have been externally validated and outperformed other risk prediction models. The KFRE can also guide the timing of preparation for kidney replacement therapy with improved healthcare resources planning and may prevent multiple complications and premature mortality among people with chronic kidney disease with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. The present review summarizes the evidence of KFRE to date and call for future research to validate and evaluate its impact on cardiovascular and mortality outcomes, as well as healthcare resource utilization in multiethnic populations and different healthcare settings.
- Drug/Regimen
- Evogliptin, a Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor, Attenuates Renal Fibrosis Caused by Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction in Mice
- Mi-Jin Kim, Na-young Kim, Yun-A Jung, Seunghyeong Lee, Gwon-Soo Jung, Jung-Guk Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Sungwoo Lee, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Keun-Gyu Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):186-192. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0271
- 5,693 View
- 97 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Renal fibrosis is considered to be the final common outcome of chronic kidney disease. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors have demonstrated protective effects against diabetic kidney disease. However, the anti-fibrotic effect of evogliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, has not been studied. Here, we report the beneficial effects of evogliptin on unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO)-induced renal fibrosis in mice. Evogliptin attenuated UUO-induced renal atrophy and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Immunohistochemistry and Western blotting demonstrated that evogliptin treatment inhibits pro-fibrotic gene expressions and extracellular matrix production.
In vitro findings showed that the beneficial effects of evogliptin on renal fibrosis are mediated by inhibition of the transforming growth factor-β/Smad3 signaling pathway. The present study demonstrates that evogliptin is protective against UUO-induced renal fibrosis, suggesting that its clinical applications could extend to the treatment of kidney disease of non-diabetic origin.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Targeting cluster of differentiation 26 / dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (CD26/DPP4) in organ fibrosis
Birte Ohm, Isabelle Moneke, Wolfgang Jungraithmayr
British Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 180(22): 2846. CrossRef - Linagliptin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis in systemic sclerosis mouse model via inhibition of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Biwei Pei, Na Zhang, Tingting Pang, Gengyun Sun
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2022; 477(4): 995. CrossRef - Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes
Yewon Na, Soo Wan Kim, Ie Byung Park, Soo Jung Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Jaehun Jung, Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(11): 3022. CrossRef - Evogliptin Directly Inhibits Inflammatory and Fibrotic Signaling in Isolated Liver Cells
Hye-Young Seo, So-Hee Lee, Eugene Han, Jae Seok Hwang, Sol Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(19): 11636. CrossRef - Optimization and validation of a fluorogenic dipeptidyl peptidase 4 enzymatic assay in human plasma
Hyunyee Yoon, Su Hee Cho, Yu Rim Seo, Kyung-Sang Yu, Sung Sup Park, Moon Jung Song
Analytical Biochemistry.2021; 612: 113952. CrossRef - Use of Anti-Diabetic Agents in Non-Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Bench to Bedside
Sungjin Chung, Gheun-Ho Kim
Life.2021; 11(5): 389. CrossRef - Targeting Dermal Fibroblast Subtypes in Antifibrotic Therapy: Surface Marker as a Cellular Identity or a Functional Entity?
Xin Huang, Yimin Khoong, Chengyao Han, Dai Su, Hao Ma, Shuchen Gu, Qingfeng Li, Tao Zan
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of evogliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, active‐controlled, randomized, double‐blind study with open‐label extension (the EVERGREEN study)
Gyuri Kim, Soo Lim, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon, Ie B. Park, Kyu J. Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park, Su K. Kwon, Hye S. Kim, Seok W. Park, Sin G. Kim, Min K. Moon, Eun S. Kim, Choon H. Chung, Kang S. Park, Mikyung Kim, Dong J. Chung, Chang B. Lee, Tae H. Kim, Moon‐Kyu Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(9): 1527. CrossRef Effect of Switching from Linagliptin to Teneligliptin Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eugene Han, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Soon Kim, Byung-wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4113. CrossRef- Efficacy and safety of novel dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 inhibitor evogliptin in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Aishwarya Krishnamurthy, LokeshKumar Sharma, Meha Sharma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 24(5): 434. CrossRef
- Targeting cluster of differentiation 26 / dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (CD26/DPP4) in organ fibrosis

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





