
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review
- Pathophysiology
- Dysfunctional Mitochondria Clearance in Situ: Mitophagy in Obesity and Diabetes-Associated Cardiometabolic Diseases
- Songling Tang, Di Hao, Wen Ma, Lian Liu, Jiuyu Gao, Peng Yao, Haifang Yu, Lu Gan, Yu Cao
- Received July 4, 2023 Accepted October 29, 2023 Published online February 15, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0213 [Epub ahead of print]
- 1,091 View
- 65 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
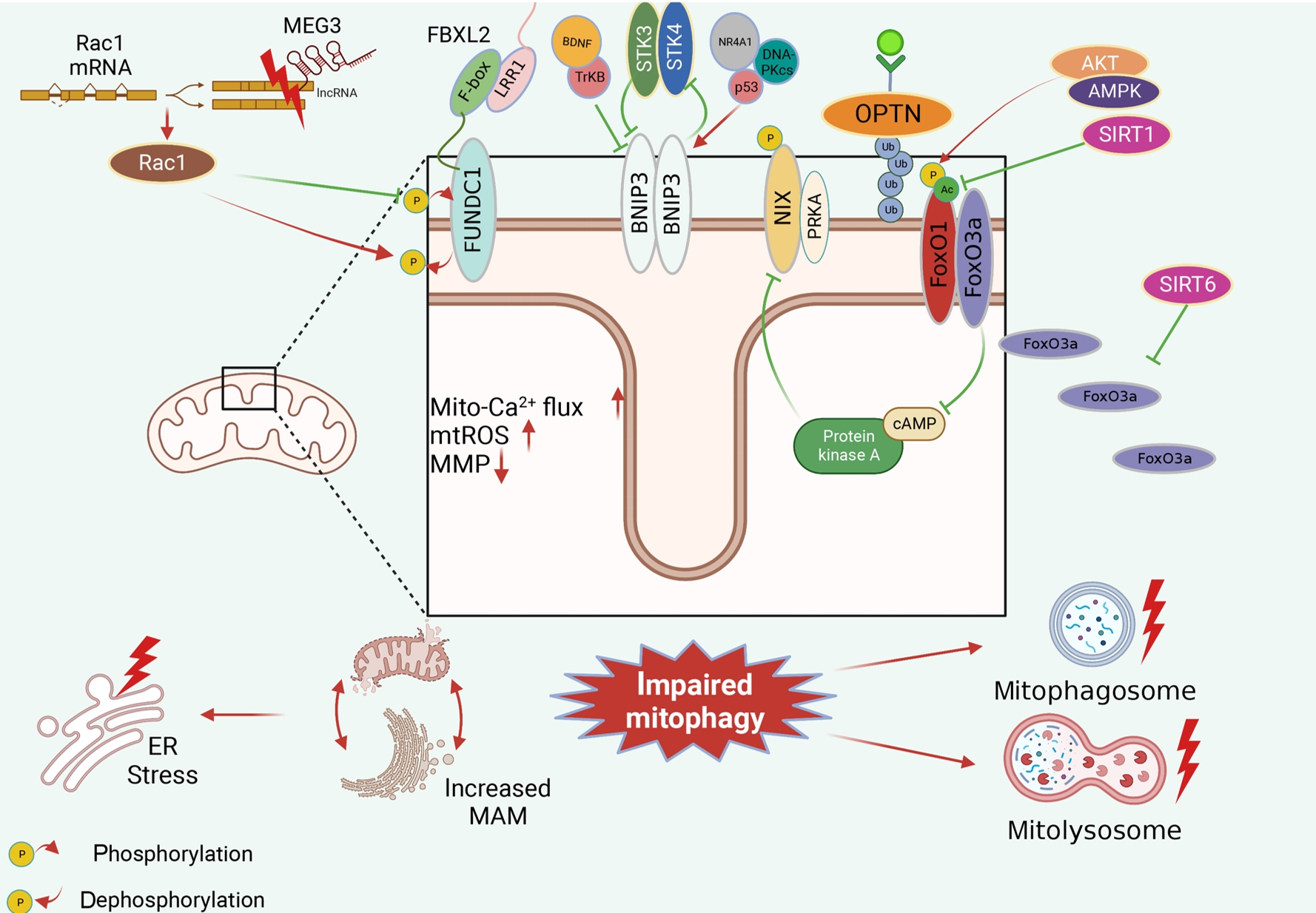
ePub - Several mitochondrial dysfunctions in obesity and diabetes include impaired mitochondrial membrane potential, excessive mitochondrial reactive oxygen species generation, reduced mitochondrial DNA, increased mitochondrial Ca2+ flux, and mitochondrial dynamics disorders. Mitophagy, specialized autophagy, is responsible for clearing dysfunctional mitochondria in physiological and pathological conditions. As a paradox, inhibition and activation of mitophagy have been observed in obesity and diabetes-related heart disorders, with both exerting bidirectional effects. Suppressed mitophagy is beneficial to mitochondrial homeostasis, also known as benign mitophagy. On the contrary, in most cases, excessive mitophagy is harmful to dysfunctional mitochondria elimination and thus is defined as detrimental mitophagy. In obesity and diabetes, two classical pathways appear to regulate mitophagy, including PTEN-induced putative kinase 1 (PINK1)/Parkin-dependent mitophagy and receptors/adapters-dependent mitophagy. After the pharmacologic interventions of mitophagy, mitochondrial morphology and function have been restored, and cell viability has been further improved. Herein, we summarize the mitochondrial dysfunction and mitophagy alterations in obesity and diabetes, as well as the underlying upstream mechanisms, in order to provide novel therapeutic strategies for the obesity and diabetes-related heart disorders.
Original Article
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Temporal Changes in Resting Heart Rate and Risk of Diabetes Mellitus
- Mi Kyoung Son, Kyoungho Lee, Hyun-Young Park
- Received August 29, 2023 Accepted November 13, 2023 Published online February 2, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0305 [Epub ahead of print]

- 630 View
- 46 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To investigate the association between the time-varying resting heart rate (RHR) and change in RHR (∆RHR) over time and the risk of diabetes mellitus (DM) by sex.
Methods
We assessed 8,392 participants without DM or atrial fibrillation/flutter from the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study, a community-based prospective cohort study that was initiated in 2001 to 2002. The participants were followed up until December 31, 2018. Updating RHR with biennial in-study re-examinations, the time-varying ∆RHR was calculated by assessing the ∆RHR at the next follow-up visit.
Results
Over a median follow-up of 12.3 years, 1,345 participants (16.2%) had DM. As compared with RHR of 60 to 69 bpm, for RHR of ≥80 bpm, the incidence of DM was significantly increased for both male and female. A drop of ≥5 bpm in ∆RHR when compared with the stable ∆RHR group (–5< ∆RHR <5 bpm) was associated significantly with lower risk of DM in both male and female. However, an increase of ≥5 bpm in ∆RHR was significantly associated with higher risk of DM only in female, not in male (hazard ratio for male, 1.057 [95% confidence interval, 0.869 to 1.285]; and for female, 1.218 [95% confidence interval, 1.008 to 1.471]).
Conclusion
In this community-based longitudinal cohort study, a reduction in ∆RHR was associated with a decreased risk of DM, while an increase in ∆RHR was associated with an increased risk of DM only in female.
Reviews
- Pathophysiology
- Epicardial Adipose Tissue and Heart Failure, Friend or Foe?
- Dong-Hyuk Cho, Seong-Mi Park
- Received June 20, 2023 Accepted December 11, 2023 Published online February 2, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0190 [Epub ahead of print]
- 929 View
- 75 Download
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Heart failure (HF) management guidelines recommend individualized assessments based on HF phenotypes. Adiposity is a known risk factor for HF. Recently, there has been an increased interest in organ-specific adiposity, specifically the role of the epicardial adipose tissue (EAT), in HF risk. EAT is easily assessable through various imaging modalities and is anatomically and functionally connected to the myocardium. In pathological conditions, EAT secretes inflammatory cytokines, releases excessive fatty acids, and increases mechanical load on the myocardium, resulting in myocardial remodeling. EAT plays a pathophysiological role in characterizing both HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). In HFrEF, EAT volume is reduced, reflecting an impaired metabolic reservoir, whereas in HFpEF, the amount of EAT is associated with worse biomarker and hemodynamic profiles, indicating increased EAT activity. Studies have examined the possibility of therapeutically targeting EAT, and recent studies using sodium glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors have shown potential in reducing EAT volume. However, further research is required to determine the clinical implications of reducing EAT activity in patients with HF.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- New Mechanisms to Prevent Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Using Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonism (GLP-1 RA) in Metabolic Syndrome and in Type 2 Diabetes: A Review
Jorge E. Jalil, Luigi Gabrielli, María Paz Ocaranza, Paul MacNab, Rodrigo Fernández, Bruno Grassi, Paulina Jofré, Hugo Verdejo, Monica Acevedo, Samuel Cordova, Luis Sanhueza, Douglas Greig
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(8): 4407. CrossRef
- New Mechanisms to Prevent Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction Using Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonism (GLP-1 RA) in Metabolic Syndrome and in Type 2 Diabetes: A Review
- Pathophysiology
- Primordial Drivers of Diabetes Heart Disease: Comprehensive Insights into Insulin Resistance
- Yajie Fan, Zhipeng Yan, Tingting Li, Aolin Li, Xinbiao Fan, Zhongwen Qi, Junping Zhang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(1):19-36. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0110
- 2,250 View
- 185 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
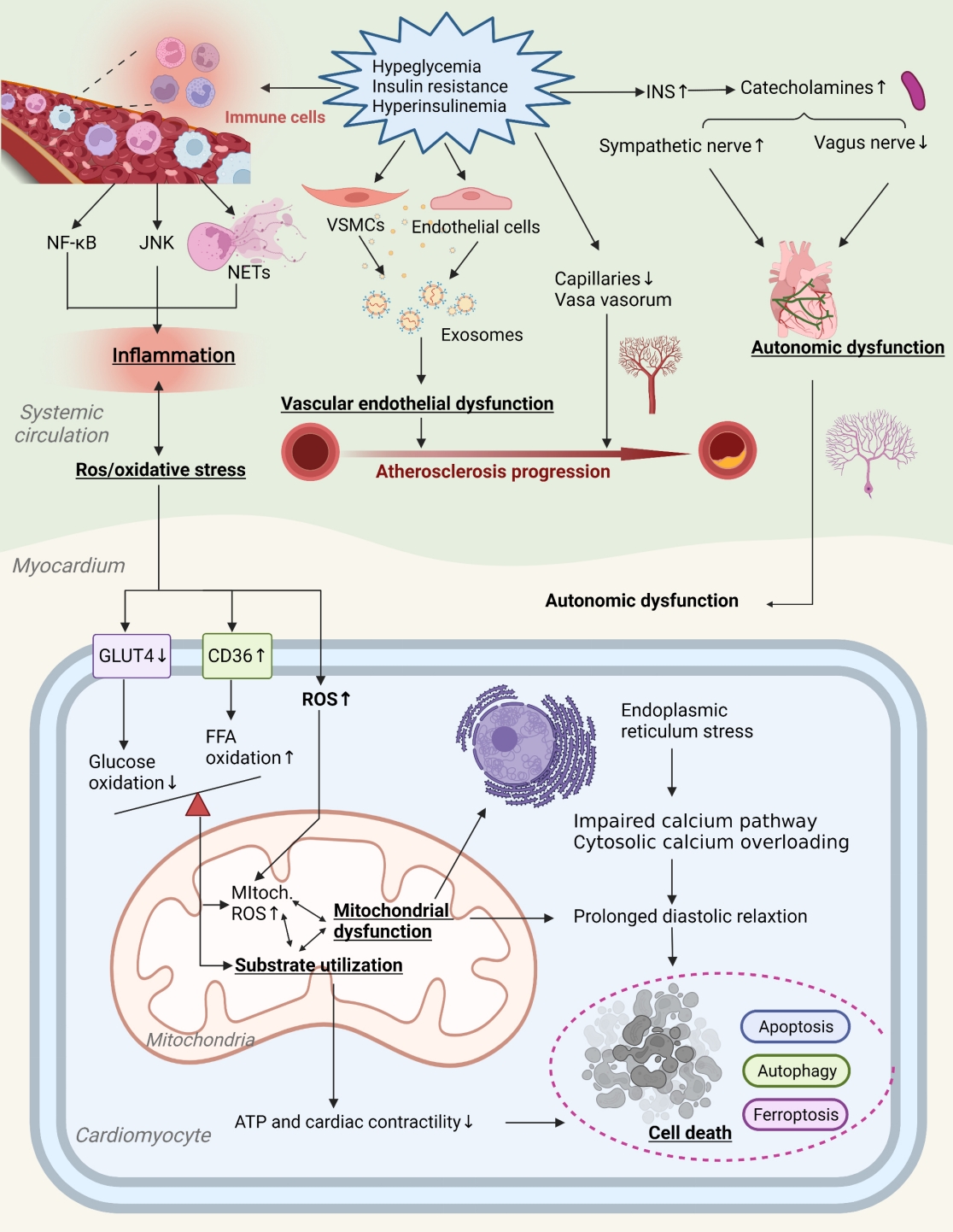
ePub - Insulin resistance has been regarded as a hallmark of diabetes heart disease (DHD). Numerous studies have shown that insulin resistance can affect blood circulation and myocardium, which indirectly cause cardiac hypertrophy and ventricular remodeling, participating in the pathogenesis of DHD. Meanwhile, hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and hyperlipidemia associated with insulin resistance can directly impair the metabolism and function of the heart. Targeting insulin resistance is a potential therapeutic strategy for the prevention of DHD. Currently, the role of insulin resistance in the pathogenic development of DHD is still under active research, as the pathological roles involved are complex and not yet fully understood, and the related therapeutic approaches are not well developed. In this review, we describe insulin resistance and add recent advances in the major pathological and physiological changes and underlying mechanisms by which insulin resistance leads to myocardial remodeling and dysfunction in the diabetic heart, including exosomal dysfunction, ferroptosis, and epigenetic factors. In addition, we discuss potential therapeutic approaches to improve insulin resistance and accelerate the development of cardiovascular protection drugs.
Original Article
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Comparison of on-Statin Lipid and Lipoprotein Levels for the Prediction of First Cardiovascular Event in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(6):837-845. Published online August 23, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0217
- 1,480 View
- 175 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
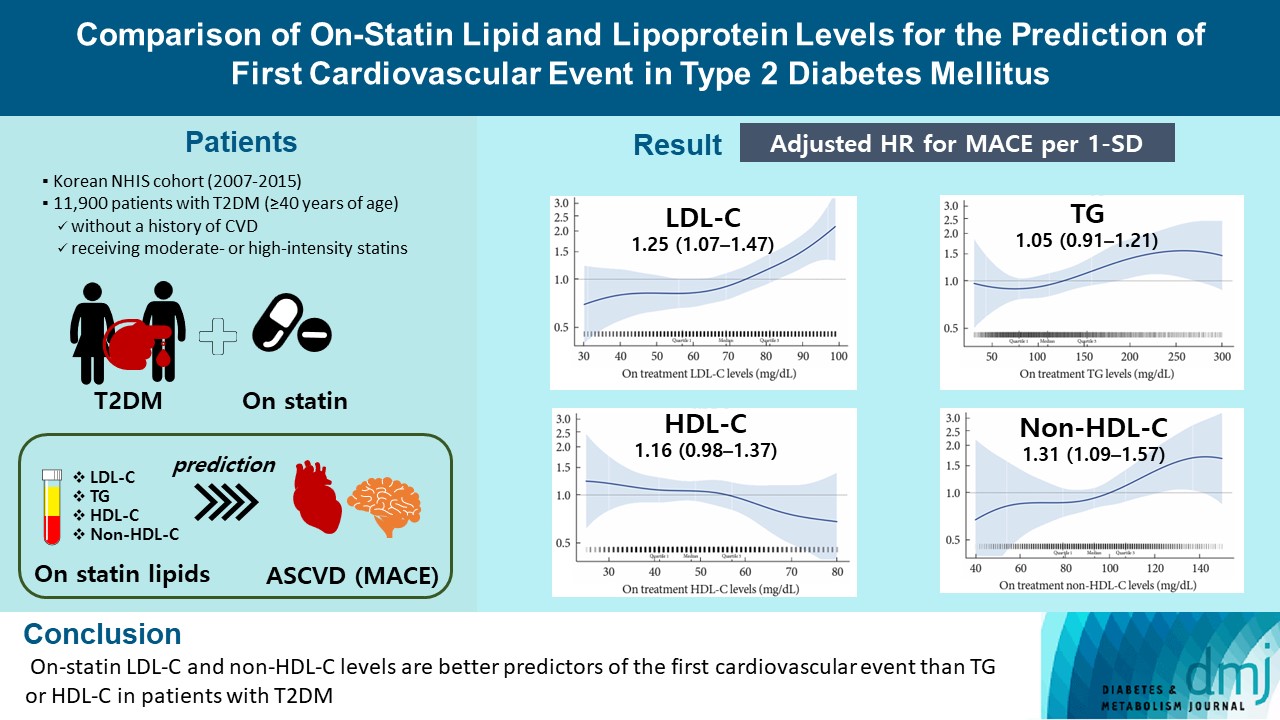
ePub - Background
A substantial cardiovascular disease risk remains even after optimal statin therapy. Comparative predictiveness of major lipid and lipoprotein parameters for cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) who are treated with statins is not well documented.
Methods
From the Korean Nationwide Cohort, 11,900 patients with T2DM (≥40 years of age) without a history of cardiovascular disease and receiving moderate- or high-intensity statins were included. The primary outcome was the first occurrence of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) including ischemic heart disease, ischemic stroke, and cardiovascular death. The risk of MACE was estimated according to on-statin levels of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), triglyceride (TG), highdensity lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), and non-HDL-C.
Results
MACE occurred in 712 patients during a median follow-up period of 37.9 months (interquartile range, 21.7 to 54.9). Among patients achieving LDL-C levels less than 100 mg/dL, the hazard ratios for MACE per 1-standard deviation change in ontreatment values were 1.25 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.07 to 1.47) for LDL-C, 1.31 (95% CI, 1.09 to 1.57) for non-HDL-C, 1.05 (95% CI, 0.91 to 1.21) for TG, and 1.16 (95% CI, 0.98 to 1.37) for HDL-C, after adjusting for potential confounders and lipid parameters mutually. The predictive ability of on-statin LDL-C and non-HDL-C for MACE was prominent in patients at high cardiovascular risk or those with LDL-C ≥70 mg/dL.
Conclusion
On-statin LDL-C and non-HDL-C levels are better predictors of the first cardiovascular event than TG or HDL-C in patients with T2DM.
Review
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- The Role of Echocardiography in Evaluating Cardiovascular Diseases in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus
- Sun Hwa Lee, Jae-Hyeong Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):470-483. Published online July 27, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0036
- 2,777 View
- 295 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
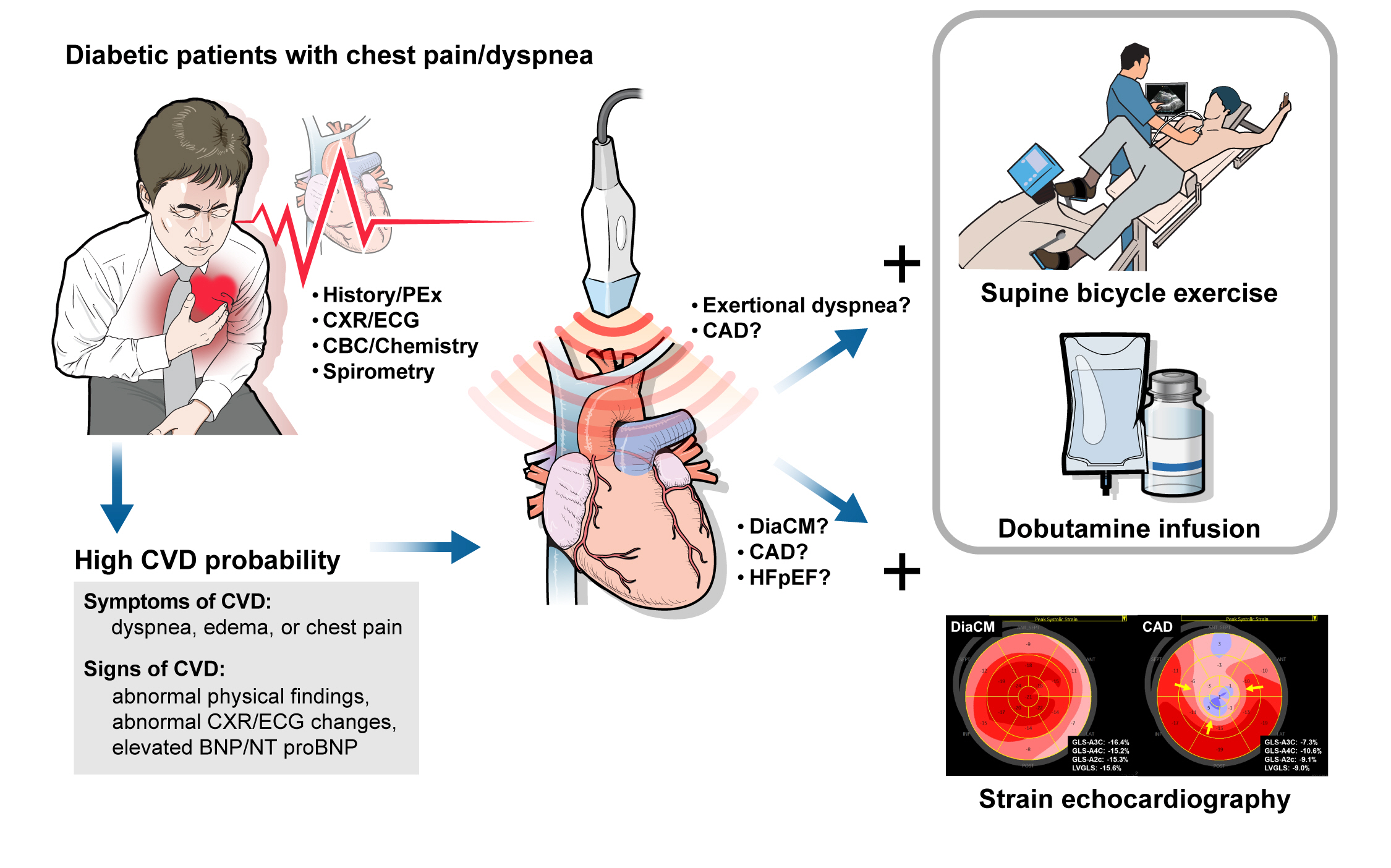
ePub - Patients with diabetes mellitus are highly susceptible to cardiovascular complications, which are directly correlated with cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. In addition to coronary artery disease, there is growing awareness of the risk and prevalence of heart failure (HF) in patients with diabetes. Echocardiography is an essential diagnostic modality commonly performed in patients with symptoms suggestive of cardiovascular diseases (CVD), such as dyspnea or chest pain, to establish or rule out the cause of symptoms. Conventional echocardiographic parameters, such as left ventricular ejection fraction, are helpful not only for diagnosing CVD but also for determining severity, treatment strategy, prognosis, and response to treatment. Echocardiographic myocardial strain, a novel echocardiographic technique, enables the detection of early changes in ventricular dysfunction before HF symptoms develop. This article aims to review the role of echocardiography in evaluating CVD in patients with diabetes mellitus and how to use it in patients with suspected cardiac diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Increased Blood Pressure Variability Over a 16-Year Period Is Associated With Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in a Population-Based Cohort
Jae-Hyeong Park, Soon-Ki Ahn, Goo-Yeong Cho, Ki-Chul Sung, Seung Ku Lee, Seong Hwan Kim, Chol Shin
American Journal of Hypertension.2024; 37(3): 168. CrossRef - Biomarkers and subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes without clinical manifestations of cardiovascular diseases
T. G. Utina, D. U. Akasheva, D. V. Korsunsky, O. N. Dzhioeva, O. M. Drapkina
Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention.2024; 23(1): 3914. CrossRef - Cardiovascular risk assessment in inflammatory bowel disease with coronary calcium score
Waqar Arif Rasool Chaudhry, Muhammad Ashfaq, Parvinder Kaur, Mahendra Kumar, Maria Faraz, Jahanzeb Malik, Amin Mehmoodi
Annals of Medicine & Surgery.2024; 86(3): 1496. CrossRef
- Increased Blood Pressure Variability Over a 16-Year Period Is Associated With Left Ventricular Diastolic Dysfunction in a Population-Based Cohort
Original Articles
- Basic Research
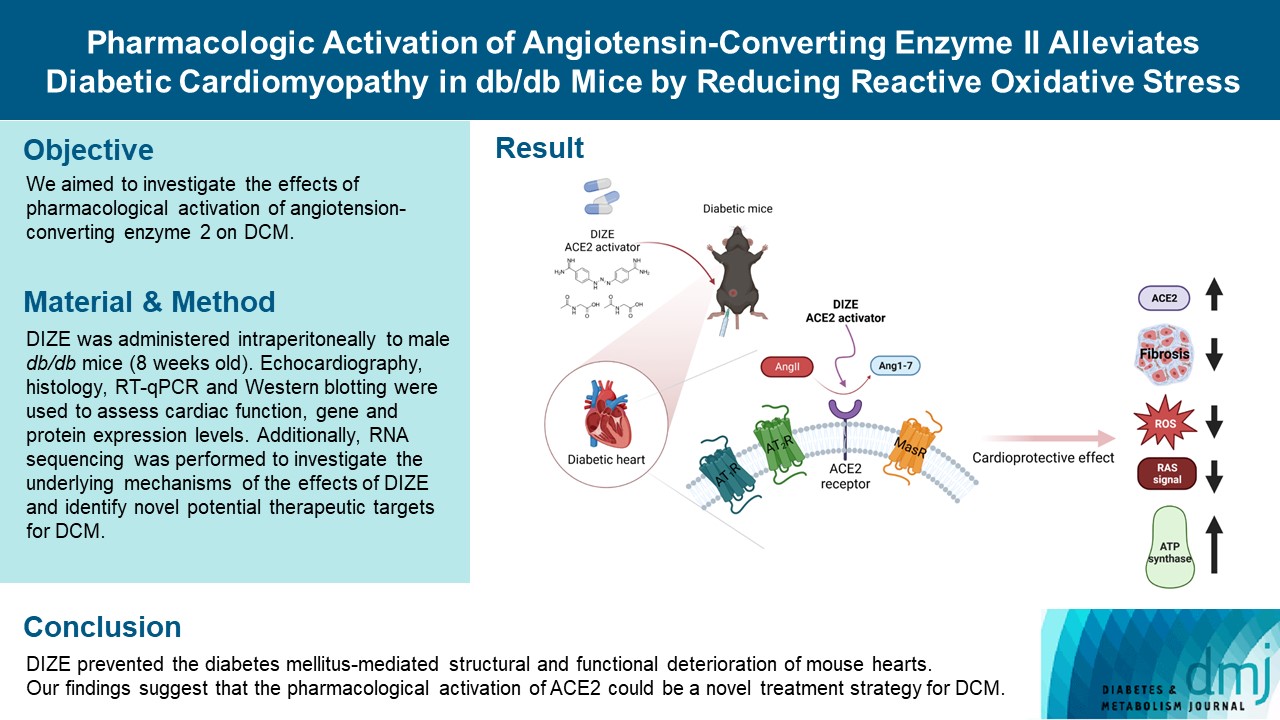
- Pharmacologic Activation of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme II Alleviates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy in db/db Mice by Reducing Reactive Oxidative Stress
- Donghyun Kim, Wooju Jeong, Yumin Kim, Jibeom Lee, Sung Woo Cho, Chang-Myung Oh, Raekil Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):487-499. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0125
- 2,328 View
- 150 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Diabetes mellitus is one of the most common chronic diseases worldwide, and cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in diabetic patients. Diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) is a phenomenon characterized by a deterioration in cardiac function and structure, independent of vascular complications. Among many possible causes, the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system and angiotensin II have been proposed as major drivers of DCM development. In the current study, we aimed to investigate the effects of pharmacological activation of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) on DCM.
Methods
The ACE2 activator diminazene aceturate (DIZE) was administered intraperitoneally to male db/db mice (8 weeks old) for 8 weeks. Transthoracic echocardiography was used to assess cardiac mass and function in mice. Cardiac structure and fibrotic changes were examined using histology and immunohistochemistry. Gene and protein expression levels were examined using quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and Western blotting, respectively. Additionally, RNA sequencing was performed to investigate the underlying mechanisms of the effects of DIZE and identify novel potential therapeutic targets for DCM.
Results
Echocardiography revealed that in DCM, the administration of DIZE significantly improved cardiac function as well as reduced cardiac hypertrophy and fibrosis. Transcriptome analysis revealed that DIZE treatment suppresses oxidative stress and several pathways related to cardiac hypertrophy.
Conclusion
DIZE prevented the diabetes mellitus-mediated structural and functional deterioration of mouse hearts. Our findings suggest that the pharmacological activation of ACE2 could be a novel treatment strategy for DCM.
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
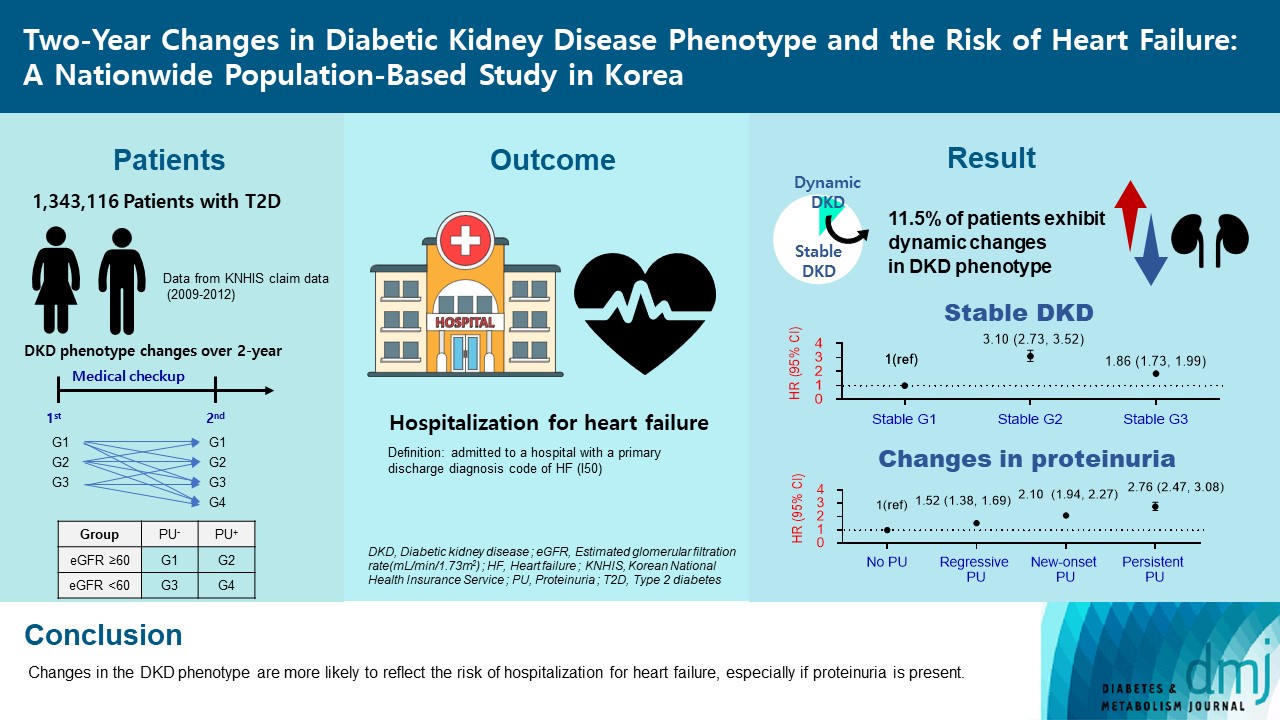
- Two-Year Changes in Diabetic Kidney Disease Phenotype and the Risk of Heart Failure: A Nationwide Population-Based Study in Korea
- Seung Eun Lee, Juhwan Yoo, Han Seok Choi, Kyungdo Han, Kyoung-Ah Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):523-534. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0096
- 1,746 View
- 100 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Diabetic kidney disease (DKD) is a risk factor for hospitalization for heart failure (HHF). DKD could be classified into four phenotypes by estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR, normal vs. low) and proteinuria (PU, negative vs. positive). Also, the phenotype often changes dynamically. This study examined HHF risk according to the DKD phenotype changes across 2-year assessments.
Methods
The study included 1,343,116 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) from the Korean National Health Insurance Service database after excluding a very high-risk phenotype (eGFR <30 mL/min/1.73 m2) at baseline, who underwent two cycles of medical checkups between 2009 and 2014. From the baseline and 2-year eGFR and PU results, participants were divided into 10 DKD phenotypic change categories.
Results
During an average of 6.5 years of follow-up, 7,874 subjects developed HHF. The cumulative incidence of HHF from index date was highest in the eGFRlowPU– phenotype, followed by eGFRnorPU+ and eGFRnorPU–. Changes in DKD phenotype differently affect HHF risk. When the persistent eGFRnorPU– category was the reference, hazard ratios for HHF were 3.10 (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.73 to 3.52) in persistent eGFRnorPU+ and 1.86 (95% CI, 1.73 to 1.99) in persistent eGFRlowPU–. Among altered phenotypes, the category converted to eGFRlowPU+ showed the highest risk. In the normal eGFR category at the second examination, those who converted from PU– to PU+ showed a higher risk of HHF than those who converted from PU+ to PU–.
Conclusion
Changes in DKD phenotype, particularly with the presence of PU, are more likely to reflect the risk of HHF, compared with DKD phenotype based on a single time point in patients with T2DM.
Review
- Guideline/Fact Sheet
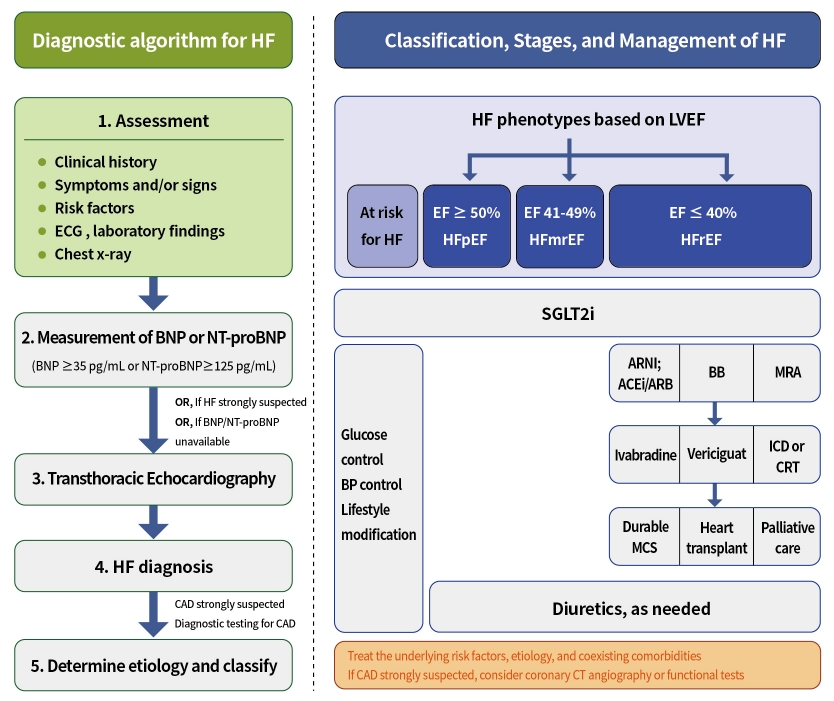
- Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
- Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon, The Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association and Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Society of Heart Failure
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):10-26. Published online January 26, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0420
- 4,402 View
- 413 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetes mellitus is a major risk factor for the development of heart failure. Furthermore, the prognosis of heart failure is worse in patients with diabetes mellitus than in those without it. Therefore, early diagnosis and proper management of heart failure in patients with diabetes mellitus are important. This review discusses the current criteria for diagnosis and screening tools for heart failure and the currently recommended pharmacological therapies for heart failure. We also highlight the effects of anti-diabetic medications on heart failure.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label Study to Compare the Effects of Gemigliptin Add-on or Escalation of Metformin Dose on Glycemic Control and Safety in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Metformin and SGLT-2 Inh
Hae Jin Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Min Kyong Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko, Eun-Jung Rhee, Kyu Yeon Hur, In-Kyung Jeong, Mark Yorek
Journal of Diabetes Research.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Comparison of the effects of gemigliptin versus glimepiride on cardiac function in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled with metformin: The gemi‐heart study
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Jun Hwa Hong, In‐Chang Hwang, Soo Lim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(8): 2181. CrossRef - Optimization of guideline-directed medical treatment for heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction
Minjung Bak, Jin-Oh Choi
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2023; 38(5): 595. CrossRef
- A Multicenter, Randomized, Open-Label Study to Compare the Effects of Gemigliptin Add-on or Escalation of Metformin Dose on Glycemic Control and Safety in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treated with Metformin and SGLT-2 Inh
Original Articles
- Drug/Regimen
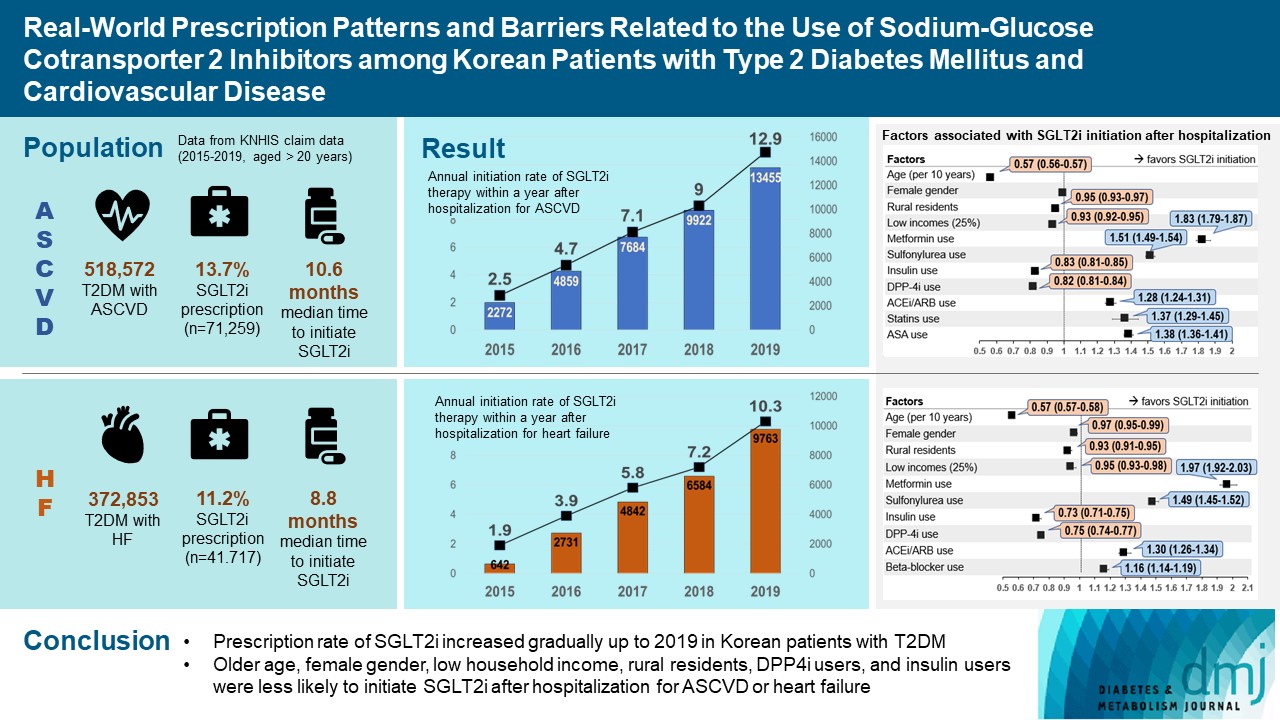
- Real-World Prescription Patterns and Barriers Related to the Use of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors among Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Cardiovascular Disease
- Jong Ha Baek, Ye Seul Yang, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Do Han, Jae Hyeon Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Jong Han Choi, Kyu Yeon Hur, Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):701-712. Published online June 3, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0002
- 4,984 View
- 319 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To evaluate prescription trends and clinical factors of the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) use according to the presence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) or heart failure (HF) in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
Prescription patterns of SGLT2i use between 2015 and 2019 were determined using the Korean National Health Insurance Service database of claims.
Results
Of all patients with T2DM (n=4,736,493), the annual prescription rate of SGLT2i increased every year in patients with ASCVD (from 2.2% to 10.7%) or HF (from 2.0% to 11.1%). After the first hospitalization for ASCVD (n=518,572), 13.7% (n=71,259) of patients initiated SGLT2i with a median of 10.6 months. After hospitalization for HF (n=372,853), 11.2% (n=41,717) of patients initiated SGLT2i after a median of 8.8 months. In multivariate regression for hospitalization, older age (per 10 years, odds ratio [OR], 0.57; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.56 to 0.57), lower household income (OR, 0.93; 95% CI, 0.92 to 0.95), rural residents (OR, 0.95; 95% CI, 0.93 to 0.97), and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP-4i) users (OR, 0.82; 95% CI, 0.81 to 0.84) were associated with lesser initiation of SGLT2i in ASCVD. Additionally, female gender (OR, 0.97; 95% CI, 0.95 to 0.99) was associated with lesser initiation of SGLT2i in HF.
Conclusion
The prescription rate of SGLT2i increased gradually up to 2019 but was suboptimal in patients with ASCVD or HF. After the first hospitalization for ASCVD or HF, older age, female gender, low household income, rural residents, and DPP-4i users were less likely to initiate SGLT2i. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effectiveness and safety of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in Asian populations
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024; 15(3): 285. CrossRef - Real-World Treatment Patterns according to Clinical Practice Guidelines in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Established Cardiovascular Disease in Korea: Multicenter, Retrospective, Observational Study
Ye Seul Yang, Nam Hoon Kim, Jong Ha Baek, Seung-Hyun Ko, Jang Won Son, Seung-Hwan Lee, Sang Youl Rhee, Soo-Kyung Kim, Tae Seo Sohn, Ji Eun Jun, In-Kyung Jeong, Chong Hwa Kim, Keeho Song, Eun-Jung Rhee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 279. CrossRef - Hospital Readmissions for Fluid Overload among Individuals with Diabetes and Diabetic Kidney Disease: Risk Factors and Multivariable Prediction Models
Jiashen Cai, Dorothy Huang, Hanis Binte Abdul Kadir, Zhihua Huang, Li Choo Ng, Andrew Ang, Ngiap Chuan Tan, Yong Mong Bee, Wei Yi Tay, Chieh Suai Tan, Cynthia C. Lim
Nephron.2024; : 1. CrossRef - Prescribing patterns of SGLT-2 inhibitors for patients with heart failure: A two-center analysis
Teja Chakrala, Roshni O. Prakash, Justin Kim, Hanzhi Gao, Umar Ghaffar, Jaymin Patel, Alex Parker, Bhagwan Dass
American Heart Journal Plus: Cardiology Research and Practice.2023; 28: 100286. CrossRef - Risk of developing chronic kidney disease in young-onset Type 2 diabetes in Korea
Joonyub Lee, Seung-Hwan Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon, Jae Hyoung Cho, Kyungdo Han, Yeoree Yang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of SGLT2 inhibitors with DPP-4 inhibitors combined with metformin in patients with acute myocardial infarction and diabetes mellitus
Young Sang Lyu, Seok Oh, Jin Hwa Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Myung Ho Jeong
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: is it preventable?
Seung-Hyun Ko
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(3): 106. CrossRef - Association between the Diabetes Drug Cost and Cardiovascular Events and Death in Korea: A National Health Insurance Service Database Analysis
Seung Min Chung, Ji-In Lee, Eugene Han, Hyun-Ae Seo, Eonju Jeon, Hye Soon Kim, Ji Sung Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(5): 759. CrossRef
- Effectiveness and safety of sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors in Asian populations
- Drug/Regimen
- Comparison of Serum Ketone Levels and Cardiometabolic Efficacy of Dapagliflozin versus Sitagliptin among Insulin-Treated Chinese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Chi-Ho Lee, Mei-Zhen Wu, David Tak-Wai Lui, Darren Shing-Hei Chan, Carol Ho-Yi Fong, Sammy Wing-Ming Shiu, Ying Wong, Alan Chun-Hong Lee, Joanne King-Yan Lam, Yu-Cho Woo, Karen Siu-Ling Lam, Kelvin Kai-Hang Yiu, Kathryn Choon-Beng Tan
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):843-854. Published online April 28, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0319
- 5,073 View
- 257 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Insulin-treated patients with long duration of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) are at increased risk of ketoacidosis related to sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitor (SGLT2i). The extent of circulating ketone elevation in these patients remains unknown. We conducted this study to compare the serum ketone response between dapagliflozin, an SGLT2i, and sitagliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, among insulin-treated T2DM patients.
Methods
This was a randomized, open-label, active comparator-controlled study involving 60 insulin-treated T2DM patients. Participants were randomized 1:1 for 24-week of dapagliflozin 10 mg daily or sitagliptin 100 mg daily. Serum β-hydroxybutyrate (BHB) levels were measured at baseline, 12 and 24 weeks after intervention. Comprehensive cardiometabolic assessments were performed with measurements of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) cholesterol efflux capacity (CEC), vibration-controlled transient elastography and echocardiography.
Results
Among these 60 insulin-treated participants (mean age 58.8 years, diabetes duration 18.2 years, glycosylated hemoglobin 8.87%), as compared with sitagliptin, serum BHB levels increased significantly after 24 weeks of dapagliflozin (P=0.045), with a median of 27% increase from baseline. Change in serum BHB levels correlated significantly with change in free fatty acid levels. Despite similar glucose lowering, dapagliflozin led to significant improvements in body weight (P=0.006), waist circumference (P=0.028), HDL-C (P=0.041), CEC (P=0.045), controlled attenuation parameter (P=0.007), and liver stiffness (P=0.022). Average E/e’, an echocardiographic index of left ventricular diastolic dysfunction, was also significantly lower at 24 weeks in participants treated with dapagliflozin (P=0.037).
Conclusion
Among insulin-treated T2DM patients with long diabetes duration, compared to sitagliptin, dapagliflozin modestly increased ketone levels and was associated with cardiometabolic benefits. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Serum thrombospondin‐2 level changes with liver stiffness improvement in patients with type 2 diabetes
Jimmy Ho Cheung Mak, David Tak‐Wai Lui, Carol Ho‐Yi Fong, Chloe Yu‐Yan Cheung, Ying Wong, Alan Chun‐Hong Lee, Ruby Lai‐Chong Hoo, Aimin Xu, Kathryn Choon‐Beng Tan, Karen Siu‐Ling Lam, Chi‐Ho Lee
Clinical Endocrinology.2024; 100(3): 230. CrossRef - SGLT-2 inhibitors as novel treatments of multiple organ fibrosis
Junpei Hu, Jianhui Teng, Shan Hui, Lihui Liang
Heliyon.2024; 10(8): e29486. CrossRef - Effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter protein-2 inhibitors on left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Yao Wang, Yujie Zhong, Zhehao Zhang, Shuhao Yang, Qianying Zhang, Bingyang Chu, Xulin Hu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on hepatic fibrosis and steatosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Peipei Zhou, Ying Tan, Zhenning Hao, Weilong Xu, Xiqiao Zhou, Jiangyi Yu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The impact of sodium-glucose Cotransporter-2 inhibitors on lipid profile: A meta-analysis of 28 randomized controlled trials
Gang Fan, Dian long Guo, Hong Zuo
European Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 959: 176087. CrossRef
- Serum thrombospondin‐2 level changes with liver stiffness improvement in patients with type 2 diabetes
- Complications
- Effect of the Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Autonomic Function in Subjects with Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Carla Greco, Daniele Santi, Giulia Brigante, Chiara Pacchioni, Manuela Simoni
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):901-911. Published online April 12, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0314
- 4,509 View
- 266 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
In addition to the metabolic effects in diabetes, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor (GLP-1R) agonists lead to a small but substantial increase in heart rate (HR). However, the GLP-1R actions on the autonomic nervous system (ANS) in diabetes remain debated. Therefore, this meta-analysis evaluates the effect of GLP-1R agonist on measures of ANS function in diabetes.
Methods
According to the Cochrane Collaboration and Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) statement, we conducted a meta-analysis considering clinical trials in which the autonomic function was evaluated in diabetic subjects chronically treated with GLP-1R agonists. The outcomes were the change of ANS function measured by heart rate variability (HRV) and cardiac autonomic reflex tests (CARTs).
Results
In the studies enrolled, HR significantly increased after treatment (P<0.001), whereas low frequency/high frequency ratio did not differ (P=0.410); no changes in other measures of HRV were detected. Considering CARTs, only the 30:15 value derived from lying-to-standing test was significantly lower after treatment (P=0.002), but only two studies reported this measurement. No differences in other CARTs outcome were observed.
Conclusion
The meta-analysis confirms the HR increase but seems to exclude an alteration of the sympatho-vagal balance due to chronic treatment with GLP-1R agonists in diabetes, considering the available measures of ANS function. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Liraglutide does not increase heart rate of diabetic patients during acute myocardial infarction
Qianyi Li, Chunxuan Wu, Shiqun Sun, Lingchao Yang, Yanyan Li, Yixin Niu, Li Zhang, Wei Li, Ying Yu
Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hormonal Gut–Brain Signaling for the Treatment of Obesity
Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3384. CrossRef - Effects of new hypoglycemic drugs on cardiac remodeling: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Yi-lin Huang, Xiao-zhuo Xu, Jing Liu, Pin-yao Wang, Xue-li Wang, Hong-lin Feng, Cheng-jiang Liu, Xu Han
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Obesity and hypertension: Obesity medicine association (OMA) clinical practice statement (CPS) 2023
Tiffany Lowe Clayton, Angela Fitch, Harold Edward Bays
Obesity Pillars.2023; 8: 100083. CrossRef - Incretins and microvascular complications of diabetes: neuropathy, nephropathy, retinopathy and microangiopathy
Jonathan Goldney, Jack A. Sargeant, Melanie J. Davies
Diabetologia.2023; 66(10): 1832. CrossRef - Diabetes-Induced Cardiac Autonomic Neuropathy: Impact on Heart Function and Prognosis
Susumu Z. Sudo, Tadeu L. Montagnoli, Bruna de S. Rocha, Aimeé D. Santos, Mauro P. L. de Sá, Gisele Zapata-Sudo
Biomedicines.2022; 10(12): 3258. CrossRef
- Liraglutide does not increase heart rate of diabetic patients during acute myocardial infarction
Review
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
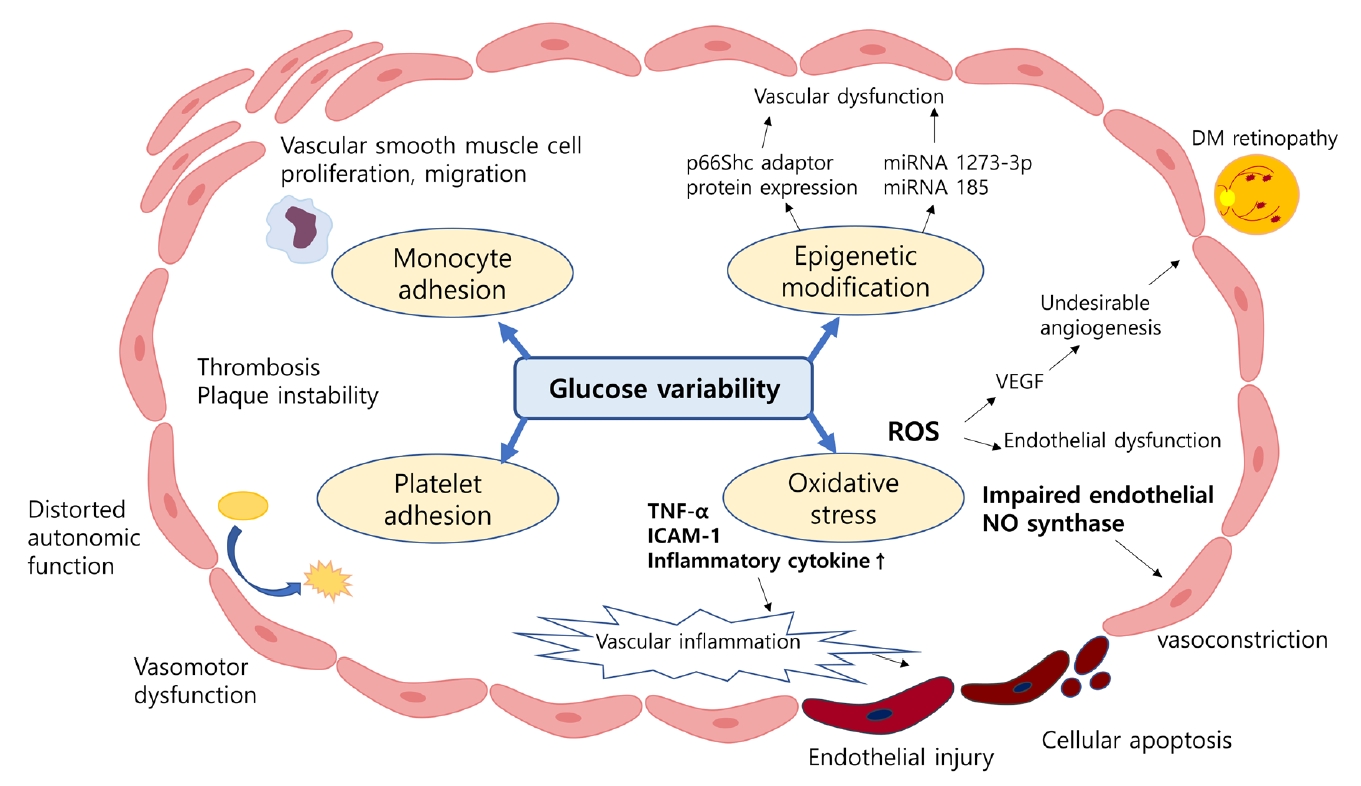
- Association between Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors and Cardiometabolic Outcomes
- Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):49-62. Published online January 27, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0316
- 5,710 View
- 221 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Despite strenuous efforts to reduce cardiovascular disease (CVD) risk by improving cardiometabolic risk factors, such as glucose and cholesterol levels, and blood pressure, there is still residual risk even in patients reaching treatment targets. Recently, researchers have begun to focus on the variability of metabolic variables to remove residual risks. Several clinical trials and cohort studies have reported a relationship between the variability of metabolic parameters and CVDs. Herein, we review the literature regarding the effect of metabolic factor variability and CVD risk, and describe possible mechanisms and potential treatment perspectives for reducing cardiometabolic risk factor variability.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Long-term variability in physiological measures in relation to mortality and epigenetic aging: prospective studies in the USA and China
Hui Chen, Tianjing Zhou, Shaowei Wu, Yaying Cao, Geng Zong, Changzheng Yuan
BMC Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Dose–response relationship between physical activity and cardiometabolic risk in obese children and adolescents: A pre-post quasi-experimental study
Zekai Chen, Lin Zhu
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of body weight change with all-cause and cause-specific mortality: A nationwide population-based study
So Yoon Kwon, Gyuri Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Jiyun Park, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 199: 110666. CrossRef - Association between lipid variability and the risk of mortality in cancer patients not receiving lipid-lowering agents
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, So Hyun Cho, Rosa Oh, Ji Yoon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyeon Kim
Frontiers in Oncology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between visit-to-visit lipid variability and risk of ischemic heart disease: a cohort study in China
Yonghao Wu, Peng Shen, Lisha Xu, Zongming Yang, Yexiang Sun, Luhua Yu, Zhanghang Zhu, Tiezheng Li, Dan Luo, Hongbo Lin, Liming Shui, Mengling Tang, Mingjuan Jin, Kun Chen, Jianbing Wang
Endocrine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors: Causative Factor or Epiphenomenon?
Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 257. CrossRef - Long-Term Variability in Physiological Measures in Relation to Mortality and Epigenetic Aging: Prospective Studies in the US and China
Hui Chen, Tianjing Zhou, Shaowei Wu, Yaying Cao, Geng Zong, Changzheng Yuan
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Long-term variability in physiological measures in relation to mortality and epigenetic aging: prospective studies in the USA and China
Original Article
- Lifestyle
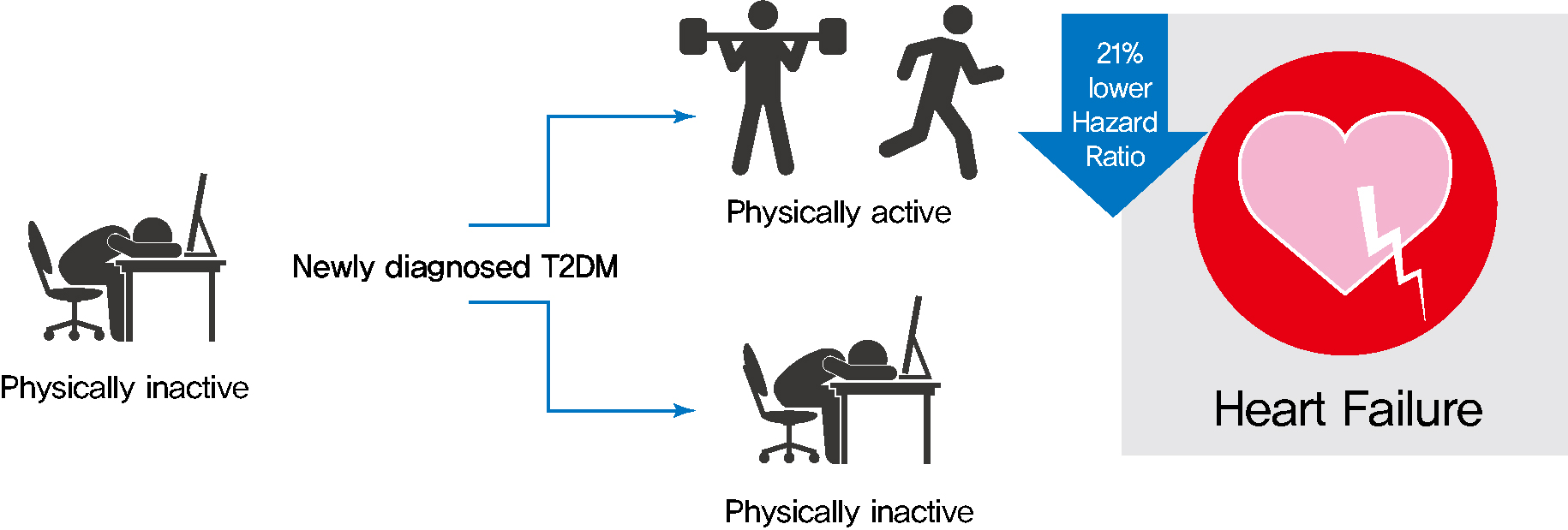
- Changes in Patterns of Physical Activity and Risk of Heart Failure in Newly Diagnosed Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Inha Jung, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Kyung-Do Han, Yong-Gyu Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):327-336. Published online November 24, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0046
- 5,428 View
- 210 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Exercise is recommended for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients to prevent cardiovascular disease. However, the effects of physical activity (PA) for reducing the risk of heart failure (HF) has yet to be elucidated. We aimed to assess the effect of changes in patterns of PA on incident HF, especially in newly diagnosed diabetic patients.
Methods
We examined health examination data and claims records of 294,528 participants from the Korean National Health Insurance Service who underwent health examinations between 2009 and 2012 and were newly diagnosed with T2DM. Participants were classified into the four groups according to changes in PA between before and after the diagnosis of T2DM: continuously inactive, inactive to active, active to inactive, and continuously active. The development of HF was analyzed until 2017.
Results
As compared with those who were continuously inactive, those who became physically active after diagnosis showed a reduced risk for HF (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR], 0.79; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.66 to 0.93). Those who were continuously active had the lowest risk for HF (aHR, 0.77; 95% CI, 0.62 to 0.96). As compared with those who were inactive, those who exercised regularly, either performing vigorous or moderate PA, had a lower HF risk (aHR, 0.79; 95% CI, 0.69 to 0.91).
Conclusion
Among individuals with newly diagnosed T2DM, the risk of HF was reduced in those with higher levels of PA after diagnosis was made. Our results suggest either increasing or maintaining the frequency of PA after the diagnosis of T2DM may lower the risk of HF. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations Between Physical Activity and the Risk of Hip Fracture Depending on Glycemic Status: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Kyoung Min Kim, Kyoung Jin Kim, Kyungdo Han, Yumie Rhee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1194. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients With Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
International Journal of Heart Failure.2023; 5(1): 1. CrossRef - Evaluation and Management of Patients with Diabetes and Heart Failure: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Heart Failure Consensus Statement
Kyu-Sun Lee, Junghyun Noh, Seong-Mi Park, Kyung Mook Choi, Seok-Min Kang, Kyu-Chang Won, Hyun-Jai Cho, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Association of plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels and frailty in community-dwelling older adults
Eun Roh, Soon Young Hwang, Eyun Song, Min Jeong Park, Hye Jin Yoo, Sei Hyun Baik, Miji Kim, Chang Won Won, Kyung Mook Choi
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The associations between changes in hepatic steatosis and heart failure and mortality: a nationwide cohort study
Jiyun Park, Gyuri Kim, Hasung Kim, Jungkuk Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Associations Between Physical Activity and the Risk of Hip Fracture Depending on Glycemic Status: A Nationwide Cohort Study
Review
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
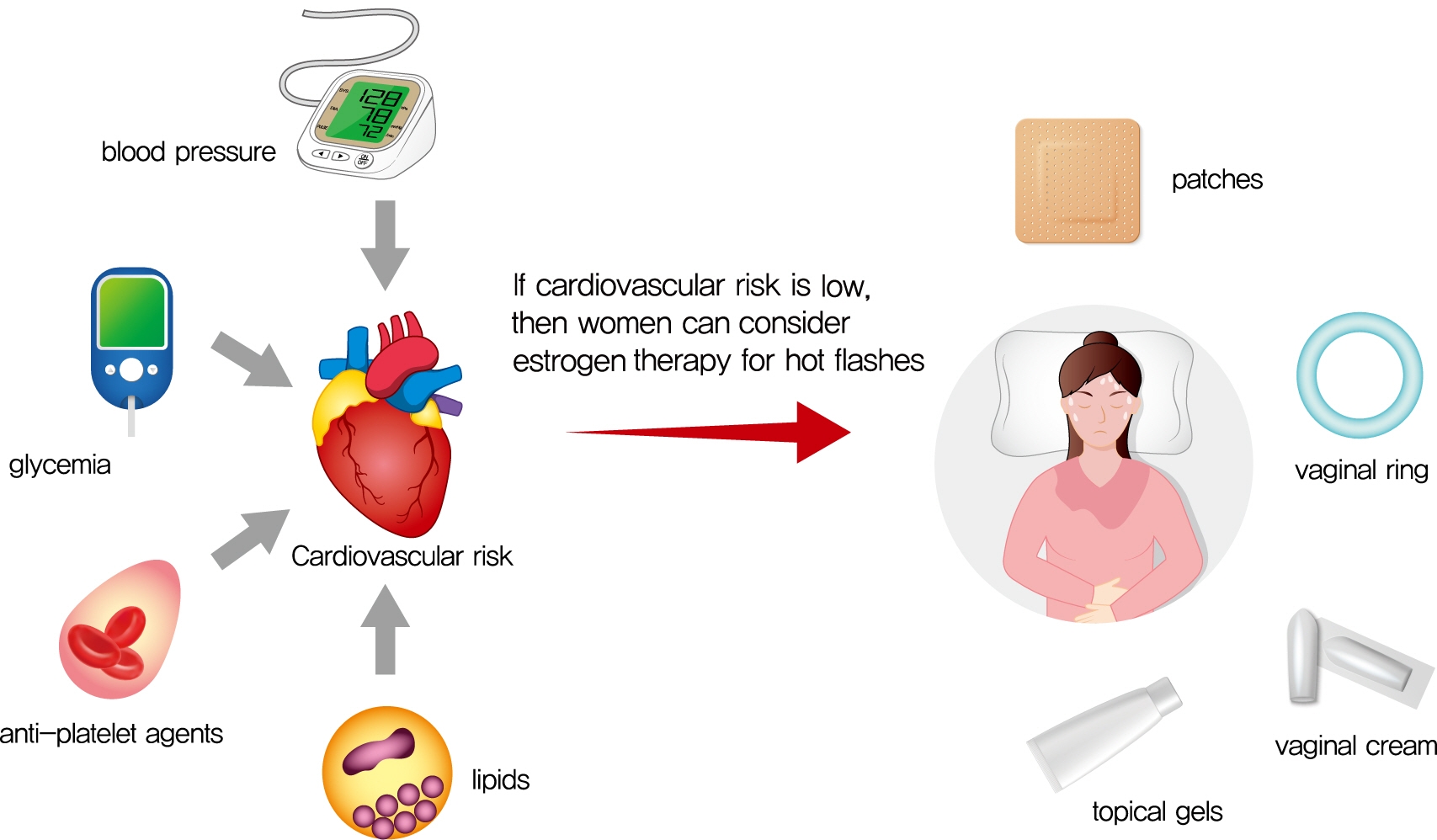
- Management of Cardiovascular Risk in Perimenopausal Women with Diabetes
- Catherine Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):492-501. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0262
- 5,713 View
- 157 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Cardiovascular disease is the primary cause of mortality in women and men with diabetes. Due to age and worsening of risk factors over the menopausal transition, risk of coronary heart disease events increases in postmenopausal women with diabetes. Randomized studies have conflicted regarding the beneficial impact of estrogen therapy upon intermediate cardiovascular disease markers and events. Therefore, estrogen therapy is not currently recommended for indications other than symptom management. However, for women at low risk of adverse events, estrogen therapy can be used to minimize menopausal symptoms. The risk of adverse events can be estimated using risk engines for the calculation of cardiovascular risk and breast cancer risk in conjunction with screening tools such as mammography. Use of estrogen therapy, statins, and anti-platelet agents can be guided by such calculators particularly for younger women with diabetes. Risk management remains focused upon lifestyle behaviors and achieving optimal levels of cardiovascular risk factors, including lipids, glucose, and blood pressure. Use of pharmacologic therapies to address these risk factors, particularly specific hypoglycemic agents, may provide some additional benefit for risk prevention. The minimal benefit for women with limited life expectancy and risk of complications with intensive therapy should also be considered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurse-led intervention in the management of patients with cardiovascular diseases: a brief literature review
Xiaoqin Qiu
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Determination of the Level of Cardiovascular Risk in 172,282 Spanish Working Women
Ángel Arturo López-González, María Albaladejo Blanco, Cristina Vidal Ribas, Pilar Tomás-Gil, Pere Riutord Sbert, José Ignacio Ramírez-Manent
Diagnostics.2023; 13(17): 2734. CrossRef - Comparison of seven surrogate insulin resistance indexes for predicting the prevalence of carotid atherosclerosis in normal-weight individuals
Zeyu Liu, Bi Deng, Qin Huang, Ruxin Tu, Fang Yu, Jian Xia, Jie Feng
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications
Joon Ho Moon, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 3. CrossRef - Reproductive Life Span and Severe Hypoglycemia Risk in Postmenopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Soyeon Kang, Yong-Moon Park, Dong Jin Kwon, Youn-Jee Chung, Jeong Namkung, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 578. CrossRef - Global hotspots and prospects of perimenopausal depression: A bibliometric analysis via CiteSpace
Mingzhou Gao, Hao Zhang, Zhan Gao, Ya Sun, Jieqiong Wang, Fengqin Wei, Dongmei Gao
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - State of metabolic processes and ways to improve them in premenopausal women due to the life extension strategy
I.V. Lakhno
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY.2021; (61): 51. CrossRef
- Nurse-led intervention in the management of patients with cardiovascular diseases: a brief literature review

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





