
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Novel Asian-Specific Visceral Adiposity Indices Are Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Korean Adults
- Jonghwa Jin, Hyein Woo, Youngeun Jang, Won-Ki Lee, Jung-Guk Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Keun-Gyu Park, Yeon-Kyung Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):426-436. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0099
- 2,519 View
- 128 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The Chinese visceral adiposity index (CVAI) and new visceral adiposity index (NVAI) are novel indices of visceral adiposity used to predict metabolic and cardiovascular diseases in Asian populations. However, the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have not been investigated. We aimed to characterize the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with the prevalence of CKD in Korean adults.
Methods
A total of 14,068 participants in the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (6,182 men and 7,886 women) were included. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses were employed to compare the associations between indices of adiposity and CKD, and a logistic regression model was used to characterize the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with CKD prevalence.
Results
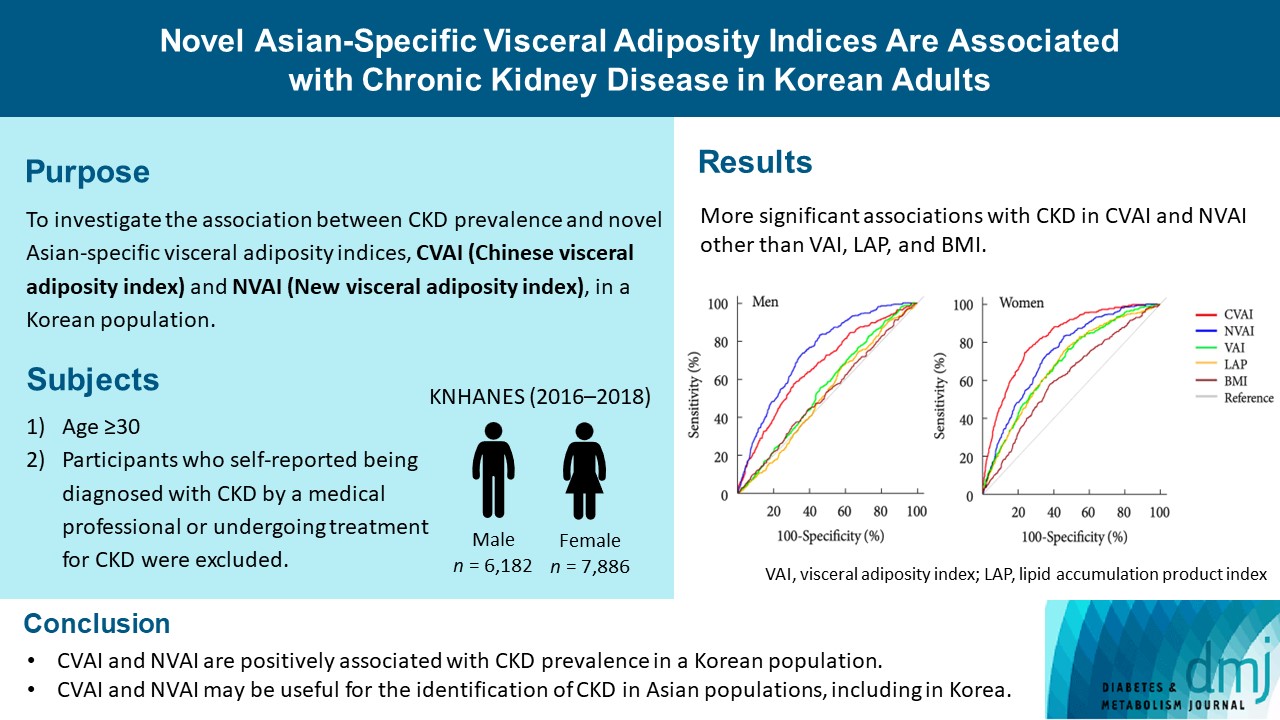
The areas under the ROC curves for CVAI and NVAI were significantly larger than for the other indices, including the visceral adiposity index and lipid accumulation product, in both men and women (all P<0.001). In addition, high CVAI or NVAI was significantly associated with a high CKD prevalence in both men (odds ratio [OR], 2.14; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.31 to 3.48 in CVAI and OR, 6.47; 95% CI, 2.91 to 14.38 in NVAI, P<0.05) and women (OR, 4.87; 95% CI, 1.85 to 12.79 in CVAI and OR, 3.03; 95% CI, 1.35 to 6.82 in NVAI, P<0.05); this association remained significant after adjustment for multiple confounding factors in men and women.
Conclusion
CVAI and NVAI are positively associated with CKD prevalence in a Korean population. CVAI and NVAI may be useful for the identification of CKD in Asian populations, including in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Chinese visceral adiposity index and risk of stroke incidence in middle-aged and elderly Chinese population: evidence from a large national cohort study
Zenglei Zhang, Lin Zhao, Yiting Lu, Xu Meng, Xianliang Zhou
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between Chinese visceral adiposity index and risk of stroke incidence in middle-aged and elderly Chinese population: evidence from a large national cohort study
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Clinical Significance of Body Fat Distribution in Coronary Artery Calcification Progression in Korean Population
- Heesun Lee, Hyo Eun Park, Ji Won Yoon, Su-Yeon Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):219-230. Published online October 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0161
- Correction in: Diabetes Metab J 2021;45(6):974

- 6,523 View
- 257 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
Although obesity differs according to ethnicity, it is globally established as a solid risk factor for cardiovascular disease. However, it is not fully understood how obesity parameters affect the progression of coronary artery calcification (CAC) in Korean population. We sought to evaluate the association of obesity-related parameters including visceral adipose tissue (VAT) measurement and CAC progression.
Methods
This retrospective observational cohort study investigated 1,015 asymptomatic Korean subjects who underwent serial CAC scoring by computed tomography (CT) with at least 1-year interval and adipose tissue measurement using non-contrast CT at baseline for a routine checkup between 2003 and 2015. CAC progression, the main outcome, was defined as a difference of ≥2.5 between the square roots of the baseline and follow-up CAC scores using Agatston units.
Results
During follow-up (median 39 months), 37.5% of subjects showed CAC progression of a total population (56.4 years, 80.6% male). Body mass index (BMI) ≥25 kg/m2, increasing waist circumferences (WC), and higher VAT/subcutaneous adipose tissue (SAT) area ratio were independently associated with CAC progression. Particularly, predominance of VAT over SAT at ≥30% showed the strongest prediction for CAC progression (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.20; P<0.001) and remained of prognostic value regardless of BMI or WC status. Further, it provided improved risk stratification of CAC progression beyond known prognosticators.
Conclusion
Predominant VAT area on CT is the strongest predictor of CAC progression regardless of BMI or WC in apparently healthy Korean population. Assessment of body fat distribution may be helpful to identify subjects at higher risk. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Gender-specific abdominal fat distribution and insulin resistance associated with organophosphate esters and phthalate metabolites exposure
Xiaoliu Shi, Wanyue Wang, Jiafan Feng, Xiaochun Ma, Mengting Xu, Cui Wang
Environmental Pollution.2024; 349: 123959. CrossRef - The association between C-reactive protein and coronary artery calcification: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Amirhossein Tajani, Masoumeh Sadeghi, Navid Omidkhoda, Amir Hooshang Mohammadpour, Sara Samadi, Vahid Jomehzadeh
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Visceral adipose tissue is an independent predictor and mediator of the progression of coronary calcification: a prospective sub-analysis of the GEA study
Neftali Eduardo Antonio-Villa, Juan Gabriel Juárez-Rojas, Rosalinda Posadas-Sánchez, Juan Reyes-Barrera, Aida Medina-Urrutia
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Deep learning-based prediction for significant coronary artery stenosis on coronary computed tomography angiography in asymptomatic populations
Heesun Lee, Bong Gyun Kang, Jeonghee Jo, Hyo Eun Park, Sungroh Yoon, Su-Yeon Choi, Min Joo Kim
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between a novel non–insulin-based metabolic score for insulin resistance (METS‐IR) and coronary artery calcification
Zhenwei Wang, Xiaofang Hui, Xu Huang, Jingjie Li, Naifeng Liu
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Abdominal Adipose Tissue Distribution and Risk of Endometrial Cancer: A Case-Control Study
Yuan Cheng, Zhongyu Wang, Xiaoxuan Jia, Rong Zhou, Jianliu Wang
Clinical Medicine Insights: Oncology.2022; 16: 117955492211407. CrossRef - Sex differences in cardiovascular risk may be related to sex differences in diet patterns: a narrative review
A. M. Tindall, V. A. Stallings
Annals of Human Biology.2021; 48(6): 517. CrossRef
- Gender-specific abdominal fat distribution and insulin resistance associated with organophosphate esters and phthalate metabolites exposure
- Lifestyle
- Body Fat Is Related to Sedentary Behavior and Light Physical Activity but Not to Moderate-Vigorous Physical Activity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Keun Hee An, Kyung Ah Han, Tae Seo Sohn, Ie Byung Park, Hae Jin Kim, Sung Dae Moon, Kyung Wan Min
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):316-325. Published online November 12, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0029
- 5,505 View
- 138 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Sedentary behavior (SB) has emerged as a new risk factor for cardiovascular accidents. We investigated whether physical activity levels or SB were related to percent body fat (%BF) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods In this cross sectional study, we measured the duration of SB, light physical activity (LPA), moderate to vigorous physical activity (MVPA), total energy expenditure, and step counts using a wireless activity tracker (Fitbit HR; FB) for 7 days in free-living conditions, along with %BF using a bio impedance analyzer (Inbody; Biospace) in 120 smartphone users with T2DM. Subjects were divided into exercise (Exe,
n =68) and non-exercise (nonExe,n =52) groups based on self-reports of whether the recommended exercises (30 min/day, 3 days/week for 3 months) were performed. SBt, LPAt, MVPAt were transformed from SB, LPA, MVPA for normally distributed variables.Results Participants were: female, 59.2%; age, 59.3±8.4 years; body mass index, 25.5±3.4 kg/m2; glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), 7.6%±1.2%; %BF, 30.4%±7.1%. They performed SB for 15.7±3.7 hr/day, LPA for 4.4±1.7 hr/day, and MVPA for 0.9±0.8 hr/day. The %BF was related to SBt and LPAt, but not to MVPA after adjustments for age, gender, and HbA1c. VPA was significantly higher in the Exe group than in the nonExe group, but SB, LPA, and moderate physical activity were not different. Predicted %BF was 89.494 to 0.105 (age), −13.047 (gender), −0.507 (HbA1c), −7.655 (LPAt) (F[4, 64]=62.929,
P <0.001), with anR 2 of 0.785 in multiple linear regression analysis.Conclusion Reduced body fat in elderly diabetic patients might be associated with reduced inactivity and increased LPA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Explanatory variables of objectively measured 24-h movement behaviors in people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review
Lotte Bogaert, Iris Willems, Patrick Calders, Eveline Dirinck, Manon Kinaupenne, Marga Decraene, Bruno Lapauw, Boyd Strumane, Margot Van Daele, Vera Verbestel, Marieke De Craemer
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2024; 18(4): 102995. CrossRef - Association between depression, anemia and physical activity using isotemporal substitution analysis
Hee-kyoung Nam, Jungmi Park, Sung-il Cho
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The Impact of Wearable Technologies in Health Research: Scoping Review
Sophie Huhn, Miriam Axt, Hanns-Christian Gunga, Martina Anna Maggioni, Stephen Munga, David Obor, Ali Sié, Valentin Boudo, Aditi Bunker, Rainer Sauerborn, Till Bärnighausen, Sandra Barteit
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2022; 10(1): e34384. CrossRef - The Correlation of Prediabetes and Type 2 Diabetes With Adiposity in Adults
Juan Sun, Zhen Liu, Zimu Zhang, Ziyang Zeng, Weiming Kang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Physical Activity Assessment of Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Using Accelerometer-Based Cut Points: Scoping Review
Ioana A Moldovan, Alexa Bragg, Anna S Nidhiry, Barbara A De La Cruz, Suzanne E Mitchell
Interactive Journal of Medical Research.2022; 11(2): e34433. CrossRef - Effects of 4 Weeks of a Technique-Specific Protocol with High-Intensity Intervals on General and Specific Physical Fitness in Taekwondo Athletes: An Inter-Individual Analysis
Alex Ojeda-Aravena, Tomás Herrera-Valenzuela, Pablo Valdés-Badilla, Jorge Cancino-López, José Zapata-Bastias, José Manuel García-García
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(7): 3643. CrossRef - Inter-Individual Variability of a High-Intensity Interval Training With Specific Techniques vs. Repeated Sprints Program in Sport-Related Fitness of Taekwondo Athletes
Alex Ojeda-Aravena, Tomás Herrera-Valenzuela, Pablo Valdés-Badilla, Jorge Cancino-López, José Zapata-Bastias, José Manuel García-García
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - EFFECT OF SPORTS MEDICINE ON REDUCING BODY FAT PERCENTAGE AND LEAN BODY MASS
Chunyan Fan
Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte.2021; 27(7): 714. CrossRef - Validation of the effectiveness of a digital integrated healthcare platform utilizing an AI-based dietary management solution and a real-time continuous glucose monitoring system for diabetes management: a randomized controlled trial
Sung Woon Park, Gyuri Kim, You-Cheol Hwang, Woo Je Lee, Hyunjin Park, Jae Hyeon Kim
BMC Medical Informatics and Decision Making.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Brain activity during a working memory task in different postures: an EEG study
Ju-Yeon Jung, Hwi-Young Cho, Chang-Ki Kang
Ergonomics.2020; 63(11): 1359. CrossRef
- Explanatory variables of objectively measured 24-h movement behaviors in people with prediabetes and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review
- Epidemiology
- Lower Leg Fat Depots Are Associated with Albuminuria Independently of Obesity, Insulin Resistance, and Metabolic Syndrome (Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys 2008 to 2011)
- Eugene Han, Nan Hee Cho, Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Soon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(4):461-473. Published online March 7, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0081
- 5,013 View
- 39 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Although the involvement of obesity in metabolic disorders is well known, leg fat depot influences on albuminuria have not been determined.
Methods This population-based, cross-sectional study used a nationally representative sample of 2,076 subjects aged ≥20 years from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys of 2008 to 2011. The ratio of leg fat to total fat (LF/TF ratio) was assessed by dual X-ray absorptiometry, and albuminuria was defined as more than one positive dipstick test or an albumin-to-creatinine ratio of ≥30 mg/g.
Results Individuals whose LF/TF ratio was in the lowest tertile showed a higher proportion of albuminuria than those in the highest tertile (odds ratio [OR], 2.82; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.01 to 3.96;
P <0.001). This association was observed in both sexes, all age groups, and all subgroups stratified by body mass index, waist circumference, homeostasis model assessments of insulin resistance, and the presence of metabolic syndrome (all,P <0.05). Multiple logistic regression analyses also demonstrated that the lowest LF/TF ratio was independently associated with albuminuria risk (OR, 1.55 to 2.16; all,P <0.05). In addition, the risk of albuminuria was higher in sarcopenic individuals with lower LF/TF ratios than in the highest LF/TF ratio subjects without sarcopenia (OR, 3.73; 95% CI, 2.26 to 6.13).Conclusion A lower LF/TF ratio was associated with an increased risk of albuminuria independent of obesity, insulin resistance, and metabolic syndrome, and when combined with sarcopenia, the albuminuria risk synergistically increased. Hence, our findings may have implications to improve risk stratification and recommendations on body fat distribution in the general population.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Efficacy and safety of evogliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: A multicentre, double‐blind, randomized, comparative trial
Eugene Han, Ji Hye Huh, Eun Y. Lee, Ji C. Bae, Sung W. Chun, Sung H. Yu, Soo H. Kwak, Kyong S. Park, Byung‐Wan Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(4): 752. CrossRef - Muscle fat contents rather than muscle mass determines nonalcoholic steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in patients with severe obesity
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Hye Won Lee, Seungwan Ryu, Hye Soon Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Youngsung Suh
Obesity.2022; 30(12): 2440. CrossRef - Albuminuria Is Associated with Steatosis Burden in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Eugene Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang, Hye Soon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(5): 698. CrossRef
- Efficacy and safety of evogliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes and non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease: A multicentre, double‐blind, randomized, comparative trial
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Relationship between Regional Body Fat Distribution and Diabetes Mellitus: 2008 to 2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
- Soo In Choi, Dawn Chung, Jung Soo Lim, Mi Young Lee, Jang Yel Shin, Choon Hee Chung, Ji Hye Huh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(1):51-59. Published online December 21, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.1.51
- 4,190 View
- 42 Download
- 35 Web of Science
- 36 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of this study was to investigate the association between regional body fat distribution, especially leg fat mass, and the prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) in adult populations.
Methods A total of 3,181 men and 3,827 postmenopausal women aged 50 years or older were analyzed based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (2008 to 2010). Body compositions including muscle mass and regional fat mass were measured using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry.
Results The odds ratios (ORs) for DM was higher with increasing truncal fat mass and arm fat mass, while it was lower with increasing leg fat mass. In a partial correlation analysis adjusted for age, leg fat mass was negatively associated with glycosylated hemoglobin in both sexes and fasting glucose in women. Leg fat mass was positively correlated with appendicular skeletal muscle mass and homeostasis model assessment of β cell. In addition, after adjusting for confounding factors, the OR for DM decreased gradually with increasing leg fat mass quartiles in both genders. When we subdivided the participants into four groups based on the median values of leg fat mass and leg muscle mass, higher leg fat mass significantly lowered the risk of DM even though they have smaller leg muscle mass in both genders (
P <0.001).Conclusion The relationship between fat mass and the prevalence of DM is different according to regional body fat distribution. Higher leg fat mass was associated with a lower risk of DM in Korean populations. Maintaining leg fat mass may be important in preventing impaired glucose tolerance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of chromium supplementation on body composition in patients with type 2 diabetes: A dose-response systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Mahdi Vajdi, Mahsa khajeh, Ehsan Safaei, Seyedehelham Moeinolsadat, Samin Mousavi, Hooria Seyedhosseini-Ghaheh, Mahdieh Abbasalizad-Farhangi, Gholamreza Askari
Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology.2024; 81: 127338. CrossRef - Connections between body composition and dysregulation of islet α- and β-cells in type 2 diabetes
Jia-xi Miao, Jia-ping Xu, Rui Wang, Yu-xian Xu, Feng Xu, Chun-hua Wang, Chao Yu, Dong-mei Zhang, Jian-bin Su
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Anthropometric and DXA-derived measures of body composition in relation to pre-diabetes among adults
Anwar Mohammad, Ali H. Ziyab, Talal Mohammad
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2023; 11(5): e003412. CrossRef - A cohort study on the predictive capability of body composition for diabetes mellitus using machine learning
Mohammad Ali Nematollahi, Amir Askarinejad, Arefeh Asadollahi, Mehdi Bazrafshan, Shirin Sarejloo, Mana Moghadami, Sarvin Sasannia, Mojtaba Farjam, Reza Homayounfar, Babak Pezeshki, Mitra Amini, Mohamad Roshanzamir, Roohallah Alizadehsani, Hanieh Bazrafsha
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Which is the best diet to reduce cardiometabolic risk: dietary counseling or home-delivered diet?
Feray Çağiran Yilmaz, Aysun Atilgan, Günay Saka
Food & Nutrition Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sedentary lifestyle and body composition in type 2 diabetes
Dan-dan Li, Yang Yang, Zi-yi Gao, Li-hua Zhao, Xue Yang, Feng Xu, Chao Yu, Xiu-lin Zhang, Xue-qin Wang, Li-hua Wang, Jian-bin Su
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impaired Lung Function and Lung Cancer Incidence: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Hye Seon Kang, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Seung Hoon Kim, Shin Young Kim, Chi Hong Kim, Kyungdo Han, Sung Kyoung Kim
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(4): 1077. CrossRef - Association between lung function and the risk of atrial fibrillation in a nationwide population cohort study
Su Nam Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko, Sung-Ho Her, Kyungdo Han, Donggyu Moon, Sung Kyoung Kim, Ki-Dong Yoo, Yu-Bae Ahn
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Is imaging-based muscle quantity associated with risk of diabetes? A meta-analysis of cohort studies
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Yang Yuan, Bo Xie, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 189: 109939. CrossRef - Research Progress of Body Composition Changes in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
鹏霞 张
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(08): 7181. CrossRef - Associations of eating speed with fat distribution and body shape vary in different age groups and obesity status
Saili Ni, Menghan Jia, Xuemiao Wang, Yun Hong, Xueyin Zhao, Liang Zhang, Yuan Ru, Fei Yang, Shankuan Zhu
Nutrition & Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Body composition, trabecular bone score and vertebral fractures in subjects with Klinefelter syndrome
W. Vena, F. Carrone, A. Delbarba, O. Akpojiyovbi, L. C. Pezzaioli, P. Facondo, C. Cappelli, L. Leonardi, L. Balzarini, D. Farina, A. Pizzocaro, A. G. Lania, G. Mazziotti, A. Ferlin
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2022; 46(2): 297. CrossRef - Genetically predicted body fat mass and distribution with diabetic kidney disease: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
Min Wang, Xin Li, Hang Mei, Zhao-Hui Huang, Yue Liu, Yong-Hong Zhu, Tian-Kui Ma, Qiu-Ling Fan
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Screening for Prediabetes and Diabetes in Korean Nonpregnant Adults: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2022
Kyung Ae Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Suk Chon, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 819. CrossRef - Age- and Sex-Related Differential Associations between Body Composition and Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Roh, Soon Young Hwang, Jung A Kim, You-Bin Lee, So-hyeon Hong, Nam Hoon Kim, Ji A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 183. CrossRef - Neck circumference and metabolic syndrome: A cross-sectional population-based study
Hooman Ebrahimi, Payam Mahmoudi, Farhad Zamani, Sedighe Moradi
Primary Care Diabetes.2021; 15(3): 582. CrossRef - Development of a clinical risk score for incident diabetes: A 10‐year prospective cohort study
Tae Jung Oh, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Nam H Cho, Hak Chul Jang
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(4): 610. CrossRef - The association of glucocorticoid receptor polymorphism with metabolic outcomes in menopausal women with adrenal incidentalomas
Sanja Ognjanović, Jadranka Antić, Tatjana Pekmezović, Bojana Popović, Tatjana Isailović, Ivana Božić Antić, Tamara Bogavac, Valentina Elezović Kovačević, Dušan Ilić, Milica Opalić, Djuro Macut
Maturitas.2021; 151: 15. CrossRef - Distinct opposing associations of upper and lower body fat depots with metabolic and cardiovascular disease risk markers
Mahasampath Gowri S, Belavendra Antonisamy, Finney S. Geethanjali, Nihal Thomas, Felix Jebasingh, Thomas V. Paul, Fredrik Karpe, Clive Osmond, Caroline H. D. Fall, Senthil K. Vasan
International Journal of Obesity.2021; 45(11): 2490. CrossRef - Body Roundness Index Is a Superior Obesity Index in Predicting Diabetes Risk Among Hypertensive Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study in China
Yingshan Liu, Xiaocong Liu, Haixia Guan, Shuting Zhang, Qibo Zhu, Xiaoying Fu, Hongmei Chen, Songtao Tang, Yingqing Feng, Jian Kuang
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Subcutaneous adipose tissue distribution and serum lipid/lipoprotein in unmedicated postmenopausal women: A B-mode ultrasound study
Imaging.2021; 13(2): 119. CrossRef - The Leg Fat to Total Fat Ratio Is Associated with Lower Risks of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Less Severe Hepatic Fibrosis: Results from Nationwide Surveys (KNHANES 2008–2011)
Hyun Min Kim, Yong-ho Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(6): 1232. CrossRef Optimal Cut-Offs of Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference to Identify Obesity in Chinese Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Qinying Zhao, Xiangjun Chen, Jinshan Wu, Lilin Gong, Jinbo Hu, Shumin Yang, Qifu Li, Zhihong Wang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 1899. CrossRef- Weight Loss after 12 Weeks of Exercise and/or Nutritional Guidance Is Not Obligatory for Induced Changes in Local Fat/Lean Mass Indexes in Adults with Excess of Adiposity
Robinson Ramírez-Vélez, Mikel Izquierdo, Karem Castro-Astudillo, Carolina Medrano-Mena, Angela Liliana Monroy-Díaz, Rocío del Pilar Castellanos-Vega, Héctor Reynaldo Triana-Reina, María Correa-Rodríguez
Nutrients.2020; 12(8): 2231. CrossRef - VISCERAL FAT, PHYSICAL FITNESS AND BIOCHEMICAL MARKERS OF BRAZILIAN MILITARY PERSONNEL
Laércio Camilo Rodrigues, Marcos de Sá Rego Fortes, Marco Antônio Muniz Lippert, Samir Ezequiel Da Rosa, José Fernandes Filho
Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte.2020; 26(1): 21. CrossRef - Comparison of 7-site skinfold measurement and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for estimating body fat percentage and regional adiposity in Taiwanese diabetic patients
Feng-Chih Kuo, Chieh-Hua Lu, Li-Wei Wu, Tung-Wei Kao, Sheng-Chiang Su, Jhih-Syuan Liu, Kuan-Chan Chen, Chia-Hao Chang, Chih-Chun Kuo, Chien-Hsing Lee, Chang-Hsun Hsieh, Mauro Lombardo
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(7): e0236323. CrossRef - Outcomes specific to patient sex after open ventral hernia repair
Kathryn A. Schlosser, Sean R. Maloney, Otto Thielan, Tanushree Prasad, Kent Kercher, Paul D. Colavita, B Todd Heniford, Vedra A. Augenstein
Surgery.2020; 167(3): 614. CrossRef Age-Related Changes in Body Composition and Bone Mineral Density and Their Relationship with the Duration of Diabetes and Glycaemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes
Ying Tang, Lilin Gong, Xiangjun Chen, Zhipeng Du, Jinbo Hu, Zhixin Xu, Jinshan Wu, Qifu Li, Zhihong Wang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4699. CrossRef- Lipodystrophy: A paradigm for understanding the consequences of "overloading" adipose tissue
Koini Lim, Afreen Haider, Claire Adams, Alison Sleigh, David Savage
Physiological Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Premeal Consumption of a Protein-Enriched, Dietary Fiber-Fortified Bar Decreases Total Energy Intake in Healthy Individuals
Chang Ho Ahn, Jae Hyun Bae, Young Min Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 879. CrossRef - Differences in dietary intakes, body compositions, and biochemical indices between metabolically healthy and metabolically abnormal obese Korean women
Eun Yeong Kang, Jung-Eun Yim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2019; 13(6): 488. CrossRef - The Association between Body Composition using Dual energy X-ray Absorptiometry and Type-2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational studies
Preeti Gupta, Carla Lanca, Alfred T. L. Gan, Pauline Soh, Sahil Thakur, Yijin Tao, Neelam Kumari, Ryan E. K. Man, Eva K. Fenwick, Ecosse L. Lamoureux
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Genes that make you fat, but keep you healthy
R. J. F. Loos, T. O. Kilpeläinen
Journal of Internal Medicine.2018; 284(5): 450. CrossRef - Overview of Epidemiology and Contribution of Obesity and Body Fat Distribution to Cardiovascular Disease: An Update
Marie-Eve Piché, Paul Poirier, Isabelle Lemieux, Jean-Pierre Després
Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases.2018; 61(2): 103. CrossRef - Relevance of human fat distribution on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism and cardiovascular disease risk
Marie-Eve Piché, Senthil K. Vasan, Leanne Hodson, Fredrik Karpe
Current Opinion in Lipidology.2018; 29(4): 285. CrossRef - Comparison of regional fat measurements by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and conventional anthropometry and their association with markers of diabetes and cardiovascular disease risk
S K Vasan, C Osmond, D Canoy, C Christodoulides, M J Neville, C Di Gravio, C H D Fall, F Karpe
International Journal of Obesity.2018; 42(4): 850. CrossRef
- Effects of chromium supplementation on body composition in patients with type 2 diabetes: A dose-response systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Clinical Relevance of Adipokines
- Matthias Blüher
- Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(5):317-327. Published online October 18, 2012
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2012.36.5.317
- 4,578 View
- 63 Download
- 128 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader The incidence of obesity has increased dramatically during recent decades. Obesity increases the risk for metabolic and cardiovascular diseases and may therefore contribute to premature death. With increasing fat mass, secretion of adipose tissue derived bioactive molecules (adipokines) changes towards a pro-inflammatory, diabetogenic and atherogenic pattern. Adipokines are involved in the regulation of appetite and satiety, energy expenditure, activity, endothelial function, hemostasis, blood pressure, insulin sensitivity, energy metabolism in insulin sensitive tissues, adipogenesis, fat distribution and insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells. Therefore, adipokines are clinically relevant as biomarkers for fat distribution, adipose tissue function, liver fat content, insulin sensitivity, chronic inflammation and have the potential for future pharmacological treatment strategies for obesity and its related diseases. This review focuses on the clinical relevance of selected adipokines as markers or predictors of obesity related diseases and as potential therapeutic tools or targets in metabolic and cardiovascular diseases.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Adipose tissue inflammation linked to obesity: A review of current understanding, therapies and relevance of phyto-therapeutics
Christiana Eleojo Aruwa, Saheed Sabiu
Heliyon.2024; 10(1): e23114. CrossRef - Lower body mass and lower adiposity are associated with differential responses to two treatment strategies for rheumatoid arthritis
Joshua F Baker, James R ODell, Bryant R England, Jon T Giles, Jefferey A Newcomb, Michael D George, Geoffrey Thiele, Larry Moreland, S Louis Bridges, Jeffrey R Curtis, Ted R Mikuls
Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.2024; 83(4): 429. CrossRef - Role of Perturbated Hemostasis in MASLD and Its Correlation with Adipokines
Salvatore Pezzino, Tonia Luca, Mariacarla Castorina, Stefano Puleo, Saverio Latteri, Sergio Castorina
Life.2024; 14(1): 93. CrossRef - Associations Between Adiponectin and the Development of Diabetes in Rheumatoid Arthritis
Joshua F Baker, Bryant R England, Katherine D Wysham, Brian Sauer, Amy M Joseph, Aleksander Lenert, Punyasha Roul, Rui Xiao, Rachel Gillcrist, Tate Johnson, Grant W Cannon, Michael Duryee, Geoffrey M Thiele, Ted R Mikuls
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Organokinler ve Biyokimyasal Etkileri
Ahmet İlhan, Umut Kökbaş
Arşiv Kaynak Tarama Dergisi.2024; 33(1): 71. CrossRef - Pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes and the impact of altered metabolic interorgan crosstalk
Jose Marcos Sanches, Li Na Zhao, Albert Salehi, Claes B. Wollheim, Philipp Kaldis
The FEBS Journal.2023; 290(3): 620. CrossRef - Female infertility in the era of obesity: The clash of two pandemics or inevitable consequence?
Sanja Medenica, Maria Elena Spoltore, Paulina Ormazabal, Ljiljana V. Marina, Antoan Stefan Sojat, Antongiulio Faggiano, Lucio Gnessi, Rossella Mazzilli, Mikiko Watanabe
Clinical Endocrinology.2023; 98(2): 141. CrossRef - Relationship Between Obesity with Galanin and Vaspin Levels
Murat TAKMET, Dilek TÜZÜN, Murat ŞAHİN, Adem DOĞANER, Metin KILINÇ
Kahramanmaraş Sütçü İmam Üniversitesi Tıp Fakültesi Dergisi.2023; 18(3): 29. CrossRef - Bioprinting: A Strategy to Build Informative Models of Exposure and Disease
Jose Caceres-Alban, Midori Sanchez, Fanny L. Casado
IEEE Reviews in Biomedical Engineering.2023; 16: 594. CrossRef - Adipokines as an important link between hidradenitis suppurativa and obesity: a narrative review
Piotr K Krajewski, Łukasz Matusiak, Jacek C Szepietowski
British Journal of Dermatology.2023; 188(3): 320. CrossRef - Chronic Resistance Training Effects on Serum Adipokines in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review
Pablo Jiménez-Martínez, Rodrigo Ramirez-Campillo, Carlos Alix-Fages, Javier Gene-Morales, Amador García-Ramos, Juan C. Colado
Healthcare.2023; 11(4): 594. CrossRef - Vaginal microbiome in obesity and its impact on reproduction
Akanksha Garg, Laura Burney Ellis, Ryan Laurence Love, Karen Grewal, Sarah Bowden, Phillip R. Bennett, Maria Kyrgiou
Best Practice & Research Clinical Obstetrics & Gynaecology.2023; 90: 102365. CrossRef - Obesity and hidradenitis suppurativa: targeting meta-inflammation for therapeutic gain
Dillon Mintoff, Rachel Agius, Farida Benhadou, Anupam Das, John W Frew, Nikolai P Pace
Clinical and Experimental Dermatology.2023; 48(9): 984. CrossRef - Autoimmune diseases and risk of gestational diabetes mellitus: a Mendelian randomization study
Xia Zhang, Xiuyan Wu, Lihong Chen, Lidan He
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 61(2): 161. CrossRef - Omentin roles in physiology and pathophysiology: an up-to-date comprehensive review
Aida A. Hussein, Noha A. Ahmed, Hader I. Sakr, Tarek Atia, Osama M. Ahmed
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Comparative Evaluation of Adipokine Metrics for the Diagnosis of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Maciej Kamiński, Radzisław Mierzyński, Elżbieta Poniedziałek-Czajkowska, Agata Sadowska, Maciej Sotowski, Bożena Leszczyńska-Gorzelak
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 25(1): 175. CrossRef - The Implications of Bone Marrow Adipose Tissue on Inflammaging
Nicole Aaron, Samantha Costa, Clifford J. Rosen, Li Qiang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Drug-induced metabolic alterations in adipose tissue - with an emphasis in epicardial adipose tissue
ARYANE C.O. PINHO, ANA BURGEIRO, MARIA JOÃO PEREIRA, EUGENIA CARVALHO
Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Low Risk for Developing Diabetes Among the Offspring of Individuals With Exceptional Longevity and Their Spouses
Iva Miljkovic, Ryan Cvejkus, Ping An, Bharat Thyagarajan, Kaare Christensen, Mary Wojczynski, Nicole Schupf, Joseph M. Zmuda
Frontiers in Clinical Diabetes and Healthcare.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Body Composition and Metabolic Changes in a Lyon Hypertensive Congenic Rat and Identification of Ercc6l2 as a Positional Candidate Gene
Karen C. Clark, Valerie A. Wagner, Katie L. Holl, John J. Reho, Monika Tutaj, Jennifer R. Smith, Melinda R. Dwinell, Justin L. Grobe, Anne E. Kwitek
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Leptin treatment has vasculo-protective effects in lipodystrophic mice
Paulina Elena Stürzebecher, Susan Kralisch, Marie Ruth Schubert, Vanina Filipova, Annett Hoffmann, Fabiana Oliveira, Bilal N. Sheikh, Matthias Blüher, Alexander Kogel, Markus Scholz, Karoline Elizabeth Kokot, Stephan Erbe, Jasmin Marga Kneuer, Thomas Eber
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipokines as potential biomarkers for type 2 diabetes mellitus in cats
Olga Sierawska, Paulina Niedźwiedzka-Rystwej
Frontiers in Immunology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Is subcutaneous adipose tissue expansion in people living with lipedema healthier and reflected by circulating parameters?
Pamela A. Nono Nankam, Manuel Cornely, Nora Klöting, Matthias Blüher
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Tea Plant (Camellia sinensis): A Current Update on Use in Diabetes, Obesity, and Cardiovascular Disease
James Michael Brimson, Mani Iyer Prasanth, Kishoree Krishna Kumaree, Premrutai Thitilertdecha, Dicson Sheeja Malar, Tewin Tencomnao, Anchalee Prasansuklab
Nutrients.2022; 15(1): 37. CrossRef - Leptin and Adiponectin Concentrations Independently Predict Future Accumulation of Visceral Fat in Nondiabetic Japanese Americans
Sun Ok Song, Seung Jin Han, Steven E. Kahn, Donna L. Leonetti, Wilfred Y. Fujimoto, Edward J. Boyko
Obesity.2021; 29(1): 233. CrossRef - Endothelial Cell–Derived Triosephosphate Isomerase Attenuates Insulin Secretion From Pancreatic Beta Cells of Male Rats
Bareket Daniel, Ariela Livne, Guy Cohen, Shirin Kahremany, Shlomo Sasson
Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Visfatin level and gestational diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Yong-Kuan Jiang, Hai-Yan Deng, Zeng-Yong Qiao, Fang-Xiao Gong
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2021; 127(5): 468. CrossRef - Association of Adipose Tissue and Adipokines with Development of Obesity-Induced Liver Cancer
Yetirajam Rajesh, Devanand Sarkar
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(4): 2163. CrossRef - Contribution of Adipose Tissue Oxidative Stress to Obesity-Associated Diabetes Risk and Ethnic Differences: Focus on Women of African Ancestry
Pamela A. Nono Nankam, Télesphore B. Nguelefack, Julia H. Goedecke, Matthias Blüher
Antioxidants.2021; 10(4): 622. CrossRef - Retinol-binding protein 4 in obesity and metabolic dysfunctions
Pamela A. Nono Nankam, Matthias Blüher
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2021; 531: 111312. CrossRef - The Potential Role of Chemerin, Lipocalin 2, and Apelin in the Diagnosis and Pathophysiology of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Radzisław Mierzyński, Elżbieta Poniedziałek-Czajkowska, Dominik Dłuski, Maciej Kamiński, Agnieszka Mierzyńska, Bożena Leszczyńska-Gorzelak, Antonio Schiattarella
Journal of Diabetes Research.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - A systematic literature review on obesity: Understanding the causes & consequences of obesity and reviewing various machine learning approaches used to predict obesity
Mahmood Safaei, Elankovan A. Sundararajan, Maha Driss, Wadii Boulila, Azrulhizam Shapi'i
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2021; 136: 104754. CrossRef - Does a Vegetarian Diet Affect the Levels of Myokine and Adipokine in Prepubertal Children?
Jadwiga Ambroszkiewicz, Joanna Gajewska, Joanna Mazur, Witold Klemarczyk, Grażyna Rowicka, Mariusz Ołtarzewski, Małgorzata Strucińska, Magdalena Chełchowska
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(17): 3995. CrossRef - Characteristics of Selected Adipokines in Ascites and Blood of Ovarian Cancer Patients
Marcin Wróblewski, Karolina Szewczyk-Golec, Iga Hołyńska-Iwan, Joanna Wróblewska, Alina Woźniak
Cancers.2021; 13(18): 4702. CrossRef - Nutrition as Prevention Factor of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: A Narrative Review
Radzisław Mierzyński, Elżbieta Poniedziałek-Czajkowska, Maciej Sotowski, Magdalena Szydełko-Gorzkowicz
Nutrients.2021; 13(11): 3787. CrossRef - The myokine meteorin‐like (metrnl) improves glucose tolerance in both skeletal muscle cells and mice by targeting AMPKα2
Jung Ok Lee, Won Seok Byun, Min Ju Kang, Jeong Ah Han, Jiyoung Moon, Min‐Jeong Shin, Ho Jun Lee, Ji Hyung Chung, Jin‐Seok Lee, Chang‐Gue Son, Kwon‐Ho Song, Tae Woo Kim, Eun‐Soo Lee, Hong Min Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Kevin R. W. Ngoei, Naomi X. Y. Ling, Jonat
The FEBS Journal.2020; 287(10): 2087. CrossRef Plasma Adipsin as a Biomarker and Its Implication in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Gebrehiwot Gebremedhin Tafere, Dawit Zewdu Wondafrash, Kaleab Alemayehu Zewdie, Brhane Teklebrhan Assefa, Muluken Altaye Ayza
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 1855. CrossRef- Low-dose naltrexone rescues inflammation and insulin resistance associated with hyperinsulinemia
Abhinav Choubey, Khyati Girdhar, Aditya K. Kar, Shaivya Kushwaha, Manoj Kumar Yadav, Debabrata Ghosh, Prosenjit Mondal
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2020; 295(48): 16359. CrossRef - Association between Adipokines and Biomarkers of Alzheimer’s Disease: A Cross-Sectional Study
Liliana Letra, Paulo Matafome, Tiago Rodrigues, Diana Duro, Raquel Lemos, Inês Baldeiras, Miguel Patrício, Miguel Castelo-Branco, Gina Caetano, Raquel Seiça, Isabel Santana
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2019; 67(2): 725. CrossRef - Role of adiponectin and its target receptors to control deposition of fat in obesity related disorders
souravh Bais, Nilesh J. Patel
Obesity Medicine.2019; 16: 100148. CrossRef - Circulatory Omentin-1 levels but not genetic variants influence the pathophysiology of Type 2 diabetes
Nirali Rathwa, Roma Patel, Sayantani Pramanik Palit, Shahnawaz D. Jadeja, Mahendra Narwaria, A.V. Ramachandran, Rasheedunnisa Begum
Cytokine.2019; 119: 144. CrossRef - Roles of omental and bone marrow adipocytes in tumor biology
Yoon Jin Cha, Ja Seung Koo
Adipocyte.2019; 8(1): 304. CrossRef - Genetic susceptibility of Iraqis for obesity and type 2 diabetes: LEPR gene polymorphisms
Maysoon K. Almyah, Adnan Issa Al-Badran
Gene Reports.2019; 15: 100386. CrossRef - New Insights into Adipokines as Potential Biomarkers for Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus
Marta Olivera-Santa Catalina, Pedro C. Redondo, Maria P. Granados, Carlos Cantonero, Jose Sanchez-Collado, Letizia Albarran, Jose J. Lopez
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2019; 26(22): 4119. CrossRef - Impact of Intragastric Balloon Treatment on Adipokines, Cytokines, and Metabolic Profile in Obese Individuals
Marcella Rodrigues Guedes, Ricardo José Fittipaldi-Fernandez, Cristina Fajardo Diestel, Márcia Regina Simas Torres Klein
Obesity Surgery.2019; 29(8): 2600. CrossRef - The cross-talk between adipokines and miRNAs in health and obesity-mediated diseases
Ahmad Ghasemi, Seyed Isaac Hashemy, Mohsen Azimi-Nezhad, Alireza Dehghani, Jafar Saeidi, Mahnaz Mohtashami
Clinica Chimica Acta.2019; 499: 41. CrossRef - Minor lipids profiling in subcutaneous and epicardial fat tissue using LC/MS with an optimized preanalytical phase
Petra Tomášová, Martina Čermáková, Helena Pelantová, Marek Vecka, Helena Kratochvílová, Michal Lipš, Jaroslav Lindner, Blanka Šedivá, Martin Haluzík, Marek Kuzma
Journal of Chromatography B.2019; 1113: 50. CrossRef - Impact of body weight gain on hepatic metabolism and hepatic inflammatory cytokines in comparison of Shetland pony geldings and Warmblood horse geldings
Carola Schedlbauer, Dominique Blaue, Martin Gericke, Matthias Blüher, Janine Starzonek, Claudia Gittel, Walter Brehm, Ingrid Vervuert
PeerJ.2019; 7: e7069. CrossRef - Lipid classes in adipose tissues and liver differ between Shetland ponies and Warmblood horses
Stephanie Adolph, Carola Schedlbauer, Dominique Blaue, Axel Schöniger, Claudia Gittel, Walter Brehm, Herbert Fuhrmann, Ingrid Vervuert, Juan J. Loor
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(3): e0207568. CrossRef - Effects of Probiotic Yogurt on Serum Omentin-1, Adropin, and Nesfatin-1 Concentrations in Overweight and Obese Participants Under Low-Calorie Diet
Mitra Zarrati, Mahsa Raji Lahiji, Eisa Salehi, Bahareh Yazdani, Elham Razmpoosh, Raheleh Shokouhi Shoormasti, Farzad Shidfar
Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins.2019; 11(4): 1202. CrossRef - Placental expressions and serum levels of adiponectin, visfatin, and omentin in GDM
Xaynaly Souvannavong-Vilivong, Chantacha Sitticharoon, Roongrit Klinjampa, Issarawan Keadkraichaiwat, Chanakarn Sripong, Saimai Chatree, Rungnapa Sririwichitchai, Tripop Lertbunnaphong
Acta Diabetologica.2019; 56(10): 1121. CrossRef - Angiotensin-(1-7), Adipokines and Inflammation
Deborah de Farias Lelis, Daniela Fernanda de Freitas, Amanda Souto Machado, Thaísa Soares Crespo, Sérgio Henrique Sousa Santos
Metabolism.2019; 95: 36. CrossRef - Recent advances in biosensor technology in assessment of early diabetes biomarkers
Armin Salek-Maghsoudi, Faezeh Vakhshiteh, Raheleh Torabi, Shokoufeh Hassani, Mohammad Reza Ganjali, Parviz Norouzi, Morteza Hosseini, Mohammad Abdollahi
Biosensors and Bioelectronics.2018; 99: 122. CrossRef - Potential role of microRNAs in the regulation of adipocytes liposecretion and adipose tissue physiology
Giulia Maurizi, Lucia Babini, Lucio Della Guardia
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2018; 233(12): 9077. CrossRef - Metabolomic and lipidomic analysis of the effect of pioglitazone on hepatic steatosis in a rat model of obese Type 2 diabetes
Hyekyung Yang, Dong Ho Suh, Dae Hee Kim, Eun Sung Jung, Kwang‐Hyeon Liu, Choong Hwan Lee, Cheol‐Young Park
British Journal of Pharmacology.2018; 175(17): 3610. CrossRef - Implications of circulating Meteorin-like (Metrnl) level in human subjects with type 2 diabetes
Hye Soo Chung, Soon Young Hwang, Ju Hee Choi, Hyun Jung Lee, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji-A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 136: 100. CrossRef - Anti-Inflammatory and Pro-Inflammatory Adipokine Profiles in Children on Vegetarian and Omnivorous Diets
Jadwiga Ambroszkiewicz, Magdalena Chełchowska, Grażyna Rowicka, Witold Klemarczyk, Małgorzata Strucińska, Joanna Gajewska
Nutrients.2018; 10(9): 1241. CrossRef - Adipokine profile as a novel screening method for cardiometabolic disease: Help or hindrance?
Ivana Veljić, Marija Polovina, Jelena P Seferović, Petar M Seferović
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2018; 25(14): 1543. CrossRef - Adipocytes and intestinal epithelium dysfunctions linking obesity to inflammation induced by high glycemic index pellet-diet in Wistar rats
Anna Beatriz Santana Luz, Júlia Braga dos Santos Figueredo, Bianca Damásio Pereira Dantas Salviano, Ana Júlia Felipe Camelo Aguiar, Luiza Gabriella Soares Dantas Pinheiro, Matheus Felipe Dantas Krause, Christina da Silva Camillo, Fernando Vagner Lobo Ladd
Bioscience Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of diet, adiposity, and weight loss on the secretion of incretin hormones in cats
K.E. McCool, A.J. Rudinsky, V.J. Parker, C.O. Herbert, C. Gilor
Domestic Animal Endocrinology.2018; 62: 67. CrossRef - Carnosine Supplementation Improves Serum Resistin Concentrations in Overweight or Obese Otherwise Healthy Adults: A Pilot Randomized Trial
Estifanos Baye, Jozef Ukropec, Maximilian de Courten, Aya Mousa, Timea Kurdiova, Josphin Johnson, Kirsty Wilson, Magdalena Plebanski, Giancarlo Aldini, Barbara Ukropcova, Barbora de Courten
Nutrients.2018; 10(9): 1258. CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome alters expression of insulin signaling-related genes in swine mesenchymal stem cells
Sabena M. Conley, Xiang-Yang Zhu, Alfonso Eirin, Hui Tang, Amir Lerman, Andre J. van Wijnen, Lilach O. Lerman
Gene.2018; 644: 101. CrossRef - Changes in Omentin Levels and Its mRNA Expression in Epicardial Adipose Tissue in Patients Undergoing Elective Cardiac Surgery: the Influence of Type 2 Diabetes and Coronary Heart Disease
Z. MATLOCH, H. KRATOCHVÍLOVÁ, A. CINKAJZLOVÁ, M. LIPŠ, P. KOPECKÝ, M. POŘÍZKA, D. HALUZÍKOVÁ, J. LINDNER, M. MRÁZ, J. KLOUČKOVÁ, Z. LACINOVÁ, M. HALUZÍK
Physiological Research.2018; : 881. CrossRef - Apport du tissu adipeux et de la fraction vasculaire stromale en chirurgie de la main
I. Nseir, F. Delaunay, C. Latrobe, A. Bonmarchand, D. Coquerel-Beghin, I. Auquit-Auckbur
Revue de Chirurgie Orthopédique et Traumatologique.2017; 103(6): 643. CrossRef - Specific Strains of Lactic Acid Bacteria Differentially Modulate the Profile of Adipokines In Vitro
Emanuel Fabersani, María Claudia Abeijon-Mukdsi, Romina Ross, Roxana Medina, Silvia González, Paola Gauffin-Cano
Frontiers in Immunology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Use of adipose tissue and stromal vascular fraction in hand surgery
I. Nseir, F. Delaunay, C. Latrobe, A. Bonmarchand, D. Coquerel-Beghin, I. Auquit-Auckbur
Orthopaedics & Traumatology: Surgery & Research.2017; 103(6): 927. CrossRef - Investigating the role of adipokines in chronic migraine
Elisa Rubino, Alessandro Vacca, Flora Govone, Annalisa Gai, Silvia Boschi, Milena Zucca, Paola De Martino, Salvatore Gentile, Lorenzo Pinessi, Innocenzo Rainero
Cephalalgia.2017; 37(11): 1067. CrossRef - Life in the fat lane: seasonal regulation of insulin sensitivity, food intake, and adipose biology in brown bears
K. S. Rigano, J. L. Gehring, B. D. Evans Hutzenbiler, A. V. Chen, O. L. Nelson, C. A. Vella, C. T. Robbins, H. T. Jansen
Journal of Comparative Physiology B.2017; 187(4): 649. CrossRef - Predictors of leptin concentration and association with cardiovascular risk in patients with coronary artery disease: results from the AtheroGene study
Christoph Bickel, Renate B. Schnabel, Tanja Zeller, Karl J. Lackner, Hans J. Rupprecht, Stefan Blankenberg, Christoph Sinning, Dirk Westermann
Biomarkers.2017; 22(3-4): 210. CrossRef - Omentin-A Novel Adipokine in Respiratory Diseases
Yan Zhou, Bo Zhang, Caixia Hao, Xiaoting Huang, Xiaohong Li, Yanhong Huang, Ziqiang Luo
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2017; 19(1): 73. CrossRef - Exercise training lowers serum chemerin concentration in obese children
F. Zehsaz, N. Farhangi, M. Ghahramani
Science & Sports.2017; 32(1): 39. CrossRef - MicroRNAs and adipocytokines: Promising biomarkers for pharmacological targets in diabetes mellitus and its complications
Mohamad Reza Ashoori, Mohammad Rahmati-Yamchi, Alireza Ostadrahimi, Sedigheh Fekri Aval, Nosratollah Zarghami
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2017; 93: 1326. CrossRef - Adiponectin, Leptin, and Leptin Receptor in Obese Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Treated with Insulin Detemir
Paweł Olczyk, Robert Koprowski, Katarzyna Komosinska-Vassev, Agnieszka Jura-Półtorak, Katarzyna Winsz-Szczotka, Kornelia Kuźnik-Trocha, Łukasz Mencner, Alicja Telega, Diana Ivanova, Krystyna Olczyk
Molecules.2017; 22(8): 1274. CrossRef - C1q/TNF-related protein-9 inhibits cytokine-induced vascular inflammation and leukocyte adhesiveness via AMP-activated protein kinase activation in endothelial cells
Chang Hee Jung, Min Jung Lee, Yu Mi Kang, Yoo La Lee, So Mi Seol, Hae Kyeong Yoon, Sang-Wook Kang, Woo Je Lee, Joong-Yeol Park
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2016; 419: 235. CrossRef - Effects of high glucose on caveolin-1 and insulin signaling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes
Sara Palacios-Ortega, Maider Varela-Guruceaga, J. Alfredo Martínez, Carlos de Miguel, Fermín I. Milagro
Adipocyte.2016; 5(1): 65. CrossRef - The Impact of Organokines on Insulin Resistance, Inflammation, and Atherosclerosis
Kyung Mook Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(1): 1. CrossRef - Molecular Pathogenesis of NASH
Alessandra Caligiuri, Alessandra Gentilini, Fabio Marra
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2016; 17(9): 1575. CrossRef - Association Between Long-term Exposure to Air Pollution and Biomarkers Related to Insulin Resistance, Subclinical Inflammation, and Adipokines
Kathrin Wolf, Anita Popp, Alexandra Schneider, Susanne Breitner, Regina Hampel, Wolfgang Rathmann, Christian Herder, Michael Roden, Wolfgang Koenig, Christa Meisinger, Annette Peters
Diabetes.2016; 65(11): 3314. CrossRef - Anti-inflammatory effects of sucrose-derived oligosaccharides produced by a constitutive mutant L. mesenteroides B-512FMCM dextransucrase in high fat diet-fed mice
Min-Gyung Kang, Hee Jae Lee, Jae-Young Cho, Kanghwa Kim, Soo Jin Yang, Doman Kim
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2016; 477(3): 350. CrossRef - UV-induced inhibition of adipokine production in subcutaneous fat aggravates dermal matrix degradation in human skin
Eun Ju Kim, Yeon Kyung Kim, Min-Kyoung Kim, Sungsoo Kim, Jin Yong Kim, Dong Hun Lee, Jin Ho Chung
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipokines in health and disease
Mathias Fasshauer, Matthias Blüher
Trends in Pharmacological Sciences.2015; 36(7): 461. CrossRef - Les cellules stromales mésenchymateuses du tissu adipeux : historique, isolement, propriétés immunomodulatrices et perspectives cliniques
N. Bertheuil, B. Chaput, C. Ménard, A. Varin, I. Garrido, J.L. Grolleau, L. Sensébé, E. Watier, K. Tarte
Annales de Chirurgie Plastique Esthétique.2015; 60(2): 94. CrossRef - Oncostatin M Modulation of Lipid Storage
Carrie Elks, Jacqueline Stephens
Biology.2015; 4(1): 151. CrossRef - Adiposité, hypoxie et apnées du sommeil : de l’obésité au syndrome métabolique
P. Böhme, P. Corbonnois, L. Duchesne, D. Quilliot, O. Ziegler
Obésité.2015; 10(3): 204. CrossRef -
ADIPOQ and IL6 variants are associated with a pro-inflammatory status in obeses with cardiometabolic dysfunction
Raquel de Oliveira, Tamiris Invencioni Moraes, Alvaro Cerda, Mario Hiroyuki Hirata, Cristina Moreno Fajardo, Marcela Correia Sousa, Egidio Lima Dorea, Márcia Martins Silveira Bernik, Rosario Dominguez Crespo Hirata
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Extensive weight loss reveals distinct gene expression changes in human subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue
Adil Mardinoglu, John T. Heiker, Daniel Gärtner, Elias Björnson, Michael R. Schön, Gesine Flehmig, Nora Klöting, Knut Krohn, Mathias Fasshauer, Michael Stumvoll, Jens Nielsen, Matthias Blüher
Scientific Reports.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Involvement of resveratrol in crosstalk between adipokine adiponectin and hepatokine fetuin-A in vivo and in vitro
Hee Jae Lee, Yunsook Lim, Soo Jin Yang
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2015; 26(11): 1254. CrossRef - Nicotinamide Riboside Ameliorates Hepatic Metaflammation by Modulating NLRP3 Inflammasome in a Rodent Model of Type 2 Diabetes
Hee Jae Lee, Young-Shick Hong, Woojin Jun, Soo Jin Yang
Journal of Medicinal Food.2015; 18(11): 1207. CrossRef - Inverse Relationship between Serum Lipoxin A4 Level and the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome in a Middle-Aged Chinese Population
Dan Yu, Zhiye Xu, Xueyao Yin, Fenping Zheng, Xihua Lin, Qianqian Pan, Hong Li, Liqing Yu
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(11): e0142848. CrossRef - Autophagy in adipose tissue of patients with obesity and type 2 diabetes
J. Kosacka, M. Kern, N. Klöting, S. Paeschke, A. Rudich, Y. Haim, M. Gericke, H. Serke, M. Stumvoll, I. Bechmann, M. Nowicki, M. Blüher
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2015; 409: 21. CrossRef - Autocrine/Paracrine Function of Globular Adiponectin: Inhibition of Lipid Metabolism and Inflammatory Response in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes
Yulia Lazra, Alona Falach, Lital Frenkel, Konstantin Rozenberg, Sanford Sampson, Tovit Rosenzweig
Journal of Cellular Biochemistry.2015; 116(5): 754. CrossRef - From leptin to other adipokines in health and disease: Facts and expectations at the beginning of the 21st century
Matthias Blüher, Christos S. Mantzoros
Metabolism.2015; 64(1): 131. CrossRef - Serum adiponectin levels in patients with acute coronary syndromes: Serial changes and relation to infarct size
Hadeel Alkofide, Gordon S Huggins, Robin Ruthazer, Joni R Beshansky, Harry P Selker
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2015; 12(6): 411. CrossRef - Peripheral Signals Mediate the Beneficial Effects of Gastric Surgery in Obesity
Silvia Barja-Fernández, Cintia Folgueira, Cecilia Castelao, Rosaura Leis, Felipe F. Casanueva, Luisa M. Seoane
Gastroenterology Research and Practice.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - Association of serum omentin-1 concentrations with the presence and severity of preeclampsia
Haiping Liu, Jianfeng Wu, Haiyu Wang, Lianbing Sheng, Ning Tang, Yunfei Li, Tianyu Hao
Annals of Clinical Biochemistry: International Journal of Laboratory Medicine.2015; 52(2): 245. CrossRef - Asthma and metabolic syndrome: Current knowledge and future perspectives
Laura Serafino-Agrusa
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2015; 3(3): 285. CrossRef - CILAIR-Based Secretome Analysis of Obese Visceral and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissues Reveals Distinctive ECM Remodeling and Inflammation Mediators
Arturo Roca-Rivada, Susana Belen Bravo, Diego Pérez-Sotelo, Jana Alonso, Ana Isabel Castro, Iván Baamonde, Javier Baltar, Felipe F. Casanueva, María Pardo
Scientific Reports.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Leptin of dermal adipose tissue is differentially expressed during the hair cycle and contributes to adipocyte‐mediated growth inhibition of anagen‐phase vibrissa hair
Chao‐Chun Yang, Hamm‐Ming Sheu, Pei‐Lun Chung, Chung‐Hsing Chang, Yau‐Sheng Tsai, Michael W. Hughes, Tai‐Lan Tuan, Lynn L. H. Huang
Experimental Dermatology.2015; 24(1): 57. CrossRef - Association of serum C1q/TNF-Related Protein-9 (CTRP9) concentration with visceral adiposity and metabolic syndrome in humans
Y-C Hwang, S Woo Oh, S-W Park, C-Y Park
International Journal of Obesity.2014; 38(9): 1207. CrossRef - Adipocyte dysfunction, inflammation and metabolic syndrome
Nora Klöting, Matthias Blüher
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2014; 15(4): 277. CrossRef - Implications of C1q/TNF-related protein-3 (CTRP-3) and progranulin in patients with acute coronary syndrome and stable angina pectoris
Kyung Mook Choi, Soon Young Hwang, Ho Chel Hong, Hae Yoon Choi, Hye Jin Yoo, Byung-Soo Youn, Sei Hyun Baik, Hong Seog Seo
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Serum Concentrations and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue mRNA Expression of Omentin in Morbid Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: the Effect of Very-Low-Calorie Diet, Physical Activity and Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy
M. URBANOVÁ, I. DOSTÁLOVÁ, P. TRACHTA, J. DRÁPALOVÁ, P. KAVÁLKOVÁ, D. HALUZÍKOVÁ, M. MATOULEK, Z. LACINOVÁ, M. MRÁZ, M. KASALICKÝ, M. HALUZÍK
Physiological Research.2014; : 207. CrossRef - Impact of Visceral Fat on Skeletal Muscle Mass and Vice Versa in a Prospective Cohort Study: The Korean Sarcopenic Obesity Study (KSOS)
Tae Nyun Kim, Man Sik Park, Ja Young Ryu, Hae Yoon Choi, Ho Cheol Hong, Hye Jin Yoo, Hyun Joo Kang, Wook Song, Seok Won Park, Sei Hyun Baik, Anne B. Newman, Kyung Mook Choi, Rozalyn M. Anderson
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(12): e115407. CrossRef - Links Between Ectopic Fat and Vascular Disease in Humans
Soo Lim, James B. Meigs
Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology.2014; 34(9): 1820. CrossRef - Circulating levels of adipokines in Parkinson's disease
Natália Pessoa Rocha, Paula Luciana Scalzo, Izabela Guimarães Barbosa, Mariana Soares de Sousa, Isabela Boechat Morato, Érica Leandro Marciano Vieira, Paulo Pereira Christo, Helton José Reis, Antônio Lúcio Teixeira
Journal of the Neurological Sciences.2014; 339(1-2): 64. CrossRef - Das Fettgewebe – ein endokrines Organ
M. Blüher
Der Internist.2014; 55(6): 687. CrossRef - The prediction role of indexes of circulating adipokines for common anthropometric and nutritional characteristics of obesity in the obese Central European population
Julie Bienertová-Vašků, Jan Novák, Filip Zlámal, Martin Forejt, Soňa Havlenová, Aneta Jackowská, Josef Tomandl, Marie Tomandlová, Zbyněk Šplíchal, Anna Vašků
Eating Behaviors.2014; 15(2): 244. CrossRef - Das Fettgewebe – ein endokrines Organ
M. Blüher
Humanmedizin kompakt.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - An exploratory investigation of links between changes in adipokines and quality of life in individuals undergoing weight loss interventions: Possible implications for cancer research
Faina Linkov, Lora E. Burke, Marina Komaroff, Robert P. Edwards, Anna Lokshin, Mindi A. Styn, Eugene Tseytlin, Kyle E. Freese, Dana H. Bovbjerg
Gynecologic Oncology.2014; 133(1): 67. CrossRef - Adipose tissue and its role in organ crosstalk
T. Romacho, M. Elsen, D. Röhrborn, J. Eckel
Acta Physiologica.2014; 210(4): 733. CrossRef - Adipokines – removing road blocks to obesity and diabetes therapy
Matthias Blüher
Molecular Metabolism.2014; 3(3): 230. CrossRef - Relationship Between Retinol-Binding Protein-4/Adiponectin and Leptin/Adiponectin Ratios with Insulin Resistance and Inflammation
Ishwarlal Jialal, Beverley Adams-Huet, Frank Duong, Gerred Smith
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2014; 12(4): 227. CrossRef - Metabolically Healthy Obesity—Does it Exist?
Patchaya Boonchaya-anant, Caroline M. Apovian
Current Atherosclerosis Reports.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Strong correlations between circulating chemerin levels and lipoprotein subfractions in nondiabetic obese and nonobese subjects
Hajnalka Lőrincz, Mónika Katkó, Mariann Harangi, Sándor Somodi, Krisztina Gaál, Péter Fülöp, György Paragh, Ildikó Seres
Clinical Endocrinology.2014; 81(3): 370. CrossRef - Physical inactivity, insulin resistance, and the oxidative-inflammatory loop
A. Gratas-Delamarche, F. Derbré, S. Vincent, J. Cillard
Free Radical Research.2014; 48(1): 93. CrossRef - Oncostatin M Is Produced in Adipose Tissue and Is Regulated in Conditions of Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
David Sanchez-Infantes, Ursula A. White, Carrie M. Elks, Ron F. Morrison, Jeffrey M. Gimble, Robert V. Considine, Anthony W. Ferrante, Eric Ravussin, Jacqueline M. Stephens
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2014; 99(2): E217. CrossRef - Bright light enhances the efficiency of physical activity in combination with a restrictive diet
Boris B. Pinkhasov, Vera G. Selyatitskaya, Ani R. Karapetyan
Health.2014; 06(03): 202. CrossRef - Impact of obesity on cardiovascular health
Marzena Chrostowska, Anna Szyndler, Michał Hoffmann, Krzysztof Narkiewicz
Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2013; 27(2): 147. CrossRef - The GH/IGF-1 axis in obesity: pathophysiology and therapeutic considerations
Darlene E. Berryman, Camilla A. M. Glad, Edward O. List, Gudmundur Johannsson
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2013; 9(6): 346. CrossRef - Phosphodiesterase 5 as target for adipose tissue disorders
Giovani Colombo, Maria Daniela H. Périco Colombo, Leonardo De Lucca Schiavon, Armando José d’Acampora
Nitric Oxide.2013; 35: 186. CrossRef - Resistance Training for Diabetes Prevention and Therapy: Experimental Findings and Molecular Mechanisms
Barbara Strasser, Dominik Pesta
BioMed Research International.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef - Adipose tissue dysfunction contributes to obesity related metabolic diseases
Matthias Blüher
Best Practice & Research Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2013; 27(2): 163. CrossRef - Importance of adipokines in glucose homeostasis
Matthias Blüher
Diabetes Management.2013; 3(5): 389. CrossRef - Association of Glypican-4 With Body Fat Distribution, Insulin Resistance, and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
H. J. Yoo, S. Y. Hwang, G. J. Cho, H. C. Hong, H. Y. Choi, T. G. Hwang, S. M. Kim, Matthias Blüher, Byung-Soo Youn, S. H. Baik, K. M. Choi
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2013; 98(7): 2897. CrossRef - Association of Serum Adiponectin, Leptin, and Resistin Concentrations with the Severity of Liver Dysfunction and the Disease Complications in Alcoholic Liver Disease
Beata Kasztelan-Szczerbinska, Agata Surdacka, Maria Slomka, Jacek Rolinski, Krzysztof Celinski, Agata Smolen, Mariusz Szczerbinski
Mediators of Inflammation.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef - RLIP76 Protein Knockdown Attenuates Obesity Due to a High-fat Diet
Sharad S. Singhal, James Figarola, Jyotsana Singhal, Marpadga A. Reddy, Xueli Liu, David Berz, Rama Natarajan, Sanjay Awasthi
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2013; 288(32): 23394. CrossRef - Tumor Necrosis Factor-α as a Predictor for the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 4-Year Follow-Up Study
Yun Yong Seo, Yong Kyun Cho, Ji-Cheol Bae, Mi Hae Seo, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2013; 28(1): 41. CrossRef - Adipose Tissue Dysfunction in Nascent Metabolic Syndrome
Andrew A. Bremer, Ishwarlal Jialal
Journal of Obesity.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef
- Adipose tissue inflammation linked to obesity: A review of current understanding, therapies and relevance of phyto-therapeutics
- Effects of Rosiglitazone on Body Fat Mass and Distribution in Type 2 Diabetic Patients.
- Hong Kyu Kim, Hyo Joong Yoon, Seung Min You, Ki Young Lee, Hye Young Park, Moon Ho Kang
- Korean Diabetes J. 2003;27(3):272-279. Published online June 1, 2003
- 1,105 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Rosiglitazone, an insulin-sensitizing drug of the thiazolidinediones class, has a high affinity for the ligands of the peroxisome proliferator activated receptor-gamma(PPAR-gamma), is highly expressed in adipose tissue, and plays an important role in the differentiation of adipocyte. The influence of rosiglitazone was investigated on the total fat mass and regional adiposity in type 2 diabetic patients. METHODS: Rosiglitazone (4 mg/day) was administered for 6 months to type 2 diabetic patients (n=20) whose glycemic control was unacceptable with the use of other treatments. Measurements of the total, trunk and leg region body fats (by dual energy X-ray absorptiometry) and abdominal fat distributions (by computed tomography) were compared before and after treatment. RESULTS: Nine patients received rosiglitazone monotherapy and 11 a combined therapy of sulfonylurea and/or metformin. The HbA1C, serum insulin level and homeostasis model assessment insulin resistance index were decreased following the rosiglitazone therapy, but the body weight and BMI were increased. As for the body fat changes, the total (19,382+/-4,786 vs. 22,940+/- 7,300 g, p<0.01), trunk (11,399+/- 2,678 vs. 13,960+/-4,698 g, p<0.01) and leg (4,734+/-1,319 vs. 6,203+/-2,231g, p<0.05) region fat masses were significantly increased. The percentage increase in the total, trunk and leg region fat masses were 20+/-25, 25+/-35 and 58+/-130%, respectively. As for abdominal fat distribution after the treatment, the visceral fat area (225+/-84 vs. 187+/-87 cm2, p<0.05) was significantly decreased, while the subcutaneous fat area tended to increase (178+/-83 vs. 201+/-80 cm2, NS), although these were not statistically significant. The visceral/subcutaneous fat ratio (V/S ratio) was significantly decreased (1.45+/- 0.64 vs. 0.95+/-0.25, p<0.05). CONCLUSION: Although the total body fat mass was increased following the rosiglitazone therapy, a shift in the body fat distribution, from the visceral to the subcutaneous region, was observed, which may be associated with an improvement in insulin resistance. However, a long-term assessment of the consequences of an increasing total fat mass and change in the body fat distribution will be required.
- Dehydroepiandrosterone-Sulfate, Sex Hormone Binding Globulin, Body Fat Distribution Pattern and Insulin Resistance in Women.
- Young Sun Hong, Jee Young Oh, Yeon Ah Sung, Nan Ho Kyung, Yeon Jin Jang
- Korean Diabetes J. 1998;22(3):328-337. Published online January 1, 2001
- 1,094 View
- 16 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) has been known to be associated with obesity, central fat accumulation and insulin resistance and thought to be a indirect marker for androgenicity in women. The relationships between circulating dehydroepiandrosterone(DHEA). dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate(DHEA-S) levels and body fat accumulation are still controversial. We conducted a cross-sectional study to eva]uate the relationships between serum levels of SHBG, DHEA-S, body fat distribution pattern and insulin sensitivity in women. METHODS: We tested 57 women(age 30~65yr; BMI 18.5~32.8kg/m, 45 premenopausal on the 5~10 day of the menstrual cycle, 12 postmenopausal who were not using hormone replacement therapy) with varying degree of glucose tolerance(32 normal glucose tolerance(NGT), 17 impaired glucose tolerance(IGT) and 8 newly diagnosed diabetes). lnsulin sensitivity was measured as minimal model derived sensitivity index(S) using insulin modified IV glucose tolerance test and fasting serum levels of SHBG and DHEA-S were measured by RIA. Body fat distribution pattern was assessed by waist to hip ratio(WHR),% body fat measured by bioelectrical impedance analyzer, subcutaneous fat area(SFA), visceral fat area(VFA) and VFA to SFA ratio(VSR) at the level of umbilicus using the computed tomography. RESULTS: 1) Measured SHBG and DHEA-S levels were not significantly different among subjects with NGT, IGT and diabetes. 2) SHBG was inversely associated with age, BMI, WHR, diastolic blood pressure, VFA, SFA, VSR,% body fat, fasting insulin and positively associated with S, whereas DHEA-S did not show any significant correlation with above variables except diastolic blood pressure. 3) SHBG level was significantly lower(p<0.05) and DHEA-S level was insignificantly lower (p=0.05) in postmenopausal women than in premenopausal women but the significance disappeared after adjustment for age, BMI, WHR and% body fat. 4) BMI was independently and negatively related to S, WHR and fasting insulin to SHBG by multiple regression analysis. CONCLUSION: We confirmed that SHBG was independently associated with central obesity and fasting hyperinsulinemia. However, S was independently associated with BMI only. It suggested that hyperinsulinemia in insulin resistance might cause the decreased level of SHBG even thaugh the directionality of the association was uncertain because of a cross-sectional nature of this study.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





