
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Drug/Regimen
- Safety and Effectiveness of Dulaglutide in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Korean Real-World Post-Marketing Study
- Jeonghee Han, Woo Je Lee, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hyoung Cho, Byung Wan Lee, Cheol-Young Park
- Received February 3, 2023 Accepted July 10, 2023 Published online February 2, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0030 [Epub ahead of print]
- 667 View
- 56 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader - Background
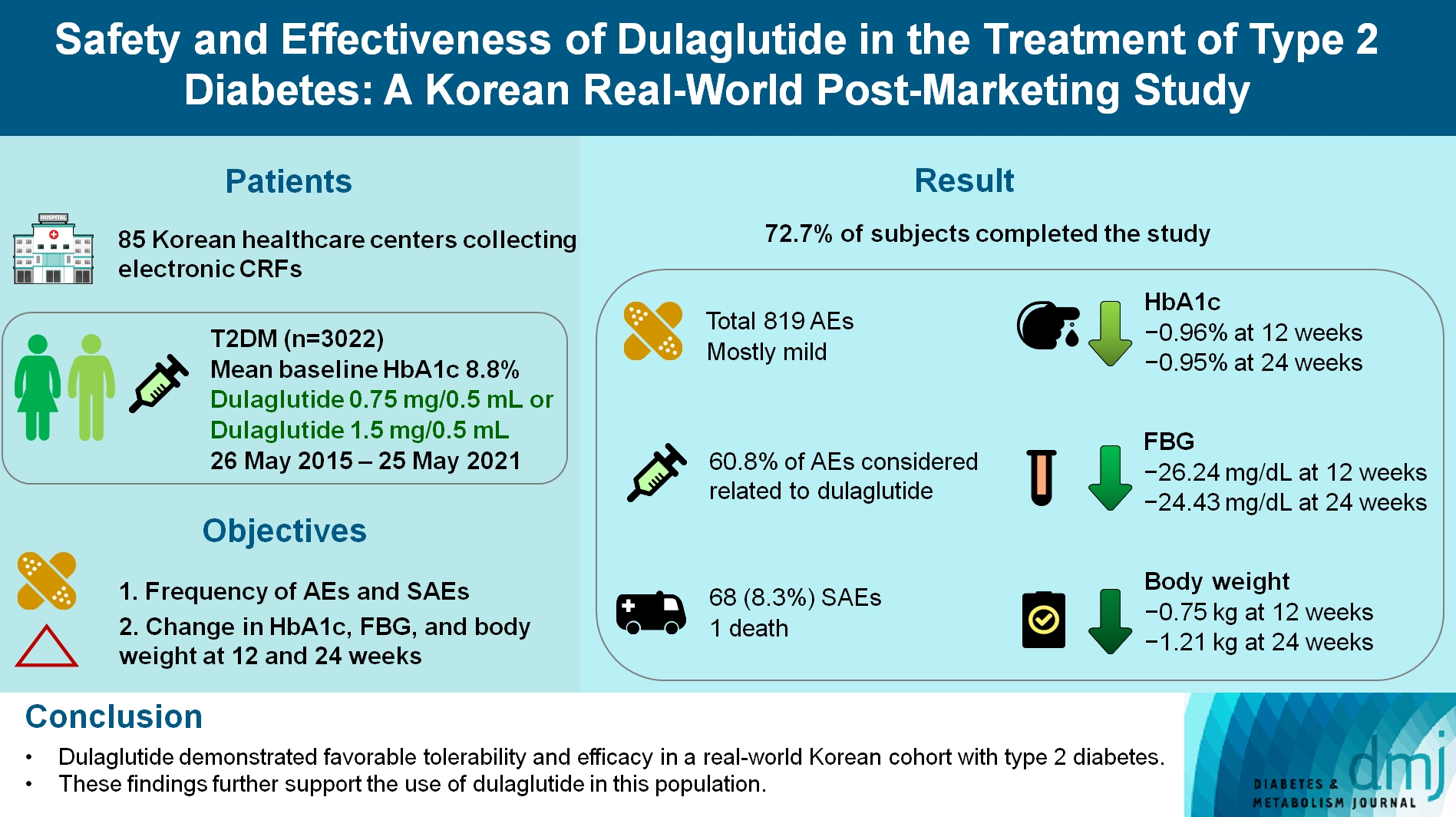
To investigate the real-world safety and effectiveness of dulaglutide in Korean adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
This was a real-world, prospective, non-interventional post-marketing safety study conducted from May 26, 2015 to May 25, 2021 at 85 Korean healthcare centers using electronic case data. Data on patients using dulaglutide 0.75 mg/0.5 mL or the dulaglutide 1.5 mg/0.5 mL single-use pens were collected and pooled. The primary objective was to report the frequency and proportion of adverse and serious adverse events that occurred. The secondary objective was to monitor the effectiveness of dulaglutide at 12 and 24 weeks by evaluating changes in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c ), fasting plasma glucose, and body weight.
Results
Data were collected from 3,067 subjects, and 3,022 subjects who received ≥1 dose (of any strength) of dulaglutide were included in the safety analysis set (53% female, mean age 56 years; diabetes duration 11.2 years, mean HbA1c 8.8%). The number of adverse events reported was 819; of these, 68 (8.3%) were serious adverse events. One death was reported. Adverse events were mostly mild in severity; 60.81% of adverse events were considered related to dulaglutide. This study was completed by 72.73% (2,198/3,022) of subjects. At 12/24 weeks there were significant (P<0.0001) reductions from baseline in least-squares mean HbA1c (0.96%/0.95%), fasting blood glucose (26.24/24.43 mg/dL), and body weight (0.75/1.21 kg).
Conclusion
Dulaglutide was generally well tolerated and effective in real-world Korean individuals with T2DM. The results from this study contribute to the body of evidence for dulaglutide use in this population.
Short Communications
- Drug/Regimen
- The Efficacy of Treatment Intensification by Quadruple Oral Therapy Compared to GLP-1RA Therapy in Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Real-World Data Study
- Minyoung Kim, Hosu Kim, Kyong Young Kim, Soo Kyoung Kim, Junghwa Jung, Jong Ryeal Hahm, Jaehoon Jung, Jong Ha Baek
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(1):135-139. Published online April 29, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0373
- 7,625 View
- 297 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
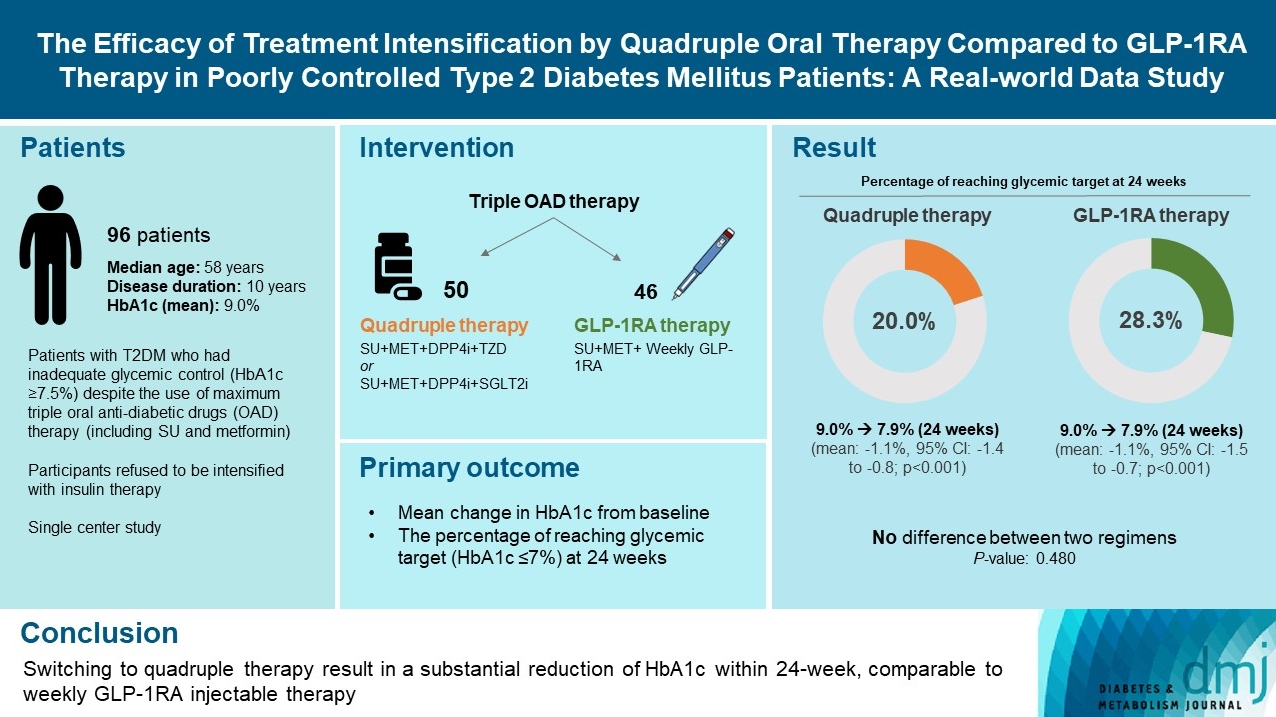
ePub - We compared the glycemic efficacy of treatment intensification between quadruple oral antidiabetic drug therapy and once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA)-based triple therapy in patients with poorly controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus refractory to triple oral therapy. For 24 weeks, changes in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) from baseline were compared between the two treatment groups. Of all 96 patients, 50 patients were treated with quadruple therapy, and 46 were treated with GLP-1RA therapy. Reductions in HbA1c for 24 weeks were comparable (in both, 1.1% reduction from baseline; P=0.59). Meanwhile, lower C-peptide level was associated with a lower glucose-lowering response of GLP-1RA therapy (R=0.3, P=0.04) but not with quadruple therapy (R=–0.13, P=0.40). HbA1c reduction by GLP-1RA therapy was inferior to that by quadruple therapy in the low C-peptide subgroup (mean, –0.1% vs. –1.3%; P=0.04). Treatment intensification by switching to quadruple oral therapy showed similar glucose-lowering efficacy to weekly GLP-1RA-based triple therapy. Meanwhile, the therapeutic response was affected by C-peptide levels in the GLP-1RA therapy group but not in the quadruple therapy group.
- Drug/Regimen
- Dulaglutide as an Effective Replacement for Prandial Insulin in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Review
- Hwi Seung Kim, Jiwoo Lee, Chang Hee Jung, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):948-953. Published online February 5, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0180

- 5,832 View
- 232 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Dulaglutide, a weekly injectable glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist, has demonstrated effectiveness when combined with basal insulin. We examined whether the efficacy of dulaglutide is comparable to that of prandial insulin in kidney transplant (KT) recipients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) undergoing multiple daily insulin injection (MDI) therapy. Thirty-seven patients, who switched from MDI therapy to basal insulin and dulaglutide, were retrospectively analyzed. Changes in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels, body weight, and basal insulin dose were evaluated over 6 months. Dulaglutide was comparable to three injections of prandial insulin in terms of glycemic control (HbA1c 7.1% vs. 7.0%; 95% confidence interval [CI], –0.53 to 0.28; P=0.53). The basal insulin and dulaglutide combination resulted in a reduction in FPG levels by 9.7 mg/dL (95% CI, 2.09 to 41.54; P=0.03), in body weight by 4.9 kg (95% CI, 2.87 to 6.98; P<0.001), and in basal insulin dose by 9.52 IU (95% CI, 5.80 to 3.23; P<0.001). Once-weekly dulaglutide may be an effective alternative for thrice-daily prandial insulin in KT recipients with T2DM currently receiving MDI therapy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Diabetic Kidney Disease in Post-Kidney Transplant Patients
Ngoc-Yen T. Pham, Diego Cruz, Luis Madera-Marin, Raja Ravender, Pablo Garcia
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(3): 793. CrossRef - Safety and efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists among kidney transplant recipients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Pajaree Krisanapan, Supawadee Suppadungsuk, Kanokporn Sanpawithayakul, Charat Thongprayoon, Pattharawin Pattharanitima, Supawit Tangpanithandee, Michael A Mao, Jing Miao, Wisit Cheungpasitporn
Clinical Kidney Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Sweet and simple as syrup: A review and guidance for use of novel antihyperglycemic agents for post‐transplant diabetes mellitus and type 2 diabetes mellitus after kidney transplantation
S. Elise Lawrence, Mary Moss Chandran, Jeong M. Park, Helen Sweiss, Thomas Jensen, Palak Choksi, Barrett Crowther
Clinical Transplantation.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel Drugs for the Management of Diabetes Kidney Transplant Patients: A Literature Review
Nancy Daniela Valencia-Morales, Beatriz Rodríguez-Cubillo, Rómulo Katsu Loayza-López, Maria Ángeles Moreno de la Higuera, Ana Isabel Sánchez-Fructuoso
Life.2023; 13(6): 1265. CrossRef - Uso de los agonistas del receptor del péptido similar al glucagón tipo 1 en pacientes trasplantados renales
Luis Alberto Vigara, Florentino Villanego, Cristhian Orellana, Myriam Eady, María Gabriela Sánchez, Marta Alonso, María Belén García, José Manuel Amaro, Teresa García, Auxiliadora Mazuecos
Nefrología.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Tolerability and Effectiveness of Switching to Dulaglutide in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Inadequately Controlled With Insulin Therapy
Youngsook Kim, Ji Hye Huh, Minyoung Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Diabetic Kidney Disease in Post-Kidney Transplant Patients

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





