
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Associations between Weight-Adjusted Waist Index and Abdominal Fat and Muscle Mass: Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
- Ji Yoon Kim, Jimi Choi, Chantal A. Vella, Michael H. Criqui, Matthew A. Allison, Nam Hoon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):747-755. Published online March 30, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0294
- 5,485 View
- 256 Download
- 30 Web of Science
- 35 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The weight-adjusted waist index (WWI) reflected body compositional changes with aging. This study was to investigate the association of WWI with abdominal fat and muscle mass in a diverse race/ethnic population.
Methods
Computed tomography (CT) data from 1,946 participants for abdominal fat and muscle areas from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (785 Whites, 252 Asians, 406 African American, and 503 Hispanics) were used. Among them, 595 participants underwent repeated CT. The WWI was calculated as waist circumference (cm) divided by the square root of body weight (kg). The associations of WWI with abdominal fat and muscle measures were examined, and longitudinal changes in abdominal composition measures were compared.
Results
In all race/ethnic groups, WWI was positively correlated with total abdominal fat area (TFA), subcutaneous fat area, and visceral fat area, but negatively correlated with total abdominal muscle area (TMA) and abdominal muscle radiodensity (P<0.001 for all). WWI showed a linear increase with aging regardless of race and there were no significant differences in the WWI distribution between Whites, Asians, and African Americans. In longitudinal analyses, over 38.6 months of follow-up, all abdominal fat measures increased but muscle measures decreased, along with increase in WWI. The more the WWI increased, the more the TFA increased and the more the TMA decreased.
Conclusion
WWI showed positive associations with abdominal fat mass and negative associations with abdominal muscle mass, which likely reflects the abdominal compositional changes with aging in a multi-ethnic population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The association between weight-adjusted-waist index and depression: Results from NHANES 2005–2018
Meng Li, Xue Yu, Wenhui Zhang, Jiahui Yin, Lu Zhang, Guoshuai Luo, Yuanxiang Liu, Jiguo Yang
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 347: 299. CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted-waist index and gallstones: an analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Si-Hua Wen, Xin Tang, Tao Tang, Zheng-Rong Ye
BMC Gastroenterology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted waist index and myopia in adolescents and young adults: results from NHANES 1999–2008
Xu Han Shi, Li Dong, Rui Heng Zhang, Wen Bin Wei
BMC Ophthalmology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between the weight-adjusted waist index and the odds of type 2 diabetes mellitus in United States adults: a cross-sectional study
Dongdong Zheng, Suzhen Zhao, Dan Luo, Feng Lu, Zhishen Ruan, Xiaokang Dong, Wenjing Chen
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Weight-Adjusted Waist Index and depressive symptoms: A nationally representative cross-sectional study from NHANES 2005 to 2018
Hangyu Liu, Jin Zhi, Chuzhao Zhang, Shiyi Huang, Yang Ma, Dandan Luo, Lungang Shi
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 350: 49. CrossRef - Relationship between cognitive function and weight-adjusted waist index in people ≥ 60 years old in NHANES 2011–2014
Xue-li Wang, Hong-lin Feng, Xiao-zhuo Xu, Jing Liu, Xu Han
Aging Clinical and Experimental Research.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted waist index and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: a population-based study
Changhui Yu, Shiming He, Maobin Kuang, Chao Wang, Xin Huang, Guotai Sheng, Yang Zou
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted waist index and serum total testosterone in males aged 6–19 years in the United States: Data from NHANES 2013–2016
Zhifei Wu, Lingling Bao, Haiyan Wang, Jiajing Zheng, Yu Chen, Wenjuan Wang, Dongkai Qiu
Heliyon.2024; 10(6): e27520. CrossRef - Associations of weight-adjusted-waist index and depression with secondary infertility
Fei Sun, Min Liu, Shanshan Hu, Ruijie Xie, Huijuan Chen, Zhaona Sun, Huiya Bi
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted-waist index and depression in US adults: A cross-sectional study
Yun Shen, Yahui Wu, Panru Luo, Minghan Fu, Kai Zhu, Jinsheng Wang
Journal of Affective Disorders.2024; 355: 299. CrossRef - Age differences in the association of body mass index-defined obesity with abdominal aortic calcification
Tangmeng Guo, Lili Huang, Zhijian Luo, Huabo Zheng, Shengshuai Shan, Bei Cheng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between weight-adjusted-waist index and diabetic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Zhaoxiang Wang, Xuejing Shao, Wei Xu, Bingshuang Xue, Shao Zhong, Qichao Yang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Assessment of existing anthropometric indices for screening sarcopenic obesity in older adults
Jin Eui Kim, Jimi Choi, Miji Kim, Chang Won Won
British Journal of Nutrition.2023; 129(5): 875. CrossRef - Relationship Between Weight-Adjusted Waist Index and Osteoporosis in the Senile in the United States from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2017-2020
Yuxiang Lin, Zijie Liang, Anxin Zhang, Nuo Xu, Xuewen Pei, Nanbu Wang, Liang Zheng, Danghan Xu
Journal of Clinical Densitometry.2023; 26(2): 101361. CrossRef - The association of asthma duration with body mass index and Weight-Adjusted-Waist index in a nationwide study of the U.S. adults
Xiaoxiao Han, Xiaofang He, Gui Hao, Lifang Cao, Yinliang Qi, Kexing Han
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between weight-adjusted-waist index and erectile dysfunction in the United State: results from NHANES 2001-2004
Shangqi Cao, Xu Hu, Yanxiang Shao, Yaohui Wang, Yaxiong Tang, Shangqing Ren, Xiang Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between weight-adjusted-waist index and total bone mineral density in adolescents: NHANES 2011–2018
Xiaohua Wang, Shuo Yang, Gansheng He, Lin Xie
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Asthma prevalence is increased in patients with high metabolism scores for visceral fat: study reports from the US
Qiushi Liu, Xiaoxiao Han, Yan Chen, Ying Gao, Wei Yang, Lewei Huang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Positive association between weight-adjusted-waist index and dementia in the Chinese population with hypertension: a cross-sectional study
Wei Zhou, Yanyou Xie, Lingling Yu, Chao Yu, Huihui Bao, Xiaoshu Cheng
BMC Psychiatry.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between weight-adjusted waist index and bone mineral density: results of a nationwide survey
Ya Zhang, Haiyang Wu, Cheng Li, Changxiong Liu, Mingjiang Liu, Xiaozhu Liu, Qiming Yin, Xianzhe Li, Ruijie Xie
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of weight-adjusted-waist index with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and liver fibrosis: a cross-sectional study based on NHANES
Qinggang Hu, Kexing Han, Jiapei Shen, Weijie Sun, Long Gao, Yufeng Gao
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Weight‐adjusted waist as an integrated index for fat, muscle and bone health in adults
Kyoung Jin Kim, Serhim Son, Kyeong Jin Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(5): 2196. CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted-waist index and female infertility: a population-based study
Zujun Wen, Xiang Li
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted-waist index and risk of cardiovascular diseases in United States adults: a cross-sectional study
Haiyang Fang, Feng Xie, Kai Li, Meng Li, Yanqing Wu
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between the weight-adjusted waist index and stroke: a cross-sectional study
Jiayi Ye, Yanjie Hu, Xinrong Chen, Zhe Yin, Xingzhu Yuan, Liping Huang, Ka Li
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between weight-adjusted-waist index and chronic kidney disease: a cross-sectional study
Xiaowan Li, Lanyu Wang, Hongyi Zhou, Hongyang Xu
BMC Nephrology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sex Differences in the Association of Weight-Adjusted-Waist Index with Sarcopenic Obesity: A Cross-Sectional Study of Hemodialysis Patients
Maolu Tian, Qin Lan, Fangfang Yu, Pinghong He, Shanshan Hu, Yan Zha
Metabolic Syndrome and Related Disorders.2023; 21(10): 596. CrossRef - Lean or Non-obese Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: Are They Really Lean?
Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 980. CrossRef - The association of body mass index and weight waist adjustment index with serum ferritin in a national study of US adults
Hao Han, Ping Ni, Siqi Zhang, Xiaojuan Ji, Mingli Zhu, Wanyu Ma, Hongfeng Ge, Hailiang Chu
European Journal of Medical Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The weight-adjusted-waist index and cognitive impairment among U.S. older adults: a population-based study
Xiao-tong Huang, Xiang Lv, Hong Jiang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between weight-adjusted-waist index and total bone mineral density in adults aged 20-59
Meiqian Guo, Yi Lei, Xueqing Liu, Xiang Li, Yong Xu, Donghui Zheng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between weight-adjusted-waist index and infertility: Results from NHANES 2013 to 2020
Huanxin Zhong, Bin Yu, Fen Zhao, Hongyin Cui, Lifang You, Dao Feng, Yi Lu
Medicine.2023; 102(48): e36388. CrossRef - The association between weight-adjusted-waist index and increased urinary albumin excretion in adults: A population-based study
Zheng Qin, Kaixi Chang, Qinbo Yang, Qiao Yu, Ruoxi Liao, Baihai Su
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between the weight-adjusted-waist index and abdominal aortic calcification in United States adults: Results from the national health and nutrition examination survey 2013–2014
Feng Xie, Yuan Xiao, Xiaozhong Li, Yanqing Wu
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between weight-adjusted-waist index and abdominal aortic calcification in adults aged ≥ 40 years: results from NHANES 2013–2014
Zheng Qin, Dongru Du, Yupei Li, Kaixi Chang, Qinbo Yang, Zhuyun Zhang, Ruoxi Liao, Baihai Su
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- The association between weight-adjusted-waist index and depression: Results from NHANES 2005–2018
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Maternal Hyperglycemia during Pregnancy Increases Adiposity of Offspring
- Hye Rim Chung, Joon Ho Moon, Jung Sub Lim, Young Ah Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Joon-Seok Hong, Soo Heon Kwak, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):730-738. Published online February 22, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0154
- 5,726 View
- 180 Download
- 6 Web of Science
- 6 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
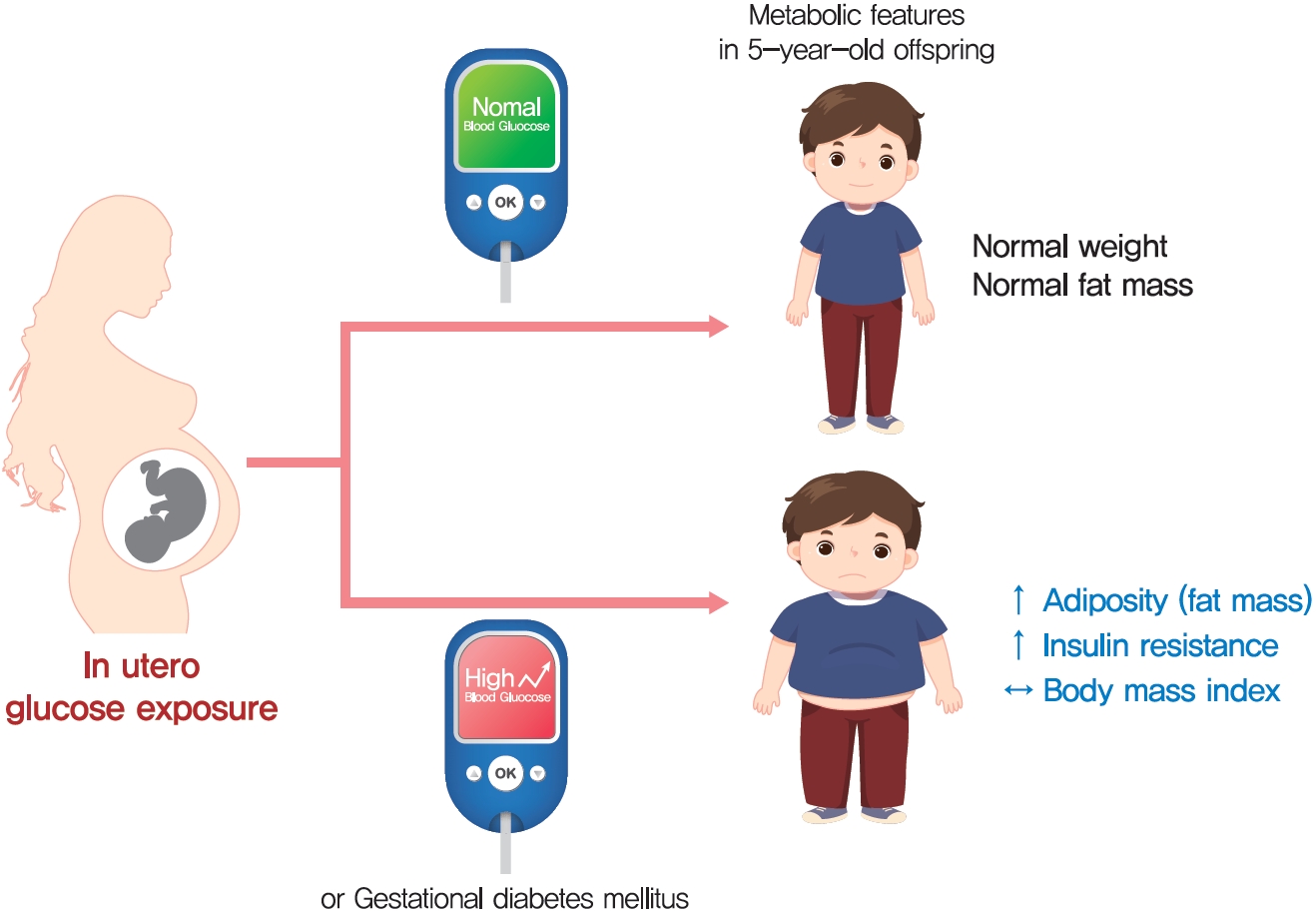
The effect of intrauterine hyperglycemia on fat mass and regional fat proportion of the offspring of mothers with gestational diabetes mellitus (OGDM) remains to be determined.
Methods
The body composition of OGDM (n=25) and offspring of normoglycemic mothers (n=49) was compared using dualenergy X-ray absorptiometry at age 5 years. The relationship between maternal glucose concentration during a 100 g oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) and regional fat mass or proportion was analyzed after adjusting for maternal prepregnancy body mass index (BMI).
Results
BMI was comparable between OGDM and control (median, 16.0 kg/m2 vs. 16.1 kg/m2 ). Total, truncal, and leg fat mass were higher in OGDM compared with control (3,769 g vs. 2,245 g, P=0.004; 1,289 g vs. 870 g, P=0.017; 1,638 g vs. 961 g, P=0.002, respectively), whereas total lean mass was lower in OGDM (15,688 g vs. 16,941 g, P=0.001). Among OGDM, total and truncal fat mass were correlated with fasting and 3-hour glucose concentrations of maternal 100 g OGTT during pregnancy (total fat mass, r=0.49, P=0.018 [fasting], r=0.473, P=0.023 [3-hour]; truncal fat mass, r=0.571, P=0.004 [fasting], r=0.558, P=0.006 [3-hour]), but there was no correlation between OGDM leg fat mass and maternal OGTT during pregnancy. Regional fat indices were not correlated with concurrent maternal 75 g OGTT values.
Conclusion
Intrauterine hyperglycemia is associated with increased fat mass, especially truncal fat, in OGDM aged 5 years. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Advances in free fatty acid profiles in gestational diabetes mellitus
Haoyi Du, Danyang Li, Laura Monjowa Molive, Na Wu
Journal of Translational Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - High-fat diet during pregnancy lowers fetal weight and has a long-lasting adverse effect on brown adipose tissue in the offspring
Mihoko Yamaguchi, Jun Mori, Nozomi Nishida, Satoshi Miyagaki, Yasuhiro Kawabe, Takeshi Ota, Hidechika Morimoto, Yusuke Tsuma, Shota Fukuhara, Takehiro Ogata, Takuro Okamaura, Naoko Nakanishi, Masahide Hamaguchi, Hisakazu Nakajima, Michiaki Fukui, Tomoko I
Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease.2023; 14(2): 261. CrossRef - Prediction of gestational diabetes mellitus in Asian women using machine learning algorithms
Byung Soo Kang, Seon Ui Lee, Subeen Hong, Sae Kyung Choi, Jae Eun Shin, Jeong Ha Wie, Yun Sung Jo, Yeon Hee Kim, Kicheol Kil, Yoo Hyun Chung, Kyunghoon Jung, Hanul Hong, In Yang Park, Hyun Sun Ko
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of early standardized management on the growth trajectory of offspring with gestational diabetes mellitus at 0–5 years old: a preliminary longitudinal study
Bingbing Guo, Jingjing Pei, Yin Xu, Yajie Wang, Xinye Jiang
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications
Joon Ho Moon, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 3. CrossRef - Increased Pro-Inflammatory T Cells, Senescent T Cells, and Immune-Check Point Molecules in the Placentas of Patients With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus
Yea Eun Kang, Hyon-Seung Yi, Min-Kyung Yeo, Jung Tae Kim, Danbit Park, Yewon Jung, Ok Soon Kim, Seong Eun Lee, Ji Min Kim, Kyong Hye Joung, Ju Hee Lee, Bon Jeong Ku, Mina Lee, Hyun Jin Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Advances in free fatty acid profiles in gestational diabetes mellitus
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Age- and Sex-Related Differential Associations between Body Composition and Diabetes Mellitus
- Eun Roh, Soon Young Hwang, Jung A Kim, You-Bin Lee, So-hyeon Hong, Nam Hoon Kim, Ji A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(2):183-194. Published online June 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0171
- 7,442 View
- 236 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
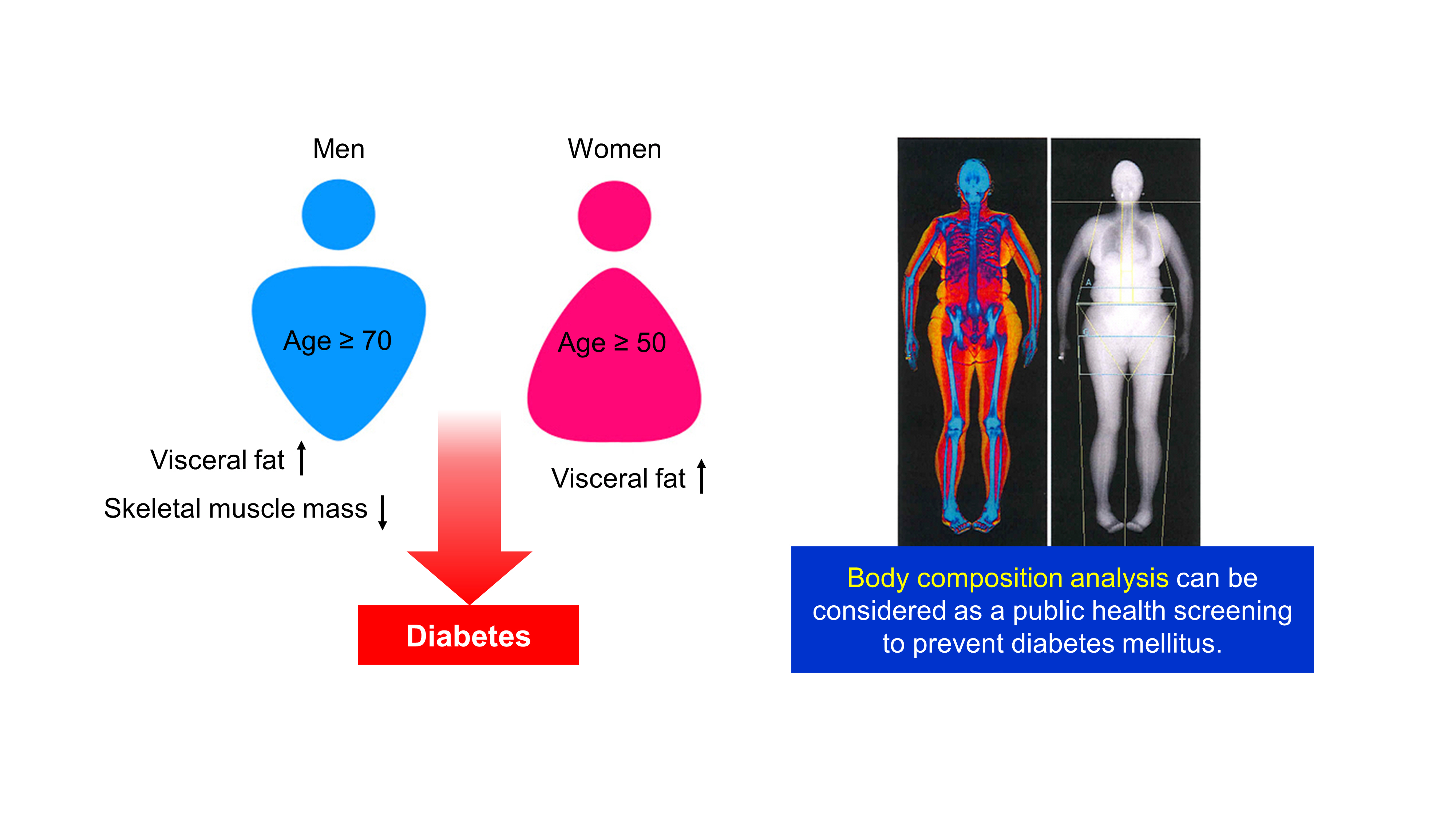
Background The age- and sex-related differences on the impacts of body composition on diabetes mellitus (DM) remain uncertain.
Methods The fourth and fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey included 15,586 subjects over 30 years of age who completed dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. We conducted a cross-sectional study to investigate whether muscle mass index (MMI), defined as appendicular skeletal muscle divided by body mass index (BMI), and fat mass index (FMI), defined as trunk fat mass divided by BMI, were differently associated with DM according to age and sex.
Results In multivariate logistic regression, the risk for DM significantly increased across quartiles of FMI in men aged ≥70. Meanwhile, MMI showed a protective association with DM in men of the same age. The odds ratios (ORs) for the highest quartile versus the lowest quartile of FMI and MMI were 3.116 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.405 to 6.914) and 0.295 (95% CI, 0.157 to 0.554), respectively. In women, the ORs of DM was significantly different across FMI quartiles in those over age 50. The highest quartile of FMI exhibited increased ORs of DM in subjects aged 50 to 69 (OR, 1.891; 95% CI, 1.229 to 2.908) and ≥70 (OR, 2.275; 95% CI, 1.103 to 4.69) compared to lowest quartile. However, MMI was not significantly associated with DM in women of all age groups.
Conclusion Both FMI and MMI were independent risk factors for DM in men aged 70 years or more. In women over 50 years, FMI was independently associated with DM. There was no significant association between MMI and DM in women.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Research Progress on Correlation between Body Composition Changes and Disease Pro-gression of Type 2 Diabetes
敏 张
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2024; 14(03): 936. CrossRef - Low Skeletal Muscle Mass Accompanied by Abdominal Obesity Additively Increases the Risk of Incident Type 2 Diabetes
Ji Eun Jun, Seung-Eun Lee, You-Bin Lee, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hwan Jee, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 108(5): 1173. CrossRef - Is imaging-based muscle quantity associated with risk of diabetes? A meta-analysis of cohort studies
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Yang Yuan, Bo Xie, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 189: 109939. CrossRef - Whole and segmental body composition changes during mid-follicular and mid-luteal phases of the menstrual cycle in recreationally active young women
Şükran Nazan Koşar, Yasemin Güzel, Mehmet Gören Köse, Ayşe Kin İşler, Tahir Hazır
Annals of Human Biology.2022; 49(2): 124. CrossRef - Body Composition and Diabetes
Hye Jin Yoo
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 238. CrossRef
- Research Progress on Correlation between Body Composition Changes and Disease Pro-gression of Type 2 Diabetes
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Association between the Thigh Muscle and Insulin Resistance According to Body Mass Index in Middle-Aged Korean Adults
- Ji Eun Heo, Jee-Seon Shim, Hokyou Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):446-457. Published online April 16, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0110
- 6,743 View
- 89 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background We examined the associations between thigh muscle area (TMA) and insulin resistance (IR) according to body mass index (BMI) in middle-aged Korean general population.
Methods TMA was measured using quantitative computed tomography and corrected by body weight (TMA/Wt) in 1,263 men, 788 premenopausal women, and 1,476 postmenopausal women all aged 30 to 64 years. The tertiles of TMA/Wt were calculated separately for men and for premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) was performed using fasting blood glucose and insulin levels, and increased IR was defined according to sex-specific, top quartiles of HOMA-IR. Associations between the TMA/Wt tertiles and increased IR according to the BMI categories (<25 and ≥25 kg/m2) were assessed using multivariable logistic regression analysis.
Results In men with higher BMIs, but not in those with lower BMIs, the presence of an increased IR had significantly higher odds ratios in the lower TMA/Wt tertiles, even after adjustment for visceral fat area. However, in premenopausal and postmenopausal women, there was no significant inverse association between TMA/Wt tertiles and increased IR, regardless of BMI category.
Conclusion Our findings suggest that the thigh muscle is inversely associated with IR in men, particularly in those with higher BMIs.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk of sleep apnea associated with higher blood pressure among Chinese and Korean Americans
Brittany N. Morey, Yuxi Shi, Soomin Ryu, Susan Redline, Ichiro Kawachi, Hye Won Park, Sunmin Lee
Ethnicity & Health.2024; 29(3): 295. CrossRef - Sex-specific equations to estimate body composition: Derivation and validation of diagnostic prediction models using UK Biobank
Yueqi Lu, Ying Shan, Liang Dai, Xiaosen Jiang, Congying Song, Bangwei Chen, Jingwen Zhang, Jing Li, Yue Zhang, Junjie Xu, Tao Li, Zuying Xiong, Yong Bai, Xiaoyan Huang
Clinical Nutrition.2023; 42(4): 511. CrossRef - Gender Differences in Relation to Body Composition, Insulin Resistance, and Islet Beta Cell Function in Newly Diagnosed Diabetic or Pre-Diabetic Patients
Minglei Ma, Tao Jiang, Zhen Wen, Dongxue Zhang, Lei Xiu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 723. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Sarcopenia and Carotid Plaque Progression Risk in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yongin Cho, Hye-Sun Park, Byung Wook Huh, Yong-ho Lee, Seong Ha Seo, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, So Hun Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(2): 232. CrossRef - Prospective External Validation of an Algorithm Predicting Hourly
Basal Insulin Infusion Rates from Characteristics of Patients with Type 1
Diabetes Treated with Insulin Pumps
Jana S. Schmelzer, Melanie Kahle-Stephan, Juris J. Meier, Michael A. Nauck
Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes.2023; 131(10): 539. CrossRef - Establishing reference values for percentage of appendicular skeletal muscle mass and their association with metabolic syndrome in Korean adolescents
Da Hye Lee, Sung-Chan Kang, Seung-Sik Hwang, Yun Jeong Lee, Hwa Young Kim, Seong Yong Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Jaehyun Kim
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(4): 237. CrossRef - Evaluating Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Simple and Easy-to-Calculate Marker for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of General Internal Medicine.2022; 37(16): 4153. CrossRef - Association between Lower-to-Upper Ratio of Appendicular Skeletal Muscle and Metabolic Syndrome
Hyun Eui Moon, Tae Sic Lee, Tae-Ha Chung
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(21): 6309. CrossRef
- Risk of sleep apnea associated with higher blood pressure among Chinese and Korean Americans
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- The Association between Z-Score of Log-Transformed A Body Shape Index and Cardiovascular Disease in Korea
- Wankyo Chung, Jung Hwan Park, Hye Soo Chung, Jae Myung Yu, Shinje Moon, Dong Sun Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):675-682. Published online April 26, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0169
- 7,751 View
- 59 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background In order to overcome the limitations of body mass index (BMI) and waist circumference (WC), the z-score of the log-transformed A Body Shape Index (LBSIZ) has recently been introduced. In this study, we analyzed the relationship between the LBSIZ and cardiovascular disease (CVD) in a Korean representative sample.
Methods Data were collected from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination VI to V. The association between CVD and obesity indices was analyzed using a receiver operating characteristic curve. The cut-off value for the LBSIZ was estimated using the Youden index, and the odds ratio (OR) for CVD was determined via multivariate logistic regression analysis. ORs according to the LBSIZ value were analyzed using restricted cubic spline regression plots.
Results A total of 31,227 Korean healthy adults were analyzed. Area under the curve (AUC) of LBSIZ against CVD was 0.686 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.671 to 0.702), which was significantly higher than the AUC of BMI (0.583; 95% CI, 0.567 to 0.599) or WC (0.646; 95% CI, 0.631 to 0.661) (
P <0.001). Similar results were observed for stroke and coronary artery diseases. The cut-off value for the LBSIZ was 0.35 (sensitivity, 64.5%; specificity, 64%; OR, 1.29, 95% CI, 1.12 to 1.49). Under restricted cubic spline regression, LBSIZ demonstrated that OR started to increase past the median value.Conclusion The findings of this study suggest that the LBSIZ might be more strongly associated with CVD risks compared to BMI or WC. These outcomes would be helpful for CVD risk assessment in clinical settings, especially the cut-off value of the LBSIZ suggested in this study.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Body Shape Index and Cardiovascular Risk in Individuals With Obesity
Nazlı Hacıağaoğlu, Can Öner, Hüseyin Çetin, Engin Ersin Şimşek
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between body shape index and risk of mortality in the United States
Heysoo Lee, Hye Soo Chung, Yoon Jung Kim, Min Kyu Choi, Yong Kyun Roh, Wankyo Chung, Jae Myung Yu, Chang-Myung Oh, Shinje Moon
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Utility of the Z-score of log-transformed A Body Shape Index (LBSIZ) in the assessment for sarcopenic obesity and cardiovascular disease risk in the United States
Wankyo Chung, Jung Hwan Park, Hye Soo Chung, Jae Myung Yu, Dong Sun Kim, Shinje Moon
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Body Shape Index and Cardiovascular Risk in Individuals With Obesity
- Epidemiology
- Longitudinal Changes of Body Composition Phenotypes and Their Association with Incident Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus during a 5-Year Follow-up in Koreans
- Hong-Kyu Kim, Min Jung Lee, Eun-Hee Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Jaewon Choe, Chul-Hee Kim, Joong-Yeol Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):627-639. Published online April 19, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0141
- 5,095 View
- 65 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background To elucidate longitudinal changes of complex body composition phenotypes and their association with incident type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Methods A total of 17,280 (mean age, 48.1±8.2 years) Korean adults who underwent medical check-ups were included. The mean follow-up duration was 5.5±0.5 years. Body compositions were assessed using a bioelectrical impedance analysis. Four body composition phenotypes were defined using the median of appendicular skeletal muscle mass (ASM) index and fat mass index: low muscle/low fat (LM/LF); high muscle (HM)/LF; LM/high fat (HF); and HM/HF groups.
Results Of the individuals in the LM/LF or HM/HF groups, over 60% remained in the same group, and over 30% were moved to the LM/HF group. Most of the LM/HF group remained in this group. In the baseline HM/LF group, approximately 30% stayed in the group, and the remaining individuals transitioned to the three other groups in similar proportions. Incident diabetes was significantly lower in participants who remained in the HM/LF group than those who transitioned to the LM/LF or LM/HF group from the baseline HM/LF group in men. ASM index was significantly associated with a decreased risk for incident diabetes in men regardless of obesity status (adjusted odds ratio [OR], 0.71 per kg/m2; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.52 to 0.97 in non-obese) (adjusted OR, 0.87; 95% CI, 0.77 to 0.98 in obese) after adjusting for other strong risk factors (e.g., baseline glycosylated hemoglobin and homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance).
Conclusion Maintenance of ASM may be protective against the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in men, regardless of obesity status.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metabolically healthy obese individuals are still at high risk for diabetes: Application of the marginal structural model
Hye Ah Lee, Hyesook Park
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(2): 431. CrossRef - Association of serum gamma-glutamyl transferase with myosteatosis assessed by muscle quality mapping using abdominal computed tomography
Han Na Jung, Yun Kyung Cho, Hwi Seung Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Joong-Yeol Park, Woo Je Lee, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Clinical Imaging.2023; 93: 4. CrossRef - More appendicular lean mass relative to body mass index is associated with lower incident diabetes in middle-aged adults in the CARDIA study
Melanie S. Haines, Aaron Leong, Bianca C. Porneala, Victor W. Zhong, Cora E. Lewis, Pamela J. Schreiner, Karen K. Miller, James B. Meigs, Mercedes R. Carnethon
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(1): 105. CrossRef - Association between hypertension and myosteatosis evaluated by abdominal computed tomography
Han Na Jung, Yun Kyung Cho, Hwi Seung Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Woo Je Lee, Hong-Kyu Kim, Chang Hee Jung
Hypertension Research.2023; 46(4): 845. CrossRef - Longitudinal association between adiposity changes and lung function deterioration
Youngmok Park, Jiyoung Kim, Young Sam Kim, Ah Young Leem, Jinyeon Jo, Kyungsoo Chung, Moo Suk Park, Sungho Won, Ji Ye Jung
Respiratory Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Relevance of body composition in phenotyping the obesities
Laura Salmón-Gómez, Victoria Catalán, Gema Frühbeck, Javier Gómez-Ambrosi
Reviews in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders.2023; 24(5): 809. CrossRef - Association of Visceral Fat Obesity, Sarcopenia, and Myosteatosis with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease without Obesity
Hong-Kyu Kim, Sung-Jin Bae, Min Jung Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Hana Park, Hwi Seung Kim, Yun Kyung Cho, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee, Jaewon Choe
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2023; 29(4): 987. CrossRef - Association between type 2 diabetes and skeletal muscle quality assessed by abdominal computed tomography scan
Eun Hee Kim, Hong‐Kyu Kim, Min Jung Lee, Sung‐Jin Bae, Kyung Won Kim, Jaewon Choe
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between fat mass index, fat‐free mass index and hemoglobin A1c in a Japanese population: The Tohoku Medical Megabank Community‐based Cohort Study
Masato Takase, Tomohiro Nakamura, Takumi Hirata, Naho Tsuchiya, Mana Kogure, Fumi Itabashi, Naoki Nakaya, Yohei Hamanaka, Junichi Sugawara, Kichiya Suzuki, Nobuo Fuse, Akira Uruno, Eiichi N Kodama, Shinichi Kuriyama, Ichiro Tsuji, Shigeo Kure, Atsushi Hoz
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(5): 858. CrossRef - Relationship between low skeletal muscle mass, sarcopenic obesity and left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in Korean adults
Jee Hee Yoo, Sung Woon Park, Ji Eun Jun, Sang‐Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Moon‐Kyu Lee, Mira Kang, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Reference Data and T-Scores of Lumbar Skeletal Muscle Area and Its Skeletal Muscle Indices Measured by CT Scan in a Healthy Korean Population
Eun Hee Kim, Kyung Won Kim, Yongbin Shin, Jiwoo Lee, Yousun Ko, Ye-Jee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Sung-Jin Bae, Sung Won Park, Jaewon Choe, Hong-Kyu Kim, Anne Newman
The Journals of Gerontology: Series A.2021; 76(2): 265. CrossRef - Age- and Sex-Related Differential Associations between Body Composition and Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Roh, Soon Young Hwang, Jung A Kim, You-Bin Lee, So-hyeon Hong, Nam Hoon Kim, Ji A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 183. CrossRef - Cardiometabolic Profile of Different Body Composition Phenotypes in Children
Yi Ying Ong, Jonathan Y Huang, Navin Michael, Suresh Anand Sadananthan, Wen Lun Yuan, Ling-Wei Chen, Neerja Karnani, S Sendhil Velan, Marielle V Fortier, Kok Hian Tan, Peter D Gluckman, Fabian Yap, Yap-Seng Chong, Keith M Godfrey, Mary F-F Chong, Shiao-Yn
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2021; 106(5): e2015. CrossRef - Age-related changes in muscle quality and development of diagnostic cutoff points for myosteatosis in lumbar skeletal muscles measured by CT scan
Hong-Kyu Kim, Kyung Won Kim, Eun Hee Kim, Min Jung Lee, Sung-Jin Bae, Yousun Ko, Taeyoung Park, Yongbin Shin, Ye-Jee Kim, Jaewon Choe
Clinical Nutrition.2021; 40(6): 4022. CrossRef - Comparison of muscle mass and quality between metabolically healthy and unhealthy phenotypes
Hong‐Kyu Kim, Min Jung Lee, Eun Hee Kim, Sung‐Jin Bae, Kyung Won Kim, Chul‐Hee Kim
Obesity.2021; 29(8): 1375. CrossRef - Association between muscle mass and insulin sensitivity independent of detrimental adipose depots in young adults with overweight/obesity
Melanie S. Haines, Laura E. Dichtel, Kate Santoso, Martin Torriani, Karen K. Miller, Miriam A. Bredella
International Journal of Obesity.2020; 44(9): 1851. CrossRef - Impact of Social Jetlag on Weight Change in Adults: Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2017
Jin Hwa Kim, Young Sang Lyu, Sang Yong Kim
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(12): 4383. CrossRef - The relationships between sarcopenic skeletal muscle loss during ageing and macronutrient metabolism, obesity and onset of diabetes
Ailsa A. Welch, Richard P. G. Hayhoe, Donnie Cameron
Proceedings of the Nutrition Society.2020; 79(1): 158. CrossRef - Impact of the Dynamic Change of Metabolic Health Status on the Incident Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Jung A Kim, Da Hye Kim, Seon Mee Kim, Yong Gyu Park, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi, Kyungdo Han, Hye Jin Yoo
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(4): 406. CrossRef
- Metabolically healthy obese individuals are still at high risk for diabetes: Application of the marginal structural model
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Proportion and Characteristics of the Subjects with Low Muscle Mass and Abdominal Obesity among the Newly Diagnosed and Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
- Jung A Kim, Soon Young Hwang, Hye Soo Chung, Nam Hoon Kim, Ji A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(1):105-113. Published online September 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0036
- 4,898 View
- 70 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Sarcopenic obesity (SO) is a serious public health concern, few studies have examined the clinical implications of SO in newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients. We evaluated the prevalence of the newly diagnosed, drug-naïve T2DM patients with low muscle mass with abdominal obesity and its association with insulin resistance and other diabetic complications.
Methods We classified 233 drug-naïve T2DM subjects into four groups according to abdominal obesity (waist circumference ≥90 cm in men and ≥85 cm in women) and low muscle mass status (appendicular skeletal muscle <7.0 kg/m2 for men and <5.4 kg/m2 for women).
Results The proportion of the subjects with low muscle mass and abdominal obesity among the newly diagnosed, drug-naïve T2DM patients was 8.2%. Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) increased linearly according to body composition group from normal to abdominal obesity to both low muscle mass and abdominal obesity. The multiple logistic regression analysis indicated that subjects with low muscle mass and abdominal obesity (odds ratio [OR], 9.39; 95% confidence interval [CI], 2.41 to 36.56) showed a higher risk for insulin resistance, defined as HOMA-IR ≥3, than those with abdominal obesity (OR, 5.36; 95% CI, 2.46 to 11.69), even after adjusting for other covariates. However, there were no differences in lipid profiles, microalbuminuria, or various surrogate markers for atherosclerosis among the four groups.
Conclusion Subjects with both low muscle mass and abdominal obesity had a higher risk of insulin resistance than those with low muscle mass or abdominal obesity only.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical observation on acupuncture for 80 patients with abdominal obesity in Germany: based on the theory of unblocking and regulating the Belt Vessel
Yuanyuan Li, Hang Xiong, Shuhui Ma, Jingzhang Dai
Journal of Acupuncture and Tuina Science.2023; 21(2): 137. CrossRef - Waist circumference and end‐stage renal disease based on glycaemic status: National Health Insurance Service data 2009–2018
Yun Kyung Cho, Ji Hye Huh, Shinje Moon, Yoon Jung Kim, Yang‐Hyun Kim, Kyung‐do Han, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung‐Hee Ihm
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(1): 585. CrossRef - Incidence of sarcopenic obesity in older patients with diabetes and association between sarcopenic obesity and higher-level functional capacity: evaluation based on a consensus statement
Satoshi Ida, Ryutaro Kaneko, Kanako Imataka, Kaoru Okubo, Kentaro Azuma, Kazuya Murata
Endocrine Journal.2023; 70(6): 591. CrossRef - A Novel Anthropometric Parameter, Weight-Adjusted Waist Index Represents Sarcopenic Obesity in Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Min Jeong Park, Soon Young Hwang, Nam Hoon Kim, Sin Gon Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 130. CrossRef - Prevalence of sarcopenic obesity in patients with diabetes and adverse outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Yuan-yuan Zhou, Jin-feng Wang, Qian Yao, Qiu-feng Jian, Zhi-peng Luo
Clinical Nutrition ESPEN.2023; 58: 128. CrossRef - The Correlation Between Leg Muscle Mass Index and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Menggege Liu, Qing Zhang, Juan Liu, Huiling Bai, Ping Yang, Xinhua Ye, Xiaoqing Yuan
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 4169. CrossRef - Sarcopenic Obesity with Normal Body Size May Have Higher Insulin Resistance in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Tingting Han, Ting Yuan, Xinyue Liang, Ningxin Chen, Jia Song, Xin Zhao, Yurong Weng, Yaomin Hu
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2022; Volume 15: 1197. CrossRef - Relationship between Visceral Adipose Index, Lipid Accumulation Product and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
停停 陈
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(04): 3350. CrossRef - Assessment of the relationship between prediabetes and low skeletal mass based on blood creatinine level
S. I. Ibragimova, G. O. Nuskabayeva, Z. N. Shalkharova, K. Zh. Sadykova, G. A. Junusbekova, M. Oran
Diabetes mellitus.2022; 25(3): 226. CrossRef - Changes in body composition and low blood urea nitrogen level related to an increase in the prevalence of fatty liver over 20 years: A cross‐sectional study
Yasushi Imamura, Seiichi Mawatari, Kohei Oda, Kotaro Kumagai, Yasunari Hiramine, Akiko Saishoji, Atsuko Kakihara, Mai Nakahara, Manei Oku, Kaori Hosoyamada, Shuji Kanmura, Akihiro Moriuchi, Hironori Miyahara, Akio ido
Hepatology Research.2021; 51(5): 570. CrossRef - Body Composition and Diabetes
Hye Jin Yoo
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2021; 22(4): 238. CrossRef - Reduced Skeletal Muscle Volume and Increased Skeletal Muscle Fat Deposition Characterize Diabetes in Individuals after Pancreatitis: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study
Andre E. Modesto, Juyeon Ko, Charlotte E. Stuart, Sakina H. Bharmal, Jaelim Cho, Maxim S. Petrov
Diseases.2020; 8(3): 25. CrossRef - Low alanine aminotransferase levels predict low muscle strength in older patients with diabetes: A nationwide cross‐sectional study in Korea
Seung Min Chung, Jun Sung Moon, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2020; 20(4): 271. CrossRef - Association between sarcopenic obesity and higher risk of type 2 diabetes in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Dima Khadra, Leila Itani, Hana Tannir, Dima Kreidieh, Dana El Masri, Marwan El Ghoch
World Journal of Diabetes.2019; 10(5): 311. CrossRef
- Clinical observation on acupuncture for 80 patients with abdominal obesity in Germany: based on the theory of unblocking and regulating the Belt Vessel
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Beneficial Effects of Aerobic Exercise Training Combined with Rosiglitazone on Glucose Metabolism in Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty Rats
- Shan-Ji Piao, So Hun Kim, Young Ju Suh, Seong-Bin Hong, Seong Hee Ahn, Da Hae Seo, In-Sun Park, Moonsuk Nam
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(6):474-485. Published online November 15, 2017
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.6.474
- 3,838 View
- 39 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Regular aerobic exercise is essential for the prevention and management of type 2 diabetes mellitus and may be particularly beneficial for those treated with thiazolidinediones, since it may prevent associated weight gain. This study aimed to evaluate the effect of combined exercise and rosiglitazone treatment on body composition and glucose metabolism in obese diabetes-prone animals.
Methods We analyzed metabolic parameters, body composition, and islet profiles in Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty rats after 28 weeks of aerobic exercise, rosiglitazone treatment, and combined exercise and rosiglitazone treatment.
Results Combined exercise with rosiglitazone showed significantly less increase in weight and epididymal fat compared to rosiglitazone treatment. Aerobic exercise alone and combined rosiglitazone and exercise treatment led to similar retention of lean body mass. All experimental groups showed a decrease in fasting glucose. However, the combined exercise and rosiglitazone therapy group showed prominent improvement in glucose tolerance compared to the other groups. Rescue of islet destruction was observed in all experimental groups, but was most prominent in the combined therapy group.
Conclusion Regular aerobic exercise combined with rosiglitazone treatment can compensate for the adverse effect of rosiglitazone treatment and has benefit for islet preservation.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impacts of an Exercise Intervention on the Health of Pancreatic Beta-Cells: A Review
Shuang Zhang, Yaru Wei, Chunxiao Wang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(12): 7229. CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms by which aerobic exercise induces insulin sensitivity
Habib Yaribeygi, Stephen L. Atkin, Luis E. Simental‐Mendía, Amirhossein Sahebkar
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2019; 234(8): 12385. CrossRef
- Impacts of an Exercise Intervention on the Health of Pancreatic Beta-Cells: A Review
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Relationship between Regional Body Fat Distribution and Diabetes Mellitus: 2008 to 2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys
- Soo In Choi, Dawn Chung, Jung Soo Lim, Mi Young Lee, Jang Yel Shin, Choon Hee Chung, Ji Hye Huh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(1):51-59. Published online December 21, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.1.51
- 4,176 View
- 42 Download
- 35 Web of Science
- 36 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The aim of this study was to investigate the association between regional body fat distribution, especially leg fat mass, and the prevalence of diabetes mellitus (DM) in adult populations.
Methods A total of 3,181 men and 3,827 postmenopausal women aged 50 years or older were analyzed based on Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (2008 to 2010). Body compositions including muscle mass and regional fat mass were measured using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry.
Results The odds ratios (ORs) for DM was higher with increasing truncal fat mass and arm fat mass, while it was lower with increasing leg fat mass. In a partial correlation analysis adjusted for age, leg fat mass was negatively associated with glycosylated hemoglobin in both sexes and fasting glucose in women. Leg fat mass was positively correlated with appendicular skeletal muscle mass and homeostasis model assessment of β cell. In addition, after adjusting for confounding factors, the OR for DM decreased gradually with increasing leg fat mass quartiles in both genders. When we subdivided the participants into four groups based on the median values of leg fat mass and leg muscle mass, higher leg fat mass significantly lowered the risk of DM even though they have smaller leg muscle mass in both genders (
P <0.001).Conclusion The relationship between fat mass and the prevalence of DM is different according to regional body fat distribution. Higher leg fat mass was associated with a lower risk of DM in Korean populations. Maintaining leg fat mass may be important in preventing impaired glucose tolerance.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of chromium supplementation on body composition in patients with type 2 diabetes: A dose-response systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Mahdi Vajdi, Mahsa khajeh, Ehsan Safaei, Seyedehelham Moeinolsadat, Samin Mousavi, Hooria Seyedhosseini-Ghaheh, Mahdieh Abbasalizad-Farhangi, Gholamreza Askari
Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology.2024; 81: 127338. CrossRef - Connections between body composition and dysregulation of islet α- and β-cells in type 2 diabetes
Jia-xi Miao, Jia-ping Xu, Rui Wang, Yu-xian Xu, Feng Xu, Chun-hua Wang, Chao Yu, Dong-mei Zhang, Jian-bin Su
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Anthropometric and DXA-derived measures of body composition in relation to pre-diabetes among adults
Anwar Mohammad, Ali H. Ziyab, Talal Mohammad
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2023; 11(5): e003412. CrossRef - A cohort study on the predictive capability of body composition for diabetes mellitus using machine learning
Mohammad Ali Nematollahi, Amir Askarinejad, Arefeh Asadollahi, Mehdi Bazrafshan, Shirin Sarejloo, Mana Moghadami, Sarvin Sasannia, Mojtaba Farjam, Reza Homayounfar, Babak Pezeshki, Mitra Amini, Mohamad Roshanzamir, Roohallah Alizadehsani, Hanieh Bazrafsha
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Which is the best diet to reduce cardiometabolic risk: dietary counseling or home-delivered diet?
Feray Çağiran Yilmaz, Aysun Atilgan, Günay Saka
Food & Nutrition Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sedentary lifestyle and body composition in type 2 diabetes
Dan-dan Li, Yang Yang, Zi-yi Gao, Li-hua Zhao, Xue Yang, Feng Xu, Chao Yu, Xiu-lin Zhang, Xue-qin Wang, Li-hua Wang, Jian-bin Su
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Impaired Lung Function and Lung Cancer Incidence: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
Hye Seon Kang, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Seung Hoon Kim, Shin Young Kim, Chi Hong Kim, Kyungdo Han, Sung Kyoung Kim
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(4): 1077. CrossRef - Association between lung function and the risk of atrial fibrillation in a nationwide population cohort study
Su Nam Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko, Sung-Ho Her, Kyungdo Han, Donggyu Moon, Sung Kyoung Kim, Ki-Dong Yoo, Yu-Bae Ahn
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Is imaging-based muscle quantity associated with risk of diabetes? A meta-analysis of cohort studies
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Yang Yuan, Bo Xie, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 189: 109939. CrossRef - Research Progress of Body Composition Changes in Type 2 Diabetes Patients
鹏霞 张
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2022; 12(08): 7181. CrossRef - Associations of eating speed with fat distribution and body shape vary in different age groups and obesity status
Saili Ni, Menghan Jia, Xuemiao Wang, Yun Hong, Xueyin Zhao, Liang Zhang, Yuan Ru, Fei Yang, Shankuan Zhu
Nutrition & Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Body composition, trabecular bone score and vertebral fractures in subjects with Klinefelter syndrome
W. Vena, F. Carrone, A. Delbarba, O. Akpojiyovbi, L. C. Pezzaioli, P. Facondo, C. Cappelli, L. Leonardi, L. Balzarini, D. Farina, A. Pizzocaro, A. G. Lania, G. Mazziotti, A. Ferlin
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2022; 46(2): 297. CrossRef - Genetically predicted body fat mass and distribution with diabetic kidney disease: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study
Min Wang, Xin Li, Hang Mei, Zhao-Hui Huang, Yue Liu, Yong-Hong Zhu, Tian-Kui Ma, Qiu-Ling Fan
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Screening for Prediabetes and Diabetes in Korean Nonpregnant Adults: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2022
Kyung Ae Lee, Dae Jung Kim, Kyungdo Han, Suk Chon, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 819. CrossRef - Age- and Sex-Related Differential Associations between Body Composition and Diabetes Mellitus
Eun Roh, Soon Young Hwang, Jung A Kim, You-Bin Lee, So-hyeon Hong, Nam Hoon Kim, Ji A Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 183. CrossRef - Neck circumference and metabolic syndrome: A cross-sectional population-based study
Hooman Ebrahimi, Payam Mahmoudi, Farhad Zamani, Sedighe Moradi
Primary Care Diabetes.2021; 15(3): 582. CrossRef - Development of a clinical risk score for incident diabetes: A 10‐year prospective cohort study
Tae Jung Oh, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Young Min Cho, Kyong Soo Park, Nam H Cho, Hak Chul Jang
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(4): 610. CrossRef - The association of glucocorticoid receptor polymorphism with metabolic outcomes in menopausal women with adrenal incidentalomas
Sanja Ognjanović, Jadranka Antić, Tatjana Pekmezović, Bojana Popović, Tatjana Isailović, Ivana Božić Antić, Tamara Bogavac, Valentina Elezović Kovačević, Dušan Ilić, Milica Opalić, Djuro Macut
Maturitas.2021; 151: 15. CrossRef - Distinct opposing associations of upper and lower body fat depots with metabolic and cardiovascular disease risk markers
Mahasampath Gowri S, Belavendra Antonisamy, Finney S. Geethanjali, Nihal Thomas, Felix Jebasingh, Thomas V. Paul, Fredrik Karpe, Clive Osmond, Caroline H. D. Fall, Senthil K. Vasan
International Journal of Obesity.2021; 45(11): 2490. CrossRef - Body Roundness Index Is a Superior Obesity Index in Predicting Diabetes Risk Among Hypertensive Patients: A Prospective Cohort Study in China
Yingshan Liu, Xiaocong Liu, Haixia Guan, Shuting Zhang, Qibo Zhu, Xiaoying Fu, Hongmei Chen, Songtao Tang, Yingqing Feng, Jian Kuang
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Subcutaneous adipose tissue distribution and serum lipid/lipoprotein in unmedicated postmenopausal women: A B-mode ultrasound study
Imaging.2021; 13(2): 119. CrossRef - The Leg Fat to Total Fat Ratio Is Associated with Lower Risks of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Less Severe Hepatic Fibrosis: Results from Nationwide Surveys (KNHANES 2008–2011)
Hyun Min Kim, Yong-ho Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(6): 1232. CrossRef Optimal Cut-Offs of Body Mass Index and Waist Circumference to Identify Obesity in Chinese Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Qinying Zhao, Xiangjun Chen, Jinshan Wu, Lilin Gong, Jinbo Hu, Shumin Yang, Qifu Li, Zhihong Wang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 1899. CrossRef- Weight Loss after 12 Weeks of Exercise and/or Nutritional Guidance Is Not Obligatory for Induced Changes in Local Fat/Lean Mass Indexes in Adults with Excess of Adiposity
Robinson Ramírez-Vélez, Mikel Izquierdo, Karem Castro-Astudillo, Carolina Medrano-Mena, Angela Liliana Monroy-Díaz, Rocío del Pilar Castellanos-Vega, Héctor Reynaldo Triana-Reina, María Correa-Rodríguez
Nutrients.2020; 12(8): 2231. CrossRef - VISCERAL FAT, PHYSICAL FITNESS AND BIOCHEMICAL MARKERS OF BRAZILIAN MILITARY PERSONNEL
Laércio Camilo Rodrigues, Marcos de Sá Rego Fortes, Marco Antônio Muniz Lippert, Samir Ezequiel Da Rosa, José Fernandes Filho
Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte.2020; 26(1): 21. CrossRef - Comparison of 7-site skinfold measurement and dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry for estimating body fat percentage and regional adiposity in Taiwanese diabetic patients
Feng-Chih Kuo, Chieh-Hua Lu, Li-Wei Wu, Tung-Wei Kao, Sheng-Chiang Su, Jhih-Syuan Liu, Kuan-Chan Chen, Chia-Hao Chang, Chih-Chun Kuo, Chien-Hsing Lee, Chang-Hsun Hsieh, Mauro Lombardo
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(7): e0236323. CrossRef - Outcomes specific to patient sex after open ventral hernia repair
Kathryn A. Schlosser, Sean R. Maloney, Otto Thielan, Tanushree Prasad, Kent Kercher, Paul D. Colavita, B Todd Heniford, Vedra A. Augenstein
Surgery.2020; 167(3): 614. CrossRef Age-Related Changes in Body Composition and Bone Mineral Density and Their Relationship with the Duration of Diabetes and Glycaemic Control in Type 2 Diabetes
Ying Tang, Lilin Gong, Xiangjun Chen, Zhipeng Du, Jinbo Hu, Zhixin Xu, Jinshan Wu, Qifu Li, Zhihong Wang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4699. CrossRef- Lipodystrophy: A paradigm for understanding the consequences of "overloading" adipose tissue
Koini Lim, Afreen Haider, Claire Adams, Alison Sleigh, David Savage
Physiological Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Premeal Consumption of a Protein-Enriched, Dietary Fiber-Fortified Bar Decreases Total Energy Intake in Healthy Individuals
Chang Ho Ahn, Jae Hyun Bae, Young Min Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 879. CrossRef - Differences in dietary intakes, body compositions, and biochemical indices between metabolically healthy and metabolically abnormal obese Korean women
Eun Yeong Kang, Jung-Eun Yim
Nutrition Research and Practice.2019; 13(6): 488. CrossRef - The Association between Body Composition using Dual energy X-ray Absorptiometry and Type-2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Observational studies
Preeti Gupta, Carla Lanca, Alfred T. L. Gan, Pauline Soh, Sahil Thakur, Yijin Tao, Neelam Kumari, Ryan E. K. Man, Eva K. Fenwick, Ecosse L. Lamoureux
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Genes that make you fat, but keep you healthy
R. J. F. Loos, T. O. Kilpeläinen
Journal of Internal Medicine.2018; 284(5): 450. CrossRef - Overview of Epidemiology and Contribution of Obesity and Body Fat Distribution to Cardiovascular Disease: An Update
Marie-Eve Piché, Paul Poirier, Isabelle Lemieux, Jean-Pierre Després
Progress in Cardiovascular Diseases.2018; 61(2): 103. CrossRef - Relevance of human fat distribution on lipid and lipoprotein metabolism and cardiovascular disease risk
Marie-Eve Piché, Senthil K. Vasan, Leanne Hodson, Fredrik Karpe
Current Opinion in Lipidology.2018; 29(4): 285. CrossRef - Comparison of regional fat measurements by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry and conventional anthropometry and their association with markers of diabetes and cardiovascular disease risk
S K Vasan, C Osmond, D Canoy, C Christodoulides, M J Neville, C Di Gravio, C H D Fall, F Karpe
International Journal of Obesity.2018; 42(4): 850. CrossRef
- Effects of chromium supplementation on body composition in patients with type 2 diabetes: A dose-response systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Effects of Body Weight Reduction on Serum Irisin and Metabolic Parameters in Obese Subjects
- Yaeko Fukushima, Satoshi Kurose, Hiromi Shinno, Ha Cao Thi Thu, Nana Takao, Hiromi Tsutsumi, Takaaki Hasegawa, Toshiaki Nakajima, Yutaka Kimura
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(5):386-395. Published online September 27, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.5.386
- 5,085 View
- 42 Download
- 30 Web of Science
- 28 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Irisin is a myokine implicated in lipid and glucose metabolism. The objective of this study is to examine the effect of a body weight reduction on the serum irisin level and physical indicators in obese Japanese patients without diabetes.
Methods The subjects were 22 patients (male/female, 5/17; age, 46.1±16.0 years; body mass index [BMI], 36.9±5.0 kg/m2) who completed a 6-month body weight reduction program at our clinic. The program included diet, exercise therapy and cognitive behavioral therapy. Blood parameters, body composition, exercise tolerance, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), and serum irisin were determined before and after intervention, and relationships among changes in these data were examined.
Results There were significant decreases in body weight and BMI after the intervention. Irisin before the intervention was significantly positively correlated with HOMA-IR (
r =0.434,P <0.05). The mean irisin level showed no significant change after the intervention in all participants. However, improvements in % body fat, subcutaneous fat area, triglycerides, and fasting glucose were significantly greater in patients with an increase in irisin compared to those with a decrease in irisin after the intervention. Patients with an increase in irisin also had significantly lower fasting insulin (9.7±4.8 vs. 16.4±8.2,P <0.05) and HOMA-IR (2.2±1.1 vs. 3.7±1.6,P <0.05) after the intervention, compared to patients with a decrease in irisin.Conclusion Body weight reduction did not alter irisin levels. However, irisin may play important roles in fat and glucose metabolism and insulin resistance, and the effects of body weight reduction on irisin kinetics may be a key for obesity treatment.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effects of 12-Week Tabata Training on Selected Health-Related Fitness Component in Healthy Untrained Students from Malaysia
N. M. Sukri, A. Ahmad, N. A. Roos, M. F. Nordin, F. N. Halim, J. V. Gnanou, F. A. Manaf
Journal of Science in Sport and Exercise.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlations between serum testosterone and irisin levels in a sample of Egyptian men with metabolic syndrome; (case-control study)
Inass Hassan Ahmad, Eman Roshdy Mohamed Mostafa, Shymaa Abdelhafeez Mohammed, Walaa Shipl, Amany Ahmed Soliman, Marwa Said
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2023; 129(1): 180. CrossRef - The Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Irisin Level: a Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Matin Bidares, Borna Safari-kish, Motahare Abedi, Hesam Malekzadeh-shoushtari, Malek Jasemnezhad, Niloufar Azarbayejani, Mahsa Aziz, Sayna Pejouhesh Jahromi, Samar Fouladi, Fatemeh Azizi-Soleiman
Obesity Surgery.2023; 33(10): 3256. CrossRef - Recent Advances in Nutraceuticals for the Treatment of Sarcopenic Obesity
Young-Chan Kim, Sang-Woo Ki, Hannah Kim, Sumin Kang, Hayoon Kim, Gwang-woong Go
Nutrients.2023; 15(17): 3854. CrossRef - Effect of Eccentric Exercise on Metabolic Health in Diabetes and Obesity
Gergő Szűcs, Márton Pipicz, Márton Richárd Szabó, Tamás Csont, László Török, Csaba Csonka
Sports Medicine - Open.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - An early prediction model for gestational diabetes mellitus based on genetic variants and clinical characteristics in China
Qi Wu, Yanmin Chen, Menglin Zhou, Mengting Liu, Lixia Zhang, Zhaoxia Liang, Danqing Chen
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of vaspin and irisin hormones levels in diabetic rats and relationship with diet
Sergen Tuğgüm, Çiğdem Bozkır, Serkan Aslan, Ahsen Yılmaz, Aliye Çelikkol
Mediterranean Journal of Nutrition and Metabolism.2022; 15(3): 419. CrossRef - Biological Response of Irisin Induced by Different Types of Exercise in Obese Subjects: A Non-Inferiority Controlled Randomized Study
Andrea D’Amuri, Valeria Raparelli, Juana Maria Sanz, Eleonora Capatti, Francesca Di Vece, Filippo Vaccari, Stefano Lazzer, Giovanni Zuliani, Edoardo Dalla Nora, Luca Maria Neri, Angelina Passaro
Biology.2022; 11(3): 392. CrossRef - The role of exercise-induced myokines in promoting angiogenesis
Chao Qi, Xianjing Song, He Wang, Youyou Yan, Bin Liu
Frontiers in Physiology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of companion-intensive multi-aspect weight management in Chinese adults with obesity: a 6-month multicenter randomized clinical trial
Wanzi Jiang, Shushu Huang, Shuai Ma, Yingyun Gong, Zhenzhen Fu, Li Zhou, Wen Hu, Guofang Mao, Zhimin Ma, Ling Yang, Guangfeng Tang, Xiaofang Sun, Ping Zhang, Jianling Bai, Lei Chen, Bimin Shi, Xinhua Ye, Hongwen Zhou
Nutrition & Metabolism.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Progress and Challenges in the Biology of FNDC5 and Irisin
Steffen Maak, Frode Norheim, Christian A Drevon, Harold P Erickson
Endocrine Reviews.2021; 42(4): 436. CrossRef - Role of Irisin in Endocrine and Metabolic Disorders—Possible New Therapeutic Agent?
Letitia Leustean, Cristina Preda, Laura Teodoriu, Laura Mihalache, Lidia Arhire, Maria-Christina Ungureanu
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(12): 5579. CrossRef - The Physiological Role of Irisin in the Regulation of Muscle Glucose Homeostasis
Naohiro Yano, Yu Tina Zhao, Ting C. Zhao
Endocrines.2021; 2(3): 266. CrossRef - Irisin, interleukin-33 and interleukin-37 in patients with ischemic heart disease and obesity
Yuliia Kovalova, Nataliia Sukhonos, Valeriia Brek, Kateryna Smolianyk
Medicinski casopis.2021; 55(3): 87. CrossRef - Synergism Effects of Ursolic Acid Supplementation on the Levels of Irisin, C-reactive Protein, IL-6, and TNF-α During High-intensity Resistance Training in Low Activity Men
Ehsan Asghari, Amir Rashidlamir, Seyyed R.A. Hosseini, Mahtab Moazzami, Saeed Samarghandian, Tahereh Farkhondeh
Cardiovascular & Hematological Disorders-Drug Targets .2020; 20(2): 138. CrossRef - Exercise-Induced Circulating Irisin Level Is Correlated with Improved Cardiac Function in Rats
Dae Yun Seo, Jun Hyun Bae, Tae Nyun Kim, Hyo-Bum Kwak, Pham Trong Kha, Jin Han
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(11): 3863. CrossRef - Effect of HIIT with Tabata Protocol on Serum Irisin, Physical Performance, and Body Composition in Men
Eugenia Murawska-Cialowicz, Pawel Wolanski, Jolanta Zuwala-Jagiello, Yuri Feito, Miroslav Petr, Jakub Kokstejn, Petr Stastny, Dawid Goliński
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(10): 3589. CrossRef - Serum Irisin, Adropin, and Preptin in Obese Patients 6 Months After Bariatric Surgery
M. Glück, J. Glück, M. Wiewióra, B. Rogala, J. Piecuch
Obesity Surgery.2019; 29(10): 3334. CrossRef - A Novel Interplay Between Irisin and PTH: From Basic Studies to Clinical Evidence in Hyperparathyroidism
Andrea Palermo, Lorenzo Sanesi, Graziana Colaianni, Gaia Tabacco, Anda Mihaela Naciu, Roberto Cesareo, Claudio Pedone, Diana Lelli, Giacomina Brunetti, Giorgio Mori, Silvia Colucci, Silvia Manfrini, Nicola Napoli, Maria Grano
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2019; 104(8): 3088. CrossRef - Irisin interaction with adipose tissue secretions by exercise training and flaxseed oil supplement
Hossein Shirvani, Saleh Rahmati-Ahmadabad
Lipids in Health and Disease.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Eccentric resistance training and β-Hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate free acid affects muscle PGC-1α expression and serum irisin, nesfatin-1 and resistin
Hossein Shirvani, Saleh Rahmati-Ahmadabad, David Robert Broom, Reza Mirnejad
Journal of Experimental Biology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Colostrum and mature breast milk analysis of serum irisin and sterol regulatory element-binding proteins-1c in gestational diabetes mellitus
Syeda Sadia Fatima, Erum Khalid, Asma Akbar Ladak, Syed Adnan Ali
The Journal of Maternal-Fetal & Neonatal Medicine.2019; 32(18): 2993. CrossRef - The influence of bariatric surgery on serum levels of irisin and nesfatin-1
Marta Majorczyk, Magdalena Staszkiewicz, Joanna Szklarczyk, Piotr Major, Magdalena Pisarska, Michał Wysocki, Tomasz Stefura, Artur Kacprzyk, Jakub Droś, Mateusz K. Hołda, Michał Pędziwiatr, Andrzej Budzyński, Jolanta Jaworek
Acta Chirurgica Belgica.2019; 119(6): 363. CrossRef - Increase in relative skeletal muscle mass over time and its inverse association with metabolic syndrome development: a 7-year retrospective cohort study
Gyuri Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Ji Eun Jun, You-Bin Lee, Jiyeon Ahn, Ji Cheol Bae, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hwan Jee, Moon-Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of serum concentrations of irisin and the adipokines adiponectin and leptin with epicardial fat in cardiovascular surgery patients
Hiroyuki Kaneda, Toshiaki Nakajima, Akiko Haruyama, Ikuko Shibasaki, Takaaki Hasegawa, Tatsuya Sawaguchi, Toshiyuki Kuwata, Syoutarou Obi, Takuo Arikawa, Masashi Sakuma, Hirohisa Amano, Shigeru Toyoda, Hirotsugu Fukuda, Teruo Inoue, Luca Vanella
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(8): e0201499. CrossRef - Relationship Between Relative Skeletal Muscle Mass and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 7‐Year Longitudinal Study
Gyuri Kim, Seung‐Eun Lee, You‐Bin Lee, Ji Eun Jun, Jiyeon Ahn, Ji Cheol Bae, Sang‐Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hwan Jee, Moon‐Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Hepatology.2018; 68(5): 1755. CrossRef - Effect of exercise on concentrations of irisin in overweight individuals: A systematic review
P. Amaro Andrade, B.K. Souza Silveira, A. Corrêa Rodrigues, F.M. Oliveira da Silva, C.O. Barbosa Rosa, R.C. Gonçalves Alfenas
Science & Sports.2018; 33(2): 80. CrossRef - Is irisin the new player in exercise-induced adaptations or not? A 2017 update
Ioannis G. Fatouros
Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM).2018; 56(4): 525. CrossRef
- Effects of 12-Week Tabata Training on Selected Health-Related Fitness Component in Healthy Untrained Students from Malaysia
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Importance of Lean Muscle Maintenance to Improve Insulin Resistance by Body Weight Reduction in Female Patients with Obesity
- Yaeko Fukushima, Satoshi Kurose, Hiromi Shinno, Ha Cao Thu, Nana Takao, Hiromi Tsutsumi, Yutaka Kimura
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(2):147-153. Published online March 27, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.2.147
- 3,576 View
- 48 Download
- 29 Web of Science
- 28 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background It has recently been suggested that skeletal muscle has an important role in insulin resistance in obesity, in addition to exercise tolerance and the fat index. The aim of this study was to identify body composition factors that contribute to improvement of insulin resistance in female patients with obesity who reduce body weight.
Methods We studied 92 female obese patients (age 40.9±10.4 years, body mass index 33.2±4.6 kg/m2) who reduced body weight by ≥5% after an intervention program including diet, exercise therapy, and cognitive behavioral therapy. Before and after the intervention, body composition was evaluated by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry to examine changes in skeletal muscle mass. Homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) was measured as an index of insulin resistance. Cardiopulmonary exercise was also performed by all patients.
Results There were significant improvements in body weight (–10.3%±4.5%), exercise tolerance (anaerobic threshold oxygen uptake 9.1%±18.4%, peak oxygen uptake 11.0%±14.2%), and HOMA-IR (–20.2%±38.3%). Regarding body composition, there were significant decreases in total body fat (–19.3%±9.6%), total fat-free mass (–2.7%±4.3%), and % body fat (–10.1%±7.5%), whereas % skeletal muscle significantly increased (8.9%±7.2%). In stepwise multiple linear regression analysis with change in HOMA-IR as the dependent variable, the change in % skeletal muscle was identified as an independent predictor (β=–0.280,
R 2=0.068,P <0.01).Conclusion Improvement of insulin resistance in female obese patients requires maintenance of skeletal muscle mass.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Sarcopenia prevalence between obese and morbid obese patients in an obesity center
Mujgan Tuna, Arzu Cennet Işık , Ozlem Hürmeydan
Journal of Surgery and Medicine.2024; 8(4): 73. CrossRef - Dietary behaviour change intervention for managing sarcopenic obesity among community-dwelling older people: a pilot randomised controlled trial
Yue-Heng Yin, Justina Yat Wa Liu, Maritta Välimäki
BMC Geriatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diet and Exercise in the Management of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome: Practical Considerations for Person-Centered Care
Giorgia E. Colombo, Stephanie Pirotta, Angelo Sabag
Seminars in Reproductive Medicine.2023; 41(01/02): 026. CrossRef - Effect of Mobility Restrictions During the Coronavirus Disease Epidemic on Body Composition and Exercise Tolerance in Patients With Obesity: Single Institutional Retrospective Cohort Study
Yoshinari Matsumoto, Satoshi Kurose, Takumi Miyauchi, Sawako Yoshiuchi, Daiki Habu, Yutaka Kimura
Journal of Physical Activity and Health.2022; 19(5): 351. CrossRef - Interrelationship of Gut Microbiota, Obesity, Body Composition and Insulin Resistance in Asians with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Che-Sheng Pai, Cheng-Yuan Wang, Wei-Wen Hung, Wei-Chun Hung, Hui-Ju Tsai, Chen-Chia Chang, Shang-Jyh Hwang, Chia-Yen Dai, Wen-Yu Ho, Yi-Chun Tsai
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2022; 12(4): 617. CrossRef - Exercise and Nutrition Strategies for Combating Sarcopenia and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Older Adults
Dionysia Argyropoulou, Nikolaos D. Geladas, Tzortzis Nomikos, Vassilis Paschalis
Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology.2022; 7(2): 48. CrossRef - Branched-Chain and Aromatic Amino Acids in Relation to Fat Mass and Fat-Free Mass Changes among Adolescents: A School-Based Intervention
Magnoudewa Priscille Pana, Pierre Ayotte, Elhadji Anassour-Laouan-Sidi, Edouard Suhas, Clémence Mahana Iti Gatti, Michel Lucas
Metabolites.2022; 12(7): 589. CrossRef - Exercising for Insulin Sensitivity – Is There a Mechanistic Relationship With Quantitative Changes in Skeletal Muscle Mass?
Jasmine Paquin, Jean-Christophe Lagacé, Martin Brochu, Isabelle J. Dionne
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The relationship between changes in serum myostatin and adiponectin levels in patients with obesity undergoing a weight loss program
Nana Takao, Satoshi Kurose, Takumi Miyauchi, Katsuko Onishi, Atsuko Tamanoi, Ryota Tsuyuguchi, Aya Fujii, Sawako Yoshiuchi, Kazuhisa Takahashi, Hiromi Tsutsumi, Yutaka Kimura
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise induces favorable metabolic changes in white adipose tissue preventing high‐fat diet obesity
Babu R. Maharjan, Sergio F. Martinez‐Huenchullan, Susan V. Mclennan, Stephen M. Twigg, Paul F. Williams
Physiological Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN INSULIN RESISTANCE AND FA-TIGUE SYMPTOM IN FIBROMYALGIA SYNDROME
Türkan Turgay, Zekiye İpek Katirci Kirmaci, Pınar Günel Karadeniz, Mehmet Baştemir
International Journal of Research -GRANTHAALAYAH.2020; 8(3): 271. CrossRef - Epicardial adipose tissue is tightly associated with exercise intolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus with asymptomatic left ventricular structural and functional abnormalities
Yousuke Sugita, Katsuhiko Ito, Shigeki Sakurai, Satoshi Sakai, Shinya Kuno
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2020; 34(5): 107552. CrossRef - Dose Frequency Optimization of the Dual Amylin and Calcitonin Receptor Agonist KBP-088: Long-Lasting Improvement in Food Preference and Body Weight Loss
Anna Thorsø Larsen, Nina Sonne, Kim V. Andreassen, Morten A. Karsdal, Kim Henriksen
Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.2020; 373(2): 269. CrossRef - Healthy dietary pattern and their corresponding gut microbiota profile are linked to a lower risk of type 2 diabetes, independent of the presence of obesity
D.A. Díaz-Rizzolo, B. Kostov, M. López-Siles, A. Serra, C. Colungo, L. González-de-Paz, M. Martinez-Medina, A. Sisó-Almirall, R. Gomis
Clinical Nutrition.2020; 39(2): 524. CrossRef Changes in Body Composition and FTO Whole Blood DNA Methylation Among Japanese Women: A Randomized Clinical Trial of Weight-Loss Program
Haruhiko Nishida, Katsuko Onishi, Satoshi Kurose, Hiromi Tsutsumi, Takumi Miyauchi, Nana Takao, Sawako Yoshiuchi, Aya Fujii, Yutaka Kimura
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 2157. CrossRef- Effects of low skeletal muscle mass and sarcopenic obesity on albuminuria: a 7-year longitudinal study
Jee Hee Yoo, Gyuri Kim, Sung Woon Park, Min Sun Choi, Jiyeon Ahn, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Moon-Kyu Lee, Mira Kang, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of body weight loss program on parameters of muscle performance in female obese adults
Gian Pietro Emerenziani, Dafne Ferrari, Silvia Migliaccio, Andrea Lenzi, Emanuela A. Greco, Chiara Marocco, Carlo Baldari, Laura Guidetti
The Journal of Sports Medicine and Physical Fitness.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Reduced Lean Body Mass and Cardiometabolic Diseases in Adult Males with Overweight and Obesity: A Pilot Study
Shirine Khazem, Leila Itani, Dima Kreidieh, Dana El Masri, Hana Tannir, Roberto Citarella, Marwan El Ghoch
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2018; 15(12): 2754. CrossRef - Physical performance measures in screening for reduced lean body mass in adult females with obesity
M. El Ghoch, A.P. Rossi, S. Calugi, S. Rubele, F. Soave, M. Zamboni, E. Chignola, G. Mazzali, P.V. Bazzani, R. Dalle Grave
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2018; 28(9): 917. CrossRef - Testosterone a key factor in gender related metabolic syndrome
V. E. Bianchi, V. Locatelli
Obesity Reviews.2018; 19(4): 557. CrossRef - Burly1 is a mouse QTL for lean body mass that maps to a 0.8-Mb region of chromosome 2
Cailu Lin, Brad D. Fesi, Michael Marquis, Natalia P. Bosak, Anna Lysenko, Mohammed Amin Koshnevisan, Fujiko F. Duke, Maria L. Theodorides, Theodore M. Nelson, Amanda H. McDaniel, Mauricio Avigdor, Charles J. Arayata, Lauren Shaw, Alexander A. Bachmanov, D
Mammalian Genome.2018; 29(5-6): 325. CrossRef - Hypoxic Training Improves Normoxic Glucose Tolerance in Adolescents with Obesity
ESTELLE DE GROOTE, FLORIAN A. BRITTO, LOÏC BULLOCK, MARIE FRANÇOIS, CARINE DE BUCK, HENRI NIELENS, LOUISE DELDICQUE
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise.2018; 50(11): 2200. CrossRef - Lipid modulation of skeletal muscle mass and function
Christopher Lipina, Harinder S Hundal
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2017; 8(2): 190. CrossRef - Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Ins/Del Polymorphism and Body Composition: The Intermediary Role of Hydration Status
Laura Bordoni, Valerio Napolioni, Francesca Marchegiani, Emilio Amadio, Rosita Gabbianelli
Lifestyle Genomics.2017; 10(1-2): 1. CrossRef - Influence of segmental body composition and adiposity hormones on resting metabolic rate and substrate utilization in overweight and obese adults
K. R. Hirsch, A. E. Smith-Ryan, M. N. M. Blue, M. G. Mock, E. T. Trexler
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2017; 40(6): 635. CrossRef - Carbohydrate-Restriction with High-Intensity Interval Training: An Optimal Combination for Treating Metabolic Diseases?
Monique E. Francois, Jenna B. Gillen, Jonathan P. Little
Frontiers in Nutrition.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Mediterranean diet and mortality risk in metabolically healthy obese and metabolically unhealthy obese phenotypes
Y-M Park, S E Steck, T T Fung, J Zhang, L J Hazlett, K Han, A T Merchant
International Journal of Obesity.2016; 40(10): 1541. CrossRef - Effects of Body Weight Reduction on Serum Irisin and Metabolic Parameters in Obese Subjects
Yaeko Fukushima, Satoshi Kurose, Hiromi Shinno, Ha Cao Thi Thu, Nana Takao, Hiromi Tsutsumi, Takaaki Hasegawa, Toshiaki Nakajima, Yutaka Kimura
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(5): 386. CrossRef
- Sarcopenia prevalence between obese and morbid obese patients in an obesity center
- Relative Skeletal Muscle Mass Is Associated with Development of Metabolic Syndrome
- Byung Sam Park, Ji Sung Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(6):458-464. Published online December 12, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.6.458
- 5,629 View
- 104 Download
- 73 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Visceral adiposity is related to insulin resistance. Skeletal muscle plays a central role in insulin-mediated glucose disposal; however, little is known about the association between muscle mass and metabolic syndrome (MS). This study is to clarify the clinical role of skeletal muscle mass in development of MS.
Methods A total of 1,042 subjects were enrolled. Subjects with prior MS and chronic diseases were excluded. After 24 months, development of MS was assessed using NCEP-ATP III criteria. Skeletal muscle mass (SMM; kg), body fat mass (BFM; kg), and visceral fat area (VFA; cm2) were obtained from bioelectrical analysis. Then, the following values were calculated as follows: percent of SMM (SMM%; %): SMM (kg)/weight (kg), skeletal muscle index (SMI; kg/m2): SMM (kg)/height (m2), skeletal muscle to body fat ratio (MFR): SMM (kg)/BFM (kg), and skeletal muscle to visceral fat ratio (SVR; kg/cm2): SMM (kg)/VFA (cm2).
Results Among 838 subjects, 88 (10.5%) were newly diagnosed with MS. Development of MS increased according to increasing quintiles of BMI, SMM, VFA, and SMI, but was negatively associated with SMM%, MFR, and SVR. VFA was positively associated with high waist circumference (WC), high blood pressure (BP), dysglycemia, and high triglyceride (TG). In contrast, MFR was negatively associated with high WC, high BP, dysglycemia, and high TG. SVR was negatively associated with all components of MS.
Conclusion Relative SMM ratio to body composition, rather than absolute mass, may play a critical role in development of MS and could be used as a strong predictor.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between adiponectin and muscle mass in patients with metabolic syndrome and obesity
Daniel de Luis, David Primo, Olatz Izaola, Juan José Lopez Gomez
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2024; 38(4): 108706. CrossRef - The longitudinal association of adipose-to-lean ratio with incident cardiometabolic morbidity: The CARDIA study
Robert Booker, Mandy Wong, Michael P. Bancks, Mercedes R. Carnethon, Lisa S. Chow, Cora E. Lewis, Pamela J. Schreiner, Shaina J. Alexandria
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2024; 38(5): 108725. CrossRef - Assessing Sarcopenic Obesity Risk in Children During the COVID-19 Pandemic: Grip-to-BMI Ratio
Bahar Öztelcan Gündüz, Aysu Duyan Çamurdan, Mücahit Yıldız, F. Nur Baran Aksakal, Emine Nüket Ünsal
Medical Research Reports.2024; 7(1): 18. CrossRef - Sex differences in body composition in youth with type 1 diabetes and its predictive value in cardiovascular disease risk assessment
Avivit Brener, Sandy Hamama, Hagar Interator, Asaf Ben Simon, Irina Laurian, Anna Dorfman, Efrat Chorna, Michal Yackobovitch‐Gavan, Asaf Oren, Ori Eyal, Yael Lebenthal
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiological, mechanistic, and practical bases for assessment of cardiorespiratory fitness and muscle status in adults in healthcare settings
Jaime A. Gallo-Villegas, Juan C. Calderón
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2023; 123(5): 945. CrossRef - The Effect of Childhood Obesity or Sarcopenic Obesity on Metabolic Syndrome Risk in Adolescence: The Ewha Birth and Growth Study
Hyunjin Park, Seunghee Jun, Hye-Ah Lee, Hae Soon Kim, Young Sun Hong, Hyesook Park
Metabolites.2023; 13(1): 133. CrossRef - Relationships of BMI, muscle-to-fat ratio, and handgrip strength-to-BMI ratio to physical fitness in Spanish children and adolescents
Samuel Manzano-Carrasco, Jorge Garcia-Unanue, Eero A. Haapala, Jose Luis Felipe, Leonor Gallardo, Jorge Lopez-Fernandez
European Journal of Pediatrics.2023; 182(5): 2345. CrossRef - Body physique rating as a factor to identify at-risk Mexicans for Metabolic Syndrome
Oscar Herrera-Fomperosa, Sergio K. Bustamante-Villagomez, Sarahí Vazquez-Álvarez, Gabriela Vázquez-Marroquín, Leonardo M. Porchia, Enrique Torres-Rasgado, Ricardo Pérez-Fuentes, M. Elba Gonzalez-Mejia
Human Nutrition & Metabolism.2023; 33: 200206. CrossRef - The association between creatinine to body weight ratio and the risk of progression to diabetes from pre-diabetes: a 5-year cohort study in Chinese adults
Tong Li, Changchun Cao, Xuan Xuan, Wenjing Liu, Xiaohua Xiao, Cuimei Wei
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Muscle-to-Fat Ratio for Predicting Metabolic Syndrome Components in Children with Overweight and Obesity
Noga Salton, Sharona Kern, Hagar Interator, Adar Lopez, Hadar Moran-Lev, Yael Lebenthal, Avivit Brener
Childhood Obesity.2022; 18(2): 132. CrossRef - Mentale Gesundheit und physische Aktivität
Wolfgang Laube
Manuelle Medizin.2022; 60(1): 13. CrossRef - Increased odds of having the metabolic syndrome with greater fat‐free mass: counterintuitive results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey database
Jean‐Christophe Lagacé, Alexis Marcotte‐Chenard, Jasmine Paquin, Dominic Tremblay, Martin Brochu, Isabelle J. Dionne
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2022; 13(1): 377. CrossRef - Lipoprotein subfractions in patients with sarcopenia and their relevance to skeletal muscle mass and function
Hui Gong, Yang Liu, Xing Lyu, Lini Dong, Xiangyu Zhang
Experimental Gerontology.2022; 159: 111668. CrossRef - Health Risks of Sarcopenic Obesity in Overweight Children and Adolescents: Data from the CHILT III Programme (Cologne)
Carolin Sack, Nina Ferrari, David Friesen, Fabiola Haas, Marlen Klaudius, Lisa Schmidt, Gabriel Torbahn, Hagen Wulff, Christine Joisten
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(1): 277. CrossRef - Creatinine-to-body weight ratio is a predictor of incident diabetes: a population-based retrospective cohort study
Jiacheng He
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Relative low muscle mass and muscle strength is associated with the prevalence of metabolic syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes
Maya Takegami, Yoshitaka Hashimoto, Masahide Hamaguchi, Ayumi Kaji, Ryosuke Sakai, Takuro Okamura, Noriyuki Kitagawa, Takafumi Osaka, Hiroshi Okada, Naoko Nakanishi, Saori Majima, Takafumi Senmaru, Emi Ushigome, Mai Asano, Masahiro Yamazaki, Michiaki Fuku
Journal of Clinical Biochemistry and Nutrition.2022; 71(2): 136. CrossRef - “Big Data” Approaches for Prevention of the Metabolic Syndrome
Xinping Jiang, Zhang Yang, Shuai Wang, Shuanglin Deng
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Teil 2: Muskeldysfunktionen – mit Training gegen Schmerz
Wolfgang Laube
Manuelle Medizin.2022; 60(3): 129. CrossRef - Impact of Low Skeletal Muscle Mass and Obesity on Hearing Loss in Asymptomatic Individuals: A Population-Based Study
Chul-Hyun Park, Kyung Jae Yoon, Yong-Taek Lee, Sung Min Jin, Sang Hyuk Lee, Tae Hwan Kim
Healthcare.2022; 10(10): 2022. CrossRef - Physical activity level, sitting time, and skeletal muscle mass between esports players and non-esports players
Zhi H. SEE, Mohamad S. ABDUL HAMID
Gazzetta Medica Italiana Archivio per le Scienze Mediche.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of changes in fat free mass with risk for type 2 diabetes: Hispanic Community Health Study/Study of Latinos
M.N. LeCroy, S. Hua, R.C. Kaplan, D. Sotres-Alvarez, Q. Qi, B. Thyagarajan, L.C. Gallo, A. Pirzada, M.L. Daviglus, N. Schneiderman, G.A. Talavera, C.R. Isasi
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 171: 108557. CrossRef - The phospholipase A2 family’s role in metabolic diseases: Focus on skeletal muscle
Iris Prunonosa Cervera, Brendan M. Gabriel, Peter Aldiss, Nicholas M. Morton
Physiological Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Bone Health in Aging Men: Does Zinc and Cuprum Level Matter?
Aleksandra Rył, Tomasz Miazgowski, Aleksandra Szylińska, Agnieszka Turoń-Skrzypińska, Alina Jurewicz, Andrzej Bohatyrewicz, Iwona Rotter
Biomolecules.2021; 11(2): 237. CrossRef - Animal Protein versus Plant Protein in Supporting Lean Mass and Muscle Strength: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Meng Thiam Lim, Bernice Jiaqi Pan, Darel Wee Kiat Toh, Clarinda Nataria Sutanto, Jung Eun Kim
Nutrients.2021; 13(2): 661. CrossRef - Effects of Exercise Intervention on Mitochondrial Stress Biomarkers in Metabolic Syndrome Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Jae Seung Chang, Jun Namkung
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(5): 2242. CrossRef - Association between sarcopenia level and metabolic syndrome
Su Hwan Kim, Ji Bong Jeong, Jinwoo Kang, Dong-Won Ahn, Ji Won Kim, Byeong Gwan Kim, Kook Lae Lee, Sohee Oh, Soon Ho Yoon, Sang Joon Park, Doo Hee Lee, Masaki Mogi
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(3): e0248856. CrossRef - Sarcopenia and Appendicular Muscle Mass as Predictors of Impaired Fasting Glucose/Type 2 Diabetes in Elderly Women
Carola Buscemi, Yvelise Ferro, Roberta Pujia, Elisa Mazza, Giada Boragina, Angela Sciacqua, Salvatore Piro, Arturo Pujia, Giorgio Sesti, Silvio Buscemi, Tiziana Montalcini
Nutrients.2021; 13(6): 1909. CrossRef - Low muscle mass in older adults and mortality: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Felipe M. de Santana, Melissa O. Premaor, Nicolas Y. Tanigava, Rosa M.R. Pereira
Experimental Gerontology.2021; 152: 111461. CrossRef - Association of obesity, visceral adiposity, and sarcopenia with an increased risk of metabolic syndrome: A retrospective study
Su Hwan Kim, Hyoun Woo Kang, Ji Bong Jeong, Dong Seok Lee, Dong-Won Ahn, Ji Won Kim, Byeong Gwan Kim, Kook Lae Lee, Sohee Oh, Soon Ho Yoon, Sang Joon Park, Mauro Lombardo
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0256083. CrossRef - Der Muskulatur mehr Aufmerksamkeit schenken!
Wolfgang Laube
Manuelle Medizin.2021; 59(4): 302. CrossRef - Dietary Protein Requirement Threshold and Micronutrients Profile in Healthy Older Women Based on Relative Skeletal Muscle Mass
Praval Khanal, Lingxiao He, Hans Degens, Georgina K. Stebbings, Gladys L. Onambele-Pearson, Alun G. Williams, Martine Thomis, Christopher I. Morse
Nutrients.2021; 13(9): 3076. CrossRef - Effects of different definitions of low muscle mass on its association with metabolic syndrome in older adults: A Korean nationwide study
Yerim Jeon, Ki Young Son
Geriatrics & Gerontology International.2021; 21(11): 1003. CrossRef - Musclin Is Related to Insulin Resistance and Body Composition, but Not to Body Mass Index or Cardiorespiratory Capacity in Adults
Yeliana L. Sánchez, Manuela Yepes-Calderón, Luis Valbuena, Andrés F. Milán, María C. Trillos-Almanza, Sergio Granados, Miguel Peña, Mauricio Estrada-Castrillón, Juan C. Aristizábal, Raúl Narvez-Sanchez, Jaime Gallo-Villegas, Juan C. Calderón
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(5): 1055. CrossRef - Relative Lean Body Mass and Waist Circumference for the Identification of Metabolic Syndrome in the Korean General Population
Eunjoo Kwon, Eun-Hee Nah, Suyoung Kim, Seon Cho
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(24): 13186. CrossRef - Impact of Skeletal Muscle Mass on Metabolic Health
Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(1): 1. CrossRef - Skeletal muscle area and density are associated with lipid and lipoprotein cholesterol levels: The Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis
Chantal A. Vella, Megan C. Nelson, Jonathan T. Unkart, Iva Miljkovic, Matthew A. Allison
Journal of Clinical Lipidology.2020; 14(1): 143. CrossRef - Creatinine/(cystatin C × body weight) ratio is associated with skeletal muscle mass index
Kensuke Nishida, Yoshitaka Hashimoto, Ayumi Kaji, Takuro Okamura, Ryousuke Sakai, Noriyuki Kitagawa, Takafumi Osaka, Masahide Hamaguchi, Michiaki Fukui
Endocrine Journal.2020; 67(7): 733. CrossRef - Testosterone Therapy for Prevention and Treatment of Obesity in Men
Monica Caliber, Farid Saad
Androgens: Clinical Research and Therapeutics.2020; 1(1): 40. CrossRef - Creatinine to Body Weight Ratio Is Associated with Incident Diabetes: Population-Based Cohort Study
Yoshitaka Hashimoto, Takuro Okamura, Masahide Hamaguchi, Akihiro Obora, Takao Kojima, Michiaki Fukui
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 227. CrossRef - Skeletal muscle – A bystander or influencer of metabolic syndrome?
Gina L. Richter-Stretton, Andrew S. Fenning, Rebecca K. Vella
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(5): 867. CrossRef - Using relative handgrip strength to identify children at risk of sarcopenic obesity
Seryozha Gontarev, Mirko Jakimovski, Georgi Georgiev
Nutrición Hospitalaria.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Associated With Low Skeletal Muscle Mass in Overweight/Obese Youths
Lucia Pacifico, Francesco Massimo Perla, Gianmarco Andreoli, Rosangela Grieco, Pasquale Pierimarchi, Claudio Chiesa
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Independent and combined associations of cardiorespiratory fitness and muscle strength with metabolic syndrome in older adults: A cross-sectional study
Marcyo Câmara, Rodrigo Alberto Vieira Browne, Gabriel Costa Souto, Daniel Schwade, Ludmila Pereira Lucena Cabral, Geovani Araújo Dantas Macêdo, Luiz Fernando Farias-Junior, Fabíola Leite Gouveia, Telma Maria Araújo Moura Lemos, Kenio Costa Lima, Todd A. D
Experimental Gerontology.2020; 135: 110923. CrossRef - A counterintuitive perspective for the role of fat‐free mass in metabolic health
Jean‐Christophe Lagacé, Martin Brochu, Isabelle J. Dionne
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2020; 11(2): 343. CrossRef - Response: The way fat‐free mass is reported may change the conclusions regarding its protective effect on metabolic health
Jean‐Christophe Lagace, Martin Brochu, Isabelle J. Dionne
Clinical Endocrinology.2020; 92(1): 79. CrossRef - The Association between Major Dietary Pattern and Low Muscle Mass in Korean Middle-Aged and Elderly Populations: Based on the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Seong-Ah Kim, Jinwoo Ha, Byeonghwi Lim, Jun-Mo Kim, Sangah Shin
Nutrients.2020; 12(11): 3543. CrossRef - Total body skeletal muscle mass and diet in children aged 6–8 years: ANIVA Study
Maria Morales-Suarez-Varela, Isabel Peraita-Costa, Carlos Guillamon Escudero, Agustin Llopis-Morales, Agustin Llopis-Gonzalez
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2019; 44(9): 944. CrossRef - The way fat‐free mass is reported may change the conclusions regarding its protective effect on metabolic health
Jean‐Christophe Lagacé, Dominic Tremblay, Jasmine Paquin, Alexis Marcotte‐Chénard, Martin Brochu, Isabelle J. Dionne
Clinical Endocrinology.2019; 91(6): 903. CrossRef - Components of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Adults: A Hospital-Based Cohort at Seoul National University Bundang Hospital
Soo Lim, Se Hee Min, Ji Hyun Lee, Lee Kyung Kim, Dong-Hwa Lee, Jie-Eun Lee, Kyoung Min Kim, Sunmi Lee, Kyoung-Chan Park, Yun Jong Lee
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2019; 28(2): 118. CrossRef - Skeletal muscle as a protagonist in the pregnancy metabolic syndrome
Raul Narvaez-Sanchez, Juan C. Calderón, Gloria Vega, Maria Camila Trillos, Sara Ospina
Medical Hypotheses.2019; 126: 26. CrossRef - Increase in relative skeletal muscle mass over time and its inverse association with metabolic syndrome development: a 7-year retrospective cohort study
Gyuri Kim, Seung-Eun Lee, Ji Eun Jun, You-Bin Lee, Jiyeon Ahn, Ji Cheol Bae, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hwan Jee, Moon-Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of Age-Related Trends in Blood Pressure and Body Composition Indices in Healthy Adults
Wei Li, Yan He, Lili Xia, Xinghua Yang, Feng Liu, Jingang Ma, Zhiping Hu, Yajun Li, Dongxue Li, Jiajia Jiang, Guangliang Shan, Changlong Li
Frontiers in Physiology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic syndrome and body shape predict differences in health parameters in farm working women
Ilze Mentoor, Maritza Kruger, Theo Nell
BMC Public Health.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of stunting in early childhood with cardiometabolic risk factors in adulthood
Emanuella De Lucia Rolfe, Giovanny Vinícius Araújo de França, Carolina Avila Vianna, Denise P. Gigante, J. Jaime Miranda, John S. Yudkin, Bernardo Lessa Horta, Ken K. Ong, C. Mary Schooling
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(4): e0192196. CrossRef - Relationship Between Relative Skeletal Muscle Mass and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A 7‐Year Longitudinal Study
Gyuri Kim, Seung‐Eun Lee, You‐Bin Lee, Ji Eun Jun, Jiyeon Ahn, Ji Cheol Bae, Sang‐Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jae Hwan Jee, Moon‐Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Hepatology.2018; 68(5): 1755. CrossRef - Relationships among Skeletal Muscle Mass, Health Related Factors, Nutrient Intake, and Physical Activities in Male Adolescents: Based on the 5th (2009-2011) Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES)
In-Kyung Jung, Jung-Hyun Kim
The Korean Journal of Community Living Science.2018; 29(2): 185. CrossRef - Using relative handgrip strength to identify children at risk of sarcopenic obesity
Michal Steffl, Jan Chrudimsky, James J. Tufano, Masaki Mogi
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(5): e0177006. CrossRef - International society of sports nutrition position stand: diets and body composition
Alan A. Aragon, Brad J. Schoenfeld, Robert Wildman, Susan Kleiner, Trisha VanDusseldorp, Lem Taylor, Conrad P. Earnest, Paul J. Arciero, Colin Wilborn, Douglas S. Kalman, Jeffrey R. Stout, Darryn S. Willoughby, Bill Campbell, Shawn M. Arent, Laurent Banno
Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between rectus abdominis muscle thickness and metabolic syndrome in middle-aged men
Eun Sil Choi, Soo Hyun Cho, Jung-Ha Kim, Etsuro Ito
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(9): e0185040. CrossRef - Health-related quality of life and activity limitation in an elderly Korean population with sarcopenia: The Fourth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES IV-2, 3), 2008–2009
T.H. Kim, S.-H. Kim, J. Kim, H.-J. Hwang
European Geriatric Medicine.2017; 8(4): 360. CrossRef - Differential association between sarcopenia and metabolic phenotype in Korean young and older adults with and without obesity
You‐Cheol Hwang, In‐Jin Cho, In‐Kyung Jeong, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Ho Yeon Chung
Obesity.2017; 25(1): 244. CrossRef - Reference Values of Skeletal Muscle Mass for Korean Children and Adolescents Using Data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2009-2011
Kirang Kim, Sangmo Hong, Eun Young Kim, Bin He
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(4): e0153383. CrossRef - Insulin sensitivity, body composition and adipose depots following 12 w combined endurance and strength training in dysglycemic and normoglycemic sedentary men
Torgrim Mikal Langleite, Jørgen Jensen, Frode Norheim, Hanne Løvdal Gulseth, Daniel Steensen Tangen, Kristoffer Jensen Kolnes, Ansgar Heck, Tryggve Storås, Guro Grøthe, Marius Adler Dahl, Anders Kielland, Torgeir Holen, Hans Jørgen Noreng, Hans Kristian S
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2016; 122(4): 167. CrossRef - Association between fat free mass and glucose homeostasis: Common knowledge revisited
Karine Perreault, Jean-Christophe Lagacé, Martin Brochu, Isabelle J. Dionne
Ageing Research Reviews.2016; 28: 46. CrossRef - Low skeletal muscle mass is associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Korean adults: the Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Hee Yeon Kim, Chang Wook Kim, Chung-Hwa Park, Jong Young Choi, Kyungdo Han, Anwar T Merchant, Yong-Moon Park
Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International.2016; 15(1): 39. CrossRef - The ratio of skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area is a main determinant linking circulating irisin to metabolic phenotype
You-Cheol Hwang, Won Seon Jeon, Cheol-Young Park, Byung-Soo Youn
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a weight loss program on body composition and the metabolic profile in obese postmenopausal women displaying various obesity phenotypes: a MONET group study
Eve Normandin, Eric Doucet, Rémi Rabasa-Lhoret, Martin Brochu
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2015; 40(7): 695. CrossRef - Analytic morphomics identifies predictors of new‐onset diabetes after liver transplantation
Valerie M. Vaughn, David C. Cron, Michael N. Terjimanian, Zachary S. Gala, Stewart C. Wang, Grace L. Su, Michael L. Volk
Clinical Transplantation.2015; 29(5): 458. CrossRef - Reduced Flexibility Associated with Metabolic Syndrome in Community-Dwelling Elders
Ke-Vin Chang, Chen-Yu Hung, Chia-Ming Li, Yu-Hung Lin, Tyng-Guey Wang, Keh-Sung Tsai, Der-Sheng Han, Diego Fraidenraich
PLOS ONE.2015; 10(1): e0117167. CrossRef - Metabolic risk factors in U.S. youth with low relative muscle mass
Sunkyung Kim, Rodolfo Valdez
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2015; 9(2): 125. CrossRef - Comparison of waist to height ratio and body indices for prediction of metabolic disturbances in the Korean population: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2008–2011
Seok Hui Kang, Kyu Hyang Cho, Jong Won Park, Jun Young Do
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - N-3 fatty acid intake altered fat content and fatty acid distribution in chicken breast muscle, but did not influence mRNA expression of lipid-related enzymes
Anna Haug, Nicole F Nyquist, Magny Thomassen, Arne T Høstmark, Tone-Kari Knutsdatter Østbye
Lipids in Health and Disease.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Métodos de análise da composição corporal em adultos obesos
Rávila Graziany Machado de Souza, Aline Corado Gomes, Carla Marques Maia do Prado, João Felipe Mota
Revista de Nutrição.2014; 27(5): 569. CrossRef
- Relationship between adiponectin and muscle mass in patients with metabolic syndrome and obesity

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





