
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Others
- Change Profiles and Functional Targets of MicroRNAs in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Obesity
- Guanhua Lu, Huanhuan Gao, Zhiyong Dong, Shuwen Jiang, Ruixiang Hu, Cunchuan Wang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):559-570. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0226
- 1,741 View
- 76 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
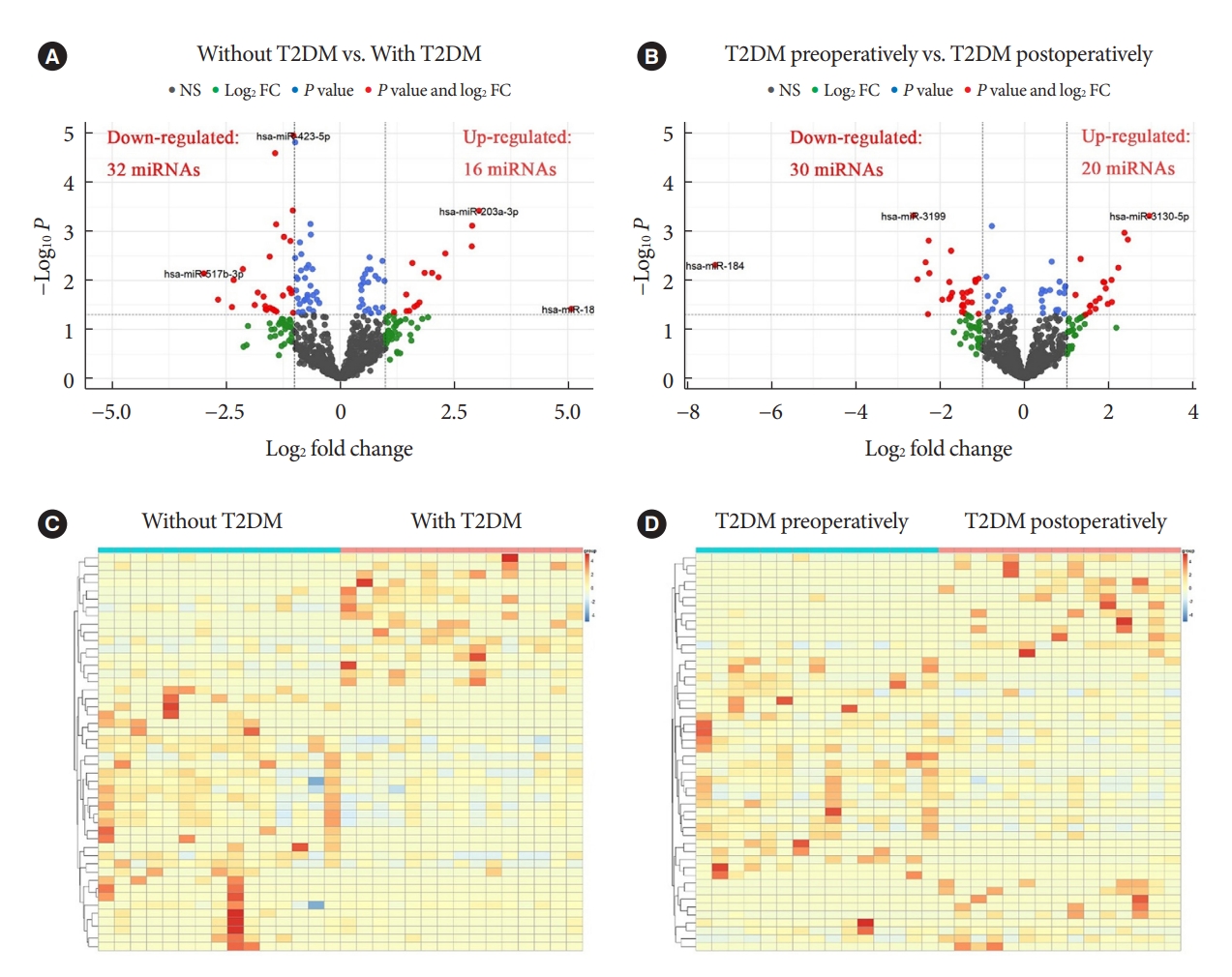
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) exert an essential contribution to obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This study aimed to investigate the differences of miRNAs in the presence and absence of T2DM in patients with obesity, as well as before and after bariatric surgery in T2DM patients with obesity. Characterization of the common changes in both was further analyzed.
Methods
We enrolled 15 patients with obesity but without T2DM and 15 patients with both obesity and T2DM. Their preoperative clinical data and serum samples were collected, as well as 1 month after bariatric surgery. The serum samples were analyzed by miRNA sequencing, and the miRNAs profiles and target genes characteristics were compared.
Results
Patients with T2DM had 16 up-regulated and 32 down-regulated miRNAs compared to patients without T2DM. Improvement in metabolic metrics after bariatric surgery of T2DM patients with obesity was correlated with changes in miRNAs, as evidenced by the upregulation of 20 miRNAs and the downregulation of 30 miRNAs. Analysis of the two miRNAs profiles identified seven intersecting miRNAs that showed opposite changes. The target genes of these seven miRNAs were substantially enriched in terms or pathways associated with T2DM.
Conclusion
We determined the expression profiles of miRNAs in the obese population, with and without diabetes, before and after bariatric surgery. The miRNAs that intersected in the two comparisons were discovered. Both the miRNAs discovered and their target genes were closely associated with T2DM, demonstrating that they might be potential targets for the regulation of T2DM.
- Technology/Device
- Glucose Profiles Assessed by Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring System during the Perioperative Period of Metabolic Surgery
- Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang, Young Suk Park, Tae Jung Oh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):713-721. Published online January 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0164
- 4,843 View
- 317 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
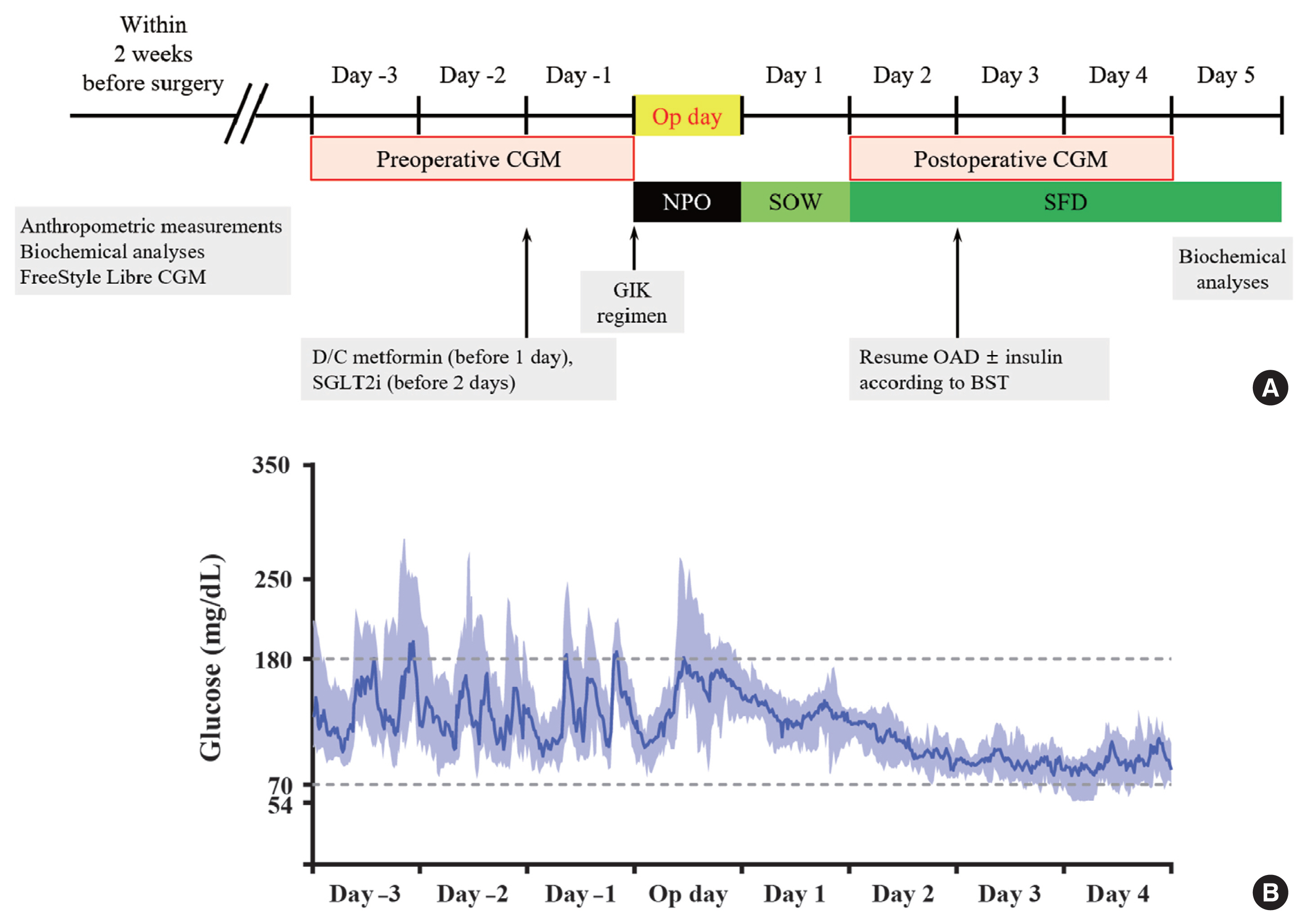
Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has been widely used in the management of diabetes. However, the usefulness and detailed data during perioperative status were not well studied. In this study, we described the immediate changes of glucose profiles after metabolic surgery using intermittently scanned CGM (isCGM) in individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
This was a prospective, single-center, single-arm study including 20 participants with T2DM. The isCGM (FreeStyle Libre CGM) implantation was performed within 2 weeks before surgery. We compared CGM metrics of 3 days before surgery and 3 days after surgery, and performed the correlation analyses with clinical variables.
Results
The mean glucose significantly decreased after surgery (147.0±40.4 to 95.5±17.1 mg/dL, P<0.001). Time in range (TIR; 70 to 180 mg/dL) did not significantly change after surgery in total. However, it was significantly increased in a subgroup of individuals with glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) ≥8.0%. Time above range (>250 or 180 mg/dL) was significantly decreased in total. In contrast, time below range (<70 or 54 mg/dL) was significantly increased in total and especially in a subgroup of individuals with HbA1c <8.0% after surgery. The coefficient of variation significantly decreased after surgery. Higher baseline HbA1c was correlated with greater improvement in TIR (rho=0.607, P=0.005).
Conclusion
The isCGM identified improvement of mean glucose and glycemic variability, and increase of hypoglycemia after metabolic surgery, but TIR was not significantly changed after surgery. We detected an increase of TIR only in individuals with HbA1c ≥8.0%. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparative Effect of Glucose-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
Ji Soo Kim, Gyeongsil Lee, Kyung-Il Park, Seung-Won Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 312. CrossRef - Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients Following Bariatric Surgery: A Scoping Review
Yang Yu, Susan W. Groth
Obesity Surgery.2023; 33(8): 2573. CrossRef - Asymptomatic Hypoglycemia after Metabolic Surgery: New Insights from Perioperative Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Sang-Man Jin
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 675. CrossRef
- Comparative Effect of Glucose-Lowering Drugs for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus on Stroke Prevention: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis
- Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome
- Metabolic Surgery for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Experience from Asia
- Wei-Jei Lee, Lwin Aung
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(6):433-443. Published online December 2, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.6.433
- 3,953 View
- 72 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a current global health priority and Asia is the epicenter of this epidemic disease. Unlike in the west, where older population is most affected, the burden of diabetes in Asian countries is disproportionately high in young to middle-age adults. The incidence of diabetic nephropathy is alarmingly high in patients with early onset T2DM, especially in those with poor glycemic control. How to control this chronic and debilitating disease is currently a very important health issue in Asia. Bariatric surgery has proven successful in treating not just obesity but also T2DM in morbid obese patients (body mass index [BMI] >35 kg/m2). Gastrointestinal metabolic surgery recently has been proposed as a new treatment modality for obesity related T2DM for patients with BMI <35 kg/m2. Many studies from Asia reported promising results of metabolic surgery to treat obese patients with T2DM which is not well controlled. It has been demonstrated that changes in gastrointestinal hormone secretion after gastrointestinal surgery would favor an early improvement of T2DM in Asians. New procedures have also been designed and proposed specifically for the treatment of diabetes in Asia. This article examines clinical trial data and accepted algorithms with a view toward elucidating the application of metabolic surgery for the treatment of T2DM in the Asia. We propose a systematic approach to surgical treatment, addressing current evidences, patient selection, procedure of choice, and timing and guideline for new procedures.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Insulin resistance levels predicted metabolic improvement and weight loss after metabolic surgery in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes
Yaoquan Cao, Ping Luo, Haibo Tang, Pengzhou Li, Guohui Wang, Weizheng Li, Zhi Song, Zhihong Su, Xulong Sun, Xianhao Yi, Zhibing Fu, Beibei Cui, Shaihong Zhu, Liyong Zhu
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases.2024; 20(1): 80. CrossRef - Long‐term outcomes of metabolic surgery in overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes in Asia
Yu‐Min Huang, Yen‐Kuang Lin, Wei‐Jei Lee, Kyoung Yul Hur, Kazunori Kasama, Anton Kui Sing Cheng, Ming‐Hsien Lee, Simon Kin‐Hung Wong, Tien‐Chou Soong, Kuo‐Ting Lee, Davide Lomanto, Muffazal Lakdawala, Yen‐Hao Su, Weu Wang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2021; 23(3): 742. CrossRef - Vertical sleeve gastrectomy induces distinctive transcriptomic responses in liver, fat and muscle
Chang Ho Ahn, Eun Hye Choi, Hyunjung Lee, Woochan Lee, Jong-Il Kim, Young Min Cho
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin Resistance Remission Following Laparoscopic Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Laparoscopic Sleeve Gastrectomy in Chinese Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients With a Body Mass Index of 27.5–32.5 kg/m2
Ping Luo, Yaoquan Cao, Pengzhou Li, Guohui Wang, Zhi Song, Weizheng Li, Zhihong Su, Hui Zhou, Xianhao Yi, Zhibing Fu, Xulong Sun, Haibo Tang, Beibei Cui, Qianqian Yu, Liyong Zhu, Shaihong Zhu
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pre- and postoperative respiratory muscle strength, body mass index and fasting glucose profile of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus submitted to metabolic surgery
Ariana de Melo Tosta, Marisa de Carvalho Borges, Élida Mara Carneiro da Silva, Alex Augusto da Silva, Eduardo Crema
Fisioterapia em Movimento.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcomes After Metabolic Surgery in Asians—a Meta-analysis
Danson Yeo, Charleen Yeo, Tze Yi Low, Saleem Ahmed, Sheena Phua, Aung Myint Oo, Jaideepraj Rao, Aaryan Koura, Kavita Venkataraman, Sanghvi Kaushal
Obesity Surgery.2019; 29(1): 114. CrossRef - Diabetes resolution after one anastomosis gastric bypass
Adam Abu-Abeid, Yonatan Lessing, Niv Pencovich, Danit Dayan, Joseph M. Klausner, Subhi Abu-Abeid
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases.2018; 14(2): 181. CrossRef - Laparoscopic metabolic surgery for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in Asia: a scoping review and evidence-based analysis
Zhiyong Dong, Sheikh Mohammed Shariful Islam, Ashley M. Yu, Rui Qu, Bingsheng Guan, Junchang Zhang, Zhao Hong, Cunchuang Wang
BMC Surgery.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical Practice Recommendations for the Management of Obesity in the United Arab Emirates
Salahedeen Abusnana, Mohammad Fargaly, Shaima Hasan Alfardan, Fatema Hasan Al Hammadi, Alaaeldin Bashier, Ghaida Kaddaha, Barbara McGowan, Rita Nawar, Amena Sadiya
Obesity Facts.2018; 11(5): 413. CrossRef - Laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy combined with single-anastomosis duodenal-jejunal bypass in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus of patients with body mass index higher than 27.5 kg/m2 but lower than 32.5 kg/m2
Ying-Xu Li, Deng-Hua Fang, Tian-Xi Liu
Medicine.2018; 97(31): e11537. CrossRef - Comparison of Great Curvature Plication with Duodenal-Jejunal Bypass (GCP-DJB) and Sleeve Gastrectomy (SG) on Metabolic Indices and Gut Hormones in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Rats
Nian-Cun Qiu, Wei Li, Miao-E Liu, Xiao-Xia Cen, Cheng-Xiang Shan, Wei Zhang, Qing Liu, Yang Wang, Ya-Ting Zhu, Ming Qiu
Obesity Surgery.2018; 28(12): 4014. CrossRef - Evolution of Diabetes Care in Hong Kong: From the Hong Kong Diabetes Register to JADE-PEARL Program to RAMP and PEP Program
Ivy H.Y. Ng, Kitty K.T. Cheung, Tiffany T.L. Yau, Elaine Chow, Risa Ozaki, Juliana C.N. Chan
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2018; 33(1): 17. CrossRef - Ethnicity Does Not Influence Glycemic Outcomes or Diabetes Remission After Sleeve Gastrectomy or Gastric Bypass in a Multiethnic Asian Cohort
Phong Ching Lee, Kwang Wei Tham, Sonali Ganguly, Hong Chang Tan, Alvin Kim Hock Eng, John B. Dixon
Obesity Surgery.2018; 28(6): 1511. CrossRef - Effects of GABAB receptor activation on spatial cognitive function and hippocampal neurones in rat models of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Xiao-Jun Cai, Lei Wang, Chun-Mei Hu
Bioscience Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolic surgery ameliorates cardiovascular risk in obese diabetic patients: Influence of different surgical procedures
Jih-Hua Wei, Ruey-Hsing Chou, Po-Hsun Huang, Wei-Jei Lee, Shu-Chun Chen, Shing-Jong Lin
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases.2018; 14(12): 1832. CrossRef - Pulmonary function evaluation in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients submitted to metabolic surgery
Ariana de Melo Tosta, Marisa de Carvalho Borges, Élida Mara Carneiro da Silva, Tharsus Dias Takeuti, Júverson Alves Terra Júnior, Eduardo Crema
Fisioterapia em Movimento.2018;[Epub] CrossRef
- Insulin resistance levels predicted metabolic improvement and weight loss after metabolic surgery in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes
- Complications
- The Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Diabetic Retinopathy: Good, Bad, or Both?
- Dora M. Gorman, Carel W. le Roux, Neil G. Docherty
- Diabetes Metab J. 2016;40(5):354-364. Published online September 27, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.5.354
- 4,353 View
- 48 Download
- 22 Web of Science
- 28 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Bariatric surgery, initially intended as a weight-loss procedure, is superior to standard lifestyle intervention and pharmacological therapy for type 2 diabetes in obese individuals. Intensive medical management of hyperglycemia is associated with improved microvascular outcomes. Whether or not the reduction in hyperglycemia observed after bariatric surgery translates to improved microvascular outcomes is yet to be determined. There is substantial heterogeneity in the data relating to the impact of bariatric surgery on diabetic retinopathy (DR), the most common microvascular complication of diabetes. This review aims to collate the recent data on retinal outcomes after bariatric surgery. This comprehensive evaluation revealed that the majority of DR cases remain stable after surgery. However, risk of progression of pre-existing DR and the development of new DR is not eliminated by surgery. Instances of regression of DR are also noted. Potential risk factors for deterioration include severity of DR at the time of surgery and the magnitude of glycated hemoglobin reduction. Concerns also exist over the detrimental effects of postprandial hypoglycemia after surgery.
In vivo studies evaluating the chronology of DR development and the impact of bariatric surgery could provide clarity on the situation. For now, however, the effect of bariatric surgery on DR remains inconclusive.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Author response to: remission of diabetes mellitus after bariatric surgery: the putative link with worsening diabetic retinopathy and a need for ongoing postoperative follow-up retinal screening
Karl Hage, Omar M. Ghanem
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of Bariatric Surgery on Treatment Burden and Progression of Diabetic Retinopathy
Ariana Allen, Hemal Patel, Sandra S. Stinnett, Jullia A. Rosdahl, Stefanie Schuman
Journal of VitreoRetinal Diseases.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of Systemic Factors in Improving the Prognosis of Diabetic Retinal Disease and Predicting Response to Diabetic Retinopathy Treatment
Joe Mellor, Anita Jeyam, Joline W.J. Beulens, Sanjeeb Bhandari, Geoffrey Broadhead, Emily Chew, Ward Fickweiler, Amber van der Heijden, Daniel Gordin, Rafael Simó, Janet Snell-Bergeon, Anniina Tynjälä, Helen Colhoun
Ophthalmology Science.2024; 4(4): 100494. CrossRef - The Importance of Glycaemic Control Before Bariatric Surgery: Preventing Microvascular and Metabolic Complications
Adhithya Sankar, Rajshekhar N. Mudaliar, Rupinder S. Kochhar, Lucinda K. M. Summers, Akheel A. Syed, Waseem Majeed
Obesity Surgery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Rapid Reduction of HbA1c and Early Worsening of Diabetic Retinopathy: A Real-world Population-Based Study in Subjects With Type 2 Diabetes
Rafael Simó, Josep Franch-Nadal, Bogdan Vlacho, Jordi Real, Ester Amado, Juana Flores, Manel Mata-Cases, Emilio Ortega, Mercedes Rigla, Joan-Anton Vallés, Cristina Hernández, Didac Mauricio
Diabetes Care.2023; 46(9): 1633. CrossRef - Early microvascular complications in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: recent developments and updates
Kalie L. Tommerdahl, Allison L. B. Shapiro, Edward J. Nehus, Petter Bjornstad
Pediatric Nephrology.2022; 37(1): 79. CrossRef - New Insights into Treating Early and Advanced Stage Diabetic Retinopathy
Rafael Simó, Cristina Hernández
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(15): 8513. CrossRef - Response to Letter to the Editor Concerning: Adam S. et al. Improvements in Diabetic Neuropathy and Nephropathy After Bariatric Surgery: a Prospective Cohort Study
Safwaan Adam, Jan Hoong Ho, Akheel A. Syed, Rayaz A. Malik, Handrean Soran
Obesity Surgery.2022; 32(10): 3460. CrossRef - Weight management and multi-morbidity
Carrie Ashby
InnovAiT: Education and inspiration for general practice.2021; 14(8): 523. CrossRef - The Safety of Pharmacological and Surgical Treatment of Diabetes in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy—A Review
Wojciech Matuszewski, Angelika Baranowska-Jurkun, Magdalena Maria Stefanowicz-Rutkowska, Katarzyna Gontarz-Nowak, Ewa Gątarska, Elżbieta Bandurska-Stankiewicz
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(4): 705. CrossRef - Safety of Semaglutide
Mark M. Smits, Daniël H. Van Raalte
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Outcomes of Diabetic Retinopathy Post-Bariatric Surgery in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ana Maria Dascalu, Anca Pantea Stoian, Alina Popa Cherecheanu, Dragos Serban, Daniel Ovidiu Costea, Mihail Silviu Tudosie, Daniela Stana, Denisa Tanasescu, Alexandru Dan Sabau, Gabriel Andrei Gangura, Andreea Cristina Costea, Vanessa Andrada Nicolae, Cata
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(16): 3736. CrossRef - Future perspectives in diabesity treatment: Semaglutide, a glucagon‑like peptide 1 receptor agonist (Review)
Mariana Tilinca, Robert Tiuca, Cristina Niculas, Andreea Varga, Ioan Tilea
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Safety of injectable semaglutide for type 2 diabetes
Rajesh Peter, Steve C. Bain
Expert Opinion on Drug Safety.2020; 19(7): 785. CrossRef - Early worsening of diabetic retinopathy due to intensive glycaemic control
Shueh Wen Lim, Peter van Wijngaarden, Colin A. Harper, Salmaan H. Al‐Qureshi
Clinical & Experimental Ophthalmology.2019; 47(2): 265. CrossRef - Worsening of diabetic retinopathy with rapid improvement in systemic glucose control: A review
Stephen C. Bain, Michael A. Klufas, Allen Ho, David R. Matthews
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2019; 21(3): 454. CrossRef - Diabetische Retinopathie bei Patienten mit Diabetes mellitus
Olga Simó-Servat, Cristina Hernández, Rafael Simó
Kompass Ophthalmologie.2019; 5(4): 157. CrossRef - Diabetic Retinopathy in the Context of Patients with Diabetes
Olga Simó-Servat, Cristina Hernández, Rafael Simó
Ophthalmic Research.2019; 62(4): 211. CrossRef - MANAGEMENT OF ENDOCRINE DISEASE: Which metabolic procedure? Comparing outcomes in sleeve gastrectomy and Roux-en Y gastric bypass
Adrian T Billeter, Javier R de la Garza Herrera, Katharina M Scheurlen, Felix Nickel, Franck Billmann, Beat P Müller-Stich
European Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 179(2): R77. CrossRef - Aggravation précoce de la rétinopathie diabétique lors de l’optimisation du contrôle glycémique
S. Feldman-Billard
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2018; 12(7): 560. CrossRef - Semaglutide, reduction in glycated haemoglobin and the risk of diabetic retinopathy
Tina Vilsbøll, Stephen C. Bain, Lawrence A. Leiter, Ildiko Lingvay, David Matthews, Rafael Simó, Ida Carøe Helmark, Nelun Wijayasinghe, Michael Larsen
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2018; 20(4): 889. CrossRef - Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists and the Risk of Incident Diabetic Retinopathy
Antonios Douros, Kristian B. Filion, Hui Yin, Oriana Hoi Yu, Mahyar Etminan, Jacob A. Udell, Laurent Azoulay
Diabetes Care.2018; 41(11): 2330. CrossRef - Early worsening of diabetic retinopathy after rapid improvement of blood glucose control in patients with diabetes
S. Feldman-Billard, É. Larger, P. Massin
Diabetes & Metabolism.2018; 44(1): 4. CrossRef - Excess visceral adiposity is associated with diabetic retinopathy in a multiethnic Asian cohort with longstanding type 2 diabetes
Angela Moh, Kumari Neelam, Xiao Zhang, Chee Fang Sum, Subramaniam Tavintharan, Keven Ang, Simon Biing Ming Lee, Wern Ee Tang, Su Chi Lim
Endocrine Research.2018; 43(3): 186. CrossRef - GLP-1R as a Target for the Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy: Friend or Foe?
Rafael Simó, Cristina Hernández
Diabetes.2017; 66(6): 1453. CrossRef - The Long-Term Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Type 2 Diabetes Remission, Microvascular and Macrovascular Complications, and Mortality: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Binwu Sheng, Khoa Truong, Hugh Spitler, Lu Zhang, Xuetao Tong, Liwei Chen
Obesity Surgery.2017; 27(10): 2724. CrossRef - Bariatric Surgery for Adolescents with Type 2 Diabetes: an Emerging Therapeutic Strategy
M. A. Stefater, T. H. Inge
Current Diabetes Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of bariatric surgery to treat diabetes: current challenges and perspectives
Chrysi Koliaki, Stavros Liatis, Carel W. le Roux, Alexander Kokkinos
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2017;[Epub] CrossRef
- Author response to: remission of diabetes mellitus after bariatric surgery: the putative link with worsening diabetic retinopathy and a need for ongoing postoperative follow-up retinal screening
- A Gut Feeling to Cure Diabetes: Potential Mechanisms of Diabetes Remission after Bariatric Surgery
- Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(6):406-415. Published online December 15, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.6.406
- 5,215 View
- 56 Download
- 52 Web of Science
- 41 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader A cure for type 2 diabetes was once a mere dream but has now become a tangible and achievable goal with the unforeseen success of bariatric surgery in the treatment of both obesity and type 2 diabetes. Popular bariatric procedures such as Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy exhibit high rates of diabetes remission or marked improvement in glycemic control. However, the mechanism of diabetes remission following these procedures is still elusive and appears to be very complex and encompasses multiple anatomical and physiological changes. In this article, calorie restriction, improved β-cell function, improved insulin sensitivity, and alterations in gut physiology, bile acid metabolism, and gut microbiota are reviewed as potential mechanisms of diabetes remission after Roux-en-Y gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of Diet Composition on the Post-operative Outcomes of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass in Mice
Matthew Stevenson, Ankita Srivastava, Maria Nacher, Christopher Hall, Thomas Palaia, Jenny Lee, Chaohui Lisa Zhao, Raymond Lau, Mohamed A. E. Ali, Christopher Y. Park, Florencia Schlamp, Sean P. Heffron, Edward A. Fisher, Collin Brathwaite, Louis Ragolia
Obesity Surgery.2024; 34(3): 911. CrossRef - A Matched Comparative Analysis of Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus Remission Between Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass and Sleeve Gastrectomy
Karl Hage, Pearl Ma, Wissam Ghusn, Kayla Ikemiya, Andres Acosta, Robert A. Vierkant, Barham K. Abu Dayyeh, Kelvin D. Higa, Omar M. Ghanem
Surgical Innovation.2024; 31(2): 148. CrossRef - Sex-Specific Changes in Body Composition Following Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery Are Associated with the Remission of Metabolic Syndrome
Xianhao Yi, Weizheng Li, Guohui Wang, Pengzhou Li, Xulong Sun, Haibo Tang, Beibei Cui, Jiapu Ling, Ping Luo, Zhibing Fu, Hui Zhou, Liyong Zhu, Shaihong Zhu
Obesity Surgery.2023; 33(9): 2780. CrossRef - East Asian perspectives in metabolic and bariatric surgery
Tae Jung Oh, Hyuk‐Joon Lee, Young Min Cho
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(5): 756. CrossRef - Long-Term Trajectories in Weight and Health Outcomes Following Multidisciplinary Publicly Funded Bariatric Surgery in Patients with Clinically Severe Obesity (≥ 3 Associated Comorbidities): A Nine-Year Prospective Cohort Study in Australia
Michelle M.C. Tan, Xingzhong Jin, Craig Taylor, Adrian K. Low, Philip Le Page, David Martin, Ang Li, David Joseph, Nic Kormas
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(15): 4466. CrossRef - Impact of Bariatric Surgery in Reducing Macrovascular Complications in Severely Obese T2DM Patients
Salman Hussain, Mohd Shahnawaz Khan, Mohammad Chand Jamali, Ali Nasir Siddiqui, Gaurav Gupta, Md Sarfaraj Hussain, Fohad Mabood Husain
Obesity Surgery.2021; 31(5): 1929. CrossRef - Vertical sleeve gastrectomy induces distinctive transcriptomic responses in liver, fat and muscle
Chang Ho Ahn, Eun Hye Choi, Hyunjung Lee, Woochan Lee, Jong-Il Kim, Young Min Cho
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Which predictors could effect on remission of type 2 diabetes mellitus after the metabolic surgery: A general perspective of current studies?
Gamze Akkus, Tamer Tetiker
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(8): 1312. CrossRef - Impact of Metabolic Surgery on Type-2 Diabetes Remission
Cejana de Abrantes Figueiredo Baiocchi, Diana Aristótelis Rocha de Sá
Current Diabetes Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Ileal Transposition Increases Pancreatic β Cell Mass and Decreases β Cell Senescence in Diet-Induced Obese Rats
Chang Ho Ahn, Eun Hye Choi, Tae Jung Oh, Young Min Cho
Obesity Surgery.2020; 30(5): 1849. CrossRef - Does Reconstruction Type After Gastric Resection Matters for Type 2 Diabetes Improvement?
Mariana Costa, Artur Trovão Lima, Tiago Morais, Rui F. Almeida, Mário Nora, Marta Guimarães, Mariana P. Monteiro
Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery.2020; 24(6): 1269. CrossRef - Epidemiology, pathophysiology and etiology of obesity in children and adolescents
Jessica Kerns, Martin Fisher
Current Problems in Pediatric and Adolescent Health Care.2020; 50(9): 100869. CrossRef - Obesity in Adolescents and Youth: The Case for and against Bariatric Surgery
Ahmed Khattab, Mark A. Sperling
The Journal of Pediatrics.2019; 207: 18. CrossRef - Outcomes of Bariatric Surgery Versus Medical Management for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: a Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Zhamak Khorgami, Saeed Shoar, Alan A. Saber, C. Anthony Howard, Goodarz Danaei, Guido M. Sclabas
Obesity Surgery.2019; 29(3): 964. CrossRef - Validating Risk Prediction Models of Diabetes Remission After Sleeve Gastrectomy
Shih-Chiang Shen, Weu Wang, Ka-Wai Tam, Hsin-An Chen, Yen-Kuang Lin, Shih-Yun Wang, Ming-Te Huang, Yen-Hao Su
Obesity Surgery.2019; 29(1): 221. CrossRef - Long-term diabetes outcomes after bariatric surgery—managing medication withdrawl
Pedro Souteiro, Sandra Belo, Daniela Magalhães, Jorge Pedro, João Sérgio Neves, Sofia Castro Oliveira, Paula Freitas, Ana Varela, Davide Carvalho
International Journal of Obesity.2019; 43(11): 2217. CrossRef - What is type 2 diabetes?
Maria Daniela Hurtado, Adrian Vella
Medicine.2019; 47(1): 10. CrossRef - Intestinal Glucose Absorption Was Reduced by Vertical Sleeve Gastrectomy via Decreased Gastric Leptin Secretion
Jinpeng Du, Chaojie Hu, Jie Bai, Miaomiao Peng, Qingbo Wang, Ning Zhao, Yu Wang, Guobin Wang, Kaixiong Tao, Geng Wang, Zefeng Xia
Obesity Surgery.2018; 28(12): 3851. CrossRef - Non-pharmacological Treatment Options in the Management of Diabetes Mellitus
Arkiath V Raveendran
European Endocrinology.2018; 14(2): 31. CrossRef - Ileal transposition rapidly improves glucose tolerance and gradually improves insulin resistance in non-obese type 2 diabetic rats
Hengliang Zhu, Huaiming Wang, Zhihai Zheng, Bailiang Ye, Xiaojiao Ruan, Xiaofeng Zheng, Guoxin Li
Gastroenterology Report.2018; 6(4): 291. CrossRef - Small Intestinal Bypass Induces a Persistent Weight-Loss Effect and Improves Glucose Tolerance in Obese Rats
Jiaqing Cao, Quan Ren, Cai Tan, Jinyuan Duan
Obesity Surgery.2017; 27(7): 1859. CrossRef - Diabetes improvement and resolution following laparoscopic vertical sleeve gastrectomy (LVSG) versus laparoscopic Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (LRYGB) procedures: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials
Emma Osland, Rossita Mohamad Yunus, Shahjahan Khan, Breda Memon, Muhammed Ashraf Memon
Surgical Endoscopy.2017; 31(4): 1952. CrossRef - The Long-Term Effects of Bariatric Surgery on Type 2 Diabetes Remission, Microvascular and Macrovascular Complications, and Mortality: a Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Binwu Sheng, Khoa Truong, Hugh Spitler, Lu Zhang, Xuetao Tong, Liwei Chen
Obesity Surgery.2017; 27(10): 2724. CrossRef - Long-term effects of duodenojejunal bypass on diabetes in Otsuka Long–Evans Tokushima Fatty rats
Sang Kuon Lee, Oh-Joo Kwon, Hae Myung Jeon, Say-June Kim
Asian Journal of Surgery.2017; 40(4): 262. CrossRef - Interaction Between Atypical Antipsychotics and the Gut Microbiome in a Bipolar Disease Cohort
Stephanie A. Flowers, Simon J. Evans, Kristen M. Ward, Melvin G. McInnis, Vicki L. Ellingrod
Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy.2017; 37(3): 261. CrossRef - THE ROLE OF THE SLEEVE GASTRECTOMY AND THE MANAGEMENT OF TYPE 2 DIABETES
Taíse FUCHS, Marcelo LOUREIRO, Gabriela Heloise BOTH, Heloise Helena SKRABA, Thaís Andrade COSTA-CASAGRANDE
ABCD. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cirurgia Digestiva (São Paulo).2017; 30(4): 283. CrossRef - Attenuated secretion of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) does not alleviate hyperphagic obesity and insulin resistance in ob/ob mice
Satoko Shimazu-Kuwahara, Norio Harada, Shunsuke Yamane, Erina Joo, Akiko Sankoda, Timothy J. Kieffer, Nobuya Inagaki
Molecular Metabolism.2017; 6(3): 288. CrossRef - Adipose tissue supports normalization of macrophage and liver lipid handling in obesity reversal
Maayan Vatarescu, Sapir Bechor, Yulia Haim, Tal Pecht, Tanya Tarnovscki, Noa Slutsky, Ori Nov, Hagit Shapiro, Avishai Shemesh, Angel Porgador, Nava Bashan, Assaf Rudich
Journal of Endocrinology.2017; 233(3): 293. CrossRef - Sleeve Gastrectomy Alters Intestinal Permeability in Diet-Induced Obese Mice
Claire Blanchard, François Moreau, Julien Chevalier, Audrey Ayer, Damien Garcon, Lucie Arnaud, Jean-Paul Pais de Barros, Thomas Gautier, Michel Neunlist, Bertrand Cariou, Cédric Le May
Obesity Surgery.2017; 27(10): 2590. CrossRef - Long-term Follow-up for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus after Gastrectomy in Non-morbidly Obese Patients with Gastric Cancer: the Legitimacy of Onco-metabolic Surgery
Tae-Hoon Lee, Chang Min Lee, Sungsoo Park, Do Hyun Jung, You Jin Jang, Jong-Han Kim, Seong-Heum Park, Young-Jae Mok
Journal of Gastric Cancer.2017; 17(4): 283. CrossRef - Preoperative Beta Cell Function Is Predictive of Diabetes Remission After Bariatric Surgery
Pedro Souteiro, Sandra Belo, João Sérgio Neves, Daniela Magalhães, Rita Bettencourt Silva, Sofia Castro Oliveira, Maria Manuel Costa, Ana Saavedra, Joana Oliveira, Filipe Cunha, Eva Lau, César Esteves, Paula Freitas, Ana Varela, Joana Queirós, Davide Carv
Obesity Surgery.2017; 27(2): 288. CrossRef - Ileal Transposition Decreases Plasma Lipopolysaccharide Levels in Association with Increased L Cell Secretion in Non-obese Non-diabetic Rats
Tae Jung Oh, Hyuk-Joon Lee, Young Min Cho
Obesity Surgery.2016; 26(6): 1287. CrossRef - The Mechanism of Metabolic Surgery: Gastric Center Hypothesis
Jiangfan Zhu, Radheshyam Gupta, Mahmood Safwa
Obesity Surgery.2016; 26(7): 1639. CrossRef - Lipids and bariatric procedures Part 2 of 2: scientific statement from the American Society for Metabolic and Bariatric Surgery (ASMBS), the National Lipid Association (NLA), and Obesity Medicine Association (OMA)
Harold Bays, Shanu N. Kothari, Dan E. Azagury, John M. Morton, Ninh T. Nguyen, Peter H. Jones, Terry A. Jacobson, David E. Cohen, Carl Orringer, Eric C. Westman, Deborah B. Horn, Wendy Scinta, Craig Primack
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases.2016; 12(3): 468. CrossRef - Metabolic Surgery for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Experience from Asia
Wei-Jei Lee, Lwin Aung
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(6): 433. CrossRef - Improved glucose metabolism following bariatric surgery is associated with increased circulating bile acid concentrations and remodeling of the gut microbiome
Lukasz Kaska, Tomasz Sledzinski, Agnieszka Chomiczewska, Agnieszka Dettlaff-Pokora, Julian Swierczynski
World Journal of Gastroenterology.2016; 22(39): 8698. CrossRef - In Vivo Models for Incretin Research: From the Intestine to the Whole Body
Tae Jung Oh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(1): 45. CrossRef - Contribution of the distal small intestine to metabolic improvement after bariatric/metabolic surgery: Lessons from ileal transposition surgery
Tae Jung Oh, Chang Ho Ahn, Young Min Cho
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2016; 7(S1): 94. CrossRef - EFFECTS OF LONG-TERM ROUX-EN-Y GASTRIC BYPASS ON BODY WEIGHT AND CLINICAL METABOLIC COMORBIDITIES IN BARIATRIC SURGERY SERVICE OF A UNIVERSITY HOSPITAL
Cátia Ferreira da SILVA, Larissa COHEN, Luciana d'Abreu SARMENTO, Felipe Monnerat Marino ROSA, Eliane Lopes ROSADO, João Régis Ivar CARNEIRO, Antônio Augusto Peixoto de SOUZA, Fernanda Cristina Carvalho Mattos MAGNO
ABCD. Arquivos Brasileiros de Cirurgia Digestiva (São Paulo).2016; 29( suppl 1): 20. CrossRef - Medication Use Among Patients Prior to Bariatric Surgery
Jennifer Padden Elliott, Erica L. Gray, Jessie Yu, Melissa A. Kalarchian
Bariatric Surgical Practice and Patient Care.2015; 10(3): 105. CrossRef - Changes in the salivary protein profile of morbidly obese women either previously subjected to bariatric surgery or not
Elsa Lamy, Carla Simões, Lénia Rodrigues, Ana Rodrigues Costa, Rui Vitorino, Francisco Amado, Célia Antunes, Isabel do Carmo
Journal of Physiology and Biochemistry.2015; 71(4): 691. CrossRef
- The Effect of Diet Composition on the Post-operative Outcomes of Roux-en-Y Gastric Bypass in Mice

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





