
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus among Korean Children, Adolescents, and Adults Younger than 30 Years: Changes from 2002 to 2016
- Yong Hee Hong, In-Hyuk Chung, Kyungdo Han, Sochung Chung, on Behalf of the Taskforce Team of the Obesity Fact Sheet of the Korean Society for the Study of Obesity
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):297-306. Published online October 26, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0038
- 9,304 View
- 343 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
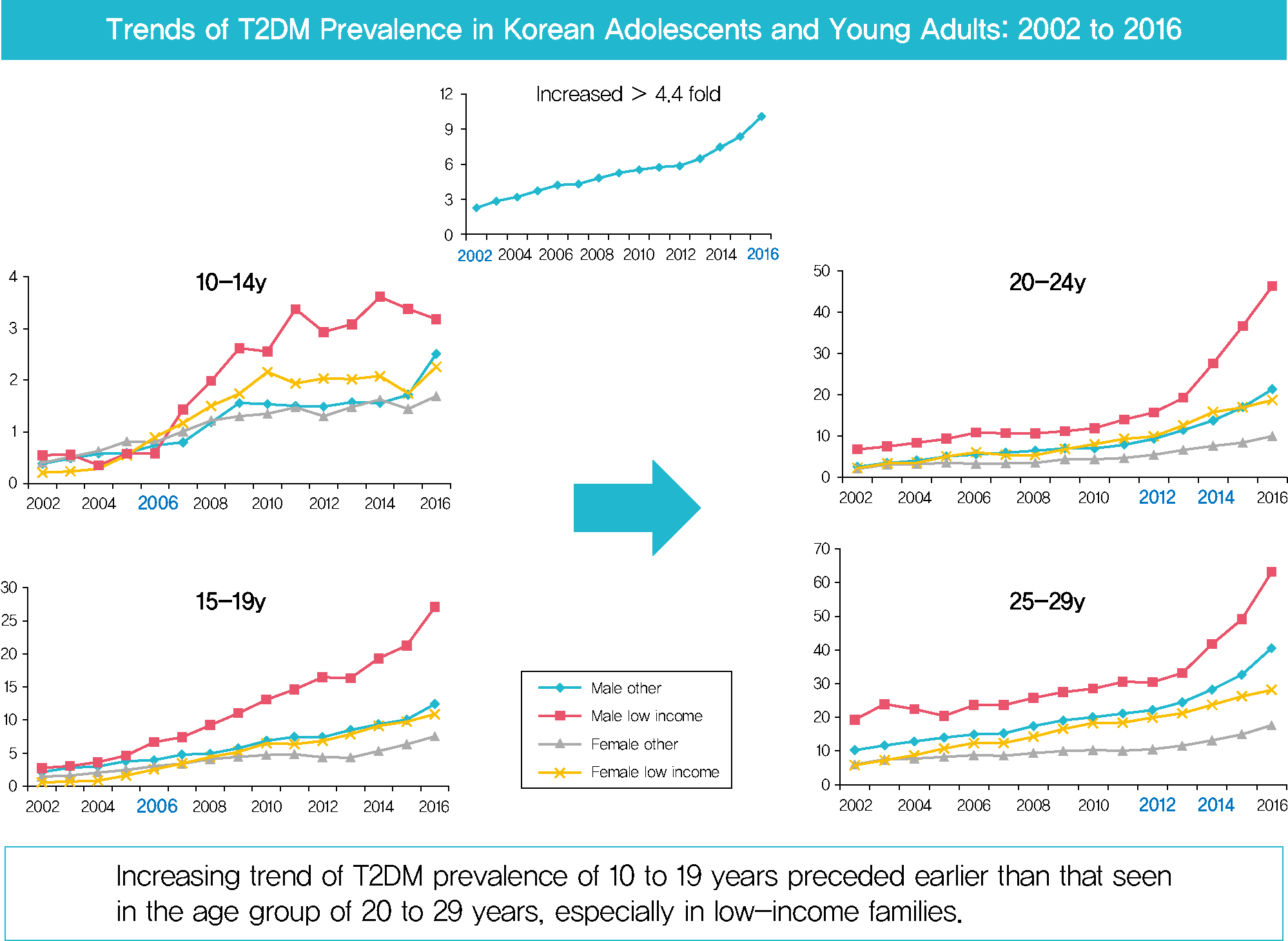
Despite the importance of and social concern regarding prevention of diabetes at younger ages, limited data are available. This study sought to analyze changes in the prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Koreans younger than 30 years according to sex, age, and level of income.
Methods
The dataset analyzed in this study was derived from health insurance claims recorded in the National Health Insurance Service (NHIS) database. Participants’ level of income was categorized as low (quintile 1, <20% of insurance premium) or others (quintile 2–5).
Results
In males and females, the prevalence of T2DM per 10,000 people steadily increased from 2.57 in 2002 to 11.41 in 2016, and from 1.96 in 2002 to 8.63 in 2016. The prevalence of T2DM in girls was higher in the age group of 5 to 14 years. Even though the prevalence was higher among those older than 20 years, the increase had started earlier, in the early 2000s, in younger age group. Adolescents aged 10 to 19 years in low-income families showed a remarkable increase in prevalence of T2DM, especially in boys.
Conclusion
The prevalence of T2DM in young Koreans increased more than 4.4-fold from 2002 to 2016, and the increase started in the early 2000s in younger age groups and in low-income families. This is the first study to examine the trend in prevalence of T2DM in children, adolescents, and young adults in Korea. Future studies and collaborations with social support systems to prevent T2DM at an early age group should be performed. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- SCORE and SCORE2 in East Asian Population
JungMin Choi, Soseul Sung, Sue K. Park, Seyong Park, Hyoyeong Kim, Myeong-Chan Cho, Bryan Williams, Hae-Young Lee
JACC: Asia.2024; 4(4): 265. CrossRef - Chronic disease management program applied to type 2 diabetes patients and prevention of diabetic complications: a retrospective cohort study using nationwide data
Min Kyung Hyun, Jang Won Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical and pathological characteristics of DKD patients with early-onset type 2 diabetes
Liang Wu, Yi-Yang Zhao, Meng-Rui Li, Dong-Yuan Chang, Ming-Hui Zhao, Min Chen
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(8): 108520. CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes and Its Association With Psychiatric Disorders in Young Adults in South Korea
Min-Kyung Lee, Su-Young Lee, Seo-Young Sohn, Jiyeon Ahn, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Hyuk Lee
JAMA Network Open.2023; 6(6): e2319132. CrossRef - Glycemic control and complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents during the COVID-19 outbreak
Kyeong Eun Oh, Yu Jin Kim, Ye Rim Oh, Eungu Kang, Hyo-Kyoung Nam, Young-Jun Rhie, Kee-Hyoung Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(4): 275. CrossRef - Position Statement on the Appropriateness and Significance of Adding the Glycated Hemoglobin Test to the National Health Examination
Ji Hye Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Jaehyun Kim, Sangjoon Park, Kyunghoon Lee, Jun Goo Kang, Eu Jeong Ku, Su Kyoung Kwon, Won Jun Kim, Young Sang Lyu, Jang Won Son, Young Sil Eom, Kyung Ae Lee, Jeongrim Lee, Jung Min Lee, Jung Hwa Lee, Jung Hwa Jung, Hochan Cho, Da
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 178. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 349. CrossRef - Prevalence trends of type 1 and type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents in North Rhine-Westphalia, the most populous federal state in Germany, 2002-2020
C. Baechle, A. Stahl-Pehe, N. Prinz, T. Meissner, C. Kamrath, R.W. Holl, J. Rosenbauer
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 190: 109995. CrossRef - Diagnostic and Therapeutic Strategies of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Youth
Hwa Young Kim, Jae Hyun Kim
The Ewha Medical Journal.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors Affecting High-Risk for Diabetes among Korean Adolescents: An Analysis Using the Eighth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2020)
Kyung-Sook Bang, Sang-Youn Jang, Ji-Hye Choe
Children.2022; 9(8): 1249. CrossRef - Characteristics of Glycemic Control and Long-Term Complications in Patients with Young-Onset Type 2 Diabetes
Han-sang Baek, Ji-Yeon Park, Jin Yu, Joonyub Lee, Yeoree Yang, Jeonghoon Ha, Seung Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Dong-Jun Lim, Hun-Sung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(4): 641. CrossRef - 젊은 2형 당뇨병 환자의 관리
재현 배
Public Health Weekly Report.2022; 15(35): 2474. CrossRef
- SCORE and SCORE2 in East Asian Population
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018
- Jiun Chae, Moon Young Seo, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):880-889. Published online July 6, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0185
- 5,868 View
- 239 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
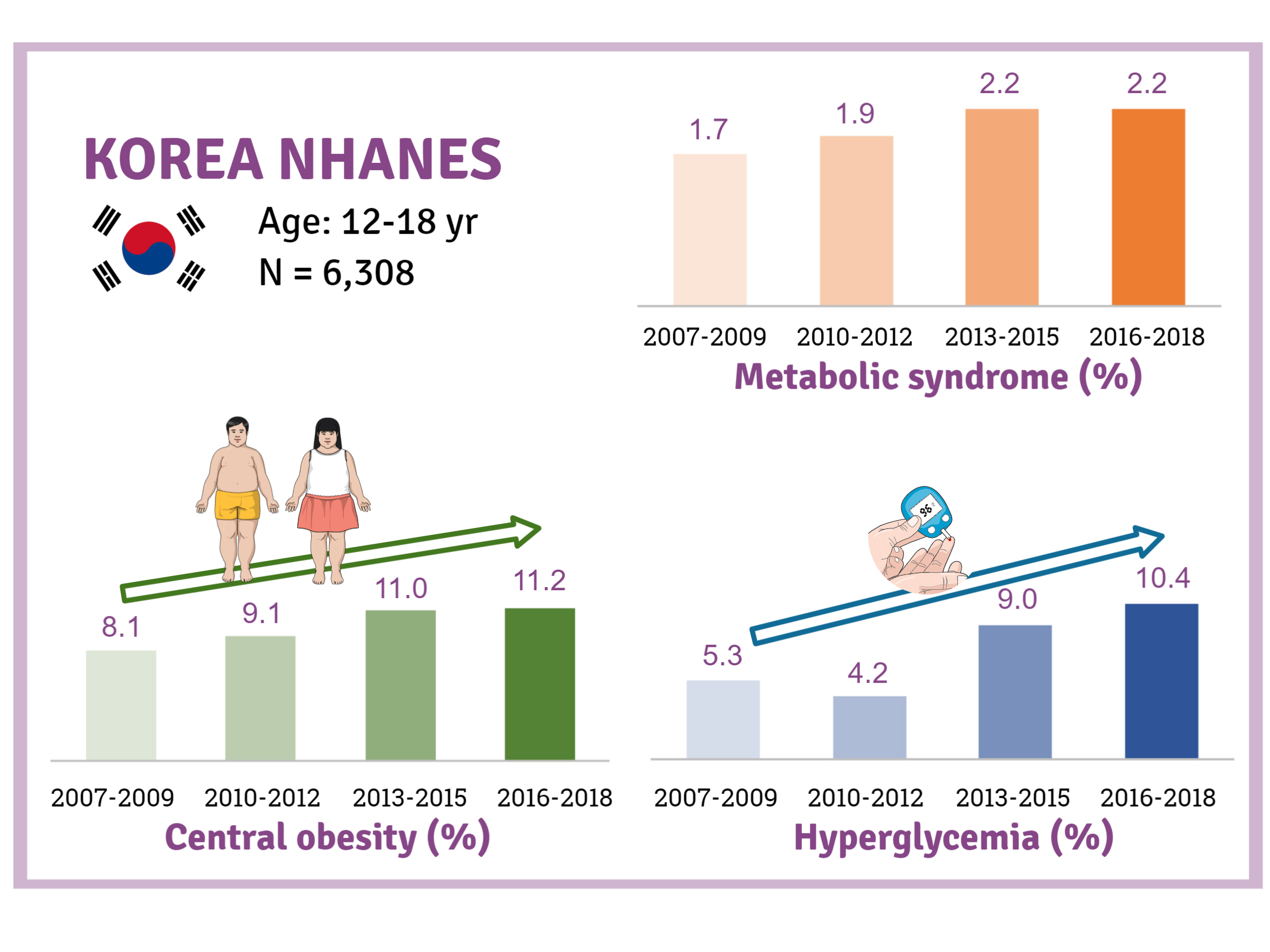
There is a lack of recent research on the changes in risk factors for metabolic syndrome (MetS) in the Asian pediatric population. We aimed to determine the 12-year trends in the prevalence of MetS and relevant lifestyle factors such as smoking, exercise, and calorie intake among Korean adolescents.
Methods
We investigated trends in MetS and lifestyle factors among 6,308 adolescents aged 12 to 18 years from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 2007 to 2018.
Results
The prevalence of MetS was stable from 2007 to 2018 (1.7% to 2.2%). There were significant increases in the prevalence of central obesity (from 8.1% to 11.2%, P=0.012) and hyperglycemia (from 5.3% to 10.4%, P<0.001) and decreases in hypo-high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterolemia (from 22.4% to 14.8%, P<0.001). Total calorie intake and calorie intake from fat significantly increased (P<0.001), whereas calorie intake from carbohydrates significantly decreased (P<0.001) during the study period. The proportions of tobacco smokers and regular walkers significantly decreased from 2007 to 2018. After controlling for all covariates, total calorie intake was positively correlated with waist circumference (P<0.05). HDL-cholesterol was negatively associated with carbohydrate consumption (P<0.01) and positively associated with fat consumption (P<0.001). Regular walking and regular strength training were associated with lower waist circumference (P<0.05). Smoking was associated with lower fasting glucose levels (P<0.01).
Conclusion
Although the prevalence rate of MetS is stable among Korean adolescents, the prevalence of central obesity and hyperglycemia has increased greatly in the recent decade. Public education on proper dietary intake and lifestyle modification is required. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of Overseas Deployment on Fatty Liver and Metabolic Diseases Among Korean Soldiers
Chang In Han, Jaejun Lee
Military Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The impacts of dietary sphingomyelin supplementation on metabolic parameters of healthy adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Chen-Zi Li, Li-Mei Wu, Chen-Xi Zhu, Huan-Yu Du, Guo-Xun Chen, Fang Yang
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between Thyroid Function and Insulin Resistance Indices in Korean Adolescents: Findings from the 2014–2015 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Eunji Mun, Hye Ah Lee, Jung Eun Choi, Rosie Lee, Kyung Hee Kim, Hyesook Park, Hae Soon Kim
Children.2024; 11(3): 370. CrossRef - Ongoing increasing trends in central precocious puberty incidence among Korean boys and girls from 2008 to 2020
Sinyoung Kang, Mi Jung Park, Jung Min Kim, Jin-Sung Yuk, Shin-Hye Kim, Jun Mori
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(3): e0283510. CrossRef - The association between urinary cotinine level and metabolic syndrome profiles among adolescents: findings from the Ewha Birth and growth study
Hyunjin Park, Ui-Jeong Kim, Eun Jeong Choi, Seunghee Jun, Bomi Park, Hye Ah Lee, Hae Soon Kim, Hyesook Park
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence-Based Speech Analysis System for Medical Support
Eui-Sun Kim, Dong Jin Shin, Sung Tae Cho, Kyung Jin Chung
International Neurourology Journal.2023; 27(2): 99. CrossRef - The effect of hypothalamic involvement and growth hormone treatment on cardiovascular risk factors during the transition period in patients with childhood-onset craniopharyngioma
Sang Hee Park, Yun Jeong Lee, Jung-Eun Cheon, Choong Ho Shin, Hae Woon Jung, Young Ah Lee
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2023; 28(2): 107. CrossRef - Increase of Prevalence of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Children and Adolescents in Korea during the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Cross-Sectional Study Using the KNHANES
Jung Eun Choi, Hye Ah Lee, Sung Won Park, Jung Won Lee, Ji Hyen Lee, Hyesook Park, Hae Soon Kim
Children.2023; 10(7): 1105. CrossRef - The Prevalence of Abdominal Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Children and Adolescents
Ja Hyang Cho
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 103. CrossRef - Temporal Trends of the Prevalence of Abdominal Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Children and Adolescents between 2007 and 2020
Jieun Lee, Sung-Chan Kang, Obin Kwon, Seung-sik Hwang, Jin Soo Moon, Hyun Wook Chae, Jaehyun Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(2): 170. CrossRef - Changes in the Number of Children and Adolescents with Complex Chronic Conditions and Medical Spending: Analyzing National Health Insurance Claims Data from 2011 to 2021
Jeong-Yoon Oh, Su-Jin Cho, Jin-Seon Jung, Jin-Suk Cho, Choon-Seon Park
Health Insurance Review & Assessment Service Research.2023; 3(2): 155. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Dae Jung Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 349. CrossRef - Trends and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome among Korean Adolescents, 2007 to 2018 (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:880-9)
Jiun Chae, Moon Young Seo, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 351. CrossRef - Comprehensive Understanding for Application in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus of the Consensus Statement on Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets by Korean Diabetes Association, Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and Korean Society of Hyperte
Jong Han Choi, Jee-Hyun Kang, Suk Chon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 377. CrossRef - Environmental polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon exposure in relation to metabolic syndrome in US adults
Xue Yang, Qingping Xue, Ying Wen, Yichao Huang, Yi Wang, Gaga Mahai, Tong Yan, Yanjun Liu, Tao Rong, Yixin Wang, Da Chen, Shuqin Zeng, Chun-Xia Yang, Xiong-Fei Pan
Science of The Total Environment.2022; 840: 156673. CrossRef - Commentary on "Single point insulin sensitivity estimator for predicting type 2 diabetes mellitus in obese adolescents"
Shin-Hye Kim
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 27(3): 155. CrossRef
- Impact of Overseas Deployment on Fatty Liver and Metabolic Diseases Among Korean Soldiers
- Epidemiology
- Association of Bisphenol A and Its Substitutes, Bisphenol F and Bisphenol S, with Obesity in United States Children and Adolescents
- Buyun Liu, Hans-Joachim Lehmler, Yangbo Sun, Guifeng Xu, Qi Sun, Linda G. Snetselaar, Robert B. Wallace, Wei Bao
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(1):59-75. Published online February 19, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0045
- 5,911 View
- 155 Download
- 92 Web of Science
- 92 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Bisphenol F (BPF) and bisphenol S (BPS) are increasingly used as substitutes for bisphenol A (BPA), an environmental obesogen. However, health effects of BPF and BPS remain unclear. In this study, we evaluated the associations of BPA, BPF, and BPS with obesity in children and adolescents.
Methods We used data from the U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2013 to 2014, a nationally representative study. We included 745 participants aged 6 to 17 years old. General obesity was defined based on the 2000 Centers for Disease Control and Prevention body mass index-for-age growth charts for the United States. Abdominal obesity was defined as waist-to-height ratio ≥0.5.
Results After adjustment for demographic, socioeconomic and lifestyle factors, and urinary creatinine levels, the odds ratio of general obesity comparing the highest with lowest quartile of urinary bisphenol levels was 1.74 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.92 to 3.31) for BPA, 1.54 (95% CI, 1.02 to 2.32) for BPF, and 1.36 (95% CI, 0.53 to 3.51) for BPS. Moreover, the associations were stronger in boys than in girls for BPA and BPF. Similar results were observed for abdominal obesity.
Conclusion This study for the first time showed that exposure to BPF, a commonly used substitute for BPA, was positively associated with higher risk of obesity in children and adolescents. The association of BPA and BPF with general and abdominal obesity was primarily observed in boys, suggesting a possible sex difference. Further investigations on the underlying mechanisms are needed.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Obesogenic effects of six classes of emerging contaminants
Siying Wu, Chaoyu Tong, Jing Liu
Journal of Environmental Sciences.2025; 151: 252. CrossRef - Bisphenol S, bisphenol F, bisphenol a exposure and body composition in US adults
Buyun Liu, Yuxiang Yan, Juan Xie, Jian Sun, Hans-Joachim Lehmler, Leonardo Trasande, Robert B. Wallace, Wei Bao
Chemosphere.2024; 346: 140537. CrossRef - Sex and Gender Differences on the Impact of Metabolism-Disrupting Chemicals on Obesity: A Systematic Review
Massimo D’Archivio, Lucia Coppola, Roberta Masella, Alessia Tammaro, Cinzia La Rocca
Nutrients.2024; 16(2): 181. CrossRef - The Role of Endocrine Disruptors Bisphenols and Phthalates in Obesity: Current Evidence, Perspectives and Controversies
Maria Dalamaga, Dimitrios Kounatidis, Dimitrios Tsilingiris, Natalia G. Vallianou, Irene Karampela, Sotiria Psallida, Athanasios G. Papavassiliou
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2024; 25(1): 675. CrossRef - Sex-specific associations of bisphenol A and its substitutes with body fat distribution among US adults: NHANES 2011–2016
Shili Zhang, Lingyan Dai, Ziyu Wan, Zhiwei Huang, Mengchen Zou, Haixia Guan
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2024; 31(5): 7948. CrossRef - EDC mixtures during pregnancy and body fat at 7 years of age in a Swedish cohort, the SELMA study
Katherine Svensson, Chris Gennings, Christian Lindh, Hannu Kiviranta, Panu Rantakokko, Sverre Wikström, Carl-Gustaf Bornehag
Environmental Research.2024; 248: 118293. CrossRef - Chemical Composition of Leachates from Hydraulic Fracturing Proppants from Surficial Releases in Southeastern New Mexico
Matthew S. Varonka, Terry G. Gregston, Michael Villalobos, Jacqueline P. Green, William H. Orem
Environmental Science & Technology Letters.2024; 11(3): 243. CrossRef - Associations of bisphenol A exposure with metabolic syndrome and its components: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Tianli Xiao, Zehua Huang, Chanjuan Zheng, Binh Quach, Yulian Zhu, Feifei Li, Wei Liang, Julien Baker, Christoph Reichetzeder, Berthold Hocher, Yide Yang
Obesity Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship of bisphenol A substitutes bisphenol F and bisphenol S with adiponectin/leptin ratio among children from the environment and development of children cohort
Hye Jin Lee, Yun Jeong Lee, Youn-Hee Lim, Hwa Young Kim, Bung-Nyun Kim, Johanna Inhyang Kim, Yong Min Cho, Yun-Chul Hong, Choong Ho Shin, Young Ah Lee
Environment International.2024; 185: 108564. CrossRef - SWATH-MS reveals that Bisphenol A and its analogs regulate pathways leading to disruption in Insulin signaling and fatty acid metabolism
Shabda Kulsange, Monika Sharma, Babasaheb Sonawane, Meera R. Jaiswal, Mahesh Kulkarni, B. Santhakumari
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2024; : 114667. CrossRef - Exposure to Bisphenol A, S, and F and its Association with Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus in General Adults of Korea: Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) 2015–2017
Min Kyong Moon, Min Joo Kim, Inae Lee, Sunmi Kim, Sohyeon Choi, Jeongim Park, Yoon Hee Cho, Sooyeon Hong, Jiyoung Yoo, Hyunwoong Park, Gi Jeong Cheon, Young Joo Park, Kyungho Choi
Exposure and Health.2023; 15(1): 53. CrossRef - Evaluation of toxicological effects of bisphenol S with an in vitro human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell: Implications for bone health
Mei Li, Tenglong Li, Juan Yin, Chunfeng Xie, Jianyun Zhu
Toxicology.2023; 484: 153408. CrossRef - In silico profiling of endocrine-disrupting potential of bisphenol analogues and their halogenated transformation products
Karolina Nowak, Žiga Jakopin
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2023; 173: 113623. CrossRef - Transient developmental exposure to low doses of bisphenol F negatively affects neurogliogenesis and olfactory behaviour in adult mice
Pieter Vancamp, Lucile Butruille, Anni Herranen, Anita Boelen, Jean-Baptiste Fini, Barbara A. Demeneix, Sylvie Remaud
Environment International.2023; 172: 107770. CrossRef - Development of human dermal PBPK models for the bisphenols BPA, BPS, BPF, and BPAF with parallel-layered skin compartment: Basing on dermal administration studies in humans
Man Hu, Zhichun Zhang, Yining Zhang, Ming Zhan, Weidong Qu, Gengsheng He, Ying Zhou
Science of The Total Environment.2023; 868: 161639. CrossRef - Postnatal exposure to Bisphenol S induces liver injury in mice: Possible implication of PPARγ receptor
Bessem Mornagui, Raja Rezg, Fadoua Neffati, Mohamed Fadhel Najjar, Ahmed Rejeb
Toxicology and Industrial Health.2023; 39(5): 237. CrossRef - JAK3/STAT5b/PPARγ Pathway Mediates the Association between Di(2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate Exposure and Lipid Metabolic Disorder in Chinese Adolescent Students
Qi Xu, Shuang Ding, Wen Qi, Xueting Zhang, Meng Zhang, Jiqiang Xing, Aipeng Ju, Liting Zhou, Lin Ye
Chemical Research in Toxicology.2023; 36(5): 725. CrossRef - Bisphenol A substitutes and childhood obesity at 7 years: a cross-sectional study in Shandong, China
Minyan Chen, Cheng Lv, Shanyu Zhang, Lap Ah Tse, Xinyu Hong, Xi Liu, Yu Ding, Ping Xiao, Ying Tian, Yu Gao
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2023; 30(29): 73174. CrossRef - Association between Bisphenol A exposure and body composition parameters in children
Yong Guo, Cui Liu, Yu-Hong Deng, Jing Ning, Li Yu, Jie-Ling Wu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Urinary neonicotinoid insecticides and adiposity measures among 7-year-old children in northern China: A cross-sectional study
Zhenping Lu, Yi Hu, Lap Ah Tse, Jinxia Yu, Zhuanning Xia, Xiaoning Lei, Yan Zhang, Rong Shi, Ying Tian, Yu Gao
International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health.2023; 251: 114188. CrossRef - Mechanism of Bisphenol F Affecting Motor System and Motor Activity in Zebrafish
Yeonhwa Kim, Seong Soon Kim, Byeong Heon Park, Kyu-Seok Hwang, Myung Ae Bae, Sung-Hee Cho, Suhyun Kim, Hae-Chul Park
Toxics.2023; 11(6): 477. CrossRef - The effects of trans fat diet intake on metabolic parameters and pancreatic tissue in offspring of prenatal bisphenol A exposed rats
Hala Abulehia, Noor Shafina Mohd Nor, Siti Hamimah Sheikh Abdul Kadir, Mardiana Abdul Aziz, Sarah Zulkifli
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Genetic background in the rat affects endocrine and metabolic outcomes of bisphenol F exposure
Valerie A Wagner, Katie L Holl, Karen C Clark, John J Reho, Melinda R Dwinell, Hans-Joachim Lehmler, Hershel Raff, Justin L Grobe, Anne E Kwitek
Toxicological Sciences.2023; 194(1): 84. CrossRef - Association of parabens and bisphenols with lung function in children aged 5–12 years from Shanghai, China
Yi Hu, Hao Chen, Yuan Tian, Dan Wu, Angela Vinturache, Guodong Ding, Guangjun Yu
International Journal of Hygiene and Environmental Health.2023; 252: 114210. CrossRef - Bisphenol A substitutes and obesity: a review of the epidemiology and pathophysiology
Shane V. Varghese, Julianne M. Hall
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Levels of Bisphenol A and its analogs in nails, saliva, and urine of children: a case control study
Yolanda Gálvez-Ontiveros, Inmaculada Moscoso-Ruiz, Vega Almazán Fernández de Bobadilla, Celia Monteagudo, Rafael Giménez-Martínez, Lourdes Rodrigo, Alberto Zafra-Gómez, Ana Rivas
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Exposure to Bisphenol A and Its Analogs among Thai School-Age Children
Nattakarn Numsriskulrat, Thanawan Teeranathada, Chansuda Bongsebandhu-Phubhakdi, Suphab Aroonparkmongkol, Kyungho Choi, Vichit Supornsilchai
Toxics.2023; 11(9): 761. CrossRef - Bisphenol analogues inhibit human and rat 17β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase 1: 3D-quantitative structure-activity relationship (3D-QSAR) and in silico docking analysis
Sailing Chen, Shaowei Wang, Jingyi Zheng, Han Lu, Huiqian Chen, Yunbing Tang, Nan Wang, Yang Zhu, Yiyan Wang, Ping Duan, Ren-shan Ge
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2023; 181: 114052. CrossRef - Associations of prenatal exposure to bisphenols with BMI growth trajectories in offspring within the first two years: evidence from a birth cohort study in China
Chao Xiong, Kai Chen, Lu-Li Xu, Yi-Ming Zhang, Hua Liu, Meng-Lan Guo, Zhi-Guo Xia, Yu-Ji Wang, Xiao-Feng Mu, Xiao-Xuan Fan, Jing-Quan Chen, Yu-Ru Liu, Yuan-Yuan Li, Wei Xia, You-Jie Wang, Ai-Fen Zhou
World Journal of Pediatrics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Ecotoxicological Evaluation of Bisphenol A and Alternatives: A Comprehensive In Silico Modelling Approach
Liadys Mora Lagares, Marjan Vračko
Journal of Xenobiotics.2023; 13(4): 719. CrossRef - Bisphenol A (BPA) and Cardiovascular or Cardiometabolic Diseases
Jeong-Hun Kang, Daisuke Asai, Riki Toita
Journal of Xenobiotics.2023; 13(4): 775. CrossRef - Report of the Scientific Committee of the Spanish Agency for Food Safety and Nutrition (AESAN) on the available evidence in relation to the potential obesogenic activity of certain chemical compounds that may be present in foods
Ana María Rivas Velasco, Irene Bretón Lesmes, Araceli Díaz Perales, Ángel Gil Izquierdo, María José González Muñoz, Victoria Moreno Arribas, María del Puy Portillo Baquedano, Silvia Pichardo Sánchez
Food Risk Assess Europe.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Regulatory and academic studies to derive reference values for human health: The case of bisphenol S
Claire Beausoleil, Brigitte Le Magueresse-Battistoni, Catherine Viguié, Sylvie Babajko, Marie-Chantal Canivenc-Lavier, Nicolas Chevalier, Claude Emond, René Habert, Nicole Picard-Hagen, Sakina Mhaouty-Kodja
Environmental Research.2022; 204: 112233. CrossRef - Urinary bisphenol concentrations and its association with metabolic disorders in the US and Korean populations
Ji Yoon Choi, Jiyun Lee, Da-An Huh, Kyong Whan Moon
Environmental Pollution.2022; 295: 118679. CrossRef - Associations of mid-childhood bisphenol A and bisphenol S exposure with mid-childhood and adolescent obesity
Priya Gajjar, Yun Liu, Nan Li, Jessie P. Buckley, Aimin Chen, Bruce P. Lanphear, Heidi J. Kalkwarf, Kim M. Cecil, Kimberly Yolton, Joseph M. Braun
Environmental Epidemiology.2022; 6(1): e187. CrossRef - Profile of Environmental Chemicals in the Korean Population—Results of the Korean National Environmental Health Survey (KoNEHS) Cycle 3, 2015–2017
Sun Kyoung Jung, Wookhee Choi, Sung Yeon Kim, Sooyeon Hong, Hye Li Jeon, Youngkyung Joo, Chulwoo Lee, Kyungho Choi, Sungkyoon Kim, Kee-Jae Lee, Jiyoung Yoo
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(2): 626. CrossRef - The bisphenol F and bisphenol S and cardiovascular disease: results from NHANES 2013–2016
Ruihua Wang, Qiaoyuan Fei, Shan Liu, Xueqiong Weng, Huanzhu Liang, Yingying Wu, Lin Wen, Guang Hao, Guangwen Cao, Chunxia Jing
Environmental Sciences Europe.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Bisphenols A and its analogues induce genotoxic damage in marine and freshwater amphipods
Serena Cosentino, Federica Aureli, Valentina Iannilli
Environmental Advances.2022; 7: 100183. CrossRef - Impact of environmental pollution on the obesogenic environment
Adriana Martínez-Esquivel, Daniela Joyce Trujillo-Silva, V Gabriela Cilia-López
Nutrition Reviews.2022; 80(7): 1787. CrossRef - Effects of BPZ and BPC on Oxidative Stress of Zebrafish under Different pH Conditions
Ying Han, Yumeng Fei, Mingxin Wang, Yingang Xue, Yuxuan Liu
Molecules.2022; 27(5): 1568. CrossRef - Race-specific associations of urinary phenols and parabens with adipokines in midlife women: The Study of Women's Health Across the Nation (SWAN)
Seulbi Lee, Carrie Karvonen-Gutierrez, Bhramar Mukherjee, William H. Herman, Sung Kyun Park
Environmental Pollution.2022; 303: 119164. CrossRef - Are BPA Substitutes as Obesogenic as BPA?
Fabiana Oliviero, Alice Marmugi, Catherine Viguié, Véronique Gayrard, Nicole Picard-Hagen, Laila Mselli-Lakhal
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(8): 4238. CrossRef - Aptamer-Based Biosensors for the Analytical Determination of Bisphenol A in Foodstuffs
Marica Erminia Schiano, Avazbek Abduvakhidov, Michela Varra, Stefania Albrizio
Applied Sciences.2022; 12(8): 3752. CrossRef - Bisphenol A exposure induces multiple effects in DOPC membrane models
Mateus D. Maximino, Cibely S. Martin, Priscila Aléssio
Journal of Molecular Liquids.2022; 359: 119253. CrossRef - Bisphenol S induces Agrp expression through GPER1 activation and alters transcription factor expression in immortalized hypothalamic neurons: A mechanism distinct from BPA-induced upregulation
Katherine J. Xu, Neruja Loganathan, Denise D. Belsham
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2022; 552: 111630. CrossRef - Bisphenol S Alters the Steroidome in the Preovulatory Follicle, Oviduct Fluid and Plasma in Ewes With Contrasted Metabolic Status
Ophélie Téteau, Philippe Liere, Antoine Pianos, Alice Desmarchais, Olivier Lasserre, Pascal Papillier, Claire Vignault, Marie-Emilie Lebachelier de la Riviere, Virginie Maillard, Aurélien Binet, Svetlana Uzbekova, Marie Saint-Dizier, Sebastien Elis
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship between bisphenol A, bisphenol S, and bisphenol F and serum uric acid concentrations among school-aged children
Yun Jeong Lee, Youn-Hee Lim, Choong Ho Shin, Bung-Nyun Kim, Johanna Inhyang Kim, Yun-Chul Hong, Yong Min Cho, Young Ah Lee, Pasquale Avino
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(6): e0268503. CrossRef - Associations of bisphenol exposure with thyroid hormones in pregnant women: a prospective birth cohort study in China
Huishen Huang, Jun Liang, Peng Tang, Chuanxiang Yu, Haoran Fan, Qian Liao, Jinghua Long, Dongxiang Pan, Xiaoyun Zeng, Shun Liu, Dongping Huang, Xiaoqiang Qiu
Environmental Science and Pollution Research.2022; 29(58): 87170. CrossRef - Association between urinary concentrations of bisphenol A substitutes and diabetes in adults
Rafael Moreno-Gómez-Toledano, Esperanza Vélez-Vélez, María I Arenas, Marta Saura, Ricardo J Bosch
World Journal of Diabetes.2022; 13(7): 521. CrossRef - Uncovering the functions of plasma proteins in ulcerative colitis and identifying biomarkers for BPA-induced severe ulcerative colitis: A plasma proteome analysis
Chen Huang, Yuqin Wang, Xiao Lin, Ting Fung Chan, Keng Po Lai, Rong Li
Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety.2022; 242: 113897. CrossRef - Relationship between emergent BPA-substitutes and renal and cardiovascular diseases in adult population
Rafael Moreno-Gómez-Toledano
Environmental Pollution.2022; 313: 120106. CrossRef - Climate change and the water quality threats posed by the emerging contaminants per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) and microplastics
Malcolm J. Gander
Water International.2022; : 1. CrossRef - Endocrine disruptor chemicals as obesogen and diabetogen: Clinical and mechanistic evidence
Niyazi Emre Kurşunoğlu, Banu Pinar Sarer Yurekli
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2022; 10(31): 11226. CrossRef - Exposure to Bisphenol A Substitutes, Bisphenol S and Bisphenol F, and Its Association with Developing Obesity and Diabetes Mellitus: A Narrative Review
Hend F. Alharbi, Raya Algonaiman, Rana Alduwayghiri, Thamer Aljutaily, Reham M. Algheshairy, Abdulkarim S. Almutairi, Razan M. Alharbi, Leena A. Alfurayh, Amjad A. Alshahwan, Amjad F. Alsadun, Hassan Barakat
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(23): 15918. CrossRef - Influence of BPA exposure, measured in saliva, on childhood weight
Leticia Heras-González, Diana Espino, Maria Jose Jimenez-Casquet, Alejandro Lopez-Moro, Fatima Olea-Serrano, Miguel Mariscal-Arcas
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Bisphenol S enhances gap junction intercellular communication in ovarian theca cells
Jeremy Gingrich, Yong Pu, Brad L. Upham, Madeline Hulse, Sarah Pearl, Denny Martin, Anita Avery, Almudena Veiga-Lopez
Chemosphere.2021; 263: 128304. CrossRef - Exposure to bisphenols and asthma morbidity among low-income urban children with asthma
Lesliam Quirós-Alcalá, Nadia N. Hansel, Meredith McCormack, Antonia M. Calafat, Xiaoyun Ye, Roger D. Peng, Elizabeth C. Matsui
Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology.2021; 147(2): 577. CrossRef - Evaluation of the effects of low nanomolar bisphenol A-like compounds’ levels on early human embryonic development and lipid metabolism with human embryonic stem cell in vitro differentiation models
Xiaoxing Liang, Renjun Yang, Nuoya Yin, Francesco Faiola
Journal of Hazardous Materials.2021; 407: 124387. CrossRef - Young children’s exposure to phenols in the home: Associations between house dust, hand wipes, silicone wristbands, and urinary biomarkers
Jessica L. Levasseur, Stephanie C. Hammel, Kate Hoffman, Allison L. Phillips, Sharon Zhang, Xiaoyun Ye, Antonia M. Calafat, Thomas F. Webster, Heather M. Stapleton
Environment International.2021; 147: 106317. CrossRef - Endocrine disrupting chemicals: Impacts on human fertility and fecundity during the peri-conception period
Mark P. Green, Alexandra J. Harvey, Bethany J. Finger, Gerard A. Tarulli
Environmental Research.2021; 194: 110694. CrossRef - Environmental Factors Involved in Maternal Morbidity and Mortality
Abee L. Boyles, Brandiese E. Beverly, Suzanne E. Fenton, Chandra L. Jackson, Anne Marie Z. Jukic, Vicki L. Sutherland, Donna D. Baird, Gwen W. Collman, Darlene Dixon, Kelly K. Ferguson, Janet E. Hall, Elizabeth M. Martin, Thaddeus T. Schug, Alexandra J. W
Journal of Women's Health.2021; 30(2): 245. CrossRef - Bisphenol-S and Bisphenol-F alter mouse pancreatic β-cell ion channel expression and activity and insulin release through an estrogen receptor ERβ mediated pathway
Laura Marroqui, Juan Martinez-Pinna, Manuel Castellano-Muñoz, Reinaldo S. dos Santos, Regla M. Medina-Gali, Sergi Soriano, Ivan Quesada, Jan-Ake Gustafsson, José A. Encinar, Angel Nadal
Chemosphere.2021; 265: 129051. CrossRef - Urinary bisphenol A concentrations and the risk of obesity in Korean adults
Shinje Moon, Moon Young Seo, Kyungho Choi, Yoon-seok Chang, Shin-Hye Kim, Mi Jung Park
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Transcriptomic pathway and benchmark dose analysis of Bisphenol A, Bisphenol S, Bisphenol F, and 3,3',5,5'-Tetrabromobisphenol A in H9 human embryonic stem cells
Vian Peshdary, Cheryl A. Hobbs, Timothy Maynor, Kim Shepard, Remi Gagné, Andrew Williams, Byron Kuo, Nikolai Chepelev, Leslie Recio, Carole Yauk, Ella Atlas
Toxicology in Vitro.2021; 72: 105097. CrossRef - Prenatal exposure to bisphenols and cognitive function in children at 7 years of age in the Swedish SELMA study
Carl-Gustaf Bornehag, Elin Engdahl, Maria Unenge Hallerbäck, Sverre Wikström, Christian Lindh, Joëlle Rüegg, Eva Tanner, Chris Gennings
Environment International.2021; 150: 106433. CrossRef - Urinary bisphenol A levels in prepubertal children with exogenous obesity according to presence of metabolic syndrome
Esra Aktağ, Kadriye Yurdakök, Siddika Songül Yalçın, Nurgün Kandemir
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 34(4): 495. CrossRef - Metabolic pathways, alterations in miRNAs expression and effects of genetic polymorphisms of bisphenol a analogues: A systematic review
Viviana Ramírez, Yolanda Gálvez-Ontiveros, Patricia Porras-Quesada, Luis Javier Martinez-Gonzalez, Ana Rivas, María Jesús Álvarez-Cubero
Environmental Research.2021; 197: 111062. CrossRef - Dietary quality and bisphenols: trends in bisphenol A, F, and S exposure in relation to the Healthy Eating Index using representative data from the NHANES 2007–2016
Irene van Woerden, Devon C Payne-Sturges, Corrie M Whisner, Meg Bruening
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2021; 114(2): 669. CrossRef - Bisphenol A and its effects on the systemic organs of children
Sarah Zulkifli, Amirah Abdul Rahman, Siti Hamimah Sheikh Abdul Kadir, Noor Shafina Mohd Nor
European Journal of Pediatrics.2021; 180(10): 3111. CrossRef - Bisphenols' occurrence in bivalves as sentinel of environmental contamination
Elena Baralla, Valeria Pasciu, Maria Vittoria Varoni, Maria Nieddu, Roberto Demuro, Maria Piera Demontis
Science of The Total Environment.2021; 785: 147263. CrossRef - Bisphenol F Exposure in Adolescent Heterogeneous Stock Rats Affects Growth and Adiposity
Valerie A Wagner, Karen C Clark, Leslie Carrillo-Sáenz, Katie A Holl, Miriam Velez-Bermudez, Derek Simonsen, Justin L Grobe, Kai Wang, Andrew Thurman, Leah C Solberg Woods, Hans-Joachim Lehmler, Anne E Kwitek
Toxicological Sciences.2021; 181(2): 246. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Exposure to Dietary Bisphenols in Adolescents
Virginia Robles-Aguilera, Yolanda Gálvez-Ontiveros, Lourdes Rodrigo, Inmaculada Salcedo-Bellido, Margarita Aguilera, Alberto Zafra-Gómez, Celia Monteagudo, Ana Rivas
Nutrients.2021; 13(5): 1553. CrossRef - Impact of short-term change of adiposity on risk of high blood pressure in children: Results from a follow-up study in China
Yi-de Yang, Ming Xie, Yuan Zeng, Shuqian Yuan, Haokai Tang, Yanhui Dong, Zhiyong Zou, Bin Dong, Zhenghe Wang, Xiangli Ye, Xiuqin Hong, Qiu Xiao, Jun Ma, Raffaella Buzzetti
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(9): e0257144. CrossRef - Life-Time Environmental Chemical Exposure and Obesity: Review of Epidemiological Studies Using Human Biomonitoring Methods
Nayan Chandra Mohanto, Yuki Ito, Sayaka Kato, Michihiro Kamijima
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Italian Children Exposure to Bisphenol A: Biomonitoring Data from the LIFE PERSUADED Project
Sabrina Tait, Fabrizia Carli, Luca Busani, Demetrio Ciociaro, Veronica Della Latta, Annalisa Deodati, Enrica Fabbrizi, Anna Paola Pala, Francesca Maranghi, Roberta Tassinari, Giacomo Toffol, Stefano Cianfarani, Amalia Gastaldelli, Cinzia La Rocca
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(22): 11846. CrossRef - Bisphenol A disrupts apolipoprotein E expression through estrogen-related receptor gamma and DNA methlylation in the liver of male rare minnow Gobiocypris rarus
Yingying Zhang, Zhu Zhu, Qiao Liu, Meng Zhang, Hui Yang, Wenzhi Wei
Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety.2021; 228: 113041. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome and Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals: An Overview of Exposure and Health Effects
Elsi Haverinen, Mariana F. Fernandez, Vicente Mustieles, Hanna Tolonen
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(24): 13047. CrossRef - Obesogens in Children—An Uncharted Territory
Mirjam Močnik, Nataša Marčun Varda
Metabolites.2021; 11(12): 882. CrossRef - Synthetic Chemicals and Cardiometabolic Health Across the Life Course Among Vulnerable Populations: a Review of the Literature from 2018 to 2019
Symielle A. Gaston, Linda S. Birnbaum, Chandra L. Jackson
Current Environmental Health Reports.2020; 7(1): 30. CrossRef - Bisphenol A analogues (BPS and BPF) present a greater obesogenic capacity in 3T3-L1 cell line
M.Á. Martínez, J. Blanco, J. Rovira, V. Kumar, J.L. Domingo, M. Schuhmacher
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2020; 140: 111298. CrossRef - Urinary bisphenol A and its analogues and haemato-biochemical alterations of pregnant women in Korea
Sora Kang, Bo Hye Shin, Jeoung A Kwon, Chan Wha Lee, Eun Kyo Park, Eun Young Park, Byungmi Kim
Environmental Research.2020; 182: 109104. CrossRef - Historical exposure to non-persistent environmental pollutants and risk of type 2 diabetes in a Spanish sub-cohort from the European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition study
E. Salamanca-Fernández, L.M. Iribarne-Durán, M. Rodríguez-Barranco, F. Vela-Soria, N. Olea, M.J. Sánchez-Pérez, J.P. Arrebola
Environmental Research.2020; 185: 109383. CrossRef - Association Between Bisphenol A Exposure and Risk of All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in US Adults
Wei Bao, Buyun Liu, Shuang Rong, Susie Y. Dai, Leonardo Trasande, Hans-Joachim Lehmler
JAMA Network Open.2020; 3(8): e2011620. CrossRef - Using three statistical methods to analyze the association between exposure to 9 compounds and obesity in children and adolescents: NHANES 2005-2010
Bangsheng Wu, Yi Jiang, Xiaoqing Jin, Li He
Environmental Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - How was the Diabetes Metabolism Journal added to MEDLINE?
Hye Jin Yoo
Science Editing.2020; 7(2): 201. CrossRef - Adipogenic effects of prenatal exposure to bisphenol S (BPS) in adult F1 male mice
Young-Ah Ahn, Hwayoung Baek, Miso Choi, Junbo Park, Soo Jin Son, Hyun Ju Seo, Jaeyun Jung, Je Kyung Seong, Jaehyouk Lee, Sungkyoon Kim
Science of The Total Environment.2020; 728: 138759. CrossRef - Bisphenol A Analogues in Food and Their Hormonal and Obesogenic Effects: A Review
Andújar, Gálvez-Ontiveros, Zafra-Gómez, Rodrigo, Álvarez-Cubero, Aguilera, Monteagudo, Rivas
Nutrients.2019; 11(9): 2136. CrossRef - Toxicological considerations of nano-sized plastics
PA Stapleton
AIMS Environmental Science.2019; 6(5): 367. CrossRef - Bisphenol A and adiposity measures in peripubertal boys from the INMA-Granada cohort
Vicente Mustieles, Maribel Casas, Patricia Ferrando-Marco, Olga Ocón-Hernández, Iris Reina-Pérez, Andrea Rodríguez-Carrillo, Fernando Vela-Soria, Rocío Pérez-Lobato, Eva María Navarrete-Muñoz, Carmen Freire, Nicolás Olea, Mariana F. Fernández
Environmental Research.2019; 173: 443. CrossRef - Trends and disparities in urinary BPA concentrations among U.S. emerging adults
Irene van Woerden, Meg Bruening, Jessica Montresor-López, Devon C. Payne-Sturges
Environmental Research.2019; 176: 108515. CrossRef - Concern about the Safety of Bisphenol A Substitutes
Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(1): 46. CrossRef - Urinary Bisphenols and Obesity Prevalence Among U.S. Children and Adolescents
Melanie H Jacobson, Miriam Woodward, Wei Bao, Buyun Liu, Leonardo Trasande
Journal of the Endocrine Society.2019; 3(9): 1715. CrossRef
- Obesogenic effects of six classes of emerging contaminants
- Epidemiology
- Association between Changes in Anthropometric Indices and in Fasting Insulin Levels among Healthy Korean Adolescents: The JS High School Study
- Ji Hye Park, Seyeon Mun, Dong Phil Choi, Joo Young Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(2):183-191. Published online January 22, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0034
- Correction in: Diabetes Metab J 2022;46(1):164
- 4,408 View
- 61 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background This study investigated the association between changes in anthropometric indices and fasting insulin levels among healthy adolescents and whether the association differed by baseline obesity status.
Methods This analysis was based on data collected for the JS High School study; 884 healthy adolescents aged 15 to 16 years followed up for 24 to 30 months were included. Changes in anthropometric indices and fasting insulin levels were computed as the difference between baseline and follow-up values. Multivariate linear regression models were used to determine the association between changes in anthropometric indices and fasting insulin levels. Based on body mass index (BMI)-for-age and waist circumference (WC)-for-age percentiles, participants were classified as normal weight (<85th percentile), overweight (85th percentile to <95th percentile), or obese (≥95th percentile).
Results Changes in BMI, WC, waist-hip ratio, and waist-height ratio were significantly associated with changes in fasting insulin levels in both sexes (
P <0.05). In analyses stratified by baseline obesity status, the association between change in BMI and change in fasting insulin was significantly stronger in overweight (males: standardized β=1.136; females: standardized β=1.262) and obese (males: standardized β=1.817; females: standardized β=2.290) participants than in those with normal weight (males: standardized β=0.957; females: standardized β=0.976) at baseline. Results were similar for changes in WC.Conclusion Changes in anthropometric indices were positively associated with fasting insulin level increases. Moreover, those who were overweight or obese at baseline had a higher absolute increase in fasting insulin levels per one standard deviation unit increase in anthropometric indices than adolescents with normal weight.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Rice-based breakfast improves fasting glucose and HOMA-IR in Korean adolescents who skip breakfast, but breakfast skipping increases aromatic amino acids associated with diabetes prediction in Korean adolescents who skip breakfast: a randomized, parallel-
Hyun Suk Kim, Su-Jin Jung, Soyoung Jang, Min Jung Kim, Youn-Soo Cha
Nutrition Research and Practice.2022; 16(4): 450. CrossRef
- Rice-based breakfast improves fasting glucose and HOMA-IR in Korean adolescents who skip breakfast, but breakfast skipping increases aromatic amino acids associated with diabetes prediction in Korean adolescents who skip breakfast: a randomized, parallel-
- Epidemiology
- Discrepancies between Glycosylated Hemoglobin and Fasting Plasma Glucose for Diagnosing Impaired Fasting Glucose and Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Youth and Young Adults
- Jieun Lee, Young Ah Lee, Jae Hyun Kim, Seong Yong Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Sei Won Yang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(2):174-182. Published online November 2, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0046
- 5,091 View
- 73 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) has been recommended as a diagnostic test for prediabetes and diabetes. Here, we evaluated the level of agreement between diagnoses based on fasting plasma glucose (FPG) versus HbA1c levels and determined optimal HbA1c cutoff values for these diseases in youth and young adults.
Methods The study included 7,332 subjects (
n =4,129, aged 10 to 19 years in youth group; andn =3,203 aged 20 to 29 years in young adult group) from the 2011 to 2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Prediabetes and diabetes were defined as 100 to 125 mg/dL (impaired fasting glucose [IFG]) and ≥126 mg/dL for FPG (diabetes mellitus [DM] by FPG [DMFPG]), and 5.7% to 6.4% and ≥6.5% for HbA1c, respectively.Results In the youth group, 32.5% with IFG had an HbA1c level of 5.7% to 6.4%, and 72.2% with DMFPG had an HbA1c ≥6.5%. In the young adult group, 27.5% with IFG had an HbA1c level of 5.7% to 6.4%, and 66.6% with DMFPG had an HbA1c ≥6.5%. Kappa coefficients for agreement between the FPG and HbA1c results were 0.12 for the youth group and 0.19 for the young adult group. In receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, the optimal HbA1c cutoff for IFG and DMFPG were 5.6% and 5.9% in youths and 5.5% and 5.8% in young adults, respectively.
Conclusion Usefulness of HbA1c for diagnosis of IFG and DMFPG in Koreans aged <30 years remains to be determined due to discrepancies between the results of glucose- and HbA1c-based tests. Additional testing might be warranted at lower HbA1c levels to detect IFG and DMFPG in this age group.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lower Dietary Magnesium Is Associated with a Higher Hemoglobin Glycation Index in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Juan Chen, Song Lin, Xingzhou Wang, Xiwei Wang, Pengxia Gao
Biological Trace Element Research.2024; 202(3): 878. CrossRef - Glycemic traits and colorectal cancer survival in a cohort of South Korean patients: A Mendelian randomization analysis
So Yon Jun, Sooyoung Cho, Min Jung Kim, Ji Won Park, Seung‐Bum Ryoo, Seung Yong Jeong, Kyu Joo Park, Aesun Shin
Cancer Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between HbA1c-derived estimated average glucose and fasting plasma glucose in patients with normal and abnormal hemoglobin patterns
Wilaiwan Sriwimol, Phattanapong Choosongsang, Pensiri Choosongsang, Warakorn Petkliang, Pittaya Treerut
Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation.2022; 82(3): 192. CrossRef - Increasing prevalence of fasting hyperglycemia in adolescents aged 10–18 years and its relationship with metabolic indicators: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Study (KNHANES), 2007–2018
Seung Eun Yoo, Ji Hyen Lee, Jung Won Lee, Hye Sook Park, Hye Ah Lee, Hae Soon Kim
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 27(1): 60. CrossRef - Differences in Clinical Indicators of Diabetes, Hypertension, and Dyslipidemia Among Workers Who Worked Long Hours and Shift Work
EunKyo Kang
Workplace Health & Safety.2021; 69(6): 268. CrossRef - Practice Patterns in the Acceptance of Medically Complex Living Kidney Donors with Obesity, Hypertension, Family History of Kidney Disease, or Donor-Recipient Age Discrepancy
Ziad Arabi, Muhammad Bukhari, Abdullah Hamad, Abdulrahman Altheaby, Saleh Kaysi
Avicenna Journal of Medicine.2021; 11(04): 172. CrossRef - Endocrine comorbidities of pediatric obesity
Jieun Lee, Jae Hyun Kim
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics.2021; 64(12): 619. CrossRef - Association between handgrip strength and cardiovascular risk factors among Korean adolescents
Kyoung Kon Kim, Kyu Rae Lee, In Cheol Hwang
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 33(9): 1213. CrossRef - Hypertriglyceridemia is associated with long-term risk of cardiovascular events and specific comorbidity in very high-risk hypertensive patients
O. Ya. Korolyuk, O. M. Radchenko
The Ukrainian Biochemical Journal.2020; 92(2): 8. CrossRef - The Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Weight Loss and Metabolic Changes in Adults with Obesity
Stanisław Głuszek, Arkadiusz Bociek, Edyta Suliga, Jarosław Matykiewicz, Magdalena Kołomańska, Piotr Bryk, Przemysław Znamirowski, Łukasz Nawacki, Martyna Głuszek-Osuch, Iwona Wawrzycka, Dorota Kozieł
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(15): 5342. CrossRef - Peculiarities of Clinical Presentations and Long–Term Complications in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease and Metabolic Syndrome, depending on their Serum Triglyceride Levels
O. Ya. Korolyuk
Ukraïnsʹkij žurnal medicini, bìologìï ta sportu.2020; 5(1): 125. CrossRef
- Lower Dietary Magnesium Is Associated with a Higher Hemoglobin Glycation Index in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Clinical Care/Education
- Frequency of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose during the School Day Is Associated with the Optimal Glycemic Control among Korean Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes
- Eun Young Joo, Ji-Eun Lee, Hee Sook Kang, Shin Goo Park, Yong Hee Hong, Young-Lim Shin, Min Sohn
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(6):480-487. Published online June 29, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0018
- 4,301 View
- 65 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between the frequency of self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels among Korean adolescents with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). Factors affecting the SMBG frequency were analyzed in order to improve their glycemic control.
Methods Sixty-one adolescents aged 13 to 18 years with T1DM were included from one tertiary center. Clinical and biochemical variables were recorded. Factors associated with SMBG frequency were assessed using structured self-reported questionnaires.
Results Average total daily SMBG frequency was 3.8±2.1 and frequency during the school day was 1.3±1.2. The mean HbA1c level was 8.6%±1.4%. As the daily SMBG frequency increased, HbA1c levels declined (
P =0.001). The adjusted odds of achieving the target HbA1c in participants who performed daily SMBG ≥5 significantly increased 9.87 folds (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.58 to 61.70) compared with those performed SMBG four times a day. In the subjects whose SMBG frequency <1/day during the school day, an 80% reduction in the adjusted odds ratio 0.2 (95% CI, 0.05 to 0.86) showed compared to the group with performing two SMBG measurements in the school setting. The number of SMBG testing performed at school was significantly high for individuals assisted by their friends (P =0.031) and for those who did SMBG in the classrooms (P =0.039).Conclusion Higher SMBG frequency was significantly associated with lower HbA1c in Korean adolescents with T1DM. It would be necessary to establish the school environments that can facilitate adequate glycemic control, including frequent SMBG.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Problems of blood glucose self-monitoring in patients with diabetes mellitus
Yu. A. Kononova, V. B. Bregovskiy, A. Yu. Babenko
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2022; (21-1): 140. CrossRef - Adherence as a Predictor of Glycemic Control Among Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes: A Retrospective Study Using Real-world Evidence
Sohayla A. Ibrahim, Maguy Saffouh El Hajj, Yaw B. Owusu, Maryam Al-Khaja, Amel Khalifa, Dalia Ahmed, Ahmed Awaisu
Clinical Therapeutics.2022; 44(10): 1380. CrossRef - Self-Care IoT Platform for Diabetic Mellitus
Jai-Chang Park, Seongbeom Kim, Je-Hoon Lee
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(5): 2006. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Adherence to Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose Among Young People with Type 1 Diabetes in China: A Cross-Sectional Study
Wencong Lv, Jiaxin Luo, Qing Long, Jundi Yang, Xin Wang, Jia Guo
Patient Preference and Adherence.2021; Volume 15: 2809. CrossRef - Habits and Routines during Transitions among Emerging Adults with Type 1 Diabetes
Kathleen M. Hanna, Jed R. Hansen
Western Journal of Nursing Research.2020; 42(6): 446. CrossRef - How was the Diabetes Metabolism Journal added to MEDLINE?
Hye Jin Yoo
Science Editing.2020; 7(2): 201. CrossRef - Differences of FreeStyle Libre Flash Glucose Monitoring System and Finger Pricks on Clinical Characteristics and Glucose Monitoring Satisfactions in Type 1 Diabetes Using Insulin Pump
Ayman A Al Hayek, Asirvatham A Robert, Mohamed A Al Dawish
Clinical Medicine Insights: Endocrinology and Diabetes.2019; 12: 117955141986110. CrossRef
- Problems of blood glucose self-monitoring in patients with diabetes mellitus
- Associations between Fatness, Fitness, IGF and IMT among Obese Korean Male Adolescents
- Eun Sung Kim, Ji-Hye Park, Mi Kyung Lee, Dong Hoon Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Hyun Chul Lee, Yoonsuk Jekal, Justin Y. Jeon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(6):610-618. Published online December 26, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.6.610
- 39,796 View
- 43 Download
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The purpose of this study was to investigate the association between obesity, fitness levels and cardiovascular (CVD) risk factors, and to identify the correlation between of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-1, IGF binding protein-3 (IGFBP-3), and carotid intima media thickness (IMT) in Korean adolescents.
Methods A total of 225 high school males with a mean age of 16.96±0.23 years participated in this study, and their fatness and fitness levels, fasting glucose, fasting insulin, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), blood lipids, IGF-1, IGFBP-3, and IMT were measured.
Results The results showed that total cholesterol (TC), triglyceride (TG), high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, IGF-1, and IGFBP-3 levels were significantly higher in the most obese group than in the other two groups (tertiles). Muscular and cardiopulmonary fitness were negatively associated with weight, body mass index (BMI), fat mass, body fat, waist circumference (WC), fasting insulin, HOMA-IR, and IMT. IGF-1 and IGFBP-3 levels were correlated with WC, hip circumference (HC), fasting glucose, TG, HDL-C, fasting insulin, and HOMA-IR. IMT levels were significantly associated with weight, BMI, muscle mass, fat mass, percent body fat, WC, HC, systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein.
Conclusion There was a significant association between increased obesity and decreased fitness and HOMA-IR, IGF, and IMT among adolescents.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship between insulin-like growth factor-1, insulin resistance and metabolic profile with pre-obesity and obesity in children
Marina Jaksic, Milica Martinovic, Najdana Gligorovic-Barhanovic, Tanja Antunovic, Mirjana Nedovic-Vukovic
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 34(3): 301. CrossRef - Enerji Metabolizması, Obezite ve Hormonlar
Derya Selda SINAR, Nasuh Evrim ACAR, İrfan YILDIRIM
Türkiye Spor Bilimleri Dergisi.2020; 4(1): 30. CrossRef - Carotid Intima‐Media Thickness but Not Carotid Artery Plaque in Healthy Individuals Is Linked to Lean Body Mass
Matthew Arnold, Andrew Linden, Robert Clarke, Yu Guo, Huaidong Du, Zheng Bian, Eric Wan, Meng Yang, Liang Wang, Yuexin Chen, Jianwei Chen, Huajun Long, Qijun Gu, Rory Collins, Liming Li, Zhengming Chen, Sarah Parish, Junshi Chen, Jun Lv, Richard Peto, Rob
Journal of the American Heart Association.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Oxidative Stress and Inflammation, Key Targets of Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression and Vulnerability: Potential Impact of Physical Activity
Pauline Mury, Erica N. Chirico, Mathilde Mura, Antoine Millon, Emmanuelle Canet-Soulas, Vincent Pialoux
Sports Medicine.2018; 48(12): 2725. CrossRef - Protein Intake in Infancy and Carotid Intima Media Thickness at 5 Years - A Secondary Analysis from a Randomized Trial
Dariusz Gruszfeld, Martina Weber, Monika Nowakowska-Rysz, Roman Janas, Rainer Kozlik-Feldmann, Annick Xhonneux, Clotilde Carlier, Enrica Riva, Elvira Verduci, Ricardo Closa-Monasterolo, Joaquin Escribano, Anna Dobrzanska, Berthold Koletzko
Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism.2015; 66(1): 51. CrossRef - High Prevalence of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Hispanic Adolescents: Correlations with Adipocytokines and Markers of Inflammation
Cynthia M. Pérez, Ana P. Ortiz, Enrique Fuentes-Mattei, Guermarie Velázquez-Torres, Damarys Santiago, Katya Giovannetti, Raúl Bernabe, Mong-Hong Lee, Sai-Ching J. Yeung
Journal of Immigrant and Minority Health.2014; 16(5): 865. CrossRef - Cross-sectional and longitudinal relation of IGF1 and IGF-binding protein 3 with lipid metabolism
Marie-Luise Eggert, Henri Wallaschofski, Anne Grotevendt, Matthias Nauck, Henry Völzke, Stefanie Samietz, Nele Friedrich
European Journal of Endocrinology.2014; 171(1): 9. CrossRef - Association between insulin‐like growth factor‐1, measures of overnutrition and undernutrition and insulin resistance in black adolescents living in the north‐west province, South Africa
Ramoteme L. Mamabolo, Cristiana Berti, Makama A. Monyeki, H. Salome Kruger
American Journal of Human Biology.2014; 26(2): 189. CrossRef - Relationship of serum insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) with nutritional status in pediatric patients with malignant diseases—a single Romanian center experience
Mihaela Ioana Chinceşan, Oana Mărginean, Ana-Maria Pitea, Minodora Dobreanu
European Journal of Pediatrics.2013; 172(10): 1401. CrossRef - Gene x environment interactions impact endometrial function and the menstrual cycle: PROGINS, life history, anthropometry, and physical activity
Elizabeth J. Rowe, Toby K. Eisenstein, Joseph Meissler, L. Christie Rockwell
American Journal of Human Biology.2013; 25(5): 681. CrossRef - Insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and clinical nutrition
Callum Livingstone
Clinical Science.2013; 125(6): 265. CrossRef - Higher Body Mass Index Leads to Longer Operative Time in Total Knee Arthroplasty
Barthelemy Liabaud, David A. Patrick, Jeffrey A. Geller
The Journal of Arthroplasty.2013; 28(4): 563. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Fitness, BMI and Risk Factors of Metabolic Syndrome Among University Students in Korea
Dong-il Kim, Ji Young Kim, Mi Kyoung Lee, Hae-Dong Lee, Ji-Won Lee, Justin Y. Jeon
The Korean Journal of Obesity.2012; 21(2): 99. CrossRef - The Insulin-Like Growth Factor System and Nutritional Assessment
Callum Livingstone
Scientifica.2012; 2012: 1. CrossRef
- Relationship between insulin-like growth factor-1, insulin resistance and metabolic profile with pre-obesity and obesity in children
- Effects of Resistance Training and Aerobic Exercise on Insulin Sensitivity in Overweight Korean Adolescents: A Controlled Randomized Trial
- Sunghwan Suh, In-Kyong Jeong, Mi Yeon Kim, Yeon Soo Kim, Sue Shin, Sun Sin Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(4):418-426. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.418
- 21,482 View
- 46 Download
- 22 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Data on the impact of resistance training on insulin resistance in overweight or obese children are inconclusive.
Methods Thirty overweight South Korean adolescents (mean age of 13.10 years) were divided by sex, and then randomly assigned to one of three treatment groups, which were the diet only (DO), diet with aerobic exercise (AE), or diet with resistance training (RT) group. Physiologic and metabolic parameters were assessed at baseline and after 12 weeks of exercise training and diet modification.
Results Both exercise groups (aerobic and resistance) showed significant improvements in their insulin area under the curve and insulin sensitivity index values when compared to their baseline values while the DO group showed no significant changes in these variables. Age-, sex-, and body mass index (BMI)-adjusted intergroup comparison analyses showed a marked reduction in BMI and a significant reduction in muscle mass in the AE group when compared to the RT group and the DO group, respectively.
Conclusion A 12-week exercise training program of either resistance or aerobic activity improved insulin sensitivity in overweight adolescents, although it failed to show superiority over a DO program. Aerobic exercise decreased both body weight and BMI, and it was noted that this group also had a significant reduction in muscle mass when compared to the DO group.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of high-intensity interval training and moderate-intensity continuous training on cardiovascular risk factors in adolescents: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Ya Wang, Shun Wang, Xiangwu Meng, Husheng Zhou
Physiology & Behavior.2024; 275: 114459. CrossRef - Exercise and Nutrition Strategies for Combating Sarcopenia and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Older Adults
Dionysia Argyropoulou, Nikolaos D. Geladas, Tzortzis Nomikos, Vassilis Paschalis
Journal of Functional Morphology and Kinesiology.2022; 7(2): 48. CrossRef - Effects and dose-response relationships of exercise intervention on weight loss in overweight and obese children: a meta-regression and system review
Rui Xu, Qiao-Ting Huang, Yu-Ting Chen, Peng-Yin Wang
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 35(9): 1117. CrossRef - The Benefits of Resistance Training in Obese Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Bruno Ribeiro, Pedro Forte, Raquel Vinhas, Daniel A. Marinho, Luís B. Faíl, Ana Pereira, Fernando Vieira, Henrique P. Neiva
Sports Medicine - Open.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Eight Weeks of Combined Training with Antioxidant Vitamins E and C on Glutathione, Glutathione Peroxidase, and Superoxide Dismutase in the Heart Tissue of Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rats
Elaheh Heydarnia, Farzaneh Taghian, Khosro Jalali Dehkodi, Mehrzad Moghadasi
Gene, Cell and Tissue.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of resistance training with and without caloric restriction on visceral fat: A systemic review and meta‐analysis
Mousa Khalafi, Abbas Malandish, Sara K. Rosenkranz, Ali A. Ravasi
Obesity Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - IMPACT OF TREADMILL RUNNING ON BLOOD GLUCOSE LEVEL OF TYPE 2 DIABETES MELLITUS PATIENTS IN GHURKI TRUST AND TEACHING HOSPITAL
Samiya Noreen, Muhammad Shafique, Tayyaba Mustafa Mian, Hafiz Abdul Rehman, Abdul Rehman, Muhammad Saad Shafiq, Ibraheem Zafar, Ramsha Masood
Pakistan BioMedical Journal.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Role of exercise on insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function: is exercise sufficient for the prevention of youth-onset type 2 diabetes?
Joon Young Kim, Justin Y. Jeon
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2020; 25(4): 208. CrossRef - Effects of HIIT and MICT on cardiovascular risk factors in adults with overweight and/or obesity: A meta-analysis
LiQiang Su, JinMei Fu, ShunLi Sun, GuangGao Zhao, Wei Cheng, ChuanChuan Dou, MingHui Quan, Belinda Parmenter
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(1): e0210644. CrossRef - What Is the Role of Resistance Exercise in Improving the Cardiometabolic Health of Adolescents with Obesity?
SoJung Lee, YoonMyung Kim, Jennifer L. Kuk
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2019; 28(2): 76. CrossRef - Does exercise training affect resting metabolic rate in adolescents with obesity?
Angela S. Alberga, Denis Prud’homme, Ronald J. Sigal, Gary S. Goldfield, Stasia Hadjiyannakis, Réjeanne Gougeon, Penny Phillips, Janine Malcolm, George A. Wells, Steve Doucette, Jinhui Ma, Glen P. Kenny
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2017; 42(1): 15. CrossRef - Iniciación al entrenamiento de fuerza en edades tempranas: revisión
G. Peña, J.R. Heredia, C. Lloret, M. Martín, M.E. Da Silva-Grigoletto
Revista Andaluza de Medicina del Deporte.2016; 9(1): 41. CrossRef - Effects of aerobic training, resistance training, or both on cardiorespiratory and musculoskeletal fitness in adolescents with obesity: the HEARTY trial
Angela S. Alberga, Denis Prud’homme, Ronald J. Sigal, Gary S. Goldfield, Stasia Hadjiyannakis, Penny Phillips, Janine Malcolm, Jinhui Ma, Steve Doucette, Rejeanne Gougeon, George A. Wells, Glen P. Kenny
Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism.2016; 41(3): 255. CrossRef - The response of circulating omentin-1 concentration to 16-week exercise training in male children with obesity
Farzad Zehsaz, Negin Farhangi, Mehri Ghahramani
The Physician and Sportsmedicine.2016; 44(4): 355. CrossRef - Epidemiology of Childhood Obesity in Korea
Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(4): 510. CrossRef - Muscle strength in youth and cardiovascular risk in young adulthood (the European Youth Heart Study)
Anders Grøntved, Mathias Ried-Larsen, Niels Christian Møller, Peter Lund Kristensen, Karsten Froberg, Søren Brage, Lars Bo Andersen
British Journal of Sports Medicine.2015; 49(2): 90. CrossRef - Position statement on youth resistance training: the 2014 International Consensus
Rhodri S Lloyd, Avery D Faigenbaum, Michael H Stone, Jon L Oliver, Ian Jeffreys, Jeremy A Moody, Clive Brewer, Kyle C Pierce, Teri M McCambridge, Rick Howard, Lee Herrington, Brian Hainline, Lyle J Micheli, Rod Jaques, William J Kraemer, Michael G McBride
British Journal of Sports Medicine.2014; 48(7): 498. CrossRef - Abdominal obesity and low physical activity are associated with insulin resistance in overweight adolescents: a cross-sectional study
Claudia-María Velásquez-Rodríguez, Marcela Velásquez-Villa, Leidy Gómez-Ocampo, Juliana Bermúdez-Cardona
BMC Pediatrics.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise and Insulin Resistance in Youth: A Meta-Analysis
Michael V. Fedewa, Nicholas H. Gist, Ellen M. Evans, Rod K. Dishman
Pediatrics.2014; 133(1): e163. CrossRef - What is the Effect of Resistance Training on the Strength, Body Composition and Psychosocial Status of Overweight and Obese Children and Adolescents? A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Natasha Schranz, Grant Tomkinson, Tim Olds
Sports Medicine.2013; 43(9): 893. CrossRef - A Review of Randomized Controlled Trials of Aerobic Exercise Training on Fitness and Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in Obese Adolescents
A. S. Alberga, A. Frappier, R. J. Sigal, D. Prud'homme, G. P. Kenny
The Physician and Sportsmedicine.2013; 41(2): 44. CrossRef - Effects of Aerobic Versus Resistance Exercise Without Caloric Restriction on Abdominal Fat, Intrahepatic Lipid, and Insulin Sensitivity in Obese Adolescent Boys
SoJung Lee, Fida Bacha, Tamara Hannon, Jennifer L. Kuk, Chris Boesch, Silva Arslanian
Diabetes.2012; 61(11): 2787. CrossRef
- Effect of high-intensity interval training and moderate-intensity continuous training on cardiovascular risk factors in adolescents: Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
- The Relationship between the Level of Fatness and Fitness during Adolescence and the Risk Factors of Metabolic Disorders in Adulthood
- Yoonsuk Jekal, Ji Eun Yun, Sang Wook Park, Sun Ha Jee, Justin Y Jeon
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(2):126-134. Published online April 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.2.126
- 3,170 View
- 27 Download
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The purpose of the current study was to investigate the association between the level of obesity and physical fitness (PF) during adolescence and the risk factors of metabolic disorders during adulthood.
Methods In the current analysis, 3,993 Korean adults (mean age, 38.70 ± 1.69 years) were recruited. The level of body index (BI) and PF were examined during adolescence through high school record, and their health examination data, including systolic blood pressure (SBP), diastolic blood pressure (DBP), fasting glucose (FG), total cholesterol (TC), and current body mass index (BMI) were obtained from National Health Insurance Corporation Data. Gender-specific analyses were administered to compare health exam data across the level of BI, the level of PF, and a mixed level of BI and PF.
Results Most obese males during high school had statistically higher SBP, DBP, FG, and BMI in adulthood, and most obese females had higher BMI, as compared to most lean males or females. Least fit males during high school had statistically higher BMI in adulthood, and least fit females had statistically higher SBP, DBP, FG, TC, and BMI, as compared to most fit males or females. There was a significant relationship between the mixed level of BI and PF and SBP, DBP, TC and current BMI in both genders.
Conclusion Maintaining a healthy level of body weight and PF during adolescence is recommended to prevent the development of metabolic diseases in adulthood.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A cross‐sectional study on the use of big data for the past H1N1 influenza epidemic in obesity after COVID‐19: Focused on the body slimming cream and leptin via DTC gene test
Jinkyung Lee, Ki Han Kwon
Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology.2022; 21(11): 5321. CrossRef - Aerobic fitness in late adolescence and the risk of cancer and cancer-associated mortality in adulthood: A prospective nationwide study of 1.2 million Swedish men
G. Högström, H. Ohlsson, C. Crump, J. Sundquist, K. Sundquist
Cancer Epidemiology.2019; 59: 58. CrossRef - Study Time after School and Habitual Eating Are Associated with Risk for Obesity among Overweight Korean Children: A Prospective Study
Eun Young Lee, Borami Kang, Yeoree Yang, Hae Kyung Yang, Hun-Sung Kim, Sun-Young Lim, Jin-Hee Lee, Seong-Su Lee, Byung-Kyu Suh, Kun-Ho Yoon
Obesity Facts.2018; 11(1): 46. CrossRef - Differences in Dietary Life and Health related Factors According to Obesity in Poor Urban Peruvian Adolescents
Hye-Kyung Chung, Hae-Young Lee, Jin Ri Kim, Eun Woo Nam
Korean Journal of Community Nutrition.2018; 23(4): 302. CrossRef - The influence of aerobic fitness on obesity and its parent-offspring correlations in a cross-sectional study among German families
Ronja Foraita, Mirko Brandes, Frauke Günther, Karin Bammann, Iris Pigeot, Wolfgang Ahrens
BMC Public Health.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Participation in Physical Activity “The Development of Fitness” Class on Physical Fitness and Risk Factors for Metabolic Syndrome of University Students in Korea
김동일, Justin Jeon, 이해동, 박지혜, 홍성현
Korean Journal of Sport Science.2012; 23(3): 478. CrossRef - Epidemiology and prevention of stroke: a worldwide perspective
Elena V Kuklina, Xin Tong, Mary G George, Pooja Bansil
Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics.2012; 12(2): 199. CrossRef - Fitness, Fatness, and Cardiovascular Disease Risk and Outcomes
John M. Jakicic, Anne E. Mishler, Renee Rogers
Current Cardiovascular Risk Reports.2011; 5(2): 113. CrossRef - Epidemiology of Physical Activity Participation and Type 2 Diabetes in Korea
Yoonsuk Jekal, Justin Y Jeon
Journal of Korean Diabetes.2011; 12(1): 13. CrossRef - Relationship Between Trajectories of Trunk Fat Mass Development in Adolescence and Cardiometabolic Risk in Young Adulthood
Lauren B. Sherar, Joe C. Eisenmann, Philip D. Chilibeck, Nazeem Muhajarine, Susanna Martin, Donald A. Bailey, Adam D.G. Baxter‐Jones
Obesity.2011; 19(8): 1699. CrossRef
- A cross‐sectional study on the use of big data for the past H1N1 influenza epidemic in obesity after COVID‐19: Focused on the body slimming cream and leptin via DTC gene test
- Self-Management and Health-Related Quality of Life in Adolescent and Adulthood Diabetic Patients.
- Bong Suk Park, Gi Nam Jin, Youn Chung Choi, Ji Hee Chung, Kyoung Hoe Kim, Mi Young Lee, Jang Hyun Koh, Choon Hee Chung
- Korean Diabetes J. 2005;29(3):254-261. Published online May 1, 2005
- 1,134 View
- 29 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
The purposes of this study are to analyze the factors that influence selfmanagement and health-related QOL, and to provide useful informations to improve the QOL in adolescent and adult diabetic patients. METHODS: For this study, we interviewed 126 adolescent and adult diabetic patients who visited the Yonsei University Wonju Christian Hospital from March 4th, 2004 to April 5th, 2004. RESULTS: We examined the relationship between the socio-demographic characteristics and the health-related quality of life(QOL). There were statistically significant relationships between the QOL-and employment, years of education, income level and marriage status, but not between the health-related QOL and age and gender. Furthermore, there were no statistically significant relationships between the health-related QOL and smoking or drinking, nor between type 1 and 2 diabetic patients. The health-related QOL was significantly higher for an increased diabetes duration and for a greater number of symptoms, but the QOL was significantly lower in the presence of complications and hospital admission. The health-related QOL was lower when the preprandial blood glucose levels and HbA1c concentrations were higher, but it was higher when the hemoglobin and hematocrit levels were higher. Regarding the treatment methods, the health-related QOL was significantly lower for those patients who took insulin injection. The QOL was higher when the general self-management and diet therapy were well-controlled. Meanwhile, those subjects who had obtained medical informations from doctors, the media(including the internet and TV) and nurses in that order, they selected diet therapy as the hardest factor in the management of their diabetes. CONCLUSION: Adolescent and adult diabetic patients need continuous education and assistance to improve their health-related QOL and to keep from developing complications

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





