- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 41(5); 2017 > Article
-
Original ArticleOthers Generation of Insulin-Expressing Cells in Mouse Small Intestine by Pdx1, MafA, and BETA2/NeuroD
-
So-Hyun Lee, Marie Rhee, Ji-Won Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon

-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2017;41(5):405-416.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.5.405
Published online: September 5, 2017
Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Kun-Ho Yoon. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, 222 Banpo-daero, Seocho-gu, Seoul 06591, Korea. yoonk@catholic.ac.kr
• Received: March 13, 2017 • Accepted: June 3, 2017
Copyright © 2017 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- To develop surrogate insulin-producing cells for diabetes therapy, adult stem cells have been identified in various tissues and studied for their conversion into β-cells. Pancreatic progenitor cells are derived from the endodermal epithelium and formed in a manner similar to gut progenitor cells. Here, we generated insulin-producing cells from the intestinal epithelial cells that induced many of the specific pancreatic transcription factors using adenoviral vectors carrying three genes: PMB (pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 [Pdx1], V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog A [MafA], and BETA2/NeuroD).
-
Methods
- By direct injection into the intestine through the cranial mesenteric artery, adenoviruses (Ad) were successfully delivered to the entire intestine. After virus injection, we could confirm that the small intestine of the mouse was appropriately infected with the Ad-Pdx1 and triple Ad-PMB.
-
Results
- Four weeks after the injection, insulin mRNA was expressed in the small intestine, and the insulin gene expression was induced in Ad-Pdx1 and Ad-PMB compared to control Ad-green fluorescent protein. In addition, the conversion of intestinal cells into insulin-expressing cells was detected in parts of the crypts and villi located in the small intestine.
-
Conclusion
- These data indicated that PMB facilitate the differentiation of mouse intestinal cells into insulin-expressing cells. In conclusion, the small intestine is an accessible and abundant source of surrogate insulin-producing cells.
- Islet transplantation has been reported as a treatment for patients with type 1 diabetes who have difficulty controlling glucose levels despite insulin therapy [1]. However, its applicability has been limited by the shortage of pancreas from donors and the requirement for immunosuppressive drugs. To overcome this problem, recent strategies have involved the differentiation of functional β-cells from other sources of non-β-cells [23]. Generation of insulin-producing cells has demonstrated that pancreatic ductal cells [4], α-cells [5], liver cells [6], bone marrow cells [7], and embryonic stem cells or induced pluripotent stem cells can differentiate into β-cells using reprogramming factors involved in proliferation and differentiation [8].
- The ectopic expression of transcription factors can convert terminally differentiated cells to insulin-producing cells by somatic cell transdifferentiation [9]. In the pancreas, pancreatic-specific transcription factors are indispensable for normal islet development. The functional expression of specific transcription factors is required for the formation of pancreatic endocrine tissue during development [10]. Pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 (Pdx1) is involved in pancreatic neogenesis and maintenance of normal β-cells [11]. Elevated levels of PDX1/VP16 can be generated by fusing mouse PDX1 to the VP16 activation domain to drive insulin biosynthesis and hyperactive proliferation of Pdx1 [12]. Additionally, other transcription factors have also been studied, including β-cell E-box transcription factor (BETA2/NeuroD) [1314] and V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog A (MafA) [15]. These are important key factors for the development and proliferation of the pancreas, regulation of survival of the β-cell, and maintenance of healthy β-cells [1011]. Pdx1, MafA, and BETA2/NeuroD (PMB) can induce hepatocytes to become insulin-producing cells [16]. It has also been reported that MafA overexpression in rat small intestinal epithelial cells (IECs) can convert intestinal cells into insulin-positive cells in vivo [17].
- Both pancreatic progenitor cells and gut progenitor cells are derived from the endodermal epithelium and proceed through related developmental pathways [1819]. In the intestine, stem cells are located in the crypt base and have the ability to self-renew and rapidly differentiate into the four distinct cell types of the intestinal epithelium, including goblet cells, paneth cells, enterocytes, and enteroendocrine cells [2021]. In addition, the IECs express pancreatic transcription factors such as Pdx1 and hepatocyte nuclear factors during the course of development [22]. Recently, it has been reported that when the three pancreatic transcription factors—Pdx1, MafA, and neurogenin 3 (Ngn3)—are ectopically expressed in the tissue of the intestine, the intestinal cells differentiate into β-like cells in immunecompetent mice [23]; the transient expression of these factors could generate β-like cells in the mouse intestine. In this study, we induced the transdifferentiation of β-cells from IECs using three adenoviral-mediated transcription factors within the intestine. Overall, our results suggest that the small intestine can become an infinite potential source of surrogate β-cells.
INTRODUCTION
- Animals
- Male C57BL/6 mice were purchased from Charles River Laboratories (Orient Bio, Seongnam, Korea). The animal care and use protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea. The C57BL/6 mice were 8 to 10 weeks old and weighed 20 to 22 g.
- Adenoviral vectors
- Recombinant adenoviruses (Ad) expressing rat green fluorescent protein (GFP), rat PDX1/VP16, mouse MafA, and hamster BETA2/NeuroD were provided by Dr. K. Hideaki (Osaka University, Osaka, Japan) [1215]. All vectors were generated with the AdEasy system (Clontech, Mountain View, CA, USA) [12]. All recombinant viruses were cloned into a shuttle vector (pAd-Track-CMV) [12]. The PDX1/VP16 and BETA2/NeuroD coding sequences also contained a GFP expressing sequence. All procedures were followed as previously described [12].
- Injection of adenoviral vectors
- We divided the animals into three groups for injection in vivo (Fig. 1). We prepared Ad-mediated pancreatic transcription factors to a titer of 1.00E+09 (pfu/mL) for Ad-GFP (n=4) control, 1.00E+09 (pfu/mL) for Ad-Pdx1 (n=5), and a mixture with 3.30E+08 (pfu/mL) each of Ad-PMB (n=4). C57BL/6 mice were injected through the cranial mesenteric artery with each corresponding group of Ad. We confirmed that the Ad injected into the artery was delivered throughout the duodenum and the colon (Supplementary Fig. 1).
- Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction
- After harvesting the mouse duodenum, total RNA was isolated using TRIzol reagent (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer's protocol. First-strand cDNA synthesis was performed using PrimeScrip 1st Strand cDNA Synthesis Kit (Takara Biomedicals, Kyoto, Japan). The cDNA products were amplified with the Perfect PreMix (Takara), and reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) was performed using the Takara PCR Thermal Cycler Dice Gradient (Takara) according to the manufacturer's protocol, followed by electrophoresis on a 1.5% agarose gel. The pancreatic transcription factor primers are indicated in Table 1.
- Quantitative real-time PCR
- Each of the cDNA products were synthesized as described above. The cDNA products were amplified with the Power SYBR Green Master Mix (Life Technologies, Carlsbad, CA, USA) and quantitative RT-PCR was performed using the Step One Plus Real-Time PCR System (Life Technologies) according to the supplied protocol. The pancreatic specific primer sequences are listed in Table 2.
- Immunohistochemistry staining
- Tissue from the small intestine was cut into 1- to 2-cm-long pieces, opened longitudinally, washed in phosphate buffered saline, and fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde overnight at 4℃. After embedding in paraffin, the tissues were subsequently cut into 4-µm sections using a microtome (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). Immunostaining was performed using the following primary antibodies: monoclonal rabbit anti-leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5 (Lgr5) immunoglobulin G (IgG, 1:50; Abcam, Cambridge, MA, USA), or mouse anti-Pdx1 IgG (1:200; Developmental Studies Hybridoma Bank, Iowa City, IA, USA) or rabbit anti-chromogranin A (CGA) IgG (1:50; Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA, USA), and rabbit anti-cytokeratin 19 (CK19) IgG (1:100; Zymed Laboratories, South San Francisco, CA, USA). After overnight incubation with the primary antibodies at 4℃, the slides were incubated with biotin-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody for 30 minutes. We performed an avidin-biotin complex reaction for 30 minutes. Diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) was added for the colorimetric reaction, and nuclear staining was performed using hematoxylin a few minutes later. The stained cells were evaluated by microscopy (Leica).
- Immunofluorescence staining
- After obtaining the tissue sections of the paraffin blocks previously described, immunostaining was performed using the monoclonal guinea pig polyclonal anti-insulin IgG (1:200; Zymed Laboratories) and polyclonal anti-C-peptide IgG (1:100; Cell Signaling, Danvers, MA, USA) antibody. After overnight incubation with the primary antibody at 4℃, the slides were incubated with biotin-conjugated anti-guinea pig IgG antibody for 30 minutes. The secondary antibody was further incubated with Texas Red-Streptavidin (1:100; Zymed Laboratories) and FITC-Streptavidin (1:100; Invitrogen) conjugated for 1 hour. Nuclear staining was performed using 2-(4-amidinophenyl)-1H-indole-6-carboxamidine (DAPI; Invitrogen). The stained cells were detected with an inverted fluorescence microscope (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany).
- Statistical analysis
- All values are given as mean±standard error. Comparisons between groups were performed using the t-test. For all comparisons, a value of P<0.05 was considered statistically significant.
METHODS
- Characterization of the mouse small intestine
- To identify the cells in the small intestine of the mice, we investigated the expression of Pdx1 (a marker of pancreatic precursor cells), CGA (a marker of endocrine and neuroendocrine cells), CK19 (a marker of epithelial cells), and leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor 5 (a marker of intestinal stem cells) in the mouse duodenum. Immunohistochemical analysis indicated that the cells in the small intestine of mice expressed Pdx1 (Fig. 1B) and CGA (Fig. 1C), and CK19 (Fig. 1D), which are well-known markers of pancreas. Lgr5+ stem cells were also detected at the bottom of the small intestine crypts but were not detected in the villus domains (Fig. 1E). The results showed that small intestine had potential to differentiate into pancreatic cells.
- Delivery of adenoviral vectors in the mouse intestine
- To establish effective gene transfer into the artery by direct injection of the adenoviral vectors, we tested two different arteries, the celiac artery and the cranial mesenteric artery (Supplementary Fig. 1A and B). When the adenovirus particles were injected into the cranial mesenteric artery, the viral solution was well infused in the entire intestine from the duodenum to the colon (Supplementary Fig. 1B and D). Then, we found the optimal dose of the virus from the survival of the mice after direct injection with Ad-GFP into the artery (Supplementary Fig. 2). Five days after the injection, GFP expression was identified in all the infected mice (Supplementary Fig. 2). We determined that the viral titer of 1.00E+09 (pfu/mL) can improve the efficiency of gene delivery and minimized irritation of the intestine.
- Ectopic expression of adenoviral vectors in the mouse intestine
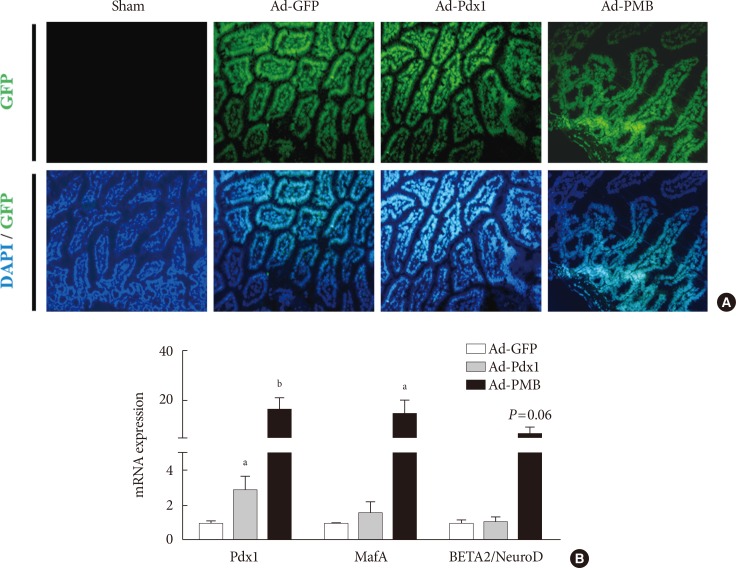
- To promote the differentiation into insulin-producing cells, the combined treatment of PMB was found to be a useful tool for the non-β-cells [16]. To apply these factors into intestinal cells, we designed and constructed adenovirus-mediated gene delivery systems consisting of a diverse combination of transcription factors to be administered into the mouse small intestine in vivo (Fig. 1A); The Ad-GFP, control, Ad-Pdx1, and Ad-PMB mixtures were injected into the artery in mouse intestine in each of the groups (Fig. 1A). After 5 days, we confirmed the GFP expression in the small intestine in all groups (except for the sham-operated group) (Fig. 2A). The Ad infected all the cells of the small intestines from the villi to the crypt regions (Fig. 2A). As shown in Fig. 2B, the levels of mRNA from the exogenous genes (PMB) were elevated. The Ad-Pdx1 group exhibited a significant increase in the expression of Pdx1 mRNA compared with the Ad-GFP groups. Furthermore, the Ad-PMB group ectopically overexpressed not only Pdx1 but also MafA and BETA2/NeuroD mRNAs compared with the control groups; particularly Pdx1 and MafA levels in this group were significantly higher than that in the Ad-Pdx1 group.
- Differentiation into insulin-producing cells of the mouse intestinal cells
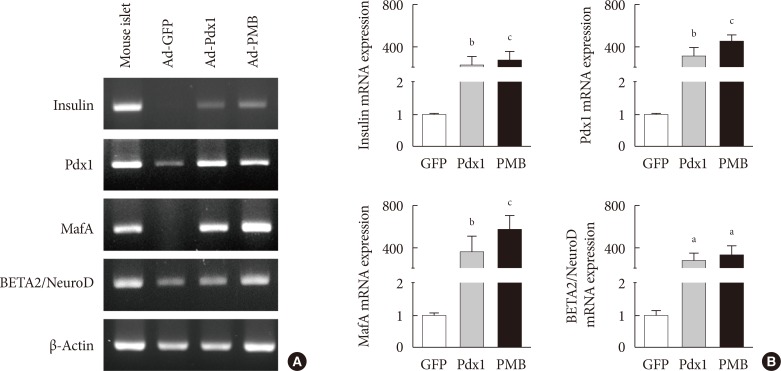
- To determine whether the intestinal cells differentiate into insulin-producing cells by adenoviral induction, we confirmed the increased levels of pancreatic key factors at 4 weeks after injection. The Ad-Pdx1 and Ad-PMB groups demonstrated significantly increased mRNA levels of the pancreatic endocrine genes (PMB). Insulin mRNA was also generated by the induction of Pdx1 in the mouse intestine (Fig. 3). In addition, the Ad-PMB group showed higher levels of genes, including PMB, and insulin (Fig. 3) than the controls. The data showed that Ad-PMB was more effective in elevating the mRNA levels of endogenous PMB, but not of insulin, compared to Ad-Pdx1 (Fig. 3B). These data indicated that pancreatic factors can be effectively transduced through an adenoviral-delivery system to induce the differentiation into insulin-producing cells in mouse intestine.
- Immunofluorescence analysis of mouse small intestine
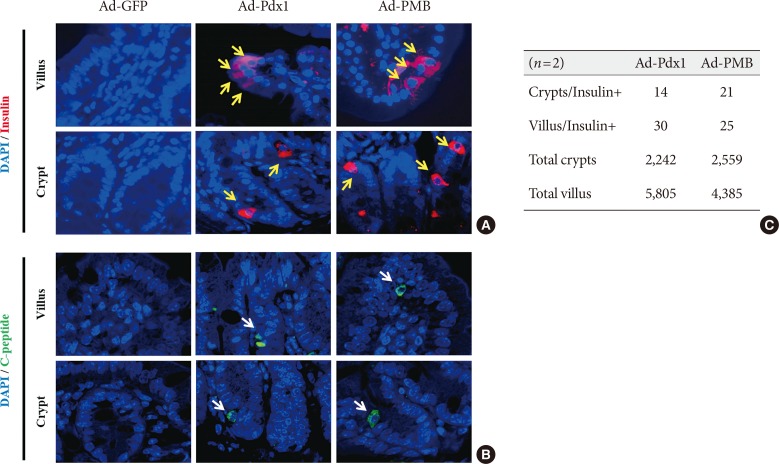
- To further investigate the β-cell differentiation in the mouse small intestine, we confirmed insulin expression in the mouse intestinal cells 4 weeks after injection. In the Ad-Pdx1 and triple injected Ad-PMB groups, insulin was expressed in the villi and crypts of the small intestine (Fig. 4A); the amounts of insulin-expressing cells were not different between the Ad-Pdx1 and triple-injected Ad-PMB groups in the villus-crypt domains (Fig. 4A). Furthermore, C-peptide was expressed in the villi and crypts of the mouse intestinal cells (Fig. 4B) in both Ad-Pdx1 and Ad-PMB injected groups. The number of insulin-positive cells was quantified by counting to confirm whether the cells had differentiated into β-cells. In the Ad-Pdx1 group, a total of 2,242 crypt cells were counted, 14 of which stained for insulin, and 5,805 villus cells were counted, with 30 cells positive for insulin (Fig. 4C). In the Ad-PMB group, 21 of 2,559 crypt cells expressed insulin, and among the 4,385 villus cells, 25 cells were positive for insulin (Fig. 4C). These results demonstrated that insulin-producing cells were induced among the small intestinal cells by adenoviral-mediated pancreatic transcription factors.
RESULTS
- Previous studies have demonstrated that differentiated insulin-producing cells from non-β-cells are useful sources to overcome the shortage of human islets for transplantation [1624252627]. In this study, we demonstrated that mouse small intestinal cells could be induced to differentiate into insulin-producing cells by genetic manipulation. To improve the efficiency of transduction, we found a specific arterial delivery system for the induction of genes combined with PMB into the small intestine. Finally, these cells could generate abundant PMB, and insulin.
- The gut is the largest endocrine organ, and it includes a monolayer of cells that undergo rapid renewal [2829]. During the process of development, the pancreas and small intestine are generated from the embryonic gut in response to intracellular signaling [30]; the progenitor cells of the pancreas and small intestine are derived from the endodermal epithelium, and the cell fate is determined by the transcriptional switch of pancreas transcription factor-1 and Pdx1 [1819313233]. Gut progenitor cells such as Lgr5+ intestinal stem cells, located in the crypts, harbor differentiation potential and self-renewing capability [34]. Differentiated IECs are generated from the Lgr5+ stem cells, and they populate the villi in the form of various differentiated cell types, then move to the villi tips and finally undergo apoptosis [21353637]. In addition, the IECs express pancreatic transcription factors similar to pancreatic β-cells, Pdx1, glucagon-like peptide-1, glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, BETA2/NeuroD, and Ngn3 [19].
- Many researchers have shown that induction by transduction of pancreatic transcription factors is essential for the differentiation of putative stem cells from various tissues into β-cells. We have previously reported that adult mouse hepatocytes can generate insulin-producing cells [38] and neonatal porcine liver-derived cells can transdifferentiate into functional insulin-producing cells with the help of triple Ad-PMB [16]. Additionally, single or triple PMB factors can promote the generation of insulin-producing cells in hepatoma cell lines and ameliorate glucose tolerance by adenoviral-PMB in the exposed livers of diabetic mice [15]. The triple Ad-PMB led to the successful differentiation into insulin-producing cells in the mouse IECs (IEC-6); insulin expression was not observed upon transduction with Ad-Pdx1 alone but only after co-transduction with MafA protein [39]. These data indicated that MafA plays a critical role in β-cell function [39]. In contrast, with IEC-6 cells, the small intestinal tissue expressed Pdx-1 and BETA2/NeuroD (Fig. 3A); thus, it might be beneficial to differentiate these into insulin-producing cells. In the current study, we developed transcription factors that were directly injected into the small intestine via an adenoviral system and tested whether Ad-PMB was more effective than Ad-Pdx1 alone. However, there was no significant difference between Ad-Pdx1 and the combination of transcription factors in insulin expression (Fig. 3). Moreover, the viral transduction of pancreas transcription factors could not lead to sufficient insulin-positive cells though the insulin mRNA production in the mouse intestine (Fig. 4). In other words, this process needs to be improved to increase the yield of β-cell differentiation from the intestinal cells to cure diabetes.
- A previous study using intestinal cells showed that the ectopic expression of Pdx1, MafA, and Ngn3 factors can induce insulin+ cells in the intestinal crypt-villus axis but not in the villi; Lgr5+ stem cells located in the crypt were converted to β-like cells and joined the ‘neoislets’ under the crypt base in vivo [23]. Of note, these data suggested the possibility that the converted insulin+ cells in the crypt would affect the production of insulin+ cells in the villus regions. We measured the insulin+ cells in the small intestinal tissue; 0.62% (Ad-Pdx1) or 0.81% (Ad-PMB) of the cells counted in the crypt base were insulin+. In the villus regions, 0.51% (Ad-Pdx1) or 0.57% (Ad-PMB) insulin+ cells were detected (Fig. 4C). These results indicated that it might be difficult to promote the sufficient differentiation into insulin-producing cells for the following reasons. First, because the Lgr5+ cells are rapidly cycling stem cells, apoptosis of the differentiated insulin-producing cells might occur at the villi tips. Second, the pancreatic transcription factors did not affect the intestinal cells continuously due to the transient delivery of the adenoviral systems in vivo. Thus, the conversion of intestinal cells to β-cells might be insufficient. Last, the Ad-Pdx1 group was infected with adenoviral constructs at a titer of 1.00E+09 (pfu/mL), whereas the Ad-PMB group was infected at a titer of 3.30E+08 (pfu/mL) of each construct. To avoid tissue damage from the high dose of virus, we tested numerous doses of the adenoviral constructs and then applied 1.00E+09 (pfu/mL) as the highest viral dose. Consequently, the amount of each transcription factor was decreased in the Ad-PMB group, and low amounts of transcription factors were introduced to the cells. Our study further suggests that the isolation of Lgr5+ stem cells from the crypts located in small intestinal tissue may be helpful for the production of cells that express pancreatic transcription factors.
- In summary, the small intestinal cells can generate insulin-producing cells by the induction of adenoviral-transcription factors. We reasoned that the small intestine is an accessible and abundant source of insulin-producing cells and might provide an interesting approach toward therapy for diabetes. We will continue to develop the appropriate transfer methods of the transcription factors to increase the gene expression levels and promote more sustainable expression to improve the β-cell differentiation efficiency. In addition, we will also study alternative sources using crypt stem cells in vitro. The isolation and establishment of these cells will be an important source of surrogate β-cells.
DISCUSSION
-
Acknowledgements
- We would like to thank Dr. Kaneto (Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, Japan) for donating the recombinant virus.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
NOTES
SUPPLEMENTARY MATERIALS
Supplementary Fig. 1
Supplementary Fig. 2
- 1. Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, Korbutt GS, Toth E, Warnock GL, Kneteman NM, Rajotte RV. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med 2000;343:230-238. ArticlePubMed
- 2. Hua H, Shang L, Martinez H, Freeby M, Gallagher MP, Ludwig T, Deng L, Greenberg E, Leduc C, Chung WK, Goland R, Leibel RL, Egli D. iPSC-derived β cells model diabetes due to glucokinase deficiency. J Clin Invest 2013;123:3146-3153. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. Bonner-Weir S, Weir GC. New sources of pancreatic beta-cells. Nat Biotechnol 2005;23:857-861. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Song KH, Ko SH, Ahn YB, Yoo SJ, Chin HM, Kaneto H, Yoon KH, Cha BY, Lee KW, Son HY. In vitro transdifferentiation of adult pancreatic acinar cells into insulin-expressing cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004;316:1094-1100. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Thorel F, Nepote V, Avril I, Kohno K, Desgraz R, Chera S, Herrera PL. Conversion of adult pancreatic alpha-cells to beta-cells after extreme beta-cell loss. Nature 2010;464:1149-1154. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 6. Sapir T, Shternhall K, Meivar-Levy I, Blumenfeld T, Cohen H, Skutelsky E, Eventov-Friedman S, Barshack I, Goldberg I, Pri-Chen S, Ben-Dor L, Polak-Charcon S, Karasik A, Shimon I, Mor E, Ferber S. Cell-replacement therapy for diabetes: generating functional insulin-producing tissue from adult human liver cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2005;102:7964-7969. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Ianus A, Holz GG, Theise ND, Hussain MA. In vivo derivation of glucose-competent pancreatic endocrine cells from bone marrow without evidence of cell fusion. J Clin Invest 2003;111:843-850. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Stadtfeld M, Brennand K, Hochedlinger K. Reprogramming of pancreatic beta cells into induced pluripotent stem cells. Curr Biol 2008;18:890-894. PubMedPMC
- 9. Takahashi K, Yamanaka S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006;126:663-676. ArticlePubMed
- 10. Murtaugh LC. Pancreas and beta-cell development: from the actual to the possible. Development 2007;134:427-438. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 11. Fujimoto K, Polonsky KS. Pdx1 and other factors that regulate pancreatic beta-cell survival. Diabetes Obes Metab 2009;11(Suppl 4):30-37. PubMedPMC
- 12. Kaneto H, Nakatani Y, Miyatsuka T, Matsuoka TA, Matsuhisa M, Hori M, Yamasaki Y. PDX-1/VP16 fusion protein, together with NeuroD or Ngn3, markedly induces insulin gene transcription and ameliorates glucose tolerance. Diabetes 2005;54:1009-1022. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 13. Naya FJ, Huang HP, Qiu Y, Mutoh H, DeMayo FJ, Leiter AB, Tsai MJ. Diabetes, defective pancreatic morphogenesis, and abnormal enteroendocrine differentiation in BETA2/neuroD-deficient mice. Genes Dev 1997;11:2323-2334. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Huang HP, Liu M, El-Hodiri HM, Chu K, Jamrich M, Tsai MJ. Regulation of the pancreatic islet-specific gene BETA2 (neuroD) by neurogenin 3. Mol Cell Biol 2000;20:3292-3307. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 15. Kaneto H, Matsuoka TA, Nakatani Y, Miyatsuka T, Matsuhisa M, Hori M, Yamasaki Y. A crucial role of MafA as a novel therapeutic target for diabetes. J Biol Chem 2005;280:15047-15052. ArticlePubMed
- 16. Ham DS, Shin J, Kim JW, Park HS, Cho JH, Yoon KH. Generation of functional insulin-producing cells from neonatal porcine liver-derived cells by PDX1/VP16, BETA2/NeuroD and MafA. PLoS One 2013;8:e79076. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Nomura S, Nakamura T, Hashimoto T, Nishio Y, Maegawa H, Kudo M, Kashiwagi A. MafA differentiates rat intestinal cells into insulin-producing cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2006;349:136-143. ArticlePubMed
- 18. Kawaguchi Y, Cooper B, Gannon M, Ray M, MacDonald RJ, Wright CV. The role of the transcriptional regulator Ptf1a in converting intestinal to pancreatic progenitors. Nat Genet 2002;32:128-134. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Fujita Y, Cheung AT, Kieffer TJ. Harnessing the gut to treat diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes 2004;5(Suppl 2):57-69. ArticlePubMed
- 20. Barker N, van Oudenaarden A, Clevers H. Identifying the stem cell of the intestinal crypt: strategies and pitfalls. Cell Stem Cell 2012;11:452-460. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Sato T, Clevers H. Growing self-organizing mini-guts from a single intestinal stem cell: mechanism and applications. Science 2013;340:1190-1194. ArticlePubMed
- 22. Richmond CA, Breault DT. Regulation of gene expression in the intestinal epithelium. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 2010;96:207-229. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 23. Chen YJ, Finkbeiner SR, Weinblatt D, Emmett MJ, Tameire F, Yousefi M, Yang C, Maehr R, Zhou Q, Shemer R, Dor Y, Li C, Spence JR, Stanger BZ. De novo formation of insulin-producing “neo-β cell islets” from intestinal crypts. Cell Rep 2014;6:1046-1058. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. You YH, Ham DS, Park HS, Rhee M, Kim JW, Yoon KH. Adenoviruses expressing PDX-1, BETA2/NeuroD and MafA induces the transdifferentiation of porcine neonatal pancreas cell clusters and adult pig pancreatic cells into beta-cells. Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:119-129. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Kim JW, Park SY, You YH, Ham DS, Park HS, Lee SH, Yang HK, Yoon KH. Targeting PGC-1α to overcome the harmful effects of glucocorticoids in porcine neonatal pancreas cell clusters. Transplantation 2014;97:273-279. ArticlePubMed
- 26. Zalzman M, Gupta S, Giri RK, Berkovich I, Sappal BS, Karnieli O, Zern MA, Fleischer N, Efrat S. Reversal of hyperglycemia in mice by using human expandable insulin-producing cells differentiated from fetal liver progenitor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003;100:7253-7258. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 27. Rhee M, Lee SH, Kim JW, Ham DS, Park HS, Yang HK, Shin JY, Cho JH, Kim YB, Youn BS, Sul HS, Yoon KH. Preadipocyte factor 1 induces pancreatic ductal cell differentiation into insulin-producing cells. Sci Rep 2016;6:23960ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 28. Ahlman H, Nilsson . The gut as the largest endocrine organ in the body. Ann Oncol 2001;12(Suppl 2):S63-S68.Article
- 29. May CL, Kaestner KH. Gut endocrine cell development. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2010;323:70-75. ArticlePubMed
- 30. Apelqvist A, Ahlgren U, Edlund H. Sonic hedgehog directs specialised mesoderm differentiation in the intestine and pancreas. Curr Biol 1997;7:801-804. ArticlePubMed
- 31. Dor Y, Brown J, Martinez OI, Melton DA. Adult pancreatic beta-cells are formed by self-duplication rather than stem-cell differentiation. Nature 2004;429:41-46. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 32. Offield MF, Jetton TL, Labosky PA, Ray M, Stein RW, Magnuson MA, Hogan BL, Wright CV. PDX-1 is required for pancreatic outgrowth and differentiation of the rostral duodenum. Development 1996;122:983-995. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 33. Ahlgren U, Jonsson J, Edlund H. The morphogenesis of the pancreatic mesenchyme is uncoupled from that of the pancreatic epithelium in IPF1/PDX1-deficient mice. Development 1996;122:1409-1416. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 34. Barker N, van Es JH, Kuipers J, Kujala P, van den Born M, Cozijnsen M, Haegebarth A, Korving J, Begthel H, Peters PJ, Clevers H. Identification of stem cells in small intestine and colon by marker gene Lgr5. Nature 2007;449:1003-1007. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 35. Carulli AJ, Samuelson LC, Schnell S. Unraveling intestinal stem cell behavior with models of crypt dynamics. Integr Biol (Camb) 2014;6:243-257. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 36. Barker N, Ridgway RA, van Es JH, van den Born M, Begthel H, van den Born M, Danenberg E, Clarke AR, Sansom OJ, Clevers H. Crypt stem cells as the cells-of-origin of intestinal cancer. Nature 2009;457:608-611. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 37. Umar S. Intestinal stem cells. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 2010;12:340-348. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 38. Ham DS, Kim JW, Park HS, Sun CL, Lee SH, Cho JH, Oh JA, Song KH, Son HY, Hideaki K, Yoon KH. Generation of insulin producing cells from the mouse primary hepatocytes. Tissue Eng Regen Med 2011;8:564-573.
- 39. Matsuoka TA, Kaneto H, Stein R, Miyatsuka T, Kawamori D, Henderson E, Kojima I, Matsuhisa M, Hori M, Yamasaki Y. MafA regulates expression of genes important to islet beta-cell function. Mol Endocrinol 2007;21:2764-2774. PubMed
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
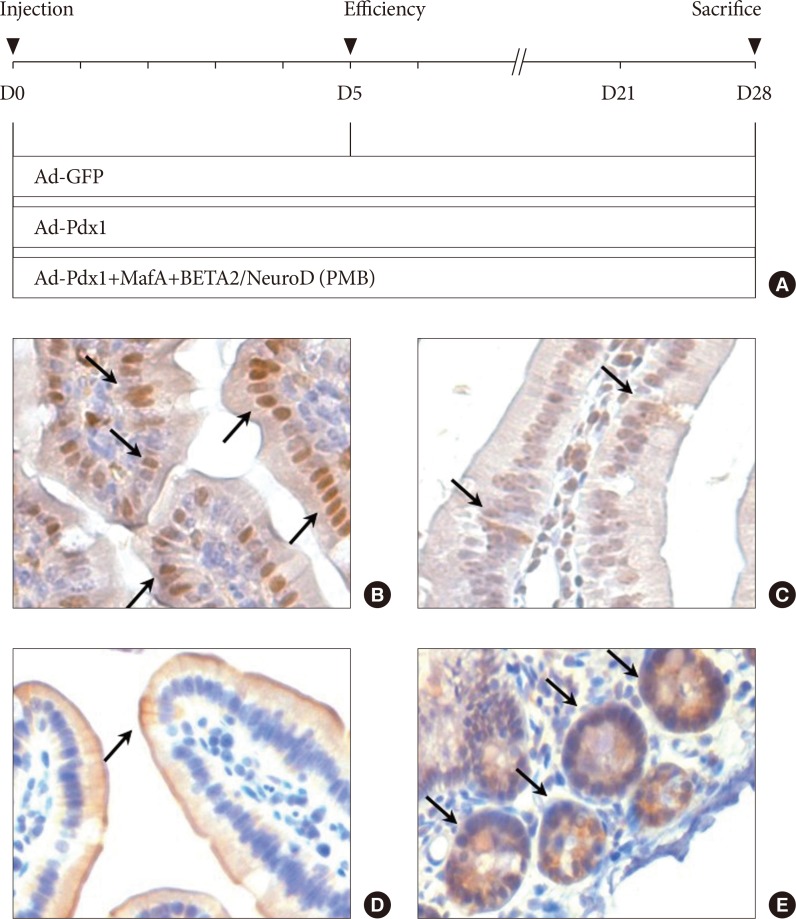
The experimental design and characterization of the small intestine. (A) The adenovirus combinations were composed of three distinct groups: adenoviruse (Ad)-green fluorescent protein (GFP; control); Ad-pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 (Pdx1); and Ad-PMB (Pdx1, V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog A [MafA], and BETA2/NeuroD). Day 0 indicated the day of adenoviral induction through the intestinal arteries in the C57BL/6 mice. On day 5, we confirmed the overexpression of the adenovirus-mediated ectopic genes, and then all the mice were harvested at 4 weeks after viral injection. The small intestine was characterized with the intestinal markers (B) Pdx-1, (C) chromogranin A, (D) cytokeratin 19, and (E) Lgr5 by immunohistochemical staining (black allows) in the mouse duodenum (×200).

Fig. 2
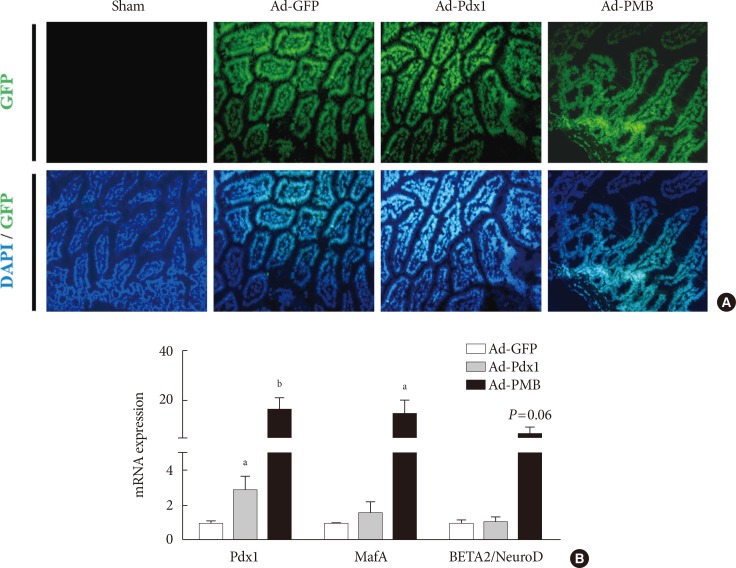
Ectopic gene expression in the mouse intestine 5 days after viral injection. (A) Signal from the green fluorescent protein (GFP) was observed in the adenoviruse (Ad)-GFP, Ad-pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 (Pdx1), and Ad-PMB (Pdx1, V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog A [MafA], and BETA2/NeuroD) groups, but not in the sham-operated group (saline injection, ×100). (B) mRNA expression levels of exogenous transcription factors (PMB) were increased at 5 days after infection with Ad-Pdx1 (gray bar) and Ad-PMB (black bar) compared to Ad-GFP (white bar) (n=2). The mean±standard error values are presented (error bars, standard error). DAPI, 2-(4-amidinophenyl)-1H-indole-6-carboxamidine. aP≤0.05, bP≤0.02.

Fig. 3
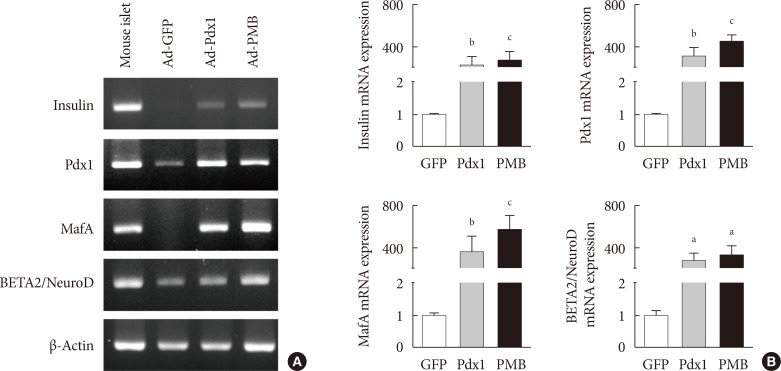
Expression of insulin mRNA in mouse intestine at 4 weeks. (A) Endogenous insulin, PMB (pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 [Pdx1], V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog A [MafA], and BETA2/NeuroD) transcription factors were evaluated by reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction analysis in the adenoviruse (Ad)-green fluorescent protein (GFP), Ad-Pdx1, and Ad-PMB groups. Mouse islets were used as positive controls. (B) Insulin, PMB transcription factors were analyzed by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in the Ad-GFP (n=4, white bar), Ad-Pdx1 (n=5, gray bar), and Ad-PMB (n=4, black bar) injected groups. The mean±standard error values are presented (error bars, standard error). aP≤0.05, bP≤0.02, cP≤0.005.

Fig. 4
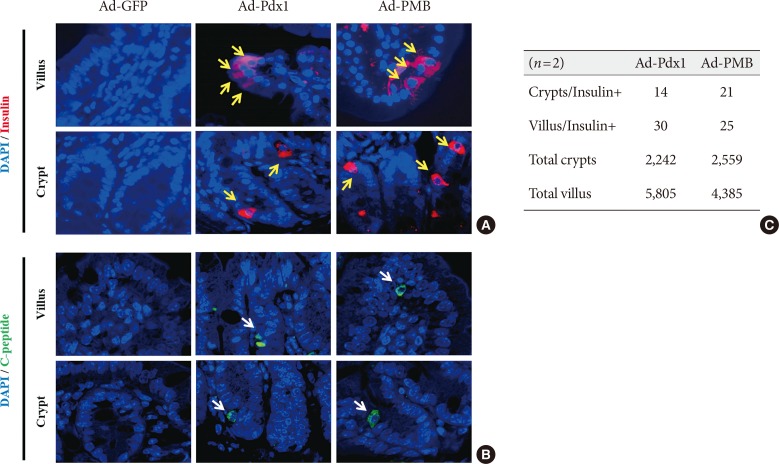
Production of insulin+ cells within the small intestinal cells located in the villus and crypt. (A) Insulin+ cells (yellow arrows) and (B) C-peptide+ cells (white arrows) were detected in the adenoviruse (Ad)-pancreatic and duodenal homeobox 1 (Pdx1) and Ad-PMB (Pdx1, V-maf musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma oncogene homolog A [MafA], and BETA2/NeuroD) groups but not in the Ad-green fluorescent protein (GFP) group (×400) by immunofluorescence analysis. (C) Quantification of insulin+ cells in the villus and crypt cells. DAPI, 2-(4-amidinophenyl)-1H-indole-6-carboxamidine.

Table 1
![dmj-41-405-i001.jpg]()
Primers for reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (sequence-specific for mice)
Table 2
![dmj-41-405-i002.jpg]()
Primers for quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (sequence-specific for mice)
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Harnessing gut cells for functional insulin production: Strategies and challenges
Kelvin Baafi, John C. March
Biotechnology Notes.2023; 4: 7. CrossRef - Differential Morphological Diagnosis of Various Forms of Congenital Hyperinsulinism in Children
Lubov Borisovna Mitrofanova, Anastasia Arkadyevna Perminova, Daria Viktorovna Ryzhkova, Anna Andreyevna Sukhotskaya, Vladimir Gireyevich Bairov, Irina Leorovna Nikitina
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Generation of iPSC-derived insulin-producing cells from patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes compared with healthy control
Min Jung Kim, Eun Young Lee, Young-Hye You, Hae Kyung Yang, Kun-Ho Yoon, Ji-Won Kim
Stem Cell Research.2020; 48: 101958. CrossRef - ERK Regulates NeuroD1-mediated Neurite Outgrowth via Proteasomal Degradation
Tae-young Lee, In-Su Cho, Narayan Bashyal, Francisco J Naya, Ming-Jer Tsai, Jeong Seon Yoon, Jung-Mi Choi, Chang-Hwan Park, Sung-Soo Kim, Haeyoung Suh-Kim
Experimental Neurobiology.2020; 29(3): 189. CrossRef - Generation of a PDX1–EGFP reporter human induced pluripotent stem cell line, KSCBi005-A-3, using the CRISPR/Cas9 system
Youngsun Lee, Hye Young Choi, Ara Kwon, Hyeyeon Park, Mi-Hyun Park, Ji-Won Kim, Min Jung Kim, Yong-Ou Kim, Sungwook Kwak, Soo Kyung Koo
Stem Cell Research.2019; 41: 101632. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite