- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 40(4); 2016 > Article
-
ReviewRoles of Reactive Oxygen Species on Insulin Resistance in Adipose Tissue
-
Chang Yeop Han

-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2016;40(4):272-279.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.4.272
Published online: June 28, 2016
Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology & Nutrition, Department of Medicine and Diabetes and Obesity Center of Excellence, University of Washington, Seattle, WA, USA.
- Corresponding author: Chang Yeop Han. Division of Metabolism, Endocrinology & Nutrition, Department of Medicine, University of Washington, Box 356426, Seattle, WA 98195-6426, USA. hancy@u.washington.edu
• Received: May 9, 2016 • Accepted: June 1, 2016
Copyright © 2016 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
- Obesity resulting from the delivery of an excess amount of energy to adipose tissue from glucose or free fatty acids is associated with insulin resistance and adipose tissue inflammation. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) have been implicated as contributors to both the onset and the progression of insulin resistance. ROS can be generated by overloading the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system, and also by nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidases (NOX) produced by either adipocytes, which only produce NOX4, or by macrophages, which produce mainly NOX2. The source of the ROS might differ in the early, intermediate and late stages of obesity, switching from NOX4-dependence in the early phases to NOX2-dependence, in the intermediate phase, and transiting to mitochondria-dependence later in the time course of obesity. Thus, depending on the stage of obesity, ROS can be generated by three distinct mechanisms: i.e., NOX4, NOX2, and mitochondria. In this review, we will discuss whether NOX4-, NOX2-, and/or mitochondria-derived ROS is/are causal in the onset of adipocyte insulin resistance as obesity progresses. Moreover, we will review the pathophysiological roles of NOX4, NOX2, and mitochondria-derived ROS on adipose tissue inflammation.
- Many lines of evidence support the proposal that visceral obesity is strongly associated with features of the metabolic/insulin resistance syndrome, and that obesity predicts the development of both type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease (CVD) [123]. Obesity is associated with a chronic low-grade inflammation [456], as evidenced by an increase in circulating inflammatory markers, such as C-reactive protein, serum amyloid A (SAA), and interleukin 6 [789]. The presence of systemic inflammation in visceral obesity has been linked to an increased risk of developing CVD and type 2 diabetes [101112]. Obesity results when there is an imbalance between energy ingested and energy expended [13]. A relative excess of energy (either genetic or diet-induced) results in two major cellular features; adipocyte expansion and infiltration of inflammatory cells into adipose tissue in both mice and humans [141516]. Adipocytes and macrophages both generate inflammatory molecules, which lead to insulin resistance and systemic inflammation. Certain saturated free fatty acids (SFAs; laurate, myristate, and palmitate) increase inflammatory genes in adipocytes [17]. These events are associated with the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) transactivation. Excess glucose and/or certain SFAs increased ROS generation and NF-κB translocation [17]. Treatment with the antioxidants, N-acetyl cysteine, catalase and superoxide dismutase (SOD) repressed ROS generation and NF-κB translocation stimulated by excess glucose 4tate, and decreased inflammatory gene expression [17]. Thus, glucose- and palmitate-stimulated ROS generation appears to play an important role in adipocyte inflammation. Although several mechanisms such as endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, hypoxia, and adipocyte death have been reported to be related to adipocyte inflammation during obesity [1819], ROS generation is upstream of ER stress and apoptosis of adipocyte occurs at later stages of obesity [1820]. ROS is a key-modulator that activates the initial the sequence of events that leads to adipose tissue inflammation. The relative contribution of ROS derived from different sources in adipocytes during the progression of obesity remains unknown. Therefore, as a first step, our review has been chosen to focus on the role of various sources of ROS generated in adipose tissue on inflammation and insulin resistance.
- ROS GENERATION AND OBESITY
- Chronic ROS production has recently been suggested to be an important contributor to the pathogenesis of obesity-associated insulin resistance [2122]. Physiologically, ROS is required for differentiation of adipocytes [2324]. These physiological ROS exist for short time and are well regulated by insulin signaling. Our review focuses on the pathophysiological roles of ROS in adipocytes inflammation; i.e., the effects of prolonged ROS generation by excess nutrients and the effect of ROS unregulated by insulin signaling. ROS in visceral adipose tissue are significantly increased in genetically obese mice and mice made obese by consumption of a high-fat diet [25]. The direct relationship between ROS generation and obesity is still not entirely clear. ROS can be generated by adipocytes during metabolism of excess nutrients. ROS also can be generated by macrophages, which accumulate in adipose tissue in obesity. Therefore, it is important to understand the source of ROS during the progression of obesity. In the early insulin sensitive state, energy flux from nutrient excess flows into lipogenesis, in which excess glucose and free fatty acid (FFA) are used for triglyceride synthesis by adipocytes. In the insulin sensitive state, insulin activates the insulin receptor tyrosine kinase which leads to stimulation of insulin receptor substrate proteins and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3-kinase) [26]. Next, PI3-kinase activates downstream protein kinases, including Akt/protein kinase B [2627]. Consequently, these events increase intracellular glucose uptake into adipocytes via insulin-stimulated translocation of glucose transporter 4 molecules to the cell membrane [27]. In this state, FFA are stored as triglyceride by activating the production of proteins involved in lipid metabolism/uptake, including lipoprotein lipase, fatty acid transport protein, and acetyl CoA-synthase [28]. However, it is totally unknown whether these ROS casually trigger the insulin resistance, or are a casual bystander of insulin resistance in adipocytes. Thus, although much is known about energy flux in adipocytes during the progression of obesity, little is known as to whether this energy flux leads to differences in the generation of ROS in the early and late stages of obesity, nor is there a good understanding of the potential pathophysiological roles of ROS derived in these stages.
- ROS AND NOX4 IN THE EARLY STAGES OF OBESITY
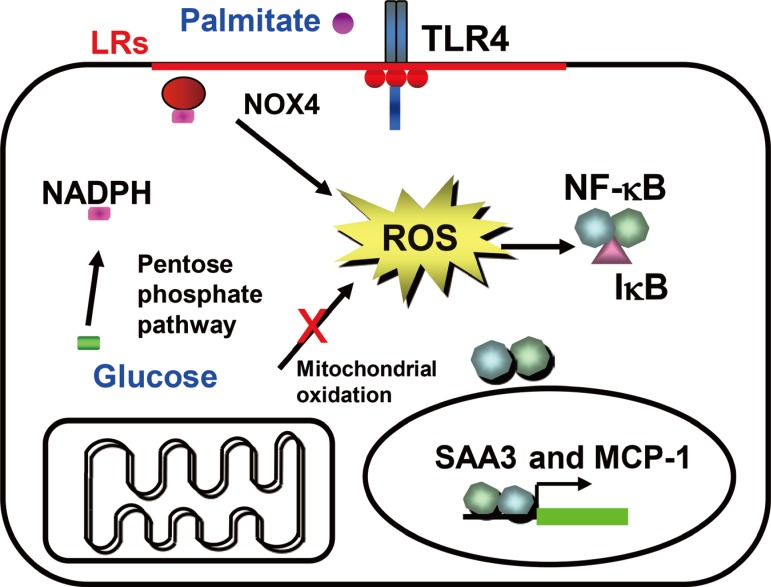
- We previously have shown that excess glucose and palmitate are not metabolized to a major extent via mitochondrial oxidation. Instead excess nutrients activate nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidases (NOX) [29]. Members of the NOX family are membrane-bound enzyme complexes that transfer electrons from NADPH to oxygen, generating superoxide. This short lived, non-membrane permeable ROS is converted, to a longer lived membrane permeable ROS, hydrogen peroxide by SOD [30] or spontaneously. The NOX family has seven isoforms, NOX1, NOX2, NOX3, NOX4, NOX5, dual oxidase 1 (DUOX1), and DUOX2, which are strongly conserved in mammals and are widely expressed in various tissues [31]. NOX1 to 3 require additional cytosolic activators (p47phox, p67phox, NADPH oxidase organizer 1) whereas NOX4 is constitutively active and independent of an activator protein (AP) [313233]. NOX5 and DUOX1/2 need intracellular calcium to activate ROS generation [3435]. It is therefore assumed that NOX1 to 3 mediates short-term effects, while NOX4 is responsible for long term effects. We have found that NOX4 is the major NOX isoform in cultured murine and human adipocytes [29]. Moreover, silencing NOX4 decreased ROS generation stimulated by excess glucose as well as palmitate, leading to inhibition of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 and SAA3 expression in vitro [29]. Thus, NOX4-derived ROS may be a common mediator induced by both excess glucose and palmitate in adipocytes (Fig. 1). Other studies showed that NOX4 activity increases in the adipose tissue with diet-induced obesity (DIO), and NOX inhibitor, apocynin treatment reduces ROS generation [25]. However, whether NOX4-derived ROS itself can promote the onset of insulin resistance in adipocytes during the progression of obesity is unknown and needs to be investigated.
- The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) generates NADPH and pentose from the 6 carbon glucose and is a major source of cellular NADPH. Glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) is the rate-limiting enzyme in the PPP. Recent studies indicate that G6PD expression is upregulated in adipose tissue in genetic and DIO, and that its overexpression is associated with increased adipocyte inflammation and ROS generation [3637]. Other studies have shown that treatment with dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), a G6PD inhibitor, reduces obesity in Zucker diabetic fatty rats [38]. We found that NADPH content and PPP activity were increased by excess glucose, but not by palmitate in 3T3-L1 adipocytes [29]. Moreover, G6PD inhibitors, DHEA and 6-aminonicotinamide, or silencing G6PD all inhibited ROS generation and monocyte chemotactic factor gene expression by both high glucose and palmitate in 3T3-L1 adipocytes [29]. These studies support the concept that PPP and G6PD could be modulators or mediators of adipose tissue inflammation (Fig. 1). During the initial stage of energy access, we hypothesize that adipocytes will continue to actively store triglycerides derived from excess nutrients, and will demonstrate increased PPP activity and NADPH content, which lead to NOX4-derived ROS generation (Fig. 1).
- However, whole body NOX4 deficiency has been reported to worsen adipose tissue inflammation in a model of DIO in mice [39]. Since NOX4 activity is essential for pre-adipocyte differentiation to adipocytes [23], blunted adipogenesis in the absence of NOX4 would reduce the number of adipocytes, allowing the remaining adipocytes to become more hypertrophic, thereby leading to adipose tissue inflammation. Indeed, expression of adipogenesis genes (peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ [PPARγ] and CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein α [C/EBPα]) was inhibited in whole body NOX4 knockout mice [39]. Therefore, it is imperative to investigate the alteration of NOX4 activity in mice during the pathophysiological progression of obesity where adipogenesis is intact, and to study the effect of adipocyte-specific deficiency of NOX4.
- ROS AND NOX2 IN THE INTERMEDIATE STAGES OF OBESITY
- Another potentially important source of ROS in obesity is from macrophages that are recruited and accumulate in obese adipose tissue. Obesity provokes changes in T-cell subsets and increases the infiltration and accumulation of activated macrophages in adipose tissue [404142]. These recruited and activated immune cells can promote the generation of ROS by NOX2, which is predominately expressed activated in T-cells and macrophages [43]. Immune cells in the inflammatory environment created by obesity could generate NOX2-derived ROS. Whole body deficiency of NOX2 shows attenuation of adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance in mice fed a high fat diet [44]. This implies that NOX2 from immune cells may play a role in adipose tissue inflammation in the intermediate stages of obesity. However, whether these NOX2-dervied ROS itself has effects in adipose tissue inflammation and can promote the onset of insulin resistance in adipocytes during the progression of obesity is unknown and needs to be investigated.
- ROS AND MITOCHONDRIA IN THE LATE STAGES OF OBESITY
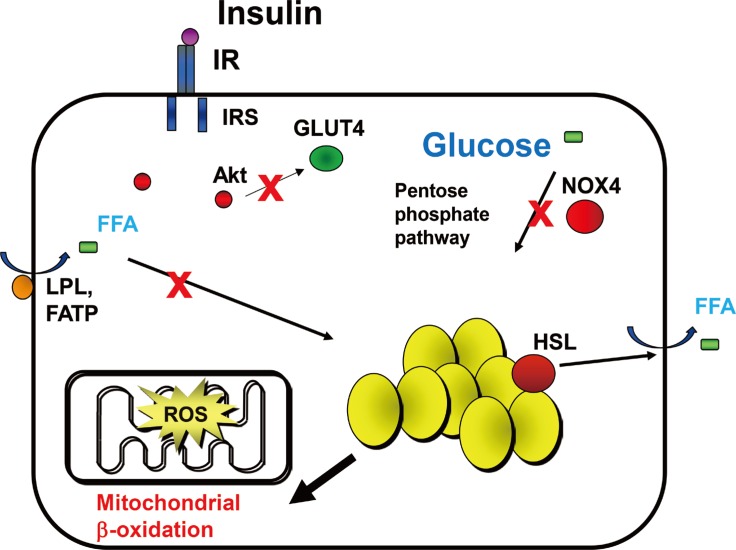
- The mitochondrial electron transport chain is a primary site for ROS production. ROS generation is accelerated when the flow of electrons through the electron transport chain is overload, resulting in leakage of electrons. Overloaded mitochondria mainly produce superoxide, which can signal intracellularly, leading to a pro-inflammatory signaling cascade that includes NF-κB and AP-1 activation [4546]. Although glucose excess presumably drives the overflow of electrons in mitochondria, other energy sources in adipocytes are preferred in the late stages of obesity since uptake of glucose is limited by the insulin resistance of adipocytes. When glucose consumption is reduced by insulin resistance, adipocytes start to use FFA from triglyceride stores for energy (Fig. 2). This alteration of energy flux into β-oxidation could overwhelm the capacity of mitochondria, leading to leakage of electrons (Fig. 2).
- When pro-inflammatory macrophages accumulate in adipose tissue as a result of the NOX4-mediated generation of macrophage chemoattractants by adipocytes, the inflammatory environment induced by these macrophages will be expected to result in adipocyte insulin resistance [47]. With the advent of sufficient insulin resistance, adipocytes will stop storing additional triglycerides, will utilize stored fatty acids from triglycerides, and will show evidence of decreased PPP activity and NADPH content. At such times, adipocyte-derived NOX4 might have a limited role in ROS generation and adipose tissue inflammation. Instead, mitochondria will now take the place of NOX4 and play a pivotal role in ROS generation and adipose tissue inflammation (Fig. 2). In support of this hypothesis are studies that show the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and macrophage chemoattractants by adipocytes at an early time point (1 week), while adipose tissue insulin resistance occurs much later (after 14 weeks) during the development of DIO in mice [4849]. These studies also show that even though some infiltration of macrophages occur at early time points, massive infiltration of macrophage happens much later (after 12 weeks) [49]. Thus, these studies strongly suggest that adipocytes become insulin resistant during the later stages of obesity, while adipocytes are insulin sensitive during the early stages of obesity. Recent studies also have reported that fasting and caloric restriction in mice in which insulin signaling is disturbed and β-oxidation of FFA is increased in adipocytes, results in the generation of chemoattractants and an increase of macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue [5051]. These studies support that mitochondria and β-oxidation of fatty acids might lead to ROS generation. Therefore, we hypothesize that mitochondria-derived ROS accounts for massive macrophage accumulation, worsening insulin resistance and systemic inflammation during the late stages of obesity (Fig. 2). Also, we hypothesize that a temporal transition of the source of ROS between NOX4 and mitochondria as obesity progresses is responsible for conversion to a more insulin resistant phase of obesity.
INTRODUCTION
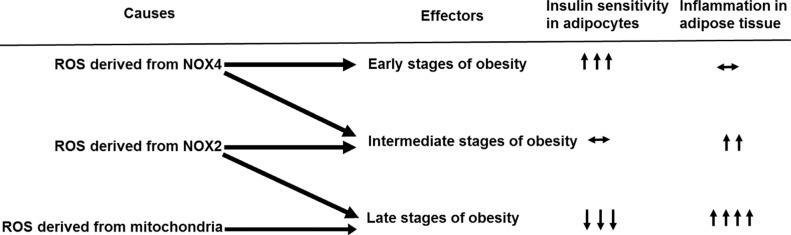
- An overall role of distinct sources of ROS for adipose tissue inflammation is that (1) in the early stages of obesity, NOX4-derived ROS from adipocytes provoke the onset of insulin resistance and initiates the recruitment of immune cells in adipose tissue, (2) in the intermediate stages of obesity, NOX2-derived ROS from infiltrated immune cells worsens adipocyte insulin resistance and adipose tissue inflammation, and (3) in the late stages of obesity, mitochondria-derived ROS from adipocytes maintain the adipose tissue inflammation and insulin resistance. We summarize how these three distinct sources of ROS might affect adipocyte insulin resistance and adipose tissue inflammation in the early, intermediate, and late stages of obesity (Fig. 3).
- Several large clinical trials have failed to show any beneficial effects of consumption of antioxidant supplements in the prevention of insulin resistance [52535455]. Nevertheless, from studies in obese mice there is increasing evidence that antioxidant might be beneficial in attenuating insulin resistance and restoring insulin signaling. For example, the antioxidant manganese tetrakis porphyrin and the cell permeable small-peptide antioxidant SS31 (D-Arg-2',6'-dimethyltyrosine-Lys-Phe-NH2) improve insulin sensitivity without altering body weight in a genetic and DIO mice [4356]. Moreover, transgenic mice overexpressing SOD2 exhibit improvements in glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity resulting from consumption of a high fat diet [57]. A discrepancy between basic research and clinical studies may be due to the fact that we have yet to address the importance of the timing of ROS generation, the source of ROS, and tissue specific effects of ROS. Findings out these discrepancies would be likely to have important translational implications related to the development of antioxidants targeting NOX4- or mitochondria-derived ROS in different stages of obesity.
CONCLUSIONS
-
Acknowledgements
- This work was supported in part by National Institutes of Health grants HL092969, 094352, DK-035816, and a Beginning Grant-in-Aid from the American Heart Association.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
NOTES
- 1. Janssen I, Katzmarzyk PT, Ross R. Body mass index, waist circumference, and health risk: evidence in support of current National Institutes of Health guidelines. Arch Intern Med 2002;162:2074-2079. ArticlePubMed
- 2. Hubert HB, Feinleib M, McNamara PM, Castelli WP. Obesity as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease: a 26-year follow-up of participants in the Framingham Heart Study. Circulation 1983;67:968-977. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Wang CC, Goalstone ML, Draznin B. Molecular mechanisms of insulin resistance that impact cardiovascular biology. Diabetes 2004;53:2735-2740. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Bulló M, Garcia-Lorda P, Megias I, Salas-Salvado J. Systemic inflammation, adipose tissue tumor necrosis factor, and leptin expression. Obes Res 2003;11:525-531. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Maachi M, Pieroni L, Bruckert E, Jardel C, Fellahi S, Hainque B, Capeau J, Bastard JP. Systemic low-grade inflammation is related to both circulating and adipose tissue TNFalpha, leptin and IL-6 levels in obese women. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2004;28:993-997. PubMed
- 6. Cancello R, Clement K. Is obesity an inflammatory illness? Role of low-grade inflammation and macrophage infiltration in human white adipose tissue. BJOG 2006;113:1141-1147. ArticlePubMed
- 7. Ouchi N, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Nakamura T, Nishida M, Kumada M, Okamoto Y, Ohashi K, Nagaretani H, Kishida K, Nishizawa H, Maeda N, Kobayashi H, Hiraoka H, Matsuzawa Y. Reciprocal association of C-reactive protein with adiponectin in blood stream and adipose tissue. Circulation 2003;107:671-674. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Poitou C, Viguerie N, Cancello R, De Matteis R, Cinti S, Stich V, Coussieu C, Gauthier E, Courtine M, Zucker JD, Barsh GS, Saris W, Bruneval P, Basdevant A, Langin D, Clement K. Serum amyloid A: production by human white adipocyte and regulation by obesity and nutrition. Diabetologia 2005;48:519-528. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 9. Fried SK, Bunkin DA, Greenberg AS. Omental and subcutaneous adipose tissues of obese subjects release interleukin-6: depot difference and regulation by glucocorticoid. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1998;83:847-850. ArticlePubMed
- 10. Lebovitz HE. Insulin resistance: a common link between type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Diabetes Obes Metab 2006;8:237-249. ArticlePubMed
- 11. Sowers JR. Obesity as a cardiovascular risk factor. Am J Med 2003;115(Suppl 8A):37S-41S. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Bray GA. Risks of obesity. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2003;32:787-804. ArticlePubMed
- 13. Bray GA, Paeratakul S, Popkin BM. Dietary fat and obesity: a review of animal, clinical and epidemiological studies. Physiol Behav 2004;83:549-555. ArticlePubMed
- 14. Wellen KE, Hotamisligil GS. Obesity-induced inflammatory changes in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 2003;112:1785-1788. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 15. Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ, Sole J, Nichols A, Ross JS, Tartaglia LA, Chen H. Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 2003;112:1821-1830. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 16. Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr. Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 2003;112:1796-1808. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 17. Yeop Han C, Kargi AY, Omer M, Chan CK, Wabitsch M, O'Brien KD, Wight TN, Chait A. Differential effect of saturated and unsaturated free fatty acids on the generation of monocyte adhesion and chemotactic factors by adipocytes: dissociation of adipocyte hypertrophy from inflammation. Diabetes 2010;59:386-396. PubMed
- 18. Strissel KJ, Stancheva Z, Miyoshi H, Perfield JW 2nd, DeFuria J, Jick Z, Greenberg AS, Obin MS. Adipocyte death, adipose tissue remodeling, and obesity complications. Diabetes 2007;56:2910-2918. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Gregor MF, Hotamisligil GS. Thematic review series: adipocyte biology. Adipocyte stress: the endoplasmic reticulum and metabolic disease. J Lipid Res 2007;48:1905-1914. ArticlePubMed
- 20. Kawasaki N, Asada R, Saito A, Kanemoto S, Imaizumi K. Obesity-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress causes chronic inflammation in adipose tissue. Sci Rep 2012;2:799ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 21. Houstis N, Rosen ED, Lander ES. Reactive oxygen species have a causal role in multiple forms of insulin resistance. Nature 2006;440:944-948. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 22. Evans JL, Goldfine ID, Maddux BA, Grodsky GM. Oxidative stress and stress-activated signaling pathways: a unifying hypothesis of type 2 diabetes. Endocr Rev 2002;23:599-622. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. Schröder K, Wandzioch K, Helmcke I, Brandes RP. Nox4 acts as a switch between differentiation and proliferation in preadipocytes. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2009;29:239-245. ArticlePubMed
- 24. Tormos KV, Anso E, Hamanaka RB, Eisenbart J, Joseph J, Kalyanaraman B, Chandel NS. Mitochondrial complex III ROS regulate adipocyte differentiation. Cell Metab 2011;14:537-544. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Furukawa S, Fujita T, Shimabukuro M, Iwaki M, Yamada Y, Nakajima Y, Nakayama O, Makishima M, Matsuda M, Shimomura I. Increased oxidative stress in obesity and its impact on metabolic syndrome. J Clin Invest 2004;114:1752-1761. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Kahn BB, Flier JS. Obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 2000;106:473-481. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 27. Summers SA, Whiteman EL, Birnbaum MJ. Insulin signaling in the adipocyte. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 2000;24(Suppl 4):S67-S70. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 28. Smith U, Axelsen M, Carvalho E, Eliasson B, Jansson PA, Wesslau C. Insulin signaling and action in fat cells: associations with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1999;892:119-126. ArticlePubMed
- 29. Han CY, Umemoto T, Omer M, Den Hartigh LJ, Chiba T, LeBoeuf R, Buller CL, Sweet IR, Pennathur S, Abel ED, Chait A. NADPH oxidase-derived reactive oxygen species increases expression of monocyte chemotactic factor genes in cultured adipocytes. J Biol Chem 2012;287:10379-10393. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Bedard K, Krause KH. The NOX family of ROS-generating NADPH oxidases: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 2007;87:245-313. ArticlePubMed
- 31. Kawahara T, Quinn MT, Lambeth JD. Molecular evolution of the reactive oxygen-generating NADPH oxidase (Nox/Duox) family of enzymes. BMC Evol Biol 2007;7:109ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 32. Martyn KD, Frederick LM, von Loehneysen K, Dinauer MC, Knaus UG. Functional analysis of Nox4 reveals unique characteristics compared to other NADPH oxidases. Cell Signal 2006;18:69-82. ArticlePubMed
- 33. Ambasta RK, Kumar P, Griendling KK, Schmidt HH, Busse R, Brandes RP. Direct interaction of the novel Nox proteins with p22phox is required for the formation of a functionally active NADPH oxidase. J Biol Chem 2004;279:45935-45941. ArticlePubMed
- 34. Bánfi B, Molnar G, Maturana A, Steger K, Hegedus B, Demaurex N, Krause KH. A Ca(2+)-activated NADPH oxidase in testis, spleen, and lymph nodes. J Biol Chem 2001;276:37594-37601. ArticlePubMed
- 35. Dupuy C, Ohayon R, Valent A, Noel-Hudson MS, Deme D, Virion A. Purification of a novel flavoprotein involved in the thyroid NADPH oxidase. Cloning of the porcine and human cdnas. J Biol Chem 1999;274:37265-37269. PubMed
- 36. Park J, Rho HK, Kim KH, Choe SS, Lee YS, Kim JB. Overexpression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is associated with lipid dysregulation and insulin resistance in obesity. Mol Cell Biol 2005;25:5146-5157. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 37. Park J, Choe SS, Choi AH, Kim KH, Yoon MJ, Suganami T, Ogawa Y, Kim JB. Increase in glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in adipocytes stimulates oxidative stress and inflammatory signals. Diabetes 2006;55:2939-2949. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 38. Cleary MP, Zisk JF. Anti-obesity effect of two different levels of dehydroepiandrosterone in lean and obese middle-aged female Zucker rats. Int J Obes 1986;10:193-204. PubMed
- 39. Li Y, Mouche S, Sajic T, Veyrat-Durebex C, Supale R, Pierroz D, Ferrari S, Negro F, Hasler U, Feraille E, Moll S, Meda P, Deffert C, Montet X, Krause KH, Szanto I. Deficiency in the NADPH oxidase 4 predisposes towards diet-induced obesity. Int J Obes (Lond) 2012;36:1503-1513. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 40. Nishimura S, Manabe I, Nagasaki M, Eto K, Yamashita H, Ohsugi M, Otsu M, Hara K, Ueki K, Sugiura S, Yoshimura K, Kadowaki T, Nagai R. CD8+ effector T cells contribute to macrophage recruitment and adipose tissue inflammation in obesity. Nat Med 2009;15:914-920. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 41. Olefsky JM, Glass CK. Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Annu Rev Physiol 2010;72:219-246. ArticlePubMed
- 42. Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 2006;444:860-867. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 43. Dang PM, Stensballe A, Boussetta T, Raad H, Dewas C, Kroviarski Y, Hayem G, Jensen ON, Gougerot-Pocidalo MA, El-Benna J. A specific p47phox -serine phosphorylated by convergent MAPKs mediates neutrophil NADPH oxidase priming at inflammatory sites. J Clin Invest 2006;116:2033-2043. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 44. Pepping JK, Freeman LR, Gupta S, Keller JN, Bruce-Keller AJ. NOX2 deficiency attenuates markers of adiposopathy and brain injury induced by high-fat diet. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2013;304:E392-E404. ArticlePubMed
- 45. Kaul N, Forman HJ. Activation of NF kappa B by the respiratory burst of macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med 1996;21:401-405. PubMed
- 46. Iles KE, Dickinson DA, Watanabe N, Iwamoto T, Forman HJ. AP-1 activation through endogenous H(2)O(2) generation by alveolar macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med 2002;32:1304-1313. ArticlePubMed
- 47. Suganami T, Ogawa Y. Adipose tissue macrophages: their role in adipose tissue remodeling. J Leukoc Biol 2010;88:33-39. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 48. Kim F, Pham M, Maloney E, Rizzo NO, Morton GJ, Wisse BE, Kirk EA, Chait A, Schwartz MW. Vascular inflammation, insulin resistance, and reduced nitric oxide production precede the onset of peripheral insulin resistance. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2008;28:1982-1988. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 49. Lee YS, Li P, Huh JY, Hwang IJ, Lu M, Kim JI, Ham M, Talukdar S, Chen A, Lu WJ, Bandyopadhyay GK, Schwendener R, Olefsky J, Kim JB. Inflammation is necessary for long-term but not short-term high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance. Diabetes 2011;60:2474-2483. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 50. Kosteli A, Sugaru E, Haemmerle G, Martin JF, Lei J, Zechner R, Ferrante AW Jr. Weight loss and lipolysis promote a dynamic immune response in murine adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 2010;120:3466-3479. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 51. Edgel KA, McMillen TS, Wei H, Pamir N, Houston BA, Caldwell MT, Mai PO, Oram JF, Tang C, Leboeuf RC. Obesity and weight loss result in increased adipose tissue ABCG1 expression in db/db mice. Biochim Biophys Acta 2012;1821:425-434. ArticlePubMed
- 52. Kataja-Tuomola M, Sundell JR, Mannisto S, Virtanen MJ, Kontto J, Albanes D, Virtamo J. Effect of alpha-tocopherol and beta-carotene supplementation on the incidence of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2008;51:47-53. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 53. Song Y, Cook NR, Albert CM, Van Denburgh M, Manson JE. Effects of vitamins C and E and beta-carotene on the risk of type 2 diabetes in women at high risk of cardiovascular disease: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr 2009;90:429-437. PubMedPMC
- 54. Liu S, Lee IM, Song Y, Van Denburgh M, Cook NR, Manson JE, Buring JE. Vitamin E and risk of type 2 diabetes in the women's health study randomized controlled trial. Diabetes 2006;55:2856-2862. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 55. Czernichow S, Couthouis A, Bertrais S, Vergnaud AC, Dauchet L, Galan P, Hercberg S. Antioxidant supplementation does not affect fasting plasma glucose in the Supplementation with Antioxidant Vitamins and Minerals (SU.VI.MAX) study in France: association with dietary intake and plasma concentrations. Am J Clin Nutr 2006;84:395-399. ArticlePubMed
- 56. Anderson EJ, Lustig ME, Boyle KE, Woodlief TL, Kane DA, Lin CT, Price JW 3rd, Kang L, Rabinovitch PS, Szeto HH, Houmard JA, Cortright RN, Wasserman DH, Neufer PD. Mitochondrial H2O2 emission and cellular redox state link excess fat intake to insulin resistance in both rodents and humans. J Clin Invest 2009;119:573-581. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 57. Hoehn KL, Salmon AB, Hohnen-Behrens C, Turner N, Hoy AJ, Maghzal GJ, Stocker R, Van Remmen H, Kraegen EW, Cooney GJ, Richardson AR, James DE. Insulin resistance is a cellular antioxidant defense mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2009;106:17787-17792. ArticlePubMedPMC
REFERENCES
Fig. 1
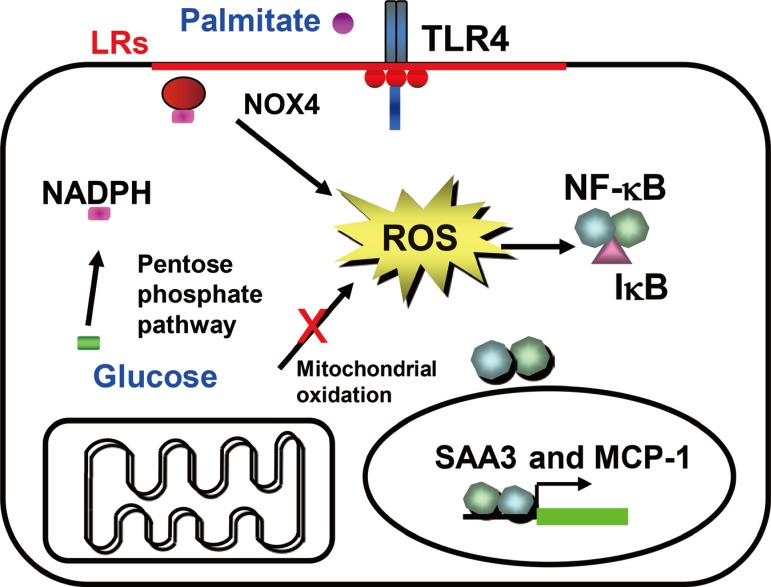
Hypothesis for a mechanism by which excess glucose and saturated free fatty acids (SFAs) affect reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in adipocytes in early stages of obesity. Excess glucose generates ROS via the pentose phosphate pathway, rather than by overloading mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation, while SFA generate ROS following activating, Toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) or lipid rafts. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase 4 (NOX4) might be the common mediator of ROS generation by both excess glucose and SFAs. ROS generated by both glucose and SFA activate nuclear factor κB (NF-κB). LR, lipid raft; SAA3, serum amyloid A3; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein-1.

Fig. 2

Hypothesis for a mechanism by which mitochondrial β-oxidation of free fatty acid (FFA) from triglyceride stores affects reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in adipocytes in the late stage of obesity. Uptake of excess glucose and FAA are inhibited, resulting in a decrease of pentose phosphate pathway and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) oxidase 4 (NOX4) activity. FFA from fat stores overload mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation and generate ROS. Mitochondria-derived ROS activate nuclear factor κB. IR, insulin receptor; IRS, insulin receptor substrate; GLUT4, glucose transporter 4; LPL, lipoprotein lipase; FATP, fatty acid transport protein; HSL, hormone-sensitive lipase.

Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- The Relationship of Alcohol Consumption and Drinking Pattern to the Risk of Glomerular Hyperfiltration in Middle-aged Japanese Men: The Kansai Healthcare Study
Mikiko Shibata, Kyoko Kogawa Sato, Hideo Koh, Izumi Shibata, Kaori Okamura, Yuka Takeuchi, Keiko Oue, Michio Morimoto, Tomoshige Hayashi
Journal of Epidemiology.2024; 34(3): 137. CrossRef - Monoamine oxidase mediated oxidative stress: a potential molecular and biochemical crux in the pathogenesis of obesity
J. P. Shirley Niveta, Cordelia Mano John, Sumathy Arockiasamy
Molecular Biology Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The obesity-autophagy-cancer axis: Mechanistic insights and therapeutic perspectives
Amir Barzegar Behrooz, Marco Cordani, Alessandra Fiore, Massimo Donadelli, Joseph W. Gordon, Daniel J. Klionsky, Saeid Ghavami
Seminars in Cancer Biology.2024; 99: 24. CrossRef - Pathogenesis and management of diabetic gastroparesis: An updated clinically oriented review
Srikar Uppaluri, Manisha Ashok Jain, Hira Ali, Jay Shingala, Dhruti Amin, Trisha Ajwani, Irum Fatima, Neil Patel, Nirja Kaka, Yashendra Sethi, Nitin Kapoor
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2024; 18(3): 102994. CrossRef - The advent of RNA-based therapeutics for metabolic syndrome and associated conditions: a comprehensive review of the literature
Helen Ye Rim Huang, Sarah Badar, Mohammad Said, Siddiqah Shah, Hareesha Rishab Bharadwaj, Krishna Ramamoorthy, Maen Monketh Alrawashdeh, Faaraea Haroon, Jawad Basit, Sajeel Saeed, Narjiss Aji, Gary Tse, Priyanka Roy, Mainak Bardhan
Molecular Biology Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The complex interplay between oxinflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction and lipotoxicity: Focus on their role in the pathogenesis of skeletal muscle insulin resistance and modulation by dietary fatty acids
Angelina Passaro, Juana Maria Sanz, Nenad Naumovski, Domenico Sergi
Advances in Redox Research.2024; 11: 100100. CrossRef - Extracellular vesicles regulate the transmission of insulin resistance and redefine noncommunicable diseases
Biao Li, Wan Li, Tiancai Liu, Longying Zha
Frontiers in Molecular Biosciences.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Oxidative stress in metabolic diseases: current scenario and therapeutic relevance
Satish K. Raut, Madhu Khullar
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2023; 478(1): 185. CrossRef - Rainbow Trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) as Source of Multifunctional Peptides with Antioxidant, ACE and DPP-IV Inhibitory Activities
Martina Bartolomei, Janna Cropotova, Carlotta Bollati, Kristine Kvangarsnes, Lorenza d’Adduzio, Jianqiang Li, Giovanna Boschin, Carmen Lammi
Nutrients.2023; 15(4): 829. CrossRef - Current Status of Obesity: Protective Role of Catechins
Tanisha Basu, Ashley Selman, Arubala P. Reddy, P. Hemachandra Reddy
Antioxidants.2023; 12(2): 474. CrossRef - Advanced Oxidation Protein Products Contribute to Chronic-Kidney-Disease-Induced Adipose Inflammation through Macrophage Activation
Nanaka Arimura, Hiroshi Watanabe, Hiromasa Kato, Tadashi Imafuku, Takehiro Nakano, Miyu Sueyoshi, Mayuko Chikamatsu, Kai Tokumaru, Taisei Nagasaki, Hitoshi Maeda, Motoko Tanaka, Kazutaka Matsushita, Toru Maruyama
Toxins.2023; 15(3): 179. CrossRef - The Role of Oxidative Stress Enhanced by Adiposity in Cardiometabolic Diseases
Iwona Świątkiewicz, Marcin Wróblewski, Jarosław Nuszkiewicz, Paweł Sutkowy, Joanna Wróblewska, Alina Woźniak
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(7): 6382. CrossRef - Understanding the Impact of Obesity on Ageing in the Radiance of DNA Metabolism
S.G. Chowdhury, S. Misra, Parimal Karmakar
The Journal of nutrition, health and aging.2023; 27(5): 314. CrossRef - Cross-talk between insulin resistance and nitrogen species in hypoxia leads to deterioration of tissue and homeostasis
Priyanshy Sharma, V. Sri Swetha Victoria, P. Praneeth Kumar, Sarbani Karmakar, Mudduluru Swetha, Amala Reddy
International Immunopharmacology.2023; 122: 110472. CrossRef - Mechanisms of Formation and Persistence of IgE Products and Potential Innovative Means of Therapy for Allergic Pathologies
D. B. Chudakov, M. V. Konovalova, M. A. Streltsova, O. A. Shustova, A. A. Generalov, G. V. Fattakhova
Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology.2023; 59(6): 754. CrossRef - Mechanism and application of Lactobacillus in type 2 diabetes-associated periodontitis
Sisi Chen, Yuhan Zhang
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Activated monocytes as a therapeutic target to attenuate vascular inflammation and lower cardiovascular disease-risk in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review of preclinical and clinical studies
Siphamandla R. Ngcobo, Bongani B. Nkambule, Tawanda M. Nyambuya, Kabelo Mokgalaboni, Aviwe Ntsethe, Vuyolwethu Mxinwa, Khanyisani Ziqubu, Yonela Ntamo, Thembeka A. Nyawo, Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 146: 112579. CrossRef - Genomic Analysis of Visceral Fat Accumulation in Holstein Cows
Larissa C. Novo, Ligia Cavani, Pablo Pinedo, Pedro Melendez, Francisco Peñagaricano
Frontiers in Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Regulation of immune cell function by nicotinamide nucleotide transhydrogenase
Thomas Regan, Rachel Conway, Leena P. Bharath
American Journal of Physiology-Cell Physiology.2022; 322(4): C666. CrossRef - d-Allulose Ameliorates Hyperglycemia Through IRE1α Sulfonation-RIDD-Sirt1 Decay Axis in the Skeletal Muscle
Hwa-Young Lee, Geum-Hwa Lee, The-Hiep Hoang, Seon-Ah Park, Juwon Lee, Junghyun Lim, Soonok Sa, Go Eun Kim, Jung Sook Han, Junghyun Kim, Han-Jung Chae
Antioxidants & Redox Signaling.2022; 37(4-6): 229. CrossRef - Impact of physical exercise and caloric restriction in patients with type 2 diabetes: Skeletal muscle insulin resistance and mitochondrial dysfunction as ideal therapeutic targets
Sinenhlanhla X.H. Mthembu, Sithandiwe E. Mazibuko-Mbeje, Khanyisani Ziqubu, Thembeka A. Nyawo, Nnini Obonye, Tawanda M. Nyambuya, Bongani B. Nkambule, Sonia Silvestri, Luca Tiano, Christo J.F. Muller, Phiwayinkosi V. Dludla
Life Sciences.2022; 297: 120467. CrossRef - The burden of overweight: Higher body mass index, but not vital exhaustion, is associated with higher DNA damage and lower DNA repair capacity
Judy Fieres, Marvin Fischer, Christine Sauter, Maria Moreno-Villanueva, Alexander Bürkle, Petra H. Wirtz
DNA Repair.2022; 114: 103323. CrossRef - The Disordered Amino Terminus of the Circadian Enzyme Nocturnin Modulates Its NADP(H) Phosphatase Activity by Changing Protein Dynamics
Anushka C. Wickramaratne, Li Li, Jesse B. Hopkins, Lukasz A. Joachimiak, Carla B. Green
Biochemistry.2022; 61(11): 1091. CrossRef - Oxidative stress and obesity
Maja Malenica, Neven Meseldžić
Arhiv za farmaciju.2022; 72(2): 166. CrossRef - Transcriptomic analysis of Simpson Golabi Behmel Syndrome cells during differentiation exhibit BAT-like function
M. Colitti, U. Ali, M. Wabitsch, D. Tews
Tissue and Cell.2022; : 101822. CrossRef - Vitamin E supplementation improves testosterone, glucose- and lipid-related metabolism in women with polycystic ovary syndrome: a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Sebastián Yalle-Vásquez, Karem Osco-Rosales, Wendy Nieto-Gutierrez, Vicente Benites-Zapata, Faustino R. Pérez-López, Christoper A. Alarcon-Ruiz
Gynecological Endocrinology.2022; 38(7): 548. CrossRef - The Immune Response in Adipocytes and Their Susceptibility to Infection: A Possible Relationship with Infectobesity
Orestes López-Ortega, Nidia Carolina Moreno-Corona, Victor Javier Cruz-Holguin, Luis Didier Garcia-Gonzalez, Addy Cecilia Helguera-Repetto, Mirza Romero-Valdovinos, Haruki Arevalo-Romero, Leticia Cedillo-Barron, Moisés León-Juárez
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(11): 6154. CrossRef - Participation of Magnesium in the Secretion and Signaling Pathways of Insulin: an Updated Review
Stéfany Rodrigues de Sousa Melo, Loanne Rocha dos Santos, Tamires da Cunha Soares, Bruna Emanuele Pereira Cardoso, Thaline Milany da Silva Dias, Jennifer Beatriz Silva Morais, Mickael de Paiva Sousa, Thayanne Gabryelle Visgueira de Sousa, Nilmara Cunha da
Biological Trace Element Research.2022; 200(8): 3545. CrossRef - Nrf2a dependent and independent effects of early life exposure to 3,3’-dichlorobiphenyl (PCB-11) in zebrafish (Danio rerio)
Monika A. Roy, Charlotte K. Gridley, Sida Li, Yeonhwa Park, Alicia R. Timme-Laragy
Aquatic Toxicology.2022; 249: 106219. CrossRef - Highly active antiretroviral therapy-silver nanoparticle conjugate interacts with neuronal and glial cells and alleviates anxiety-like behaviour in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats
Sodiq Kolawole Lawal, Samuel Oluwaseun Olojede, Ayobami Dare, Oluwaseun Samuel Faborode, Sheu Oluwadare Sulaiman, Edwin Coleridge Naidu, Carmen Olivia Rennie, Onyemaechi Okpara Azu
IBRO Neuroscience Reports.2022; 13: 57. CrossRef - Vitamin C attenuates predisposition to high-fat diet-induced metabolic dysregulation in GLUT10-deficient mouse model
Chung-Lin Jiang, Chang-Yu Tsao, Yi-Ching Lee
Genes & Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Adipose Tissue Aging and Metabolic Disorder, and the Impact of Nutritional Interventions
Xiujuan Wang, Meihong Xu, Yong Li
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3134. CrossRef - Production of Reactive Oxygen Species by Epicardial Adipocytes Is Associated with an Increase in Postprandial Glycemia, Postprandial Insulin, and a Decrease in Serum Adiponectin in Patients with Severe Coronary Atherosclerosis
Natalia V. Naryzhnaya, Olga A. Koshelskaya, Irina V. Kologrivova, Tatiana E. Suslova, Olga A. Kharitonova, Sergey L. Andreev, Alexander S. Gorbunov, Boris K. Kurbatov, Alla A. Boshchenko
Biomedicines.2022; 10(8): 2054. CrossRef - Aberrant mitochondrial homeostasis at the crossroad of musculoskeletal ageing and non-small cell lung cancer
Konstantinos Prokopidis, Panagiotis Giannos, Oliver C. Witard, Daniel Peckham, Theocharis Ispoglou, Ajay Pratap Singh
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(9): e0273766. CrossRef - Nutraceutical Prevention of Diabetic Complications—Focus on Dicarbonyl and Oxidative Stress
Mark F. McCarty, James J. DiNicolantonio, James H. O’Keefe
Current Issues in Molecular Biology.2022; 44(9): 4314. CrossRef - Fructose promotes more than glucose the adipocytic differentiation of pig mesenchymal stem cells
Francisco Campos‐Maldonado, María L. González‐Dávalos, Enrique Piña, Miriam Aracely Anaya‐Loyola, Armando Shimada, Alfredo Varela‐Echavarria, Ofelia Mora
Journal of Food Biochemistry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding the effect of obesity on papillary thyroid cancer: is there a need for tailored diagnostic and therapeutic management?
Antonio Matrone, Alessio Basolo, Ferruccio Santini, Rossella Elisei
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 17(6): 475. CrossRef - The Role of Inflammation as a Preponderant Risk Factor in Cardiovascular
Diseases
Rodrigo Damián García, Joana Antonela Asensio, Diahann Jeanette Perdicaro, María de los Ángeles Peral
Current Vascular Pharmacology.2022; 20(3): 244. CrossRef - Synthesis and Catalytic Studies of Nanoalloy Particles Based on Bismuth, Silver, and Rhenium
Konrad Wojtaszek, Katarzyna Skibińska, Filip Cebula, Tomasz Tokarski, Marc Escribà-Gelonch, Volker Hessel, Marek Wojnicki
Metals.2022; 12(11): 1819. CrossRef - Endothelium-Derived Relaxing Factors and Endothelial Function: A Systematic Review
Francesco Nappi, Antonio Fiore, Joyce Masiglat, Teresa Cavuoti, Michela Romandini, Pierluigi Nappi, Sanjeet Singh Avtaar Singh, Jean-Paul Couetil
Biomedicines.2022; 10(11): 2884. CrossRef - MicroRNAs in the Regulation of NADPH Oxidases in Vascular Diabetic and Ischemic Pathologies: A Case for Alternate Inhibitory Strategies?
Sean R. Wallace, Patrick J. Pagano, Damir Kračun
Antioxidants.2022; 12(1): 70. CrossRef - Potential Roles of Adipocyte Extracellular Vesicle–Derived miRNAs in Obesity-Mediated Insulin Resistance
Yujeong Kim, Ok-Kyung Kim
Advances in Nutrition.2021; 12(2): 566. CrossRef - Mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium ameliorates diabetic serum‐induced insulin resistance in 3T3‐L1 cells
Avinash Sanap, Ramesh Bhonde, Kalpana Joshi
Chronic Diseases and Translational Medicine.2021; 7(1): 47. CrossRef - F13A1 transglutaminase expression in human adipose tissue increases in acquired excess weight and associates with inflammatory status of adipocytes
M. T. Kaartinen, M. Arora, S. Heinonen, A. Hang, A. Barry, J. Lundbom, A. Hakkarainen, N. Lundholm, A. Rissanen, J. Kaprio, K. H. Pietiläinen
International Journal of Obesity.2021; 45(3): 577. CrossRef - Obesity and the prevention of thyroid cancer: Impact of body mass index and weight change on developing thyroid cancer – Pooled results of 24 million cohorts
Mohanad R. Youssef, Adin S.C. Reisner, Abdallah S. Attia, Mohamed Hosny Hussein, Mahmoud Omar, Anna LaRussa, Carlos A. Galvani, Mohamed Aboueisha, Mohamed Abdelgawad, Eman Ali Toraih, Gregory W. Randolph, Emad Kandil
Oral Oncology.2021; 112: 105085. CrossRef - Thioredoxin deficiency exacerbates vascular dysfunction during diet‐induced obesity in small mesenteric artery in mice
Shannon Dunn, Robert H. Hilgers, Kumuda C. Das
Microcirculation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Protein Digests and Pure Peptides from Chia Seed Prevented Adipogenesis and Inflammation by Inhibiting PPARγ and NF-κB Pathways in 3T3L-1 Adipocytes
Mariana Grancieri, Hércia Stampini Duarte Martino, Elvira Gonzalez de Mejia
Nutrients.2021; 13(1): 176. CrossRef - The Interplay Between Adipose Tissue and Vasculature: Role of Oxidative Stress in Obesity
Yawen Zhou, Huige Li, Ning Xia
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Peri-renal adipose inflammation contributes to renal dysfunction in a non-obese prediabetic rat model: Role of anti-diabetic drugs
Safaa H. Hammoud, Ibrahim AlZaim, Nahed Mougharbil, Sahar Koubar, Ali H. Eid, Assaad A. Eid, Ahmed F. El-Yazbi
Biochemical Pharmacology.2021; 186: 114491. CrossRef - Hydrogen Nano-Bubble Water Suppresses ROS Generation, Adipogenesis, and Interleukin-6 Secretion in Hydrogen-Peroxide- or PMA-Stimulated Adipocytes and Three-Dimensional Subcutaneous Adipose Equivalents
Li Xiao, Nobuhiko Miwa
Cells.2021; 10(3): 626. CrossRef - Redox Homeostasis in Pancreatic β-Cells: From Development to Failure
Štěpánka Benáková, Blanka Holendová, Lydie Plecitá-Hlavatá
Antioxidants.2021; 10(4): 526. CrossRef - Htd2 deficiency-associated suppression of α-lipoic acid production provokes mitochondrial dysfunction and insulin resistance in adipocytes
Mengqi Zeng, Jie Xu, Zhengyi Zhang, Xuan Zou, Xueqiang Wang, Ke Cao, Weiqiang Lv, Yuting Cui, Jiangang Long, Zhihui Feng, Jiankang Liu
Redox Biology.2021; 41: 101948. CrossRef - Nutraceutical, Dietary, and Lifestyle Options for Prevention and Treatment of Ventricular Hypertrophy and Heart Failure
Mark F. McCarty
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(7): 3321. CrossRef - Contribution of Adipose Tissue Oxidative Stress to Obesity-Associated Diabetes Risk and Ethnic Differences: Focus on Women of African Ancestry
Pamela A. Nono Nankam, Télesphore B. Nguelefack, Julia H. Goedecke, Matthias Blüher
Antioxidants.2021; 10(4): 622. CrossRef - Effects of different models of sucrose intake on the oxidative status of the uterus and ovary of rats
Joanna Sadowska, Wioleta Dudzińska, Izabela Dziaduch, Mahmoud A.O. Dawood
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(5): e0251789. CrossRef - Oxidative stress in oocyte aging and female reproduction
Ling Wang, Jinhua Tang, Lei Wang, Feng Tan, Huibin Song, Jiawei Zhou, Fenge Li
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2021; 236(12): 7966. CrossRef - Temporal correlation of morphological and biochemical changes with the recruitment of different mechanisms of reactive oxygen species formation during human SW872 cell adipogenic differentiation
Mara Fiorani, Rita De Matteis, Barbara Canonico, Giulia Blandino, Alessandro Mazzoli, Mariele Montanari, Andrea Guidarelli, Orazio Cantoni
BioFactors.2021; 47(5): 837. CrossRef - Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of gamma- oryzanol attenuates insulin resistance by increasing GLUT- 4 expression in skeletal muscle of obese animals
Letícia Mattei, Fabiane Valentini Francisqueti-Ferron, Jéssica Leite Garcia, Artur Junio Togneri Ferron, Carol Cristina Vágula de Almeida Silva, Cristina Schmitt Gregolin, Erika Tiemi Nakandakare-Maia, Janaína das Chagas Paixão Silva, Fernando Moreto, Igo
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2021; 537: 111423. CrossRef - Serum Bilirubin Levels in Overweight and Obese Individuals: The Importance of Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Responses
Lovro Žiberna, Zala Jenko-Pražnikar, Ana Petelin
Antioxidants.2021; 10(9): 1352. CrossRef - The level of reactive oxygen species production by adipocytes of epicardial adipose tissue is associated with an increase in postprandial glycemia in patients with severe coronary atherosclerosis
O. A. Koshelskaya, N. V. Naryzhnaya, I. V. Kologrivova, T. E. Suslova, O. A. Kharitonova, V. V. Evtushenko, S. L. Andreev, A. S. Gorbunov, A. A. Gudkova
The Siberian Journal of Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2021; 36(3): 59. CrossRef - Exercise training results in depot-specific adaptations to adipose tissue mitochondrial function
Amy E. Mendham, Steen Larsen, Cindy George, Kevin Adams, Jon Hauksson, Tommy Olsson, Melony C. Fortuin-de Smidt, Pamela A. Nono Nankam, Olah Hakim, Louise M. Goff, Carmen Pheiffer, Julia H. Goedecke
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Oxidative stress resulting from the removal of endogenous catalase induces obesity by promoting hyperplasia and hypertrophy of white adipocytes
Su-Kyung Shin, Hyun-Woo Cho, Seung-Eun Song, Seung-Soon Im, Jae-Hoon Bae, Dae-Kyu Song
Redox Biology.2020; 37: 101749. CrossRef - Pathogenic Role of Air Pollution Particulate Matter in Cardiometabolic Disease: Evidence from Mice and Humans
Timoteo Marchini, Andreas Zirlik, Dennis Wolf
Antioxidants & Redox Signaling.2020; 33(4): 263. CrossRef - Fumarate and oxidative stress synergize to promote stability of C/EBP homologous protein in the adipocyte
Allison M. Manuel, Michael D. Walla, Margaret T. Dorn, Ross M. Tanis, Gerardo G. Piroli, Norma Frizzell
Free Radical Biology and Medicine.2020; 148: 70. CrossRef - TNF-α G-308A genetic variants, serum CRP-hs concentration and DNA damage in obese women
Marta Włodarczyk, Michał Ciebiera, Grażyna Nowicka
Molecular Biology Reports.2020; 47(2): 855. CrossRef - Lipolysis modulates the biosynthesis of inflammatory lipid mediators derived from linoleic acid in adipose tissue of periparturient dairy cows
G. Andres Contreras, Jenne De Koster, Jonas de Souza, Juliana Laguna, Vengai Mavangira, Rahul K. Nelli, Jeff Gandy, Adam L. Lock, Lorraine M. Sordillo
Journal of Dairy Science.2020; 103(2): 1944. CrossRef - Dietary Fat and Cancer—Which Is Good, Which Is Bad, and the Body of Evidence
Bianka Bojková, Pawel J. Winklewski, Magdalena Wszedybyl-Winklewska
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(11): 4114. CrossRef - Adipose tissue macrophages: Unique polarization and bioenergetics in obesity
Heather L. Caslin, Monica Bhanot, W. Reid Bolus, Alyssa H. Hasty
Immunological Reviews.2020; 295(1): 101. CrossRef - Conditioned medium of adipose derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells reverse insulin resistance through downregulation of stress induced serine kinases
Avinash Sanap, Ramesh Bhonde, Kalpana Joshi
European Journal of Pharmacology.2020; 881: 173215. CrossRef - Quercetin metabolites from Hibiscus sabdariffa contribute to alleviate glucolipotoxicity-induced metabolic stress in vitro
María Herranz-López, Mariló Olivares-Vicente, Esther Rodríguez Gallego, Jose Antonio Encinar, Almudena Pérez-Sánchez, Verónica Ruiz-Torres, Jorge Joven, Enrique Roche, Vicente Micol
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2020; 144: 111606. CrossRef - Elastin-derived peptide VGVAPG decreases differentiation of mouse embryo fibroblast (3T3-L1) cells into adipocytes
Konrad A. Szychowski, Bartosz Skóra, Jakub Tobiasz, Jan Gmiński
Adipocyte.2020; 9(1): 234. CrossRef - Pharmacological potential of the combination of Salvia miltiorrhiza (Danshen) and Carthamus tinctorius (Honghua) for diabetes mellitus and its cardiovascular complications
John O. Orgah, Shuang He, Yule Wang, Miaomiao Jiang, Yuefei Wang, Emmanuel A. Orgah, Yajun Duan, Buchang Zhao, Boli Zhang, Jihong Han, Yan Zhu
Pharmacological Research.2020; 153: 104654. CrossRef - Microbiota-Mitochondria Inter-Talk: A Potential Therapeutic Strategy in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
Teresa Vezza, Zaida Abad-Jiménez, Miguel Marti-Cabrera, Milagros Rocha, Víctor Manuel Víctor
Antioxidants.2020; 9(9): 848. CrossRef - Transglutaminases and Obesity in Humans: Association of F13A1 to Adipocyte Hypertrophy and Adipose Tissue Immune Response
Mari T. Kaartinen, Mansi Arora, Sini Heinonen, Aila Rissanen, Jaakko Kaprio, Kirsi H. Pietiläinen
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(21): 8289. CrossRef - Phytosterols: Nutritional Health Players in the Management of Obesity and Its Related Disorders
Teresa Vezza, Francisco Canet, Aranzazu M. de Marañón, Celia Bañuls, Milagros Rocha, Víctor Manuel Víctor
Antioxidants.2020; 9(12): 1266. CrossRef - Metabolic programming of macrophage functions and pathogens control
Sue-jie Koo, Nisha J. Garg
Redox Biology.2019; 24: 101198. CrossRef - Effects of bariatric surgery on telomere length and T-cell aging
F. Jongbloed, R. W. J. Meijers, J. N. M. IJzermans, R. A. Klaassen, M. E. T. Dollé, S. van den Berg, M. G. H. Betjes, R. W. F. de Bruin, E. van der Harst, N. H. R. Litjens
International Journal of Obesity.2019; 43(11): 2189. CrossRef - Shared pathways for neuroprogression and somatoprogression in neuropsychiatric disorders
Gerwyn Morris, Basant K. Puri, Adam J. Walker, Michael Maes, Andre F. Carvalho, Chiara C. Bortolasci, Ken Walder, Michael Berk
Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews.2019; 107: 862. CrossRef - Adipose oxidative stress and protein carbonylation
Amy K. Hauck, Yimao Huang, Ann V. Hertzel, David A. Bernlohr
Journal of Biological Chemistry.2019; 294(4): 1083. CrossRef - Modulatory functions of bioactive fruits, vegetables and spices in adipogenesis and angiogenesis
Priyanka Sarkar, Kavitha Thirumurugan
Journal of Functional Foods.2019; 53: 318. CrossRef - Spontaneous ketonuria and risk of incident diabetes: a 12 year prospective study
Gyuri Kim, Sang-Guk Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Ele Ferrannini, Yong-ho Lee, Nam H. Cho
Diabetologia.2019; 62(5): 779. CrossRef - Obesity, DNA Damage, and Development of Obesity-Related Diseases
Marta Włodarczyk, Grażyna Nowicka
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(5): 1146. CrossRef - Weight change is significantly associated with risk of thyroid cancer: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Hyemi Kwon, Kyung-Do Han, Cheol-Young Park
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The Role of NADPH Oxidases in the Etiology of Obesity and Metabolic Syndrome: Contribution of Individual Isoforms and Cell Biology
Evan DeVallance, Yao Li, Michael J. Jurczak, Eugenia Cifuentes-Pagano, Patrick J. Pagano
Antioxidants & Redox Signaling.2019; 31(10): 687. CrossRef - Phenolic compounds as natural and multifunctional anti-obesity agents: A review
Celia Rodríguez-Pérez, Antonio Segura-Carretero, María del Mar Contreras
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2019; 59(8): 1212. CrossRef - Oxygenic metabolism in nutritional obesity induced by olive oil. The influence of vitamin C
Eraci Drehmer, Mari Ángeles Navarro-Moreno, Sandra Carrera, Vincent M. Villar, Mari Luz Moreno
Food & Function.2019; 10(6): 3567. CrossRef - High Glucose Level Impairs Human Mature Bone Marrow Adipocyte Function Through Increased ROS Production
Tareck Rharass, Stéphanie Lucas
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Redox TRPs in diabetes and diabetic complications: Mechanisms and pharmacological modulation
Pratik Adhya, Shyam Sunder Sharma
Pharmacological Research.2019; 146: 104271. CrossRef - Linking Arrhythmias and Adipocytes: Insights, Mechanisms, and Future Directions
Maria A. Pabon, Kevin Manocha, Jim W. Cheung, James C. Lo
Frontiers in Physiology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Strawberry extract attenuates oxidative stress in 3T3-L1 cells
Tamara Y. Forbes-Hernández, Sadia Afrin, Danila Cianciosi, Piera Pia Manna, Jiaojiao Zhang, Massimiliano Gasparrini, Patricia Reboredo-Rodríguez
Journal of Berry Research.2018; 8(3): 193. CrossRef - The mitochondrial unfolded protein response and mitohormesis: a perspective on metabolic diseases
Hyon-Seung Yi, Joon Young Chang, Minho Shong
Journal of Molecular Endocrinology.2018; 61(3): R91. CrossRef - Emerging Roles for Adipose Tissue in Cardiovascular Disease
Elizabeth E. Ha, Robert C. Bauer
Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - miR-199a-3p regulates brown adipocyte differentiation through mTOR signaling pathway
Yao Gao, Yan Cao, Xianwei Cui, Xingyun Wang, Yahui Zhou, Fangyan Huang, Xing Wang, Juan Wen, Kaipeng Xie, Pengfei Xu, Xirong Guo, Lianghui You, Chenbo Ji
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2018; 476: 155. CrossRef - Reduced expression of Twist 1 is protective against insulin resistance of adipocytes and involves mitochondrial dysfunction
Sumei Lu, Hong Wang, Rui Ren, Xiaohong Shi, Yanmei Zhang, Wanshan Ma
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Zanthoxylum ailanthoides Suppresses Oleic Acid-Induced Lipid Accumulation through an Activation of LKB1/AMPK Pathway in HepG2 Cells
Eun-Bin Kwon, Myung-Ji Kang, Soo-Yeon Kim, Yong-Moon Lee, Mi-Kyeong Lee, Heung Joo Yuk, Hyung Won Ryu, Su Ui Lee, Sei-Ryang Oh, Dong-Oh Moon, Hyun-Sun Lee, Mun-Ock Kim
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Supplementation of Lactobacillus plantarum Improves Markers of Metabolic Dysfunction Induced by a High Fat Diet
Alice Martinic, Javad Barouei, Zach Bendiks, Darya Mishchuk, Dustin D. Heeney, Roy Martin, Maria L. Marco, Carolyn M. Slupsky
Journal of Proteome Research.2018; 17(8): 2790. CrossRef - The novel NADPH oxidase 4 selective inhibitor GLX7013114 counteracts human islet cell death in vitro
Xuan Wang, Andris Elksnis, Per Wikström, Erik Walum, Nils Welsh, Per-Ola Carlsson, Harald H. H. W. Schmidt
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(9): e0204271. CrossRef - Involvement of adipose tissue inflammation and dysfunction in virus-induced type 1 diabetes
James C Needell, Madalyn N Brown, Danny Zipris
Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 238(1): 61. CrossRef - Autophagy as an emerging target in cardiorenal metabolic disease: From pathophysiology to management
Yingmei Zhang, Adam T. Whaley-Connell, James R. Sowers, Jun Ren
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2018; 191: 1. CrossRef - Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in an Obese State and the Protective Effects of Gallic Acid
Phiwayinkosi Dludla, Bongani Nkambule, Babalwa Jack, Zibusiso Mkandla, Tinashe Mutize, Sonia Silvestri, Patrick Orlando, Luca Tiano, Johan Louw, Sithandiwe Mazibuko-Mbeje
Nutrients.2018; 11(1): 23. CrossRef - Adipocyte-Specific Deficiency of NADPH Oxidase 4 Delays the Onset of Insulin Resistance and Attenuates Adipose Tissue Inflammation in Obesity
Laura J. Den Hartigh, Mohamed Omer, Leela Goodspeed, Shari Wang, Tomasz Wietecha, Kevin D. O’Brien, Chang Yeop Han
Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology.2017; 37(3): 466. CrossRef - Novel lipid-mimetic prodrugs delivering active compounds to adipose tissue
Andrea Mattarei, Andrea Rossa, Veronica Bombardelli, Michele Azzolini, Martina La Spina, Cristina Paradisi, Mario Zoratti, Lucia Biasutto
European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2017; 135: 77. CrossRef - Combined metformin and insulin treatment reverses metabolically impaired omental adipogenesis and accumulation of 4-hydroxynonenal in obese diabetic patients
Morana Jaganjac, Shamma Almuraikhy, Fatima Al-Khelaifi, Mashael Al-Jaber, Moataz Bashah, Nayef A. Mazloum, Kamelija Zarkovic, Neven Zarkovic, Georg Waeg, Wael Kafienah, Mohamed A. Elrayess
Redox Biology.2017; 12: 483. CrossRef - A Novel Index Using Soluble CD36 Is Associated with the Prevalence of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Comparison Study with Triglyceride-Glucose Index
Ho Jin Kim, Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Joong Hee Kim, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(3): 375. CrossRef - Xanthine oxidase inhibition by febuxostat attenuates stress-induced hyperuricemia, glucose dysmetabolism, and prothrombotic state in mice
Maimaiti Yisireyili, Motoharu Hayashi, Hongxian Wu, Yasuhiro Uchida, Koji Yamamoto, Ryosuke Kikuchi, Mohammad Shoaib Hamrah, Takayuki Nakayama, Xian Wu Cheng, Tadashi Matsushita, Shigeo Nakamura, Toshimitsu Niwa, Toyoaki Murohara, Kyosuke Takeshita
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Differential Effect of Sucrose and Fructose in Combination with a High Fat Diet on Intestinal Microbiota and Kidney Oxidative Stress
Adriana Rosas-Villegas, Mónica Sánchez-Tapia, Azalia Avila-Nava, Victoria Ramírez, Armando Tovar, Nimbe Torres
Nutrients.2017; 9(4): 393. CrossRef - Neovascular deterioration, impaired NADPH oxidase and inflammatory cytokine expression in adipose-derived multipotent cells from subjects with metabolic syndrome
Wilfredo Oliva-Olivera, Said Lhamyani, Leticia Coín-Aragüez, Daniel Castellano-Castillo, Juan Alcaide-Torres, Elena María Yubero-Serrano, Rajaa El Bekay, Francisco José Tinahones
Metabolism.2017; 71: 132. CrossRef - Fatty acid binding protein 4/aP2-dependent BLT1R expression and signaling
Ann V. Hertzel, Hongliang Xu, Michael Downey, Nicholas Kvalheim, David A. Bernlohr
Journal of Lipid Research.2017; 58(7): 1354. CrossRef - Metformin prevents glucotoxicity by alleviating oxidative and ER stress–induced CD36 expression in pancreatic beta cells
Jun Sung Moon, Udayakumar Karunakaran, Suma Elumalai, In-Kyu Lee, Hyoung Woo Lee, Yong-Woon Kim, Kyu Chang Won
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(1): 21. CrossRef - Teneligliptin, a dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor, attenuated pro-inflammatory phenotype of perivascular adipose tissue and inhibited atherogenesis in normoglycemic apolipoprotein-E-deficient mice
Hotimah Masdan Salim, Daiju Fukuda, Yasutomi Higashikuni, Kimie Tanaka, Yoichiro Hirata, Shusuke Yagi, Takeshi Soeki, Michio Shimabukuro, Masataka Sata
Vascular Pharmacology.2017; 96-98: 19. CrossRef - Obesity-induced vascular dysfunction and arterial stiffening requires
endothelial cell arginase 1
Anil Bhatta, Lin Yao, Zhimin Xu, Haroldo A. Toque, Jijun Chen, Reem T. Atawia, Abdelrahman Y. Fouda, Zsolt Bagi, Rudolf Lucas, Ruth B. Caldwell, Robert W. Caldwell
Cardiovascular Research.2017; 113(13): 1664. CrossRef - Change in serum albumin concentration is inversely and independently associated with risk of incident metabolic syndrome
Sang-Man Jin, Yong Joo Hong, Jae Hwan Jee, Ji Cheol Bae, Kyu Yeon Hur, Moon-Kyu Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
Metabolism.2016; 65(11): 1629. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA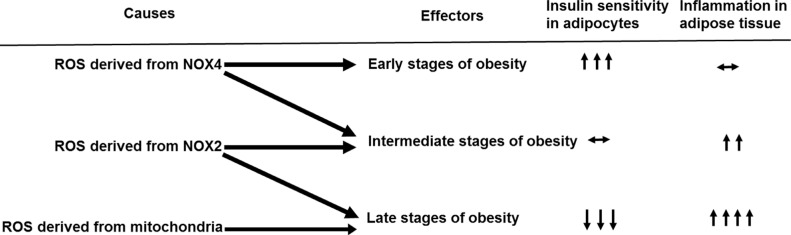
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite