- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 45(3); 2021 > Article
-
Original ArticleCOVID-19 Use of Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System Inhibitors and Severe COVID-19 Outcomes in Patients with Hypertension: A Nationwide Cohort Study
-
Jae Hyun Bae1,*
 , Sun Kyu Choi2,*
, Sun Kyu Choi2,* , Nam Hoon Kim1, Juneyoung Lee2
, Nam Hoon Kim1, Juneyoung Lee2 , Sin Gon Kim1
, Sin Gon Kim1
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2021;45(3):430-438.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0279
Published online: February 22, 2021
1Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Department of Biostatistics, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
-
Corresponding authors: Sin Gon Kim
 Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, 73 Goryeodae-ro, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul 02841, Korea E-mail: k50367@korea.ac.kr
Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Anam Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, 73 Goryeodae-ro, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul 02841, Korea E-mail: k50367@korea.ac.kr
-
Juneyoung Lee
 Department of Biostatistics, Korea University College of Medicine, 73 Goryeodae-ro, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul 02841, Korea E-mail: jyleeuf@korea.ac.kr
Department of Biostatistics, Korea University College of Medicine, 73 Goryeodae-ro, Seongbuk-gu, Seoul 02841, Korea E-mail: jyleeuf@korea.ac.kr
- *Jae Hyun Bae and Sun Kyu Choi contributed equally to this study as first authors.
Copyright © 2021 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 facilitates the entry of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 into the human body. We investigated the association of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitor use with severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) outcomes in hypertensive patients.
-
Methods
- We identified hypertensive patients with confirmed COVID-19 from the Korean Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service from inception to May 15, 2020. The primary outcome was the composite of intensive care unit (ICU) admission, invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV), continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT), extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), and death from COVID-19. The individual components were evaluated as secondary outcomes.
-
Results
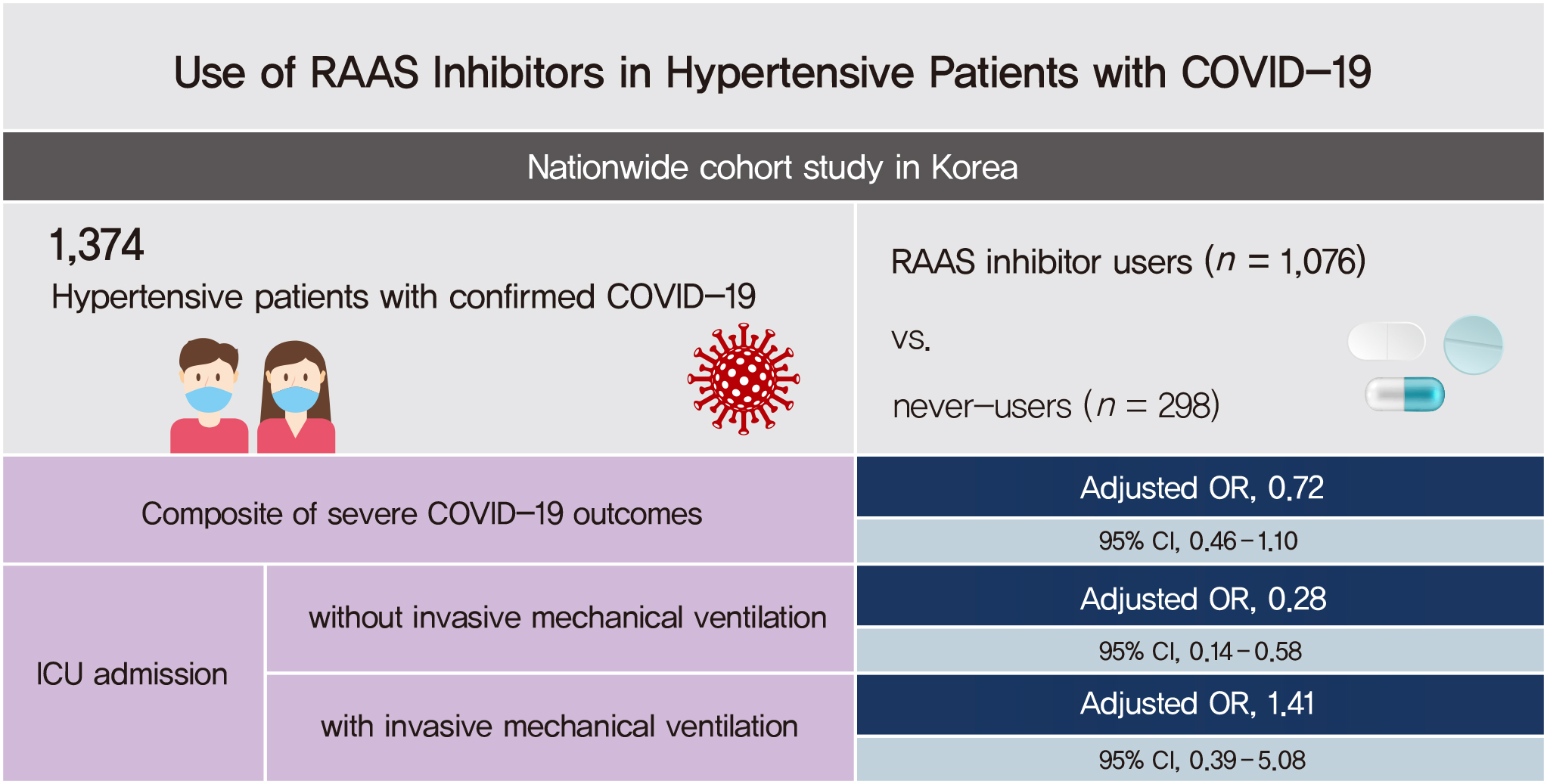
- Of 1,374 hypertensive patients with COVID-19, 1,076 (78.3%) and 298 (21.7%) were users and never-users of RAAS inhibitors, respectively. The RAAS inhibitor users were not associated with the risk of the primary outcome (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 0.72; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.46 to 1.10). The risk of ICU admission was significantly lower in the users than the never-users (aOR, 0.44; 95% CI, 0.24 to 0.84). The RAAS inhibitors were beneficial only in ICU admissions that did not require IMV (aOR, 0.28; 95% CI, 0.14 to 0.58). The risk of death from COVID-19 was comparable between the groups (aOR, 1.09; 95% CI, 0.64 to 1.85). We could not evaluate the risks of CRRT and ECMO owing to the small number of events.
-
Conclusion
- RAAS inhibitor use was not associated with the composite of severe outcomes in the hypertensive patients with COVID-19 but significantly lowered the risk of ICU admission, particularly in patients who did not require IMV.
- The global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) that began in late 2019 still threatens the health of people worldwide, causing 1,444,596 deaths by November 29, 2020 [1,2]. Hence identifying the risk factors for severe clinical outcomes of COVID-19, which include acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and death, is one of the most important issues.
- However, many areas of uncertainty remain to be clarified, including the effect of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors. Several studies have been conducted on the hypothesis that the use of RAAS inhibitors, including angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (ACEIs) and angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs), affects COVID-19 susceptibility and clinical outcomes because it may alter the expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) at the cell surface, which is known as the entry of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) [3,4]. Epidemiological studies have reported inconsistent results about the use of RAAS inhibitors being harmful [5], neutral [6,7], and beneficial [8,9] to SARSCoV-2 infection or clinical outcomes of COVID-19. This warranted the review of the existing evidence and hypothesis. ACE2 upregulation may increase the viral load via an increase in the cellular entry of SARS-CoV-2 [10]. By contrast, it may exert beneficial effects, especially on the cardiovascular and renal system via counterregulatory actions on the RAAS [11]. Meanwhile, experimental studies indicated that the effects of RAAS inhibitors on the ACE2 expression may vary according to classes or individual properties of the drugs and the tissues in which it is expressed [12,13]. These findings imply that RAAS inhibitors might have complex or mixed effects in patients with COVID-19.
- Therefore, a more precise approach is needed to refine the COVID-19 outcomes related to the use of RAAS inhibitors. In this regard, we investigated the effects of RAAS inhibitors on severe outcomes of COVID-19, including respiratory failure and hemodynamic derangement, in patients with hypertension on the basis of the Korean national registry data.
INTRODUCTION
- The Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service (HIRA) of South Korea is a repository of claims data generated for reimbursing providers [14]. Under the universal coverage system based on the fee-for-service payment system in Korea, HIRA data contains comprehensive information, including examinations, prescriptions, procedures, and surgeries, and covers 98% of the Korean population [14]. As the COVID-19 pandemic continues to spread, the Korean government decided to share the de-identified nationwide COVID-19 patient data with domestic and international researchers [15]. After their initial release, the data were updated with claims submitted to the HIRA by May 15, 2020 [16]. The updated data consisted of COVID-19-related items (classification, real-time polymerase chain reaction, disease, and fee codes) and information on prior use of healthcare services (Supplementary table 1). Owing to the increased number of patients, the duration of healthcare service use history was reduced from 5 to 3 years. As the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention data of confirmed cases were connected to the HIRA claims data, COVID-19 confirmation and death codes were also added. Ultimately, the claim statements of 7,590 patients among 11,018 confirmed cases were included [16].
- Study population
- We identified patients with prior hypertension who had confirmed COVID-19. Hypertension was defined as the Tenth Revision of the International Statistical Classification of Diseases and Related Health Problems (ICD-10) codes I10, I15, O10, and O13–O16 and at least one claim in 6 months for the prescription of antihypertensive agents (identified using the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical code). A confirmed COVID-19 case was defined as a person with laboratory-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection on the basis of the diagnostic testing criteria, regardless of clinical manifestations [17]. Real-time reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction tests were performed on nasopharyngeal/oropharyngeal swab or sputum samples [17]. The index date was defined as the day of diagnosis of COVID-19. All the study participants were followed up until their death or the end of the study, on May 15, 2020.
- Use of RAAS inhibitors
- The exposure of interest was the use of RAAS inhibitors, including ARBs and ACEIs. RAAS inhibitor users were defined as individuals with at least one prescription of ARBs or ACEIs within 6 months before the index date. RAAS inhibitor ex-users were defined as individuals who had received ARBs or ACEIs between 3 years and 6 months but not within 6 months before the index date. RAAS inhibitor never-users were defined as individuals who had never received ARBs or ACEIs within 3 years before the index date. We included both RAAS inhibitor users and never-users in the analysis.
- Study outcomes
- The primary outcome was defined as the composite of intensive care unit (ICU) admission, invasive mechanical ventilation (IMV), continuous renal replacement therapy (CRRT), extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), and death from COVID-19 (Supplementary table 2). Each of the individual components was used as secondary outcomes.
- Statistical analysis
- The patients’ characteristics and the number of events are presented as the mean±standard deviation or number (%). We performed unadjusted and adjusted (multivariable) logistic regression analyses to estimate odds ratios (ORs) and their 95% confidence intervals (CIs) for the study outcomes. For the multivariable model, the covariates of age; sex; comorbidities, including diabetes mellitus (DM), hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular disease (CVD), chronic kidney disease (CKD), chronic pulmonary disease; concomitant use of medications, including antihypertensive, glucose-lowering, lipid-lowering, and antithrombotic agents (Supplementary table 3); and the Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) [18] were adjusted as confounders. Subgroup analyses were performed by age, sex, the presence of DM, hyperlipidemia, CVD, CKD, the treatment of DM, and the use of statins, antithrombotic agents, and inhaled corticosteroids. All statistical analyses were performed using SAS version 9.4 (SAS Institute Inc., Cary, NC, USA) with a two-sided test, and statistical significance was set at α=0.05.
- Ethical statement
- The study protocol was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Korea University Anam Hospital (IRB No. 2020-AN-0182). As all data were de-identified in a retrospective study, the study protocol was exempted from review and informed consent was waived.
METHODS
- Characteristics of the study participants
- Of 7,590 patients with confirmed COVID-19, 1,374 with prior hypertension were included. Of the included patients, 1,076 (1,037 [96.4%] used ARBs and 39 [3.6%] used ACEIs) and 298 were RAAS inhibitor users and never-users, respectively. We excluded 17 patients who received both ARBs and ACEIs during the same period. A flow diagram of the patient selection is depicted in Fig. 1. The baseline characteristics of the study participants are shown in Table 1. Comorbidities, including DM (60.7% vs. 49.0%, P<0.001) and hyperlipidemia (54.0% vs. 39.6%, P<0.001), were more prevalent in the RAAS inhibitor users than in the never-users. Compared with the never-users, RAAS inhibitor users were more likely to have been taking antihypertensive agents (diuretics and β-blockers), glucose-lowering agents (metformin, sulfonylurea, and dipeptidyl peptidase-4 [DPP-4] inhibitors), and statins.
- Severe outcomes of COVID-19
- The primary composite outcome of ICU admission, IMV, CRRT, ECMO, and death occurred in 144 patients. The RAAS inhibitor users were not associated with the risk of the composite outcome as compared with the never-users (adjusted OR [aOR], 0.72; 95% CI, 0.46 to 1.10). This finding was consistent across the ARB (aOR, 0.71; 95% CI, 0.46 to 1.10) and ACEI users (aOR, 0.81; 95% CI, 0.31 to 2.11) (Table 2).
- ICU admission occurred in 52 patients. The RAAS inhibitor users were significantly associated with a lower risk of ICU admission as compared with the never-users (aOR, 0.44; 95% CI, 0.24 to 0.84). The result was attributed to the ARB users (aOR, 0.42; 95% CI, 0.22 to 0.81) rather than the ACEI users (aOR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.21 to 2.48). The beneficial effect of RAAS inhibitors on ICU admission was observed in the patients who did not require IMV (aOR, 0.28; 95% CI, 0.14 to 0.58), but not in those who required IMV (aOR, 1.41; 95% CI, 0.39 to 5.08) (Table 2). The risk of death (n=106) was similar between the RAAS inhibitor users and never-users (aOR, 1.09; 95% CI, 0.64 to 1.85). The ORs of the other secondary outcomes, including CRRT (n=0) and ECMO (n=1), could not be calculated owing to the small number of events.
- The subgroup analyses revealed that the absence of DM (aOR, 0.48; 95% CI, 0.23 to 0.99) and chronic pulmonary disease (aOR, 0.58; 95% CI, 0.37 to 0.91), the presence of hyperlipidemia (aOR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.29 to 0.86), and the use of antithrombotic agents (aOR, 0.44; 95% CI, 0.25 to 0.77) were associated with a lower risk of the composite outcome (Supplementary table 4).
- Risk factors for the primary composite outcome and ICU admission
- The multivariable analysis revealed that older age (as a continuous variable), male sex, DM, CVD, CKD, and increased CCI were associated with a higher risk of the composite outcome (Fig. 2A). Several factors, including male sex, prior CVD, and increased CCI, were also associated with a higher risk of ICU admission (Fig. 2B). On the contrary, the use of RAAS inhibitors and ARBs was associated with a lower risk of ICU admission. These findings were similar in the patients admitted to the ICU without IMV (Fig. 2C), but not in those with IMV (Fig. 2D).
RESULTS
- In this study, we found that the use of RAAS inhibitors did not increase the risk of serious health outcomes in the hypertensive patients with COVID-19. In addition, the use of RAAS inhibitors was associated with some health benefits, including a 56% reduction in the risk of ICU admission, mostly resulted from ICU admissions not requiring IMV. This pattern was similarly observed for both ARBs and ACEIs, but statistically significant results were only observed for ARBs, not for ACEIs, which might be owing to the small number of patients and events.
- Overall, the results of this study are in line with those of the existing large-scale epidemiological studies, which showed that the use of RAAS inhibitors was not harmful to COVID-19 susceptibility and outcomes [6,7,19]. The noteworthy finding in this study is that RAAS inhibitors may have different clinical effects depending on the affected organs and tissues. This is, in part, due to their different responses to altered expression of ACE2 by RAAS inhibitors or blockade per se.
- ACE2 degrades angiotensin II to angiotensin-(1–7) and cleaves angiotensin I to angiotensin-(1–9), and thereby its primary action is the counterregulation of the RAAS [11]. Recent studies on the relationship between RAAS inhibitor use and the development or outcomes of COVID-19 were based on the assumption that RAAS inhibitors would induce changes in ACE2 expression or activity. With a few exceptions [20,21], experimental studies generally supported the original assumption that RAAS inhibitor treatment induced an increase in ACE2 expression or activity [22,23]. The degree of this increase varied depending on the type of drugs and the tissues in which ACE2 was expressed. For example, losartan treatment significantly increased ACE2 activity in both heart and kidney tissues, but lisinopril treatment increased that only in kidney and not in heart tissue [12,13]. On the basis of these findings, we can speculate that changes in ACE2 and related clinical consequences would not be uniform depending on the diverse RAAS inhibitors and affected organs such as the lung, heart, or kidney.
- Previous studies reported that hypertension and CVD were the major comorbidities and risk factors for COVID-19 [6,24,25]. Similarly, in our study, CVD was identified as a significant risk factor for most outcomes. Evidence suggested that ACE2 downregulation by SARS-CoV-2 infection possibly contributed to the exacerbation of underlying CVD and even direct injury to cardiomyocytes in patients with COVID-19 [26,27]. In a previous autopsy study of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus, myocardial damage was associated with the downregulation of myocardial ACE2 [28]. Thus, RAAS inhibitors, through the alteration of ACE2 activity or its own actions such as vasodilation, anti-inflammation, and anti-fibrosis, may have beneficial effects on the cardiovascular outcomes of COVID-19. In this regard, our study adds evidence of the possible benefits of RAAS inhibitors on COVID-19 outcomes. On the other hand, RAAS inhibitors had no beneficial effect on ICU admissions that required IMV. Failure to reduce the number of IMV cases, which is mainly related to severe lung injury, may be explained by the reduced benefits of RAAS inhibitors on ACE2 after acute lung injury. However, this is just a hypothesis and should be proved by further studies.
- In our study, the use of metformin, DPP-4 inhibitors, and statins was higher in the RAAS users than the never-users in accordance with the prevalence of DM and hyperlipidemia. Several studies have reported that these medications are associated with clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19. In retrospective cohort studies, metformin was significantly associated with lower inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) [29] and reduced in-hospital mortality in women with T2DM and obesity [30]. In a case-control study [31] and a case series [32] from northern Italy, DPP-4 inhibitor treatment was associated with decreased mortality in patients hospitalized for COVID-19. On the other hand, in-hospital statin use was associated with a lower risk of mortality in Chinese patients with COVID-19 [33]. In this study, adding ACEIs or ARBs did not affect statin-associated outcome among patients with COVID-19 and hypertension [33]. Although these medications have anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects [34-36], which might be beneficial for treating infectious diseases, there is little evidence supporting the protective or detrimental role in patients with COVID-19 [37]. In our study, RAAS inhibitor users were associated with a significantly lower risk of ICU admission in the hypertensive patients with COVID-19 after adjusting for confounders, including the use of metformin, DPP-4 inhibitors, and statins. Given the shortcomings and limitations of the retrospective nature of the study, well-designed, randomized controlled trials are required to elucidate its mechanism and potential interaction with other medications in patients with COVID-19.
- This study has several limitations. First, because we approached the database retrospectively, detailed information on the in-hospital progress of the patients, including laboratory findings or imaging studies, could not be obtained. Therefore, we considered the use of IMV, CRRT, and ECMO as an indirect indicator of severe lung injury and hemodynamic derangement. Second, the dose and duration of RAAS inhibitors might affect the study outcomes. However, owing to the limitation on data availability, we could not evaluate their influence on the results. Third, information on the ACE2 expression or activity, which may have as a causal relationship between RAAS inhibitor use and COVID-19 outcomes, could not be obtained. Fourth, the number of patients who used ACEIs was insufficient. Therefore, we could not ascertain whether ACEIs have the same benefits for COVID-19 outcomes as ARBs.
- This study demonstrated that the use of RAAS inhibitors did not increase serious health risks, including death, in the hypertensive patients with COVID-19. In addition, as inferred from the benefits for ICU admission without IMV, this study suggests that the use of RAAS inhibitors may exert different effects depending on the organ systems in COVID-19. The results of ongoing clinical trials of RAAS inhibitors in patients with COVID-19 may provide a clearer conclusion.
DISCUSSION
Supplementary Materials
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
Conception or design: J.H.B., J.L., S.G.K.
Acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data: J.H.B., S.K.C., N.H.K., J.L., S.G.K.
Drafting the work or revising: J.H.B., S.K.C., N.H.K., J.L., S.G.K.
Final approval of the manuscript: J.H.B., S.K.C., N.H.K., J.L., S.G.K.
-
FUNDING
None
NOTES
-
Acknowledgements
- The authors appreciate the healthcare professionals dedicated to the treatment of patients with COVID-19 in Korea, the Ministry of Health and Welfare, and the HIRA of Korea for promptly sharing invaluable national health insurance claims data.

| Characteristic | Total (n=1,374) | RAAS inhibitor users (n=1,076) | RAAS inhibitor never-users (n=298) | P value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, yr | 65.0±13.2 | 64.5±12.8 | 66.7±14.9 | 0.017 | |
| <65 | 727 (52.9) | 599 (55.7) | 128 (43.0) | ||
| ≥65 | 647 (47.1) | 477 (44.3) | 170 (57.0) | ||
| Men | 569 (41.4) | 459 (42.7) | 110 (36.9) | 0.075 | |
| Comorbidities | |||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 799 (58.2) | 653 (60.7) | 146 (49.0) | <0.001 | |
| Hyperlipidemia | 699 (50.9) | 581 (54.0) | 118 (39.6) | <0.001 | |
| Cardiovascular diseasea | 594 (43.2) | 454 (42.2) | 140 (47.0) | 0.140 | |
| Chronic kidney disease | 55 (4.0) | 46 (4.3) | 9 (3.0) | 0.328 | |
| Chronic pulmonary diseaseb | 275 (20.0) | 210 (19.5) | 65 (21.8) | 0.381 | |
| Charlson Comorbidity Index | 2.00±1.57 | 2.01±1.56 | 1.95±1.58 | 0.813 | |
| Medications | |||||
| Diuretics | 366 (26.6) | 323 (30.0) | 43 (14.4) | <0.001 | |
| Calcium channel blocker | 705 (51.3) | 539 (50.1) | 166 (55.7) | 0.086 | |
| β-Blocker | 204 (14.9) | 143 (13.3) | 61 (20.5) | 0.002 | |
| Metformin | 326 (23.7) | 279 (25.9) | 47 (15.8) | <0.001 | |
| Sulfonylurea | 140 (10.2) | 123 (11.4) | 17 (5.7) | 0.004 | |
| Thiazolidinedione | 35 (2.6) | 29 (2.7) | 6 (2.0) | 0.509 | |
| DPP-4 inhibitor | 199 (14.5) | 174 (16.2) | 25 (8.4) | 0.001 | |
| SGLT2 inhibitor | 31 (2.3) | 28 (2.6) | 3 (1.0) | 0.101 | |
| GLP-1 receptor agonist | 7 (0.5) | 7 (0.7) | 0 | 0.358 | |
| Insulin | 26 (1.9) | 23 (2.1) | 3 (1.0) | 0.205 | |
| Statin | 654 (47.6) | 542 (50.4) | 112 (37.6) | <0.001 | |
| Antithrombotic agent | 389 (28.3) | 305 (28.4) | 84 (28.2) | 0.957 | |
| Inhaled corticosteroids | 102 (7.4) | 77 (7.2) | 25 (8.4) | 0.472 | |
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
RAAS, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; DPP-4, dipeptidyl peptidase-4; SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide-1.
a Cardiovascular disease includes ischemic heart disease, cerebral infarction, heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and arrhythmia,
b Chronic pulmonary disease includes chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and asthma.
| Outcomes (vs. RAAS inhibitor never-users) |
RAAS inhibitors (n=1,076) |
ARB (n=1,037) |
ACEI (n=39) |
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No. of events (%) | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | Adjusted OR (95% CI)b | No. of events (%) | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | Adjusted OR (95% CI)b | No. of events (%) | Unadjusted OR (95% CI) | Adjusted OR (95% CI)b | |||
| Primary outcomea (n=144) | 106 (9.9) | 0.75 (0.50–1.11) | 0.72 (0.46-1.10) | 99 (9.6) | 0.72 (0.49–1.08) | 0.71 (0.46–1.10) | 7 (18.0) | 1.50 (0.62–3.63) | 0.81 (0.31–2.11) | ||
| Secondary outcomes | |||||||||||
| ICU admission (n=52) | 34 (3.2) | 0.51 (0.28–0.91) | 0.44 (0.24–0.84) | 30 (2.9) | 0.46 (0.26–0.84) | 0.42 (0.22–0.81) | 4 (10.3) | 1.78 (0.57–5.55) | 0.72 (0.21–2.48) | ||
| Not requiring IMV (n=34) | 21 (2.0) | 0.35 (0.18–0.68) | 0.28 (0.14–0.58) | 19 (1.8) | 0.33 (0.17–0.65) | 0.28 (0.14–0.58) | 2 (5.1) | 0.96 (0.21–4.31) | 0.31 (0.06–1.56) | ||
| Requiring IMV (n=17) | 14 (1.3) | 1.30 (0.37–4.54) | 1.41 (0.39–5.08) | 12 (1.2) | 1.15 (0.32–4.11) | 1.30 (0.36–4.76) | 2 (5.1) | 5.32 (0.86–32.86) | 3.57 (0.52–24.71) | ||
| IMV (n=17) | 14 (1.3) | 1.30 (0.37–4.54) | 1.41 (0.39–5.08) | 12 (1.2) | 1.15 (0.31–4.11) | 1.30 (0.36–4.76) | 2 (5.1) | 5.32 (0.86–32.86) | 3.57 (0.52–24.71) | ||
| CRRT (n=0) | 0 | NA | NA | 0 | NA | NA | 0 | NA | NA | ||
| ECMO (n=1) | 1 (0.1) | NA | NA | 1 (0.1) | NA | NA | 0 | NA | NA | ||
| Death (n=106) | 82 (7.6) | 0.94 (0.59–1.51) | 1.09 (0.64–1.85) | 79 (7.6) | 0·94 (0.59–1.52) | 1.12 (0.66–1.90) | 3 (7.7) | 0.95 (0.27–3.32) | 0.62 (0.17–2.35) | ||
RAAS, renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; ARB, angiotensin-receptor blocker; ACEI, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval; ICU, intensive care unit; IMV, invasive mechanical ventilation; CRRT, continuous renal replacement therapy; NA, not applicable; ECMO, extracorporeal membrane oxygenation.
a The primary outcome was defined as the composite of ICU admission, IMV, CRRT, ECMO, and death from coronavirus disease 2019,
b Adjusted variables included age; sex; comorbidities, including diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and chronic pulmonary disease; medications, including antihypertensive, glucose-lowering, lipid-lowering, and antithrombotic agents; and the Charlson Comorbidity Index.
- 1. Mahase E. Covid-19: WHO declares pandemic because of “alarming levels” of spread, severity, and inaction. BMJ 2020;368:m1036.ArticlePubMed
- 2. World Health Organization: World Health Organization COVID-19 dashboard. Available from: https://covid19.who.int(cited 2021 Jan 21).
- 3. Zheng YY, Ma YT, Zhang JY, Xie X. COVID-19 and the cardiovascular system. Nat Rev Cardiol 2020;17:259-60.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 4. Soler MJ, Ye M, Wysocki J, William J, Lloveras J, Batlle D. Localization of ACE2 in the renal vasculature: amplification by angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade using telmisartan. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 2009;296:F398-405.ArticlePubMed
- 5. Oussalah A, Gleye S, Clerc Urmes I, Laugel E, Callet J, Barbe F, et al. Long-term ACE inhibitor/ARB use is associated with severe renal dysfunction and acute kidney injury in patients with severe COVID-19: results from a referral center cohort in the northeast of France. Clin Infect Dis 2020;71:2447-56.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. de Abajo FJ, Rodriguez-Martin S, Lerma V, Mejia-Abril G, Aguilar M, Garcia-Luque A, et al. Use of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and risk of COVID-19 requiring admission to hospital: a case-population study. Lancet 2020;395:1705-14.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 7. Mancia G, Rea F, Ludergnani M, Apolone G, Corrao G. Reninangiotensin-aldosterone system blockers and the risk of Covid-19. N Engl J Med 2020;382:2431-40.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Meng J, Xiao G, Zhang J, He X, Ou M, Bi J, et al. Renin-angiotensin system inhibitors improve the clinical outcomes of COVID-19 patients with hypertension. Emerg Microbes Infect 2020;9:757-60.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 9. Zhang P, Zhu L, Cai J, Lei F, Qin JJ, Xie J, et al. Association of inpatient use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and angiotensin ii receptor blockers with mortality among patients with hypertension hospitalized with COVID-19. Circ Res 2020;126:1671-81.PubMedPMC
- 10. Hoffmann M, Kleine-Weber H, Schroeder S, Kruger N, Herrler T, Erichsen S, et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell 2020;181:271-80.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 11. Forrester SJ, Booz GW, Sigmund CD, Coffman TM, Kawai T, Rizzo V, et al. Angiotensin II signal transduction: an update on mechanisms of physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 2018;98:1627-738.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Ferrario CM, Jessup J, Chappell MC, Averill DB, Brosnihan KB, Tallant EA, et al. Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II receptor blockers on cardiac angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. Circulation 2005;111:2605-10.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Jessup JA, Gallagher PE, Averill DB, Brosnihan KB, Tallant EA, Chappell MC, et al. Effect of angiotensin II blockade on a new congenic model of hypertension derived from transgenic Ren2 rats. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2006;291:H2166-72.ArticlePubMed
- 14. Kim JA, Yoon S, Kim LY, Kim DS. Towards actualizing the value potential of Korea Health Insurance Review and Assessment (HIRA) data as a resource for health research: strengths, limitations, applications, and strategies for optimal use of HIRA data. J Korean Med Sci 2017;32:718-28.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 15. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service of Korea. Guidelines for COVID-19 international research co-hosted by MoHW and HIRA of Korea. Sejong: MoHW and HIRA; 2020.
- 16. Ministry of Health and Welfare, Health Insurance Review and Assessment Service of Korea. Data update notice for the Global Research Collaboration Project on COVID-19. Sejong: MoHW and HIRA; 2020.
- 17. Central Disease Control Headquarters. Guidelines for the operation of COVID-19 screening clinics. Cheongju: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, 2020.
- 18. Charlson ME, Pompei P, Ales KL, MacKenzie CR. A new method of classifying prognostic comorbidity in longitudinal studies: development and validation. J Chronic Dis 1987;40:373-83.ArticlePubMed
- 19. Reynolds HR, Adhikari S, Pulgarin C, Troxel AB, Iturrate E, Johnson SB, et al. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors and risk of COVID-19. N Engl J Med 2020;382:2441-8.ArticlePubMed
- 20. Hamming I, van Goor H, Turner AJ, Rushworth CA, Michaud AA, Corvol P, et al. Differential regulation of renal angiotensinconverting enzyme (ACE) and ACE2 during ACE inhibition and dietary sodium restriction in healthy rats. Exp Physiol 2008;93:631-8.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 21. Burchill LJ, Velkoska E, Dean RG, Griggs K, Patel SK, Burrell LM. Combination renin-angiotensin system blockade and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 in experimental myocardial infarction: implications for future therapeutic directions. Clin Sci (Lond) 2012;123:649-58.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 22. Vaduganathan M, Vardeny O, Michel T, McMurray JJV, Pfeffer MA, Solomon SD. Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors in patients with COVID-19. N Engl J Med 2020;382:1653-9.ArticlePubMed
- 23. South AM, Diz DI, Chappell MC. COVID-19, ACE2, and the cardiovascular consequences. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 2020;318:H1084-90.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 24. Chen N, Zhou M, Dong X, Qu J, Gong F, Han Y, et al. Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 99 cases of 2019 novel coronavirus pneumonia in Wuhan, China: a descriptive study. Lancet 2020;395:507-13.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Wang D, Hu B, Hu C, Zhu F, Liu X, Zhang J, et al. Clinical characteristics of 138 hospitalized patients with 2019 novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA 2020;323:1061-9.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 26. Inciardi RM, Lupi L, Zaccone G, Italia L, Raffo M, Tomasoni D, et al. Cardiac involvement in a patient with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA Cardiol 2020;5:819-24.ArticlePubMed
- 27. Yousif MH, Dhaunsi GS, Makki BM, Qabazard BA, Akhtar S, Benter IF. Characterization of angiotensin-(1-7) effects on the cardiovascular system in an experimental model of type-1 diabetes. Pharmacol Res 2012;66:269-75.ArticlePubMed
- 28. Oudit GY, Kassiri Z, Jiang C, Liu PP, Poutanen SM, Penninger JM, et al. SARS-coronavirus modulation of myocardial ACE2 expression and inflammation in patients with SARS. Eur J Clin Invest 2009;39:618-25.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Cheng X, Liu YM, Li H, Zhang X, Lei F, Qin JJ, et al. Metformin is associated with higher incidence of acidosis, but not mortality, in individuals with COVID-19 and pre-existing type 2 diabetes. Cell Metab 2020;32:537-47.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 30. Bramante CT, Ingraham NE, Murray TA, Marmor S, Hovertsen S, Gronski J, et al. Metformin and risk of mortality in patients hospitalised with COVID-19: a retrospective cohort analysis. Lancet Healthy Longev 2020;2:e34-41.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 31. Solerte SB, D’Addio F, Trevisan R, Lovati E, Rossi A, Pastore I, et al. Sitagliptin treatment at the time of hospitalization was associated with reduced mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19: a multicenter, case-control, retrospective, observational study. Diabetes Care 2020;43:2999-3006.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 32. Mirani M, Favacchio G, Carrone F, Betella N, Biamonte E, Morenghi E, et al. Impact of comorbidities and glycemia at admission and dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes with covid-19: a case series from an academic hospital in Lombardy, Italy. Diabetes Care 2020;43:3042-9.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 33. Zhang XJ, Qin JJ, Cheng X, Shen L, Zhao YC, Yuan Y, et al. Inhospital use of statins is associated with a reduced risk of mortality among individuals with COVID-19. Cell Metab 2020;32:176-87.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. Scheen AJ. Metformin and COVID-19: from cellular mechanisms to reduced mortality. Diabetes Metab 2020;46:423-6.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Mulvihill EE, Drucker DJ. Pharmacology, physiology, and mechanisms of action of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors. Endocr Rev 2014;35:992-1019.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 36. Parihar SP, Guler R, Brombacher F. Statins: a viable candidate for host-directed therapy against infectious diseases. Nat Rev Immunol 2019;19:104-17.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 37. Lim S, Bae JH, Kwon HS, Nauck MA. COVID-19 and diabetes mellitus: from pathophysiology to clinical management. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2021;17:11-30.ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Systematic review and meta-analysis of the clinical outcomes of ACEI/ARB in East-Asian patients with COVID-19
Nancy Xurui Huang, Qi Yuan, Fang Fang, Bryan P. Yan, John E. Sanderson, Masaki Mogi
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(1): e0280280. CrossRef - Renin‐Angiotensin Aldosterone System Inhibitors and COVID‐19: A Systematic Review and Meta‐Analysis Revealing Critical Bias Across a Body of Observational Research
Jordan Loader, Frances C. Taylor, Erik Lampa, Johan Sundström
Journal of the American Heart Association.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system blockers in Bulgarian COVID-19 patients with or without chronic kidney disease
Rumen Filev, Lionel Rostaing, Mila Lyubomirova, Boris Bogov, Krassimir Kalinov, Dobrin Svinarov
Medicine.2022; 101(48): e31988. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite