
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Articles
- Basic Research
- Role of SUMO-Specific Protease 2 in Leptin-Induced Fatty Acid Metabolism in White Adipocytes
- Praise Chanmee Kim, Ji Seon Lee, Sung Soo Chung, Kyong Soo Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):382-393. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0156
- 3,197 View
- 158 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
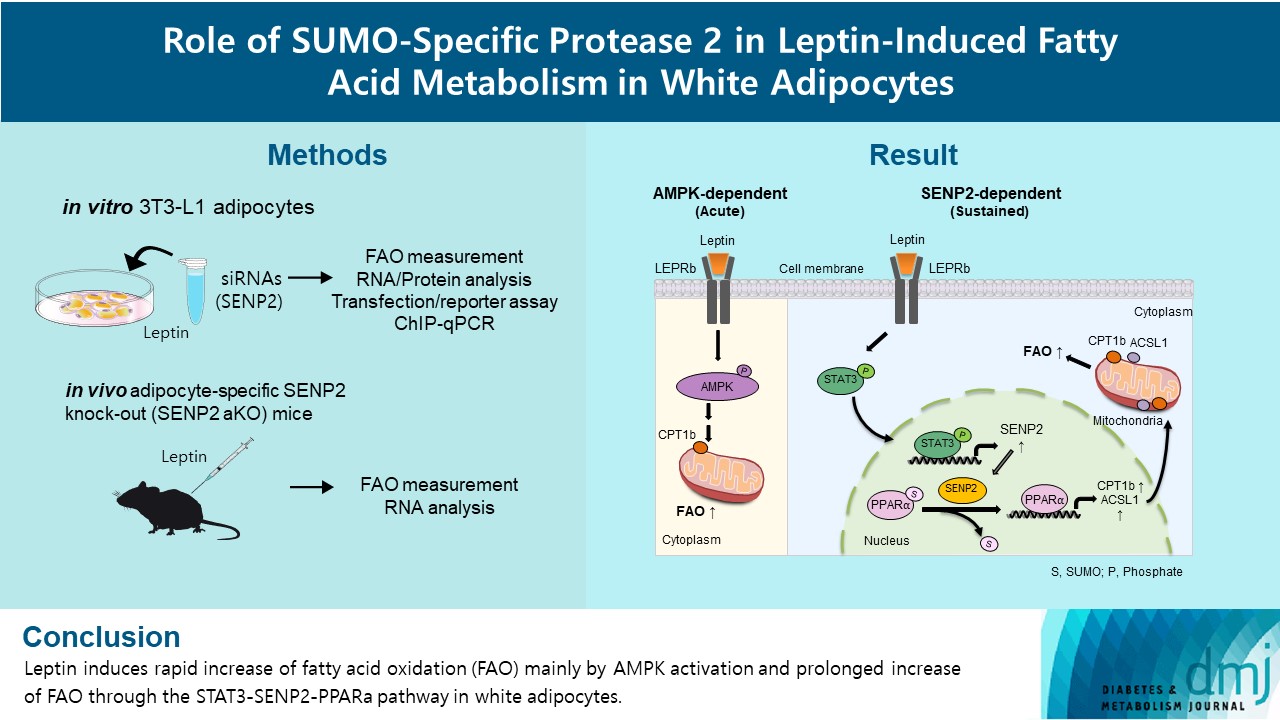
Leptin is a 16-kDa fat-derived hormone with a primary role in controlling adipose tissue levels. Leptin increases fatty acid oxidation (FAO) acutely through adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and on delay through the SUMO-specific protease 2 (SENP2)–peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ/γ (PPARδ/γ) pathway in skeletal muscle. Leptin also directly increases FAO and decreases lipogenesis in adipocytes; however, the mechanism behind these effects remains unknown. Here, we investigated the role of SENP2 in the regulation of fatty acid metabolism by leptin in adipocytes and white adipose tissues.
Methods
The effects of leptin mediated by SENP2 on fatty acid metabolism were tested by siRNA-mediated knockdown in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. The role of SENP2 was confirmed in vivo using adipocyte-specific Senp2 knockout (Senp2-aKO) mice. We revealed the molecular mechanism involved in the leptin-induced transcriptional regulation of carnitine palmitoyl transferase 1b (Cpt1b) and long-chain acyl-coenzyme A synthetase 1 (Acsl1) using transfection/reporter assays and chromatin immunoprecipitation.
Results
SENP2 mediated the increased expression of FAO-associated enzymes, CPT1b and ACSL1, which peaked 24 hours after leptin treatment in adipocytes. In contrast, leptin stimulated FAO through AMPK during the initial several hours after treatment. In white adipose tissues, FAO and mRNA levels of Cpt1b and Acsl1 were increased by 2-fold 24 hours after leptin injection in control mice but not in Senp2-aKO mice. Leptin increased PPARα binding to the Cpt1b and Acsl1 promoters in adipocytes through SENP2.
Conclusion
These results suggest that the SENP2-PPARα pathway plays an important role in leptin-induced FAO in white adipocytes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Intermittent cold stimulation affects energy metabolism and improves stress resistance in broiler heart
Tingting Li, Haidong Wei, Shijie Zhang, Xiaotao Liu, Lu Xing, Yuanyuan Liu, Rixin Gong, Jianhong Li
Poultry Science.2024; 103(1): 103190. CrossRef
- Intermittent cold stimulation affects energy metabolism and improves stress resistance in broiler heart
- The Association Between White Blood Cell Count and Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
- Wan Sub Shim, Hae Jin Kim, Soo Kyung Kim, Shin Ae Kang, Eun Seok Kang, Yu Mie Rhee, Chul Woo Ahn, Sung Kil Lim, Kyung Rae Kim, Hyun Chul Lee, Bong Soo Cha
- Korean Diabetes J. 2005;29(5):460-468. Published online September 1, 2005
- 1,230 View
- 20 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGOUND: Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, and inflammation is also closely associated with cardiovascular disease. The white blood cell count, which is a marker of systemic inflammation, has been found to correlated with the risk of cardiovascular disease. The aim of this study was to evaluate the association between metabolic syndrome and the WBC count in type 2 diabetic patients. METHODS: 606 patients (males 318, females 288, BMI 25.6+/-3.2 kg/m2 and duration of diabetes 4.8+/-5.9year) were enrolled. The WBC and differential counts, anthropometry, blood pressure, fasting glucose, insulin and lipid profiles were measured. RESULTS: According to the quartiles of the WBC count, the number of components of metabolic syndrome and percentage of patients with metabolic syndrome were increased in the highest WBC count quartile. The WBC, neutrophil, lymphocyte, monocyte and eosinophil counts increased with increasing number of components of metabolic syndrome, but not that of the basophil count. The WBC, neutrophil, lymphocyte, monocyte and eosinophil counts were higher in patients with metabolic syndrome than in those without. The WBC count was found to be positively correlated with the waist circumference(gamma=0.090), systolic blood pressure(gamma=0.090), diastolic blood pressure(gamma=0.104), triglyceride(gamma=0.252), insulin(gamma=0.168) and HOMAIR(gamma=0.170), but negatively with high-density lipoprotein cholesterol(gamma= -0.167)(P<0.05, respectively). CONCLUSION: Chronic inflammation, as indicated by a higher than normal WBC count, may increased with the increasing number of components of metabolic syndrome.

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





