
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
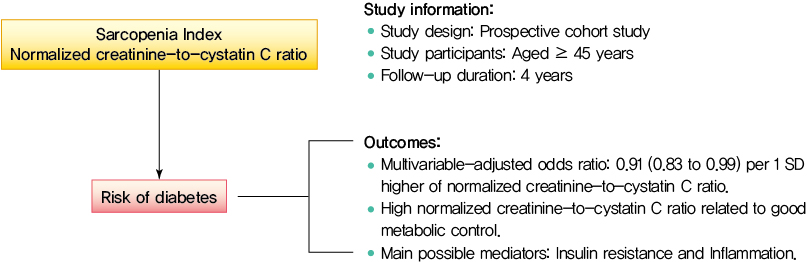
- Normalized Creatinine-to-Cystatin C Ratio and Risk of Diabetes in Middle-Aged and Older Adults: The China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study
- Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Bo Xie, Yang Yuan, Zilin Sun, Tongzhi Wu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(3):476-485. Published online March 7, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0074
- 4,748 View
- 205 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio is recently suggested to be a surrogate marker for sarcopenia. However, little is known about its association with diabetes. This study aimed to fill in this gap based on a large-scale prospective cohort.
Methods
A population-based representative sample of 5,055 participants aged ≥45 years from the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study was enrolled between 2011 and 2012 and followed at least once during the subsequent surveys at 2013, 2015, or 2018. Creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio was calculated and normalized by body weight. Incident diabetes was ascertained by plasma glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin, self-reported history, or use of anti-diabetic drugs. Logistic regression analysis and mediation analysis were employed.
Results
During follow-up, 634 participants developed diabetes. The risk of diabetes was gradually and significantly decreased with increased normalized creatinine–cystatin C ratio. The multivariable-adjusted odds ratio for diabetes was 0.91 (95% confidence interval, 0.83 to 0.99) per 1 standard deviation higher of normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio, and this relationship remained significant after controlling for muscle strength. The risk reduction in diabetes was significantly larger in participants with normal-weight and high normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio compared with those with overweight/obesity and high normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio (Pinteraction=0.01). Insulin resistance and inflammation appeared to be key mediators accounting for the observed relationship between normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio and risk of diabetes, with their mediating effect being 93.1% and 22.0%, respectively.
Conclusion
High normalized creatinine-to-cystatin C ratio is associated with reduced risk of diabetes in middle-aged and older adults. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Muscle Quality in Relation to Prediabetes Phenotypes: A Population-Based Study With Mediation Analysis
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Xiaoying Zhou, Jinshui Xu, Zilin Sun, Haijian Guo, Tongzhi Wu
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 109(3): e1151. CrossRef - Sex‐specific associations between skeletal muscle mass and incident diabetes: A population‐based cohort study
Dan Liu, Nan Li, Yiling Zhou, Miye Wang, Peige Song, Changzheng Yuan, Qingyang Shi, Hui Chen, Kaixin Zhou, Huan Wang, Tao Li, Xiong‐Fei Pan, Haoming Tian, Sheyu Li
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(3): 820. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus Should Be Considered While Analysing Sarcopenia-Related Biomarkers
Justyna Rentflejsz, Zyta Beata Wojszel
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(4): 1107. CrossRef - Associations of muscle mass and strength with new-onset diabetes among middle-aged and older adults: evidence from the China health and retirement longitudinal study (CHARLS)
Yun-Yun He, Mei-Ling Jin, Xiang-Yang Fang, Xiao-Juan Wang
Acta Diabetologica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The serum creatinine to cystatin C to waist circumference ratios predicts risk for type 2 diabetes: A Chinese cohort study
Yinfei Chen, Weiheng Wen, Zhiliang Mai, Ming Wang, Hong Chen, Jia Sun
Journal of Diabetes.2023; 15(10): 808. CrossRef - Associations of sarcopenia with peak expiratory flow among community-dwelling elderly population: based on the China Health and Retirement Longitudinal Study (CHARLS)
Yun-Yun He, Mei-Ling Jin, Jing Chang, Xiao-Juan Wang
European Geriatric Medicine.2023; 15(1): 95. CrossRef - Additive impact of diabetes and sarcopenia on all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: A longitudinal nationwide population-based study
Eyun Song, Soon Young Hwang, Min Jeong Park, Ahreum Jang, Kyeong Jin Kim, Ji Hee Yu, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi
Metabolism.2023; 148: 155678. CrossRef
- Muscle Quality in Relation to Prediabetes Phenotypes: A Population-Based Study With Mediation Analysis
- The Correlations between Extremity Circumferences with Total and Regional Amounts of Skeletal Muscle and Muscle Strength in Obese Women with Type 2 Diabetes
- Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Ah Han, Hee Jung Ahn, Jae Hyuk Lee, Gang Seo Park, Kyung Wan Min
- Diabetes Metab J. 2011;35(4):374-383. Published online August 31, 2011
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.4.374
- 4,306 View
- 43 Download
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Insulin resistance is related to central obesity and the amount of skeletal muscle. A simple and practical anthropometric marker for muscle mass is not known, although waist circumference (WC) is used as an indicator of abdominal obesity. The aims of this study were to investigate whether arm (AC) and thigh circumferences (TC) can be used as an indicator of muscle mass and if they are related to muscle strength.
Methods A total of 110 obese (body mass index [BMI]≥25 kg/m2) women with type 2 diabetes were enrolled, and WC, AC, and TC were measured. Abdominal visceral fat (AVF), subcutaneous fat (ASF), and total fat (ATF) were assessed by computed tomography, regional muscle (MM), and fat mass by dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, muscle strength by one repetition maximum (1RM) of both extremities (chest and leg press) and insulin resistance by KITT.
Results The mean age was 56.2±7.3 years, duration of diabetes was 4.2±4.4 years, and BMI was 27.2±2.8 kg/m2. WC was correlated with ATF, AVF, and ASF (
r =0.728,P <0.001;r =0.515,P <0.001;r =0.608,P <0.001, respectively). Arm MM was correlated with AC (r =0.500,P <0.001), and leg MM with TC (r =0.291,P =0.002). Upper 1RM was related to AC/WC ratio (r =0.359,P <0.001), and lower 1RM was to TC/WC ratio (r =0.286,P =0.003). Insulin resistance had significant relations with AVF, WC, and total MM (r =-0.262,P =0.008;r =-0.217,P =0.029;r =0.160,P =0.031, respectively).Conclusion The muscle mass was related to extremity circumferences, and muscle strength was to extremity/waist circumference ratio in obese women with type 2 diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Inflammation and Loss of Skeletal Muscle Mass in Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia
Joana Ferreira, Alexandre Carneiro, Isabel Vila, Cristina Silva, Cristina Cunha, Adhemar Longatto-Filho, Amílcar Mesquita, Jorge Cotter, Armando Mansilha, Margarida Correia-Neves, Pedro Cunha
Annals of Vascular Surgery.2023; 88: 164. CrossRef - Thigh-hip ratio is significantly associated with all-cause mortality among Japanese community-dwelling men
Ryuichi Kawamoto, Asuka Kikuchi, Daisuke Ninomiya, Teru Kumagi, Fredirick Lazaro mashili
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(10): e0292287. CrossRef - Association of Skeletal Muscle and Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Patients with Lower Extremity Arterial Disease
Joana Ferreira, Alexandre Lima Carneiro, Isabel Vila, Cristina Cunha, C ristina Silva, Adhemar Longatto-Filho, Amesqui Mesquita, Jorge Cotter, Armando Mansilha, Margarida Correia-Neves, Pedro Cunha
Annals of Vascular Surgery.2022; 80: 223. CrossRef - A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to evaluate the hypoglycemic efficacy of the mcIRBP-19-containing Momordica charantia L. fruit extracts in the type 2 diabetic subjects
Yi-Sun Yang, Nian-Yi Wu, Edy Kornelius, Chien-Ning Huang, Nae-Cherng Yang
Food & Nutrition Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Thigh circumference and handgrip strength are significantly associated with all-cause mortality: findings from a study on Japanese community-dwelling persons
Ryuichi Kawamoto, Asuka Kikuchi, Taichi Akase, Daisuke Ninomiya, Teru Kumagi
European Geriatric Medicine.2021; 12(6): 1191. CrossRef Thigh Circumference and Risk of All-Cause, Cardiovascular and Cerebrovascular Mortality: A Cohort Study
Chao-lei Chen, Lin Liu, Jia-yi Huang, Yu-ling Yu, Geng Shen, Kenneth Lo, Yu-qing Huang, Ying-qing Feng
Risk Management and Healthcare Policy.2020; Volume 13: 1977. CrossRef- Mid-arm muscle circumference as an indicator of osteoporosis in community-dwelling older men
Yuan-Ping Chao, Tung-Wei Kao, Wei-Liang Chen, Tao-Chun Peng, Li-Wei Wu
Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics.2020; 87: 103998. CrossRef - Carnitine deficiency is associated with decreased exercise activity in hemodialysis patients
Junko Yano, Yusuke Kaida, Yosuke Nakayama, Sakuya Ito, Yuka Kurokawa, Nao Nakamura, Takuma Hazama, Takashi Maeda, Ryuki Hashida, Kyoko Tashiro, Takahiro Inokuchi, Hiroo Matsuse, Kei Fukami
Renal Replacement Therapy.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Preliminary study of the anabolic/catabolic balance in patients with interstitial pulmonary fibrosis
Ahmed El Hosainy, Safy Kaddah, Mohamed Saied, Aml Ibrahim, Rania Darwish
Egyptian Journal of Chest Diseases and Tuberculosis.2017; 66(3): 497. CrossRef - Anthropometric dimensions provide reliable estimates of abdominal adiposity: A validation study
Z. Pintér, A. Pósa, C. Varga, I. Horváth, A. Palkó, Z. Just, G. Pálfi
HOMO.2017; 68(5): 398. CrossRef - Creatine kinase in the U.S. population
Michael D. George, Neilia-Kay McGill, Joshua F. Baker
Medicine.2016; 95(33): e4344. CrossRef - Relationship of calf circumference with bone mineral density and hip geometry: a hospital-based cross-sectional study
Rekha Singh, Sushil Gupta
Archives of Osteoporosis.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Acupuncture for Management of Balance Impairment in a Patient with Bipolar Disorder
Kun Hyung Kim, Jae Kyu Kim, Gi Young Yang, Byung Ryul Lee, Seung Hee Noh
Journal of Acupuncture and Meridian Studies.2013; 6(1): 56. CrossRef - The association of insulin resistance and carotid atherosclerosis with thigh and calf circumference in patients with type 2 diabetes
Jong Suk Park, Min Ho Cho, Chul Woo Ahn, Kyung Rae Kim, Kap Bum Huh
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2012;[Epub] CrossRef
- Inflammation and Loss of Skeletal Muscle Mass in Chronic Limb Threatening Ischemia
- The Effects of Resistance Training on Muscle and Body Fat Mass and Muscle Strength in Type 2 Diabetic Women
- Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Ah Han, Yun Hyi Ku, Hee Jung Ahn, Bo-Kyung Koo, Ho Chul Kim, Kyung Wan Min
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(2):101-110. Published online April 30, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.2.101
- 4,968 View
- 73 Download
- 55 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Our goal was to investigate the effects of low intensity resistance training on body fat, muscle mass and strength, cardiovascular fitness, and insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetes.
Methods Twenty-eight overweight women with type 2 diabetes were randomly assigned to a resistance training group (RG,
n = 13) or a control group (CG,n = 15). RG performed resistance training using elastic bands, of which strength was equal to 40 to 50% of one repetition maximum (1RM), for three days per week. Each exercise consisted of three sets for 60 minutes. We assessed abdominal fat using computed tomography, muscle mass using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry, and muscle strength using Keiser's chest and leg press. Insulin sensitivity was measured using the insulin tolerance test, and aerobic capacity was expressed as oxygen uptake at the anaerobic threshold (AT-VO2) before and after the 12-week exercise program.Results The age of participants was 56.4 ± 7.1 years, duration of diabetes was 5.9 ± 5.5 years, and BMI was 27.4 ± 2.5 kg/m2, without significant differences between two groups. During intervention, a greater increase in muscle mass and greater decreases in both total fat mass and abdominal fat were observed in RG compared to those of CG (
P = 0.015,P = 0.011,P = 0.010, respectively). Increase in 1RM of upper and lower extremities was observed in the RG (P = 0.004,P = 0.040, respectively), without changes in AT-VO2 and insulin resistance in either group.Conclusion In conclusion, the low intensity resistance training was effective in increasing muscle mass and strength and reducing total fat mass without change of insulin sensitivity in type 2 diabetic patients.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Impact of Resistance Exercise Training on Glycemic Control Among Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Yuwen Wan, Zhanguo Su
Biological Research For Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Current trends in the development of soy-based foods containing probiotics and paving the path for soy-synbiotics
Minnu Sasi, Sandeep Kumar, Muzaffar Hasan, Arpitha S. R., Enriqueta Garcia-Gutierrez, Sweta Kumari, Om Prakash, Lata Nain, Archana Sachdev, Anil Dahuja
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2023; 63(29): 9995. CrossRef - Communication Strategies and Resources for Health and Fitness Professionals to Minimize Diabetes-Related Social Stigma
Lindsay J. Della, Annika Reitenga, Kristi M. King
ACSM'S Health & Fitness Journal.2023; 27(2): 54. CrossRef - IMPACTS OF MUSCLE TRAINING LOADS ON COLLEGE STUDENTS' PHYSICAL FITNESS
Wang Lu, Zheng Hua, Wang Tailin, Wei Xuanxi
Revista Brasileira de Medicina do Esporte.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of resistance training on HbA1c in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and the moderating effect of changes in muscular strength: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Anna K Jansson, Li X Chan, David R Lubans, Mitch J Duncan, Ronald C Plotnikoff
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(2): e002595. CrossRef - Role of genetic factors (biology of telomeres) in cardiac rehabilitation
D. M. Aronov, O. M. Drapkina, M. G. Bubnova
Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention.2022; 21(6): 3272. CrossRef - Effects of 12-Week Progressive Sandbag Exercise Training on Glycemic Control and Muscle Strength in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Combined with Possible Sarcopenia
Yu-Hsuan Chien, Chia-Jen Tsai, Dean-Chuan Wang, Pin-Hung Chuang, Hwai-Ting Lin
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2022; 19(22): 15009. CrossRef - Effects of Online Live Pilates Training during the COVID-19 Pandemic on Body Composition, Cardiovascular Function, and Physical Fitness in Sedentary Middle-aged Obese Women
Jung-Heon Choi, Ko-Eun Choi, Man-Gyoon Lee
Korean Journal of Sport Science.2022; 33(4): 521. CrossRef - Muscular Strength, Functional Fitness, Body Composition, and Quality of Life after 12 Weeks of Detraining in Older Females
Matúš Krčmár, Nora Halmová, Jaroslav Krajčovič, Bohumila Krčmárová
Physical & Occupational Therapy In Geriatrics.2021; 39(2): 129. CrossRef - Comparison between different types of exercise training in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and network metanalysis of randomized controlled trials
Edoardo Mannucci, Allegra Bonifazi, Matteo Monami
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2021; 31(7): 1985. CrossRef - DETERMINING NEW ANTHROPOMETRIC MARKERS FOR SCREENING TYPE 2 DM IN A CARIBBEAN REGION.
Amruta Rajput, Upendra K Gupta, Guri Tzivion, Ravindrasingh Rajput
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF SCIENTIFIC RESEARCH.2021; : 58. CrossRef - Effect of elastic band resistance training with green coffee extract supplementation on adiposity indices and TyG-related Indicators in Obese Women
Zahra Rashidi, Rezvan Beigi, Majid Mardaniyan Ghahfarrokhi, Mohammad Faramarzi, Ebrahim Banitalebi, Tina Jafari, Conrad P. Earnest, Julien S. Baker
Obesity Medicine.2021; 24: 100351. CrossRef - Effect of resistance training with and without caloric restriction on visceral fat: A systemic review and meta‐analysis
Mousa Khalafi, Abbas Malandish, Sara K. Rosenkranz, Ali A. Ravasi
Obesity Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Effect of Elastic Resistance Band Training on Postural Control and Body Composition in Sedentary Women
Yağmur KOCAOĞLU, Nurtekin ERKMEN
Spor Bilimleri Araştırmaları Dergisi.2021; 6(1): 233. CrossRef - Strength Training and Insulin Resistance: The Mediating Role of Body Composition
McKayla J. Niemann, Larry A. Tucker, Bruce W. Bailey, Lance E. Davidson
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Beyond general resistance training. Hypertrophy versus muscular endurance training as therapeutic interventions in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Pedro Acosta‐Manzano, María Rodriguez‐Ayllon, Francisco M. Acosta, David Niederseer, Josef Niebauer
Obesity Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistance Exercise Intensity is Correlated with Attenuation of HbA1c and Insulin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yubo Liu, Weibing Ye, Qian Chen, Yong Zhang, Chia-Hua Kuo, Mallikarjuna Korivi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 16(1): 140. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Exercise Intervention in Reducing Body Weight and Glycosylated Hemoglobin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Ji-Eun Jang, Yongin Cho, Byung Wan Lee, Ein-Soon Shin, Sun Hee Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(3): 302. CrossRef - Effects of a moderate-to-high intensity resistance circuit training on fat mass, functional capacity, muscular strength, and quality of life in elderly: A randomized controlled trial
Pablo Jorge Marcos-Pardo, Francisco Javier Orquin-Castrillón, Gemma María Gea-García, Ruperto Menayo-Antúnez, Noelia González-Gálvez, Rodrigo Gomes de Souza Vale, Alejandro Martínez-Rodríguez
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Resistance Exercise on Glycated Hemoglobin and Functional Performance in Older Patients with Comorbid Diabetes Mellitus and Knee Osteoarthritis: A Randomized Trial
Shu-Mei Chen, Feng-Chih Shen, Jung-Fu Chen, Wen-Dien Chang, Nai-Jen Chang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2019; 17(1): 224. CrossRef - Effects of low‐intensity resistance training on muscular function and glycemic control in older adults with type 2 diabetes
Eri Takenami, ShinMin Iwamoto, Noriko Shiraishi, Akiko Kato, Yuichi Watanabe, Yoshifumi Yamada, Satoru Yamada, Naokata Ishii
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2019; 10(2): 331. CrossRef - Effect of 12-Month Resistance Training on Changes in Abdominal Adipose Tissue and Metabolic Variables in Patients with Prediabetes: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Juan Yan, Xia Dai, Jitao Feng, Xiaodan Yuan, Jianing Li, Lihong Yang, Panpan Zuo, Zhaohui Fang, Chao Liu, Cunyi Hsue, Junya Zhu, Joshua D. Miller, Qingqing Lou
Journal of Diabetes Research.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Positive Effects of a Short-Term Intense Elastic Resistance Training Program on Body Composition and Physical Functioning in Overweight Older Women
Nicole B. Fritz, Álvaro Juesas, Pedro Gargallo, Joaquín Calatayud, Julio Fernández-Garrido, Michael E. Rogers, Juan C. Colado
Biological Research For Nursing.2018; 20(3): 321. CrossRef - Protein timing during the day and its relevance for muscle strength and lean mass
Samuel L. Buckner, Jeremy P. Loenneke, Paul D. Loprinzi
Clinical Physiology and Functional Imaging.2018; 38(2): 332. CrossRef - Exercise training modalities in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Bei Pan, Long Ge, Yang-qin Xun, Ya-jing Chen, Cai-yun Gao, Xue Han, Li-qian Zuo, Hou-qian Shan, Ke-hu Yang, Guo-wu Ding, Jin-hui Tian
International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Resistance training reduces metabolic syndrome and inflammatory markers in older women: A randomized controlled trial
Crisieli M. Tomeleri, Mariana F. Souza, Roberto C. Burini, Cláudia R. Cavaglieri, Alex S. Ribeiro, Melissa Antunes, João P. Nunes, Danielle Venturini, Décio S. Barbosa, Luís B. Sardinha, Edilson S. Cyrino
Journal of Diabetes.2018; 10(4): 328. CrossRef - Effect of Resistance Training with Blood Flow Restriction on Follistatin to Myostatin Ratio, Body Composition and Anaerobic Power of Trained-Volleyball Players
Reza Bagheri, Amir Rashidlamir, Seyyed Reza Attarzadeh Hosseini
Medical Laboratory Journal.2018; 12(6): 28. CrossRef - Effects of 8-week kettlebell training on body composition, muscle strength, pulmonary function, and chronic low-grade inflammation in elderly women with sarcopenia
Hung-Ting Chen, Huey-June Wu, Yu-Jen Chen, Sung-Yen Ho, Yu-Chun Chung
Experimental Gerontology.2018; 112: 112. CrossRef - F inding the O ptimal volume and intensity of R esistance T raining E xercise for Type 2 Diabetes: The FORTE Study, a Randomized Trial
Pearl Yang, Walter Swardfager, Daniel Fernandes, Sheila Laredo, George Tomlinson, Paul I. Oh, Scott Thomas
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2017; 130: 98. CrossRef - Exercise and ectopic fat in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
A. Sabag, K.L. Way, S.E. Keating, R.N. Sultana, H.T. O’Connor, M.K. Baker, V.H. Chuter, J. George, N.A. Johnson
Diabetes & Metabolism.2017; 43(3): 195. CrossRef - Resistance training to improve type 2 diabetes: working toward a prescription for the future
Dominik H. Pesta, Renata L. S. Goncalves, Anila K. Madiraju, Barbara Strasser, Lauren M. Sparks
Nutrition & Metabolism.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Improvement of obesity-linked skeletal muscle insulin resistance by strength and endurance training
Sergio Di Meo, Susanna Iossa, Paola Venditti
Journal of Endocrinology.2017; 234(3): R159. CrossRef - Leisure time sedentary behavior, physical activity and frequency of protein consumption on lower extremity strength and lean mass
P D Loprinzi, J P Loenneke, D L Hamilton
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2017; 71(12): 1399. CrossRef - Strength Training Prevents Hyperinsulinemia, Insulin Resistance, and Inflammation Independent of Weight Loss in Fructose-Fed Animals
José D. Botezelli, Andressa Coope, Ana C. Ghezzi, Lucieli T. Cambri, Leandro P. Moura, Pedro P. M. Scariot, Rodrigo Stellzer Gaspar, Rania A. Mekary, Eduardo Rochete Ropelle, José Rodrigo Pauli
Scientific Reports.2016;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Elastic Band Resistance Training on Glucose Control, Body Composition, and Physical Function in Women With Short- vs. Long-Duration Type-2 Diabetes
Bong-Sup Park, Andy V. Khamoui, Lee E. Brown, Do-Youn Kim, Kyung-Ah Han, Kyung-Wan Min, Geun-Hee An
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research.2016; 30(6): 1688. CrossRef - Neuromuscular dysfunction in type 2 diabetes: underlying mechanisms and effect of resistance training
Giorgio Orlando, Stefano Balducci, Ilenia Bazzucchi, Giuseppe Pugliese, Massimo Sacchetti
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2016; 32(1): 40. CrossRef - Physical exercises with free weights and elastic bands can improve body composition parameters in postmenopausal women
Simoni T. Bittar, Sergio S. Maeda, Marília M.S. Marone, Cláudio Santili
Menopause.2016; 23(4): 383. CrossRef - Effects of exercise training using resistance bands on glycaemic control and strength in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials
Samantha K. McGinley, Marni J. Armstrong, Normand G. Boulé, Ronald J. Sigal
Acta Diabetologica.2015; 52(2): 221. CrossRef - Effect of exercise training on neuromuscular function of elbow flexors and knee extensors of type 2 diabetic patients
I. Bazzucchi, G. De Vito, F. Felici, S. Dewhurst, A. Sgadari, M. Sacchetti
Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology.2015; 25(5): 815. CrossRef - Effects of short term elastic resistance training on muscle mass and strength in untrained older adults: a randomized clinical trial
Wagner Rodrigues Martins, Marisete Peralta Safons, Martim Bottaro, Juscelino Castro Blasczyk, Leonardo Rios Diniz, Romulo Maia Carlos Fonseca, Ana Clara Bonini-Rocha, Ricardo Jacó de Oliveira
BMC Geriatrics.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Brain-derived neurotrophic factor correlated with muscle strength in subjects undergoing stationary bicycle exercise training
Sen-Wei Tsai, Yin-Ching Chan, Francois Liang, Chiann-Yi Hsu, I-Te Lee
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2015; 29(3): 367. CrossRef - Implementation of Resources to Support Patient Physical Activity through Diabetes Centres in Nova Scotia: The Effectiveness of Enhanced Support for Exercise Participation
Jonathon R. Fowles, Chris Shields, Lisette d’Entremont, Stephanie McQuaid, Brittany Barron, Peggy Dunbar
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2014; 38(6): 423. CrossRef - Changes in insulin sensitivity in response to different modalities of exercise: a review of the evidence
S. Mann, C. Beedie, S. Balducci, S. Zanuso, J. Allgrove, F. Bertiato, A. Jimenez
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2014; 30(4): 257. CrossRef - The surprising influence of family history to type 2 diabetes on anaerobic performance of young male élite athletes
Antonino Bianco, Francesco Pomara, Antonino Patti, Ewan Thomas, Marco Petrucci, Marianna Bellafiore, Giuseppe Battaglia, Antonio Paoli, Antonio Palma
SpringerPlus.2014;[Epub] CrossRef - Skeletal muscle and organ masses differ in overweight adults with type 2 diabetes
Lance E. Davidson, David E. Kelley, Stanley Heshka, John Thornton, F. Xavier Pi-Sunyer, Lawrence Boxt, Ashok Balasubramanyam, Dympna Gallagher
Journal of Applied Physiology.2014; 117(4): 377. CrossRef - The effects of elastic band resistance training combined with blood flow restriction on strength, total bone‐free lean body mass and muscle thickness in postmenopausal women
Robert S. Thiebaud, Jeremy P. Loenneke, Christopher A. Fahs, Lindy M. Rossow, Daeyeol Kim, Takashi Abe, Mark A. Anderson, Kaelin C. Young, Debra A. Bemben, Michael G. Bemben
Clinical Physiology and Functional Imaging.2013; 33(5): 344. CrossRef - Predicting Aerobic Fitness Improvements after Participation in a Hybrid Supervised and Home-Based Exercise Program in People with Type 2 Diabetes
Pearl Yang, Paul Oh
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2013; 37(6): 388. CrossRef - Impacto do treinamento resistido na força e hipertrofia muscular em HIV-soropositivos
Ciro José Brito, Edmar Lacerda Mendes, Aparecido Pimentel Ferreira, Sérgio Oliveira De Paula, Otávio de Tolêdo Nóbrega, Cláudio Córdova
Motriz: Revista de Educação Física.2013; 19(2): 313. CrossRef - Resistance Training for Diabetes Prevention and Therapy: Experimental Findings and Molecular Mechanisms
Barbara Strasser, Dominik Pesta
BioMed Research International.2013; 2013: 1. CrossRef - Resistance training, visceral obesity and inflammatory response: a review of the evidence
B. Strasser, M. Arvandi, U. Siebert
Obesity Reviews.2012; 13(7): 578. CrossRef - The effects of resistance training on ApoB/ApoA-I ratio, Lp(a) and inflammatory markers in patients with type 2 diabetes
Nikolaos P. E. Kadoglou, Grigorios Fotiadis, Zoi Athanasiadou, Ioulia Vitta, Stylianos Lampropoulos, Ioannis S. Vrabas
Endocrine.2012; 42(3): 561. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta‐analysis of the effect of aerobic vs. resistance exercise training on visceral fat
I. Ismail, S. E. Keating, M. K. Baker, N. A. Johnson
Obesity Reviews.2012; 13(1): 68. CrossRef - Aging, Resistance Training, and Diabetes Prevention
Kyle D. Flack, Kevin P. Davy, Matthew W. Hulver, Richard A. Winett, Madlyn I. Frisard, Brenda M. Davy
Journal of Aging Research.2011; 2011: 1. CrossRef - The Effects of Aerobic/Resistance Exercise on Body Fat Mass, Muscle Strength and Endothelial Function in Korean Type 2 Diabetes mellitus Patients
Kyung Wan Min
Journal of Korean Diabetes.2011; 12(1): 6. CrossRef - Exercise and Type 2 Diabetes
Sheri R. Colberg, Ronald J. Sigal, Bo Fernhall, Judith G. Regensteiner, Bryan J. Blissmer, Richard R. Rubin, Lisa Chasan-Taber, Ann L. Albright, Barry Braun
Diabetes Care.2010; 33(12): e147. CrossRef
- The Impact of Resistance Exercise Training on Glycemic Control Among Adults with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Effects of Aerobic Exercise on Abdominal Fat, Thigh Muscle Mass and Muscle Strength in Type 2 Diabetic Subject
- Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Wan Min, Hee Jung Ahn, Hee Geum Seok, Bo Kyung Koo, Ho Chul Kim, Kyung Ah Han
- Korean Diabetes J. 2010;34(1):23-31. Published online February 28, 2010
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2010.34.1.23
- 3,652 View
- 43 Download
- 18 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Aerobic exercise can effectively reduce visceral fat. However, few studies have examined the effect of daily physical activity on obesity and cardiopulmonary function in the subjects with diabetes. We examined the effect of moderate intensity of walking in obese diabetes patients by monitoring of daily activity and measuring the change in abdominal fat area, muscle are and maximal muscle strength.
Methods We randomly assigned 27 obese women with type 2 diabetes to an aerobic exercise group (AG, n = 13) and control group (CG, n = 14). The AG performed moderate intensity walking for 60 minutes per exercise, 5 times per week, and for 12 weeks. The activity energy expenditure was monitored by a multi-record accelerometer. The CG maintained routine daily activities. At the time of the initiation of the study and after 12 weeks of exercise, the aerobic exercise capacity was assessed using oxygen consumption rate at anaerobic threshold (VO2-AT). The abdominal fat area and the quadriceps muscle area were measured by computed tomography, and the maximum muscle strength of the upper and lower limbs was measured by a chest press and a leg press, respectively.
Results The mean age of the study subjects was 56.6 ± 8.0 years, the mean duration of diabetes was 6.3 ± 6.0 years, and the body weight index (BMI) was 27.3 ± 2.7 kg/m2. The BMI of the AG was significantly decreased (
P = 0.003). In the AG, the visceral fat area and subcutaneous fat area were also significantly decreased (P = 0.018 andP < 0.001, respectively) but not in CG. VO2-AT of the AG was significantly improved, while that of the CG did not change (P = 0.009 andP = 0.115, respectively). The quadriceps muscle mass and the maximal muscle strength of the AG did not change, however, the CG showed a significant decrease. Duration of moderate intensity exercise was correlated with the decrease in total abdominal fat area (r = -0.484;P = 0.011) and that of high intensity exercise was correlated with improvement of cardiopulmonary function (r = 0.414;P = 0.032).Conclusion Daily moderate intensity aerobic exercise is effective at reducing abdominal fat mass, while high intensity exercise improves cardiopulmonary function.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Relationship Between Visceral Fat Tissue and Exercise
Ebru Ceviz
Türk Spor Bilimleri Dergisi.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Walking for subjects with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and joint AMD/SID/SISMES evidence-based practical guideline
P. Moghetti, S. Balducci, L. Guidetti, P. Mazzuca, E. Rossi, F. Schena, P. Moghetti, S. Balducci, L. Guidetti, F. Schena, P. Mazzuca, E. Rossi
Sport Sciences for Health.2021; 17(1): 1. CrossRef - Effect of exercise intervention dosage on reducing visceral adipose tissue: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Yu-Hsuan Chang, Hui-Ying Yang, Shiow-Ching Shun
International Journal of Obesity.2021; 45(5): 982. CrossRef - Comparison between different types of exercise training in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and network metanalysis of randomized controlled trials
Edoardo Mannucci, Allegra Bonifazi, Matteo Monami
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2021; 31(7): 1985. CrossRef - The Therapeutic Effects of Mild to Moderate Intensity Aerobic Exercise on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials
Siyao Gao, Jialing Tang, Guozhong Yi, Zhong Li, Zhenyin Chen, Ling Yu, Feng Zheng, Yajing Hu, Zhangui Tang
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(10): 2767. CrossRef - Walking for subjects with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and joint AMD/SID/SISMES evidence-based practical guideline
P. Moghetti, S. Balducci, L. Guidetti, P. Mazzuca, E. Rossi, F. Schena
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2020; 30(11): 1882. CrossRef - Effect of Coordinative Locomotor Training Program on Body Fat and Muscle mass of Male University students
Hyung chun Nam, Nam jeong Cho, Jae yong Choi
Archives of Orthopedic and Sports Physical Therapy.2019; 15(2): 109. CrossRef - Exercise training modalities in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and network meta-analysis
Bei Pan, Long Ge, Yang-qin Xun, Ya-jing Chen, Cai-yun Gao, Xue Han, Li-qian Zuo, Hou-qian Shan, Ke-hu Yang, Guo-wu Ding, Jin-hui Tian
International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise and ectopic fat in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
A. Sabag, K.L. Way, S.E. Keating, R.N. Sultana, H.T. O’Connor, M.K. Baker, V.H. Chuter, J. George, N.A. Johnson
Diabetes & Metabolism.2017; 43(3): 195. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta‐analysis on the effects of exercise training versus hypocaloric diet: distinct effects on body weight and visceral adipose tissue
R. J. H. M. Verheggen, M. F. H. Maessen, D. J. Green, A. R. M. M. Hermus, M. T. E. Hopman, D. H. T. Thijssen
Obesity Reviews.2016; 17(8): 664. CrossRef - Effects of Aerobic Exercise Associated with Abdominal Microcurrent: A Preliminary Study
Andreia Noites, Rita Nunes, Ana Isabel Gouveia, Alexandra Mota, Cristina Melo, Ágata Viera, Nuno Adubeiro, José Mesquita Bastos
The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine.2015; 21(4): 229. CrossRef - Brain-derived neurotrophic factor correlated with muscle strength in subjects undergoing stationary bicycle exercise training
Sen-Wei Tsai, Yin-Ching Chan, Francois Liang, Chiann-Yi Hsu, I-Te Lee
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2015; 29(3): 367. CrossRef - Impact of Walking on Glycemic Control and Other Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis
Shanhu Qiu, Xue Cai, Uwe Schumann, Martina Velders, Zilin Sun, Jürgen Michael Steinacker, Lamberto Manzoli
PLoS ONE.2014; 9(10): e109767. CrossRef - A systematic review and meta‐analysis of the effect of aerobic vs. resistance exercise training on visceral fat
I. Ismail, S. E. Keating, M. K. Baker, N. A. Johnson
Obesity Reviews.2012; 13(1): 68. CrossRef - The Effects of Regular Pilates Exercise on Blood pressure and Pulmonary Variables
Gyu-Chang Lee, Dong-Yeop Lee, Jae-Ho Yu
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2011; 12(7): 3088. CrossRef - The Effects of Aerobic/Resistance Exercise on Body Fat Mass, Muscle Strength and Endothelial Function in Korean Type 2 Diabetes mellitus Patients
Kyung Wan Min
Journal of Korean Diabetes.2011; 12(1): 6. CrossRef - The Evaluation of Workplace Obesity Intervention Program using Six Sigma Methodology
Ji Yeon Kang, Ill Keun Park, Yun Kyun Chang, Sook Hee Sung, Yoo Kyoung Park, Sang Woon Cho, Yun Mi Paek, Tae In Choi
The Korean Journal of Obesity.2011; 20(4): 193. CrossRef - How Can We Measure the Effects of Exercise in Daily Life?
Sang Yong Kim
Korean Diabetes Journal.2010; 34(1): 21. CrossRef
- Relationship Between Visceral Fat Tissue and Exercise
- Relationship of Maximal Muscle Strength with Body Mass Index and Aerobics Capacity in Type 2 Diabetic Patients.
- Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Ah Han, Yun Hyi Ku, Hee Jung Ahn, Bo Kyung Koo, Kyung Wan Min
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(6):511-517. Published online December 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.6.511
- 2,183 View
- 31 Download
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
Combination fitness regimens (including aerobic and resistance exercises) are effective for improving cardio-respiratory fitness, reducing visceral fat and increasing insulin sensitivity in diabetic patients. The combination exercise intensity that a patient is capable of is limited by his or her aerobic capacity and one repetition maximum (1RM). We investigated the relationships between 1RM, aerobic exercise capacity and body mass index in patients with type 2 diabetes. METHODS: A total of 177 (men: 85, women: 92) diabetic subjects with HbA1c < or = 10% were enrolled. Muscle strength and 1RM were assessed bychest press (upper body) and leg press (lower body). We assessed aerobic capacity by VO2max and muscle mass by bioimpedance analysis. RESULTS: There was no correlation between 1RM and VO2max in type 2 diabetic patients (upper: P = 0.122, lower: P = 0.138 for men, and upper: P = 0.952, lower: P = 0.570 for women). However, 1RM was significantly correlated with muscle mass both in men and women (upper: r = 0.493, P < 0.001, r = 0.315, P = 0.002 lower: r = 0.437 P < 0.001, r = 0.307, P =0.003, respectively). There was also a significant correlation between 1RM and BMI. In obese male subjects with BMI > or = 25 kg/m2, we observed a significant correlation between muscle mass and BMI (r = 0.374, P = 0.032), but this correlation was not observed in women. CONCLUSION: Clinicians treating Korean type 2 diabetic subjects should recommend resistance exercise to their patients. In particular, obese women with diabetes may receive greater benefits by increasing muscle mass through resistance exercises. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Evaluation of Muscle Strength and Endurance in Postmenopausal Women: A Cross-sectional Study
Arati V Mahishale, Manali P Kulkarni
Journal of South Asian Federation of Obstetrics and Gynaecology.2021; 13(3): 163. CrossRef - The Correlations between Extremity Circumferences with Total and Regional Amounts of Skeletal Muscle and Muscle Strength in Obese Women with Type 2 Diabetes
Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Ah Han, Hee Jung Ahn, Jae Hyuk Lee, Gang Seo Park, Kyung Wan Min
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(4): 374. CrossRef - The Effects of Aerobic/Resistance Exercise on Body Fat Mass, Muscle Strength and Endothelial Function in Korean Type 2 Diabetes mellitus Patients
Kyung Wan Min
Journal of Korean Diabetes.2011; 12(1): 6. CrossRef - The Effects of Resistance Training on Muscle and Body Fat Mass and Muscle Strength in Type 2 Diabetic Women
Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Ah Han, Yun Hyi Ku, Hee Jung Ahn, Bo-Kyung Koo, Ho Chul Kim, Kyung Wan Min
Korean Diabetes Journal.2010; 34(2): 101. CrossRef
- Evaluation of Muscle Strength and Endurance in Postmenopausal Women: A Cross-sectional Study
- Maximal Muscle Strength Deteriorates with Age in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus.
- Hwi Ryun Kwon, Yun Hyi Ku, Hee Jung Ahn, Ji Yun Jeong, Sang Ryol Ryu, Bo Kyung Koo, Kyung Ah Han, Kyung Wan Min
- Korean Diabetes J. 2009;33(5):412-420. Published online October 1, 2009
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/kdj.2009.33.5.412
- 2,422 View
- 23 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF - BACKGROUND
It is difficult to improve muscle strength with only aerobic exercise training in type 2 diabetes patients. Resistance training is effective for improving muscle mass, muscle strength and insulin sensitivity. One repetition maxima (1RM), or the maximum amount of weight a subject can lift in a single repetition, may be a useful unit for evaluating the results of resistance training in type 2 diabetic patients. This study was aimed to assess baseline values for 1RM in a sample of Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus patients that are scaled for intensity and load of exercise, and to assess the relationship of 1RM to age. METHODS: A total of 266 (male: 95, female: 171) Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus were included in the study sample. Maximal muscle strength was assessed by measuring 1RM for each subject (KEISER, Fresno, CA, USA). Two different exercises were used to measure 1RM: the chest press for the upper extremities, and the leg press for the lower extremities. RESULTS: Both upper and lower values of 1RM decreased with age in men and women; upper 1RM: r = -0.454, P<0.001 in men, r = -0.480, P< 0.001 in women, lower 1RM: r = -0.569, P<0.001 in men, and r = -0.452, P<0.001 in women. Values of 1RM significantly decreased in men only after the age of 70. In women, values of 1RM continuously decreased after the age of 60. CONCLUSION: The maximal muscle strength of individuals with type 2 diabetes decreases with age. We believe that resistance training is especially beneficial for type 2 diabetes mellitus patients after the sixth decade of life. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effects of Floor-seated Exercise Program on Physical Fitness, Depression, and Sleep in Older Adults: A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial
Min-Jung Choi, Kyeong-Yae Sohng
International Journal of Gerontology.2018; 12(2): 116. CrossRef - The Effects of Aerobic/Resistance Exercise on Body Fat Mass, Muscle Strength and Endothelial Function in Korean Type 2 Diabetes mellitus Patients
Kyung Wan Min
Journal of Korean Diabetes.2011; 12(1): 6. CrossRef - The Correlations between Extremity Circumferences with Total and Regional Amounts of Skeletal Muscle and Muscle Strength in Obese Women with Type 2 Diabetes
Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Ah Han, Hee Jung Ahn, Jae Hyuk Lee, Gang Seo Park, Kyung Wan Min
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(4): 374. CrossRef - The Effects of Resistance Training on Muscle and Body Fat Mass and Muscle Strength in Type 2 Diabetic Women
Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Ah Han, Yun Hyi Ku, Hee Jung Ahn, Bo-Kyung Koo, Ho Chul Kim, Kyung Wan Min
Korean Diabetes Journal.2010; 34(2): 101. CrossRef - Relationship of Maximal Muscle Strength with Body Mass Index and Aerobics Capacity in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Hwi Ryun Kwon, Kyung Ah Han, Yun Hyi Ku, Hee Jung Ahn, Bo Kyung Koo, Kyung Wan Min
Korean Diabetes Journal.2009; 33(6): 511. CrossRef
- The Effects of Floor-seated Exercise Program on Physical Fitness, Depression, and Sleep in Older Adults: A Cluster Randomized Controlled Trial

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





