
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Review
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Management of Cardiovascular Risk in Perimenopausal Women with Diabetes
- Catherine Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(4):492-501. Published online July 30, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0262
- 5,701 View
- 156 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
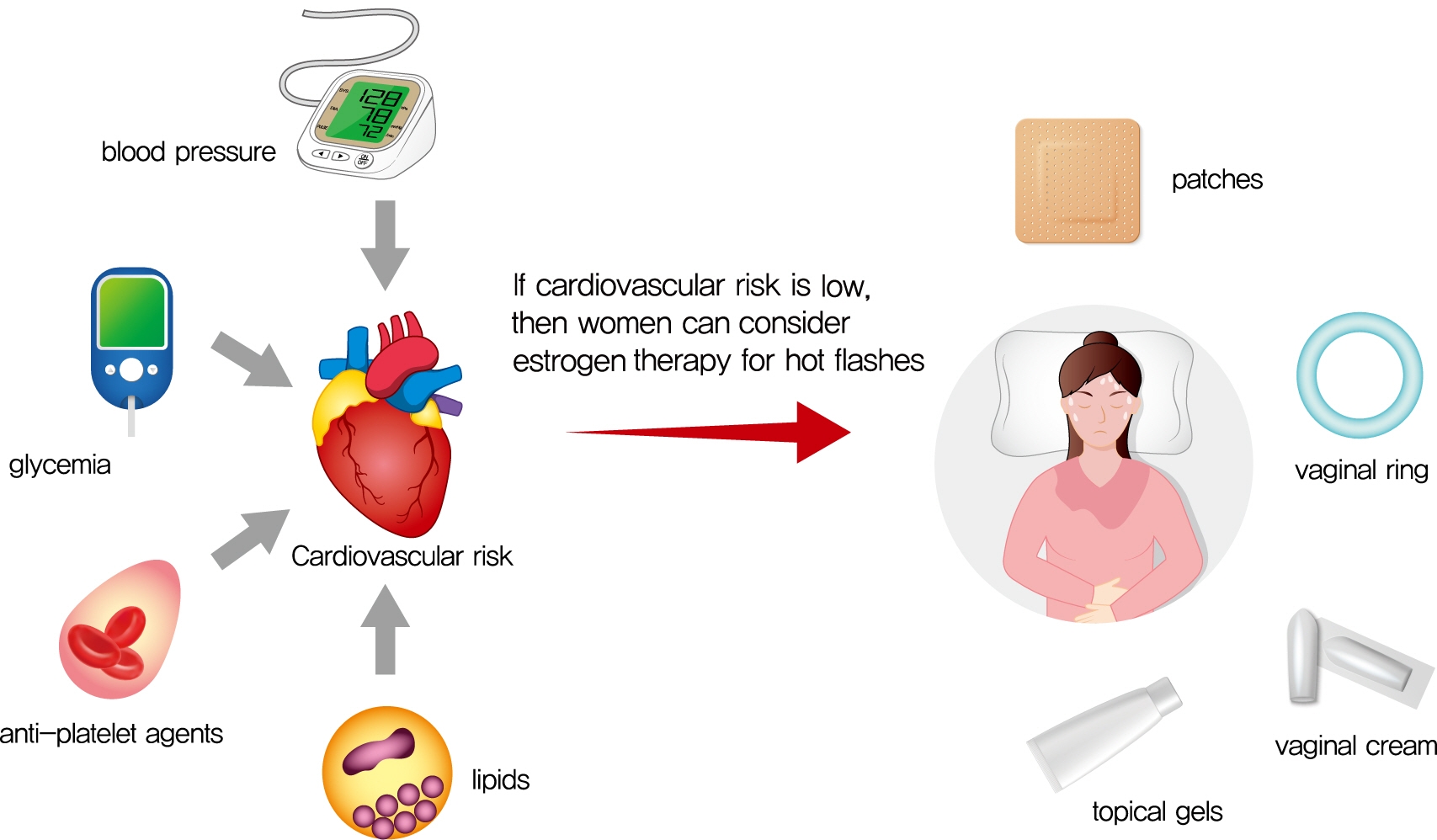
- Cardiovascular disease is the primary cause of mortality in women and men with diabetes. Due to age and worsening of risk factors over the menopausal transition, risk of coronary heart disease events increases in postmenopausal women with diabetes. Randomized studies have conflicted regarding the beneficial impact of estrogen therapy upon intermediate cardiovascular disease markers and events. Therefore, estrogen therapy is not currently recommended for indications other than symptom management. However, for women at low risk of adverse events, estrogen therapy can be used to minimize menopausal symptoms. The risk of adverse events can be estimated using risk engines for the calculation of cardiovascular risk and breast cancer risk in conjunction with screening tools such as mammography. Use of estrogen therapy, statins, and anti-platelet agents can be guided by such calculators particularly for younger women with diabetes. Risk management remains focused upon lifestyle behaviors and achieving optimal levels of cardiovascular risk factors, including lipids, glucose, and blood pressure. Use of pharmacologic therapies to address these risk factors, particularly specific hypoglycemic agents, may provide some additional benefit for risk prevention. The minimal benefit for women with limited life expectancy and risk of complications with intensive therapy should also be considered.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Nurse-led intervention in the management of patients with cardiovascular diseases: a brief literature review
Xiaoqin Qiu
BMC Nursing.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Determination of the Level of Cardiovascular Risk in 172,282 Spanish Working Women
Ángel Arturo López-González, María Albaladejo Blanco, Cristina Vidal Ribas, Pilar Tomás-Gil, Pere Riutord Sbert, José Ignacio Ramírez-Manent
Diagnostics.2023; 13(17): 2734. CrossRef - Comparison of seven surrogate insulin resistance indexes for predicting the prevalence of carotid atherosclerosis in normal-weight individuals
Zeyu Liu, Bi Deng, Qin Huang, Ruxin Tu, Fang Yu, Jian Xia, Jie Feng
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Diagnostic Approaches and Maternal-Offspring Complications
Joon Ho Moon, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 3. CrossRef - Reproductive Life Span and Severe Hypoglycemia Risk in Postmenopausal Women with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Soyeon Kang, Yong-Moon Park, Dong Jin Kwon, Youn-Jee Chung, Jeong Namkung, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 578. CrossRef - Global hotspots and prospects of perimenopausal depression: A bibliometric analysis via CiteSpace
Mingzhou Gao, Hao Zhang, Zhan Gao, Ya Sun, Jieqiong Wang, Fengqin Wei, Dongmei Gao
Frontiers in Psychiatry.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - State of metabolic processes and ways to improve them in premenopausal women due to the life extension strategy
I.V. Lakhno
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY.2021; (61): 51. CrossRef
- Nurse-led intervention in the management of patients with cardiovascular diseases: a brief literature review

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





