
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Others
- Risk Prediction and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease in People Living with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Ying-Guat Ooi, Tharsini Sarvanandan, Nicholas Ken Yoong Hee, Quan-Hziung Lim, Sharmila S. Paramasivam, Jeyakantha Ratnasingam, Shireene R. Vethakkan, Soo-Kun Lim, Lee-Ling Lim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):196-207. Published online January 26, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2023.0244
- 1,949 View
- 366 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - People with type 2 diabetes mellitus have increased risk of chronic kidney disease and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Improved care delivery and implementation of guideline-directed medical therapy have contributed to the declining incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease in high-income countries. By contrast, the global incidence of chronic kidney disease and associated mortality is either plateaued or increased, leading to escalating direct and indirect medical costs. Given limited resources, better risk stratification approaches to identify people at risk of rapid progression to end-stage kidney disease can reduce therapeutic inertia, facilitate timely interventions and identify the need for early nephrologist referral. Among people with chronic kidney disease G3a and beyond, the kidney failure risk equations (KFRE) have been externally validated and outperformed other risk prediction models. The KFRE can also guide the timing of preparation for kidney replacement therapy with improved healthcare resources planning and may prevent multiple complications and premature mortality among people with chronic kidney disease with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. The present review summarizes the evidence of KFRE to date and call for future research to validate and evaluate its impact on cardiovascular and mortality outcomes, as well as healthcare resource utilization in multiethnic populations and different healthcare settings.
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Glycemic Control and Adverse Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from KNOW-CKD
- Ga Young Heo, Hee Byung Koh, Hyung Woo Kim, Jung Tak Park, Tae-Hyun Yoo, Shin-Wook Kang, Jayoun Kim, Soo Wan Kim, Yeong Hoon Kim, Su Ah Sung, Kook-Hwan Oh, Seung Hyeok Han
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):535-546. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0112
- 2,689 View
- 163 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The optimal level of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) to prevent adverse clinical outcomes is unknown in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
We analyzed 707 patients with CKD G1-G5 without kidney replacement therapy and T2DM from the KoreaN Cohort Study for Outcome in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease (KNOW-CKD), a nationwide prospective cohort study. The main predictor was time-varying HbA1c level at each visit. The primary outcome was a composite of development of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) or all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes included the individual endpoint of MACEs, all-cause mortality, and CKD progression. CKD progression was defined as a ≥50% decline in the estimated glomerular filtration rate from baseline or the onset of end-stage kidney disease.
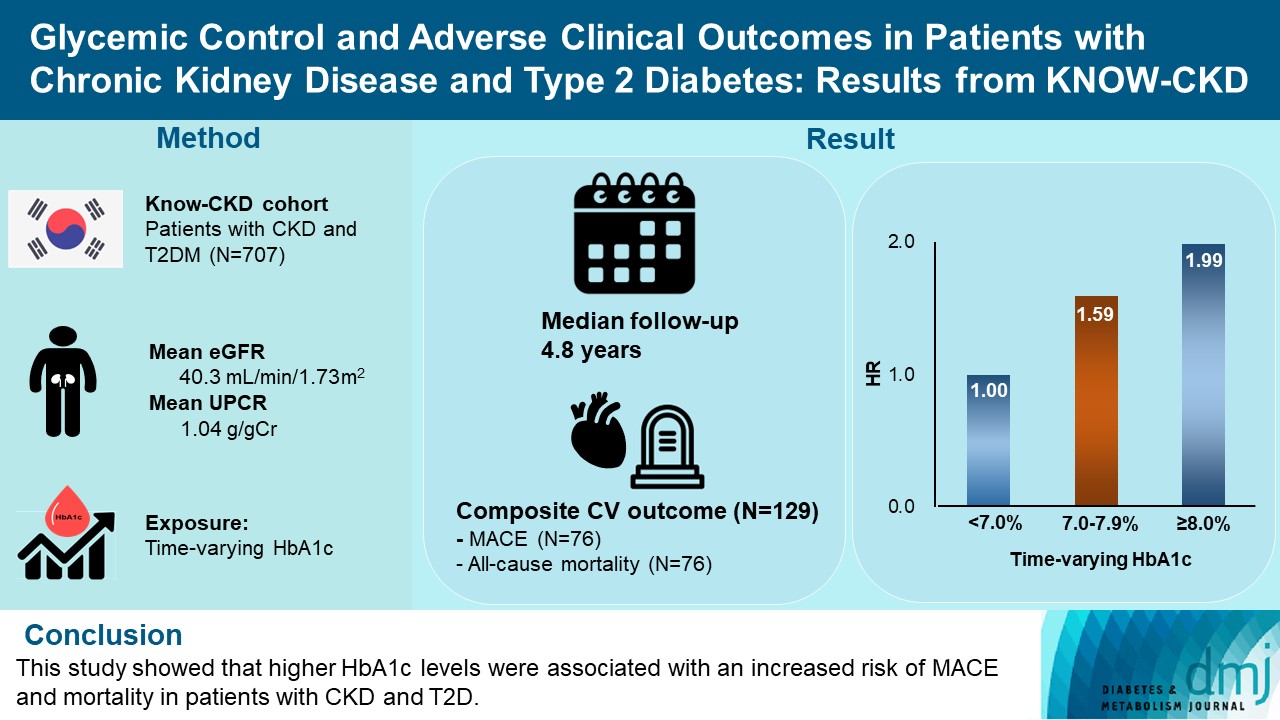
Results
During a median follow-up of 4.8 years, the primary outcome occurred in 129 (18.2%) patients. In time-varying Cox model, the adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) for the primary outcome were 1.59 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01 to 2.49) and 1.99 (95% CI, 1.24 to 3.19) for HbA1c levels of 7.0%–7.9% and ≥8.0%, respectively, compared with <7.0%. Additional analysis of baseline HbA1c levels yielded a similar graded association. In secondary outcome analyses, the aHRs for the corresponding HbA1c categories were 2.17 (95% CI, 1.20 to 3.95) and 2.26 (95% CI, 1.17 to 4.37) for MACE, and 1.36 (95% CI, 0.68 to 2.72) and 2.08 (95% CI, 1.06 to 4.05) for all-cause mortality. However, the risk of CKD progression did not differ between the three groups.
Conclusion
This study showed that higher HbA1c levels were associated with an increased risk of MACE and mortality in patients with CKD and T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Beneficial Effect of Glycemic Control against Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
Dong-Hwa Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(4): 484. CrossRef - Prevalence and predictors of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetic patients worldwide, systematic review and meta-analysis
Eneyew Talie Fenta, Habitu Birhan Eshetu, Natnael Kebede, Eyob Ketema Bogale, Amare Zewdie, Tadele Derbew Kassie, Tadele Fentabil Anagaw, Elyas Melaku Mazengia, Sintayehu Shiferaw Gelaw
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of teneligliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a Bayesian network meta-analysis
Miao Zhu, Ruifang Guan, Guo Ma
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Beneficial Effect of Glycemic Control against Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
- Others
- Opening the Precision Diabetes Care through Digital Healthcare
- Joonyub Lee, Jin Yu, Kun-Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):307-314. Published online March 29, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0386

- 5,455 View
- 247 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - The national healthcare systems of every country in the world cannot sustain the rise in healthcare expenditure caused by chronic diseases and their complications. To sustain the national healthcare system, a novel system should be developed to improve the quality of care and minimize healthcare costs. For 20 years, our team developed patient-communicating digital healthcare platforms and proved their efficacy. National scale randomized control trials are underway to systematically measure the efficacy and economic benefits of this digital health care system. Precision medicine aims to maximize effectiveness of disease management by considering individual variability. Digital health technologies enable precision medicine at a reasonable cost that was not available before. The government launched the “National Integrated Bio-big Data Project” which will collect diverse health data from the participants. Individuals will share their health information to physicians or researchers at their will by gateway named “My-Healthway.’ Taken together, now we stand in front of the evolution of medical care, so-called “Precision medicine.” led by various kinds of technologies and a huge amount of health information exchange. We should lead these new trends as pioneers, not as followers, to establish and implement the best care for our patients that can help them to withstand their devastating diseases.
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Novel Asian-Specific Visceral Adiposity Indices Are Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Korean Adults
- Jonghwa Jin, Hyein Woo, Youngeun Jang, Won-Ki Lee, Jung-Guk Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Keun-Gyu Park, Yeon-Kyung Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(3):426-436. Published online March 6, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0099
- 2,516 View
- 128 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 1 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The Chinese visceral adiposity index (CVAI) and new visceral adiposity index (NVAI) are novel indices of visceral adiposity used to predict metabolic and cardiovascular diseases in Asian populations. However, the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with chronic kidney disease (CKD) have not been investigated. We aimed to characterize the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with the prevalence of CKD in Korean adults.
Methods
A total of 14,068 participants in the 7th Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (6,182 men and 7,886 women) were included. Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analyses were employed to compare the associations between indices of adiposity and CKD, and a logistic regression model was used to characterize the relationships of CVAI and NVAI with CKD prevalence.
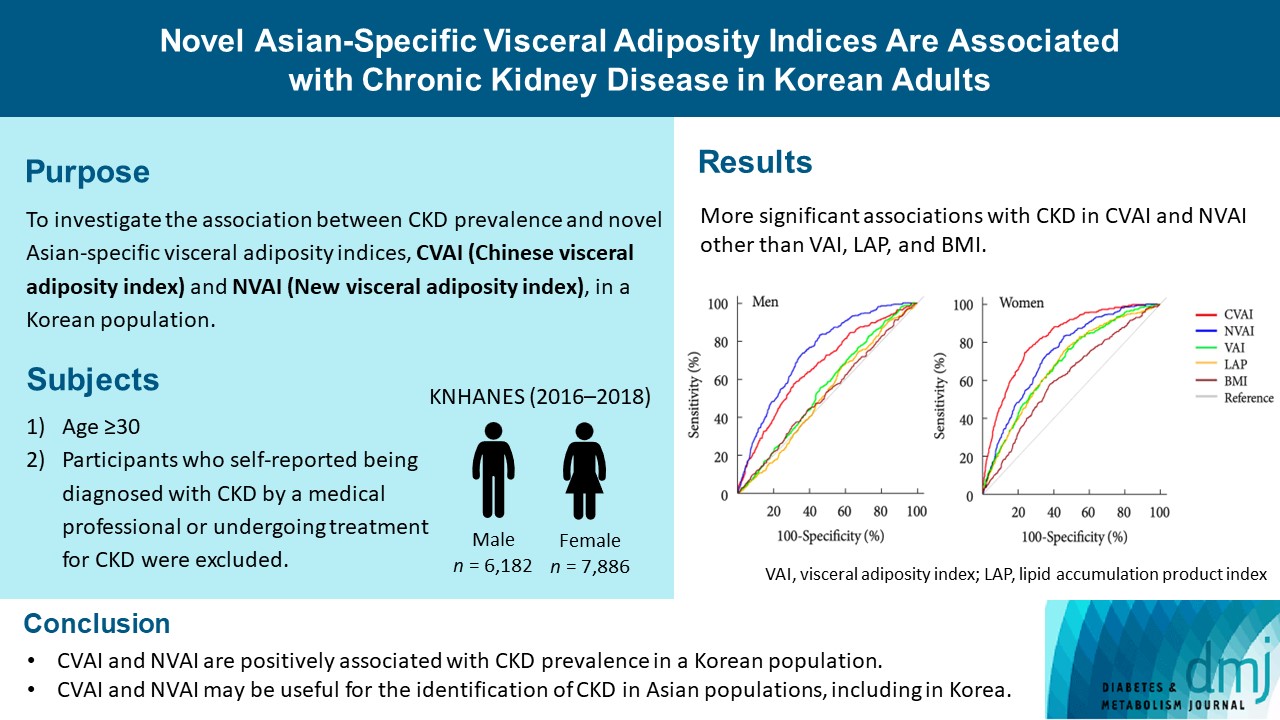
Results
The areas under the ROC curves for CVAI and NVAI were significantly larger than for the other indices, including the visceral adiposity index and lipid accumulation product, in both men and women (all P<0.001). In addition, high CVAI or NVAI was significantly associated with a high CKD prevalence in both men (odds ratio [OR], 2.14; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.31 to 3.48 in CVAI and OR, 6.47; 95% CI, 2.91 to 14.38 in NVAI, P<0.05) and women (OR, 4.87; 95% CI, 1.85 to 12.79 in CVAI and OR, 3.03; 95% CI, 1.35 to 6.82 in NVAI, P<0.05); this association remained significant after adjustment for multiple confounding factors in men and women.
Conclusion
CVAI and NVAI are positively associated with CKD prevalence in a Korean population. CVAI and NVAI may be useful for the identification of CKD in Asian populations, including in Korea. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association between Chinese visceral adiposity index and risk of stroke incidence in middle-aged and elderly Chinese population: evidence from a large national cohort study
Zenglei Zhang, Lin Zhao, Yiting Lu, Xu Meng, Xianliang Zhou
Journal of Translational Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association between Chinese visceral adiposity index and risk of stroke incidence in middle-aged and elderly Chinese population: evidence from a large national cohort study
- Complications
- Advanced Liver Fibrosis Is Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
- Da Hea Seo, Young Ju Suh, Yongin Cho, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongha Seo, Seongbin Hong, Yong-ho Lee, Young Ju Choi, Eunjig Lee, So Hun Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):630-639. Published online January 26, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0130
- 5,567 View
- 274 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 16 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD). However, the causal relationship between NAFLD and CKD is uncertain, particularly in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). We aimed to investigate the association between the presence and severity of NAFLD and incident CKD in patients with T2DM.
Methods
In this longitudinal cohort study of patients with T2DM, 3,188 patients with preserved renal function were followed up for the occurrence of incident CKD. NAFLD was defined as the presence of hepatic steatosis on ultrasonography, without any other causes of chronic liver disease. Advanced liver fibrosis of NAFLD was defined as a fibrosis-4 index ≥2.67. CKD was defined as an estimated glomerular filtration rate <60 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Results
At baseline, 1,729 (54.2%) patients had NAFLD, of whom 94 (5.4%) had advanced liver fibrosis. During the follow-up of 8.3±3.6 years, 472 (14.8%) patients developed incident CKD: 220 (15.1%) in the non-NAFLD group, 231 (14.1%) in the NAFLD without advanced fibrosis group and 28 (31.1%) in the NAFLD with advanced fibrosis group. There was no increased risk of incident CKD in the NAFLD group compared to the non-NAFLD group (P=0.435). However, among patients with NAFLD, advanced liver fibrosis was associated with an increased risk of CKD (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.75; 95% confidence interval, 1.15 to 2.66; P=0.009).
Conclusion
Advanced liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD is independently associated with an increased risk of incident CKD in patients with T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Esteatosis hepática metabólica y nefropatía diabética: una llamada a la acción
Salvador Benlloch, Francesc Moncho, Jose Luis Górriz
Nefrología.2024; 44(2): 129. CrossRef - Longitudinal Outcomes Associated With Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: A Meta-analysis of 129 Studies
Kai En Chan, Elden Yen Hng Ong, Charlotte Hui Chung, Christen En Ya Ong, Benjamin Koh, Darren Jun Hao Tan, Wen Hui Lim, Jie Ning Yong, Jieling Xiao, Zhen Yu Wong, Nicholas Syn, Apichat Kaewdech, Margaret Teng, Jiong-Wei Wang, Nicholas Chew, Dan Yock Young
Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.2024; 22(3): 488. CrossRef - Association of NAFLD/NASH, and MAFLD/MASLD with chronic kidney disease: an updated narrative review
Amedeo Lonardo
Metabolism and Target Organ Damage.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting metabolic-associated fatty liver disease in diabetic kidney disease: A call to action
Salvador Benlloch, Francesc Moncho, Jose Luis Górriz
Nefrología (English Edition).2024;[Epub] CrossRef - MAFLD and NAFLD in the prediction of incident chronic kidney disease
So Yoon Kwon, Jiyun Park, So Hee Park, You-Bin Lee, Gyuri Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Janghyun Koh, Jae Hwan Jee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Mira Kang, Sang-Man Jin
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations of non-invasive indices of liver steatosis and fibrosis with progressive kidney impairment in adults with type 2 diabetes
Mei Chung Moh, Sharon Li Ting Pek, Kenny Ching Pan Sze, Serena Low, Tavintharan Subramaniam, Keven Ang, Wern Ee Tang, Simon Biing Ming Lee, Chee Fang Sum, Su Chi Lim
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(6): 827. CrossRef - Pancreatic beta-cell specific BAG3 knockout results in chronic hyperinsulinemia inducing insulin resistance
Verena Damiani, Alessia Lamolinara, Ilaria Cicalini, Maria Concetta Cufaro, Francesco Del Pizzo, Federica Di Marco, Piero Del Boccio, Beatrice Dufrusine, Michael Hahne, Rossano Lattanzio, Damiana Pieragostino, Manuela Iezzi, Massimo Federici, Maria Cateri
Molecular Metabolism.2023; 74: 101752. CrossRef - Utility of non-invasive liver fibrosis markers to predict the incidence of chronic kidney disease (CKD): A systematic review, meta-analysis, and meta-regression
Rudi Supriyadi, Theo Audi Yanto, Timotius Ivan Hariyanto, Ketut Suastika
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(8): 102814. CrossRef - Significance of Diabetic Kidney Disease Biomarkers in Predicting Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease
Jaehyun Bae, Byung-Wan Lee
Biomedicines.2023; 11(7): 1928. CrossRef - Hepatic Fibrosis Evaluated in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes with and without Chronic Kidney Disease
Therese Adrian, Mads Hornum, Filip Krag Knop, Karl Bang Christensen, Thomas Almdal, Peter Rossing, Lisa Í Lídaa, Niels Søndergaard Heinrich, Vincent Oltman Boer, Anouk Marsman, Esben Thade Petersen, Hartwig Roman Siebner, Bo Feldt-Rasmussen
Nephron.2023; 147(11): 673. CrossRef - Clinical Interest of Serum Alpha-2 Macroglobulin, Apolipoprotein A1, and Haptoglobin in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, with and without Type 2 Diabetes, before or during COVID-19
Olivier Deckmyn, Thierry Poynard, Pierre Bedossa, Valérie Paradis, Valentina Peta, Raluca Pais, Vlad Ratziu, Dominique Thabut, Angelique Brzustowski, Jean-François Gautier, Patrice Cacoub, Dominique Valla
Biomedicines.2022; 10(3): 699. CrossRef - Fibrosis Risk in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Is Related to Chronic Kidney Disease in Older Type 2 Diabetes Patients
Yifan Sun, Liang Hong, Zhe Huang, Lihong Wang, Yanqin Xiong, Shuhang Zong, Rui Zhang, Jun Liu, Shufei Zang
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(9): e3661. CrossRef - Beyond Liver Disease: Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Advanced Liver Fibrosis in Kidney Disease
Eugene Han
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 564. CrossRef - A higher FIB‐4 index is associated with an increased incidence of renal failure in the general population
Eva Maria Schleicher, Simon Johannes Gairing, Peter Robert Galle, Julia Weinmann‐Menke, Jörn M. Schattenberg, Karel Kostev, Christian Labenz
Hepatology Communications.2022; 6(12): 3505. CrossRef - Advanced Liver Fibrosis Is Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:630-9)
Ji Hye Huh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 953. CrossRef - Advanced Liver Fibrosis Is Associated with Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:630-9)
Da Hea Seo, So Hun Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(6): 956. CrossRef
- Esteatosis hepática metabólica y nefropatía diabética: una llamada a la acción
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Performance of Diabetes and Kidney Disease Screening Scores in Contemporary United States and Korean Populations
- Liela Meng, Keun-Sang Kwon, Dae Jung Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Jeehyoung Kim, Abhijit V. Kshirsagar, Heejung Bang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):273-285. Published online September 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0054
- 65,535 View
- 239 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Risk assessment tools have been actively studied, and they summarize key predictors with relative weights/importance for a disease. Currently, standardized screening scores for type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM) and chronic kidney disease (CKD)—two key global health problems—are available in United States and Korea. We aimed to compare and evaluate screening scores for DM (or combined with prediabetes) and CKD, and assess the risk in contemporary United States and Korean populations.
Methods
Four (2×2) models were evaluated in the United States-National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES 2015–2018) and Korea-NHANES (2016–2018)—8,928 and 16,209 adults. Weighted statistics were used to describe population characteristics. We used logistic regression for predictors in the models to assess associations with study outcomes (undiagnosed DM and CKD) and diagnostic measures for temporal and cross-validation.
Results
Korean adult population (mean age 47.5 years) appeared to be healthier than United States counterpart, in terms of DM and CKD risks and associated factors, with exceptions of undiagnosed DM, prediabetes and prehypertension. Models performed well in own country and external populations regarding predictor-outcome association and discrimination. Risk tests (high vs. low) showed area under the curve >0.75, sensitivity >84%, specificity >45%, positive predictive value >8%, and negative predictive value >99%. Discrimination was better for DM, compared to the combined outcome of DM and prediabetes, and excellent for CKD due to age.
Conclusion
Four easy-to-use screening scores for DM and CKD are well-validated in contemporary United States and Korean populations. Prevention of DM and CKD may serve as first-step in public health, with these self-assessment tools as basic tools to help health education and disparity. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A meta‐analysis of diabetes risk prediction models applied to prediabetes screening
Yujin Liu, Sunrui Yu, Wenming Feng, Hangfeng Mo, Yuting Hua, Mei Zhang, Zhichao Zhu, Xiaoping Zhang, Zhen Wu, Lanzhen Zheng, Xiaoqiu Wu, Jiantong Shen, Wei Qiu, Jianlin Lou
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(5): 1593. CrossRef - Performance Analysis and Assessment of Type 2 Diabetes Screening Scores in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Norma Latif Fitriyani, Muhammad Syafrudin, Siti Maghfirotul Ulyah, Ganjar Alfian, Syifa Latif Qolbiyani, Chuan-Kai Yang, Jongtae Rhee, Muhammad Anshari
Mathematics.2023; 11(10): 2266. CrossRef - A Comprehensive Analysis of Chinese, Japanese, Korean, US-PIMA Indian, and Trinidadian Screening Scores for Diabetes Risk Assessment and Prediction
Norma Latif Fitriyani, Muhammad Syafrudin, Siti Maghfirotul Ulyah, Ganjar Alfian, Syifa Latif Qolbiyani, Muhammad Anshari
Mathematics.2022; 10(21): 4027. CrossRef
- A meta‐analysis of diabetes risk prediction models applied to prediabetes screening
- Complications
- High Incidence of Chronic Kidney Disease among Iranian Diabetic Adults: Using CKD-EPI and MDRD Equations for Estimated Glomerular Filtration Rate
- Seyyed Saeed Moazzeni, Reyhane Hizomi Arani, Mitra Hasheminia, Maryam Tohidi, Fereidoun Azizi, Farzad Hadaegh
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(5):684-697. Published online March 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0109
- 5,857 View
- 157 Download
- 13 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
To investigate the population based incidence rate of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and its potential risk factors among Iranian diabetic adults during over 14 years of follow-up.
Methods
Two different equations (Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration [CKD-EPI] and Modification of Diet in Renal Disease [MDRD]) were applied for the calculating the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR). Among a total of 1,374 diabetic Tehranian adults, 797 and 680 individuals were eligible for CKD-EPI and MDRD analyses, respectively. CKD was defined as eGFR lower than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2. Multivariable Cox proportional hazard models were used to estimate the hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CI) for all potential risk factors.
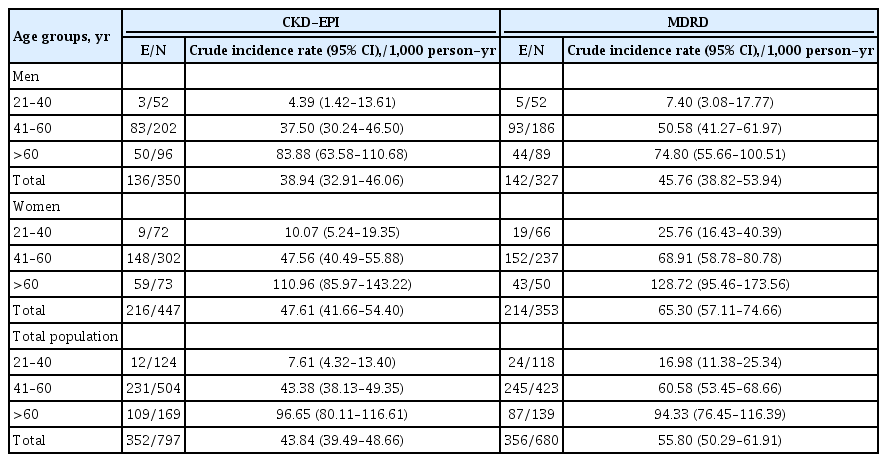
Results
The incidence rates (95% CI) of CKD per 1,000 person-years were 43.84 (39.49 to 48.66) and 55.80 (50.29 to 61.91) based on CKD-EPI and MDRD equations, respectively. Being older, a history of cardiovascular disease, and having lower levels of eGFR were significant risk factors in both equations. Moreover, in CKD-EPI, using glucose-lowering medications and hypertension, and in MDRD, female sex and fasting plasma glucose ≥10 mmol/L were also independent risk factors. Regarding the discrimination index, CKD-EPI equation showed a higher range of C-index for the predicted probability of incident CKD in the full-adjusted model, compared to MDRD equation (0.75 [0.72 to 0.77] vs. 0.69 [0.66 to 0.72]).
Conclusion
We found an incidence rate of more than 4%/year for CKD development among our Iranian diabetic population. Compared to MDRD, it can be suggested that CKD-EPI equation can be a better choice to use for prediction models of incident CKD among the Iranian diabetic populations. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Effect of the Holy Quran Recitation on Inflammatory Markers in Hemodialysis Patients in Iran: A Randomized Clinical Trial
Maedeh Teimourzadeh, Hassan Babamohamadi, Maliheh Yarmohamadi, Raheb Ghorbani, Harold G. Koenig
Journal of Religion and Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of anemia and its associated factors among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a referral diabetic clinic in the north of Iran
Reyhane Hizomi Arani, Farima Fakhri, Mohammad Naeimi Tabiee, Fatemeh Talebi, Zahra Talebi, Negin Rashidi, Maryam Zahedi
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between fasting plasma glucose variability and incident eGFR decline: evidence from two cohort studies
Niloofar Deravi, Yasaman Sharifi, Fatemeh Koohi, Seyed Saeed Tamehri Zadeh, Soroush Masrouri, Fereidoun Azizi, Farzad Hadaegh
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Low LncRNA LUCAT1 Expression Assists in the Diagnosis of Chronic Heart Failure and Predicts Poor Prognosis
Jian Wang, Xujin Wu, Li Wang, Chengyong Zhao
International Heart Journal.2023; 64(3): 409. CrossRef - Comparison of eGFR formulas (CKD-EPI and MDRD) in patients with multiple myeloma
Osman ERİNÇ, Soner YEŞİLYURT, Meliha NALCACİ
Cukurova Medical Journal.2023; 48(2): 336. CrossRef - Comparison and evaluation of the 2009 and 2021 chronic kidney disease-epidemiological collaboration equations among Jordanian patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Randa I. Farah, Abdulrahman Alhajahjeh, Oraib Al-farahid, Hana Abuzaid, Dana Hiasat, Rama Rayyan, Laith Bdier, Izzat AlAwwa, Kamel Ajlouni
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 61(2): 169. CrossRef - Effect of teaching health-promoting behaviors on the care burden of family caregivers of hemodialysis patients: a four-group clinical trial
Mehrdad Hayati, Razieh Bagherzadeh, Mehdi Mahmudpour, Fatemeh Heidari, Hakimeh Vahedparast
BMC Nursing.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of social and clinical factors on the diagnostic delay of chronic kidney disease: an evaluation study
Mousa Ghelichi-Ghojogh, Mohammad fararouei, Mozhgan Seif, Bahram Shahryari, Maryam Pakfetrat
International Urology and Nephrology.2022; 54(7): 1603. CrossRef - Chronic kidney disease and its health-related factors: a case-control study
Mousa Ghelichi-Ghojogh, Mohammad Fararouei, Mozhgan Seif, Maryam Pakfetrat
BMC Nephrology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Incidence and risk factors of severe non‐proliferative/proliferative diabetic retinopathy: More than a decade follow up in the Tehran Lipids and Glucose Study
Mahsa Sardarinia, Samaneh Asgari, Reyhane Hizomi Arani, Fatemeh Eskandari, Fereidoun Azizi, Davood Khalili, Farzad Hadaegh
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2022; 13(2): 317. CrossRef - Pathophysiologic Mechanisms and Potential Biomarkers in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Chan-Young Jung, Tae-Hyun Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 181. CrossRef - Prevalence of chronic kidney diseases and its determinants among Iranian adults: results of the first phase of Shahedieh cohort study
Ali Dehghani, Sadegh Alishavandi, Nader Nourimajalan, Hossein Fallahzadeh, Vahid Rahmanian
BMC Nephrology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Construct a classification decision tree model to select the optimal equation for estimating glomerular filtration rate and estimate it more accurately
Zhenliang Fan, Qiaorui Yang, Zhuohan Xu, Ke Sun, Mengfan Yang, Riping Yin, Dongxue Zhao, Junfen Fan, Hongzhen Ma, Yiwei Shen, Hong Xia
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Novel biomarkers for diabetic kidney disease
Chan-Young Jung, Tae-Hyun Yoo
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 41(Suppl 2): S46. CrossRef - Prevalence and Associated Factors of Kidney Dysfunction in Patients with Hypertension and/or Diabetes Mellitus from a Primary Care Population in Northwest China
Mengyue Lin, Mulalibieke Heizhati, Lin Wang, Lin Gan, Mei Li, Wenbo Yang, Ling Yao, Zhongrong Wang, Zhikang Yang, Reyila Abudoyreyimu, Zihao Wu, Nanfang Li
International Journal of General Medicine.2021; Volume 14: 7567. CrossRef
- The Effect of the Holy Quran Recitation on Inflammatory Markers in Hemodialysis Patients in Iran: A Randomized Clinical Trial
- Complications
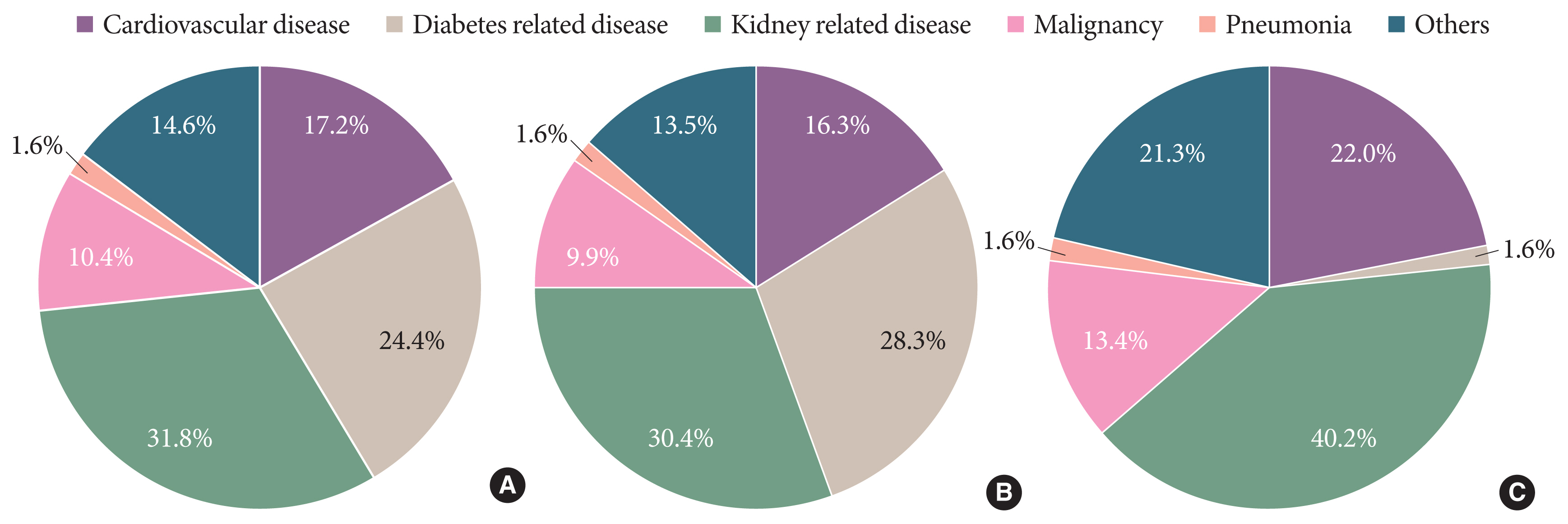
- Trends in the Incidence, Prevalence, and Mortality of End-Stage Kidney Disease in South Korea
- Min-Jeong Lee, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim, Inwhee Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):933-937. Published online December 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0156
- 5,838 View
- 239 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 14 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Knowledge of the epidemiologic characteristics of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) patients is essential. The trends in the prevalence, incidence, and mortality rates of ESKD were analyzed retrospectively using the Korean National Health Insurance ServiceNational Sample Cohort database between 2006 and 2015. From 2006 to 2015, the incidence of ESKD decreased from 28.6 to 24.0 per 100,000 people and showed a decreasing pattern with or without diabetes mellitus. However, the incidence of those aged ≥75 years increased, as did the mean age at the onset of ESKD. From 2007 to 2015, the prevalence of ESKD increased in all age groups, but particularly in those aged ≥75 years. The prevalence of ESKD differed by sex and diabetes mellitus status and this gap widened over time. Mortality rates in ESKD patients remained relatively constant throughout the study period. However, mortality rates in ESKD without diabetes decreased over the same period.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Kidney Health Plan 2033 in Korea: bridging the gap between the present and the future
Do Hyoung Kim, Young Youl Hyun, Jin Joo Cha, Sua Lee, Hyun Kyung Lee, Jong Wook Choi, Su-Hyun Kim, Sang Youb Han, Cheol Whee Park, Eun Young Lee, Dae Ryong Cha, Sung Gyun Kim, Chun Soo Lim, Sun-Hee Park
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 43(1): 8. CrossRef - Remnant cholesterol is an independent risk factor for the incidence of chronic kidney disease in newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population-based study
Soo Yeon Jang, Minwoong Kang, Eyun Song, Ahreum Jang, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Hye Jin Yoo
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 210: 111639. CrossRef - Waist circumference and end‐stage renal disease based on glycaemic status: National Health Insurance Service data 2009–2018
Yun Kyung Cho, Ji Hye Huh, Shinje Moon, Yoon Jung Kim, Yang‐Hyun Kim, Kyung‐do Han, Jun Goo Kang, Seong Jin Lee, Sung‐Hee Ihm
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle.2023; 14(1): 585. CrossRef - Usefulness of continuous glucose monitoring of blood glucose control in patients with diabetes undergoing hemodialysis: A pilot study
Sua Lee, Soyoung Lee, Kyeong Min Kim, Jong Ho Shin
Frontiers in Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between N-Terminal Prohormone Brain Natriuretic Peptide and Decreased Skeletal Muscle Mass in a Healthy Adult Population: A Cross-Sectional Study
Tae Kyung Yoo, Marie Yung-Chen Wu, Moon Soo Kim, Mi-Yeon Lee, Yong-Taek Lee, Kyung Jae Yoon, Chul-Hyun Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(2): 269. CrossRef - Age at Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Who Underwent Kidney Transplantation: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Sun Ok Song, Eugene Han, Kang Ju Son, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3160. CrossRef - Epigenome-wide association study of diabetic chronic kidney disease progression in the Korean population: the KNOW-CKD study
Hye Youn Sung, Sangjun Lee, Miyeun Han, Woo Ju An, Hyunjin Ryu, Eunjeong Kang, Yong Seek Park, Seung Eun Lee, Curie Ahn, Kook-Hwan Oh, Sue K. Park, Jung-Hyuck Ahn
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Dapagliflozin in Asian Patients With Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction in DAPA-HF
Kieran F. Docherty, Inder S. Anand, Chern-En Chiang, Vijay K. Chopra, Akshay S. Desai, Masafumi Kitakaze, Subodh Verma, Pham N. Vinh, Silvio E. Inzucchi, Lars Køber, Mikhail N. Kosiborod, Felipe A. Martinez, Olof Bengtsson, Piotr Ponikowski, Marc S. Sabat
JACC: Asia.2022; 2(2): 139. CrossRef - Glomerular filtration rate as a kidney outcome of diabetic kidney disease: a focus on new antidiabetic drugs
Hyo Jin Kim, Sang Soo Kim, Sang Heon Song
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2022; 37(3): 502. CrossRef - The risk of Parkinson's disease according to diabetic kidney disease status in a Korean population
Seung Eun Lee, Juhwan Yoo, Han Seok Choi, Kyungdo Han, Kyoung-Ah Kim
Parkinsonism & Related Disorders.2022; 100: 13. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - The Incidence and Risk Factors of Renal Insufficiency among Korean HIV infected Patients: The Korea HIV/AIDS Cohort Study
Jun Hyoung Kim, Heeseon Jang, Jung Ho Kim, Joon Young Song, Shin-Woo Kim, Sang Il Kim, Bo Youl Choi, Jun Yong Choi
Infection & Chemotherapy.2022; 54(3): 534. CrossRef - Sex difference in the association among nutrition, muscle mass, and strength in peritoneal dialysis patients
Jun Young Do, Seok Hui Kang
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Additive interaction of diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease in cancer patient mortality risk
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef
- Kidney Health Plan 2033 in Korea: bridging the gap between the present and the future
- Drug/Regimen
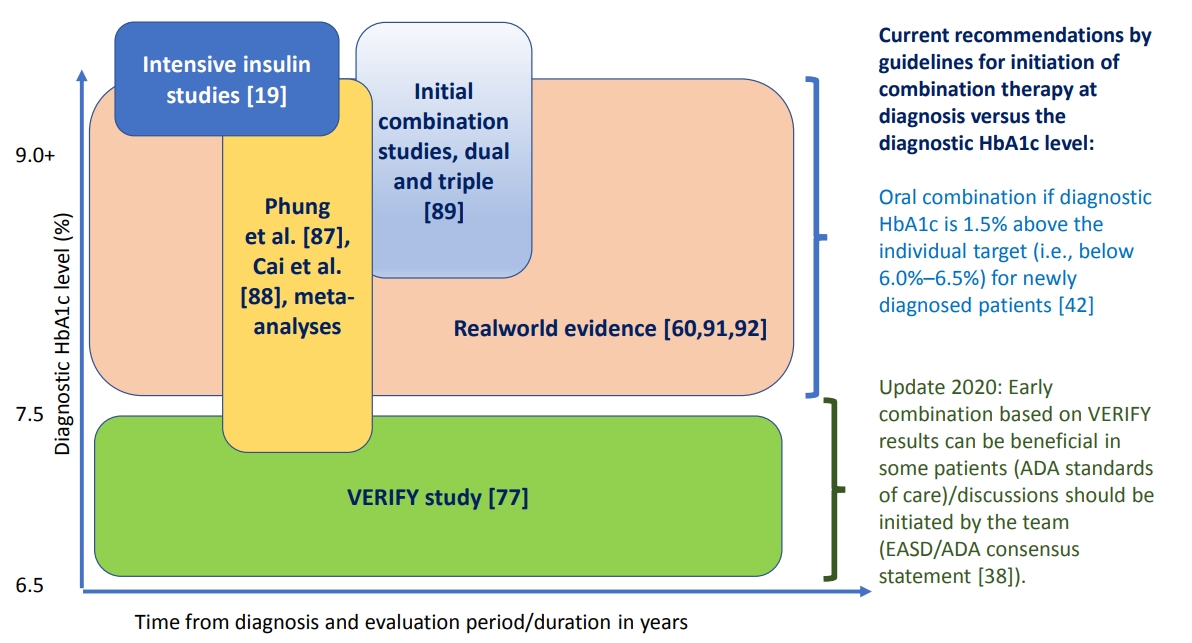
- Evaluating the Evidence behind the Novel Strategy of Early Combination from Vision to Implementation
- Päivi Maria Paldánius
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):785-801. Published online September 15, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0179
- 7,114 View
- 287 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a complex and progressive chronic disease characterised by elevating hyperglycaemia and associated need to gradually intensify therapy in order to achieve and maintain glycaemic control. Treating hyperglycaemia with sequential therapy is proposed to allow holistic assessment of the efficacy and risk-to-benefit ratio of each added component. However, there is an array of evidence supporting the scientific rationale for using synergistic, earlier, modern drug combinations to achieve glycaemic goals, delay the deterioration of glycaemic control, and, therefore, potentially preserve or slow down the declining β-cell function. Additionally, implementation of early combination(s) may lead to opportunities to combat clinical inertia and other hurdles to optimised disease management outcomes. This review aims to discuss the latest empirical evidence for long-term clinical benefits of this novel strategy of early combination in people with newly diagnosed T2DM versus the current widely-implemented treatment paradigm, which focuses on control of hyperglycaemia using lifestyle interventions followed by sequentially intensified (mostly metformin-based) monotherapy. The recent reported Vildagliptin Efficacy in combination with metfoRmin For earlY treatment of T2DM (VERIFY) study results have provided significant new evidence confirming long-term glycaemic durability and tolerability of a specific early combination in the management of newly diagnosed, treatment-naïve patients worldwide. These results have also contributed to changes in clinical treatment guidelines and standards of care while clinical implementation and individualised treatment decisions based on VERIFY results might face barriers beyond the existing scientific evidence.
- Basic Research
- Histone Deacetylase 9: Its Role in the Pathogenesis of Diabetes and Other Chronic Diseases
- Siqi Hu, Eun-Hee Cho, Ji-Young Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):234-244. Published online March 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0243
- 6,390 View
- 161 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 21 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader As a member of the class IIa histone deacetylases (HDACs), HDAC9 catalyzes the deacetylation of histones and transcription factors, commonly leading to the suppression of gene transcription. The activity of HDAC9 is regulated transcriptionally and post-translationally. HDAC9 is known to play an essential role in regulating myocyte and adipocyte differentiation and cardiac muscle development. Also, recent studies have suggested that HDAC9 is involved in the pathogenesis of chronic diseases, including cardiovascular diseases, osteoporosis, autoimmune disease, cancer, obesity, insulin resistance, and liver fibrosis. HDAC9 modulates the expression of genes related to the pathogenesis of chronic diseases by altering chromatin structure in their promotor region or reducing the transcriptional activity of their respective transcription factors. This review summarizes the current knowledge of the regulation of HDAC9 expression and activity. Also, the roles of HDAC9 in the pathogenesis of chronic diseases are discussed, along with potential underlying mechanisms.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Impact of housing temperature on adipose tissue HDAC9 expression and adipogenic differentiation in high fat‐fed mice
Samah Ahmadieh, Brandee Goo, Abdalrahman Zarzour, David Kim, Hong Shi, Praneet Veerapaneni, Ronnie Chouhaita, Nicole K. H. Yiew, Carla Dominguez Gonzalez, Akash Chakravartty, James Pennoyer, Nazeera Hassan, Tyler W. Benson, Mourad Ogbi, David J. Fulton, R
Obesity.2024; 32(1): 107. CrossRef - HDAC9 inhibition reduces skeletal muscle atrophy and enhances regeneration in mice with cigarette smoke-induced COPD
Guixian Zheng, Chao Li, Xiaoli Chen, Zhaohui Deng, Ting Xie, Zengyu Huo, Xinyan Wei, Yanbing Huang, Xia Zeng, Yu Luo, Jing Bai
Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Basis of Disease.2024; 1870(3): 167023. CrossRef - Identification of HDAC9 and ARRDC4 as potential biomarkers and targets for treatment of type 2 diabetes
Jing Liu, Lingzhen Meng, Zhihong Liu, Ming Lu, Ruiying Wang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - HDAC9 as a Privileged Target: Reviewing its Role in Different Diseases
and Structure-activity Relationships (SARs) of its Inhibitors
Totan Das, Samima Khatun, Tarun Jha, Shovanlal Gayen
Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry.2024; 24(7): 767. CrossRef - Targeting histone deacetylases for cancer therapy: Trends and challenges
Tao Liang, Fengli Wang, Reham M. Elhassan, Yongmei Cheng, Xiaolei Tang, Wengang Chen, Hao Fang, Xuben Hou
Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B.2023; 13(6): 2425. CrossRef - Therapeutic approach of natural products that treat osteoporosis by targeting epigenetic modulation
Guokai Zhang, Zhenying Liu, Zihan Li, Bing Zhang, Pengyu Yao, Yun Qiao
Frontiers in Genetics.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Research Progress on Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors
玉姜 汤
Hans Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.2023; 11(02): 116. CrossRef - HDAC9 Inhibition as a Novel Treatment for Stroke
Hugh S. Markus
Stroke.2023; 54(12): 3182. CrossRef - Histone deacetylase 9 exacerbates podocyte injury in hyperhomocysteinemia through epigenetic repression of Klotho
Min Liu, Yang Zhang, Ping Zhan, Wenjuan Sun, Chuanqiao Dong, Xiaohan Liu, Yujie Yang, Xiaojie Wang, Yusheng Xie, Chengjiang Gao, Huili Hu, Benkang Shi, Ziying Wang, Chun Guo, Fan Yi
Pharmacological Research.2023; 198: 107009. CrossRef - Molecular mechanism and therapeutic potential of HDAC9 in intervertebral disc degeneration
Ming Lei, Hui Lin, Deyao Shi, Pan Hong, Hui Song, Bomansaan Herman, Zhiwei Liao, Cao Yang
Cellular & Molecular Biology Letters.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Interindividual variability in transgene mRNA and protein production following adeno-associated virus gene therapy for hemophilia A
Sylvia Fong, Bridget Yates, Choong-Ryoul Sihn, Aras N. Mattis, Nina Mitchell, Su Liu, Chris B. Russell, Benjamin Kim, Adebayo Lawal, Savita Rangarajan, Will Lester, Stuart Bunting, Glenn F. Pierce, K. John Pasi, Wing Yen Wong
Nature Medicine.2022; 28(4): 789. CrossRef - Active RhoA Exerts an Inhibitory Effect on the Homeostasis and Angiogenic Capacity of Human Endothelial Cells
Michael Hauke, Robert Eckenstaler, Anne Ripperger, Anna Ender, Heike Braun, Ralf A. Benndorf
Journal of the American Heart Association.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - HDAC9 Contributes to Serous Ovarian Cancer Progression through Regulating Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition
Long Xu, Jian Wang, Buhan Liu, Jiaying Fu, Yuanxin Zhao, Sihang Yu, Luyan Shen, Xiaoyu Yan, Jing Su
Biomedicines.2022; 10(2): 374. CrossRef - Common protein-coding variants influence the racing phenotype in galloping racehorse breeds
Haige Han, Beatrice A. McGivney, Lucy Allen, Dongyi Bai, Leanne R. Corduff, Gantulga Davaakhuu, Jargalsaikhan Davaasambuu, Dulguun Dorjgotov, Thomas J. Hall, Andrew J. Hemmings, Amy R. Holtby, Tuyatsetseg Jambal, Badarch Jargalsaikhan, Uyasakh Jargalsaikh
Communications Biology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Proposed minimal essential co-expression and physical interaction networks involved in the development of cognition impairment in human mid and late life
Zahra Salehi, Masoud Arabfard, Omid Sadatpour, Mina Ohadi
Neurological Sciences.2021; 42(3): 951. CrossRef - Emerging roles of SIRT6 in human diseases and its modulators
Gang Liu, Haiying Chen, Hua Liu, Wenbo Zhang, Jia Zhou
Medicinal Research Reviews.2021; 41(2): 1089. CrossRef - Quis Custodiet Ipsos Custodes (Who Controls the Controllers)? Two Decades of Studies on HDAC9
Claudio Brancolini, Eros Di Giorgio, Luigi Formisano, Teresa Gagliano
Life.2021; 11(2): 90. CrossRef - circ_0003204 Regulates Cell Growth, Oxidative Stress, and Inflammation in ox-LDL-Induced Vascular Endothelial Cells via Regulating miR-942-5p/HDAC9 Axis
Huan Wan, Ting You, Wei Luo
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Histone deacetylase (HDAC) 9: versatile biological functions and emerging roles in human cancer
Chun Yang, Stéphane Croteau, Pierre Hardy
Cellular Oncology.2021; 44(5): 997. CrossRef - Dual HDAC/BRD4 inhibitors against cancer
Negar Omidkhah, Farzin Hadizadeh, Razieh Ghodsi
Medicinal Chemistry Research.2021; 30(10): 1822. CrossRef - miR‐211‐5p is down‐regulated and a prognostic marker in bladder cancer
Weisheng Wang, Zhiming Liu, Xuegang Zhang, Junning Liu, Junqing Gui, Maorong Cui, Yong Li
The Journal of Gene Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef
- Impact of housing temperature on adipose tissue HDAC9 expression and adipogenic differentiation in high fat‐fed mice
- Drug/Regimen
- Evogliptin, a Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor, Attenuates Renal Fibrosis Caused by Unilateral Ureteral Obstruction in Mice
- Mi-Jin Kim, Na-young Kim, Yun-A Jung, Seunghyeong Lee, Gwon-Soo Jung, Jung-Guk Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Sungwoo Lee, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Keun-Gyu Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(1):186-192. Published online October 31, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0271
- 5,670 View
- 97 Download
- 10 Web of Science
- 10 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Renal fibrosis is considered to be the final common outcome of chronic kidney disease. Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitors have demonstrated protective effects against diabetic kidney disease. However, the anti-fibrotic effect of evogliptin, a DPP-4 inhibitor, has not been studied. Here, we report the beneficial effects of evogliptin on unilateral ureteral obstruction (UUO)-induced renal fibrosis in mice. Evogliptin attenuated UUO-induced renal atrophy and tubulointerstitial fibrosis. Immunohistochemistry and Western blotting demonstrated that evogliptin treatment inhibits pro-fibrotic gene expressions and extracellular matrix production.
In vitro findings showed that the beneficial effects of evogliptin on renal fibrosis are mediated by inhibition of the transforming growth factor-β/Smad3 signaling pathway. The present study demonstrates that evogliptin is protective against UUO-induced renal fibrosis, suggesting that its clinical applications could extend to the treatment of kidney disease of non-diabetic origin.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Targeting cluster of differentiation 26 / dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (CD26/DPP4) in organ fibrosis
Birte Ohm, Isabelle Moneke, Wolfgang Jungraithmayr
British Journal of Pharmacology.2023; 180(22): 2846. CrossRef - Linagliptin ameliorates pulmonary fibrosis in systemic sclerosis mouse model via inhibition of endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Biwei Pei, Na Zhang, Tingting Pang, Gengyun Sun
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry.2022; 477(4): 995. CrossRef - Association Between DPP4 Inhibitor Use and the Incidence of Cirrhosis, ESRD, and Some Cancers in Patients With Diabetes
Yewon Na, Soo Wan Kim, Ie Byung Park, Soo Jung Choi, Seungyoon Nam, Jaehun Jung, Dae Ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(11): 3022. CrossRef - Evogliptin Directly Inhibits Inflammatory and Fibrotic Signaling in Isolated Liver Cells
Hye-Young Seo, So-Hee Lee, Eugene Han, Jae Seok Hwang, Sol Han, Mi Kyung Kim, Byoung Kuk Jang
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(19): 11636. CrossRef - Optimization and validation of a fluorogenic dipeptidyl peptidase 4 enzymatic assay in human plasma
Hyunyee Yoon, Su Hee Cho, Yu Rim Seo, Kyung-Sang Yu, Sung Sup Park, Moon Jung Song
Analytical Biochemistry.2021; 612: 113952. CrossRef - Use of Anti-Diabetic Agents in Non-Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Bench to Bedside
Sungjin Chung, Gheun-Ho Kim
Life.2021; 11(5): 389. CrossRef - Targeting Dermal Fibroblast Subtypes in Antifibrotic Therapy: Surface Marker as a Cellular Identity or a Functional Entity?
Xin Huang, Yimin Khoong, Chengyao Han, Dai Su, Hao Ma, Shuchen Gu, Qingfeng Li, Tao Zan
Frontiers in Physiology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of evogliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes: A multicentre, active‐controlled, randomized, double‐blind study with open‐label extension (the EVERGREEN study)
Gyuri Kim, Soo Lim, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon, Ie B. Park, Kyu J. Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park, Su K. Kwon, Hye S. Kim, Seok W. Park, Sin G. Kim, Min K. Moon, Eun S. Kim, Choon H. Chung, Kang S. Park, Mikyung Kim, Dong J. Chung, Chang B. Lee, Tae H. Kim, Moon‐Kyu Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(9): 1527. CrossRef Effect of Switching from Linagliptin to Teneligliptin Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors in Older Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Eugene Han, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Hye Soon Kim, Byung-wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4113. CrossRef- Efficacy and safety of novel dipeptidyl-peptidase-4 inhibitor evogliptin in the management of type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis
Deep Dutta, Saptarshi Bhattacharya, Aishwarya Krishnamurthy, LokeshKumar Sharma, Meha Sharma
Indian Journal of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 24(5): 434. CrossRef
- Targeting cluster of differentiation 26 / dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (CD26/DPP4) in organ fibrosis
- Complications
- Higher Prevalence and Progression Rate of Chronic Kidney Disease in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Kyung-Soo Kim, Seok Won Park, Yong-Wook Cho, Soo-Kyung Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(3):224-232. Published online May 31, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0065
- 5,268 View
- 73 Download
- 31 Web of Science
- 33 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background To evaluate the prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and progression rate to CKD in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods We investigated the medical records of 190 elderly patients (65 years or older) with T2DM from 2005 to 2011 in 6-month increments. Mean follow-up duration was 64.5 months. CKD was defined as estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 and/or the presence of albuminuria.
Results The mean age was 70.4 years and mean diabetes duration was 10.6 years. Among all the participants, 113 patients (59.5%) had CKD. The eGFR was significantly decreased between baseline (65.7±15.0 mL/min/1.73 m2) and the end of follow-up (52.7±17.5 mL/min/1.73 m2,
P <0.001). At the end of follow-up, the prevalence of eGFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2 had increased by 61.6% (at baseline, 44.2%). Furthermore, in patients with eGFR ≥60 mL/min/1.73 m2, the progression rate to more than CKD stage 3 was 39.6% at the end of follow-up; 30.2% of elderly diabetic patients had progressed to albuminuria from normoalbuminuria. Kaplan-Meier analysis showed that the time interval to worsening nephropathy was significantly shorter in elderly patients with diabetes duration ≥10 years than in those with diabetes duration <5 years (P =0.018).Conclusion CKD was commonly observed in older patients with T2DM, and the progression rate to CKD is also high. Consequently, it is important to identify and manage CKD as early as possible in elderly patients with T2DM, especially in those with diabetes duration ≥10 years.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Assessing heatwave effects on disabled persons in South Korea
Yeji Kang, Ingul Baek, Jongchul Park
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Combination of Risks of BMI and Health-Related Lifestyles on Kidney Function in the Prediabetic Japanese Population: A Prospective Cohort Study
Jou-Yin Chen, Shiqi Deng, Yukiko Wagatsuma
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(7): 5338. CrossRef - Hormonal imbalance in patients with chronic renal failure in the pre-dialysis and dialysis periods (part1)
I.P. Katerenchuk, S.T. Rustamyan, V.V. Talash, T.I. Yarmola
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF ENDOCRINOLOGY (Ukraine).2023; 19(1): 65. CrossRef - The Beneficial Effect of Glycemic Control against Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
Dong-Hwa Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(4): 484. CrossRef - Association Between Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Glycemia Risk Index and Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes
Jee Hee Yoo, Ji Yoon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(10): 726. CrossRef - Global burden and influencing factors of chronic kidney disease due to type 2 diabetes in adults aged 20–59 years, 1990–2019
Dandan Xie, Tianpeng Ma, Haoliang Cui, Jing Li, Aihua Zhang, Zhifeng Sheng, Yiqiang Xie
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effectiveness of Early Advanced Glycation End Product Accumulation Testing in the Diagnosis of Diabetes: A Health Risk Factor Analysis Using the Body Mass Index as a Moderator
Yi Zhang, Tian Jiang, Chao Liu, Honglin Hu, Fang Dai, Li Xia, Qiu Zhang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Causal association pathways between fetuin-A and kidney function: a mediation analysis
Philip Etabee Bassey, Pawin Numthavaj, Sasivimol Rattanasiri, Piyamitr Sritara, Mark McEvoy, Boonsong Ongphiphadhanakul, Ammarin Thakkinstian
Journal of International Medical Research.2022; 50(4): 030006052210828. CrossRef - Advanced glycation end products and diabetes and other metabolic indicators
Tian Jiang, Yi Zhang, Fang Dai, Chao Liu, Honglin Hu, Qiu Zhang
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Type 2 diabetes management in people aged over seventy-five years: targets and treatment strategies
Theocharis Koufakis, Maria Grammatiki, Kalliopi Kotsa
Maturitas.2021; 143: 118. CrossRef - Comparative Efficacy of Lobeglitazone Versus Pioglitazone on Albuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(1): 171. CrossRef - Chronic kidney disease progression in aged patients
Murat Tuğcu, Dilek Barutçu Ataş
International Urology and Nephrology.2021; 53(12): 2619. CrossRef - Factors determining the clinical significance of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in the treatment of elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
I. V. Glinkina, A. V. Balashova, A. S. Shyman, A. V. Oderij, S. A. Khan, G. E. Runova, T. B. Morgunova, V. V. Fadeev
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2021; (7): 56. CrossRef - Effect of Oral carnosine supplementation on urinary TGF-β in diabetic nephropathy: a randomized controlled trial
Narongrit Siriwattanasit, Bancha Satirapoj, Ouppatham Supasyndh
BMC Nephrology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Estimation of the prevalence of type 2 diabetes in combination with diabetic kidney disease and identification of the associated factors in patients attending primary hospitals in Anhui Province, China
Li Xia, Lanlan Cheng, Tian Jiang, Chao Liu, Shiqi Zhang, Honglin Hu, Fang Dai, Qiu Zhang, Yunxia Lu
Journal of International Medical Research.2021; 49(10): 030006052110512. CrossRef - A STUDY TO EVALUATE THE EFFECT OF ANAEMIA IN TYPE-2 DIABETIC PATIENTS
Radhika Maheshwari, Divya J., J. Sahayaraj, Muthukrishnan R.
GLOBAL JOURNAL FOR RESEARCH ANALYSIS.2021; : 117. CrossRef - Metformin treatment for patients with diabetes and chronic kidney disease: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology consensus statement
Kyu Yeon Hur, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Miyeun Han, Dong Won Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 39(1): 32. CrossRef - Metformin Treatment for Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
Kyu Yeon Hur, Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung Hyun Ko, Miyeun Han, Dong Won Lee, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 3. CrossRef - The prevalence of diabetic chronic kidney disease in adult Greek subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A series from hospital-based diabetes clinics
Ilias N. Migdalis, Nikolaos Papanas, Athanasios E. Raptis, Ioannis M. Ioannidis, Alexios E. Sotiropoulos, George D. Dimitriadis
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 166: 108243. CrossRef - Proteinuria Is Associated with Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis in Non-Albuminuric Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jaehyun Bae, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 136. CrossRef - Renal status in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes
Kazunaga Takamatsu
Clinical and Experimental Nephrology.2020; 24(1): 53. CrossRef - The fat mass, estimated glomerular filtration rate, and chronic inflammation in type 2 diabetic patients
Tomáš Šálek, Alena Adamíková, Petr Ponížil
Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin: Trigger and Target of Renal Functions
Ana F. Pina, Diego O. Borges, Maria João Meneses, Patrícia Branco, Rita Birne, Antonio Vilasi, Maria Paula Macedo
Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Rate of kidney function decline and factors predicting progression of kidney disease in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with reduced kidney function: A nationwide retrospective cohort study
Wisit Kaewput, Charat Thongprayoon, Api Chewcharat, Ram Rangsin, Bancha Satirapoj, Chalermrat Kaewput, Picha Suwannahitatorn, Tarun Bathini, Michael A. Mao, Liam D. Cato, Andrew M. Harrison, Pradeep Vaitla, Wisit Cheungpasitporn
Therapeutic Apheresis and Dialysis.2020; 24(6): 677. CrossRef - Association Between Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Time in Range, Other Core Metrics, and Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes
Jee Hee Yoo, Min Sun Choi, Jiyeon Ahn, Sung Woon Park, Yejin Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Sang-Man Jin, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2020; 22(10): 768. CrossRef - Comparison of Renal Effects of Ezetimibe–Statin Combination versus Statin Monotherapy: A Propensity-Score-Matched Analysis
Jaehyun Bae, Namki Hong, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Yong-ho Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(3): 798. CrossRef - Metformin Use and Risk of All-Cause Mortality and Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Yao Hu, Min Lei, Guibao Ke, Xin Huang, Xuan Peng, Lihui Zhong, Ping Fu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Treatment with Cinacalcet in Hemodialysis Patients with Severe Secondary Hyperparathyroidism, Influences Bone Mineral Metabolism and Anemia Parameters
Maria Aktsiali, Theodora Papachrysanthou , Ioannis Griveas, Christos Andriopoulos, Panagiotis Sitaras, Ioannis K. Triantafyllopoulos , George I. Lambrou
Current Drug Therapy.2020; 15(3): 249. CrossRef - Gemigliptin Attenuates Renal Fibrosis Through Down-Regulation of the NLRP3 Inflammasome
Jung Beom Seo, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Hye-In Woo, Yun-A Jung, Sungwoo Lee, Seunghyeong Lee, Mihyang Park, In-Kyu Lee, Gwon-Soo Jung, Keun-Gyu Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 830. CrossRef - Glucometabolic characteristics and higher vascular complication risk in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes with non-albumin proteinuria
Yongin Cho, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-soo Cha, Byung-wan Lee
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(8): 585. CrossRef - Assessment of kidney function and associated risk factors among type 2 diabetic patients
Moyad Jamal Shahwan, Nageeb Abdul galil Hassan, Rima Ahd Shaheen
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(4): 2661. CrossRef - Influence of diabetes mellitus on patients with lumbar spinal stenosis: A nationwide population-based study
Chang Kyu Lee, Sun Kyu Choi, Dong Ah Shin, Seong Yi, Yoon Ha, Keung Nyun Kim, Insoo Kim, Gregory W.J. Hawryluk
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(3): e0213858. CrossRef - Predictores de progresión de enfermedad renal en el paciente anciano
Manuel Heras Benito, Mª José Fernández Reyes Luis
Enfermería Nefrológica.2019; 22(1): 19. CrossRef
- Assessing heatwave effects on disabled persons in South Korea
- Pathophysiology
- Role of NO/VASP Signaling Pathway against Obesity-Related Inflammation and Insulin Resistance
- Yu Mi Kang, Francis Kim, Woo Je Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2017;41(2):89-95. Published online November 15, 2016
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.2.89
- 4,473 View
- 59 Download
- 20 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Obesity has quickly become a worldwide pandemic, causing major adverse health outcomes such as dyslipidemia, type 2 diabetes mellitus, cardiovascular disease and cancers. Obesity-induced insulin resistance is the key for developing these metabolic disorders, and investigation to understand the molecular mechanisms involved has been vibrant for the past few decades. Of these, low-grade chronic inflammation is suggested as a critical concept in the development of obesity-induced insulin resistance, and the anti-inflammatory effect of nitric oxide (NO) signaling has been reported to be linked to improvement of insulin resistance in multiple organs involved in glucose metabolism. Recently, a body of evidence suggested that vasodilatory-stimulated phosphoprotein (VASP), a downstream mediator of NO signaling plays a crucial role in the anti-inflammatory effect and improvement of peripheral insulin resistance. These preclinical studies suggest that NO/VASP signaling could be an ideal therapeutic target in the treatment of obesity-related metabolic dysfunction. In this review, we introduce studies that investigated the protective role of NO/VASP signaling against obesity-related inflammation and insulin resistance in various tissues.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hippocampal proteomic changes in high-fat diet-induced obese mice associated with memory decline
Ping Lu, Cun-Xiu Gao, Fei-Jian Luo, Yu-Ting Huang, Mei-Mei Gao, Yue-Sheng Long
The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry.2024; 125: 109554. CrossRef - Leptina, obesidad y enfermedades cardiovasculares
Jorly Mejia-Montilla , Nadia Reyna-Villasmil, Andreina Fernández-Ramírez, Eduardo Reyna-Villasmil
Revista Repertorio de Medicina y Cirugía.2023; 32(3): 218. CrossRef - Urinary and circulatory netrin-1 as biomarker in diabetes and its related complications: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Amir Hossein Behnoush, Amirmohammad Khalaji, Zahra Shokri Varniab, Afshin Rahbarghazi, Elahe Amini, Aleksandra Klisic
Endocrine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of ultraviolet radiation on cardiovascular and metabolic disorders: The role of nitric oxide and vitamin D
Qing‐Ling Quan, Kyeong‐No Yoon, Ji Su Lee, Eun Ju Kim, Dong Hun Lee
Photodermatology, Photoimmunology & Photomedicine.2023; 39(6): 573. CrossRef - Beneficial Metabolic Effects of Praliciguat, a Soluble Guanylate Cyclase Stimulator, in a Mouse Diet-Induced Obesity Model
Chad D. Schwartzkopf, John R. Hadcock, Guang Liu, Peter Germano, Julien Roux, Courtney M. Shea, Emmanuel S. Buys, Juli E. Jones
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes Complicated With Heart Failure: Research on Therapeutic Mechanism and Potential Drug Development Based on Insulin Signaling Pathway
Hui Ye, Yanan He, Chuan Zheng, Fang Wang, Ming Yang, Junzhi Lin, Runchun Xu, Dingkun Zhang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of low-dose tadalafil once daily on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes and erectile dysfunction: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled pilot study
Min-Kyung Lee, Jae-Hyuk Lee, Seo-Young Sohn, Seo Yeon Lee, Tae-Yoong Jeong, Sae Chul Kim
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - In situ hydrogel capturing nitric oxide microbubbles accelerates the healing of diabetic foot
Yingzheng Zhao, Lanzi Luo, Lantian Huang, Yingying Zhang, Mengqi Tong, Hanxiao Pan, Jianxun Shangguan, Qing Yao, Shihao Xu, Helin Xu
Journal of Controlled Release.2022; 350: 93. CrossRef - Amelioration effect of black seed oil against high‐fat diet‐induced obesity in rats through Nrf2/HO‐1 pathway
Nada F. Abo El‐Magd, Mohamed El‐Mesery, Amro El‐Karef, Mamdouh M. El‐Shishtawy
Journal of Food Biochemistry.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - An exploratory, randomised, placebo-controlled, 14 day trial of the soluble guanylate cyclase stimulator praliciguat in participants with type 2 diabetes and hypertension
John P. Hanrahan, Jelena P. Seferovic, James D. Wakefield, Phebe J. Wilson, Jennifer G. Chickering, Joon Jung, Kenneth E. Carlson, Daniel P. Zimmer, Andrew L. Frelinger, Alan D. Michelson, Linda Morrow, Michael Hall, Mark G. Currie, G. Todd Milne, Albert
Diabetologia.2020; 63(4): 733. CrossRef - Advantages of Phosphodiesterase Type 5 Inhibitors in the Management of Glucose Metabolism Disorders: A Clinical and Translational Issue
Cristina Antinozzi, Paolo Sgrò, Luigi Di Luigi
International Journal of Endocrinology.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Association of endothelial dysfunction with incident prediabetes, type 2 diabetes and related traits: the KORA F4/FF4 study
Marie-Theres Huemer, Cornelia Huth, Florian Schederecker, Stefanie J Klug, Christa Meisinger, Wolfgang Koenig, Wolfgang Rathmann, Annette Peters, Barbara Thorand
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2020; 8(1): e001321. CrossRef - Embelin from Embelia ribes ameliorates oxidative stress and inflammation in high-fat diet-fed obese C57BL/6 mice
Priyanka Bansal, Uma Bhandari, Sayeed Ahmad
Pharmacognosy Magazine.2020; 16(5): 443. CrossRef - Weight change is significantly associated with risk of thyroid cancer: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Hyemi Kwon, Kyung-Do Han, Cheol-Young Park
Scientific Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes and Cancer: Cancer Should Be Screened in Routine Diabetes Assessment
Sunghwan Suh, Kwang-Won Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 733. CrossRef - Antioxidant, antihyperglycemic, and antidiabetic activity of Apis mellifera bee tea
Janielle da Silva Melo da Cunha, Tamaeh Monteiro Alfredo, Jéssica Maurino dos Santos, Valter Vieira Alves Junior, Luiza Antas Rabelo, Emerson Silva Lima, Ana Paula de Araújo Boleti, Carlos Alexandre Carollo, Edson Lucas dos Santos, Kely de Picoli Souza, M
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(6): e0197071. CrossRef - Relationship Between Circulating Netrin-1 Concentration, Impaired Fasting Glucose, and Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes
Jisook Yim, Gyuri Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Jeong-Ho Kim, Jin Won Cho, Sang-Guk Lee, Yong-ho Lee
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycyrrhizin ameliorates high fat diet-induced obesity in rats by activating NrF2 pathway
Nada F. Abo El-Magd, Mohamed El-Mesery, Amro El-Karef, Mamdouh M. El-Shishtawy
Life Sciences.2018; 193: 159. CrossRef - cGMP-dependent protein kinase I (cGKI) modulates human hepatic stellate cell activation
Andras Franko, Marketa Kovarova, Susanne Feil, Robert Feil, Robert Wagner, Martin Heni, Alfred Königsrainer, Marc Ruoß, Andreas K. Nüssler, Cora Weigert, Hans-Ulrich Häring, Stefan Z. Lutz, Andreas Peter
Metabolism.2018; 88: 22. CrossRef
- Hippocampal proteomic changes in high-fat diet-induced obese mice associated with memory decline
- Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Epidemiology to Clinical Perspectives
- Cheol Whee Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(4):252-260. Published online August 20, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.4.252
- 6,545 View
- 58 Download
- 76 Web of Science
- 69 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader With worldwide epidemic of diabetes mellitus, diabetic nephropathy which is one of the major causes of microvascular complication has become a serious concern in Korea as well as the rest of the world. In view of its significance, there is an urgent and paramount need for proper managements that could either deter or slow the progression of diabetic nephropathy. Despite advances in care, ever increasing number of patients suffering from diabetic kidney disease and from end-stage renal disease implies that the current management is not adequate in many aspects. The reasons for these inadequacies compromise lack of early diagnosis, failure to intervene with timely and aggressive manner, and lack of understanding on the kind of interventions required. Another issue equally important for the adequate care of patients with diabetic nephropathy is an understanding of past, present and future epidemiology of diabetic nephropathy which serves, especially in Korea, as a material determining standard diagnosis and treatment and a national health-policy decision.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation in diabetic kidney disease
Jiaan Huang, Fan Yang, Yan Liu, Yuehua Wang
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2024; 171: 116185. CrossRef - Association of advanced chronic kidney disease with diabetic retinopathy severity in older patients with diabetes: a retrospective cross-sectional study
Geun Woo Lee, Chul Ho Lee, Seong Gyu Kim
Journal of Yeungnam Medical Science.2023; 40(2): 146. CrossRef - Age at Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Who Underwent Kidney Transplantation: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Sun Ok Song, Eugene Han, Kang Ju Son, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(9): 3160. CrossRef - Single‐cell RNA‐seq with spatial transcriptomics to create an atlas of human diabetic kidney disease
Duo Chen, Mingwei Shao, Yi Song, Gaofei Ren, Feng Guo, Xunjie Fan, Yanyan Wang, Wei Zhang, Guijun Qin
The FASEB Journal.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Metabolomic profiling of amino acids study reveals a distinct diagnostic model for diabetic kidney disease
Jiao Wang, Chunyu Zhou, Qing Zhang, Zhangsuo Liu
Amino Acids.2023; 55(11): 1563. CrossRef - New insights into the mechanisms of diabetic kidney disease: Role of circadian rhythm and Bmal1
Zhimei Peng, Yanting Liang, Xueying Liu, Jie Shao, Nan Hu, Xinzhou Zhang
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 166: 115422. CrossRef - Physical exercise as a friend not a foe in acute kidney diseases through immune system modulation
Ana Carolina Costanti-Nascimento, Leonilia Brelaz-Abreu, Elayne Bragança-Jardim, Welbert de Oliveira Pereira, Niels Olsen Saraiva Camara, Mariane Tami Amano
Frontiers in Immunology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sodium-dependent glucose transporter 2 inhibitor alleviates renal lipid deposition and improves renal oxygenation levels in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a randomized controlled trial
Li Zhang, Tongdan Wang, Yan Kong, Haizhen Sun, Yuling Zhang, Junmei Wang, Zhida Wang, Shan Lu, Pei Yu, Saijun Zhou
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Neutrophil lymphocyte ratio: a reliable biomarker for diabetic nephropathy?
Ashutosh Singh, Anshu Kumar Jha, Bipul Chandra Kalita, Dharmendra Kumar Jha, Yash Alok
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2022; 42(3): 523. CrossRef - miR-193a as a potential mediator of WT-1/synaptopodin in the renoprotective effect of Losartan on diabetic kidney
Dan Gao, Pei Yu, Sanhui Jing, Chengcheng Yan, Dandan Ding, Yingjin Qiao, Ge Wu
Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology.2022; 100(1): 26. CrossRef - 3-Hydroxybutyrate Ameliorates the Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy
Jeeyoun Jung, Woo Yeong Park, Yun Jin Kim, Mikyung Kim, Misun Choe, Kyubok Jin, Ji Hae Seo, Eunyoung Ha
Antioxidants.2022; 11(2): 381. CrossRef - Emerging Role of Epitranscriptomics in Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications
Xinqian Geng, Zheng Li, Ying Yang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Analysis of serum circulating MicroRNAs level in Malaysian patients with gestational diabetes mellitus
Sajad Jamalpour, Shamsul Mohd Zain, Reza Vazifehmand, Zahurin Mohamed, Yuh Fen Pung, Hesam Kamyab, Siti Zawiah Omar
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Combined Single-Cell RNA-Seq and Spatial Transcriptomics Reveal an Atlas of Human Diabetic Kidney Disease
Duo Chen, Mingwei Shao, Yi Song, Gaofei Ren, Feng Guo, Xunjie Fan, Yanyan Wang, Wei Zhang, Guijun Qin
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - How to inhibit transforming growth factor beta safely in diabetic kidney disease
Yuxin Yang, Kexin Shi, Devang M. Patel, Fang Liu, Tieqiao Wu, Zhonglin Chai
Current Opinion in Nephrology & Hypertension.2021; 30(1): 115. CrossRef - Plasma miR-193a-3p can be a potential biomarker for the diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy
Yan Hong, Jidong Wang, Lai Zhang, Wenjuan Sun, Xuefang Xu, Kaiyue Zhang
Annals of Clinical Biochemistry: International Journal of Laboratory Medicine.2021; 58(2): 141. CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia and the risk of end stage renal disease in type 2 diabetes
Jae-Seung Yun, Yong-Moon Park, Kyungdo Han, Hyung-Wook Kim, Seon-Ah Cha, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Integrin β3 overexpression contributes to podocyte injury through inhibiting RhoA/YAP signaling pathway
Zhuo Li, Zhiwen Lian, Jianchao Ma, Li Zhang, Xingji Lian, Shuangxin Liu, Jianteng Xie, Zhonglin Feng, Ting Lin, Hong Zhang, Xinling Liang
Bioengineered.2021; 12(1): 1138. CrossRef - A Nonlinear Relationship Between Serum 25-Hydroxyvitamin D and Urine Albumin to Creatinine Ratio in Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study in China
Qian Liang, Haofei Hu, Han Wu, Xuan Chen, Wei Wang, Ying Le, Shufen Yang, Lijing Jia
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 2581. CrossRef - Proteinuria as a significant predictive factor for the progression of carotid artery atherosclerosis in non-albuminuric type 2 diabetes
Young-eun Kim, Minyoung Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 181: 109082. CrossRef - USP9X prevents AGEs-induced upregulation of FN and TGF-β1 through activating Nrf2-ARE pathway in rat glomerular mesangial cells
Kaipeng Huang, Xilin Zhao
Experimental Cell Research.2020; 393(2): 112100. CrossRef - D-dimer Levels in Chronic Kidney Illness: A Comprehensive and Systematic Literature Review
Sahar Vahdat, Shahrzad Shahidi
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, India Section B: Biological Sciences.2020; 90(5): 911. CrossRef - Circulating Expression Level of LncRNA Malat1 in Diabetic Kidney Disease Patients and Its Clinical Significance
Lian-ji Zhou, Da-wei Yang, Li-Na Ou, Xing-Rong Guo, Biao-liang Wu
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Impact of chronic kidney disease definition on assessment of its incidence and risk factors in patients with newly diagnosed type 1 and type 2 diabetes in the UK: A cohort study using primary care data from the United Kingdom
Antonio González-Pérez, Maria E. Saéz, David Vizcaya, Marcus Lind, Luis A. García Rodríguez
Primary Care Diabetes.2020; 14(4): 381. CrossRef Resveratrol Inhibits Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Extracellular Matrix Accumulation and Inflammation in Rat Glomerular Mesangial Cells by SphK1/S1P2/NF-κB Pathway
Wenyan Gong, Jie Li, Wenying Chen, Fuzhen Feng, Yanhui Deng
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 4495. CrossRef- Effects of dietary iron restriction on kidney mitochondria function and oxidative stress in streptozotocin-diabetic rats
Donovan J. Peña-Montes, Maribel Huerta-Cervantes, Mónica Ríos-Silva, Xóchitl Trujillo, Christian Cortés-Rojo, Miguel Huerta, Alfredo Saavedra-Molina
Mitochondrion.2020; 54: 41. CrossRef - Significance of glycated LDL in different stages of diabetic nephropathy
Khalid Siddiqui, Teena P. George, Shaik Sarfaraz Nawaz, Maram Yaslam, Ebtehal Almogbel, Khalid Al-Rubeaan
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(1): 548. CrossRef - Prognostic value of visit-to-visit systolic blood pressure variability related to diabetic kidney disease among patients with type 2 diabetes
Zhe-Bin Yu, Jian-Bing Wang, Die Li, Xue-Yu Chen, Hong-Bo Lin, Kun Chen
Journal of Hypertension.2019; 37(7): 1411. CrossRef - Epigenetics and epigenomics in diabetic kidney disease and metabolic memory
Mitsuo Kato, Rama Natarajan
Nature Reviews Nephrology.2019; 15(6): 327. CrossRef - Resveratrol inhibits high glucose-induced activation of AP-1 and NF-κB via SphK1/S1P2 pathway to attenuate mesangial cells proliferation and inflammation
Yanhui Deng, Wenyan Gong, Qiang Li, Xian Wu, Liyao Wu, Xiaoxia Zheng, Wenying Chen, Heqing Huang
Journal of Functional Foods.2019; 55: 86. CrossRef - Predictive Factors for Efficacy of AST-120 Treatment in Diabetic Nephropathy: a Prospective Single-Arm, Open-Label, Multi-Center Study
You-Cheol Hwang, Se Won Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Bong-Soo Cha, In Joo Kim, Tae Sun Park, Sei Hyun Baik, Kun Ho Yoon, Kwan Woo Lee, In Kyu Lee, Moon-Kyu Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Potential Diagnostic Hemorheological Indexes for Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes
Hoyoon Lee, Wonwhi Na, Sang Bae Lee, Chul Woo Ahn, Jun Sung Moon, Kyu Chang Won, Sehyun Shin
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing the Effect of Dipeptidyl-Peptidase 4 Inhibitors and Sulfonylureas on Albuminuria in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Prospective Open-Label Study
Po-Chung Cheng, Shang-Ren Hsu, Jeng-Fu Kuo, Yun-Chung Cheng, Yu-Hsiu Liu, Shih-Te Tu
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(10): 1715. CrossRef - Mechanisms of Adiponectin Action: Implication of Adiponectin Receptor Agonism in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Yaeni Kim, Cheol Whee Park
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2019; 20(7): 1782. CrossRef - Regulatory T cells in acute and chronic kidney diseases
Rahul Sharma, Gilbert R. Kinsey
American Journal of Physiology-Renal Physiology.2018; 314(5): F679. CrossRef - Herba Artemisiae Capillaris Extract Prevents the Development of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Nephropathy of Rat
Jianan Geng, Xiaoyan Yu, Chunyu Liu, Chengbo Sun, Menghuan Guo, Zhen Li, Yingli Jin, Yinggang Zou, Jinghua Yu
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Overview of the burden of illness and the role of once-weekly glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist therapy in type 2 diabetes
Deborah Hinnen
Journal of the American Association of Nurse Practitioners.2018; 30(1): S4. CrossRef - Previous Exercise Training Reduces Markers of Renal Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Female Rats
Liliany Souza de Brito Amaral, Cláudia Silva Souza, Rildo Aparecido Volpini, Maria Heloisa Massola Shimizu, Ana Carolina de Bragança, Daniele Canale, Antonio Carlos Seguro, Terezila Machado Coimbra, Amélia Cristina Mendes de Magalhães, Telma de Jesus Soar
Journal of Diabetes Research.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Critical Shear Stress is Associated with Diabetic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Seung Min Chung, Jung Hyun Oh, Jun Sung Moon, Yu Kyung Kim, Ji Sung Yoon, Kyu Chang Won, Hyoung Woo Lee
Scientific Reports.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Losartan Alleviates Renal Fibrosis and Inhibits Endothelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Under High-Fat Diet-Induced Hyperglycemia
Yufeng Yao, Yong Li, Xiaofei Zeng, Zheng Ye, Xia Li, Lu Zhang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between poor psychosocial conditions and diabetic nephropathy in Japanese type 2 diabetes patients: A cross‐sectional study
Hiroyo Ninomiya, Naoto Katakami, Taka‐aki Matsuoka, Mitsuyoshi Takahara, Hitoshi Nishizawa, Norikazu Maeda, Michio Otsuki, Akihisa Imagawa, Hiroyasu Iso, Tetsuya Ohira, Iichiro Shimomura
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2018; 9(1): 162. CrossRef - Urinary Microvesicle-Bound Uromodulin: A Potential Molecular Biomarker in Diabetic Kidney Disease
Neng-jun Lou, Yi-hong Ni, Hong-ying Jia, Jing-ti Deng, Lu Jiang, Feng-jie Zheng, Ai-li Sun
Journal of Diabetes Research.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Renoprotective effect of fucoidan from Acaudina molpadioides in streptozotocin/high fat diet-induced type 2 diabetic mice
Shiwei Hu, Jinhui Wang, Jingfeng Wang, Shijie Li, Wei Jiang, Yu Liu
Journal of Functional Foods.2017; 31: 123. CrossRef - Analysis and comparison of the cost-effectiveness of statins according to the baseline low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level in Korea
Y. J. Jeong, H. Kim, S. J. Baik, T. M. Kim, S. J. Yang, S.-H. Lee, J.-H. Cho, H. Lee, H. W. Yim, I. Y. Choi, K.-H. Yoon, H.-S. Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2017; 42(3): 292. CrossRef - Visualization of kidney fibrosis in diabetic nephropathy by long diffusion tensor imaging MRI with spin-echo sequence
Jun-Ya Kaimori, Yoshitaka Isaka, Masaki Hatanaka, Satoko Yamamoto, Naotsugu Ichimaru, Akihiko Fujikawa, Hiroshi Shibata, Akira Fujimori, Sosuke Miyoshi, Takashi Yokawa, Kagayaki Kuroda, Toshiki Moriyama, Hiromi Rakugi, Shiro Takahara
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Rutin suppresses high glucose-induced ACTA2 and p38 protein expression in diabetic nephropathy
Chun-Shan Han, Kai Liu, Ning Zhang, Shi-Wen Li, Hai-Cheng Gao
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2017; 14(1): 181. CrossRef - Emodin self-emulsifying platform ameliorates the expression of FN, ICAM-1 and TGF-β1 in AGEs-induced glomerular mesangial cells by promoting absorption
Jiani Huang, Wenyan Gong, Zhiquan Chen, Junying Huang, Qiuhong Chen, Heqing Huang, Chunshun Zhao
European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences.2017; 99: 128. CrossRef - New therapeutic agents in diabetic nephropathy
Yaeni Kim, Cheol Whee Park
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(1): 11. CrossRef - Urine clusterin/apolipoprotein J is linked to tubular damage and renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Sang Soo Kim, Sang Heon Song, Jong Ho Kim, Yun Kyung Jeon, Bo Hyun Kim, Min‐Cheol Kang, Sung Wan Chun, Soo Hyun Hong, Michelle Chung, Yong Ki Kim, In Joo Kim, Young‐Bum Kim
Clinical Endocrinology.2017; 87(2): 156. CrossRef - Treatment of diabetic kidney disease: current and future targets
Mi-Kyung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(4): 622. CrossRef - Sphingosine kinase 1 mediates AGEs-induced fibronectin upregulation in diabetic nephropathy
Cheng Chen, Wenyan Gong, Changzheng Li, Fengxiao Xiong, Shaogui Wang, Junying Huang, Yu Wang, Zhiquan Chen, Qiuhong Chen, Peiqing Liu, Tian Lan, Heqing Huang
Oncotarget.2017; 8(45): 78660. CrossRef - Comparison between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin in Renal Function Decline among Patients with Diabetes
Eugene Han, Gyuri Kim, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Beom Seok Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(2): 274. CrossRef - Glycemic Management of Patients Undergoing Dialysis
Mi-Kyung Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2016; 17(3): 164. CrossRef - Probucol in Albuminuric Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients on Renin–Angiotensin System Blockade
Sang-Man Jin, Kyung Ah Han, Jae Myung Yu, Tae Seo Sohn, Sung Hee Choi, Choon Hee Chung, Ie Byung Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Sei Hyun Baik, Tae Sun Park, In-Kyu Lee, Seung-Hyun Ko, You-Cheol Hwang, Bong Soo Cha, Hyoung Woo Lee, Moon-Suk Nam, Moon-Kyu Lee
Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology.2016; 36(10): 2108. CrossRef - MicroRNA-27a promotes renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis via suppressing PPARγ pathway in diabetic nephropathy
Xiaoyan Hou, Jianwei Tian, Jian Geng, Xiao Li, Xun Tang, Jun Zhang, Xiaoyan Bai
Oncotarget.2016; 7(30): 47760. CrossRef - Lipoprotein(a) predicts a new onset of chronic kidney disease in people with Type 2 diabetes mellitus
J.‐S. Yun, Y.‐B. Ahn, K.‐H. Song, K.‐D. Yoo, Y.‐M. Park, H.‐W. Kim, S.‐H. Ko
Diabetic Medicine.2016; 33(5): 639. CrossRef - Metabolic biomarkers for chronic kidney disease
Marc Breit, Klaus M. Weinberger
Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics.2016; 589: 62. CrossRef - Effect of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitor, Dapagliflozin, on Renal Renin-Angiotensin System in an Animal Model of Type 2 Diabetes
Seok Joon Shin, Sungjin Chung, Soo Jung Kim, Eun-Mi Lee, Young-Hye Yoo, Ji-Won Kim, Yu-Bae Ahn, Eun-Sook Kim, Sung-Dae Moon, Myung-Jun Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kwang-Hyun Baek
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(11): e0165703. CrossRef - Renoprotective Effect of Gemigliptin, a Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitor, in Streptozotocin-Induced Type 1 Diabetic Mice
Gwon-Soo Jung, Jae-Han Jeon, Mi Sun Choe, Sung-Woo Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Mi-Kyung Kim, Keun-Gyu Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(3): 211. CrossRef - Beneficial effects of previous exercise training on renal changes in streptozotocin-induced diabetic female rats
Liliany S de Brito Amaral, Fernanda A Silva, Vicente B Correia, Clara EF Andrade, Bárbara A Dutra, Márcio V Oliveira, Amélia CM de Magalhães, Rildo A Volpini, Antonio C Seguro, Terezila M Coimbra, Telma de J Soares
Experimental Biology and Medicine.2016; 241(4): 437. CrossRef - Adenosine monophosphate–activated protein kinase in diabetic nephropathy
Yaeni Kim, Cheol Whee Park
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2016; 35(2): 69. CrossRef - Estimated Glucose Disposal Rate (eGDR) – A Marker for the Assessment of Insulin Resistance in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Mihaela L. Bîcu, Daniel Bîcu, Sigina Gârgavu, Magdalena Sandu, Mihaela I. Vladu, Diana Clenciu, Eugen Moţa, Maria Moţa
Romanian Journal of Diabetes Nutrition and Metabolic Diseases.2016; 23(2): 177. CrossRef - Polydatin attenuates AGEs-induced upregulation of fibronectin and ICAM-1 in rat glomerular mesangial cells and db/db diabetic mice kidneys by inhibiting the activation of the SphK1-S1P signaling pathway
Cheng Chen, Kaipeng Huang, Jie Hao, Junying Huang, Zhiying Yang, Fengxiao Xiong, Peiqing Liu, Heqing Huang
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2016; 427: 45. CrossRef - Glycated albumin and the risk of micro- and macrovascular complications in subjects with Type 1 Diabetes
Hye-jin Yoon, Yong-ho Lee, So Ra Kim, Tyler Hyungtaek Rim, Eun Young Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Byung-Wan Lee
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Tripterygium Glycosides Tablet Ameliorates Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis via the Toll-Like Receptor 4/Nuclear Factor Kappa B Signaling Pathway in High-Fat Diet Fed and Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
Ze-jun Ma, Xiao-na Zhang, Li Li, Wei Yang, Shan-shan Wang, Xin Guo, Pei Sun, Li-ming Chen
Journal of Diabetes Research.2015; 2015: 1. CrossRef - The association between abnormal heart rate variability and new onset of chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A ten-year follow-up study
Jae-Seung Yun, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Dong Yoo, Hyung-Wook Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2015; 108(1): 31. CrossRef - Finerenone: third-generation mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist for the treatment of heart failure and diabetic kidney disease
Licette CY Liu, Elise Schutte, Ron T Gansevoort, Peter van der Meer, Adriaan A Voors
Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs.2015; 24(8): 1123. CrossRef - Effects of pentoxifylline on proteinuria and glucose control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a prospective randomized double-blind multicenter study
Seung Jin Han, Hae Jin Kim, Dae Jung Kim, Seung Soo Sheen, Choon Hee Chung, Chul Woo Ahn, Se Hwa Kim, Yong-Wook Cho, Seok Won Park, Soo-Kyung Kim, Chul Sik Kim, Kyung Wook Kim, Kwan Woo Lee
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Proteomic Profile in Glomeruli of Type-2 Diabetic KKAy Mice using 2-Dimensional Differential Gel Electrophoresis
Lining Wang
Medical Science Monitor.2014; 20: 2705. CrossRef
- N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation in diabetic kidney disease
- Prevalence and Determinants of Diabetic Nephropathy in Korea: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Jae Hee Ahn, Ji Hee Yu, Seung-Hyun Ko, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Dae Jung Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim, Chul Sik Kim, Kee-Ho Song, Jong Chul Won, Soo Lim, Sung Hee Choi, Kyungdo Han, Bong-Yun Cha, Nan Hee Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2014;38(2):109-119. Published online April 18, 2014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2014.38.2.109
- 5,355 View
- 99 Download
- 58 Web of Science
- 58 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Diabetic nephropathy is a leading cause of end stage renal disease and is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular mortality. It manifests as albuminuria or impaired glomerular filtration rate (GFR), and the prevalence of diabetic nephropathy varies with ethnicity. The prevalence of diabetic nephropathy and its determinants in Korean adults have not previously been studied at the national level. This cross-sectional study was undertaken to ascertain the prevalence and determinants of albuminuria and chronic kidney disease (CKD) in Korean patients with diabetes.
Methods The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES) V, conducted in 2011, was used to define albuminuria (
n =4,652), and the dataset of KNHANES IV-V (2008-2011) was used to define CKD (n =21,521). Selected samples were weighted to represent the entire civilian population in Korea. Albuminuria was defined as a spot urine albumin/creatinine ratio >30 mg/g. CKD was defined as a GFR <60 mL/min/1.73 m2.Results Among subjects with diabetes, 26.7% had albuminuria, and 8.6% had CKD. Diabetes was associated with an approximate 2.5-fold increased risk of albuminuria, with virtually no difference between new-onset and previously diagnosed diabetes. Only systolic blood pressure was significantly associated with albuminuria, and old age, high serum triglyceride levels, and previous cardiovascular disease (CVD) were related with CKD in subjects with diabetes.
Conclusion Korean subjects with diabetes had a higher prevalence of albuminuria and CKD than those without diabetes. Blood pressure was associated with albuminuria, and age, triglyceride level, and previous CVD were independent determinants of CKD in subjects with diabetes.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Associations between dietary patterns and renal impairment in individuals with diabetes: a cross‐sectional study
Ziling Ding, Xingzhe Wu, Chao Liu, Ruixue Ying, Yi Zhang, Shiqi Zhang, Qiu Zhang, Honglin Hu, Fang Dai
Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics.2024; 37(1): 193. CrossRef - Determinants of diabetic nephropathy among adult diabetic patients on follow-up at public hospitals in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia: A case-control study
Diriba Etana Tola, Zenebu Begna Bayissa, Tamene Abera Desissa, Lencho Kajela Solbana, Azeb Haile Tesfaye, Bikila Fufa Eba
SAGE Open Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Kidney Health Plan 2033 in Korea: bridging the gap between the present and the future
Do Hyoung Kim, Young Youl Hyun, Jin Joo Cha, Sua Lee, Hyun Kyung Lee, Jong Wook Choi, Su-Hyun Kim, Sang Youb Han, Cheol Whee Park, Eun Young Lee, Dae Ryong Cha, Sung Gyun Kim, Chun Soo Lim, Sun-Hee Park
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 43(1): 8. CrossRef - Risk Factors of Microalbuminuria among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A Cross-Sectional Study Based on 2019–2020 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey Data
Eun Sook Bae, Jung Yi Hur, Hyung Soon Jang, Jeong Suk Kim, Hye Seung Kang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2023; 20(5): 4169. CrossRef - CORRELATION OF VASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL FUNCTION AND INFLAMMATORY FACTORS WITH RENAL FUNCTION IN PATIENTS WITH DIABETIC NEPHROPATHY
A. Y. Mammadzada, Sh. G. Ismayilova, Sh. S. Ibrahimova, N. I. Huseynova, L. A. Huseyn
World of Medicine and Biology.2023; 19(85): 129. CrossRef - Synopsis of the Korean Society of Nephrology 2023 Practical Recommendations for the Management of Diabetic Kidney Disease
Sungjin Chung
The Korean Journal of Medicine.2023; 98(6): 270. CrossRef - 3-Hydroxybutyrate Ameliorates the Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy
Jeeyoun Jung, Woo Yeong Park, Yun Jin Kim, Mikyung Kim, Misun Choe, Kyubok Jin, Ji Hae Seo, Eunyoung Ha
Antioxidants.2022; 11(2): 381. CrossRef - Development and Validation of a Model That Predicts the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jing Yang, Sheng Jiang
International Journal of General Medicine.2022; Volume 15: 5089. CrossRef - Renoprotective Mechanism of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors: Focusing on Renal Hemodynamics
Nam Hoon Kim, Nan Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 543. CrossRef - Development and assessment of diabetic nephropathy prediction model using hub genes identified by weighted correlation network analysis
Xuelian Zhang, Yao Wang, Zhaojun Yang, Xiaoping Chen, Jinping Zhang, Xin Wang, Xian Jin, Lili Wu, Xiaoyan Xing, Wenying Yang, Bo Zhang
Aging.2022; 14(19): 8095. CrossRef - Neutrophil–lymphocyte ratio as an inflammatory biomarker of diabetic nephropathy among type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A comparative cross-sectional study
Mesfin Zewude Gurmu, Solomon Genet, Solomon Tebeje Gizaw, Teka Obsa Feyisa, Natesan Gnanasekaran
SAGE Open Medicine.2022; 10: 205031212211402. CrossRef - Did Sejong the Great have ankylosing spondylitis? The oldest documented case of ankylosing spondylitis
JiHwan Lee
International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases.2021; 24(2): 203. CrossRef - Protective effects of klotho on palmitate-induced podocyte injury in diabetic nephropathy
Jeong Suk Kang, Seung Seob Son, Ji-Hye Lee, Seong Woo Lee, Ah Reum Jeong, Eun Soo Lee, Seung-Kuy Cha, Choon Hee Chung, Eun Young Lee, Partha Mukhopadhyay
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(4): e0250666. CrossRef - Nomogram for the prediction of diabetic nephropathy risk among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on a questionnaire and biochemical indicators: a retrospective study
Yuhong Hu, Rong Shi, Ruohui Mo, Fan Hu
Aging.2020; 12(11): 10317. CrossRef - Differential Urinary Proteome Analysis for Predicting Prognosis in Type 2 Diabetes Patients with and without Renal Dysfunction
Hee-Sung Ahn, Jong Ho Kim, Hwangkyo Jeong, Jiyoung Yu, Jeonghun Yeom, Sang Heon Song, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, Kyunggon Kim
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(12): 4236. CrossRef - Urine E-cadherin: A Marker for Early Detection of Kidney Injury in Diabetic Patients
Michael Koziolek, Gerhard A. Mueller, Gry H. Dihazi, Klaus Jung, Constanze Altubar, Manuel Wallbach, Ivana Markovic, Dirk Raddatz, Olaf Jahn, Hülya Karaköse, Christof Lenz, Henning Urlaub, Abdelhi Dihazi, Abdellatif El El Meziane, Hassan Dihazi
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(3): 639. CrossRef - Study of serum pentraxin 3 level in patients with diabetic nephropathy
Alaaeldin Abdelsalam Dawood, Mai Ashraf Kamel, Thoria Ahmed Omar, Ahmed Ahmed Mohammed Agaba
The Egyptian Journal of Internal Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Limitations of Deep Learning Attention Mechanisms in Clinical Research: Empirical Case Study Based on the Korean Diabetic Disease Setting
Junetae Kim, Sangwon Lee, Eugene Hwang, Kwang Sun Ryu, Hanseok Jeong, Jae Wook Lee, Yul Hwangbo, Kui Son Choi, Hyo Soung Cha
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2020; 22(12): e18418. CrossRef - Long-term effects of various types of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase inhibitors on changes in glomerular filtration rate in Korea
Seo Yeon Baik, Hyunah Kim, So Jung Yang, Tong Min Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Kun-Ho Yoon, Hun-Sung Kim
Frontiers of Medicine.2019; 13(6): 713. CrossRef - Plasma endoglin in Type2 diabetic patients with nephropathy
Ahmed S. Doghish, Atef A. Bassyouni, Mohamed H. Mahfouz, Heba G. Abd El-Aziz, Rania Y. Zakaria
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2019; 13(1): 764. CrossRef - Cigarette smoking as a risk factor for diabetic nephropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies
Dan Liao, Liang Ma, Jing Liu, Ping Fu, Noël C. Barengo
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(2): e0210213. CrossRef - Risk factors for diabetic nephropathy complications in community patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Shanghai: Logistic regression and classification tree model analysis
Jieqiong Lou, Limei Jing, Hui Yang, Fei Qin, Wen Long, Rong Shi
The International Journal of Health Planning and Management.2019; 34(3): 1013. CrossRef - Predictive Factors for Efficacy of AST-120 Treatment in Diabetic Nephropathy: a Prospective Single-Arm, Open-Label, Multi-Center Study
You-Cheol Hwang, Se Won Kim, Kyu Yeon Hur, Bong-Soo Cha, In Joo Kim, Tae Sun Park, Sei Hyun Baik, Kun Ho Yoon, Kwan Woo Lee, In Kyu Lee, Moon-Kyu Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycated Albumin Is a More Useful Glycation Index than HbA1c for Reflecting Renal Tubulopathy in Subjects with Early Diabetic Kidney Disease
Ji Hye Huh, Minyoung Lee, So Young Park, Jae Hyeon Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(3): 215. CrossRef - Meta‑analysis of the benefit of sitagliptin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes complicated with incipient nephropathy
Wei Liu, Jiangyi Yu, Qianhua Yan, Lijuan Wang, Nan Li, Wei Xiong
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - MicroRNA‐326‐3p ameliorates high glucose and ox‐LDL‐IC‐ induced fibrotic injury in renal mesangial cells by targeting FcγRIII
Yiting Wang, Rui Zhang, Junlin Zhang, Fang Liu
Nephrology.2018; 23(11): 1031. CrossRef - The Global Epidemiology of Diabetes and Kidney Disease
Digsu N. Koye, Dianna J. Magliano, Robert G. Nelson, Meda E. Pavkov
Advances in Chronic Kidney Disease.2018; 25(2): 121. CrossRef - Evaluation of the association between the number of natural teeth and anemia among Korean adults using nationally representative data
Kyungdo Han, Jun‐Beom Park
Journal of Periodontology.2018; 89(10): 1184. CrossRef - Correlation of vascular endothelial function and coagulation factors with renal function and inflammatory factors in patients with diabetic nephropathy
Jie Sun, Caiyan Liu
Experimental and Therapeutic Medicine.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Cigarette smoking and risk of albuminuria in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies
Haili Xu, Jinliu Suo, Jing Lian
International Urology and Nephrology.2018; 50(5): 911. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea, 2016: An Appraisal of Current Status
Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyuk Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Kyu Chang Won, Dae Jung Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(5): 415. CrossRef - Association between the number of natural teeth and diabetic retinopathy among type 2 diabetes mellitus
Su Jeong Song, Kyungdo Han, Seong-su Lee, Jun-Beom Park
Medicine.2017; 96(47): e8694. CrossRef - Arterial Stiffness Is More Associated with Albuminuria than Decreased Glomerular Filtration Rate in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: The REBOUND Study
Jong Ho Kim, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, Bo Hyun Kim, Ja Young Park, Chang Won Lee, Ji Hye Suk, Sun Hae Shin, Sung Pyo Son, Min Chul Kim, Jun Hyeob Ahn, Kwang Jae Lee, Min Jung Kwon, Soon Hee Lee, Jeong Hyun Park
Journal of Diabetes Research.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Determinants of diabetic nephropathy in Ayder Referral Hospital, Northern Ethiopia: A case-control study
Solomon Hintsa, Lamessa Dube, Mebrahtu Abay, Teklit Angesom, Abdulhalik Workicho, Petter Bjornstad
PLOS ONE.2017; 12(4): e0173566. CrossRef - Comparison between Atorvastatin and Rosuvastatin in Renal Function Decline among Patients with Diabetes
Eugene Han, Gyuri Kim, Ji-Yeon Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Beom Seok Kim, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(2): 274. CrossRef - Association between underweight and tooth loss among Korean adults
In-Seok Song, Kyungdo Han, Jae-Jun Ryu, Jun-Beom Park
Scientific Reports.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Variability in glycated albumin levels predicts the progression of diabetic nephropathy
Su Bin Park, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim, Yoon Jeong Nam, Kang Hee Ahn, Jong Ho Kim, Yun Kyung Jeon, Bo Hyun Kim, Sang Heon Song, Ihm Soo Kwak, Eun Kyung Lee, Yong Ki Kim
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(6): 1041. CrossRef - Low serum bilirubin level predicts the development of chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Kang Hee Ahn, Sang Soo Kim, Won Jin Kim, Jong Ho Kim, Yun Jeong Nam, Su Bin Park, Yun Kyung Jeon, Bo Hyun Kim, In Joo Kim, Yong Ki Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(5): 875. CrossRef - Periodontitis is associated with diabetic retinopathy in non-obese adults
Su Jeong Song, Seong-su Lee, Kyungdo Han, Jun-Beom Park
Endocrine.2017; 56(1): 82. CrossRef - Baseline Cardiovascular Characteristics of Adult Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease from the KoreaN Cohort Study for Outcomes in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease (KNOW-CKD)
Hyoungnae Kim, Tae-Hyun Yoo, Kyu Hun Choi, Kook-Hwan Oh, Joongyub Lee, Soo Wan Kim, Tae Hee Kim, Suah Sung, Seung Hyeok Han
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2017; 32(2): 231. CrossRef - Addition of nonalbumin proteinuria to albuminuria improves prediction of type 2 diabetic nephropathy progression
Jong Ho Kim, Seo Young Oh, Eun Heui Kim, Min Jin Lee, Yun Kyung Jeon, Bo Hyun Kim, Jin Mi Kim, Yong Ki Kim, Sang Soo Kim, In Joo Kim
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Smoking and the risk of diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis of observational studies
Ning Jiang, Feng Huang, Xiurong Zhang
Oncotarget.2017; 8(54): 93209. CrossRef - Treatment of diabetic kidney disease: current and future targets
Mi-Kyung Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(4): 622. CrossRef - Analysis and comparison of the cost-effectiveness of statins according to the baseline low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level in Korea
Y. J. Jeong, H. Kim, S. J. Baik, T. M. Kim, S. J. Yang, S.-H. Lee, J.-H. Cho, H. Lee, H. W. Yim, I. Y. Choi, K.-H. Yoon, H.-S. Kim
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2017; 42(3): 292. CrossRef - Mechanistic Insight and Management of Diabetic Nephropathy: Recent Progress and Future Perspective
Rui Xue, Dingkun Gui, Liyang Zheng, Ruonan Zhai, Feng Wang, Niansong Wang
Journal of Diabetes Research.2017; 2017: 1. CrossRef - Nonalbuminuric Renal Insufficiency: Can It Be a Novel Category of Diabetic Nephropathy?
Masami Tanaka, Hiroshi Itoh
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(4): 533. CrossRef - Current Challenges in Diabetic Nephropathy: Early Diagnosis and Ways to Improve Outcomes
Sang Soo Kim, Jong Ho Kim, In Joo Kim
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(2): 245. CrossRef - Functional mechanisms for diabetic nephropathy-associated genetic variants
Chengxin Gong, Yonghu Xu, Yongfang Fan, Xingzi Liu, Chaopeng Xiong, Luling He, Changle Liu, Shenqiang Rao, Wen Xiao, Lu Ding, Lan Tang, Fangfang Hu, Mengqi Xiong, Mei Yang, Shangdong Liang, Hong Xu
Genes & Genomics.2016; 38(7): 595. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Intention to Receive Examination of Diabetes Complications
Yi-Lin Hsieh, Fang-Hsin Lee, Chien-Liang Chen, Ming-Fong Chang, Pei-Hsuan Han
Asian Nursing Research.2016; 10(4): 289. CrossRef - Associations between the number of natural teeth and renal dysfunction
Hye Min Choi, Kyungdo Han, Yong Gyu Park, Jun-Beom Park
Medicine.2016; 95(34): e4681. CrossRef - Decreased plasma α-Klotho predict progression of nephropathy with type 2 diabetic patients
Sang Soo Kim, Sang Heon Song, In Joo Kim, Eun Young Lee, Su Mi Lee, Choon Hee Chung, Ihm Soo Kwak, Eun Kyung Lee, Yong Ki Kim
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2016; 30(5): 887. CrossRef - The Association Between Smoking Tobacco After a Diagnosis of Diabetes and the Prevalence of Diabetic Nephropathy in the Korean Male Population
Hyungseon Yeom, Jung Hyun Lee, Hyeon Chang Kim, Il Suh
Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health.2016; 49(2): 108. CrossRef - Effects of Small Dense LDL in Diabetic Nephropathy in Females with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Seongyul Ryu, Youngwoo Kim, Mee Kyoung Kim, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki-Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Kyung-Jin Yun
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2016; 5(1): 11. CrossRef - Translational genomics for human diseases: toward a new era of precision medicine
Yoon Shin Cho, Ki Wha Chung, Nam-Soo Kim
Genes & Genomics.2016; 38(7): 573. CrossRef - Lipoprotein(a) predicts a new onset of chronic kidney disease in people with Type 2 diabetes mellitus
J.‐S. Yun, Y.‐B. Ahn, K.‐H. Song, K.‐D. Yoo, Y.‐M. Park, H.‐W. Kim, S.‐H. Ko
Diabetic Medicine.2016; 33(5): 639. CrossRef - The association between abnormal heart rate variability and new onset of chronic kidney disease in patients with type 2 diabetes: A ten-year follow-up study
Jae-Seung Yun, Yu-Bae Ahn, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Dong Yoo, Hyung-Wook Kim, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2015; 108(1): 31. CrossRef - Central obesity is an independent risk factor for microalbuminuria in both the general Korean women and nondiabetic nonhypertensive subpopulation: Association of microalbuminuria and metabolic syndrome from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examinat
John Hoon Rim, Yong-ho Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Sang-Guk Lee, Jeong-Ho Kim
Clinica Chimica Acta.2015; 448: 74. CrossRef - Diabetic Kidney Disease: From Epidemiology to Clinical Perspectives
Cheol Whee Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2014; 38(4): 252. CrossRef
- Associations between dietary patterns and renal impairment in individuals with diabetes: a cross‐sectional study

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





