
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Complications
- Peripheral Neuropathy Phenotyping in Rat Models of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Evaluating Uptake of the Neurodiab Guidelines and Identifying Future Directions
- Md Jakir Hossain, Michael D. Kendig, Meg E. Letton, Margaret J. Morris, Ria Arnold
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(2):198-221. Published online March 24, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0347
- 5,220 View
- 225 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) affects over half of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients, with an urgent need for effective pharmacotherapies. While many rat and mouse models of T2DM exist, the phenotyping of DPN has been challenging with inconsistencies across laboratories. To better characterize DPN in rodents, a consensus guideline was published in 2014 to accelerate the translation of preclinical findings. Here we review DPN phenotyping in rat models of T2DM against the ‘Neurodiab’ criteria to identify uptake of the guidelines and discuss how DPN phenotypes differ between models and according to diabetes duration and sex. A search of PubMed, Scopus and Web of Science databases identified 125 studies, categorised as either diet and/or chemically induced models or transgenic/spontaneous models of T2DM. The use of diet and chemically induced T2DM models has exceeded that of transgenic models in recent years, and the introduction of the Neurodiab guidelines has not appreciably increased the number of studies assessing all key DPN endpoints. Combined high-fat diet and low dose streptozotocin rat models are the most frequently used and well characterised. Overall, we recommend adherence to Neurodiab guidelines for creating better animal models of DPN to accelerate translation and drug development.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- SIRT3 alleviates painful diabetic neuropathy by mediating the FoxO3a‐PINK1‐Parkin signaling pathway to activate mitophagy
Jing Yang, Zhuoying Yu, Ye Jiang, Zixian Zhang, Yue Tian, Jie Cai, Min Wei, Yanhan Lyu, Dongsheng Yang, Shixiong Shen, Guo‐Gang Xing, Min Li
CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Compound Qiying Granules alleviates diabetic peripheral neuropathy by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis
Yan Hu, Chen Chen, Zhengting Liang, Tao Liu, Xiaoling Hu, Guanying Wang, Jinxia Hu, Xiaolin Xie, Zhiyan Liu
Molecular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - HCV affects KATP channels through GnT-IVa-mediated N-glycosylation of GLUT2 on the surface of pancreatic β-cells leading to impaired insulin secretion
Ben Niu, Lijing Ma, Lixuan Yao, Yating Zhang, Heng Su
Endocrine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Multimodal Comparison of Diabetic Neuropathy in Aged Streptozotocin-Treated Sprague–Dawley and Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats
Annalisa Canta, Valentina A. Carozzi, Alessia Chiorazzi, Cristina Meregalli, Norberto Oggioni, Virginia Rodriguez-Menendez, Barbara Sala, Roberto Cosimo Melcangi, Silvia Giatti, Raffaella Lombardi, Roberto Bianchi, Paola Marmiroli, Guido Cavaletti
Biomedicines.2022; 11(1): 20. CrossRef
- SIRT3 alleviates painful diabetic neuropathy by mediating the FoxO3a‐PINK1‐Parkin signaling pathway to activate mitophagy
- Complications
- Influence of Glucose Fluctuation on Peripheral Nerve Damage in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Yu Ji Kim, Na Young Lee, Kyung Ae Lee, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):117-128. Published online September 9, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0275
- 5,229 View
- 179 Download
- 4 Web of Science
- 4 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
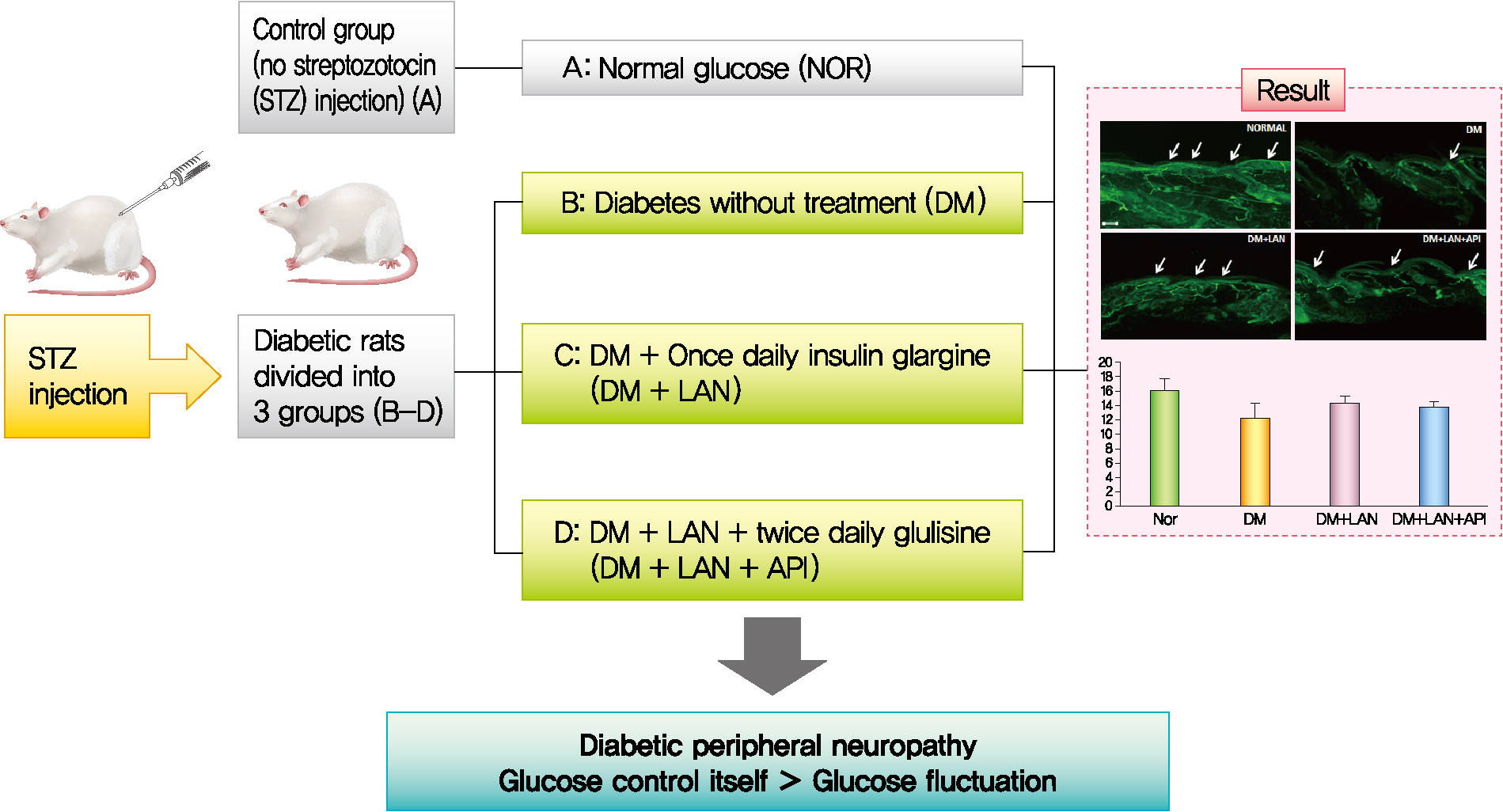
- Background
It is unclear whether glycemic variability (GV) is a risk factor for diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN), and whether control of GV is beneficial for DPN. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of GV on peripheral nerve damage by inducing glucose fluctuation in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats.
Methods
Rats were divided into four groups: normal (normal glucose group [NOR]), diabetes without treatment (sustained severe hyperglycemia group; diabetes mellitus [DM]), diabetes+once daily insulin glargine (stable hyperglycemia group; DM+LAN), and diabetes+once daily insulin glargine with twice daily insulin glulisine (unstable glucose fluctuation group; DM+Lantus [LAN]+Apidra [API]). We measured anti-oxidant enzyme levels and behavioral responses against tactile, thermal, and pressure stimuli in the plasma of rats. We also performed a quantitative comparison of cutaneous and sciatic nerves according to glucose fluctuation.
Results
At week 24, intraepidermal nerve fiber density was less reduced in the insulin-administered groups compared to the DM group (P<0.05); however, a significant difference was not observed between the DM+LAN and DM+LAN+API groups irrespective of glucose fluctuation (P>0.05; 16.2±1.6, 12.4±2.0, 14.3±0.9, and 13.9±0.6 for NOR, DM, DM+LAN, and DM+LAN+API, respectively). The DM group exhibited significantly decreased glutathione levels compared to the insulin-administered groups (2.64±0.10 μmol/mL, DM+LAN; 1.93±0.0 μmol/mL, DM+LAN+API vs. 1.25±0.04 μmol/mL, DM; P<0.05).
Conclusion
Our study suggests that glucose control itself is more important than glucose fluctuation in the prevention of peripheral nerve damage, and intra-day glucose fluctuation has a limited effect on the progression of peripheral neuropathy in rats with diabetes. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Glucose Fluctuation Inhibits Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Hippocampal Tissues and Exacerbates Cognitive Impairment in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
Haiyan Chi, Yujing Sun, Peng Lin, Junyu Zhou, Jinbiao Zhang, Yachao Yang, Yun Qiao, Deshan Liu, Eusebio Chiefari
Journal of Diabetes Research.2024; 2024: 1. CrossRef - Artesunate Inhibits Apoptosis and Promotes Survival in Schwann Cells via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR Axis in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Xin Zhang, Zhifang Liang, Ying Zhou, Fang Wang, Shan Wei, Bing Tan, Yujie Guo
Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin.2023; 46(6): 764. CrossRef - The Potential of Glucose Treatment to Reduce Reactive Oxygen Species Production and Apoptosis of Inflamed Neural Cells In Vitro
Juin-Hong Cherng, Shu-Jen Chang, Hsin-Da Tsai, Chung-Fang Chun, Gang-Yi Fan, Kenneth Dean Reeves, King Hei Stanley Lam, Yung-Tsan Wu
Biomedicines.2023; 11(7): 1837. CrossRef - Relationship between acute glucose variability and cognitive decline in type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Haiyan Chi, Min Song, Jinbiao Zhang, Junyu Zhou, Deshan Liu, Victor Manuel Mendoza-Nuñez
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(9): e0289782. CrossRef
- Glucose Fluctuation Inhibits Nrf2 Signaling Pathway in Hippocampal Tissues and Exacerbates Cognitive Impairment in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Drug/Regimen
- Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats
- Sun Hee Kim, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):842-853. Published online May 28, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0190
- 6,171 View
- 177 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
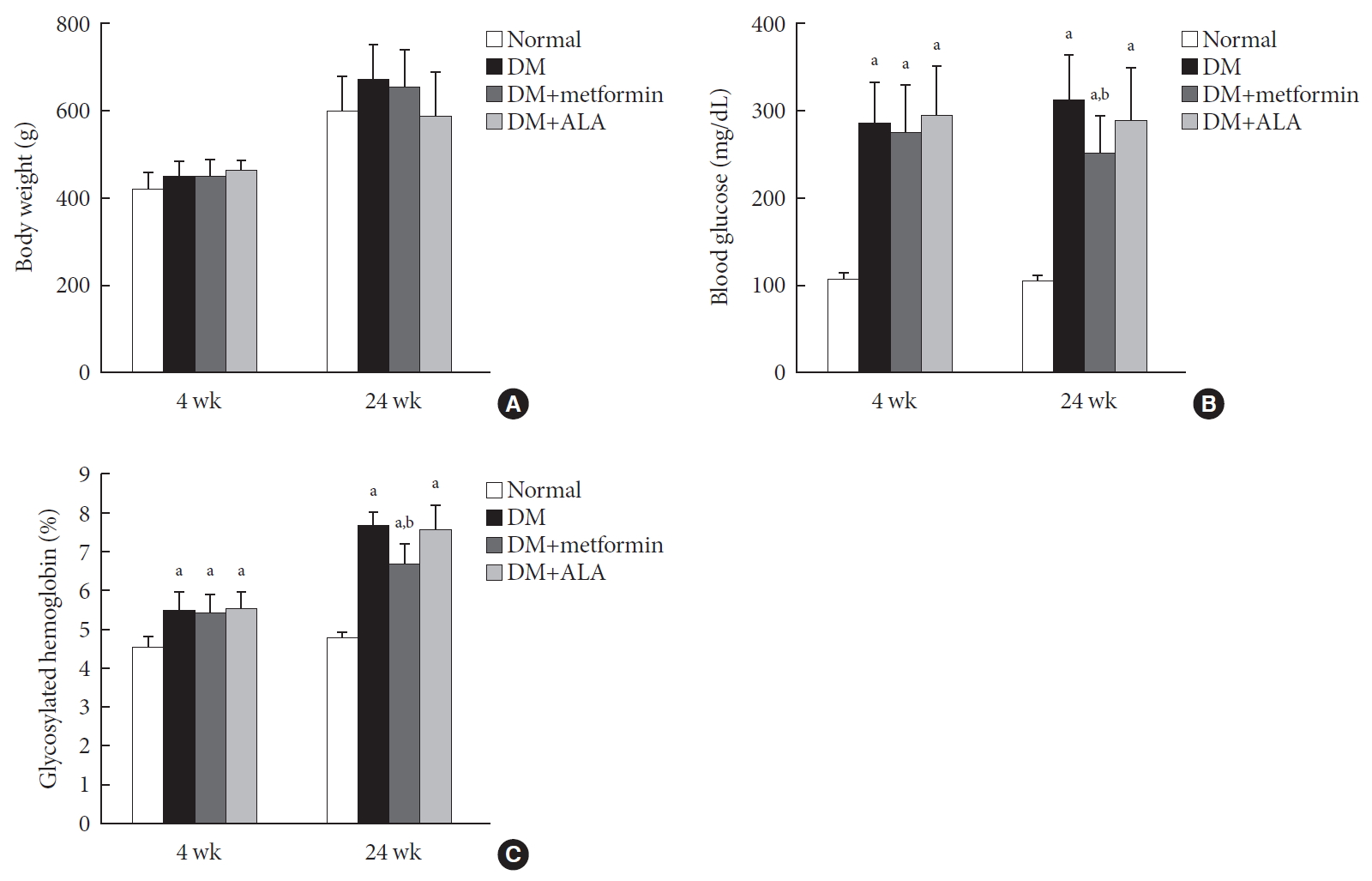
ePub Background Metformin is widely marketed medication for the treatment of diabetes, but its pharmacological effect on diabetic peripheral neuropathy remains unclear. In this study, the effect of metformin on peripheral nerves in diabetic rats was investigated using diverse neuronal parameters of nerve fibers.
Methods Rats were assigned to one of four groups (
n =7 to 10 per group): normal, diabetes mellitus (DM), DM+metformin (100 mg/kg), and DM+alpha lipoic acid (ALA, 100 mg/kg). DM was induced by streptozotocin/high-fat diet (STZ/HFD). After 12 weeks, the sensory thresholds to mechanical and heat stimuli were assessed. Repeated sensory tests, immunofluorescence microscopic comparison of peripheral nerves, and biochemical blood analysis were performed after 24 weeks.Results Both DM+metformin and DM+ALA groups showed similar trends to diverse sensory tests at 24 weeks compared to DM group although the degree of change were different according to the stimulated senses. There was no significant difference in the comparison of the intraepidermal nerve fiber density (IENFD) of peripheral nerves between the DM+metformin and DM+ALA groups (11.83±0.07 fibers/mm vs. 12.37±1.82 fibers/mm, respectively). Both groups showed preserved IENFD significantly compared with DM group (8.46±1.98 fibers/mm,
P <0.05). Sciatic nerve morphology of the experimental animals showed a similar trend to the IENFD, with respect to axonal diameter, myelin sheath thickness, and myelinated fiber diameter.Conclusion Metformin has beneficial pharmacological effects on the preservation of peripheral nerves in diabetic rats and its effects are comparable to those of ALA.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Metformin improves diabetic neuropathy by reducing inflammation through up-regulating the expression of miR-146a and suppressing oxidative stress
Fengmin Liu, Fangqin You, Lihang Yang, Siyun Wang, Diya Xie
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2024; 38(6): 108737. CrossRef - Effect of Metformin on the Functional and Electrophysiological Recovery of Crush Injury-Induced Facial Nerve Paralysis in Diabetic Rats
Kyung Hoon Sun, Cheol Hee Choi, Gwang-Won Cho, Chul Ho Jang
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2023; 13(9): 1317. CrossRef - Is metformin neuroprotective against diabetes mellitus-induced neurodegeneration? An updated graphical review of molecular basis
Fatemeh Karami, Hamidreza Jamaati, Natalie Coleman-Fuller, Maryam Shokrian Zeini, A. Wallace Hayes, Mina Gholami, Mahsa Salehirad, Mohammad Darabi, Majid Motaghinejad
Pharmacological Reports.2023; 75(3): 511. CrossRef - Early Diagnosis through Estimation of Inflammatory Biomarkers and the Neuroprotective Role of Metformin in Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Laxmi Sri, Prabhakar Orsu
International Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Nanotechnology(IJPSN).2023; 16(2): 6427. CrossRef - Bidirectional association between diabetic peripheral neuropathy and vitamin B12 deficiency: Two longitudinal 9-year follow-up studies using a national sample cohort
Heung Yong Jin, Kyung Ae Lee, Yu Ji Kim, In Sun Gwak, Tae Sun Park, Sang Woo Yeom, Jong Seung Kim
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(5): 436. CrossRef - An overview of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Diagnosis and treatment advancements
Jonathan M. Hagedorn, Alyson M. Engle, Tony K. George, Jay Karri, Newaj Abdullah, Erik Ovrom, Jhon E. Bocanegra-Becerra, Ryan S. D'Souza
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 188: 109928. CrossRef - The role of MicroRNA networks in tissue-specific direct and indirect effects of metformin and its application
Qinzhi Yang, Gang Wang, Dan Fang, Xiaojun Gao, Yu Liang, Liqun Wang, Jianbo Wu, Min Zeng, Mao Luo
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2022; 151: 113130. CrossRef - Is metformin a possible treatment for diabetic neuropathy?
Juechun Wei, Yanling Wei, Meiyan Huang, Peng Wang, Shushan Jia
Journal of Diabetes.2022; 14(10): 658. CrossRef - Metformin as a potential therapeutic for neurological disease: mobilizing AMPK to repair the nervous system
Sarah Demaré, Asha Kothari, Nigel A. Calcutt, Paul Fernyhough
Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics.2021; 21(1): 45. CrossRef - Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:842-53)
Bo Kyung Koo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 125. CrossRef - Metformin Preserves Peripheral Nerve Damage with Comparable Effects to Alpha Lipoic Acid in Streptozotocin/High-Fat Diet Induced Diabetic Rats (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:842-53)
Sun Hee Kim, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 127. CrossRef - Impacts of statin and metformin on neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: Korean Health Insurance data
Hong Ki Min, Se Hee Kim, Jong Han Choi, Kyomin Choi, Hae-Rim Kim, Sang-Heon Lee
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(33): 10198. CrossRef
- Metformin improves diabetic neuropathy by reducing inflammation through up-regulating the expression of miR-146a and suppressing oxidative stress
- Complications
- Effect of Empagliflozin, a Selective Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor, on Kidney and Peripheral Nerves in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
- Kyung Ae Lee, Heung Yong Jin, Na Young Lee, Yu Ji Kim, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(4):338-342. Published online April 25, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.0095
- 3,996 View
- 64 Download
- 17 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader The effect of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors on peripheral nerves and kidneys in diabetes mellitus (DM) remains unexplored. Therefore, this study aimed to explore the effect of empagliflozin in diabetic rats. DM in rats was induced by streptozotocin injection, and diabetic rats were treated with empagliflozin 3 or 10 mg/kg. Following 24-week treatment, response thresholds to four different stimuli were tested and found to be lower in diabetic rats than in normal rats. Empagliflozin significantly prevented hypersensitivity (
P <0.05) and the loss of skin intraepidermal nerve fibers, and mesangial matrix expansion in diabetic rats. Results of this study demonstrate the potential therapeutic effects of empagliflozin for the treatment of diabetic peripheral neuropathy and nephropathy.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Effect of empagliflozin in peripheral diabetic neuropathy of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Sahar Mohamed El-Haggar, Yasser Mostafa Hafez, Amira Mohamed El Sharkawy, Maha Khalifa
Medicina Clínica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A Review of Recent Pharmacological Advances in the Management of Diabetes-Associated Peripheral Neuropathy
Osman Syed, Predrag Jancic, Nebojsa Nick Knezevic
Pharmaceuticals.2023; 16(6): 801. CrossRef - Renal intrinsic cells remodeling in diabetic kidney disease and the regulatory effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors
Wenwen Guo, Han Li, Yixuan Li, Wen Kong
Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy.2023; 165: 115025. CrossRef - A systematic review on renal effects of SGLT2 inhibitors in rodent models of diabetic nephropathy
Aqsa Ashfaq, Myriam Meineck, Andrea Pautz, Ebru Arioglu-Inan, Julia Weinmann-Menke, Martin C. Michel
Pharmacology & Therapeutics.2023; 249: 108503. CrossRef - The impact of canagliflozin on the risk of neuropathy events: A post-hoc exploratory analysis of the CREDENCE trial
Jinlan Liao, Amy Kang, Chao Xia, Tamara Young, Gian Luca Di Tanna, Clare Arnott, Carol Pollock, Arun V. Krishnan, Rajiv Agarwal, George Bakris, David M. Charytan, Dick de Zeeuw, Hiddo J.L. Heerspink, Adeera Levin, Bruce Neal, David C. Wheeler, Hong Zhang,
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(4): 101331. CrossRef - Sodium Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor Protects Against Diabetic Neuropathy and Nephropathy in Modestly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes: Follow-Up Study
Fukashi Ishibashi, Aiko Kosaka, Mitra Tavakoli
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Protective effect of empagliflozin on gentamicin-induced acute renal injury via regulation of SIRT1/NF-κB signaling pathway
Sandy R. Botros, Asmaa I. Matouk, Aliaa Anter, Mohamed M.A. Khalifa, Gehan H. Heeba
Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology.2022; 94: 103907. CrossRef - Empagliflozin mitigates type 2 diabetes-associated peripheral neuropathy: a glucose-independent effect through AMPK signaling
Noha F. Abdelkader, Marawan A. Elbaset, Passant E. Moustafa, Sherehan M. Ibrahim
Archives of Pharmacal Research.2022; 45(7): 475. CrossRef - Pathogenesis and Treatment of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Seon Mee Kang
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2022; 23(4): 222. CrossRef - Empagliflozin and neohesperidin protect against methotrexate-induced renal toxicity via suppression of oxidative stress and inflammation in male rats
Adel T. Osman, Souty M.Z. Sharkawi, Mohamed I.A. Hassan, Amira M. Abo-youssef, Ramadan A.M. Hemeida
Food and Chemical Toxicology.2021; 155: 112406. CrossRef - Effect of exenatide on peripheral nerve excitability in type 2 diabetes
Tushar Issar, Natalie C.G. Kwai, Ann M. Poynten, Ria Arnold, Kerry-Lee Milner, Arun V. Krishnan
Clinical Neurophysiology.2021; 132(10): 2532. CrossRef - Effectiveness of Empagliflozin With Vitamin D Supplementation in Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Sanjana Mehta, Parminder Nain, Bimal K Agrawal, Rajinder P Singh, Jaspreet Kaur, Sabyasachi Maity, Aniruddha Bhattarcharjee, Jagannadha Peela, Shreya Nauhria, Samal Nauhria
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeting oxidative stress, proinflammatory cytokines, apoptosis and toll like receptor 4 by empagliflozin to ameliorate bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis
Ahmed M. Kabel, Remon S. Estfanous, Majed M. Alrobaian
Respiratory Physiology & Neurobiology.2020; 273: 103316. CrossRef - Empagliflozin reduces high glucose-induced oxidative stress and miR-21-dependent TRAF3IP2 induction and RECK suppression, and inhibits human renal proximal tubular epithelial cell migration and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
Nitin A. Das, Andrea J. Carpenter, Anthony Belenchia, Annayya R. Aroor, Makoto Noda, Ulrich Siebenlist, Bysani Chandrasekar, Vincent G. DeMarco
Cellular Signalling.2020; 68: 109506. CrossRef - Differential Effects of Empagliflozin on Microvascular Complications in Murine Models of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Stephanie A. Eid, Phillipe D. O’Brien, Lucy M. Hinder, John M. Hayes, Faye E. Mendelson, Hongyu Zhang, Lixia Zeng, Katharina Kretzler, Samanthi Narayanan, Steven F. Abcouwer, Frank C. Brosius, Subramaniam Pennathur, Masha G. Savelieff, Eva L. Feldman
Biology.2020; 9(11): 347. CrossRef - Pre-treatment with Empagliflozin ameliorates Cisplatin induced acute kidney injury by suppressing apoptosis
Maaly A. Abd Elmaaboud, Ahmed M. Kabel, Mohamed Elrashidy
Journal of Applied Biomedicine.2019; 17(1): 90. CrossRef - Effects of ticagrelor, empagliflozin and tamoxifen against experimentally-induced vascular reactivity defects in rats in vivo and in vitro
Yasmin Moustafa Ahmed, Basim Anwar Shehata Messiha, Mahmoud El-Sayed El-Daly, Ali Ahmed Abo-Saif
Pharmacological Reports.2019; 71(6): 1034. CrossRef - SGLT2 inhibition with empagliflozin attenuates myocardial oxidative stress and fibrosis in diabetic mice heart
Chenguang Li, Jie Zhang, Mei Xue, Xiaoyu Li, Fei Han, Xiangyang Liu, Linxin Xu, Yunhong Lu, Ying Cheng, Ting Li, Xiaochen Yu, Bei Sun, Liming Chen
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Empagliflozin Contributes to Polyuria via Regulation of Sodium Transporters and Water Channels in Diabetic Rat Kidneys
Sungjin Chung, Soojeong Kim, Mina Son, Minyoung Kim, Eun Sil Koh, Seok Joon Shin, Seung-Hyun Ko, Ho-Shik Kim
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Effect of empagliflozin in peripheral diabetic neuropathy of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- Complication
- Morphologic Comparison of Peripheral Nerves in Adipocyte Tissue from
db/db Diabetic versus Normal Mice - Kyung Ae Lee, Na Young Lee, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(2):169-172. Published online March 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.42.2.169
- 3,397 View
- 43 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Present study investigated the morphologic changes of autonomic nerves in the adipose tissue in diabetic animal model. Male obese type 2 diabetic
db/db mice and age matched non-diabeticdb/m control mice were used. Epididymal adipose tissue from diabeticdb/db mice with that from control heterozygousdb/m mice was compared using confocal microscopy-based method to visualize intact whole adipose tissue. Immunohistochemistry with tyrosine hydroxylase for sympathetic (SP), choline acetyltransferase for parasympathetic (PSP), and protein gene product 9.5 (PGP 9.5) for whole autonomic nerves was performed. The quantity of immunostained portion of SP, PSP, and PGP 9.5 stained nerve fibers showed decreased trend in diabetic group; however, the ratio of SP/PSP of adipose tissue was higher in diabetic group compared with control group as follows (0.70±0.30 vs. 0.95±0.25,P <0.05; normal vs. diabetic, respectively). Both SP and PSP nerve fibers were observed in white adipose tissue and PSP nerve fibers were suggested as more decreased in diabetes based on our observation.
- Effect of Granulocyte Colony-Stimulating Factor on the Peripheral Nerves in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rat
- Kyung Ae Lee, Kyung Taek Park, Hea Min Yu, Heung Yong Jin, Hong Sun Baek, Tae Sun Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2013;37(4):286-290. Published online August 14, 2013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.4.286
- 3,212 View
- 26 Download
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader There are controversial reports about the effect of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) in peripheral nerve protection. Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate the effect of G-CSF on peripheral nerves in streptozotocin (STZ) induced diabetic rats. After STZ or vehicle injection, rats were divided into five groups (
n =6) as follows: normal+vehicle, normal+G-CSF (50 µg/kg for 5 days), diabetes mellitus (DM)+vehicle, DM+G-CSF (50 µg/kg for 5 days), and DM+G-CSF extension (50 µg/kg for 5 days and followed by two injections per week up to 24 weeks). Our results showed that the current perception threshold was not significantly different among experimental groups. G-CSF treatment inhibited the loss of cutaneous nerves and gastric mucosal small nerve fibers in morphometric comparison, but statistical significance was not observed. The present results demonstrated that G-CSF has no harmful but minimal beneficial effects with respect to peripheral nerve preservation in diabetic rats.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Colony stimulating factors in the nervous system
Violeta Chitu, Fabrizio Biundo, E. Richard Stanley
Seminars in Immunology.2021; 54: 101511. CrossRef - Non-glucose risk factors in the pathogenesis of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Kyung Ae Lee, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
Endocrine.2020; 70(3): 465. CrossRef - Two to Tango: Dialogue between Adaptive and Innate Immunity in Type 1 Diabetes
Lin Sun, Shugang Xi, Guangyu He, Zhuo Li, Xiaokun Gang, Chenglin Sun, Weiying Guo, Guixia Wang
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Transplantation of human mobilized mononuclear cells improved diabetic neuropathy
Se Hee Min, Jung Hee Kim, Yu Mi Kang, Seung Hak Lee, Byung-Mo Oh, Kyou-Sup Han, Meihua Zhang, Hoe Suk Kim, Woo Kyung Moon, Hakmo Lee, Kyong Soo Park, Hye Seung Jung
Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 239(3): 277. CrossRef - Granulocyte-colony stimulating factor as a treatment for diabetic neuropathy in rat
Kyung-Soo Kim, Yi-Sun Song, Jiyong Jin, Jun-Ho Joe, Byung-Im So, Jun-Young Park, Cheng-Hu Fang, Mi Jung Kim, Youl-Hee Cho, Sejin Hwang, Young-Suck Ro, Hyuck Kim, You-Hern Ahn, Hak-Joon Sung, Jung-Joon Sung, Sung-Hye Park, Stuart A. Lipton
Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology.2015; 414: 64. CrossRef
- Colony stimulating factors in the nervous system

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





