
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
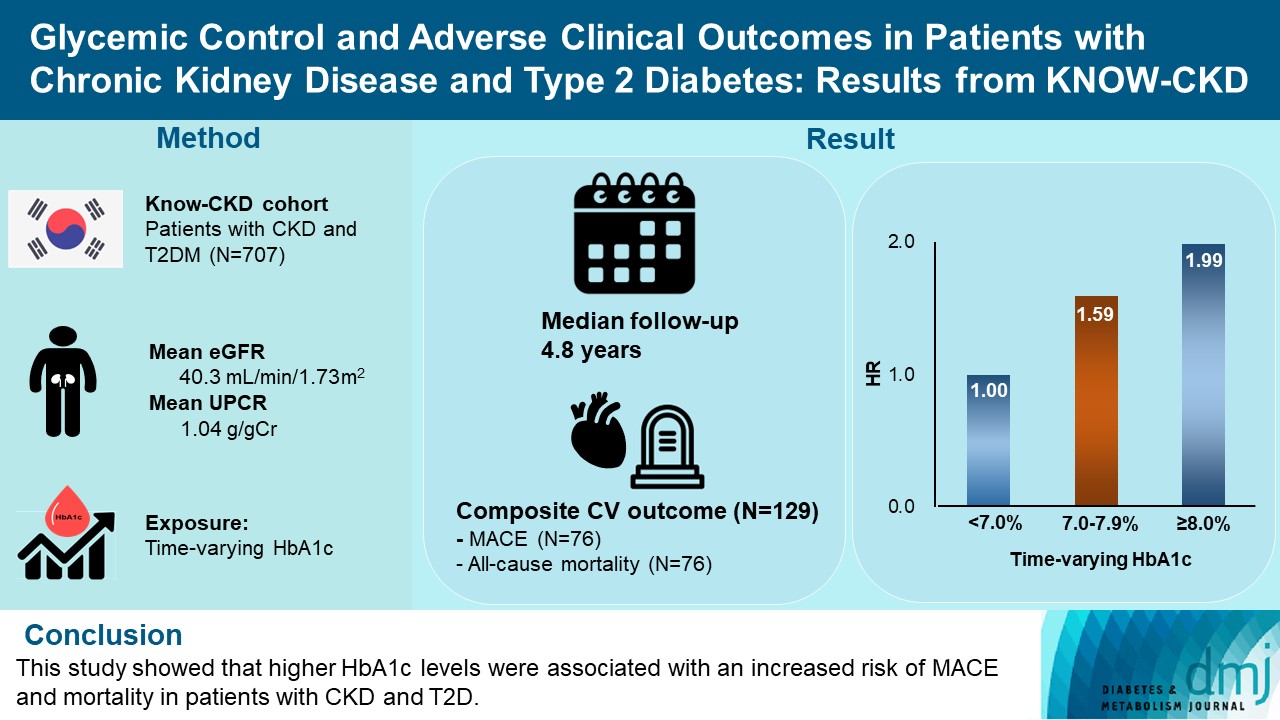
- Glycemic Control and Adverse Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Results from KNOW-CKD
- Ga Young Heo, Hee Byung Koh, Hyung Woo Kim, Jung Tak Park, Tae-Hyun Yoo, Shin-Wook Kang, Jayoun Kim, Soo Wan Kim, Yeong Hoon Kim, Su Ah Sung, Kook-Hwan Oh, Seung Hyeok Han
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(4):535-546. Published online April 25, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0112
- 2,655 View
- 162 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
The optimal level of glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) to prevent adverse clinical outcomes is unknown in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
We analyzed 707 patients with CKD G1-G5 without kidney replacement therapy and T2DM from the KoreaN Cohort Study for Outcome in Patients With Chronic Kidney Disease (KNOW-CKD), a nationwide prospective cohort study. The main predictor was time-varying HbA1c level at each visit. The primary outcome was a composite of development of major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) or all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes included the individual endpoint of MACEs, all-cause mortality, and CKD progression. CKD progression was defined as a ≥50% decline in the estimated glomerular filtration rate from baseline or the onset of end-stage kidney disease.
Results
During a median follow-up of 4.8 years, the primary outcome occurred in 129 (18.2%) patients. In time-varying Cox model, the adjusted hazard ratios (aHRs) for the primary outcome were 1.59 (95% confidence interval [CI], 1.01 to 2.49) and 1.99 (95% CI, 1.24 to 3.19) for HbA1c levels of 7.0%–7.9% and ≥8.0%, respectively, compared with <7.0%. Additional analysis of baseline HbA1c levels yielded a similar graded association. In secondary outcome analyses, the aHRs for the corresponding HbA1c categories were 2.17 (95% CI, 1.20 to 3.95) and 2.26 (95% CI, 1.17 to 4.37) for MACE, and 1.36 (95% CI, 0.68 to 2.72) and 2.08 (95% CI, 1.06 to 4.05) for all-cause mortality. However, the risk of CKD progression did not differ between the three groups.
Conclusion
This study showed that higher HbA1c levels were associated with an increased risk of MACE and mortality in patients with CKD and T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The Beneficial Effect of Glycemic Control against Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
Dong-Hwa Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(4): 484. CrossRef - Prevalence and predictors of chronic kidney disease among type 2 diabetic patients worldwide, systematic review and meta-analysis
Eneyew Talie Fenta, Habitu Birhan Eshetu, Natnael Kebede, Eyob Ketema Bogale, Amare Zewdie, Tadele Derbew Kassie, Tadele Fentabil Anagaw, Elyas Melaku Mazengia, Sintayehu Shiferaw Gelaw
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of teneligliptin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a Bayesian network meta-analysis
Miao Zhu, Ruifang Guan, Guo Ma
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef
- The Beneficial Effect of Glycemic Control against Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Abnormal Responses in Cognitive Impulsivity Circuits Are Associated with Glycosylated Hemoglobin Trajectories in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus and Impaired Metabolic Control
- Helena Jorge, Isabel C. Duarte, Sandra Paiva, Ana Paula Relvas, Miguel Castelo-Branco
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):866-878. Published online March 22, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0307
- 4,400 View
- 173 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Risky health decisions and impulse control profiles may impact on metabolic control in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). We hypothesize that the neural correlates of cognitive impulsivity and decision-making in T1DM relate to metabolic control trajectories.
Methods
We combined functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), measures of metabolic trajectories (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] over multiple time points) and behavioral assessment using a cognitive impulsivity paradigm, the Balloon Analogue Risk Task (BART), in 50 participants (25 T1DM and 25 controls).
Results
Behavioral results showed that T1DM participants followed a rigid conservative risk strategy along the iterative game. Imaging group comparisons showed that patients showed larger activation of reward related, limbic regions (nucleus accumbens, amygdala) and insula (interoceptive saliency network) in initial game stages. Upon game completion differences emerged in relation to error monitoring (anterior cingulate cortex [ACC]) and inhibitory control (inferior frontal gyrus). Importantly, activity in the saliency network (ACC and insula), which monitors interoceptive states, was related with metabolic trajectories, which was also found for limbic/reward networks. Parietal and posterior cingulate regions activated both in controls and patients with adaptive decision-making, and positively associated with metabolic trajectories.
Conclusion
We found triple converging evidence when comparing metabolic trajectories, patients versus controls or risk averse (non-learners) versus patients who learned by trial and error. Dopaminergic reward and saliency (interoceptive and error monitoring) circuits show a tight link with impaired metabolic trajectories and cognitive impulsivity in T1DM. Activity in parietal and posterior cingulate are associated with adaptive trajectories. This link between reward-saliency-inhibition circuits suggests novel strategies for patient management. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The usefulness of an intervention with a serious video game as a complementary approach to cognitive behavioural therapy in eating disorders: A pilot randomized clinical trial for impulsivity management
Cristina Vintró‐Alcaraz, Núria Mallorquí‐Bagué, María Lozano‐Madrid, Giulia Testa, Roser Granero, Isabel Sánchez, Janet Treasure, Susana Jiménez‐Murcia, Fernando Fernández‐Aranda
European Eating Disorders Review.2023; 31(6): 781. CrossRef - Adaptations of the balloon analog risk task for neuroimaging settings: a systematic review
Charline Compagne, Juliana Teti Mayer, Damien Gabriel, Alexandre Comte, Eloi Magnin, Djamila Bennabi, Thomas Tannou
Frontiers in Neuroscience.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Trust-based health decision-making recruits the neural interoceptive saliency network which relates to temporal trajectories of Hemoglobin A1C in Diabetes Type 1
Helena Jorge, Isabel C. Duarte, Miguel Melo, Ana Paula Relvas, Miguel Castelo-Branco
Brain Imaging and Behavior.2023; 18(1): 171. CrossRef
- The usefulness of an intervention with a serious video game as a complementary approach to cognitive behavioural therapy in eating disorders: A pilot randomized clinical trial for impulsivity management
- Technology/Device
- A 4-Week, Two-Center, Open-Label, Single-Arm Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of EOPatch in Well-Controlled Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jiyun Park, Nammi Park, Sangjin Han, You-Bin Lee, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Woo Je Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(6):941-947. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0299
- 5,174 View
- 269 Download
- 2 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - This study evaluated the safety and efficacy of tubeless patch pump called EOPatch in patients with well-controlled type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). This 4-week, two-center, open-label, single-arm study enrolled 10 adult patients diagnosed with T1DM with glycosylated hemoglobin less than 7.5%. The co-primary end points were patch pump usage time for one attachment and number of serious adverse events related to the patch pump. The secondary end points were total amount of insulin injected per patch and changes in glycemic parameters including continuous glucose monitoring data compared to those at study entry. The median usage time per patch was 84.00 hours (interquartile range, 64.50 to 92.50). Serious adverse events did not occur during the trial. Four weeks later, time in range 70 to 180 mg/dL was significantly improved (70.71%±17.14 % vs. 82.96%±9.14%, P=0.01). The times spent below range (<54 mg/dL) and above range (>180 mg/dL) also improved (All P<0.05). Four-week treatment with a tubeless patch pump was safe and led to clinical improvement in glycemic control.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Multilayer track‐etched membrane‐based electroosmotic pump for drug delivery
Qian Yang, Zebo Zhang, Junshu Lin, Boyu Zhu, Rongying Yu, Xinru Li, Bin Su, Bo Zhao
ELECTROPHORESIS.2024; 45(5-6): 433. CrossRef - Comparison between a tubeless, on-body automated insulin delivery system and a tubeless, on-body sensor-augmented pump in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Eun Seok Kang, Soo Heon Kwak, Yeoree Yang, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyun Bae, Jun Sung Moon, Chang Hee Jung, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh, Sun Joon Moon, Sun Ok Song, Suk Chon, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A true continuous healthcare system for type 1 diabetes
Jiyong Kim, Salman Khan, Eun Kyu Kim, Hye-Jun Kil, Bo Min Kang, Hyo Geon Lee, Jin-Woo Park, Jun Young Yoon, Woochul Kim
Nano Energy.2023; 113: 108553. CrossRef
- Multilayer track‐etched membrane‐based electroosmotic pump for drug delivery
- Drug/Regimen
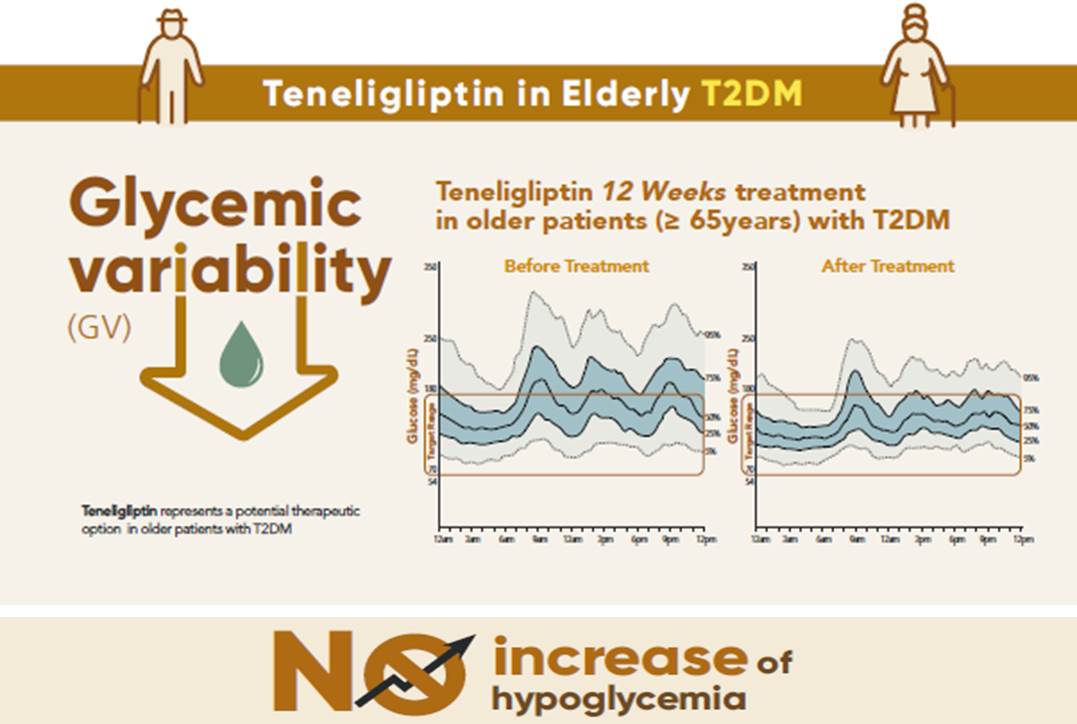
- Effects of Teneligliptin on HbA1c levels, Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Time in Range and Glycemic Variability in Elderly Patients with T2DM (TEDDY Study)
- Ji Cheol Bae, Soo Heon Kwak, Hyun Jin Kim, Sang-Yong Kim, You-Cheol Hwang, Sunghwan Suh, Bok Jin Hyun, Ji Eun Cha, Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):81-92. Published online June 16, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0016
- 7,563 View
- 431 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To evaluate the effects of teneligliptin on glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM)-derived time in range, and glycemic variability in elderly type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Methods
This randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled study was conducted in eight centers in Korea (clinical trial registration number: NCT03508323). Sixty-five participants aged ≥65 years, who were treatment-naïve or had been treated with stable doses of metformin, were randomized at a 1:1 ratio to receive 20 mg of teneligliptin (n=35) or placebo (n=30) for 12 weeks. The main endpoints were the changes in HbA1c levels from baseline to week 12, CGM metrics-derived time in range, and glycemic variability.
Results
After 12 weeks, a significant reduction (by 0.84%) in HbA1c levels was observed in the teneligliptin group compared to that in the placebo group (by 0.08%), with a between-group least squares mean difference of –0.76% (95% confidence interval [CI], –1.08 to –0.44). The coefficient of variation, standard deviation, and mean amplitude of glycemic excursion significantly decreased in participants treated with teneligliptin as compared to those in the placebo group. Teneligliptin treatment significantly decreased the time spent above 180 or 250 mg/dL, respectively, without increasing the time spent below 70 mg/dL. The mean percentage of time for which glucose levels remained in the 70 to 180 mg/dL time in range (TIR70–180) at week 12 was 82.0%±16.0% in the teneligliptin group, and placebo-adjusted change in TIR70–180 from baseline was 13.3% (95% CI, 6.0 to 20.6).
Conclusion
Teneligliptin effectively reduced HbA1c levels, time spent above the target range, and glycemic variability, without increasing hypoglycemia in our study population. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Comparison of teneligliptin and other gliptin-based regimens in addressing insulin resistance and glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients: a cross-sectional study
Harmanjit Singh, Ravi Rohilla, Shivani Jaswal, Mandeep Singla
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2024; 19(1): 81. CrossRef - Potential approaches using teneligliptin for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: current status and future prospects
Harmanjit Singh, Jasbir Singh, Ravneet Kaur Bhangu, Mandeep Singla, Jagjit Singh, Farideh Javid
Expert Review of Clinical Pharmacology.2023; 16(1): 49. CrossRef - Mechanism of molecular interaction of sitagliptin with human DPP4 enzyme - New Insights
Michelangelo Bauwelz Gonzatti, José Edvar Monteiro Júnior, Antônio José Rocha, Jonathas Sales de Oliveira, Antônio José de Jesus Evangelista, Fátima Morgana Pio Fonseca, Vânia Marilande Ceccatto, Ariclécio Cunha de Oliveira, José Ednésio da Cruz Freire
Advances in Medical Sciences.2023; 68(2): 402. CrossRef - A prospective multicentre open label study to assess effect of Teneligliptin on glycemic control through parameters of time in range (TIR) Metric using continuous glucose monitoring (TOP-TIR study)
Banshi Saboo, Suhas Erande, A.G. Unnikrishnan
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2022; 16(2): 102394. CrossRef - Association between Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors and Cardiometabolic Outcomes
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 49. CrossRef
- Comparison of teneligliptin and other gliptin-based regimens in addressing insulin resistance and glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients: a cross-sectional study
- Drug/Regimen
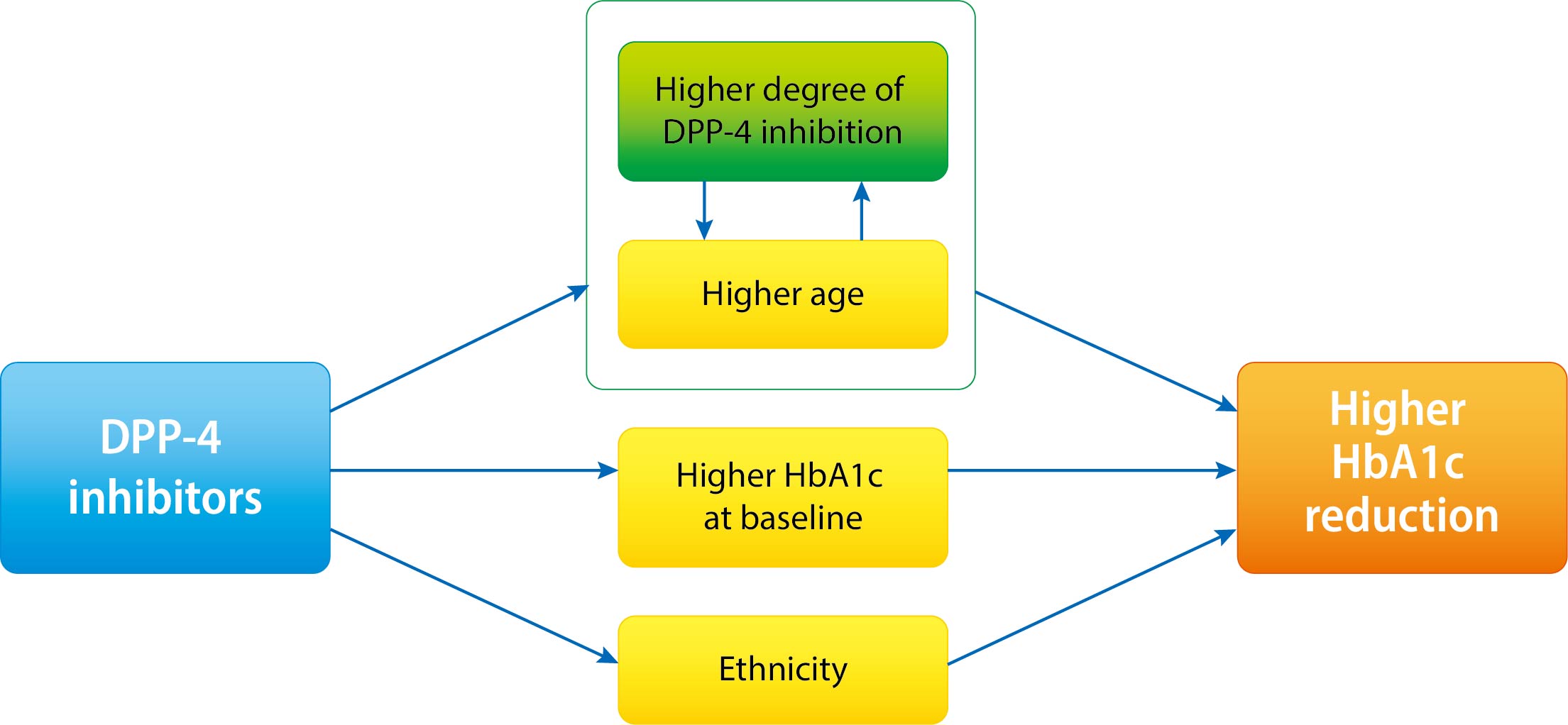
- Increasing Age Associated with Higher Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibition Rate Is a Predictive Factor for Efficacy of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors
- Sangmo Hong, Chang Hee Jung, Song Han, Cheol-Young Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(1):63-70. Published online April 19, 2021
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0253
- 65,535 View
- 287 Download
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
It is not known which type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients would most benefit from dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-4) inhibitor treatment. We aimed to investigate the predictors of response to DPP-4 inhibitors considering degree of DPP-4 inhibition.
Methods
This study is a post hoc analysis of a 24-week, randomized, double-blind, phase III trial that compared the efficacy and safety of a DPP-4 inhibitor (gemigliptin vs. sitagliptin) in patients with T2DM. Subjects were classified into tertiles of T1 <65.26%, T2=65.26%–76.35%, and T3 ≥76.35% by DPP-4 inhibition. We analyzed the change from baseline in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) according to DPP-4 inhibition with multiple linear regression adjusting for age, ethnicity, body mass index, baseline HbA1c, and DPP-4 activity at baseline.
Results
The mean age was greater in the high tertile group compared with the low tertile group (T1: 49.8±8.3 vs. T2: 53.1±10.5 vs. T3: 55.3±9.5, P<0.001) of DPP-4 inhibition. Although HbA1c at baseline was not different among tertiles of DPP-4 inhibition (P=0.398), HbA1c after 24-week treatment was lower in the higher tertile compares to the lower tertile (T1: 7.30%±0.88% vs. T2: 7.12%±0.78% vs. T3: 7.00%±0.78%, P=0.021). In multiple regression analysis, DPP-4 enzyme inhibition rate was not a significant determent for HbA1c reduction due to age. In subgroup analysis by tertile of DPP-4 inhibition, age was the only significant predictor and only in the highest tertile (R2=0.281, B=–0.014, P=0.024).
Conclusion
This study showed that HbA1c reduction by DPP-4 inhibitor was associated with increasing age, and this association was linked with higher DPP-4 inhibition.
- Type 1 Diabetes
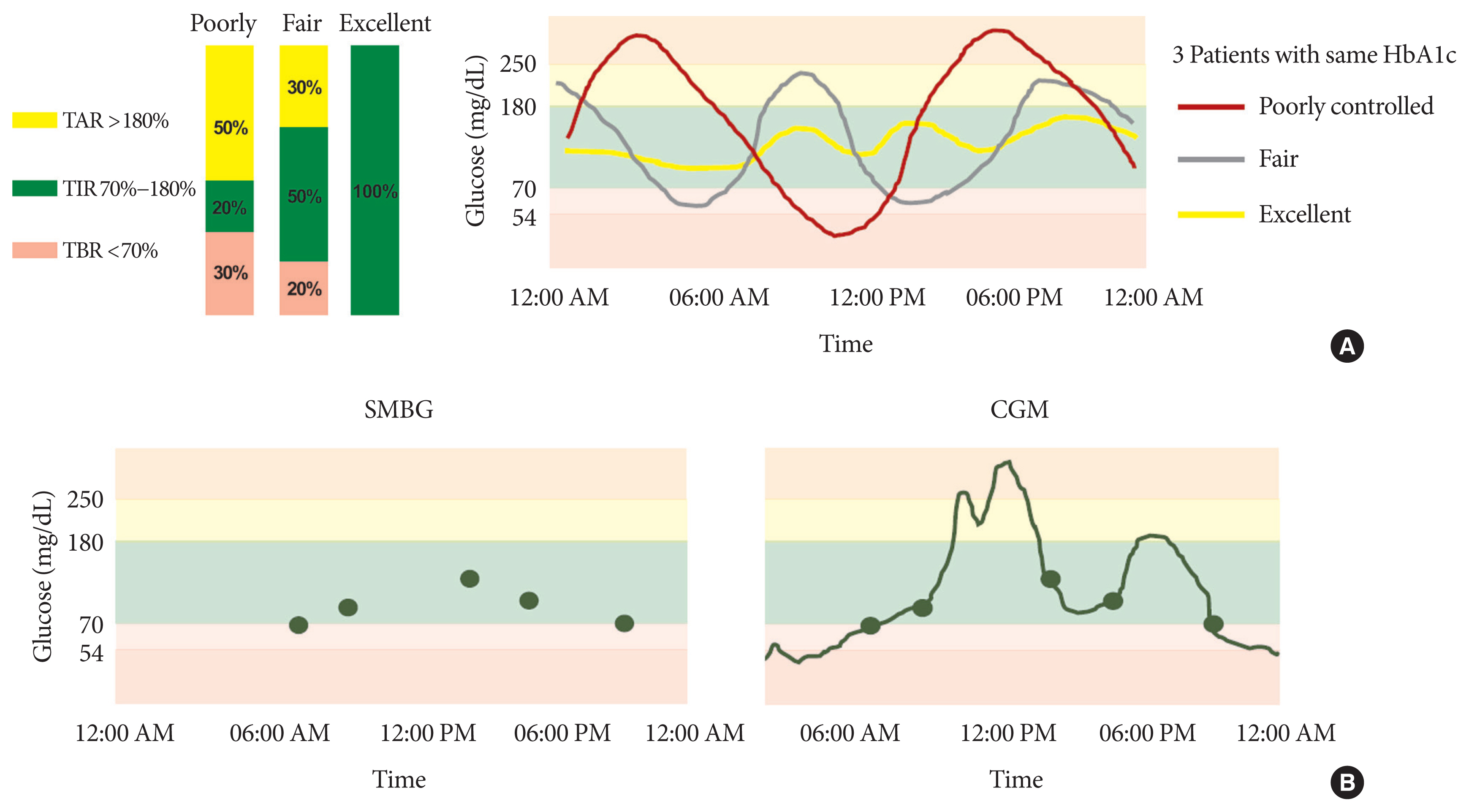
- Time in Range from Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Novel Metric for Glycemic Control
- Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):828-839. Published online December 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0257
- Correction in: Diabetes Metab J 2021;45(5):795
- 9,826 View
- 467 Download
- 31 Web of Science
- 36 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) has been the sole surrogate marker for assessing diabetic complications. However, consistently reported limitations of HbA1c are that it lacks detailed information on short-term glycemic control and can be easily interfered with by various clinical conditions such as anemia, pregnancy, or liver disease. Thus, HbA1c alone may not represent the real glycemic status of a patient. The advancement of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has enabled both patients and healthcare providers to monitor glucose trends for a whole single day, which is not possible with HbA1c. This has allowed for the development of core metrics such as time spent in time in range (TIR), hyperglycemia, or hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability. Among the 10 core metrics, TIR is reported to represent overall glycemic control better than HbA1c alone. Moreover, various evidence supports TIR as a predictive marker of diabetes complications as well as HbA1c, as the inverse relationship between HbA1c and TIR reveals. However, there are more complex relationships between HbA1c, TIR, and other CGM metrics. This article provides information about 10 core metrics with particular focus on TIR and the relationships between the CGM metrics for comprehensive understanding of glycemic status using CGM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Acute and Chronic Adverse Outcomes of Type 1 Diabetes
Rachel Longendyke, Jody B. Grundman, Shideh Majidi
Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America.2024; 53(1): 123. CrossRef - La plongée sous-marine en scaphandre autonome avec un diabète de type 1. Une belle histoire du dernier millénaire
Lise Dufaitre Patouraux, Agnès Sola-Gazagnes, Boris Lormeau, Corinne Lormeau
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2024; 18(1): 67. CrossRef - S100A9 exerts insulin-independent antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory effects
Gloria Ursino, Giulia Lucibello, Pryscila D. S. Teixeira, Anna Höfler, Christelle Veyrat-Durebex, Soline Odouard, Florian Visentin, Luca Galgano, Emmanuel Somm, Claudia R. Vianna, Ariane Widmer, François R. Jornayvaz, Andreas Boland, Giorgio Ramadori, Rob
Science Advances.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hybrid Closed-Loop Versus Manual Insulin Delivery in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: A Post Hoc Analysis Using the Glycemia Risk Index
Melissa H. Lee, Sara Vogrin, Timothy W. Jones, David N. O’Neal
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinically relevant stratification of patients with type 2 diabetes by using continuous glucose monitoring data
Xiaopeng Shao, Jingyi Lu, Rui Tao, Liang Wu, Yaxin Wang, Wei Lu, Hongru Li, Jian Zhou, Xia Yu
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a 2-Week Kinect-Based Mixed-Reality Exercise Program on Prediabetes: A Pilot Trial during COVID-19
So Young Ahn, Si Woo Lee, Hye Jung Shin, Won Jae Lee, Jun Hyeok Kim, Hyun-Jun Kim, Wook Song
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2024; 33(1): 54. CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring with structured education in adults with type 2 diabetes managed by multiple daily insulin injections: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kang Hee Sim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Jun Sung Moon, Soo Lim, Eun Seok Kang, Cheol-Young Park, Sin Gon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison between a tubeless, on-body automated insulin delivery system and a tubeless, on-body sensor-augmented pump in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Eun Seok Kang, Soo Heon Kwak, Yeoree Yang, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyun Bae, Jun Sung Moon, Chang Hee Jung, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh, Sun Joon Moon, Sun Ok Song, Suk Chon, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Anagliptin twice‐daily regimen improves glycaemic variability in subjects with type 2 diabetes: A double‐blind, randomized controlled trial
Yong‐ho Lee, Doo‐Man Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Kyung Mook Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Kang Seo Park, Hyun‐Shik Son, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Soon Hee Lee, Ki‐Ho Song, Su Kyoung Kwon, Hyeong Kyu Park, Kyu Chang Won, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(5): 1174. CrossRef - Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 27. CrossRef - Status of continuous glucose monitoring use and management in tertiary hospitals of China: a cross-sectional study
Liping Chen, Xiaoqin Liu, Qin Lin, Hongmei Dai, Yong Zhao, Zumin Shi, Liping Wu
BMJ Open.2023; 13(2): e066801. CrossRef - Real-world outcomes of continuous glucose monitoring in adults with diabetes mellitus attending an Irish tertiary hospital
Aoife Courtney, Diarmuid Smith, Hannah Forde
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2023; 192(6): 2763. CrossRef - Insight into continuous glucose monitoring: from medical basics to commercialized devices
Ayman Chmayssem, Małgorzata Nadolska, Emily Tubbs, Kamila Sadowska, Pankaj Vadgma, Isao Shitanda, Seiya Tsujimura, Youssef Lattach, Martin Peacock, Sophie Tingry, Stéphane Marinesco, Pascal Mailley, Sandrine Lablanche, Pierre Yves Benhamou, Abdelkader Zeb
Microchimica Acta.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of polyethylene glycol loxenatide versus insulin glargine on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, open-label, parallel-group trial
Shuo Zhang, Chuanyan Zhang, Jingxian Chen, Feiying Deng, Zezhen Wu, Dan Zhu, Fengwu Chen, Yale Duan, Yue Zhao, Kaijian Hou
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control and its derived metrics in type 1 diabetes: a longitudinal study
So Hyun Cho, Seohyun Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Glycemia Risk Index and Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes
Jee Hee Yoo, Ji Yoon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(10): 726. CrossRef - Acute Glycemic Variability and Early Outcomes After Cardiac Surgery:
A Meta-Analysis
Shuo Chang, Mian Xu, Yu Wang, Yanbo Zhang
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2023; 55(11): 771. CrossRef - Comparison of Glycemia Risk Index with Time in Range for Assessing Glycemic Quality
Ji Yoon Kim, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(12): 883. CrossRef - Correlação entre tempo no alvo e hemoglobina glicada de pessoas com diabetes mellitus: revisão sistemática
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlación entre tiempo en rango y hemoglobina glicosilada en personas con diabetes mellitus: revisión sistemática
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation between time on target and glycated hemoglobin in people with diabetes mellitus: systematic review
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef - Novel Glycemic Index Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Predict Poor Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Il Rae Park, Yin Young Lee, Eun Young Choi, Jun Sung Moon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypoglycemic agents and glycemic variability in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
SuA Oh, Sujata Purja, Hocheol Shin, Minji Kim, Eunyoung Kim
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2022; 19(3): 147916412211068. CrossRef - Advanced Glycation End Products and Their Effect on Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jeongmin Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3086. CrossRef - Influence of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on glycemic variability in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Shangyu Chai, Ruya Zhang, Ye Zhang, Richard David Carr, Yiman Zheng, Swapnil Rajpathak, Miao Yu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Glucose Profiles Assessed by Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring System during the Perioperative Period of Metabolic Surgery
Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang, Young Suk Park, Tae Jung Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 713. CrossRef - Deterioration in glycemic control on schooldays among children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A continuous glucose monitoring-based study
Yu Ding, Wenhao Zhang, Xiumei Wu, Tian Wei, Xulin Wang, Xueying Zheng, Sihui Luo
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of repeated bolus and continuous glucose infusion on a panel of circulating biomarkers in healthy volunteers
Roland Feldbauer, Matthias Wolfgang Heinzl, Carmen Klammer, Michael Resl, Johannes Pohlhammer, Klemens Rosenberger, Verena Almesberger, Florian Obendorf, Lukas Schinagl, Thomas Wagner, Margot Egger, Benjamin Dieplinger, Martin Clodi, Stephen L. Atkin
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(12): e0279308. CrossRef - Relationship between glycemic intraday variations evaluated in continuous glucose monitoring and HbA1c variability in type 2 diabetes: pilot study
Akemi Tokutsu, Yosuke Okada, Keiichi Torimoto, Yoshiya Tanaka
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Time-in-range for monitoring glucose control: Is it time for a change?
Virginia Bellido, Pedro José Pinés-Corrales, Rocío Villar-Taibo, Francisco Javier Ampudia-Blasco
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 177: 108917. CrossRef - Glucose Management Indicator for People with Type 1 Asian Diabetes Is Different from That of the Published Equation: Differences by Glycated Hemoglobin Distribution
Jee Hee Yoo, Seung Hee Yang, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life, Family Conflicts and Fear of Injecting: Perception Differences between Preadolescents and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes and Their Mothers
Marta Tremolada, Maria Cusinato, Sabrina Bonichini, Arianna Fabris, Claudia Gabrielli, Carlo Moretti
Behavioral Sciences.2021; 11(7): 98. CrossRef - Daytime Glycemic Variability and Frailty in Older Patients with Diabetes: a Pilot Study Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Seung Min Chung, Yun Hee Lee, Chang Oh Kim, Ji Yeon Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Seung-Hyun Yoo, Jun Sung Moon, Kwang Joon Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Benefits of a Switch from Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring (isCGM) to Real-Time (rt) CGM in Diabetes Type 1 Suboptimal Controlled Patients in Real-Life: A One-Year Prospective Study §
Yannis Préau, Sébastien Galie, Pauline Schaepelynck, Martine Armand, Denis Raccah
Sensors.2021; 21(18): 6131. CrossRef - Recent Advances of Integrative Bio-Omics Technologies to Improve Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) Care
Nisha Karwal, Megan Rodrigues, David D. Williams, Ryan J. McDonough, Diana Ferro
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(24): 11602. CrossRef
- Acute and Chronic Adverse Outcomes of Type 1 Diabetes
- Drug/Regimen
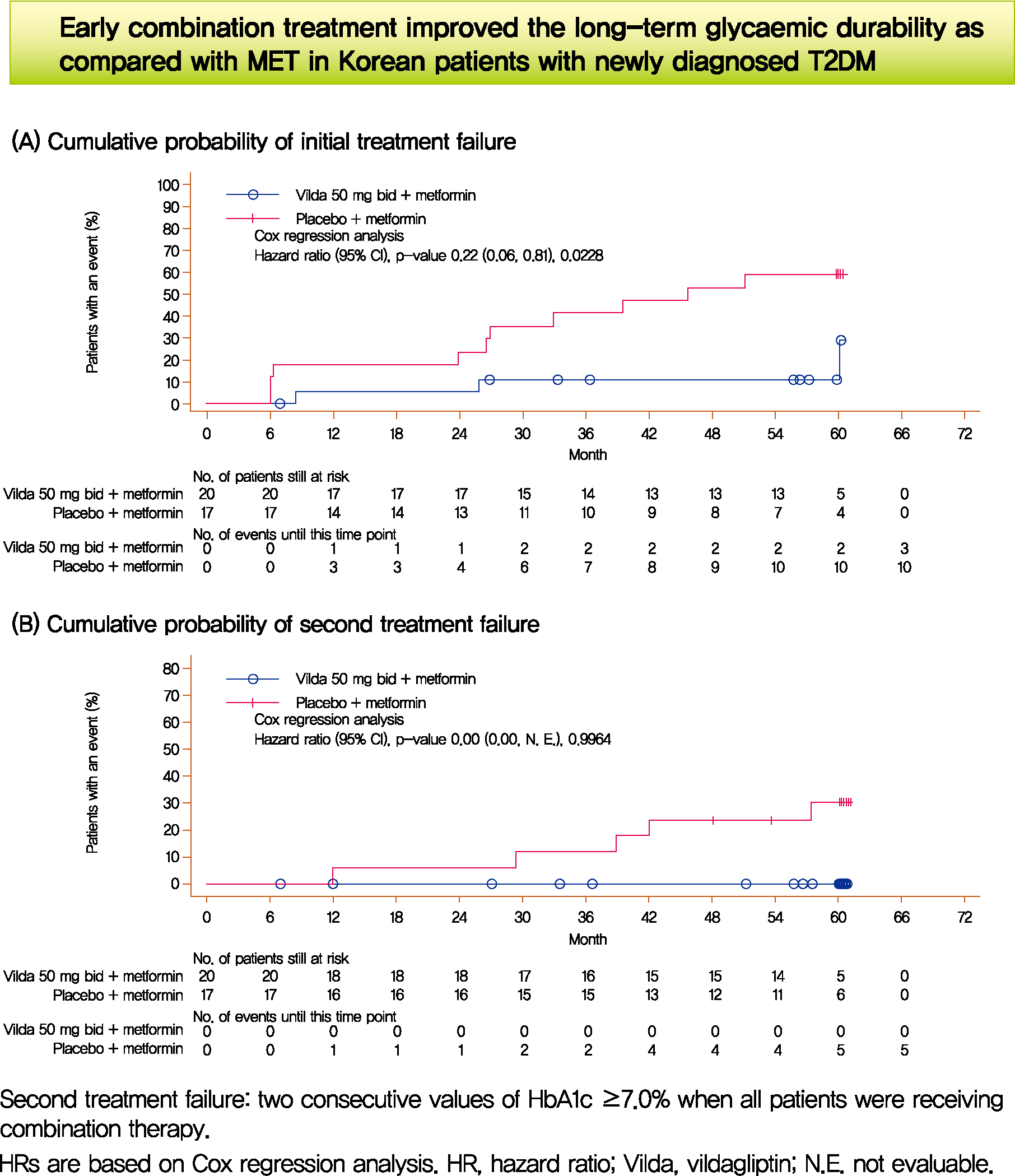
- Long-Term Glycaemic Durability of Early Combination Therapy Strategy versus Metformin Monotherapy in Korean Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Soon-Jib Yoo, Sang-Ah Chang, Tae Seo Sohn, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Jong Min Lee, Sungdae Moon, Pieter Proot, Päivi M Paldánius, Kun Ho Yoon
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(6):954-959. Published online November 12, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0173
- 55,052 View
- 367 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 2 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- We assessed the glycaemic durability with early combination (EC; vildagliptin+metformin [MET], n=22) versus MET monotherapy (n=17), among newly-diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) enrolled (between 2012 and 2014) in the VERIFY study from Korea (n=39). Primary endpoint was time to initial treatment failure (TF) (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] ≥7.0% at two consecutive scheduled visits after randomization [end of period 1]). Time to second TF was assessed when both groups were receiving and failing on the combination (end of period 2). With EC the risk of initial TF significantly reduced by 78% compared to MET (n=3 [15%] vs. n=10 [58.7%], P=0.0228). No secondary TF occurred in EC group versus five patients (29.4%) in MET. Patients receiving EC treatment achieved consistently lower HbA1c levels. Both treatment approaches were well tolerated with no hypoglycaemic events. In Korean patients with newly diagnosed T2DM, EC treatment significantly and consistently improved the long-term glycaemic durability as compared with MET.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Han Choi, Kyung Ae Lee, Joon Ho Moon, Suk Chon, Dae Jung Kim, Hyun Jin Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo, Mee Kyoung Kim, Jeong Hyun Lim, YoonJu Song, Ye Seul Yang, Jae Hyeon Kim, You-Bin Lee, Junghyun Noh, Kyu Yeon Hur, Jong Suk Park, Sang Youl Rhee, Hae J
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(5): 575. CrossRef - 2021 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
Kyu Yeon Hur, Min Kyong Moon, Jong Suk Park, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seung-Hwan Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Jong Ha Baek, Junghyun Noh, Byung-Wan Lee, Tae Jung Oh, Suk Chon, Ye Seul Yang, Jang Won Son, Jong Han Choi, Kee Ho Song, Nam Hoon Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Jin Wha Kim,
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 461. CrossRef
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
- Complications
-
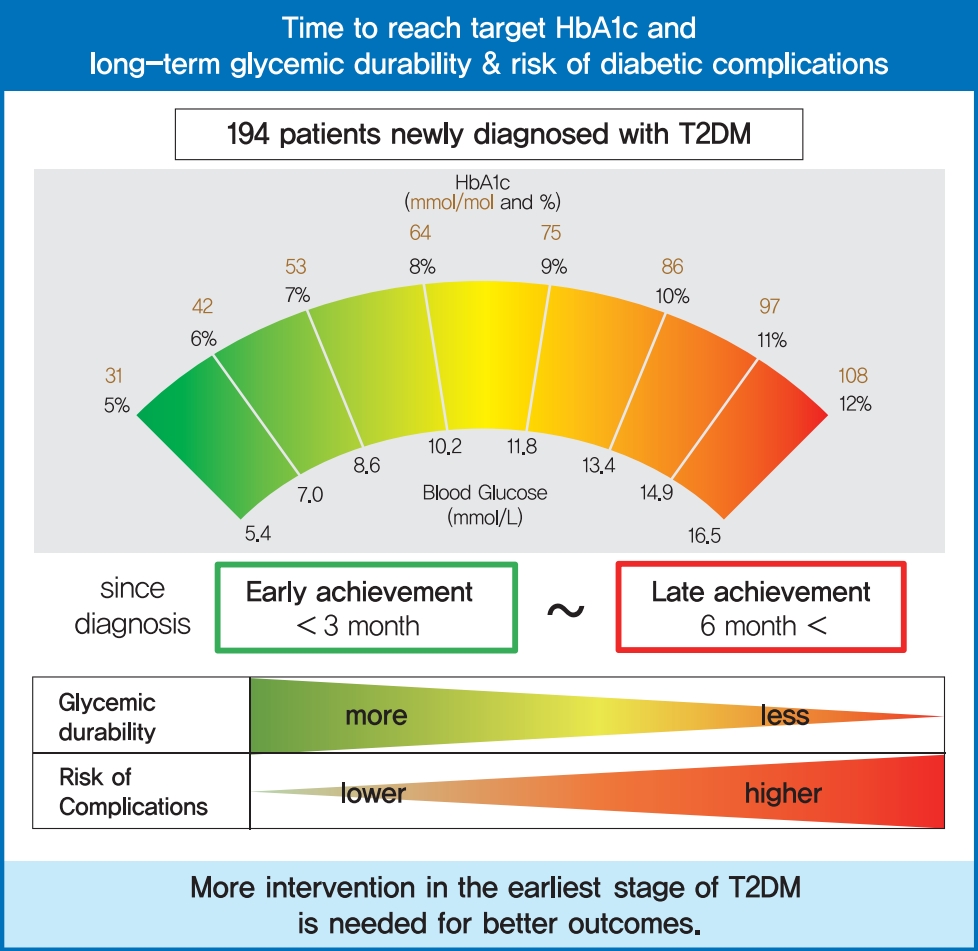
- Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study
- Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyeong Jin Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):368-378. Published online October 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0046
- 9,379 View
- 343 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
To evaluate the association of time to reach the target glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level with long-term durable glycemic control and risk of diabetic complications in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
In a longitudinal observational cohort, 194 patients with T2DM newly diagnosed between January 2011 and March 2013 were followed up over 6 years. Patients were classified according to the time needed to reach the target HbA1c (<7.0%): <3, 3 to 6 (early achievement group), and ≥6 months (late achievement group). Risks of microvascular complications including diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy as well as macrovascular events including ischemic heart disease, ischemic stroke, and peripheral arterial disease were assessed by multivariable Cox proportional hazards analysis.
Results
During a median follow-up of 6.53 years, 66 microvascular and 14 macrovascular events occurred. Maintenance of durable glycemic control over 6 years was more likely in the early achievement groups than in the late achievement group (34.5%, 30.0%, and 16.1% in <3, 3 to 6, and ≥6 months, respectively, P=0.039). Early target HbA1c achievement was associated with lower risk of composite diabetic complications (adjusted hazard ratio [HR, 0.47; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.26 to 0.86 in <3 months group) (adjusted HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.23 to 1.10 in 3 to 6 months group, in reference to ≥6 months group). Similar trends were maintained for risks of microvascular and macrovascular complications, although statistical significance was not reached for macrovascular complications.
Conclusion
Early target HbA1c achievement was associated with long-term durable glycemic control and reduced risk of diabetic complications in newly diagnosed T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- HbA1c As Diabetes Mellitus Biomarker and Its Methods Evolution
Liong Boy Kurniawan
INDONESIAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY AND MEDICAL LABORATORY.2024; 30(2): 191. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
Young Sang Lyu, Sangmo Hong, Si Eun Lee, Bo Young Cho, Cheol-Young Park
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of health quotient and time management skills on self-management behavior and glycemic control among individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Mengjie Chen, Man Liu, Ying Pu, Juan Wu, Mingjiao Zhang, Hongxia Tang, Laixi Kong, Maoting Guo, Kexue Zhu, Yuxiu Xie, Zhe Li, Bei Deng, Zhenzhen Xiong
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic control and cardiovascular complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus
I. V. Druk, S. S. Safronova
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2023; (13): 130. CrossRef - Effect of viscous soluble dietary fiber on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis on randomized clinical trials
Kun Lu, Tingqing Yu, Xinyi Cao, Hui Xia, Shaokang Wang, Guiju Sun, Liang Chen, Wang Liao
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Construction and validation of a clinical prediction model for asymptomatic obstructive coronary stenosis in patients with carotid stenosis
Cuijie Qin, Chuang Li, Yunpeng Luo, Zhen Li, Hui Cao
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk assessment of rectal anastomotic leakage (RAREAL) after DIXON in non-emergency patients with rectal cancer
Xue-Cong Zheng, Jin-Bo Su, Jin-Jie Zheng
BMC Gastroenterology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Left Ventricular Function in Diabetes Patients with Microvascular Disease by Three-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Imaging
青 周
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(12): 18908. CrossRef - Validity of the diagnosis of diabetic microvascular complications in Korean national health insurance claim data
Hyung Jun Kim, Moo-Seok Park, Jee-Eun Kim, Tae-Jin Song
Annals of Clinical Neurophysiology.2022; 24(1): 7. CrossRef - Metformin plus a low hypoglycemic risk antidiabetic drug vs. metformin monotherapy for untreated type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Wei-Tse Hung, Yuan-Jung Chen, Chun-Yu Cheng, Bruce Ovbiagele, Meng Lee, Chia-Yu Hsu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 189: 109937. CrossRef - Peripheral arterial disease progression and ankle brachial index: a cohort study with newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes
João Soares Felício, Franciane Trindade Cunha de Melo, Giovana Miranda Vieira, Vitória Teixeira de Aquino, Fernanda de Souza Parente, Wanderson Maia da Silva, Nivin Mazen Said, Emanuele Rocha da Silva, Ana Carolina Contente Braga de Souza, Maria Clara Ner
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of long-term visit-to-visit variability of HbA1c and fasting glycemia with hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chen Long, Yaling Tang, Jiangsheng Huang, Suo Liu, Zhenhua Xing
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Degree of Glycemic Control for the First Three Months Determines the Next Seven Years
Nami Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of advanced glycation end products and protein oxidation by leaf extracts and phenolics from Chilean bean landraces
Felipe Ávila, Nadia Cruz, Jazmin Alarcon-Espósito, Nélida Nina, Hernán Paillan, Katherine Márquez, Denis Fuentealba, Alberto Burgos-Edwards, Cristina Theoduloz, Carmina Vejar-Vivar, Guillermo Schmeda-Hirschmann
Journal of Functional Foods.2022; 98: 105270. CrossRef - Mediation Effect of Self-Efficacy Between Health Beliefs and Glycated Haemoglobin Levels in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study
Anqi Zhang, Jinsong Wang, Xiaojuan Wan, Jing Zhang, Zihe Guo, Yamin Miao, Shuhan Zhao, Shuo Bai, Ziyi Zhang, Weiwei Yang
Patient Preference and Adherence.2022; Volume 16: 3015. CrossRef - Early Glycosylated Hemoglobin Target Achievement Predicts Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Joonyub Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 337. CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
Ja Young Jeon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 613. CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyeong Jin Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 617. CrossRef - Plasma Nesfatin-1: Potential Predictor and Diagnostic Biomarker for Cognitive Dysfunction in T2DM Patient
Dandan Xu, Yue Yu, Yayun Xu, Jinfang Ge
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 3555. CrossRef
- HbA1c As Diabetes Mellitus Biomarker and Its Methods Evolution
- Lifestyle
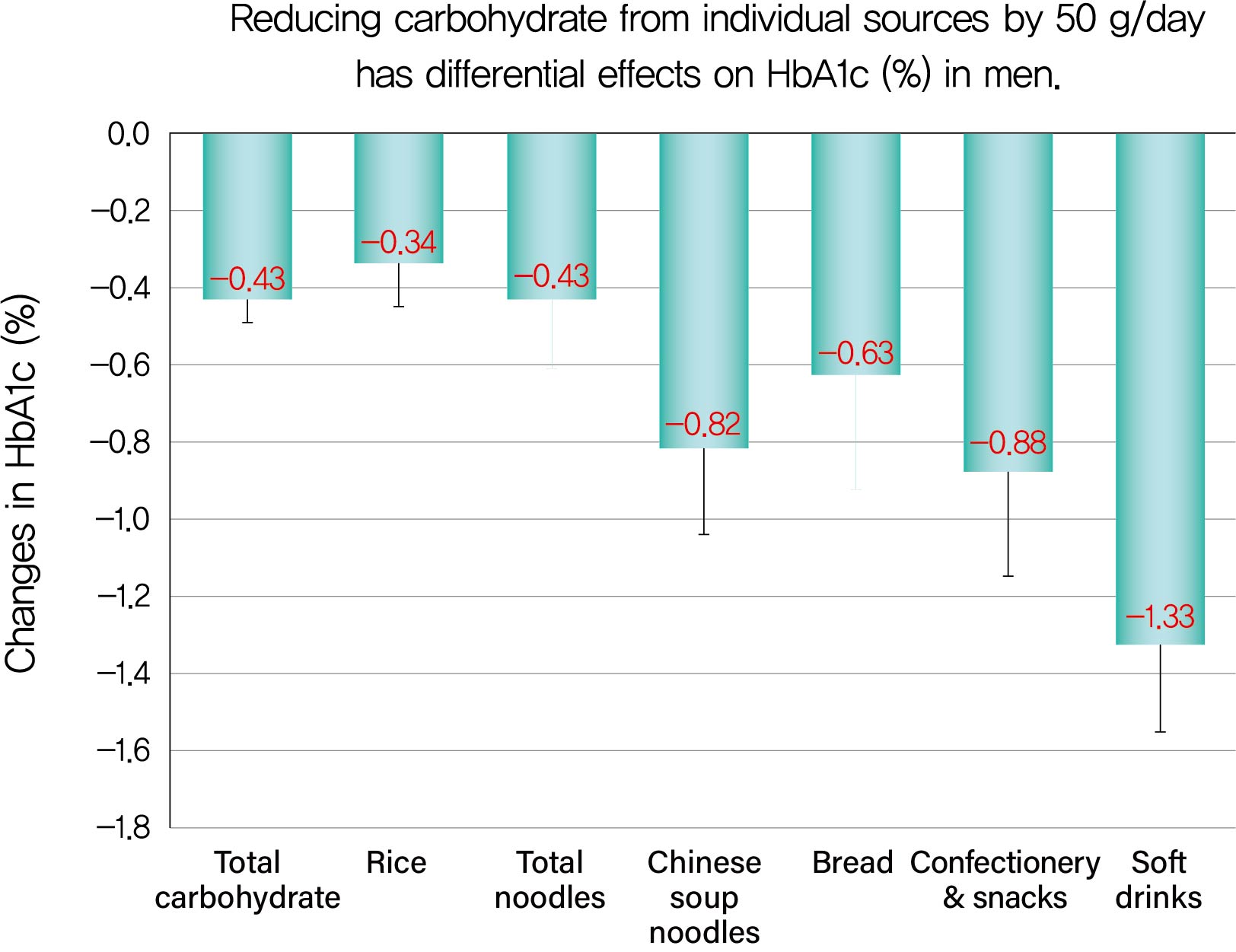
- Reducing Carbohydrate from Individual Sources Has Differential Effects on Glycosylated Hemoglobin in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients on Moderate Low-Carbohydrate Diets
- Hajime Haimoto, Shiho Watanabe, Keiko Maeda, Takashi Murase, Kenji Wakai
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):390-403. Published online July 21, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0033
- 5,786 View
- 160 Download
- 3 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
Background We evaluated decreases in glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) achieved by reducing carbohydrate from various sources in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
Methods We followed up 138 male and 107 female outpatients on a moderate low-carbohydrate diet without diabetic medication for 6 months. Changes in carbohydrate sources (Δcarbohydrate) were assessed from 3-day dietary records at baseline and 6 months, and associations with changes in HbA1c (ΔHbA1c) were examined with Spearman's correlation coefficients (
r s) and multiple regression analysis.Results ΔHbA1c was −1.5%±1.6% in men and −0.9%±1.3% in women, while Δtotal carbohydrate was −115.3±103.7 g/day in men and −63.6±71.1 g/day in women. Positive associations with ΔHbA1c were found for Δtotal carbohydrate (
r s=0.584), Δcarbohydrate from soft drinks (0.368), confectionery (0.361), rice (0.325), bread (0.221), Chinese soup noodles (0.199) in men, and Δtotal carbohydrate (0.547) and Δcarbohydrate from rice (0.376) and confectionery (0.195) in women. Reducing carbohydrate sources by 50 g achieved decreases in HbA1c of 0.43% for total carbohydrate, 1.33% for soft drinks, 0.88% for confectionery, 0.63% for bread, 0.82% for Chinese soup noodles and 0.34% for rice in men and 0.45% for total carbohydrate, 0.67% for confectionery and 0.34% for rice in women, although mean reductions in carbohydrate from these sources were much smaller than that from rice.Conclusion Decreases in HbA1c achieved by reducing carbohydrate from soft drinks, confectionery, bread and Chinese soup noodles were 2- to 4-fold greater than that for rice. Our results will enable patients to decrease HbA1c efficiently (UMIN000009866).
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring diet associations with Covid-19 and other diseases: a Network Analysis–based approach
Rashmeet Toor, Inderveer Chana
Medical & Biological Engineering & Computing.2022; 60(4): 991. CrossRef - Comprehensive Understanding for Application in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus of the Consensus Statement on Carbohydrate-Restricted Diets by Korean Diabetes Association, Korean Society for the Study of Obesity, and Korean Society of Hyperte
Jong Han Choi, Jee-Hyun Kang, Suk Chon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(3): 377. CrossRef - Associations of Dietary Salt and Its Sources with Hemoglobin A1c in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Not Taking Anti-Diabetic Medications: Analysis Based on 6-Month Intervention with a Moderate Low-Carbohydrate Diet
Hajime Haimoto, Takashi Murase, Shiho Watanabe, Keiko Maeda, Kenji Wakai
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 4569. CrossRef
- Exploring diet associations with Covid-19 and other diseases: a Network Analysis–based approach
- Complications
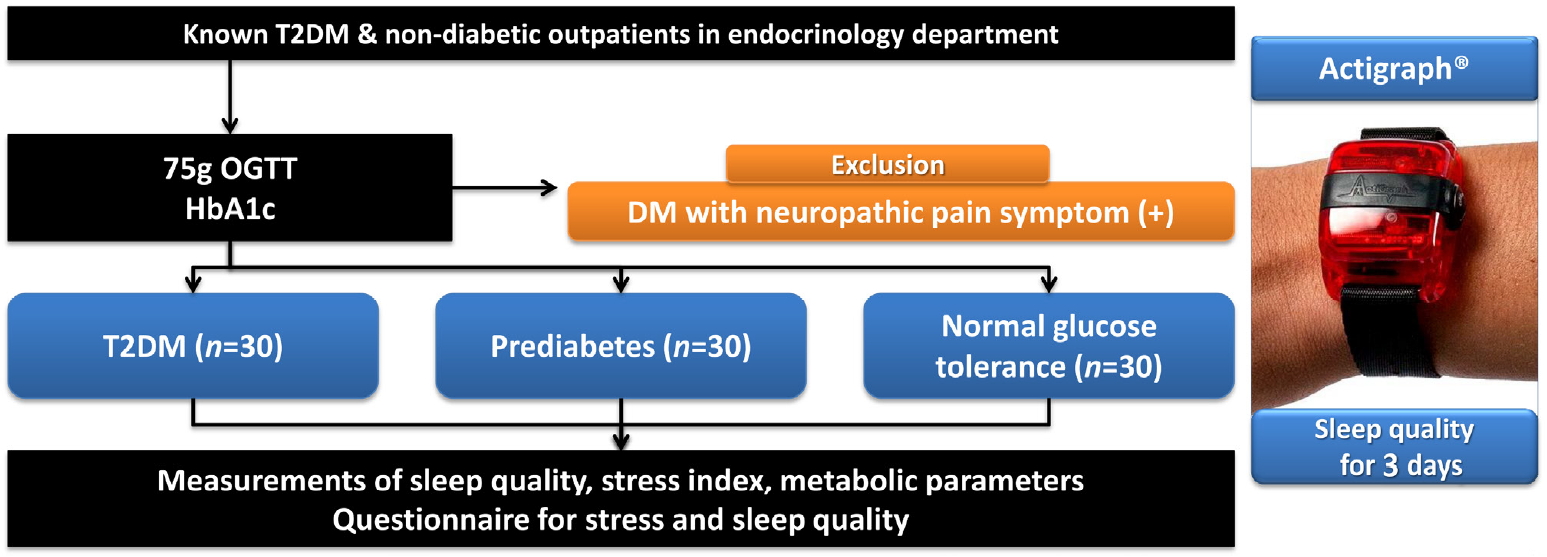
- Deterioration of Sleep Quality According to Glycemic Status
- Myung Haeng Hur, Mi-Kyoung Lee, Kayeon Seong, Jun Hwa Hong
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(5):679-686. Published online April 17, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0125
- 4,875 View
- 113 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is a progressive disease with multiple complications. The present study aimed to determine the effects of glycemic status on sleep quality in individuals with T2DM, prediabetes, and normal glucose tolerance (NGT).
Methods A total of 90 participants were categorized into three groups, T2DM (
n =30), prediabetes (n =30), and NGT (n =30). Objective sleep quality was measured with the actigraph wrist-worn device over 3 nights and subjective sleep quality was evaluated with a questionnaire.Results The duration of diabetes in the T2DM group was 2.23 years and the glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels in the T2DM, prediabetes, and NGT groups were 7.83%, 5.80%, and 5.31%, respectively. Sleep efficiency decreased across the T2DM, prediabetes, and NGT groups (86.25%, 87.99%, and 90.22%, respectively;
P =0.047). Additionally, HbA1c levels revealed a significant negative correlation with sleep efficiency (r =−0.348,P =0.001). The sleep quality questionnaire results were similar among the three groups.Conclusion Although the participants in the present study were not necessarily conscious of their sleep disturbances, deterioration in sleep quality progressed according to glycemic status.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Risk factors of non communicable diseases among recently diagnosed diabetic patients in a tertiary care Hospital
Yusra Amin, Sonia Mushtaq, Rukhsana Farooq
Indian Journal of Clinical Anatomy and Physiology.2024; 10(4): 205. CrossRef - Metabolic health tracking using Ultrahuman M1 continuous glucose monitoring platform in non- and pre-diabetic Indians: a multi-armed observational study
Monik Chaudhry, Mohit Kumar, Vatsal Singhal, Bhuvan Srinivasan
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Relation between sleep quality and glycemic control among type 2 diabetic patients
Asmaa Ali Elsayed Ali
Frontiers of Nursing.2023; 10(1): 115. CrossRef - Heart rate variability in different sleep stages is associated with metabolic function and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Wenquan Cheng, Hongsen Chen, Leirong Tian, Zhimin Ma, Xingran Cui
Frontiers in Physiology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Diabetic Retinopathy and Insomnia Risk: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Yoo Hyun Um, Tae-Won Kim, Jong-Hyun Jeong, Seung-Chul Hong, Ho-Jun Seo, Kyung-Do Han
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Nutritional Biomarkers and Factors Correlated with Poor Sleep Status among Young Females: A Case-Control Study
Sara AL-Musharaf, Lama AlAjllan, Ghadeer Aljuraiban, Munirah AlSuhaibani, Noura Alafif, Syed Danish Hussain
Nutrients.2022; 14(14): 2898. CrossRef - The impact of sleep disorders on microvascular complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (SLEEP T2D): the protocol of a cohort study and feasibility randomised control trial
Christina Antza, Ryan Ottridge, Smitaa Patel, Gemma Slinn, Sarah Tearne, Matthew Nicholls, Brendan Cooper, Asad Ali, Abd A. Tahrani
Pilot and Feasibility Studies.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Early Development of Bidirectional Associations between Sleep Disturbance and Diabetes
Yongin Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 668. CrossRef
- Risk factors of non communicable diseases among recently diagnosed diabetic patients in a tertiary care Hospital
- Epidemiology
- Low-Normal Free Thyroxine Levels in Euthyroid Male Are Associated with Prediabetes
- Sung Woo Kim, Jae-Han Jeon, Jun Sung Moon, Eon Ju Jeon, Mi-Kyung Kim, In-Kyu Lee, Jung Beom Seo, Keun-Gyu Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(5):718-726. Published online March 19, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0222
- 4,318 View
- 51 Download
- 2 Web of Science
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Abnormal thyroid function is associated with impaired glucose homeostasis. This study aimed to determine whether free thyroxine (FT4) influences the prevalence of prediabetes in euthyroid subjects using a cross-sectional survey derived from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, conducted between 2013 and 2015. We studied 2,399 male participants of >20 years of age who were euthyroid and non-diabetic. Prediabetic participants had lower FT4 concentrations than those without prediabetes, but their thyrotropin concentrations were similar. We stratified the population into tertiles according to FT4 concentration. After adjusting for multiple confounding factors, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels significantly decreased with increasing FT4 tertile, whereas fasting plasma glucose (FPG) levels were not associated with FT4 tertiles (HbA1c,
P <0.01 in T3 vs. T1; FPG,P =0.489 in T3 vs. T1). The prevalence of prediabetes was significantly higher in T1 (odds ratio, 1.426; 95% confidence interval, 1.126 to 1.806;P <0.01) than in T3. In conclusion, subjects with low-normal serum FT4 had high HbA1c and were more likely to have prediabetes. These results suggest that low FT4 concentration is a risk factor for prediabetes in male, even when thyroid function is within the normal range.
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Predictors of the Therapeutic Efficacy and Consideration of the Best Combination Therapy of Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter 2 Inhibitors
- Ji-Yeon Lee, Yongin Cho, Minyoung Lee, You Jin Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Bong-Soo Cha, Eun Seok Kang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(2):158-173. Published online January 25, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0057
- 5,938 View
- 160 Download
- 15 Web of Science
- 15 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background We investigated the predictive markers for the therapeutic efficacy and the best combination of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors (empagliflozin, dapagliflozin, and ipragliflozin) therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods A total of 804 patients with T2DM who had taken SGLT2 inhibitor as monotherapy or an add-on therapy were analyzed. Multivariate regression analyses were performed to identify the predictors of SGLT2 inhibitor response including the classes of baseline anti-diabetic medications.
Results After adjusting for age, sex, baseline body mass index (BMI), diabetes duration, duration of SGLT2 inhibitor use, initial glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level, estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and other anti-diabetic agent usage, multivariate analysis revealed that shorter diabetes duration, higher initial HbA1c and eGFR were associated with better glycemic response. However, baseline BMI was inversely correlated with glycemic status; lean subjects with well-controlled diabetes and obese subjects with inadequately controlled diabetes received more benefit from SGLT2 inhibitor treatment. In addition, dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitor use was related to a greater reduction in HbA1c in patients with higher baseline HbA1c ≥7%. Sulfonylurea users experienced a larger change from baseline HbA1c but the significance was lost after adjustment for covariates and metformin and thiazolidinedione use did not affect the glycemic outcome.
Conclusion A better response to SGLT2 inhibitors is expected in Korean T2DM patients who have higher baseline HbA1c and eGFR with a shorter diabetes duration. Moreover, the add-on of an SGLT2 inhibitor to a DPP4 inhibitor is likely to show the greatest glycemic response.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Predictors of efficacy of Sodium‐GLucose Transporter‐2 inhibitors and Glucagon‐Like Peptide 1 receptor agonists: A retrospective cohort study
Daniele Scoccimarro, Giacomo Cipani, Ilaria Dicembrini, Edoardo Mannucci
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Short-term effectiveness of dapagliflozin versus DPP-4 inhibitors in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes: a multicentre retrospective study
M. L. Morieri, I. Raz, A. Consoli, M. Rigato, A. Lapolla, F. Broglio, E. Bonora, A. Avogaro, G. P. Fadini, Federica Ginestra, Gloria Formoso, Agostino Consoli, Francesco Andreozzi, Giorgio Sesti, Salvatore Turco, Luigi Lucibelli, Adriano Gatti, Raffaella
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2023; 46(7): 1429. CrossRef - Treatment effect heterogeneity following type 2 diabetes treatment with GLP1-receptor agonists and SGLT2-inhibitors: a systematic review
Katherine G. Young, Eram Haider McInnes, Robert J. Massey, Anna R. Kahkoska, Scott J. Pilla, Sridharan Raghavan, Maggie A. Stanislawski, Deirdre K. Tobias, Andrew P. McGovern, Adem Y. Dawed, Angus G. Jones, Ewan R. Pearson, John M. Dennis, Deirdre K. Tobi
Communications Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of HbA1c treatment response to add-on medication following metformin monotherapy: a population-based cohort study
Wei Ying Tan, Wynne Hsu, Mong Li Lee, Ngiap Chuan Tan
Scientific Reports.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Evogliptin Add-on Therapy to Dapagliflozin/Metformin Combinations in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week Multicenter Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel-Design Phase-3 Trial with a 28-Week Extensio
Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Hae Jin Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Chang Won, Kyung Ah Han, Cheol-Young Park, Jong Chul Won, Dong Jun Kim, Gwan Pyo Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Chang Beom Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 808. CrossRef - Effect of Dapagliflozin as an Add-on Therapy to Insulin on the Glycemic Variability in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (DIVE): A Multicenter, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Randomized Study
Seung-Hwan Lee, Kyung-Wan Min, Byung-Wan Lee, In-Kyung Jeong, Soon-Jib Yoo, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 339. CrossRef - Angiotensin II up-regulates sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 expression and SGLT2 inhibitor attenuates Ang II-induced hypertensive renal injury in mice
Kana N. Miyata, Chao-Sheng Lo, Shuiling Zhao, Min-Chun Liao, Yuchao Pang, Shiao-Ying Chang, Junzheng Peng, Matthias Kretzler, Janos G. Filep, Julie R. Ingelfinger, Shao-Ling Zhang, John S.D. Chan
Clinical Science.2021; 135(7): 943. CrossRef - Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor for Renal Function Preservation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology Consensus Statement
Tae Jung Oh, Ju-Young Moon, Kyu Yeon Hur, Seung Hyun Ko, Hyun Jung Kim, Taehee Kim, Dong Won Lee, Min Kyong Moon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(4): 489. CrossRef - Differential indication for SGLT-2 inhibitors versus GLP-1 receptor agonists in patients with established atherosclerotic heart disease or at risk for congestive heart failure
Francesco Giorgino, Irene Caruso, Julia Moellmann, Michael Lehrke
Metabolism.2020; 104: 154045. CrossRef - Clinical Predictors of the Hypoglycemic Effect of Sodium–Glucose Co-transporter-2 Inhibitors in Hyperuricemic Patients: A Retrospective Descriptive Observational Study
Toshinori Hirai, Yuya Kawagoe, Motoki Kei, Ryuichi Ogawa, Toshimasa Itoh
Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin.2020; 43(5): 782. CrossRef - Sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor for renal function preservation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A Korean Diabetes Association and Korean Society of Nephrology consensus statement
Tae Jung Oh, Ju-Young Moon, Kyu Yeon Hur, Seung Hyun Ko, Hyun Jung Kim, Taehee Kim, Dong Won Lee, Min Kyong Moon
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 39(3): 269. CrossRef - Efficacy of Once-Weekly Semaglutide vs Empagliflozin Added to Metformin in Type 2 Diabetes: Patient-Level Meta-analysis
Ildiko Lingvay, Matthew S Capehorn, Andrei-Mircea Catarig, Pierre Johansen, Jack Lawson, Anna Sandberg, Robert Shaw, Abby Paine
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2020; 105(12): e4593. CrossRef - Letter: Predictors of the Therapeutic Efficacy and Consideration of the Best Combination Therapy of Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter 2 Inhibitors (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:158–73)
Kyung-Soo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(3): 377. CrossRef - Response: Predictors of the Therapeutic Efficacy and Consideration of the Best Combination Therapy of Sodium-Glucose Co-transporter 2 Inhibitors (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43:158–73)
Ji-Yeon Lee, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(3): 379. CrossRef - An Age of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor Priority: Are We Ready?
Ji A Seo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(5): 578. CrossRef
- Predictors of efficacy of Sodium‐GLucose Transporter‐2 inhibitors and Glucagon‐Like Peptide 1 receptor agonists: A retrospective cohort study
- Complications
- Glycosylated Hemoglobin in Subjects Affected by Iron-Deficiency Anemia
- Jari Intra, Giuseppe Limonta, Fabrizio Cappellini, Maria Bertona, Paolo Brambilla
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(4):539-544. Published online November 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0072
- 4,849 View
- 99 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Previous studies have suggested that iron-deficiency anemia affects glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) measurements, but the results were contradictory. We conducted a retrospective case-control study to determine the effects of iron deficiency on HbA1c levels. Starting with the large computerized database of the Italian Hospital of Desio, including data from 2000 to 2016, all non-pregnant individuals older than 12 years of age with at least one measurement of HbA1c, cell blood count, ferritin, and fasting blood glucose on the same date of blood collection were enrolled. A total of 2,831 patients met the study criteria. Eighty-six individuals were diagnosed with iron-deficiency anemia, while 2,745 had a normal iron state. The adjusted means of HbA1c were significantly higher in anemic subjects (5.59% [37.37 mmol/mol]), than those measured in individuals without anemia (5.34% [34.81 mmol/mol]) (
P <0.0001). These results suggest that clinicians should be cautious about diagnosing prediabetes and diabetes in individuals with anemia.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fingerprinting hyperglycemia using predictive modelling approach based on low-cost routine CBC and CRP diagnostics
Amna Tahir, Kashif Asghar, Waqas Shafiq, Hijab Batool, Dilawar Khan, Omar Chughtai, Safee Ullah Chaudhary
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Implications of Iron Deficiency Anaemia on Glycemic Dynamics in Diabetes Mellitus: A Critical Risk Factor in Cardiovascular Disease
Eman Elsheikh, Sereen S Aljohani , Munirah M Alshaikhmubarak, Meshari A Alhawl, Alhanouf W Alsubaie, Norah Alsultan, Asmaa F Sharif, Sayed Ibrahim Ali
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Usefulness of glucose management indicator derived from continuous glucose monitoring to assess glycemic condition in hospitalized patients with diabetic kidney disease treated with insulin pumps
Yi Lu, Qian Zhang, Xiangyu Wang, Ya Jiang, Yaoming Xue
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(11): 108613. CrossRef - Serum Iron Profile in Type 2 Diabetes, A Role Beyond Anemic Marker!
Happy Chutia, Sungdirenla Jamir, Md Yasir, Gautam Handique
The Journal of Medical Research.2023; 9(5): 129. CrossRef - Association between Anemia and Myopia in Korean Adults
Minyi Seo, Sangshin Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(4): 314. CrossRef - Large-scale retrospective analyses of the effect of iron deficiency anemia on hemoglobin A1c concentrations
Lokinendi V. Rao, George W. Pratt, Caixia Bi, Martin H. Kroll
Clinica Chimica Acta.2022; 529: 21. CrossRef - Integrity loss of glycosylated hemoglobin with deepening anemia
Bünyamin AYDIN, Aysun GÖNDEREN
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2022; 5(3): 839. CrossRef - Association between hemoglobin within the normal range and hemoglobin A1c among Chinese non-diabetes adults
Yi Lai, Zhihong Lin, Zhongxin Zhu
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association between Daily Total Dietary Nutrient Intake and Recent Glycemic Control States of Non-Pregnant Adults 20+ Years Old from NHANES 1999–2018 (Except for 2003–2004)
Yin Bai, Hao Zhang, Jie Yang, Lei Peng
Nutrients.2021; 13(11): 4168. CrossRef
- Fingerprinting hyperglycemia using predictive modelling approach based on low-cost routine CBC and CRP diagnostics
- Clinical Diabetes & Therapeutics
- Effectiveness of Exercise Intervention in Reducing Body Weight and Glycosylated Hemoglobin Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Ji-Eun Jang, Yongin Cho, Byung Wan Lee, Ein-Soon Shin, Sun Hee Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(3):302-318. Published online November 19, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0062
- 5,295 View
- 97 Download
- 11 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background This study aimed to assess the effectiveness of exercise intervention in reducing body weight and glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Korea.
Methods Cochrane, PubMed, Embase, KoreaMed, KMbase, NDSL, KCI, RISS, and DBpia databases were used to search randomized controlled trials and controlled clinical trials that compared exercise with non-exercise intervention among patients with non-insulin-treated T2DM in Korea. The effectiveness of exercise intervention was estimated by the mean difference in body weight changes and HbA1c level. Weighted mean difference (WMD) with its corresponding 95% confidence interval (CI) was used as the effect size. The pooled mean differences of outcomes were calculated using a random-effects model.
Results We identified 7,692 studies through literature search and selected 23 articles (723 participants). Compared with the control group, exercise intervention (17 studies) was associated with a significant decline in HbA1c level (WMD, −0.58%; 95% CI, −0.89 to −0.27;
I 2=73%). Although no significant effectiveness on body weight was observed, eight aerobic training studies showed a significant reduction in body weight (WMD, −2.25 kg; 95% CI, −4.36 to −0.13;I 2=17%) in the subgroup analysis.Conclusion Exercise significantly improves glycemic control; however, it does not significantly reduce body weight. Aerobic training can be beneficial for patients with non-insulin-treated T2DM in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- The anti-inflammatory effects of aerobic exercise training in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Georgia Papagianni, Chrystalla Panayiotou, Michail Vardas, Nikolaos Balaskas, Constantinos Antonopoulos, Dimitrios Tachmatzidis, Triantafyllos Didangelos, Vaia Lambadiari, Nikolaos P.E. Kadoglou
Cytokine.2023; 164: 156157. CrossRef - Glucose Control in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus according to Body Mass Index
Ye-lim Shin, Heesoh Yoo, Joo Young Hong, Jooeun Kim, Kyung-do Han, Kyu-Na Lee, Yang-Hyun Kim
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2023; 32(1): 55. CrossRef - Exercise therapy for diabetes mellitus
Chaiho Jeong, Tae-Seo Sohn
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2023; 66(7): 427. CrossRef - Effects of an evidence‐based nursing intervention on prevention of anxiety and depression in the postpartum period
Jun Meng, Junying Du, Xiaoli Diao, Yingxia Zou
Stress and Health.2022; 38(3): 435. CrossRef - Effect of exercise intervention dosage on reducing visceral adipose tissue: a systematic review and network meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Yu-Hsuan Chang, Hui-Ying Yang, Shiow-Ching Shun
International Journal of Obesity.2021; 45(5): 982. CrossRef - Development and validation of the type 2 diabetes mellitus 10-year risk score prediction models from survey data
Gregor Stiglic, Fei Wang, Aziz Sheikh, Leona Cilar
Primary Care Diabetes.2021; 15(4): 699. CrossRef - Pioglitazone for NAFLD Patients With Prediabetes or Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Meta-Analysis
Jingxuan Lian, Jianfang Fu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise Training: The Holistic Approach in Cardiovascular Prevention
Francesco Giallauria, Teresa Strisciuglio, Gianluigi Cuomo, Anna Di Lorenzo, Andrea D’Angelo, Mario Volpicelli, Raffaele Izzo, Maria Virginia Manzi, Emanuele Barbato, Carmine Morisco
High Blood Pressure & Cardiovascular Prevention.2021; 28(6): 561. CrossRef - Effect of chronic High Intensity Interval Training on glycosylated haemoglobin in people with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis
María Cristina Arrieta-Leandro, Jessenia Hernández-Elizondo, Judith Jiménez-Díaz
Human Movement.2021; 24(1): 32. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Fatty Liver Research Group of the Korean Diabetes Association
Byung-Wan Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Cheol-Young Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee, Nan-Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Keun-Gyu Park, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Bong-Soo Cha, Dae Ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 382. CrossRef - Beneficial effect of anti-diabetic drugs for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung-Soo Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Clinical and Molecular Hepatology.2020; 26(4): 430. CrossRef - Factors Influencing Glycemic Control among Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients: The Sixth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2013~2015)
Mee Ock Gu
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2019; 31(3): 235. CrossRef
- The anti-inflammatory effects of aerobic exercise training in patients with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- Epidemiology
- Discrepancies between Glycosylated Hemoglobin and Fasting Plasma Glucose for Diagnosing Impaired Fasting Glucose and Diabetes Mellitus in Korean Youth and Young Adults
- Jieun Lee, Young Ah Lee, Jae Hyun Kim, Seong Yong Lee, Choong Ho Shin, Sei Won Yang
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(2):174-182. Published online November 2, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0046
- 5,090 View
- 73 Download
- 9 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) has been recommended as a diagnostic test for prediabetes and diabetes. Here, we evaluated the level of agreement between diagnoses based on fasting plasma glucose (FPG) versus HbA1c levels and determined optimal HbA1c cutoff values for these diseases in youth and young adults.
Methods The study included 7,332 subjects (
n =4,129, aged 10 to 19 years in youth group; andn =3,203 aged 20 to 29 years in young adult group) from the 2011 to 2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Prediabetes and diabetes were defined as 100 to 125 mg/dL (impaired fasting glucose [IFG]) and ≥126 mg/dL for FPG (diabetes mellitus [DM] by FPG [DMFPG]), and 5.7% to 6.4% and ≥6.5% for HbA1c, respectively.Results In the youth group, 32.5% with IFG had an HbA1c level of 5.7% to 6.4%, and 72.2% with DMFPG had an HbA1c ≥6.5%. In the young adult group, 27.5% with IFG had an HbA1c level of 5.7% to 6.4%, and 66.6% with DMFPG had an HbA1c ≥6.5%. Kappa coefficients for agreement between the FPG and HbA1c results were 0.12 for the youth group and 0.19 for the young adult group. In receiver operating characteristic curve analysis, the optimal HbA1c cutoff for IFG and DMFPG were 5.6% and 5.9% in youths and 5.5% and 5.8% in young adults, respectively.
Conclusion Usefulness of HbA1c for diagnosis of IFG and DMFPG in Koreans aged <30 years remains to be determined due to discrepancies between the results of glucose- and HbA1c-based tests. Additional testing might be warranted at lower HbA1c levels to detect IFG and DMFPG in this age group.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Lower Dietary Magnesium Is Associated with a Higher Hemoglobin Glycation Index in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Juan Chen, Song Lin, Xingzhou Wang, Xiwei Wang, Pengxia Gao
Biological Trace Element Research.2024; 202(3): 878. CrossRef - Glycemic traits and colorectal cancer survival in a cohort of South Korean patients: A Mendelian randomization analysis
So Yon Jun, Sooyoung Cho, Min Jung Kim, Ji Won Park, Seung‐Bum Ryoo, Seung Yong Jeong, Kyu Joo Park, Aesun Shin
Cancer Medicine.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Associations between HbA1c-derived estimated average glucose and fasting plasma glucose in patients with normal and abnormal hemoglobin patterns
Wilaiwan Sriwimol, Phattanapong Choosongsang, Pensiri Choosongsang, Warakorn Petkliang, Pittaya Treerut
Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation.2022; 82(3): 192. CrossRef - Increasing prevalence of fasting hyperglycemia in adolescents aged 10–18 years and its relationship with metabolic indicators: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Study (KNHANES), 2007–2018
Seung Eun Yoo, Ji Hyen Lee, Jung Won Lee, Hye Sook Park, Hye Ah Lee, Hae Soon Kim
Annals of Pediatric Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 27(1): 60. CrossRef - Differences in Clinical Indicators of Diabetes, Hypertension, and Dyslipidemia Among Workers Who Worked Long Hours and Shift Work
EunKyo Kang
Workplace Health & Safety.2021; 69(6): 268. CrossRef - Practice Patterns in the Acceptance of Medically Complex Living Kidney Donors with Obesity, Hypertension, Family History of Kidney Disease, or Donor-Recipient Age Discrepancy
Ziad Arabi, Muhammad Bukhari, Abdullah Hamad, Abdulrahman Altheaby, Saleh Kaysi
Avicenna Journal of Medicine.2021; 11(04): 172. CrossRef - Endocrine comorbidities of pediatric obesity
Jieun Lee, Jae Hyun Kim
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics.2021; 64(12): 619. CrossRef - Association between handgrip strength and cardiovascular risk factors among Korean adolescents
Kyoung Kon Kim, Kyu Rae Lee, In Cheol Hwang
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 33(9): 1213. CrossRef - Hypertriglyceridemia is associated with long-term risk of cardiovascular events and specific comorbidity in very high-risk hypertensive patients
O. Ya. Korolyuk, O. M. Radchenko
The Ukrainian Biochemical Journal.2020; 92(2): 8. CrossRef - The Effect of Bariatric Surgery on Weight Loss and Metabolic Changes in Adults with Obesity
Stanisław Głuszek, Arkadiusz Bociek, Edyta Suliga, Jarosław Matykiewicz, Magdalena Kołomańska, Piotr Bryk, Przemysław Znamirowski, Łukasz Nawacki, Martyna Głuszek-Osuch, Iwona Wawrzycka, Dorota Kozieł
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(15): 5342. CrossRef - Peculiarities of Clinical Presentations and Long–Term Complications in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease and Metabolic Syndrome, depending on their Serum Triglyceride Levels
O. Ya. Korolyuk
Ukraïnsʹkij žurnal medicini, bìologìï ta sportu.2020; 5(1): 125. CrossRef
- Lower Dietary Magnesium Is Associated with a Higher Hemoglobin Glycation Index in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





