
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
- Complications
- Impact of Hyperglycemia on Complication and Mortality after Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Sun Joon Moon, Chang Ho Ahn, Yun Bin Lee, Young Min Cho
- Diabetes Metab J. 2024;48(2):302-311. Published online January 3, 2024
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0255
- 796 View
- 120 Download
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Current guidelines regarding periprocedural glycemic control to prevent complications after nonsurgical invasive procedures are insufficient. Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a widely used treatment for unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma. We aimed to investigate the association between diabetes mellitus (DM) per se and the degree of hyperglycemia with postprocedural complications after TACE.
Methods
A total of 22,159 TACE procedures performed at Seoul National University Hospital from 2005 to 2018 were retrospectively analyzed. The associations between DM, preprocedural glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), and periprocedural average glucose with postprocedural adverse outcomes were evaluated. The primary outcome was occurrence of postprocedural bacteremia. Secondary outcomes were acute kidney injury (AKI), delayed discharge and death within 14 days. Periprocedural glucose was averaged over 3 days: the day of, before, and after the TACE procedures. Propensity score matching was applied for procedures between patients with or without DM.
Results
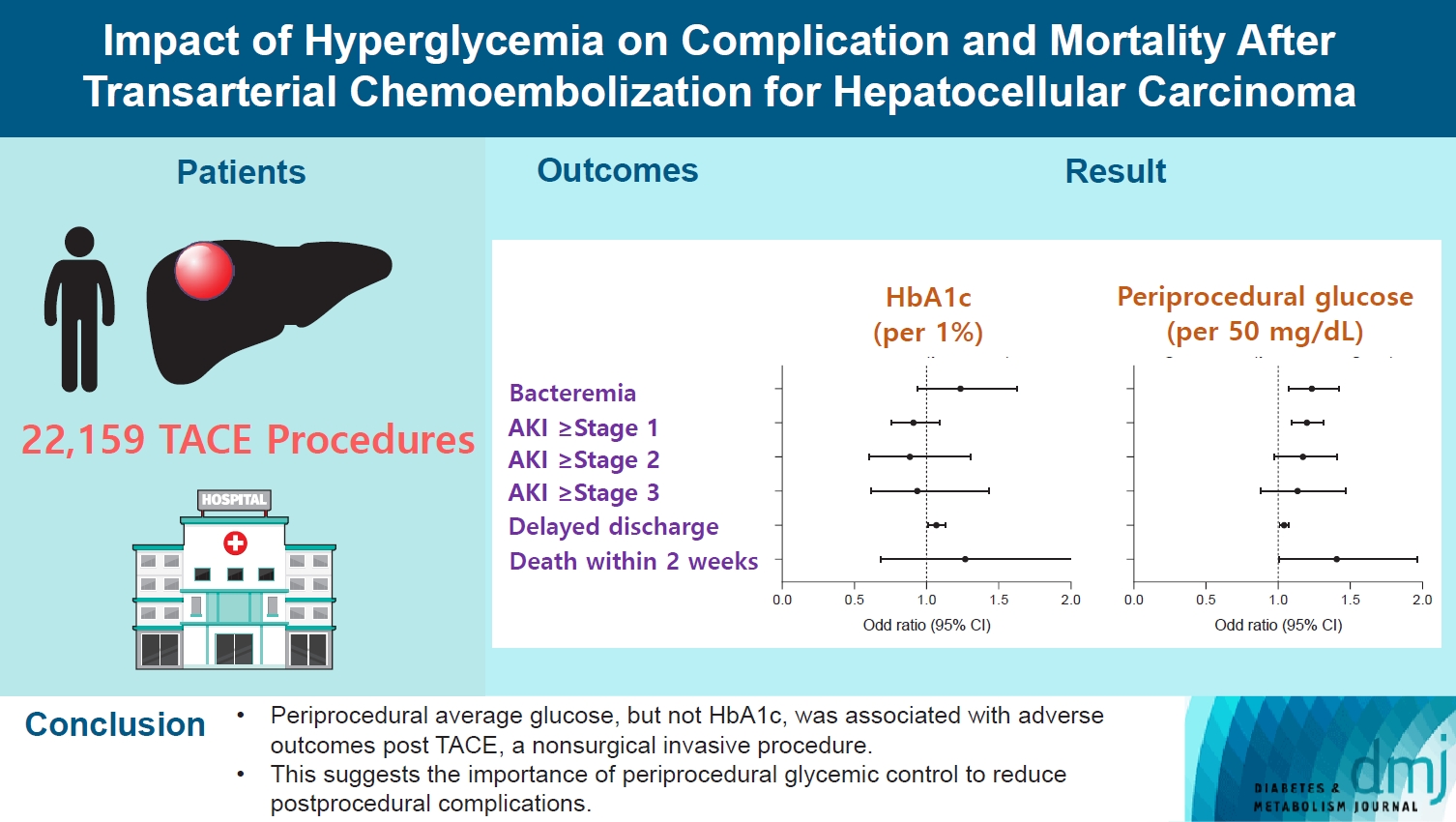
Periprocedural average glucose was significantly associated with bacteremia (adjusted odds ratio per 50 mg/dL of glucose, 1.233; 95% confidence interval, 1.071 to 1.420; P=0.004), AKI, delayed discharge, and death within 14 days. DM per se was only associated with bacteremia and AKI. Preprocedural HbA1c was associated with delayed discharge. Average glucose levels above 202 and 181 mg/dL were associated with a significantly higher risk of bacteremia and AKI, respectively, than glucose levels of 126 mg/dL or lower.
Conclusion
Periprocedural average glucose, but not HbA1c, was associated with adverse outcomes after TACE, which is a nonsurgical invasive procedure. This suggests the importance of periprocedural glycemic control to reduce postprocedural complications.
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Intensified Multifactorial Intervention in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Takayoshi Sasako, Toshimasa Yamauchi, Kohjiro Ueki
- Diabetes Metab J. 2023;47(2):185-197. Published online January 12, 2023
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2022.0325
- 5,126 View
- 358 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
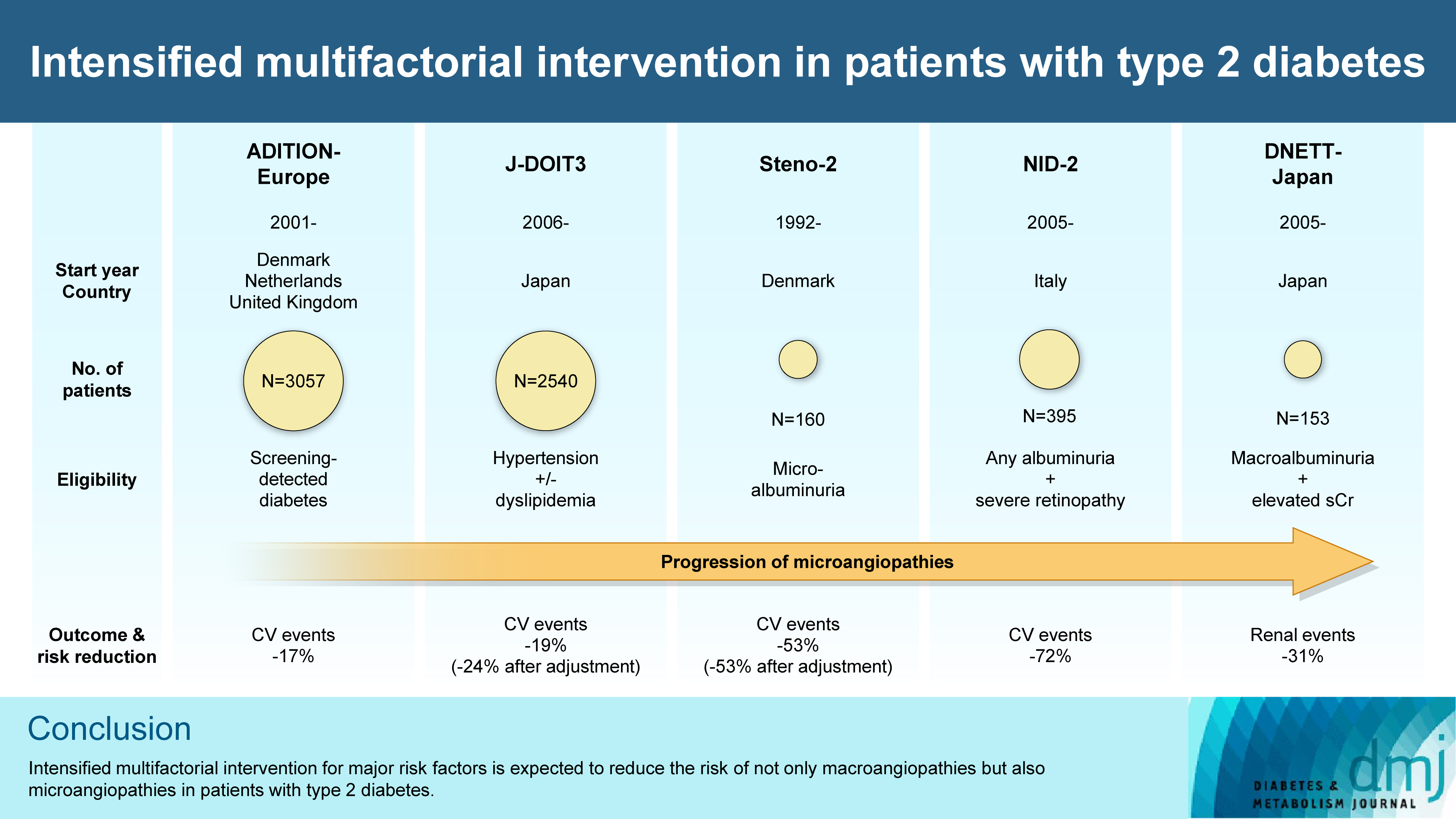
ePub - In the management of diabetes mellitus, one of the most important goals is to prevent its micro- and macrovascular complications, and to that end, multifactorial intervention is widely recommended. Intensified multifactorial intervention with pharmacotherapy for associated risk factors, alongside lifestyle modification, was first shown to be efficacious in patients with microalbuminuria (Steno-2 study), then in those with less advanced microvascular complications (the Anglo-Danish-Dutch Study of Intensive Treatment In People with Screen Detected Diabetes in Primary Care [ADDITION]-Europe and the Japan Diabetes Optimal Treatment study for 3 major risk factors of cardiovascular diseases [J-DOIT3]), and in those with advanced microvascular complications (the Nephropathy In Diabetes-Type 2 [NID-2] study and Diabetic Nephropathy Remission and Regression Team Trial in Japan [DNETT-Japan]). Thus far, multifactorial intervention led to a reduction in cardiovascular and renal events, albeit not necessarily significant. It should be noted that not only baseline characteristics but also the control status of the risk factors and event rates during intervention among the patients widely varied from one trial to the next. Further evidence is needed for the efficacy of multifactorial intervention in a longer duration and in younger or elderly patients. Moreover, now that new classes of antidiabetic drugs are available, it should be addressed whether strict and safe glycemic control, alongside control of other risk factors, could lead to further risk reductions in micro- and macrovascular complications, thereby decreasing all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Exploring mechanisms underlying diabetes comorbidities and strategies to prevent vascular complications
Takayoshi Sasako
Diabetology International.2024; 15(1): 34. CrossRef - Targeting ERS-mitophagy in hippocampal neurons to explore the improvement of memory by tea polyphenols in aged type 2 diabetic rats
Wenjuan Feng, Chenhui Lv, Le Cheng, Xin Song, Xuemin Li, Haoran Xie, Shuangzhi Chen, Xi Wang, Lushan Xue, Cheng Zhang, Jie Kou, Lili Wang, Haifeng Zhao
Free Radical Biology and Medicine.2024; 213: 293. CrossRef - Risk of Dementia Among Patients With Diabetes in a Multidisciplinary, Primary Care Management Program
Kailu Wang, Shi Zhao, Eric Kam-Pui Lee, Susan Zi-May Yau, Yushan Wu, Chi-Tim Hung, Eng-Kiong Yeoh
JAMA Network Open.2024; 7(2): e2355733. CrossRef - Causes of In-Hospital Death and Pharmaceutical Associations with Age of Death during a 10-Year Period (2011–2020) in Individuals with and without Diabetes at a Japanese Community General Hospital
Minae Hosoki, Taiki Hori, Yousuke Kaneko, Kensuke Mori, Saya Yasui, Seijiro Tsuji, Hiroki Yamagami, Saki Kawata, Tomoyo Hara, Shiho Masuda, Yukari Mitsui, Kiyoe Kurahashi, Takeshi Harada, Shingen Nakamura, Toshiki Otoda, Tomoyuki Yuasa, Akio Kuroda, Itsur
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(5): 1283. CrossRef - External validation of a minimal-resource model to predict reduced estimated glomerular filtration rate in people with type 2 diabetes without diagnosis of chronic kidney disease in Mexico: a comparison between country-level and regional performance
Camilla Sammut-Powell, Rose Sisk, Ruben Silva-Tinoco, Gustavo de la Pena, Paloma Almeda-Valdes, Sonia Citlali Juarez Comboni, Susana Goncalves, Rory Cameron
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Gut Microbiota Targeted Approach by Natural Products in Diabetes Management: An Overview
Priyanka Sati, Praveen Dhyani, Eshita Sharma, Dharam Chand Attri, Arvind Jantwal, Rajni Devi, Daniela Calina, Javad Sharifi-Rad
Current Nutrition Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Cardiovascular Risk Reduction in Type 2 Diabetes: Further Insights into the Power of Weight Loss and Exercise
Seung-Hwan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2023; 38(3): 302. CrossRef - Sarcopenia: Loss of mighty armor against frailty and aging
Takayoshi Sasako, Kohjiro Ueki
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(10): 1145. CrossRef
- Exploring mechanisms underlying diabetes comorbidities and strategies to prevent vascular complications
- Complication
- Waist Circumference and Body Mass Index Variability and Incident Diabetic Microvascular Complications: A Post Hoc Analysis of ACCORD Trial
- Daniel Nyarko Hukportie, Fu-Rong Li, Rui Zhou, Jia-Zhen Zheng, Xiao-Xiang Wu, Xian-Bo Wu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(5):767-780. Published online May 10, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0258
- 3,806 View
- 221 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Obesity is associated with adverse health events among diabetic patients, however, the relationship between obesity fluctuation and risk of microvascular complications among this specific population is unclear. We aimed to examine the effect of waist circumference (WC) and body mass index (BMI) variability on the risk of diabetic microvascular outcome
Methods
Annually recorded anthropometric data in the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) study was used to examine the association of WC and BMI variability defined as variability independent of mean, with the risk of microvascular outcomes, including neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy. Cox proportional hazards models were used to estimate the hazard ratios (HRs) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs) (Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov., no. NCT00000620).
Results
There were 4,031, 5,369, and 2,601 cases of neuropathy, nephropathy, and retinopathy during a follow-up period of 22,524, 23,941, and 23,850 person-years, respectively. Higher levels of WC and BMI variability were associated with an increased risk of neuropathy. Compared with the lowest quartile, the fully-adjusted HR (95% CI) for the highest quartile of WC and BMI variability for neuropathy risk were 1.21 (1.05 to 1.40) and 1.16 (1.00 to 1.33), respectively. Also, higher quartiles of BMI variability but not WC variability were associated with increased risk of nephropathic events. The fully-adjusted HR (95% CI) for the highest quartile compared with the lowest quartile of BMI variability was 1.31 (1.18 to 1.46). However, the results for retinopathic events were all insignificant.
Conclusion
Among participants with type 2 diabetes mellitus, WC and BMI variability were associated with a higher risk of neuropathic events, whereas BMI variability was associated with an increased risk of nephropathic events. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of body mass index and blood pressure variability with 10-year mortality and renal disease progression in type 2 diabetes
Stephen Fava, Sascha Reiff
Acta Diabetologica.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Waist Circumference and Body Mass Index Variability and Incident Diabetic Microvascular Complications: A Post Hoc Analysis of ACCORD Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:767-80)
Yun Kyung Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 147. CrossRef - Waist Circumference and Body Mass Index Variability and Incident Diabetic Microvascular Complications: A Post Hoc Analysis of ACCORD Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2022;46:767-80)
Daniel Nyarko Hukportie, Fu-Rong Li, Rui Zhou, Jia-Zhen Zheng, Xiao-Xiang Wu, Xian-Bo Wu
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 150. CrossRef - Weight variability and diabetes complications
Francesco Prattichizzo, Chiara Frigé, Rosalba La Grotta, Antonio Ceriello
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 199: 110646. CrossRef - Risk Factors for Diabetic Retinopathy in Latin America (Mexico) and the World: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Oscar Vivanco-Rojas, Sonia López-Letayf, Valentina Londoño-Angarita, Fátima Sofía Magaña-Guerrero, Beatriz Buentello-Volante, Yonathan Garfias
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(20): 6583. CrossRef - Effects of body weight variability on risks of macro- and microvascular outcomes in individuals with type 2 diabetes: The Rio de Janeiro type 2 diabetes cohort
Claudia R.L. Cardoso, Nathalie C. Leite, Gil F. Salles
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2023; 205: 110992. CrossRef - Correlation Between the Variability of Different Obesity Indices and Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study Based on Populations in Taiwan
Zhenzhen Sun, Kun Wang, Chuan Yun, Fang Bai, Xiaodan Yuan, Yaujiunn Lee, Qingqing Lou
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 2791. CrossRef - Unraveling shared risk factors for diabetic foot ulcer: a comprehensive Mendelian randomization analysis
Kangli Yin, Tianci Qiao, Yongkang Zhang, Jiarui Liu, Yuzhen Wang, Fei Qi, Junlin Deng, Cheng Zhao, Yongcheng Xu, Yemin Cao
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2023; 11(6): e003523. CrossRef
- Association of body mass index and blood pressure variability with 10-year mortality and renal disease progression in type 2 diabetes
- Metabolic Risk/Epidemiology
- Effect of Different Types of Diagnostic Criteria for Gestational Diabetes Mellitus on Adverse Neonatal Outcomes: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis, and Meta-Regression
- Fahimeh Ramezani Tehrani, Marzieh Saei Ghare Naz, Razieh Bidhendi-Yarandi, Samira Behboudi-Gandevani
- Diabetes Metab J. 2022;46(4):605-619. Published online March 8, 2022
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0178
- 5,129 View
- 298 Download
- 7 Web of Science
- 7 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
Evidence supporting various diagnostic criteria for diagnose gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) are consensus-based, needs for additional evidence related to outcomes. Therefore, the aim of this systematic-review and meta-analysis was to assess the impact of different GDM diagnostic-criteria on the risk of adverse-neonatal-outcomes.
Methods
Electronic databases including Scopus, PubMed, and Web of Sciences were searched to retrieve English original, population-based studies with the universal GDM screening approach, up to January-2020. GDM diagnostic criteria were classified in seven groups and International Association of the Diabetes and Pregnancy Study Groups (IADPSG) was considered as reference one. We used the Mantel–Haenszel method to calculate the pooled odds of events. The possibility of publication bias was examined by Begg’s test.
Results
A total of 55 population-based studies consisting of 1,604,391 pregnant women with GDM and 7,770,855 non-GDM counterparts were included. Results showed that in all diagnostic-criteria subgroups, the risk of adverse neonatal outcomes including macrosomia, hyperbilirubinemia, respiratory distress syndrome, neonatal hypoglycemia, neonatal intensive care unit admission, preterm birth, and birth-trauma were significantly higher than the non-GDM counterparts were significantly higher than non-GDM counterparts. Meta-regression analysis revealed that the magnitude of neonatal risks in all diagnostic-criteria subgroups are similar.
Conclusion
Our results showed that the risk of adverse-neonatal-outcome increased among women with GDM, but the magnitude of risk was not different among those women who were diagnosed through more or less intensive strategies. These findings may help health-care-providers and policy-makers to select the most cost-effective approach for the screening of GDM among pregnant women. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Hyperglycemia in pregnancy did not worsen the short-term outcomes of very preterm infants: a propensity score matching study
Ying Li, Wei Shen, Rong Zhang, Jian Mao, Ling Liu, Yan-Mei Chang, Xiu-Zhen Ye, Yin-Ping Qiu, Li Ma, Rui Cheng, Hui Wu, Dong-Mei Chen, Ling Chen, Ping Xu, Hua Mei, San-Nan Wang, Fa-Lin Xu, Rong Ju, Xiao-Mei Tong, Xin-Zhu Lin, Fan Wu
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetesscreening in der Schwangerschaft
Ute Schäfer-Graf
Die Gynäkologie.2023; 56(2): 103. CrossRef - One-step versus two-step screening for diagnosis of gestational diabetes mellitus in Iranian population: A randomized community trial
Fahimeh Ramezani Tehrani, Maryam Rahmati, Farshad Farzadfar, Mehrandokht Abedini, Maryam Farahmand, Farhad Hosseinpanah, Farzad Hadaegh, Farahnaz Torkestani, Majid Valizadeh, Fereidoun Azizi, Samira Behboudi-Gandevani
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Predictors of Neonatal Intensive Care Unit Admission and Adverse Outcomes Related to Gestational Diabetes
Abdullah M Al-shahrani
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Positive association between circulating Caveolin-1 and microalbuminuria in overt diabetes mellitus in pregnancy
Y. Shu, Y. Xiong, Y. Song, S. Jin, X. Bai
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2023; 47(1): 201. CrossRef - Early-to-mid pregnancy sleep and circadian markers in relation to birth outcomes: An epigenetics pilot study
Erica C. Jansen, Kelvin Pengyuan Zhang, Dana C. Dolinoy, Helen J. Burgess, Louise M. O’Brien, Elizabeth Langen, Naquia Unwala, Jessa Ehlinger, Molly C. Mulcahy, Jaclyn M. Goodrich
Chronobiology International.2023; 40(9): 1224. CrossRef - Various screening and diagnosis approaches for gestational diabetes mellitus and adverse pregnancy outcomes: a secondary analysis of a randomized non-inferiority field trial
Fahimeh Ramezani Tehrani, Ali Sheidaei, Maryam Rahmati, Farshad Farzadfar, Mahsa Noroozzadeh, Farhad Hosseinpanah, Mehrandokht Abedini, Farzad Hadaegh, Majid Valizadeh, Farahnaz Torkestani, Davood Khalili, Faegheh Firouzi, Masoud Solaymani-Dodaran, Afshin
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2023; 11(6): e003510. CrossRef
- Hyperglycemia in pregnancy did not worsen the short-term outcomes of very preterm infants: a propensity score matching study
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Time in Range from Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Novel Metric for Glycemic Control
- Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(6):828-839. Published online December 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0257
- Correction in: Diabetes Metab J 2021;45(5):795
- 9,878 View
- 469 Download
- 31 Web of Science
- 36 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
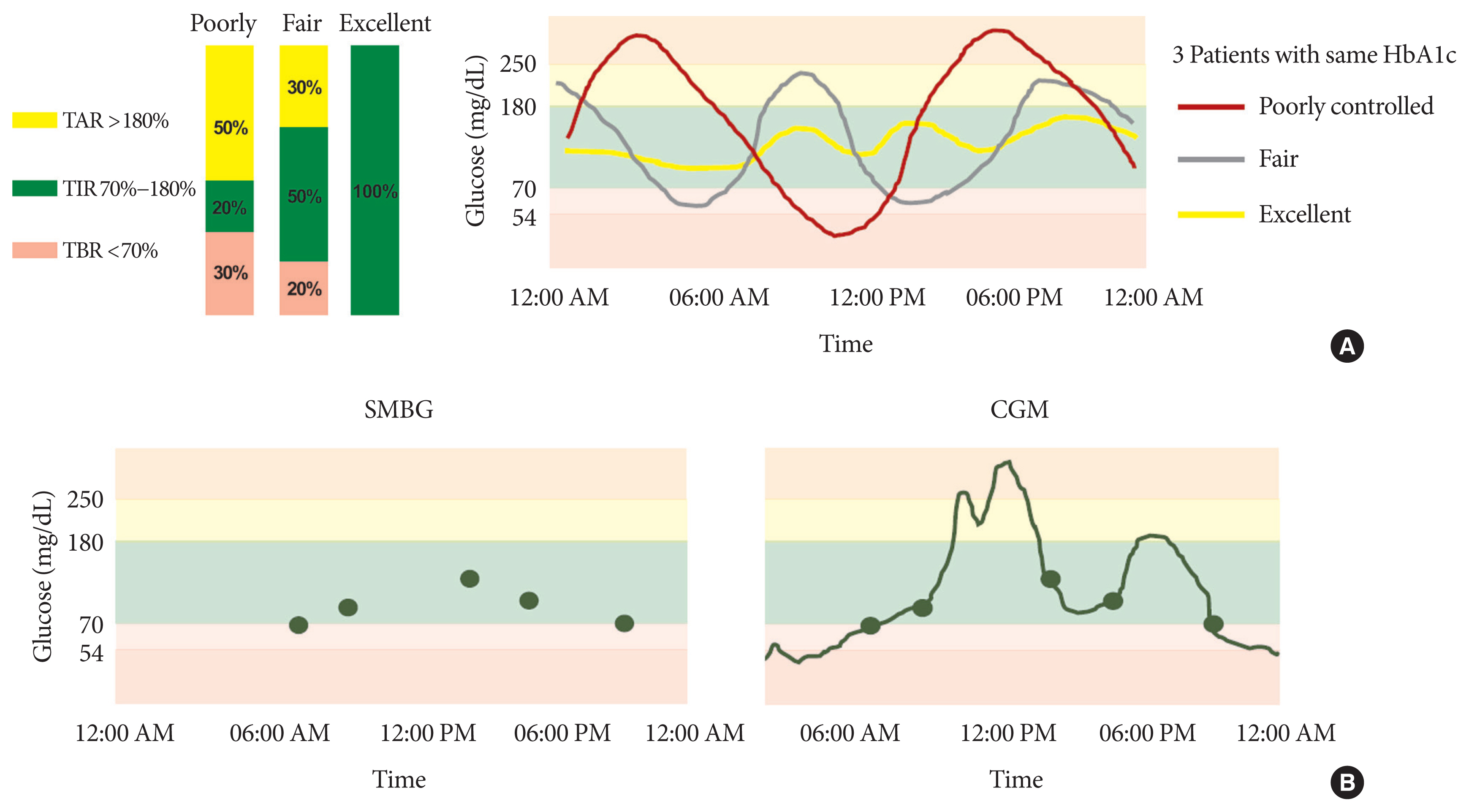
ePub - Glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) has been the sole surrogate marker for assessing diabetic complications. However, consistently reported limitations of HbA1c are that it lacks detailed information on short-term glycemic control and can be easily interfered with by various clinical conditions such as anemia, pregnancy, or liver disease. Thus, HbA1c alone may not represent the real glycemic status of a patient. The advancement of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) has enabled both patients and healthcare providers to monitor glucose trends for a whole single day, which is not possible with HbA1c. This has allowed for the development of core metrics such as time spent in time in range (TIR), hyperglycemia, or hypoglycemia, and glycemic variability. Among the 10 core metrics, TIR is reported to represent overall glycemic control better than HbA1c alone. Moreover, various evidence supports TIR as a predictive marker of diabetes complications as well as HbA1c, as the inverse relationship between HbA1c and TIR reveals. However, there are more complex relationships between HbA1c, TIR, and other CGM metrics. This article provides information about 10 core metrics with particular focus on TIR and the relationships between the CGM metrics for comprehensive understanding of glycemic status using CGM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Acute and Chronic Adverse Outcomes of Type 1 Diabetes
Rachel Longendyke, Jody B. Grundman, Shideh Majidi
Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America.2024; 53(1): 123. CrossRef - La plongée sous-marine en scaphandre autonome avec un diabète de type 1. Une belle histoire du dernier millénaire
Lise Dufaitre Patouraux, Agnès Sola-Gazagnes, Boris Lormeau, Corinne Lormeau
Médecine des Maladies Métaboliques.2024; 18(1): 67. CrossRef - S100A9 exerts insulin-independent antidiabetic and anti-inflammatory effects
Gloria Ursino, Giulia Lucibello, Pryscila D. S. Teixeira, Anna Höfler, Christelle Veyrat-Durebex, Soline Odouard, Florian Visentin, Luca Galgano, Emmanuel Somm, Claudia R. Vianna, Ariane Widmer, François R. Jornayvaz, Andreas Boland, Giorgio Ramadori, Rob
Science Advances.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Hybrid Closed-Loop Versus Manual Insulin Delivery in Adults With Type 1 Diabetes: A Post Hoc Analysis Using the Glycemia Risk Index
Melissa H. Lee, Sara Vogrin, Timothy W. Jones, David N. O’Neal
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinically relevant stratification of patients with type 2 diabetes by using continuous glucose monitoring data
Xiaopeng Shao, Jingyi Lu, Rui Tao, Liang Wu, Yaxin Wang, Wei Lu, Hongru Li, Jian Zhou, Xia Yu
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a 2-Week Kinect-Based Mixed-Reality Exercise Program on Prediabetes: A Pilot Trial during COVID-19
So Young Ahn, Si Woo Lee, Hye Jung Shin, Won Jae Lee, Jun Hyeok Kim, Hyun-Jun Kim, Wook Song
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2024; 33(1): 54. CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring with structured education in adults with type 2 diabetes managed by multiple daily insulin injections: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kang Hee Sim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Jun Sung Moon, Soo Lim, Eun Seok Kang, Cheol-Young Park, Sin Gon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison between a tubeless, on-body automated insulin delivery system and a tubeless, on-body sensor-augmented pump in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Eun Seok Kang, Soo Heon Kwak, Yeoree Yang, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyun Bae, Jun Sung Moon, Chang Hee Jung, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh, Sun Joon Moon, Sun Ok Song, Suk Chon, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Anagliptin twice‐daily regimen improves glycaemic variability in subjects with type 2 diabetes: A double‐blind, randomized controlled trial
Yong‐ho Lee, Doo‐Man Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Kyung Mook Choi, Sin Gon Kim, Kang Seo Park, Hyun‐Shik Son, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Soon Hee Lee, Ki‐Ho Song, Su Kyoung Kwon, Hyeong Kyu Park, Kyu Chang Won, Hak Chul Jang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(5): 1174. CrossRef - Advances in Continuous Glucose Monitoring and Integrated Devices for Management of Diabetes with Insulin-Based Therapy: Improvement in Glycemic Control
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(1): 27. CrossRef - Status of continuous glucose monitoring use and management in tertiary hospitals of China: a cross-sectional study
Liping Chen, Xiaoqin Liu, Qin Lin, Hongmei Dai, Yong Zhao, Zumin Shi, Liping Wu
BMJ Open.2023; 13(2): e066801. CrossRef - Real-world outcomes of continuous glucose monitoring in adults with diabetes mellitus attending an Irish tertiary hospital
Aoife Courtney, Diarmuid Smith, Hannah Forde
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2023; 192(6): 2763. CrossRef - Insight into continuous glucose monitoring: from medical basics to commercialized devices
Ayman Chmayssem, Małgorzata Nadolska, Emily Tubbs, Kamila Sadowska, Pankaj Vadgma, Isao Shitanda, Seiya Tsujimura, Youssef Lattach, Martin Peacock, Sophie Tingry, Stéphane Marinesco, Pascal Mailley, Sandrine Lablanche, Pierre Yves Benhamou, Abdelkader Zeb
Microchimica Acta.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy of polyethylene glycol loxenatide versus insulin glargine on glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, open-label, parallel-group trial
Shuo Zhang, Chuanyan Zhang, Jingxian Chen, Feiying Deng, Zezhen Wu, Dan Zhu, Fengwu Chen, Yale Duan, Yue Zhao, Kaijian Hou
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of continuous glucose monitoring on glycemic control and its derived metrics in type 1 diabetes: a longitudinal study
So Hyun Cho, Seohyun Kim, You-Bin Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Kyu Yeon Hur, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Glycemia Risk Index and Albuminuria in Type 2 Diabetes
Jee Hee Yoo, Ji Yoon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(10): 726. CrossRef - Acute Glycemic Variability and Early Outcomes After Cardiac Surgery:
A Meta-Analysis
Shuo Chang, Mian Xu, Yu Wang, Yanbo Zhang
Hormone and Metabolic Research.2023; 55(11): 771. CrossRef - Comparison of Glycemia Risk Index with Time in Range for Assessing Glycemic Quality
Ji Yoon Kim, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2023; 25(12): 883. CrossRef - Correlação entre tempo no alvo e hemoglobina glicada de pessoas com diabetes mellitus: revisão sistemática
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlación entre tiempo en rango y hemoglobina glicosilada en personas con diabetes mellitus: revisión sistemática
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Correlation between time on target and glycated hemoglobin in people with diabetes mellitus: systematic review
Rafael Aparecido Dias Lima, Daiane Rubinato Fernandes, Rute Aparecida Casas Garcia, Lucas Ariel da Rocha Carvalho, Renata Cristina de Campos Pereira Silveira, Carla Regina de Souza Teixeira
Revista Latino-Americana de Enfermagem.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Smart Insulin Pen: Managing Insulin Therapy for People with Diabetes in the Digital Era
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(4): 190. CrossRef - Novel Glycemic Index Based on Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Predict Poor Clinical Outcomes in Critically Ill Patients: A Pilot Study
Eun Yeong Ha, Seung Min Chung, Il Rae Park, Yin Young Lee, Eun Young Choi, Jun Sung Moon
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Hypoglycemic agents and glycemic variability in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
SuA Oh, Sujata Purja, Hocheol Shin, Minji Kim, Eunyoung Kim
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2022; 19(3): 147916412211068. CrossRef - Advanced Glycation End Products and Their Effect on Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jeongmin Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Nutrients.2022; 14(15): 3086. CrossRef - Influence of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors on glycemic variability in patients with type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Shangyu Chai, Ruya Zhang, Ye Zhang, Richard David Carr, Yiman Zheng, Swapnil Rajpathak, Miao Yu
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Glucose Profiles Assessed by Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring System during the Perioperative Period of Metabolic Surgery
Kyuho Kim, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang, Young Suk Park, Tae Jung Oh
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(5): 713. CrossRef - Deterioration in glycemic control on schooldays among children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes: A continuous glucose monitoring-based study
Yu Ding, Wenhao Zhang, Xiumei Wu, Tian Wei, Xulin Wang, Xueying Zheng, Sihui Luo
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Effect of repeated bolus and continuous glucose infusion on a panel of circulating biomarkers in healthy volunteers
Roland Feldbauer, Matthias Wolfgang Heinzl, Carmen Klammer, Michael Resl, Johannes Pohlhammer, Klemens Rosenberger, Verena Almesberger, Florian Obendorf, Lukas Schinagl, Thomas Wagner, Margot Egger, Benjamin Dieplinger, Martin Clodi, Stephen L. Atkin
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(12): e0279308. CrossRef - Relationship between glycemic intraday variations evaluated in continuous glucose monitoring and HbA1c variability in type 2 diabetes: pilot study
Akemi Tokutsu, Yosuke Okada, Keiichi Torimoto, Yoshiya Tanaka
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Time-in-range for monitoring glucose control: Is it time for a change?
Virginia Bellido, Pedro José Pinés-Corrales, Rocío Villar-Taibo, Francisco Javier Ampudia-Blasco
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 177: 108917. CrossRef - Glucose Management Indicator for People with Type 1 Asian Diabetes Is Different from That of the Published Equation: Differences by Glycated Hemoglobin Distribution
Jee Hee Yoo, Seung Hee Yang, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Health-Related Quality of Life, Family Conflicts and Fear of Injecting: Perception Differences between Preadolescents and Adolescents with Type 1 Diabetes and Their Mothers
Marta Tremolada, Maria Cusinato, Sabrina Bonichini, Arianna Fabris, Claudia Gabrielli, Carlo Moretti
Behavioral Sciences.2021; 11(7): 98. CrossRef - Daytime Glycemic Variability and Frailty in Older Patients with Diabetes: a Pilot Study Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Seung Min Chung, Yun Hee Lee, Chang Oh Kim, Ji Yeon Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Seung-Hyun Yoo, Jun Sung Moon, Kwang Joon Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Benefits of a Switch from Intermittently Scanned Continuous Glucose Monitoring (isCGM) to Real-Time (rt) CGM in Diabetes Type 1 Suboptimal Controlled Patients in Real-Life: A One-Year Prospective Study §
Yannis Préau, Sébastien Galie, Pauline Schaepelynck, Martine Armand, Denis Raccah
Sensors.2021; 21(18): 6131. CrossRef - Recent Advances of Integrative Bio-Omics Technologies to Improve Type 1 Diabetes (T1D) Care
Nisha Karwal, Megan Rodrigues, David D. Williams, Ryan J. McDonough, Diana Ferro
Applied Sciences.2021; 11(24): 11602. CrossRef
- Acute and Chronic Adverse Outcomes of Type 1 Diabetes
- Complications
-
- Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study
- Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyeong Jin Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):368-378. Published online October 20, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0046
- 9,411 View
- 344 Download
- 19 Web of Science
- 19 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
- Background
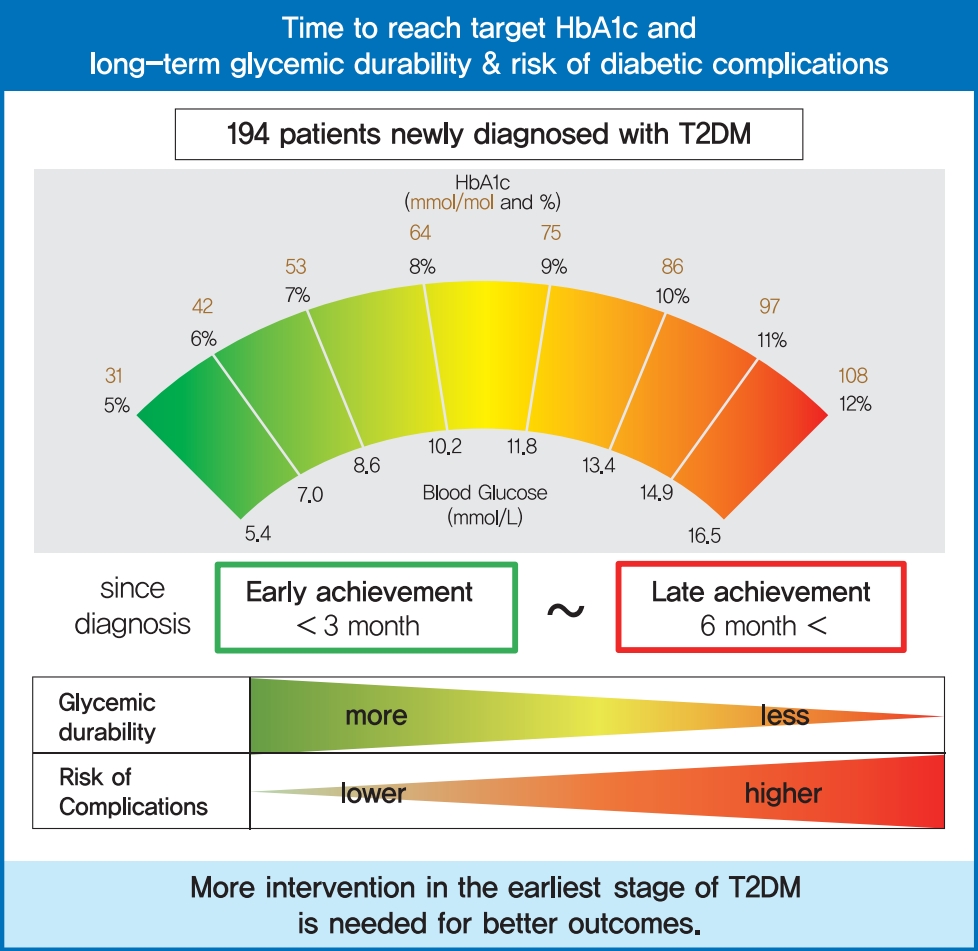
To evaluate the association of time to reach the target glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level with long-term durable glycemic control and risk of diabetic complications in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
In a longitudinal observational cohort, 194 patients with T2DM newly diagnosed between January 2011 and March 2013 were followed up over 6 years. Patients were classified according to the time needed to reach the target HbA1c (<7.0%): <3, 3 to 6 (early achievement group), and ≥6 months (late achievement group). Risks of microvascular complications including diabetic retinopathy, nephropathy, and neuropathy as well as macrovascular events including ischemic heart disease, ischemic stroke, and peripheral arterial disease were assessed by multivariable Cox proportional hazards analysis.
Results
During a median follow-up of 6.53 years, 66 microvascular and 14 macrovascular events occurred. Maintenance of durable glycemic control over 6 years was more likely in the early achievement groups than in the late achievement group (34.5%, 30.0%, and 16.1% in <3, 3 to 6, and ≥6 months, respectively, P=0.039). Early target HbA1c achievement was associated with lower risk of composite diabetic complications (adjusted hazard ratio [HR, 0.47; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.26 to 0.86 in <3 months group) (adjusted HR, 0.50; 95% CI, 0.23 to 1.10 in 3 to 6 months group, in reference to ≥6 months group). Similar trends were maintained for risks of microvascular and macrovascular complications, although statistical significance was not reached for macrovascular complications.
Conclusion
Early target HbA1c achievement was associated with long-term durable glycemic control and reduced risk of diabetic complications in newly diagnosed T2DM. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- HbA1c As Diabetes Mellitus Biomarker and Its Methods Evolution
Liong Boy Kurniawan
INDONESIAN JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PATHOLOGY AND MEDICAL LABORATORY.2024; 30(2): 191. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of enavogliflozin vs. dapagliflozin as add-on therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus based on renal function: a pooled analysis of two randomized controlled trials
Young Sang Lyu, Sangmo Hong, Si Eun Lee, Bo Young Cho, Cheol-Young Park
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - The effect of health quotient and time management skills on self-management behavior and glycemic control among individuals with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Mengjie Chen, Man Liu, Ying Pu, Juan Wu, Mingjiao Zhang, Hongxia Tang, Laixi Kong, Maoting Guo, Kexue Zhu, Yuxiu Xie, Zhe Li, Bei Deng, Zhenzhen Xiong
Frontiers in Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic control and cardiovascular complications of type 2 diabetes mellitus
I. V. Druk, S. S. Safronova
Meditsinskiy sovet = Medical Council.2023; (13): 130. CrossRef - Effect of viscous soluble dietary fiber on glucose and lipid metabolism in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis on randomized clinical trials
Kun Lu, Tingqing Yu, Xinyi Cao, Hui Xia, Shaokang Wang, Guiju Sun, Liang Chen, Wang Liao
Frontiers in Nutrition.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Construction and validation of a clinical prediction model for asymptomatic obstructive coronary stenosis in patients with carotid stenosis
Cuijie Qin, Chuang Li, Yunpeng Luo, Zhen Li, Hui Cao
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk assessment of rectal anastomotic leakage (RAREAL) after DIXON in non-emergency patients with rectal cancer
Xue-Cong Zheng, Jin-Bo Su, Jin-Jie Zheng
BMC Gastroenterology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluation of Left Ventricular Function in Diabetes Patients with Microvascular Disease by Three-Dimensional Speckle Tracking Imaging
青 周
Advances in Clinical Medicine.2023; 13(12): 18908. CrossRef - Validity of the diagnosis of diabetic microvascular complications in Korean national health insurance claim data
Hyung Jun Kim, Moo-Seok Park, Jee-Eun Kim, Tae-Jin Song
Annals of Clinical Neurophysiology.2022; 24(1): 7. CrossRef - Metformin plus a low hypoglycemic risk antidiabetic drug vs. metformin monotherapy for untreated type 2 diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials
Wei-Tse Hung, Yuan-Jung Chen, Chun-Yu Cheng, Bruce Ovbiagele, Meng Lee, Chia-Yu Hsu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 189: 109937. CrossRef - Peripheral arterial disease progression and ankle brachial index: a cohort study with newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes
João Soares Felício, Franciane Trindade Cunha de Melo, Giovana Miranda Vieira, Vitória Teixeira de Aquino, Fernanda de Souza Parente, Wanderson Maia da Silva, Nivin Mazen Said, Emanuele Rocha da Silva, Ana Carolina Contente Braga de Souza, Maria Clara Ner
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of long-term visit-to-visit variability of HbA1c and fasting glycemia with hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chen Long, Yaling Tang, Jiangsheng Huang, Suo Liu, Zhenhua Xing
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Degree of Glycemic Control for the First Three Months Determines the Next Seven Years
Nami Lee, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of advanced glycation end products and protein oxidation by leaf extracts and phenolics from Chilean bean landraces
Felipe Ávila, Nadia Cruz, Jazmin Alarcon-Espósito, Nélida Nina, Hernán Paillan, Katherine Márquez, Denis Fuentealba, Alberto Burgos-Edwards, Cristina Theoduloz, Carmina Vejar-Vivar, Guillermo Schmeda-Hirschmann
Journal of Functional Foods.2022; 98: 105270. CrossRef - Mediation Effect of Self-Efficacy Between Health Beliefs and Glycated Haemoglobin Levels in Elderly Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Cross-Sectional Study
Anqi Zhang, Jinsong Wang, Xiaojuan Wan, Jing Zhang, Zihe Guo, Yamin Miao, Shuhan Zhao, Shuo Bai, Ziyi Zhang, Weiwei Yang
Patient Preference and Adherence.2022; Volume 16: 3015. CrossRef - Early Glycosylated Hemoglobin Target Achievement Predicts Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Joonyub Lee, Jae Hyoung Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 337. CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
Ja Young Jeon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 613. CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:368-78)
Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyeong Jin Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 617. CrossRef - Plasma Nesfatin-1: Potential Predictor and Diagnostic Biomarker for Cognitive Dysfunction in T2DM Patient
Dandan Xu, Yue Yu, Yayun Xu, Jinfang Ge
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 3555. CrossRef
- HbA1c As Diabetes Mellitus Biomarker and Its Methods Evolution
- Complications
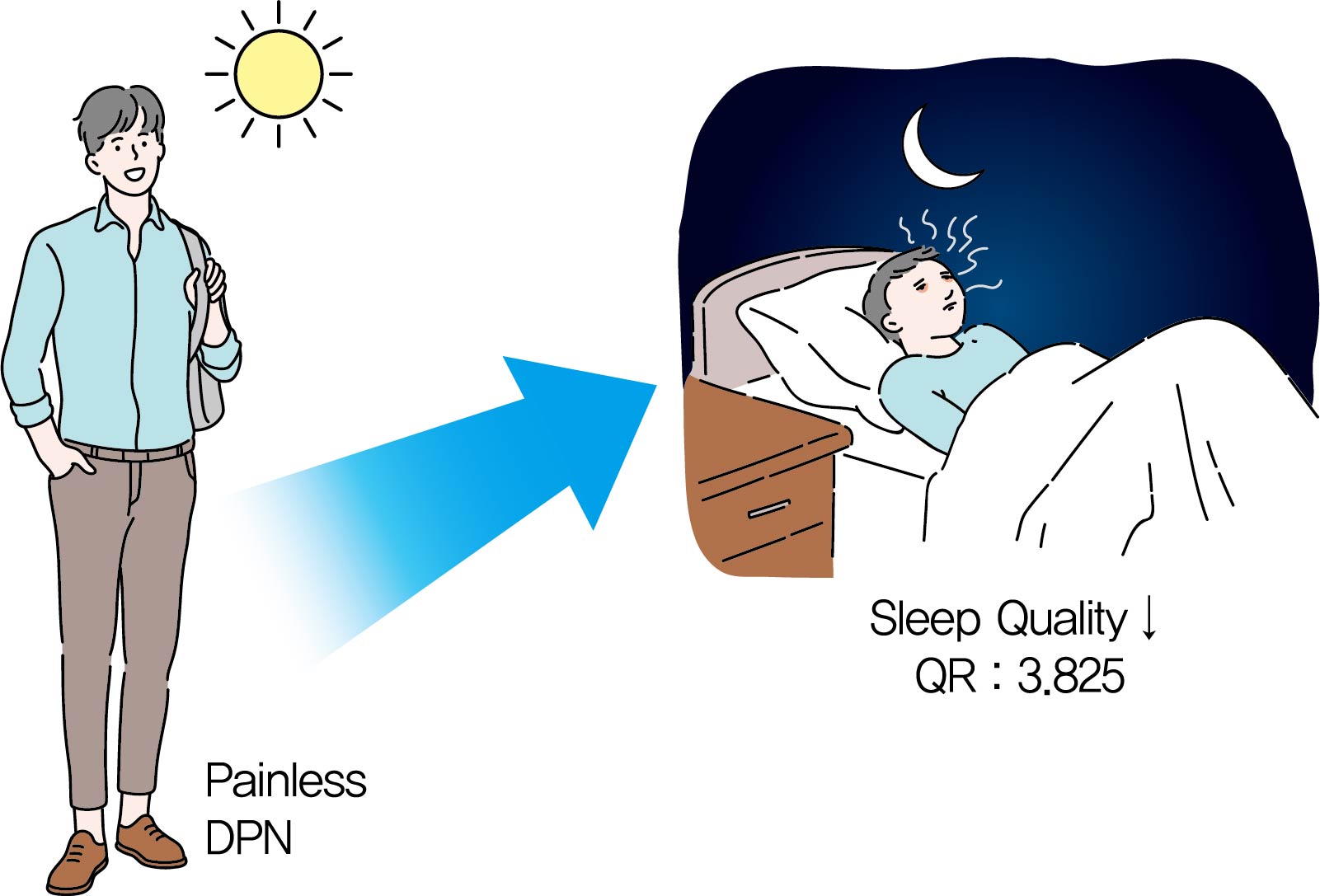
- Association between Sleep Quality and Painless Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Assessed by Current Perception Threshold in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
- Dughyun Choi, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chan-Hee Jung, Chul-Hee Kim, Ji-Oh Mok
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(3):358-367. Published online August 6, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0219
- 5,963 View
- 155 Download
- 1 Web of Science
- 3 Crossref
-
 Graphical Abstract
Graphical Abstract
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub 
Background It is known that the painful sensation of diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) results in sleep problems in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). However, it is not known that the painless DPN also is associated with poor sleep quality in T2DM. The purpose of the current study was to investigate the association between painless DPN and poor sleep quality in T2DM.
Methods A total of 146 patients of T2DM who do not have any painful symptoms of DPN were recruited into the study. Among the patients, painless DPN was diagnosed by using the current perception threshold test. Sleep quality was assessed using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index questionnaire.
Results The percentage of painless DPN was significantly higher in the poor sleep quality group than the good sleep quality group (70.0% vs. 35.5%,
P <0.001). In the subscale results, stimulus values at 2,000 Hz, hypoesthesia and hyperesthesia were more common in the poor sleep quality group than in the good sleep quality group (45.7% vs. 25.0%,P =0.009; 34.3% vs. 18.4%,P =0.029; 40.0% vs. 19.7%,P =0.007, respectively). The association of painless DPN and poor sleep quality remained significant after adjustment for significant covariates (odds ratio, 3.825; 95% confidence interval, 1.674 to 8.742;P <0.001).Conclusion The current study showed that painless DPN was associated with poor sleep quality. Future studies are required to clarify the pathophysiologic causal relationship between painless DPN and sleep quality.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Deteriorated sleep quality and associate factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Lin Fu, Liping Zhong, Xin Liao, Lingrui Wang, Youyi Wang, Xiuquan Shi, Yanna Zhou
PeerJ.2024; 12: e16789. CrossRef - Sleep impairment: Is it an overlooked burden in painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy? A single-centre, cross-sectional study from south India
Adlin Lawrence, Himsikhar Khataniar, Sinimol Joseph, Thenmozhi Nagarajan, Soumya Umesh, John Michael Raj A
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2022; 16(8): 102568. CrossRef - Sleep: an emerging therapeutic target in diabetes care
Nishant Raizada, S. V. Madhu
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2021; 41(1): 1. CrossRef
- Deteriorated sleep quality and associate factors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated with diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- Type 1 Diabetes
- Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
- Jong Ha Baek, Woo Je Lee, Byung-Wan Lee, Soo Kyoung Kim, Gyuri Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Jae Hyeon Kim
- Diabetes Metab J. 2021;45(1):46-54. Published online July 10, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0134

- 6,855 View
- 231 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 12 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub Background The aim of this study was to evaluate characteristics and risk of diabetic complications according to age at diagnosis among young adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM).
Methods A total of 255 T1DM patients aged less than 40 years were included. Patients were categorized into three groups (<20, 20 to 29, and 30 to 40 years) according to age at diagnosis. Diabetic nephropathy (DN) was defined when spot urine-albumin creatinine ratio was 300 mg/g or more and/or estimated glomerular filtration ratio (eGFR) level was 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 or less.
Results Median age at diagnosis was 25 years and disease duration was 14 years. Individuals diagnosed with T1DM at childhood/adolescent (age <20 years) had lower stimulated C-peptide levels. They received more intensive insulin treatment with higher total daily insulin doses compared to older onset groups. The prevalence of DN was higher in the childhood/adolescent-onset group than in older onset groups (25.3% vs. 15.3% vs. 9.6%,
P =0.022). The eGFR was inversely associated with disease duration whilst the degree of decrease was more prominent in the childhood/adolescent-onset group than in the later onset group (aged 30 to 40 years;P <0.001). Childhood/adolescent-onset group was independently associated with the risk of DN compared to the older onset group (aged 30 to 40 years; odds ratio, 3.47; 95% confidence interval, 1.45 to 8.33;P =0.005).Conclusion In individuals with childhood/adolescent-onset T1DM, the reduction in renal function is more prominent with disease duration. Early age-onset T1DM is an independent risk of DN.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Age at onset of type 1 diabetes between puberty and 30 years old is associated with increased diabetic nephropathy risk
Yen-Bo Lin, Wayne Huey-Herng Sheu, Su-Huey Lo, Yen-Po Yeh, Chien-Ning Huang, Chii-Min Hwu, Chang-Hsun Hsieh, Horng-Yi Ou, Lee-Ming Chuang, Jung-Fu Chen, Yu-Cheng Chen, Yun-Hsing Peng, Szu-Tah Chen, Shang-Ren Hsu, Yi-Ling Hsieh, Chih-Hsun Chu, Chieg-Hsiang
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Targeted mapping and utilization of the perihepatic surface for therapeutic beta cell replacement and retrieval in diabetic non-human primates
David J. Leishman, Scott H. Oppler, Laura L. Hocum Stone, Timothy D. O’Brien, Sabarinathan Ramachandran, Bradley J. Willenberg, Andrew B. Adams, Bernhard J. Hering, Melanie L. Graham
Frontiers in Transplantation.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison between a tubeless, on-body automated insulin delivery system and a tubeless, on-body sensor-augmented pump in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Eun Seok Kang, Soo Heon Kwak, Yeoree Yang, Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyun Bae, Jun Sung Moon, Chang Hee Jung, Ji Cheol Bae, Sunghwan Suh, Sun Joon Moon, Sun Ok Song, Suk Chon, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring with structured education in adults with type 2 diabetes managed by multiple daily insulin injections: a multicentre randomised controlled trial
Ji Yoon Kim, Sang-Man Jin, Kang Hee Sim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Jae Hyoung Cho, Jun Sung Moon, Soo Lim, Eun Seok Kang, Cheol-Young Park, Sin Gon Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetologia.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Network-based identification and prioritization of key transcriptional factors of diabetic kidney disease
Ikhlak Ahmed, Mubarak Ziab, Sahar Da’as, Waseem Hasan, Sujitha P. Jeya, Elbay Aliyev, Sabah Nisar, Ajaz A. Bhat, Khalid Adnan Fakhro, Ammira S. Alshabeeb Akil
Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal.2023; 21: 716. CrossRef - Comparison of diabetes distress and depression screening results of emerging adults with type 1 diabetes onset at different ages: findings from the German early-onset T1D study and the German Diabetes Study (GDS)
Anna Stahl-Pehe, Christina Bächle, Kálmán Bódis, Oana-Patricia Zaharia, Karin Lange, Reinhard W. Holl, Michael Roden, Joachim Rosenbauer, M. Roden, H. Al-Hasani, B Belgardt, GJ. Bönhof, V Burkart, A. E. Buyken, G. Geerling, C. Herder, A. Icks, K. Jandelei
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Hemoperfusion and functional state of the macula after simultaneous pancreas and kidney transplantation
IV Vorobyeva, EV Bulava, LK Moshetova, AV Pinchuk
Bulletin of Russian State Medical University.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Sigesbeckia orientalis Extract Ameliorates the Experimental Diabetic Nephropathy by Downregulating the Inflammatory and Oxidative Stress Signaling Pathways
Chung-Ming Chen, Jer-Yiing Houng, Tsui-Ling Ko, Shu-Hui Juan, Hsiu-Chu Chou, Xing Li
Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - Impact of low-protein diet on cardiovascular risk factors and kidney function in diabetic nephropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized-controlled trials
Mohammad Hassan Sohouli, Parvin Mirmiran, Shaikh Sanjid Seraj, Emad Kutbi, Hadil Ali Mohammed Alkahmous, Faisal Almuqayyid, Omar Ahnaf Arafah, Abdul Rahman Riad Barakeh, Ahmed Abu-Zaid
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 191: 110068. CrossRef - Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:46-54)
Jong Ha Baek, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 281. CrossRef - Age at Diagnosis and the Risk of Diabetic Nephropathy in Young Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (Diabetes Metab J 2021;45:46-54)
Ye Seul Yang, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 277. CrossRef - Role of magnetic resonance diffusion weighted imaging in diagnosis of diabetic nephropathy in children living with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Eman Nabil Wahba, Ashraf Elsharkawy, Mohammad Hosny Awad, Ashraf Abdel Rahman, Amr Sarhan
Journal of Pediatric Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 34(12): 1585. CrossRef
- Age at onset of type 1 diabetes between puberty and 30 years old is associated with increased diabetic nephropathy risk
- Complications
- Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports
- Na-young Kim, Eunyeong Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Yong-Hoon Lee, Eun Young Choi
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(2):349-353. Published online April 23, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2020.0091

- 8,670 View
- 186 Download
- 65 Web of Science
- 71 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Since the first case was contracted by coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19) in Daegu, Korea in February 2020, about 6,800 cases and 130 deaths have been reported on April 9, 2020. Recent studies have reported that patients with diabetes showed higher mortality and they had a worse prognosis than the group without diabetes. In poorly controlled patients with diabetes, acute hyperglycemic crises such as diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) or hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS) also might be precipitated by COVID-19. Thus, intensive monitoring and aggressive supportive care should be needed to inadequately controlled patients with diabetes and COVID-19 infection. Here, we report two cases of severe COVID-19 patients with acute hyperglycemic crises in Korea.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Clinical Characteristics and Predictors of Mortality in Obese African-Americans with COVID-19: a Single-Center Retrospective Study
Pavani Reddy Garlapati, Suneet Kumar, Meet Patel, Bidyut Sarker, Benjamin Tiongson, Sreedhar Adapa, Sohail Abdul Salim, Mark K. Adler, Vijay Reddy Gayam
Journal of Racial and Ethnic Health Disparities.2023; 10(1): 160. CrossRef - Diabetes and the COVID-19 pandemic
Kamlesh Khunti, Jonathan Valabhji, Shivani Misra
Diabetologia.2023; 66(2): 255. CrossRef - Adult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes Development Following COVID-19 mRNA Vaccination
Hyeyeon Moon, Sunghwan Suh, Mi Kyoung Park
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID‐19 associated ketosis and diabetic ketoacidosis: A rapid review
Tharun T. Alamuri, Sandhya Mahesh, Kevin Dell'Aquila, Taylor Jan Leong, Rebecca Jennings, Tim Q. Duong
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(7): 1785. CrossRef - Risks associated with acute pancreatitis (AP) with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) in COVID-19 patients: a literature review
Sundru Manjulata Devi, Annapurna Pamreddy, Venkata Ramana Narendra
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2023; 22(1): 135. CrossRef - A Review of Hyperglycemia in COVID-19
Maryam Zahedi, Saba Kordrostami, Mohammadreza Kalantarhormozi, Marziyeh Bagheri
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - A UK nationwide study of adults admitted to hospital with diabetic ketoacidosis or hyperosmolar hyperglycaemic state and COVID‐19
Benjamin C. T. Field, Yue Ruan, Kinga A. Várnai, Jim Davies, Robert E. J. Ryder, Rajiv Gandhi, Sophie Harris, Dinesh Nagi, Dipesh Patel, Punith Kempegowda, Sarah H. Wild, Emma G. Wilmot, Kamlesh Khunti, Rustam Rea, Parth Narendran
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(7): 2012. CrossRef - Diabetic Ketoacidosis in COVID-19 Patients: Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes – A Retrospective Study in a Single Tertiary Care Hospital, Dubai, United Arab Emirates
Hana AL Sughaiyer, Abeer AL Haj, Samia Murad Ibrahim Abdulrahman
Dubai Diabetes and Endocrinology Journal.2023; 29(2): 107. CrossRef - COVID-19 and diabetes
Artur Furga
Probacja.2023; 3: 235. CrossRef - COVID-19 SALGININDA DİYABET YÖNETİMİ VE HEMŞİRENİN ROLÜ
Dilek BÜYÜKKAYA BESEN, Merve DERVİŞOĞLU
Gazi Sağlık Bilimleri Dergisi.2022; 7(2): 78. CrossRef - Diabetic ketoacidosis and COVID-19: what have we learned so far?
Caio Oliveira de Sá-Ferreira, Camila Helena Macedo da Costa, João Campos Wiltgen Guimarães, Nathasha Souza Sampaio, Leticia de Moraes Lopes Silva, Larissa Paula de Mascarenhas, Nicollas Garcia Rodrigues, Talita Labonia dos Santos, Solange Campos, Esther C
American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 322(1): E44. CrossRef - COVID-19 and hyperglycaemic emergencies: perspectives from a developing country
Raisa Bhikoo, Marli Conradie-Smit, Gerhard Van Wyk, Sa’ad Lahri, Elizabeth Du Plessis, Jaco Cilliers, Susan Hugo, Ankia Coetzee
Journal of Endocrinology, Metabolism and Diabetes of South Africa.2022; 27(1): 42. CrossRef - Potential impact of combined influenza and pneumococcal vaccines on the severity of respiratory illness in COVID-19 infection among type 2 diabetic patients
Amr Shaaban Hanafy, Waseem M. Seleem, Hany A. Elkattawy
Clinical and Experimental Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The COVID-19-diabetes mellitus molecular tetrahedron
Mehdi Mahmudpour, Katayoun Vahdat, Mohsen Keshavarz, Iraj Nabipour
Molecular Biology Reports.2022; 49(5): 4013. CrossRef - Diabetes and COVID-19; A Bidirectional Interplay
Paraskevi Kazakou, Vaia Lambadiari, Ignatios Ikonomidis, Aikaterini Kountouri, Georgios Panagopoulos, Stavros Athanasopoulos, Eleni Korompoki, Ioannis Kalomenidis, Meletios A. Dimopoulos, Asimina Mitrakou
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The mechanism underlying extrapulmonary complications of the coronavirus disease 2019 and its therapeutic implication
Qin Ning, Di Wu, Xiaojing Wang, Dong Xi, Tao Chen, Guang Chen, Hongwu Wang, Huiling Lu, Ming Wang, Lin Zhu, Junjian Hu, Tingting Liu, Ke Ma, Meifang Han, Xiaoping Luo
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Challenges in hyperglycemia management in critically ill patients with COVID-19
Rajesh Kethireddy, Darshan Gandhi, Asim Kichloo, Love Patel
World Journal of Critical Care Medicine.2022; 11(4): 219. CrossRef - New-Onset and Persistent Insulin-Dependent Diabetes in Patients With COVID-19: A Peruvian Experience
Anthony Ramos-Yataco, Emanuel A Salcedo Davila, Kelly Meza, Inga Harbuz-Miller
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and COVID-19: A Narrative Review
Cristina Rey-Reñones, Sara Martinez-Torres, Francisco M. Martín-Luján, Carles Pericas, Ana Redondo, Carles Vilaplana-Carnerero, Angela Dominguez, María Grau
Biomedicines.2022; 10(9): 2089. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 Infections, Impaired Tissue, and Metabolic Health: Pathophysiology and Potential Therapeutics
Shailendra Pratap Singh, Aayushi Bhatnagar, Sujeet Kumar Singh, Sanjib K. Patra, Navjot Kanwar, Abhinav Kanwal, Salomon Amar, Ranata Manna
Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry.2022; 22(16): 2102. CrossRef - Collateral damage due to COVID-19
Farhan Fazal, Nitin Gupta, Wasim Khot, Yogiraj Ray
Tropical Doctor.2021; 51(1): 126. CrossRef - Diabetic emergencies during the COVID‐19 pandemic: A case–control study
M. S. B. Huda, S. Shaho, B. Trivedi, G. Fraterrigo, L. Chandrarajan, P. Zolfaghari, T. M. Dovey, C. G. Garrett, T. A Chowdhury
Diabetic Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Euglycemic Diabetic Ketoacidosis With COVID-19 Infection in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes Taking SGLT2 Inhibitors
Rebecca J. Vitale, Yannis K. Valtis, Marie E. McDonnell, Nadine E. Palermo, Naomi D.L. Fisher
AACE Clinical Case Reports.2021; 7(1): 10. CrossRef - Outcomes and Healthcare Provider Perceptions of Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring (rtCGM) in Patients With Diabetes and COVID-19 Admitted to the ICU
Kenneth W. Chow, Danielle J. Kelly, Mary C. Rieff, Patricia A. Skala, Igor Kravets, Marina M. Charitou, Eric J. Morley, Rajarsi Gupta, Joshua D. Miller
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2021; 15(3): 607. CrossRef - Diabetic ketoacidosis presented with COVID-19 infection: A rare case report
Deniz Çekiç, Selçuk Yaylacı, Sümeyye Çekiç, Kubilay İşsever, Hamad Dheir, Havva Kocayiğit, Mehmet Halil Öztürk, Oğuz Karabay
Journal of Clinical Medicine of Kazakhstan.2021; 18(1): 79. CrossRef - Renin-angiotensin system modulators and other risk factors in COVID-19 patients with hypertension: a Korean perspective
Hee-Sung Kim, Minseok Kang, Gilwon Kang
BMC Infectious Diseases.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Increased Incidence of Pediatric Diabetic Ketoacidosis After COVID-19: A Two-Center Retrospective Study in Korea
Min Jeong Han, Jun Ho Heo
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 783. CrossRef - Diabetes, obesity, and insulin resistance in COVID-19: molecular interrelationship and therapeutic implications
Andrey Santos, Daniéla Oliveira Magro, Rosana Evangelista-Poderoso, Mario José Abdalla Saad
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Neuropsychiatric Symptoms of COVID-19 Explained by SARS-CoV-2 Proteins’ Mimicry of Human Protein Interactions
Hale Yapici-Eser, Yunus Emre Koroglu, Ozgur Oztop-Cakmak, Ozlem Keskin, Attila Gursoy, Yasemin Gursoy-Ozdemir
Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - COVID-19 and Diabetic Ketoacidosis: Report of Eight Cases
Balraj Singh, Prem Patel , Parminder Kaur , Nicole Majachani, Michael Maroules
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Machine Learning Applied to Clinical Laboratory Data in Spain for COVID-19 Outcome Prediction: Model Development and Validation
Juan L Domínguez-Olmedo, Álvaro Gragera-Martínez, Jacinto Mata, Victoria Pachón Álvarez
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2021; 23(4): e26211. CrossRef - Effect of COVID-19 on management of type 1 diabetes: Pushing the boundaries of telemedical healthcare
Ines Bilic Curcic, Maja Cigrovski Berkovic, Tomislav Kizivat, Silvija Canecki Varzic, Robert Smolic, Martina Smolic
World Journal of Diabetes.2021; 12(6): 780. CrossRef - COVID-19 and Diabetes: Understanding the Interrelationship and Risks for a Severe Course
Cyril P. Landstra, Eelco J. P. de Koning
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Real-World Studies Support Use of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Independently of Treatment Regimen
James R. Gavin, Clifford J. Bailey
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2021; 23(S3): S-19. CrossRef - Evaluation of Characteristics and Outcomes for Patients with Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) With and Without COVID-19 in Elmhurst Queens During Similar Three-Month Periods in 2019 and 2020
Urja Patel, Linda Deluxe, Carlos Salama, Aaron Ross Jimenez, Adrian Whiting, Cedrick Lubin, Nancy Tarlin
Cureus.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Temporal trends in emergency admissions for diabetic ketoacidosis in people with diabetes in England before and during the COVID-19 pandemic: a population-based study
Shivani Misra, Emma Barron, Eszter Vamos, Stephen Thomas, Ketan Dhatariya, Partha Kar, Bob Young, Kamlesh Khunti, Jonathan Valabhji
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2021; 9(10): 671. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus and COVID-19: Understanding the association in light of current evidence
Saikat Sen, Raja Chakraborty, Pratap Kalita, Manash Pratim Pathak
World Journal of Clinical Cases.2021; 9(28): 8327. CrossRef - Follow-Up Study of the Cardiopulmonary and Psychological Outcomes of COVID-19 Survivors Six Months After Discharge in Sichuan, China
Shuiping Dai, Bennan Zhao, Dafeng Liu, Yongzhao Zhou, Yaling Liu, Lijuan Lan, Yalun Li, Wenxin Luo, Yilan Zeng, Weimin Li
International Journal of General Medicine.2021; Volume 14: 7207. CrossRef - Diabetic ketoacidosis in patients with SARS-CoV-2: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Saad Alhumaid, Abbas Al Mutair, Zainab Al Alawi, Ali A. Rabaan, Mohammed A. Alomari, Sadiq A. Al Salman, Ahmed S. Al-Alawi, Mohammed H. Al Hassan, Hesham Alhamad, Mustafa A. Al-kamees, Fawzi M. Almousa, Hani N. Mufti, Ali M. Alwesabai, Kuldeep Dhama, Jaff
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - In-hospital clinical complications of COVID-19: a brief overview
Kevin John John, Jemimah Nayar, Ajay Kumar Mishra, Vijairam Selvaraj, Mohammad Saud Khan, Amos Lal
Future Virology.2021; 16(11): 717. CrossRef - Combined Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome and Diabetic Ketoacidosis Associated with COVID-19 in a Pediatric Patient
Yu Shan Tseng, Bradley Tilford, Usha Sethuraman, Katherine Cashen, Mehmet Doganay
Case Reports in Critical Care.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Toddler With New Onset Diabetes and Atypical Hemolytic-Uremic Syndrome in the Setting of COVID-19
Faraz Alizadeh, Amanda O’Halloran, Areej Alghamdi, Charlotte Chen, Maria Trissal, Avram Traum, Danielle DeCourcey
Pediatrics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Complicated Case of COVID-19 and Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome in an Adolescent Male
Anisha Gohil, Stefan Malin, Kamal Abulebda, Tamara S. Hannon
Hormone Research in Paediatrics.2021; 94(1-2): 71. CrossRef - COVID-19 in People with Diabetes: Perspectives from Saudi Arabia
Asirvatham Alwin Robert, Mohamed Abdulaziz Al Dawish
Current Diabetes Reviews.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - A Case of COVID-19 with Acute Myocardial Infarction and Cardiogenic Shock
Hong Nyun Kim, Jang Hoon Lee, Hun Sik Park, Dong Heon Yang, Se Yong Jang, Myung Hwan Bae, Yongkeun Cho, Shung Chull Chae, Yong-Hoon Lee
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Clinical profile and outcomes in COVID-19 patients with diabetic ketoacidosis: A systematic review of literature
Rimesh Pal, Mainak Banerjee, Urmila Yadav, Sukrita Bhattacharjee
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(6): 1563. CrossRef - Diabetic Ketoacidosis in COVID-19: Unique Concerns and Considerations
Nadine E Palermo, Archana R Sadhu, Marie E McDonnell
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2020; 105(8): 2819. CrossRef - A Case of Combined Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State in a Patient With COVID-19
Shemitha Rafique, Fahad W Ahmed
Cureus.2020;[Epub] CrossRef COVID’s Razor: RAS Imbalance, the Common Denominator Across Disparate, Unexpected Aspects of COVID-19
Maureen Czick, Christine Shapter, Robert Shapter
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 3169. CrossRef- Letter: Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:349–53)
Ja Young Jeon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 480. CrossRef - COVID-19 in people with diabetes: understanding the reasons for worse outcomes
Matteo Apicella, Maria Cristina Campopiano, Michele Mantuano, Laura Mazoni, Alberto Coppelli, Stefano Del Prato
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2020; 8(9): 782. CrossRef - Diabetes and COVID-19: Global and regional perspectives
In-Kyung Jeong, Kun Ho Yoon, Moon Kyu Lee
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 166: 108303. CrossRef - Hyperglycemia, Hypertriglyceridemia, and Acute Pancreatitis in COVID-19 Infection
Chiranjeevi Gadiparthi, Mehak Bassi, Balaji Yegneswaran, Sammy Ho, Capecomorin S. Pitchumoni
Pancreas.2020; 49(7): e62. CrossRef - Response: Acute Hyperglycemic Crises with Coronavirus Disease-19: Case Reports (Diabetes Metab J 2020;44:349–53)
Na-young Kim, Eunyeong Ha, Jun Sung Moon, Yong-Hoon Lee, Eun Young Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 484. CrossRef - Diabetic ketoacidosis precipitated by COVID-19: A report of two cases and review of literature
Pavan Kumar Reddy, Mohammad Shafi Kuchay, Yatin Mehta, Sunil Kumar Mishra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(5): 1459. CrossRef - COVID-19 and diabetes: What have we learned so far?
Nida Taher, Mohammed SB Huda, Tahseen A Chowdhury
Clinical Medicine.2020; 20(4): e87. CrossRef - High dose ascorbic acid treatment in COVID-19 patients raised some problems in clinical chemistry testing
Fatih Yesildal, Ferruh Kemal Isman
Turkish Journal of Biochemistry.2020; 45(5): 491. CrossRef - Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Diabetes: The Epidemic and the Korean Diabetes Association Perspective
Junghyun Noh, Hyun-Ha Chang, In-Kyung Jeong, Kun Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 372. CrossRef - Practical considerations for pregnant women with diabetes and severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection
Glenn P. Boyles, Stephen Thung, Steven G. Gabbe, Mark B. Landon, Maged M. Costantine
American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology MFM.2020; 2(4): 100210. CrossRef - Protracted ketonaemia in hyperglycaemic emergencies in COVID-19: a retrospective case series
Eleni Armeni, Umaira Aziz, Sulmaaz Qamar, Sadia Nasir, Chidambaram Nethaji, Rupert Negus, Nicholas Murch, Huw Clarke Beynon, Pierre Bouloux, Miranda Rosenthal, Sidrah Khan, Ahmed Yousseif, Ravi Menon, Efthimia Karra
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2020; 8(8): 660. CrossRef - Development of a tablet PC-based portable device for colorimetric determination of assays including COVID-19 and other pathogenic microorganisms
Woo Sik Yoo, Hyung Soo Han, Jung Gon Kim, Kitaek Kang, Hyo-Sung Jeon, Jin-Young Moon, Hyeonmi Park
RSC Advances.2020; 10(54): 32946. CrossRef - Machine Learning to Predict Mortality and Critical Events in a Cohort of Patients With COVID-19 in New York City: Model Development and Validation
Akhil Vaid, Sulaiman Somani, Adam J Russak, Jessica K De Freitas, Fayzan F Chaudhry, Ishan Paranjpe, Kipp W Johnson, Samuel J Lee, Riccardo Miotto, Felix Richter, Shan Zhao, Noam D Beckmann, Nidhi Naik, Arash Kia, Prem Timsina, Anuradha Lala, Manish Paran
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2020; 22(11): e24018. CrossRef - COVID-19: the endocrine opportunity in a pandemic
Subhankar Chatterjee, Ritwik Ghosh, Payel Biswas, Souvik Dubey, Rishi T. Guria, Chandra B. Sharma, Sanjay Kalra
Minerva Endocrinologica.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Management of Diabetes in Coronavirus Disease 2019: Prognosis and Practical Issues
Hye Soon Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2020; 21(3): 120. CrossRef - Short term follow-up of patients presenting with acute onset diabetes and diabetic ketoacidosis during an episode of COVID-19
Mohammad Shafi Kuchay, Pavan Kumar Reddy, Sakshi Gagneja, Anu Mathew, Sunil Kumar Mishra
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2020; 14(6): 2039. CrossRef - Diabetic ketoacidosis precipitated by Coronavirus disease 2019 infection: Case series
Ibrahim Alsadhan, Shahad Alruwashid, Maram Alhamad, Sarah Alajmi, Sara Alshehri, Eman Alfadhli, Aishah Ekhzaimy
Current Therapeutic Research.2020; 93: 100609. CrossRef - Determinants of survival after severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 infection in Mexican outpatients and hospitalised patients
F.-J. Prado-Galbarro, C. Sanchez-Piedra, A.E. Gamiño-Arroyo, C. Cruz-Cruz
Public Health.2020; 189: 66. CrossRef - SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Factors ACE2 and TMPRSS2 Are Expressed in the Microvasculature and Ducts of Human Pancreas but Are Not Enriched in β Cells
Katie C. Coate, Jeeyeon Cha, Shristi Shrestha, Wenliang Wang, Luciana Mateus Gonçalves, Joana Almaça, Meghan E. Kapp, Maria Fasolino, Ashleigh Morgan, Chunhua Dai, Diane C. Saunders, Rita Bottino, Radhika Aramandla, Regina Jenkins, Roland Stein, Klaus H.
Cell Metabolism.2020; 32(6): 1028. CrossRef - Caring for Hospitalized Patients with Diabetes Mellitus, Hyperglycemia, and COVID-19: Bridging the Remaining Knowledge Gaps
Amisha Wallia, Grace Prince, Emilie Touma, Malek El Muayed, Jane Jeffrie Seley
Current Diabetes Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Recovery From Acute Kidney Injury With Diabetic Ketoacidosis Following SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Case Report and Literature Review
Chang Xu, Umer Zia
Cureus.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Outbreak of COVID-19 and Diabetes in Korea: “We Will Find a Way as We Have Always Done”
Kyu Chang Won, Kun Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 211. CrossRef
- Clinical Characteristics and Predictors of Mortality in Obese African-Americans with COVID-19: a Single-Center Retrospective Study
- Cardiovascular Risk/Epidemiology
- Impact of Diabetes Control on Subclinical Atherosclerosis: Analysis from Coronary Computed Tomographic Angiography Registry
- Gyung-Min Park, Chang Hoon Lee, Seung-Whan Lee, Sung-Cheol Yun, Young-Hak Kim, Yong-Giun Kim, Ki-Bum Won, Soe Hee Ann, Shin-Jae Kim, Dong Hyun Yang, Joon-Won Kang, Tae-Hwan Lim, Eun Hee Koh, Woo Je Lee, Min-Seon Kim, Joong-Yeol Park, Hong-Kyu Kim, Jaewon Choe, Sang-Gon Lee
- Diabetes Metab J. 2020;44(3):470-479. Published online November 22, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2019.0073
- 8,698 View
- 69 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 8 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background There are limited data on the impact of diabetes control on the risk of subclinical coronary atherosclerosis.
Methods We analyzed 6,434 consecutive asymptomatic individuals without previous history of coronary artery disease who underwent coronary computed tomographic angiography (CCTA) (mean age, 53.7±7.6 years and 4,694 men [73.0%]). The degree and extent of subclinical coronary atherosclerosis were assessed by CCTA, and ≥50% diameter stenosis was defined as significant. A cardiac event was defined as a composite of all-cause death, myocardial infarction, unstable angina, or coronary revascularization. Study participants were categorized as normal (
n =5,319), controlled diabetes (glycosylated hemoglobin [HbA1c] <7%,n =747), or uncontrolled diabetes (HbA1c ≥7%,n =368), respectively.Results Compared with normal individuals, there were no statistically significant differences in the risk of for any atherosclerotic plaque (odds ratio [OR], 1.16; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.98 to 1.38;
P =0.086) and significant coronary artery stenosis (OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 0.82 to 1.42;P =0.583) in controlled diabetic individuals. In contrast, uncontrolled diabetic individuals had consistently higher risks of any atherosclerotic plaque (OR, 2.16; 95% CI, 1.70 to 2.75;P <0.001) and significant coronary artery stenosis (OR, 3.34; 95% CI, 2.52 to 4.43;P <0.001) than normal individuals. During a follow-up of median 5.4 years, there was no significant difference in cardiac events between normal and controlled diabetic individuals (P =0.365). However, uncontrolled diabetes was associated with an increased risk of cardiac events compared with normal individuals (P <0.001) and controlled diabetic individuals (P =0.023).Conclusion Asymptomatic uncontrolled diabetes was associated with significant subclinical coronary atherosclerosis with subsequent high risk for cardiac events.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Carotid Ultrasound Abnormalities of People Living With HIV in Kunming, China: Multiple Correspondence Analysis Approach to Identify Influencing Factors
Shuishui Pan, Haiyan Fu, Zhiqiong Ai, Chongxi Li, Jinsong Bai
International Journal of STD & AIDS.2023; 34(10): 710. CrossRef - Differential Impact of Degree of Hypertension on Subclinical Coronary Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic Subjects With and Without Diabetes Mellitus
Hyun Woo Park, Sangyong Jo, Kyung Sun Park, Hyeji Lee, Young-Jee Jeon, Sangwoo Park, Soe Hee Ann, Yong-Giun Kim, Seong Hoon Choi, Woon Jung Kwon, Young-Rak Cho, Jon Suh, Gyung-Min Park
The American Journal of Cardiology.2023; 203: 343. CrossRef - Exosomal MALAT1 Derived from High Glucose-Treated Macrophages Up-Regulates Resistin Expression via miR-150-5p Downregulation
Kou-Gi Shyu, Bao-Wei Wang, Wei-Jen Fang, Chun-Ming Pan, Chiu-Mei Lin
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2022; 23(3): 1095. CrossRef - Comparison of Framingham risk score and pooled cohort equations for the prediction of coronary atherosclerosis in patients who meet the target LDL-C level of Korean dyslipidemia guideline
Su Bin Kim, Hae Won Jung
Medicine.2022; 101(47): e31816. CrossRef - Time to Reach Target Glycosylated Hemoglobin Is Associated with Long-Term Durable Glycemic Control and Risk of Diabetic Complications in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 6-Year Observational Study
Kyoung Jin Kim, Jimi Choi, Jae Hyun Bae, Kyeong Jin Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A Seo, Nan Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Sin Gon Kim, Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 368. CrossRef - Frequency and Significance of Right Bundle Branch Block and Subclinical Coronary Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic Individuals
Hyeji Lee, Young-Jee Jeon, Byung Ju Kang, Tae Young Lee, Eun Ji Park, Sangwoo Park, Soe Hee Ann, Yong-Giun Kim, Yongjik Lee, Seong Hoon Choi, Gyung-Min Park
The American Journal of Cardiology.2021; 158: 30. CrossRef - The association between glucose-related variables and plaque morphology in patients with ST-segment elevated myocardial infarction
Jinxin Liu, Shanjie Wang, Can Cui, Hengxuan Cai, Rong Sun, Weili Pan, Shaohong Fang, Bo Yu
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Choosing Antithrombotic Therapy in Patients with Coronary Heart Disease and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: How to Reduce the Risk of Death
N. A. Koziolova, P. G. Karavaev, A. S. Veklich
Kardiologiia.2020; 60(4): 109. CrossRef
- Carotid Ultrasound Abnormalities of People Living With HIV in Kunming, China: Multiple Correspondence Analysis Approach to Identify Influencing Factors
- Clinical Care/Education
- Impact of Continuous Care on Health Outcomes and Cost for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Analysis Using National Health Insurance Cohort Database
- Ji Hyun Nam, Changwoo Lee, Nayoung Kim, Keun Young Park, Jeonghoon Ha, Jaemoon Yun, Dong Wook Shin, Euichul Shin
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(6):776-784. Published online October 21, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0189
- 5,419 View
- 74 Download
- 14 Web of Science
- 11 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background The objective of the study was to determine the impact of continuous care on health outcomes and cost of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) in Korea.
Methods A nationwide retrospective, observational case-control study was conducted. Continuity of treatment was measured using Continuity of Care (COC) score. Information of all patients newly diagnosed with T2DM in 2004 was retrieved from the National Health Insurance database for the period of 2002 to 2013. The study examined 2,373 patients after applying exclusion criteria, such as for patients who died from conditions not related to T2DM. Statistical analyses were performed using frequency distribution, simple analysis (
t -test and chi-squared test), and multi-method analysis (simple linear regression, logistic regression, and survival analysis).Results The overall COC score was 0.8±0.24. The average incidence of diabetic complications was 0.39 per patient with a higher COC score, whereas it was 0.49 per patient with a lower COC score. In both survival and logistic analyses, patients who had high COC score were significantly less likely to have diabetic complications (hazard ratio, 0.69; 95% confidence interval, 0.54 to 0.88). The average medical cost was approximately 3,496 United States dollar (USD) per patient for patients with a higher COC score, whereas it was 3,973 USD per patient for patients with a lower COC score during the 2006 to 2013 period, with a difference of around 477 USD, which is statistically significant after adjusting for other factors (β=−0.152).
Conclusion Continuity of care for diabetes significantly reduced health complications and medical costs from patients with T2DM.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Continuity of primary care for type 2 diabetes and hypertension and its association with health outcomes and disease control: insights from Central Vietnam
Quynh-Anh Le Ho Thi, Peter Pype, Johan Wens, Huy Nguyen Vu Quoc, Anselme Derese, Wim Peersman, Nhon Bui, Huyen Nguyen Thi Thanh, Tam Nguyen Minh
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Application of continuing nursing intervention on wound infection and ulcers in patients with diabetic foot: A meta‐analysis
Xu‐Xiang Li, Jing Xu, Juan Chen, Feng Gao, Qing‐Ju Wang, Shi‐Hu Yang
International Wound Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Impact of the family doctor system on the continuity of care for diabetics in urban China: a difference-in-difference analysis
Xinyi Liu, Luying Zhang, Wen Chen
BMJ Open.2023; 13(2): e065612. CrossRef - The associations of continuity of care with inpatient, outpatient, and total medical care costs among older adults with urinary incontinence
Eunkyung Han, Wankyo Chung, Antonio Trujillo, Joel Gittelsohn, Leiyu Shi
BMC Health Services Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between initial continuity of care status and diabetes-related health outcomes in older patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A nationwide retrospective cohort study in South Korea
Hyun Woo Jung, Woo-Ri Lee
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(6): 600. CrossRef - Relationship between continuity of care and clinical outcomes in patients with dyslipidemia in Korea: a real world claims database study
Juhee Lee, Eunyoung Choi, Eunjung Choo, Siachalinga Linda, Eun Jin Jang, Iyn-Hyang Lee
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Team-Based Continuity of Care and Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases Among Patients With Diabetes: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Kam Suen Chan, Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Weng Yee Chin, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Ivy Lynn Mak, Will Ho Gi Cheng, Margaret Kay Ho, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Diabetes Care.2022; 45(5): 1162. CrossRef - Personal continuity of GP care and outpatient specialist visits in people with type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional survey
Anne Helen Hansen, May-Lill Johansen, Dylan A. Mordaunt
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(10): e0276054. CrossRef - Clinical Study Using Healthcare Claims Database
Jin-Su Park, Chan Hee Lee
Journal of Rheumatic Diseases.2021; 28(3): 119. CrossRef - Effects of continuity of care on health outcomes among patients with diabetes mellitus and/or hypertension: a systematic review
Kam-Suen Chan, Eric Yuk-Fai Wan, Weng-Yee Chin, Will Ho-Gi Cheng, Margaret Kay Ho, Esther Yee-Tak Yu, Cindy Lo-Kuen Lam
BMC Family Practice.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Young-onset type 2 diabetes in South Korea: a review of the current status and unmet need
Ye Seul Yang, Kyungdo Han, Tae Seo Sohn, Nam Hoon Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2021; 36(5): 1049. CrossRef
- Continuity of primary care for type 2 diabetes and hypertension and its association with health outcomes and disease control: insights from Central Vietnam
- Epidemiology
- Diabetes Mellitus and Cause-Specific Mortality: A Population-Based Study
- Sen Li, Jiaxin Wang, Biao Zhang, Xinyi Li, Yuan Liu
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(3):319-341. Published online April 19, 2019
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0060
- 20,104 View
- 243 Download
- 122 Web of Science
- 135 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF Supplementary Material
Supplementary Material PubReader
PubReader Background To investigate whether diabetes contributes to mortality for major types of diseases.
Methods Six National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey data cycles (1999 to 2000, 2001 to 2002, 2003 to 2004, 2005 to 2006, 2007 to 2008, and 2009 to 2010) and their linked mortality files were used. A population of 15,513 participants was included according to the availability of diabetes and mortality status.
Results Participants with diabetes tended to have higher all-cause mortality and mortality due to cardiovascular disease, cancer, chronic lower respiratory diseases, cerebrovascular disease, influenza and pneumonia, and kidney disease. Confounder-adjusted Cox proportional hazard models showed that both diagnosed diabetes category (yes or no) and diabetes status (diabetes, prediabetes, or no diabetes) were associated with all-cause mortality and with mortality due to cardiovascular disease, chronic lower respiratory diseases, influenza and pneumonia, and kidney disease. No associations were found for cancer-, accidents-, or Alzheimer's disease-related mortality.
Conclusion The current study's findings provide epidemiological evidence that diagnosed diabetes at the baseline is associated with increased mortality risk due to cardiovascular disease, chronic lower respiratory diseases, influenza and pneumonia, and kidney disease, but not with cancer or Alzheimer's disease.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Association of type 2 diabetes mellitus with dementia‐related and non–dementia‐related mortality among postmenopausal women: A secondary competing risks analysis of the women's health initiative
Tyler J. Titcomb, Phyllis Richey, Ramon Casanova, Lawrence S. Phillips, Simin Liu, Shama D. Karanth, Nazmus Saquib, Tomas Nuño, JoAnn E. Manson, Aladdin H. Shadyab, Longjian Liu, Terry L. Wahls, Linda G. Snetselaar, Robert B. Wallace, Wei Bao
Alzheimer's & Dementia.2024; 20(1): 234. CrossRef - Antiglycation potential of metal ions and polyphenolic extract of chickpea on thiol-protease inhibitor: A management for diabetic complications
Mohd Shahnawaz Khan, Sheraz Ahmad Bhat, Monnera Saud Albagmi, Mohammed Arshad, Mohammad Tarique, Bilqees Bano
Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal.2024; 32(1): 101916. CrossRef - GLP-1 receptor agonists, SGLT2 inhibitors and noncardiovascular mortality in type 2 diabetes: Insights from a meta-analysis
Mainak Banerjee, Rimesh Pal, Indira Maisnam, Satinath Mukhopadhyay
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2024; 18(1): 102943. CrossRef - Assessment of the radial peripapillary capillary plexus and retinal nerve fiber layer thickness in diabetic patients in comparison to normal age-matched individuals
Christina S.I. Farag, Heba M.A. El-Saied, Hala M. El-Mofty, Randa M.A.M. El-Mofty
Journal of the Egyptian Ophthalmological Society.2024; 117(1): 43. CrossRef - Fasting GLP-1 Levels and Albuminuria Are Negatively Associated in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Cheol-Won Jang, Tae Yang Yu, Jin Woo Jeong, Se Eun Ha, Rajan Singh, Moon Young Lee, Seungil Ro
Journal of Personalized Medicine.2024; 14(3): 280. CrossRef - The Benefits and Harms of Lung Cancer Screening in Individuals With Comorbidities
Minal S. Kale, Keith Sigel, Arushi Arora, Bart S. Ferket, Juan Wisnivesky, Chung Yin Kong
JTO Clinical and Research Reports.2024; 5(3): 100635. CrossRef - Risk factor control and cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Do Kyeong Song, Young Sun Hong, Yeon-Ah Sung, Hyejin Lee, Hidetaka Hamasaki
PLOS ONE.2024; 19(2): e0299035. CrossRef - Liraglutide Attenuates Diabetic Cardiomyopathy via the ILK/PI3K/AKT/PTEN Signaling Pathway in Rats with Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Shatha M. Alobaid, Rahaf M. Alshahrani, Asma S. Alonazi, Nawal M. Alrasheed, Maha A. Alamin, Tahani K. Alshammari, Anfal F. Bin Dayel, Doaa M. Elnagar, Rana R. Alotaibi, Lama A. Almuthnabi, Dalia H. Almasud, Shahad E. Al-Ammar, Shahad O. Almadhi, Reema A.
Pharmaceuticals.2024; 17(3): 374. CrossRef - Effects of high-intensity interval training and its different protocols on lipid profile and glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis
Nandiny Paula Cavalli, Mariana Brondani de Mello, Natiele Camponogara Righi, Felipe Barreto Schuch, Luis Ulisses Signori, Antônio Marcos Vargas da Silva
Journal of Sports Sciences.2024; 42(4): 333. CrossRef - Role of renin-angiotensin system/angiotensin converting enzyme-2 mechanism and enhanced COVID-19 susceptibility in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Ashwin Kumar Shukla, Komal Awasthi, Kauser Usman, Monisha Banerjee
World Journal of Diabetes.2024; 15(4): 606. CrossRef - Precision Medicine in Bariatric Procedures
Khushboo Gala, Wissam Ghusn, Andres Acosta
Gastrointestinal Endoscopy Clinics of North America.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Gamma‐glutamyl transferase and the risk of all‐cause and disease‐specific mortality in patients with diabetes: A nationwide cohort study
Goh Eun Chung, Su‐Min Jeong, Su Jong Yu, Jeong‐Ju Yoo, Yuri Cho, Kyu‐na Lee, Dong Wook Shin, Yoon Jun Kim, Jung‐Hwan Yoon, Kyungdo Han, Eun Ju Cho
Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Trends in cause-specific mortality among people with type 2 and type 1 diabetes from 2002 to 2019: a Danish population-based study
Tinne Laurberg, Susanne B. Graversen, Annelli Sandbæk, Sarah H. Wild, Rimke C. Vos, Henrik Støvring
The Lancet Regional Health - Europe.2024; 41: 100909. CrossRef - Behavioral Therapy for People With Diabetes Who Smoke: A Scoping Review
Roberta Sammut, Joseph Grech, Riccardo Polosa, Davide Campagna, Agostino Di Ciaula, Tabinda Dugal, Andre Kenge, Anoop Misra, Syed Abbas Raza, Cristina Russo, Noel Somasundaram, Magdalena Walicka, Le Dinh Phoung, Graziella Chiara Prezzavento, Mirko Casu, G
Journal of Primary Care & Community Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Inhibition of sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 and liver-related complications in individuals with diabetes: a Mendelian randomization and population-based cohort study
Sung Won Chung, Hye-Sung Moon, Hyunjae Shin, Hyein Han, Sehoon Park, Heejin Cho, Jeayeon Park, Moon Haeng Hur, Min Kyung Park, Sung-Ho Won, Yun Bin Lee, Eun Ju Cho, Su Jong Yu, Dong Ki Kim, Jung-Hwan Yoon, Jeong-Hoon Lee, Yoon Jun Kim
Hepatology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Design of the DAVOS Study: Diabetes Smartphone App, a Fully Automatic Transmission of Data From the Blood Glucose Meter and Insulin Pens Using Wireless Technology to Enhance Diabetes Self-Management—A Study Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial
Franziska Grosser, Sandra Herrmann, Maxi Bretschneider, Patrick Timpel, Janko Schildt, Markus Bentrup, Peter E. H. Schwarz
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2023; 17(3): 742. CrossRef - Low diet quality is associated with adverse levels of metabolic health markers and clustering of risk factors in adults with type 2 diabetes
Namrata Sanjeevi, Jeanne H. Freeland‐Graves
Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics.2023; 36(1): 31. CrossRef - Need for improving immunization status and preventive care in diabetes mellitus patients
Teresa Gisinger, Alexandra Kautzky-Willer, Michael Leutner
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift.2023; 135(13-14): 336. CrossRef - Nanoparticles encapsulating sesame seeds (Sesamum indicum) oil: Physicochemical, antioxidant and enzymatic inhibition properties
Narimane Lammari, Mehdi Louaer, Ouahida Louaer, Chawki Bensouici, Ahmed Zermane, Abdelhamid Elaissari, Abdeslam Hassen Meniai
Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology.2023; 79: 104003. CrossRef - Significant Association between Subclinical Left Cardiac Dysfunction and Liver Stiffness in Metabolic Syndrome Patients with Diabetes Mellitus and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Alexandru Apostu, Daniel Malita, Sergiu-Florin Arnautu, Mirela-Cleopatra Tomescu, Dan Gaiță, Alina Popescu, Ruxandra Mare, Ramona Gidea, Diana-Aurora Arnautu
Medicina.2023; 59(2): 328. CrossRef - An examination of causal associations and shared risk factors for diabetes and cardiovascular diseases in the East Asian population: A Mendelian randomization study
Yulin Guo, Jie Gao, Yan Liu, Yanxiong Jia, Xiangguang An, Xitao Zhang, Pixiong Su
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Synthesis, Cytotoxicity and In Vitro α-Glucosidase Inhibition of New N-Substituted Glitazone and Rhodanine Derivatives
N. R. Tshiluka, M. V. Bvumbi, S. S. Mnyakeni-Moleele
Russian Journal of Bioorganic Chemistry.2023; 49(2): 384. CrossRef - Prevalence of QT prolongation and its risk factors in patients with type 2 diabetes
Khaled Aburisheh, Mohammad F. AlKheraiji, Saleh I. Alwalan, Arthur C. Isnani, Mohamed Rafiullah, Muhammad Mujammami, Assim A. Alfadda
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Adapted Diabetes Complications Severity Index and Charlson Comorbidity Index in predicting all-cause and cause-specific mortality among patients with type 2 diabetes
Yu-Wen Hu, Chiu-Mei Yeh, Chia-Jen Liu, Tzeng-Ji Chen, Nicole Huang, Yiing-Jenq Chou
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2023; 11(2): e003262. CrossRef - Influenza: Diabetes as a risk factor for severe related-outcomes and the effectiveness of vaccination in diabetic population. A meta-analysis of observational studies
Ilaria Dicembrini, Giovanni Antonio Silverii, Alessandra Clerico, Riccardo Fornengo, Giovanni Gabutti, Valeria Sordi, Silvio Tafuri, Ottavia Peruzzi, Edoardo Mannucci
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2023; 33(6): 1099. CrossRef - Research progress on classification, sources and functions of dietary polyphenols for prevention and treatment of chronic diseases
Wei Li, Haihong Chen, Bing Xu, Yi Wang, Canyang Zhang, Yong Cao, Xinhui Xing
Journal of Future Foods.2023; 3(4): 289. CrossRef - Greater efficiency of polyherbal drug encapsulated biosynthesized chitosan nano-biopolymer on diabetes and its complications
G. Revathi, S. Elavarasi, K. Saravanan, M. Ashokkumar, Chukwuebuka Egbuna
International Journal of Biological Macromolecules.2023; 240: 124445. CrossRef - Variations in all-cause mortality, premature mortality and cause-specific mortality among persons with diabetes in Ontario, Canada
Laura C Rosella, Kathy Kornas, Ednah Negatu, Limei Zhou
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2023; 11(3): e003378. CrossRef - The relationship between family support and the level of self care in type 2 diabetes patients
Fatma Gul Zeren, Ozlem Canbolat
Primary Care Diabetes.2023; 17(4): 341. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus-related hospital admissions and prescriptions of antidiabetic agents in England and Wales: an ecological study
Gayda Abdel Rahman AbuHammad, Abdallah Y. Naser, Loay Khaled Mohammad Hassouneh
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Administration of alloxan and streptozotocin in Sprague Dawley rats and the challenges in producing diabetes model
Indah Fajarwati, Dedy Duryadi Solihin, Tutik Wresdiyati, Irmanida Batubara
IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science.2023; 1174(1): 012035. CrossRef - Impacts of SARS-CoV-2 on diabetes mellitus: A pre and post pandemic evaluation
A H M Nurun Nabi, Akio Ebihara, Hossain Uddin Shekhar
World Journal of Virology.2023; 12(3): 151. CrossRef - Risk Stratification for Herpes Simplex Virus Pneumonia Using Elastic Net Penalized Cox Proportional Hazard Algorithm with Enhanced Explainability
Yu-Chiang Wang, Wan-Ying Lin, Yi-Ju Tseng, Yiwen Fu, Weijia Li, Yu-Chen Huang, Hsin-Yao Wang
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(13): 4489. CrossRef - Bee Honey Extract Attenuates Hyperglycemia in Induced Type 1 Diabetes: Impact of Antioxidant and Angiogenesis Activities on Diabetic Severity In Vivo
Ahmed H. Alghamdi, Ibrahim M. Shatla, Soliman Shreed, Atif H. Khirelsied, Mohamed F. El-Refaei
Applied Sciences.2023; 13(14): 8045. CrossRef - Increased Left Atrial Stiffness is Significantly Associated with Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation in Diabetic Patients
Diana-Aurora Arnautu, Sergiu-Florin Arnautu, Mirela-Cleopatra Tomescu, Silvia Luca, Constantin-Tudor Luca
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity.2023; Volume 16: 2077. CrossRef - Cost-effectiveness analysis of implementing polygenic risk score in a workplace cardiovascular disease prevention program
Deo Mujwara, Jen Kintzle, Paolo Di Domenico, George B. Busby, Giordano Bottà
Frontiers in Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes associates with mortality in critically ill patients with SARS-CoV-2 pneumonia: No diabetes paradox in COVID-19
Priscila Bellaver, Larissa Schneider, Ariell F. Schaeffer, Lilian Rodrigues Henrique, Joíza Lins Camargo, Fernando Gerchman, Cristiane B. Leitão, Tatiana H. Rech
Heliyon.2023; 9(8): e18554. CrossRef - New Insights into the Role of Oxidative Stress in the Development of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications
Julia Matzenbacher dos Santos, Qing Zhong, Sandra A. Benite-Ribeiro, Thiago Gomes Heck
Journal of Diabetes Research.2023; 2023: 1. CrossRef - A paradigm shift for cardiovascular outcome evaluation in diabetes: Major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE) to major adverse vascular events (MAVE)
Ashu Rastogi, Anand Sudhayakumar, Nicolaas C. Schaper, Edward B. Jude
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(11): 102875. CrossRef - Assessing Elevated Blood Glucose Levels Through Blood Glucose Evaluation and Monitoring Using Machine Learning and Wearable Photoplethysmography Sensors: Algorithm Development and Validation
Bohan Shi, Satvinder Singh Dhaliwal, Marcus Soo, Cheri Chan, Jocelin Wong, Natalie W C Lam, Entong Zhou, Vivien Paitimusa, Kum Yin Loke, Joel Chin, Mei Tuan Chua, Kathy Chiew Suan Liaw, Amos W H Lim, Fadil Fatin Insyirah, Shih-Cheng Yen, Arthur Tay, Seng
JMIR AI.2023; 2: e48340. CrossRef - Cost-Utility of an Exercise Referral Scheme Versus Doing Nothing in Flemish Adults: Exploring the Impact of Key Assumptions
Amber Werbrouck, Masja Schmidt, Koen Putman, Steven Simoens, Nick Verhaeghe, Lieven Annemans
Journal of Physical Activity and Health.2023; : 1. CrossRef - Community-based models of care for management of type 2 diabetes mellitus among non-pregnant adults in sub-Saharan Africa: A scoping review
Emmanuel Firima, Lucia Gonzalez, Fabiola Ursprung, Elena Robinson, Jacqueline Huber, Jennifer M. Belus, Fabian Raeber, Ravi Gupta, Gibrilla F. Deen, Alain Amstutz, Bailah Leigh, Maja Weisser, Niklaus Daniel Labhardt, Rehana Abdus Salam
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(11): e0278353. CrossRef - Omega-3 supplementation and diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Felipe Mendes Delpino, Lílian Munhoz Figueiredo, Bruna Gonçalves Cordeiro da Silva, Taiciane Gonçalves da Silva, Gicele Costa Mintem, Renata Moraes Bielemann, Denise Petrucci Gigante
Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.2022; 62(16): 4435. CrossRef - The effect of real‐time monitoring of physical activity intensity in diabetic patients
Rumi Tanaka, Kimie Fujita, Satoko Maeno, Kanako Yakushiji, Satomi Tanaka, Keizo Ohnaka, Kenji Ashida, Shohei Sakamoto, Masatoshi Nomura
Japan Journal of Nursing Science.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Factors associated with influenza vaccine coverage among patients with diabetes: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2016–2018
A. Lum Han
International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries.2022; 42(2): 297. CrossRef - Interacción entre el estadio de la enfermedad renal crónica y la diabetes mellitus como factores asociados con mortalidad en pacientes con enfermedad renal crónica: un estudio de cohortes externas
Laura E. Villegas Sierra, Melisa Buriticá Agudelo, Carlos Enrique Yepes Delgado, Yanett Marcela Montoya Jaramillo, Fabián Jaimes Barragan
Nefrología.2022; 42(5): 540. CrossRef - Influence of glucose supplementation on biofilm formation of Candida albicans and Candida glabrata isolated from diabetic and non-diabetic individuals
Pedro Castania Amadio Domingues, Viviane de Cássia Oliveira, Felipe Lazarini Bim, Carolina Patrícia Aires, André Pereira dos Santos, Denise Tornavoi de Castro, Cláudia Helena Silva-Lovato, Denise de Andrade, Evandro Watanabe
Archives of Oral Biology.2022; 134: 105339. CrossRef - The influence of the disclosure of diabetes on the cognitive, physical ability and diabetes self‐management in diabetic employed adults in Saudi Arabia
Sitah Alshutwi, Eman Miligi, Lujain Alhumidan, Adel F. Almutairi
Nursing Open.2022; 9(2): 978. CrossRef - Effect of fermented cassava tuber on the gene expression of PI3K/Akt signaling and AMPK pathway in STZ-NA-induced diabetic rats
Rio Jati Kusuma, Desty Ervira Puspaningtyas, Puspita Mardika Sari
Nutrition & Food Science .2022; 52(2): 213. CrossRef - A fractional order control model for Diabetes and COVID-19 co-dynamics with Mittag-Leffler function
Andrew Omame, Ugochukwu K. Nwajeri, M. Abbas, Chibueze P. Onyenegecha
Alexandria Engineering Journal.2022; 61(10): 7619. CrossRef - Enhancing Choices Regarding the Administration of Insulin Among Patients With Diabetes Requiring Insulin Across Countries and Implications for Future Care
Ileana Mardare, Stephen M. Campbell, Johanna C. Meyer, Israel Abebrese Sefah, Amos Massele, Brian Godman
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dyslipidemia Among Patients With Type 1 Diabetes and Its Associated Factors in Saudi Arabia: An Analytical Cross-Sectional Study
Abdullah A Alrasheed
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Prickly Pear Cacti (Opuntia spp.) Cladodes as a Functional Ingredient for Hyperglycemia Management: A Brief Narrative Review
Rao Raahim Kashif, Nathan M. D’Cunha, Duane D. Mellor, Natalie I. Alexopoulos, Domenico Sergi, Nenad Naumovski
Medicina.2022; 58(2): 300. CrossRef - Machine learning for predicting chronic diseases: a systematic review
F.M. Delpino, Â.K. Costa, S.R. Farias, A.D.P. Chiavegatto Filho, R.A. Arcêncio, B.P. Nunes
Public Health.2022; 205: 14. CrossRef - Effects of blueberry and cranberry on type 2 diabetes parameters in individuals with or without diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
Felipe Mendes Delpino, Lílian Munhoz Figueiredo, Taiciane Gonçalves da Silva, Thaynã Ramos Flores
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2022; 32(5): 1093. CrossRef - Momordica charantia nanoparticles potentiate insulin release and modulate antioxidant gene expression in pancreas of diabetic rats
Olusola Olalekan Elekofehinti
Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - GLP-1 receptor agonists in diabetic kidney disease: current evidence and future directions
Ji Hee Yu, So Young Park, Da Young Lee, Nan Hee Kim, Ji A Seo
Kidney Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 41(2): 136. CrossRef - Pharmacological Study: Synergistic Antidiabetic Activity of Cinnamon Bark and Zingiber Extract in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
Eva Nurinda, Nurul Kusumawardani, Ari Susiana Wulandari , Annisa Fatmawati, E. Emelda, Husnatun Nisa, Nurjani A. Hasan, Wahyu Fajar Iriyanti, Mardiatun Rohmah, Puji Lestari, Veriani Aprilia
Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences.2022; 10(T8): 1. CrossRef - Integrating a Polygenic Risk Score for Coronary Artery Disease as a Risk‐Enhancing Factor in the Pooled Cohort Equation: A Cost‐Effectiveness Analysis Study
Deo Mujwara, Geoffrey Henno, Stephen T. Vernon, Siyang Peng, Paolo Di Domenico, Brock Schroeder, George B. Busby, Gemma A Figtree, Giordano Bottà
Journal of the American Heart Association.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of mechanistic pathways of bariatric surgery in patients with diabetes mellitus: A Bayesian network meta‐analysis
Chaoxing Lin, Trevor James Jun‐Ming Yeong, Wen Hui Lim, Cheng Han Ng, Chun En Yau, Yip Han Chin, Mark D. Muthiah, Poay Huan Loh, Roger S. Y. Foo, Shao Feng Mok, Asim Shabbir, Georgios K. Dimitriadis, Chin Meng Khoo, Nicholas W. S. Chew
Obesity.2022; 30(7): 1380. CrossRef - Diabetes and COVID-19: Biological profile of type 2 diabetic patients with COVID-19 in Pointe-Noire, Congo
Anicet Boumba Luc Magloire, Batchy Aladin Atandi, Elenga-Bongo Charley, Pouki Freddy Saturnin, Kibouilou Fredy, Balanda Christ Nkouanga, Dabo Tidiane Cheick Ahmed, Wahar Saar Abdoul, Mahouanga Didel Mampassi, Voumbi Ghislain Loubano, Moukassa Donatien
Global Journal of Clinical Virology.2022; 7(1): 001. CrossRef - Integrated Nutritional Supports for Diabetic Patients During COVID-19
Infection: A Comprehensive Review
A.K. Obidul Huq, Abu Naim Mohammad Bazlur Rahim, S.M. Golam Moktadir, Ielias Uddin, Mohammad Zahidul Manir, Muhammad Abu Bakr Siddique, Khaleda Islam, Md. Sirajul Islam
Current Diabetes Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mechanisms of COVID-19 pathogenesis in diabetes
Chandrakala Aluganti Narasimhulu, Dinender K. Singla
American Journal of Physiology-Heart and Circulatory Physiology.2022; 323(3): H403. CrossRef - Improvement in Age at Mortality and Changes in Causes of Death in the Population with Diabetes: An Analysis of Data from the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(3): 466. CrossRef - Gender difference in association between diabetes mellitus and all-cause mortality in atrial fibrillation patients
Li Tian, Yan-min Yang, Jun Zhu, Han Zhang, Xing-hui Shao
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2022; 36(9): 108265. CrossRef - An Overview of Diabetes Mellitus in Egypt and the Significance of Integrating Preventive Cardiology in Diabetes Management
Mohamed R Abouzid, Karim Ali, Ibrahim Elkhawas, Shorouk M Elshafei
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between diabetes mellitus and functionality in knee osteoarthritis: a cross-sectional study
Serdar KAYMAZ, Sanem Aslıhan AYKAN
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2022; 5(4): 1114. CrossRef - In-hospital hyperglycemia but not diabetes mellitus alone is associated with increased in-hospital mortality in community-acquired pneumonia (CAP): a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies prior to COVID-19
Rahul D Barmanray, Nathan Cheuk, Spiros Fourlanos, Peter B Greenberg, Peter G Colman, Leon J Worth
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2022; 10(4): e002880. CrossRef - The association between leukocyte telomere length and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease is partially mediated by inflammation: a meta-analysis and population-based mediation study
Tieshan Wang, Zhaoqi Jia, Sen Li, Yuxin Li, Tingting Yu, Tao Lu, Yuanyuan Shi
BMC Pulmonary Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Influence of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy on the Duration of Sciatic Nerve Block with 1.3% Liposomal Bupivacaine and 0.25% Bupivacaine Hydrochloride in a Mouse Model
Liljana Markova, Erika Cvetko, Chiedozie Kenneth Ugwoke, Simon Horvat, Nejc Umek, Tatjana Stopar Pintarič
Pharmaceutics.2022; 14(9): 1824. CrossRef - Free, Conjugated, and Bound Phenolics in Peel and Pulp from Four Wampee Varieties: Relationship between Phenolic Composition and Bio-Activities by Multivariate Analysis
Xue Lin, Yousheng Shi, Pan Wen, Xiaoping Hu, Lu Wang
Antioxidants.2022; 11(9): 1831. CrossRef - Protocol: Developing a framework to improve glycaemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Kinshasa, Democratic Republic of the Congo
Jean-Pierre Fina Lubaki, Olufemi Babatunde Omole, Joel Msafiri Francis, David Desseauve
PLOS ONE.2022; 17(9): e0268177. CrossRef - Triglyceride-glucose index is associated with poor sleep quality in apparently healthy subjects: A cross-sectional study
Daniela Carolina Avelino, Alessandra da Silva, Larissa Oliveira Chaves, Júlia Cristina Cardoso Carraro, Fernanda de Carvalho Vidigal, Josefina Bressan
Archives of Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Molecular mechanisms interlinking biological clock and diabetes mellitus: Effective tools for better management
Chandrasekaran Sankaranarayanan, Perumal Subramanian
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2022; 16(11): 102639. CrossRef - Amyloid Fibrillation of Insulin: Amelioration Strategies and Implications for Translation
Megren H. A. Fagihi, Sourav Bhattacharjee
ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science.2022; 5(11): 1050. CrossRef - Potential Roles of Anti-Inflammatory Plant-Derived Bioactive Compounds Targeting Inflammation in Microvascular Complications of Diabetes
Yahia A. Kaabi
Molecules.2022; 27(21): 7352. CrossRef - Additive interaction of diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease in cancer patient mortality risk
Seohyun Kim, Gyuri Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Re-understanding and focusing on normoalbuminuric diabetic kidney disease
Na An, Bi-tao Wu, Yu-wei Yang, Zheng-hong Huang, Jia-fu Feng
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Coexistent Lichen Amyloidosis and Acquired Reactive Perforating Collagenosis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Post-Thyroidectomy Hypothyroidism Due to Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma: A Rare Case
Eva Krishna Sutedja, Muhamad Radyn Haryadi Widjaya, Hartati Purbo Dharmadji, Pati Aji Achdiat, Laila Tsaqilah
International Medical Case Reports Journal.2022; Volume 15: 745. CrossRef - Interaction between the stage of chronic kidney disease and diabetes mellitus as factors associated with mortality in chronic kidney disease patients: An external cohort study
Laura E. Villegas Sierra, Melisa Buriticá Agudelo, Carlos Enrique Yepes Delgado, Yanett Marcela Montoya Jaramillo, Fabián Jaimes Barragan
Nefrología (English Edition).2022; 42(5): 540. CrossRef - Effects of Pea Protein on Satiety, Postprandial Glucose Response and Appetite Hormones: A Literature Review
Amy Choi
Undergraduate Research in Natural and Clinical Science and Technology (URNCST) Journal.2022; 6(10): 1. CrossRef - Hemoglobin glycation index is associated with incident chronic kidney disease in subjects with impaired glucose metabolism: A 10-year longitudinal cohort study
Wonjin Kim, Taehwa Go, Dae Ryong Kang, Eun Jig Lee, Ji Hye Huh
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2021; 35(1): 107760. CrossRef - Coronavirus Disease 2019 (SARS-CoV-2) and polycystic ovarian disease: Is there a higher risk for these women?
Giuseppe Morgante, Libera Troìa, Vincenzo De Leo
The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology.2021; 205: 105770. CrossRef - Regional differences in diabetes across Europe – regression and causal forest analyses
Péter Elek, Anikó Bíró
Economics & Human Biology.2021; 40: 100948. CrossRef - Active ingredients and mechanisms of Phellinus linteus (grown on Rosa multiflora) for alleviation of Type 2 diabetes mellitus through network pharmacology
Ki Kwang Oh, Md. Adnan, Dong Ha Cho
Gene.2021; 768: 145320. CrossRef - Application of Telemedicine in Diabetes Care: The Time is Now
Felix Aberer, Daniel A. Hochfellner, Julia K. Mader
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(3): 629. CrossRef - Long-term outcomes after kidney transplant failure and variables related to risk of death and probability of retransplant: Results from a single-center cohort study in Brazil
Lúcio R. Requião-Moura, Cássio R. Moreira Albino, Paula Rebello Bicalho, Érika de Arruda Ferraz, Luciana Mello de Mello Barros Pires, Maurício Fregonesi Rodrigues da Silva, Alvaro Pacheco-Silva, Justyna Gołębiewska
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(1): e0245628. CrossRef - Estimating the disease burden of Korean type 2 diabetes mellitus patients considering its complications
Juyoung Kim, Seok-Jun Yoon, Min-Woo Jo, Brecht Devleesschauwer
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(2): e0246635. CrossRef - Susceptibility for Some Infectious Diseases in Patients With Diabetes: The Key Role of Glycemia
Jesús Chávez-Reyes, Carlos E. Escárcega-González, Erika Chavira-Suárez, Angel León-Buitimea, Priscila Vázquez-León, José R. Morones-Ramírez, Carlos M. Villalón, Andrés Quintanar-Stephano, Bruno A. Marichal-Cancino
Frontiers in Public Health.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prediabetes, Diabetes, and the Risk of All-Cause and Cause-Specific Mortality in a Japanese Working Population: Japan Epidemiology Collaboration on Occupational Health Study
Zobida Islam, Shamima Akter, Yosuke Inoue, Huan Hu, Keisuke Kuwahara, Tohru Nakagawa, Toru Honda, Shuichiro Yamamoto, Hiroko Okazaki, Toshiaki Miyamoto, Takayuki Ogasawara, Naoko Sasaki, Akihiko Uehara, Makoto Yamamoto, Takeshi Kochi, Masafumi Eguchi, Tai
Diabetes Care.2021; 44(3): 757. CrossRef - Proportion and mortality of Iranian diabetes mellitus, chronic kidney disease, hypertension and cardiovascular disease patients with COVID-19: a meta-analysis
Hamid Mirjalili, Seyed Alireza Dastgheib, Seyed Hossein Shaker, Reza Bahrami, Mahta Mazaheri, Seyed Mohamad Hossein Sadr-Bafghi, Jalal Sadeghizadeh-Yazdi, Hossein Neamatzadeh
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(1): 905. CrossRef - Prevalence and associated factors of diabetes mellitus among tuberculosis patients in Brunei Darussalam: A 6-year retrospective cohort study
Nurfakhrina Omar, Justin Wong, Kyaw Thu, Md Fathi Alikhan, Liling Chaw
International Journal of Infectious Diseases.2021; 105: 267. CrossRef - Diabetes and COVID-19
Zohair Jamil Gazzaz
Open Life Sciences.2021; 16(1): 297. CrossRef - Review of potential risk groups for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19)
M. Naveed, M. Naeem, M. ur Rahman, M. Gul Hilal, M.A. Kakakhel, G. Ali, A. Hassan
New Microbes and New Infections.2021; 41: 100849. CrossRef - COVID-19 from the interdisciplinary standpoint. Round table
M. N. Mamedov, Yu. V. Rodionova, I. S. Yavelov, M. I. Smirnova, E. N. Dudinskaya, V. I. Potievskaya
Cardiovascular Therapy and Prevention.2021; 20(3): 2849. CrossRef - Diabetes is a major cause of influenza-associated mortality in Mexico
A. Gómez-Gómez, E.L. Sánchez-Ramos, D.E. Noyola
Revue d'Épidémiologie et de Santé Publique.2021; 69(4): 205. CrossRef - Ameliorative potential of Operculina turpethum against streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats: biochemical and histopathological studies
Neeraj Choudhary, Gopal L. Khatik, Rekha Sharma, Navneet Khurana, Richard Lobo, Shvetank Bhatt, Devesh Tewari, Ashish Suttee
3 Biotech.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Current utilization patterns for long-acting insulin analogues including biosimilars among selected Asian countries and the implications for the future
Brian Godman, Mainul Haque, Santosh Kumar, Salequl Islam, Jaykaran Charan, Farhana Akter, Amanj Kurdi, Eleonora Allocati, Muhammed Abu Bakar, Sagir Abdur Rahim, Nusrat Sultana, Farzana Deeba, M. A. Halim Khan, A. B. M Muksudul Alam, Iffat Jahan, Zubair Ma
Current Medical Research and Opinion.2021; 37(9): 1529. CrossRef - Association between cardiometabolic risk factors and COVID-19 susceptibility, severity and mortality: a review
Yasaman Sharifi, Moloud Payab, Erfan Mohammadi-Vajari, Seyed Morsal Mosallami Aghili, Farshad Sharifi, Neda Mehrdad, Elham Kashani, Zhaleh Shadman, Bagher Larijani, Mahbube Ebrahimpur
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(2): 1743. CrossRef - Association of ACE I/D and PAI-1 4G/5G polymorphisms with susceptibility to type 2 diabetes mellitus
Somaye Miri, Mohammad Hasan Sheikhha, Seyed Alireza Dastgheib, Seyed Amir Shaker, Hossein Neamatzadeh
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(2): 1191. CrossRef - Assessment and Management of Diabetic Patients During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Amit K Verma, Mirza Masroor Ali Beg, Deepti Bhatt, Kapil Dev, Mohammed A Alsahli, Arshad Husain Rahmani, Yamini Goyal
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2021; Volume 14: 3131. CrossRef - Higher admission activated partial thromboplastin time, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, serum sodium, and anticoagulant use predict in-hospital COVID-19 mortality in people with Diabetes: Findings from Two University Hospitals in the U.K
Ahmed Iqbal, Marni Greig, Muhammad Fahad Arshad, Thomas H. Julian, Sher Ee Tan, Jackie Elliott
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 178: 108955. CrossRef - Risk factors for severe outcomes in people with diabetes hospitalised for COVID-19: a cross-sectional database study
Emilio Ortega, Rosa Corcoy, Mònica Gratacòs, Francesc Xavier Cos Claramunt, Manel Mata-Cases, Ramon Puig-Treserra, Jordi Real, Bogdan Vlacho, Esmeralda Castelblanco, Pere Domingo, Kamlesh Khunti, Josep Franch-Nadal, Didac Mauricio
BMJ Open.2021; 11(7): e051237. CrossRef - Diabetes increases the risk of COVID-19 in an altitude dependent manner: An analysis of 1,280,806 Mexican patients
Juan Alonso Leon-Abarca, Arianna Portmann-Baracco, Mayte Bryce-Alberti, Carlos Ruiz-Sánchez, Roberto Alfonso Accinelli, Jorge Soliz, Gustavo Francisco Gonzales, Chiara Lazzeri
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(8): e0255144. CrossRef - Botanical Interventions to Improve Glucose Control and Options for Diabetes Therapy
Peter Smoak, Susan J. Burke, J. Jason Collier
SN Comprehensive Clinical Medicine.2021; 3(12): 2465. CrossRef - Antidiabetic bioactive compounds from Tetrastigma angustifolia (Roxb.) Deb and Oxalis debilis Kunth.: Validation of ethnomedicinal claim by in vitro and in silico studies
Julfikar Ali Junejo, Kamaruz Zaman, Mithun Rudrapal, Ismail Celik, Emmanuel Ifeanyi Attah
South African Journal of Botany.2021; 143: 164. CrossRef - SGLT2 Inhibition for Cardiovascular Diseases, Chronic Kidney Disease, and NAFLD
Moein Ala
Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Hospitalization costs with degludec versus glargine U100 for patients with type 2 diabetes at high cardiovascular risk: Canadian costs applied to SAEs from a randomized outcomes trial
Jean-Eric Tarride, Mansoor Husain, Andreas Andersen, Jens Gundgaard, Maria Luckevich, Thomas Mark, Lily Wagner, Thomas R. Pieber
Journal of Medical Economics.2021; 24(1): 1318. CrossRef - Traditional Uses, Pharmacological Effects, and Molecular Mechanisms of Licorice in Potential Therapy of COVID-19
Qian-hui Zhang, Hao-zhou Huang, Min Qiu, Zhen-feng Wu, Zhan-chang Xin, Xin-fu Cai, Qiang Shang, Jun-zhi Lin, Ding-kun Zhang, Li Han
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Recent Updates on Free Fatty Acid Receptor 1 (GPR-40) Agonists for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Lata Rani, Ajmer Singh Grewal, Neelam Sharma, Sukhbir Singh
Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry.2021; 21(4): 426. CrossRef - Low Levels of Influenza Vaccine Uptake among the Diabetic Population in Spain: A Time Trend Study from 2011 to 2020
Jose J. Zamorano-Leon, Rodrigo Jimenez-Garcia, Ana Lopez-de-Andres, Javier de-Miguel-Diez, David Carabantes-Alarcon, Romana Albaladejo-Vicente, Rosa Villanueva-Orbaiz, Khaoula Zekri-Nechar, Sara Sanz-Rojo
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 11(1): 68. CrossRef - Effects of Short-term Mobile Application Use on Weight Reduction for Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Seung Eun Lee, Su-Kyung Park, Ye-Seul Park, Kyoung-Ah Kim, Han Seok Choi, Sang Woo Oh
Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome.2021; 30(4): 345. CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus in combination with COVID-19: modern views on therapy
V.I. Tsymbaliuk, M.D. Tronko, Y.G. Antypkin, S.V. Kushnirenko, V.V. Popova
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY.2021; (57): 8. CrossRef - Dietary aldose reductase inhibitors and prevention of diabetic complications
Ameena Anjum, Janamolla Sreeja, Yarlagadda Swapna, Rajesh Bolleddu, Sama Venkatesh
Indian Journal of Health Sciences and Biomedical Research (KLEU).2021; 14(2): 194. CrossRef - Cohort Profile: The Maule Cohort (MAUCO)
Catterina Ferreccio, Andrea Huidobro, Sandra Cortés, Claudia Bambs, Pablo Toro, Vanessa Van De Wyngard, Johanna Acevedo, Fabio Paredes, Pía Venegas, Hugo Verdejo, Ximena Oyarzún-González, Paz Cook, Pablo F Castro, Claudia Foerster, Claudio Vargas, Jill Ko
International Journal of Epidemiology.2020; 49(3): 760. CrossRef - Treating Dyslipidemias in the Primary Prevention of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease in Older Adults with Diabetes Mellitus
MengHee Tan, Mark Paul MacEachern
Clinics in Geriatric Medicine.2020; 36(3): 457. CrossRef - Increased Mortality Risk in People with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Lithuania
Donata Linkeviciute-Ulinskiene, Auguste Kaceniene, Audrius Dulskas, Ausvydas Patasius, Lina Zabuliene, Giedre Smailyte
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(18): 6870. CrossRef - Proteinuria Is Associated with Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis in Non-Albuminuric Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jaehyun Bae, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 136. CrossRef - COVID-19 and diabetes: Knowledge in progress
Akhtar Hussain, Bishwajit Bhowmik, Nayla Cristina do Vale Moreira
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 162: 108142. CrossRef - Peripheral arterial endothelial dysfunction predicts future cardiovascular events in diabetic patients with albuminuria: a prospective cohort study
Bo Kyung Koo, Woo-Young Chung, Min Kyong Moon
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Risk Factors in and Long-Term Survival of Patients with Post-Transplantation Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Ching-Yao Cheng, Cheng-Hsu Chen, Ming-Fen Wu, Ming-Ju Wu, Jun-Peng Chen, Ying-Mei Liu, Yu-Chi Hou, Hue-Yu Wang
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2020; 17(12): 4581. CrossRef - Fasting Plasma Glucose Variability and Gastric Cancer Risk in Individuals Without Diabetes Mellitus: A Nationwide Population-Based Cohort Study
So-hyeon Hong, Eunjin Noh, Jinsil Kim, Soon Young Hwang, Jun A. Kim, You-Bin Lee, Eun Roh, Kyung Mook Choi, Sei Hyun Baik, Geum Joon Cho, Hye Jin Yoo
Clinical and Translational Gastroenterology.2020; 11(9): e00221. CrossRef - Trimetazidine Inhibits Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells to Mesenchymal Transition in Diabetic Rats via Upregulation of Sirt1
Yong Yang, Yong Wang, Zuowen He, Yunchang Liu, Chen Chen, Yan Wang, Dao Wen Wang, Hong Wang
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Beta Cell Imaging—From Pre-Clinical Validation to First in Man Testing
Stephane Demine, Michael L. Schulte, Paul R. Territo, Decio L. Eizirik
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2020; 21(19): 7274. CrossRef - The role of dental insurance in mitigating mortality among working‐age U.S. adults with periodontitis
Naveed Sadiq, Janice C. Probst, Anwar T. Merchant, Amy B. Martin, Deepika Shrestha, M. Mahmud Khan
Journal of Clinical Periodontology.2020; 47(11): 1294. CrossRef - Antidiabetic Activity of Triterpenoids from Anisophyllea disticha
Miftahul Fikriyah, Muhammad Almurdani, Yum Eryanti, Hilwan Y. Teruna
Journal of Physics: Conference Series.2020; 1655(1): 012033. CrossRef - Therapeutic efficacy of umbilical cord-derived stem cells for diabetes mellitus: a meta-analysis study
Dina H. Kassem, Mohamed M. Kamal
Stem Cell Research & Therapy.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Loss of Smell in COVID-19 Patients: Lessons and Opportunities
Dennis Mathew
Frontiers in Human Neuroscience.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus and COVID-19: current issues of pathogenesis, clinic and therapy. Literature review
В. І. Цимбалюк, М. Д. Тронько, Ю. Г. Антипкін, В. В. Попова
REPRODUCTIVE ENDOCRINOLOGY.2020; (54): 8. CrossRef - Increased Age of Death and Change in Causes of Death Among Persons With Diabetes Mellitus From the Korean National Health Insurance and Statistical Information Service, 2006 to 2018
Eugene Han, Sun Ok Song, Hye Soon Kim, Kang Ju Son, Sun Ha Jee, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
SSRN Electronic Journal .2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Purva Rupeeyam of bhela indriya sthana-an explorative study
Kshama Gupta, Prasad Mamidi
International Journal of Complementary & Alternative Medicine.2020; 13(6): 228. CrossRef - The COVID-19 pandemic and diabetes mellitus
Athanasia Papazafiropoulou, Stavros Antonopoulos
Archives of Medical Science – Atherosclerotic Diseases.2020; 5(1): 200. CrossRef - Diabetes and Cancer: Cancer Should Be Screened in Routine Diabetes Assessment
Sunghwan Suh, Kwang-Won Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(6): 733. CrossRef - Diabetes Mellitus, Still Major Threat to Mortality from Various Causes
Nam Hoon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(3): 273. CrossRef - The Need to Improve the Quality of Diabetes Care in Korea
Seung Jin Han, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef
- Association of type 2 diabetes mellitus with dementia‐related and non–dementia‐related mortality among postmenopausal women: A secondary competing risks analysis of the women's health initiative
- Complications
- Glycosylated Hemoglobin in Subjects Affected by Iron-Deficiency Anemia
- Jari Intra, Giuseppe Limonta, Fabrizio Cappellini, Maria Bertona, Paolo Brambilla
- Diabetes Metab J. 2019;43(4):539-544. Published online November 28, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0072
- 4,885 View
- 100 Download
- 8 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Previous studies have suggested that iron-deficiency anemia affects glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) measurements, but the results were contradictory. We conducted a retrospective case-control study to determine the effects of iron deficiency on HbA1c levels. Starting with the large computerized database of the Italian Hospital of Desio, including data from 2000 to 2016, all non-pregnant individuals older than 12 years of age with at least one measurement of HbA1c, cell blood count, ferritin, and fasting blood glucose on the same date of blood collection were enrolled. A total of 2,831 patients met the study criteria. Eighty-six individuals were diagnosed with iron-deficiency anemia, while 2,745 had a normal iron state. The adjusted means of HbA1c were significantly higher in anemic subjects (5.59% [37.37 mmol/mol]), than those measured in individuals without anemia (5.34% [34.81 mmol/mol]) (
P <0.0001). These results suggest that clinicians should be cautious about diagnosing prediabetes and diabetes in individuals with anemia.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Fingerprinting hyperglycemia using predictive modelling approach based on low-cost routine CBC and CRP diagnostics
Amna Tahir, Kashif Asghar, Waqas Shafiq, Hijab Batool, Dilawar Khan, Omar Chughtai, Safee Ullah Chaudhary
Scientific Reports.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Implications of Iron Deficiency Anaemia on Glycemic Dynamics in Diabetes Mellitus: A Critical Risk Factor in Cardiovascular Disease
Eman Elsheikh, Sereen S Aljohani , Munirah M Alshaikhmubarak, Meshari A Alhawl, Alhanouf W Alsubaie, Norah Alsultan, Asmaa F Sharif, Sayed Ibrahim Ali
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Usefulness of glucose management indicator derived from continuous glucose monitoring to assess glycemic condition in hospitalized patients with diabetic kidney disease treated with insulin pumps
Yi Lu, Qian Zhang, Xiangyu Wang, Ya Jiang, Yaoming Xue
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(11): 108613. CrossRef - Serum Iron Profile in Type 2 Diabetes, A Role Beyond Anemic Marker!
Happy Chutia, Sungdirenla Jamir, Md Yasir, Gautam Handique
The Journal of Medical Research.2023; 9(5): 129. CrossRef - Association between Anemia and Myopia in Korean Adults
Minyi Seo, Sangshin Park
Journal of Health Informatics and Statistics.2023; 48(4): 314. CrossRef - Large-scale retrospective analyses of the effect of iron deficiency anemia on hemoglobin A1c concentrations
Lokinendi V. Rao, George W. Pratt, Caixia Bi, Martin H. Kroll
Clinica Chimica Acta.2022; 529: 21. CrossRef - Integrity loss of glycosylated hemoglobin with deepening anemia
Bünyamin AYDIN, Aysun GÖNDEREN
Journal of Health Sciences and Medicine.2022; 5(3): 839. CrossRef - Association between hemoglobin within the normal range and hemoglobin A1c among Chinese non-diabetes adults
Yi Lai, Zhihong Lin, Zhongxin Zhu
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association between Daily Total Dietary Nutrient Intake and Recent Glycemic Control States of Non-Pregnant Adults 20+ Years Old from NHANES 1999–2018 (Except for 2003–2004)
Yin Bai, Hao Zhang, Jie Yang, Lei Peng
Nutrients.2021; 13(11): 4168. CrossRef
- Fingerprinting hyperglycemia using predictive modelling approach based on low-cost routine CBC and CRP diagnostics
- Complications
- Association between Serum Cystatin C and Vascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus without Nephropathy
- Hye Jeong Kim, Dong Won Byun, Kyoil Suh, Myung Hi Yoo, Hyeong Kyu Park
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(6):513-518. Published online October 15, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0006
- 3,590 View
- 43 Download
- 12 Web of Science
- 9 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader Background Recent studies have correlated serum cystatin C (CysC) with vascular complications, but few studies have investigated this correlation in diabetes patients without nephropathy. This study aimed to evaluate if higher serum CysC levels increase the risk for vascular complications in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with normal renal function or mild renal impairment.
Methods A total of 806 consecutive patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who were admitted to the diabetes center of Soonchunhyang University Hospital for blood glucose control were retrospectively reviewed. Patients with nephropathy were excluded. Subjects were categorized into quartiles of serum CysC levels (Q1, ≤0.65 mg/L; Q2, 0.66 to 0.79 mg/L; Q3, 0.80 to 0.94 mg/L; and Q4, ≥0.95 mg/L).
Results The proportion of patients with diabetic retinopathy (DR) (
P for trend <0.001), coronary heart disease (CHD) (P for trend <0.001), and stroke (P for trend <0.001) increased across the serum CysC quartiles. After adjustment for confounding factors, the highest serum CysC level remained a significant risk factor for DR (odds ratio [OR], 1.929; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.007 to 4.144;P =0.040). Compared with Q1, a significant positive association was observed between serum CysC and CHD in Q2 (OR, 7.321; 95% CI, 1.114 to 48.114;P =0.012), Q3 (OR, 6.027; 95% CI, 0.952 to 38.161;P =0.020), and Q4 (OR, 8.122; 95% CI, 1.258 to 52.453;P =0.007). No associations were observed between CysC and stroke after additional adjustment for confounding variables.Conclusion Serum CysC levels are independently associated with DR and CHD, suggesting that CysC may be useful for identifying type 2 diabetes mellitus patients without nephropathy who are at high risk for vascular complications.
-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- A systematic literature review of machine learning based risk prediction models for diabetic retinopathy progression
Tiwalade Modupe Usman, Yakub Kayode Saheed, Augustine Nsang, Abel Ajibesin, Sandip Rakshit
Artificial Intelligence in Medicine.2023; 143: 102617. CrossRef - Serum cystatin C for risk stratification of prediabetes and diabetes populations
Kun Xiong, Shiran Zhang, Pingting Zhong, Zhuoting Zhu, Yanping Chen, Wenyong Huang, Wei Wang
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(11): 102882. CrossRef - Serum VEGF, high-sensitivity CRP, and cystatin-C assist in the diagnosis of type 2 diabetic retinopathy complicated with hyperuricemia
Jing Wei, Jincheng Zhang, Yanan Shi, Huiqin Zhang, Yan Wu
Open Medicine.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diagnostic circulating biomarkers to detect vision‐threatening diabetic retinopathy: Potential screening tool of the future?
Karen Frudd, Sobha Sivaprasad, Rajiv Raman, Subramanian Krishnakumar, Yeddula Rebecca Revathy, Patric Turowski
Acta Ophthalmologica.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between circulating cystatin C and hyperuricemia: a cross-sectional study
Yanjun Guo, Hangkai Huang, Yishu Chen, Chao Shen, Chengfu Xu
Clinical Rheumatology.2022; 41(7): 2143. CrossRef - Multicenter Evaluation of Diagnostic Circulating Biomarkers to Detect Sight-Threatening Diabetic Retinopathy
Sarega Gurudas, Karen Frudd, Jayapal Jeya Maheshwari, Yeddula Rebecca Revathy, Sobha Sivaprasad, Shruthi Mahalakshmi Ramanathan, Vignesh Pooleeswaran, A. Toby Prevost, Eleni Karatsai, Sandra Halim, Shruti Chandra, Paul Nderitu, Dolores Conroy, Subramanian
JAMA Ophthalmology.2022; 140(6): 587. CrossRef - A Cross-Sectional Study of Serum and Urine Fluoride in Diabetes in Fluoride Exposed Population
Sai Deepika Ram Mohan, Shashidhar Kurpad Nagaraj, Raveesha Anjanappa, Muninarayana Chandrappa
Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences.2021; 10(11): 798. CrossRef - Cystatin C predicts the risk of incident cerebrovascular disease in the elderly
Xin Zheng, Hong-da She, Qiao-xin Zhang, Tong Si, Ku-sheng Wu, Ying-xiu Xiao
Medicine.2021; 100(28): e26617. CrossRef - Proteinuria Is Associated with Carotid Artery Atherosclerosis in Non-Albuminuric Type 2 Diabetes: A Cross-Sectional Study
Jaehyun Bae, Yong-ho Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Byung-Wan Lee
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(1): 136. CrossRef
- A systematic literature review of machine learning based risk prediction models for diabetic retinopathy progression
- Complications
- Diagnosing Diabetic Neuropathy: Something Old, Something New
- Ioannis N. Petropoulos, Georgios Ponirakis, Adnan Khan, Hamad Almuhannadi, Hoda Gad, Rayaz A. Malik
- Diabetes Metab J. 2018;42(4):255-269. Published online August 21, 2018
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2018.0056
- 8,318 View
- 117 Download
- 68 Web of Science
- 72 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader There are potentially many ways of assessing diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN). However, they do not fulfill U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) requirements in relation to their capacity to assess therapeutic benefit in clinical trials of DPN. Over the past several decades symptoms and signs, quantitative sensory and electrodiagnostic testing have been strongly endorsed, but have consistently failed as surrogate end points in clinical trials. Therefore, there is an unmet need for reliable biomarkers to capture the onset and progression and to facilitate drug discovery in DPN. Corneal confocal microscopy (CCM) is a non-invasive ophthalmic imaging modality for
in vivo evaluation of sensory C-fibers. An increasing body of evidence from multiple centers worldwide suggests that CCM fulfills the FDA criteria as a surrogate endpoint of DPN.-
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Painful Diabetic Neuropathy: The Need for New Approaches
Andrea M. Yeung, Jingtong Huang, Kevin T. Nguyen, Nicole Y. Xu, Lorenzo T. Hughes, Brajesh K. Agrawal, Niels Ejskjaer, David C. Klonoff
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2024; 18(1): 159. CrossRef - COMMENT ON: Diabetic peripheral neuropathy is associated with diabetic kidney disease and cardiovascular disease: The silesia diabetes-heart project
Laksh Kumar, Syed Ali Arsal
Current Problems in Cardiology.2024; 49(4): 102227. CrossRef - Risk factors for peripheral artery disease and diabetic peripheral neuropathy among patients with type 2 diabetes
Tian Chen, Shengjue Xiao, Zhengdong Chen, Yiqing Yang, Bingquan Yang, Naifeng Liu
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2024; 207: 111079. CrossRef - Laser-Induced Graphene-Based Smart Insole to Measure Plantar Temperature
Amith Khandakar, Md. Ahasan Atick Faisal, Muhammad E. H. Chowdhury, Mamun Bin Ibne Reaz, Sawal Hamid Md Ali, Mohd Ibrahim bin Shapiai Abd. Razak, Ahmad Ashrif A. Bakar, Sakib Mahmud, Rayaz A. Malik
IEEE Sensors Journal.2024; 24(2): 1190. CrossRef - Morphometry of the sural nerve in diabetic neuropathy: a systematic review
Zhang Ludi, Matthias Yi Quan Liau, Bryan Song Jun Yong, Amanda Sze Yen Auyong, Quah Hui Ting Lynette, Samuel Jianjie Yeo, Khin Swee Elizabeth Tan, Sreenivasulu Reddy Mogali, Ramya Chandrasekaran, Vivek Perumal, Ranganath Vallabhajosyula
Journal of Ultrasound.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding the Clinical Relationship Between Diabetic Retinopathy, Nephropathy, and Neuropathy: A Comprehensive Review
Aditi Kulkarni, Archana R Thool, Sachin Daigavane
Cureus.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Development and validation of risk prediction model for diabetic neuropathy among diabetes mellitus patients at selected referral hospitals, in Amhara regional state Northwest Ethiopia, 2005–2021
Negalgn Byadgie Gelaw, Achenef Asmamaw Muche, Adugnaw Zeleke Alem, Nebiyu Bekele Gebi, Yazachew Moges Chekol, Tigabu Kidie Tesfie, Tsion Mulat Tebeje, Jacopo Sabbatinelli
PLOS ONE.2023; 18(8): e0276472. CrossRef - Biomarkers in diabetic neuropathy
Kaveri M. Adki, Yogesh A. Kulkarni
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2023; 129(2): 460. CrossRef - Early detection and treatment device for diabetic foot neuropathy
Hunduma Tolossa Kumsa, Lelisa Getaneh Abdisa, Lelisa Tesema Tolessa, Sosina Ayele Wubneh, Wadajo Feyisa Kusa, Shimelis Nigusu Hordofa, Hundessa Daba Nemomssa
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2023; 192(1): 143. CrossRef - Differences in motor unit behavior during isometric contractions in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy at various disease severities
Mateus André Favretto, Felipe Rettore Andreis, Sandra Cossul, Francesco Negro, Anderson Souza Oliveira, Jefferson Luiz Brum Marques
Journal of Electromyography and Kinesiology.2023; 68: 102725. CrossRef - Association of peripheral neuropathy with subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in patients with type 2 diabetes
Yanyan Chen, Yi Wang, Ying Zhang, Mengying Li, Weiqing Zhang, Yingni Zhou, Xiangyang Liu, Jianfang Fu, Zuowei Lu, Qian Xu, Tao Liu, Zeping Li, Xiaomiao Li, Jie Zhou
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2023; 37(2): 108406. CrossRef - Quantifying gait intralimb coordination patterns in individuals with different levels of diabetic neuropathy: a vector coding analysis
Michelle Bazilio Milan, Guilherme Augusto Gomes De Villa, Eneida Yuri Suda, Isabel de Camargo Neves Sacco, Marcus Fraga Vieira
Research on Biomedical Engineering.2023; 39(1): 311. CrossRef - Mechanisms underlying altered neuromuscular function in people with DPN
Antonin Le Corre, Nathan Caron, Nicolas A. Turpin, Georges Dalleau
European Journal of Applied Physiology.2023; 123(7): 1433. CrossRef - Peripheral Neuropathy in Diabetes Mellitus: Pathogenetic Mechanisms and Diagnostic Options
Raffaele Galiero, Alfredo Caturano, Erica Vetrano, Domenico Beccia, Chiara Brin, Maria Alfano, Jessica Di Salvo, Raffaella Epifani, Alessia Piacevole, Giuseppina Tagliaferri, Maria Rocco, Ilaria Iadicicco, Giovanni Docimo, Luca Rinaldi, Celestino Sardu, T
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(4): 3554. CrossRef - Nerve conduction velocity is independently associated with bone mineral density in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Xiao-jing Chen, Xiao-feng Wang, Zheng-can Pan, Deng Zhang, Ke-cheng Zhu, Tao Jiang, Xiao-ke Kong, Rui Xie, Li-hao Sun, Bei Tao, Jian-min Liu, Hong-yan Zhao
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Precision of Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument (MNSI) Tool for the Diagnosis of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Among People with Type 2 Diabetes—A Study from South India
Vijay Viswanathan, Balkhiwala Ahmed Khan, Sukanya Nachimuthu, Satyavani Kumpatla
The International Journal of Lower Extremity Wounds.2023; : 153473462311632. CrossRef - Ankle Fractures in Diabetic Patients
Ellen M. Goldberg, William S. Polachek, Kelly Hynes
JBJS Reviews.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing the Ipswich Touch Test (IpTT) and 10gm-SMWF (10-gm Semmes–Weinstein mono-filament) in Indian population subset with type 2 diabetes mellitus to detect diabetes neuropathy
Sivasubramaniyam Senthilkumar, Ramesh Dasarathan, Pushkar Pazhani, Archana Gaur, Varatharajan Sakthivadivel
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1971 -).2023; 192(6): 2793. CrossRef - Diabetic neuropathy: Pathogenesis and evolving principles of management
Basem Zaino, Rashika Goel, Sanjana Devaragudi, Ananya Prakash, Yogeshkumar Vaghamashi, Yashendra Sethi, Neil Patel, Nirja Kaka
Disease-a-Month.2023; 69(9): 101582. CrossRef - Association between Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy as Measured Using a Point-of-Care Sural Nerve Conduction Device and Urinary Albumin Excretion in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Tatsuya Fukuda, Akiko Fujii, Taro Akihisa, Naoya Otsubo, Masanori Murakami, Tetsuya Yamada, Chisato Maki
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2023; 12(12): 4089. CrossRef - Sudomotor dysfunction in diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) and its testing modalities: A literature review
Muhammad Akbar, Alvian Wandy, Gita Vita Soraya, Yudy Goysal, Mimi Lotisna, Muhammad Iqbal Basri
Heliyon.2023; 9(7): e18184. CrossRef - Novel insights into the nervous system affected by prolonged hyperglycemia
Kamila Zglejc-Waszak, Konark Mukherjee, Agnieszka Korytko, Bogdan Lewczuk, Andrzej Pomianowski, Joanna Wojtkiewicz, Marta Banach, Michał Załęcki, Natalia Nowicka, Julia Jarosławska, Bernard Kordas, Krzysztof Wąsowicz, Judyta K. Juranek
Journal of Molecular Medicine.2023; 101(8): 1015. CrossRef - (Pre)diabetes and a higher level of glycaemic measures are continuously associated with corneal neurodegeneration assessed by corneal confocal microscopy: the Maastricht Study
Sara B. A. Mokhtar, Frank C. T. van der Heide, Karel A. M. Oyaert, Carla J. H. van der Kallen, Tos T. J. M. Berendschot, Fabio Scarpa, Alessia Colonna, Bastiaan E. de Galan, Marleen M. J. van Greevenbroek, Pieter C. Dagnelie, Casper G. Schalkwijk, Rudy M.
Diabetologia.2023; 66(11): 2030. CrossRef - Potential Retinal Biomarkers in Alzheimer’s Disease
Mariana Yolotzin García-Bermúdez, Rupali Vohra, Kristine Freude, Peter van Wijngaarden, Keith Martin, Maj Schneider Thomsen, Blanca Irene Aldana, Miriam Kolko
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(21): 15834. CrossRef - The effect of polyneuropathy severity on nerve conduction and pain syndrome in patients with type 2 diabetes
A.Ya. Sabovchyk, M.M. Oros
INTERNATIONAL NEUROLOGICAL JOURNAL.2023; 19(6): 161. CrossRef - Artificial intelligence utilising corneal confocal microscopy for the diagnosis of peripheral neuropathy in diabetes mellitus and prediabetes
Frank G. Preston, Yanda Meng, Jamie Burgess, Maryam Ferdousi, Shazli Azmi, Ioannis N. Petropoulos, Stephen Kaye, Rayaz A. Malik, Yalin Zheng, Uazman Alam
Diabetologia.2022; 65(3): 457. CrossRef - 10.6-μm infrared laser as adjuvant therapy for diabetic peripheral neuropathy: study protocol for a double-blind, randomized controlled trial
Lin Lin, Yi Chen, Yuxia Li, Ke Cheng, Haiping Deng, Jianping Lu, Ling Zhao, Xueyong Shen
Trials.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetic corneal neuropathy as a surrogate marker for diabetic peripheral neuropathy
WeiZheng So, NatalieShi Qi Wong, HongChang Tan, MollyTzu Yu Lin, IsabelleXin Yu Lee, JodhbirS Mehta, Yu-Chi Liu
Neural Regeneration Research.2022; 17(10): 2172. CrossRef - SUDOSCAN in Combination with the Michigan Neuropathy Screening Instrument Is an Effective Tool for Screening Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy
Tae Jung Oh, Yoojung Song, Hak Chul Jang, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(2): 319. CrossRef - Performance Analysis of Conventional Machine Learning Algorithms for Diabetic Sensorimotor Polyneuropathy Severity Classification Using Nerve Conduction Studies
Fahmida Haque, Mamun B. I. Reaz, Muhammad E. H. Chowdhury, Serkan Kiranyaz, Sawal H. M. Ali, Mohammed Alhatou, Rumana Habib, Ahmad A. A. Bakar, Norhana Arsad, Geetika Srivastava, Paolo Crippa
Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience.2022; 2022: 1. CrossRef - The Presence of Clonal Hematopoiesis Is Negatively Associated with Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy in Type 2 Diabetes
Tae Jung Oh, Han Song, Youngil Koh, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2022; 37(2): 243. CrossRef - An overview of painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy: Diagnosis and treatment advancements
Jonathan M. Hagedorn, Alyson M. Engle, Tony K. George, Jay Karri, Newaj Abdullah, Erik Ovrom, Jhon E. Bocanegra-Becerra, Ryan S. D'Souza
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2022; 188: 109928. CrossRef - Prevalence and risk of diabetic complications in young-onset versus late-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus
Yongin Cho, Hye-Sun Park, Byung Wook Huh, Seong Ha Seo, Da Hea Seo, Seong Hee Ahn, Seongbin Hong, Young Ju Suh, So Hun Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism.2022; 48(6): 101389. CrossRef - Artificial Intelligence and Corneal Confocal Microscopy: The Start of a Beautiful Relationship
Uazman Alam, Matthew Anson, Yanda Meng, Frank Preston, Varo Kirthi, Timothy L. Jackson, Paul Nderitu, Daniel J. Cuthbertson, Rayaz A. Malik, Yalin Zheng, Ioannis N. Petropoulos
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(20): 6199. CrossRef - INvesTigating the Abnormality of detrusor ConTractility by uroflowmetry in diabetic children (INTACT Trial): protocol of a prospective, observational study
Ágnes Rita Martonosi, Piroska Pázmány, Szabolcs Kiss, Annamária Zsákai, László Szabó
BMJ Open.2022; 12(11): e062198. CrossRef - Diabetic foot ulcers: A devastating complication of diabetes mellitus continues non-stop in spite of new medical treatment modalities
Gamze Akkus, Murat Sert
World Journal of Diabetes.2022; 13(12): 1106. CrossRef - Corneal nerves in diabetes—The role of the in vivo corneal confocal microscopy of the subbasal nerve plexus in the assessment of peripheral small fiber neuropathy
Anna M. Roszkowska, Carmelo Licitra, Giuseppe Tumminello, Elisa I. Postorino, Michele R. Colonna, Pasquale Aragona
Survey of Ophthalmology.2021; 66(3): 493. CrossRef - Association between Sleep Quality and Painless Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Assessed by Current Perception Threshold in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Dughyun Choi, Bo-Yeon Kim, Chan-Hee Jung, Chul-Hee Kim, Ji-Oh Mok
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 358. CrossRef - Glycaemic control for painful diabetic peripheral neuropathy is more than fasting plasma glucose and glycated haemoglobin
Y.-W. Pai, C.-L. Tang, C.-H. Lin, S.-Y. Lin, I.-T. Lee, M.-H. Chang
Diabetes & Metabolism.2021; 47(1): 101158. CrossRef - Diagnosis of Neuropathy and Risk Factors for Corneal Nerve Loss in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes: A Corneal Confocal Microscopy Study
Maryam Ferdousi, Alise Kalteniece, Shazli Azmi, Ioannis N. Petropoulos, Georgios Ponirakis, Uazman Alam, Omar Asghar, Andrew Marshall, Catherine Fullwood, Maria Jeziorska, Caroline Abbott, Giuseppe Lauria, Catharina G. Faber, Handrean Soran, Nathan Efron,
Diabetes Care.2021; 44(1): 150. CrossRef - Widespread sensory neuropathy in diabetic patients hospitalized with severe COVID-19 infection
Ariel Odriozola, Lucía Ortega, Lidia Martinez, Samantha Odriozola, Ainhoa Torrens, David Corroleu, Silvia Martínez, Meritxell Ponce, Yolanda Meije, Mercedes Presas, Alejandra Duarte, M. Belén Odriozola, Rayaz A. Malik
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2021; 172: 108631. CrossRef - Lost in Translation? Measuring Diabetic Neuropathy in Humans and Animals
Heung Yong Jin, Seong-Su Moon, Nigel A. Calcutt
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(1): 27. CrossRef - Early Detection of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Focus on Small Nerve Fibres
Jamie Burgess, Bernhard Frank, Andrew Marshall, Rashaad S. Khalil, Georgios Ponirakis, Ioannis N. Petropoulos, Daniel J. Cuthbertson, Rayaz A. Malik, Uazman Alam
Diagnostics.2021; 11(2): 165. CrossRef - Role of interdigital sensory nerve conduction study as a noninvasive approach for early diagnosis of diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Hamid R. Fateh, Seyed Pezhman Madani
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2021; 20(1): 71. CrossRef - Performance Analysis of Conventional Machine Learning Algorithms for Diabetic Sensorimotor Polyneuropathy Severity Classification
Fahmida Haque, Mamun Bin Ibne Reaz, Muhammad Enamul Hoque Chowdhury, Geetika Srivastava, Sawal Hamid Md Ali, Ahmad Ashrif A. Bakar, Mohammad Arif Sobhan Bhuiyan
Diagnostics.2021; 11(5): 801. CrossRef - Advances in Screening, Early Diagnosis and Accurate Staging of Diabetic Neuropathy
Josie Carmichael, Hassan Fadavi, Fukashi Ishibashi, Angela C. Shore, Mitra Tavakoli
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Vibration Perception Threshold and Related Factors for Balance Assessment in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jisang Jung, Min-Gyu Kim, Youn-Joo Kang, Kyungwan Min, Kyung-Ah Han, Hyoseon Choi
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(11): 6046. CrossRef - Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy Affects Pinch Strength and Hand Dexterity in Elderly Patients
Qi Zhang, Yifang Lin, Xinhua Liu, Li Zhang, Yan Zhang, Dong Zhao, Qi Lu, Jie Jia, Jia-Jia Wu
Neural Plasticity.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Association of Combined TCF7L2 and KCNQ1 Gene Polymorphisms with Diabetic Micro- and Macrovascular Complications in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Rujikorn Rattanatham, Nongnuch Settasatian, Nantarat Komanasin, Upa Kukongviriyapan, Kittisak Sawanyawisuth, Phongsak Intharaphet, Vichai Senthong, Chatri Settasatian
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(4): 578. CrossRef - Neuropeptide Y: a potential theranostic biomarker for diabetic peripheral neuropathy in patients with type-2 diabetes
Noo Ree Cho, Yeuni Yu, Chang-Kyu Oh, Dai Sik Ko, Kyungjae Myung, Yoonsung Lee, Hee Sam Na, Yun Hak Kim
Therapeutic Advances in Chronic Disease.2021; 12: 204062232110419. CrossRef - Prediction of Diabetic Sensorimotor Polyneuropathy Using Machine Learning Techniques
Dae Youp Shin, Bora Lee, Won Sang Yoo, Joo Won Park, Jung Keun Hyun
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(19): 4576. CrossRef - Reduced association between dendritic cells and corneal sub‐basal nerve fibers in patients with fibromyalgia syndrome
Alexander Klitsch, Dimitar Evdokimov, Johanna Frank, Dominique Thomas, Nadine Saffer, Caren Meyer zu Altenschildesche, Marco Sisignano, Daniel Kampik, Rayaz A. Malik, Claudia Sommer, Nurcan Üçeyler
Journal of the Peripheral Nervous System.2020; 25(1): 9. CrossRef - Diet-Induced Rodent Models of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy, Retinopathy and Nephropathy
Inês Preguiça, André Alves, Sara Nunes, Pedro Gomes, Rosa Fernandes, Sofia D. Viana, Flávio Reis
Nutrients.2020; 12(1): 250. CrossRef - Diabetic Distal Symmetrical Polyneuropathy: Correlation of Clinical, Laboratory, and Electrophysiologic Studies in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yi-Ching Weng, Sung-Sheng Tsai, Rong-Kuo Lyu, Chun-Che Chu, Long-Sun Ro, Ming-Feng Liao, Hong-Shiu Chang, Chiung-Mei Chen, Jawl-Shan Hwang, Hung-Chou Kuo
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: Is it Underdiagnosed?
Rizaldy T. Pinzon, M. Kes, Rosa De Lima R. Sa
Asian Journal of Biological Sciences.2020; 13(2): 168. CrossRef - Deterioration of Sleep Quality According to Glycemic Status
Myung Haeng Hur, Mi-Kyoung Lee, Kayeon Seong, Jun Hwa Hong
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(5): 679. CrossRef - Microvascular Complications of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Charles Faselis, Alexandra Katsimardou, Konstantinos Imprialos, Pavlos Deligkaris, Manolis Kallistratos, Kiriakos Dimitriadis
Current Vascular Pharmacology.2020; 18(2): 117. CrossRef - Computational methods for automated analysis of corneal nerve images: Lessons learned from retinal fundus image analysis
Tooba Salahuddin, Uvais Qidwai
Computers in Biology and Medicine.2020; 119: 103666. CrossRef - TIR generated by continuous glucose monitoring is associated with peripheral nerve function in type 2 diabetes
Fengwen Li, Yinan Zhang, Huizhi Li, Jingyi Lu, Lan Jiang, Robert A. Vigersky, Jian Zhou, Congrong Wang, Yuqian Bao, Weiping Jia
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 166: 108289. CrossRef - A Phase 2 Clinical Trial on the Use of Cibinetide for the Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema
Noemi Lois, Evie Gardner, Margaret McFarland, David Armstrong, Christine McNally, Nuala Jane Lavery, Christina Campbell, Rita I Kirk, Daiva Bajorunas, Ann Dunne, Anthony Cerami, Michael Brines
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2020; 9(7): 2225. CrossRef - Diabetic neuropathy and neuropathic pain: a (con)fusion of pathogenic mechanisms?
Nigel A. Calcutt
Pain.2020; 161(Supplement): S65. CrossRef - Lumos for the long trail: Strategies for clinical diagnosis and severity staging for diabetic polyneuropathy and future directions
Tatsuhito Himeno, Hideki Kamiya, Jiro Nakamura
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2020; 11(1): 5. CrossRef - Corneal confocal microscopy detects small nerve fibre damage in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy
Alise Kalteniece, Maryam Ferdousi, Shazli Azmi, Womba M. Mubita, Andrew Marshall, Giuseppe Lauria, Catharina G. Faber, Handrean Soran, Rayaz A. Malik
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The Association of Fasting C-peptide with Corneal Neuropathy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Anju Zuo, Chuan Wang, Lili Li, Jingru Qu, Juan Cao, Li Chen, Solomon Tesfaye, Wenjuan Li, Xinguo Hou, Vincenza Spallone
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Performance analysis of noninvasive electrophysiological methods for the assessment of diabetic sensorimotor polyneuropathy in clinical research: a systematic review and meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis
Fahmida Haque, Mamun Bin Ibne Reaz, Sawal Hamid Md Ali, Norhana Arsad, Muhammad Enamul Hoque Chowdhury
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Tear film substance P: A potential biomarker for diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Shyam Sunder Tummanapalli, Mark D.P. Willcox, Tushar Issar, Aimy Yan, Jana Pisarcikova, Natalie Kwai, Ann M. Poynten, Arun V. Krishnan, Maria Markoulli
The Ocular Surface.2019; 17(4): 690. CrossRef - Characterizing distal peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes mellitus in a semi-urban community setting in Peru
Meera F Iyengar, Antonio Bernabe-Ortiz
Journal of Global Health Reports.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetic peripheral neuropathy: advances in diagnosis and strategies for screening and early intervention
Dinesh Selvarajah, Debasish Kar, Kamlesh Khunti, Melanie J Davies, Adrian R Scott, Jeremy Walker, Solomon Tesfaye
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2019; 7(12): 938. CrossRef - Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy as a Risk Factor for Sarcopenia
Tae Jung Oh, Yoojung Song, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang
Annals of Geriatric Medicine and Research.2019; 23(4): 170. CrossRef - Diabetic Neuropathy: New Insights to Early Diagnosis and Treatments
Mark Yorek, Rayaz A. Malik, Nigel A. Calcutt, Aaron Vinik, Soroku Yagihashi
Journal of Diabetes Research.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - Use of parenteral vitamin B complexes in treatment of polyneuropathy
O. V. Kurushina, A. E. Barulin, O. I. Agarkova
Medical Council.2018; (18): 62. CrossRef - Circulating microRNAs as biomarkers for diabetic neuropathy: A novel approach
Eleni Xourgia, Athanasia Papazafiropoulou, Andreas Melidonis
World Journal of Experimental Medicine.2018; 8(3): 18. CrossRef
- Painful Diabetic Neuropathy: The Need for New Approaches

 KDA
KDA
 First
First Prev
Prev





