- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 41(5); 2017 > Article
-
ReviewClinical Diabetes & Therapeutics Antihyperglycemic Agent Therapy for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 2017: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
-
Seung-Hyun Ko1, Kyu-Yeon Hur2, Sang Youl Rhee3, Nan-Hee Kim4, Min Kyong Moon5, Seok-O Park6, Byung-Wan Lee7, Hyun Jin Kim8, Kyung Mook Choi4
 , Jin Hwa Kim9, Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline of Korean Diabetes Association
, Jin Hwa Kim9, Committee of Clinical Practice Guideline of Korean Diabetes Association -
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2017;41(5):337-348.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2017.41.5.337
Published online: October 17, 2017
1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
3Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
5Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul Metropolitan Government Boramae Medical Center, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
6Department of Internal Medicine, Gwangmyeong Sungae Hospital, Gwangmyeong, Korea.
7Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
8Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Chungnam National University School of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
9Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Kyung Mook Choi. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University Guro Hospital, Korea University College of Medicine, 148 Gurodong-ro, Guro-gu, Seoul 08308, Korea. medica7@gmail.com
- *Seung-Hyun Ko and Kyu-Yeon Hur contributed equally to this study as first authors.
Copyright © 2017 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
- In 2017, the Korean Diabetes Association (KDA) published a position statement on the use of antihyperglycemic agents for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The KDA regularly updates its Clinical Practice Guidelines, but since the last update in 2015, many results from clinical trials have been introduced, and domestic data from studies performed in Korean patients with T2DM have been published. Recently, evidence from large clinical studies assessing cardiovascular outcomes following the use of sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors and glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists in patients with T2DM were incorporated into the recommendations. Additionally, new data from clinical trials using dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors and thiazolidinediones in Korean patients with T2DM were added. Following a systematic review and assessment of recent evidence, the KDA updated and modified its clinical practice recommendations regarding the use of antihyperglycemic agents and revised the treatment algorithm for Korean adult patients with T2DM.
- The Clinical Practice Guidelines for type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) provided by the Korean Diabetes Association (KDA) include comprehensive and evidence-based treatment and management guidelines to improve the level of care for adults with T2DM in Korea according to Korean standards. The target users of this guideline are primary care physicians and other healthcare professionals who treat adults with T2DM. Since the first edition was published in 1990, the Clinical Practice Guidelines for adult patients with T2DM have been periodically updated by the Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines of the KDA [1]. However, since the fifth edition was published in 2015, many results from large clinical trials of antidiabetic drugs have been introduced, and clinical evidence from studies assessing Korean patients with T2DM who use dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) inhibitors, glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs), or sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors have accumulated [2345]. All novel evidence and results were reviewed to extract recommendations for the treatment of these patients.
- The 2017 KDA position statement was written by the Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines under a formal review process after a systematic and extensive review of articles published from January 1, 2015 to May 31, 2017. The grading system for the scientific evidence was defined by the KDA and modeled after the evidence-grading system of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) with some modifications [6]. Therefore, the level of evidence and strength of the recommendation were not treated as separate entities. The KDA classified recommendation levels into four ratings (A, B, C, and E) according to the quality of evidence (Table 1). If domestic data were limited or evidence was difficult to apply to Korean patients with T2DM, the Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines made a final decision after intensive discussion. In the absence of qualified supporting evidence, or if the recommendation was based on the consensus of the Expert Committees, a grade E was assigned.
- In this 2017 position statement regarding pharmacological therapies for non-pregnant adult patients with T2DM, the KDA updated the previous recommendations published in 2015. In principle, these recommendations were based on extensive review of scientific evidences; therefore, criteria for the health insurance coverage in Korea were not considered. The treatment algorithm for use of antihyperglycemic agents was also revised. Specifically, the previous algorithm was divided into treatment with non-insulin antihyperglycemic agents and treatment with insulin, whereas the updated 2017 position statement is believed to provide the most recent evidence-based treatment recommendations for adult Korean patients with T2DM.
INTRODUCTION
- Oral antihyperglycemic agents and GLP-1RAs for type 2 diabetes mellitus
- 1. Active lifestyle modification (LSM) and appropriate pharmacotherapy are needed following the initial diagnosis of diabetes [A].
- 2. An appropriate selection of pharmacotherapies should be made after considering the patient's clinical characteristics and the efficacy, side effects, mechanism of action, risk of hypoglycemia, effect on body weight, patient preference, and combined comorbidity [E].
- 1. Metformin is the preferred initial oral antihyperglycemic agent [A].
- 2. If metformin is contraindicated or intolerable as the initial treatment, then another class of antihyperglycemic agent can be used depending on the clinical situation [E].
- 3. If monotherapy fails to achieve the glycemic goal, then combination therapy using a second agent with a different mechanism of action should be initiated [A].
- 4. Dual combination therapy can be used as the initial management strategy depending on the patient [B].
- 5. Although the maximal dosage of a single oral agent may be prescribed, early initiation of combination therapy is suitable after considering the glucose-lowering efficacy and side effects of the drug [B].
- 6. When selecting a class of antihyperglycemic agents for combination therapy, the glucose-lowering efficacy, risk of hypoglycemia, body weight gain, and cardiovascular benefits associated with the drugs are preferentially considered [E].
- 7. The different mechanisms of action, drug interactions, and patient preferences for combination therapy with more than two classes of antihyperglycemic agents should be considered [C].
- 8. Although insulin therapy is recommended after failed oral combination therapy, changing or adding another class of oral antihyperglycemic agent can be performed [C].
- Glycemic control within the target range has beneficial effects for reducing the risk of cardiovascular and/or microvascular complications [7]. The glycemic goal for non-pregnant adult patients with T2DM is ideally a glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level <6.5%, but this can be tailored to individual circumstances [189]. Factors to consider when setting a glycemic target goal include age, duration of diabetes, life expectancy, presence of advanced diabetic complications, comorbidities, repeated episodes of hypoglycemia, cognitive dysfunction, and patient preference [168]. More stringent goals are required for preoperative and postoperative situations, pregnancy, and acute-onset disease. A patient-centered approach is emphasized to successfully achieve the glycemic goal [168910].
- LSM is an essential component of treatment for all patients with T2DM and should be initiated promptly and simultaneously with antidiabetic medications after diagnosis. Patient education within a structured program should be received from a healthcare professional at the time of diagnosis and then followed up with regular reinforcement checks [111213]. For patients with newly diagnosed T2DM, LSM includes medical nutrition therapy, weight control, physical activity, smoking cessation, and avoidance of alcohol should be initiated. Although LSM is a very important component of treatment for T2DM, the administration of antihyperglycemic agents should not be delayed. Pharmacotherapy can be initiated simultaneously and in conjunction with LSM.
- T2DM is a chronic metabolic disease with a progressive nature [14]. A gradual decline in β-cell function and progressive increases in insulin resistance lead to a deteriorated glycemic control status and the need for increasingly intensive pharmacotherapies [15]. Therefore, in addition to LSM, a transition from monotherapy to combination therapy with antihyperglycemic agents is usually inevitable. The initiation or add-on to a current therapy of most oral antihyperglycemic agents yields an additional reduction in HbA1c levels of 0.5% to 1.25%, whereas thiazolidinediones (TZDs) and sulfonylureas (SUs) lower HbA1c levels by approximately 1.0% to 1.25% [16].
- As an initial therapy for newly diagnosed patients with an HbA1c level ≤7.5%, metformin monotherapy is recommended [171819]. Metformin should not be used in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate <30 mL/min/1.73 m2, severe renal or hepatic dysfunction, heart failure, severe infection, or dehydration [678910]. If metformin is not tolerable or is contraindicated, the alternative choices for monotherapy include DPP4 inhibitors, SGLT2 inhibitors, TZDs, GLP-1RAs, SUs, glinides (meglitinide), α-glucosidase inhibitors (AGIs), and insulin according to patient circumstances (Table 2, Fig. 1). The factors to consider when choosing an antihyperglycemic medication include its efficacy, complementary mechanism of action, risk of hypoglycemia, effect on weight gain, side effects, patient preference, and comorbidities [20212223]. In the Practical Evidence of Antidiabetic Monotherapy (PEAM) study, the glucose-lowering efficacies of SUs (glimepiride), biguanide (metformin), and TZDs (rosiglitazone) as antidiabetic monotherapies administered for 48 weeks were similar in drug-naive Korean patients with T2DM (decrease in HbA1c levels from 7.8% to 6.9% for glimepiride, P<0.001; from 7.9% to 7.0% for metformin, P<0.001; and from 7.8% to 7.0% for rosiglitazone, P<0.001; P=0.62) [24]. Glimepiride and rosiglitazone significantly increased body weight, while metformin reduced body weight. Symptomatic hypoglycemia was more frequent in the glimepiride group, while diarrhea was more frequent in the metformin group [24].
- If the initial HbA1c level of a patient is ≥7.5% or the HbA1c target is not achieved within 3 months initiating monotherapy, dual combination therapy can be considered [678910252627282930]. If the HbA1c target is not achieved within 3 months of initiating dual therapy, a third agent with a complementary mechanism of action can be added for triple combination therapy [31]. Metformin is maintained as background therapy during dual or triple combination therapy. If metformin is not tolerable or is contraindicated, avoid the use of metformin and proceed to the next category in the algorithm (Fig. 1). The reductions in HbA1c values are similar across all drug classes used as monotherapies and metformin-based combinations. Body weight is reduced or maintained with metformin, DPP4 inhibitors, GLP-1RAs, and SGLT2 inhibitors but increased with SUs and TZDs [2526272829]. Hypoglycemia is more frequent with SUs [18192829]. As a monotherapy, DPP4 inhibitors exhibit a lower risk of hypoglycemia, lower risks of side effects and weight gain, and a better glucose-lowering efficacy in Asians compared with other ethnic groups [30]. When added to metformin and SUs, GLP-1RAs are associated with the lowest risk of hypoglycemia (odds ratio, 0.60; 95% confidence interval, 0.39 to 0.94) [19], but gastrointestinal side effects are highest with metformin and GLP-1RAs. SGLT2 inhibitors have greater associations with the potential side effects of urinary tract infection and euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis [2632].
- If postprandial hyperglycemia occurs, meglitinides, AGIs, DPP4 inhibitors, or GLP-1RAs can be considered [3334]. The early initiation of combination therapy is preferred over maximizing the dosage of a single agent after considering glucoselowering efficacy and side effects [3536]. SUs or DPP4 inhibitors are not associated with increased risks of major cardiovascular events in patients with T2DM, irrespective of comparator or background medications [637]. However, for patients with longstanding suboptimally controlled T2DM and established atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, the ADA recommends empagliflozin or liraglutide, because these drugs have been shown to reduce cardiovascular and all-cause mortality rates [63839]. Ongoing studies investigating the cardiovascular benefits of the SGLT2 inhibitors, DPP4 inhibitors, and GLP-1RAs are being conducted [6].
- Injections for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: insulin and GLP-1RAs
- 1. Insulin therapy should be initiated if the patient fails to achieve the target glycemic goal despite appropriate treatment with oral antihyperglycemic agents [A].
- 2. Insulin can be used as an initial treatment at the time of diagnosis of T2DM for patients with metabolic decompensation and/or HbA1c levels >9.0% and/or symptomatic hyperglycemia [E].
- 3. Initiate insulin therapy in cases of decompensated renal or hepatic insufficiency, myocardial infarction, stroke, acute severe illness, and/or major surgery [B].
- 1. A basal insulin regimen or premixed insulin injections (once or twice daily) should be used depending on the patient's circumstances [B].
- 2. If the glycemic goal is not achieved with a basal insulin or premixed insulin regimen, then a multiple-component insulin regimen should be used [A].
- 3. A combination therapy of oral antihyperglycemic agents and insulin can be employed depending on the patient's condition [A].
- 1. A GLP-1RA can be used as monotherapy or combination therapy with oral antihyperglycemic agents or basal insulin [A].
- Insulin therapy should be initiated if the patient fails to achieve the target glycemic goal despite the appropriate treatment with oral antihyperglycemic agents. The KDA recommends insulin therapy in two circumstances: as the initial treatment after diagnosis of T2DM and after oral antihyperglycemic agent failure.
- Initiation of insulin treatment at the diagnosis of T2DM is recommended if the patient has severe hyperglycemia (HbA1c levels >9.0%) with hyperglycemic symptoms (polyuria, polydipsia, and weight loss) and/or metabolic decompensation [1640]. Insulin therapy should also be considered in patients with decompensated hepatic or renal insufficiency, myocardial infarction, stroke, and/or critical illness, as well as those undergoing major surgery [164142].
- For patients with T2DM who fail to achieve the glycemic goal following adequate treatment with oral antihyperglycemic agents, insulin injection therapy is the next step [678919434445]. Basal insulin alone or in combination with oral antihyperglycemic agents is easy to administer and is the preferred choice. Basal insulin alone, including both intermediate-acting and long-acting analogs, is the most convenient initial insulin regimen. Although the glucose-lowering effects are similar, hypoglycemia occurs less frequently with long-acting basal insulin analogs (insulin glargine or detemir) than with neutral protamine Hagedorn (NPH) insulin (human isophane insulin) [46]. A recently introduced ultra-long-acting insulin, degludec, showed a lower rate of nocturnal hypoglycemia and reduced mean fasting plasma glucose level compared with glargine in patients with T2DM [4748].
- Basal insulin is typically combined with metformin and/or other classes of oral antihyperglycemic agents. The addition of DPP4 inhibitors to a basal insulin regimen results in significant improvements in glycemic control relative to placebo without increasing hypoglycemia or body weight [495051]. Compared with a 25% increase in the insulin dose, the addition of sitagliptin to an insulin-based regimen is more effective at lowering HbA1c levels and is associated with less hypoglycemia and weight gain in Korean patients with uncontrolled T2DM [51]. SGLT2 inhibitors achieve better glycemic control and weight reduction than do DPP4 inhibitors without increasing the risk of hypoglycemia in patients with T2DM inadequately controlled by insulin [52].
- The addition of a GLP-1RA to basal insulin or switching to a premixed insulin regimen (once or twice daily) is another option, but this depends on the patient's clinical situation (Table 3) [53]. Premixed insulin products contain a basal component as well as a prandial component (NPH/Regular 70/30, 70/30 aspart mix, 75/25 lispro mix, and 50/50 lispro mix), which provides coverage for both basal and prandial needs in a single injection [678910]. For patients with T2DM who are unable to achieve glycemic control despite basal insulin titration, the addition of a GLP-1RA to the titrated basal insulin results in HbA1c reductions that are similar to those seen with standard basal-bolus or basal-plus insulin regimens, in conjunction with a lower relative risk of hypoglycemia and a greater decrease in body weight [545556].
- If glycemic control in patients treated with basal insulin alone or in combination with oral antihyperglycemic agents is not within the target range, treatment intensification via addition of a prandial insulin, such as a rapid-acting insulin analog (lispro, aspart, or glulisine), at the main meal (basal-plus) or at each meal (basal-bolus) is recommended (Table 4, Fig. 2). An insulin intensification strategy might also consist of upward titration of the insulin dose and regimen modification. As prandial insulin, rapid-acting insulin analogs are preferred to regular insulin because of their rapid onset, lower frequency of hypoglycemia, and ease of use (injection before meal) [678910]. If the HbA1c goal is not reached following the administration of premixed insulin given twice daily, consider switching to a premixed insulin analog (70/30 aspart mix, 75/25 lispro mix, 50/50 lispro mix) given three times daily for intensification. There are no clinically relevant differences in terms of the efficacies of basal-bolus versus premixed insulin regimens for decreasing HbA1c levels in patients with T2DM [53].
- The effects of two insulin-based strategies, glargine once daily and premixed insulin once or twice daily, were compared in subjects with T2DM who did not achieve adequate glycemic control with oral agents. More patients using premixed insulin achieved their target, with less frequent symptomatic hypoglycemia, compared with glargine. Glargine (with or without glulisine) and premix strategies result in similar rates of well-controlled diabetes without hypoglycemia, in that more patients achieve their target HbA1c levels with premixed insulin, whereas overall symptomatic hypoglycemia occurs less frequently with glargine [4053].
- When deciding intensify an insulin regimen, physicians should consider the various advantages and disadvantages of each option, including flexibility, complexity, and the frequency of hypoglycemia. Furthermore, healthcare professionals should provide comprehensive self-care education that includes insulin injection skills, self-monitoring of blood glucose levels, hypoglycemia management, and simple dosage adjustment prior to the initiation of insulin therapy [57].
RECOMMENDATIONS
Principles of initial management after diagnosis of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Principles of treatment with antihyperglycemic agents
Indications for insulin treatment for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Choice of type of insulin treatment
GLP-1RAs
-
Acknowledgements
- Financial support for the development of these guidelines was provided by the KDA operating budget; there was no support or involvement from industry sources.
- This position statement on antihyperglycemic agent therapy was written by the KDA Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines. We gratefully acknowledge the following experts who provided a critical review and discussion of this update: Tae-Nyun Kim, Inje University College of Medicine, Busan; Yong-ho Lee, Severance Hospital, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul; Jin-Hwa Kim, Chosun University Hospital, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju; Eun-Gyoung Hong, Hallym University Dongtan Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Hwaseong; Jaetaek Kim, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul; Won-Young Lee, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul; Bokrye Song, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul; Ji Young Kim, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul; Dong Hee Yang, Inje University Ilsan Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Goyang; Taeyoung Yang, Taeyoung 21 Hospital, Gwangju; and Hyeongjin Kim, Kim HJ Medical Clinic, Paju, Korea.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
-
This manuscript is simultaneously published in the Diabetes Metabolism Journal and the Korean Journal of Internal Medicine by the Korean Diabetes Association and the Korean Association of Internal Medicine.
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
NOTES
- 1. Ko SH, Kim SR, Kim DJ, Oh SJ, Lee HJ, Shim KH, Woo MH, Kim JY, Kim NH, Kim JT, Kim CH, Kim HJ, Jeong IK, Hong EK, Cho JH, Mok JO, Yoon KH. Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association. 2011 Clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:431-436. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 2. Min KW, Ku BJ, Lee JH, Kim MS, Ahn KJ, Lee MK, Kokubo S, Yoshida S, Cho HJ, Cha BS. Addition of ipragliflozin to metformin treatment in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: subgroup analysis of a phase 3 trial. Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:135-145. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 3. Kim JH, Kim SS, Baek HS, Lee IK, Chung DJ, Sohn HS, Bae HY, Kim MK, Park JH, Choi YS, Kim YI, Hahm JR, Lee CW, Jo SR, Park MK, Lee KJ, Kim IJ. Comparison of vildagliptin and pioglitazone in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin. Diabetes Metab J 2016;40:230-239. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 4. Yoon KH, Nishimura R, Lee J, Crowe S, Salsali A, Hach T, Woerle HJ. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes from Asian countries: pooled data from four phase III trials. Diabetes Obes Metab 2016;18:1045-1049. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Yoon KH, Hardy E, Han J. Exenatide versus insulin lispro added to basal insulin in a subgroup of Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:69-74. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2017. Diabetes Care 2017;40(Suppl 1):S1-S135. PubMed
- 7. Intensive blood-glucose control with sulphonylureas or insulin compared with conventional treatment and risk of complications in patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 33). Lancet 1998;352:837-853. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Garber AJ, Abrahamson MJ, Barzilay JI, Blonde L, Bloomgarden ZT, Bush MA, Dagogo-Jack S, DeFronzo RA, Einhorn D, Fonseca VA, Garber JR, Garvey WT, Grunberger G, Handelsman Y, Hirsch IB, Jellinger PS, McGill JB, Mechanick JI, Rosenblit PD, Umpierrez GE. Consensus statement by the American association of clinical endocrinologists and American college of endocrinology on the comprehensive type 2 diabetes management algorithm: 2017 executive summary. Endocr Pract 2017;23:207-238. ArticlePubMed
- 9. McGuire H, Longson D, Adler A, Farmer A, Lewin I. Guideline Development Group. Management of type 2 diabetes in adults: summary of updated NICE guidance. BMJ 2016;353:i1575ArticlePubMed
- 10. Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR. Management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, 2015: a patient-centered approach: update to a position statement of the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015;38:140-149. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 11. Kim JM, Hong JW, Noh JH, Kim DJ. Factors associated with participation in diabetes education: the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2007 to 2009. Diabetes Metab J 2016;40:447-453. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 12. Yong YM, Shin KM, Lee KM, Cho JY, Ko SH, Yoon MH, Kim TW, Jeong JH, Park YM, Ko SH, Ahn YB. Intensive individualized reinforcement education is important for the prevention of hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab J 2015;39:154-163. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 13. Ha KH, Kim DJ. Current status of managing diabetes mellitus in Korea. Korean J Intern Med 2016;31:845-850. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 14. Chon S, Gautier JF. An update on the effect of incretin-based therapies on β-cell function and mass. Diabetes Metab J 2016;40:99-114. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 15. Turner RC, Cull CA, Frighi V, Holman RR. Glycemic control with diet, sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: progressive requirement for multiple therapies (UKPDS 49). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. JAMA 1999;281:2005-2012. ArticlePubMed
- 16. Sherifali D, Nerenberg K, Pullenayegum E, Cheng JE, Gerstein HC. The effect of oral antidiabetic agents on A1C levels: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Care 2010;33:1859-1864. PubMedPMC
- 17. Effect of intensive blood-glucose control with metformin on complications in overweight patients with type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 34). UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) Group. Lancet 1998;352:854-865. PubMed
- 18. Maruthur NM, Tseng E, Hutfless S, et al. Diabetes medications as monotherapy or metformin-based combination therapy for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 2016;164:740-751. ArticlePubMed
- 19. Palmer SC, Mavridis D, Nicolucci A, Johnson DW, Tonelli M, Craig JC, Maggo J, Gray V, De Berardis G, Ruospo M, Natale P, Saglimbene V, Badve SV, Cho Y, Nadeau-Fredette AC, Burke M, Faruque L, Lloyd A, Ahmad N, Liu Y, Tiv S, Wiebe N, Strippoli GF. Comparison of clinical outcomes and adverse events associated with glucose-lowering drugs in patients with type 2 diabetes: a meta-analysis. JAMA 2016;316:313-324. ArticlePubMed
- 20. Esposito K, Chiodini P, Maiorino MI, Bellastella G, Capuano A, Giugliano D. Glycaemic durability with dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of long-term randomised controlled trials. BMJ Open 2014;4:e005442.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 21. Storgaard H, Gluud LL, Bennett C, Grondahl MF, Christensen MB, Knop FK, Vilsboll T. Benefits and harms of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2016;11:e0166125. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Yun JS, Ko SH. Risk factors and adverse outcomes of severe hypoglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Metab J 2016;40:423-432. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 23. Cha SA, Yun JS, Lim TS, Hwang S, Yim EJ, Song KH, Yoo KD, Park YM, Ahn YB, Ko SH. Severe hypoglycemia and cardiovascular or all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Metab J 2016;40:202-210. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 24. Yoon KH, Shin JA, Kwon HS, Lee SH, Min KW, Ahn YB, Yoo SJ, Ahn KJ, Park SW, Lee KW, Sung YA, Park TS, Kim MS, Kim YK, Nam MS, Kim HS, Park IeB, Park JS, Woo JT, Son HY. Comparison of the efficacy of glimepiride, metformin, and rosiglitazone monotherapy in korean drug-naïve type 2 diabetic patients: the practical evidence of antidiabetic monotherapy study. Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:26-33. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Foroutan N, Muratov S, Levine M. Safety and efficacy of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors vs sulfonylurea in metformin-based combination therapy for type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Invest Med 2016;39:E48-E62. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 26. Zhong X, Lai D, Ye Y, Yang X, Yu B, Huang Y. Efficacy and safety of empagliflozin as add-on to metformin for type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2016;72:655-663. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 27. Mishriky BM, Cummings DM, Tanenberg RJ. The efficacy and safety of DPP4 inhibitors compared to sulfonylureas as add-on therapy to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2015;109:378-388. ArticlePubMed
- 28. Zhou JB, Bai L, Wang Y, Yang JK. The benefits and risks of DPP4-inhibitors vs. sulfonylureas for patients with type 2 diabetes: accumulated evidence from randomised controlled trial. Int J Clin Pract 2016;70:132-141. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 29. Del Prato S, Nauck M, Duran-Garcia S, Maffei L, Rohwedder K, Theuerkauf A, Parikh S. Long-term glycaemic response and tolerability of dapagliflozin versus a sulphonylurea as add-on therapy to metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes: 4-year data. Diabetes Obes Metab 2015;17:581-590. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 30. Kim YG, Hahn S, Oh TJ, Kwak SH, Park KS, Cho YM. Differences in the glucose-lowering efficacy of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors between Asians and non-Asians: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetologia 2013;56:696-708. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 31. Mearns ES, Saulsberry WJ, White CM, Kohn CG, Lemieux S, Sihabout A, Salamucha I, Coleman CI. Efficacy and safety of antihyperglycaemic drug regimens added to metformin and sulphonylurea therapy in type 2 diabetes: a network meta-analysis. Diabet Med 2015;32:1530-1540. ArticlePubMed
- 32. Taylor SI, Blau JE, Rother KI. SGLT2 inhibitors may predispose to ketoacidosis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015;100:2849-2852. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 33. Oh S, Chon S, Ahn KJ, Jeong IK, Kim BJ, Kang JG. The role of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in type 2 diabetes: understanding how data can inform clinical practice in Korea. Diabetes Metab J 2015;39:177-187. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. Kim MK, Suk JH, Kwon MJ, Chung HS, Yoon CS, Jun HJ, Ko JH, Kim TK, Lee SH, Oh MK, Rhee BD, Park JH. Nateglinide and acarbose for postprandial glucose control after optimizing fasting glucose with insulin glargine in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2011;92:322-328. ArticlePubMed
- 35. Olansky L, Reasner C, Seck TL, Williams-Herman DE, Chen M, Terranella L, Mehta A, Kaufman KD, Goldstein BJ. A treatment strategy implementing combination therapy with sitagliptin and metformin results in superior glycaemic control versus metformin monotherapy due to a low rate of addition of antihyperglycaemic agents. Diabetes Obes Metab 2011;13:841-849. ArticlePubMed
- 36. Phung OJ, Sobieraj DM, Engel SS, Rajpathak SN. Early combination therapy for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus: systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes Obes Metab 2014;16:410-417. ArticlePubMed
- 37. Varvaki Rados D, Catani Pinto L, Reck Remonti L, Bauermann Leitão C, Gross JL. The association between sulfonylurea use and all-cause and cardiovascular mortality: a meta-analysis with trial sequential analysis of randomized clinical trials. PLoS Med 2016;13:e1001992. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 38. Marso SP, Daniels GH, Brown-Frandsen K, Kristensen P, Mann JF, Nauck MA, Nissen SE, Pocock S, Poulter NR, Ravn LS, Steinberg WM, Stockner M, Zinman B, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB. LEADER Steering Committee. LEADER Trial Investigators. Liraglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2016;375:311-322. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 39. Zinman B, Wanner C, Lachin JM, Fitchett D, Bluhmki E, Hantel S, Mattheus M, Devins T, Johansen OE, Woerle HJ, Broedl UC, Inzucchi SE. EMPA-REG OUTCOME Investigators. Empagliflozin, cardiovascular outcomes, and mortality in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2015;373:2117-2128. ArticlePubMed
- 40. Hwang YC, Kang JG, Ahn KJ, Cha BS, Ihm SH, Lee S, Kim M, Lee BW. The glycemic efficacies of insulin analogue regimens according to baseline glycemic status in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes: sub-analysis from the A(1)chieve((R)) study. Int J Clin Pract 2014;68:1338-1344. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 41. Malmberg K, Norhammar A, Wedel H, Ryden L. Glycometabolic state at admission: important risk marker of mortality in conventionally treated patients with diabetes mellitus and acute myocardial infarction: long-term results from the Diabetes and Insulin-Glucose Infusion in Acute Myocardial Infarction (DIGAMI) study. Circulation 1999;99:2626-2632. ArticlePubMed
- 42. Griesdale DE, de Souza RJ, van Dam RM, Heyland DK, Cook DJ, Malhotra A, Dhaliwal R, Henderson WR, Chittock DR, Finfer S, Talmor D. Intensive insulin therapy and mortality among critically ill patients: a meta-analysis including NICE-SUGAR study data. CMAJ 2009;180:821-827. ArticlePubMed
- 43. Fonseca V, Gill J, Zhou R, Leahy J. An analysis of early insulin glargine added to metformin with or without sulfonylurea: impact on glycaemic control and hypoglycaemia. Diabetes Obes Metab 2011;13:814-822. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 44. Park CY, Kang JG, Chon S, Noh J, Oh SJ, Lee CB, Park SW. Comparison between the therapeutic effect of metformin, glimepiride and their combination as an add-on treatment to insulin glargine in uncontrolled patients with type 2 diabetes. PLoS One 2014;9:e87799. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 45. Zhong X, Zhang T, Liu Y, Wei X, Zhang X, Qin Y, Jin Z, Chen Q, Ma X, Wang R, He J. Effects of three injectable antidiabetic agents on glycaemic control, weight change and drop-out in type 2 diabetes suboptimally controlled with metformin and/or a sulfonylurea: a network meta-analysis. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2015;109:451-460. ArticlePubMed
- 46. Horvath K, Jeitler K, Berghold A, Ebrahim SH, Gratzer TW, Plank J, Kaiser T, Pieber TR, Siebenhofer A. Long-acting insulin analogues versus NPH insulin (human isophane insulin) for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2007;(2):CD005613ArticlePubMed
- 47. Russell-Jones D, Gall MA, Niemeyer M, Diamant M, Del Prato S. Insulin degludec results in lower rates of nocturnal hypoglycaemia and fasting plasma glucose vs. insulin glargine: a meta-analysis of seven clinical trials. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2015;25:898-905. ArticlePubMed
- 48. Marso SP, McGuire DK, Zinman B, Poulter NR, Emerson SS, Pieber TR, Pratley RE, Haahr PM, Lange M, Brown-Frandsen K, Moses A, Skibsted S, Kvist K, Buse JB. DEVOTE Study Group. Efficacy and safety of degludec versus glargine in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2017;377:723-732. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 49. Yki-Jarvinen H, Rosenstock J, Duran-Garcia S, Pinnetti S, Bhattacharya S, Thiemann S, Patel S, Woerle HJ. Effects of adding linagliptin to basal insulin regimen for inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes: a ≥52-week randomized, double-blind study. Diabetes Care 2013;36:3875-3881. PubMedPMC
- 50. Kothny W, Foley J, Kozlovski P, Shao Q, Gallwitz B, Lukashevich V. Improved glycaemic control with vildagliptin added to insulin, with or without metformin, in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Obes Metab 2013;15:252-257. ArticlePubMed
- 51. Hong ES, Khang AR, Yoon JW, Kang SM, Choi SH, Park KS, Jang HC, Shin H, Walford GA, Lim S. Comparison between sitagliptin as add-on therapy to insulin and insulin dose-increase therapy in uncontrolled Korean type 2 diabetes: CSI study. Diabetes Obes Metab 2012;14:795-802. ArticlePubMed
- 52. Min SH, Yoon JH, Hahn S, Cho YM. Comparison between SGLT2 inhibitors and DPP4 inhibitors added to insulin therapy in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review with indirect comparison meta-analysis. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 2017;33:e2818.ArticlePDF
- 53. Giugliano D, Chiodini P, Maiorino MI, Bellastella G, Esposito K. Intensification of insulin therapy with basal-bolus or premixed insulin regimens in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Endocrine 2016;51:417-428. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 54. Diamant M, Nauck MA, Shaginian R, Malone JK, Cleall S, Reaney M, de Vries D, Hoogwerf BJ, MacConell L, Wolffenbuttel BH. 4B Study Group. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist or bolus insulin with optimized basal insulin in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2014;37:2763-2773. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 55. Eng C, Kramer CK, Zinman B, Retnakaran R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist and basal insulin combination treatment for the management of type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet 2014;384:2228-2234. ArticlePubMed
- 56. Mathieu C, Rodbard HW, Cariou B, Handelsman Y, Philis-Tsimikas A, Ocampo Francisco AM, Rana A, Zinman B. BEGIN: VICTOZA ADD-ON (NN1250-3948) study group. A comparison of adding liraglutide versus a single daily dose of insulin aspart to insulin degludec in subjects with type 2 diabetes (BEGIN: VICTOZA ADD-ON). Diabetes Obes Metab 2014;16:636-644. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 57. Choi SH, Oh TJ, Jang HC. Comparison of antidiabetic regimens in patients with type 2 diabetes uncontrolled by combination therapy of sulfonylurea and metformin: results of the MOHAS Disease Registry in Korea. Diabetes Metab J 2017;41:170-178. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
REFERENCES
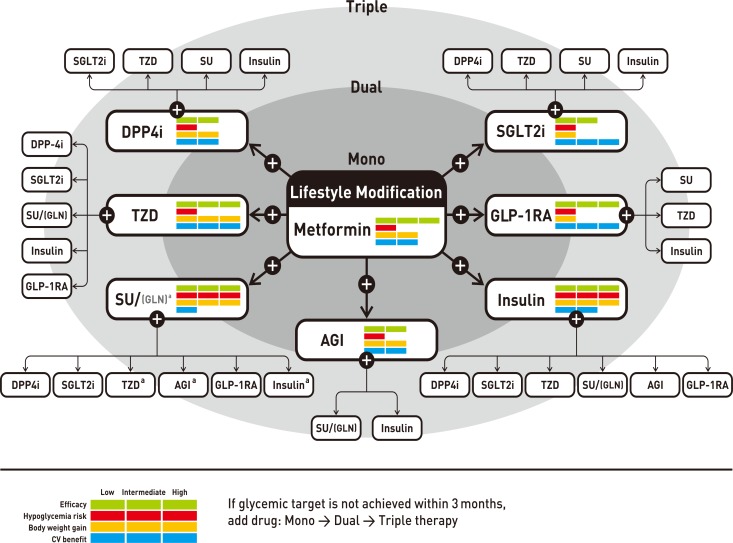
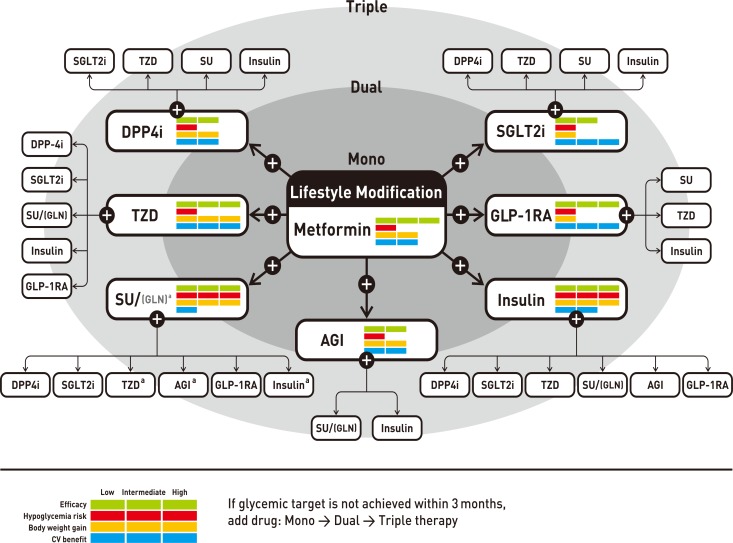
Antihyperglycemic therapy algorithm for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). The algorithm stratifies the choice of medications for T2DM based on initial glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels and demonstrates drug arrangement in a centrifugal direction. This algorithm includes only U.S. Food and Drug Administration-approved classes of medications for T2DM that are prescribed in Korea. For newly diagnosed T2DM, begin with lifestyle modification (LSM) at the time of diagnosis and subsequently maintain these changes for the duration of treatment. The HbA1c target is <6.5%; if this is not achieved within 3 months after implementing LSM, then the use of an antihyperglycemic agent should be initiated promptly. If the HbA1c level is <7.5%, metformin monotherapy is the preferred choice for pharmacotherapy in conjunction with LSM. If there are contraindications for metformin or side effects, then consider other monotherapy options such as a dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor (DPP4i), sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitor (SGLT2i) thiazolidinedione (TZD), glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RAs), sulfonylurea (SU), α-glucosidase inhibitor (AGI), or insulin as the initial therapy according to the patient's condition. If the initial HbA1c level is <7.5% or the HbA1c target is not achieved within 3 months of monotherapy, dual combination therapy can be considered. In this case, a second-line drug is added to metformin; however, any other combination of drugs with different mechanisms of action can be used depending on the patient's clinical characteristics. If the HbA1c target is not achieved within 3 months after commencing dual therapy, then proceed to triple combination therapy. In no particular order of preference, efficacy, risk of hypoglycemia, weight gain, impact on cardiovascular (CV) outcomes, and presence of clinical data in the Korean population should be considered for this arrangement. To aid the physician's choice, the characteristics of antihyperglycemic agent classes are shown as a bar scale. Efficacy (green), hypoglycemia risk (red), body weight gain (yellow), and CV benefit (blue color) were assigned ratings of low, intermediate, or high based on recently published studies identified in an extensive literature review; the scale bar is not constructed according to strict definitions but should be used as a guide for clinical decisions. GLN, glinide (meglitinide). aGLN can be used as dual combination therapy with metformin, TZD, AGI, or insulin or as a triple combination therapy with metformin and AGI, metformin and TZD, or metformin and insulin.
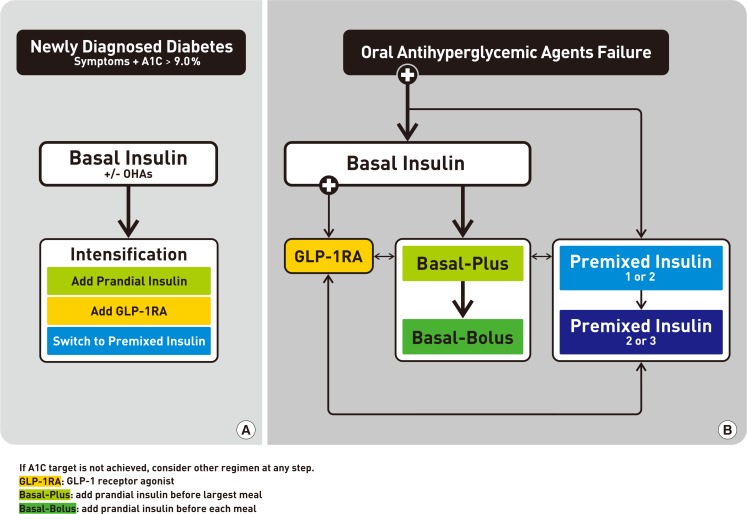
Treatment algorithm for insulin therapy. (A) Initiation of insulin treatment. If the initial glycosylated hemoglobin (A1C) level is >9.0% and symptomatic hyperglycemia or metabolic decompensation is present, insulin therapy can be initiated with or without oral antihyperglycemic agents (OHAs) in patients with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). If the HbA1c target range is not achieved after implementing a basal insulin regimen, then proceed to intensification treatment, for example, addition of a glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist (GLP-1RA) or a prandial insulin or switching to a premixed insulin regimen. (B) For adult patients with T2DM who have not achieved their glycemic target following adequate treatment using OHAs. When OHAs fail, proceed to basal insulin either with or without OHAs. The addition of a GLP-1RA or switching to a premixed insulin regimen could be another option depending on the patient's clinical situation. The width of each black line reflects the strength of the expert consensus recommendations.
Evidence-grading system of the Korean Diabetes Association
Oral antihyperglycemic agents for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus used in Korea
HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; GI, gastrointestinal; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; DPP4, dipeptidyl peptidase 4; GLP-1, glucagon-like peptide 1; GIP, gastric inhibitory polypeptide; CKD, chronic kidney disease; SGLT2, sodium-glucose cotransporter 2; DKA, diabetic ketoacidosis.
aMonotherapy.
Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Properties of different insulins
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Comparative Study on Efficacy of Empagliflozin Versus Sitagliptin, as an Add-on Therapy to Metformin in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Harsh Salankar, Sonali Rode, C. Arjun, Rajeeta Joseph, Gourav B. Deshmane, Radhika P. Vijayan
Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences.2024; 16(Suppl 1): S335. CrossRef - Two-Year Therapeutic Efficacy and Safety of Initial Triple Combination of Metformin, Sitagliptin, and Empagliflozin in Drug-Naïve Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients
Young-Hwan Park, Minji Sohn, So Yeon Lee, Soo Lim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2024; 48(2): 253. CrossRef - Association of preoperative blood glucose level with delirium after non-cardiac surgery in diabetic patients
Soo Jung Park, Ah Ran Oh, Jong-Hwan Lee, Kwangmo Yang, Jungchan Park
Korean Journal of Anesthesiology.2024; 77(2): 226. CrossRef - Systematic review and meta-analysis of teneligliptin for treatment of type 2 diabetes
R. Pelluri, S. Kongara, V. R. Nagasubramanian, S. Mahadevan, J. Chimakurthy
Journal of Endocrinological Investigation.2023; 46(5): 855. CrossRef - Effects of dapagliflozin compared with glimepiride on body composition in Asian patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin: The BEYOND study
Hyeong Kyu Park, Kyoung‐Ah Kim, Kyung‐Wan Min, Tae‐Seo Sohn, In Kyung Jeong, Chul Woo Ahn, Nan‐Hee Kim, Ie Byung Park, Ho Chan Cho, Choon Hee Chung, Sung Hee Choi, Kang Seo Park, Seoung‐Oh Yang, Kwan Woo Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(9): 2743. CrossRef - Paradigm Shift in Management of Hyperglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Glucocentric versus Organ Protection
Jong Chul Won
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2023; 24(2): 59. CrossRef - A Comparison of the Effects of Empagliflozin and Sitagliptin, When Combined With Metformin, on Lipid Levels in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Clinical Investigation
Mazhar Ahmed, Asjad Saeed, Muhammad Zarar Khan, Sana Z Javaid, Farhan Aslam, Savida Ilyas Dar
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Evogliptin Add-on Therapy to Dapagliflozin/Metformin Combinations in Patients with Poorly Controlled Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A 24-Week Multicenter Randomized Placebo-Controlled Parallel-Design Phase-3 Trial with a 28-Week Extensio
Jun Sung Moon, Il Rae Park, Hae Jin Kim, Choon Hee Chung, Kyu Chang Won, Kyung Ah Han, Cheol-Young Park, Jong Chul Won, Dong Jun Kim, Gwan Pyo Koh, Eun Sook Kim, Jae Myung Yu, Eun-Gyoung Hong, Chang Beom Lee, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2023; 47(6): 808. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Mulberry Twig Alkaloids Tablet for Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Multicenter Clinical Study
Ling Qu, Xiao-chun Liang, Guo-qing Tian, Gai-li Zhang, Qun-li Wu, Xiu-mei Huang, Ya-zhong Cui, Yu-ling Liu, Zhu-fang Shen, Guo-qing Ma, Hao Lu, Yi Li, Hong Jiang, Xi-yan Yang, Guang-de Zhang, Chen-hua Yang
Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine.2022; 28(4): 304. CrossRef - Risk for Imbalanced Blood Glucose Pattern: Construct Analysis and Nursing Diagnosis Proposal
Rafael Oliveira Pitta Lopes, Jéssica de Castro Santos, Hudson Carmo de Oliveira, Juliana Faria Campos, Cândida Caniçali Primo, Camila Takáo Lopes, Marcos Antônio Gomes Brandão
Clinical Nursing Research.2022; 31(7): 1241. CrossRef - Long‐term clinical outcomes of oral antidiabetic drugs as fixed‐dose combinations: A nationwide retrospective cohort study
Sang‐Jun Cho, In‐Sun Oh, Han Eol Jeong, Young Min Cho, Yul Hwangbo, Oriana Hoi Yun Yu, Ju‐Young Shin
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2022; 24(10): 2051. CrossRef - Randomized Clinical Trial on Efficacy of Empagliflozin Versus Sitagliptin, In Addition to Metformin in Type 2 Diabetic Patients
Muaz Mubashir, Mazhar Ahmed, Hassan Atique, Ahmed Wassan, Mehdi Naqvi, Muneeb Ullah
Cureus.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - The Mediating Effect of Acceptance Action in the Relationship between Diabetes Distress and Self-stigma among Old Adults with Diabetes in South Korea
Hyesun Kim, Kawoun Seo
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2022; 33(4): 446. CrossRef - Increasing Individual Target Glucose Levels to Prevent Hypoglycemia in Patients with Diabetes
Juyoung Shin, Hyunah Kim, Hun-Sung Kim, Churlmin Kim, Whan-Seok Choi
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2021; 42(4): 269. CrossRef - Phase III, randomized, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of teneligliptin monotherapy in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled with diet and exercise
Linong Ji, Jianhua Ma, Weiping Lu, Jingdong Liu, Jiao’e Zeng, Jialin Yang, Wei Li, Xiuzhen Zhang, Xinhua Xiao, Gen Takayanagi, Yi Wang
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(4): 537. CrossRef - Umbilical Cord-Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Conditioned Medium Improves Insulin Resistance in C2C12 Cell
Kyung-Soo Kim, Yeon Kyung Choi, Mi Jin Kim, Jung Wook Hwang, Kyunghoon Min, Sang Youn Jung, Soo-Kyung Kim, Yong-Soo Choi, Yong-Wook Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(2): 260. CrossRef - Blood glucose levels and bodyweight change after dapagliflozin administration
Hyunah Kim, Seung‐Hwan Lee, Hyunyong Lee, Hyeon Woo Yim, Jae‐Hyoung Cho, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Hun‐Sung Kim
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(9): 1594. CrossRef - Effects of liraglutide combined with metformin and Diamicron on glucose–lipid metabolism and islet β-cell function in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Chunzhi Zhao, Xing Li, Jianhua Ma, Zhengtai Zhu, Hua Li, Fangli Lou, Yuefang Zhai, Hui Chen, Shujun Xiao, Qinhui Peng, Huilian Hua, Qing Zhang, Fangyong Lou
All Life.2021; 14(1): 333. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Mulberry Twig Alkaloids Tablet for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Double-Dummy, and Parallel Controlled Clinical Trial
Ling Qu, Xiaochun Liang, Guoqing Tian, Gaili Zhang, Qunli Wu, Xiumei Huang, Yazhong Cui, Yuling Liu, Zhufang Shen, Changqing Xiao, Yingfen Qin, Heng Miao, Yongyan Zhang, Ziling Li, Shandong Ye, Xuezhi Zhang, Jing Yang, Guiwen Cao, Yi Li, Gangyi Yang, Ji H
Diabetes Care.2021; 44(6): 1324. CrossRef - Clinical Impact of Combination Therapy in Diabetic Neuropathy and Nephropathy
Harmeet Kaur, Arvinder Kaur, Pankaj Kumar Prashar, Anamika Gautam, Ankita Sood, Sachin Kumar Singh, Monica Gulati, Narendra Kumar Pandey, Bimlesh Kumar
Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology.2021; : 3471. CrossRef - Effect of Voluntary Participation on Mobile Health Care in Diabetes Management: Randomized Controlled Open-Label Trial
Da Young Lee, Seung-Hyun Yoo, Kyong Pil Min, Cheol-Young Park
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2020; 8(9): e19153. CrossRef - Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Fatty Liver Research Group of the Korean Diabetes Association
Byung-Wan Lee, Yong-ho Lee, Cheol-Young Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee, Nan-Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Keun-Gyu Park, Yeon-Kyung Choi, Bong-Soo Cha, Dae Ho Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(3): 382. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Pioglitazone versus Glimepiride after Metformin and Alogliptin Combination Therapy: A Randomized, Open-Label, Multicenter, Parallel-Controlled Study
Jeong Mi Kim, Sang Soo Kim, Jong Ho Kim, Mi Kyung Kim, Tae Nyun Kim, Soon Hee Lee, Chang Won Lee, Ja Young Park, Eun Sook Kim, Kwang Jae Lee, Young Sik Choi, Duk Kyu Kim, In Joo Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(1): 67. CrossRef - Clinical Characteristics and Prevalence of Comorbidities according to Metformin Use in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Sang Ouk Chin, In Gyoon Ha, Sang Youl Rhee, Su Jin Jeong, Suk Chon, Sung Hoon Kim, Kyu Jeung Ahn, Sei Hyun Baik, Yongsoo Park, Moon Suk Nam, Kwan Woo Lee, Jeong Taek Woo
International Journal of Endocrinology.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Differentially Affects Brain Activation in Response to Visual Food Cues in Lean and Obese Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jae Hyun Bae, Hyung Jin Choi, Kang Ik Kevin Cho, Lee Kyung Kim, Jun Soo Kwon, Young Min Cho
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(2): 248. CrossRef Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Interactions Between Evogliptin and Glimepiride in Healthy Male Subjects
Hyounggyoon Yoo, Yun Kim, In-Jin Jang, Kyung-Sang Yu, SeungHwan Lee
Drug Design, Development and Therapy.2020; Volume 14: 5179. CrossRef- Clinical parameters affecting the therapeutic efficacy of empagliflozin in patients with type 2 diabetes
Yun Kyung Cho, Jiwoo Lee, Yu Mi Kang, Jee Hee Yoo, Joong-Yeol Park, Chang Hee Jung, Woo Je Lee, Tatsuo Shimosawa
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(8): e0220667. CrossRef - Teneligliptin versus sitagliptin in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled with metformin and glimepiride: A randomized, double‐blind, non‐inferiority trial
Yonghyun Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Hak Chul Jang, Dong Jun Kim, Taekeun Oh, Eun Sook Kim, Nan‐Hee Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Sung‐Rae Kim, JiYoung You, Se‐Jin Kim, Moon‐Kyu Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2019; 21(3): 631. CrossRef - Pharmacotherapy of Diabetes Focused on Stroke
Young-Sang Lyu, Jin-Hwa Kim, Sang-Yong Kim
Journal of the Korean Neurological Association.2019; 37(3): 235. CrossRef - Letter: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43;276-86)
Hannah Seok, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 545. CrossRef - Nationwide Trends in Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Cancer Risk Among Patients With Newly Diagnosed Type 2 Diabetes Receiving Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 Inhibitors
Minyoung Lee, Jiyu Sun, Minkyung Han, Yongin Cho, Ji-Yeon Lee, Chung Mo Nam, Eun Seok Kang
Diabetes Care.2019; 42(11): 2057. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Tae Jung Oh, Jae Myung Yu, Kyung Wan Min, Hyun Shik Son, Moon Kyu Lee, Kun Ho Yoon, Young Duk Song, Joong Yeol Park, In Kyung Jeong, Bong Soo Cha, Yong Seong Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, In Joo Kim, Doo Man Kim, Sung Rae Kim, Kwan Woo Lee, Jeong Hyung Park, In Kyu
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(3): 276. CrossRef - 2019 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Korea
Mee Kyoung Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Bo-Yeon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Junghyun Noh, Soo-Kyung Kim, Seok-O Park, Kyu Yeon Hur, Suk Chon, Min Kyong Moon, Nan-Hee Kim, Sang Yong Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Kang-Woo Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Eun-Jung Rhee, SungWan Chun, Sung Hoon Yu
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 398. CrossRef - Medical Big Data Is Not Yet Available: Why We Need Realism Rather than Exaggeration
Hun-Sung Kim, Dai-Jin Kim, Kun-Ho Yoon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2019; 34(4): 349. CrossRef - Monotherapy in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients 2017: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Sang Youl Rhee
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(1): 15. CrossRef - Glucose Control in Intensive Care Unit Patients: Recent Updates
Sang Youl Rhee
Journal of Neurocritical Care.2018; 11(2): 81. CrossRef - Educational Strategies for Insulin Injection Therapy in Elderly Diabetic Patients
Eun Chong Shin
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(2): 101. CrossRef - Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Hyun Jin Kim
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2018; 19(1): 35. CrossRef - Fifty Years of Compassionate Care and Harmonious Collaboration of the Korean Diabetes Association: The 50th Anniversary of Korean Diabetes Association
Jong Chul Won, Eun-Jung Rhee, Hyung Joon Yoo
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(6): 475. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of ipragliflozin as an add‐on therapy to sitagliptin and metformin in Korean patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized controlled trial
Kyung‐Ah Han, Suk Chon, Choon Hee Chung, Soo Lim, Kwan‐Woo Lee, SeiHyun Baik, Chang Hee Jung, Dong‐Sun Kim, Kyong Soo Park, Kun‐Ho Yoon, In‐Kyu Lee, Bong‐Soo Cha, Taishi Sakatani, Sumi Park, Moon‐Kyu Lee
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2018; 20(10): 2408. CrossRef - Monotherapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 349. CrossRef - Insulin therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2017
Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Kyung Mook Choi
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 967. CrossRef - New anti-diabetic agents
Doo-Man Kim
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2017; 60(12): 992. CrossRef - Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Hyun Jin Kim, Seok O Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Sang Youl Rhee, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(6): 423. CrossRef - Insulin Therapy for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2017
Byung-Wan Lee, Jin Hwa Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 367. CrossRef
- Figure
- Related articles
-
- 2023 Clinical Practice Guidelines for Diabetes Mellitus of the Korean Diabetes Association
- The Beneficial Effect of Glycemic Control against Adverse Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease
- Screening for Prediabetes and Diabetes in Korean Nonpregnant Adults: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association, 2022

 KDA
KDA PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite