- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 40(4); 2016 > Article
-
Original ArticleOthers Comparison of the Usefulness of the Updated Homeostasis Model Assessment (HOMA2) with the Original HOMA1 in the Prediction of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Koreans
-
Young Seok Song1, You-Cheol Hwang2
 , Hong-Yup Ahn3, Cheol-Young Park1
, Hong-Yup Ahn3, Cheol-Young Park1
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2016;40(4):318-325.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.4.318
Published online: May 27, 2016
1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
3Department of Statistics, Dongguk University, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: You-Cheol Hwang. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kyung Hee University Hospital at Gangdong, Kyung Hee University School of Medicine, 892 Dongnam-ro, Gangdong-gu, Seoul 05278, Korea. khmcilyong@naver.com
- Corresponding author: Cheol-Young Park. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 29 Saemunan-ro, Jongno-gu, Seoul 03181, Korea. cydoctor@chol.com
Copyright © 2016 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- The original homeostasis model assessment (HOMA1) and the updated HOMA model (HOMA2) have been used to evaluate insulin resistance (IR) and β-cell function, but little is known about the usefulness of HOMA2 for the prediction of diabetes in Koreans. The aim of this study was to demonstrate the usefulness of HOMA2 as a predictor of type 2 diabetes mellitus in Koreans without diabetes.
-
Methods
- The study population consisted of 104,694 Koreans enrolled at a health checkup program and followed up from 2001 to 2012. Participants were divided into a normal glucose tolerance (NGT) group and a pre-diabetes group according to fasting glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin levels. Anthropometric and laboratory data were measured at the baseline checkup, and HOMA values were calculated at the baseline and follow-up checkups. The hazard ratios (HRs) of the HOMA1 and HOMA2 values and the prevalence of diabetes at follow-up were evaluated using a multivariable Cox proportional hazards model and Kaplan-Meier analysis.
-
Results
- After adjusting for several diabetes risk factors, all of the HOMA values except 1/HOMA1-β and 1/HOMA2-β in the NGT group were significant predictors of the progression to diabetes. In the NGT group, there was no significant difference in HOMA1-IR (HR, 1.09; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.04 to 1.14) and HOMA2-IR (HR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.04 to 1.19). However, in the pre-diabetes group, 1/HOMA2-β was a more powerful marker (HR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.26 to 1.31) than HOMA1-IR (HR, 1.23; 95% CI, 1.19 to 1.28) or 1/HOMA1-β (HR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.12 to 1.16). In the non-diabetic group (NGT+pre-diabetes), 1/HOMA2-β was also a stronger predictor of diabetes (HR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.25 to 1.29) than HOMA1-IR (HR, 1.14; 95% CI, 1.12 to 1.15) or 1/HOMA1-β (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.11 to 1.14).
-
Conclusion
- HOMA2 is more predictive than HOMA1 for the progression to diabetes in pre-diabetes or non-diabetic Koreans.
- The pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) involves insulin resistance (IR) and β-cell dysfunction [1234]. Accordingly, estimating IR and β-cell function is essential for screening high-risk subjects for T2DM and making a treatment plan. There are several methods for estimating IR and β-cell function, including the hyperinsulinemic euglycemic clamp, frequently sampled intravenous glucose tolerance, C-peptide to glucose ratio, and homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) model [567].
- Among these, the original HOMA (HOMA1) has been broadly used due to its simplicity and cost effectiveness. Previous studies show that an increase of HOMA1-IR and a decrease of HOMA1-β are associated with an increased incidence of diabetes and future cardiovascular events in patients with T2DM [89]. The relationship between the HOMA value and future risk of diabetes in Korean male subjects has been examined [10]. However, the HOMA1 model is not always reliable because it does not consider the variations in the glucose resistance of the peripheral tissue and liver, increases in the insulin secretion curve for blood glucose concentrations above 180 mg/dL, and contribution of circulating pro-insulin [1112].
- An updated HOMA (HOMA2), the correctly solved computer model that considers such variations, was announced in 1998. HOMA2 was recalibrated to give steady-state β-cell function (% B) and insulin sensitivity (% S) of 100% in normal young adults when using currently available assays for insulin, specific insulin, or C-peptide [11]. HOMA2 was better than HOMA1 in predicting oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT)-based indexes of β-cell function and glucose resistance in Italians [1314]. In addition, HOMA2 has been used to study IR and metabolic syndrome in Brazilians [15]. A study targeting people in Iraq observed a correlation between glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and HOMA2-IR [16].
- Despite the diverse ethnic groups included in HOMA research, a study of the correlation between HOMA2 and HO MA1 and the development of overt diabetes has not yet been conducted in Koreans. Therefore, the aim of this study was to compare the usefulness of HOMA1 and HOMA2 for predicting progression to diabetes in Koreans.
INTRODUCTION
- Study population and design
- We designed a retrospective observational study of participants in a medical health checkup program at the Health Promotion Center at Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, from January 2001 to December 2012. The purpose of this medical health check-up program is to promote the health of the employees through regular health checkups and the early detection of existing disease. Most examinees are employees of Korean industrial companies and their family members.
- Among the 136,158 subjects, we excluded subjects who had a history of diabetes or were taking oral hypoglycemic agents, as well as those with a fasting blood glucose ≥126 mg/dL or HbA1c ≥6.5% at the baseline checkup. In addition, subjects with missing data and pregnant subjects were excluded from the final analysis. These exclusions (n=31,464) resulted in a final study population of 104,694 subjects.
- At the baseline checkup, the subjects were divided by fasting blood glucose and HbA1c levels into the normal glucose tolerance (NGT, fasting blood glucose <100 mg/dL and HbA1c <5.7%) group and the pre-diabetes (100 mg/dL≤fasting blood glucose<126 mg/dL or 5.7%≤HbA1c<6.5%) group. Collectively, all of the subjects constituted the non-diabetic group. In subsequent medical checkups, those subjects with a fasting blood glucose ≥126 mg/dL or HbA1c ≥6.5% were defined as having diabetes. The primary purpose of this study was to compare the predictive ability of HOMA1 and HOMA2 for diabetes, so we calculated the hazard ratios (HRs) of the HOMA values (i.e., HOMA1-IR, 1/HOMA1-β, HOMA2-IR, and 1/HOMA2-β). We monitored changes of the HbA1c, blood glucose, and HOMA values in each group over time. In addition, the subjects were divided into four groups based on each quartile of HOMA values, and we calculated the cumulative prevalence of diabetes in each group.
- No specific informed consent was obtained. The requirement for written or verbal consent was waived by the Institutional Review Board during the planning phase of this study. Researchers were only allowed to assess the database for analysis purposes, and the database did not contain any personal identifying information.
- Anthropometric and laboratory measurements
- Height, weight, waist circumference, and systolic blood pressure were measured in duplicate, and the results were averaged. Systolic blood pressure was taken with a standardized sphygmomanometer after at least 5 minutes of rest, according to the hypertension detection and follow-up protocol [17]. Body mass index (BMI) was calculated by dividing the weight in kilogram by the square of the height in meters. A family history of diabetes was defined as having at least one parent or sibling with diabetes. A current smoker was defined as smoking occasionally or on a daily basis.
- After 12 hours of fasting, the fasting blood glucose, total cholesterol, triglyceride, high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C), low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), and HbA1c levels were checked. The hexokinase method (Advia 1650 Autoanalyzer; Bayer Diagnostics, Leverkusen, Germany) was used to measure blood glucose levels, and an enzymatic colorimetric test was used to measure total cholesterol and triglyceride levels. The selective inhibition method was used to measure the level of HDL-C, and the homogeneous enzymatic calorimetric test was used to measure the level of LDL-C. Serum insulin concentration was measured with an immunoradiometric assay (INS-IRMA; Biosource, Nivelles, Belgium). Estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was calculated by the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study equation.
- HOMA1-IR was defined as [fasting insulin (µU/mL)× fasting glucose (mmol/L)]/22.5. HOMA1-β was calculated using (20×fasting insulin)/(fasting glucose–3.5) [9]. HOMA2-IR and HOMA2-β data were calculated with a HOMA2 calculator released by the Diabetes Trials Unit, University of Oxford: HOMA Calculator. This calculator is available at: http://www.dtu.ox.ac.uk/homacalculator/index.php (updated January 8, 2013). HOMA1-β and HOMA2-β have a negative correlation with diabetes risk, so we took the inverse value to compare them with HOMA-IR or HOMA2-IR.
- Statistical analysis
- Continuous variables are presented as mean±standard deviation, and the categorical variables are presented as frequency and proportion. HOMA1 and HOMA2 were compared for independent incident diabetes development by use of HRs from multivariable Cox proportional hazards models. The Kaplan-Meier method was used to compare the cumulative prevalence of diabetes for each HOMA value quartile. All of the data were analyzed using R version 3.1.1 (http://www.R-project.org). Statistical significance was defined as P<0.05.
METHODS
- Baseline characteristics of study subjects are shown in Table 1. The median follow-up duration was 6.2 years (range, 1.5 to 15.1), and the mean subject age was 38.9±7.4 years. Our study population included 72,915 NGT subjects (69.6%) and 31,779 pre-diabetes subjects (30.4%). After follow-up, 1,939 subjects (1.9%) were newly diagnosed with T2DM. The subjects in the pre-diabetes group tended to be older, were more often male, and had higher systolic blood pressure, BMI, HbA1c, HDL-C, non-HDL-C, aspartate aminotransferase, alanine transaminase, HOMA-IR, and HOMA2-IR and lower eGFR, HO MA1-β, and HOMA2-β than the NGT group. There were statistically significant differences for all of the variables in the baseline characteristics.
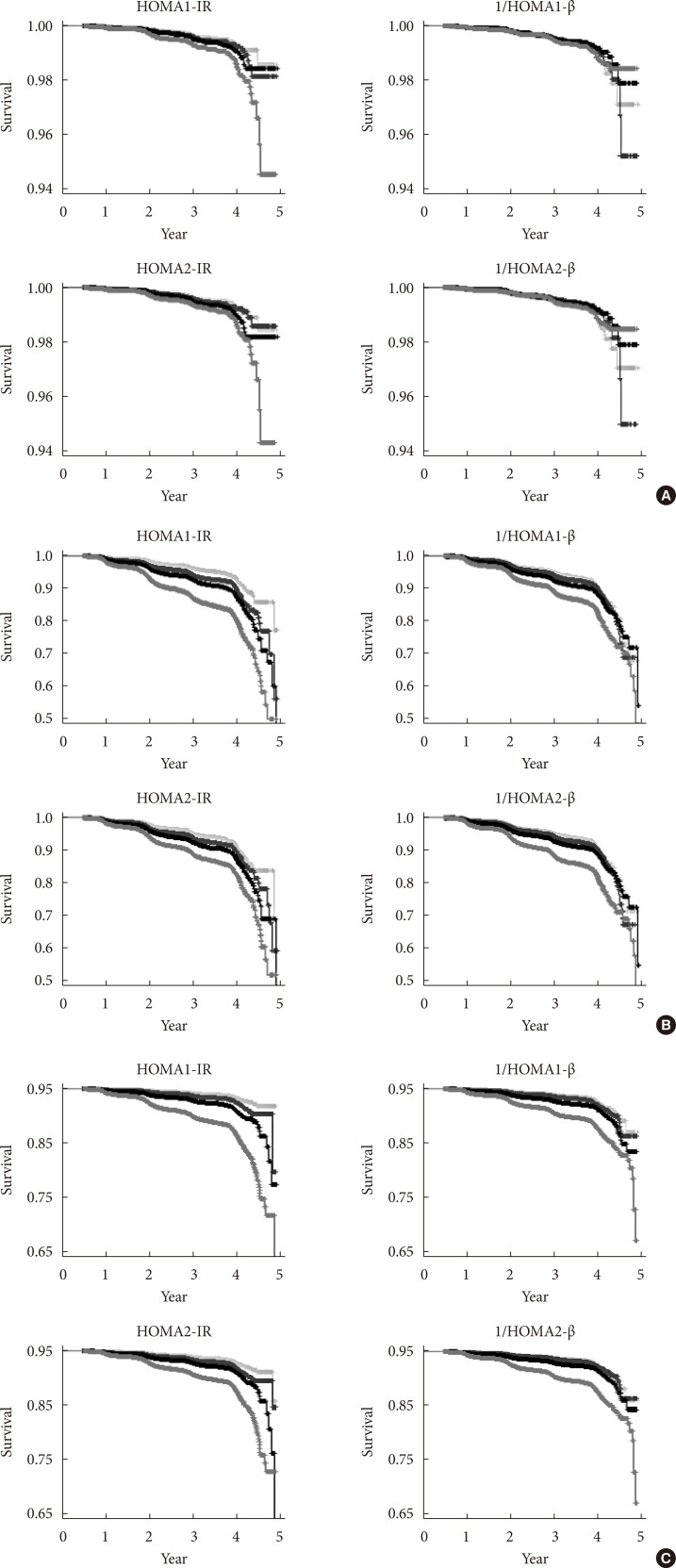
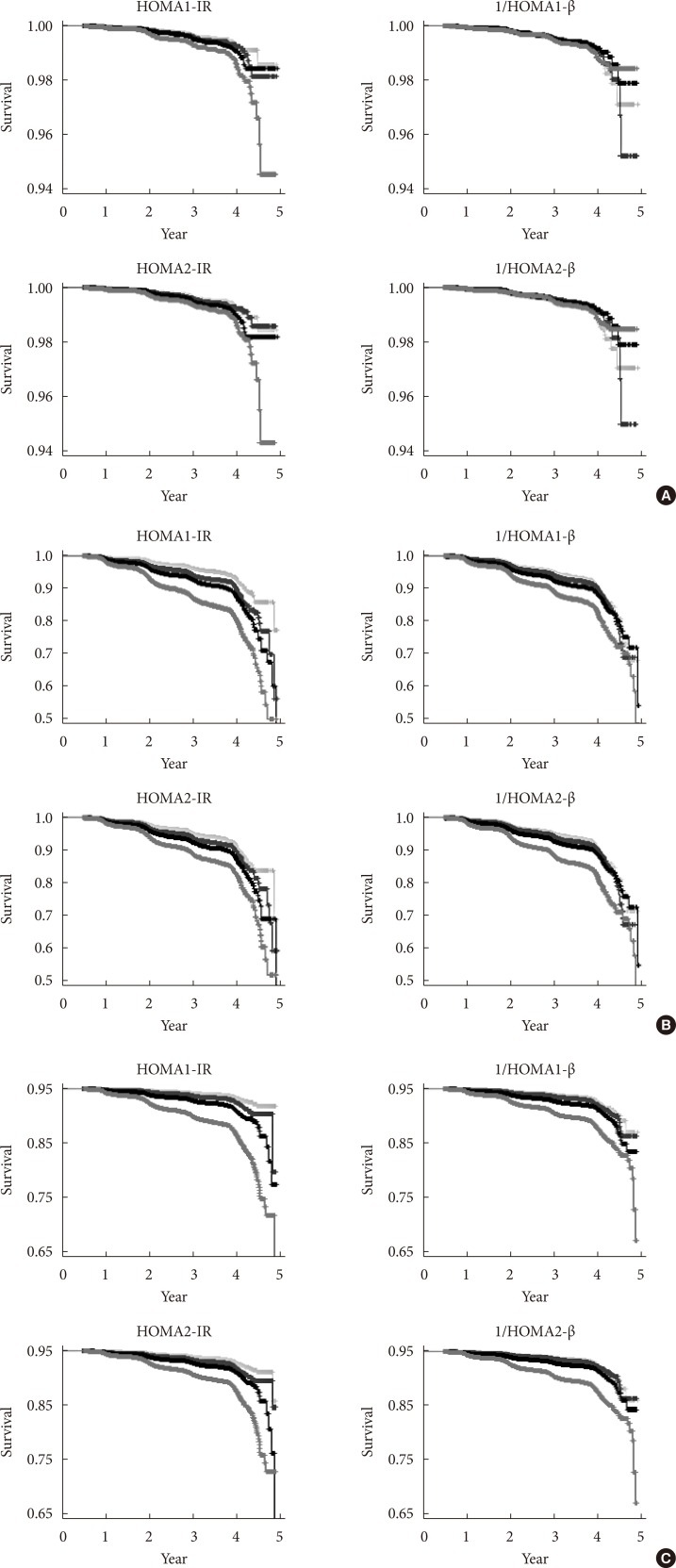
- The cumulative incidence of diabetes by quartile for each HOMA value in the NGT group is shown in Fig. 1A, the pre-diabetes group is shown in Fig. 1B, and all subjects together are shown in Fig. 1C. The cumulative prevalence of diabetes tends to increase significantly along with the quartile of HOMA1 and HOMA2 except for 1/HOMA1-β and 1/HO MA2-β in the NGT group. Generally, the high HOMA-IR quartile group had a higher cumulative prevalence of diabetes at follow-up and vice versa in the HOMA-β quartile.
- Table 2 compares the HRs for the development of diabetes based on the HOMA1 and HOMA2 estimations as the value increased by the standard deviation. In the NGT subjects, HOMA2-IR (HR, 1.18; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.13 to 1.23; P<0.001) was more predictive than HOMA1-IR (HR, 1.13; 95% CI, 1.1 to 1.17; P<0.001), but there was no significant difference between HOMA2-IR and HOMA1-IR (P> 0.05). HOMA1-β and HOMA2-β did predict progression to diabetes. In the pre-diabetes group, HOMA1-IR (HR, 1.42; 95% CI, 1.38 to 1.46; P<0.001) was a more powerful marker than HOMA2-IR (HR, 1.33; 95% CI, 1.29 to 1.38; P<0.001) or HOMA2-β (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.23 to 1.29; P<0.001). In the non-diabetic group, HOMA2-IR (HR, 1.25; 95% CI, 1.23 to 1.26; P<0.001) and HOMA2-β (HR, 1.26; 95% CI, 1.25 to 1.28; P<0.001) had stronger predictive power than the HOMA1 values.
- HOMA-IR values were associated with the development of T2DM independent of age, sex, BMI, family history of diabetes, smoking history, systolic blood pressure, lipid profile, and HbA1c, but there were no differences between HOMA1-IR (HR, 1.09; 95% CI, 1.04 to 1.14; P<0.001) and HOMA2-IR (HR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.04 to 1.19; P<0.001) in the NGT group. HOMA2-β was the most significant predictive marker in both the pre-diabetic group (HR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.26 to 1.31; P< 0.001) and the non-diabetic group (HR, 1.27; 95% CI, 1.25 to 1.29; P<0.001) (Table 3).
RESULTS
- In this study, after adjusting for diabetes-related variables, both HOMA1-IR and HOMA2-IR were statistically significant markers for predicting the development of diabetes in the NGT group. All HOMA values were predictive in the pre-diabetes and non-diabetic groups. In particular, HOMA2-β was the potential marker for predicting the future development of T2DM in the pre-diabetes and non-diabetic groups.
- A previous study compared the performance of HOMA2 with HOMA1 in pre-diabetic and diabetic patients using the OGTT and found that HOMA2 reflected IR and β-cell function more accurately than HOMA1 [13]. In another study, HOMA2 more significantly affected the identification of IR and the detection of metabolic syndrome and polycystic ovarian disease than HOMA1 [18]. In this study, HOMA1-IR and HOMA2-IR were not significantly different in their ability to predict the progression to T2DM in the NGT group, but HOMA2, especially HOMA2-β, was more predictive in pre-diabetic and non-diabetic Koreans than HOMA1. In particular, HOMA2-β was the most predictive marker for the pre-diabetic group, probably due to differences in age, race, and BMI. The β-cell function of Asians is usually lower than in Western ethnic groups [1920] based on a multiethnic cohort study of diet and cancer [21]. Further, the low HOMA-β group had a higher risk of progression to diabetes than the high HOMA-IR group in a prospective study of Korean men [10]. These outcomes point to the need for a standard model appropriate for Koreans because the factors that affect the development of diabetes vary depending on ethnicity. At a minimum, if we use the established HOMA model, we need to select the best model according to glycemic status.
- We also observed that HOMA1-β and HOMA2-β were not significantly predictive in the NGT group. The normoglycemic state results from the homeostasis of glucose production, and consumption is mediated by the liver, skeletal muscle, and pancreas β-cells [22]. Accordingly, both IR and impaired insulin secretion are thought to be critical to the pathophysiology of pre-diabetes although controversy remains about the leading factor for diabetes. Both IR and impaired insulin secretion are independent determinants of the progression from NGT to pre-diabetes and from pre-diabetes to diabetes [232425]. In the NGT group, the level of insulin secretion was low to normal in a person with good insulin sensitivity, so it is difficult to think that HOMA-β alone can predict the progression to diabetes in a healthy person.
- The strength of this study is that it was a longitudinal observational study, not a cross-sectional study, and it investigated the usefulness of HOMA2 in a large number of Koreans. Our large sample size gave us the ability to divide the subjects into the NGT and pre-diabetic groups, allowing us to compare the performance of HOMA1 and HOMA2 in the NGT and prediabetes groups.
- Even so, this study had several limitations. First, all of the study subjects were enrolled in the health screening center of our hospital, and the study was conducted at a single center. Therefore, the results may not be representative of the entire Korean population. In addition, except for oral hypoglycemic agents, we did not confirm previous medication history, which could affect IR or β-cell function. Finally, we defined pre-diabetes using fasting plasma glucose, so there were no data about the progression to diabetes according to impaired glucose tolerance.
- In conclusion, HOMA2, especially HOMA2-β, was more predictive for the progression to diabetes in pre-diabetes or non-diabetic Koreans. HOMA2 may offer a meaningful predictor of diabetes in Koreans if appropriate values are selected depending on individual glycemic status.
DISCUSSION
-
Acknowledgements
- This study was supported by Health Promotion Funds from the Korean Ministry for Health, Welfare, and Family Affairs and by the Welfare Bureau of the Seoul Metropolitan Government and SBRI (Samsung Biomedical Research Institute) Grant to CYP.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
NOTES
- 1. Kahn SE. The relative contributions of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction to the pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia 2003;46:3-19. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Meier JJ, Bonadonna RC. Role of reduced beta-cell mass versus impaired beta-cell function in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2013;36(Suppl 2):S113-S119. PubMedPMC
- 3. Matthews DR. Insulin resistance and beta-cell function: a clinical perspective. Diabetes Obes Metab 2001;3(Suppl 1):S28-S33. PubMed
- 4. Li CL, Tsai ST, Chou P. Relative role of insulin resistance and beta-cell dysfunction in the progression to type 2 diabetes: the Kinmen Study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2003;59:225-232. PubMed
- 5. Borai A, Livingstone C, Kaddam I, Ferns G. Selection of the appropriate method for the assessment of insulin resistance. BMC Med Res Methodol 2011;11:158ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 6. Meier JJ, Menge BA, Breuer TG, Muller CA, Tannapfel A, Uhl W, Schmidt WE, Schrader H. Functional assessment of pancreatic beta-cell area in humans. Diabetes 2009;58:1595-1603. PubMedPMC
- 7. Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC. Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985;28:412-419. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Sung KC, Reaven GM, Kim SH. Utility of homeostasis model assessment of beta-cell function in predicting diabetes in 12,924 healthy Koreans. Diabetes Care 2010;33:200-202. PubMed
- 9. Bonora E, Formentini G, Calcaterra F, Lombardi S, Marini F, Zenari L, Saggiani F, Poli M, Perbellini S, Raffaelli A, Cacciatori V, Santi L, Targher G, Bonadonna R, Muggeo M. HOMA-estimated insulin resistance is an independent predictor of cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetic subjects: prospective data from the Verona Diabetes Complications Study. Diabetes Care 2002;25:1135-1141. PubMed
- 10. Choi ES, Rhee EJ, Kim JH, Won JC, Park CY, Lee WY, Oh KW, Park SW, Kim SW. Insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion determined by homeostasis model assessment and future risk of diabetes mellitus in Korean men. Korean Diabetes J 2008;32:498-505.Article
- 11. Levy JC, Matthews DR, Hermans MP. Correct homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) evaluation uses the computer program. Diabetes Care 1998;21:2191-2192. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Wallace TM, Levy JC, Matthews DR. Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 2004;27:1487-1495. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 13. Caumo A, Perseghin G, Lattuada G, Ragogna F, Brunani A, Luzi L. Comparing the original (HOMA1) and the updated (HOMA2) method: evidence that HOMA2 is more reliable than HOMA1. Diabetes 2007;56(Suppl 1):A406.
- 14. Caumo A, Perseghin G, Brunani A, Luzi L. New insights on the simultaneous assessment of insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function with the HOMA2 method. Diabetes Care 2006;29:2733-2734. PubMed
- 15. Geloneze B, Vasques AC, Stabe CF, Pareja JC, Rosado LE, Queiroz EC, Tambascia MA. BRAMS Investigators. HOMA1-IR and HOMA2-IR indexes in identifying insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome: Brazilian Metabolic Syndrome Study (BRAMS). Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 2009;53:281-287. ArticlePubMed
- 16. Al-Hakeim HK, Abdulzahra MS. Correlation between glycated hemoglobin and HOMA indices in type 2 diabetes mellitus: prediction of beta-cell function from glycated hemoglobin. J Med Biochem 2015;34:191-199.PubMedPMC
- 17. Hypertension Detection and Follow-up Program Cooperative Group. Five-year findings of the hypertension detection and follow-up program. I. Reduction in mortality of persons with high blood pressure, including mild hypertension. JAMA 1979;242:2562-2571. ArticlePubMed
- 18. Safar FH, Mojiminiyi OA, Al-Rumaih HM, Diejomaoh MF. Computational methods are significant determinants of the associations and definitions of insulin resistance using the homeostasis model assessment in women of reproductive age. Clin Chem 2011;57:279-285. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 19. Møller JB, Dalla Man C, Overgaard RV, Ingwersen SH, Tornoe CW, Pedersen M, Tanaka H, Ohsugi M, Ueki K, Lynge J, Vasconcelos NM, Pedersen BK, Kadowaki T, Cobelli C. Ethnic differences in insulin sensitivity, beta-cell function, and hepatic extraction between Japanese and Caucasians: a minimal model analysis. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2014;99:4273-4280. PubMed
- 20. Torréns JI, Skurnick J, Davidow AL, Korenman SG, Santoro N, Soto-Greene M, Lasser N, Weiss G;. Study of Women's Health Across the Nation (SWAN). Ethnic differences in insulin sensitivity and beta-cell function in premenopausal or early perimenopausal women without diabetes: the Study of Women's Health Across the Nation (SWAN). Diabetes Care 2004;27:354-361. PubMed
- 21. Maskarinec G, Grandinetti A, Matsuura G, Sharma S, Mau M, Henderson BE, Kolonel LN. Diabetes prevalence and body mass index differ by ethnicity: the Multiethnic Cohort. Ethn Dis 2009;19:49-55. PubMedPMC
- 22. DeFronzo RA. Lilly lecture 1987. The triumvirate: beta-cell, muscle, liver. A collusion responsible for NIDDM. Diabetes 1988;37:667-687. PubMed
- 23. Haffner SM, Miettinen H, Gaskill SP, Stern MP. Decreased insulin action and insulin secretion predict the development of impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetologia 1996;39:1201-1207. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 24. Haffner SM, Miettinen H, Gaskill SP, Stern MP. Decreased insulin secretion and increased insulin resistance are independently related to the 7-year risk of NIDDM in Mexican-Americans. Diabetes 1995;44:1386-1391. ArticlePubMed
- 25. Weyer C, Tataranni PA, Bogardus C, Pratley RE. Insulin resistance and insulin secretory dysfunction are independent predictors of worsening of glucose tolerance during each stage of type 2 diabetes development. Diabetes Care 2001;24:89-94. ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
Kaplan-Meier curves for the cumulative prevalence of type 2 diabetes mellitus for the quartile of homeostasis model assessment (HOMA) values. (A) In the normal glucose tolerance group. (B) In the pre-diabetic group. (C) In the non-diabetic group. In each figure, the 1Q group is displayed in gray, the 2Q group is displayed in blue, the 3Q group in black, and the highest quartile in red. IR, insulin resistance.
Baseline characteristics of the study participants
Values are presented as mean±standard deviation or number (%).
NGT, normal glucose tolerance; BMI, body mass index; DM, diabetes mellitus; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine transaminase; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; SBP, systolic blood pressure; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; HOMA1, original homeostasis model assessment; IR, insulin resistance; HOMA2, updated HOMA model.
aThe NGT group is with a plasma glucose <100 mg/dL at the baseline checkup, bThe pre-diabetes group is with a plasma glucose ≥100 and <126 mg/dL at the baseline checkup, cNon-diabetic group: NGT+pre-diabetes group, dNGT group vs. pre-diabetes group.
Univariate Cox proportional hazards analysis model of HOMA values for developing type 2 diabetes mellitus
HOMA, homeostasis model assessment; NGT, normal glucose tolerance; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; HOMA1, original HOMA; IR, insulin resistance; HOMA2, updated HOMA model.
aWhen increased by the standard deviation from the mean value of each HOMA value. Reference is the mean value of each HOMA model.
Multivariatea Cox proportional hazards analysis model of HOMA values for developing type 2 diabetes mellitus
HOMA, homeostasis model assessment; NGT, normal glucose tolerance; HR, hazard ratio; CI, confidence interval; HOMA1, original HOMA; IR, insulin resistance; HOMA2, updated HOMA model.
aAll estimates reflect adjustment for age, sex, body mass index, family history of diabetes, history of smoking, systolic blood pressure, glycosylated hemoglobin, triglyceride, and high density lipoprotein cholesterol, bWhen increased by the standard deviation from the mean value of each HOMA value. Reference is the mean value of each HOMA model.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Non-linear associations of HOMA2-IR with all-cause mortality in general populations: insights from NHANES 1999–2006
Aikai Zhang, Lingchen Huang, Min Tang
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - An acute exercise at low to moderate intensity attenuated postprandial lipemia and insulin responses
Lisa L. Ji, Vicki S. Fretwell, Abel Escamilla, Wanxiang Yao, Tianou Zhang, Meizi He, John Q. Zhang
Journal of Exercise Science & Fitness.2024; 22(1): 14. CrossRef - Insufficient compensatory pancreatic β-cells function might be closely associated with hyperuricemia in U.S. adults: evidence from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Tianran Shen, Qiutong Zheng, Liling Zhong, Xia Zeng, Xiaojing Yuan, Fengxin Mo, Shiheng Zhu, Wenhan Yang, Qingsong Chen
BMC Public Health.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycated haemoglobin, HOMA2‐B, C‐peptide to glucose ratio and type 2 diabetes clusters as predictors for therapy failure in individuals with type 2 diabetes without insulin therapy: A registry analysis
Faisal Aziz, Christoph Sternad, Caren Sourij, Lisa Knoll, Harald Kojzar, Anna Schranz, Alexandra Bürger, Harald Sourij, Felix Aberer
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2024; 26(3): 1082. CrossRef - Nghiên cứu tương quan giữa chỉ số đề kháng insulin và chỉ số khối cơ thể ở bệnh nhân tiền đái tháo đường có tăng huyết áp
Linh Dương
Journal of Clinical Medicine- Hue Central Hospital.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Bridelia ferruginea inhibits key carbohydrate digesting enzyme and intestinal glucose absorption and modulates glucose metabolism in diabetic rats
Olajumoke Oyebode, Lindiwe Zuma, Ochuko Lucky Erukainure, Neil Koorbanally, Md. Shahidul Islam
Archives of Physiology and Biochemistry.2023; 129(3): 671. CrossRef - Impact of Pancreatic β-Cell Function on Clopidogrel Responsiveness and Outcomes in Chinese Nondiabetic Patients Undergoing Elective Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Xiliang Zhao, Jin Wang, Quan Li, Yicong Ye, Yong Zeng
Cardiovascular Drugs and Therapy.2023; 37(3): 487. CrossRef - Development and validation of an insulin resistance model for a population without diabetes mellitus and its clinical implication: a prospective cohort study
Shang-Feng Tsai, Chao-Tung Yang, Wei-Ju Liu, Chia-Lin Lee
eClinicalMedicine.2023; 58: 101934. CrossRef - Association of the triglyceride‐glucose index with subclinical left ventricular dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A retrospective cross‐sectional study
Qi‐chao Sun, Jie Liu, Ran Meng, Ning Zhang, Jing Yao, Fan Yang, Da‐long Zhu
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2023; 14(8): 953. CrossRef - Fasting indices of glucose-insulin-metabolism across life span and prediction of glycemic deterioration in children with obesity from new diagnostic cut-offs
Maximiliane Chiara Hammel, Robert Stein, Jürgen Kratzsch, Mandy Vogel, Alexander J. Eckert, Rima Destya Triatin, Marco Colombo, Christof Meigen, Ronny Baber, Juraj Stanik, Ulrike Spielau, Anette Stoltze, Kerstin Wirkner, Anke Tönjes, Harold Snieder, Reinh
The Lancet Regional Health - Europe.2023; 30: 100652. CrossRef - The role of bariatric surgery on beta-cell function and insulin resistance in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and steatohepatitis
Adisa Poljo, Stephan Kopf, Alba Sulaj, Stephanie Roessler, Thomas Albrecht, Benjamin Goeppert, Sarah Bojko, Beat P. Müller-Stich, Adrian T. Billeter
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases.2023; 19(12): 1421. CrossRef - Glutamine Defended the Kidneys Versus Lead Intoxication Via Elevating Endogenous Antioxidants, Reducing Inflammation and Carbonyl Stress, as well as Improving Insulin Resistance and Dyslipidemia
Sina Mahdavifard, Najafzadeh Nowruz
Biological Trace Element Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Sex and genetic background define the metabolic, physiologic, and molecular response to protein restriction
Cara L. Green, Heidi H. Pak, Nicole E. Richardson, Victoria Flores, Deyang Yu, Jay L. Tomasiewicz, Sabrina N. Dumas, Katherine Kredell, Jesse W. Fan, Charlie Kirsh, Krittisak Chaiyakul, Michaela E. Murphy, Reji Babygirija, Gregory A. Barrett-Wilt, Joshua
Cell Metabolism.2022; 34(2): 209. CrossRef - Associations of the HOMA2‐%B and HOMA2‐IR with progression to diabetes and glycaemic deterioration in young and middle‐aged Chinese
Baoqi Fan, Hongjiang Wu, Mai Shi, Aimin Yang, Eric S. H. Lau, Claudia H. T. Tam, Dandan Mao, Cadmon K. P. Lim, Alice P. S. Kong, Ronald C. W. Ma, Elaine Chow, Andrea O. Y. Luk, Juliana C. N. Chan
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Triglyceride and glucose index is a simple and easy‐to‐calculate marker associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Kyung‐Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Hong‐Yup Ahn, Cheol‐Young Park
Obesity.2022; 30(6): 1279. CrossRef - Protective effect of acetylcysteine, histidine, and their combination against diabetes vascular complications in type-2 diabetic rats via reducing NF-kβ pathway signaling
Sina Mahdavifard, Manochehr Nakhjavani
Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders.2022; 21(2): 1233. CrossRef - Visceral fat might impact left ventricular remodeling through changes in arterial stiffness in type 2 diabetes: A cross-sectional study
Haishan Huang, Jing Jin, Yanshan Chen, Lina Wang, Jingyi Zhong, Zhenguo Chen, Lingling Xu
International Journal of Cardiology.2022; 368: 78. CrossRef - The effect of berberine and fenugreek seed co-supplementation on inflammatory factor, lipid and glycemic profile in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a double-blind controlled randomized clinical trial
Shima Nematollahi, Gholam Reza Pishdad, Mehrnoosh Zakerkish, Foroogh Namjoyan, Kambiz Ahmadi Angali, Fatemeh Borazjani
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Association between changes in pancreatic morphology and vascular complications in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a retrospective study
Yuichiro Iwamoto, Tomohiko Kimura, Fuminori Tatsumi, Toshitomo Sugisaki, Masato Kubo, Erina Nakao, Kazunori Dan, Ryo Wamata, Hideyuki Iwamoto, Kaio Takahashi, Junpei Sanada, Yoshiro Fushimi, Yukino Katakura, Masashi Shimoda, Shuhei Nakanishi, Tomoatsu Mun
Scientific Reports.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Clustering patterns of metabolic syndrome: A cross-sectional study in children and adolescents in Kyiv
Maiia H. Aliusef, Ganna V. Gnyloskurenko, Alina V. Churylina, Inga O. Mityuryayeva
Frontiers in Pediatrics.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Circulating spexin levels are influenced by the glycemic status and correlated with pancreatic β-cell function in Chinese subjects
Jiarong Dai, Yunzhi Ni, Di Wu, Yaojing Jiang, Shuoshuo Jin, Shan Zhang, Xuemei Yu, Rui Liu
Acta Diabetologica.2022; 60(2): 305. CrossRef - Association between the triglyceride–glucose index and diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes: A cross‐sectional study
Li Liu, Rui Xia, Xiaoqing Song, Benping Zhang, Wentao He, Xinrong Zhou, Shengzhong Li, Gang Yuan
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2021; 12(4): 557. CrossRef - The insulin resistance by triglyceride glucose index and risk for dementia: population-based study
Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Determinants of type 2 diabetes remission after bariatric surgery in obese Japanese patients: a retrospective cohort study
Masahiro Ohira, Yasuhiro Watanabe, Takashi Yamaguchi, Atsuhito Saiki, Shoko Nakamura, Shou Tanaka, Naomi Shimizu, Taiki Nabekura, Takashi Oshiro, Ichiro Tatsuno
Diabetology International.2021; 12(4): 379. CrossRef - Sakarya Eğitim ve Araştırma Hastanesine Başvuran Hastaların HOMA-IR Değerlerinin Yaş ve Cinsiyet Faktörü Açısından Değerlendirilmesi
Mehmet ÖZDİN, Hayrullah YAZAR, Durhasan MUNDAN
Mustafa Kemal Üniversitesi Tıp Dergisi.2021; 12(42): 1. CrossRef - Feeding pattern, biochemical, anthropometric and histological effects of prolonged ad libitum access to sucrose, honey and glucose-fructose solutions in Wistar rats
Carmen Alejandrina Virgen-Carrillo, Alma Gabriela Martínez Moreno, Juan José Rodríguez-Gudiño, Jessica Elizabeth Pineda-Lozano
Nutrition Research and Practice.2021; 15(2): 187. CrossRef - The effect of curcumin and zinc co‐supplementation on glycemic parameters in overweight or obese prediabetic subjects: A phase 2 randomized, placebo‐controlled trial with a multi‐arm, parallel‐group design
Majid Karandish, Hassan Mozaffari‐khosravi, Seyed Mohammad Mohammadi, Bahman Cheraghian, Maryam Azhdari
Phytotherapy Research.2021; 35(8): 4377. CrossRef - The Association Between Second-Line Oral Antihyperglycemic Medication on Types of Dementia in Type 2 Diabetes: A Nationwide Real-World Longitudinal Study
Won Jun Kim, Jung Hyun Noh, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of Alzheimer's Disease.2021; 81(3): 1263. CrossRef - Personalized Type 2 Diabetes Management Using a Mobile Application Integrated with Electronic Medical Records: An Ongoing Randomized Controlled Trial
Eun-Young Lee, Jae-Seung Yun, Seon-Ah Cha, Sun-Young Lim, Jin-Hee Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Kun-Ho Yoon, Seung-Hyun Ko
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2021; 18(10): 5300. CrossRef - Enhancement of Serum Myonectin Levels by Progressive Resistance Training in Rats Fed with High-Fat Diet and Sucrose Solution
Alireza Safarzade, Hadi Safarpour
Zahedan Journal of Research in Medical Sciences.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Pancreatic β-Cell Dysfunction Is Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease
Xu Chen, Jinghe Xiao, Juan Pang, Shen Chen, Qing Wang, Wenhua Ling
Nutrients.2021; 13(9): 3139. CrossRef - The correlation between serum resistin and toll-like receptor-4 with insulin resistance in hypertensive subjects with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus
Mustafa Al-Taie, Rayah Baban, Mouayed Hamed
Baghdad Journal of Biochemistry and Applied Biological Sciences.2021; 2(04): 203. CrossRef - Significant fibrosis predicts new-onset diabetes mellitus and arterial hypertension in patients with NASH
Javier Ampuero, Rocío Aller, Rocío Gallego-Durán, Javier Crespo, José Luis Calleja, Carmelo García-Monzón, Judith Gómez-Camarero, Joan Caballería, Oreste Lo Iacono, Luis Ibañez, Javier García-Samaniego, Agustín Albillos, Rubén Francés, Conrado Fernández-R
Journal of Hepatology.2020; 73(1): 17. CrossRef - Are the Different Diabetes Subgroups Correlated With All-Cause, Cancer-Related, and Cardiovascular-Related Mortality?
Peng-Fei Li, Wei-Liang Chen
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2020; 105(12): e4240. CrossRef - Avoiding holiday seasonal weight gain with nutrient-supported intermittent energy restriction: a pilot study
Steven P. Hirsh, Marianne Pons, Steven V. Joyal, Andrew G. Swick
Journal of Nutritional Science.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Peripartum Management of Gestational Diabetes Using a Digital Health Care Service: A Pilot, Randomized Controlled Study
Ji-Hee Sung, Da Young Lee, Kyoung Pil Min, Cheol-Young Park
Clinical Therapeutics.2019; 41(11): 2426. CrossRef - Development of type 2 diabetes mellitus in people with intermediate hyperglycaemia
Bernd Richter, Bianca Hemmingsen, Maria-Inti Metzendorf, Yemisi Takwoingi
Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - The cut-off values of surrogate measures for insulin resistance in the Korean population according to the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study (KOGES)
Bongyoung Kim, Hyun Young Choi, Wonhee Kim, Chiwon Ahn, Juncheol Lee, Jae Guk Kim, Jihoon Kim, Hyungoo Shin, Jae Myung Yu, Shinje Moon, Taulant Muka
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(11): e0206994. CrossRef - Testing for HbA1c, in addition to the oral glucose tolerance test, in screening for abnormal glucose regulation helps to reveal patients with early β-cell function impairment
Yu-Hsuan Li, Wayne Huey-Herng Sheu, Wen-Jane Lee, I-Te Lee, Shih-Yi Lin, Wen-Lieng Lee, Kae-Woei Liang, Jun-Sing Wang
Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (CCLM).2018; 56(8): 1345. CrossRef - Metabolic clustering of risk factors: evaluation of Triglyceride-glucose index (TyG index) for evaluation of insulin resistance
Sikandar Hayat Khan, Farah Sobia, Najmusaqib Khan Niazi, Syed Mohsin Manzoor, Nadeem Fazal, Fowad Ahmad
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Pancreatic β-Cell Function and Prognosis of Nondiabetic Patients With Ischemic Stroke
Yuesong Pan, Weiqi Chen, Jing Jing, Huaguang Zheng, Qian Jia, Hao Li, Xingquan Zhao, Liping Liu, Yongjun Wang, Yan He, Yilong Wang
Stroke.2017; 48(11): 2999. CrossRef - Association of serum pancreatic derived factor ( PANDER) with beta-cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes mellitus
Miral M. Shehata, Mohamed M. Kamal, Mohamed H. El-Hefnawy, Hala O. EL-Mesallamy
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2017; 31(4): 748. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite