- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 40(3); 2016 > Article
-
Original ArticleComplications Severe Hypoglycemia and Cardiovascular or All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
-
Seon-Ah Cha1, Jae-Seung Yun1, Tae-Seok Lim1, Seawon Hwang1, Eun-Jung Yim1, Ki-Ho Song1, Ki-Dong Yoo2, Yong-Moon Park3, Yu-Bae Ahn1, Seung-Hyun Ko1

-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2016;40(3):202-210.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2016.40.3.202
Published online: April 5, 2016
1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
2Division of Cardiology, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea, Seoul, Korea.
3Epidemiology Branch, National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, National Institutes of Health, Research Triangle Park, NC, USA.
- Corresponding author: Seung-Hyun Ko. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, St. Vincent's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea, 93 Jungbu-daero, Paldal-gu, Suwon 16247, Korea. kosh@catholic.ac.kr
Copyright © 2016 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- We investigated the association between severe hypoglycemia (SH) and the risk of cardiovascular (CV) or all-cause mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes.
-
Methods
- The study included 1,260 patients aged 25 to 75 years with type 2 diabetes from the Vincent Type 2 Diabetes Resgistry (VDR), who consecutively enrolled (n=1,260) from January 2000 to December 2010 and were followed up until May 2015 with a median follow-up time of 10.4 years. Primary outcomes were death from any cause or CV death. We investigated the association between the CV or all-cause mortality and various covariates using Cox proportional hazards regression analysis.
-
Results
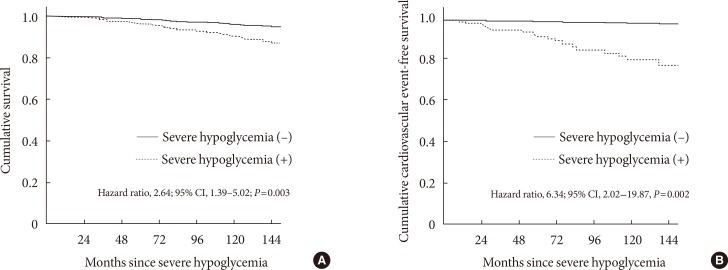
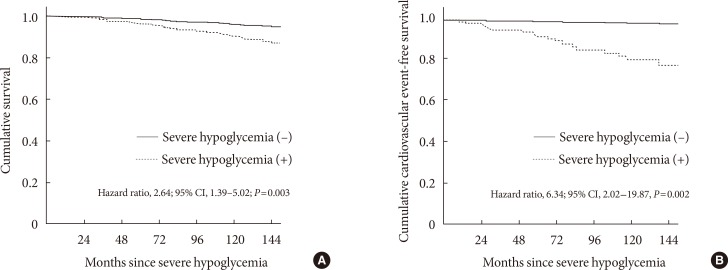
- Among the 906 participants (71.9%) who completed follow-up, 85 patients (9.4%) had at least one episode of SH, and 86 patients (9.5%) died (9.1 per 1,000 patient-years). Patients who had died were older, had a longer duration of diabetes and hypertension, received more insulin, and had more diabetic microvascular complications at baseline, as compared with surviving patients. The experience of SH was significantly associated with an increased risk of all-cause mortality (hazard ratio [HR], 2.64; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.39 to 5.02; P=0.003) and CV mortality (HR, 6.34; 95% CI, 2.02 to 19.87; P=0.002) after adjusting for sex, age, diabetic duration, hypertension, mean glycosylated hemoglobin levels, diabetic nephropathy, lipid profiles, and insulin use.
-
Conclusion
- We found a strong association between SH and increased risk of all-cause and CV mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes.
- Hypoglycemia is a well-known acute complication of diabetes treatment and regarded as a major obstacle to reach glycemic targets in patients with type 2 diabetes [1]. Because intensive glycemic control has demonstrated beneficial effects of lowering glucose on microvascular or macrovascular complications, the incidence of severe hypoglycemia (SH) has increased significantly according to the implementation of stringent glycemic control and use of intensive insulin therapy [234]. In both the Action in Diabetes and Vascular Disease: Preterax and Diamicron Modified Release Controlled Evaluation (ADVANCE) and Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes (ACCORD) studies, incidence of SH was significantly higher in the intensive therapy group compared with the standard treatment group [56].
- Because accumulated evidence from cardiovascular (CV) trials has suggested that not all patients benefit from intensive glycemic treatment, recent clinical practice guidelines recommend individualized glycemic target goals to avoid SH episodes or weight gain [789]. The UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS), comprising subjects with recently diagnosed diabetes, showed that an improvement in glycemic control reduced microvascular complication and myocardial infarction (MI) [2]. Meanwhile, in the ACCORD study, individuals with older age, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) of 7.5% or more, and cardiovascular disease (CVD) or additional CV risk factors were recruited and compared with those in UKPDS. These differences suggested that individuals in the ACCORD study receiving intensive therapy had greater risk factors for CV morbidity and mortality compared with those in the UKPDS [25].
- Further, many studies related to SH and CV outcomes have been performed. A meta-analysis of six observational studies, including 903,510 people with type 2 diabetes, showed that SH was strongly associated with a higher risk of CVD [10]. In addition, the ADVANCE study also revealed that SH was strongly associated with increased risks of adverse clinical outcomes, including vascular events and death in patients with long-standing type 2 diabetes [6].
- Although the pathogenic mechanisms implicated in CV outcome or CV mortality among patients with hypoglycemia or SH remain elusive, recent evidence suggests that hypoglycemia or SH may contribute to the increased risk of adverse CV events. These findings suggested that SH is of greater clinical significance as a predictable marker for future development of serious CV events. If so, patients with type 2 diabetes with SH episodes, beyond hypoglycemia management, should be recommended for the evaluation of CV risk or active screening for the presence of asymptomatic CVD.
- Therefore, we investigated whether experience of SH was associated with an increased risk of CV mortality or death from any cause in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes using the Vincent Type 2 Diabetes Registry (VDR), a long-term prospective observational cohort study.
INTRODUCTION
- Population
- One thousand four hundred twenty-eight patients with type 2 diabetes, aged 25 to 75 years from the VDR, were consecutively recruited from January 2000 to December 2010, and underwent follow-up until May 2015 at the university-affiliated Diabetes Center of St. Vincent's Hospital in South Korea [11]. Patients were excluded if they were older than 75 years; were mentally ill; were unable to undertake self-care behaviors; had a previous episode of SH; or had cognitive dysfunction, alcoholism, or any severe illness, such as malignancy, end-stage rerenal disease, severe infection, or liver cirrhosis. All subjects underwent follow-up every 3 to 6 months on an outpatient basis. After participants were enrolled, their clinical outcomes were monitored until their time of death or May 2015.
- This prospective cohort study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of St. Vincent's Hospital, College of Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea (IRB No. VC10OISE0152). The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was obtained from all participants.
- Evaluation of SH
- SH was defined as hypoglycemic episodes requiring the assistance of medical care in an emergency department, or hospitalization [1213]. Patients were asked if they had experienced SH episodes or visited an emergency department because of SH during the enrollment period. If patients did not visit our clinic for any reason, we attempted to contact the patient by telephone to evaluate the occurrence of SH. Even if the patients visited other hospitals, we reviewed all medical records describing their SH episodes and confirmed the events.
- Evaluation of CV death or all-cause death
- The primary outcome of this study was death from any cause or CV death. CV death included deaths resulting from an acute MI, sudden cardiac death, death because of heart failure, and other CV causes [14].
- CVD was defined as a diagnosis of coronary artery disease (CAD) and stroke. CAD was defined as a diagnosis history of angina pectoris, MI, or coronary revascularization (coronary bypass surgery or coronary angioplasty) [15]. Stroke manifestation included previous transient ischemic attack or cerebral infarction [1516]. Diagnosis of clinically established CVD was based on verified medical records, and the diagnosis was confirmed by a specialist (cardiologist, neurologist, or neurosurgeon). All patients were followed up for mortality or CV mortality preponderantly, from the time of enrollment to May 2015. Causes of death were determined from the death certificates, clinical records, and hospital records.
- Assessment of clinical variables
- Anthropometric measurements and participants' information, including medical history, current cigarette smoking status, and the use of medications, were obtained using a detailed questionnaire. Hypertension was defined as systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg, diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg, or the use of antihypertensive medications [17]. Blood samples were collected after fasting for 8 hours overnight. Fasting and 2-hour postprandial plasma glucose, lipid profiles for total cholesterol, triglyceride, and high density lipoprotein cholesterol were measured by an enzymatic method using an automatic analyzer (model 736-40; Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan). The HbA1c level was measured every 6 months during the follow-up period. The estimated glomerular filtration rate was used to determine a classification of stages of chronic kidney disease using the 4-component Modification of Diet in Renal Disease equation [18].
- Diabetic retinopathy was assessed from retinal photographs at baseline, and the findings were reviewed by an ophthalmologist. Diabetic nephropathy was considered if a patient showed microalbuminuria (30 to 300 mg/day) or macroalbuminuria (≥300 mg/day). The urinary albumin excretion rate was measured from a 24-hour urine collection using immunoturbidimetry (Eiken, Tokyo, Japan).
- Statistical analysis
- All results were expressed as the mean±standard deviation or as proportions or median (interquartile range). P<0.05 was considered significant. Chi-square tests were used to test differences in the proportion of categorical variables, and independent Student t-tests were used for continuous variables. If a patient had multiple SH events, the first recorded event was used in this analysis. After verifying the proportional hazards assumption by means of log-minus log-survival plots and testing with the methods described elsewhere [19], univariable and multivariable Cox proportional hazards regression analysis was applied to test associations between the CV or all-cause mortality and potential explanatory variables. The relationships were analyzed after adjustment for the following prognostic factors: sex, age, duration of diabetes, presence of hypertension, diabetic nephropathy, mean HbA1c throughout the study, and the use of insulin, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor, angiotensin receptor blocker, or CVD history. The results were presented as hazard ratios (HR) and 95% confidence intervals (CIs). All statistical analyses were performed using SAS version 9.2 (SAS Institute, Cary, NC, USA).
METHODS
- Clinical characteristics
- In total, 1,428 patients were recruited, and 168 patients were excluded from the study. Among the 1,260 patients who were enrolled, 906 (71.9%) completed the follow-up. The median follow-up time was 10.4 years. Further, 354 patients did not receive follow-up care, and 86 patients (9.5%) died during the follow-up period. There were no significant differences between the participants who completed the follow-up evaluation and those who did not with respect to sex ratio (P=0.303), age (55.7±10.0 years vs. 57.0±10.8 years, P=0.055), diabetes duration (8.2±6.7 years vs. 8.2±7.1 years, P=0.907), presence of hypertension (P=0.742), or history of prior CVD (P=0.100).
- The mean age and diabetic duration in the patients who completed follow-up were 55.7±10.0 and 8.2±6.7 years, respectively. Among 906 patients who completed follow-up, 85 patients (9.5%) experienced at least one episode of SH. Eighty-two of the participants (9.1%) had a history of CVD before enrollment.
- Table 1 shows baseline data of the patients with SH and those without SH. Patients with SH were older (P<0.001), had a longer duration of diabetes (P=0.003), had a history of CVD (P<0.001), and used more insulin (P<0.001) at baseline, compared with patients without SH. In addition, the patients with SH experienced higher incidences of diabetic retinopathy (P=0.002). However, there were no statistically significant differences in baseline HbA1c between the two groups (P=0.094) (Table 1).
- CV or all-cause mortality
- After excluding 82 patients with CVD history, 153 patients (15.6%) experienced CV events among 824 patients without prior CVD episodes during the follow-up period. During the same period, 86 patients (9.5%) were dead, and 21 patients died from CV events. The most common causes of death were sepsis (29.1%) and CV events (24.4%). In addition, patients died from malignancy (21.1%), hemorrhagic stroke (5.8%), acute exacerbation of chronic disease (9.3%), and unknown or other causes (9.3%) in this cohort. The median time from the onset of SH to the first CV death or death from any cause was 2.25 and 3 years, respectively.
- Table 2 shows baseline clinical parameters of the patients who survived and those who died. Patients who died were older, had a longer duration of diabetes, hypertension, and more diabetic microvascular complications; and received more insulin at baseline, compared with surviving patients. Patients who died demonstrated a significantly higher incidence of SH (19.8% vs. 8.3%, P=0.001) or history of CVD (19.8% vs. 7.9%, P<0.001) compared with the surviving group (Table 2).
- Association between SH and all-cause or CV mortality
- In univariable Cox regression analysis, age, diabetes duration (≥10 years), presence of hypertension, smoking, history of CVD, treatment with insulin and acetylsalicylic acid, diabetic nephropathy, SH, and estimated GFR were significantly associated with all-cause mortality or CV mortality (Table 3). After adjustment for multiple confounding factors, we found a significantly higher risk for all-cause mortality in the patients with SH than in those without SH (HR, 2.64; 95% CI, 1.39 to 5.02; P=0.003) in multivariable Cox regression analysis (Table 4, Fig. 1A).
- In addition, SH remained a significant prognostic factor for death from CV events (HR, 6.34; 95% CI, 2.02 to 19.87; P=0.002) after adjusting for various confounding factors (Table 4, Fig. 1B).
RESULTS
- In this long-term, prospective observational cohort study, we found that SH was significantly associated with increased risks of death from both CV events and any cause in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes. Especially, in this study, patients with experience of SH had 2.64 times higher risk of all-cause mortality during the follow-up period, as compared with those without an SH episode. The results were independent of glycemic control status, diabetic duration, age, diabetic nephropathy, use of insulin, or history of CVD.
- Large epidemiologic studies have shown the relationship between SH events and CV or all-cause mortality. According to the Hong Kong Diabetes Registry, patients with SH had a higher incidence of mortality (32.8% vs. 11.2%, P<0.0001) than those without SH did. Moreover, SH was associated with advanced age, renal dysfunction, poor glycemic control, and cancer sub-phenotypes [20]. In the retrospective study using data from Taiwan National Health Research Institutes, including 77,611 people with type 2 diabetes, clinically mild or severe symptomatic hypoglycemia was associated with an increased risk of CV events (HR, 2.09; 95% CI, 1.63 to 2.67), all-cause hospitalization (HR, 2.51; 95% CI, 2.00 to 3.16), and all-cause mortality (HR, 2.48; 95% CI, 1.41 to 4.38) [21]. In the Edinburgh Type 2 Diabetes Study and ORIGIN trial, a significant association was observed between a history of preceding SH and a higher frequency of subsequent macrovascular events [2223]. Recent studies have suggested that SH reflects the effects of comorbidities and unmeasured confounding variables; therefore, it is a marker of an increased risk of adverse clinical outcomes rather than a direct cause [624].
- Consistent with previous studies, we also found that subjects with SH events have a higher mortality rate than those without SH do in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes. In our study, CVD events accounted for 24.4% of all-cause death. Remarkably, death from sepsis or infection (29.1%) and malignancy (22.1%) were the major causes of death in our study population. Moreover, the median time from the onset of SH to the first CV death or death from any cause was within 3 years. Therefore, SH episodes seemed to reflect combined critical comorbidity or denote patients who are vulnerable to any cause of death [19]. In other words, the presence of SH should raise clinical suspicion of the patients' susceptibility to CV death or any cause of death, and patients with SH events need more clinical attention to prevent adverse outcomes.
- There has been increasing debate about the causality between hypoglycemia and CV mortality, and its mechanism. Although the pathogenic mechanism between SH and CVD also remains inconclusive, there have been several hypotheses to explain their relationship. Hypoglycemia has been suggested to have acute effects on sympathoadrenal activation, inflammation, increased platelet and neutrophil activation, coagulation, endothelial function, and inflammatory mediators or cytokines [2225], all of which have potential adverse effects on myocardium or vascular hemodynamics [1023]. In addition, cardiac ischemia, corrected QT interval prolongation, or fatal arrhythmia during SH may be responsible for the increased risk of CVD or sudden CV death among patients with SH [262728]. In addition, an interaction between hypoglycemia and CV autonomic neuropathy contributes to the risk of sudden death in patients with diabetes [29].
- The main strength of our study is the long-term, well-characterized prospective approach, which was conducted in a large hospital-based cohort in Korea, to ascertain the risk factors of SH and CV mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes. There are few long-term observational, prospective high-quality cohort studies analyzing the relationship between SH and CV mortality [6]. Some of them were based on self-reporting of SH and had small number of participants or short observation period and; therefore, may be unreliable or prone to recall bias [2030]. We also confirmed CV outcomes or SH episodes with strict criteria and verification procedures.
- Despite these strengths, our study has some limitations. First, this cohort study was conducted in a relatively small area by single-center experience and in one ethnic group. We analyzed only SH episodes, but the effect of minor hypoglycemia episodes on mortality was not evaluated. Last, peripheral artery disease and carotid endarterectomy were not included in the definition of CVD.
- In conclusion, we demonstrated that the SH was an independent risk factor for CV or all-cause mortality in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes. To reduce the risk of CV mortality or all-cause mortality, it is important to not only take measures to prevent SH but also carefully screen the type 2 diabetes population with a high risk of CVD and a history of SH. Moreover, additional studies are needed to clarify the underlying mechanisms linking CVD and SH.
DISCUSSION
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
NOTES
- 1. Cryer PE. Hypoglycaemia: the limiting factor in the glycaemic management of type I and type II diabetes. Diabetologia 2002;45:937-948. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 2. Stratton IM, Adler AI, Neil HA, Matthews DR, Manley SE, Cull CA, Hadden D, Turner RC, Holman RR. Association of glycaemia with macrovascular and microvascular complications of type 2 diabetes (UKPDS 35): prospective observational study. BMJ 2000;321:405-412. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 3. Holstein A, Patzer OM, Machalke K, Holstein JD, Stumvoll M, Kovacs P. Substantial increase in incidence of severe hypoglycemia between 1997-2000 and 2007-2010: a German longitudinal population-based study. Diabetes Care 2012;35:972-975. PubMedPMC
- 4. Kim JT, Oh TJ, Lee YA, Bae JH, Kim HJ, Jung HS, Cho YM, Park KS, Lim S, Jang HC, Lee HK. Increasing trend in the number of severe hypoglycemia patients in Korea. Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:166-172. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Study Group. Gerstein HC, Miller ME, Byington RP, Goff DC Jr, Bigger JT, Buse JB, Cushman WC, Genuth S, Ismail-Beigi F, Grimm RH Jr, Probstfield JL, Simons-Morton DG, Friedewald WT. Effects of intensive glucose lowering in type 2 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2008;358:2545-2559. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Zoungas S, Patel A, Chalmers J, de Galan BE, Li Q, Billot L, Woodward M, Ninomiya T, Neal B, MacMahon S, Grobbee DE, Kengne AP, Marre M, Heller S. ADVANCE Collaborative Group. Severe hypoglycemia and risks of vascular events and death. N Engl J Med 2010;363:1410-1418. ArticlePubMed
- 7. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2014. Diabetes Care 2014;37(Suppl 1):S14-S80. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 8. Inzucchi SE, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Diamant M, Ferrannini E, Nauck M, Peters AL, Tsapas A, Wender R, Matthews DR. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes: a patient-centered approach. Position statement of the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2012;55:1577-1596. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 9. Ko SH, Kim SR, Kim DJ, Oh SJ, Lee HJ, Shim KH, Woo MH, Kim JY, Kim NH, Kim JT, Kim CH, Kim HJ, Jeong IK, Hong EK, Cho JH, Mok JO, Yoon KH. Committee of Clinical Practice Guidelines, Korean Diabetes Association. 2011 Clinical practice guidelines for type 2 diabetes in Korea. Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:431-436. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Goto A, Arah OA, Goto M, Terauchi Y, Noda M. Severe hypoglycaemia and cardiovascular disease: systematic review and meta-analysis with bias analysis. BMJ 2013;347:f4533ArticlePubMed
- 11. Yun JS, Kim JH, Song KH, Ahn YB, Yoon KH, Yoo KD, Park YM, Ko SH. Cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction predicts severe hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes: a 10-year follow-up study. Diabetes Care 2014;37:235-241. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Workgroup on Hypoglycemia. American Diabetes Association. Defining and reporting hypoglycemia in diabetes: a report from the American Diabetes Association Workgroup on Hypoglycemia. Diabetes Care 2005;28:1245-1249. PubMed
- 13. Yun JS, Ko SH. Avoiding or coping with severe hypoglycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. Korean J Intern Med 2015;30:6-16. ArticlePubMed
- 14. Hicks KA, Hung HM, Mahaffey KW, Mehran R, Nissen SE, Stockbridge NL, Targum SL, Temple R. on behalf of the Standardized Data Collection for Cardiovascular Trials Initiative: Standardized definitions for cardiovascular and stroke endpoint events in clinical trials updated 2014 Aug 20. Available from: http://www.cdisc.org.
- 15. Koivisto VA, Stevens LK, Mattock M, Ebeling P, Muggeo M, Stephenson J, Idzior-Walus B. Cardiovascular disease and its risk factors in IDDM in Europe. EURODIAB IDDM Complications Study Group. Diabetes Care 1996;19:689-697. PubMed
- 16. Desouza CV, Bolli GB, Fonseca V. Hypoglycemia, diabetes, and cardiovascular events. Diabetes Care 2010;33:1389-1394. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 17. Fahrmann ER, Adkins L, Loader CJ, Han H, Rice KM, Denvir J, Driscoll HK. Severe hypoglycemia and coronary artery calcification during the diabetes control and complications trial/epidemiology of diabetes interventions and complications (DCCT/EDIC) study. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2015;107:280-289. ArticlePubMed
- 18. Levey AS, Bosch JP, Lewis JB, Greene T, Rogers N, Roth D. A more accurate method to estimate glomerular filtration rate from serum creatinine: a new prediction equation. Modification of Diet in Renal Disease Study Group. Ann Intern Med 1999;130:461-470. ArticlePubMed
- 19. Grambsch PM, Therneau TM. Proportional hazards tests and diagnostics based on weighted residuals. Biometrika 1994;81:515-526.Article
- 20. Kong AP, Yang X, Luk A, Ma RC, So WY, Ozaki R, Ting R, Cheung K, Ho CS, Chan MH, Chow CC, Chan JC. Severe hypoglycemia identifies vulnerable patients with type 2 diabetes at risk for premature death and all-site cancer: the Hong Kong diabetes registry. Diabetes Care 2014;37:1024-1031. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 21. Hsu PF, Sung SH, Cheng HM, Yeh JS, Liu WL, Chan WL, Chen CH, Chou P, Chuang SY. Association of clinical symptomatic hypoglycemia with cardiovascular events and total mortality in type 2 diabetes: a nationwide population-based study. Diabetes Care 2013;36:894-900. PubMedPMC
- 22. Bedenis R, Price AH, Robertson CM, Morling JR, Frier BM, Strachan MW, Price JF. Association between severe hypoglycemia, adverse macrovascular events, and inflammation in the Edinburgh Type 2 Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 2014;37:3301-3308. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 23. ORIGIN Trial Investigators. Mellbin LG, Ryden L, Riddle MC, Probstfield J, Rosenstock J, Diaz R, Yusuf S, Gerstein HC. Does hypoglycaemia increase the risk of cardiovascular events? A report from the ORIGIN trial. Eur Heart J 2013;34:3137-3144. ArticlePubMed
- 24. Bonds DE, Miller ME, Bergenstal RM, Buse JB, Byington RP, Cutler JA, Dudl RJ, Ismail-Beigi F, Kimel AR, Hoogwerf B, Horowitz KR, Savage PJ, Seaquist ER, Simmons DL, Sivitz WI, Speril-Hillen JM, Sweeney ME. The association between symptomatic, severe hypoglycaemia and mortality in type 2 diabetes: retrospective epidemiological analysis of the ACCORD study. BMJ 2010;340:b4909ArticlePubMedPMC
- 25. Frier BM, Schernthaner G, Heller SR. Hypoglycemia and cardiovascular risks. Diabetes Care 2011;34(Suppl 2):S132-S137. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 26. Vinik AI, Maser RE, Mitchell BD, Freeman R. Diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Diabetes Care 2003;26:1553-1579. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 27. Stahn A, Pistrosch F, Ganz X, Teige M, Koehler C, Bornstein S, Hanefeld M. Relationship between hypoglycemic episodes and ventricular arrhythmias in patients with type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular diseases: silent hypoglycemias and silent arrhythmias. Diabetes Care 2014;37:516-520. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 28. Cox AJ, Azeem A, Yeboah J, Soliman EZ, Aggarwal SR, Bertoni AG, Carr JJ, Freedman BI, Herrington DM, Bowden DW. Heart rate-corrected QT interval is an independent predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes: the Diabetes Heart Study. Diabetes Care 2014;37:1454-1461. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 29. Adler GK, Bonyhay I, Failing H, Waring E, Dotson S, Freeman R. Antecedent hypoglycemia impairs autonomic cardiovascular function: implications for rigorous glycemic control. Diabetes 2009;58:360-366. PubMedPMC
- 30. Algra A, Tijssen JG, Roelandt JR, Pool J, Lubsen J. QTc prolongation measured by standard 12-lead electrocardiography is an independent risk factor for sudden death due to cardiac arrest. Circulation 1991;83:1888-1894. ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Cumulative overall survival and cumulative cardiovascular event-free survival of patients with severe hypoglycemia (SH) estimated by Cox regression analysis. (A) Overall survival after SH. (B) Cardiovascular event-free survival after SH. CI, confidence interval.
Baseline characteristics of the groups with and without severe hypoglycemia
Values are presented as number (%), mean±standard deviation, or median (interquartile range).
SH, severe hypoglycemia; BMI, body mass index; CVD, cardiovascular disease; ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; UAE, urinary albumin excretion.
aDiabetic retinopathy was assessed from retinal photographs and the findings were reviewed by one ophthalmologist.
Comparison of baseline parameters between the patients who survived and died
Values are presented as number (%), mean±standard deviation, or median (interquartile range).
CVD, cardiovascular disease; ACE, angiotensin-converting enzyme; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; UAE, urinary albumin excretion.
Univariable Cox proportional hazards model of severe hypoglycemia for predicting cardiovascular mortality and all-cause mortality
CV, cardiovascular; CI, confidence interval; CVD, cardiovascular disease; ACEi, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor; ARB, angiotensin receptor blocker; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; HbA1c, glycosylated hemoglobin; SH, severe hypoglycemia.
Multivariable Cox proportional hazards model of severe hypoglycemia for cardiovascular mortality and all-cause mortality
Multivariable Cox proportional hazards models were adjusted for the following covariates: model 1, sex, age; model 2: model 1+diabetes duration, hypertension, cardiovascular disease history, smoking, body mass index, mean glycosylated hemoglobin, diabetic nephropathy; model 3: model 2+fasting plasma glucose, estimated glomerular filtration rate, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; model 4: model 3+insulin, angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blockers, statin, acetylsalicylic acid.
CI, confidence interval; CV, cardiovascular; SH, severe hypoglycemia.
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- The prognostic value of the stress hyperglycemia ratio for all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with diabetes or prediabetes: insights from NHANES 2005–2018
Lei Ding, Hongda Zhang, Cong Dai, Aikai Zhang, Fengyuan Yu, Lijie Mi, Yingjie Qi, Min Tang
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Navigating the future of diabetes: innovative nomogram models for predicting all-cause mortality risk in diabetic nephropathy
Sensen Wu, Hui Wang, Dikang Pan, Julong Guo, Fan Zhang, Yachan Ning, Yongquan Gu, Lianrui Guo
BMC Nephrology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Association of hypoglycaemia with the risks of arrhythmia and mortality in individuals with diabetes - a systematic review and meta-analysis
Gangfeng Li, Shuping Zhong, Xingmu Wang, Fuyuan Zhuge
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Diabetes mellitus und Straßenverkehr – ein Positionspapier der Österreichischen Diabetesgesellschaft (Update 2023)
Heidemarie Abrahamian, Birgit Salamon, Angelika Lahnsteiner, Christian Schelkshorn, Alexander Bräuer, Lars Stechemesser, Gerd Köhler, Martin Clodi
Wiener klinische Wochenschrift.2023; 135(S1): 319. CrossRef - Validation of the hypoglycemia awareness questionnaire to assess hypoglycemia awareness in patients with type 2 diabetes treated with insulin
Diana Cristina Henao-Carrillo, Fabio Alexander Sierra-Matamoros, Ana Julia Carrillo Algarra, Julieth Patricia García-Lugo, Sandra Milena Hernández-Zambrano
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2023; 17(12): 102917. CrossRef - Basal insulin analogues in people with diabetes and chronic kidney disease
David León‐Jiménez, José Pablo Miramontes‐González, Laura Márquez‐López, Francisco Astudillo‐Martín, Luis M. Beltrán‐Romero, Fernando Moreno‐Obregón, Javier Escalada‐San Martín
Diabetic Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Severe Hypoglycemia Increases Dementia Risk and Related Mortality: A Nationwide, Population-based Cohort Study
Eugene Han, Kyung-do Han, Byung-Wan Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Seung-Hyun Ko, Yong-ho Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(5): e1976. CrossRef - Validación transcultural del HypoA-Q para medir conciencia de hipoglucemia en pacientes diabéticos
Ana Julia Carrillo-Algarra, Sandra Milena Hernandez-Zambrano, Fabio Alexander Sierra-Matamoros, Diana Cristina Henao-Carrillo, Ana María Gómez-Medina, Daniel Esteban Hurtado-Barrera
Revista Ciencia y Cuidado.2022; 19(1): 42. CrossRef - Validity of the diagnosis of diabetic microvascular complications in Korean national health insurance claim data
Hyung Jun Kim, Moo-Seok Park, Jee-Eun Kim, Tae-Jin Song
Annals of Clinical Neurophysiology.2022; 24(1): 7. CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a risk factor for cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes: is it preventable?
Seung-Hyun Ko
Cardiovascular Prevention and Pharmacotherapy.2022; 4(3): 106. CrossRef - Evaluation of a Clinical Platform to Promote Chronic Disease Management
Laura Greene, Nila Sathe, John A. House, Laura L. Schott, Stella Safo
Population Health Management.2021; 24(4): 470. CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia as a preventable risk factor for cardiovascular disease in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Soo-Yeon Choi, Seung-Hyun Ko
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2021; 36(2): 263. CrossRef - Meta-Analysis: Association Between Hypoglycemia and Serious Adverse Events in Older Patients Treated With Glucose-Lowering Agents
Katharina Mattishent, Yoon K. Loke
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Epidemiology and outcomes from severe hypoglycemia in Kuwait: a prospective cohort study
Dalal Al Hasan, Ameen Yaseen, Mohammad Al Roudan, Lee Wallis
BMC Emergency Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The incidence of hypoglycemia and its risk factors among diabetic patients in the Eastern Province of Saudi Arabia
Ahmed Elshebiny, Hassan Alali, Zainab Alamer, Yasmin Alsultan, Hashim Alkhalaf, Abdullah Alkishi, Mohammed Alsuwaylih
International Journal of Medicine in Developing Countries.2021; : 614. CrossRef - Current trends in epidemiology of cardiovascular disease and cardiovascular risk management in type 2 diabetes
Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Metabolism.2021; 123: 154838. CrossRef - Real-world Evaluation of glycemic control and hypoglycemic Events among type 2 Diabetes mellitus study (REEDS): a multicentre, cross-sectional study in Thailand
Bancha Satirapoj, Thongchai Pratipanawatr, Boonsong Ongphiphadhanakul, Sompongse Suwanwalaikorn, Yupin Benjasuratwong, Wannee Nitiyanant
BMJ Open.2020; 10(2): e031612. CrossRef Predictors of Diabetes Self-Care Practice Among Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in Public Hospitals in Northeastern Ethiopia: A Facility-Based Cross-Sectional Study
Tesfaye Molla Gulentie, Ebrahim Mohammed Yesuf, Taklo Simeneh Yazie, Belayneh Kefale
Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy.2020; Volume 13: 3137. CrossRef- Hypoglycemia in Older Patients
Byron J. Hoogwerf
Clinics in Geriatric Medicine.2020; 36(3): 395. CrossRef - Severe hypoglycaemia and absolute risk of cause-specific mortality in individuals with type 2 diabetes: a UK primary care observational study
Francesco Zaccardi, Suping Ling, Claire Lawson, Melanie J. Davies, Kamlesh Khunti
Diabetologia.2020; 63(10): 2129. CrossRef - Insulin Glargine U100 Improved Glycemic Control and Reduced Nocturnal Hypoglycemia in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Chronic Kidney Disease Stages 3 and 4
Carolina C. Betônico, Silvia Maria O. Titan, Aécio Lira, Tatiana S. Pelaes, Maria Lúcia C. Correa-Giannella, Márcia Nery, Márcia Queiroz
Clinical Therapeutics.2019; 41(10): 2008. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Degludec Compared to Glargine 300 Units/mL in Insulin-Experienced Patients With Type 2 Diabetes: Trial Protocol Amendment (NCT03078478)
Athena Philis-Tsimikas, Irene Stratton, Lone Nørgård Troelsen, Britta Anker Bak, Lawrence A. Leiter
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2019; 13(3): 498. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of insulin glargine/lixisenatide (iGlarLixi) fixed-ratio combination in older adults with type 2 diabetes
Yehuda Handelsman, Christina Chovanes, Terry Dex, Francesco Giorgino, Neil Skolnik, Elisabeth Souhami, William Stager, Elisabeth Niemoeller, Juan Pablo Frias
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(3): 236. CrossRef - Urinary glucose excretion after dapagliflozin treatment: An exposure‐response modelling comparison between Japanese and non‐Japanese patients diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus
Victor Sokolov, Tatiana Yakovleva, Shinya Ueda, Joanna Parkinson, David W. Boulton, Robert C. Penland, Weifeng Tang
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2019; 21(4): 829. CrossRef - Effects on clinical outcomes of intensifying triple oral antidiabetic drug (OAD) therapy by initiating insulin versus enhancing OAD therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide population‐based, propensity‐score‐matched cohort study
Shihchen Kuo, Chun‐Ting Yang, Jin‐Shang Wu, Huang‐Tz Ou
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2019; 21(2): 312. CrossRef - Cardiovascular safety and lower severe hypoglycaemia of insulin degludec versus insulin glargine U100 in patients with type 2 diabetes aged 65 years or older: Results from DEVOTE (DEVOTE 7)
Richard E. Pratley, Scott S. Emerson, Edward Franek, Matthew P. Gilbert, Steven P. Marso, Darren K. McGuire, Thomas R. Pieber, Bernard Zinman, Charlotte T. Hansen, Melissa V. Hansen, Thomas Mark, Alan C. Moses, John B. Buse
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2019; 21(7): 1625. CrossRef - Review of the cardiovascular safety of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and the clinical relevance of the CAROLINA trial
Marile Santamarina, Curt J. Carlson
BMC Cardiovascular Disorders.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of a 12-week moderate-intensity exercise training on blood glucose response in patients with type 2 diabetes
Shang-Lin Chiang, Margaret McLean Heitkemper, Yi-Jen Hung, Wen-Chii Tzeng, Meei-Shyuan Lee, Chia-Huei Lin
Medicine.2019; 98(36): e16860. CrossRef - Impaired Awareness of Hypoglycaemia in Insulin-treated Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Mohammad J. Alkhatatbeh, Nedaa A. Abdalqader , Mohammad A.Y. Alqudah
Current Diabetes Reviews.2019; 15(5): 407. CrossRef - Hypoglycaemia, cardiovascular disease, and mortality in diabetes: epidemiology, pathogenesis, and management
Stephanie A Amiel, Pablo Aschner, Belinda Childs, Philip E Cryer, Bastiaan E de Galan, Brian M Frier, Linda Gonder-Frederick, Simon R Heller, Timothy Jones, Kamlesh Khunti, Lawrence A Leiter, Yingying Luo, Rory J McCrimmon, Ulrik Pedersen-Bjergaard, Eliza
The Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology.2019; 7(5): 385. CrossRef - Sulfonylureas as initial treatment for type 2 diabetes and the risk of adverse cardiovascular events: A population‐based cohort study
Kristian B. Filion, Antonios Douros, Laurent Azoulay, Hui Yin, Oriana H. Yu, Samy Suissa
British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology.2019; 85(10): 2378. CrossRef - Selectivity of beta-blockers, cardiovascular and all-cause mortality in people with hypoglycaemia: An observational study
F. Zaccardi, L.L. Nystrup Husemoen, B.L. Thorsted, D.R. Webb, S.K. Paul, M.J. Davies, K. Khunti
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2019; 29(5): 481. CrossRef - Cost-effectiveness of a primary care multidisciplinary Risk Assessment and Management Program for patients with diabetes mellitus (RAMP-DM) over lifetime
Fangfang Jiao, Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Colman Siu Cheung Fung, Anca Ka Chun Chan, Sarah Morag McGhee, Ruby Lai Ping Kwok, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Endocrine.2019; 63(2): 259. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of sensor-augmented pump therapy (SAPT) with predictive low-glucose management in patients diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus previously treated with SAPT and low glucose suspend
Ana María Gómez, Diana Cristina Henao, Angelica Imitola, Oscar Mauricio Muñoz, Martín Alonso Rondón Sepúlveda, Laura Kattah, Juan Sebastian Guerrero, Elly Morros, Juan Pablo Llano, Maira García Jaramillo, Fabián León-Vargas
Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición.2018; 65(8): 451. CrossRef - Recent diabetes-related mortality trends in Romania
Sorin Ioacara, Elisabeta Sava, Olivia Georgescu, Anca Sirbu, Simona Fica
Acta Diabetologica.2018; 55(8): 821. CrossRef - Use of sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors from clinical trial results to practical application in Russia
D. A. Lebedev, A. Yu. Babenko
Medical Council.2018; (16): 100. CrossRef - Severe hypoglycemia is a risk factor for atrial fibrillation in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Nationwide population-based cohort study
Seung-Hyun Ko, Yong-Moon Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Seon-Ah Cha, Eue-Keun Choi, Kyungdo Han, Eugene Han, Yong-ho Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2018; 32(2): 157. CrossRef - Antioxidant effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate on the aTC1-6 pancreatic alpha cell line
Ting Cao, Xiong Zhang, Dan Yang, Yue-Qian Wang, Zheng-Dong Qiao, Jian-Ming Huang, Peng Zhang
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2018; 495(1): 693. CrossRef - Hemoglobin glycation index predicts cardiovascular disease in people with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A 10-year longitudinal cohort study
Mee Kyoung Kim, Jee Sun Jeong, Jae-Seung Yun, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Ki Hyun Baek, Ki-Ho Song, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2018; 32(10): 906. CrossRef - Day-to-day fasting glycaemic variability in DEVOTE: associations with severe hypoglycaemia and cardiovascular outcomes (DEVOTE 2)
Bernard Zinman, Steven P. Marso, Neil R. Poulter, Scott S. Emerson, Thomas R. Pieber, Richard E. Pratley, Martin Lange, Kirstine Brown-Frandsen, Alan Moses, Ann Marie Ocampo Francisco, Jesper Barner Lekdorf, Kajsa Kvist, John B. Buse
Diabetologia.2018; 61(1): 48. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of sensor-augmented pump therapy (SAPT) with predictive low-glucose management in patients diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus previously treated with SAPT and low glucose suspend
Ana María Gómez, Diana Cristina Henao, Angelica Imitola, Oscar Mauricio Muñoz, Martín Alonso Rondón Sepúlveda, Laura Kattah, Juan Sebastian Guerrero, Elly Morros, Juan Pablo Llano, Maira García Jaramillo, Fabián León-Vargas
Endocrinología, Diabetes y Nutrición (English ed.).2018; 65(8): 451. CrossRef - Time- and frequency-domain measures of heart rate variability predict cardiovascular outcome in patients with type 2 diabetes
Seon-Ah Cha, Yong-Moon Park, Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hwan Lee, Yu-Bae Ahn, Sung-Rae Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2018; 143: 159. CrossRef - Newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes in an ethnic minority population: clinical presentation and comparison to other populations
Michael Morkos, Bettina Tahsin, Louis Fogg, Leon Fogelfeld
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2018; 6(1): e000568. CrossRef - DEVOTE 3: temporal relationships between severe hypoglycaemia, cardiovascular outcomes and mortality
Thomas R. Pieber, Steven P. Marso, Darren K. McGuire, Bernard Zinman, Neil R. Poulter, Scott S. Emerson, Richard E. Pratley, Vincent Woo, Simon Heller, Martin Lange, Kirstine Brown-Frandsen, Alan Moses, Jesper Barner Lekdorf, Lucine Lehmann, Kajsa Kvist,
Diabetologia.2018; 61(1): 58. CrossRef - Intervention effects of Compound Houttuyniae Herba to diabetic renal damage based on SOCS-JAK/STAT negative feedback regulation
Yun Fang, Sai-cong Shao, Hai-ying Wang
Chinese Herbal Medicines.2018; 10(4): 424. CrossRef - Monotherapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 349. CrossRef - Monotherapy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Sang Youl Rhee, Hyun Jin Kim, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu Yeon Hur, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 959. CrossRef - Antihyperglycemic agent therapy for adult patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus 2017: a position statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Sang Youl Rhee, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2017; 32(6): 947. CrossRef - Cardiovascular effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor in diabetic patients with and without established cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis and systematic review
Shishi Xu, Xinyue Zhang, Lizhi Tang, Fang Zhang, Nanwei Tong
Postgraduate Medicine.2017; 129(2): 205. CrossRef - Antihyperglycemic Agent Therapy for Adult Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus 2017: A Position Statement of the Korean Diabetes Association
Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyu-Yeon Hur, Sang Youl Rhee, Nan-Hee Kim, Min Kyong Moon, Seok-O Park, Byung-Wan Lee, Hyun Jin Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Jin Hwa Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(5): 337. CrossRef - Effects of propofol on myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats with type-2 diabetes mellitus
Ying Wang, Xiuru Qi, Chunliang Wang, Danning Zhao, Hongjie Wang, Jianxin Zhang
Biomedical Reports.2017; 6(1): 69. CrossRef - Cardiovascular risk assessment in patients with diabetes
Marcello Casaccia Bertoluci, Viviane Zorzanelli Rocha
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Pathogenetic features of the combined course of arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus 2 type
O.M. Bilovol, L.R. Bobronnikova, O.V. Al-Trawneh
Shidnoevropejskij zurnal vnutrisnoi ta simejnoi medicini.2017; 2017(1): 4. CrossRef - Risk Factors and Adverse Outcomes of Severe Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Jae-Seung Yun, Seung-Hyun Ko
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(6): 423. CrossRef - Real-world evidence for the safety of ipragliflozin in elderly Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (STELLA-ELDER): final results of a post-marketing surveillance study
Koutaro Yokote, Yasuo Terauchi, Ichiro Nakamura, Haruko Sugamori
Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy.2016; 17(15): 1995. CrossRef - Hypoglycemia: Culprit or Bystander?
You-Cheol Hwang
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2016; 40(3): 190. CrossRef - Schwere Hypoglykämien erhöhen die Mortalität
E. Fritschka
MMW - Fortschritte der Medizin.2016; 158(S3): 46. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite