- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 39(4); 2015 > Article
-
ReviewComplications Glycemic Variability: How Do We Measure It and Why Is It Important?
- Sunghwan Suh1, Jae Hyeon Kim2
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2015;39(4):273-282.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2015.39.4.273
Published online: August 17, 2015
1Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A Medical Center, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Jae Hyeon Kim. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, 81 Irwon-ro, Gangnam-gu, Seoul 06351, Korea. jaehyeon@skku.edu
Copyright © 2015 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- ABSTRACT
- INTRODUCTION
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY
- MEASUREMENT OF GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY
- SERUM MARKERS OF GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY
- GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY AND DIABETES COMPLICATIONS
- GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY AND HYPOGLYCEMIA
- GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY AS A TREATMENT TARGET
- HOW TO MINIMIZE GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY
- CONCLUSIONS
- NOTES
- REFERENCES
ABSTRACT
- Chronic hyperglycemia is the primary risk factor for the development of complications in diabetes mellitus (DM); however, it is believed that frequent or large glucose fluctuations may independently contribute to diabetes-related complications. Postprandial spikes in blood glucose, as well as hypoglycemic events, are blamed for increased cardiovascular events in DM. Glycemic variability (GV) includes both of these events; hence, minimizing GV can prevent future cardiovascular events. Correcting GV emerges as a target to be pursued in clinical practice to safely reduce the mean blood glucose and to determine its direct effects on vascular complications in diabetes. Modern diabetes management modalities, including glucagon-related peptide-1-based therapy, newer insulins, modern insulin pumps and bariatric surgery, significantly reduce GV. However, defining GV remains a challenge primarily due to the difficulty of measuring it and the lack of consensus regarding the optimal approach for its management. The purpose of this manuscript was not only to review the most recent evidence on GV but also to help readers better understand the available measurement options and how the various definitions relate differently to the development of diabetic complications.
- Glycemic variability (GV), which refers to swings in blood glucose levels, has a broader meaning because it alludes to blood glucose oscillations that occur throughout the day, including hypoglycemic periods and postprandial increases, as well as blood glucose fluctuations that occur at the same time on different days. The broad definition of GV considers the intraday glycemic excursions, including episodes of hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
- The concept of variability is often used in a negative sense when referring to human pathology. However, variability plays a fundamental role in all of the primary control systems in our body. The circadian rhythm of the hormones involved in glucose metabolism has been related to variations in glucose tolerance and insulin action [1]. Therefore, GV is not always negative because changes in glycemia are the physiological consequence not only of the circadian rhythm of hormones involved in the control of glucose metabolism, but also of carbohydrate intake. Although a certain degree of variability is also observed in subjects with normal glucose tolerance [2], GV is increased in people with diabetes and in people with impaired blood glucose regulation. Therefore, it is crucial not only to identify the boundary beyond which GV takes on a pathological meaning but also, more importantly, to better define the concept of GV. However, the literature on glucose GV is extensive yet inconsistent, especially regarding cardiovascular (CV) mortality [3456]. In this review, we will discuss the most recent reports, clinical implications, and measures for controlling GV in clinical practice.
INTRODUCTION
- According to various studies, the occurrence of various microvascular and macrovascular complications in diabetes is attributed to hyperglycemia and dysglycemia (peaks and nadirs). Several pathophysiological mechanisms were reported, unifying the two primary mechanisms: excessive protein glycation end products and activation of oxidative stress, which causes vascular complications. Intermittent high blood glucose exposure, rather than constant exposure to high blood glucose, has been shown to have deleterious effects in experimental studies [78]. In vitro and in vivo data have presented the mechanisms that are at the basis of the adverse CV effects of GV, which are mainly associated with oxidative stress; the atherogenic action of postprandial glucose (PPG) also involves insulin sensitivity, the postprandial increase of serum lipids and the glycemic index of food [9]. In In vitro experimental settings and in animal studies, glycemic fluctuations display a more deleterious effect on the parameters of CV risk, such as endothelial dysfunction [10]. There is a significant association between GV and the increased incidence of hypoglycemia [11]. Hypoglycemic events may trigger inflammation by inducing the release of inflammatory cytokines. Hypoglycemia also induces increased platelet and neutrophil activation. The sympathoadrenal response during hypoglycemia increases adrenaline secretion and may induce arrhythmias and increase the cardiac workload. Underlying endothelial dysfunction leading to decreased vasodilation may contribute to CV risk [12]. Published studies have demonstrated that GV, particularly when associated with severe hypoglycemia, could be harmful not only to people with diabetes but also to nondiabetic patients in critical care settings [17]. Overall, the pathophysiological evidence appears to be highly suggestive of GV being an important key determinant of vascular damage [13].
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY
- Extensive clinical trials have confirmed the association between hyperglycemia and the development of long-term complications in type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) [9]. The majority of these studies have used time-averaged glucose values measured as glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), an indicator of the degree of glycemic control, which is why HbA1c has become the reference parameter for therapies aimed at reducing the risk of complications from diabetes. Chronic hyperglycemia is almost universally assessed by HbA1c, which in a longitudinal study by Nathan et al. [14] has been shown to correlate closely with mean glucose levels over time, as determined by continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). However, the relative contribution of postprandial glycemic excursions and fasting to overall hyperglycemia has been the subject of considerable debate. Monnier et al. [15] suggested that the relative contributions of fasting and postprandial glucose differ according to the level of overall glycemic control. Fasting glucose concentrations present the most important contribution to hemoglobin glycosylation, whereas at lower levels of HbA1c, the relative contribution of postprandial hyperglycemia becomes predominant [1516]. Collectively, GV is likely to be incompletely expressed by HbA1c, particularly in patients with good metabolic control as shown in Fig. 1.
- The studies identified here illustrate that a large number of different methods are currently used to assess GV (Table 1). Currently, a clear consensus on the gold-standard method for measuring GV in clinical practice and research is lacking, although numerous indicators have been proposed [1]. On the contrary, an excessive amount of variability indices could lead to an increase of the existing confusion surrounding this important issue. Several of these indices can now be obtained by downloading self-monitoring blood glucose (SMBG) data, thereby making them available not only to diabetologists but also to patients. However, other indices are particularly complex, even when determined using the most innovative blood glucose monitoring systems, such as CGM. The majority of studies that have examined the degree of correlation between different assessment methods demonstrated that the most widely used methods are closely correlated among themselves and with previously developed measures [17]. Additionally, GV mandates restriction to a description of glucose excursions exclusive of a time component. Glycemic exposure (glucose excursion×time) and slope (glucose excursion/time) are indicators of the rate of glucose change but not its extent [18]. More details on the methodology for each of the indicators are described in a 2013 review by Service [18]. Rather than comment on all of the indicators, we would like to discuss a few salient points regarding the most commonly used measures. Although standard deviation (SD) is widely used, it has a limitation in that its use implies that glucose measures are normally distributed, which is typically not the case. However, SD remains a fairly robust measure because a linear relation has been established between the interquartile range and the SD [19]. The mean amplitude of glucose excursion (MAGE) was designed to capture mealtime-related glucose excursions. To separate mealtime-induction from other glucose excursions, investigations conducted in healthy volunteers found that excursions larger than 1.0 SD of the glucose measurements obtained were consistently related to mealtime. Detailed calculation of MAGE is depicted in Fig. 2. MAGE has also been criticized on five points [20]. First, with the introduction of CGM, postprandial excursions can be assessed more precisely by using the area under the curve and the trapezoidal method. Second, the calculation of MAGE is operator-dependent and not unambiguously defined. Third, the outcome differs depending on whether ascending or descending limbs are used for calculating MAGE. Fourth, there is a high correlation with the SD. Fifth, it is questionable whether only mealtime excursions or excursions larger than 1.0 SD would have clinical importance. The methods used for evaluating GV represent a critical issue because all of the methods suffer from the fact that GV is significantly influenced by the mean blood glucose: higher mean blood glucose levels are associated with higher GV values, unless they are corrected for the mean blood glucose. Correcting for the mean glucose of any relation between GV and a given outcome is important because high correlations between GV and the mean glucose have been demonstrated [20]. Because many studies have not made this correction, the reliability of their results could be questionable. For reasons outlined in this counterpoint, the coefficient of variation (CoV) has been proposed as the preferred measure of GV [2021]. The CoV in CGM was significantly associated with the presence of CV autonomic neuropathy in patients with inadequately controlled T2DM [22]. Jin et al. [23] identified independent factors associated with measures of GV. Fasting C-peptide levels inversely correlated with CoV in T1DM and insulin-treated T2DM. In T2DM without insulin therapy, high density lipoprotein and low density lipoprotein levels and the use of sulfonylurea were significantly correlated with the CoV [23].
- SMBG revolutionized the management of diabetes, becoming an integral part of the standard diabetes treatment in daily practice and recommended in the guidelines for managing therapy [24]. Frequent blood glucose monitoring is essential for managing the therapy of insulin-treated diabetes and in reducing HbA1c and the risk of hypoglycemia [25]. However, it should be noted that SMBG may not be appropriate for assessing GV because of the high number of determinations (at least hourly) that are needed to evaluate the parameters, such as SD, MAGE, and continuous overall net glycemic action (CONGA) [26]. Another major limitation of the methods for measuring GV associated with SMBG-based measures is that they provide an unsophisticated measure of variability, with a significant dependence on patient cooperation that makes the planning of long-term studies difficult. This observation casts doubt on the significance of the lack of correlation between GV and complications when GV is assessed with 7-point blood glucose profiles [11]. CGM, which is a new frontier for the overall assessment of GV, has revolutionized the management of patients with T1DM and has allowed for better troubleshooting in several patients with T2DM [2728]. CGM can provide information on daily glucose fluctuations and can show how those numbers are affected by everyday activities and stress levels. For this reason, clinical studies on CGM use may be easily performed to provide valuable data with minimal inconvenience to patients. CGM is particularly useful in clinical practice for various conditions as shown in Table 2. A meta-analysis suggests that, compared with SMBG, CGM is associated with a short-term reduction of HbA1c of 0.26% [29]. However, the long-term effectiveness of CGM needs to be determined. It also plays an integral part in emerging technology billed as an "artificial pancreas" partnering with continuous sensing technology to form a closed-loop glycemic control system that includes an insulin pump and controlling algorithms.
- For routine clinical practice, it is likely that the SD and corresponding CoV obtained using either SMBG or CGM will be sufficient to permit the assessment of changes in GV with time or following therapeutic interventions, and to permit comparisons with reference populations of patients with a similar type, duration, and level of control of HbA1c or mean glucose [2127]. Despite the various formulas offered, simple and standard clinical tools for defining GV have yet to evolve and different indexes of GV should be used, depending on the metabolic profile of the studied population.
MEASUREMENT OF GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY
- In addition to the indices mentioned, simple markers of glycemia, such as glycated albumin (GA) and 1,5-anhydroglucitol (1,5-AG), may have clinical utility for diagnosing and evaluating GV and predicting diabetic complications [3031]. We have already shown that these glycemic markers are significantly correlated with all of the GV parameters from CGM [16]. GA was demonstrated to be a more useful glycation index than HbA1c for monitoring short-term glycemic control in patients with T2DM [32], especially those with fluctuating and poorly controlled glycemic conditions [33]. Additionally, a high GA/HbA1c ratio reflects higher glycemic excursions, irrespective of the type of diabetes [34]. The 1,5-AG level is also reflective of the short-term glucose status, postprandial hyperglycemia, and GV that is not captured using HbA1c assay in patients with T1DM and T2DM [3536]. Simultaneous measurements of GA, 1,5-AG, and HbA1c may help to identify a group of patients who warrant closer monitoring in relation to GV.
SERUM MARKERS OF GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY
- There is considerable clinical evidence that supports the negative role of GV in the development of diabetes complications. The role of GV in the development of microvascular complications was initially suggested by the analysis of the diabetes control and complications trial (DCCT) data [37], which showed that increased HbA1c explained only 11% of the variation in the risk of retinopathy, meaning that factors independent of HbA1c must presumably explain the remaining 89%. In recent years, GV has been proposed to be an additional risk factor for complications of diabetes independent of hyperglycemia [3839]. Growing evidence indicates that significant GV, particularly when accompanied by hypoglycemia, can have a harmful effect not only on the onset and progression of diabetes complications but also in clinical conditions other than diabetes treated in intensive care units (ICUs) [20]. Regarding GV, it is important to note the differences among patients with T1DM, patients with insulin-treated T2DM and patients with T2DM using dietary therapy or oral hypoglycemic agents [24]. GV is always important in T1DM, where alternating hyperglycemia, normoglycemia and hypoglycemia are linked to an absolute insulin deficiency, erratic absorption of exogenous insulin, incomplete suppression of hepatic glucose production and altered hormonal counterregulation, among other factors. Recent studies using CGM showed a significant fluctuation in the blood glucose values of children with T1DM, as well as in those with excellent HbA1c values. This finding suggests that in addition to HbA1c, GV may have a predictive value for the development of T1DM complications [40]. A recent study identified the important association between GV and diabetes-related quality of life and treatment satisfaction in patients with T1DM [41].
- In insulin-treated T2DM, the relevance of GV varies according to the heterogeneity of the disease, the presence of residual insulin secretion and insulin resistance, in addition to the factors mentioned above. The findings from studies on T2DM support the likelihood that increased levels of short-term GV may play a substantial role in the development of microvascular complications [20]. Hsu et al. [42] showed a significant association of GV with diabetes retinopathy in patients with T1DM and T2DM. Jin et al. [43] found a significant association between urinary albumin excretion and GV measured by CGM. Less clear is the relationship between GV and CV events and overall mortality [11]. Several years ago, Muggeo et al. [44] found that all-cause and CV mortality in elderly people with T2DM was primarily associated with the variability/instability of fasting glucose levels, rather than its absolute values. The second clue in favor of this hypothesis is based primarily on the observation that in individuals with diabetes and in those with impaired glucose tolerance (IGT), blood glucose two hours after oral glucose loading has a higher predictive value for CV events than fasting plasma glucose (FPG) [45]. A third supporting element is based on the consideration that an increase in postprandial glycemia may have a particularly harmful effect on the onset of CV complications, a concept supported by the study to prevent non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (study to prevent non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus [STOP-NIDDM]) [46], but not by a study of hyperglycemia and its effect after acute myocardial infarction on CV outcomes in patients with T2DM (hyperglycemia and its effect after acute myocardial infarction on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus [HEART2D]) [3], which has led to a heated debate. Another supporting factor is based on the fact that the presence of acute hyperglycemia during acute myocardial infarction [47] or in intensive care patients [48] is associated with worse prognosis in individuals with diabetes or without diabetes. Therefore, PPG is not only a key determinant of HbA1c but also an independent parameter in the risk stratification of CV events and total mortality [4]. Since 1997, more than 15 observational studies have been published showing that elevated PPG, even in the high nondiabetic IGT range, contributes to an approximately 3-fold increase in the risk of developing coronary heart disease or a CV event [13]. Moreover, the meta-analysis of the published data from 20 studies of 95,783 individuals found a progressive relationship between the GV and CV risk [49]. In summary, the accumulated data that GV seems to be associated with the development of microvascular complications appear to be impressive. However, the evidence is less convincing in terms of a unique role for the long-term prediction of macrovascular complications above and beyond other glycemic parameters, such as FPG and HbA1c. Nevertheless, we should still include GV in the list of potential risk factors for diabetes complications.
GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY AND DIABETES COMPLICATIONS
- The hypothesis that the maintenance of close glycemic control is of importance in all of the clinical settings is highlighted by the recent evidence that in individuals with normal glucose tolerance, glycemia is maintained within a narrow range between 68.4 and 138.6 mg/dL [50]. Translated into clinical terms, this suggests that maintaining a normal glycemic level is important not only in diabetes but also in clinical contexts in which glycemia tends to increase. However, caution is required in treatment, particularly with insulin, to avoid excessive fluctuations and the risk of hypoglycemia, especially in ICUs. It is advisable to make every effort to maintain stable glycemic values, even above strictly physiological levels.
- Severe hypoglycemia is strongly associated with the increased risks of a range of adverse clinical outcomes in patient with diabetes [51]. In the DCCT trial, a 10% to 30% incidence of hypoglycemia was observed in the intensive insulin arm group. Hypoglycemia was the primary accompanying complication when the desired glucose target was intensively achieved. The frequency of severe hypoglycemia increases exponentially when lowering blood glucose [52] and several studies have reported that low GV coincided with decreased occurrence of hypoglycemia [53]. HbA1c is a poor predictor of hypoglycemic episodes because it only considers 8% of the likelihood of severe hypoglycemia [54]; on the contrary, GV can account for an estimated 40% to 50% of future hypoglycemic episodes. In a study by Kilpatrick et al. [55] using datasets of the DCCT, GV was independently predictive of hypoglycemia, similar to the mean blood glucose. They also showed that HbA1c is a poor predictor of hypoglycemic risk, whereas GV is a strong predictor of hypoglycemic episodes. Kim et al. [56] found that Korean T1DM patients with hypoglycemic events had a significantly higher GV index, as calculated from the CGM data. Collectively, patients at risk for hypoglycemia (i.e., those receiving insulin or insulin secretagogues) constitute one category that requires GV monitoring.
GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY AND HYPOGLYCEMIA
- The primary purpose of diabetes treatment is to obtain the most optimal metabolic control to avoid metabolic imbalance related to diabetes itself and the onset of complications. Of the various parameters required to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of a given agent, in addition to the parameters that are most frequently used, such as fasting glycemia, postprandial glycemia and HbA1c, the options include GV. The target GV has been a topic of debate. Monnier and Colette [57] proposed that a MAGE value of 40 mg/dL as the target level of GV and found that GV was an independent predictor of chronic diabetic complications, in addition to HbA1c. An independent association exists between increased GV and higher mortality in ICU patients [58]. In nondiabetic critically ill patients, diminishing hyperglycemic excursions will improve mortality [7]. As in recent studies, for example, the action to control cardiovascular risk in diabetes (ACCORD) study, hypoglycemia must be avoided. The study of Brunner et al. [59] showed that strict glycemic control using CGM did not decrease GV. Therefore, it is difficult, if not impossible, to decrease GV. The importance of GV and PPG has also been demonstrated in the results of intervention studies [60]. It appears indisputable that PPG excursions play an important role in determining the overall metabolic control in diabetes mellitus because an increase in PPG has a greater prognostic significance in terms of GV [61]. Thus, trials specifically aimed at correcting GV have not been conducted; however, trials that tended to correct PPG, at least in theory, have been conducted (i.e., STOP-NIDDM, HEART2D, nateglinide and valsartan in impaired glucose tolerance outcomes research [NAVIGATOR]) and are ongoing (acarbose cardiovascular evaluation [ACE]). If all of the intervention studies are taken together, there is no definite proof that targeting postprandial hyperglycemia results in a more beneficial outcome of CV complications in subjects with IGT or overt T2DM [13]. However, we should note that PPG and GV are not identical, even if they are closely related. Moreover, the absence of a uniformly accepted standard of how to estimate postprandial hyperglycemia and GV adds another challenge to this debate. Additional studies are warranted for confirming or refuting the role of GV as a treatment target.
GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY AS A TREATMENT TARGET
- The attention dedicated to GV is derived from the above evidence concerning its effects on oxidative stress and, from the latter, on chronic diabetes complications. Control of GV has been the focus of a number of interventional studies aimed at reducing this fluctuation. Diet and weight reduction are the first therapeutic instrument that can be used for reducing GV. Glucagon-like peptide-1 analogs and dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 inhibitors demonstrated a significant impact on GV in people with T2DM [17]. Regarding insulin therapy, the evolution of fast-acting and long-acting insulin has had a positive impact on the control of GV. One of the aims of the ultraslow analog degludec, which was recently approved for clinical use, is to reduce GV by virtue of its smaller pharmacodynamic variability. To date, the published results show that degludec is capable of reducing the frequency of episodes of hypoglycemia in patients with T1DM and postprandial glycemia oscillations in patients with T2DM, suggesting potential efficacy in the control of GV [62]. Continuous Subcutaneous Insulin Infusion (CSII) and bariatric surgery were also associated with significant reductions in hyperglycemic excursions along with the mean glucose [763]. Lastly, the development of new technologies for diabetes education, monitoring and therapy, particularly in T1DM, has made it possible to identify GV as an emerging target for improving overall diabetes treatment [1]. There should be no doubt that pharmacological advances directed at the ultimate goal of physiological insulin replacement will continue to the point where the postprandial glycemic curve will be bent to conform to that of nondiabetic subjects. In that ideal situation, the currently available measures of GV can be retired.
HOW TO MINIMIZE GLYCEMIC VARIABILITY
- GV is a physiological phenomenon that assumes an even more important dimension in the presence of diabetes because it not only contributes to increasing the mean blood glucose values but it also favors the development of chronic diabetes complications. It appears that GV is poised to become a future target parameter for optimum glycemic control over and above standard glycemic parameters, such as blood glucose and HbA1c. Avoiding both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia by careful use of SMBG and the availability of new agents to correct hyperglycemia without inducing hypoglycemia is expected to reduce the burden of premature mortality and disabling CV events associated with diabetes mellitus. However, defining GV remains a challenge primarily due to the difficulty of measuring it and the lack of consensus regarding the most optimal approach for patient management.
CONCLUSIONS
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST: No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
NOTES
- 1. Frontoni S, Di Bartolo P, Avogaro A, Bosi E, Paolisso G, Ceriello A. Glucose variability: an emerging target for the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2013;102:86-95. ArticlePubMed
- 2. Wang C, Lv L, Yang Y, Chen D, Liu G, Chen L, Song Y, He L, Li X, Tian H, Jia W, Ran X. Glucose fluctuations in subjects with normal glucose tolerance, impaired glucose regulation and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2012;76:810-815. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Siegelaar SE, Kerr L, Jacober SJ, Devries JH. A decrease in glucose variability does not reduce cardiovascular event rates in type 2 diabetic patients after acute myocardial infarction: a reanalysis of the HEART2D study. Diabetes Care 2011;34:855-857. PubMedPMC
- 4. Cavalot F, Petrelli A, Traversa M, Bonomo K, Fiora E, Conti M, Anfossi G, Costa G, Trovati M. Postprandial blood glucose is a stronger predictor of cardiovascular events than fasting blood glucose in type 2 diabetes mellitus, particularly in women: lessons from the San Luigi Gonzaga Diabetes Study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2006;91:813-819. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Muggeo M, Zoppini G, Bonora E, Brun E, Bonadonna RC, Moghetti P, Verlato G. Fasting plasma glucose variability predicts 10-year survival of type 2 diabetic patients: the Verona Diabetes Study. Diabetes Care 2000;23:45-50. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 6. Nalysnyk L, Hernandez-Medina M, Krishnarajah G. Glycaemic variability and complications in patients with diabetes mellitus: evidence from a systematic review of the literature. Diabetes Obes Metab 2010;12:288-298. ArticlePubMed
- 7. Satya Krishna SV, Kota SK, Modi KD. Glycemic variability: clinical implications. Indian J Endocrinol Metab 2013;17:611-619. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 8. Risso A, Mercuri F, Quagliaro L, Damante G, Ceriello A. Intermittent high glucose enhances apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells in culture. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2001;281:E924-E930. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Cavalot F. Do data in the literature indicate that glycaemic variability is a clinical problem? Glycaemic variability and vascular complications of diabetes. Diabetes Obes Metab 2013;15(Suppl 2):3-8. Article
- 10. Ceriello A, Esposito K, Piconi L, Ihnat M, Thorpe J, Testa R, Bonfigli AR, Giugliano D. Glucose "peak" and glucose "spike": impact on endothelial function and oxidative stress. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2008;82:262-267. ArticlePubMed
- 11. Smith-Palmer J, Brandle M, Trevisan R, Orsini Federici M, Liabat S, Valentine W. Assessment of the association between glycemic variability and diabetes-related complications in type 1 and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2014;105:273-284. ArticlePubMed
- 12. Desouza CV, Bolli GB, Fonseca V. Hypoglycemia, diabetes, and cardiovascular events. Diabetes Care 2010;33:1389-1394. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 13. Standl E, Schnell O, Ceriello A. Postprandial hyperglycemia and glycemic variability: should we care? Diabetes Care 2011;34(Suppl 2):S120-S127. PubMedPMC
- 14. Nathan DM, Turgeon H, Regan S. Relationship between glycated haemoglobin levels and mean glucose levels over time. Diabetologia 2007;50:2239-2244. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 15. Monnier L, Lapinski H, Colette C. Contributions of fasting and postprandial plasma glucose increments to the overall diurnal hyperglycemia of type 2 diabetic patients: variations with increasing levels of HbA(1c). Diabetes Care 2003;26:881-885. PubMed
- 16. Suh S, Joung JY, Jin SM, Kim MY, Bae JC, Park HD, Lee MS, Lee MK, Kim JH. Strong correlation between glycaemic variability and total glucose exposure in type 2 diabetes is limited to subjects with satisfactory glycaemic control. Diabetes Metab 2014;40:272-277. ArticlePubMed
- 17. Rodbard D. New and improved methods to characterize glycemic variability using continuous glucose monitoring. Diabetes Technol Ther 2009;11:551-565. ArticlePubMed
- 18. Service FJ. Glucose variability. Diabetes 2013;62:1398-1404. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 19. Rodbard D. Optimizing display, analysis, interpretation and utility of self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) data for management of patients with diabetes. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2007;1:62-71. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 20. DeVries JH. Glucose variability: where it is important and how to measure it. Diabetes 2013;62:1405-1408. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 21. Rodbard D. Clinical interpretation of indices of quality of glycemic control and glycemic variability. Postgrad Med 2011;123:107-118. ArticlePubMed
- 22. Jun JE, Jin SM, Baek J, Oh S, Hur KY, Lee MS, Lee MK, Kim JH. The association between glycemic variability and diabetic cardiovascular autonomic neuropathy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc Diabetol 2015;14:70ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 23. Jin SM, Kim TH, Bae JC, Hur KY, Lee MS, Lee MK, Kim JH. Clinical factors associated with absolute and relative measures of glycemic variability determined by continuous glucose monitoring: an analysis of 480 subjects. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2014;104:266-272. ArticlePubMed
- 24. Inchiostro S, Candido R, Cavalot F. How can we monitor glycaemic variability in the clinical setting? Diabetes Obes Metab 2013;15(Suppl 2):13-16. ArticlePubMed
- 25. Schiffrin A, Belmonte M. Multiple daily self-glucose monitoring: its essential role in long-term glucose control in insulin-dependent diabetic patients treated with pump and multiple subcutaneous injections. Diabetes Care 1982;5:479-484. ArticlePubMed
- 26. Baghurst PA, Rodbard D, Cameron FJ. The minimum frequency of glucose measurements from which glycemic variation can be consistently assessed. J Diabetes Sci Technol 2010;4:1382-1385. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 27. American Diabetes Association. (6) Glycemic targets. Diabetes Care 2015;38(Suppl):S33-S40. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 28. Kim SK, Kim HJ, Kim T, Hur KY, Kim SW, Lee MK, Min YK, Kim KW, Chung JH, Kim JH. Effectiveness of 3-day continuous glucose monitoring for improving glucose control in type 2 diabetic patients in clinical practice. Diabetes Metab J 2014;38:449-455. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 29. Yeh HC, Brown TT, Maruthur N, Ranasinghe P, Berger Z, Suh YD, Wilson LM, Haberl EB, Brick J, Bass EB, Golden SH. Comparative effectiveness and safety of methods of insulin delivery and glucose monitoring for diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Intern Med 2012;157:336-347. ArticlePubMed
- 30. Selvin E, Francis LM, Ballantyne CM, Hoogeveen RC, Coresh J, Brancati FL, Steffes MW. Nontraditional markers of glycemia: associations with microvascular conditions. Diabetes Care 2011;34:960-967. PubMedPMC
- 31. Koga M. 1,5-Anhydroglucitol and glycated albumin in glycemia. Adv Clin Chem 2014;64:269-301. ArticlePubMed
- 32. Koga M, Kasayama S. Clinical impact of glycated albumin as another glycemic control marker. Endocr J 2010;57:751-762. ArticlePubMed
- 33. Lee EY, Lee BW, Kim D, Lee YH, Kim KJ, Kang ES, Cha BS, Lee EJ, Lee HC. Glycated albumin is a useful glycation index for monitoring fluctuating and poorly controlled type 2 diabetic patients. Acta Diabetol 2011;48:167-172. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 34. Ogawa A, Hayashi A, Kishihara E, Yoshino S, Takeuchi A, Shichiri M. New indices for predicting glycaemic variability. PLoS One 2012;7:e46517ArticlePubMedPMC
- 35. Kim WJ, Park CY. 1,5-Anhydroglucitol in diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 2013;43:33-40. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 36. Seok H, Huh JH, Kim HM, Lee BW, Kang ES, Lee HC, Cha BS. 1,5-Anhydroglucitol as a useful marker for assessing short-term glycemic excursions in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab J 2015;39:164-170. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 37. Lachin JM, Genuth S, Nathan DM, Zinman B, Rutledge BN. DCCT/EDIC Research Group. Effect of glycemic exposure on the risk of microvascular complications in the diabetes control and complications trial: revisited. Diabetes 2008;57:995-1001. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 38. Brownlee M, Hirsch IB. Glycemic variability: a hemoglobin A1c-independent risk factor for diabetic complications. JAMA 2006;295:1707-1708. ArticlePubMed
- 39. Sartore G, Chilelli NC, Burlina S, Di Stefano P, Piarulli F, Fedele D, Mosca A, Lapolla A. The importance of HbA1c and glucose variability in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: outcome of continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). Acta Diabetol 2012;49(Suppl 1):S153-S160. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 40. Salardi S, Zucchini S, Santoni R, Ragni L, Gualandi S, Cicognani A, Cacciari E. The glucose area under the profiles obtained with continuous glucose monitoring system relationships with HbA(lc) in pediatric type 1 diabetic patients. Diabetes Care 2002;25:1840-1844. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 41. Ayano-Takahara S, Ikeda K, Fujimoto S, Hamasaki A, Harashima S, Toyoda K, Fujita Y, Nagashima K, Tanaka D, Inagaki N. Glycemic variability is associated with quality of life and treatment satisfaction in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015;38:e1-e2. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 42. Hsu CR, Chen YT, Sheu WH. Glycemic variability and diabetes retinopathy: a missing link. J Diabetes Complications 2015;29:302-306. ArticlePubMed
- 43. Jin SM, Kim TH, Oh S, Baek J, Joung JY, Park SM, Cho YY, Sohn SY, Hur KY, Lee MS, Lee MK, Kim JH. Association between the extent of urinary albumin excretion and glycaemic variability indices measured by continuous glucose monitoring. Diabet Med 2015;32:274-279. ArticlePubMed
- 44. Muggeo M, Verlato G, Bonora E, Zoppini G, Corbellini M, de Marco R. Long-term instability of fasting plasma glucose, a novel predictor of cardiovascular mortality in elderly patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: the Verona Diabetes Study. Circulation 1997;96:1750-1754. ArticlePubMed
- 45. Ceriello A. Postprandial hyperglycemia and diabetes complications: is it time to treat? Diabetes 2005;54:1-7. PubMed
- 46. Chiasson JL, Josse RG, Gomis R, Hanefeld M, Karasik A, Laakso M. STOP-NIDDM Trial Research Group. Acarbose treatment and the risk of cardiovascular disease and hypertension in patients with impaired glucose tolerance: the STOP-NIDDM trial. JAMA 2003;290:486-494. ArticlePubMed
- 47. Deedwania P, Kosiborod M, Barrett E, Ceriello A, Isley W, Mazzone T, Raskin P. American Heart Association Diabetes Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Hyperglycemia and acute coronary syndrome: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Diabetes Committee of the Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism. Circulation 2008;117:1610-1619. ArticlePubMed
- 48. Langouche L, Vanhorebeek I, Van den Berghe G. Therapy insight: the effect of tight glycemic control in acute illness. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2007;3:270-278. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 49. Coutinho M, Gerstein HC, Wang Y, Yusuf S. The relationship between glucose and incident cardiovascular events. A metaregression analysis of published data from 20 studies of 95,783 individuals followed for 12.4 years. Diabetes Care 1999;22:233-240. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 50. Waden J, Forsblom C, Thorn LM, Gordin D, Saraheimo M, Groop PH. Finnish Diabetic Nephropathy Study Group. A1C variability predicts incident cardiovascular events, microalbuminuria, and overt diabetic nephropathy in patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2009;58:2649-2655. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 51. Zoungas S, Patel A, Chalmers J, de Galan BE, Li Q, Billot L, Woodward M, Ninomiya T, Neal B, MacMahon S, Grobbee DE, Kengne AP, Marre M, Heller S, Group AC. Severe hypoglycemia and risks of vascular events and death. N Engl J Med 2010;363:1410-1418. ArticlePubMed
- 52. Nathan DM, Cleary PA, Backlund JY, Genuth SM, Lachin JM, Orchard TJ, Raskin P, Zinman B. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial/Epidemiology of Diabetes Interventions and Complications (DCCT/EDIC) Study Research Group. Intensive diabetes treatment and cardiovascular disease in patients with type 1 diabetes. N Engl J Med 2005;353:2643-2653. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 53. Jeha GS, Karaviti LP, Anderson B, Smith EO, Donaldson S, McGirk TS, Haymond MW. Insulin pump therapy in preschool children with type 1 diabetes mellitus improves glycemic control and decreases glucose excursions and the risk of hypoglycemia. Diabetes Technol Ther 2005;7:876-884. ArticlePubMed
- 54. The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Hypoglycemia in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes 1997;46:271-286. ArticlePubMed
- 55. Kilpatrick ES, Rigby AS, Goode K, Atkin SL. Relating mean blood glucose and glucose variability to the risk of multiple episodes of hypoglycaemia in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2007;50:2553-2561. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 56. Kim SK, Suh S, Kim MY, Chung HS, Hur KY, Kim SW, Chung JH, Lee MS, Min YK, Kim KW, Kim JH. Three-day continuous glucose monitoring for rapid assessment of hypoglycemic events and glycemic variability in type 1 diabetic patients. Endocr J 2011;58:535-541. ArticlePubMed
- 57. Monnier L, Colette C. Glycemic variability: should we and can we prevent it? Diabetes Care 2008;31(Suppl 2):S150-S154. PubMed
- 58. Krinsley JS. Glycemic variability: a strong independent predictor of mortality in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 2008;36:3008-3013. ArticlePubMed
- 59. Brunner R, Adelsmayr G, Herkner H, Madl C, Holzinger U. Glycemic variability and glucose complexity in critically ill patients: a retrospective analysis of continuous glucose monitoring data. Crit Care 2012;16:R175ArticlePubMedPMC
- 60. van Haeften TW, Pimenta W, Mitrakou A, Korytkowski M, Jenssen T, Yki-Jarvinen H, Gerich JE. Relative conributions of beta-cell function and tissue insulin sensitivity to fasting and postglucose-load glycemia. Metabolism 2000;49:1318-1325. ArticlePubMed
- 61. Avignon A, Radauceanu A, Monnier L. Nonfasting plasma glucose is a better marker of diabetic control than fasting plasma glucose in type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 1997;20:1822-1826. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 62. Vora J, Cariou B, Evans M, Gross JL, Harris S, Landstedt-Hallin L, Mithal A, Rodriguez MR, Meneghini L. Clinical use of insulin degludec. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2015;109:19-31. ArticlePubMed
- 63. Heinemann L, Fleming GA, Petrie JR, Holl RW, Bergenstal RM, Peters AL. Insulin pump risks and benefits: a clinical appraisal of pump safety standards, adverse event reporting, and research needs: a joint statement of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes and the American Diabetes Association Diabetes Technology Working Group. Diabetes Care 2015;38:716-722. ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
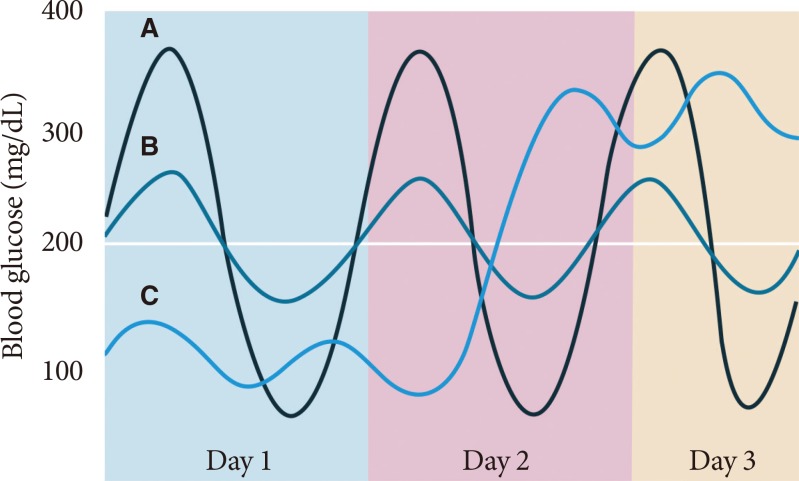
Fig. 1
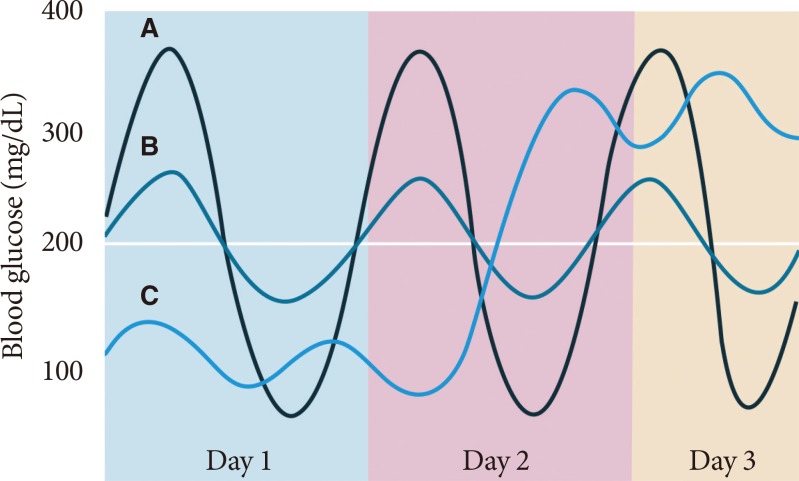
Glycemic variability in three hypothetical patients who have the same mean blood glucose concentration. Patient B has relatively small variations during the day and on different days; this patient should have little difficulty in lowering daily mean blood glucose concentrations without inducing hypoglycemia. In comparison, patient A has marked blood glucose variations on the same day and patient C has marked blood glucose variations on different days.

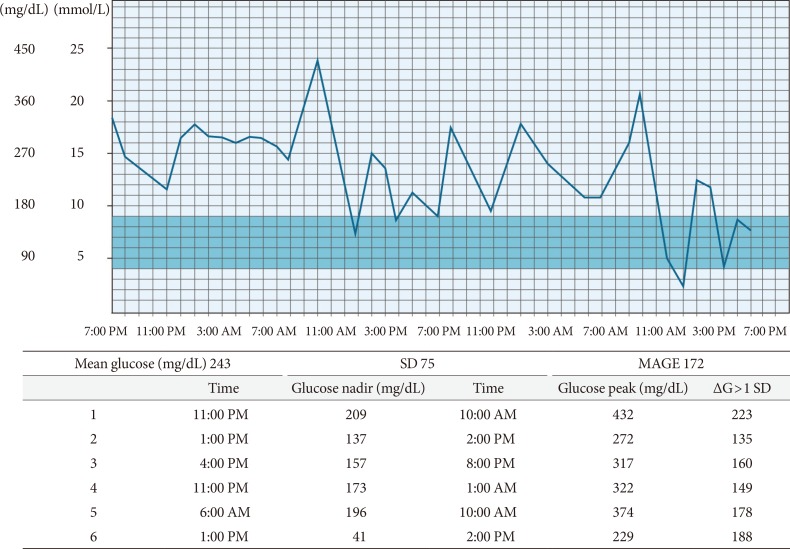
Fig. 2

Calculation of mean amplitude of glucose excursion (MAGE). In the first step, all the local maximum/minimum values are determined. The next step is an assessment of maximum/minimum pairs against the standard deviation (SD). If the difference from minimum to maximum is greater than the SD, this variation from mean measure is retained. If the local maximum/minimum is less than 1 SD it is excluded from further calculations. These troughs are retained and summed to achieve the MAGE.

Table 1
![dmj-39-273-i001.jpg]()
Glycemic variability indices
Table 2
![dmj-39-273-i002.jpg]()
Indications for continuous glucose monitoring
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Evaluation of Effects of Continuous Glucose Monitoring on Physical Activity Habits and Blood Lipid Levels in Persons With Type 1 Diabetes Managed With Multiple Daily Insulin Injections: An Analysis Based on the GOLD Randomized Trial (GOLD 8)
Thomas Nyström, Erik Schwarz, Sofia Dahlqvist, Magnus Wijkman, Magnus Ekelund, Helen Holmer, Jan Bolinder, Jarl Hellman, Henrik Imberg, Irl B. Hirsch, Marcus Lind
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2024; 18(1): 89. CrossRef - Washed microbiota transplantation reduces glycemic variability in unstable diabetes
Yangyang Li, Qing Liu, Lingyu Zhang, Jing Zou, Rongbo He, Ying Zhou, Chen Qian, Yuxiao Zhu, Rourou Chen, Ying Zhang, Pengpeng Cai, Miao Wang, Wei Shao, Minjun Ji, Hao Wu, Faming Zhang, Zejian Liu, Yu Liu
Journal of Diabetes.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic variability: Measurement, target, impact on complications of diabetes and does it really matter?
Yifei Mo, Jingyi Lu, Jian Zhou
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2024; 15(1): 5. CrossRef - Statistical Packages and Algorithms for the Analysis of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data: A Systematic Review
Mikkel Thor Olsen, Carina Kirstine Klarskov, Arnold Matovu Dungu, Katrine Bagge Hansen, Ulrik Pedersen-Bjergaard, Peter Lommer Kristensen
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin pump treatment vs. multiple daily insulin injections in patients with poorly controlled Type 2 diabetes mellitus: a comparison of cardiovascular effects
Saverio Tremamunno, Linda Tartaglione, Alessandro Telesca, Alessandro Rizzi, Tamara Felici, Francesco Mazzotta, Antonio De Vita, Emanuele Rizzo, Nello Cambise, Antonietta Belmusto, Dario Pitocco, Gaetano Antonio Lanza
Endocrine.2024; 84(1): 128. CrossRef - To What Extent Is HbA1c Associated with Glycemic Variability in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes? A Retrospective, Noninterventional Study
Sandra Lazar, Ioana Ionita, Delia Reurean-Pintilei, Romulus Timar, Silvia Ana Luca, Bogdan Timar
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2024; 13(2): 450. CrossRef - Short-term glycemic variability in non-diabetic, non-obese dogs assessed by common glycemic variability indices
Tobias Urbanschitz, Lukas Huber, Alexander Tichy, Iwan Anton Burgener, Florian Karl Zeugswetter
Research in Veterinary Science.2024; 169: 105156. CrossRef - Enhancement of Ambulatory Glucose Profile for Decision Assistance and Treatment Adjustments
V. K. R. Rajeswari Satuluri, Vijayakumar Ponnusamy
Diagnostics.2024; 14(4): 436. CrossRef - Glycemic variability assessed using continuous glucose monitoring in individuals without diabetes and associations with cardiometabolic risk markers: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Anna Hjort, David Iggman, Fredrik Rosqvist
Clinical Nutrition.2024; 43(4): 915. CrossRef - Oral metformin for type-2 diabetes mellitus treatment in a black-tufted marmoset (Callithrix penicillata)
Janyni Duz, Lívia E. Surita, Letícia Machado, Priscila M.D. Costa, Bruna S. Machado, Stella F. Valle, Marcelo M. Alievi, Álan G. Pöppl
Pesquisa Veterinária Brasileira.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - A low-glucose eating pattern is associated with improvements in glycemic variability among women at risk for postmenopausal breast cancer: an exploratory analysis
Michelle R. Jospe, Yue Liao, Erin D. Giles, Barry I. Hudson, Joyce M. Slingerland, Susan M. Schembre
Frontiers in Nutrition.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycaemic Variability as a Predictor of Graft Failure following Infra-Inguinal Bypass for Peripheral Arterial Disease. A Retrospective Cohort Study.
Daniel J. Farndon, Philip C. Bennett, Ian Nunney, Ketan Dhatariya
Annals of Vascular Surgery.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Insulin Titration Guidelines for Patients With Type 1 Diabetes: It Is About Time!
John Walsh, Ruth Roberts, Timothy S. Bailey, Lutz Heinemann
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2023; 17(4): 1066. CrossRef - A randomised crossover trial: Exploring the dose–response effect of carbohydrate restriction on glycaemia in people with well‐controlled type 2 diabetes
Ebaa Al‐Ozairi, Al Awadi Reem, Abeer El Samad, Etab Taghadom, Jumana Al‐Kandari, Muhammad Abdul‐Ghani, Nick Oliver, Brandon Whitcher, Nicola Guess
Journal of Human Nutrition and Dietetics.2023; 36(1): 51. CrossRef - Monitoring of continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion treatment in Portugal and its implications for diabetes management
Ana Rita Figueiredo, Tânia Matos, Sónia do Vale
Hormones.2023; 22(1): 87. CrossRef - A composite measure of sleep health is associated with glycaemic target achievement in young adults with type 1 diabetes
Stephanie Griggs, Grant Pignatiello, Ronald L. Hickman
Journal of Sleep Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of Point-of-Care and Laboratory Glycated Hemoglobin A1c and Its Relationship to Time-in-Range and Glucose Variability: A Real-World Study
Ayman Al Hayek, Wael M Alzahrani, Samia H Sobki, Abdulghani H Al-Saeed, Mohamed Al Dawish
Cureus.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - HIF-1α accumulation in response to transient hypoglycemia may worsen diabetic eye disease
Chuanyu Guo, Monika Deshpande, Yueqi Niu, Isha Kachwala, Miguel Flores-Bellver, Haley Megarity, Taylor Nuse, Savalan Babapoor-Farrokhran, Michael Ramada, Jaron Sanchez, Neelay Inamdar, Thomas V. Johnson, Maria Valeria Canto-Soler, Silvia Montaner, Akrit S
Cell Reports.2023; 42(1): 111976. CrossRef - Machine Learning–Based Time in Patterns for Blood Glucose Fluctuation Pattern Recognition in Type 1 Diabetes Management: Development and Validation Study
Nicholas Berin Chan, Weizi Li, Theingi Aung, Eghosa Bazuaye, Rosa M Montero
JMIR AI.2023; 2: e45450. CrossRef - Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Dogs and Cats
Francesca Del Baldo, Federico Fracassi
Veterinary Clinics of North America: Small Animal Practice.2023; 53(3): 591. CrossRef - Hypoglycemia and glycemic variability of people with type 1 diabetes with lower and higher physical activity loads in free-living conditions using continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion with predictive low-glucose suspend system
Denise Montt-Blanchard, Raimundo Sánchez, Karen Dubois-Camacho, Jaime Leppe, María Teresa Onetto
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2023; 11(2): e003082. CrossRef - In vivo photoacoustic monitoring of vasoconstriction induced by acute hyperglycemia
Joongho Ahn, Jin Woo Baik, Donggyu Kim, Karam Choi, Seunghyun Lee, Sung-Min Park, Jin Young Kim, Sung Hyun Nam, Chulhong Kim
Photoacoustics.2023; 30: 100485. CrossRef - Oscillating Glucose Induces the Increase in Inflammatory Stress through Ninjurin-1 Up-Regulation and Stimulation of Transport Proteins in Human Endothelial Cells
Laura Toma, Gabriela M. Sanda, Camelia S. Stancu, Loredan S. Niculescu, Mina Raileanu, Anca V. Sima
Biomolecules.2023; 13(4): 626. CrossRef - The association between fasting plasma glucose variability and incident eGFR decline: evidence from two cohort studies
Niloofar Deravi, Yasaman Sharifi, Fatemeh Koohi, Seyed Saeed Tamehri Zadeh, Soroush Masrouri, Fereidoun Azizi, Farzad Hadaegh
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Insight into continuous glucose monitoring: from medical basics to commercialized devices
Ayman Chmayssem, Małgorzata Nadolska, Emily Tubbs, Kamila Sadowska, Pankaj Vadgma, Isao Shitanda, Seiya Tsujimura, Youssef Lattach, Martin Peacock, Sophie Tingry, Stéphane Marinesco, Pascal Mailley, Sandrine Lablanche, Pierre Yves Benhamou, Abdelkader Zeb
Microchimica Acta.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - The efficacy and tolerability of intermittent prandial acarbose to reduce glucose spikes in healthy individuals
A. Isman, A. Nyquist, M. Moel, X. Zhang, S. Zalzala
Translational Medicine of Aging.2023; 7: 12. CrossRef - Development of an artificial intelligence system to identify hypoglycaemia via ECG in adults with type 1 diabetes: protocol for data collection under controlled and free-living conditions
Owain Cisuelo, Katy Stokes, Iyabosola B Oronti, Muhammad Salman Haleem, Thomas M Barber, Martin O Weickert, Leandro Pecchia, John Hattersley
BMJ Open.2023; 13(4): e067899. CrossRef - Self-Management and Glycemic Targets in Adult Haitian Immigrants With Type 2 Diabetes
Cherlie Magny-Normilus, Robin Whittemore, Marcella Nunez-Smith, Christopher S. Lee, Jeffrey Schnipper, Deborah Wexler, Julie A. Sanders, Margaret Grey
Nursing Research.2023; 72(3): 211. CrossRef - The effect of traditional diet on glucose homoeostasis in carriers and non-carriers of a common TBC1D4 variant in Greenlandic Inuit: a randomised crossover study
Jack Ivor Lewis, Mads Vendelbo Lind, Grith Møller, Torben Hansen, Hanne Pedersen, Marie Mathilde Bjerg Christensen, Jens Christian Laursen, Sara Nielsen, Charlotte B. Ottendahl, Christina V. Lytken Larsen, Ken D. Stark, Peter Bjerregaard, Marit E. Jørgens
British Journal of Nutrition.2023; 130(11): 1871. CrossRef - Screening for Impaired Glucose Homeostasis: A Novel Metric of Glycemic Control
Jaycee M. Kaufman, Lennaert van Veen, Yan Fossat
Mayo Clinic Proceedings: Digital Health.2023; 1(2): 189. CrossRef - Impact of a Low-Carbohydrate Compared with Low-Fat Breakfast on Blood Glucose Control in Type 2 Diabetes: A Randomized Trial
Barbara F. Oliveira, Courtney R. Chang, Kate Oetsch, Kaja Falkenhain, Kara Crampton, Matthew Stork, Malvinder Hoonjan, Thomas Elliott, Monique E. Francois, Jonathan P. Little
The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2023; 118(1): 209. CrossRef - Time in Range Estimation in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes is Improved by Incorporating Fasting and Postprandial Glucose Levels
Rui Sun, Yanli Duan, Yumei Zhang, Lingge Feng, Bo Ding, Rengna Yan, Jianhua Ma, Xiaofei Su
Diabetes Therapy.2023; 14(8): 1373. CrossRef - Glucose variability: a new risk factor for cardiovascular disease
Martina Belli, Alfonso Bellia, Domenico Sergi, Lucy Barone, Davide Lauro, Francesco Barillà
Acta Diabetologica.2023; 60(10): 1291. CrossRef - Effect of Repeated Bolus and Continuous Glucose Infusion on DNA Damage and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in Healthy Male Volunteers
Laura Bragagna, Christina Polak, Lisa Schütz, Lina Maqboul, Carmen Klammer, Roland Feldbauer, Agnes Draxler, Martin Clodi, Karl-Heinz Wagner
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2023; 24(17): 13608. CrossRef - Association between inpatient glycemic variability and COVID-19 mortality: a prospective study
Salma Ali El Chab Parolin, Rebecca Benicio Stocco, Julia do Carmo Kneipp Lopes, Marcos Roberto Curcio Pereira, Milena Massae Yamashita, Maria Eduarda Domareski Goulart, Henrique Demeneck, Marcia Olandoski, Larissa Hermann de Souza Nunes, Victor Keniche Mo
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Understanding temporal changes and seasonal variations in glycemic trends using wearable data
Prajakta Belsare, Abigail Bartolome, Catherine Stanger, Temiloluwa Prioleau
Science Advances.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of mulberry twig alkaloids(Sangzhi alkaloids) and metformin on blood glucose fluctuations in combination with premixed insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes
Ziyu Meng, Chengye Xu, Haoling Liu, Xinyuan Gao, Xinyu Li, Wenjian Lin, Xuefei Ma, Changwei Yang, Ming Hao, Kangqi Zhao, Yuxin Hu, Yi Wang, Hongyu Kuang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Baricitinib and β-Cell Function in Patients with New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes
Michaela Waibel, John M. Wentworth, Michelle So, Jennifer J. Couper, Fergus J. Cameron, Richard J. MacIsaac, Gabby Atlas, Alexandra Gorelik, Sara Litwak, Laura Sanz-Villanueva, Prerak Trivedi, Simi Ahmed, Francis J. Martin, Madeleine E. Doyle, Jessica E.
New England Journal of Medicine.2023; 389(23): 2140. CrossRef - Metabolic Stress of Red Blood Cells Induces Hemoglobin Glutathionylation
P. I. Zaripov, Yu. D. Kuleshova, Yu. M. Poluektov, S. V. Sidorenko, O. K. Kvan, G. V. Maksimov, V. A. Mitkevich, A. A. Makarov, I. Yu. Petrushanko
Molecular Biology.2023; 57(6): 1176. CrossRef - How to Measure Glycemic Variability? A Literature Review
Sandra Lazar, Ioana Ionita, Delia Reurean-Pintilei, Bogdan Timar
Medicina.2023; 60(1): 61. CrossRef - A New Analysis Tool for Continuous Glucose Monitor Data
Evan Olawsky, Yuan Zhang, Lynn E Eberly, Erika S Helgeson, Lisa S Chow
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2022; 16(6): 1496. CrossRef - Variations in Sleep Characteristics and Glucose Regulation in Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes
Stephanie Griggs, Margaret Grey, Kingman P Strohl, Sybil L Crawford, Seunghee Margevicius, Sangeeta R Kashyap, Chiang-Shan R Li, Sanjay Rajagopalan, Ronald L Hickman
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(3): e1085. CrossRef - Influence of Fasting Plasma Glucose Targets on Glycemic Variability in Chinese Participants With Type 2 Diabetes: A Post Hoc Analysis of the FPG GOAL Trial (BEYOND III)
Ling Li, Tao Yang, Yaoming Xue, Pengfei Ruan, Juan Du, Yunguang Li, Xia Zhang, Nan Cui, Wenying Yang
Advances in Therapy.2022; 39(1): 421. CrossRef - Diet and Physical Activity as Determinants of Continuously Measured Glucose Levels in Persons at High Risk of Type 2 Diabetes
Su Hyun Park, Jiali Yao, Xin Hui Chua, Suresh Rama Chandran, Daphne S. L. Gardner, Chin Meng Khoo, Falk Müller-Riemenschneider, Clare Whitton, Rob M. van Dam
Nutrients.2022; 14(2): 366. CrossRef - Expert Panel Recommendations for Use of Standardized Glucose Reporting System Based on Standardized Glucometrics Plus Visual Ambulatory Glucose Profile (AGP) Data in Clinical Practice
Selcuk Dagdelen, Oguzhan Deyneli, Nevin Dinccag, Hasan Ilkova, Zeynep Osar Siva, Ilhan Yetkin, Temel Yilmaz
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Influence of Glucose Fluctuation on Peripheral Nerve Damage in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Rats
Yu Ji Kim, Na Young Lee, Kyung Ae Lee, Tae Sun Park, Heung Yong Jin
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 117. CrossRef - Effects of Teneligliptin on HbA1c levels, Continuous Glucose Monitoring-Derived Time in Range and Glycemic Variability in Elderly Patients with T2DM (TEDDY Study)
Ji Cheol Bae, Soo Heon Kwak, Hyun Jin Kim, Sang-Yong Kim, You-Cheol Hwang, Sunghwan Suh, Bok Jin Hyun, Ji Eun Cha, Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 81. CrossRef - Glycemic variability and other risk factors for diabetic retinopathy: A pilot case-control study
AmrutaS Kulkarni, KarakkattuV Kavitha, NikitaS Sarkar, VedavatiB Purandare, Savita Bhat, Shalbha Tiwari, AmbikaG Unnikrishnan
Chronicle of Diabetes Research and Practice.2022; 1(1): 14. CrossRef - Association between Variability of Metabolic Risk Factors and Cardiometabolic Outcomes
Min Jeong Park, Kyung Mook Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(1): 49. CrossRef - Intraoperative Glycemic Variability and Mean Glucose are Predictors for Postoperative Delirium After Cardiac Surgery: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Hoon Choi, Chul Soo Park, Jaewon Huh, Jungmin Koo, Joonpyo Jeon, Eunsung Kim, Sangmin Jung, Hwan Wook Kim, Ju Yong Lim, Wonjung Hwang
Clinical Interventions in Aging.2022; Volume 17: 79. CrossRef - The Impact and Clinical Prediction of Hyperglycemia During Parenteral Nutrition for Nondiabetic Patients After Gastrectomy for Gastric Cancer
Ning Lan, Xiaohua Chen, Ying Lu, Yujie Zhou, Fei Kong, Yining Zhao, Fuzhi Jiao, Lin Zhang, Wenzhen Yuan
Frontiers in Nutrition.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - High glycemic variability: An underestimated determinant of stroke functional outcome following large vessel occlusion
J. Baudu, E. Gerbaud, B. Catargi, M. Montaudon, M.-C. Beauvieux, S. Sagnier, S. Debruxelles, P. Renou, M. Poli, S. Olindo, M. Couture, G. Marnat, I. Sibon
Revue Neurologique.2022; 178(7): 732. CrossRef - Glycaemic Variability and Hyperglycaemia as Prognostic Markers of Major Cardiovascular Events in Diabetic Patients Hospitalised in Cardiology Intensive Care Unit for Acute Heart Failure
Edouard Gerbaud, Ambroise Bouchard de La Poterie, Thomas Baudinet, Michel Montaudon, Marie-Christine Beauvieux, Anne-Iris Lemaître, Laura Cetran, Benjamin Seguy, François Picard, Fritz-Line Vélayoudom, Alexandre Ouattara, Rémi Kabore, Pierre Coste, Pierre
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2022; 11(6): 1549. CrossRef - The Emerging Role of Continuous Glucose Monitoring in the Management of Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy: A Narrative Review
Evanthia Gouveri, Nikolaos Papanas
Diabetes Therapy.2022; 13(5): 931. CrossRef - Objective Sleep-Wake Characteristics Are Associated With Diabetes Symptoms in Young Adults With Type 1 Diabetes
Stephanie Griggs, Margaret Grey, Garrett I. Ash, Chiang-shan R. Li, Sybil L. Crawford, Ronald L. Hickman
The Science of Diabetes Self-Management and Care.2022; 48(3): 149. CrossRef - The Reproducibility and Usefulness of Estimated Average Glucose for Hyperglycemia Management during Health Checkups: A Retrospective Cross-Sectional Study
Eun-Hee Nah, Seon Cho, Hyeran Park, Dongwon Noh, Eunjoo Kwon, Han-Ik Cho
Healthcare.2022; 10(5): 824. CrossRef - Effects of a Novel Blood Glucose Forecasting Feature on Glycemic Management and Logging in Adults With Type 2 Diabetes Using One Drop: Retrospective Cohort Study
Steven D Imrisek, Matthew Lee, Dan Goldner, Harpreet Nagra, Lindsey M Lavaysse, Jamillah Hoy-Rosas, Jeff Dachis, Lindsay E Sears
JMIR Diabetes.2022; 7(2): e34624. CrossRef - Glucose variability is associated with an adverse vascular profile but only in the presence of insulin resistance in individuals with type 1 diabetes: An observational study
Noppadol Kietsiriroje, Sam M Pearson, Lauren L O’Mahoney, Daniel J West, Robert AS Ariëns, Ramzi A Ajjan, Matthew D Campbell
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2022; 19(3): 147916412211032. CrossRef - Hypoglycemic agents and glycemic variability in individuals with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and network meta-analysis
SuA Oh, Sujata Purja, Hocheol Shin, Minji Kim, Eunyoung Kim
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2022; 19(3): 147916412211068. CrossRef - Helpful or harmful? The impact of the ketogenic diet on eating disorder outcomes in type 1 diabetes mellitus
Suzanne Schneider, Deborah L Biggerstaff, Thomas M Barber
Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 17(4): 319. CrossRef - Feline Comorbidities: Clinical perspective on diabetes mellitus and pancreatitis
Panagiotis G Xenoulis, Federico Fracassi
Journal of Feline Medicine and Surgery.2022; 24(7): 651. CrossRef - Intralymphatic GAD-Alum (Diamyd®) Improves Glycemic Control in Type 1 Diabetes With HLA DR3-DQ2
Christoph Nowak, Marcus Lind, Zdenek Sumnik, Terezie Pelikanova, Lía Nattero-Chavez, Elena Lundberg, Itxaso Rica, Maria A Martínez-Brocca, MariSol Ruiz de Adana, Jeanette Wahlberg, Ragnar Hanas, Cristina Hernandez, Maria Clemente-León, Ana Gómez-Gila, Mar
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2022; 107(9): 2644. CrossRef - Serum Glucose Variability Increases the Risk of Complications Following Aseptic Revision Hip and Knee Arthroplasty
Graham S. Goh, Noam Shohat, Mohammad S. Abdelaal, Ilan Small, Terence Thomas, Kerri-Anne Ciesielka, Javad Parvizi
Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery.2022; 104(18): 1614. CrossRef - Glycemic Variability in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Pregnancies—Novel Parameters in Predicting Large-for-Gestational-Age Neonates: A Prospective Cohort Study
Gloria Leksic, Maja Baretić, Lara Gudelj, Marija Radic, Iva Milicic, Marina Ivanišević, Dubravka Jurisic-Erzen
Biomedicines.2022; 10(9): 2175. CrossRef - Nomogram for prediction of diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A retrospective study
Hongyan Yang, Miao Xia, Zanchao Liu, Yuwei Xing, Weili Zhao, Yang Li, Minzhen Wang, Zengyi Zhao
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2022; 36(11): 108313. CrossRef - Menopause is associated with postprandial metabolism, metabolic health and lifestyle: The ZOE PREDICT study
Kate M. Bermingham, Inbar Linenberg, Wendy L. Hall, Kirstin Kadé, Paul W. Franks, Richard Davies, Jonathan Wolf, George Hadjigeorgiou, Francesco Asnicar, Nicola Segata, JoAnn E. Manson, Louise R. Newson, Linda M. Delahanty, Jose M. Ordovas, Andrew T. Chan
eBioMedicine.2022; 85: 104303. CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring for detection of glycemic variability, hypoglycemia, and hyperglycemia in women with eating disorders
Nao Uotani, Shun’ichi Noma, Momoko Akamine, Takashi Miyawaki
BioPsychoSocial Medicine.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Mining associations between glycemic variability in awake-time and in-sleep among non-diabetic adults
Zilu Liang
Frontiers in Medical Technology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Dynamic circadian fluctuations of glycemia in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Manuel Vásquez-Muñoz, Alexis Arce-Álvarez, Cristian Álvarez, Rodrigo Ramírez-Campillo, Fernando A. Crespo, Dayana Arias, Camila Salazar-Ardiles, Mikel Izquierdo, David C. Andrade
Biological Research.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Menopause Is Associated With Postprandial Metabolism, Metabolic Health and Lifestyle: The ZOE PREDICT Study
Kate Bermingham, Inbar Linenberg, Wendy L. Hall, Kirstin Kadé, Paul Franks, Richard Davies, Jonathan Wolf, Francesco Asnicar, Nicola Segata, JoAnn E. Manson, Louise Newson, Linda M. Delahanty, Jose Ordovas, Andrew T. Chan, Tim D. Spector, Ana Valdes, Sara
SSRN Electronic Journal .2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring-assisted insulin dose titration in the Indian outpatient setting
SriRamya Ganti, KalyanChakravarthy Gurazada
International Journal of Diabetes and Technology.2022; 1(2): 75. CrossRef - Effectiveness of blood glucose control protocol for open heart surgery patients
Hye Jin Yoo, Eunyoung E. Suh, JaeLan Shim
Journal of Advanced Nursing.2021; 77(1): 275. CrossRef - Effect of Dapagliflozin as an Add-on Therapy to Insulin on the Glycemic Variability in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus (DIVE): A Multicenter, Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind, Randomized Study
Seung-Hwan Lee, Kyung-Wan Min, Byung-Wan Lee, In-Kyung Jeong, Soon-Jib Yoo, Hyuk-Sang Kwon, Yoon-Hee Choi, Kun-Ho Yoon
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2021; 45(3): 339. CrossRef - Comparison of Glycemic Excursion Using Flash Continuous Glucose Monitoring in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Before and After Treatment with Voglibose
Selvam Kasthuri, Subramani Poongothai, Ranjit Mohan Anjana, Jayvel Selvakumar, Subramaniam Muthukumar, Sengottuevel Kayalvizhi, Syed Tariq, Evangelin Honey, Prasanna Kumar Gupta, Ulagamathesan Venkatesan, Viswanathan Mohan
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2021; 23(3): 213. CrossRef - Comparison of CGM-Derived Measures of Glycemic Variability Between Pancreatogenic Diabetes and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Channabasappa Shivaprasad, Yalamanchi Aiswarya, Shah Kejal, Atluri Sridevi, Biswas Anupam, Barure Ramdas, Kolla Gautham, Premchander Aarudhra
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2021; 15(1): 134. CrossRef - Spousal Influence on Diabetes Self-care: Moderating Effects of Distress and Relationship Quality on Glycemic Control
Emily C Soriano, James M Lenhard, Jeffrey S Gonzalez, Howard Tennen, Sy-Miin Chow, Amy K Otto, Christine Perndorfer, Biing-Jiun Shen, Scott D Siegel, Jean-Philippe Laurenceau
Annals of Behavioral Medicine.2021; 55(2): 123. CrossRef - Effects of structured Aerobic Exercise on selected clinical profiles of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review with meta-analysis
NmachukwuIfeoma Ekechukwu, StellaUdumma Anwara, UkamakaGloria Mgbeojedo, OliveU Chijioke, OkechukwuSteven Onwukwe, UchechukwuAnthonia Ezugwu, EchezonaNelson Dominic Ekechukwu, IjeomaL Okoronkwo
International Journal of Medicine and Health Development.2021; 26(1): 17. CrossRef - New Innovation: Use of Flash Glucose Monitoring for Evaluating Glycaemic Variability, Patient Satisfaction and Clinical Utility in Pregnant Women with Diabetes
Saxena Pikee, Kumari Khushbu, Prakash Anupam, Puri Manju, Jain Sachin
The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India.2021; 71(2): 136. CrossRef - Comprehensive elaboration of glycemic variability in diabetic macrovascular and microvascular complications
Bao Sun, Zhiying Luo, Jiecan Zhou
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Added and Interpretative Value of CGM-Derived Parameters in Type 1 Diabetes Depends on the Level of Glycemic Control
Simon Helleputte, Tine De Backer, Patrick Calders, Bart Pauwels, Samyah Shadid, Bruno Lapauw
Endocrine Practice.2021; 27(1): 44. CrossRef - Short-term glycemic variability and hemorrhagic transformation after successful endovascular thrombectomy
Tae Jung Kim, Ji Sung Lee, Soo-Hyun Park, Sang-Bae Ko
Translational Stroke Research.2021; 12(6): 968. CrossRef - The relationship between glycemic variability and blood pressure variability in normoglycemic normotensive individuals
Havva Sezer, Dilek Yazici, Sidar Copur, Tuncay Dagel, Oguzhan Deyneli, Mehmet Kanbay
Blood Pressure Monitoring.2021; 26(2): 102. CrossRef - Current concepts and clinical importance of glycemic variability
Ramya Ravi, V Balasubramaniam, Gowthamarajan Kuppusamy, Sivasankaran Ponnusankar
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2021; 15(2): 627. CrossRef - Oscillatory pattern of glycemic control in patients with diabetes mellitus
Manuel Vasquez-Muñoz, Alexis Arce-Alvarez, Magdalena von Igel, Carlos Veliz, Gonzalo Ruiz-Esquide, Rodrigo Ramirez-Campillo, Cristian Alvarez, Robinson Ramirez-Velez, Fernando A. Crespo, Mikel Izquierdo, Rodrigo Del Rio, David C. Andrade
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparing the Efficacies of Telemedicine and Standard Prenatal Care on Blood Glucose Control in Women With Gestational Diabetes Mellitus: Randomized Controlled Trial
Ying Tian, Suhan Zhang, Feiling Huang, Liangkun Ma
JMIR mHealth and uHealth.2021; 9(5): e22881. CrossRef - Interpreting blood GLUcose data with R package iglu
Steven Broll, Jacek Urbanek, David Buchanan, Elizabeth Chun, John Muschelli, Naresh M. Punjabi, Irina Gaynanova, Laura Pyle
PLOS ONE.2021; 16(4): e0248560. CrossRef - Weight fluctuation and risk of hepatocellular carcinoma: a nationwide population-based 8-million-subject study
Young Chang, Jeong-Ju Yoo, Eun Ju Cho, Kyungdo Han, Dahye Kim, Bo-Yeon Kim, Goh Eun Chung, Yuri Cho, Dong Wook Shin, Su Jong Yu
Hepatology International.2021; 15(2): 482. CrossRef - Glucose variability predicts 6-month mortality in patients hospitalized with acute heart failure
Filipe M. Cunha, Catarina Cidade-Rodrigues, Catarina Elias, Diana Oliveira, Paulo Bettencourt, Patrícia Lourenço
Internal and Emergency Medicine.2021; 16(8): 2121. CrossRef - Glucose Variability and Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients with Diabetes: A Nationwide Population-Based Study
Jeong-Ju Yoo, Eun Ju Cho, Kyungdo Han, Soo Seong Heo, Bo-Yeon Kim, Dong Wook Shin, Su Jong Yu
Cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention.2021; 30(5): 974. CrossRef - Sleep-wake characteristics, daytime sleepiness, and glycemia in young adults with type 1 diabetes
Stephanie Griggs, Ronald L. Hickman, Kingman P. Strohl, Nancy S. Redeker, Sybil L. Crawford, Margaret Grey
Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine.2021; 17(9): 1865. CrossRef - Glycemic Variability in Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus Saudis Using Ambulatory Glucose Profile
Bader Alzahrani, Saad Alzahrani, Mussa H Almalki, Souha S Elabd, Shawana Abdulhamid Khan, Badurudeen Buhary, Naji Aljuhani, Anwar A Jammah
Clinical Medicine Insights: Endocrinology and Diabetes.2021; 14: 117955142110137. CrossRef - Effect of glucose concentration and culture substrate on HUVECs viability in in vitro cultures: A literature review and own results
Anna Ciechanowska, Ilona Gora, Stanislawa Sabalinska, Piotr Foltynski, Piotr Ladyzynski
Biocybernetics and Biomedical Engineering.2021; 41(4): 1390. CrossRef - Probabilistic Model of Transition between Categories of Glucose Profiles in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Using a Compositional Data Analysis Approach
Lyvia Biagi, Arthur Bertachi, Marga Giménez, Ignacio Conget, Jorge Bondia, Josep Antoni Martín-Fernández, Josep Vehí
Sensors.2021; 21(11): 3593. CrossRef - Engineering digital biomarkers of interstitial glucose from noninvasive smartwatches
Brinnae Bent, Peter J. Cho, Maria Henriquez, April Wittmann, Connie Thacker, Mark Feinglos, Matthew J. Crowley, Jessilyn P. Dunn
npj Digital Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Non-invasive wearables for remote monitoring of HbA1c and glucose variability: proof of concept
Brinnae Bent, Peter J Cho, April Wittmann, Connie Thacker, Srikanth Muppidi, Michael Snyder, Matthew J Crowley, Mark Feinglos, Jessilyn P Dunn
BMJ Open Diabetes Research & Care.2021; 9(1): e002027. CrossRef - Circadian characteristics of the rest-activity rhythm, executive function, and glucose fluctuations in young adults with type 1 diabetes
Stephanie Griggs, Kingman P. Strohl, Margaret Grey, Eric Barbato, Seunghee Margevicius, Ronald L. Hickman
Chronobiology International.2021; 38(10): 1477. CrossRef - Glucose forecasting using genetic programming and latent glucose variability features
Sergio Contador, J. Manuel Velasco, Oscar Garnica, J. Ignacio Hidalgo
Applied Soft Computing.2021; 110: 107609. CrossRef - On the efficacy of behavior change techniques in mHealth for self-management of diabetes: A meta-analysis
Omar El-Gayar, Martinson Ofori, Nevine Nawar
Journal of Biomedical Informatics.2021; 119: 103839. CrossRef - Daytime Glycemic Variability and Frailty in Older Patients with Diabetes: a Pilot Study Using Continuous Glucose Monitoring
Seung Min Chung, Yun Hee Lee, Chang Oh Kim, Ji Yeon Lee, Sang-Man Jin, Seung-Hyun Yoo, Jun Sung Moon, Kwang Joon Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Glucose Patterns in Very Old Adults: A Pilot Study in a Community-Based Population
Elizabeth Selvin, Dan Wang, Olive Tang, Melissa Minotti, Justin B. Echouffo-Tcheugui, Josef Coresh
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Uma Visão Bioquímica Dos Exames Laboratoriais Prévios Para Iniciantes Na Prática De Corrida De Forma Recreativa E A Importância De Realizá-Los
João Henrique Pereira De Oliveira
Revista Científica Multidisciplinar Núcleo do Conhecimento.2021; : 81. CrossRef - Retrospective study of glycemic variability, BMI, and blood pressure in diabetes patients in the Digital Twin Precision Treatment Program
Paramesh Shamanna, Mala Dharmalingam, Rakesh Sahay, Jahangir Mohammed, Maluk Mohamed, Terrence Poon, Nathan Kleinman, Mohamed Thajudeen
Scientific Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The role of T‐cell immunity in COVID‐19 severity amongst people living with type II diabetes
Zhen Wei Marcus Tong, Emma Grant, Stephanie Gras, Melanie Wu, Corey Smith, Helen L. Barrett, Linda A. Gallo, Kirsty R. Short
The FEBS Journal.2021; 288(17): 5042. CrossRef - The Role of Glycemic Variability in Cardiovascular Disorders
Valentina Alfieri, Veronika A. Myasoedova, Maria Cristina Vinci, Maurizio Rondinelli, Paola Songia, Ilaria Massaiu, Nicola Cosentino, Donato Moschetta, Vincenza Valerio, Michele Ciccarelli, Giancarlo Marenzi, Stefano Genovese, Paolo Poggio
International Journal of Molecular Sciences.2021; 22(16): 8393. CrossRef - Impact of tacrolimus variability on pediatric heart transplant outcomes
Megan Sirota, Caroline Heyrend, Zhining Ou, Susan Masotti, Eric Griffiths, Kimberly Molina
Pediatric Transplantation.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of glycemic variability and factors associated with the glycemic arrays among end-stage kidney disease patients on chronic hemodialysis
Abdul Hanif Khan Yusof Khan, Nor Fadhlina Zakaria, Muhammad Adil Zainal Abidin, Nor Azmi Kamaruddin
Medicine.2021; 100(30): e26729. CrossRef - Efficacy of Ketogenic Diets on Type 2 Diabetes: a Systematic Review
Delphine Tinguely, Justine Gross, Christophe Kosinski
Current Diabetes Reports.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Glucose variability and low bone turnover in people with type 2 diabetes
Jakob Starup-Linde, Simon Lykkeboe, Aase Handberg, Peter Vestergaard, Pernille Høyem, Jesper Fleischer, Troels Krarup Hansen, Per Løgstrup Poulsen, Esben Laugesen
Bone.2021; 153: 116159. CrossRef - Use of continuous glucose monitoring in obesity research: A scoping review
Elizabeth Hegedus, Sarah-Jeanne Salvy, Choo Phei Wee, Monica Naguib, Jennifer K. Raymond, D. Steven Fox, Alaina P. Vidmar
Obesity Research & Clinical Practice.2021; 15(5): 431. CrossRef - The Association Between Mean Glycated Haemoglobin or Glycaemic Variability and the Development of Retinopathy in People with Diabetes: A Retrospective Observational Cohort Study
Ketan Dhatariya, Alexander Humberstone, Abul Hasnat, Rebecca Wright, Morgan Lujan, Ian Nunney
Diabetes Therapy.2021; 12(10): 2755. CrossRef - Improved Glycemic Control and Variability: Application of Healthy Ingredients in Asian Staples
Stefan Gerardus Camps, Bhupinder Kaur, Joseph Lim, Yi Ting Loo, Eunice Pang, Terence Ng, Christiani Jeyakumar Henry
Nutrients.2021; 13(9): 3102. CrossRef - Glycemic Variability Impacted by SGLT2 Inhibitors and GLP 1 Agonists in Patients with Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Heeyoung Lee, Se-eun Park, Eun-Young Kim
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2021; 10(18): 4078. CrossRef - Glycemic variability of acute stroke patients and clinical outcomes: a continuous glucose monitoring study
Lina Palaiodimou, Vasileios-Arsenios Lioutas, Vaia Lambadiari, Aikaterini Theodorou, Marios Themistocleous, Laura Aponte, Georgia Papagiannopoulou, Aikaterini Foska, Eleni Bakola, Rodrigo Quispe, Laura Mendez, Magdy Selim, Vera Novak, Elias Tzavellas, Pan
Therapeutic Advances in Neurological Disorders.2021; 14: 175628642110458. CrossRef - Glycemic variability: Importance, relationship with physical activity, and the influence of exercise
Joshua R. Sparks, Erin E. Kishman, Mark A. Sarzynski, J. Mark Davis, Peter W. Grandjean, J. Larry Durstine, Xuewen Wang
Sports Medicine and Health Science.2021; 3(4): 183. CrossRef - The Effect of Physical Activity on Glycemic Variability in Patients With Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Xingyun Zhu, Lina Zhao, Jing Chen, Chu Lin, Fang Lv, Suiyuan Hu, Xiaoling Cai, Li Zhang, Linong Ji
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Cgmquantify: Python and R Software Packages for Comprehensive Analysis of Interstitial Glucose and Glycemic Variability from Continuous Glucose Monitor Data
Brinnae Bent, Maria Henriquez, Jessilyn Dunn
IEEE Open Journal of Engineering in Medicine and Biology.2021; 2: 263. CrossRef - In-Hospital Mortality and Glycemic Control in Patients with Hospital Hyperglycemia
María Paula Russo, Santiago Nicolas Marquez Fosser, Cristina María Elizondo, Diego Hernán Giunta, Nora Angélica Fuentes, María Florencia Grande-Ratti
Review of Diabetic Studies.2021; 17(2): 50. CrossRef - Perspectives of glycemic variability in diabetic neuropathy: a comprehensive review
Xiaochun Zhang, Xue Yang, Bao Sun, Chunsheng Zhu
Communications Biology.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between Intra-Hospital Uncontrolled Glycemia and Health Outcomes in Patients with Diabetes: A Systematic Review of Observational Studies
Renata Cunha Carvalho, Fernanda Ayache Nishi, Tatiane Bomfim Ribeiro, Gustavo Galvão França, Patricia Melo Aguiar
Current Diabetes Reviews.2021; 17(3): 304. CrossRef - Glycaemic Variability Heavily Affects Outcomes of Diabetic Patients Hospitalized for Acute Heart Failure
Edouard Gerbaud, Ambroise Bouchard de la Poterie, Thomas Baudinet, Michel Montaudon, Marie-Christine Beauvieux, Anne-Iris Lemaître, Laura Cetran, Benjamin Seguy, Francois Picard, Fritz-Line Vélayoudom, Alexandre Ouattara, Rémi Kabore, Pierre Coste, Pierre
SSRN Electronic Journal .2021;[Epub] CrossRef - GLU: a software package for analysing continuously measured glucose levels in epidemiology
Louise A C Millard, Nashita Patel, Kate Tilling, Melanie Lewcock, Peter A Flach, Debbie A Lawlor
International Journal of Epidemiology.2020; 49(3): 744. CrossRef - Glycemic variability and subsequent malignancies among the population without diabetes
Daiki Kobayashi, Hiroshi Noto, Osamu Takahashi, Takuro Shimbo
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 159: 107987. CrossRef - The relationship between glycaemic variability and cardiovascular autonomic dysfunction in patients with type 1 diabetes: A systematic review
Simon Helleputte, Tine De Backer, Bruno Lapauw, Samyah Shadid, Bert Celie, Birgit Van Eetvelde, Karsten Vanden Wyngaert, Patrick Calders
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Actualización sobre hiperglucemia posprandial: fisiopatología, prevalencia, consecuencias e implicaciones para el tratamiento de la diabetes
P.J. Pinés Corrales, V. Bellido Castañeda, F.J. Ampudia-Blasco
Revista Clínica Española.2020; 220(1): 57. CrossRef - Sleep, self‐management, neurocognitive function, and glycemia in emerging adults with Type 1 diabetes mellitus: A research protocol
Stephanie Griggs, Nancy S. Redeker, Sybil L. Crawford, Margaret Grey
Research in Nursing & Health.2020; 43(4): 317. CrossRef - GLP 1 receptor agonists, glycemic variability, oxidative stress and acute coronary syndrome
Maria Isabel del Olmo García, Juan Francisco Merino-Torres
Medical Hypotheses.2020; 136: 109504. CrossRef - Risk factors for hospitalization in youth with type 1 diabetes: Development and validation of a multivariable prediction model
Juan D Mejia‐Otero, Soumya Adhikari, Perrin C White
Pediatric Diabetes.2020; 21(7): 1268. CrossRef - Acute and Chronic Effects of Exercise on Continuous Glucose Monitoring Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes: A Meta-Analysis
Matthew Munan, Camila L. P. Oliveira, Alexis Marcotte-Chénard, Jordan L. Rees, Carla M. Prado, Eléonor Riesco, Normand G. Boulé
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Age‐specific associations of glycated haemoglobin variability with cardiovascular disease and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A 10‐ year cohort study
Eric Yuk Fai Wan, Esther Yee Tak Yu, Weng Yee Chin, Florence Ting Yan Ng, Shu Ming Cheryl Chia, Ian Chi Kei Wong, Esther Wai Yin Chan, Cindy Lo Kuen Lam
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(8): 1316. CrossRef - Comparison of Glycemic Variability Indices: Blood Glucose, Risk Index, and Coefficient of Variation in Predicting Adverse Outcomes for Patients Undergoing Cardiac Surgery
Valluvan Rangasamy, Xinling Xu, Ammu Thampi Susheela, Balachundhar Subramaniam
Journal of Cardiothoracic and Vascular Anesthesia.2020; 34(7): 1794. CrossRef - Low Blood Glucose Index and Hypoglycaemia Risk: Insulin Glargine 300 U/mL Versus Insulin Glargine 100 U/mL in Type 2 Diabetes
Boris Kovatchev, Zhaoling Meng, Anna M. G. Cali, Riccardo Perfetti, Marc D. Breton
Diabetes Therapy.2020; 11(6): 1293. CrossRef - Non-Dietary Factors Associated with Glycemic Status among Adults Diagnosed with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Malawi
Getrude Mphwanthe, Dave Weatherspoon, Alexander Kalimbira, Lorraine Weatherspoon
Social Work in Public Health.2020; 35(6): 380. CrossRef - Glycaemic profile in the second and third trimesters of normal pregnancy compared to non-pregnant adult females
Aruna Nigam, Neha Varun, Sumedha Sharma, YP Munjal, Anupam Prakash
Obstetric Medicine.2020; 13(1): 30. CrossRef - The Effect of Acarbose on Glycemic Variability in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Using Premixed Insulin Compared to Metformin (AIM): An Open-Label Randomized Trial
Fei Gao, Xiaojing Ma, Jiahui Peng, Jingyi Lu, Wei Lu, Wei Zhu, Yuqian Bao, Robert A. Vigersky, Weiping Jia, Jian Zhou
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2020; 22(4): 256. CrossRef - Circulating Wnt1-inducible signaling pathway protein-1 (WISP-1/CCN4) is a novel biomarker of adiposity in subjects with type 2 diabetes
Vadim V. Klimontov, Dinara M. Bulumbaeva, Olga N. Fazullina, Alexander P. Lykov, Natalia P. Bgatova, Nikolay B. Orlov, Vladimir I. Konenkov, Andreas F.H. Pfeiffer, Olga Pivovarova-Ramich, Natalia Rudovich
Journal of Cell Communication and Signaling.2020; 14(1): 101. CrossRef - Glycemic variability in newly diagnosed diabetic cats treated with the glucagon‐like peptide‐1 analogue exenatide extended release
Anna L. Krämer, Angelina Riederer, Federico Fracassi, Felicitas S. Boretti, Nadja S. Sieber‐Ruckstuhl, Thomas A. Lutz, Barbara Contiero, Eric Zini, Claudia E. Reusch
Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine.2020; 34(6): 2287. CrossRef - Glycemic variability in type 2 diabetes mellitus and acute coronary syndrome: liraglutide compared with insulin glargine: a pilot study
Maria Isabel del Olmo-García, David Hervás Marín, Jana Caudet Esteban, Antonio Ballesteros Martin-Portugués, Alba Cerveró Rubio, Miguel Angel Arnau Vives, Ana Catalá Gregori, Maite Penalba Martínez, Juan Francisco Merino-Torres
Journal of International Medical Research.2020; 48(6): 030006052092606. CrossRef - Capturing glucose variability in patients with diabetes
David Laight
Prescriber.2020; 31(9): 20. CrossRef - Diabetes of the Exocrine Pancreas Related to Hereditary Pancreatitis, an Update
Gabriel Xavier Ramalho, Marcio Garrison Dytz
Current Diabetes Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Robust estimation of the effect of an exposure on the change in a continuous outcome
Yilin Ning, Nathalie C. Støer, Peh Joo Ho, Shih Ling Kao, Kee Yuan Ngiam, Eric Yin Hao Khoo, Soo Chin Lee, E-Shyong Tai, Mikael Hartman, Marie Reilly, Chuen Seng Tan
BMC Medical Research Methodology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Comparison of the effects of gemigliptin and dapagliflozin on glycaemic variability in type 2 diabetes: A randomized, open‐label, active‐controlled, 12‐week study (STABLE II study)
Soo Heon Kwak, You‐Cheol Hwang, Jong Chul Won, Ji Cheol Bae, Hyun Jin Kim, Sunghwan Suh, Eun Young Lee, Subin Lee, Sang‐Yong Kim, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2020; 22(2): 173. CrossRef - Acarbose-metformin is more effective in glycemic variability control than repaglinide-metformin in T2DM patients inadequately controlled with metformin: a retrospective cohort study
Guoli Du, Wanrun Xie, Yinxia Su, Yao Ma, Xiaoming Gao, Sheng Jiang, Huazheng Liang
PeerJ.2020; 8: e9905. CrossRef - Association between sleep disturbances, fear of hypoglycemia and psychological well-being in adults with type 1 diabetes mellitus, data from cross-sectional VARDIA study
Valentine Suteau, Pierre-Jean Saulnier, Matthieu Wargny, Linda Gonder-Frederick, Elise Gand, Lucy Chaillous, Ingrid Allix, Séverine Dubois, Fabrice Bonnet, Anne-Marie Leguerrier, Gerard Fradet, Ingrid Delcourt Crespin, Véronique Kerlan, Didier Gouet, Caro
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2020; 160: 107988. CrossRef - Update on postprandial hyperglycemia: The pathophysiology, prevalence, consequences and implications of treating diabetes
P.J. Pinés Corrales, V. Bellido Castañeda, F.J. Ampudia-Blasco
Revista Clínica Española (English Edition).2020; 220(1): 57. CrossRef - How tightly controlled do fluctuations in blood glucose levels need to be to reduce the risk of developing complications in people with Type 1 diabetes?
R. Livingstone, J. G. Boyle, J. R. Petrie
Diabetic Medicine.2020; 37(4): 513. CrossRef - In-Silico Evaluation of Glucose Regulation Using Policy Gradient Reinforcement Learning for Patients with Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Jonas Nordhaug Myhre, Miguel Tejedor, Ilkka Kalervo Launonen, Anas El Fathi, Fred Godtliebsen
Applied Sciences.2020; 10(18): 6350. CrossRef - Association of Glycemic Indices (Hyperglycemia, Glucose Variability, and Hypoglycemia) with Oxidative Stress and Diabetic Complications
Eleftheria Papachristoforou, Vaia Lambadiari, Eirini Maratou, Konstantinos Makrilakis, Celestino Sardu
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Simple Linear Support Vector Machine Classifier Can Distinguish Impaired Glucose Tolerance Versus Type 2 Diabetes Using a Reduced Set of CGM-Based Glycemic Variability Indices
Enrico Longato, Giada Acciaroli, Andrea Facchinetti, Alberto Maran, Giovanni Sparacino
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2020; 14(2): 297. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of trelagliptin in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes with severe renal impairment or end‐stage renal disease: Results from a randomized, phase 3 study
Kohei Kaku, Kazuyuki Ishida, Kohei Shimizu, Meguru Achira, Yuusuke Umeda
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2020; 11(2): 373. CrossRef - Finding the clinical utility of 1,5-anhydroglucitol among primary care practitioners
John Peabody, David Paculdo, M. Czarina Acelajado, Trever Burgon, Jeffrey R. Dahlen
Journal of Clinical & Translational Endocrinology.2020; 20: 100224. CrossRef - Effects of Exercise on Blood Glucose and Glycemic Variability in Type 2 Diabetic Patients with Dawn Phenomenon
Xin Zheng, Yanyan Qi, Lina Bi, Wenli Shi, Yan Zhang, Dan Zhao, Su Hu, Meixin Li, Qin Li
BioMed Research International.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Effects of Cardiovascular Risk Factor Variability on Health Outcomes
Seung-Hwan Lee, Mee Kyoung Kim, Eun-Jung Rhee
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 217. CrossRef - Increased Preoperative Glucose Variability Is Associated with Adverse Perioperative Outcomes Following Orthopedic Surgery in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Si-jie Yuan, Jie Shen
Current Medical Science.2020; 40(3): 523. CrossRef - Clinically Accurate Prediction of Glucose Levels in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes
Yotam Amar, Smadar Shilo, Tal Oron, Eran Amar, Moshe Phillip, Eran Segal
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2020; 22(8): 562. CrossRef - Higher glycemic variability within the first day of ICU admission is associated with increased 30-day mortality in ICU patients with sepsis
Wen-Cheng Chao, Chien-Hua Tseng, Chieh-Liang Wu, Sou-Jen Shih, Chi-Yuan Yi, Ming-Cheng Chan
Annals of Intensive Care.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of Glucose Fluctuation Targeted Intervention on the Prognosis of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes following the First Episode of Cerebral Infarction
Qingqing Lou, Xiaodan Yuan, Shujie Hao, Joshua D. Miller, Juan Yan, Panpan Zuo, Jianing Li, Lihong Yang, Hong Li
Journal of Diabetes Research.2020; 2020: 1. CrossRef - Rationale and design of the LIBERATES trial: Protocol for a randomised controlled trial of flash glucose monitoring for optimisation of glycaemia in individuals with type 2 diabetes and recent myocardial infarction
Colin C Everett, Catherine Reynolds, Catherine Fernandez, Deborah D Stocken, Linda D Sharples, Thozhukat Sathyapalan, Simon Heller, Robert F Storey, Ramzi A Ajjan
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2020; 17(5): 147916412095793. CrossRef - Comparison between a flash glucose monitoring system and a portable blood glucose meter for monitoring dogs with diabetes mellitus
Francesca Del Baldo, Claudia Canton, Silvia Testa, Harry Swales, Ignazio Drudi, Stefania Golinelli, Federico Fracassi
Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine.2020; 34(6): 2296. CrossRef - Effect of Variability in Blood Pressure, Glucose and Cholesterol Concentrations, and Body Weight on Emergency Hospitalization and 30‐Day Mortality in the General Population
Seung‐Hwan Lee, Kyungdo Han, Hyuk‐Sang Kwon, Kun‐Ho Yoon, Mee Kyoung Kim
Journal of the American Heart Association.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Accumulating Physical Activity in Short or Brief Bouts for Glycemic Control in Adults With Prediabetes and Diabetes
Courtney R. Chang, Brooke M. Russell, Paddy C. Dempsey, Hannah E. Christie, Matthew D. Campbell, Monique E. Francois
Canadian Journal of Diabetes.2020; 44(8): 759. CrossRef - Time in Range from Continuous Glucose Monitoring: A Novel Metric for Glycemic Control
Jee Hee Yoo, Jae Hyeon Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2020; 44(6): 828. CrossRef - Flash glucose monitoring in diabetic dogs: a feasible method for evaluating glycemic control
Florian K. Zeugswetter, Andrea Sellner
Tierärztliche Praxis Ausgabe K: Kleintiere / Heimtiere.2020; 48(05): 330. CrossRef - Letter: Efficacy and Safety of Voglibose Plus Metformin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Randomized Controlled Trial (Diabetes Metab J 2019;43;276-86)
Hannah Seok, Tae Seo Sohn
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 545. CrossRef - Efficacy of Real-Time Continuous Glucose Monitoring to Improve Effects of a Prescriptive Lifestyle Intervention in Type 2 Diabetes: A Pilot Study
Penelope J. Taylor, Campbell H. Thompson, Natalie D. Luscombe-Marsh, Thomas P. Wycherley, Gary Wittert, Grant D. Brinkworth
Diabetes Therapy.2019; 10(2): 509. CrossRef - The mechanisms of glycemic variability accelerate diabetic central neuropathy and diabetic peripheral neuropathy in diabetic rats
Junpeng Yang, Zhigang Zhao, Huijuan Yuan, Xiangxiang Ma, Yakun Li, Huimeng Wang, Xiaojun Ma, Guijun Qin
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2019; 510(1): 35. CrossRef - Assessment of glucose variability in subjects with prediabetes
Nevena Chakarova, Rumyana Dimova, Greta Grozeva, Tsvetalina Tankova
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2019; 151: 56. CrossRef - Phase 1 Study of the Pharmacology of BTI320 Before High‐Glycemic Meals
David R. Luke, Karen Ka Yan Lee, Carl W. Rausch, Camille Cheng
Clinical Pharmacology in Drug Development.2019; 8(3): 395. CrossRef - Design and Prestudy Assessment of a Dashboard for Presenting Self-Collected Health Data of Patients With Diabetes to Clinicians: Iterative Approach and Qualitative Case Study
Alain Giordanengo, Eirik Årsand, Ashenafi Zebene Woldaregay, Meghan Bradway, Astrid Grottland, Gunnar Hartvigsen, Conceição Granja, Torbjørn Torsvik, Anne Helen Hansen
JMIR Diabetes.2019; 4(3): e14002. CrossRef - Early dysglycemia and mortality in traumatic brain injury and subarachnoid hemorrhage
Simone Pappacena, Michael Bailey, Luca Cabrini, Giovanni Landoni, Andrew Udy, David V. Pilcher, Paul Young, Rinaldo Bellomo
Minerva Anestesiologica.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - The state of variability: A vision for descriptors of glycaemia
Tony Zhou, Jennifer L. Knopp, J. Geoffrey Chase
Annual Reviews in Control.2019; 48: 472. CrossRef - Variability in Glycated Hemoglobin and Risk of Poor Outcomes Among People With Type 2 Diabetes in a Large Primary Care Cohort Study
Julia A. Critchley, Iain M. Carey, Tess Harris, Stephen DeWilde, Derek G. Cook
Diabetes Care.2019; 42(12): 2237. CrossRef - Efficacy and safety of a morning injection of insulin glargine 300 units/mL versus insulin glargine 100 units/mL in adult patients with type 1 diabetes: A multicentre, randomized controlled trial using continuous glucose monitoring
Jeremy Pettus, Jasvinder Gill, Sachin Paranjape, John Stewart, Shilpy Malla, Steven Edelman, Richard M. Bergenstal, Bruce Bode
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2019; 21(8): 1906. CrossRef - Improved outcome of patients with diabetes mellitus with good glycemic control in the cardiac intensive care unit: a retrospective study
Kassem Sharif, Suheil Ghadir, Daniela Jakubowicz, Howard Amital, Nicola Luigi Bragazzi, Abdulla Watad, Julio Wainstein, Yosefa Bar-Dayan
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Short‐term exercise training reduces glycaemic variability and lowers circulating endothelial microparticles in overweight and obese women at elevated risk of type 2 diabetes
Hossein Rafiei, Emily Robinson, Julianne Barry, Mary Elizabeth Jung, Jonathan Peter Little
European Journal of Sport Science.2019; 19(8): 1140. CrossRef - Rapid gastric emptying in diabetes mellitus: Pathophysiology and clinical importance
Raj K. Goyal, Vivian Cristofaro, Maryrose P. Sullivan
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(11): 107414. CrossRef - Fine-Scale Online Evaluation of Glycemic Control Performance Based on Temporal Feature Analysis
Hong Zhao, Chunhui Zhao
Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research.2019; 58(11): 4374. CrossRef - Breakfast replacement with a liquid formula improves glycaemic variability in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomised clinical trial
Jiahui Peng, Jingyi Lu, Xiaojing Ma, Lingwen Ying, Wei Lu, Wei Zhu, Yuqian Bao, Jian Zhou
British Journal of Nutrition.2019; 121(5): 560. CrossRef - Dapagliflozin: A Review in Type 1 Diabetes
Julia Paik, Hannah A. Blair
Drugs.2019; 79(17): 1877. CrossRef - Data-Driven Blood Glucose Pattern Classification and Anomalies Detection: Machine-Learning Applications in Type 1 Diabetes
Ashenafi Zebene Woldaregay, Eirik Årsand, Taxiarchis Botsis, David Albers, Lena Mamykina, Gunnar Hartvigsen
Journal of Medical Internet Research.2019; 21(5): e11030. CrossRef - Quantitative Assessment of Autonomic Regulation of the Cardiac System
Jian Kang Wu, Zhipei Huang, Zhiqiang Zhang, Wendong Xiao, Hong Jiang
Journal of Healthcare Engineering.2019; 2019: 1. CrossRef - Different Types of Physical Activity and Metabolic Control in People With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus
Iztok Štotl, Tim Kambič, Vedran Hadžić, Anže Zdolšek
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - A Randomized Pilot Study of the Effect of Trelagliptin and Alogliptin on Glycemic Variability in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Rimei Nishimura, Takeshi Osonoi, Yasuhiro Koike, Kouji Miyata, Yukio Shimasaki
Advances in Therapy.2019; 36(11): 3096. CrossRef - No association between fear of hypoglycemia and blood glucose variability in type 1 diabetes: The cross-sectional VARDIA study
Pierre Jean Saulnier, Claire Briet, Elise Gand, Lucy Chaillous, Severine Dubois, Fabrice Bonnet, Anne Marie Leguerrier, Gérard Fradet, Ingrid Delcourt Crespin, Veronique Kerlan, Didier Gouet, Caroline Perlemoine, Pierre Henri Ducluzeau, Matthieu Pichelin,
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2019; 33(8): 554. CrossRef - Limited benefit of haemoglobin glycation index as risk factor for cardiovascular disease in type 2 diabetes patients
H.B. Østergaard, T. Mandrup-Poulsen, G.F.N. Berkelmans, Y. van der Graaf, F.L.J. Visseren, J. Westerink
Diabetes & Metabolism.2019; 45(3): 254. CrossRef - Glycemic Variability Is a Powerful Independent Predictive Factor of Midterm Major Adverse Cardiac Events in Patients With Diabetes With Acute Coronary Syndrome
Edouard Gerbaud, Romain Darier, Michel Montaudon, Marie-Christine Beauvieux, Christine Coffin-Boutreux, Pierre Coste, Hervé Douard, Alexandre Ouattara, Bogdan Catargi
Diabetes Care.2019; 42(4): 674. CrossRef - General Assembly, Prevention, Host Risk Mitigation - General Factors: Proceedings of International Consensus on Orthopedic Infections
William Jiranek, James W.M. Kigera, Brian A. Klatt, Fatih Küçükdurmaz, Jay Lieberman, Claus Moser, Kevin Mulhall, Hasan Nahouli, Edward Schwarz, Noam Shohat, Majd Tarabichi
The Journal of Arthroplasty.2019; 34(2): S43. CrossRef - Fenofibrate increases very-long-chain sphingolipids and improves blood glucose homeostasis in NOD mice
Laurits J. Holm, Martin Haupt-Jorgensen, Jano D. Giacobini, Jane P. Hasselby, Mesut Bilgin, Karsten Buschard
Diabetologia.2019; 62(12): 2262. CrossRef - Ghrelin deficiency in patients with type 2 diabetes: the relationships with obesity, adipose tissue dysfunction and glucose variability
V V Klimontov, D M Bulumbaeva, O N Fazullina, N B Orlov, V I Konenkov
Terapevticheskii arkhiv.2019; 91(10): 28. CrossRef - Treatment preference for weekly versus daily DPP-4 inhibitors in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: outcomes from the TRINITY trial
Shu Meguro, Shingo Matsui, Hiroshi Itoh
Current Medical Research and Opinion.2019; 35(12): 2071. CrossRef - Glucose Variables in Type 1 Diabetes Studies With Dapagliflozin: Pooled Analysis of Continuous Glucose Monitoring Data From DEPICT-1 and -2
Chantal Mathieu, Paresh Dandona, Moshe Phillip, Tal Oron, Marcus Lind, Lars Hansen, Fredrik Thorén, John Xu, Anna Maria Langkilde
Diabetes Care.2019; 42(6): 1081. CrossRef - Time in Range: Ein neuer Parameter – komplementär zum HbA 1c
Thomas Danne, Olga Kordonouri, Torben Biester, Thorsten Siegmund, Jens Kröger, Peter Bramlage, Thomas Haak
Deutsches Ärzteblatt Online.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Glucose variability during delirium in diabetic and non-diabetic intensive care unit patients: A prospective cohort study
Kris van Keulen, Wilma Knol, Svetlana V. Belitser, Irene J. Zaal, Paul D. van der Linden, Eibert R. Heerdink, Toine C. G. Egberts, Arjen J. C. Slooter, Noël C. Barengo
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(11): e0205637. CrossRef - Association of various glycemic variability indices and vascular outcomes in type-2 diabetes patients
Lei Tong, Chen Chi, Zhiguo Zhang
Medicine.2018; 97(21): e10860. CrossRef - Glycemic Variability: How to Measure and Its Clinical Implication for Type 2 Diabetes
Guillermo E. Umpierrez, Boris P. Kovatchev
The American Journal of the Medical Sciences.2018; 356(6): 518. CrossRef - Glycemic Variability Percentage: A Novel Method for Assessing Glycemic Variability from Continuous Glucose Monitor Data
Thomas A. Peyser, Andrew K. Balo, Bruce A. Buckingham, Irl B. Hirsch, Arturo Garcia
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2018; 20(1): 6. CrossRef - Impact of Insulin Degludec in Hospitalized Patients With and Without Type 2 Diabetes Requiring Parenteral/Enteral Nutrition: An Observational Study
Giuseppe Fatati, Agnese Di Donato, Ilenia Grandone, Pina Menicocci, Eva Mirri, Giuseppe Prosperini, Marco Scardapane, Maria Chiara Rossi, Mariangela Palazzi
Advances in Therapy.2018; 35(6): 809. CrossRef - Long-lasting Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Analogue Exendin-4 Ameliorates the Secretory and Synthetic Function of Islets Isolated From Severely Scalded Rats
Dongxu Zhao, Li Ma, Chuanan Shen, Dawei Li, Wenfeng Cheng, Yuru Shang, Zhaoxing Liu, Xin Wang, Kai Yin
Journal of Burn Care & Research.2018; 39(4): 545. CrossRef - Social support effects on diabetes management by South African emerging adults: A replication and extension study
Elné Visagie, Esmé van Rensburg, Elmarí Deacon
Journal of Psychology in Africa.2018; 28(6): 504. CrossRef - All Patients Should Be Screened for Diabetes Before Total Joint Arthroplasty
Noam Shohat, Karan Goswami, Majd Tarabichi, Emily Sterbis, Timothy L. Tan, Javad Parvizi
The Journal of Arthroplasty.2018; 33(7): 2057. CrossRef - Devoting attention to glucose variability and hypoglycaemia in type 2 diabetes
Martin K. Rutter
Diabetologia.2018; 61(1): 43. CrossRef - Duration of storage influences the hemoglobin rising effect of red blood cells in patients undergoing major abdominal surgery
Oliver Hunsicker, Katarina Hessler, Alexander Krannich, Willehad Boemke, Ioana Braicu, Jalid Sehouli, Oliver Meyer, Axel Pruß, Claudia Spies, Aarne Feldheiser
Transfusion.2018; 58(8): 1870. CrossRef - Different Indexes of Glycemic Variability as Identifiers of Patients with Risk of Hypoglycemia in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Ana M. Gómez, Oscar M. Muñoz, Alejandro Marin, Maria Camila Fonseca, Martin Rondon, María Alejandra Robledo Gómez, Andrei Sanko, Dilcia Lujan, Maira García-Jaramillo, Fabian Mauricio León Vargas
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2018; 12(5): 1007. CrossRef - Glucose concentrations after insulin‐induced hypoglycemia and glycemic variability in healthy and diabetic cats
Eric Zini, Elena Salesov, Perrine Dupont, Laura Moretto, Barbara Contiero, Thomas A. Lutz, Claudia E. Reusch
Journal of Veterinary Internal Medicine.2018; 32(3): 978. CrossRef - Assessment of Glycemic Variability May Be the Next Step in Optimizing Patients for Total Joint Arthroplasty
Charles N. Cornell
Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery.2018; 100(13): e92. CrossRef - Glucose Variability and the Use of Continuous Glucose Monitors in People With Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Betty Lu, Jennifer D. Goldman
AADE in Practice.2018; 6(6): 22. CrossRef - Emerging Technologies for Diabetes Care
Timothy S. Bailey, John Walsh, Jenine Y. Stone
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2018; 20(S2): S2-78. CrossRef - Exercise Timing in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review
SHAUN Y. M. TEO, JILL A. KANALEY, KYM J. GUELFI, SUMMER B. COOK, JEFFREY J. HEBERT, MITCHELL R. L. FORREST, TIMOTHY J. FAIRCHILD
Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise.2018; 50(12): 2387. CrossRef - FATORES DE RISCO ASSOCIADOS À HIPOGLICEMIA E ANÁLISE DE EVENTOS ADVERSOS EM UMA TERAPIA INTENSIVA
Keroulay Estebanez Roque, Andrea Rodrigues Gomes da Silva, Mario Henrique Bravo de Almeida Santos, Enirtes Caetano Prates Melo
Texto & Contexto - Enfermagem.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Decreased Retinal Thickness in Type 1 Diabetic Children with Signs of Nonproliferative Diabetic Retinopathy
P. Ruiz-Ocaña, P. Espinoza Requena, A. Alonso-Ojembarrena, P. Alemany Márquez, S. Jiménez Carmona, A. M. Lechuga-Sancho
International Journal of Endocrinology.2018; 2018: 1. CrossRef - The impact of dapagliflozin on glucose excursions related to early proatherogenic derangement in the aortic wall
Agnieszka Stelmaszyk, Anna Wesołowska, Karolina Pomieczyńska, Saule Iskakova, Magdalena Frydrychowicz, Grzegorz Dworacki, Marzena Dworacka
Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal.2018; 26(8): 1192. CrossRef - The Relationship Between Social Support and Type 2 Diabetes Risk
Kristin G. Maki
Communication Research Reports.2018; 35(1): 12. CrossRef - Early glycemia and mortality in critically ill septic patients: Interaction with insulin-treated diabetes
Fraser Magee, Michael Bailey, David V. Pilcher, Johan Mårtensson, Rinaldo Bellomo
Journal of Critical Care.2018; 45: 170. CrossRef - Glycemic behavior in patients with type 2 diabetes during a short period of a combined training program
Daniela Bassi, Almir Vieira Dibai-Filho, Leonardo Hesley Durans, Renata Gonçalves Mendes, Flávia Cristina Rossi Caruso, Vivian Maria Arakelian, Audrey Borghi-Silva
Motriz: Revista de Educação Física.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Glycemic variability in the development of cardiovascular complications in diabetes
Annunziata Nusca, Dario Tuccinardi, Marzia Albano, Camilla Cavallaro, Elisabetta Ricottini, Silvia Manfrini, Paolo Pozzilli, Germano Di Sciascio
Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Continuous glucose monitoring: data management and evaluation by patients and health care professionals – current situation and developments
Guido Freckmann, Jochen Mende
LaboratoriumsMedizin.2018; 42(6): 225. CrossRef - Glucotypes reveal new patterns of glucose dysregulation
Heather Hall, Dalia Perelman, Alessandra Breschi, Patricia Limcaoco, Ryan Kellogg, Tracey McLaughlin, Michael Snyder, Jason Locasale
PLOS Biology.2018; 16(7): e2005143. CrossRef - The Role of Glycemic Control and Variability in Diabetic Retinopathy
Irini P. Chatziralli
Diabetes Therapy.2018; 9(1): 431. CrossRef - Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Predicts Higher HbA1c Variability in Subjects with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus
Yeoree Yang, Eun-Young Lee, Jae-Hyoung Cho, Yong-Moon Park, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kun-Ho Yoon, Moo-Il Kang, Bong-Yun Cha, Seung-Hwan Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(6): 496. CrossRef - Verapamil is a potential therapy for hypoglycaemic brain injury
Janice J. Hwang, Robert S. Sherwin
Nature Reviews Endocrinology.2018; 14(8): 443. CrossRef - The effect of impaired glucose metabolism on weight loss in multidisciplinary childhood obesity treatment
Julie T. Kloppenborg, Michael Gamborg, Cilius E. Fonvig, Tenna R. H. Nielsen, Oluf Pedersen, Jesper Johannesen, Torben Hansen, Jens‐Christian Holm
Pediatric Diabetes.2018; 19(3): 366. CrossRef - Increased glycemic variability in type 2 diabetes patients treated with insulin - a real-life clinical practice, continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) study
Cristian-Ioan Crăciun, Anca-Elena Crăciun, Adriana Rusu, Corina Ioana Bocşan, Nicolae Hâncu, Anca Dana Buzoianu
Revista Romana de Medicina de Laborator.2018; 26(3): 345. CrossRef - Lixisenatide reduces glycaemic variability in insulin‐treated patients with type 2 diabetes
Guillermo E. Umpierrez, David O'Neal, Andres DiGenio, Ronald Goldenberg, Eric Hernandez‐Triana, Jay Lin, Cheol‐Young Park, Eric Renard, Boris Kovatchev
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2017; 19(9): 1317. CrossRef - The relationship between fasting blood glucose variability and coronary artery collateral formation in type 2 diabetes patients with coronary artery disease
Gang Cheng, Hilda Mahmoudi, Binna Chokshi, Marlena Fernandez, Vahid Kazemi, Nader Lamaa
Coronary Artery Disease.2017; 28(6): 486. CrossRef - How Can We Realize the Clinical Benefits of Continuous Glucose Monitoring?
Ramzi A. Ajjan
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2017; 19(S2): S-27. CrossRef - Effect of gemigliptin on glycaemic variability in patients with type 2 diabetes (STABLE study)
Se E. Park, Byung W. Lee, Jae H. Kim, Woo J. Lee, Jae H. Cho, Chang H. Jung, Seung H. Lee, Sunghwan Suh, Gwong C. Hur, Sung H. Kim, Young H. Jang, Cheol Y. Park
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2017; 19(6): 892. CrossRef - Glucose variability indices predict the episodes of nocturnal hypoglycemia in elderly type 2 diabetic patients treated with insulin
Vadim V. Klimontov, Natalia E. Myakina
Diabetes & Metabolic Syndrome: Clinical Research & Reviews.2017; 11(2): 119. CrossRef - A Multicenter Real-Life Study on the Effect of Flash Glucose Monitoring on Glycemic Control in Patients with Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Ranjit Mohan Anjana, Jothydev Kesavadev, Deshpande Neeta, Mangesh Tiwaskar, Rajendra Pradeepa, Saravanan Jebarani, Suresh Thangamani, Nadiminty Ganapathi Sastry, Srivastava Brijendra Kumar, Muthu Ramu, Pokal Prasanna Kumar Gupta, Jayaprakash Vignesh, Sund
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2017; 19(9): 533. CrossRef - Association Between Coronary Artery Calcification and the Hemoglobin Glycation Index: The Kangbuk Samsung Health Study
Eun-Jung Rhee, Jung-Hwan Cho, Hyemi Kwon, Se Eun Park, Cheol-Young Park, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Won-Young Lee
The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.2017; 102(12): 4634. CrossRef - Comparison of Glucose Area Under the Curve Measured Using Minimally Invasive Interstitial Fluid Extraction Technology with Continuous Glucose Monitoring System in Diabetic Patients
Mei Uemura, Yutaka Yano, Toshinari Suzuki, Taro Yasuma, Toshiyuki Sato, Aya Morimoto, Samiko Hosoya, Chihiro Suminaka, Hiromu Nakajima, Esteban C. Gabazza, Yoshiyuki Takei
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(4): 265. CrossRef - Glycemic Variability and Its Association With Demographics and Lifestyles in a General Adult Population
Francisco Gude, Pablo Díaz-Vidal, Cintia Rúa-Pérez, Manuela Alonso-Sampedro, Carmen Fernández-Merino, Jesús Rey-García, Carmen Cadarso-Suárez, Marcos Pazos-Couselo, José Manuel García-López, Arturo Gonzalez-Quintela
Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology.2017; 11(4): 780. CrossRef - Glycaemic variability in patients with severe sepsis or septic shock admitted to an Intensive Care Unit
L.M. Silveira, A. Basile-Filho, E.A. Nicolini, C.A.M. Dessotte, G.C.S. Aguiar, A.M. Stabile
Intensive and Critical Care Nursing.2017; 41: 98. CrossRef - Exenatide once weekly improved 24‐hour glucose control and reduced glycaemic variability in metformin‐treated participants with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, placebo‐controlled trial
Juan P. Frías, Samer Nakhle, James A. Ruggles, Sergey Zhuplatov, Eric Klein, Rong Zhou, Poul Strange
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2017; 19(1): 40. CrossRef - Individualized, patient-centered use of lixisenatide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Markolf Hanefeld, Denis Raccah, Louis Monnier
Expert Opinion on Drug Metabolism & Toxicology.2017; 13(3): 311. CrossRef - Glucocorticoid-Induced Diabetes Mellitus: An Important but Overlooked Problem
Sunghwan Suh, Mi Kyoung Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(2): 180. CrossRef - Urinary N-acetyl-β-D-glucosaminidase, an early marker of diabetic kidney disease, might reflect glucose excursion in patients with type 2 diabetes
So Ra Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Sang-Guk Lee, Eun Seok Kang, Bong-Soo Cha, Jeong-Ho Kim, Byung-Wan Lee
Medicine.2016; 95(27): e4114. CrossRef - Insulin degludec + liraglutide: a complementary combination
K. Stinkens, B. Peene, C. Mathieu
Expert Opinion on Biological Therapy.2016; 16(9): 1171. CrossRef - GLP1-RA Add-on Therapy in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Currently on a Bolus Containing Insulin Regimen
Marie L. Davies, David Q. Pham, Scott R. Drab
Pharmacotherapy: The Journal of Human Pharmacology and Drug Therapy.2016; 36(8): 893. CrossRef - Teneligliptin: Heralding Change in Type 2 Diabetes
Manish Maladkar, Srividya Sankar, Kushal Kamat
Journal of Diabetes Mellitus.2016; 06(02): 113. CrossRef - Association between estimated blood glucose levels and glycated hemoglobin levels
Seon-Ah Cha, Seung-Hyun Ko
The Korean Journal of Internal Medicine.2016; 31(3): 457. CrossRef - Metformin attenuates fluctuating glucose-induced endothelial dysfunction through enhancing GTPCH1-mediated eNOS recoupling and inhibiting NADPH oxidase
Huijie An, Rui Wei, Jing Ke, Jin Yang, Ye Liu, Xian Wang, Guang Wang, Tianpei Hong
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2016; 30(6): 1017. CrossRef - The impact of glycemic variability on diabetic peripheral neuropathy
Heung Yong Jin, Kyung Ae Lee, Tae Sun Park
Endocrine.2016; 53(3): 643. CrossRef - The association of serum glycated albumin with the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Won Seon Jeon, Se Eun Park, Eun-Jung Rhee, Won-Young Lee, Ki-Won Oh, Sung-Woo Park, Cheol-Young Park
Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice.2016; 116: 46. CrossRef - Management of Steroid-induced Hyperglycemia
Sunghwan Suh, Mi Kyoung Park
The Journal of Korean Diabetes.2016; 17(3): 174. CrossRef - Comparison of Different Treatment Modalities for Type 1 Diabetes, Including Sensor-Augmented Insulin Regimens, in 52 Weeks of Follow-Up: A COMISAIR Study
Jan Šoupal, Lenka Petruželková, Milan Flekač, Tomáš Pelcl, Martin Matoulek, Martina Daňková, Jan Škrha, Štěpán Svačina, Martin Prázný
Diabetes Technology & Therapeutics.2016; 18(9): 532. CrossRef - Heart rate variability is associated with interstitial glucose fluctuations in type 2 diabetic women treated with insulin
Vadim V. Klimontov, Natalia E. Myakina, Nadezda V. Tyan
SpringerPlus.2016;[Epub] CrossRef

 KDA
KDA PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite