- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 45(5); 2021 > Article
-
Sulwon Lecture 2020Pathophysiology Rho-Kinase as a Therapeutic Target for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases
-
Inês Sousa-Lima1
 , Hyun Jeong Kim2, John Jones3, Young-Bum Kim2
, Hyun Jeong Kim2, John Jones3, Young-Bum Kim2
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2021;45(5):655-674.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2021.0197
Published online: September 30, 2021
1CEDOC-Chronic Disease Research Center, NOVA Medical School/ Faculty of Medical Sciences, New University of Lisbon, Lisbon, Portugal
2Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Metabolism, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center and Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA
3Center for Neuroscience and Cell Biology, University of Coimbra, Marquis of Pombal Square, Coimbra, Portugal
-
Corresponding author: Young-Bum Kim
 Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, 330 Brookline Avenue, Boston, MA 02215, USA E-mail: ykim2@bidmc.harvard.edu
Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes and Metabolism, Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, 330 Brookline Avenue, Boston, MA 02215, USA E-mail: ykim2@bidmc.harvard.edu
Copyright © 2021 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- ABSTRACT
- Graphical abstract
- INTRODUCTION
- PATHOLOGY OF NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASES
- Rho-KINASE INHIBITOR AMELIORATES NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASES
- THE IMPACT OF HEPATIC ROCK1 ON OBESITY AND INSULIN SENSITIVITY
- CONTROL OF DE NOVO LIPOGENESIS BY ROCK1
- ROCK1 MEDIATES ENDOCANNABINOID INDUCED LIPOGENESIS
- THE REGULATORY MECHANISMS UNDERLYING ROCK1-MEDIATED LIPOGENESIS
- SUMMARY
- NOTES
- REFERENCES
ABSTRACT
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a major public health problem and the most common form of chronic liver disease, affecting 25% of the global population. Although NAFLD is closely linked with obesity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes mellitus, knowledge on its pathogenesis remains incomplete. Emerging data have underscored the importance of Rho-kinase (Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing kinase [ROCK]) action in the maintenance of normal hepatic lipid homeostasis. In particular, pharmacological blockade of ROCK in hepatocytes or hepatic stellate cells prevents the progression of liver diseases such as NAFLD and fibrosis. Moreover, mice lacking hepatic ROCK1 are protected against obesity-induced fatty liver diseases by suppressing hepatic de novo lipogenesis. Here we review the roles of ROCK as an indispensable regulator of obesity-induced fatty liver disease and highlight the key cellular pathway governing hepatic lipid accumulation, with focus on de novo lipogenesis and its impact on therapeutic potential. Consequently, a comprehensive understanding of the metabolic milieu linking to liver dysfunction triggered by ROCK activation may help identify new targets for treating fatty liver diseases such as NAFLD.
- The Sulwon Award for Scientific Achievement is the Korean Diabetes Association’s highest scientific award and honors an individual who has excellently contributed to the progress in the field of diabetes and metabolism. The Sulwon Award is named after an emeritus professor, Eung Jin Kim, who founded Korean Diabetes Association. Prof. Young-Bum Kim received the 12th Sulwon Award at the 2020 International Congress of Diabetes and Metabolism which was held as a virtual congress from September 18 to 19 in 2020.
Graphical abstract
- During the 20th century, dramatic changes in lifestyle and eating habits led to a remarkable increase in obesity, which is a major risk factor for the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) [1,2]. NAFLD, known as the hepatic manifestation of the metabolic syndrome, is the most common form of chronic liver disease. This condition is closely associated with insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and obesity [3]. NAFLD is an umbrella term covering a broad spectrum of liver diseases characterized by different grades of severity in fat accumulation, inflammation, injury, and fibrosis [4]. The pathological manifestation of NAFLD ranges from simple steatosis or nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) to nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and fibrosis/cirrhosis that can ultimately lead to hepatocellular carcinoma and liver failure [1,2,4]. NAFL or fatty liver refers to simple steatosis characterized by storage of excess macrovesicular fat in more than 5% of hepatocytes. NASH is considered the most severe disease grade which includes inflammation, hepatocyte damage and pericellular fibrosis, and ultimately can progress to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma [5].
- The worldwide prevalence of NAFLD is 6% to 35% (median 20%) [6], whereas the estimated prevalence in the United States varies from 18% in the overall population to 28% in overweight individuals [7]. Individuals with NAFLD are generally obese and often present other pathophysiologic features of the metabolic syndrome, including insulin resistance, hypertension, dyslipidemia, and diabetes [8,9]. In fact, NAFLD prevalence amongst individuals with T2DM is 55.5% and 37.3% for NASH [10]. Thus, identifying new insights into the biological foundations of obesity-related fatty liver is highly crucial given the substantial rise in NAFLD prevalence worldwide. In this review, we discuss the emerging roles of Rho-kinase in the development of fatty liver disease and the consequences on systemic glucose homeostasis, with a particular focus on a molecular link with hepatic de novo lipogenesis (DNL).
INTRODUCTION
- The liver is an important metabolic organ that is essential for maintaining whole-body glucose and lipid homeostasis [1]. Impaired liver functions lead to insulin resistance causing T2DM and is often found in obesity-associated metabolic diseases such as NAFLD [1,11]. The pathophysiological mechanism(s) underlying NAFLD onset and progression appears to be a ‘multiple-hit’ process that includes insulin resistance, hormones secreted from the adipose tissue, nutritional factors, gut microbiota as well as genetic and epigenetic factors [12]. Initially, an increase in liver fat accumulation through a disruption of the homeostatic balance between triglyceride synthesis and clearance is detected. However, hepatic lipogenic pathways and concomitant inflammation are activated when obesity develops [12]. Specifically, pro-inflammatory cytokines secreted by adipose tissue is involved in the pathological process of ectopic fat accumulation within the hepatocyte and overall steatosis [13]. This development implies that the liver is not necessarily responsible for the initial development of metabolic inflammation but, with the gradual progression of obesity, is an important contributor to perpetuating this overall state of inflammation. Additionally, mitochondrial dysfunction in the liver is crucial in NAFLD development in metabolic disorders such as metabolic syndrome, obesity, and T2DM [14,15]. The delicate metabolic homeostasis between lipid accumulation and fuel utilization in liver cells is regulated by mitochondrial activity, including β-oxidation of free fatty acids, electron transfer and adenosine triphosphate production, as well as reactive oxygen species (ROS). Any imbalance between pro- and anti-oxidant activities leads to a decrease in β-oxidation and an increase in ROS production [14], which could ultimately contribute to NAFLD’s pathogenesis.
- Several types of the cells were found in the liver, including hepatic parenchymal cells, sinusoidal endothelial cells, hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), Kupffer cells, and dendritic cells [16]. HSCs comprise approximately 10% of all liver cells. These cells are typically found in the space of Disse, lying between liver sinusoidal endothelial cells and hepatocytes [17]. In a non-pathological state, HSCs are dormant, displaying a quiescent, nonproliferative phenotype (qHSCs). This cell stores vitamin A, cholesteryl esters and triglycerides in lipid vacuoles in the cytosol [18]. HSCs, in physiological conditions, regulate extracellular matrix (ECM) homeostasis through the release of ECM proteins, degrading enzymes (matrix metalloproteinases), and their tissue inhibitors. qHSCs are also known to produce a range of growth factors and other metabolic mediators such as the hepatocyte growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor [19]. Following liver injury, HSCs are activated into myofibroblasts that drive expressing fibrogenic genes, including collagen type 1, α-smooth muscle actin, and the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase. They proliferate and migrate to the liver injury site, where ECM secretion is stimulated [20]. Several studies have shown that fibrosis can be reversed upon the injury’s removal, specifically, myofibroblasts will undergo apoptosis and inactivation, promoting fibrosis regression [21,22].
- Kupffer cells are liver resident macrophages located within the lumen of the sinusoids and are adherent to the endothelial cells composing the blood vessel walls [18]. These cells play a key role in preventing undesired immune response under normal conditions, whereas they are activated under the pathophysiological conditions such as NAFLD. Activated Kupffer cells induce numerous inflammatory chemokines and cytokines secretion, resulting in detrimental effects on hepatic function, inflammation, and insulin resistance [18,23]. In fact, chemical-mediated ablation of Kupffer cells protects hepatic insulin resistance and hepatic steatosis in response to a highfat diet (HFD) [24,25], highlighting the vital role for Kupffer cells in the progression of hepatic lipid accumulation. Notably, Kupffer cells also induce HSCs from a quiescent state to an ac tivated state, leading to the production of collages and initiation of liver fibrogenesis [26]. The regulatory mechanisms underlying this phenomenon remain to be elucidated.
PATHOLOGY OF NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASES
- Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing kinase (ROCK) is a serine/threonine protein kinase identified as a guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-Rho-binding protein [27]. Two isoforms of ROCK, ROCK1 (also known as ROKβ) [28,29] and ROCK2 (also known as ROKα) [28,30] were identified. ROCK has a kinase domain at its N-terminal domain, a coiled-coil domain in its middle portion, and a putative pleckstrin-homology domain at its C-terminal domain split by the insertion of a Cysrich region. The Rho binding domain of ROCK is in the C-terminal portion of the coiled-coil domain [27]. ROCK activity increases when bound with (Rho-GTP) Rho-GTP through a Rho-binding domain [27]. The amino acid sequences of the two ROCK isoforms have 65% overall identity, with their kinase domains exhibiting 92% identity [27].
- The initial study of the ROCK inhibitor led by the Narumiya group demonstrated that treating a hypertensive animal with a high dose of the ROCK inhibitor (Y27632, 100 mg/kg/day for 5 months) results in decreased blood pressure [31]. These data suggest the ROCK inhibitor is a potential therapeutic target for many diseases resulting from abnormally high smooth muscle contraction. Since the introduction of this work, numerous studies have consistently revealed that ROCK inhibition is beneficial for multiple cardiovascular-related illnesses [32-34]. Beyond these investigations, a pharmacotherapy with the ROCK inhibitor has also been found to be effective in treating liver diseases, including NAFLD, NASH, and fibrosis as shown in Table 1 [35-53]. Data supporting a role of ROCK on liver diseases include the fact that a ROCK chemical inhibitor ameliorated hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in rats fed a choline-deficient/ L-amino acid-defined (CDAA) diet and choline-deficient diet [35-37]. These findings are also accompanied by decreased alanine aminotransferase (ALT)/aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and serum lipids levels [37]. The cellular mechanism(s) underlying this phenomenon could include involvement of the inactivation of HSCs [35-37], which have a crucial role in the development of hepatic fibrosis [54]. In support of this, the experimental evidence has demonstrated that selective delivery of the ROCK inhibitor to HSCs reduces chronic carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced liver fibrosis or cirrhosis by inhibiting activated HSCs in mice [38,39], highlighting an essential role for ROCK action in HSCs. Similar observations have been found in various animal models, including HFD-fed mice [40], HFD and streptozotocin (STZ)-treated rats [41], STZ-induced diabetic rats [42], dimethylnitrosamine- induced hepatic fibrosis rats [43], and endotoxintreated mice [44,45]. In animal models of CCl4-induced liver fibrosis, the ability of a ROCK inhibitor to reduce HSCs activation is greatly enhanced, leading to the prevention of liver fibrosis development [39,46-48]. Given the fact that ROCK inhibitors, including Y27632 and fasudil (HA1077), inhibit both ROCK1 and ROCK2 kinase activity [55,56], it is conceivable that the blockage of both isoforms may play a pivotal role in the protective effects of progressive liver diseases. This limitation has been an issue in the field and appears to result from limited knowledge on the isoform specificity of ROCK inhibitor. In this respect, an orally bioavailable ROCK2 inhibitor (ANG4201), which is >200 fold selective for ROCK2 versus ROCK1, has recently been developed by Angion Biomedica Corp. (San Francisco, CA, USA) [57]. Consistent with the aforementioned findings, the treatment of NASH mice with ANG4201 for 2 months also leads to a significant improvement in fibrosis, which is associated with decreased ALT/AST and cholesterol [57]. Equally, another ROCK2 selective inhibitor (RXC007) has been found to have the antifibrotic effect [58]. However, these results will need to be confirmed by a more specific genetic approach where ROCK2 in HSCs or hepatocytes is genetically deleted selectively, providing definitive knowledge as to whether ROCK2 is an indispensable regulator of liver diseases. Nevertheless, these data highlight compelling evidence that the hyper-activation of ROCK in the liver may contribute to the etiopathogenesis of hepatic dysfunction and that ROCK is a potential therapeutic target for obesity-induced fatty liver diseases such as NAFLD.
Rho-KINASE INHIBITOR AMELIORATES NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASES
- Earlier studies demonstrated that aberrant ROCK1 expression and/or activity are associated with numerous metabolic syndrome- related disorders, including cardiovascular disease, insulin resistance, obesity, and T2DM and its complications [59-63]. These works have never explored ROCK expression and/or activity in the liver of altered metabolic states such as obesity. Our study focused on investigating whether the expression or activity of ROCK1 in the liver changes in metabolic-linked diseases. In rodents, a marked increase in ROCK1 activity or expression is observed in the liver and adipose tissue of insulin- resistant, obese, or T2DM animal models [49]. In contrast, a significant decrease in ROCK1 activity is detected in the hypothalamus of these animals [63], suggesting site-specific regulation of ROCK1 in metabolically active organs. In individuals with fatty liver disease, ROCK1 expression greatly increased in the liver and strongly correlated with risk factors clustering with fatty liver diseases or liver damage [49]. These data demonstrate that ROCK1 has a vital role in the pathogenesis of obesity-linked metabolic diseases, including NAFLD.
- Given the fact that obesity is a major risk factor for developing NAFLD and drives hepatic ROCK1 expression [1,49], our laboratory has undertaken studies to establish the physiological function of ROCK1 in the liver, using animal models with genetic modifications of hepatic ROCK1. Mice lacking hepatic ROCK1 are resistant to the development of obesity during high-fat feeding, primarily due to increased energy expenditure. Hepatic ROCK1 deletion also significantly improves glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity in mice on high-fat or regular chow diets [49]. Support for this comes from a pharmacological study showing that 6 weeks of treatment of a ROCK inhibitor ameliorates diet-induced obesity and glucose intolerance as well as energy expenditure in mice [64]. Similarly, it was reported that 4 weeks of treatment with a ROCK inhibitor decreased body weight and improved glucose tolerance in obese Zucker animals [65]. However, it should be noted that long-term ROCK inhibition by a chemical inhibitor reduces body weight in insulin-resistant obese animals, which could possibly be secondary to insulin-sensitizing effects [64,65]. In keeping with these observations, our study further demonstrates that high-fat feeding greatly promotes obesity and insulin resistance in transgenic mice expressing a constitutively active form of hepatic ROCK1 compared with control mice. The importance of hepatic ROCK1 action on glucose metabolism is further underscored by the finding that leptin-deficient ob/ob mice lacking hepatic ROCK1 display improved insulin sensitivity compared with control ob/ob mice [49]. Collectively, these data demonstrate that hepatic ROCK1 is necessary and sufficient for regulating normal body-weight homeostasis and glucose metabolism, establishing a key role of hepatic ROCK1 in fuel metabolism.
THE IMPACT OF HEPATIC ROCK1 ON OBESITY AND INSULIN SENSITIVITY
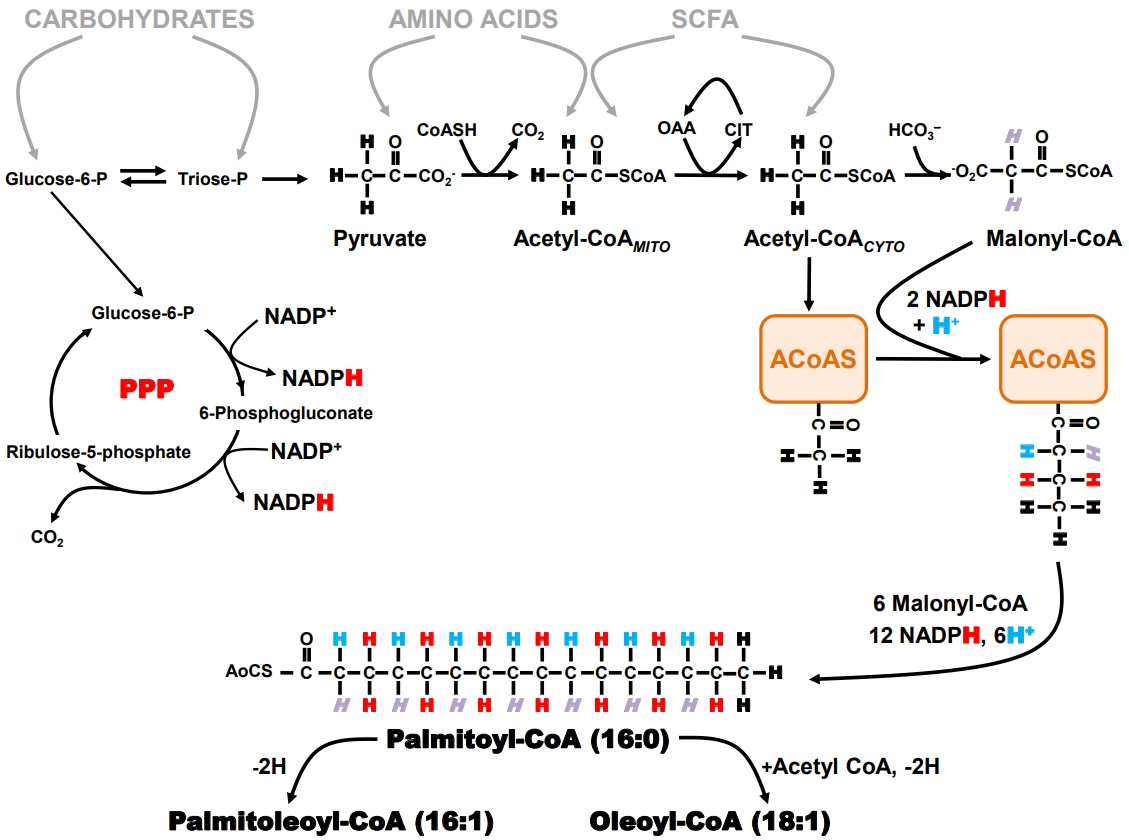
- Biochemistry and physiology of hepatic de novo lipogenesis
- When an organism ingests an amount of food that exceeds its immediate energy needs, the excess nutrients are directed into the formation of storage products that can be later mobilized for energy generation when food is less available. Triglyceride represents an energy-dense and physiologically benign storage product and is the principal sink for the disposal of excess nutrient carbons. The biosynthesis of triglyceride can be considered a two-stage process: first, the formation of long-chain fatty acyl CoA (LCFA-CoA) by a process known as DNL whose pathway is summarized in Fig. 1, and second, the sequential esterification of glycerol-3-phosphate by three LCFA-CoA to form triacylglycerol. DNL is usually the rate-limiting step for the synthesis of triglyceride from non-lipid precursors [66]. Therefore, expression and activity of the enzymes that constitute the DNL pathway, coupled with the availability of precursor substrates, determine the rate of hepatic triglyceride synthesis [67]. DNL occurs in the cytosol and relies on the generation of cytosolic acetyl coenzyme A (acetyl-CoA) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH). With the exception of a few substrates, such as the short-chain fatty acid acetate which can be converted to acetyl-CoA in the cytosol via acyl-coenzyme A synthetase short-chain family member 2 (ACSS2) [68], almost all other nutrients are catabolized to mitochondrial acetyl-CoA, which is then transferred to the cytosol via the citrate shuttle.
- The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) is the primary source of NADPH generation. Recent studies indicate that oxidative pentose pathway flux is highly coupled to that of DNL, at least during high-sugar feeding [69]. The generation of two NADPH equivalents via the PPP requires oxidation of one carbohydrate carbon to CO2, therefore synthesis of one equivalent of palmitoyl- CoA involves the oxidation of 1.17 equivalents of glucose- 6-P for the generation of NADPH alone. In part, because of its strong dependence on PPP activity, DNL is more responsive to the availability of carbohydrates compared to other nutrients. DNL activity is highly modulated by insulin through positiveand negative-feedback loops which are conditional on carbohydrate availability and feeding state [70,71] and stimulated by sugar-sensing factors such as carbohydrate-responsive element- binding protein (ChREBP) [72]. Thus, diets high in simple sugars such as glucose and fructose promote high hepatic DNL rates [73,74]. In addition to contributing directly to the hepatic lipid burden, DNL also attenuates hepatic fatty acid oxidation by generating malonyl-CoA, a potent inhibitor of long-chain fatty acid transported into the mitochondria via the carnitine shuttle. Normally, DNL is acutely suppressed following intake of high fat/low carbohydrate diets. However, the development of insulin resistance can result in maintaining DNL activity in this setting in part because of the increased availability of hepatic glucose-6-phosphate resulting from chronic hyperglycemia and/or uncontrolled hepatic gluconeogenesis. This is associated with increased ChREBP activity that upregulates DNL independently of any impairments of hepatic insulin signaling [75].
- Measurement of hepatic DNL with deuterated water (2H2O)
- Tracers that directly measure DNL provide estimates of fractional synthetic rates (i.e., the percent contribution of DNL to the total triglyceride pool over a defined interval). These estimates are derived from the precursor enrichment analysis, measured either directly or inferred from mass isotopomer distribution analysis (MIDA) of the product [76]. Although earlier studies of DNL were performed with infused [1-13C]- or [1-14C] acetate, there has been a widespread shift to the use of 2H2O, in large part because it is less costly than the acetate tracer and can be administered orally over an unlimited period of time. This latter aspect is important for the study of DNL contributions to lipid pools because of their relatively slow turnover rates, particularly for humans. In addition, 2H2O can be administered to humans on an outpatient basis under “real life” conditions [77] or to animals without disrupting their normal feeding routines [78].
- As shown in Fig. 1, the hydrogens of the fatty acid product of DNL can be traced to four specific sources: (1) body water; (2) the methyl hydrogens of the first acetyl-CoA molecule that binds to fatty acyl-CoA synthase; (3) malonyl-CoA; and (4) NADPH. The PPP NADPH hydrogens are in turn derived from hydrogens 1 and 3 of glucose-6-phosphate. When 2H2O is administered, the 2H rapidly mixes with the hydrogens of body water and is directly incorporated into the nascent fatty acid chain during the second hydrogenation step. In addition, the 2H present in body water can be incorporated into acetyl- CoA and malonyl-CoA precursors via specific exchange processes that occur during the formation of these metabolites. The NADPH hydrogens become enriched in part through exchange as well as by acquisition of 2H from glucose-6-P that was itself enriched from body water 2H via metabolic exchange processes associated with gluconeogenesis and Cori cycle activity. As a result, all the fatty acyl product hydrogens become enriched with 2H with the level of enrichment of a particular hydrogen relying on that of the body water precursor and the extent to which the exchange processes are complete. Although early studies suggested that 2H enrichment of newlysynthesized fatty acids was only ~50% to 70% of the theoretical value, thereby requiring a correction factor for determining DNL rates [79], a more recent analysis suggests that under some conditions, 2H/1H exchanges approach 100% [69]. Fatty acids that undergo elongation also incorporate 2H by the same exchange mechanisms, but only into the elongated front portion. Positional analysis of fatty acid enrichment by 2H nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) allows elongation and DNL rates to be resolved [80] and for transfer of hydrogen from glucose via NADPH to be followed [69].
- DNL measurements in animal models and humans
- The deuterated water method has been widely applied to study the involvement of DNL in NAFLD pathogenesis in both humans and animal models. The main constraint of this measurement in humans is that direct sampling of liver triglyceride via needle biopsy is typically not performed per se because of the unacceptable risk/benefit. As a less invasive alternative, triglycerides from circulating very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) are sampled, with the assumption that these derived from the hepatic triglyceride pool and therefore report the same tracer enrichment levels as hepatic triglyceride [81]. Conversion of fractional synthetic rates to absolute DNL rates requires an independent measurement of triglyceride turnover. In the liver, this is complicated by the appearance of fatty acids from sources other than DNL, such as from chylomicron remnants and circulating non-esterified fatty acids, and a disposal of fatty acids by several processes other than VLDL export, such as mitochondrial and peroxisomal oxidation. Finally, due to an extensive interchange of fatty acids between adipose tissues— particularly visceral adipose tissue—and the liver, a portion of hepatic fatty acid and VLDL labeling may in fact have originated from adipocyte DNL activity [77]. For humans, the liver is considered the principal site of DNL synthesis; hence, adipocyte contributions to hepatic fatty acid labeling may be minor. However, for many animals including rodents and pigs, adipocyte lipogenesis activity contributes substantially more to whole body DNL rates and could therefore have a significant influence on hepatic lipid labeling and activity attributed to hepatic DNL [82,83]. Because altered DNL is highly implicated in the pathogenesis of NAFLD [84,85], this pathway activity has become a focus both toward enhancing our understanding of NAFLD pathogenesis and as a putative pharmacological target for NAFLD treatment. Table 2 provides an overview of selected hepatic DNL studies in human subjects with NAFLD. In summary, hepatic DNL contributes about 5% to 10% of hepatic triglyceride appearance in healthy post-absorptive humans, whereas this rate is significantly elevated to 15% to 25% for patients with NAFLD [11,81,84,86-88]. Elevated DNL activity is tightly associated with increased hepatic lipid levels. Decreases in hepatic steatosis resulting from either dietary intervention (typically, a reduction in caloric intake), and pharmacological inhibition of fatty acids synthase, are associated with decreases in fractional DNL rates.
- Role of ROCK1 in hepatic DNL activity
- Our research efforts first sought to identify a central role of ROCK1 in the liver mediating DNL [49]. In obese mice where hepatic steatosis was induced by high-fat feeding, liver-specific deletion of ROCK1 expression resulted in an amelioration of hepatic triglyceride levels [49]. We explored the physiologic mechanisms by which ROCK1 regulates hepatic lipid accumulation by assessing DNL activity, fatty acid uptake and oxidation, and hepatic VLDL release. A marked reduction in fractional DNL rates determined by 2H NMR of deuterated water 2H2O in liver-specific ROCK1-deficient mice fed a HFD was observed. Because these studies were performed with body-weight matching ROCK1-deficient mice, the possible confounding effects of adiposity can be excluded. In relation to DNL measurement, differences in whole body triglyceride pools could modify hepatic fatty acid 2H-enrichment independently of changes in absolute hepatic DNL rates. To demonstrate that this effect could not be attributed to some uncharacterized physiological aspect of liver-specific ROCK1-deficient mice beside adiposity, we further studied liver-specific ROCK1-deficient mice fed a normal chow diet that had a similar body weight to control mice. We found that DNL rates significantly reduced for this group of mice. However, deleting hepatic ROCK1 had no effects on hepatocyte fatty acid uptake or oxidation, and hepatic VLDL export rates. This suggests the decrease in hepatic lipid accumulation caused by ROCK1 deficiency is solely explained by significant reductions in fractional DNL rates. In conjunction with DNL activity, we also investigated whether decreased hepatic lipid accumulation by ROCK1 deletion is due to changes in gene expression of key enzymes involved in glucose and lipid metabolism. Consistent with the results of DNL rates, deficiency of ROCK1 in the liver caused a significant decrease in gene expressions of key enzymes involved in lipogenesis but not gluconeogenesis, glycolysis, fatty acid oxidation and uptake. Importantly, these effects were also observed in ob/ob mice lacking hepatic ROCK1 independent of changes in body weight. Together, these data suggest the major mechanism by which deletion of ROCK1 in the liver prevents hepatic steatosis could be through decreased DNL, mediated by the reduced expression of lipogenic enzymes. Thus, our studies identify hepatic ROCK1 as a principal regulator of fat metabolism and further implicate that inhibition of hepatic ROCK1 could be a novel therapeutic target for the treatment of NAFLD.
CONTROL OF DE NOVO LIPOGENESIS BY ROCK1
- The endocannabinoid system is comprised of the cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1 receptor) and 2 (CB2 receptor), their endogenous lipidic ligands (endocannabinoids), and the enzymes involved in endocannabinoid synthesis and degradation [89]. The CB1 receptor is mainly found in the brain and is responsible for the psychotropic and behavioral effects after the use of cannabinoids. The CB2 receptor is expressed in metabolically active peripheral organs such as the liver, adipose tissue, and pancreas [90,91] and functions as a key modulator of innate immunity and fuel metabolism, amongst other roles [91,92]. In particular, during the progression of liver diseases, CB1 receptor expression is induced in hepatocytes, hepatic myofibroblasts, and endothelial cells of the liver, whereas CB2 receptor expression is up-regulated in Kupffer cells [89,93]. In this regard, a significant increase in CB1 and CB2 receptor expression in the liver of humans with NAFLD was observed [94,95], suggesting that dysregulation of the endocannabinoid system may contribute to the pathogenesis of liver diseases.
- Two arachidonic acid-containing endocannabinoids, arachidonoylethanolamide (anandamide [AEA]) and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), are identified as ligands for the CB1 and CB2 receptors [96-99]. AEA and 2-AG play important roles in regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. These functions entail lipogenic enzymes activation and fat accumulation in the liver [100], modulation of insulin secretion in islets [101,102], stimulation of lipoprotein lipase activity in adipose tissue [103], and decreases in insulin-stimulated glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation in muscle [103,104]. All these features are key hallmarks involved in the pathogenesis of metabolic syndrome.
- Antagonism and agonism of the CB1 and CB2 receptors have been extensively studied in the experimental settings of liver diseases and diet-induced obesity [105]. Numerous studies have been performed with an inverse agonist/antagonist rimonabant for the CB1 receptor. These investigations have obtained consistent outcomes on the metabolic benefits of hepatic lipid metabolism in various liver diseases models [106-111]. Recent studies have also demonstrated that inverse agonist/ antagonists targeting the peripheral CB1 receptor ameliorate metabolic parameters in animal models of obesity and diabetes [111-115]. For example, treating diet-induced obese mice with a pyrazole-based inverse agonist of the CB1 receptor (RTI1092769) that has minimal brain exposure decreased hepatic triglyceride contents and improved hepatic steatosis [111]. Another peripherally-restricted inverse agonist for the CB1 receptor, JD5037, is found to have a therapeutic potential in metabolic disorders of the peripheral tissues such as the liver [113,114]. In fact, JD5037 attenuated HSCs activation of liver fibrosis by inhibiting β-arrestin1/Akt signaling in humans and rodents [115]. These pharmacological observations have been supported by the evidence from a genetic model of liver-specific CB1 receptor knockout mice [100]. Mice lacking the CB1 receptor in the liver have significantly less hepatic steatosis, hyperglycemia, and dyslipidemia during over-nutrition [100], highlighting an important role for the CB1 receptor in regulating normal hepatic metabolism. Selective studies of the endocannabinoid system in the context of liver diseases are showed in Table 3 [106-111,116-124].
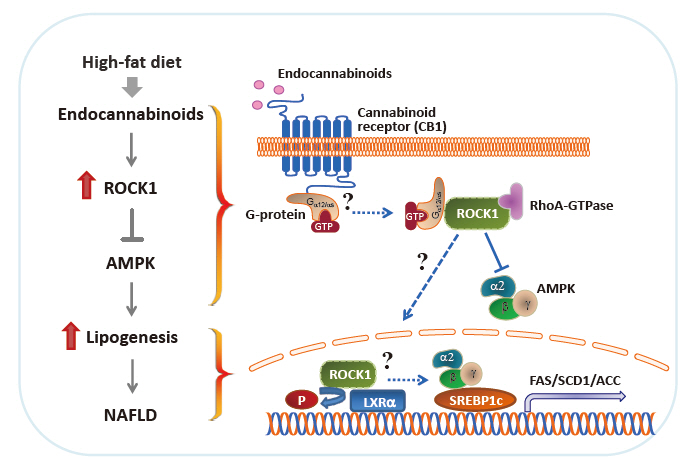
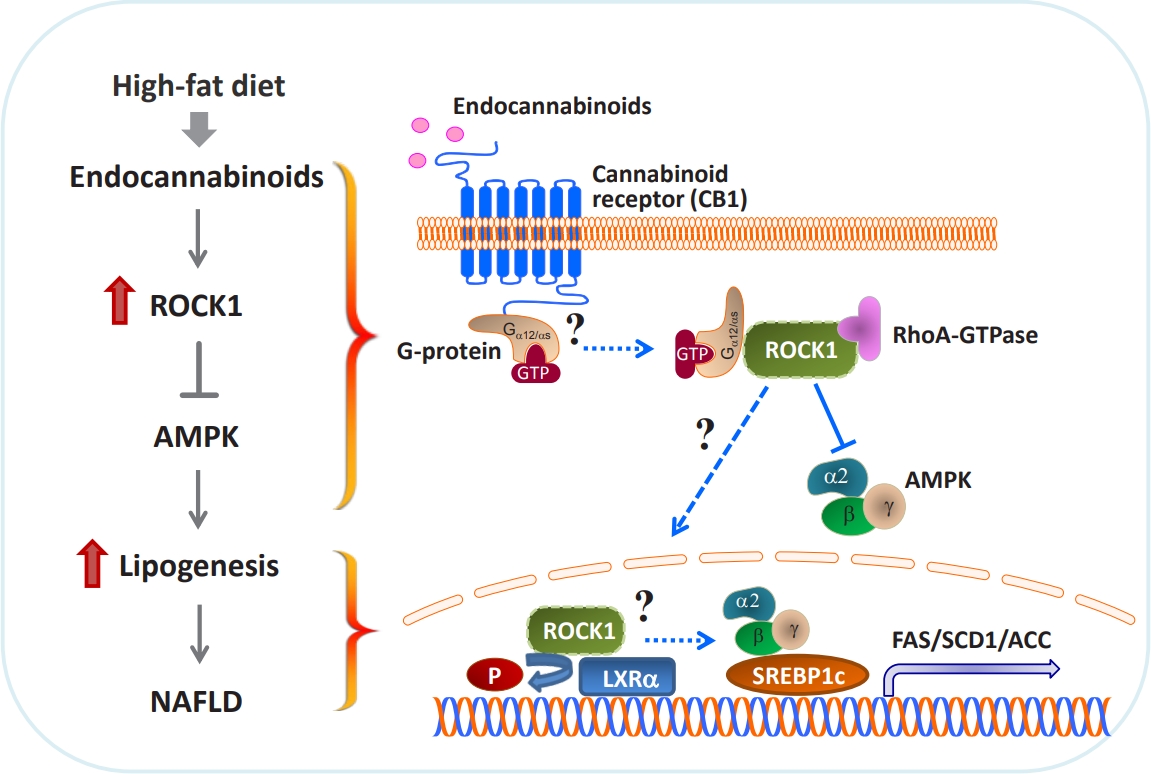
- In proof-of-concept studies, we made the novel observation that endocannabinoids, AEA and 2-AG, strongly increased the catalytic activity of ROCK1 in the liver and HepG2 cells [49] and DNL rate in hepatocytes. Concurrently, gene expression of key lipogenic enzymes, including fatty acid synthase (FAS), stearoyl-CoA desaturase-1 (SCD1), acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), and sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1c (SREBP1c) also markedly increased in response to 2-AG in the liver. However, the lack of endocannabinoids’ response on lipogenic gene expression was noted when hepatic ROCK1 was absent, suggesting that ROCK1 activation is necessary to regulate the endocannabinoid-mediated lipogenic program. We further hypothesize that ROCK1-dependent lipogenesis is mediated through inhibition of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK), as evidenced from our data showing that 2-AG suppressed the activity of hepatic AMPK in control mice but not in liver-specific ROCK1-deficient mice. In addition, ROCK1 deletion stimulated AMPK activity but ROCK1 activation suppressed AMPK activity in the liver, further highlighting a negative regulation of ROCK1 for AMPK. Therefore, our work has provided mechanistic insight into the fundamental function of ROCK1 in regulating the endocannabinoid-dependent lipogenic program.
ROCK1 MEDIATES ENDOCANNABINOID INDUCED LIPOGENESIS
- Experimental evidence has demonstrated that AMPK plays a pivotal role in regulating glucose and fatty acid metabolism. AMPK, a highly conserved serine/threonine protein kinase, was viewed as a cellular sensor that responds to depletion in cellular energy reserves by switching off anabolic pathways and enhancing catabolic processes [125]. Activation of the AMPK and its downstream signaling pathways was found to suppress hepatic lipid synthesis [126], increase muscle fatty acid oxidation [127], and enhance insulin action [128]. In particular, ac tivated AMPK decreases the hepatic gene expression of the lipogenic transcription factor SREBP1c and its downstream targets ACC, SCD1, and FAS [126]. Although ROCK1 has not been suspected to be involved in AMPK signaling, our work reveals that AMPK acts as a downstream regulator of ROCK1 in the context of hepatic DNL [49]. In fact, ROCK1 negatively regulates AMPK activity, as demonstrated by the evidence that AMPK activity increased due to ROCK1 deletion but decreased by ROCK1 activation in the liver. Correspondingly, reciprocal changes in hepatic lipogenesis are seen (i.e., decrteased or enhanced fatty acid synthesis caused by AMPK activation or suppression due to ROCK1 deletion or hyperactivation, respectively). Pharmacological modulations of AMPK activity in hepatocytes are enabled to regulate gene expression of key lipogenic enzymes despite the metabolic conditions where ROCK1 is either absent or activated, further confirming that ROCK1 is an upstream component of AMPK signaling. Thus, our data suggest the hepatic ROCK1 → AMPK signaling cascade is a crucial determinant of hepatic lipid synthesis (Fig. 2) [49]. This novel pathway appears to be functional in response to an insulin sensitizer metformin [129], which further implicates clinical significance and relevance of ROCK1 signaling. Of note, our recent work further identified Gα12 or Gαs as an upstream component of ROCK1 → AMPK signaling during melanocortin stimulation in the hypothalamus [130]. Thus, it is important to know that Gα12 or Gαs plays a role in the development of NAFLD in the context of ROCK1 action (Fig. 2).
- The liver X receptors (LXRs), LXRα and LXRβ, play a pivotal role in regulating lipid and glucose metabolism in insulintarget tissues by controlling its downstream targets’ gene expression [131,132]. Insulin induces LXRα in hepatocytes, resulting in an increased expression of key enzymes in lipogenesis, including SREBP1c, the master regulator of hepatic lipogenesis, and its several downstream genes such as FAS and SCD1 [133-135]. A central role for LXRs in the regulation of lipogenesis is further established by the study showing that deleting LXRs from ob/ob mice reduces hepatic triglyceride amounts and lipogenic gene expression [136]. Conversely, treating mice with synthetic LXR agonists promotes triglyceride synthesis in the liver by inducing lipogenic gene expression [137,138], thereby leading to hypertriglyceridemia, a risk factor for developing insulin resistance and obesity [133]. The fact that deficiency of hepatic ROCK1 selectively suppresses gene expression of lipogenic key enzymes in the liver [49] allowed this research to raise the possibility that LXRα is involved in ROCK1 action in the context of lipogenesis. Interestingly, coimmunoprecipitation assay indicates that ROCK1 physically binds to LXRα in the liver and possibly could phosphorylate LXRα serine residues in vitro (not shown). Whether LXRα is a critical determinant for the metabolic regulation of ROCK1- mediated DNL by controlling its target gene expression is an intriguing question that future studies should address. These investigations will establish the biological significance of ROCK1-dependent LXRα action in hepatic metabolism and provide a novel mechanism for the ROCK1 → LRXα signaling axis that is linked to lipogenesis (Fig. 2).
THE REGULATORY MECHANISMS UNDERLYING ROCK1-MEDIATED LIPOGENESIS
- Significant progress in comprehending the critical signaling pathways that regulate normal glucose and lipid homeostasis has been made in the field. In particular, much attention has focused on hepatic fatty acid metabolism in the context of obesity- related NAFLD. Growing evidence from pharmacological and genetic studies demonstrated that ROCK1 plays an essential role in the homeostatic regulation of DNL in the liver and its activation is the key defect that underlies the etiology of obesity-linked NAFLD. In addition, the ROCK1 → AMPK signaling cascade is required to mediate hepatic DNL provoked by endocannabinoid generated from HSCs. Thus, the emergence of ROCK1 as a pivotal player of hepatic lipid metabolism provides new insight into the etiopathogenesis of NAFLD and may lead to new treatment approaches for obesity- related metabolic disorders such as NAFLD.
- Outstanding questions are as follows:
- • What are the specific roles of ROCK1 or ROCK2 in HSCs in the development of liver diseases?
- • What are the functions of ROCK1 or ROCK2 in Kupper cells?
- • Is ROCK1 involved in the regulation of LXRα-mediated lipogenic programs?
- • What are the key downstream pathways of ROCK1 → AMPK signaling?
- • What is the physiological role of the ROCK1 → AMPK signaling pathways in other metabolic organs?
- • Does Gα12 or Gαs act as an upstream signal of ROCK1 in the liver?
SUMMARY
-
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
-
FUNDING
None
NOTES
-
Acknowledgements
- We thank Maria Paula Macedo and Inês Couto Coelho for their helpful discussion.

| Animal models with liver diseases | Treatments | Major findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fibrosis induced by CDAA in rats | Y-27632 (1 mg/kg) was treated for 12 weeks | Improvement of hepatic fibrosis and steatosis | [35] |
| Decreased ALT and HA levels | |||
| Reduced hepatic TNFα expression | |||
| Steatosis induced by choline-deficient diet for 6 weeks in rats and the liver was subjected to IR injury | Vitamin A-coupled liposomes carrying Y-27632 for targeted HSCs was administered before ischemia induction | Improved the survival rate after IR injury, the liver blood flow, and the portal perfusion pressure | [37] |
| Decreased AST levels | |||
| Steatosis induced by choline-deficient diet for 6 weeks and the liver was s ubjected to IR injury in rats | Fasudil (10 mg/kg) was administered for 30 minutes before ischemia induction | Attenuation of HSCs activation | [36] |
| Improvement of IR injury | |||
| Decreased AST and ALT levels | |||
| Reduced ET-1 serum levels | |||
| Fibrosis induced by CCl4 treatment for 12 weeks in rats | Y-27635 (30 mg/kg) was treated for 6 weeks | Prevented the development of liver fibrosis | [46,50] |
| Decreased αSMA and TGFβ1-positive cell | |||
| Decreased total collagen | |||
| Increased survival rate after hepatectomy | |||
| CCl4-induced acute liver injury in mice | Y-27632 (1.5 mg/kg) was injected at 24 and 48 hours after CCl4 injection | Reduction of local activation of HSCs | [47] |
| Decreased αSMA | |||
| CCl4-induced acute liver injury in mice | Single injection of HA-1077 (10 mg/kg) | Reduced hepatic apoptosis | [51] |
| Decreased ALT levels | |||
| Fibrosis induced by CCl4 treatment for 7 weeks in mice | Y27632 conjugate (45 mg/kg/day) that is taken up in activated HSCs for 2 weeks | Inhibited activation of HSCs | [39] |
| Decreased ALT and AST level | |||
| Reduced liver fibrosis | |||
| Cirrhosis induced by CCl4-intoxication and BDL in rats | Y-27635 coupled with mannose-6- phosphate targeting HSCs activation | Decreased the portal pressure | [38] |
| Decreased the hepatic-portal resistance | |||
| No extrahepatic effects | |||
| Cirrhosis induced by BDL or CCl4 in rats | Y27632 coupled with human serum albumin substituted with PDGFRβ- recognizing peptides (Y27pPBHSA) | Lower portal pressure, hepatic vascular resistance without effect on systemic vascular resistance | [48] |
| Reduced intrahepatic resistance by decreased moesin and MLC | |||
| Mouse model of NAFLD induced by HFD | RKI-1447 (2 and 8 mg/kg) was treated for 3 weeks | Decreased ALT and AST levels | [40] |
| Decreased serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels | |||
| Ameliorated hepatic steatosis | |||
| Diabetic rats made by a combination of HFD and streptozotocin | Fasudil (10 mg/kg) was treated for 14 weeks | Amelioration of liver fibrosis | [41] |
| Inhibited TGFβ1/CTGF pathway and αSMA expression | |||
| Streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetic rats | Fasudil (2 mg/kg b.i.d., 10 mg/kg b.i.d., H-Fas group) was treated for 8 weeks | Suppression of inflammation and accumulation of the extracellular matrix | [42] |
| Downregulated TGFβ1 and MMP9/TIMP-1 | |||
| Decreased NF-κB activation | |||
| Rat model of DMN-induced fibrosis | Y27632 (30 mg/kg) was orally administered for 4 weeks | Decrease liver fibrosis | [43] |
| Reduced hepatic collagen and hydroxyproline | |||
| Decreased hepatic αSMA expression | |||
| Endotoxin-induced mice made by a combination of LPS and D-galactosamine | Fasudil (40 mg/kg) or Y-27632 (10 mg/kg) by a single injection | Decreased ALT and AST levels | [45] |
| Decreased hepatic apoptosis | |||
| Attenuated LPS-induced liver injury | |||
| Reduced LPS-induced leukocyte adhesion | |||
| Decreased hepatic TNFα and CXC chemokines expression | |||
| LPS-induced acute liver injury in mice | Y-27632 (10 mg/kg) was injected prior to LPS injection | Attenuated LPS-induced liver injury | [44] |
| Reduced the LPS-induced hepatic inflammatory response and oxidative stress | |||
| Protective effects on hepatic mitochondrial function | |||
| Obstructive cholestasis induced by BDL in mice (hepatocellular damage) | Y-27632 (1 and 10 mg/kg) was injected prior to BDL | Decreased serum AST and ALT levels | [52] |
| Reduced CXC chemokines and leukocyte recruitment | |||
| Restored sinusoidal perfusion | |||
| Rats underwent intrahepatic tumor implantation followed by orthotopic liver transplantation | Y-27632 (10 mg/kg) for 28 days | Suppression of cancer cell migration | [53] |
| Suppression of tumor recurrence | |||
| Increased survival rate | |||
| Mice lacking hepatic ROCK1 | HFD for 16 weeks | Prevented HFD-induced fatty liver | [49] |
| Decreased hepatic TG and cholesterol in serum and liver | |||
| Decreased de novo lipogenesis | |||
| Mice overexpressing a constitutively active mutant of ROCK1 in the liver | HFD for 12 weeks | Promoted HFD-induced fatty liver | [49] |
| Increased serum TG and cholesterol levels | |||
| Increased hepatic TG | |||
| Leptin-deficient mice (ob/ob) mice lacking hepatic ROCK1 | No treatment | Prevented the development of fatty liver | [49] |
| Decreased hepatic TG and cholesterol levels |
CDAA, choline-deficient/L-amino acid-defined; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; HA, hyaluronic acid; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha; IR, ischemia-reperfusion; HSC, hepatic stellate cell; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ET-1, endothelin-1; CCl4, carbon tetrachloride; αSMA, α-smooth muscle actin; TGFβ, transforming growth factor-β; BDL, bile duct ligation; PDGFRβ, platelet-derived growth factor receptor β; MLC, myosin light chain; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; HFD, high-fat diet; CTGF, connective tissue growth factor; b.i.d., twice a day; MMP9, matrix metallopeptidase 9; TIMP-1, tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases-1; NF-κB, Nuclear factor kappa B; DMN, dimethylnitrosamine; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; ROCK1, Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing kinase; TG, triglyceride.
| Study outline | Tracer method for DNL assay | Major findings | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| DNL rates were measured in lean healthy subjects and in overweight patients with suspected NAFLD based on transaminase levels and hepatic ultrasound tests. | 2H2O given over 20 hours and enrichment of palmitate within TG-rich lipoprotein measured after a breakfast meal. | This was among the first published study of DNL in NAFLD subjects using the 2H2O tracer. The contribution of DNL to the appearance rate of plasma TG was ~3-fold higher for the NAFLD subjects compared to the healthy controls. | [86] |
| Comparison of DNL contributions to liver TG appearance in obese subjects with low or with high liver fat but matched for other metabolic factors | 2H2O given over 11 days and enrichment of palmitate within TG-rich lipoprotein measured. | Subjects with high liver fat levels had a DNL contribution to liver fat appearance that was twice that of subjects with low liver TG levels. | [84] |
| Determine the sources of fatty acids contributing to hepatic TG and in secreted lipoprotein of NAFLD patients during both fed and fasted states | [1-13C]acetate infused over 4 days. Hepatic TG directly sampled by liver biopsy and plasma lipoprotein TG also sampled. | Analysis of plasma lipoprotein TG yielded similar flux estimates to those of liver TG. DNL accounted for about one-quarter of liver and plasma lipoprotein TG synthesis. DNL was active during both fed and fasted states. | [81] |
| Determine the effect of age-induced skeletal muscle insulin resistance on postprandial hepatic lipid kinetics by studying elderly subjects and young subjects matched for body composition and physical activity | 2H2O given over 2 days and enrichment of palmitate within VLDL measured. | Hepatic DNL rates were two-fold higher in the elderly cohort. Hepatic lipid levels were three-fold higher in the elderly cohort. These were associated with increased fasting plasma glucose levels and increased muscle insulin resistance as seen by impaired muscle glycogen synthesis rates. | [87] |
| Determine the effects of a fatty acid synthase inhibitor (FT-4101) on hepatic DNL rates in NAFLD patients | 2H2O given over 14 days and enrichment of VLDL-palmitate measured during a period of fructose ingestion. | 12 Weeks of FT-4101 administration significantly decreased fractional DNL rates over placebo in a dose-dependent manner. This was accompanied by a significant decrease in liver TG levels. | [88] |
| Compare DNL rates in lean subjects without NAFLD, obese subjects without NAFLD and obese subjects with NAFLD before and after placement on a weight-loss diet | 2H2O given over 3−5 weeks and enrichment of palmitate within TG-rich lipoprotein measured. | DNL rates were highest in obese-NAFLD subjects and were directly correlated with plasma insulin and glucose concentrations. Moderate weight loss resulted in significant decreases in both DNL rates and liver TG levels that was linked to significant decreases in plasma glucose and insulin levels. | [11] |
| Animal model of metabolic dysfunction | Treatments | Major findings | Major findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obese Zucker fa/fa rats | Rimonabant (30 mg/kg/day) was orally administered for 8 weeks | Decreased plasma ALT, GGT, and ALP levels | [106] |
| Decreased hepatic TNFα levels | |||
| Reduced plasma TG and cholesterol levels | |||
| Improved hepatic steatosis | |||
| OLETF rats | Rimonabant (10 mg/kg/day) was orally administered for 6 weeks | Decreased serum ALT and AST levels | [107] |
| Decreased hepatic TG levels | |||
| Improved hepatic steatosis | |||
| C56BL/6J mice fed a HFD for 20 weeks | Rimonabant (10 mg/kg) was orally administered from 18th to 20th week | Decreased serum AST and ALT levels | [108] |
| Reduced hepatic palmitic, stearic, and oleic acid proportion | |||
| Ameliorated hepatic steatosis | |||
| Sprague-Dawley rats fed a choline-deficient diet for 12 weeks | Rimonabant (10 mg/kg) orally administered from 10th week to 12th week | Decreased serum AST and ALT levels | [109] |
| Decreased hepatic malondialdehyde levels | |||
| Increased hepatic glutathione peroxidase activity | |||
| Reduced hepatic TGFβ immunoreactive area | |||
| Male C57BL/6 mice fed a HFD for 20 weeks | Rimonabant (10 mg/kg) was orally administered from 18th week to 20th week | Decreased serum AST and ALT levels | [110] |
| Decreased adipokines levels (leptin, visfatin, IL-6, IFNγ levels in adipose tissue) | |||
| Reduced hepatic-6, IFNγ levels | |||
| Improved hepatic steatosis | |||
| C57Bl/6J male mice fed a HFD underwent hypoxia exposure for 10 weeks | CB1 receptor agonist (WIN55212-2, 1 mg/kg) was treated for 4 weeks | Hypoxia-induced improvement in hepatic steatosis was abolished by CB1 receptor agonist | [116] |
| Increased hepatic CB1 and SREBP1 expression | |||
| Male Sprague-Dawley and WKY rats injected with LPS/D-galactosamine (acute liver injury model) | CB2 agonist (JWH-133, 2.5 mg/kg) or CB1 antagonist (AM6545, 10 mg/kg) was acutely injected | CB1 antagonist or CB2 agonist had no effect on LPS/D-galactosamine-induced liver injury | [117] |
| NAFLD was induced by a high-fat cholesterol diet for 6 weeks | Cannabis extracts (5 mg/kg) were administrated orally every 3 days for 6 weeks | No change in hepatic lipid accumulation | [118] |
| CBD-rich extracts increased hepatic iNOS and TNFα expression | |||
| THC-rich extracts decreased liver enzymes | |||
| Mice lacking CHOP fed a HFD for 14 weeks | CB1R blocker (JD5037, 3 mg/kg) was administered for 7 days | Failed to reverse DIO-induced reduction of sOB-R levels and hepatic steatosis | [119] |
| Liver fibrosis induced by thioacetamide (200 mg/kg) treatment for 6 weeks in rats | AM1241 (CB2 receptor activator, 3 and 6 mg/kg) was injected for 3 weeks | Suppressed hepatic TNFα, IL-1b, and IL-6 levels | [120] |
| Decreased hepatic TLR4, TGFβ1, αSMA, and miR-155 gene expression | |||
| Inhibited the development of fibrosis | |||
| APOE∗3-Leiden.CETP transgenic mice fed Western-type diet for 20 weeks | Rimonabant (20 mg/kg/day) for 4 weeks | Decreased plasma TG and non-HDL levels | [121] |
| Increased plasma HDL-C levels | |||
| Reduced VLDL-TG production | |||
| Increased VLDL-TG turnover | |||
| Prevented atherosclerosis | |||
| Obese mice fed on a HFD | RTI1092769 (inverse agonist/antagonist of CB1) | Decreased hepatic TG contents | [111] |
| Decreased plasma AST and ALT levels | |||
| Improved hepatic steatosis | |||
| C57BL/6J and fat-1 transgenic mice fed a LFD for 10 weeks +10 weeks of a HFD | Fatty acids SAF oil or LIN oil were supplemented to a LFD for 10 weeks, prior to HFD exposure | Decreased hepatic AEA and 2-AG contents in LIN-treated mice | [122] |
| Improved glucose tolerance and insulin tolerance in LIN-treated mice | |||
| Global CB1 receptor knockout mice | SR161716A (10 mg/kg) was injected before and after CCl4 | Reduced fibrosis associated with chronic liver injury | [123] |
| Decreased hepatic TGFβ1 expression | |||
| Global CB1 receptor knockout mice | No treatment | Decreased hepatic TG levels | [124] |
| Reduced hepatic PLIN2 expression | |||
| Suppressed lipogenesis |
ALT, alanine aminotransferase; GGT, gamma glutamyltransferase; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha; TG, triglyceride; OLETF, Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima Fatty; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; HFD, high-fat diet; TGFβ, transforming growth factor-β; IL-6, interleukin 6; IFNγ, interferon gamma; CB1, cannabinoid receptor type 1; SREBP1, sterol regulatory element-binding protein 1; WKY, Wistar Kyoto; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; CB2, cannabinoid receptor type 2; NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; CBD, cannabidiol; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; THC, tetrahydrocannabinol; CHOP, C/EBP homologous protein; CB1R, cannabinoid receptor type 1 receptor; DIO, diet-induced obesity; sOb-R, soluble leptin receptor; IL-1b, interleukin 1b; TLR4, toll like receptor 4; αSMA, α-smooth muscle actin; HDL, high-density lipoprotein; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; VLDL, very low-density lipoprotein; LFD, low-fat diet; SAF, safflower oil; LIN, linseed oil; AEA, arachidonoylethanolamide; 2-AG, 2-arachidonoylglycerol; CCl4, carbon tetrachloride; PLIN2, perilipin 2.
- 1. Birkenfeld AL, Shulman GI. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, hepatic insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes. Hepatology 2014;59:713-23.ArticlePubMed
- 2. Kopelman PG. Obesity as a medical problem. Nature 2000;404:635-43.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Thibaut R, Gage MC, Pineda-Torra I, Chabrier G, Venteclef N, Alzaid F. Liver macrophages and inflammation in physiology and physiopathology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. FEBS J 2021 Apr 15 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.15877.Article
- 4. Ayonrinde OT. Historical narrative from fatty liver in the nineteenth century to contemporary NAFLD: reconciling the present with the past. JHEP Rep 2021;3:100261.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 5. Wong RJ, Aguilar M, Cheung R, Perumpail RB, Harrison SA, Younossi ZM, et al. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis is the second leading etiology of liver disease among adults awaiting liver transplantation in the United States. Gastroenterology 2015;148:547-55.ArticlePubMed
- 6. Bellentani S. The epidemiology of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int 2017;37 Suppl 1:81-4.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 7. Sayiner M, Koenig A, Henry L, Younossi ZM. Epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in the United States and the rest of the world. Clin Liver Dis 2016;20:205-14.ArticlePubMed
- 8. Samuel VT, Shulman GI. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease as a nexus of metabolic and hepatic diseases. Cell Metab 2018;27:22-41.ArticlePubMed
- 9. Loomba R, Friedman SL, Shulman GI. Mechanisms and disease consequences of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Cell 2021;184:2537-64.ArticlePubMed
- 10. Younossi ZM, Golabi P, de Avila L, Paik JM, Srishord M, Fukui N, et al. The global epidemiology of NAFLD and NASH in patients with type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol 2019;71:793-801.ArticlePubMed
- 11. Smith BW, Adams LA. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes mellitus: pathogenesis and treatment. Nat Rev Endocrinol 2011;7:456-65.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 12. Buzzetti E, Pinzani M, Tsochatzis EA. The multiple-hit pathogenesis of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Metabolism 2016;65:1038-48.ArticlePubMed
- 13. Katsarou A, Moustakas II, Pyrina I, Lembessis P, Koutsilieris M, Chatzigeorgiou A. Metabolic inflammation as an instigator of fibrosis during non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 2020;26:1993-2011.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 14. Prasun P. Mitochondrial dysfunction in metabolic syndrome. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 2020;1866:165838.ArticlePubMed
- 15. Masarone M, Rosato V, Dallio M, Gravina AG, Aglitti A, Loguercio C, et al. Role of oxidative stress in pathophysiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2018;2018:9547613.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 16. Bourebaba N, Marycz K. Hepatic stellate cells role in the course of metabolic disorders development: a molecular overview. Pharmacol Res 2021;170:105739.ArticlePubMed
- 17. Blaner WS, O’Byrne SM, Wongsiriroj N, Kluwe J, D’Ambrosio DM, Jiang H, et al. Hepatic stellate cell lipid droplets: a specialized lipid droplet for retinoid storage. Biochim Biophys Acta 2009;1791:467-73.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Zisser A, Ipsen DH, Tveden-Nyborg P. Hepatic stellate cell activation and inactivation in NASH-fibrosis: roles as putative treatment targets? Biomedicines 2021;9:365.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 19. Kitto LJ, Henderson NC. Hepatic stellate cell regulation of liver regeneration and repair. Hepatol Commun 2020;5:358-70.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 20. Berumen J, Baglieri J, Kisseleva T, Mekeel K. Liver fibrosis: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 2021;13:e1499.ArticlePDF
- 21. Kisseleva T, Cong M, Paik Y, Scholten D, Jiang C, Benner C, et al. Myofibroblasts revert to an inactive phenotype during regression of liver fibrosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2012;109:9448-53.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 22. Iredale JP, Benyon RC, Pickering J, McCullen M, Northrop M, Pawley S, et al. Mechanisms of spontaneous resolution of rat liver fibrosis: hepatic stellate cell apoptosis and reduced hepatic expression of metalloproteinase inhibitors. J Clin Invest 1998;102:538-49.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 23. Duarte N, Coelho IC, Patarrao RS, Almeida JI, Penha-Goncalves C, Macedo MP. How inflammation impinges on NAFLD: a role for Kupffer cells. Biomed Res Int 2015;2015:984578.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 24. Lanthier N, Molendi-Coste O, Cani PD, van Rooijen N, Horsmans Y, Leclercq IA. Kupffer cell depletion prevents but has no therapeutic effect on metabolic and inflammatory changes induced by a high-fat diet. FASEB J 2011;25:4301-11.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 25. Neyrinck AM, Cani PD, Dewulf EM, De Backer F, Bindels LB, Delzenne NM. Critical role of Kupffer cells in the management of diet-induced diabetes and obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2009;385:351-6.ArticlePubMed
- 26. Nguyen-Lefebvre AT, Horuzsko A. Kupffer cell metabolism and function. J Enzymol Metab 2015;1:101.PubMedPMC
- 27. Matsui T, Amano M, Yamamoto T, Chihara K, Nakafuku M, Ito M, et al. Rho-associated kinase, a novel serine/threonine kinase, as a putative target for small GTP binding protein Rho. EMBO J 1996;15:2208-16.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 28. Nakagawa O, Fujisawa K, Ishizaki T, Saito Y, Nakao K, Narumiya S. ROCK-I and ROCK-II, two isoforms of Rho-associated coiled-coil forming protein serine/threonine kinase in mice. FEBS Lett 1996;392:189-93.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 29. Ishizaki T, Maekawa M, Fujisawa K, Okawa K, Iwamatsu A, Fujita A, et al. The small GTP-binding protein Rho binds to and activates a 160 kDa Ser/Thr protein kinase homologous to myotonic dystrophy kinase. EMBO J 1996;15:1885-93.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 30. Leung T, Manser E, Tan L, Lim L. A novel serine/threonine kinase binding the Ras-related RhoA GTPase which translocates the kinase to peripheral membranes. J Biol Chem 1995;270:29051-4.ArticlePubMed
- 31. Uehata M, Ishizaki T, Satoh H, Ono T, Kawahara T, Morishita T, et al. Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by a Rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension. Nature 1997;389:990-4.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 32. Hirooka Y, Shimokawa H. Therapeutic potential of rho-kinase inhibitors in cardiovascular diseases. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs 2005;5:31-9.ArticlePubMed
- 33. Hu E, Lee D. Rho kinase as potential therapeutic target for cardiovascular diseases: opportunities and challenges. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2005;9:715-36.ArticlePubMed
- 34. Shimokawa H, Sunamura S, Satoh K. RhoA/Rho-kinase in the cardiovascular system. Circ Res 2016;118:352-66.ArticlePubMed
- 35. Kitamura K, Tada S, Nakamoto N, Toda K, Horikawa H, Kurita S, et al. Rho/Rho kinase is a key enzyme system involved in the angiotensin II signaling pathway of liver fibrosis and steatosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2007;22:2022-33.ArticlePubMed
- 36. Kuroda S, Tashiro H, Igarashi Y, Tanimoto Y, Nambu J, Oshita A, et al. Rho inhibitor prevents ischemia-reperfusion injury in rat steatotic liver. J Hepatol 2012;56:146-52.ArticlePubMed
- 37. Kuroda S, Tashiro H, Kimura Y, Hirata K, Tsutada M, Mikuriya Y, et al. Rho-kinase inhibitor targeting the liver prevents ischemia/reperfusion injury in the steatotic liver without major systemic adversity in rats. Liver Transpl 2015;21:123-31.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 38. Klein S, Van Beuge MM, Granzow M, Beljaars L, Schierwagen R, Kilic S, et al. HSC-specific inhibition of Rho-kinase reduces portal pressure in cirrhotic rats without major systemic effects. J Hepatol 2012;57:1220-7.ArticlePubMed
- 39. van Beuge MM, Prakash J, Lacombe M, Gosens R, Post E, Reker-Smit C, et al. Reduction of fibrogenesis by selective delivery of a Rho kinase inhibitor to hepatic stellate cells in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2011;337:628-35.ArticlePubMed
- 40. Wang J, Jiang W. The effects of RKI-1447 in a mouse model of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease induced by a high-fat diet and in HepG2 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells treated with oleic acid. Med Sci Monit 2020;26:e919220.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 41. Zhou H, Fang C, Zhang L, Deng Y, Wang M, Meng F. Fasudil hydrochloride hydrate, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, ameliorates hepatic fibrosis in rats with type 2 diabetes. Chin Med J (Engl) 2014;127:225-31.ArticlePubMed
- 42. Xie Y, Song T, Huo M, Zhang Y, Zhang YY, Ma ZH, et al. Fasudil alleviates hepatic fibrosis in type 1 diabetic rats: involvement of the inflammation and RhoA/ROCK pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 2018;22:5665-77.PubMed
- 43. Tada S, Iwamoto H, Nakamuta M, Sugimoto R, Enjoji M, Nakashima Y, et al. A selective ROCK inhibitor, Y27632, prevents dimethylnitrosamine-induced hepatic fibrosis in rats. J Hepatol 2001;34:529-36.ArticlePubMed
- 44. Ding R, Han J, Zhao D, Hu Z, Ma X. Pretreatment with Rhokinase inhibitor ameliorates lethal endotoxemia-induced liver injury by improving mitochondrial function. Int Immuno-pharmacol 2016;40:125-30.Article
- 45. Thorlacius K, Slotta JE, Laschke MW, Wang Y, Menger MD, Jeppsson B, et al. Protective effect of fasudil, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, on chemokine expression, leukocyte recruitment, and hepatocellular apoptosis in septic liver injury. J Leukoc Biol 2006;79:923-31.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 46. Murata T, Arii S, Mori A, Imamura M. Therapeutic significance of Y-27632, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, on the established liver fibrosis. J Surg Res 2003;114:64-71.ArticlePubMed
- 47. van Beuge MM, Prakash J, Lacombe M, Post E, Reker-Smit C, Beljaars L, et al. Increased liver uptake and reduced hepatic stellate cell activation with a cell-specific conjugate of the Rhokinase inhibitor Y27632. Pharm Res 2011;28:2045-54.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 48. Klein S, Frohn F, Magdaleno F, Reker-Smit C, Schierwagen R, Schierwagen I, et al. Rho-kinase inhibitor coupled to peptidemodified albumin carrier reduces portal pressure and increases renal perfusion in cirrhotic rats. Sci Rep 2019;9:2256.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 49. Huang H, Lee SH, Sousa-Lima I, Kim SS, Hwang WM, Dagon Y, et al. Rho-kinase/AMPK axis regulates hepatic lipogenesis during overnutrition. J Clin Invest 2018;128:5335-50.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 50. Murata T, Arii S, Nakamura T, Mori A, Kaido T, Furuyama H, et al. Inhibitory effect of Y-27632, a ROCK inhibitor, on progression of rat liver fibrosis in association with inactivation of hepatic stellate cells. J Hepatol 2001;35:474-81.ArticlePubMed
- 51. Ikeda H, Kume Y, Tejima K, Tomiya T, Nishikawa T, Watanabe N, et al. Rho-kinase inhibitor prevents hepatocyte damage in acute liver injury induced by carbon tetrachloride in rats. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 2007;293:G911-7.ArticlePubMed
- 52. Laschke MW, Dold S, Jeppsson B, Schilling MK, Menger MD, Thorlacius H. Rho-kinase inhibitor attenuates cholestasis-induced CXC chemokine formation, leukocyte recruitment, and hepatocellular damage in the liver. J Surg Res 2010;159:666-73.ArticlePubMed
- 53. Ogawa T, Tashiro H, Miyata Y, Ushitora Y, Fudaba Y, Kobayashi T, et al. Rho-associated kinase inhibitor reduces tumor recurrence after liver transplantation in a rat hepatoma model. Am J Transplant 2007;7:347-55.ArticlePubMed
- 54. Mann DA, Smart DE. Transcriptional regulation of hepatic stellate cell activation. Gut 2002;50:891-6.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 55. Narumiya S, Ishizaki T, Uehata M. Use and properties of ROCK-specific inhibitor Y-27632. Methods Enzymol 2000;325:273-84.ArticlePubMed
- 56. Ono-Saito N, Niki I, Hidaka H. H-series protein kinase inhibitors and potential clinical applications. Pharmacol Ther 1999;82:123-31.ArticlePubMed
- 57. Ali Q, Dalapati S, Prakash N, Narayan P, Paka L, Li J, et al. Novel Rho associated coiled kinase 2 (ROCK2) inhibitor reduces steatosis and fibrosis in mice model of liver disease. FASEB J 2020;34(S1):1.Article
- 58. Ali Q, Prakash N, Dalapati S, Li J, Goldberg I, Paka L. Novel Rho associated coiled kinase inhibitor improves hepatic fibrosis in mice model of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). J Hepatol 2020;73:S524.Article
- 59. Wingard C, Fulton D, Husain S. Altered penile vascular reactivity and erection in the Zucker obese-diabetic rat. J Sex Med 2007;4:348-63.ArticlePubMed
- 60. Kikuchi Y, Yamada M, Imakiire T, Kushiyama T, Higashi K, Hyodo N, et al. A Rho-kinase inhibitor, fasudil, prevents development of diabetes and nephropathy in insulin-resistant diabetic rats. J Endocrinol 2007;192:595-603.ArticlePubMed
- 61. Kolavennu V, Zeng L, Peng H, Wang Y, Danesh FR. Targeting of RhoA/ROCK signaling ameliorates progression of diabetic nephropathy independent of glucose control. Diabetes 2008;57:714-23.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 62. Mishra RK, Alokam R, Sriram D, Yogeeswari P. Potential role of Rho kinase inhibitors in combating diabetes-related complications including diabetic neuropathy: a review. Curr Diabetes Rev 2013;9:249-66.ArticlePubMed
- 63. Huang H, Lee SH, Ye C, Lima IS, Oh BC, Lowell BB, et al. ROCK1 in AgRP neurons regulates energy expenditure and locomotor activity in male mice. Endocrinology 2013;154:3660-70.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 64. Noda K, Nakajima S, Godo S, Saito H, Ikeda S, Shimizu T, et al. Rho-kinase inhibition ameliorates metabolic disorders through activation of AMPK pathway in mice. PLoS One 2014;9:e110446.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 65. Kanda T, Wakino S, Homma K, Yoshioka K, Tatematsu S, Hasegawa K, et al. Rho-kinase as a molecular target for insulin resistance and hypertension. FASEB J 2006;20:169-71.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 66. Alves-Bezerra M, Cohen DE. Triglyceride metabolism in the liver. Compr Physiol 2017;8:1-8.PubMedPMC
- 67. Solinas G, Boren J, Dulloo AG. De novo lipogenesis in metabolic homeostasis: more friend than foe? Mol Metab 2015;4:367-77.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 68. Moffett JR, Puthillathu N, Vengilote R, Jaworski DM, Namboodiri AM. Acetate revisited: a key biomolecule at the nexus of metabolism, epigenetics and oncogenesis. Part 1: acetyl-CoA, acetogenesis and acyl-CoA short-chain synthetases. Front Physiol 2020;11:580167.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 69. Belew GD, Silva J, Rito J, Tavares L, Viegas I, Teixeira J, et al. Transfer of glucose hydrogens via acetyl-CoA, malonyl-CoA, and NADPH to fatty acids during de novo lipogenesis. J Lipid Res 2019;60:2050-6.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 70. Girard J, Perdereau D, Foufelle F, Prip-Buus C, Ferre P. Regulation of lipogenic enzyme gene expression by nutrients and hormones. FASEB J 1994;8:36-42.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 71. Najjar SM, Yang Y, Fernstrom MA, Lee SJ, Deangelis AM, Rjaily GA, et al. Insulin acutely decreases hepatic fatty acid synthase activity. Cell Metab 2005;2:43-53.ArticlePubMed
- 72. Eissing L, Scherer T, Todter K, Knippschild U, Greve JW, Buurman WA, et al. De novo lipogenesis in human fat and liver is linked to ChREBP-β and metabolic health. Nat Commun 2013;4:1528.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 73. Beysen C, Ruddy M, Stoch A, Mixson L, Rosko K, Riiff T, et al. Dose-dependent quantitative effects of acute fructose administration on hepatic de novo lipogenesis in healthy humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2018;315:E126-32.ArticlePubMed
- 74. McDevitt RM, Bott SJ, Harding M, Coward WA, Bluck LJ, Prentice AM. De novo lipogenesis during controlled overfeeding with sucrose or glucose in lean and obese women. Am J Clin Nutr 2001;74:737-46.ArticlePubMed
- 75. Ter Horst KW, Vatner DF, Zhang D, Cline GW, Ackermans MT, Nederveen AJ, et al. Hepatic insulin resistance is not pathway selective in humans with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Care 2021;44:489-98.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 76. Strawford A, Antelo F, Christiansen M, Hellerstein MK. Adipose tissue triglyceride turnover, de novo lipogenesis, and cell proliferation in humans measured with 2H2O. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2004;286:E577-88.ArticlePubMed
- 77. Smith GI, Shankaran M, Yoshino M, Schweitzer GG, Chondronikola M, Beals JW, et al. Insulin resistance drives hepatic de novo lipogenesis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest 2020;130:1453-60.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 78. Silva JCP, Marques C, Martins FO, Viegas I, Tavares L, Macedo MP, et al. Determining contributions of exogenous glucose and fructose to de novo fatty acid and glycerol synthesis in liver and adipose tissue. Metab Eng 2019;56:69-76.ArticlePubMed
- 79. Diraison F, Pachiaudi C, Beylot M. In vivo measurement of plasma cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis with deuterated water: determination of the average number of deuterium atoms incorporated. Metabolism 1996;45:817-21.ArticlePubMed
- 80. Duarte JA, Carvalho F, Pearson M, Horton JD, Browning JD, Jones JG, et al. A high-fat diet suppresses de novo lipogenesis and desaturation but not elongation and triglyceride synthesis in mice. J Lipid Res 2014;55:2541-53.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 81. Donnelly KL, Smith CI, Schwarzenberg SJ, Jessurun J, Boldt MD, Parks EJ. Sources of fatty acids stored in liver and secreted via lipoproteins in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J Clin Invest 2005;115:1343-51.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 82. Bergen WG, Mersmann HJ. Comparative aspects of lipid metabolism: impact on contemporary research and use of animal models. J Nutr 2005;135:2499-502.ArticlePubMed
- 83. Schmidt NH, Svendsen P, Albarran-Juarez J, Moestrup SK, Bentzon JF. High-fructose feeding does not induce steatosis or non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in pigs. Sci Rep 2021;11:2807.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 84. Lambert JE, Ramos-Roman MA, Browning JD, Parks EJ. Increased de novo lipogenesis is a distinct characteristic of individuals with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2014;146:726-35.ArticlePubMed
- 85. Postic C, Girard J. The role of the lipogenic pathway in the development of hepatic steatosis. Diabetes Metab 2008;34(6 Pt 2):643-8.ArticlePubMed
- 86. Diraison F, Moulin P, Beylot M. Contribution of hepatic de novo lipogenesis and reesterification of plasma non esterified fatty acids to plasma triglyceride synthesis during non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Diabetes Metab 2003;29:478-85.ArticlePubMed
- 87. Flannery C, Dufour S, Rabol R, Shulman GI, Petersen KF. Skeletal muscle insulin resistance promotes increased hepatic de novo lipogenesis, hyperlipidemia, and hepatic steatosis in the elderly. Diabetes 2012;61:2711-7.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 88. Beysen C, Schroeder P, Wu E, Brevard J, Ribadeneira M, Lu W, et al. Inhibition of fatty acid synthase with FT-4101 safely reduces hepatic de novo lipogenesis and steatosis in obese subjects with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: results from two early-phase randomized trials. Diabetes Obes Metab 2021;23:700-10.PubMed
- 89. Mallat A, Teixeira-Clerc F, Deveaux V, Manin S, Lotersztajn S. The endocannabinoid system as a key mediator during liver diseases: new insights and therapeutic openings. Br J Pharmacol 2011;163:1432-40.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 90. Baldassarre M, Giannone FA, Napoli L, Tovoli A, Ricci CS, Tufoni M, et al. The endocannabinoid system in advanced liver cirrhosis: pathophysiological implication and future perspectives. Liver Int 2013;33:1298-308.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 91. Gotfried J, Naftali T, Schey R. Role of cannabis and its derivatives in gastrointestinal and hepatic disease. Gastroenterology 2020;159:62-80.ArticlePubMed
- 92. Silvestri C, Di Marzo V. The endocannabinoid system in energy homeostasis and the etiopathology of metabolic disorders. Cell Metab 2013;17:475-90.ArticlePubMed
- 93. Batkai S, Osei-Hyiaman D, Pan H, El-Assal O, Rajesh M, Mukhopadhyay P, et al. Cannabinoid-2 receptor mediates protection against hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. FASEB J 2007;21:1788-800.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 94. Auguet T, Berlanga A, Guiu-Jurado E, Terra X, Martinez S, Aguilar C, et al. Endocannabinoid receptors gene expression in morbidly obese women with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Biomed Res Int 2014;2014:502542.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 95. Mendez-Sanchez N, Zamora-Valdes D, Pichardo-Bahena R, Barredo-Prieto B, Ponciano-Rodriguez G, Bermejo-Martinez L, et al. Endocannabinoid receptor CB2 in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Liver Int 2007;27:215-9.ArticlePubMed
- 96. Devane WA, Hanus L, Breuer A, Pertwee RG, Stevenson LA, Griffin G, et al. Isolation and structure of a brain constituent that binds to the cannabinoid receptor. Science 1992;258:1946-9.ArticlePubMed
- 97. Mechoulam R, Ben-Shabat S, Hanus L, Ligumsky M, Kaminski NE, Schatz AR, et al. Identification of an endogenous 2-monoglyceride, present in canine gut, that binds to cannabinoid receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 1995;50:83-90.ArticlePubMed
- 98. Sugiura T, Kondo S, Sukagawa A, Nakane S, Shinoda A, Itoh K, et al. 2-Arachidonoylglycerol: a possible endogenous cannabinoid receptor ligand in brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1995;215:89-97.PubMed
- 99. Rahman SM, Uyama T, Hussain Z, Ueda N. Roles of endocannabinoids and endocannabinoid-like molecules in energy homeostasis and metabolic regulation: a nutritional perspective. Annu Rev Nutr 2021 Jun 11 [Epub]. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-nutr-043020-090216.Article
- 100. Osei-Hyiaman D, DePetrillo M, Pacher P, Liu J, Radaeva S, Batkai S, et al. Endocannabinoid activation at hepatic CB1 receptors stimulates fatty acid synthesis and contributes to dietinduced obesity. J Clin Invest 2005;115:1298-305.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 101. Bermudez-Silva FJ, Suarez J, Baixeras E, Cobo N, Bautista D, Cuesta-Munoz AL, et al. Presence of functional cannabinoid receptors in human endocrine pancreas. Diabetologia 2008;51:476-87.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 102. Juan-Pico P, Fuentes E, Bermudez-Silva FJ, Javier Diaz-Molina F, Ripoll C, Rodriguez de Fonseca F, et al. Cannabinoid receptors regulate Ca(2+) signals and insulin secretion in pancreatic beta-cell. Cell Calcium 2006;39:155-62.ArticlePubMed
- 103. Silvestri C, Ligresti A, Di Marzo V. Peripheral effects of the endocannabinoid system in energy homeostasis: adipose tissue, liver and skeletal muscle. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 2011;12:153-62.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 104. Eckardt K, Sell H, Taube A, Koenen M, Platzbecker B, Cramer A, et al. Cannabinoid type 1 receptors in human skeletal muscle cells participate in the negative crosstalk between fat and muscle. Diabetologia 2009;52:664-74.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 105. Bazwinsky-Wutschke I, Zipprich A, Dehghani F. Endocannabinoid system in hepatic glucose metabolism, fatty liver disease, and cirrhosis. Int J Mol Sci 2019;20:2516.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 106. Gary-Bobo M, Elachouri G, Gallas JF, Janiak P, Marini P, Ravinet-Trillou C, et al. Rimonabant reduces obesity-associated hepatic steatosis and features of metabolic syndrome in obese Zucker fa/fa rats. Hepatology 2007;46:122-9.ArticlePubMed
- 107. Chang E, Kim DH, Yang H, Lee DH, Bae SH, Park CY. CB1 receptor blockade ameliorates hepatic fat infiltration and inflammation and increases Nrf2-AMPK pathway in a rat model of severely uncontrolled diabetes. PLoS One 2018;13:e0206152.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 108. Jorgacevic B, Vucevic D, Duricic I, Sobajic S, Mladenovic D, Veskovic M, et al. The effect of cannabinoid receptor 1 blockade on hepatic free fatty acid profile in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Chem Phys Lipids 2017;204:85-93.ArticlePubMed
- 109. Hussien NI, El-Kerdasy HI, Ibrahim ME. Protective effect of rimonabant, a canabinoid receptor 1 antagonist, on nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a rat model through modulation of the hepatic expression of activin A and follistatin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2017;95:1433-41.ArticlePubMed
- 110. Jorgacevic B, Vucevic D, Veskovic M, Mladenovic D, Vukicevic D, Vukicevic RJ, et al. The effect of cannabinoid receptor 1 blockade on adipokine and proinflammatory cytokine concentration in adipose and hepatic tissue in mice with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 2019;97:120-9.ArticlePubMed
- 111. Khan N, Laudermilk L, Ware J, Rosa T, Mathews K, Gay E, et al. Peripherally selective CB1 receptor antagonist improves symptoms of metabolic syndrome in mice. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci 2021;4:757-64.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 112. Tam J, Cinar R, Liu J, Godlewski G, Wesley D, Jourdan T, et al. Peripheral cannabinoid-1 receptor inverse agonism reduces obesity by reversing leptin resistance. Cell Metab 2012;16:167-79.ArticlePubMed
- 113. Cinar R, Godlewski G, Liu J, Tam J, Jourdan T, Mukhopadhyay B, et al. Hepatic cannabinoid-1 receptors mediate diet-induced insulin resistance by increasing de novo synthesis of long-chain ceramides. Hepatology 2014;59:143-53.ArticlePubMed
- 114. Gruden G, Barutta F, Kunos G, Pacher P. Role of the endocannabinoid system in diabetes and diabetic complications. Br J Pharmacol 2016;173:1116-27.ArticlePubMed
- 115. Tan S, Liu H, Ke B, Jiang J, Wu B. The peripheral CB1 receptor antagonist JD5037 attenuates liver fibrosis via a CB1 receptor/β-arrestin1/Akt pathway. Br J Pharmacol 2020;177:2830-47.PubMedPMC
- 116. Yang Q, Sun S, Liu W, Liu Q, Wang J. Hypoxia training improves hepatic steatosis partly by downregulation of CB1 receptor in obese mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2020;525:639-45.ArticlePubMed
- 117. Killilea M, Kerr DM, Mallard BM, Roche M, Wheatley AM. Exacerbated LPS/GalN-induced liver injury in the stress-sensitive Wistar Kyoto rat is associated with changes in the endocannabinoid system. Molecules 2020;25:3834.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 118. Assa-Glazer T, Gorelick J, Sela N, Nyska A, Bernstein N, Madar Z. Cannabis extracts affected metabolic syndrome parameters in mice fed high-fat/cholesterol diet. Cannabis Cannabinoid Res 2020;5:202-14.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 119. Drori A, Gammal A, Azar S, Hinden L, Hadar R, Wesley D, et al. CB1R regulates soluble leptin receptor levels via CHOP, contributing to hepatic leptin resistance. Elife 2020;9:e60771.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 120. Ali AM, El-Tawil OS, Al-Mokaddem AK, Abd El-Rahman SS. Promoted inhibition of TLR4/miR-155/NFkB p65 signaling by cannabinoid receptor 2 agonist (AM1241), aborts inflammation and progress of hepatic fibrosis induced by thioacetamide. Chem Biol Interact 2021;336:109398.ArticlePubMed
- 121. van Eenige R, Ying Z, Tambyrajah L, Pronk AC, Blomberg N, Giera M, et al. Cannabinoid type 1 receptor inverse agonism attenuates dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis in APOE*3-Leiden.CETP mice. J Lipid Res 2021;62:100070.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 122. Demizieux L, Piscitelli F, Troy-Fioramonti S, Iannotti FA, Borrino S, Gresti J, et al. Early low-fat diet enriched with linolenic acid reduces liver endocannabinoid tone and improves late glycemic control after a high-fat diet challenge in mice. Diabetes 2016;65:1824-37.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 123. Teixeira-Clerc F, Julien B, Grenard P, Tran Van Nhieu J, Deveaux V, Li L, et al. CB1 cannabinoid receptor antagonism: a new strategy for the treatment of liver fibrosis. Nat Med 2006;12:671-6.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 124. Irungbam K, Churin Y, Matono T, Weglage J, Ocker M, Glebe D, et al. Cannabinoid receptor 1 knockout alleviates hepatic steatosis by downregulating perilipin 2. Lab Invest 2020;100:454-65.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 125. Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D, Hardie DG. AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab 2005;1:15-25.ArticlePubMed
- 126. Li Y, Xu S, Mihaylova MM, Zheng B, Hou X, Jiang B, et al. AMPK phosphorylates and inhibits SREBP activity to attenuate hepatic steatosis and atherosclerosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. Cell Metab 2011;13:376-88.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 127. Minokoshi Y, Kim YB, Peroni OD, Fryer LG, Muller C, Carling D, et al. Leptin stimulates fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nature 2002;415:339-43.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 128. Weikel KA, Ruderman NB, Cacicedo JM. Unraveling the actions of AMP-activated protein kinase in metabolic diseases: systemic to molecular insights. Metabolism 2016;65:634-45.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 129. Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X, Fenyk-Melody J, et al. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Invest 2001;108:1167-74.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 130. Kim SS, Hwang WM, Yang WM, Lee H, Park KS, Dagon Y, et al. Rho-kinase mediates the anorexigenic action of melanocortin by suppressing AMPK. bioRxiv 2019 Jun 21. https://doi.org/10.1101/677880.Article
- 131. Hong C, Tontonoz P. Liver X receptors in lipid metabolism: opportunities for drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 2014;13:433-44.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 132. Steffensen KR, Gustafsson JA. Putative metabolic effects of the liver X receptor (LXR). Diabetes 2004;53 Suppl 1:S36-42.ArticlePubMedPDF
- 133. Bradley MN, Hong C, Chen M, Joseph SB, Wilpitz DC, Wang X, et al. Ligand activation of LXR beta reverses atherosclerosis and cellular cholesterol overload in mice lacking LXR alpha and apoE. J Clin Invest 2007;117:2337-46.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 134. Joseph SB, Laffitte BA, Patel PH, Watson MA, Matsukuma KE, Walczak R, et al. Direct and indirect mechanisms for regulation of fatty acid synthase gene expression by liver X receptors. J Biol Chem 2002;277:11019-25.ArticlePubMed
- 135. Chu K, Miyazaki M, Man WC, Ntambi JM. Stearoyl-coenzyme A desaturase 1 deficiency protects against hypertriglyceridemia and increases plasma high-density lipoprotein cholesterol induced by liver X receptor activation. Mol Cell Biol 2006;26:6786-98.ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 136. Beaven SW, Matveyenko A, Wroblewski K, Chao L, Wilpitz D, Hsu TW, et al. Reciprocal regulation of hepatic and adipose lipogenesis by liver X receptors in obesity and insulin resistance. Cell Metab 2013;18:106-17.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 137. Laffitte BA, Chao LC, Li J, Walczak R, Hummasti S, Joseph SB, et al. Activation of liver X receptor improves glucose tolerance through coordinate regulation of glucose metabolism in liver and adipose tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2003;100:5419-24.ArticlePubMedPMC
- 138. Chisholm JW, Hong J, Mills SA, Lawn RM. The LXR ligand T0901317 induces severe lipogenesis in the db/db diabetic mouse. J Lipid Res 2003;44:2039-48.ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- THE ROLE OF N6-METHYLADENOSINE METHYLTRANSFERASE RBM15 IN NONALCOHOLIC FATTY LIVER DISEASE
Shiqing Li, Shengyi Lian, Wei Cheng, Tao Zhang, Xiaobing Gong
Shock.2024; 61(2): 311. CrossRef - Exploring the potential of drug repurposing for liver diseases: A comprehensive study
Fares E.M. Ali, Mustafa Ahmed Abdel-Reheim, Emad H.M. Hassanein, Mostafa K. Abd El-Aziz, Hanan S. Althagafy, Khalid S.A. Badran
Life Sciences.2024; : 122642. CrossRef - Targeting of G-protein coupled receptor 40 alleviates airway hyperresponsiveness through RhoA/ROCK1 signaling pathway in obese asthmatic mice
Xixi Lin, Like Wang, Xiaojie Lu, Yuanyuan Zhang, Rongying Zheng, Ruijie Chen, Weixi Zhang
Respiratory Research.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Selectivity matters: selective ROCK2 inhibitor ameliorates established liver fibrosis via targeting inflammation, fibrosis, and metabolism
Alexandra Zanin-Zhorov, Wei Chen, Julien Moretti, Melanie S. Nyuydzefe, Iris Zhorov, Rashmi Munshi, Malavika Ghosh, Cindy Serdjebi, Kelli MacDonald, Bruce R. Blazar, Melissa Palmer, Samuel D. Waksal
Communications Biology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Insight Into Rho Kinase Isoforms in Obesity and Energy Homeostasis
Lei Wei, Jianjian Shi
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Paeoniflorin alleviates liver injury in hypercholesterolemic rats through the ROCK/AMPK pathway
Tong Liu, Ning Zhang, Lingya Kong, Sijie Chu, Ting Zhang, Guangdi Yan, Donglai Ma, Jun Dai, Zhihong Ma
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2022;[Epub] CrossRef - Fasudil Increased the Sensitivity to Gefitinib in NSCLC by Decreasing Intracellular Lipid Accumulation
Tingting Liao, Jingjing Deng, Wenjuan Chen, Juanjuan Xu, Guanghai Yang, Mei Zhou, Zhilei Lv, Sufei Wang, Siwei Song, Xueyun Tan, Zhengrong Yin, Yumei Li, Yang Jin
Cancers.2022; 14(19): 4709. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA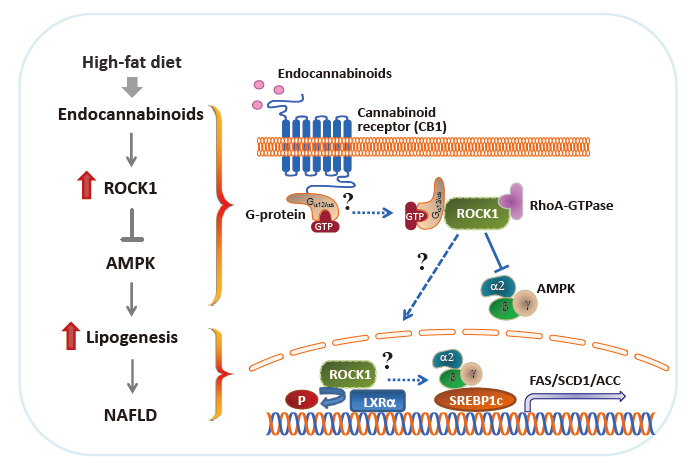
 PubReader
PubReader ePub Link
ePub Link Cite
Cite