
- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 35(3); 2011 > Article
-
Original ArticleThe Effect of an Angiotensin Receptor Blocker on Arterial Stiffness in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Hypertension
- Ji Hyun Kim1, Su Jin Oh1, Jung Min Lee1, Eun Gyoung Hong2, Jae Myung Yu2, Kyung Ah Han3, Kyung Wan Min3, Hyun Shik Son1, Sang Ah Chang1
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2011;35(3):236-242.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2011.35.3.236
Published online: June 30, 2011
1Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
2Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
3Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Sang Ah Chang. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, St. Paul's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, 620-56 Jeonnong 1-dong, Dongdaemun-gu, Seoul 130-709, Korea. sangah@catholic.ac.kr
Copyright © 2011 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- Hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus are major risk factors for cardiovascular disease. This study analyzed the changes in central aortic waveforms and pulse wave velocity as well as related parameters after treatment with valsartan, an angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker, in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension.
-
Methods
- We used pulse wave analysis to measure central aortic waveform in a total of 98 subjects. In 47 of these patients, pulse wave velocity measurements were obtained before and after 12 weeks of treatment with valsartan.
-
Results
- In the central aortic waveform analysis, the aortic pulse pressure and augmentation index were significantly decreased after valsartan treatment, as was the aortic pulse wave velocity. Factors contributing to the improvement in pulse wave velocity were the fasting blood glucose and haemoglobin A1c levels.
-
Conclusion
- Short-term treatment with valsartan improves arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes and hypertension, and the glucose status at baseline was associated with this effect.
- Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is the largest cause of morbidity and mortality in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) [1]. Hypertension is a common comorbidity in patients with T2DM, and these two diseases are major risk factors for CVD [2]. In T2DM, hypertension often initiates and accelerates the progression of macrovascular events by increasing arterial stiffness, which results in the aggravation of ventricular afterload and the impairment of coronary perfusion [3,4]. Increased arterial stiffness was recently reported to be a powerful and independent risk factor for early mortality, and presented more clinical prognostic value than previously known CVD risk factors such as age, gender, smoking, and dyslipidemia [5]. Therefore, the measurement of arterial stiffness and the control of other risk factors would be important strategies for the prevention and early treatment of cardiovascular events.
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers (ARBs) have been shown to have a beneficial effect on angiopathy resulting from hypertension and impaired glucose metabolism. ARBs are regarded as first-line treatment for T2DM with hypertension and some studies have reported an effect of the blockade of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) on arterial stiffness in T2DM and hypertension [6-8]. However, the effect of ARBs on arterial stiffness, as well as the mechanism and related factors, are poorly understood in T2DM with hypertension. Valsartan is an angiotensin II type 1 (AT1) receptor blocker that has antihypertensive effects. To examine the effect of the ARB valsartan on arterial stiffness and related parameters in T2DM with hypertension, we analyzed the changes in central aortic waveforms and aortic pulse wave velocity (PWV) after treatment with valsartan for 12 weeks.
INTRODUCTION
- Research setting and study population
- Our study population included patients between 30 and 75 years of age who had T2DM and who visited one of three centers from February 2006 to February 2008. Patients with a <10-year recorded history of T2DM diagnosed according to the American Diabetes Association criteria, a verified body mass index (BMI) between 20 and 30 kg/m2, and a verified Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) level between 6.5% and 10% were eligible for this study. Eligibility criteria also included mild to moderate hypertension as defined by the Joint National Committee on Prevention, Detection, Evaluation, and Treatment of High Blood Pressure, i.e., brachial systolic blood pressure (SBP) of 140 to 160 mm Hg and diastolic blood pressure (DBP) of 90 to 100 mm Hg. Exclusion criteria included a history of ischemic heart disease in the preceding 3 months, biochemical evidence of renal impairment (creatinine >1.5 mg/dL), liver enzyme levels more than three times the normal limits, and pregnancy or nursing at the time of the study. Additional exclusion criteria included the concomitant use of medications such as ACE inhibitors or other ARBs at entry and the use of insulin or antidiabetic drugs such as thiazolidinedione or metformin in the preceding 3 months. A total of 107 Korean subjects were recruited for this study. After nine subjects withdrew, 98 subjects (41 men and 57 women) were available for analysis.
- Study design
- This study was a multi-centre, open label, controlled study to investigate the short-term effect of a 12-week treatment with valsartan on arterial stiffness in T2DM with hypertension. Patients receiving other antihypertensive agents for systolic hypertension were permitted to enter the trial after a 2-week wash-out of the drug and hypertension was controlled by valsartan thereafter. Arterial blood pressure was measured in the right arm using a mercury sphygmomanometer, three times under resting conditions in the morning by a selected physician, and the mean values were calculated for this study. All study subjects underwent anthropometric measurements, including height, weight, and BMI, as well as blood chemistry analysis, including fasting blood glucose, HbA1c, insulin, BUN, creatinine, and uric acid levels; liver function tests; and lipid profiles. An estimate of insulin resistance was obtained by homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance (HOMA-IR), which was calculated using the following formula: fasting insulin (mU/L)×fasting glucose (mmol/L)/22.5. The central aortic waveform was measured using pulse wave analysis by applanation tonometry (Sphygmocor; AtCor Medical Inc., Sydney, Australia) in all study subjects, and aortic PWV measurements were taken in 47 of the study subjects.
- After the screening examination, all participants received an initial daily dose of 80 mg of valsartan. After 4 weeks, the valsartan dose was increased to 160 mg/day for 8 weeks. All subjects were advised to consume their usual diet and medications other than valsartan were not changed during the study. Basic assessment, blood sampling, and central aortic waveform measurement were evaluated before and after the 12-week administration. Aortic PWV was measured in 47 randomly selected among subjects who measured pulse wave analysis (PWA). To evaluate the factors contributing to the improvement of PWV with valsartan administration, these patients were divided into two groups: one group in which PWV decreased and the other in which PWV did not decrease. The Ethics Committee of each hospital approved this study protocol, and informed consent was obtained from all subjects.
- Measurement of arterial stiffness
- Central aortic waveform measurements were made using pulse wave analysis by applanation tonometry (Sphygmocor). Radial artery pressure waveforms were obtained from the wrist using a tonometer, and a corresponding central waveform was generated with a validated generalized transfer function, using the Sphygmocor. The Sphygmocor generates ascending aortic pressure waveforms from the radial pulse and provides substantially equivalent values of aortic systolic, pulse, mean, and diastolic pressures [9]. The integrated Sphygmocor software was used to determine the augmentation index (AIx), which is a composite measure of systemic arterial stiffness and wave-reflection amplitude, as well as the ejection duration (ED) and subendocardial viability ratio (SEVR). The aortic (carotid to femoral) PWV and relevant transient times were measured noninvasively by tonometry, using the Sphygmocor system as mentioned above. For each subject, the distance travelled by the pulse wave between the carotid-femoral arteries was measured in a straight line. The investigators who performed the measurements had been fully trained in the technique of applanation tonometry. The precision of the method was determined by the interobserver and intraobserver variabilities, which were 0.93 and 0.95, respectively, for AIx and 0.9 and 0.9 for PWV.
- Statistical analysis
- Treatment-related changes in parameters were analyzed using a Wilcoxon test. We analyzed the relationship between the change in arterial stiffness and changes in other parameters using Spearman's correlation test. Continuous values are expressed as means±standard deviation (SD). A P value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. Statistical analysis was performed using SPSS version 10.0 (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
METHODS
- A total of 98 (41 men and 57 women) patients were eligible for analysis in the study. The demographic characteristics of the patients and the alterations in their clinical and laboratory parameters are shown in Table 1. In the central aortic waveform analysis, aortic pulse pressure (44.4±8.5 vs. 38.9±10.2 mm Hg, P<0.05) and AIx (29.5±7.4% vs. 27.8±7.9%, P<0.05) were significantly decreased after valsartan treatment without increase of heart rate. However, the SEVR and ED did not change significantly (Table 2). At the end of the 12-week treatment, there were significant decreases in SBP (148.6±5.7 vs. 132.3±13.0 mm Hg, P<0.001) and DBP (91.4±2.7 vs. 81.2±10.1 mm Hg, P<0.001) (Table 3). There were no observed changes in the levels of total cholesterol, triglycerides, low density lipoprotein cholesterol, high density lipoprotein cholesterol, fasting glucose, HbA1c, and HOMA-IR (Table 3). The change in SBP correlated only with the decreases in AIx (P<0.01) and aortic pulse pressure (P<0.01) (data not shown).
- In a subgroup analysis of the 47 patients with measured PWV, the mean aortic PWV was significantly decreased (10.9±1.1 vs. 10.0±1.2 m/sec, P<0.05) without a change in heart rate after valsartan treatment (Table 2). Among the baseline parameters, there were significant differences in the levels of fasting blood glucose (138.2±34.7 vs. 163.7±39.9 mg/dL) and HbA1c (7.1±1.0% vs. 8.6±1.1%) between the two groups (P<0.05). The change in mean arterial pressure was not different between the two groups.
- In logistic regression analysis, HbA1c was the only independent factor associated with aortic PWV improvement (hazard ratio, 2.638; P<0.05) (Table 4). Patients with improved PWV presented significantly better blood glucose levels at baseline compared to those with no PWV improvement.
RESULTS
- Hypertension and T2DM are major risk factors for cardiovascular disease, and the degree of atherosclerosis can be determined by measuring arterial stiffness. The detection of arterial stiffness and the control of risk factors are becoming important strategies in the prevention and early treatment of cardiovascular events. Arterial stiffness can be assessed by the simple, validated, and reproducible technique of applanation tonometry, which noninvasively measures PWA and PWV [10]. This study demonstrated that valsartan reduced central hemodynamic parameters, AIx and aortic pulse pressure. These findings are consistent with those of previous reports that ARBs reduce arterial stiffness [6-8]. Central blood pressure and AIx, a composite measure of systemic arterial stiffness, can be assessed with PWA of the radial artery waveform. The pressure wave can reflect the status of the peripheral vasculature, i.e., branching, resistance, stenosis, and return towards the heart. When vessels are stiffened, the returned wave may add to the ejection pressure. In addition, the late systolic augmentation of the central pressure waveform is associated with an increased left ventricular mass index. Therefore, an increased AIx is associated with coronary artery disease. Increased stiffness of the aorta and large arteries leads to an increase in the pulse pressure, through a reduction in arterial compliance, and a premature return of reflected waves in late systole, which increases the load on the ventricle and the myocardial oxygen demand [11]. In our study, SEVR and ED were not changed after valsartan administration. These results could be explained by the results of previous studies showing that the mean aortic pressure and pulse pressure did not contribute to the SEVR and ED [12,13]. No changes were observed in glucose metabolism, insulin resistance or lipid profiles after valsartan administration. Valsartan reduced systolic and diastolic blood pressures, but only the alteration of SBP was correlated with the changes in central hemodynamic parameters showing arterial stiffness in this study.
- Aortic PWV is a one of the well-validated parameters of central arterial stiffness and generalized atherosclerosis [14]. Moreover, it is considered an independent predictor for cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in subjects with T2DM [15]. In our data, aortic PWV was also reduced by valsartan treatment. It could be a passive effect of the reduction of mean arterial pressure by 12 mm Hg after valsartan treatment (data not shown). However, in some patients of our study, a lack of reduction in aortic PWV was shown in state of decline in central blood pressure. Our results suggest that baseline glucose control status is associated with modulation of arterial stiffness by valsartan. Although one possible mechanism by which valsartan decreases arterial stiffness is via a decrease in blood pressure, ARBs modulate arterial stiffness independently of the brachial, central BP lowering and of the passive effect of pressure on arterial elastic properties [7]. Therefore, ARBs may act on arterial stiffness by other mechanisms.
- Among local hormone factors associated with the modification of the arterial wall, angiotensin II may play an important role through the AT1 receptor, because it induces proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells and increases collagen synthesis by fibroblasts [16,17]. Angiotensin II contributes to cell injury, endothelial dysfunction, and vascular toxicity and fibrosis [18,19]. It also mediates the accumulation and activation of inflammatory cells, and an increase in vascular permeability, which results in premature vascular complications [20]. Therefore, ARB reverses these changes in the vascular wall and may improve the stiffness.
- In patients with T2DM, over-activation of the RAAS occurs and affects cardiovascular homeostasis. Owing to the inhibition of the RAAS, ACE inhibitors and ARBs may have greater cardio-protective benefits in T2DM patients [21-23]. ARBs can reduce the negative influence of angiotensin II on the endothelium, with subsequent improvement of arterial elasticity. Other advantageous aspects of ARBs are a reduction in oxidative stress, expression of proinflammatory vascular cell adhesion molecules and stimulation of adipogenesis, leading to improved glucose transport [24,25].
- Patients with both diabetes and hypertension have higher arterial stiffness than those with diabetes or hypertension alone [26]. In patients with both diseases, angiotensin II receptor blockade is expected to play a more important role in protection against cardiovascular disease, by improving arterial stiffness. Few previous reports regarding T2DM with hypertension have focused on the effect of ARBs on arterial stiffness and related parameters [7,26,27]. Our findings that valsartan significantly reduces arterial stiffness as demonstrated be estimation of PWA and PWV in T2DM patients with hypertension, was based on observational findings during a relatively short period, of 12 weeks. Moreover, baseline glucose control status is associated with modulation of arterial stiffness by valsartan, i.e., with better diabetes control, valsartan treatment will be more effective for treating T2DM patients with hypertension. A previous study analyzing the effects of T2DM with hypertension on the arterial wall has reported a highly significant correlation between PWV and the fasting glucose level, among the various risk factors [26]. The mechanism by which arterial stiffness is increased in diabetes is largely unknown. However, one possible mechanism is related to changes in elastin and collagen within the walls. Therefore, hyperglycemia due to diabetes is thought to affect atherosclerosis of large arteries, and promote the formation of advanced glycation end-products in the arterial wall [26]. Advanced glycation end-products are believed to cause the cross-linking of collagen molecules, leading to a loss of collagen elasticity and a subsequent increase in arterial stiffness [28]. Chronic hyperglycaemia and hyperinsulinaemia also increase local RAAS activity and the expression of the AT1 receptor in vascular tissue, promoting development of wall hypertrophy and fibrosis [29]. Low-grade inflammation and endothelial dysfunction may partly explain the increase in arterial stiffness related to diabetes [30]. In this regard, concomitant blood glucose control and treatment with ARBs are expected to induce favorable cardio-protective effects in this population. Such treatments would be recommended in the early stages of diabetes and hypertension, before vascular modulation has progressed.
- Our study has some limitations. First, there was no control group treated with another class of anti-hypertensive drug. We can not establish whether valsartan reduced arterial stiffness independently of its blood pressure lowering effect. Second, the failure of valsartan to improve arterial stiffness in patients with uncontrolled diabetes was not completely understood. We suggest that the vascular changes over the 12-week treatment period may be insufficient to positively affect arterial stiffness under conditions in which glucose is uncontrolled. The changes in aortic PWV were supposed to be influenced by long term pressure-dependent vascular structure changes. The differential impact of ARB on aortic PWV could not be reflected sufficiently because of the short-term period of this study. Nevertheless, this study is one of very few studies, especially in Asian people, evaluating the effect of ARB on arterial stiffness and related parameters in T2DM with hypertension. Further investigations will elucidate the mechanism by which the glucose control status affects arterial stiffness after valsartan treatment.
- In conclusion, this study shows that treatment with the ARB, valsartan, improved arterial stiffness over a relatively short treatment period of 12 weeks in T2DM patients with hypertension. The fasting glucose and HbA1c levels are independently associated with PWV improvement attributable to the action of valsartan. Valsartan may be useful for delaying and reducing the influence of cardiovascular risk factors on arterial stiffness in high-risk patients such as those with T2DM with hypertension.
DISCUSSION
- 1. Haffner SM, Lehto S, Ronnemaa T, Pyorala K, Laakso M. Mortality from coronary heart disease in subjects with type 2 diabetes and in nondiabetic subjects with and without prior myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 1998;339:229-234. ArticlePubMed
- 2. Cockcroft JR, Webb DJ, Wilkinson IB. Arterial stiffness, hypertension and diabetes mellitus. J Hum Hypertens 2000;14:377-380. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 3. Lehmann ED, Gosling RG, Sonksen PH. Arterial wall compliance in diabetes. Diabet Med 1992;9:114-119. ArticlePubMed
- 4. Dart AM, Kingwell BA. Pulse pressure: a review of mechanisms and clinical relevance. J Am Coll Cardiol 2001;37:975-984. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Willum-Hansen T, Staessen JA, Torp-Pedersen C, Rasmussen S, Thijs L, Ibsen H, Jeppesen J. Prognostic value of aortic pulse wave velocity as index of arterial stiffness in the general population. Circulation 2006;113:664-670. ArticlePubMed
- 6. Agata J, Nagahara D, Kinoshita S, Takagawa Y, Moniwa N, Yoshida D, Ura N, Shimamoto K. Angiotensin II receptor blocker prevents increased arterial stiffness in patients with essential hypertension. Circ J 2004;68:1194-1198. ArticlePubMed
- 7. Karalliedde J, Smith A, DeAngelis L, Mirenda V, Kandra A, Botha J, Ferber P, Viberti G. Valsartan improves arterial stiffness in type 2 diabetes independently of blood pressure lowering. Hypertension 2008;51:1617-1623. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Okura T, Watanabe S, Kurata M, Koresawa M, Irita J, Enomoto D, Jotoku M, Miyoshi K, Fukuoka T, Higaki J. Long-term effects of angiotensin II receptor blockade with valsartan on carotid arterial stiffness and hemodynamic alterations in patients with essential hypertension. Clin Exp Hypertens 2008;30:415-422. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Pauca AL, O'Rourke MF, Kon ND. Prospective evaluation of a method for estimating ascending aortic pressure from the radial artery pressure waveform. Hypertension 2001;38:932-937. ArticlePubMed
- 10. Wilkinson IB, Fuchs SA, Jansen IM, Spratt JC, Murray GD, Cockcroft JR, Webb DJ. Reproducibility of pulse wave velocity and augmentation index measured by pulse wave analysis. J Hypertens 1998;16(12 Pt 2):2079-2084. ArticlePubMed
- 11. Nichols WW, O'Rourke MF. . McDonald's blood flow in arteries: theoretical, experimental and clinical principles. 1990. 3rd ed. London: Lea and Febier; p. 77-142. p. 216-269. p. 283-359. p. 398-437.
- 12. Chemla D, Nitenberg A, Teboul JL, Richard C, Monnet X, le Clesiau H, Valensi P, Brahimi M. Subendocardial viability ratio estimated by arterial tonometry: a critical evaluation in elderly hypertensive patients with increased aortic stiffness. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2008;35:909-915. ArticlePubMed
- 13. Brooks BA, Molyneaux LM, Yue DK. Augmentation of central arterial pressure in type 2 diabetes. Diabet Med 2001;18:374-380. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Cohn JN, Finkelstein S, McVeigh G, Morgan D, LeMay L, Robinson J, Mock J. Noninvasive pulse wave analysis for the early detection of vascular disease. Hypertension 1995;26:503-508. ArticlePubMed
- 15. Cruickshank K, Riste L, Anderson SG, Wright JS, Dunn G, Gosling RG. Aortic pulse-wave velocity and its relationship to mortality in diabetes and glucose intolerance: an integrated index of vascular function? Circulation 2002;106:2085-2090. ArticlePubMed
- 16. Kim S, Iwao H. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of angiotensin II-mediated cardiovascular and renal diseases. Pharmacol Rev 2000;52:11-34. PubMed
- 17. Williams B. Angiotensin II and the pathophysiology of cardiovascular remodeling. Am J Cardiol 2001;87(8A):10C-17C.ArticlePubMed
- 18. Johnston CI. Tissue angiotensin converting enzyme in cardiac and vascular hypertrophy, repair, and remodeling. Hypertension 1994;23:258-268. ArticlePubMed
- 19. Kuwahara F, Kai H, Tokuda K, Takeya M, Takeshita A, Egashira K, Imaizumi T. Hypertensive myocardial fibrosis and diastolic dysfunction: another model of inflammation? Hypertension 2004;43:739-745. ArticlePubMed
- 20. Luft FC. Angiotensin, inflammation, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. Curr Hypertens Rep 2001;3:61-67. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 21. Heart Outcomes Prevention Evaluation Study Investigators. Effects of ramipril on cardiovascular and microvascular outcomes in people with diabetes mellitus: results of the HOPE study and MICRO-HOPE substudy. Lancet 2000;355:253-259. ArticlePubMed
- 22. Dahlof B, Devereux RB, Kjeldsen SE, Julius S, Beevers G, de Faire U, Fyhrquist F, Ibsen H, Kristiansson K, Lederballe-Pedersen O, Lindholm LH, Nieminen MS, Omvik P, Oparil S, Wedel H. LIFE Study Group. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): a randomised trial against atenolol. Lancet 2002;359:995-1003. ArticlePubMed
- 23. Lindholm LH, Ibsen H, Dahlof B, Devereux RB, Beevers G, de Faire U, Fyhrquist F, Julius S, Kjeldsen SE, Kristiansson K, Lederballe-Pedersen O, Nieminen MS, Omvik P, Oparil S, Wedel H, Aurup P, Edelman J, Snapinn S. LIFE Study Group. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in patients with diabetes in the Losartan Intervention For Endpoint reduction in hypertension study (LIFE): a randomised trial against atenolol. Lancet 2002;359:1004-1010. ArticlePubMed
- 24. Dandona P, Kumar V, Aljada A, Ghanim H, Syed T, Hofmayer D, Mohanty P, Tripathy D, Garg R. Angiotensin II receptor blocker valsartan suppresses reactive oxygen species generation in leukocytes, nuclear factor-kappa B, in mononuclear cells of normal subjects: evidence of an antiinflammatory action. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2003;88:4496-4501. PubMed
- 25. Schling P, Loffler G. Effects of angiotensin II on adipose conversion and expression of genes of the renin-angiotensin system in human preadipocytes. Horm Metab Res 2001;33:189-195. ArticlePubMed
- 26. Tedesco MA, Natale F, Di Salvo G, Caputo S, Capasso M, Calabro R. Effects of coexisting hypertension and type II diabetes mellitus on arterial stiffness. J Hum Hypertens 2004;18:469-473. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 27. Tropeano AI, Boutouyrie P, Pannier B, Joannides R, Balkestein E, Katsahian S, Laloux B, Thuillez C, Struijker-Boudier H, Laurent S. Brachial pressure-independent reduction in carotid stiffness after long-term angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition in diabetic hypertensives. Hypertension 2006;48:80-86. ArticlePubMed
- 28. Aronson D. Cross-linking of glycated collagen in the pathogenesis of arterial and myocardial stiffening of aging and diabetes. J Hypertens 2003;21:3-12. ArticlePubMed
- 29. Creager MA, Luscher TF, Cosentino F, Beckman JA. Diabetes and vascular disease: pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy. Part I. Circulation 2003;108:1527-1532. ArticlePubMed
- 30. Wakabayashi I, Masuda H. Association of acute-phase reactants with arterial stiffness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Clin Chim Acta 2006;365:230-235. ArticlePubMed
REFERENCES
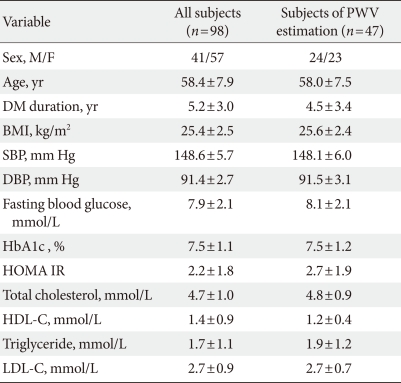
Continuous parameters are presented as mean±standard deviation.
PWV, pulse wave velocity; DM, diabetes mellitus; BMI, body mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; HbA1c, haemoglobin A1c; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; HOMA IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol.

Continuous parameters are presented as mean±standard deviation.
BMI, body mass index; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; HbA1c, haemoglobin A1c; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; HOMA IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol.
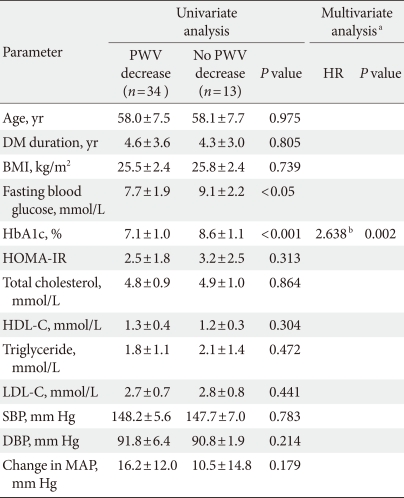
PWV, pulse wave velocity; HR, hazard ratio; DM, diabetes mellitus; BMI, body mass index; HbA1c, haemoglobin A1c; HOMA-IR, homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; SBP, systolic blood pressure; DBP, diastolic blood pressure; MAP, mean arterial pressure.
aMultivariate analysis was performed using binary logistic regression model with 'Forward: LR' method, bThe HR is predictive risk for 'no decrease of PWV value' in the case of an increase in the HbA1c level, and the accuracy rate of classification is 78.3% (95% CI, 1.447 to 4.810).
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Mechanisms underlying the blood pressure‐lowering effects of empagliflozin, losartan and their combination in people with type 2 diabetes: A secondary analysis of a randomized crossover trial
Rosalie A. Scholtes, Charlotte M. Mosterd, Anne C. Hesp, Mark M. Smits, Hiddo J. L. Heerspink, Daniël H. van Raalte
Diabetes, Obesity and Metabolism.2023; 25(1): 198. CrossRef - Distinct effects of losartan and atenolol on vascular stiffness in Marfan syndrome
Ami B Bhatt, J Stewart Buck, Jonah P Zuflacht, Jessica Milian, Samoneh Kadivar, Kimberlee Gauvreau, Michael N Singh, Mark A Creager
Vascular Medicine.2015; 20(4): 317. CrossRef - The impact of angiotensin receptor blockers on arterial stiffness: a meta-analysis
Feng Peng, Hongming Pan, Bin Wang, Jinxiu Lin, Wenquan Niu
Hypertension Research.2015; 38(9): 613. CrossRef - Arterial stiffness in atherosclerotic renovascular hypertension
Ljiljana Fodor, Vedran Premužić, Vanja Ivković, Dražen Perkov, Mario Laganović, Tajana Željković Vrkić, Živka Dika, Marijana Živko, Bojan Jelaković
Journal of Hypertension.2014; 32(11): 2238. CrossRef - Improvement of arterial wall characteristics by the low-dose fluvastatin and valsartan combination in type 1 diabetes mellitus patients
Vedran Savić, Barbara Eržen, Miodrag Janić, Mojca Lunder, Maja Boncelj, Karin Kanc, Andrej Janež, Mišo Šabovič
Diabetes and Vascular Disease Research.2013; 10(5): 420. CrossRef - The association between regional arterial stiffness and diabetic retinopathy in type 2 diabetes
Won Jun Kim, Cheol-Young Park, Se Eun Park, Eun Jung Rhee, Won Young Lee, Ki Won Oh, Sung Woo Park, Sun Woo Kim, SuJeong Song
Atherosclerosis.2012; 225(1): 237. CrossRef - Letter: The Effect of an Angiotensin Receptor Blocker on Arterial Stiffness in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Hypertension (Diabetes Metab J 2011;35:236-42)
Chul-Hee Kim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2011; 35(4): 427. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite



