- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 37(6); 2013 > Article
-
Original ArticleEpidemiology Prevalence and Management of Dyslipidemia in Korea: Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey during 1998 to 2010
- Eun Roh1, Seung-Hyun Ko2, Hyuk-Sang Kwon2, Nan Hee Kim3, Jae Hyeon Kim4, Chul Sik Kim5, Kee-Ho Song6, Jong Chul Won7, Dae Jung Kim8, Sung Hee Choi1, Soo Lim1, Bong-Yun Cha2, Taskforce Team of Diabetes Fact Sheet of the Korean Diabetes Association
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2013;37(6):433-449.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.6.433
Published online: December 12, 2013
1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
2Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
3Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
4Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
5Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Hallym University Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Anyang, Korea.
6Department of Internal Medicine, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
7Department of Internal Medicine, Mitochondrial Research Group, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
8Department of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Bong-Yun Cha. Division of Endocrinology and Metabolism, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, 222 Banpo-daero, Seocho-gu, Seoul 137-701, Korea. bycha@catholic.ac.kr
- Corresponding author: Soo Lim. Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 82 Gumi-ro 173beon-gil, Bundang-gu, Seongnam 463-707, Korea. limsoo@snu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2013 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- Dyslipidemia is a major risk factor of cardiovascular disease. The aim of this study was to investigate the changing trends in the prevalence and management status of dyslipidemia among Korean adults.
-
Methods
- The prevalence of dyslipidemia and the rates of awareness, treatment, and control of dyslipidemia were investigated in adults aged ≥20 years from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Surveys (KNHANES) 1998 to 2010. The updated National Cholesterol Education Program criteria was used, which define dyslipidemia as having one or more of the following lipid abnormalities: hypercholesterolemia (total cholesterol ≥240 mg/dL or diagnosis of dyslipidemia or use of lipid-lowering drugs), hypertriglyceridemia (≥150 mg/dL), hyper-low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterolemia (≥160 mg/dL or diagnosis of dyslipidemia or use of lipid-lowering drugs), and hypo-high density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterolemia (<40 mg/dL in men and <50 mg/dL in women).
-
Results
- The number of participants was 6,921, 4,894, 5,312, 2,733, 6,295, 6,900, and 5,738 in KNHANES 1998, 2001, 2005, 2007, 2008, 2009, and 2010, respectively. Age-standardized prevalence rates of dyslipidemia were 54.0%, 65.8%, 66.5%, 60.6%, 58.7%, 58.9%, and 59.0% in 1998, 2001, 2005, 2007, 2008, 2009, and 2010, respectively. Hypertriglyceridemia and hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia were the two most frequent lipid abnormalities. The overall prevalence of hypercholesterolemia and hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia increased by 1.36- and 1.35-fold in 2010 compared with 2007, respectively. Awareness, treatment, and control rates of dyslipidemia improved over the period of surveys in both sexes. In 2010, about 30% of dyslipidemic patients who received lipid-lowering treatment reached target levels.
-
Conclusion
- Although the management status of dyslipidemia has improved during recent years, effective strategy is required for achieving better prevention, treatment, and control of dyslipidemia.
- Cardiovascular disease is one of main causes of death worldwide [1]. In Korea, cardiovascular disease accounted for approximately 1 of every 10 deaths from 2011 mortality data [2]. Metabolic syndrome is an important risk factor for cardiovascular disease [3,4] and adult Koreans with the metabolic syndrome are more likely to have a history of cardiovascular disease than those without the syndrome [5]. Among the five components of the metabolic syndrome, dyslipidemia, and abdominal obesity were the major factors influencing the increased prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Koreans for the past 10 years [6]. Previous epidemiologic studies revealed that high-carbohydrate diet, abdominal obesity, and physical inactivity were related with greater risk of elevated triglyceride and low high density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels in Korean population [7,8].
- Since dyslipidemia has been considered as an important risk factor that contributes to the development of cardiovascular disease, the assessment of the prevalence and management status of dyslipidemia in recent years would be an initial step for planning preventive strategy reducing the development of cardiovascular disease. Studies from the United States using the data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys (NHANES) 1988 to 2010 reported a decrease in total cholesterol and low density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), an increase in triglyceride, and an unchanged HDL-C level in United States [9]. Meanwhile, in Japanese general population, the total cholesterol level and triglyceride level (only in men) increased in past 10 years (1990 to 2000) [10]. Lee et al. [11] reported that prevalence of dyslipidemia in Korea gradually increased from 1998 to 2005 through the data from Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey (KNHANES) 1998, 2001, and 2005. However, a relatively short duration of the study, as well as the differences in the definition of dyslipidemia between KNHANES 2005 and 1998/2001 make direct comparisons difficult [11].
- In this study, we investigated the recent changes in the prevalence, awareness, treatment, and control rates of dyslipidemia among Korean adults in KNHANES 1998 to 2010 by adopting an updated National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel (NCEP-ATP) III definition [12]. We also investigated the changes in the factors constituting dyslipidemia among Korean adults.
INTRODUCTION
- Data source and study population
- This study was performed using the data from KNHANES I (1998), II (2001), III (2005), and IV (2007 to 2009), V (2010). KNHANES is a nationwide, community-based cross-sectional survey examining the general health and nutrition status of the noninstitutionalized civilians of Korea, conducted by the Division of Health and Nutritional Survey under the Korean Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (KCDCP). It consisted of three distinct surveys: health interview survey, health examination survey, and nutrition survey. Participants were selected from sampling units based on geographical area-, sex-, and age-groups using household registries with a stratified, multistage, clustered, probability sampling design. This sampling method is certified as producing representative statistics by the Korea Department of Statistics. KNHANES was conducted according to the guidelines laid down in the Declaration of Helsinki. All participants in the survey signed an informed consent form. The Institutional Review Board of KCDCP approved the protocol.
- In KNHANES I (1998) and II (2001), individuals were not asked about their prior diagnosis and management in the health interview survey because the prevalence of dyslipidemia was considered to be very low in Korea at that time period. Self-reported prior diagnosis of dyslipidemia and current use of lipid-lowering drugs were available since 2005. We analyzed subjects over 20 years old and completed the health examination and health interview survey as well. In the analysis, any measurements that were missing total cholesterol, HDL-C, or triglycerides were excluded. All individuals voluntarily agreed to participate in this survey and informed consent was obtained from all of them. The survey protocol was approved by an Institutional Review Board of KCDCP.
- Dyslipidemia was defined entirely based on the blood test results in the health examination performed in 1998 and 2001. The definition of dyslipidemia was made according to the presence of one or more of the following criteria: hypercholesterolemia (total cholesterol ≥240 mg/dL); hypertriglyceridemia (triglyceride ≥150 mg/dL); hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia (LDL-C ≥160 mg/dL); and hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia (HDL-C <40 mg/dL in men and <50 mg/dL in women). Since 2005, dyslipidemia was determined with fasting blood tests as well as health interview survey data. Hypercholesterolemia was defined by previous diagnosis by physician or current use of lipid-lowering drugs or total cholesterol of ≥240 mg/dL. Hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia was defined by previous diagnosis by medical doctor or current use of lipid-lowering medications or LDL-C of ≥160 mg/dL. Hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia and hypertriglyceridemia were defined in the same manner as in 1998 and 2001.
- And then, we divided the participants into diabetic and nondiabetic subjects to compare the prevalence and management status of dyslipidemia between the two groups. The diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus were obtained from the American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines [13]: diabetes was diagnosed in subjects whose level of fasting plasma glucose was over 126 mg/dL or who responded to health interview survey as having had a previous diagnosis of diabetes by physician or treated with antidiabetic agents or insulin. We categorized the lipid-related risks of coronary artery disease in diabetic participants according to the updated NCEP-ATP III and the 2008 ADA/American College of Cardiology Statement [14]. Patients with diabetes alone should be considered to be at high risk, while patients with diabetes and one or more additional risk factors of coronary artery disease are considered to be at very high risk. The major risk factors of coronary artery disease included high LDL-C (≥160 mg/dL), cigarette smoking, hypertension (systolic/diastolic blood pressure ≥140/90 mm Hg or use of antihypertensive medication), low HDL-C (<40 mg/dL), and age (men ≥45 years, women ≥55 years). When HDL-C concentration was ≥60 mg/dL, one risk factor was subtracted from a patient's overall risk profile.
- Awareness rate, treatment rate, and control rate of dyslipidemia were defined using the health interview survey and the health examination survey results from KNHANES. Awareness rate was defined as the number of individuals who were identified in the health interview survey as having had a previous diagnosis of dyslipidemia by a physician divided by the number of people with dyslipidemia. Treatment rate was defined as participants whose response to the health interview survey indicated that they have been taking lipid-lowering drugs among those with dyslipidemia. Treatment goal was defined according to the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists guidelines for management of dyslipidemia [15]. Control rate was defined based on individuals who reached treatment goal (LDL-C levels <160 mg/dL, triglyceride levels <150 mg/dL, HDL-C levels >40 mg/dL in men and >50 mg/dL in women) among who have taken lipid-lowering drugs. For the definition of control rate in diabetic participants, LDL-C target of <100 mg/dL was used. Dyslipidemic patients with a very high risk of coronary artery disease had LDL-C target of <70 mg/dL.
- Biochemical measurements
- The blood samples were drawn from antecubital vein of each participant in the morning after fasting for at least 8 hours. Samples were properly processed, refrigerated at 2℃ to 8℃, and immediately sent to the Central Testing Institute in Seoul, Korea, where plasma was separated immediately by centrifugation. The fasting plasma concentrations of glucose and lipids were measured enzymatically in a central laboratory; a 747-chemistry analyzer was used (Hitachi, Tokyo, Japan) in the 1998 and 2001 studies, while an Advia 1,650/2,400 was employed (Siemens, New York, NY, USA) in 2005 and 2007, and a Hitachi Automatic Analyzer 7600 (Hitachi) was used in 2008, 2009, and 2010. Because the analysis tool and the method of measuring HDL-C were changed due to changes in clinical laboratory organization, revised HDL-C level was derived since 2007 according to the Lipid Standardization Program [16] made by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) in the United States. LDL-C was calculated using Friedewald's formula [17] in individuals with triglycerides ≤400 mg/dL. LDL-C level has been directly measured using automated enzymatic techniques since 2009 in KNHANES IV.
- Statistical analysis
- Statistical analyses were performed with complex-samples analysis procedures in SPSS version 19.0 (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). We used KNHANES stratification variables and sampling weights designated by KCDCP, which were based on the sample design of each survey year. Data were presented as percentage (standard error) for nominal data or means±standard error for continuous variables. The age-standardized prevalence of dyslipidemia and other lipid abnormalities were calculated by the age- and sex-specific structure of the 2010 Korean population. As the definition of dyslipidemia changed in KNHANES 2005 and revised HDL-C level have been available since the KNHANES 2007, we compared the prevalence of dyslipidemia during 2007 to 2010. In order to compare the prevalence rates of each year, logistic regression analyses were used. Every comparison among the studies was done after age adjustment.
METHODS
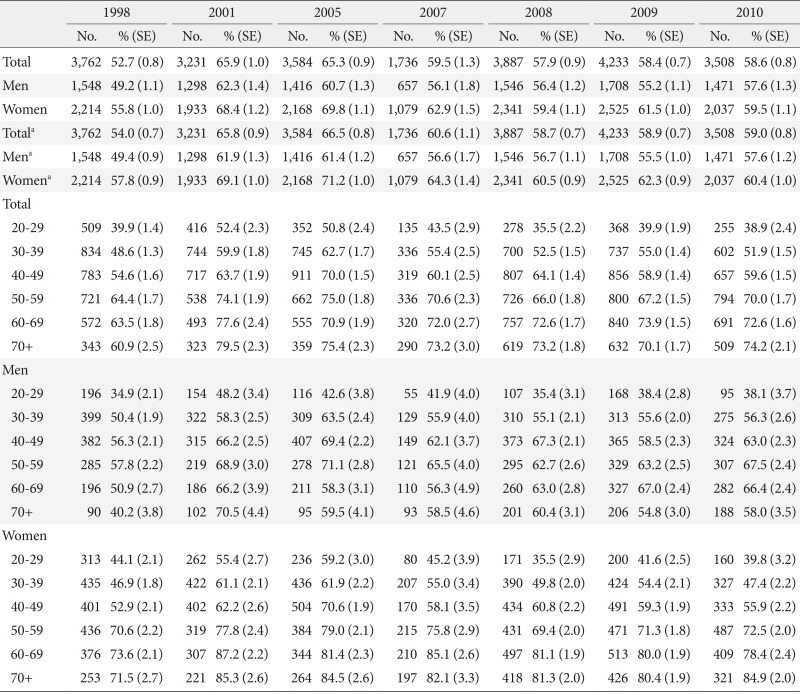
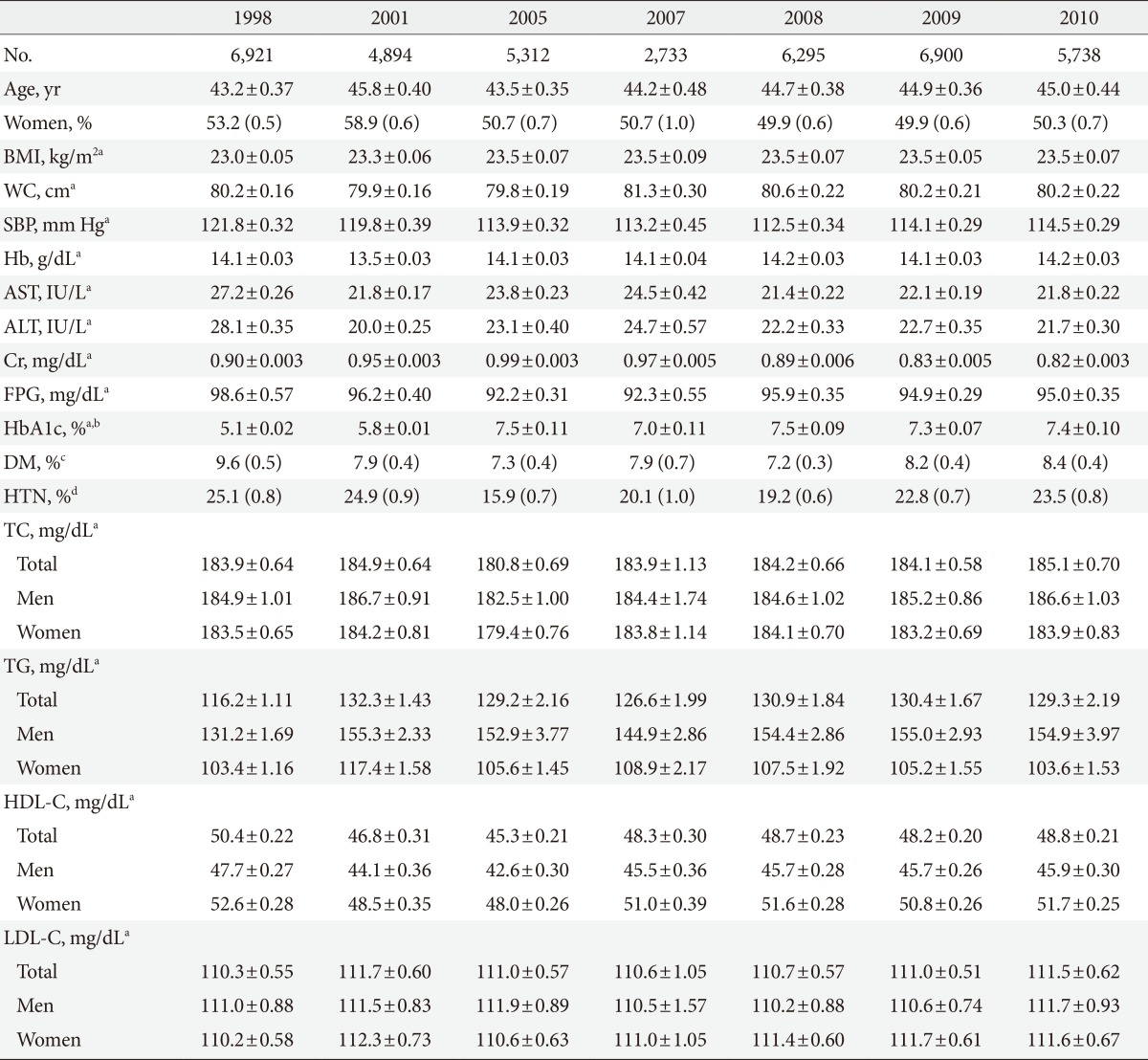
- A total of 6,921 (aged 43.2±0.37 years), 4,894 (45.8±0.40), 5,312 (43.5±0.35), 2,733 (44.2±0.48), 6,295 (44.7±0.38), 6,900 (44.9±0.36), and 5,738 (45.0±0.44) respondents were available for analysis from KNHANES in the 1998, 2001, 2005, 2007, 2008, 2009, and 2010, respectively. Table 1 shows the characteristics of participants in KNHANES during 1998 to 2010. Age-standardized prevalence rates of dyslipidemia were 54.0% in 1998, 65.8% in 2001, 66.5% in 2005, 60.6% in 2007, 58.7% in 2008, 58.9% in 2009, and 59.0% in 2010. The prevalence of dyslipidemia was higher in women than in men every year (57.6% in men and 60.4% in women in 2010).
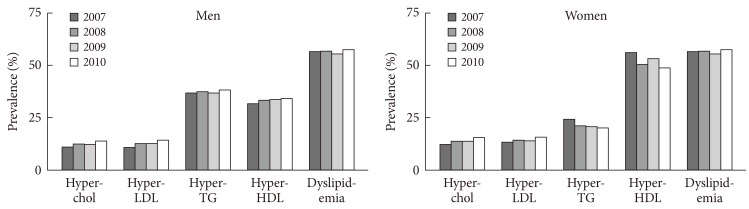
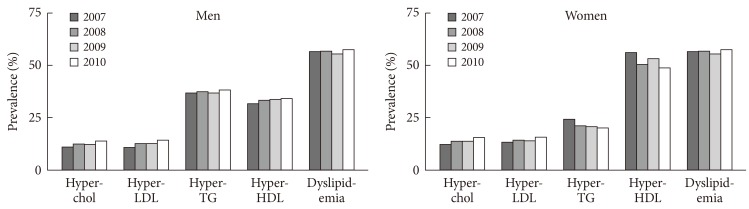
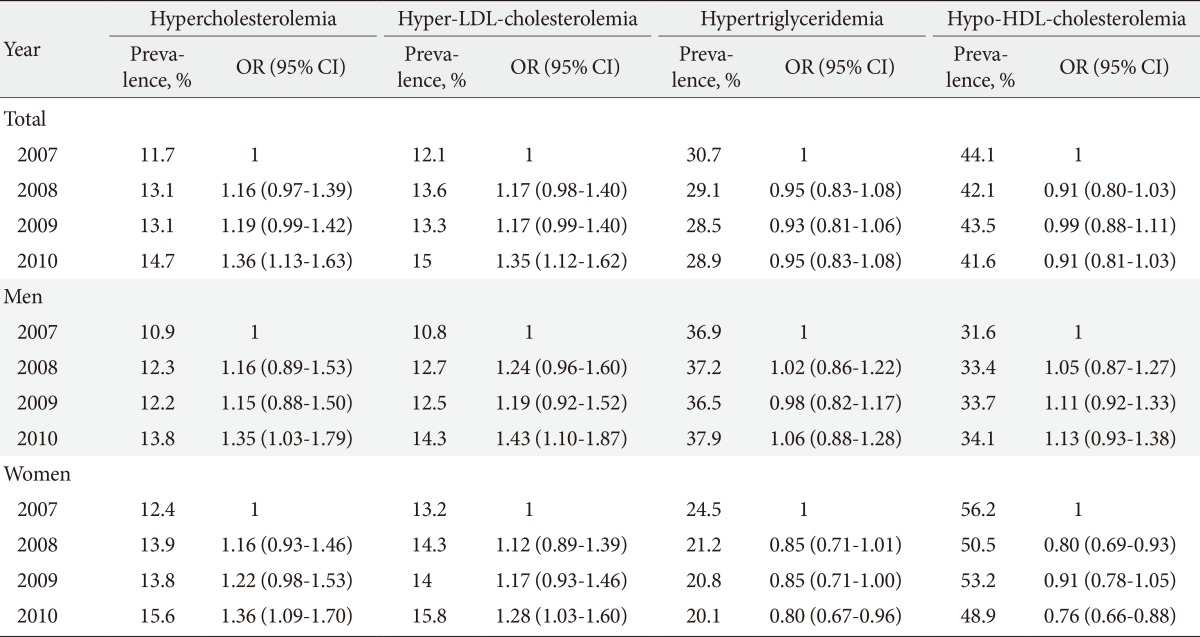
- Table 2, Fig. 1 show age-standardized prevalence rates of dyslipidemia and each lipid abnormalities of it in KNHANES during 2007 to 2010. In women, the prevalence of hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia tended to decrease and the prevalence in 2010 has decreased by 0.76-fold (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.66 to 0.88) compared with the prevalence reported in 2007. In men, the prevalence of hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia was the second frequent lipid abnormality and accounted for almost one third of all dyslipidemia. In contrast to women, the prevalence of hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia in men tended to increase: prevalence in 2010 had increased by 1.13-fold (95% CI, 0.93 to 1.38) compared with that in 2007. The prevalence of hypertriglyceridemia, most frequent lipid abnormality in men, has not changed significantly in men, while a significantly decreasing tendency was found in women. Compared with the prevalence in 2007, the prevalence in 2010 has decreased by 0.80-fold (95% CI, 0.67 to 0.96) in women. On the other hand, the prevalence of hypercholesterolemia and hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia, the two lowest frequent lipid abnormalities, has significantly increased in both sexes after 2007. In 2010, the overall prevalence of hypercholesterolemia and hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia has increased by 1.36- and 1.35-fold compared with the prevalence in 2007, respectively.
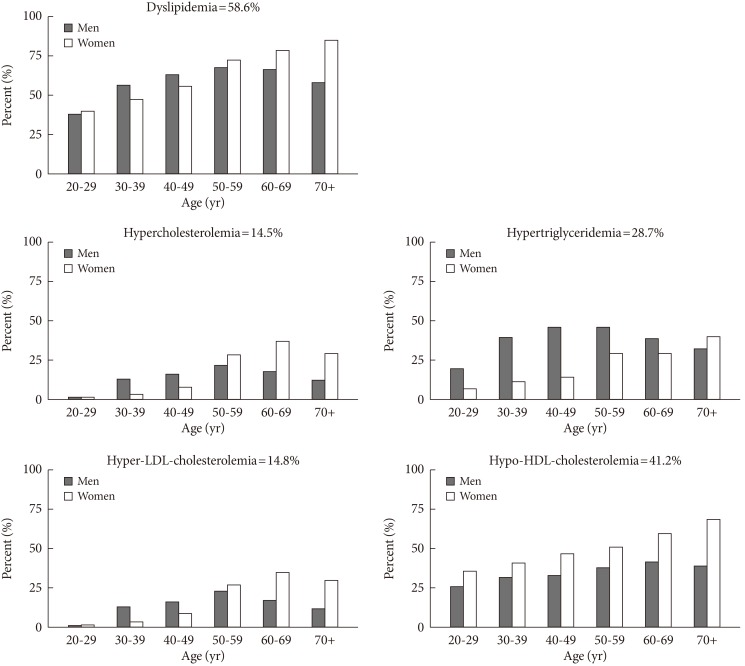
- The prevalence of dyslipidemia and its individual lipid abnormalities by sex- and age-category in 2010 are shown in Fig. 2. The prevalence of dyslipidemia peaked in the 50 to 60 year age groups in men and has decreased after age 70 years. In contrast, the prevalence had rapidly increasing trend as age increased in women. In subjects ≥70 years the prevalence of dyslipidemia in women was about 1.5 times higher than that of men. The prevalence of hypercholesterolemia and hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia were higher in men than in women in the 30 to 40 age groups, although the prevalence rate was higher in women after age 50. The prevalence of hypertriglyceridemia was much higher in men in younger age groups. Women had a higher prevalence of hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia in all age groups than men. The percentage of women with HDL-cholesterolemia below 45 mg/dL was similar to that of men with hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia (HDL-C <40 mg/dL) in KNHANES during 1998 to 2010 (data not shown). The prevalence of dyslipidemia and its respective components by sex- and age-category during 1998 to 2010 are described in detail in Appendixes 1-5 (1, prevalence of dyslipidemia; 2, prevalence of hypercholesterolemia; 3, prevalence of hypertriglyceridemia; 4, prevalence of hyper-LDL-cholesteroleamia; 5, prevalence of hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia).
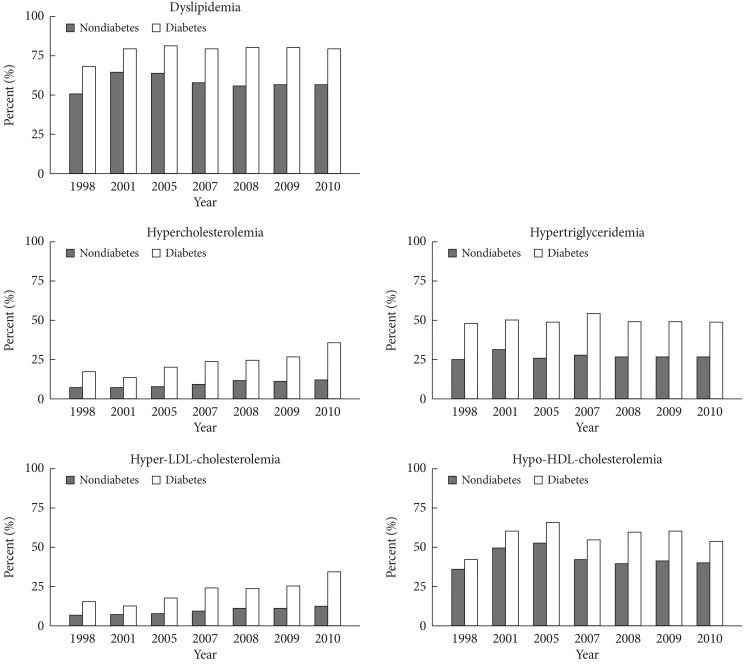
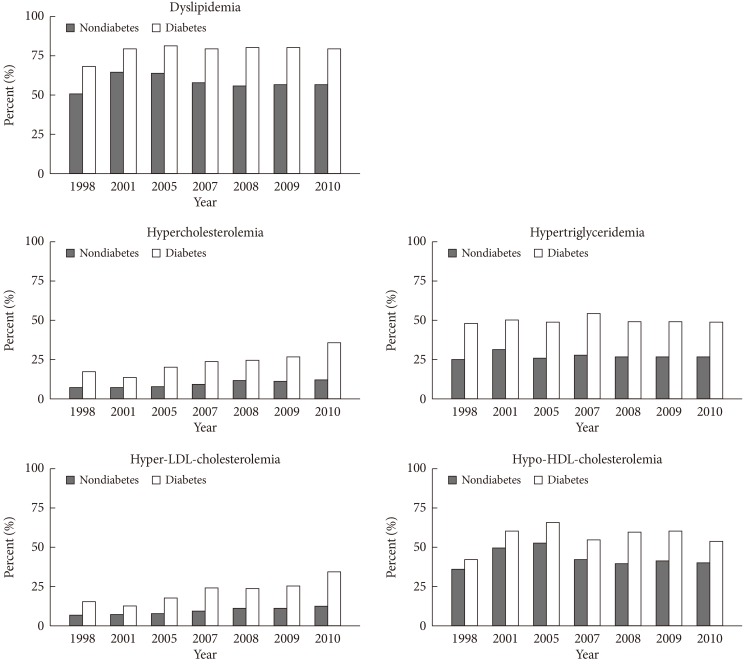
- Participants with diabetes had a higher prevalence of dyslipidemia and more respective lipid abnormalities than nondiabetic subjects during 1998 to 2010 period (Fig. 3). In 2010, the prevalence of dyslipidemia was 79.6% in diabetic and 56.7% in nondiabetic subjects. The prevalences of hypercholesterolemia and hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia were 36.0% and 35.1% in diabetic and 12.5% and 12.9% in nondiabetic subjects, respectively. The prevalence of hypertriglyceridemia was 49.3% in diabetic and 26.8% in nondiabetic subjects. The prevalence of hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia was 53.7% in diabetic and 40.0% in nondiabetic subjects in 2010.
- Awareness rate had increased annually during 2005 to 2010 from 6.1% in 2005 to 13.7% in 2010. Treatment rate tended to increase: it was 1.9% in 2005 and 7.4% in 2010 (Table 3). The rates of awareness and treatment in diabetic subjects were much higher than nondiabetic subjects in both sexes. In 2010, awareness rate was 34.6% in diabetic and 11.0% in nondiabetic subjects. Treatment rate in 2010 was 23.6% in diabetic and 5.3% in nondiabetic subjects. Control rate of dyslipidemia among treated patients showed an increasing tendency (Table 4). The rate of dyslipidemic subjects who reached treatment goal (LDL-C levels <160 mg/dL, triglyceride levels <150 mg/dL, HDL-C levels >40 mg/dL in men and >50 mg/dL in women) among who have taken lipid-lowering drugs was 21.8% in 2005 and 29.7% in 2010. The rate of diabetic patients who reached treatment goal (LDL-C levels <100 mg/dL, triglyceride levels <150 mg/dL, HDL-C levels >40 mg/dL in men and >50 mg/dL in women) increased from 5.8% in 2005 to17.4% in 2010. The control rate in LDL-C defined as below 100 mg/dL in diabetic subjects tended to increase from 41.9% in 2005 to 62.6% in 2010. Among diabetic subjects with a very high risk of cardiovascular disease treated with lipid-lowering drug, the rate of subjects who had LDL-C level <70 mg/dL increased from 8.6% in 2005 to 22.2% in 2010.
RESULTS
- This is the first national-scale epidemiologic study to evaluate the changing trends of the prevalence of dyslipidemia and individual components of dyslipidemia including awareness, treatment, and control rates in Korean adults. The prevalence of dyslipidemia was greater than 50% in both men and women during the past 12 years. About one half of the women had a low level of HDL-cholesterolemia. However, the prevalence of hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia has decreased in women, while it showed an increasing tendency in men during recent 4 years. The proportion of adults with elevated levels of triglyceride significantly decreased in women while it has not changed recently in men. The increase in the prevalence of hypercholesterolemia and hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia, the two lowest frequent lipid abnormalities in both sexes, was significant during recent 4 years in Korea. The proportion of dyslipidemic subjects who had been previously diagnosed by a medical doctor and who have been taking lipid-lowering medications and who reached treatment goals after treatment with lipid-lowering drugs increased over the past 5 years.
- Elevated total cholesterol and LDL-C levels are independent risk factors of development of cardiovascular disease [18,19]. A 10 mg/dL increase of total cholesterol was associated with 9% increase of death from cardiovascular disease during in a 30-year follow-up study [20]. Reducing plasma LDL-C levels with the use of statins reduced the incidence of death from cardiovascular causes [21,22]. A large-scale epidemiological study in United States observed the decreases in total and LDL-C levels in recent 20 years due to the increase in the percentage of adults taking lipid-lowering drugs [9]. A previous report on trends in total cholesterol worldwide indicated mean cholesterol levels declined in developed countries (North America, Western Europe, Australia, and some Asian regions) [9,23]. A recent increasing trend of the prevalence of hypercholesterolemia and hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia in Korea is consistent with the increasing prevalence of cardiovascular disease [2]. A relatively low proportion of adults taking lipid-lowering drugs (7.4% from KNHANES 2010 vs. 15.5% from NHANES 2007 to 2010 [9]) might have affected the increasing trend of the prevalence of hypercholesterolemia and hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia.
- Low-carbohydrate diet contributes to favorable effects on atherogenic dyslipidemia including elevated serum triglyceride and reduced HDL-C [24,25]. The high prevalence of hypertriglyceridemia and hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia in Korean adults could be related with high-carbohydrate diet. A recent Korean study revealed that previous traditional Korean diet with high-carbohydrate content was related with elevated triglyceride and low HDL-C [7]. It is also well-known that body mass index is inversely related to the concentration of HDL-C [26] and positively with triglyceride levels [27]. The recent decreasing trend in the prevalence of hypertriglyceridemia and hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia in Korean women is consistent with a decreased prevalence of obesity in young and middle-aged Korean women [28]. A social preference for thin body image may have affected the decreasing trend of the prevalence of obesity in these female age subgroups [29,30]. Meanwhile, an increasing trend in the prevalence of obesity in Korean men might be one of the reasons of recently increased prevalence of hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia in men [28].
- HDL-C is known as an inverse predictor of cardiovascular disease [31-33]. A 1 mg/dL increase of HDL-C is associated with 2% reduction in the relative risk of cardiovascular disease in men and 3% reduction in women [34]. Triglyceride is a risk factor of cardiovascular disease for both men and women in the general population, independent of HDL-C [35]. High body mass index, abdominal obesity, cigarette smoking, and physical inactivity were associated with a greater risk of low HDL-C levels in Korean adults [8]. Thus, smoking cessation, increasing physical activity, and decreasing body weight would all contribute to increasing HDL-C levels in Korean population [36].
- The characteristic features of diabetic dyslipidemia are high plasma triglyceride concentration, low HDL-C concentration, and increased concentration of small, dense LDL-C particles [37]. In this study, we found that Korean diabetic patients had a higher prevalence of all lipid abnormalities of dyslipidemia than that of nondiabetic subjects. A higher prevalence of hypercholesterolemia and hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia in diabetic subjects is considered to be affected by a higher rate of self-reported prior diagnosis or current use of lipid-lowering drugs in diabetic participants.
- This study had some limitations. Although KNHANES collected nationally representative data, it is a cross-sectional evaluation of the health and nutritional status of Koreans. To prevent the potential errors in survey methods, the prevalence estimated in each KNHANES was standardized according to the 2010 Korean population. Each KNHANES was conducted with different subjects and since it was based on self-administered questionnaire, recall bias, confounding factors, and unintentional errors should be considered. The change in the definition of hypercholesterolemia and hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia in 2005 by an introduction of questionnaire for previous diagnosis of dyslipidemia by physician and current use of lipid-lowering drugs made it difficult to analyze trends over time using the 1998 and 2001 KNAHNES data. Also, the change in the protocol of HDL-C measurement could have affected the HDL-C results. For this reason, the values were standardized according to the United States Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Lipid Standardization Program to minimize method effects since 2007.
- In conclusion, more than half of Korean adults have had dyslipidemia from KNHANES 1998 to KNHANES 2010. Elevated triglyceride and low HDL-C levels were the two most frequent lipid abnormalities in Korean population. A recent increasing trend of hypercholesterolemia and hyper-LDL-cholesterolemia is associated with an increasing prevalence of cardiovascular mortality in Korea. Although the awareness and treatment rates of dyslipidemia have improved during this period, the low control rate in dyslipidemia suggests a need for a national strategy to prevent increasing trend of atherogenic dyslipidemia. Proper lifestyle management with weight loss, low carbohydrate diet, and regular exercise are recommended to reduce the burden of dyslipidemia and cardiovascular mortality.
DISCUSSION
- 1. World Health Organization. World health statistics 2012 cited 2012 May 16. Available from: http://www.who.int/gho/publications/world_health_statistics/2012/en/index.html.
- 2. Statistics Korea. Annual report on the causes of death statistics, 2011 updated 2012 Sep 13. Available from: http://www.kostat.go.kr.
- 3. Isomaa B, Almgren P, Tuomi T, Forsen B, Lahti K, Nissen M, Taskinen MR, Groop L. Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality associated with the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes Care 2001;24:683-689. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 4. Lakka HM, Laaksonen DE, Lakka TA, Niskanen LK, Kumpusalo E, Tuomilehto J, Salonen JT. The metabolic syndrome and total and cardiovascular disease mortality in middle-aged men. JAMA 2002;288:2709-2716. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Kim MH, Kim MK, Choi BY, Shin YJ. Prevalence of the metabolic syndrome and its association with cardiovascular diseases in Korea. J Korean Med Sci 2004;19:195-201. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 6. Lim S, Shin H, Song JH, Kwak SH, Kang SM, Won Yoon J, Choi SH, Cho SI, Park KS, Lee HK, Jang HC, Koh KK. Increasing prevalence of metabolic syndrome in Korea: the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey for 1998-2007. Diabetes Care 2011;34:1323-1328. PubMedPMC
- 7. Song Y, Joung H. A traditional Korean dietary pattern and metabolic syndrome abnormalities. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 2012;22:456-462. ArticlePubMed
- 8. Kim SM, Han JH, Park HS. Prevalence of low HDL-cholesterol levels and associated factors among Koreans. Circ J 2006;70:820-826. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Carroll MD, Kit BK, Lacher DA, Shero ST, Mussolino ME. Trends in lipids and lipoproteins in US adults, 1988-2010. JAMA 2012;308:1545-1554. ArticlePubMed
- 10. Arai H, Yamamoto A, Matsuzawa Y, Saito Y, Yamada N, Oikawa S, Mabuchi H, Teramoto T, Sasaki J, Nakaya N, Itakura H, Ishikawa Y, Ouchi Y, Horibe H, Kita T. Serum lipid survey and its recent trend in the general Japanese population in 2000. J Atheroscler Thromb 2005;12:98-106. ArticlePubMed
- 11. Lee MH, Kim HC, Ahn SV, Hur NW, Choi DP, Park CG, Suh I. Prevalence of dyslipidemia among Korean adults: Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey 1998-2005. Diabetes Metab J 2012;36:43-55. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Grundy SM, Cleeman JI, Merz CN, Brewer HB Jr, Clark LT, Hunninghake DB, Pasternak RC, Smith SC Jr, Stone NJ. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. American College of Cardiology Foundation. American Heart Association. Implications of recent clinical trials for the National Cholesterol Education Program Adult Treatment Panel III guidelines. Circulation 2004;110:227-239. ArticlePubMed
- 13. American Diabetes Association. Standards of medical care in diabetes: 2013. Diabetes Care 2013;36(Suppl 1):S11-S66. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 14. Brunzell JD, Davidson M, Furberg CD, Goldberg RB, Howard BV, Stein JH, Witztum JL. Lipoprotein management in patients with cardiometabolic risk: consensus conference report from the American Diabetes Association and the American College of Cardiology Foundation. J Am Coll Cardiol 2008;51:1512-1524. PubMed
- 15. Jellinger PS, Smith DA, Mehta AE, Ganda O, Handelsman Y, Rodbard HW, Shepherd MD, Seibel JA. AACE Task Force for Management of Dyslipidemia and Prevention of Atherosclerosis. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists' Guidelines for Management of Dyslipidemia and Prevention of Atherosclerosis: executive summary. Endocr Pract 2012;18:269-293. ArticlePubMed
- 16. Myers GL, Cooper GR, Winn CL, Smith SJ. The Centers for Disease Control-National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute Lipid Standardization Program. An approach to accurate and precise lipid measurements. Clin Lab Med 1989;9:105-135. ArticlePubMed
- 17. Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 1972;18:499-502. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 18. Kannel WB, Castelli WP, Gordon T. Cholesterol in the prediction of atherosclerotic disease. New perspectives based on the Framingham study. Ann Intern Med 1979;90:85-91. ArticlePubMed
- 19. Castelli WP. Epidemiology of coronary heart disease: the Framingham study. Am J Med 1984;76:4-12. ArticlePubMed
- 20. Anderson KM, Castelli WP, Levy D. Cholesterol and mortality. 30 years of follow-up from the Framingham study. JAMA 1987;257:2176-2180. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Randomised trial of cholesterol lowering in 4,444 patients with coronary heart disease: the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (4S). Lancet 1994;344:1383-1389. PubMed
- 22. Shepherd J, Cobbe SM, Ford I, Isles CG, Lorimer AR, MacFarlane PW, McKillop JH, Packard CJ. West of Scotland Coronary Prevention Study Group. Prevention of coronary heart disease with pravastatin in men with hypercholesterolemia. N Engl J Med 1995;333:1301-1307. ArticlePubMed
- 23. Farzadfar F, Finucane MM, Danaei G, Pelizzari PM, Cowan MJ, Paciorek CJ, Singh GM, Lin JK, Stevens GA, Riley LM, Ezzati M. Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors of Chronic Diseases Collaborating Group (Cholesterol). National, regional, and global trends in serum total cholesterol since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 321 country-years and 3.0 million participants. Lancet 2011;377:578-586. ArticlePubMed
- 24. Bonow RO, Eckel RH. Diet, obesity, and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med 2003;348:2057-2058. ArticlePubMed
- 25. Volek JS, Phinney SD, Forsythe CE, Quann EE, Wood RJ, Puglisi MJ, Kraemer WJ, Bibus DM, Fernandez ML, Feinman RD. Carbohydrate restriction has a more favorable impact on the metabolic syndrome than a low fat diet. Lipids 2009;44:297-309. ArticlePubMed
- 26. Knuiman JT, West CE, Burema J. Serum total and high density lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations and body mass index in adult men from 13 countries. Am J Epidemiol 1982;116:631-642. PubMed
- 27. National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (U.S.). Clinical guidelines on the identification, evaluation, and treatment of overweight and obesity in adults: the evidence report. Bethesda: National Institutes of Health, National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute; 1998. p. 14.
- 28. Rhee SY, Park SW, Kim DJ, Woo J. Gender disparity in the secular trends for obesity prevalence in Korea: analyses based on the KNHANES 1998-2009. Korean J Intern Med 2013;28:29-34. ArticlePubMed
- 29. Demarest J, Allen R. Body image: gender, ethnic, and age differences. J Soc Psychol 2000;140:465-472. ArticlePubMed
- 30. Sakamaki R, Amamoto R, Mochida Y, Shinfuku N, Toyama K. A comparative study of food habits and body shape perception of university students in Japan and Korea. Nutr J 2005;4:31ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 31. Despres JP, Lemieux I, Dagenais GR, Cantin B, Lamarche B. HDL-cholesterol as a marker of coronary heart disease risk: the Quebec cardiovascular study. Atherosclerosis 2000;153:263-272. ArticlePubMed
- 32. Barter P, Gotto AM, LaRosa JC, Maroni J, Szarek M, Grundy SM, Kastelein JJ, Bittner V, Fruchart JC. Treating to New Targets Investigators. HDL cholesterol, very low levels of LDL cholesterol, and cardiovascular events. N Engl J Med 2007;357:1301-1310. ArticlePubMed
- 33. Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration. Di Angelantonio E, Sarwar N, Perry P, Kaptoge S, Ray KK, Thompson A, Wood AM, Lewington S, Sattar N, Packard CJ, Collins R, Thompson SG, Danesh J. Major lipids, apolipoproteins, and risk of vascular disease. JAMA 2009;302:1993-2000. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 34. Gordon DJ, Probstfield JL, Garrison RJ, Neaton JD, Castelli WP, Knoke JD, Jacobs DR Jr, Bangdiwala S, Tyroler HA. High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. Four prospective American studies. Circulation 1989;79:8-15. ArticlePubMed
- 35. Hokanson JE, Austin MA. Plasma triglyceride level is a risk factor for cardiovascular disease independent of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level: a meta-analysis of population-based prospective studies. J Cardiovasc Risk 1996;3:213-219. ArticlePubMed
- 36. Goldbourt U, Yaari S, Medalie JH. Isolated low HDL cholesterol as a risk factor for coronary heart disease mortality. A 21-year follow-up of 8000 men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 1997;17:107-113. PubMed
- 37. Mooradian AD. Dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Nat Clin Pract Endocrinol Metab 2009;5:150-159. ArticlePubMedPDF
REFERENCES
Appendix
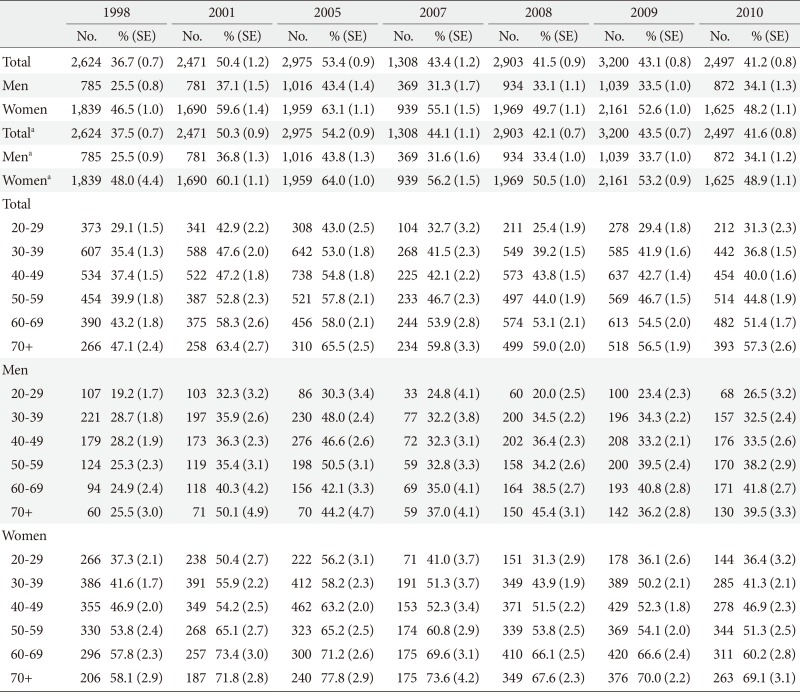
Prevalence rates of dyslipidemia in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey during 1998 to 2010 by sex- and age-category
Prevalence rates of hypercholesterolemia in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey during 1998 to 2010 by sex- and age-category
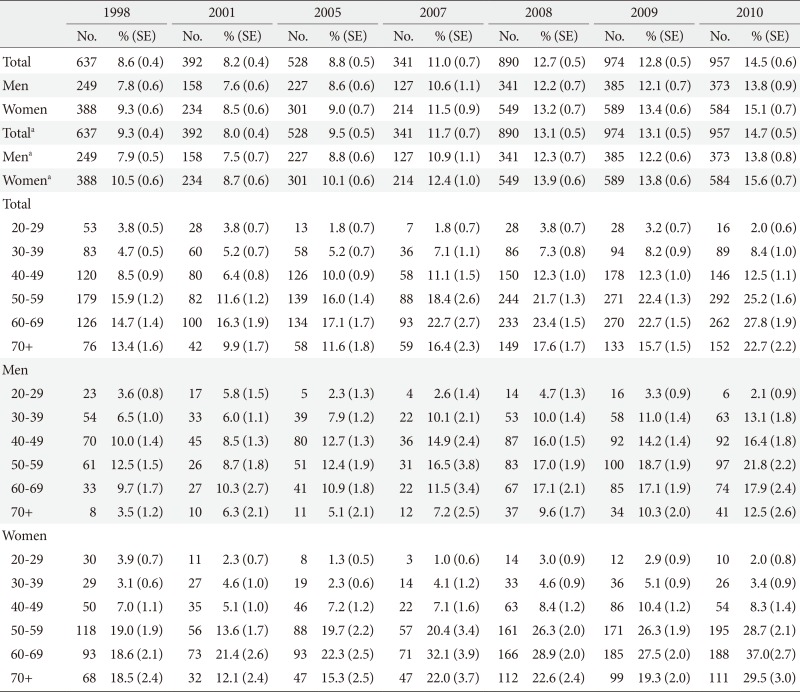
Prevalence rates of hypertriglyceridemia in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey during 1998 to 2010 by sex- and age-category
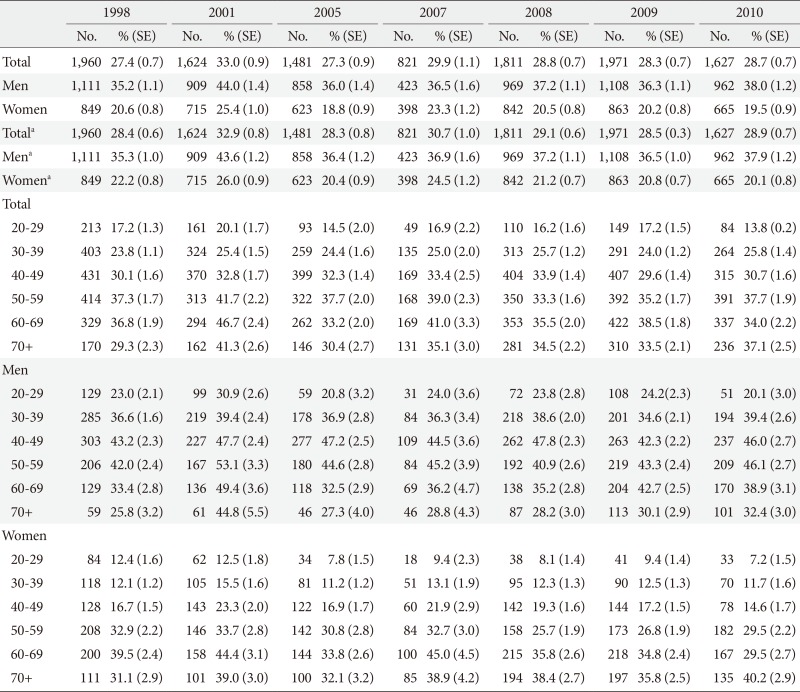
Prevalence rates of hyper-low density lipoprotein cholesterolemia in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey during 1998 to 2010 by sex- and age-category
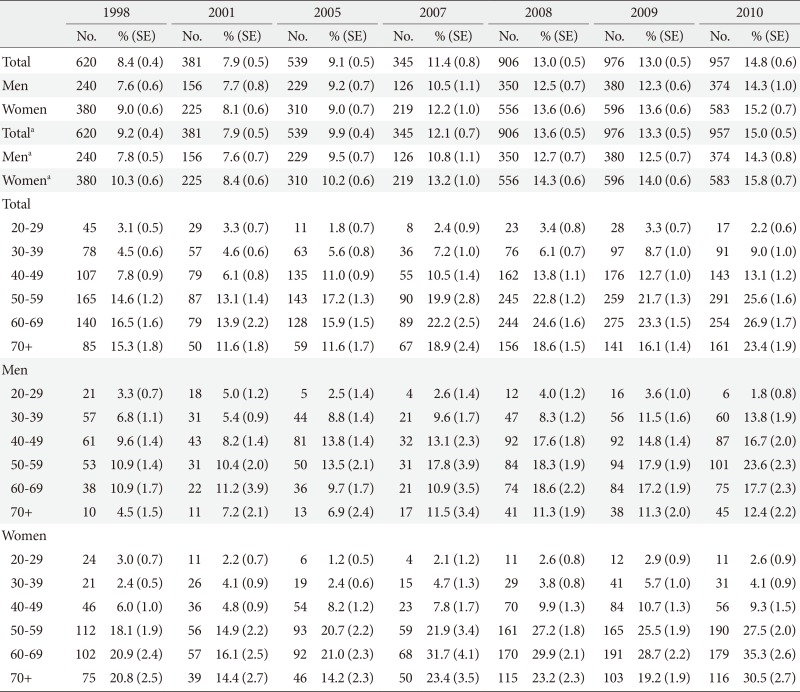
Prevalence rates of hypo-high density lipoprotein cholesterolemia in the Korea National Health and Nutrition Survey during 1998 to 2010 by sex- and age-category

Values are presented as mean±standard error or percentage (standard error).
BMI, body mass index; WC, waist circumference; SBP, systolic blood pressure; Hb, hemoglobin; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; Cr, creatinine; FPG, fasting plasma glucose; HbA1c, glycated hemoglobin; DM, diabetes mellitus; HTN, hypertension; TC, total cholesterol; TG, triglyceride; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol.
aAge-adjusted value, bHbA1c were measured mainly among patients with diabetes mellitus, cDiabetes mellitus was diagnosed in subjects whose level of fasting plasma glucose ≥126 mg/dL or who responded to health interview survey as having had a previous diagnosis of diabetes by physician or treated with antidiabetic agents or insulin, dHypertension were defined based on systolic blood pressure ≥140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure ≥90 mm Hg or current use of antihypertensive medication.
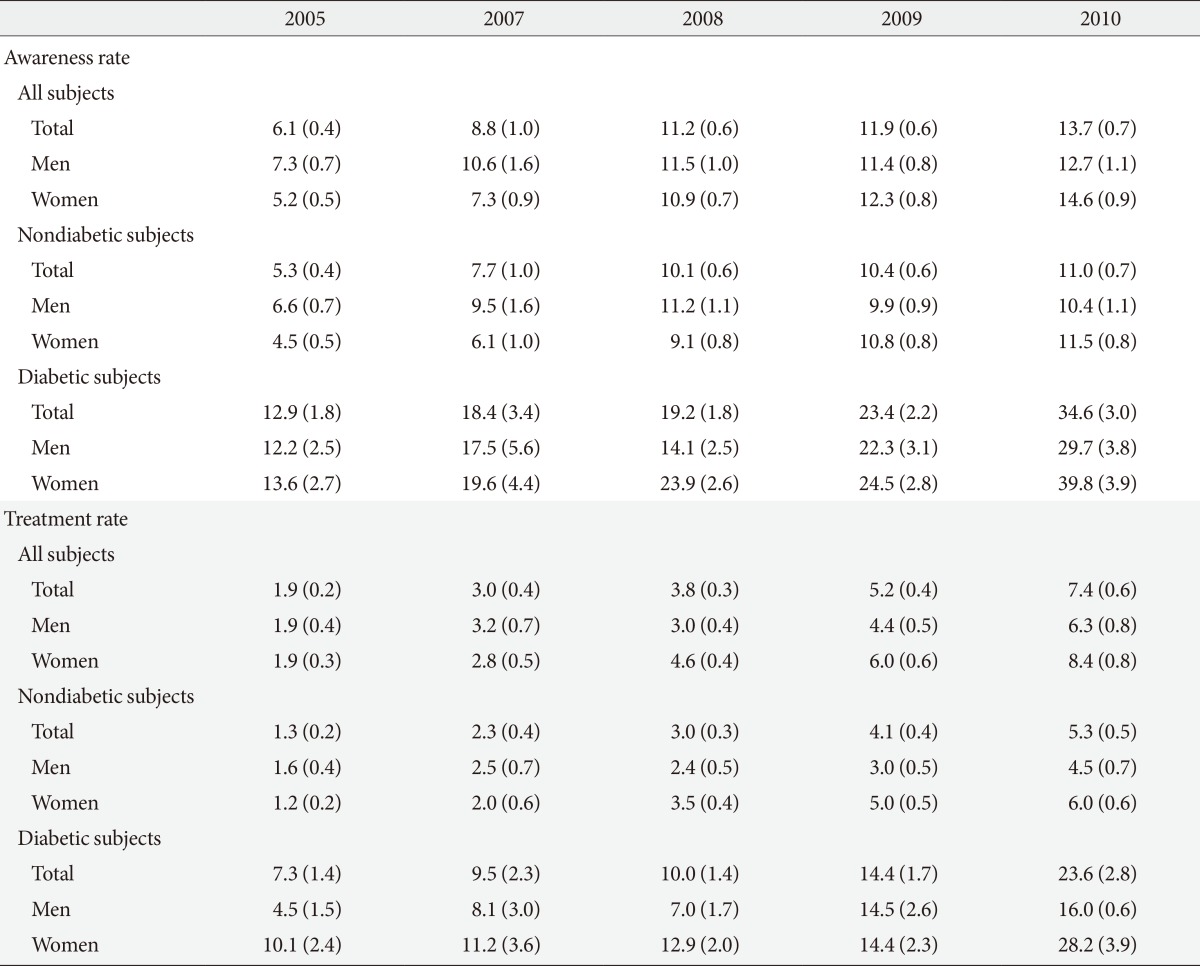
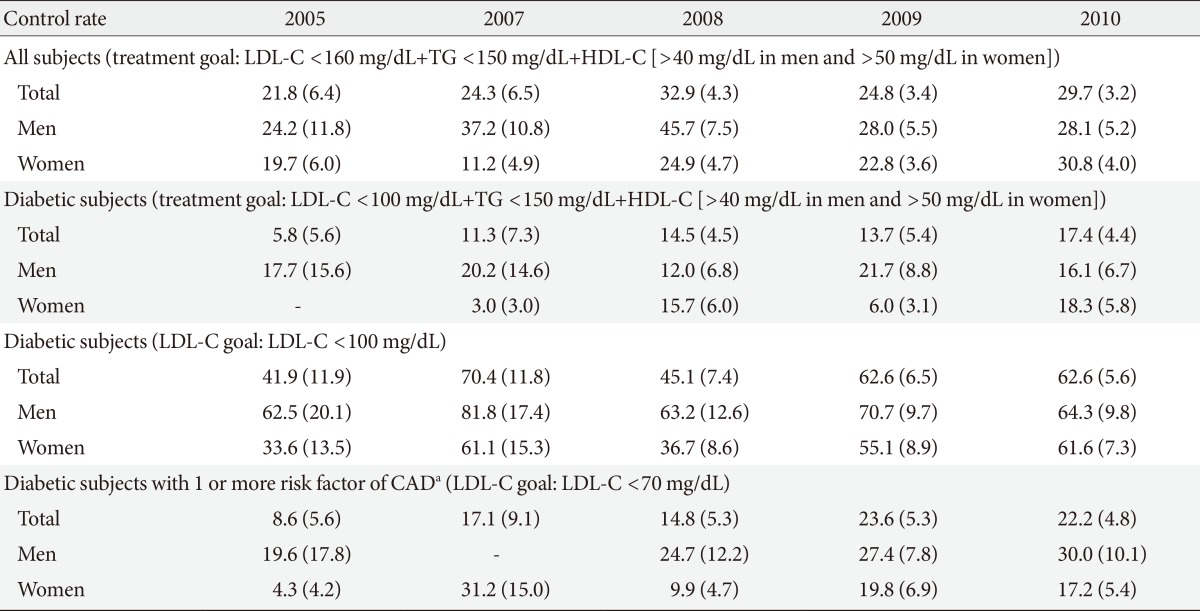
Values are presented as percentage (standard error).
LDL-C, low density lipoprotein cholesterol; TG, hypertriglyceride; HDL-C, high density lipoprotein cholesterol; CAD, coronary artery disease.
aRisk factors of coronary artery disease are high LDL-C (≥160 mg/dL), cigarette smoking, hypertension (systolic/diastolic blood pressure ≥140/90 mm Hg or use of antihypertensive medication), low HDL-C (<40 mg/dL), and age (men ≥45 years, women ≥55 years). Subtract one risk factor if the person has high HDL-C (≥60 mg/dL).
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- SCORE and SCORE2 in East Asian Population
JungMin Choi, Soseul Sung, Sue K. Park, Seyong Park, Hyoyeong Kim, Myeong-Chan Cho, Bryan Williams, Hae-Young Lee
JACC: Asia.2024; 4(4): 265. CrossRef - Statin use and the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma among patients with chronic hepatitis B: an emulated target trial using longitudinal nationwide population cohort data
Dong Hyun Sinn, Danbee Kang, Yewan Park, Hyunsoo Kim, Yun Soo Hong, Juhee Cho, Geum-Youn Gwak
BMC Gastroenterology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Menopause management: A manual for primary care practitioners and nurse practitioners
Neelam Aggarwal, Meeta Meeta, Nirja Chawla
Journal of Mid-life Health.2022; 13(5): 2. CrossRef - New, Novel Lipid-Lowering Agents for Reducing Cardiovascular Risk: Beyond Statins
Kyuho Kim, Henry N. Ginsberg, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2022; 46(4): 517. CrossRef - Status of dyslipidemia management and statin undertreatment in Korean cancer survivors: A Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey study
Sujeong Shin, Dong Wook Shin, In Young Cho, Su-Min Jeong, Hyein Jung
European Journal of Preventive Cardiology.2021; 28(8): 864. CrossRef - Triglyceride glucose (TyG) index as a predictor of incident type 2 diabetes among nonobese adults: a 12-year longitudinal study of the Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study cohort
Byoungjin Park, Hye Sun Lee, Yong-Jae Lee
Translational Research.2021; 228: 42. CrossRef - Temporal change in the diagnosis and treatment rates of osteoporosis: results from the Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Y. J. Choi, H.-B. Shin, B. Park, D. J. Kim, Y.-S. Chung
Osteoporosis International.2021; 32(9): 1777. CrossRef - Hypertriglyceridemia and Other Plasma Lipid Profile Abnormalities among People Living with Diabetes Mellitus in Ethiopia: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Baye Dagnew, Yigizie Yeshaw, Demeke Geremew, Dessie Abebaw Angaw, Henok Dagne, Mekuriaw Alemayehu, Meseret Derbew Molla, Yonas Akalu, Carlos R. Bueno Junior
BioMed Research International.2021; 2021: 1. CrossRef - Triglyceride to HDL-Cholesterol Ratio and the Incident Risk of Ischemic Heart Disease Among Koreans Without Diabetes: A Longitudinal Study Using National Health Insurance Data
Byoungjin Park, Dong Hyuk Jung, Hye Sun Lee, Yong Jae Lee
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Three Musketeers for Lowering Cholesterol: Statins, Ezetimibe and Evolocumab
Qian Xu, Yiming Deng, Jun Xiao, Xiangrui Liu, Min Zhou, Zhong Ren, Juan Peng, Yaling Tang, Zhisheng Jiang, Zhihan Tang, Lushan Liu
Current Medicinal Chemistry.2021; 28(5): 1025. CrossRef - Achievement of LDL-C Targets Defined by ESC/EAS (2011) Guidelines in Risk-Stratified Korean Patients with Dyslipidemia Receiving Lipid-Modifying Treatments
Ye Seul Yang, Seo Young Lee, Jung-Sun Kim, Kyung Mook Choi, Kang Wook Lee, Sang-Chol Lee, Jung Rae Cho, Seung-Jin Oh, Ji-Hyun Kim, Sung Hee Choi
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2020; 35(2): 367. CrossRef - Statin Use and the Risk of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Chronic Hepatitis B
Myung Ji Goh, Dong Hyun Sinn, Seonwoo Kim, Sook Young Woo, Hyun Cho, Wonseok Kang, Geum‐Youn Gwak, Yong‐Han Paik, Moon Seok Choi, Joon Hyeok Lee, Kwang Cheol Koh, Seung Woon Paik
Hepatology.2020; 71(6): 2023. CrossRef - Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol goal attainment rates in high-risk patients with cardiovascular diseases and diabetes mellitus in Korea: a retrospective cohort study
Ye Seul Yang, Bo Ram Yang, Mi-Sook Kim, Yunji Hwang, Sung Hee Choi
Lipids in Health and Disease.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalencia de hipertrigliceridemia en adultos y factores cardiometabólicos asociados. Estudio SIMETAP-HTG
Antonio Ruiz-García, Ezequiel Arranz-Martínez, Beatriz López-Uriarte, Montserrat Rivera-Teijido, David Palacios-Martínez, Gema M. Dávila-Blázquez, Antonio Rosillo-González, José Antonio González-Posada Delgado, José Enrique Mariño-Suárez, Enrique Revilla-
Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis.2020; 32(6): 242. CrossRef - The Effect of High Carbohydrate-to-fat Intake Ratios on Hypo-HDL-cholesterolemia Risk and HDL-cholesterol Levels over a 12-year Follow-up
Hye Ah Lee, Hyoin An
Scientific Reports.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Design and rationale of a randomized control trial testing the effectiveness of combined therapy with STAtin plus FENOfibrate and statin alone in non-diabetic, combined dyslipidemia patients with non-intervened intermediate coronary artery disease - STAFE
Taek-Geun Kwon, Albert Youngwoo Jang, Sang Wook Kim, Young Joon Hong, Jang-Ho Bae, Sung Yun Lee, Sang-Hyun Kim, Seung Hwan Han
Trials.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Small-area variation of cardiovascular diseases and select risk factors and their association to household and area poverty in South Africa: Capturing emerging trends in South Africa to better target local level interventions
Ntabozuko Dwane, Njeri Wabiri, Samuel Manda, David Watkins
PLOS ONE.2020; 15(4): e0230564. CrossRef - Comprehensive Identification of Key Genes Involved in Development of Diabetes Mellitus-Related Atherogenesis Using Weighted Gene Correlation Network Analysis
Qi Huang, Guoxiong Deng, Rongguo Wei, Qiaoye Wang, Donghua Zou, Jinru Wei
Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The triglyceride-glucose index predicts ischemic heart disease risk in Koreans: a prospective study using National Health Insurance Service data
Byoungjin Park, Yong-Jae Lee, Hye Sun Lee, Dong-Hyuk Jung
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - Prevalence of hypertriglyceridemia in adults and related cardiometabolic factors. SIMETAP-HTG study
Antonio Ruiz-García, Ezequiel Arranz-Martínez, Beatriz López-Uriarte, Montserrat Rivera-Teijido, David Palacios-Martínez, Gema M. Dávila-Blázquez, Antonio Rosillo-González, José Antonio González-Posada Delgado, José Enrique Mariño-Suárez, Enrique Revilla-
Clínica e Investigación en Arteriosclerosis (English Edition).2020; 32(6): 242. CrossRef - Incident cardiovascular disease and particulate matter air pollution in South Korea using a population-based and nationwide cohort of 0.2 million adults
Ok-Jin Kim, Soo Hyun Lee, Si-Hyuck Kang, Sun-Young Kim
Environmental Health.2020;[Epub] CrossRef - The association between low frequency of having breakfast and dyslipidemia in South Korean men and women
Doo Woong Lee, Dong-Woo Choi, Yeong Jun Ju, Sang Ah Lee, Eun-Cheol Park
European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.2019; 73(6): 896. CrossRef - Estimated glycemic load (eGL) of mixed meals and its associations with cardiometabolic risk factors among Korean adults: data from the 2013 ~ 2016 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Kyungho Ha, Kisun Nam, YoonJu Song
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(4): 354. CrossRef - Working hours and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease according to sleep duration
Hwanjin Park, Soo-Jin Lee
Chronobiology International.2019; 36(12): 1671. CrossRef - An analysis of the associations between gender and metabolic syndrome components in Korean adults: a national cross-sectional study
Young-Mo Yang, Byung-Cheul Shin, Chihyoung Son, In-Hyuk Ha
BMC Endocrine Disorders.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Time‐ and Dose‐Dependent Association of Statin Use With Risk of Clinically Relevant New‐Onset Diabetes Mellitus in Primary Prevention: A Nationwide Observational Cohort Study
Min Jung Ko, Ae Jeong Jo, Yun Jung Kim, Shin Hee Kang, Songhee Cho, Sang‐Ho Jo, Cheol‐Young Park, Sung‐Cheol Yun, Woo Je Lee, Duk‐Woo Park
Journal of the American Heart Association.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Dyslipidemia associated with body constitution in Traditional Chinese Medicine
Qiuping Li, Qing Kong, Zihui Tang
Traditional Medicine and Modern Medicine.2019; 02(02): 59. CrossRef - Effect of Sulgidduk containing pine needle juice on lipid metabolism in high fat-cholesterol diet induced dyslipidemic rats
Yunjung Lee, Jae-Hee Park, Eunju Park
Journal of Nutrition and Health.2019; 52(1): 6. CrossRef - Increased Serum Angiopoietin-Like 6 Ahead of Metabolic Syndrome in a Prospective Cohort Study
Jun Namkung, Joon Hyung Sohn, Jae Seung Chang, Sang-Wook Park, Jang-Young Kim, Sang-Baek Koh, In Deok Kong, Kyu-Sang Park
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2019; 43(4): 521. CrossRef - Total cholesterol variability and risk of atrial fibrillation: A nationwide population-based cohort study
Eun Roh, Hye Soo Chung, Ji Sung Lee, Jung A. Kim, You-Bin Lee, So-hyeon Hong, Nam Hoon Kim, Hye Jin Yoo, Ji A. Seo, Sin Gon Kim, Nan Hee Kim, Sei Hyun Baik, Kyung Mook Choi, Stefan Kiechl
PLOS ONE.2019; 14(4): e0215687. CrossRef - Low Levels of Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol and Mortality Outcomes in Non-Statin Users
Sung, Huh, Ryu, Lee, Scorletti, Byrne, Kim, Hyun, Ko
Journal of Clinical Medicine.2019; 8(10): 1571. CrossRef - The differential effects of changes in individual macronutrient intake on changes in lipid concentrations during childhood: From the Ewha Birth & Growth Cohort
Hye Ah Lee, Hyo Jeong Hwang, Se Young Oh, Eun Ae Park, Su Jin Cho, Hae Soon Kim, Hyesook Park
Clinical Nutrition.2018; 37(3): 1027. CrossRef - Association between cotinine‐verified smoking status and risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Nam Hee Kim, Yoon Suk Jung, Hyun Pyo Hong, Jung Ho Park, Hong Joo Kim, Dong Il Park, Yong Kyun Cho, Chong Il Sohn, Woo Kyu Jeon, Byung Ik Kim
Liver International.2018; 38(8): 1487. CrossRef - The prevalence, awareness, and treatment of lipid abnormalities in Iranian adults: Surveillance of risk factors of noncommunicable diseases in Iran 2016
Zahra Aryan, Negar Mahmoudi, Ali Sheidaei, Shahabeddin Rezaei, Zohreh Mahmoudi, Kimyia Gohari, Nazila Rezaei, Mohammad Javad Hajipour, Arezou Dilmaghani-Marand, Farideh Razi, Mahdi Sabooni, Farzad Kompani, Alireza Delavari, Bagher Larijani, Farshad Farzad
Journal of Clinical Lipidology.2018; 12(6): 1471. CrossRef - Low-carbohydrate diet and the risk of metabolic syndrome in Korean adults
K. Ha, H. Joung, Y. Song
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2018; 28(11): 1122. CrossRef - Association of change in total cholesterol level with mortality: A population-based study
Su-Min Jeong, Seulggie Choi, Kyuwoong Kim, Sung-Min Kim, Gyeongsil Lee, Joung Sik Son, Jae-Moon Yun, Sang Min Park, Katriina Aalto-Setala
PLOS ONE.2018; 13(4): e0196030. CrossRef - Diabetes Fact Sheet in Korea, 2016: An Appraisal of Current Status
Jong Chul Won, Jae Hyuk Lee, Jae Hyeon Kim, Eun Seok Kang, Kyu Chang Won, Dae Jung Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2018; 42(5): 415. CrossRef - Evaluating the prevalence, awareness, and control of hypertension, diabetes, and dyslipidemia in Korea using the NHIS-NSC database
Sunjoo Boo, Young Joo Yoon, Hyunjin Oh
Medicine.2018; 97(51): e13713. CrossRef - New and Future Parenteral Therapies for the Management of Lipid Disorders
Roberto Garcia, Jaime Burkle
Archives of Medical Research.2018; 49(8): 538. CrossRef - Association between Dietary Pattern and Incidence of Cholesterolemia in Korean Adults: The Korean Genome and Epidemiology Study
Jieul Lee, Jihye Kim
Nutrients.2018; 10(1): 53. CrossRef - Efficacy and Safety of Adding Omega-3 Fatty Acids in Statin-treated Patients with Residual Hypertriglyceridemia: ROMANTIC (Rosuvastatin-OMAcor iN residual hyperTrIglyCeridemia), a Randomized, Double-blind, and Placebo-controlled Trial
Chee Hae Kim, Kyung Ah Han, Jaemyung Yu, Sang Hak Lee, Hui Kyung Jeon, Sang Hyun Kim, Seok Yeon Kim, Ki Hoon Han, Kyungheon Won, Dong-Bin Kim, Kwang-Jae Lee, Kyungwan Min, Dong Won Byun, Sang-Wook Lim, Chul Woo Ahn, SeongHwan Kim, Young Joon Hong, Jidong
Clinical Therapeutics.2018; 40(1): 83. CrossRef - Effects of Abdominal Obesity and Risk Drinking on the Hypertension Risk in Korean Adults
Eun Sook Lee
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing.2018; 29(3): 349. CrossRef - Does Adjuvant Treatment With Ginkgo Biloba to Statins Have Additional Benefits in Patients With Dyslipidemia?
Yu Fan, Xin Jin, Changfeng Man, Dandan Gong
Frontiers in Pharmacology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - Relationship with Smoking and Dyslipidemia in Korean Adults
Dong Youl Shin, Young Keun Jang, Jae Hoon Lee, Jeong Hoon Wee, Dong Ho Chun
Journal of the Korean Society for Research on Nicotine and Tobacco.2017; 8(2): 73. CrossRef - Prevalence and Clinical Characteristics of Dyslipidemia in Koreans
Jee-Sun Jeong, Hyuk-Sang Kwon
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2017; 32(1): 30. CrossRef - Management Status of Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors for Dyslipidemia among Korean Adults
Jongseok Lee, Heejeong Son, Ohk-Hyun Ryu
Yonsei Medical Journal.2017; 58(2): 326. CrossRef - Application of the 2013 American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Cholesterol Guideline to the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Surveys from 1998 to 2012
Young Shin Song, Tae Jung Oh, Kyoung Min Kim, Jae Hoon Moon, Sung Hee Choi, Hak Chul Jang, Kyong Soo Park, Soo Lim
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2017; 41(1): 38. CrossRef - Dietary carbohydrate and fat intakes are differentially associated with lipid abnormalities in Korean adults
SuJin Song, Won O. Song, YoonJu Song
Journal of Clinical Lipidology.2017; 11(2): 338. CrossRef - Metabolic Syndrome Causes Cardiovascular Disease under Stable Statin Medication
Sang-Cheol Cho, Hoonhee Lee, Hyo-Jung Nam, Ki Hoon Han
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2017; 6(2): 75. CrossRef - Improved trends in cardiovascular complications among subjects with type 2 diabetes in Korea: a nationwide study (2006–2013)
Chang Hee Jung, Jin Ook Chung, Kyungdo Han, Seung-Hyun Ko, Kyung Soo Ko, Joong-Yeol Park
Cardiovascular Diabetology.2017;[Epub] CrossRef - Association Between the Awareness of Dyslipidemia and Health Behavior for Control of Lipid Levels Among Korean Adults with Dyslipidemia
In Young Cho, Hwa Yeon Park, Kiheon Lee, Woo Kyung Bae, Se Young Jung, Hye Jin Ju, Jae Kyeong Song, Jong Soo Han
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2017; 38(2): 64. CrossRef - Effect of statin on hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with type 2 diabetes: A nationwide nested case‐control study
Gyuri Kim, Suk‐Yong Jang, Eugene Han, Yong‐ho Lee, Se‐young Park, Chung Mo Nam, Eun Seok Kang
International Journal of Cancer.2017; 140(4): 798. CrossRef - Association of dietary intakes of total and subtypes of fat substituted for carbohydrate with metabolic syndrome in Koreans
Kyong Won Lee, Yoonsu Cho, Garam Jo, Yoo Kyoung Park, Min-Jeong Shin
Endocrine Journal.2016; 63(11): 991. CrossRef - Pre-treatment with simvastatin prevents the induction of diet-induced atherosclerosis in a rabbit model
Nikolaos Oikonomidis, Nikolaos Kavantzas, Laskarina-Maria Korou, Panagiotis Konstantopoulos, Vasilios Pergialiotis, Evangelos Misiakos, Ioannis Rizos, Christos Verikokos, Despina N. Perrea
Biomedical Reports.2016; 5(6): 667. CrossRef - Comparative analysis of the efficacy of omega-3 fatty acids for hypertriglyceridaemia management in Korea
H.-S. Kim, H. Kim, Y. J. Jeong, S. J. Yang, S. J. Baik, H. Lee, S.-H. Lee, J. H. Cho, I.-Y. Choi, H. W. Yim, K.-H. Yoon
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2016; 41(5): 508. CrossRef - Parks and Green Areas Are Associated with Decreased Risk for Hyperlipidemia
Hye-Jin Kim, Jin-Young Min, Hyun-Jin Kim, Kyoung-Bok Min
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health.2016; 13(12): 1205. CrossRef - Analysis and comparison of statin prescription patterns and outcomes according to clinical department
H.-S. Kim, H. Kim, H. Lee, B. Park, S. Park, S.-H. Lee, J. H. Cho, H. Song, J. H. Kim, K.-H. Yoon, I. Y. Choi
Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics.2016; 41(1): 70. CrossRef - Dyslipidemia patterns are differentially associated with dietary factors
SuJin Song, Hee Young Paik, Minseon Park, YoonJu Song
Clinical Nutrition.2016; 35(4): 885. CrossRef - Epidemiology of dyslipidemia in Korea
Hyeon Chang Kim
Journal of the Korean Medical Association.2016; 59(5): 352. CrossRef - Difference between old and young adults in contribution of β‐cell function and sarcopenia in developing diabetes mellitus
Bo Kyung Koo, Eun Roh, Ye Seul Yang, Min Kyong Moon
Journal of Diabetes Investigation.2016; 7(2): 233. CrossRef - Economic Evaluation of Rosuvastatin and Atorvastatin for the Treatment of Dyslipidemia from a Korean Health System Perspective
Sunghwan Suh, Chang Hee Jung, Soon-Jun Hong, Jung-Sun Kim, Byung Ju Song, Hyun Soon Sohn, Sung Hee Choi
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2016; 5(1): 61. CrossRef - Obesity and Hyperglycemia in Korean Men with Klinefelter Syndrome: The Korean Endocrine Society Registry
Seung Jin Han, Kyung-Soo Kim, Wonjin Kim, Jung Hee Kim, Yong-ho Lee, Ji Sun Nam, Ji A Seo, Bu Kyung Kim, Jihyun Lee, Jin Ook Chung, Min-Hee Kim, Tae-Seo Sohn, Han Seok Choi, Seong Bin Hong, Yoon-Sok Chung
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2016; 31(4): 598. CrossRef - Effects of mulberry leaf extract on blood glucose and serum lipid profiles in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review
Seung-Ok Shin, Hyun-Ju Seo, Hyunyoung Park, Hyun Jin Song
European Journal of Integrative Medicine.2016; 8(5): 602. CrossRef - Diabetic Cardiovascular Autonomic Neuropathy Predicts Recurrent Cardiovascular Diseases in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
Seon-Ah Cha, Jae-Seung Yun, Tae-Seok Lim, Kyoungil Min, Ki-Ho Song, Ki-Dong Yoo, Yong-Moon Park, Yu-Bae Ahn, Seung-Hyun Ko, James M Wright
PLOS ONE.2016; 11(10): e0164807. CrossRef - Effects of Age, Sex, and Menopausal Status on Blood Cholesterol Profile in the Korean Population
Ji Hye Park, Myung Ha Lee, Jee-Seon Shim, Dong Phil Choi, Bo Mi Song, Seung Won Lee, Hansol Choi, Hyeon Chang Kim
Korean Circulation Journal.2015; 45(2): 141. CrossRef - Is nutritional labeling associated with individual health? The effects of labeling-based awareness on dyslipidemia risk in a South Korean population
Jong Yeob Kim, Ki Hong Kweon, Min Jae Kim, Eun-Cheol Park, Suk-Yong Jang, Woorim Kim, Kyu-Tae Han
Nutrition Journal.2015;[Epub] CrossRef - Cost-effectiveness analysis of low density lipoprotein cholesterol-lowering therapy in hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes in Korea: single-pill regimen (amlodipine/atorvastatin) versus double-pill regimen (amlodipine+atorvastatin)
Ji-Hyun Park, Yong-Ho Lee, Su-Kyoung Ko, Bong-Soo Cha
Epidemiology and Health.2015; 37: e2015010. CrossRef - Application of New Cholesterol Guidelines to the Korean Adult Diabetic Patients
Bu Kyung Kim, Hyeon Chang Kim, Kyoung Hwa Ha, Dae Jung Kim
Journal of Korean Medical Science.2015; 30(11): 1612. CrossRef - Undiagnosed diabetes is prevalent in younger adults and associated with a higher risk cardiometabolic profile compared to diagnosed diabetes
Yong-ho Lee, Ehrin J. Armstrong, Gyuri Kim, Jaewon Oh, Seok-Min Kang, Byung-Wan Lee, Chul Woo Ahn, Bong Soo Cha, Hyun Chul Lee, Christos S. Mantzoros, Eun Seok Kang
American Heart Journal.2015; 170(4): 760. CrossRef - New Drugs for Treating Dyslipidemia: Beyond Statins
Chang Ho Ahn, Sung Hee Choi
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal.2015; 39(2): 87. CrossRef - Can increased visceral adiposity without body weight changes accelerate carotid atherosclerosis in South Korean participants with type 2 diabetes?
Chul Sik Kim, Soo-Kyung Kim, Maria Rosario G. Araneta, Eun Jig Lee, Elizabeth Barrett-Connor, Kab Bum Huh
Journal of Diabetes and its Complications.2015; 29(8): 1085. CrossRef - Prevalence and Management of Dyslipidemia Among Korean Adults: KNHANES 2010-2012
Sungok Jang, Jongseok Lee
Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial cooperation Society.2015; 16(11): 7978. CrossRef - Prevalence and Gender-Related Characteristics of Metabolic Syndrome in Korean Community
Kyung-Taek Park, Hack-Lyoung Kim, Sang-Hyun Kim, Myung-A Kim, Euijae Lee, Jonghanne Park, Sang-Ho Jo, Sung Rae Kim, Jaetaek Kim, Chee Jeong Kim, Moon-Kyu Lee, Hyun Ho Shin
Journal of Lipid and Atherosclerosis.2014; 3(2): 89. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite