- Current
- Browse
- Collections
-
For contributors
- For Authors
- Instructions to authors
- Article processing charge
- e-submission
- For Reviewers
- Instructions for reviewers
- How to become a reviewer
- Best reviewers
- For Readers
- Readership
- Subscription
- Permission guidelines
- About
- Editorial policy
Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > Diabetes Metab J > Volume 37(5); 2013 > Article
-
Original ArticleObesity and Metabolic Syndrome Effect of Treadmill Exercise on Interleukin-15 Expression and Glucose Tolerance in Zucker Diabetic Fatty Rats
- Hee-Jae Kim1, Jae Young Park2, Seung Lyul Oh1, Yong-An Kim1, Byunghun So1, Je Kyung Seong3, Wook Song1,4
-
Diabetes & Metabolism Journal 2013;37(5):358-364.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.4093/dmj.2013.37.5.358
Published online: October 17, 2013
1Health and Exercise Science Laboratory, The Institute of Sports Science, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
2Department of Sport, Kyungil University College of Arts and Sports, Gyeongsan, Korea.
3Department of Anatomy and Cell Biology, Research Institute for Veterinary Science, Seoul National University College of Veterinary Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
4Institute on Aging, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- Corresponding author: Wook Song. Health and Exercise Science Laboratory, The Institute of Sports Science, Seoul National University, and Institute on Aging, Seoul National University College of Medicine, 1 Gwanak-ro, Gwanak-gu, Seoul 151-742, Korea. songw3@snu.ac.kr
Copyright © 2013 Korean Diabetes Association
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
ABSTRACT
-
Background
- Interleukin-15 (IL-15), a well-known myokine, is highly expressed in skeletal muscle and is involved in muscle-fat crosstalk. Recently, a role of skeletal muscle-derived IL-15 in the improvement of glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity has been proposed. However, little is known regarding the influence of endurance training on IL-15 expression in type 2 diabetic skeletal muscles. We investigated the effect of endurance exercise training on glucose tolerance and IL-15 expression in skeletal muscles using type 2 diabetic animal models.
-
Methods
- Male Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF) and ZDF lean control (ZLC) rats were randomly divided into three groups: sedentary ZLC, sedentary ZDF (ZDF-Con), and exercised ZDF (ZDF-Ex). The ZDF-Ex rats were forced to run a motor-driven treadmill for 60 minutes once a day 5 times per week for 12 weeks. Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT) was performed after 12 weeks. Expression of IL-15 was measured using ELISA in extracted soleus (SOL) and gastrocnemius medial muscles.
-
Results
- After 12 weeks of treadmill training, reduction of body weight was observed in ZDF-Ex compared to ZDF-Con rats. Glucose tolerance using IPGTT in diabetic rats was significantly improved in ZDF-Ex rats. Furthermore, the expression of IL-15 was significantly increased (P<0.01) only in the SOL of ZDF-Ex rats compared to ZDF-Con. Additionally, IL-15 expression in SOL muscles was negatively correlated with change of body weight (R=-0.424, P=0.04).
-
Conclusion
- The present study results suggest that 12 weeks of progressive endurance training significantly improved glucose tolerance with concomitant increase of IL-15 expression in SOL muscles of type 2 diabetic rats.
- Myokines, known as cytokines and peptides, that are produced, expressed, and released by muscle fibers and exertion of these substances in either paracrine or endocrine fashion should be classified [1]. Previously, researchers have searched for a muscle contraction-induced hormonal factor, an exercise factor, which could mediate some of the exercise-induced changes in other organs such as the liver and adipose tissue [1]. Among various myokines, interleukin-15 (IL-15) has been identified as an anabolic factor, which is highly expressed in skeletal muscle [2]. Quinn et al. [3] have proposed an important role of IL-15 in skeletal muscle by demonstrating that IL-15 can stimulate differentiated myocytes and muscle fibers to accumulate increased amounts of contractile proteins. The action of IL-15 stimulates muscle-specific myosin heavy chain accumulation by differentiated myocytes and muscle fibers in culture, suggesting a role in skeletal muscle fiber growth in vivo [4]. In addition, overexpression of IL-15 in mouse C2C12 cells leads to clear muscle hypertrophy [5]. Recently, the functional role of IL-15 in regulating metabolic diseases, including obesity and diabetes, has been emphasized. Modulation of glucose uptake in incubated skeletal muscles and muscle cell cultures by IL-15 implies that cytokines may play a role in the inhibition of the development of diabetes [4]. Indeed, in vivo administration of IL-15 results in an elevation of 2-deoxyglucose uptake in skeletal muscle. Additionally, in vitro treatment of IL-15 increases GLUT4 content in muscle cell cultures [6].
- These findings suggest the possibility that IL-15 can serve as an important mediator of skeletal muscle fiber growth, hypertrophy, and glucose uptake. One study demonstrated that high intensity resistance training leads to a transient increase in serum IL-15 concentration [7], while another study reported that plasma IL-15 concentration is not altered by heavy resistance training [8]. Endurance exercise did not increase IL-15 mRNA content in skeletal muscle or circulating IL-15 concentration from 1 up to 6 hours after exercise [9-12]. However, a recent study implied that endurance exercise increases circulating IL-15 concentration 10 minutes after the exercise [13]. These findings suggest that exercise-induced IL-15 may mediate the systemic as well as local beneficial effects of endurance exercise, including insulin-sensitizing, antiadipogenic effects, and anabolic actions in skeletal muscle [13].
- Skeletal muscle is the principle site of glucose uptake under insulin-stimulated conditions and strongly influences glucose intolerance [14]. Impaired glucose transport in skeletal muscles leads to impaired whole-body glucose uptake, and facilitates the development of type 2 diabetes. Subjects with glucose intolerance have an increased risk of type 2 diabetes, therefore improvement of glucose tolerance is considered important for the prevention of diabetes [15,16].
- Collectively, the results of previous studies clearly indicate that expression of IL-15 in skeletal muscles may regulate glucose metabolism in various metabolic diseases including diabetes. Although exercise is considered an important preventive measure for patients with diabetes, data regarding the influence of endurance training on IL-15 expression in type 2 diabetic skeletal muscles by fiber types are lacking. Therefore, in the present study, we examined the effect of endurance exercise training on glucose tolerance and IL-15 expression in skeletal muscles using type 2 diabetic rats.
INTRODUCTION
- Animals
- Male and female Zucker diabetic fatty (ZDF, fa/+) rats were purchased from Genetic Models (Indianapolis, ME, USA) and allowed to mate. They were housed in conventional cages under adequate temperature (23℃) and humidity (60%), control with a 12-hour light/12-hour dark cycle, and free access to food and water. Purina 5008 rodent diet (7.5% fat) was provided as recommended by Genetic Models Co. (Purina, St. Louis, MO, USA). The fa gene genotype was determined using the strategy described in our previous study [17]. Twenty-four male lean (ZDF lean control, ZLC, +/+) and diabetic (ZDF, fa/fa) Zucker rats (8-week-old) were separated into three groups, lean control (sedentary ZLC, ZLC-Con, n=8), diabetic control (sedentary ZDF, ZDF-Con, n=8), and diabetic exercise-trained (exercised ZDF, ZDF-Ex, n=8).
- All animals in the training group had a treadmill adaptation period of 1 week. At 8 weeks (pre-exercise) and 20 weeks (postexercise) of age, body weight (mettle instrument AG CH-8606; Mettler Toledo, Greifensee, Switzerland) and fasting plasma glucose level (Roche Diagnostics Ltd., Mannheim, Germany) were measured in all animals. The handling and caring procedures for the animals adhered to the guidelines in compliance with the current international law and policies (National Institutes of Health [NIH] Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, NIH Publication No. 85-23, 1985, revised 1996). All experiments were conducted to minimize the number of animals used and the suffering caused by the procedures in the present study.
- Progressive endurance exercise training
- The rats in the ZDF-Ex were forced to run a motor-driven treadmill for 60 minutes once a day 5 times per week for 12 weeks. The ZDF-Ex rats were acclimated to the treadmill exercise before training. The exercise intensity (running speed) was set at the speed of 15 to 20 m/min at their lactate threshold [18]. The initial treadmill speed was set to 15 and 2 m/min was added every 2 weeks to simulate the intensity and effect of exercise training. The maximal treadmill speed was limited to 20 m/min in the last 2 weeks.
- Tissue collection
- Skeletal muscle tissue collection was performed 2 days after the last session of the exercise training program. Rats were anesthetized by Zoletil 50 (intraperitoneal injection, 10 mg/kg; Vibac Laboratories, Carros, France) and sacrificed. The tissues were collected from the soleus (SOL) and the gastrocnemius medial (GM) muscles. The samples were quickly weighed, frozen with liquid nitrogen, and then stored at -80℃ until used. Each tissue was homogenized in radio immunoprecipitation assay buffer. The homogenized tissues were then centrifuged at 14,000 rpm for 20 minutes at 4℃, and the total protein concentration of the supernatant was determined using the Bradford assay.
- IL-15 protein analysis
- Protein extracts from the skeletal muscle were prepared by centrifugation of the tissue homogenates according to the manufacturer's specifications (Rat IL-15 ELISA Kit; Cusabio Biotec Co., Ltd., Newark, DE, USA). Detection range was 1.56 to 100 pg/mL for each assay. All samples were assayed in duplicate to guarantee the precision of the results, and all samples were run within the range of the standard curve. The results were expressed as concentration of IL-15 (pg/mL) read from standard curves.
- Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test
- Glucose tolerance was assessed using the intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IPGTT) in rats during the last week of the training session. IPGTT was performed by injecting glucose (2 g/kg in 20% solution) intraperitoneally in overnight-fasted rats. Blood samples were obtained by cutting the tile tip before and 0, 15, 30, 60, 90, and 120 minutes after glucose administration. Blood glucose concentration was measured using an Accu-Chek glucose analyzer (Roche Diagnostics Ltd., Mannheim, Germany).
- Statistical analysis
- Statistical analysis was performed using the Origin 8.0 and SPSS version 18.0 software package (IBM Co., Armonk, NY, USA). Data were analyzed using two samples t-test to examine the body weight, fasting glucose levels, IL-15 levels, and area under the curve (AUC) of IPGTT. Data were presented as mean±standard error of mean with significance set at P<0.05. Associations of IL-15 expression in SOL with body weight and fasting blood glucose were calculated with Pearson correlation coefficient.
METHODS
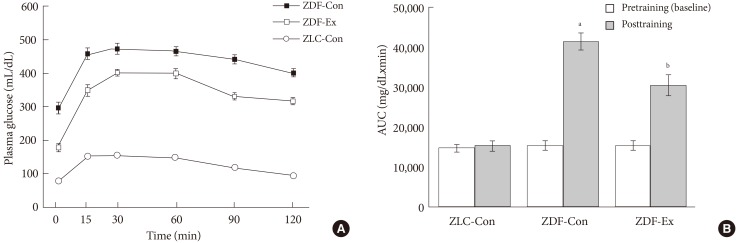
- As shown in Fig. 1A, the body weight of ZDF-Con rats was markedly increased (P<0.05) compared to ZLC-Con rats at the end of exercise training. After the 12-week treadmill exercise program, body weight was lower (P<0.05) in the ZDF-Ex group compared to ZDF-Con group. However, there was no significant change in body weight following the treadmill exercise in ZLC rats (data not shown). The fasting blood glucose concentration in ZDF-Con rats (297.2±18.5 mg/dL) was significantly higher (P<0.05) than in ZLC-Con rats (78.4±5.4 mg/dL). After the last exercise session, the fasting blood glucose level was lower in ZDF-Ex (178.2±12.9 mg/dL) than in ZDF-Con rats (Fig. 1B).
- IPGTT was performed on every weekend to verify the improvement of glucose tolerance. The representative result was found at the last measurement, 2 days after the last session of the exercise program. The significant increase of blood glucose concentration was found within 30 minutes after dextrose injection (2 g/kg, intraperitoneal) in all experimental groups (Fig. 2A). In ZLC-Con rats, the increased blood glucose due to injection of dextrose was gradually eliminated within 2 hours, whereas, the regulatory capacity of blood glucose was significantly attenuated in ZDF-Con rats (Fig. 2A). In parallel, the AUC values of blood glucose levels during IPGTT in ZDF-Con rats were increased to approximately 2.8-fold compared to ZLC-Con rats (Fig. 2B). However, the blood glucose levels in ZDF-Ex rats were significantly reduced during IPGTT, and the total AUC for the glucose response was markedly lower compared to ZDF-Con rats (Fig. 2B).
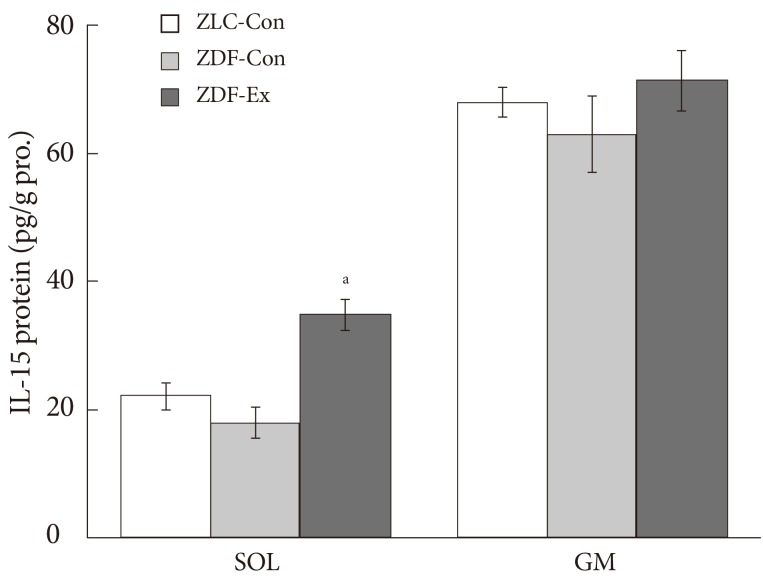
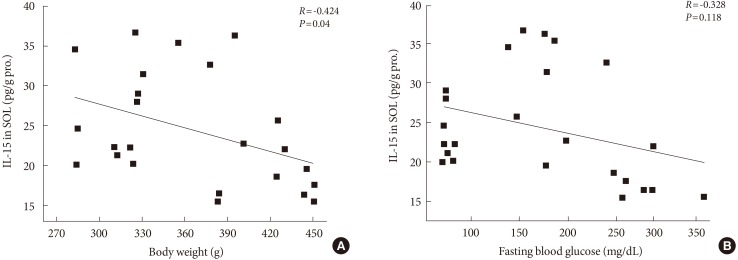
- The expressions of IL-15 in SOL and GM muscles were measured at the end of the 12-week endurance training. In SOL muscle, there was no significant change of IL-15 proteins between ZLC-Con and ZDF-Con rats. In addition, the expression of IL-15 in SOL of ZDF-Ex rats was higher compared to ZDF-Con rats (P<0.05) (Fig. 3). However, no significant effects of diabetes and endurance training were detected in IL-15 expression in GM muscle. Additionally, we found a negative correlation between expression of IL-15 in SOL muscle and body weight (R=-0.424, P=0.04) (Fig. 4A), whereas, statistical correlation between IL-15 expression in SOL muscle and concentration of fasting blood glucose was not observed (R=-0.328, P=0.118) (Fig. 4B).
RESULTS
- In the present study, we investigated whether 12 weeks of physical exercise training improves glucose tolerance and expression of IL-15 in diabetic skeletal muscles. Our data demonstrated that body weight and fasting blood glucose levels were positively changed in trained diabetic rats. Additionally, the glucose tolerance significantly improved following 12 weeks of treadmill exercise training. The expression of IL-15 in skeletal muscles, especially in the SOL muscle, significantly increased after treadmill exercise in diabetic animals. To our knowledge, this is the first study to investigate the effect of exercise training on the expression of IL-15 in skeletal muscles with concomitant improvement of glucose tolerance in transgenic diabetic animals.
- Our result demonstrated a body weight reduction in ZDF-Ex rats. Based on our observation, we could not find any significant differences in food and water intake between control and exercise groups (data not shown). Additionally, there was no visible symptom of under nutrition during the entire training program. Although the change of body composition was not measured in our study, regular physical exercise is known to decrease body fat mass which leads to weight reduction. The results showing body weight reduction and lower fasting blood glucose levels are typical results obtained from exercise in type 2 diabetic models, indicating the training program was adequately designed and implemented.
- In previous IL-15 metabolism studies, IL-15 reportedly stimulated glucose uptake and lipid oxidation in muscle tissue [6,19]. Furthermore, systemic injection of IL-15 reduced fat deposition in normal and obese rodents, which was associated with inhibition of lipogenesis in the liver and adipose tissues [20,21]. Additionally, circulating IL-15 protein regulated body composition including adipose tissue deposition [22]. A recent study reported that IL-15 improves glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in obese mice [23]. In the present study, we found the increase of IL-15 expression in SOL muscle with concomitant improvement of glucose tolerance in diabetic rats after training. Systemic effect of exercise-induced IL-15 on improvement of glucose metabolism is unknown, and IL-15 may be a potent mediator to elucidate the beneficial effect of exercise on metabolic diseases such as obesity or type 2 diabetes.
- Previous studies showed inconsistent results regarding the effects of exercise on IL-15 expression in skeletal muscle and plasma [24]. Nieman et al. [12] reported no changes in muscle IL-15 mRNA following 2 hours of intensive strength training. Similarly, Ostrowski et al. [11] observed no changes in plasma IL-15 following 2 hours of treadmill running. In contrast, plasma IL-15 levels increased following resistance exercise [8,25] and treadmill running in healthy young men [13]. To date, however, most of the previous research subjects were normal individuals, and alteration of IL-15 expression in diabetic skeletal muscle was not found. Only one study reported that treadmill exercise promotes IL-15 expression in skeletal muscle of high-fat induced obese rats [26]. In our results, IL-15 expression was increased in skeletal muscle following exercise training especially in the SOL muscle when using a transgenic diabetic model.
- Having an important role in the determination of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, skeletal muscle is affected by insulin resistance in diabetic conditions. In patients and animals with type 2 diabetes, skeletal muscles showed lower oxidative enzyme activity than normal subjects [27-29]. Additionally, the alteration of muscle fiber types and fiber specific oxidative enzyme activities in skeletal muscles of patients with type 2 diabetes have been reported [30]. In various type 2 diabetic animals including Otsuka Long Evans Tokushima Fatty, Goto-Kakizaki, and ZDF rats, skeletal muscle had a lower percentage of type IIA fibers compared to age-matched nondiabetic rats [31,32]. Additionally, Yasuda et al. [33] reported the SOL muscle in ZDF rats has a lower percentage of type IIA fibers than lean controls. Due to different metabolic properties of the muscle fiber classification, type I (slow-twitch, oxidative) and type II (fast-twitch, glycolytic) skeletal muscles are differently affected by diabetes. In the present study, IL-15 expression was markedly increased in SOL (mostly type I fiber) but not in GM (type II dominant) muscles. Based on our results, in diabetic skeletal muscle, response of type I muscle fibers may be more sensitive to IL-15 expression than type II muscle fibers following exercise training.
- Although this study investigates a new perspective of exercise-induced improvement in type 2 diabetes, several limitations in the experimental design and variables remain. IL-15 expression should have been measured in both skeletal muscle and circulating plasma following exercise training. However, not enough plasma was obtained to analyze insulin and plasma IL-15 levels in this experiment.
- In conclusion, our data showed that 12 weeks of treadmill exercise induced an increase of IL-15 expression in SOL muscle with concomitant improvement of glucose tolerance. Based on the current knowledge, including our own findings, increased IL-15 following endurance exercise might be a potent mediator of glucose regulation in type 2 diabetes. Further studies will be required to investigate the mechanisms by which different expressions of IL-15 are regulated by different muscle fiber types under diabetic conditions, and how the increased expression of IL-15 exerts preventive effects including improvement of glucose tolerance in diabetic models.
DISCUSSION
-
Acknowledgements
- This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by Ministry of Education, Science and Technology (2010-0009915), MEST 2011-0030133, and also supported by the grants from KGEMC (20120008875).
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
- 1. Pedersen BK, Akerstrom TC, Nielsen AR, Fischer CP. Role of myokines in exercise and metabolism. J Appl Physiol 2007;103:1093-1098. ArticlePubMed
- 2. Grabstein KH, Eisenman J, Shanebeck K, Rauch C, Srinivasan S, Fung V, Beers C, Richardson J, Schoenborn MA, Ahdieh M, Johnson L, Alderson MR, Watson JD, Anderson DM, Giri JG. Cloning of a T cell growth factor that interacts with the beta chain of the interleukin-2 receptor. Science 1994;264:965-968. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Quinn LS, Haugk KL, Grabstein KH. Interleukin-15: a novel anabolic cytokine for skeletal muscle. Endocrinology 1995;136:3669-3672. ArticlePubMed
- 4. Argiles JM, Lopez-Soriano FJ, Busquets S. Therapeutic potential of interleukin-15: a myokine involved in muscle wasting and adiposity. Drug Discov Today 2009;14:208-213. ArticlePubMed
- 5. Quinn LS, Anderson BG, Drivdahl RH, Alvarez B, Argiles JM. Overexpression of interleukin-15 induces skeletal muscle hypertrophy in vitro: implications for treatment of muscle wasting disorders. Exp Cell Res 2002;280:55-63. ArticlePubMed
- 6. Busquets S, Figueras M, Almendro V, Lopez-Soriano FJ, Argiles JM. Interleukin-15 increases glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. An antidiabetogenic effect of the cytokine. Biochim Biophys Acta 2006;1760:1613-1617. ArticlePubMed
- 7. Argiles JM, Busquets S, Felipe A, Lopez-Soriano FJ. Muscle wasting in cancer and ageing: cachexia versus sarcopenia. Adv Gerontol 2006;18:39-54. PubMed
- 8. Riechman SE, Balasekaran G, Roth SM, Ferrell RE. Association of interleukin-15 protein and interleukin-15 receptor genetic variation with resistance exercise training responses. J Appl Physiol 2004;97:2214-2219. ArticlePubMed
- 9. Nielsen AR, Mounier R, Plomgaard P, Mortensen OH, Penkowa M, Speerschneider T, Pilegaard H, Pedersen BK. Expression of interleukin-15 in human skeletal muscle effect of exercise and muscle fibre type composition. J Physiol 2007;584(Pt 1):305-312. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 10. Chan MH, Carey AL, Watt MJ, Febbraio MA. Cytokine gene expression in human skeletal muscle during concentric contraction: evidence that IL-8, like IL-6, is influenced by glycogen availability. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 2004;287:R322-R327. ArticlePubMed
- 11. Ostrowski K, Hermann C, Bangash A, Schjerling P, Nielsen JN, Pedersen BK. A trauma-like elevation of plasma cytokines in humans in response to treadmill running. J Physiol 1998;513(Pt 3):889-894. ArticlePubMedPMC
- 12. Nieman DC, Davis JM, Brown VA, Henson DA, Dumke CL, Utter AC, Vinci DM, Downs MF, Smith JC, Carson J, Brown A, McAnulty SR, McAnulty LS. Influence of carbohydrate ingestion on immune changes after 2 h of intensive resistance training. J Appl Physiol 2004;96:1292-1298. ArticlePubMed
- 13. Tamura Y, Watanabe K, Kantani T, Hayashi J, Ishida N, Kaneki M. Upregulation of circulating IL-15 by treadmill running in healthy individuals: is IL-15 an endocrine mediator of the beneficial effects of endurance exercise? Endocr J 2011;58:211-215. ArticlePubMed
- 14. DeFronzo RA, Bonadonna RC, Ferrannini E. Pathogenesis of NIDDM. A balanced overview. Diabetes Care 1992;15:318-368. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 15. Bergman RN, Finegood DT, Ader M. Assessment of insulin sensitivity in vivo. Endocr Rev 1985;6:45-86. ArticlePubMed
- 16. Tuomilehto J, Lindstrom J, Eriksson JG, Valle TT, Hamalainen H, Ilanne-Parikka P, Keinanen-Kiukaanniemi S, Laakso M, Louheranta A, Rastas M, Salminen V, Uusitupa M. Finnish Diabetes Prevention Study Group. Prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus by changes in lifestyle among subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. N Engl J Med 2001;344:1343-1350. ArticlePubMed
- 17. Hwang IK, Yi SS, Kim YN, Kim IY, Lee IS, Yoon YS, Seong JK. Reduced hippocampal cell differentiation in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus in a rat model of type II diabetes. Neurochem Res 2008;33:394-400. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 18. Chang H, Park JY, Suk MH, Lee HJ, Kang HJ, Choi KM, Song W. Comparison of lactate threshold, glucose, and insulin levels between OLETF and LETO rats after all-out exercise. J Sports Sci Med 2009;8:381-387. PubMedPMC
- 19. Almendro V, Busquets S, Ametller E, Carbo N, Figueras M, Fuster G, Argiles JM, Lopez-Soriano FJ. Effects of interleukin-15 on lipid oxidation: disposal of an oral [(14)C]-triolein load. Biochim Biophys Acta 2006;1761:37-42. PubMed
- 20. Alvarez B, Carbo N, Lopez-Soriano J, Drivdahl RH, Busquets S, Lopez-Soriano FJ, Argiles JM, Quinn LS. Effects of interleukin-15 (IL-15) on adipose tissue mass in rodent obesity models: evidence for direct IL-15 action on adipose tissue. Biochim Biophys Acta 2002;1570:33-37. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Carbo N, Lopez-Soriano J, Costelli P, Alvarez B, Busquets S, Baccino FM, Quinn LS, Lopez-Soriano FJ, Argiles JM. Interleukin-15 mediates reciprocal regulation of adipose and muscle mass: a potential role in body weight control. Biochim Biophys Acta 2001;1526:17-24. ArticlePubMed
- 22. Quinn LS, Anderson BG, Strait-Bodey L, Stroud AM, Argiles JM. Oversecretion of interleukin-15 from skeletal muscle reduces adiposity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2009;296:E191-E202. ArticlePubMed
- 23. Barra NG, Chew MV, Holloway AC, Ashkar AA. Interleukin-15 treatment improves glucose homeostasis and insulin sensitivity in obese mice. Diabetes Obes Metab 2012;14:190-193. ArticlePubMed
- 24. Quinn LS, Anderson BG. Interleukin-15, IL-15 receptor-alpha, and obesity: Concordance of Laboratory Animal and Human Genetic Studies. J Obes 2011;2011:456347ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 25. Lambert CP, Flynn MG, Sullivan DH, Evans WJ. Effects of megestrol acetate on circulating interleukin-15 and interleukin-18 concentrations in healthy elderly men. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 2004;59:855-858. ArticlePubMed
- 26. Yang H, Chang J, Chen W, Zhao L, Qu B, Tang C, Qi Y, Zhang J. Treadmill exercise promotes interleukin 15 expression in skeletal muscle and interleukin 15 receptor alpha expression in adipose tissue of high-fat diet rats. Endocrine 2013;43:579-585. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 27. Marin P, Andersson B, Krotkiewski M, Bjorntorp P. Muscle fiber composition and capillary density in women and men with NIDDM. Diabetes Care 1994;17:382-386. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 28. Hickey MS, Carey JO, Azevedo JL, Houmard JA, Pories WJ, Israel RG, Dohm GL. Skeletal muscle fiber composition is related to adiposity and in vitro glucose transport rate in humans. Am J Physiol 1995;268(3 Pt 1):E453-E457. ArticlePubMed
- 29. Nyholm B, Qu Z, Kaal A, Pedersen SB, Gravholt CH, Andersen JL, Saltin B, Schmitz O. Evidence of an increased number of type IIb muscle fibers in insulin-resistant first-degree relatives of patients with NIDDM. Diabetes 1997;46:1822-1828. ArticlePubMed
- 30. Oberbach A, Bossenz Y, Lehmann S, Niebauer J, Adams V, Paschke R, Schon MR, Bluher M, Punkt K. Altered fiber distribution and fiber-specific glycolytic and oxidative enzyme activity in skeletal muscle of patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2006;29:895-900. ArticlePubMedPDF
- 31. Yasuda K, Adachi T, Kikuchi N, Tsujimoto G, Aoki N, Tsuda K, Ishihara A. Effects of running exercise on fibre-type distribution of soleus and plantaris muscles in diabetic Otsuka Long-Evans Tokushima fatty rats. Diabetes Obes Metab 2006;8:311-321. ArticlePubMed
- 32. Yasuda K, Nishikawa W, Iwanaka N, Nakamura E, Seino Y, Tsuda K, Ishihara A. Abnormality in fibre type distribution of soleus and plantaris muscles in non-obese diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 2002;29:1001-1008. ArticlePubMed
- 33. Adachi T, Kikuchi N, Yasuda K, Anahara R, Gu N, Matsunaga T, Yamamura T, Mori C, Tsujimoto G, Tsuda K, Ishihara A. Fibre type distribution and gene expression levels of both succinate dehydrogenase and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma coactivator-1alpha of fibres in the soleus muscle of Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Exp Physiol 2007;92:449-455. PubMed
REFERENCES
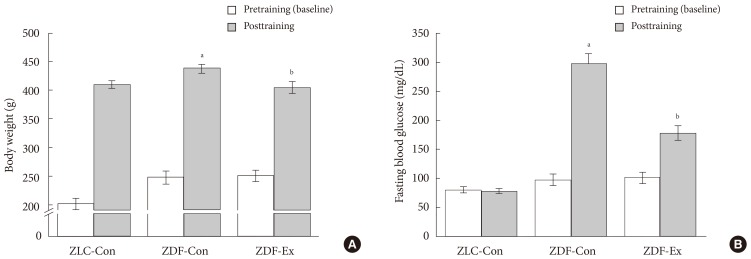


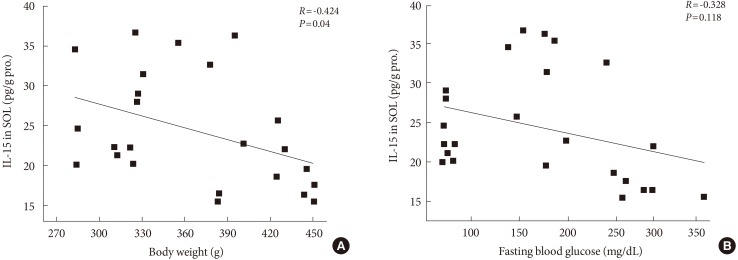
Figure & Data
References
Citations

- Beyond muscles: Investigating immunoregulatory myokines in acute resistance exercise – A systematic review and meta‐analysis
Miriam Ringleb, Florian Javelle, Simon Haunhorst, Wilhelm Bloch, Lena Fennen, Sabine Baumgart, Sebastian Drube, Philipp A. Reuken, Mathias W. Pletz, Heiko Wagner, Holger H. W. Gabriel, Christian Puta
The FASEB Journal.2024;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise‐regulated white adipocyte differentitation: An insight into its role and mechanism
Linjing Yan, Liang Guo
Journal of Cellular Physiology.2023; 238(8): 1670. CrossRef - Effects of short-term physical training on the interleukin-15 signalling pathway and glucose tolerance in aged rats
Luciele Guerra Minuzzi, Luciana Renata da Conceição, Vitor Rosetto Muñoz, Renan Fudoli Lins Vieira, Rafael Calais Gaspar, Adelino S.R. da Silva, Dennys Esper Cintra, Leandro Pereira de Moura, Eduardo Rochete Ropelle, Ana Maria Teixeira, José Rodrigo Pauli
Cytokine.2021; 137: 155306. CrossRef - Swimming Program on Mildly Diabetic Rats in Pregnancy
Nathália C. D. Macedo, Isabela L. Iessi, Franciane Q. Gallego, Aline O. Netto, Yuri K. Sinzato, Gustavo T. Volpato, Elena Zambrano, Débora C. Damasceno
Reproductive Sciences.2021; 28(8): 2223. CrossRef - Exercise training and de-training effects on serum leptin and TNF-α in high fat induced diabetic rats
Hamideh Dinari Ghozhdi, Ali Heidarianpour, Maryam Keshvari, Hassan Tavassoli
Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - Exercise-Induced Myokines can Explain the Importance of Physical Activity in the Elderly: An Overview
Jenny Hyosun Kwon, Kyoung Min Moon, Kyueng-Whan Min
Healthcare.2020; 8(4): 378. CrossRef - Myokine/Adipokine Response to “Aerobic” Exercise: Is It Just a Matter of Exercise Load?
Zihong He, Ye Tian, Pedro L. Valenzuela, Chuanye Huang, Jiexiu Zhao, Ping Hong, Zilin He, Shuhui Yin, Alejandro Lucia
Frontiers in Physiology.2019;[Epub] CrossRef - Overexpression of Interleukin-15 exhibits improved glucose tolerance and promotes GLUT4 translocation via AMP-Activated protein kinase pathway in skeletal muscle
Taku Fujimoto, Ken Sugimoto, Toshimasa Takahashi, Yukiko Yasunobe, Keyu Xie, Minoru Tanaka, Yuri Ohnishi, Shino Yoshida, Hitomi Kurinami, Hiroshi Akasaka, Yoichi Takami, Yasushi Takeya, Koichi Yamamoto, Hiromi Rakugi
Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications.2019; 509(4): 994. CrossRef - Insights from Exercise-induced Cardioprotection-from Clinical Application to Basic Research
Hao Jiang, Beijian Zhang, Daile Jia, Wenlong Yang, Aijun Sun, Junbo Ge
Current Pharmaceutical Design.2019; 25(35): 3751. CrossRef - Myokine Response to High-Intensity Interval vs. Resistance Exercise: An Individual Approach
Zihong He, Ye Tian, Pedro L. Valenzuela, Chuanye Huang, Jiexiu Zhao, Ping Hong, Zilin He, Shuhui Yin, Alejandro Lucia
Frontiers in Physiology.2018;[Epub] CrossRef - A systematic review of “myokines and metabolic regulation”
Henry H. León-Ariza, María P. Mendoza-Navarrete, María I. Maldonado-Arango, Daniel A. Botero-Rosas
Apunts. Medicina de l'Esport.2018; 53(200): 155. CrossRef - Exercise benefits in cardiovascular disease: beyond attenuation of traditional risk factors
Carmen Fiuza-Luces, Alejandro Santos-Lozano, Michael Joyner, Pedro Carrera-Bastos, Oscar Picazo, José L. Zugaza, Mikel Izquierdo, Luis M. Ruilope, Alejandro Lucia
Nature Reviews Cardiology.2018; 15(12): 731. CrossRef - Effects of 8 Weeks Resistance Exercise on GSH, SOD, TBARS Activities and GLUT2 mRNA Expression of Pancreas in OLETF Rats
Min-Ki Lee, Jin-Hwan Yoon
The Korean Journal of Physical Education.2017; 56(3): 551. CrossRef - Exercise effects on perivascular adipose tissue: endocrine and paracrine determinants of vascular function
B C S Boa, J S Yudkin, V W M van Hinsbergh, E Bouskela, E C Eringa
British Journal of Pharmacology.2017; 174(20): 3466. CrossRef - IL15RA is required for osteoblast function and bone mineralization
Emanuele Loro, Girish Ramaswamy, Abhishek Chandra, Wei-Ju Tseng, Manoj K. Mishra, Eileen M. Shore, Tejvir S. Khurana
Bone.2017; 103: 20. CrossRef - Interleukin‐15 in obesity and metabolic dysfunction: current understanding and future perspectives
Y. Duan, F. Li, W. Wang, Q. Guo, C. Wen, Y. Li, Y. Yin
Obesity Reviews.2017; 18(10): 1147. CrossRef - Effects of interval aerobic training combined with strength exercise on body composition, glycaemic and lipid profile and aerobic capacity of obese rats
Irene Coll-Risco, Virginia A. Aparicio, Elena Nebot, Daniel Camiletti-Moirón, Rosario Martínez, Garyfallia Kapravelou, María López-Jurado, Jesús M. Porres, Pilar Aranda
Journal of Sports Sciences.2016; 34(15): 1452. CrossRef - Exercise-induced alterations in pancreatic oxidative stress and mitochondrial function in type 2 diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats
Haider Raza, Annie John, Jasmin Shafarin, Frank C. Howarth
Physiological Reports.2016; 4(8): e12751. CrossRef - Interval aerobic training combined with strength-endurance exercise improves metabolic markers beyond caloric restriction in Zucker rats
V.A. Aparicio, I. Coll-Risco, D. Camiletti-Moirón, E. Nebot, R. Martínez, M. López-Jurado, P. Aranda
Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases.2016; 26(8): 713. CrossRef - IL-15 expression increased in response to treadmill running and inhibited endoplasmic reticulum stress in skeletal muscle in rats
Hong-Tao Yang, Li-Jie Luo, Wen-Jia Chen, Lei Zhao, Chao-Shu Tang, Yong-Fen Qi, Jing Zhang
Endocrine.2015; 48(1): 152. CrossRef - Time course of IL-15 expression after acute resistance exercise in trained rats: effect of diabetes and skeletal muscle phenotype
Mahdieh Molanouri Shamsi, Zuhair Mohammad Hassan, LeBris S. Quinn, Reza Gharakhanlou, Leila Baghersad, Mehdi Mahdavi
Endocrine.2015; 49(2): 396. CrossRef - The search for exercise factors in humans
Milène Catoire, Sander Kersten
The FASEB Journal.2015; 29(5): 1615. CrossRef - Muscle-specific deletion of exons 2 and 3 of theIL15RAgene in mice: effects on contractile properties of fast and slow muscles
Grant O'Connell, Ge Guo, Janelle Stricker, LeBris S. Quinn, Averil Ma, Emidio E. Pistilli
Journal of Applied Physiology.2015; 118(4): 437. CrossRef - Exercise-induced myokines in health and metabolic diseases
Byunghun So, Hee-Jae Kim, Jinsoo Kim, Wook Song
Integrative Medicine Research.2014; 3(4): 172. CrossRef

 KDA
KDA PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite